Page 1

Cisco Smart Business
Communications System
Feature Reference Guide
December 2010
Page 2
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 27
Introduction
Cisco® Configuration Assistant simplifies the task of configuring, deploying, and administering the Cisco Smart
Business Communications System (SBCS)—a complete system of advanced voice, data, security, and wireless
networking products designed specifically for small and medium-sized businesses. Cisco Configuration Assistant
improves network security and performance and substantially reduces deployment and configuration time. This PCbased application features a simple graphical user interface (GUI) and provides everything required to quickly set up
a small office network.
Cisco Configuration Assistant provides:
●
Configuration, deployment, and ongoing network management support for the Cisco Smart Business
Communications System
●
Multiple network views
●
Simplified network reporting
●
Drag-and-drop software updates
●
Troubleshooting
This document lists Cisco SBCS system features that can be configured using Cisco Configuration Assistant versions
2.2(5) and 3.0. Feature configuration information is categorized by network and voice, switching, wireless, and
security. A comprehensive, A-to-Z guide to SBCS system features is also included. For device- and platform-specific
features, see the data sheets and platform reference guides available on Cisco.com (www.cisco.com/go/sbcs)
Download Cisco Configuration Assistant at no charge at www.cisco.com/go/configassist by selecting the “Download
Software” link.
Page 3
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 27
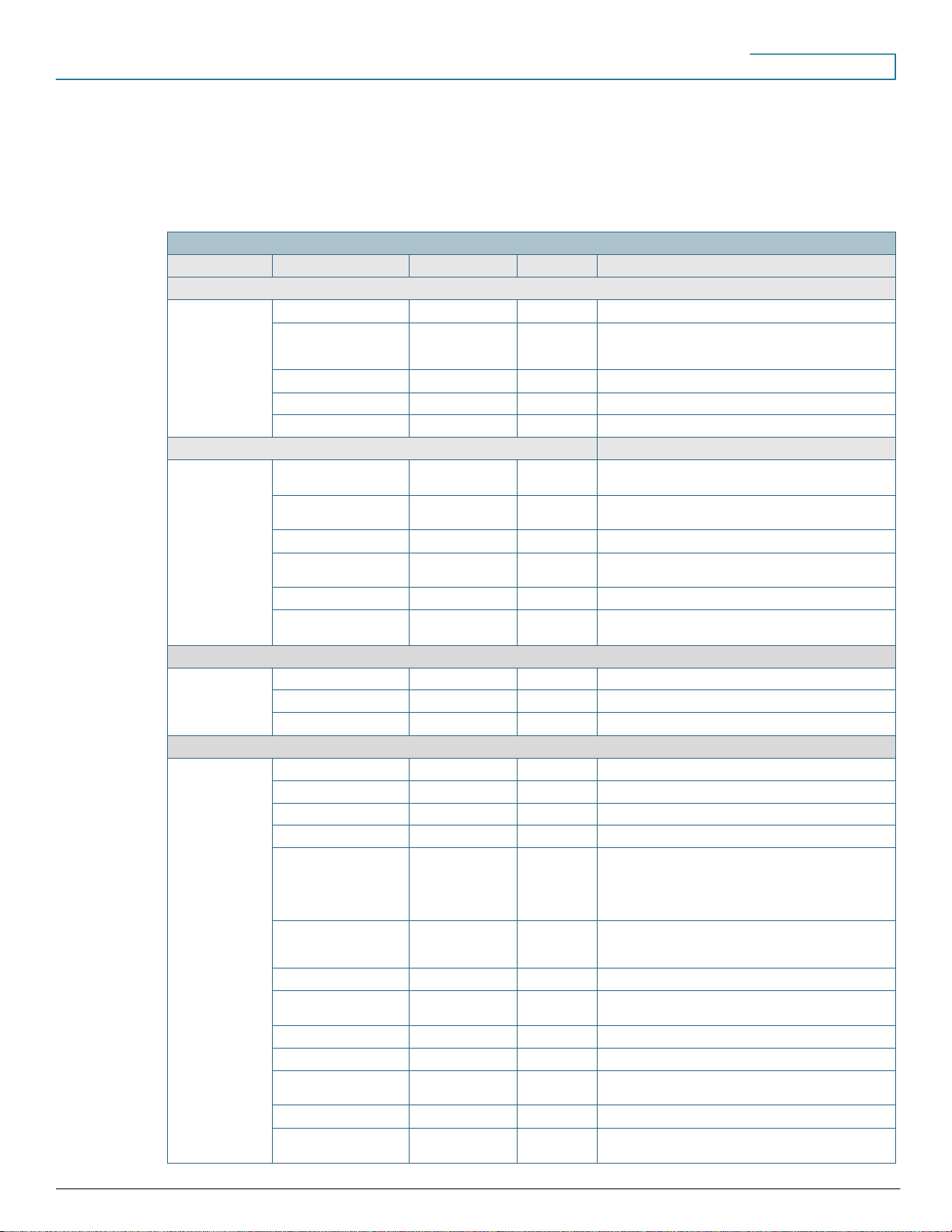
Cisco Configuration Assistant Network and Voice Feature Support
Category
Feature
v2.2(5)
v3.0
Description
Basic Network Configuration
WAN IP address
X X
Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol
(DHCP)
X X
Time zone
X X
Data and voice VLANs
X X
Routing
X X Only static routing supported
Voice Deployment Scenarios
Key System mode
X X Supported for Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) and T1/E1
channel associated signaling (CAS)
Private Branch
Exchange (PBX) mode
X X Support for direct inward dialing (DID) and direct outward
dialing (DOD)
Remote teleworker
X X
Multisite SBCS
deployment
X X Up to 5-site multisite deployment
Phone VPN client
X X
Video streaming to IP
phone
X X
Cisco Unified Communications (UC) 500 Series Platforms Supported
UC520
X X
UC540
X X
UC560
X X
Basic Managed Device Support
System time
X X
Users and passwords
X X
IP address
X X
Device access
X X
Access device
configuration utility from
Cisco Configuration
Assistant Topology
View
X X
Simple Network
Management Protocol
(SNMP)
X X Varies by device
Save configuration
X X
Backup and restore
configuration
X X
Firmware upgrade
X X
Inventory
X X
System messages
(logging)
X X
Hostname
X X
Reset to factory
defaults
X X
Section One: Feature Comparisons by Release
Cisco Configuration Assistant Network and Voice Feature Support
Table 1 lists network and voice features that are supported by Cisco Configuration Assistant versions 2.2(5) and 3.0.
Table 1. Cisco Configuration Assistant Network and Voice Feature Support
Page 4
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 27
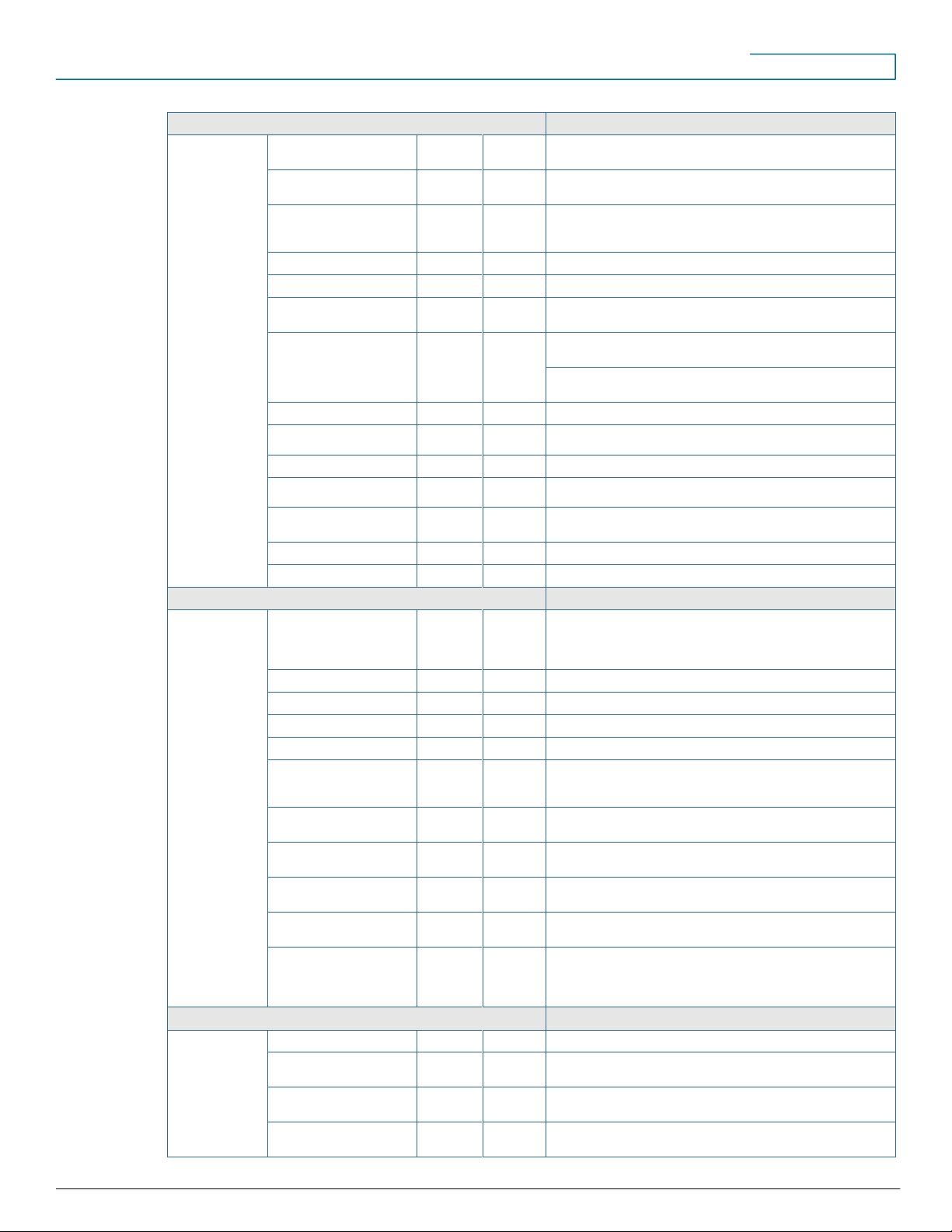
Dial Plan
Inbound call handling
X X Call handling for FXO, Basic Rate Interface (BRI)/T1/E1 incoming call
handling mechanism
Outbound call handling
X X Ability to specify multiple emergency numbers, customized call
blocking capability
Public Switched Telephone
Network (PSTN) number
mapping (DID)
X X Ability to perform 1-to-1 and 1-to-many DID to internal extension
mapping.
Call forward busy
X X
Call forward no answer
X X
Inbound caller ID support
X X Supported on FXO, BRI, Primary Rate Interface (PRI), Session
Initiation Protocol (SIP)
Outbound caller ID support
X
X
Supported on BRI, PRI, and SIP. If DID range is noncontiguous,
outbound caller ID is the auto attendant (AA) number.
Supported for configuring caller ID per PSTN trunk and overriding
trunk-level caller ID for individual extensions.
Caller ID blocking
X X
Call blocking
X X Added ability to customize up to 5 call block numbers or ranges
Customizable dial plan
X X
Trunk failover
X X Support for SIP trunk to PSTN or PSTN to SIP trunk failover
Multiple access codes
X X Support for multiple access codes for any string of digits in the dial
plan
Digit collection timeout
X X
Dial plan test diagnostic
X X
PSTN Trunks
Central office (CO) trunk
(FXO)
X X Call handling per FXO port can be customized to redirect to
AA/operator/hunt group/shared line; Cisco Configuration Assistant
2.2(5) adds support for overlay on CO trunk line. Cisco Configuration
Assistant 3.0 adds support for detailed FXO trunk settings.
Analog DID
X X Supported only on the expansion voice interface card (VIC) slot
BRI X X T1 (PRI) including fractional
X X
E1 (PRI) including fractional
X X
T1 (CAS) including fractional
X X Ear and mouth (E&M) (Wink Start and Immediate Start signaling types
supported). For Foreign Exchange Station (FXS)/FXO, loop start and
ground start signaling types supported.
E1 (CAS) including fractional
X X E&M (Wink Start and Immediate Start signaling types supported). For
FXS/FXO, loop start and ground start signaling types supported.
Analog station ports
(integrated FXS)
X X
ISDN BRI/PRI parameter
customization
X X Configurable bearer-cap and static TEI settings
International call progress
tones
X X Configurable call progress tone for international locales
SIP trunks
X X Support for AT&T, Cbeyond, Nuvox, Paetec, XO, Broadview and
British Telecom, FiberNet, and generic SIP provider. Cisco
Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for Cablevision, Qwest, and
Portugal Telecom.
Voice System Features
Call pickup
X X
Call park
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for call park extension
timeout and recall settings.
Call hold
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for call hold audible
alert settings.
Hunt groups
X X Includes sequential, peer, simultaneous (call blast), and longest idle
hunt group types
Page 5
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 27
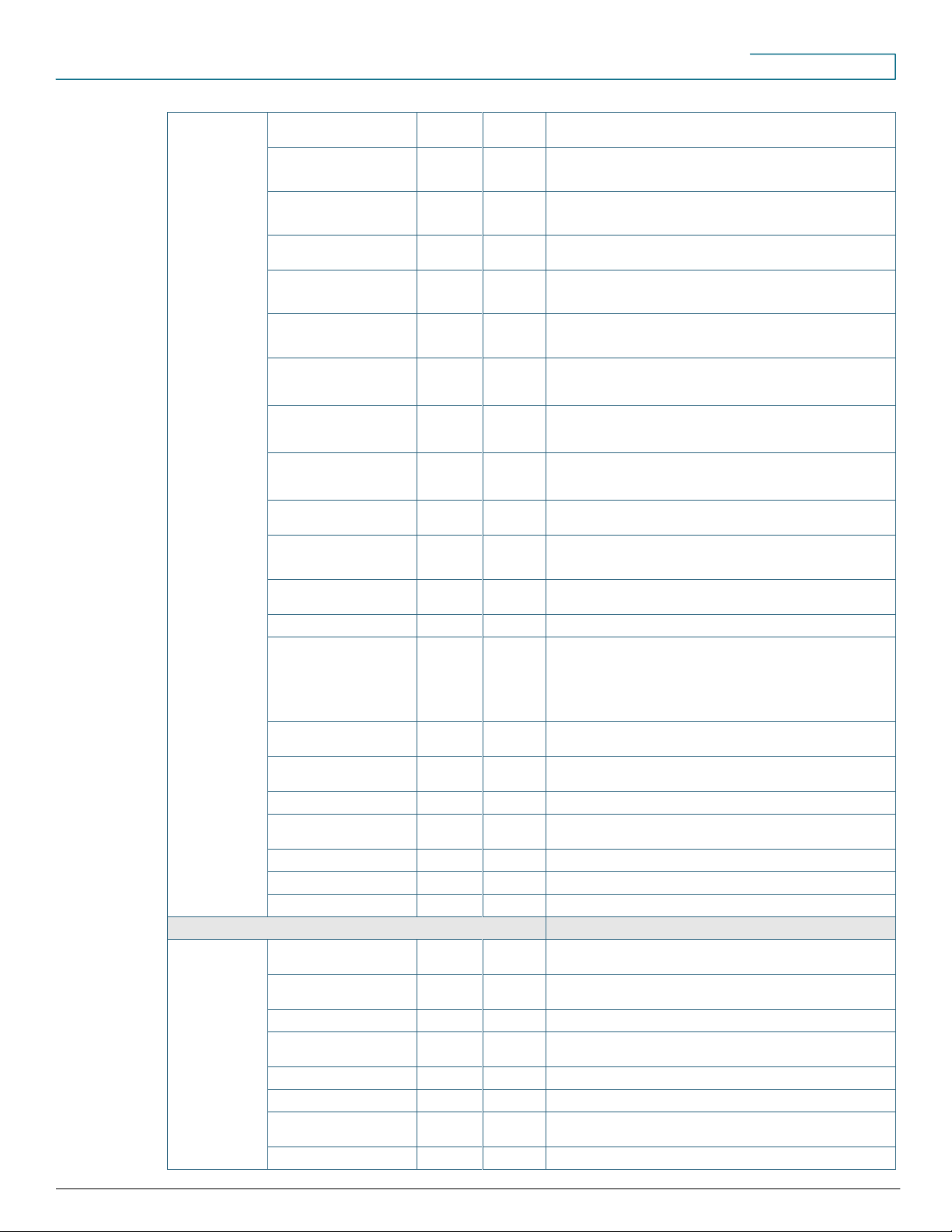
Paging groups
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) adds support for combined
paging groups with one level of nesting
Intercom (with or without
mute)
X X Including multiple intercom support and ability to configure intercom on
nonprimary buttons
Dialable intercom (with or
without mute, overlay option)
X X Dialable intercom on primary button is not supported.
Whisper intercom
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) adds whisper intercom support on
all buttons except the primary button.
Single Number Reach
(SNR)
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for SNR timeout
settings.
Conferencing
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for enabling and
disabling conference join and leave tones
Ad hoc conferencing
X X For UC540 system, max number of conferences is 24 (up to 8
concurrent users per conference). For UC 560 system, this limit is 56 (up
to 8 concurrent users per conference)
Meet-me conferencing
X X For UC540 system, max number of conferences is 6 (up to 32
concurrent users per conference). For UC560 system, this limit is 12 (up
to 32 concurrent users per conference)
cBarge and privacy
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) adds support for configuring
cBarge with or without Privacy button (requires shared octo-line
extensions on phones)
Basic automatic call
distribution
X X
Night service
X X Support for night service schedule, night service bell, night service call
forward, and night service toggle code
Phone services URL
provisioning
X X
Fax support
X X
T.37 fax to email
X Support for enabling voice mailboxes to receive incoming faxes, voice
and fax detection, fax printing, and integration with voicemail
notifications or IMAP to allow users to receiving email notifications with
faxes attached in TIFF format. Administrators can use the default
system prompts for voice and fax detection or record a custom
prompt.
T.38 fax relay
X X Supported for Cisco Certified SIP trunk providers. Generic SIP trunk
providers supported in Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.4.
Arc Express 2.1
compatibility
X X Arc Express client must be configured separately.
FXO hook flash
X X
Advanced FXO port settings
X Configure advanced FXO port settings, including supervisory
disconnect, audio, and timer settings.
Busy lamp field (BLF)
X X
Line monitoring
X X
Trunk monitors
X X
Users/Phones/Extensions
Multiple extensions per
phone
X X
Floating/phantom extensions
X Create extensions that are not associated with any phone. Within
Cisco Configuration Assistant, these are called floating extensions.
Extension mobility
X Support normal and shared line only.
Email and voicemail
Notifications
X
Shared line
X X
2 calls per line
X X
Phone display header
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) adds support for editing the
description displayed in the phone header
Overlay DN
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.5 adds support for configuring an
Page 6
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 27
overlay on the CO Line button. Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds
support for configuring overlay with intercom.
Octo-lines
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) adds support for octo-lines on
shared extensions
Busy line monitoring
X X
Custom button label
X X
PSTN line appearance
X X
Personal speed dials
X X
System speed dials
X X
Soft key templates
X X Phone templates are not customizable through Cisco Configuration
Assistant.
Cisco CP-500G Series
X X
Cisco CP-500SG Series
X X
Cisco SPA300 Series
phones
X X
Cisco SPA525G wireless IP
phone
X X
Cisco SPA525G2 wireless
IP phones
X X
Cisco 7915 and 7916
sidecar
X X
Cisco 7937 conference
station
X X
Cisco Unified IP Phones
