Page 1

Cisco Small Business
RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router
ADMINISTRATION
GUIDE
Page 2

© 2013 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. OL-25648-01
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks,
go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner
does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Page 3

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this
equipment.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
Radiation Exposure Statement
1. 20 cm minimum when the product is operated alone without co-transmitting
with a plug-in 3G USB dongle device.
2. 33 cm minimum when the product is operated with a plug-in 3G USB device
which has maximum of 7 W ERP output power.
3. For co-transmission scenario which is not covered above, please consult the RF
technician or device supplier.
© 2013 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. OL-25648-01
Page 4

Contents
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement 3
Radiation Exposure Statement 3
Chapter 1: Getting Started 5
Product Overview 5
Front Panel 6
Back Panel 8
Default Settings 9
Mounting the RV315W 10
Placement Tips 10
Wall-Mounting 10
Connecting the RV315W 11
Getting Started with the Configuration 13
Before You Begin 13
Logging in to the Configuration Utility 13
Using the Help System 14
Performing Basic Configuration Tasks 14
Changing the Default Administrator Password 14
Upgrading Your Firmware After Your First Login 15
Backing Up Your Configuration 15
Chapter 2: Using the Setup Wizard 17
Starting the Setup Wizard 17
Configuring WAN Connection 17
Configuring Default LAN Settings 22
Configuring Wireless Connection 23
Completing the Setup Wizard 28
Chapter 3: Viewing System Status 30
Device Information 30
WAN Connection 31
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 1
Page 5

Contents
3G Wireless Connection 31
LAN Interfaces 33
WLAN Connection 33
DHCP Clients 33
Application Information 34
Processes Information 34
Refresh Rate 35
Chapter 4: Port Management 36
Configuring WAN 36
Viewing WAN Connection Information 36
Configuring WAN Connections 37
Configuring Default Route of the Physical WAN Interface 41
Configuring Multi-WAN 41
Configuring WAN1/LAN0 Interface 43
Configuring LAN 43
Configuring LAN Interface Settings 44
Configuring VLAN Settings 45
Configuring WLAN 46
Configuring Wireless Radio Settings 46
Configuring Wireless Network Settings 47
Configuring 3G Wireless Connection 53
Chapter 5: Networking 56
Configuring DDNS 56
Configuring Port Forwarding 57
Configuring Single Port Forwarding 57
Configuring Port Range Forwarding 58
Configuring Port Triggering 59
Configuring DMZ 60
Configuring Software DMZ 60
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 2
Page 6
Contents
Configuring Hardware DMZ 61
Configuring UPnP 61
Configuring Port Mirroring 62
Configuring Routing 62
Configuring Basic Routing Settings 62
Configuring Routing Mode 62
Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing 63
Configuring Static Routing 63
Configuring Policy-based Routing 64
Configuring Dynamic Routing 65
Viewing the Routing Table 66
Configuring IGMP 67
Chapter 6: VPN 68
Viewing IPsec VPN Status 68
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies 69
Setting Up a Site-to-Site VPN 69
Setting Up a PC-to-Site VPN 73
Chapter 7: Quality of Service (QoS) 76
Configuring Bandwidth Management 76
Configuring Flow Control Policies 77
Configuring Session Limits 79
Chapter 8: Security 80
Configuring the Firewall 80
Configuring DoS Protection 81
Configuring Content Filtering 82
Configuring Access Control 83
Configuring MAC Address Filtering 84
Preventing ARP Attacks 85
Configuring ALG 86
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 3
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 9: System Management 87
Rebooting the RV315W 88
Configuring Password Complexity 88
Configuring User Accounts 89
Viewing User Information 89
Creating a New User 90
Changing User Password 90
Deleting a Local User 91
Restoring Factory Default Settings 91
Managing System Configuration 92
Upgrading the Firmware 93
Using Diagnostic Utilities 94
Ping 94
Traceroute 95
HTTP Get 95
DNS Query 95
Configuring System Time 96
Configuring TR-069 Settings 96
Configuring SNMP 98
Configuring Remote Management 99
Configuring Remote Access Protocols and Ports 99
Configuring Trusted Remote Hosts 100
Configuring SSH 100
Log Management 102
Configuring Log Settings 102
Configuring Log Facilities 103
Viewing Logs 105
Configuring Firewall Logs 105
Appendix A: Where to Go From Here 106
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 4
Page 8

Getting Started
This chapter provides information to familiarize you with the product features,
guide you through the installation process, and get started using web-based
Configuration Utility. Refer to the following sections:
• Product Overview
• Mounting the RV315W
• Connecting the RV315W
• Getting Started with the Configuration
• Performing Basic Configuration Tasks
1
Product Overview
Thank you for choosing the Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router. The
RV315W provides routing, switching, security, wireless, 3G, Virtual Private
Network (VPN), quality of service (QoS), and flow-control capabilities for small
businesses.
Before you use the RV315W, become familiar with the lights on the front panel and
the ports on the rear panel.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 5
Page 9

Getting Started
Product Overview
1
Front Panel
The lights are located on the front panel of the RV315W.
POWER • Solid green when the RV315W is powered on and is
operating normally.
• Off when the RV315W is powered off or the power has
problems.
SYS • Solid green when the RV315W is connected to the Internet
through your cable or DSL modem.
• Flashes green when the RV315W is attempting to connect
to the Internet, the RV315W cannot connect to the Internet,
or the system is upgrading the firmware.
• Solid red when the system has problems.
• Flashes red when the system is overloaded, such as the
CPU utilization or the memory utilization exceeds the
limitation.
• Off when there is no Internet connection.
WAN0 • Solid green when the RV315W is connected to the Internet
through the WAN0 port, but there is no traffic over this port.
• Flashes green when the RV315W is sending or receiving
data over the WAN0 port.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 6
• Off when the WAN0 port has no connection.
Page 10
Getting Started
Product Overview
1
WAN1 If the WAN1/LAN0 port on the back panel is set to a secondary
WAN inter face ( WAN1) :
• Solid green when the RV315W is connected to the Internet
through the WAN1 port, but there is no traffic over this port.
• Flashes green when the RV315W is sending or receiving
data over the WAN1 port.
• Off when the WAN1 port has no connection.
LAN0 If the WAN1/LAN0 port on the back panel is set to an additional
LAN interface (LAN0):
• Solid green when the RV315W is connected to a device
through the LAN0 port, but there is no traffic over this port.
• Flashes green when the RV315W is sending or receiving
data over the LAN0 port.
• Off when the LAN0 port has no connection.
LAN1-8 The numbered lights correspond to the LAN ports on the back
panel of the RV315W.
• Solid green when the RV315W is connected to a device
through the corresponding port (LAN1 to 8), but there is no
traffic over that port.
• Flashes green when the RV315W is sending or receiving
data over the corresponding LAN port.
• Off when the corresponding LAN port has no connection.
USB • Solid green when a USB device is detected, but has no read
and write operations.
• Flashes green when a USB device is detected and has read
and write operations.
• Off when the RV315W does not detect a USB device.
3G • Solid green when the RV315W is connected to a 3G
wireless network, but there is no traffic over the 3G USB
port.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 7
• Flashes green when the RV315W is sending or receiving
data over the 3G USB port.
• Off when the RV315W does not connect to a 3G wireless
network.
Page 11

Getting Started
Product Overview
1
WLAN • Solid green when the wireless module is enabled, but there
is no traffic over the wireless network.
• Flashes green when the RV315W is sending or receiving
data on the wireless module.
• Off when the wireless module is disabled.
VPN • Solid green when there are active VPN tunnels.
• Flashes green once per two seconds when the RV315W is
attempting to establish a VPN tunnel, or the attempt of
establishing a new VPN tunnel fails.
• Off when there is no VPN connection.
NMS • Solid green when the RV315W is connected to an
upper-level Network Management System (NMS) but has no
operations.
Back Panel
• Flashes green when the RV315W is connected to an
upper-level NMS and has operations.
• Off when the RV315W does not connect to an upper-level
NMS.
WARNING 33 cm minimum when the product is operated with a plug-in 3G USB device which
has maximum of 7 W ERP output power.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 8
Page 12

Getting Started
Product Overview
1
3G USB Port The 3G USB port connects your RV315W to a 3G wireless
network through a 3G USB device. To obtain the list of 3G
USB dongle models supported by the RV315W, go to
www.cisco.com/go/rv315w.
USB Port The USB port connects to a USB storage device to save
syslog messages.
WAN0 Por t The WAN0 (Internet) port is connected to your Internet
device, such as a cable or DSL modem.
WAN1/LAN0 Port The WAN1/LAN0 port can be set to a secondary WAN
interface (WAN1) or an additional LAN interface (LAN0).
LAN1-8 Ports These ports provide a LAN connection to network devices,
such as PCs, print servers, or switches.
RESET The RESET button has two functions:
• Reboot: Press the RESET button for at least 1, but no
more than 5 seconds with a paper clip or a pencil tip
to reboot the unit.
• Restore to Factory Defaults: Press and hold the
RESET button for more than 5 seconds to reboot the
unit and restore to factory defaults. Changes that you
have previously made to the RV315W settings are
lost.
POWER (12VDC) The POWER port is where you connect the supplied power
adapter (12 V/3 A).
Power Switch Powers the unit on or off.
Default Settings
These are the default settings used when configuring your RV315W for the first
time.
Parameter Default Value
Username cisco
Password cisco
LAN IP 192.168.1.1
DHCP Range 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.200
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 9
Page 13

Getting Started
1
2
4
3
Mounting the RV315W
NOTE Press and hold the RESET button for more than 5 seconds with a paper clip or a
pencil tip to reboot the unit and restore the factory defaults. Changes that you have
previously made to the RV315W settings are lost.
Mounting the RV315W
You can place your RV315W on a desktop or mount it on a wall.
Placement Tips
• Ambient Temperature—To prevent the RV315W from overheating, do not
operate it in an area that exceeds an ambient temperature of 104°F (40°C).
1
• Air Flow—Be sure that there is adequate air flow around the RV315W.
• Mechanical Loading—Be sure that the RV315W is level and stable to avoid
any hazardous conditions.
Place the RV315W horizontally on a flat surface so that it sits on its four rubber
feet.
Wall-Mounting
The RV315W can be wall-mounted. The wall-mounting hardware is
user-supplied. The ports on the back panel must face either upward or downward
when mounting the RV315W to the wall.
The recommended dimensions for the mount kit are as follows:
1 8 mm/0.31 in 2 25 mm/0.98 in 3 6.5 mm/0.26 in 4 17.9 mm/0.7 in
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 10
Page 14

Getting Started
Connecting the RV315W
WARNING Insecure mounting might damage the device or cause injury. Cisco is not
STEP 1 Determine where you want to mount the RV315W. Verify that the surface is
STEP 2 Drill two pilot holes into the surface 5.9 inches (150 mm) apart.
STEP 3 Insert a screw into each hole, leaving a gap between the surface and the base of
STEP 4 Place the RV315W wall-mount slots over the screws and slide the RV315W down
1
responsible for damages incurred by insecure wall-mounting.
To mount the RV315W to the wall:
smooth, flat, dry, and sturdy.
the screw head of at least 0.1 inches (3 mm).
until the screws fit snugly into the wall-mount slots.
Connecting the RV315W
NOTE The wireless module of the RV315W is enabled by default. You can connect one
PC with an Ethernet cable or through a wireless connection to perform the initial
configuration. Use the default wireless network name (SSID) and pre-shared key
that are provided on the product label at the bottom of the RV315W to connect the
PC to your wireless network for the first time.
STEP 1 Power off all equipment, including the cable or DSL modem, the PC that you will
use to connect to the RV315W, and the RV315W.
STEP 2 Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to your cable or DSL modem. Connect the
other end to the WAN0 port on the back panel of the RV315W.
STEP 3 Connect one end of a different Ethernet cable to one of the LAN ports on the back
panel. Connect the other end to an Ethernet port on the PC that you will use to run
web-based Configuration Utility.
NOTE Skip this step if you want to connect the PC to the RV315W through a
wireless connection.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 11
Page 15

Getting Started
Connecting the RV315W
STEP 4 Connect the supplied power adapter to the POWER port on the back panel. Plug
STEP 5 Power on all connected devices including the cable or DSL modem and the PC
STEP 6 Power on the RV315W.
STEP 7 To connect the PC to your wireless network for the first time, you can configure the
1
the other end of the power adapter into an electrical outlet. Make sure that the
power switch is turned off.
NOTE Use only the power adapter that is supplied with the unit. Using a different
power adapter could damage the unit.
and wait until the connections are active.
wireless connection using the default SSID name and pre-shared key that are
provided on the product label.
A sample configuration is illustrated here.
Wireless
Devices
Internet
Access
Devices
Network
Devices
Power
Supply
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 12
Page 16
Getting Started
Getting Started with the Configuration
Getting Started with the Configuration
You can use web-based Configuration Utility of the RV315W to view the system
information, configure key parameters, upgrade system firmware, reboot the unit,
or restore the unit to its factory default settings.
Before You Begin
Before you begin to use web-based Configuration Utility, make sure that you have
a PC with Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 (or later) or Mozilla Firefox 3.0 (or later).
NOTE The minimum recommended display resolution for the PC running the web browser
used to access the utility is 1024 x 768.
1
Logging in to the Configuration Utility
To log in to the utility:
STEP 1 Connect a PC to an available LAN port on the back panel. After you power on the
PC, your PC becomes a DHCP client of the RV315W and receives an IP address in
the 192.168.1.xxx range.
STEP 2 Start a web browser. In the address bar, enter the default IP address of the
RV315W: 192.168.1.1.
STEP 3 When the login page appears, choose the language that you prefer to use in the
utility and enter the username and password.
The default username is cisco. The default password is cisco. Both usernames
and passwords are case sensitive.
STEP 4 Click Login. The Change Password page opens.
For security purposes, change the password from its default settings at your first
login to prevent unauthorized access.
STEP 5 Enter the old password.
STEP 6 Enter the new password. Passwords should contain at least three of these
character classes: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special
characters. Passwords must be at least eight characters in length.
NOTE Checking Disable Password Strength Enforcement will not enforce the
minimum password complexity requirements for password changes.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 13
Page 17