6900 Series
X Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for Cisco Unified IP
Phone 6901, 6911, 6921, 6941, and 6961 models only
Cisco SPA500 Series IP
phones
X X
Cisco SPA500S sidecar
X X
Voicemail
Personal mailbox
X X
General delivery mailbox
X X
Floating/phantom mailbox
X Assign a voice mailbox to an extension that is not associated with a
physical phone (floating extension).
Unified messaging (Internet
Message Access Protocol
[IMAP])
X X Automatically configured by Cisco Configuration Assistant. IMAP client
must be configured separately.
VoiceView Express
X X
Voicemail notification
X Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for voicemail
notifications sent to phone or email. Voicemail notifications can be
used in conjunction with T.37 fax-to-mail to enable users to receive
incoming faxes as attachments.
Greeting
X X
Call recording
X X Support for Live Record softkey. Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0
adds support for Live Record beep tone settings.
Direct transfer to voicemail
X X
Play caller ID
X X
Auto Attendant (AA)
Multiple AAs
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant allows configuration of up to three AAs
on a single Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series.
Multilevel AA
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant allows configuration of up to three levels
of AA menus.
AA transfer script
customization
X X In Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5), the AA_SBCS_v03 AA script
becomes the default AA script, which supports configuration of an
optional drop-through number.
Separate prompts and
actions for open/closed
hours
X X
Page 7
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 27
Custom script management
X X Custom scripts can be uploaded. For custom scripts, only the AA
extension and PSTN main number can be configured using Cisco
Configuration Assistant.
Prompt management
X X AA prompt management allows assignment of prompt recording and
management privileges to users and configuration of prompt
management extension.
Holiday/business hours
X X Configure up to 4 separate business schedules; up to 26 holidays.
Night service schedule
X X AA closed hour prompts and actions are presented during night
service hours.
Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series Administration
Backup/restore of
configuration/data
X X Cisco Configuration Assistant can back up and restore both Cisco
Unified Communications 500 Series configuration and user data, such
as voicemails and passwords.
Reset to factory default
X X
Disk cleanup
X X
Cisco IOS® Software
upgrade
X X Drag and drop or through the Cisco Unified Communications 500
Series software pack upgrade.
Cisco Unified
Communications Manager
Express/Cisco Unity®
Express localization
X X Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series locale packs and language
files posted on free software download page.
Administrators can switch between active and alternate phone
languages and voicemail languages.
Phone load management
X X Phone loads should be in the phone load folder in Cisco Configuration
Assistant.
Drag-and-drop upgrades are supported for Cisco SPA 500 Series and
SPA 300 Series IP Phones.
Flash file management
X
X
Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0 adds support for uploading and
downloading files to the Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series
flash from the File Management window.
Music on hold (MOH)
X X
Cisco Unity Express
upgrade
X X Supported through Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series
software pack upgrade.
Cisco Unified
Communications 500 Series
license upgrade
X
X
License upgrade up to 32, 64, and 104 users, depending on
Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series platform.
Cisco UC540 and UC560 license upgrade through a product
authorization key (PAK).
Reboot phone from topology
view
X X
Display phone detailed
status GUI from topology
view
X X
Telephony setup wizard
X X Requires factory default Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series
VPN phone setup wizard
X X Step-by-step wizard for enabling and configuring SSL VPN client
settings for Cisco SPA525G and SPA525G2 phones (day 0 and day
2).
Cisco WebEx™
PhoneConnect
X X
Timecard View
X X
System Dashboard
X X
Network Topology View
X X
Network diagnostics
X X Ping, trace, DHCP bindings, and system status.
Voice diagnostics and
debugging
X X Collect per phone debugs for SIP, H.323, and Skinny Client Control
Protocol (SCCP) troubleshooting, perform T1/E1 loopback circuit
diagnostics.
Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) adds support for PCM capture,
SIP trunk registration diagnostics, and Cisco Unity Express
connectivity diagnostics.
Security diagnostics
X X Collect VPN and firewall/ NAT debug logs.
Expert mode telephony
monitoring and reporting
X X View detailed reports for phones and extensions, hunt groups, call
blast groups, TFTP server files, dial peers, translation profiles, SIP
Page 8
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 8 of 27
trunk status, phone templates, voicemail status, DSP status, and
software pack status.
Expert mode monitoring and
troubleshooting
X
X
Enter Cisco IOS Software and Cisco Unity Express exec mode
commands and view output.
View show command output for selected Cisco IOS Software and
Cisco Unity Express commands.
CLI postview
X X Enable display of Cisco IOS Software commands sent to Cisco Unified
Communications 500 Series when telephony configuration is applied.
Online Help
X X
Remote Teleworker Deployment
Soft phone (Cisco IP
Communicator)
X X
Cisco 871W Integrated
Services Router
X X EzVPN client on 871W, EzVPN server on Cisco Unified
Communications 500 Series
Cisco SR500 Series Secure
Routers
X X EzVPN client on 871W, EzVPN server on Cisco Unified
Communications 500 Series
Codec configuration
X X
Firewall/NAT Traversal
(MTP)
X X Configured automatically for Cisco IP Communicator phones in Cisco
Configuration Assistant
Transcoding
X X
VPN Phone Setup Wizard
X X Step-by-step wizard for enabling and configuring SSL VPN client
settings for Cisco SPA525G and SPA525G2 phones (day 0 and day
2)
Multisite SBCS Deployment
H.323 and SIP voice over IP
(VoIP) parameters
X X
Call admission control
(CAC)
X X
Dynamic DNS (DDNS)
X X
Quality of service (QoS)
traffic shaping
X X
Cisco Configuration Assistant Switch Feature Support
Category
Feature
v2.2(5)
v3.0
Description
Layer 2 Switching
Cisco Small Business ESW
500 Series Switches
X X Access the ESW 500 Series Switch Configuration Utility from the
Cisco Configuration Assistant Topology View to configure additional
features.
Cisco Catalyst® Express
500 Series Switches
X X
Spanning Tree Protocol
X
X
Catalyst Express 500 Series only
Fast convergence using 802.1w, enabled by default
Portfast: supported on “Desktop,” “Phone + Desktop,” “Printer,” and
“Server” Smartports roles
MAC addresses
X X Catalyst Express 500 Series only
Read-only display of MAC address table from switch
Virtual LANs (VLANs)
X X Up to 32 VLANs (1000 range) and support for 802.1Q trunking using
Cisco Smartports
Number and type of queues
X
X
4 queues per port
Shaped Round Robin (SRR) queuing
Cisco Configuration Assistant Switching Feature Support
Table 2 lists the switching features that are supported by Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) and Cisco
Configuration Assistant 3.0.
Table 2. Cisco Configuration Assistant Switch Feature Support
Page 9
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 27
Support for differentiated services code point (DSCP) and class of
service (CoS) using Cisco Smartports
Port grouping
X
X
Catalyst Express 500 Series only
Support for Cisco EtherChannel and IEEE 802.3ad
Up to 6 groups
Up to 8 ports per group
Smartports (Preset Cisco Recommended Network Enhancements, QoS, and Security)
Desktop
X
X
Optimized for desktop connectivity
Configurable VLAN setting
Port security enabled to limit unauthorized access to the network
IP phone plus desktop
X
X
Optimized QoS for IP phone plus desktop configurations
Voice traffic is placed on “Cisco-Voice” VLAN
Configurable data VLAN
QoS level assures VoIP traffic takes precedence
Port security enabled to limit unauthorized access to the network
Router
X X Configured for optimal connection to a router or firewall for WAN
connectivity
Switch
X
X
Configured as an uplink port to a backbone switch for fast
convergence
Enables 802.1Q trunking
Access point
X
X
Configured for optimal connection to a wireless access point
Configurable VLAN
Server
X
X
Catalyst Express 500 Series only
Can be classified as trusted, critical, business, or standard server:
●
Trusted: For use with Cisco Communications Manager Express;
same QoS setting as voice (VoIP traffic is prioritized)
●
Critical: For critical servers with QoS set higher than default
●
Business: Default setting; QoS higher than desktop Internet traffic
●
Standard: For servers set to same level as regular desktop
Internet traffic; configurable VLAN port security enabled to limit
unauthorized access to the network
Printer
X
X
Catalyst Express 500 Series only
QoS settings for “Printer” are the same as “Desktop,” “Access Point,”
and “Standard Server.”
Configurable VLAN
Port security enabled to limit unauthorized access to the network.
Guest
X
X
Catalyst Express 500 Series only
Guests are allowed access to the Internet, but not to the company
network.
All guest ports are placed on the “Cisco-Guest” VLAN.
Port security enabled to limit unauthorized access to the network.
Other X X
“Other” Smartports role allows for flexible connectivity of nonspecified
devices and diagnostic on ESW 500 Series.
Configurable VLAN
No security
No QoS policy
Diagnostic
X X Customers can connect diagnostics devices to monitor traffic on other
switches (configurable using Cisco Configuration Assistant only).
On ESW 500 Series switches, this functionality is provided by setting
the Smartports role to Other and using port mirroring.
Page 10