Getting Started
Performing Basic Configuration Tasks
STEP 7 Enter the new password again to confirm and click Save. You are required to log in
to the utility again with the new password.
Using the Help System
The utility provides a context-sensitive help file for all configuration tasks. To view
the help page, click the Help link in the top right corner of the screen. A new
window opens with information about the page that you are currently viewing.
Performing Basic Configuration Tasks
We recommend that you complete the tasks in this section before you configure
the RV315W.
1
Changing the Default Administrator Password
The default administrator account (cisco) has full privilege to set the configuration
and read the system status. For security purposes, we recommend that you
change the default administrator password after your first login.
To change the default administrative password:
STEP 1 Click System Management > User Management. The User Management page
opens.
STEP 2 Check the default administrator account (cisco) and click Change Password.
STEP 3 Enter the following information:
• Old Password: Enter the current administrator password.
• New Password: Enter a new administrator password. Passwords are case
sensitive. By default, passwords should contain at least three of these
character classes: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special
characters. Passwords must be at least eight characters in length.
• Password Confirm: Enter the password again for confirmation.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 14
Page 18

Getting Started
Performing Basic Configuration Tasks
Upgrading Your Firmware After Your First Login
After you log in to web-based Configuration Utility for the first time, we
recommend that you upgrade your firmware to the latest version before you do
any other tasks.
NOTE This feature requires that you have an active WAN connection to access the
Internet.
To upgrade the firmware:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Firmware Upgrade. The Firmware Upgrade page
opens.
STEP 2 In the Download the latest firmware area, click Download to download the latest
version of the firmware from the specified website to your local PC. Make sure that
you have an active WAN connection.
1
STEP 3 In the Locate & select the upgrade file area, click Browse to locate and select the
downloaded firmware image from your local PC.
STEP 4 Click Upgrade.
After the new firmware image is validated, the system first overwrites the
secondary firmware with the new version in the flash, and then reboots with the
new firmware image. The new firmware image becomes the primary firmware
image and the previous primary firmware image becomes the secondary
firmware image.
Backing Up Your Configuration
At any point during the configuration process, you can back up your configuration.
Later, if you make changes that you want to abandon, you can easily restore the
saved configuration.
To back up your configuration:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Configuration Management. The Configuration
Management page opens.
STEP 2 Click Backup Configuration to back up the settings currently used on your
RV315W.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 15
Page 19
Getting Started
Performing Basic Configuration Tasks
STEP 3 Select where to locate the configuration file, and then click Save.
1
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 16
Page 20

Using the Setup Wizard
This chapter describes how to use the Setup Wizard to quickly configure the initial
settings of your RV315W. Refer to the following sections:
• Starting the Setup Wizard
• Configuring WAN Connection
• Configuring Default LAN Settings
• Configuring Wireless Connection
• Completing the Setup Wizard
2
Starting the Setup Wizard
STEP 1 Click Setup Wizard in the left-hand navigation pane. The Setup Wizard launches.
STEP 2 If you are an expert, you can exit the Setup Wizard and click the menu in the left-
hand navigation pane to configure the specific feature directly. If you want to
continue, click Next to proceed to the WAN Configuration page. Or you can click
Exit to exit the Setup Wizard.
Configuring WAN Connection
From the WAN Configuration page you can configure the WAN connection by
using information provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Depending on the requirements of your ISP, choose the Internet connection type
and configure the corresponding fields. The RV315W supports four types of
network addressing modes: DHCP, Static IP, PPPoE, and L2TP.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 17
Page 21

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring WAN Connection
STEP 3 Choose WAN0 or WAN1 (only available when the WAN1/LAN0 port on the back
STEP 4 Choose a proper network addressing method from the Internet Connection Type
2
panel is set to a secondary WAN port) from the WAN Port drop-down menu to
connect to the Internet.
drop-down menu and specify the corresponding settings.
The following table provides the configuration instruction for each Internet
connection type. Confirm that you have proper network information from your ISP
or a peer router to configure the RV315W to access the Internet.
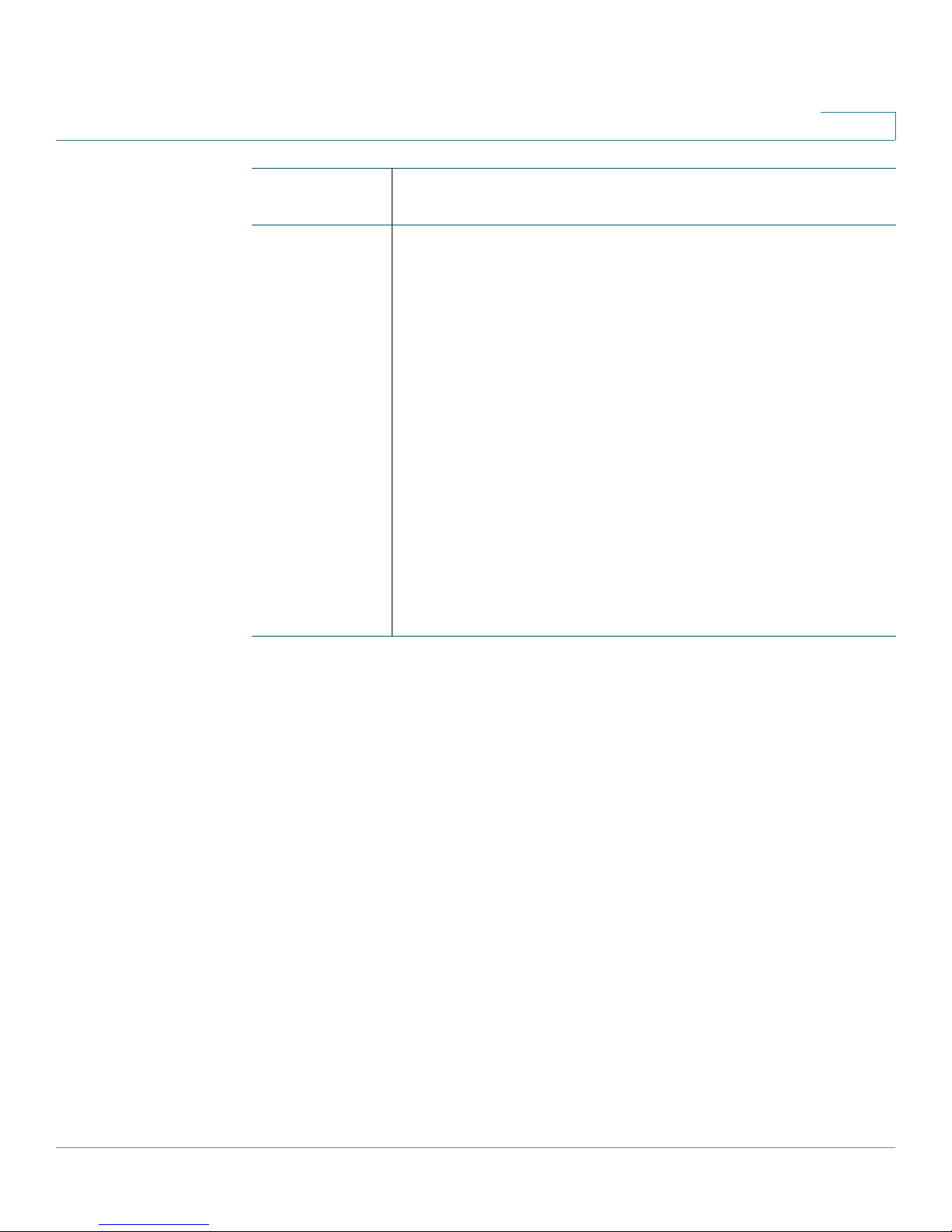
Connection
Type
DHCP Connection type often used with cable modems. Choose this
Configuration
option if your ISP dynamically assigns an IP address on
connection, and enter the following information:
• Enable DNS Server: Click Enable to enable the DNS
server, or click Disable to disable this feature.
• Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the
primary DNS server.
• Secondary DNS Server: (Optional) Enter the IP
address of the secondary DNS server.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 18
Page 22
Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring WAN Connection
2
Connection
Type
Static IP Choose this option if your ISP provides you with a static
Configuration
(permanent) IP address and does not assign it dynamically,
and use the corresponding information from your ISP to
complete the following fields:
• IP Address: Enter the IP address of the WAN port that
can be accessible from the Internet.
• Subnet Mask: Enter the IP address of the subnet mask.
• Default Gateway: Enter the IP address of default
gateway.
• Primary DNS Server: DNS servers map Internet
domain names to IP addresses. Enter the IP address of
the primary DNS server. You can get the DNS server
address from your ISP.
• Secondary DNS Server: (Optional) Enter the IP
address of the secondary DNS server.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 19
Page 23

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring WAN Connection
2
Connection
Type
PPPoE Choose this option if your ISP provides the username and
Configuration
password to connect to the Internet, and use the
corresponding information from your ISP to complete the
following fields:
• Username: Enter the username that is required to log
into the ISP.
• Password: Enter the password that is required to log
into the ISP.
• Service Name: Enter the name for the PPPoE service.
• Enable DNS Server: Click Enable to enable the DNS
server, or click Disable to disable this feature.
• Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the
primary DNS server.
• Secondary DNS Server: (Optional) Enter the IP
address of the secondary DNS server.
• Keep Alive: Choose one of the following options:
- Connect on Demand: Let the RV315W disconnect
from the Internet after a specified period of
inactivity (Idle Time). This option is recommended if
your ISP fees are based on the time that you spend
online. If you choose this option, enter the idle time
in the Maximum Idle Time field. The default value is
300 seconds.
- Keep Alive: Keep the connection always on,
regardless of the level of activity. This option is
recommended if you pay a flat fee for your Internet
service. If you choose this option, enter the interval
to automatically reestablish the WAN connection
after the connection is down. The default value is 30
seconds.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 20
Page 24

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring WAN Connection
2
Connection
Type
L2TP Choose this option if you want to use Layer 2 Tunneling
Configuration
Protocol (L2TP) to connect to the Internet, and use the
necessary information from your ISP to complete the L2TP
configuration:
• Auto Get IP: Click Enable to automatically obtain an IP
address from your service provider, or click Disable to
disable this feature.
• L2TP Server IP Address: Enter the IP address of the
L2TP server.
• Username: Enter the username that is required to log in
to the L2TP server.
• Password: Enter the password that is required to log in
to the L2TP server.
• Enable DNS Server: Click Enable to enable the DNS
server, or click Disable to disable this feature.
• Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the
primary DNS server.
• Secondary DNS Server: (Optional) Enter the IP
address of the secondary DNS server.
• Keep Alive: Choose one of the following options:
- Connect on Demand: Let the RV315W disconnect
from the Internet after a specified period of
inactivity (Idle Time). This option is recommended if
your ISP fees are based on the time that you spend
online. If you choose this option, enter the idle time
in the Maximum Idle Time field. The default value is
300 seconds.
- Keep Alive: Keep the connection always on,
regardless of the level of activity. This option is
recommended if you pay a flat fee for your Internet
service. If you choose this option, enter the interval
to automatically reestablish the WAN connection
after the connection is down. The default value is 30
seconds.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 21
Page 25
Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring Default LAN Settings
STEP 5 In the Enable VLAN area, click Enable when the ISP uses the VLAN ID to add the
tag to the users, and enter the following information:
• VLAN ID: Enter the tag of the VLAN ID.
• 802.1p Priority: Enter the value of the 802.1p priority.
STEP 6 In the MTU area, choose Auto to use the default MTU size or choose Manual if you
want to specify another size. If you choose Manual, enter the custom MTU size in
bytes.
STEP 7 If you want to continue, click Next to proceed to the LAN Configuration page. If you
want to return to the previous page, click Back. If you want to exit the Setup
Wizard, click Exit.
Configuring Default LAN Settings
2
From the LAN Configuration page you can configure the default LAN settings of
the RV315W.
STEP 8 Enter the following information:
• VLAN: Select a VLAN from the drop-down menu. See Configuring VLAN
Settings for more information on configuring the VLANs.
• IP Address: Enter the subnet IP address of the default LAN.
• Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask of the default LAN.
• DHCP Server: Click Enable to allow the RV315W to act as a DHCP server
and assign IP addresses to all devices that are connected to the LANs. Any
new DHCP client joining the LANs is assigned an IP address of the DHCP
pool. Click Disable to disable the DHCP server on the RV315W.
• Start IP: Enter the starting IP address of the DHCP pool if you enable the
DHCP server.
• End IP: Enter the ending IP address of the DHCP pool if you enable the DHCP
server.
• Lease Time: Enter the maximum connection time in minutes that a dynamic
IP address is “leased” to a network user. When the time elapses, the dynamic
IP address of the user is automatically renewed. The default is 0, indicates
that the lease time is 1 day.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 22
Page 26

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring Wireless Connection
STEP 9 If you want to continue, click Next to proceed to the Wireless Configuration page.
If you want to return to the previous page, click Back. If you want to exit the Setup
Wizard, click Exit.
Configuring Wireless Connection
From the Wireless Configuration page you can configure the wireless network of
the RV315W and the security settings for the selected SSID.
STEP 10 Enter the following information:
• Current SSID: Select the SSID as the default wireless access point of the
RV315W.
• SSID Name: Displays the name of the selected SSID. You can edit the SSID
name. Enter a unique name for the SSID for identification.
2
• Enable Current SSID: Click Enable to enable this SSID, or click Disable to
disable the SSID.
• Security Mode: Choose the security mode and configure the
corresponding security settings. For security purposes, we strongly
recommend that you use WPA2 for wireless security.
The following table lists all available security modes:
Security Mode Configuration
Disable Any wireless device that is in range can connect to the
SSID.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 23
Page 27

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring Wireless Connection
Security Mode Configuration
WEP WEP encryption is an older encryption method that is not
2
considered to be secure and can easily be broken.
Choose this option only if you need to allow access to
devices that do not support WPA or WPA2, and enter the
following information:
• Authentication Type: Choose either Open System
or Shared key. The default is Open System.
• Key Length: Choose either 64 bits or 128 bits. The
default is 64 bits. The larger size keys provide
stronger encryption, which makes the key more
difficult to crack.
• Passphrase: If you want to generate WEP keys by
using a Passphrase, enter any alphanumeric phrase
(between 4 to 63 characters) and then click
Generate to generate 4 unique WEP keys. Select
one key to use as the key that devices must have to
use the wireless network.
• Key Index: Choose a key index as the default
transmit key. Key indexes 1 through 4 are available.
• Key 1-4: If a WEP Passphrase is not specified, a key
can be entered directly into one of the Key boxes.
The length of the key should be 5 ASCII characters
(or 10 hex characters) for 64-bit encryption and 13
ASCII characters (or 26 hex characters) for 128-bit
encryption.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 24
Page 28

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring Wireless Connection
Security Mode Configuration
2
WPA-Personal
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) provides better security
than WEP because it uses dynamic key encryption. This
standard was implemented as an intermediate measure to
replace WEP, pending final completion of the 802.11i standard for WPA2.
WPA-Personal supports Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP) or Advanced Encryption System (AES) encryption
mechanisms for data encryption (default is TKIP+AES).
TKIP uses dynamic keys and incorporates Message
Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection against hackers.
AES uses symmetric 128-bit block data encryption.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Pre-Shared Key: The Pre-shared Key (PSK) is
the shared secret key for WPA. Enter a string of at
least 8 characters to a maximum of 63 characters.
• Show Password: Check to show the pre-shared
key in plaintext.
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 25
• WPA Encryption: Choose either AES or TKIP+AES
as the encryption algorithm for data encryption. The
default is TKIP+AES.
Page 29