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 10 of 27
Switch Security
SSL X X
SSL support: Encrypts all HTTP traffic, allowing secure access to the
browser-based management GUI in the switch
Can be configured through Cisco Configuration Assistant; for Catalyst
Express 500 Series only
Security policy slider
X
X
Catalyst Express 500 Series only
Three security levels: Low, medium, and high (configurable using
Cisco Configuration Assistant only):
●
Low: For business environments where there is limited guest
access; limited number of devices are allowed per port (broadcast
storm control and port security enabled).
●
Medium: For business environments where security is important;
only authorized devices (by MAC address) are allowed on the
company network.
●
High: For business environments where security is critical; only
authorized devices (by MAC address) and authenticated users
(using IEEE 802.1x) are allowed on the company network.
Multicast
X
X
Available through Cisco Configuration Assistant for Catalyst Express
500 Series only
High-bandwidth video traffic is optimized so that it does not affect
other applications on the network
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) (v1, v2, and v3)
snooping: IGMP snooping constrains multicast traffic at Layer 2 by
configuring Layer 2 LAN ports dynamically to forward multicast traffic
only to those ports that want to receive it.
Cisco Configuration Assistant Wireless Feature Support
Category
Feature
v2.2(5)
v3.0
Description
Basic Device Configuration
Host name
X X Cisco 521 Wireless Express Access Point, Cisco AP541N Wireless
Access Pont
System time
X X Cisco 521, AP541N
Daylight saving time
X X Cisco 521, AP541N
Time zone
X X Cisco 521, AP541N
NTP X X
Cisco 521, AP541N
HTTP authentication
X X Cisco 521, AP541N
Enable password
X X Cisco 521, AP541N
Local user name and
password
X X Cisco 521, AP541N
Telnet and console
passwords
X X Cisco 521 only
WLAN
X X For Cisco 521, VLAN is created as part of WLANs. Maximum three
WLANs supported; AP541N
Data, voice, and guest
VLANs usability
X X Cisco 526 Wireless Express Mobility Controller, AP541N
Save configuration
X X
WLAN Deployment Scenarios
Wireless Voice Setup
Wizard
X X Simple setup wizard for configuring wireless LAN security, QoS for
Cisco Unified Communications 500W, 521, or AP541N and SPA525G
wireless IP phones
Data WLAN usability
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x, AP541N
Cisco Configuration Assistant Wireless Feature Support
Table 3 lists the wireless features that are supported by Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) and Cisco Configuration
Assistant 3.0.
Table 3. Cisco Configuration Assistant Wireless Feature Support
Page 11

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 11 of 27
Voice WLAN usability
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x, AP541N
Guest VLAN usability
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x, AP541N
Secure authentication
X X Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Extensible Authentication protocol
(EAP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), WPA Preshare Key (WPAPSK), WPA2, WPA2-PSK, MAC, MAC+EAP, AP541
Web authentication
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x
Fast roaming (Cisco
Centralized Key
Management)
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x
Voice CAC
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x
Support for 10 autonomous
access points
X X Cisco 526 controller, AP541N
WLAN Users
Guest user
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x
Nonguest user
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x
Web login page
X X Cisco 526 controller only with version 4.2.x.x; both internal and
customized web login page
Convert to LAP
Convert authoritative access
point (AAP) to lightweight
access point (LAP)
X X Cisco 521 only
Reports
Inventory
X X Cisco 521 LAPs are displayed under their respective Cisco 526
controller, AP541N
Wireless radios
X X Cisco 526 controller, AP541N
Wireless clients
X X Cisco 526 controller, AP541N
Views
Topology
X X
Front panel view
X X Cisco 526 controller only
Monitor
Events
X X Includes acknowledgments
System messages
X X
Maintenance
Software upgrade
X X
Configuration archive
X X Includes RMA setup
Restart (that is, reboot)
X X
Reset to factory default
X X
Upload troubleshooting log
X X
Out-of-Box Setup
Wireless Setup Wizard
X X Cisco 521, AP541N, SPA525G, and SPA525G2 IP phones operating
in Wireless-G mode
Cisco Configuration Assistant Security Feature Support
Table 4 lists the security features that are supported by Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2(5) and Cisco Configuration
Assistant 3.0.
Page 12

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 12 of 27
Cisco Configuration Assistant Security Feature Support
Category
Feature
v 2.2(5)
v3.0
Description
Firewall
Application firewall
X
X
Provides high, medium, and low security levels for firewall policy
settings to enable accelerated and easy deployment:
●
Low: For business environments that do not need to track peer
to peer (P2P) and IM applications on the network or check for
protocol conformance
●
Medium: For business environments where security is
important and there is a need to track the use of IM and P2P
applications and check for HTTP and email protocol
conformance
●
High: For business environments where security is critical, and
there is a need for protocol anomaly detection services to drop
nonconformant HTTP and email traffic and prevent use of P2P
and IM applications
Zone-based firewall
X X Advanced firewall supported by default on Cisco SR500 Series
Secure Router.
URL filtering
X X Supported on Cisco SR500 Series Secure Router only.
Intrusion prevention system
(IPS)
X X Supported on Cisco SR500 Series Secure Router only.
VPN
Cisco Easy VPN Remote
X X Scalable, easy-to-manage, secure remote access for teleworkers
for Cisco SR500 Series
Cisco Easy VPN Server
X X Offers wizard-based configuration of remote-access VPN server
configuration for Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
VPN
X X
Split tunneling
X X
Disable split tunneling
X X Uses Dynamic Virtual Tunnel Interface (DVTI) to allow
WAN/Internet access only from VPN hub site
Security Features
Security Setup Wizard
X X Cisco SA500 software version 1.1.42 and earlier are not supported
by Cisco Configuration Assistant.
All other SA500 features are configured through the SA500
Configuration Utility, which is accessible from the Cisco
Configuration Assistant Topology view.
SSL- and SSH v2-based
secure remote access
X X Provides for secure management between PC and Cisco Unified
Communications 500 Series.
Network Address Translation
(NAT)
X X 1-to-1 static port mapping for TCP and User Datagram Protocol
(UDP) ports. VoIP pass-through enabled by default on Cisco
SR500 Series Secure Router. Cisco Configuration Assistant 3.0
adds support for 1-to-many static NAT mappings.
Remove NAT and firewall
X X Remove NAT and firewall from Cisco Unified Communications 500
Series and Cisco SR500 Series Secure Router for deployments in
network with existing firewall
DMZ X X
A DMZ network enables Internet users to access a company’s
public servers, including web and FTP servers, while maintaining
security for the company’s private LAN.
Security audit
X
X
Assesses vulnerability of existing Cisco Unified Communications
500 Series and Cisco SR500 Series Secure Router.
Provides quick compliance with best-practices (Cisco Technical
Assistance Center [TAC], ICSA recommendations) security policies
for Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series and Cisco SR500
Series Secure Router.
Security diagnostics
X X Collect firewall/NAT and VPN debug logs.
Monitoring
X X EzVPN client and server, site-to-site VPN, SSL VPN, firewall, NAT,
and VPN status reports.
Table 4. Cisco Configuration Assistant Security Feature Support
Page 13