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring Wireless Connection
Security Mode Configuration
WPA2-Personal WPA2 provides the best security for wireless
2
transmissions. This method implements the security
standards specified in the final version of 802.11i. WPA2Personal always uses AES encryption mechanism for data
encryption.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Pre-Shared Key: The Pre-shared Key (PSK) is
the shared secret key for WPA. Enter a string of at
least 8 characters to a maximum of 63 characters.
• Show Password: Check to show the pre-shared
key in plaintext.
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
• WPA Encryption: Choose either AES or TKIP+AES
as the encryption algorithm for data encryption. The
default is AES.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 26
Page 30

Using the Setup Wizard
Configuring Wireless Connection
Security Mode Configuration
WPA-Enterprise WPA-Enterprise uses WPA with RADIUS authentication.
2
This mode supports TKIP and AES encryption
mechanisms (default is TKIP+AES) and requires the use of
a RADIUS server to authenticate users.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
• WPA Encryption: Choose AES or TKIP+AES as the
encryption algorithm for data encryption. The
default is TKIP+AES.
• RADIUS Server IP Address: Enter the IP address
of the RADIUS server.
• RADIUS Server Port: Enter the port number of the
primary RADIUS server. The default value is 1812.
• RADIUS Server Key: Enter the key for
authentication used by the RADIUS server and the
RV315W.
• Show Password: Check to show the key for
authentication in plaintext.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 27
Page 31

Using the Setup Wizard
Completing the Setup Wizard
2
Security Mode Configuration
WPA2-Enterprise WPA2-Enterprise uses WPA2 with RADIUS authentication.
This mode always uses AES encryption mechanism for
data encryption and requires the use of a RADIUS server
to authenticate users.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
• WPA Encryption: Choose AES or TKIP+AES as the
encryption algorithm for data encryption. The
default is AES.
STEP 11 If you want to continue, click Next to proceed to the Complete Setup Wizard page.
If you want to return to the previous page, click Back. If you want to exit the Setup
Wizard, click Exit.
Completing the Setup Wizard
From the Complete Setup Wizard page you can see the summary information for
all configurations.
• RADIUS Server IP Address: Enter the IP address
of the RADIUS server.
• RADIUS Server Port: Enter the port number of the
primary RADIUS server. The default value is 1812.
• RADIUS Server Key: Enter the key for
authentication used by the RADIUS server and the
RV315W.
• Show Password: Check to show the key for
authentication in plaintext.
STEP 12 If you want to return to the previous page, click Back. If you want to exit the Setup
Wizard, click Exit.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 28
Page 32

Using the Setup Wizard
Completing the Setup Wizard
STEP 13 If the configuration is correct, click Finish to apply the settings and complete the
2
Setup Wizard configuration.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 29
Page 33

Viewing System Status
This chapter describes how to view real-time statistics and other information
about the RV315W. Refer to the following sections:
• Device Information
• WAN Connection
• 3G Wireless Connection
• LAN Interfaces
• WLAN Connection
• DHCP Clients
3
• Application Information
• Processes Information
• Refresh Rate
Click System Summary. The System Summary page opens.
Device Information
The Device Information area displays the following information:
• Product Name: Product name of the unit.
• Device Model: Product model of the unit.
• VID: Version ID of the unit.
• Serial Number: Serial number of the unit.
• Hardware Version: Hardware version that the unit is currently using.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 30
Page 34

Viewing System Status
WAN Connection
WAN Connection
The WAN Connections area displays the following information:
3
• Primary Firmware Version: Firmware version that the unit is currently
using.
• Secondary Firmware Version: Firmware version that is used as backup.
• System Up Time: Duration for which the system has been running.
• CPU Utilization: Current CPU utilization in percentage of the unit.
• Memory Utilization: Current memory utilization in percentage of the unit.
• WAN Port: Name of the physical WAN interface.
• Port Status: Shows if the physical WAN interface is active or inactive for
routing.
• WAN Connection Name: Connection name through the WAN interface or
its WAN subinterface.
• IP Address: IP address of the WAN interface or its WAN subinterface.
3G Wireless Connection
The 3G Wireless Connection area displays the following information:
• 3G Wireless Network: Displays whether the RV315W is connected to a 3G
wireless network or not.
• 3G Modem Status: Displays whether a 3G USB dongle is detected or not.
The 3G USB dongle should be inserted into the 3G USB port on the back
panel.
• UIM Card Status: Displays whether the UIM card is detected or not. The
UIM card should be inserted into the 3G USB dongle.
• Signal Strength: Displays current 3G wireless signal strength if the
RV315W is connected to a 3G wireless network.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 31
Page 35

Viewing System Status
3G Wireless Connection
STEP 1 Click Details. The following information is displayed:
3
To see complete details of the 3G wireless connection:
• 3G Modem Information: Displays information of the 3G USB dongle that is
detected by the RV315W:
- 3G Modem Status: Displays whether the RV315W is connected to a 3G
wireless network or not.
- Device Model: Model number of the detected 3G USB dongle.
- Manufacturer: Manufacturer name of the detected 3G USB dongle.
- Network Access License: Identification number of the network access
certificate.
- Serial Number: Serial number of the 3G USB dongle.
- Hardware Version: Hardware version of the 3G USB dongle.
- Firmware Version: Software version that the 3G USB dongle is currently
using.
- PRL Version: PRL version of the 3G USB dongle.
• UIM Card Information: Displays information of the UIM card that is detected
by the 3G USB dongle:
- UIM Card Status: Current status of the UIM card.
- IMSI: IMSI number of the UIM card.
- Voltage: Current voltage of the UIM card.
• 3G Network Information: Displays information of the 3G wireless network:
- Service Operator: Name of the 3G network service provider.
- Operating Status: Displays whether the RV315W is connected to a 3G
wireless network or not.
- Flow Rate: Current flow rate of the 3G wireless network.
- Transfer Rate: Current transfer rate of the 3G wireless network.
- Uptime: Duration for which the 3G wireless connection has been running.
- Signal Strength: Wi-Fi signal strength of the 3G wireless connection.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 32
Page 36

Viewing System Status
LAN Interfaces
STEP 2 Click Back to return to the System Summary page.
LAN Interfaces
The LAN Interfaces area displays the connection status for each LAN port.
• LANx: Displays the LAN port number.
• Status: Displays whether the LAN port is connected or disconnected.
WLAN Connection
3
DHCP Clients
STEP 1 Click Details and choose a DHCP server from the drop-down menu.
The WLAN Connections area displays the following information for all wireless
access points supported on the RV315W:
• SSID: Name of the wireless access point.
• Status: Shows if the wireless access point is enabled or disabled.
• Number of Connected Devices: Number of the client stations that are
connected to the wireless access point.
The DHCP Clients area displays information for all DHCP servers defined on the
RV315W and its DHCP clients.
To see complete details for all clients that are connected to the RV315W:
The following information is displayed:
• Hostname: Hostname of the connected device.
• IP Address: IP address of the connected device.
• MAC Address: MAC address of the connected device.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 33
Page 37

Viewing System Status
Application Information
• Lease Time: Duration for which the IP address is leased to the connected
device.
• Interface: Shows how the client is connected to the RV315W.
STEP 2 Click Back to return to the System Summary page.
Application Information
The Application Information area displays the following information for the
applications (such as IPsec VPN) that are running on the RV315W:
• Application Name: Name of the running service or application.
3
• Status: Shows if the service or application is enabled or disabled.
Processes Information
The Processes area displays information for active Internet connections.
To see complete details for active Internet connections:
STEP 1 Click Details. The following information is displayed:
• Proto: The protocol (TCP, UDP, or raw) used by the socket.
• Recv-Q: The count of bytes not copied by the user program connected to
this socket.
• Send-Q: The count of bytes not acknowledged by the remote host.
• Local Address: Address and port number of the local end of the socket.
• Foreign Address: Address and port number of the remote end of the socket.
• State: The state of the socket. Because there are no states in raw mode and
usually no states used in UDP, this column may be left blank. Normally the
state can be one of several values:
- ESTABLISHED: The socket has an established connection.
- SYN_SENT: The socket is actively attempting to establish a connection.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 34
Page 38

Viewing System Status
Refresh Rate
3
- SYN_RECV: A connection request has been received from the network.
- FIN_WAIT1: The socket is closed, and the connection is shutting down.
- FIN_WAIT2: The connection is closed, and the socket is waiting for a
shutdown from the remote end.
- TIME_WAIT: The socket is waiting after the closing to handle packets still
in the network.
- CLOSED: The socket is not being used.
- CLOSE_WAIT: The remote end has shut down, waiting for the socket to
close.
- LAST_ACK: The remote end has shut down, and the socket is closed.
Waiting for acknowledgement.
- LISTEN: The socket is listening for incoming connections. Such sockets
are not included in the output unless you specify the --listening (-l) or --all
(-a) option.
STEP 2 Click Back to return to the System Summary page.
Refresh Rate
- CLOSING: Both sockets are shut down but we still do not have all our
data sent.
- UNKNOWN: The state of the socket is unknown.
Choose a refresh rate from the Refresh Rate drop-down menu, or choose
Manually Refresh to manually refresh the page at any time by clicking Refresh.
This operation causes the page to re-read the statistics from the RV315W and
refresh the page.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 35
Page 39

Port Management
This chapter describes how to configure your Internet connection, LAN, wireless
network, and 3G wireless network. Refer to the following sections:
• Configuring WAN
• Configuring LAN
• Configuring WLAN
• Configuring 3G Wireless Connection
Configuring WAN
4
By default, the RV315W is configured to receive a public IP address from your ISP
automatically through DHCP. Depending on the requirements of your ISP, you may
need to modify the WAN settings to ensure the Internet connectivity.
Viewing WAN Connection Information
Click Port Settings > WAN > WAN Interface Settings. The WAN Interface
Settings page opens.
This page displays the following information:
Parameter Description
Port Port number of the physical WAN interface, such as
WAN0 or WA N1.
Connection Name WAN connection name through the physical WAN
interface or its subinterface.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 36
Page 40

Port Management
Configuring WAN
4
Parameter Description
Internet Connection
Type
IP Address IP address of the WAN interface.
DNS IP address of the DNS server for the WAN interface.
Status Shows if the WAN interface is active or inactive for
Network addressing mode used to connect to the
Internet. See Configuring WAN Connection for more
information.
routing.
Configuring WAN Connections
By default, the WAN1/LAN0 port on the back panel of the RV315W is set to a
secondary WAN interface so that the RV315W can support a second Internet
connection to ensure continuous connectivity or to increase available bandwidth
and balance traffic.
The RV315W allows you to add multiple subinterfaces on a physical WAN
interface. Each WAN subinterface can be used to set up an Internet connection but
only one of these connections can be used as the default route of the physical
WAN interface. Up to eight WAN subinterfaces can be added on the physical WAN
interfaces.
To configure a WAN connection through a physical WAN interface or its
subinterface:
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > WAN > WAN Interface Settings. The WAN Interface
Settings page opens.
STEP 2 To add a WAN subinterface on a physical WAN interface, click Add Subinterface.
STEP 3 Choose either Route Mode or Bridge Mode for a WAN subinterface from the
Internet Connection Type drop-down menu.
NOTE The Route Mode is always selected for a physical WAN interface.
STEP 4 If Route Mode is selected, select one of the following options to connect to the
Internet and specify the corresponding fields:
• DHCP: Choose this option if your ISP dynamically assigns an IP address on
connection and enter the following information:
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 37
Page 41

Port Management
Configuring WAN
4
- Enable DNS Server: Click Enable to enable the DNS server, or click
Disable to disable this feature.
- Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
- Secondary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS
server.
• Static IP: Choose this option if the ISP provides you with a static
(permanent) IP address and does not assign it dynamically, and use the
corresponding information from your ISP to complete the following fields:
- IP Address: Enter the IP address of the WAN port that can be accessible
from the Internet.
- Subnet Mask: Enter the IP address of the subnet mask.
- Default Gateway: Enter the IP address of default gateway.
- Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
- Secondary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS
server.
• PPPoE: Choose this option if your ISP provides you with client software,
username, and password, and use the necessary PPPoE information from
your ISP to complete the PPPoE configuration:
- Username: Enter the username that is required to log into the ISP.
- Password: Enter the password that is required to log into the ISP.
- Service Name: Enter the name for the PPPoE service.
- Enable DNS Server: Click Enable to enable the DNS server, or click
Disable to disable this feature.
- Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
- Secondary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS
server.
- Keep Alive: Choose one of the following options:
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 38
Connect on Demand: Choose this option to let the RV315W disconnect
from the Internet after a specified period of inactivity (Idle Time). This
option is recommended if your ISP fees are based on the time that you
spend online. Enter the idle time in the Maximum Idle Time field. The
default value is 300 seconds.
Page 42

Port Management
Configuring WAN
4
Keep Alive: Choose this option to keep the connection always on,
regardless of the level of activity. This option is recommended if you pay
a flat fee for your Internet service. You can specify the interval to
automatically reestablish the WAN connection after the connection is
down. The default value is 30 seconds.
• L2TP: Choose this option if you want to use Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
(L2TP) to connect to the Internet, and use the necessary information from
your ISP to complete the L2TP configuration:
- Auto Get IP (DHCP): Click Enable to automatically obtain an IP address
from your service provider, or click Disable to disable this feature.
- L2TP Server IP Address: Enter the IP address of the L2TP server.
- Username: Enter the username that is required to log into the L2TP
server.
- Password: Enter the password that is required to log into the L2TP
server.
- Enable DNS Server: Click Enable to enable the DNS server, or click
Disable to disable this feature.
- Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
- Secondary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS
server.
- Keep Alive: Choose one of the following options:
Connect on Demand: Let the RV315W disconnect from the Internet after
a specified period of inactivity (Idle Time). This option is recommended if
your ISP fees are based on the time that you spend online. Enter the idle
time in the Maximum Idle Time field. The default value is 300 seconds.
Keep Alive: Keep the connection always on, regardless of the level of
activity. This option is recommended if you pay a flat fee for your Internet
service. You can specify the interval to automatically reestablish the WAN
connection after the connection is down. The default value is 30 seconds.
STEP 5 Specify other settings if Route Mode is selected:
• Enable NAT: Click Enable to enable NAT, or click Disable to disable NAT.
Disable this feature if the WAN connection is only used for management
purposes.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 39
Page 43