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 13 of 27
Video Monitoring/IP Cameras
Cisco PVC2300 and
WVC2300 Business Internet
Video Camera support
X X
Video monitor setup wizard
X X Step-by-step wizard for enabling viewing of video from Cisco
PVC2300 or WVC2300 Business Internet Video Cameras on
SPA525G and SPA525G2 IP phones
Bonjour discovery
X X Ability to discover Cisco and third-party devices running the
Bonjour protocol. Devices that can run Bonjour include video
cameras and network printers. Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.2
can launch the web GUI of Bonjour discovered devices that are not
natively supported in Cisco Configuration Assistant.
Page 14

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 14 of 27
Feature
Category
Description
Abbreviated
dialing speed
dial
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This feature allows you to quickly dial a phone number by entering an assigned index code (1-99) on the phone
keypad. Abbreviated dialing can be useful if your phone model does not provide speed-dial buttons or if you want
to configure more speed-dial numbers than the number of speed-dial buttons on your phone.
You can assign index codes from the User Options webpage or on the phone using Services, My Phone Apps, or
Speed Dial.
The associated softkey is AbbrDial.
Access to a
greeting
management
system from
the telephone
user interface
(TUI)
Voicemail
Subscribers with administrative privileges can access a greeting management system (GMS) for recording
alternate greetings and prompts through their phone. This feature is also referred to as Administration via
Telephone (AvT) or prompt management. Administrators can change Auto Attendant greetings remotely for snow
days, for example.
Account code
entry
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Account code entry allows you to enter account codes during call setup or when connected to an active call using
the Acct softkey (a nonforced option). Account codes are inserted into call detail records (CDRs) on the Cisco
Unified Communications 500 Series for Small Business for later interpretation by billing software.
The account code also appears in the “account-code” attribute of the CDR. To enter an account code during call
setup or when in a connected state, press the Acct softkey, enter the account code using the phone keypad, and
then press the # key to notify the Cisco Unified Communications 500 that you have entered the last digit of the
code. The Cisco Unified Communications 500 processes the account code digits upon receipt of the #.
Ad hoc
conferencing
Voice-system
features
You can have multiparty impromptu conferencing. Conference calls can include other IP phones, analog phones,
or external calls through SIP or PSTN trunks. With an analog phone you can set up only three-party conferences.
Agent
availability and
hunt groups
Voice-system
features
Three options increase the flexibility of hunt groups:
●
Dynamic hunt-group membership allows an authorized agent to join and leave hunt groups.
●
Agent status control allows an agent to manually activate a toggle to temporarily enter a not-ready state, in
which hunt-group calls bypass the agent’s phone.
●
Automatic agent status not-ready automatically puts an agent’s phone in a not-ready state after a specified
number of hunt-group calls are unanswered by the agent’s phone.
Alternate
automatedattendant
greetings and
prompts
Voicemail
You can record alternate automated-attendant greetings and prompts that you can upload or download as
needed. These alternate greetings and prompts are in addition to the default greetings and prompts that ship with
the Cisco Unified Communications 500.
Analog phone
support
Voice-system
features
You can add analog phones for fax machines or other devices that you can connect to built-in analog station
(FXS) ports on the Cisco Unified Communications 500. In user mode, these analog FXS ports require a user
license and can use IP phone features such as voicemail and conferencing. In common area or fax mode, these
ports do not consume a user license and are restricted to making and receiving calls.
You can connect additional analog phones using an analog telephone adapter (ATA).
ATA (Cisco
Analog
Telephone
Adapters)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The Cisco ATA analog telephone adaptors are handset-to-Ethernet adaptors that allow regular analog telephones
to operate on IP-based telephony networks.
Audio paging
Voice-system
features
Audio paging provides a one-to-many voice message to phones that are designated to receive paging. When a
caller dials the paging number, each idle IP phone that is configured with the paging number automatically
answers using its speakerphone. Only the voice from the phone originating the page is heard. The phones
receiving the audio page can only listen.
Automatic
agent status
not-ready;
electronic
phone
(ephone) hunt
groups
Voice-system
features
This feature automatically puts an agent’s phone in a not-ready state after a specified number of hunt-group calls
are unanswered by the agent. Typically used with basic automatic call distributors (BACDs), this feature is also
called auto logout.
Automatic line
selection
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Picking up the handset answers the first ringing line or, if no line is ringing, selects the first idle line.
Section Two: SBCS Feature Descriptions
Table 5 lists and describes all of the available Cisco Smart Business Communications System features. Not all of
these features require configuration.
Table 5. SBCS Feature Descriptions
Page 15

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 15 of 27
Auto Attendant
Voicemail
The Auto Attendant provided with Cisco Unified Communications 500 provides simplified self-service for callers by
allowing them to quickly reach a person, hear an audio directory, or hear recorded guidance without the
assistance of an operator. It is navigated using touch-tone entries from your phone. The Auto Attendant can have
different options based on time of day and holiday schedules. It can also redirect to another menu layer in the
Auto Attendant.
Basic
Automated Call
Distribution
(Basic ACD)
Voice System
Features
Basic ACD provides automatic answering and distribution of incoming calls through interactive menus and hunt
groups. A Basic ACD application consists of one call queue service and up to 10 Basic ACD services. For each
Basic ACD service, users configure a pilot number for the service, hunt group parameters, prompts, destination
for unanswered calls, timeout, number of retries, and other settings.
The Basic ACD call flow implemented in Configuration Assistant is limited to drop- through mode, in which the
Auto Attendant serves as the top-level entry point and control is transferred to Basic ACD for second-level menu
actions.
Barge,
Conference
Barge (cBarge)
Voice-system
features
The barge feature allows phone users who share a directory number to join an active call on the shared line by
pressing a softkey. When the initiator barges into a call, a conference is created between the barge initiator, the
target party, and the other party connected in the call. Parties see the call information on their phones and, if the
conference join tone is configured, they hear a tone.
If a phone that is using the shared line has privacy enabled, call information does not appear on the other phones
that share the line and the call cannot be barged. Connected parties hear the barge tone (single beep) after the
conference is set up. When a party leaves the conference, a barge leave tone is played to the remaining parties.
Billing records
Voice-system
features
The accounting process collects accounting data for each call leg created on the Cisco Unified Communications
500. You can use this information for activities such as generating billing records and network analysis. The
feature captures accounting data in the form of CDRs containing attributes defined by Cisco. The feature can
send CDRs to a RADIUS server, syslog server, or to a file in comma-separated value (CSV) format for storing to
flash memory or an FTP server.
Blast hunt
group
Voice-system
features
With this feature enabled, incoming calls simultaneously ring multiple phones or multiple destinations, including
PSTN, SIP trunk, and multisite numbers. This feature is also called parallel hunt groups. In Cisco Unified
Communications 500 Software Pack 7.0.2 and later versions, this feature is supported across all IP phones.
Busy lamp
field (BLF)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This feature provides a visible line status indicating whether or not the line is in use. A monitor-line lamp is off or
unlit only when its line is in the idle call state. The idle state occurs before a call is made and after a call is
completed. For all other call states, the monitor line lamp is lit. A receptionist who monitors the line can see that it
is in use and can decide not to send additional calls to that extension, assuming that other transfer and forwarding
options are available. BLF for phones is also available; refer to the BLF notification feature that follows.
BLF
notification
(“watch
mode”)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
A line button that is configured for watch mode on one phone provides BLF notification for all lines on another
phone (watched phone) for which the watched directory number is the primary line. Watch mode allows a phone
user, such as a receptionist, to visually monitor the in-use status of an individual phone. The line and line button
on the watching phone are available in watch mode for visual status only. Calls cannot be made or received using
a line button that has been set in watch mode. Incoming calls on a line button that is in watch mode do not ring
and do not display caller ID or call-waiting caller ID.
Blocking caller
ID
Voice-system
features
You can selectively choose to block your name or number on outbound calls. Caller ID blocking on outbound calls
does not apply to PSTN calls through analog FXO ports. Caller ID features on analog FXO-connected subscriber
lines are under the control of the PSTN service provider, who may require you to use the provider’s caller ID
blocking service.
Busy timeout
Voice-system
features
Busy timeout sets the length of time after which calls that are transferred to busy destinations are disconnected.
Call forwarding
Voice-system
features
Call forwarding allows you to divert incoming calls to an extension to a specific destination under different
conditions:
●
All calls: All incoming calls are diverted based on destination configured by the administrator or entered by
a user.
●
No answer: All incoming calls are diverted when the extension does not answer the call for a specific timeout
to a destination such as voicemail configured by the administrator.
●
Busy: All incoming calls are diverted when the extension is busy and call waiting is not active to a destination
such as voicemail configured by the administrator.
●
Night service: All incoming calls are automatically diverted during designated hours, defined by night service
schedule, to a destination such as an automated attendant configured by the administrator.
An extension can have all four types of call forwarding defined at the same time, with a different forwarding
destination defined for each type of call forwarding.
Call history
Voice-system
features
This feature helps collect call-detail information for reporting activities such as generating billing records and voice
network analysis. The system captures accounting data in the form of CDRs that can be stored as a text file (CSV
format) for storing to flash memory or exporting to an FTP server for third-party application integration.
Call hold
Voice-system
features
The system by default allows you to place a call on hold by using the Hold softkey on any active call. For calls
placed on hold, the system can enable the optional on-hold indicator, which generates a ring burst on idle phones
or call-waiting beeps for phones on another call.
Call hunt
Voice-system
features
Call hunt allows you to use the same extensions on multiples phones or lines on the same phone to provide
coverage for a single called number. It uses preference to control the order in which the extensions are matched
and a huntstop option to determine when the call should be forwarded to the no answer destination.
Page 16

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 16 of 27
Call park
Voice-system
features
Call park allows you to place a call on hold at a special extension called “park slot” such that you can retrieve the
parked call from any other phone in the system. The system supports basic call park; directed call park, where
you can transfer the call to a predefined park-slot extension; and dedicated call park, which reserves specific callpark slots for a specific phone.
Call pickup
Voice-system
features
Call pickup allows you to answer a call that is ringing on another phone. The system supports three types of call
pickup: ● Directed call pickup, where you can pick up a ringing call on another phone
●
Local group pickup, where you can pick up a ringing call on another phone by pressing the GPickup softkey
and then the asterisk (*) if both phones are in the same pickup group
●
Group pickup, where you can answer a ringing phone in a different pickup group by pressing the GPickUp
softkey and then dialing the pickup group number
Call transfer
Voice-system
features
Call transfer allows you to transfer the current active call on your phone to a different destination. Call transfers
can be blind, where the transferring extension connects you to the target destination before the target phone
rings, or consultative, where the transferring extension either connects you to a ringing phone or speaks with the
target destination before connecting you to the target.
Call waiting
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Call waiting allows you to be alerted when you receive an incoming call while you are on another call. While you
are on an active call, you get an audible call-waiting tone such as beep or ring and also visually see the callingparty information on your phone screen.
Call waiting for
overlaid
ephone
directorynumber
extensions
Users,
phones, and
extensions
For extensions in an overlay set (refer to “Ephone-dn, overlaid” later in this table), by default call waiting is
disabled. If enabled, call waiting causes idle phones to ring and phones with active calls to generate an audible
call-waiting notification such as a beep or ring along with visual call-waiting notification by displaying caller ID on
the phone screen.
Call-waiting
beep
Users,
phones, and
extensions
By default, the audible indication for call waiting on the system is to use beeps. The administrator can turn this
indication off if required.
Called-name
display
Users,
phones, and
extensions
When phone users answer calls for several different departments, it is often helpful for them to see a display of
the name of the called extension, rather than the number. The called-name display feature can display either the
name associated with an extension in a local directory or the name associated with an overlay extension.
Caller ID
blocking
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can block the display of caller ID information for outgoing calls from an extension on a per-call basis, allowing
you to maintain your privacy when necessary. The system administrator defines a code for caller ID blocking,
which you then dial before making any call on which you do not want your caller ID sent. Alternatively, the system
can also block caller ID on specific dial patterns or trunks if required. Outbound caller ID blocking does depend on
the PSTN trunks being used - you cannot use it on analog lines because the control of caller ID in this case is with
the service provider.
Call detail
records
Voice-system
features
Refer to “Call history”
Channel
huntstop
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The system by default allows two calls per line on each phone. If this feature is enabled, a second incoming call is
sent to a line to the call-forward busy target if an active call is already on that line. (Refer also to “Call hunt.”)
Cisco IP
Communicator
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Cisco IP Communicator is the Windows softphone client that is supported on the system. It typically acts as a
remote teleworker phone for users at remote sites (teleworkers).
Conference
gain control
Voice-system
features
Gain control on conference calls keeps the volume for callers at the same volume for ease of use.
Conferencing
Voice-system
features
Conferencing allows you to connect three or more parties in a telephone conversation. Conferences can be
hardware- or software-based, depending on the number of parties.
Consulting call
transfers (SIP
call control
only)
Voice-system
features
Voicemail permits attended and semiattended call-transfer modes in addition to blind transfers. You cannot
configure this feature through the GUI.
Dedicated FXO
trunk lines
Voice-system
features
You can configure IP phones running SCCP to have buttons for dedicated PSTN FXO trunk lines, also known as
FXO lines. FXO lines are ideal for companies whose employees require private PSTN numbers. FXO lines can
use PSTN service provider voicemail: when the line button is pressed, the line is seized, allowing you to hear the
stutter dial tone provided by the PSTN to indicate that voice messages are available.
Because FXO lines behave as private lines, you do not have to dial a prefix, such as 9 or 8, to reach an outside
line. To reach phone users within the company, FXO-line users must dial numbers that use the company’s PSTN
number. For calls to non-PSTN destinations, such as local IP phones, a second directory number must be
provisioned.
Calls placed to or received on an FXO line have restricted Cisco Unified Communications 500 services and
cannot be transferred by the application. However, phone users are able to access hookflash-controlled PSTN
services using the Flash softkey.
Page 17

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 17 of 27
DHCP setup
Voice-system
features
When a Cisco Unified IP Phone is connected to the Cisco Unified Communications 500 system, it automatically
queries for a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server (onboard or external to the application). The DHCP
server responds by assigning an IP address to the Cisco Unified IP Phone and providing the IP address of the
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server through DHCP option 150. Then the phone registers with the Cisco
Unified Communications 500 and attempts to get configuration and phone firmware files from the TFTP server.
Differentiated
Services Code
Point
Voice-system
features
DSCP packet marking specifies the class of service for each packet. Cisco Unified IP Phones get their DSCP
information from the configuration file that is downloaded to the device.
Directed call
pickup
Voice-system
features
Any local phone user can pick up a ringing call on another phone by pressing a softkey and then dialing the
extension. You do not need to belong to a pickup group to use this method. The softkey that you press, either
GPickUp or PickUp, depends on your configuration.
Directories
Voice-system
features
Local, called-name display, and directory search use directory services.
Called-name
display
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The called-name display feature can display either of the following types of names:
●
Name for a directory number in a local directory
●
Name associated with an overlay directory number
Calls to the first directory number in a set of overlay numbers display a caller ID. Calls to the remaining directory
numbers in the overlay set display the name associated with the directory number.
Display phone
header bar
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can customize the content of an IP phone header bar, which is the top line of the IP phone display.
The IP phone header bar, or top line, of a Cisco Unified IP Phone normally replicates the text that appears next to
the first line button. The header bar can contain a user-definable message instead of the extension number. For
example, the header bar can be used to display a name or the full E.164 number of the phone. If no description is
specified, the header bar replicates the extension number that appears next to the first button on the phone.
Phone systemmessage
display
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The system-message display feature allows you to specify a custom text or display messages to appear in the
lower part of the display window on display-capable IP phones. If you do not set a custom text or display
message, a default message is displayed.
Distinctive ring
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Distinctive ring is used to identify internal and external incoming calls. An internal call is defined as a call
originating from any Cisco Unified IP Phone that is registered in the Cisco Unified Communications 500 or is
routed through the local FXS port.
Do not disturb
(DND)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The DND feature prevents incoming calls from audibly ringing a phone. When DND is enabled, the phone flashes
an alert to visually indicate an incoming call instead of ringing, and you can answer the call if desired.
DSP
Voice-system
features
A digital-signal-processor (DSP) chip provides analog FXS and FXO and digital BRI/PRI to IP connectivity, in
addition to conferencing features for audio calls.
Direct station
select (DSS)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
DSS allows a multibutton phone user to transfer calls to an idle monitored line by pressing the Transfer key and
the appropriate monitored line button. A monitored line is one that appears on two phones; one phone can use the
line to make and receive calls and the other phone simply monitors whether the line is in use. Consultative
transfers can occur during DSS transfers (transferring calls to idle monitored lines).
Dual-tone
multifrequency
(DTMF) relay
(SIP call
control only)
Voice-system
features
DTMF relay handles incoming and outgoing DTMF signals for SIP calls.
DTMF relay for
H.323
networks
Voice-system
features
For IP phones on H.323 networks, DTMF is relayed using the H.245 alphanumeric method, which is defined by
the ITU H.245 standard. This method separates DTMF digits from the voice stream and sends them as ASCII
characters in H.245 user input indication messages through the H.245 signaling channel instead of the Real-Time
Transport Protocol (RTP) channel.
DTMF relay for
SIP trunks
Voice-system
features
To use remote voicemail or interactive-voice-response (IVR) applications on SIP networks from Cisco Unified
Communications 500 phones, the DTMF digits used by these phones must be converted to the RFC 2833 in-band
DTMF relay mechanism used by SIP phones. The SIP DTMF relay method is needed in the following situations:
●
When SIP is used to connect a Cisco Unified Communications 500 system to a remote SIP-based IVR or
voicemail applications
●
When SIP is used to connect a Cisco Unified Communications 500 system to a remote SIP-PSTN voice
gateway that goes through the PSTN to a voicemail or IVR application; SIP phones natively support in-band
DTMF relay as specified in RFC 2833
Encrypting
stored
personal
identification
numbers
(PINs)
Voice-system
features
Voicemail PIN codes are stored in encrypted form for security reasons.
Ephone
Voice-system
features
Ephone is a term for Cisco Unified Communications 500 configuration for phones using SCCP or the singlechannel-per-carrier (SCPC) protocol.
Extension
mobility
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Extension mobility provides the benefit of phone mobility for end users. It offers a user login service that allows
phone users to temporarily access a physical phone other than their own phone and use their personal settings,
such as directory number, speed-dial lists, and services, as if the phone were their own desk phone. The phone
Page 18

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 18 of 27
user can make and receive calls on that phone using the same personal directory number as on their own desk
phone.
Hunt groups
(ephone-hunt)
Voice-system
features
Hunt groups allow you to direct incoming calls to a specific number (pilot number) to a defined group of extension
numbers. There are four different types of hunt groups: sequential, peer, longest-idle, and parallel. Each type uses
a different strategy to determine the first number that rings for successive calls to the pilot number, as described
later in the table.
ephone-dn
overview
Voice-system
features
You can associate buttons on a phone with a line. Lines are of various types; some allow only a single call,
whereas others allow two or more calls. You can associate a phone with multiple line buttons with multiple lines,
allowing one phone to have multiple numbers. You can also share a given line across multiple phones, allowing
one number to ring multiple phones.
ephone-dn,
overlay
Voice-system
features
Overlaid lines allow you to increase the capacity of a line to up to 25 simultaneous calls. This feature is useful in a
helpdesk- or call center-like setup where calls to a single number are answered by multiple people at different
phones.
Feature access
code (FAC)
Voice-system
features
FACs are special patterns of characters that are dialed from a telephone keypad to invoke particular features. For
example, you might press **1, and then press 2345 to forward all incoming calls to extension 2345. FAC is
typically used only on an analog phone that does not have softkey.
Fax
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The fax feature allows the voicemail system to include fax-machine support using analog (FXS) lines. Fax traffic is
handled using SCCP and pass-through by default, or it can be set up for T.37 or T.38 with support for G2 and G3
speeds.
Fax relay
Voice-system
features
The fax-relay feature allows two fax machines to exchange faxes over an IP network. It recognizes that a call is a
fax and not a voice call, and by doing so it provides a more robust transport of the facsimile data.
Feature ring
Users,
phones, and
extensions
When a phone has more than one line associated with it, you can configure one of the lines with a feature ring.
The feature ring allows you to easily recognize that an incoming call is ringing a specific line.
Fixed holidays
Voice-system
features
The Auto Attendant greetings are controlled by a calendar. You can identify certain days as fixed holidays
because they fall on the same date every year. On holidays the Auto Attendant plays a greeting that is appropriate
for a day when the business is closed.
Fixed line and
feature button
set
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G has a large number of buttons. You can select from two fixed button-layout
formats to assign functions to certain line buttons on the phone to support key-system phone behavior.
Flash softkey
and FXO
hookflash
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The Flash softkey provides hookflash functions for calls made on analog trunks. Certain PSTN services, such as
three-way calling and call waiting, require hookflash intervention from a phone user. The Flash softkey provides
this function for IP phones.
Forwarding
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Call forwarding diverts calls to an alternative specified number under one or more of the following conditions:
●
Always
●
Upon no answer
●
Upon busy
●
When night service is active
FXS (analog)
ports
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Call processing supports FXS analog phone ports. FXS ports behave like a regular phone line from the phone
company and allow you to connect a regular analog phone or fax machine.
Group call
pickup
Voice-system
features
With group call pickup, you can answer a ringing phone in any pickup group by pressing the GPickUp softkey and
then dialing the pickup group number. If only one pickup group is defined in the Cisco Unified Communications
500 system, you can pick up the call simply by pressing the GPickUp softkey. You do not need to belong to a
pickup group to use this method.
Hairpin call
routing
Voice-system
features
The Cisco Unified Communications 500 supports hairpin call routing. When a call that originally terminated on a
FXO port from the PSTN is transferred or forwarded by a phone back out to the PSTN (for example, an outside
caller makes a call to a Cisco Unified Communications 500 phone and the call is forwarded to the callee’s cell
phone), the application reoriginates the call and routes it back out to the PSTN through another FXO port. This
looping back from and to the PSTN is called hairpinning. Hairpin routing of transferred and forwarded calls also
causes the generation of separate billing records for each call leg, so that the transferred or forwarded call leg is
typically billed to the user who initiates the transfer or forward.
Hardwarebased
conferencing
Voice-system
features
Conferencing allows you to connect three or more parties in a telephone conversation. Conferences can be
hardware- or software-based, depending on the number of parties. Hardware-based Ad Hoc conferencing
(maximum of 8 parties) uses DSPs to allow more parties than software-based Ad Hoc conferencing, which allows
3 parties only. Meet-me hardware-based conferences (maximum of 32 parties) are created by parties calling a
designated conference number. If you configure software-based conferencing, you cannot have meet-me
conferences.
Header-bar
display
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The header-bar display is the text on the top line of the IP phone display.
Historical
reports
Voice-system
features
Historical reports refers to the ability of the Cisco Unified Communications 500 to provide reports about call
activities and application activities on the system.
Page 19