Port Management
Configuring WAN
4
• Enable VLAN: Click Enable to enable VLAN if your ISP uses the VLAN ID to
identify the users, and specify the VLAN ID and the 802.1p priority in the
VLAN ID and 802.1p Priority fields.
• MTU: Choose Auto to use the default MTU size or choose Manual if you
want to specify another size. If you choose Manual, enter the custom MTU
size in bytes.
• Service Binding: Choose one of the following service types for the WAN
connection:
- Management: Only use for management purpose.
- Internet: Only use for Internet access purpose.
- Management_Internet: Use for both management and Internet access
purposes.
- VoIP: Only use for VoIP traffic.
- IPTV: Only use for IPTV traffic.
- Other: Use for other purposes.
STEP 6 If Bridge Mode is selected, enter the following information:
• Enable NAT: Click Enable to enable NAT or click Disable to disable NAT.
Disable this feature if the WAN connection is only used for management
purpose.
• Enable VLAN: Click Enable to enable VLAN if your ISP uses the VLAN ID to
identify the users, and specify the VLAN ID and the 802.1p priority in the
VLAN ID and 802.1p Priority fields.
• MTU: Choose Auto to use the default MTU size or choose Manual if you
want to specify another size. If you choose Manual, enter the custom MTU
size in bytes.
• Binding Ports: Specify the port as the subinterface's downstream path.
STEP 7 Click Save to save your settings and return to the WAN Interface Settings page.
To edit the settings of a WAN connection through a physical WAN interface or a
WAN su binter face , clic k Edit. To delete a WAN connection through a WAN
subinterface, click Delete.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 40
Page 44

Port Management
Configuring WAN
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > WAN > WAN Interface Settings. The WAN Interface
STEP 2 In the WAN Port Default Route area, choose the default route interface for each
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
4
Configuring Default Route of the Physical WAN Interface
If multiple WAN connections are defined on a physical WAN interface, you must
choose the default route of the physical WAN interface.
To configure the default route of the physical WAN interface:
Settings page opens.
physical WAN interface.
Configuring Multi-WAN
If you have two ISP links, one for WAN0 and another for WAN1, you can configure
the WAN redundancy to determine how the two ISP links are used.
NOTE Multi-WAN is only available when the WAN0/LAN1 port on the back panel is set to
a secondary WAN port (WAN1).
To configure Multi-WAN:
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > WAN > Multi-WAN. The Multi-WAN page opens.
STEP 2 In the Multi-WAN area, enter the following information:
• WAN Failover: Click Enable to enable the WAN Failover feature, or click
Disable to disable it. When WAN Failover is enabled, the RV315W diverts all
Internet traffic to the backup link if a failure is detected on the primary link.
When the primary link regains connectivity, all Internet traffic is directed to
the primary link and the backup link becomes idle. By default, WAN0 is set
as the primary link and the WAN1 is set as the backup link.
• Link Query Interval: The RV315W detects the WAN failure by pinging the
specified IP address. Enter the interval in seconds between two ping
detections. The default is 60 seconds.
• Ping Timeout: If the connection to the ISP is down, the RV315W tries to
connect to the ISP after a specified timeout. Enter the timeout, in seconds, to
reconnect to the ISP. The default is 5 seconds.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 41
Page 45

Port Management
Configuring WAN
STEP 3 In the Failover Detection area, specify the IP address used to detect the WAN
STEP 4 In the WAN Interfaces area, specify the priorities for the WAN interfaces, including
4
• Number of Pings: Enter the number of pings. The default is 1.
• Recover the connection after x connection queries: Enter the number of
successful ping detections to recover the connection. The WAN connection
with the higher priority will be recovered.
failure. By default, RV315W pings the IP address of default WAN gateway with the
higher priority. If the default WAN gateway can be detected, the network
connection is active. You can also ping a specific remote host to detect the WAN
failure.
• Gateway: Pings the IP address of default WAN gateway.
• User-defined: Pings a specific remote host. If you choose this option, enter
the IP address of the specific remote host to ping.
the 3G USB port:
• Interface: Name of the WAN interface.
• Status: Connection status of the WAN interface.
• Priority: Choose the priority of the WAN interface from the drop-down
menu.
STEP 5 In the WAN Interface Details area, view the following information of the WAN
interfaces:
• Interface: Name of the WAN interface.
• IP Address: IP address of the WAN interface.
• Subnet Mask: Subnet mask of the WAN interface.
• Gateway: Default gateway IP address of the WAN interface.
STEP 6 In the Load Balancing area, click Enable to enable Load Balancing to distribute the
bandwidth to two WAN ports by the weighted percentages, or click Disable to
disable this feature.
STEP 7 In the Load Balancing Settings area, specify the weighted percentage for each
WAN interface, such as 50% bandwidth for WAN0, 50% bandwidth for WAN1, and
0% for USB_3G, which indicates that 50% bandwidth is distributed to WAN0 and
50% bandwidth is distributed to WAN1. The value of zero (0) indicates that Load
Balancing is disabled on the 3G WAN interface.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 42
Page 46

Port Management
!
Configuring LAN
STEP 8 Click Save to save your settings.
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > WAN > WAN1/LAN0. The WAN1/LAN0 page opens.
STEP 2 Click LAN0 to set this port to an additional LAN port, or click WAN1 to set this port
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
4
Configuring WAN1/LAN0 Interface
The WAN1/LAN0 interface on the back panel of the RV315W can be configured to
a secondary WAN interface (WAN1) or an additional LAN interface (LAN0).
To set the port type of the WAN1/LAN0 interface:
to a secondary WAN port.
CAUTION Changing the port type of the WAN1/LAN0 interface requires the RV315W to be
rebooted. Note that changing the port type from WAN1 to LAN0 will reboot the
RV315W with the factory default settings. The previous settings that you made on
the RV315W will be lost.
Configuring LAN
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a group of endpoints in a network that are associated by
function or other shared characteristics. Unlike LANs, which are usually
geographically based, VLANs can group endpoints without regard to the physical
location of the equipment or users.
The VLANs allow you to segregate the network into LANs that are isolated from
one another. Any PC that is connected to the specified LAN port is on a separate
VLAN and cannot access other VLANs.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 43
Page 47

Port Management
Configuring LAN
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > LAN > LAN Configuration. The LAN Configuration page
STEP 2 In the LAN Configuration area, specify the following information for a VLAN:
4
Configuring LAN Interface Settings
Use the LAN Configuration page to configure the LAN interface settings for a
VLAN.
To configure the LAN interface settings for a VLAN:
opens.
• VLAN: Choose a VLAN that you want to configure from the drop-down menu.
To add a new VLAN and assign physical LAN interfaces or wireless
interfaces to the VLAN, go to the VLAN Settings page. See Configuring
VLAN Settings for more information.
• IP Address: Enter the subnet IP address for the VLAN.
• Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask for the VLAN.
• DHCP Service: Click Enable to allow the RV315W to act as a DHCP server
and assign IP addresses to all devices that are connected to the VLAN. Any
new DHCP client joining the VLAN is assigned an IP address of the DHCP
pool. Click Disable to disable the DHCP server on the RV315W.
• Start IP: Enter the starting IP address of the DHCP pool if you enable the
DHCP service.
• End IP: Enter the ending IP address of the DHCP pool if you enable the DHCP
service.
• Gateway Address: Enter the IP address for default gateway.
• Lease Time: Enter the maximum connection time that a dynamic IP address
is “leased” to a network user. When the time elapses, the user is
automatically renewed the dynamic IP address. The default value is 1 day.
• DNS Proxy: Click Enable to enable the DNS proxy feature, or click Disable
to disable this feature.
• DNS Server 1: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
• DNS Server 2: Optionally, enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
• Reserve Address: Click Enable to allow you to reserve some IP addresses
of the DHCP pool for specific hosts, or click Disable to disable this feature.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 44
Page 48