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 19 of 27
Hold
Users,
phones, and
extensions
When a call is in progress, you can use the Hold softkey to place the call on hold. The person on the other end
typically hears music while on hold. Pressing Resume reconnects to the caller.
Hunt groups
Voice-system
features
Hunt groups allow you to direct incoming calls to a specific number (pilot number) to a defined group of extension
numbers.
Password and
PIN security
protection
Voice-system
features
This feature provides both temporary and permanent lockout for passwords and PINs to help prevent security
breaches; it includes set minimum lengths and expiry times for passwords and PINs.
Integrated
messaging
Voice-system
features
Cisco Unified Communications 500 voicemail subscribers can access and manage their voice and fax messages
using an Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)-enabled email client such as Microsoft Outlook and Outlook
Express. Integrated messaging brings voice, fax, and email together at the email client.
Intercom lines
Users,
phones, and
extensions
An intercom line is a dedicated two-way audio path between two phones. The Cisco Unified Communications 500
supports intercom functions for one-way and press-to-answer voice connections using a dedicated pair of
intercom directory numbers on two phones that speed-dial each other.
When you press an intercom speed-dial button, a call is speed-dialed to the directory number that is the other half
of the dedicated pair. The called phone automatically answers the call in speakerphone mode with mute activated,
providing a one-way voice path from the initiator to the recipient. A beep is sounded when the call is
autoanswered to alert the recipient to the incoming call. To respond to the intercom call and open a two-way voice
path, the recipient deactivates the mute function by pressing the Mute button.
Interdigit
timeout
Voice-system
features
Interdigit timeout is the number of seconds the system waits between dialed digits. The default is 10 seconds.
International
languages and
tones
Users,
phones, and
extensions
International languages and tones refer to the language used for text displays and the country-specific tones and
cadences required for connection to the local telephone network.
Key system
Voice-system
features
In a key system, most phones have nearly identical configurations, in which each phone can answer any incoming
PSTN call on any line without the aid of a receptionist, an automated-attendant service, or (expensive) directinward-dialing (DID) lines. Also, the lines act as shared lines - you can put a call on hold on one phone and
resume the call on another phone without invoking call transfer.
Keyswitch
telephone
system
Voice-system
features
This Cisco Unified Communications 500 configuration option sets the system up to act as a key system; refer also
to “Key system” and “Dedicated FXO trunk lines.”
Languages and
tones
Voice-system
features
Refer to “International languages and tones.”
Leaving
multiple voice
messages in
the same
session
Voice-system
features
You can leave multiple voice messages for the same or different subscribers without having to hang up and call
back to the system each time.
License
upgrades
Voice-system
features
An enforced system determines how many phones can register to the system using the Cisco Licensing System.
Customers wanting additional phones can purchase a software license upgrade, receive a PAK ID, register this
PAK ID on Cisco.com, and receive a license file by email (or within Cisco Configuration Assistant); the file is
applied to the system, stored in ROM, and used to allow additional phones to connect or register.
Live record
Applications
The live-record feature enables IP phone users in a Cisco Unified Communications 500 system to record a phone
conversation with the Cisco Unified Communications 500 voicemail system. Callers will hear a brief pause and
optional tone at the start of call recording. By option (required in some states or countries), an audible notification,
by either announcement or periodic beep, alerts participants that the conversation is being recorded.
Live reply
Voice-system
features
Live reply enables voicemail subscribers to make a phone call to the sender of a voice message while listening to
the message by pressing 4-4.
Local directory
Voice-system
features
The local directory lists all internal users with extension number by name plus the option to add 250 external
additional names and phone numbers that a user can search then autodial using the IP Phone display.
Local group
pickup
Voice-system
features
You can pick up another phone ringing in the same group without dialing the group number.
Locale installer
Voice-system
features
You can easily add new IP phone country locales (text on display phones plus tones heard).
Longest-idle
ephone hunt
groups
Voice-system
features
New calls to this hunt-group type ring the directory number that has been idle for the longest duration. An option is
for the phone instead of the directory number to be used for timing. This feature is used with BACDs.
Manual backup
and restore
Voice-system
features
Cisco Unified Communications 500 configuration includes backing up voicemail using Cisco Configuration
Assistant by choosing the backup option. Scheduled backups are not currently supported.
Maximum calls
per button
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can configure each button on an IP phone to handle one to eight calls at one time. Only one call is active;
other states include call waiting, hold, and hold and place new call. The Cisco Unified IP Phone 7940, 7960, and
7970 models support one to eight calls per button; the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931 supports only one call; and
the Cisco Unified Communications 500 Series phones support one or two calls per button.
Meet-me
conference
Voice-system
features
A meet-me conference is a voice conference bridge initiated by one IP phone user, where other users (internal or
external by DID or Auto Attendant) join. No scheduling or password option exists for meet-me conferencing. Up to
32 phones can join a single meet-me session on Cisco Unified Communications 500.
Page 20

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 20 of 27
Message
properties
(envelope)
customization
Voice-system
features
This systemwide option lets you choose the information about each voicemail message that is played (envelope
information) before the message is played. Options include sender, time and date, receive date (if more than 30
minutes from send time), message number, priority, and type.
Monitor mode
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can assign a button on your IP phone to show the idle or busy status of a shared directory number. Also
known as busy lamp field (BLF), in this case this feature is only for a directory number, not a phone. You should
use watch mode to show the status of the phone.
Monitor-line
speed dial
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can assign a button on your IP phone to show the idle or busy status of another directory number on the
system; this feature is also known as BLF with an additional option to have the Idle button act as a speed-dial
button to call that phone. For example, an administrator will use the monitor-line speed dial feature to watch the
supervisor’s phone, and can press the button when idle to easily call the supervisor.
MTP
Voice-system
features
Media termination point (MTP) is an IP phone feature that forces all RTP voice streams to transverse though the
Cisco Unified Communications 500 unit (like a proxy) for proper call handling with NAT and firewalls.
Multiple lines
per phone
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Multibutton IP phones offer the option to support more than one directory number per phone. Cisco Unified
Communications 500 also supports up to 10 directory numbers on a per-button basis using overlays.
Multi-site
Voice-system
features
Multi-site is the common name for the ability to connect multiple UC or SR 500s across the internet using VPN
connection(s). The VPN connection(s) encrypt data, voice and video traffic for secure communications.
You can connect up to 5 sites using a full-mesh topology. That means each site can have up to 4 direct VPN
connections to other sites.
Music on hold
Voice-system
features
Outside callers placed on hold will hear recorded music. The source can be a WAV file saved to flash memory or
a live source. Only one source for all phones is supported.
New voicemail
subscriber
feature
Voice-system
features
New voicemail users when first calling in to the system are given a minitutorial on use, recording their voice name,
recording a greeting, and setting a PIN.
Network Time
Protocol (NTP)
reference
Voice-system
features
Cisco Unified Communications 500 needs the current time and date to show on IP phones and time stamp for
voice messages. NTP reference service allows the application to get the current time and date from an external
server, which allows all devices in a network to be kept synchronized.
Night service
Voice-system
features
You can configure a different set of phones to ring when night service is enabled. You can activate night service
by dialing a code, using speed dial, or automatically setting it for certain days of week and hours per day.
Octo-lines
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The octo-line feature supports up to eight active calls (octo) per directory number assigned to a button. This
feature is supported on Cisco Unified IP Phone 794x, 796x, and 797x models.
Off-premises
extension
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The Cisco Unified Communications 500 system supports remote teleworker phones and off-premises phones.
The phones can be IP-based using VPN or analog using telco-provided wiring.
On-hook
dialing
Users,
phones, and
extensions
An IP phone user can dial a number (internal or external) without going off hook.
On-hook
transfer
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The call transfer feature supports the on-hook (hangup) action as a possible last step to complete a call transfer.
With the on-hook transfer implementation, user B can hang up after dialing the number of user C, and the transfer
completes.
Online help
Voice-system
features
Online help is a detailed, transparent help function embedded in Cisco Configuration Assistant that provides an
extensive glossary and powerful search engine that helps you quickly and easily find the information you need to
apply specific settings. With these online help features, you often can troubleshoot and resolve problems without
having to call for technical support.
Outgoing call
restrictions
Voice-system
features
The class-of-restrictions (COR) feature allows you to deny certain call attempts based on the incoming and
outgoing class of restrictions provisioned on the dial peers. This function provides flexibility in network design,
allows you to block calls (for example, to 900 numbers), and applies different restrictions to call attempts from
different originators.
COR is used to specify which incoming dial peer can use which outgoing dial peer to make a call. You can
provision each dial peer with an incoming and an outgoing COR list. The incoming COR list indicates the
capability of the dial peer to initiate certain classes of calls. The outgoing COR list indicates the capability required
for an incoming dial peer to deliver a call through this outgoing dial peer. If the capabilities of the incoming dial
peer are not the same or are a superset of the capabilities required by the outgoing dial peer, the call cannot be
completed using this outgoing dial peer.
Page 21

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 21 of 27
Paging
Voice-system
features
You can define a paging number to relay audio pages to a group of designated phones. When a caller dials the
paging number, each idle IP phone that is configured with the paging number automatically answers using its
speakerphone mode. Displays on the phones that answer the page show the caller ID that has been set using the
name command under the paging ephone-dn. When the caller finishes speaking the message and hangs up, the
phones are returned to their idle states.
Audio paging provides a one-way voice path to the phones that have been designated to receive paging. It does
not have a press-to-answer option like the intercom feature. A paging group is created using a dummy ephone-dn,
known as the paging ephone-dn, which can be associated with any number of local IP phones. The paging
ephone-dn can be dialed from anywhere, including on-net.
After you have created two or more simple paging groups, you can unite them into combined paging groups. By
creating combined paging groups, you provide phone users with the flexibility to page a small local paging group
(for example, paging four phones in a store’s jewelry department) or to page a combined set of several paging
groups (for example, paging a group that consists of both the jewelry and the accessories departments).
Park
Voice-system
features
The call park feature allows you to place a call on hold at a special extension so you can retrieve it from any other
phone in the system. You can park the call at the extension, known as the call-park slot, by pressing the Park
softkey. Cisco Unified Communications 500 chooses the next available call-park slot and displays that number on
the phone. A user on another phone can then retrieve the call by dialing the extension number of the call-park
slot.
You can define either a single extension number or a range of extension numbers to use as call-park slots. Each
call-park slot can hold one call at a time, so the number of calls that you can park is equal to the number of slots
you create. If the secondary number is used to group calls together, calls are retrieved in the order in which they
were parked; the call that has been parked the longest is the first call retrieved from the call-park slot.
A caller who is parked in a park slot hears the MOH audio stream if the call uses the G.711 codec or if the call
uses G.729 with transcoding; otherwise, the caller hears a tone on hold. Users who attempt to park a call at a
busy slot hear a busy tone.
Parallel hunt
groups (call
blast)
Voice-system
features
In a parallel hunt group, calls simultaneously ring multiple phones. Using parallel hunt groups is also referred to as
application-level forking because it enables the forking of a call to multiple destinations. In versions earlier than
Cisco Unified Communications 500 Version 4.3, only SIP phones support parallel hunt groups. In Cisco Unified
Communications 500 Version 4.3 and later versions, SCCP phones also support voice hunt groups.
You can enable functions similar to parallel hunt groups on SCCP phones by using the ephone-dn overlay feature
for shared lines.
The number of ringing calls that a parallel hunt group can support depends on whether call waiting is enabled on
the SIP phones.
IP phone
password
setting
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can change your phone password from your User Options webpages. Phone passwords are used for
computer telephony integration/Telephony Application Programming Interface (CTI/TAPI) integrations, extension
mobility, toll-bar override, and user page login.
PBX system
Voice-system
features
When setting up a Cisco Unified Communications 500 system, you need to decide if call handling should be
similar to that of a PBX, similar to that of a keyswitch, or a hybrid of both. The Cisco Unified Communications 500
Series provides significant flexibility in this area, but you must have a clear understanding of the model that you
choose. The simplest model is the PBX model, in which most of the IP phones in your system have a single,
unique extension number. Incoming PSTN calls are routed to a receptionist at an attendant console or to an
automated attendant. Phone users can be in separate offices or geographically separated and therefore often use
the telephone to contact each other.
Peer ephone
hunt groups
Voice-system
features
This feature defines a hunt group in which the first extension to ring is the number to the right (in the list) of the
extension that was the last one to ring when the hunt group was last called. Ringing proceeds in a circular
manner, left to right, for the number of hops specified when the ephone hunt group is defined.
Personal
address book
(PAB)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
PAB is a directory for personal contacts. It is stored locally on the Cisco SPA525G 5-line IP Phone with Color
Display.
Personal
speed dial
Users,
phones, and
extensions
With this feature, you can configure a maximum of 24 personal speed-dial numbers per phone; the numbers are
accessed through the Directory, Personal Speed Dial listing. Each phone can have up to 99 fast dials. You can
configure each phone using the Options webpage or through the phone using Services, MyPhoneApps, Speed
dial.
Phantom
extension
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This feature allows you to create an extension without associating it with any phone.
Phantom
mailbox
Voicemail
This feature lets you create a mailbox without associating it with any phone.
Page 22
Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 22 of 27
Phone display
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Phone display features comprise the following functions:
●
Caller-name display: When phone agents answer calls for several different departments or people, it is often
helpful for them to see a display of the name, rather than the number, of the called party. The caller-name
display feature can display either of the following types of name: name for a directory number in a local
directory or name associated with an overlay directory number.
●
Header bar: Refer to “Phone header bar display.”
●
System message display: The system message display feature allows you to specify a custom text or display
message to appear in the lower part of the display window on display-capable IP phones. If you do not set a
custom text or display message, the default message “UC5X0” is displayed. When you specify a text
message, the number of characters that can be displayed is not fixed because IP phones typically use a
proportional (as opposed to fixed-width) font. There is room for approximately 30 alphanumeric characters.
Phone header
bar display
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can customize the content of an IP phone header bar, which is the top line of the IP phone display. The
header bar can contain a user-definable message instead of the extension number. If no description is specified,
the header bar replicates the extension number that appears next to the first button on the phone.
Phone labels
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Phone labels are configurable text strings that can be displayed instead of extension numbers next to line buttons
on a Cisco Unified IP Phone. By default, the number that is associated to a directory number and assigned to a
phone is displayed next to the applicable button. The label feature allows you to enter a meaningful text string for
each directory number so that a phone user with multiple lines can select a line by label instead of by phone
number, thus eliminating the need to consult in-house phone directories.
Phone lock
(Cisco Unified
Wireless IP
Phone 7921G
and 7925G WiFi phone
models)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can secure access to your Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7920 by enabling the phone-lock feature. After
powering on the phone, you must enter a password before the phone can authenticate with the wireless network.
This feature is not available with desktop phones.
Phone
services
Users,
phones, and
extensions
With this feature, you can use Cisco Unified IP Phones to deploy customized client services with which users can
interact through the keypad and display. Services deploy using HTTP from standard web servers.
You can access these features using the Services and Directories buttons or menu options (availability varies by
phone model). When you press the Services button (or choose the Services menu item), a menu of configured
services appears. You can then choose a service from the list, and the phone displays the service.
The following list gives typical services that are supplied to the phones when connected to the Cisco Unified
Communications 500 system:
●
Visual voicemail (VoiceView Express)
●
System speed dial
●
Personal speed dial
●
Call history
●
Local directory
Phone
softkeys
Users,
phones, and
extensions
With this feature, you can customize the display and order of softkeys that appear during various call states on
individual IP phones. Softkeys that are appropriate in each call state are displayed by default. Using phone
templates, you can delete softkeys that would normally appear or change the order in which the softkeys appear.
For example, you might want to display the CFwdAll and Confrn softkeys on a manager’s phone and remove
these softkeys from a receptionist’s phone.
You change the softkey order by defining a phone template and applying the template to one or more phones.
You can create up to 20 phone templates for SCCP phones and 10 templates for SIP phones. You can apply only
one template to a phone.
Pickup groups
Voice-system
features
With this feature, you can answer a ringing phone in any pickup group by pressing the GPickUp softkey and then
dialing the pickup group number. If only one pickup group is defined in the Cisco Unified Communications 500
system, you can pick up the call simply by pressing the GPickUp softkey. You do not need to belong to a pickup
group to use this method. If both phones are in the same pickup group, you can pick up a ringing call on another
phone by pressing a softkey and then the asterisk (*). The softkey that you press, either GPickUp or PickUp,
depends on your configuration.
PIN setting
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This feature sets a PIN to be used by a phone user to access voicemail.
Placed call list
Voice-system
features
You can view records of your placed calls. While viewing call logs, you can use softkeys to display details for a
call record, erase call records, and dial from call records. If you are on another call when dialing, your phone might
prompt you with options (Hold, Transfer, Conference, EndCall) for handling the first call before placing the second
call.
Power failure
transfer
Voice-system
features
With no power, the first FXO trunk will be connected to the first FXS port, allowing for calls to be answered or
placed until power is restored.
Predial
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can enter a phone number before getting a dial tone and complete the call by going off hook (lifting the
handset, pressing the speakerphone button, and so on).
Page 23

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 23 of 27
Primary Rate
Interface (PRI)
Voice-system
features
The PRI is a high-capacity digital trunk for carrying voice and data between the service provider and customer; it
is based on the ISDN telecommunications standard. In the United States PRI is based on a T1 line and offers 23
channels; in Europe it is based on an E1 line and offers 29 channels.
All data and voice channels operate at 64 kbps. The primary difference between T1/E1 channel associated
signaling (CAS) and PRI is that PRI reserves one channel for signaling and providing features not available with
standard T1/E1 circuits such as DID and feature-rich caller ID. The Cisco Unified Communications 500 system
supports only voice PRI; shared data and voice circuits are not supported.
Private-line
automated
ringdown
(PLAR)
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Private-line automated ringdown allows the administrator to set up an analog or IP phone on going off hook to
automatically ring a predetermined number. An example is that a phone placed inside an elevator on going off
hook would automatically ring the receptionist or other defined number, internal or external.
Programmable
buttons
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Administrators can choose button features for Cisco IP Phones, including a directory number, a shared line for
trunks, speed dial, BLF showing the status of another phone with speed dial to that phone, or blank.
PSTN failover
Voice-system
features
PSTN failover automatically routes calls over the PSTN network if the IP network is down.
Redial
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can automatically dial the last placed call from your IP phone.
Remote
teleworker
phones
Voice-system
features
IP phones used by remote teleworkers are called remote teleworker phones. A remote teleworker is a user who is
not physically present at the main office and uses secure IP network to connect remotely.
Remove
conference
participants
Voice-system
features
This feature allows removal of the last user who joined a conference call.
Repeat last
number dialed
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can automatically dial the last placed call from your IP phone; this feature is also known as redial. You can
also use directory, placed calls to redial any of the last 30 calls placed.
Resetting
phones
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can reset an IP phone remotely from the call control agent (IP PBX). The call control agent sends out control
messages to the IP phone to reset itself and start the bootup process.
Resetting TAPI
session
Users,
phones, and
extensions
TAPI sessions are used for controlling IP phones. A Windows desktop application Telephony Service Provider
(TSP) is installed and configured with an application like Microsoft Outlook to control the user’s IP Phone. The
TSP using the Windows telephony API communicates to the UC 500 call-control agent to control the operation of
the IP phone. Resetting a TAPI session flushes out the current session parameters and forces the TSP to
reestablish communication with the call-control agent. This is sometimes necessary due to TSP or application
issues.
Restriction
tables
Voice-system
features
These tables are used to control a list of numbers (or dial patterns) that are not allowed to be dialed.
Restore to
factory
defaults
Voice-system
features
This operation restores the system to its factory default setting. It resets all the configuration parameters as well
as any database maintained by the system.
Resume
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This softkey feature on IP phones allows you to reclaim a call on hold. While on hold, the other end hears MOH.
When resumed, a two-way audio is established between the users.
Ringer settings
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This setting selects the ring tone on an IP phone. You can set ringers on a per-directory number basis.
Ringing-line
preference
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This feature enables you to pick up the handset and get connected to the line that is ringing on your IP phone.
This feature is used when multiple lines are configured on an IP phone.
Ringing
timeout
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Ringing timeout is associated with no answer on an incoming call. By default, Cisco Configuration Assistant
configures this value to 30 seconds on IP phones; for voice ports it is 180 seconds.
Ring-tone
setting
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can select the ring tone on your IP phone. You can set ringers on a per directory number basis.
Rollover
buttons for
overlaid
ephone-dns
Voice-system
features
Phones with overlaid ephone-dns can use the button command with the x keyword to dedicate one or more
additional buttons to receive overflow calls. If an overlay button is busy, an incoming call to any of the other
ephone-dns in the overlay set rings on the first available overflow button on each phone that is configured to
receive the overflow.
SCCPcontrolled
analog (FXS)
ports
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can configure analog voice ports (FXS) to be controlled by the call-control agent using the same protocol that
is used to communicate with IP phones. The FXS ports appear as IP phones to the Cisco Unified
Communications 500, and you can configure the phones with most of the features available for IP phones,
including voicemail.
Page 24

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 24 of 27
Schedules for
holidays and
business
hours
Voice-system
features
The Auto Attendant on Cisco Unified Communications 500 offers holiday and business schedules to enable timeof-the-day routing of incoming calls.
Secondary dial
tone
Voice-system
features
A secondary dial tone is available for Cisco Unified IP Phones connected to Cisco Unified Communications 500 in
the PBX mode. The secondary dial tone is generated when you dial a predefined PSTN access prefix and
terminates when you dial additional digits.
Secure Socket
Layer (SSL)
Phone Client
Voice-system
features
The SSL Phone Client on the SPA525G IP phone provides secure connectivity to a UC500 or SR500 series over
the internet. The SSL Phone Client at the remote site does not need a teleworker router, making it an ideal
solution for simple scenarios that require voice-only connectivity.
Sequential
ephone hunt
groups
Voice-system
features
The sequencing method of hunting always starts with the first member of the hunt group and hunts through all the
members in the sequential order.
Session
Initiation
Protocol (SIP)
Voice-system
features
SIP is a signaling protocol widely used for controlling multimedia communication sessions such as voice and
video calls over IP. Cisco Unified Communications 500 supports Cisco SIP endpoint devices as well as SIP trunks
to SIP providers.
SIP IP Phone
dial plans
Voice-system
features
SIP dial plans enable call routing using the SIP protocol. The dial plans route calls toward a SIP server, which
could be either another Cisco Unified Communications 500 at a remote site or a SIP server hosted by a SIP
provider.
A dial plan is a set of dial patterns that SIP phones use to determine when digit collection is complete after you go
off-hook and dial a destination number. Dial plans allow SIP phones to perform local digit collection and recognize
dial patterns as your input is collected. After a pattern is recognized, the SIP phone sends an INVITE message to
the Cisco Unified Communications 500 to initiate the call to the number matching your input. All of the digits you
entered are presented as a block to the Cisco Unified Communications 500 for processing. Because digit
collection is done by the phone, dial plans reduce signaling messages overhead compared to Keypad Markup
Language (KPML) digit collection.
SIP dial plans eliminate the need for you to press the Dial softkey or # key, or to wait for the interdigit timeout to
trigger an outgoing INVITE. You can configure a SIP dial plan and associate the dial plan with a SIP phone. The
dial plan is downloaded to the phone in the configuration file.
SIP IP phones
Users,
phones, and
extensions
IP phones can communicate using several protocols, including H.323, SIP, and Media Gateway Control Protocol
(MGCP). SIP IP phones use the SIP protocol to communicate with a SIP server.
SIP trunk
Voice-system
features
SIP trunks provide an alternative to the traditional PSTN (digital and analog) connectivity options. SIP trunks are
provisioned through SIP service providers that provide PSTN connectivity.
SIP
supplementary
services,
disabling
Voice-system
features
The SIP call transfer and call forwarding supplementary services feature introduces the ability of SIP gateways to
initiate blind, or attended, call transfers by passing the call control back to the originating devices. Disabling these
supplementary services forces the SIP gateway to handle these call conditions locally.
Shared lines
Users,
phones, and
extensions
A shared directory number allows the same number to appear on two different IP phones. A call made to a shared
directory number rings all the IP phones that have a button assigned to the shared number. A call made from the
shared directory number ties up the shared-dn-buttons on the rest of the IP phones. If a call on the shared
directory number is put on hold, any of the IP phones can resume the on-hold call.
Shared-line
overlay
ephone-dns
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The overlay feature allows a single IP phone button to be associated with multiple directory numbers. A call to any
of the associated directory numbers rings the IP phone on the overlaid button. Shared directory numbers can also
be part of the overlay configuration. Primary extensions cannot be part of the shared overlay ephone-dns.
Simple Auto
Attendant
script
Voice-system
features
The basic Auto Attendant is included in the Cisco Unified Communications 500 as aa_simple.aef script. It
supports dial-by-extension, alternate, holiday, and business-hours greetings.
Single number
reach (SNR)
Voice-system
features
SNR allows you to have incoming calls to a single number simultaneously ring an IP phone and a remote
destination such as a home or mobile phone. You can answer incoming calls to your SNR number on your IP
phone or at your remote destination and pick up in-progress calls on your desktop phone or the remote
destination without losing the connection.
If you do not answer the call within 5 seconds, the Cisco Unified Communications 500 system rings the remote
number while continuing to ring your IP phone extension. If you answer the call on your IP phone, you can send
the call to the remote phone by pressing the Mobility softkey.
If you answer the call on your remote phone, you can pull back the call to the IP phone by pressing the Resume
softkey. You can also change the SNR remote destination using the IP Phone menu.
Softkeys
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Softkeys are keys that appear on the bottom of the IP phone LCD. They allow you to access various features such
as call forward, call transfer, conferencing, and call park. The softkeys available for use change dynamically
according to whether the phone is in connected, ringing, idle, or seized (handset is lifted). Additional softkeys are
also automatically enabled when advanced features, such as SNR and live record, are enabled.
Softwarebased
conferencing
Voice-system
features
Software conferencing is the type of voice conferencing that is supported by default on the Cisco Unified
Communications 500. It does not require any hardware resources; the audio mixing is done within the application
software. Software conferencing allows a maximum of three parties in a conference, with maximum of eight
simultaneous conferences.
Page 25

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 25 of 27
Speakerphone
mode
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Speakerphone mode allows you to talk and listen hands-free (without using a handset or headset). It is typically
activated by pressing the Speakerphone button on an IP phone. Conference phones such as the Cisco Unified IP
Phone 7936 and 7937G use speakerphone for all calls. Speakerphones on lower-end Cisco Unified IP Phone
7906G and 7911G model phones allow you to hear audio only.
Speed dialing
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Speed dial allows you to quickly dial a number from a list. The different types of speed dial include local speeddial menu, personal speed-dial menu, and speed-dial buttons. The local speed-dial menu is configured by the
administrator and is shared between all IP phones on the system. You can configure personal speed dials and
speed-dial buttons on your individual IP phones.
SRTP
Voice-system
features
Media encryption (SRTP) encrypts the voice media for calls made between IP phones registered to the same
Cisco Unified Communications 500, without the need for a dedicated VPN tunnel.
Station volume
controls
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can adjust the volume for your incoming call ringer and phone speaker. You can also adjust the outgoing
volume of the phone microphone on a hands-free call.
Support for
caller ID
information in
incoming
messages
Users,
phones, and
extensions
The Cisco Unified Communications 500 can play back the caller ID number of the caller who recorded the
message, when you listen to new voicemail messages.
Support for
multiple
languages
Voice-system
features
You can install multiple concurrent languages on a single Cisco Unified Communications 500. The IP phone
display and voicemail prompts can be different on a per-user basis.
Support for
vCard
information
from remote
subscribers
Voice-system
features
This feature permits vCard information from remote subscribers to update their directory entries.
System
message
display
Voice-system
features
This feature allows you to specify a custom text or display message to appear in the lower part of the display
window on your IP phones. If you do not set a custom text or display message, the default message “UC5X0” is
displayed.
Teleworker
remote phones
Voice-system
features
IP phones or instances of Cisco IP Communicator can be connected to a Cisco Unified Communications 500
over a VPN connection to support teleworkers who are at remote locations from the application. Cisco IP
Communicator Softphones can connect to the Cisco Unified Communications 500 over a VPN tunnel
established using Cisco VPN client installed on a PC. Hardware IP phones connect to the Cisco Unified
Communications 500 over a VPN tunnel established using a Cisco Secure Router 500 Series teleworker router
The product data sheet is at
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/solutions/small_business/products/routers_switches/500_series_secure_router
s/index.html. The Cisco Unified Communications 500 supports a maximum of 10 teleworker sites, with a
maximum of 5 teleworker phones at each site.
The VPN client on Cisco SPA525G IP phones can be configured through the Cisco Configuration Assistant Phone
VPN Setup Wizard and deployed at remote sites.
T1/E1 digital
trunk interface
Voice-system
features
This feature provides PBX support for direct digital trunk interfaces, such as ISDN PRI and T1 or E1 CAS circuits.
T1 CAS
(channel
associated
signaling)
Voice-system
features
CAS is also referred to as robbed-bit signaling. In this type of signaling, the least significant bit of information in a
T1 signal is “robbed” from the channels that carry voice and is used to transmit framing and clocking information.
This protocol is sometimes called “in-band” signaling. CAS is a method of signaling each traffic channel rather
than having a dedicated signaling channel (such as ISDN). In other words, the signaling for a particular traffic
circuit is permanently associated with that circuit. The most common forms of CAS signaling are loopstart and
groundstart. In addition to receiving and placing calls, CAS signaling also processes the receipt of Dialed Number
Identification Service (DNIS) and automatic-number-identification (ANI) information.
Time zones
Voice-system
features
Support for time zones on the Cisco Unified Communications 500 allows the correct time and date information to
be displayed on IP phones and played back on the voicemail. Correct time-zone information is also essential for
integration with applications that use time information, such as Cisco WebEx™ PhoneConnect.
Toll-fraud
prevention
Voice-system
features
The Cisco Unified Communications 500 implements several security features to prevent unauthorized phones
from both internal and external users when using the Cisco Configuration Assistant tool for configuration.
Toll
restrictions
Voice-system
features
This feature allows you to prevent specified phones from making long-distance (toll) calls.
Touchscreen
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can press the phone screen to choose menu items, softkeys, and feature tabs (on Cisco Unified IP Phones
with touch-sensitive phone screens).
Trace
(debugging)
Voice-system
features
Real-time troubleshooting tools are available through on-demand debugs for the Cisco Unified Communications
500 and within Cisco Configuration Assistant 2.1 and later.
Transcoder
resources
Voice-system
features
This feature provides translation of RTP streams from one codec format into another.
Transfer
Users,
phones, and
extensions
When you are connected to another party, call transfer allows you to shift the connection of the other party to a
different number. The transferred call (transferee) and transfer destination (transfer-to) can be a local extension or
PSTN number. On the Cisco Unified Communications 500, IP phones, analog phones, and Auto Attendant can
initiate call transfers.
Page 26

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 26 of 27
Transfer to
voicemail
Voice-system
features
Transfer to voicemail allows you or the Auto Attendant feature to transfer incoming calls directly to a voice
mailbox. Unlike normal call transfers, callers who are transferred to a voice mailbox can leave a message
immediately, instead of waiting until the phone rings and call forwards to voicemail. IP phone users can transfer
calls to voicemail by pressing the TrnsfVM softkey, or by entering the transfer to voicemail prefix.
Translation
rules and
profiles
Voice-system
features
Translation rules manipulate dialed numbers to conform to internal or external numbering schemes. Voice
translation profiles allow you to group translation rules together and apply them to the following types of numbers:
●
Called numbers (DNIS)
●
Calling numbers (ANI)
●
Redirected called numbers
The Cisco Unified Communications 500 uses translation rules and profiles for many purposes, including
translating incoming numbers from ISDN or SIP trunks to internal extension numbers and stripping off the access
code for outbound dialing to the PSTN.
Trunk groups
Voice-system
features
Trunk groups are an administrator-controlled feature that allows administrators to easily configure outbound and
inbound calls to have common call-handing properties. For example, all FXO and analog trunks would be in one
trunk group and SIP trunks would be in another.
Trunk-to-trunk
connections
Voice-system
features
Outside callers can be connected to another PSTN trunk when a phone is set to forward (or SNR) or transferred
by a user.
Undelete voice
messages
Voice-system
features
During a voicemail session you can listen once again to a deleted voicemail message.
Vibration alert
Users,
phones, and
extensions
This feature is supported on Cisco Unified IP Phone 7921 and 7925 models for incoming calls; it is also referred to
as vibration mode.
Video
Streaming
Voice-system
features
This feature allows a live video feed from a Cisco 2300 Series Business Internet Video Camera to be streamed to
the display of a Cisco SPA525G IP Phone.
Video support
Voice-system
features
Video telephony is as easy as making a voice call. When a Cisco Unified Video Advantage camera and a Cisco
Unified IP Phone 7900 Series phone or video endpoint is in use by two users when connected over the LAN or
WAN, then a video telephony session will automatically start between the two devices. With no special dialing or
button to push, it is very easy to set up and use.
Voice hunt
group
Voice-system
features
You can set up a voice hunt group to ring all phones at one time; the voice hunt group is also known as a blast or
parallel hunt group
VoiceView
Express
Applications
This Cisco Unified Communications 500 Smart Productivity Application for Cisco IP Phones with a larger display
allows you to interact with the voicemail system as an XML application; it is included without charge. You can
listen to new messages play though the phone, forward, send a message, save, delete, set greetings, change
password, and manage groups and notification options - all without listening to the voicemail system prompts.
View
conference list
Voice-system
features
With this View Participant IP Phone softkey option when participating on a conference call (ad hoc or meet-me),
you can see all the users currently participating in the conference. (This feature is not supported with SIP-based
phones or when using third-party conferencing).
Viewing angle
settings
Users,
phones, and
extensions
With this feature of the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7940, 7960, and 7970 models, you can tilt your phone to change
the viewing angle.
Voice activity
detection
(VAD)
Voice-system
features
This call-processing feature sends no packets when no audio is heard between endpoints, saving bandwidth and
offering you a better quality-of-service (QoS) experience.
Note that with Cisco solutions side tones are provided, so even with VAD enabled (by default) you still feel as if
connected.
Voice
messaging
Voice-system
features
Whether you are an external or internal caller, you can record an audio message to be played back to the receiver
at a later time. In most cases when calling a phone that is not answered or busy, you have the option to leave a
voice message. When you leave a voice message, notification of the new message is made available to the
person you called by a light on the phone, email notification, or by the system calling that person and playing a
new-message prompt. Automated voice-messaging systems allow business users to receive and listen to
messages without the need for an operator or message desk employees, saving costs.
Voice mailbox
PINless login
Voice-system
features
This feature allows you to call in to your voicemail internally without entering a PIN or code. You should enable
this feature only when voicemail security is not required.
Voice
translation
rules and
profiles
Voice-system
features
Refer to “Translation rules and profiles.”
Voicemail
notification
Voicemail
You can enable notifying subscribers of new messages in their voice mailboxes. These notifications can be sent
to phone or email.
Volume
settings
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can set the ringing, handset, and headset volume on your IP phone.
Page 27

Feature Description Guide
© 2010 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 27 of 27
Cisco Unified
Video
Advantage
Users,
phones, and
extensions
Cisco Unified Video Advantage (formerly Cisco VT Advantage) adds video telephony features to Cisco Unified IP
Phones (Cisco Unified IP Phone 7900 models plus Cisco IP Communicator softphone).
Cisco Unified Video Advantage offers a Cisco Video Advantage camera (or third-party USB camera) plus
Windows software. The camera is connected to the Windows PC, and the PC is connected to the Cisco Unified IP
Phone 7900, which is then connected to the network. When you make a call from one video-enabled endpoint
(within the site, or site to site over the WAN), video is displayed automatically.
Watch button
Users,
phones, and
extensions
You can configure a button on your IP phone or sidecar to show the status of another IP phone on the network;
this button is also known as the busy-lamp-field (BLF) button. Watch status shows a phone idle or in use, no
matter which directory number on the phone is in use. Refer also to “Busy lamp field.”
Cisco WebEx
PhoneConnect
Applications
With this free application with Cisco Unified Communications 500, an XML application shows Cisco WebEx
meetings you are either hosting or being invited to. In addition, a notification on the phone reminds you of
upcoming Cisco WebEx meetings; a softkey call button autodials you in to the meeting.
Printed in USA C07-557625-03 12/10
 Loading...
Loading...