Port Management
Configuring LAN
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
STEP 4 In the DHCP Service List area, the DHCP service status and its DHCP pool
4
• Manually Add Hosts: Specify the following information to reserve an IP
address for a host and then click Add:
- Hostname: Enter the name of the host for identification.
- IP Address: Enter the IP address that you want to reserve for the host.
- Host MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the host.
settings for each VLAN are displayed. To delete a DHCP server, check the VLAN
and click Delete. Default VLAN 1 cannot be deleted.
Configuring VLAN Settings
Use the VLAN Settings page to create new VLANs and assign physical LAN ports
and/or wireless interfaces to the specified VLANs.
To c r e a t e a n e w V L A N :
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > LAN > VLAN Settings. The VLAN Settings page opens.
STEP 2 To create a new VLAN, select the Add radio button and enter a unique
identification number for the VLAN in the VLAN ID field (VLAN1 and VLAN2 are
reserved by default).
STEP 3 Assign the physical LAN interfaces or wireless interfaces to the VLAN by moving
them from the list of Available Ports to the list of Selected Ports. Traffic through
the selected interfaces is mapped to the VLAN.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
STEP 5 To delete a VLAN, select the Delete radio button and choose the VLAN ID from the
Choose VLAN drop-down men, and then click Save. The reserved VLAN1 and
VLAN2 cannot be deleted.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 45
Page 49

Port Management
Configuring WLAN
Configuring WLAN
The wireless module of the RV315W is enabled by default. To connect to the
default wireless network of the RV315W for the first time, use the default wireless
network name (SSID) and pre-shared key that are provided on the product label at
the bottom of the RV315W.
Configuring Wireless Radio Settings
To configure wireless radio settings:
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > Wireless. The Wireless page opens.
STEP 2 In the Wireless Radio Settings area, enter the following information:
4
• Wireless Radio: Click Enable to turn the wireless radio on, or click Disable
to turn the wireless radio off. The wireless radio is turned on by default.
• Wireless Network Mode: Choose one of the following options:
- 802.11b/g/n mixed: Choose this option if you have Wireless-N,
Wireless-B, and Wireless-G devices in your network. This is the default
setting (recommended).
- 802.11b/g mixed: Choose this option if you have Wireless-B and
Wireless-G devices in your network.
- 802.11b: Choose this option if you have only Wireless-B devices in your
network.
- 802.11g: Choose this option if you have only Wireless-G devices in your
network.
- 802.11n: Choose this option if you have only Wireless-N devices in your
network.
• Wireless Band Selection: Choose either 20 MHz or 20/40 MHz as the
wireless bandwidth on your network.
• Wireless Channel: Choose the wireless channel from the drop-down menu
or choose Auto to let the system determine the optimal channel to use based
on the environmental noise levels for the available channels.
- Choose any channel from 1 to 13 channels when the wireless bandwidth
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 46
is set to 20 MHz.
Page 50

Port Management
Configuring WLAN
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
4
- Choose any channel from 3 to 11 channels when the wireless bandwidth
is set to 20/40 MHz (the default is 11 channel).
• Wi-Fi Power: Choose the Wi-Fi power on your network. The default is High.
• Station Isolation: Check so that the wireless clients on the same SSID
cannot see each other, or uncheck so that the wireless clients on the same
SSID can see each other.
• Wireless QoS: Check to enable WiFi MultiMedia (WMM), or uncheck to
disable this feature.
Configuring Wireless Network Settings
To configure the settings for a wireless network:
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > Wireless. The Wireless page opens.
The Wireless Basic and Security Settings area displays the following information
for a wireless network:
• SSID: Name of the SSID.
• Security Mode: Security settings of the SSID.
• Status: Shows whether the SSID is enabled or disabled.
STEP 2 To enable a SSID, check the corresponding SSID and click Enable.
STEP 3 To disable a SSID, check the corresponding SSID and click Disable.
STEP 4 To edit the settings of a SSID, check the corresponding SSID and click Edit.
STEP 5 Enter the following information:
• SSID Name: Enter a unique name of the wireless access point for
identification.
• Hide Wireless Network: Check to prevent auto-detection of the SSID. In this
case, users must know the SSID to set up a wireless connection to this SSID.
Uncheck to enable SSID broadcast and broadcast the SSID in its beacon
frames. All wireless devices within range are able to see the SSID when they
scan for available networks.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 47
Page 51

Port Management
Configuring WLAN
4
• Allow Remote Management: Check to allow you to remotely access the
RV315W through the wireless network and configure the settings of the
RV315W.
• User Limit: Click Enable to specify the maximum number of users that can
simultaneously connect to this SSID. Enter a value in the range of 0 to 30. The
default value is zero (0), which indicates that there is no limit for this SSID.
• Security Mode: Choose one of the following security modes for the SSID
and configure the corresponding security settings. For security purposes,
we strongly recommend that you use WPA2 for wireless security.
Security Mode Configuration
Disable Any wireless device that is in range can connect to the
SSID. This is the default setting but not recommended.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 48
Page 52

Port Management
Configuring WLAN
4
Security Mode Configuration
WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a data encryption
protocol for 802.11 wireless networks. All wireless
stations and SSIDs on the network are configured with a
static 64-bit or 128-bit shared key for data encryption.
The higher the bit for data encryption, the more secure for
your network.
WEP encryption is an older encryption method that is not
considered to be secure and can easily be broken.
Choose this option only if you need to allow access to
devices that do not support WPA or WPA2.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• Authentication Type: Choose either Open System
or Shared key. The default is Open System.
• Encryption: Choose the encryption type: 64 bits
(10 hex digits), 64 bits (5 ASCII), 128 bits (26 hex
digits), or 128 bits (13 ASCII). The default is 64 bits
(10 hex digits). The larger size keys provide
stronger encryption, thus making the key more
difficult to crack.
• Passphrase: If you want to generate WEP keys by
using a Passphrase, enter any alphanumeric phrase
(between 4 to 63 characters) and then click
Generate to generate 4 unique WEP keys. Select
one key to use as the key that devices must have to
use the wireless network.
• Default Transmit Key: Choose a key index as the
default transmit key. Key indexes 1 through 4 are
available.
• Key 1-4: If a WEP Passphrase is not specified, a
key can be entered directly into one of the Key
boxes. The length of the key should be 5 ASCII
characters (or 10 hex characters) for 64-bit
encryption and 13 ASCII characters (or 26 hex
characters) for 128-bit encryption.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 49
Page 53

Port Management
Configuring WLAN
4
Security Mode Configuration
WPA-Personal Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) provides better security
than WEP because it uses dynamic key encryption. This
standard was implemented as an intermediate measure to
replace WEP, pending final completion of the 802.11i
standard for WPA2.
WPA-Personal supports Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP) or Advanced Encryption System (AES) encryption
mechanisms for data encryption (default is TKIP+AES).
TKIP uses dynamic keys and incorporates Message
Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection against hackers.
AES uses symmetric 128-bit block data encryption.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Pre-Shared Key: The Pre-shared Key (PSK) is
the shared secret key for WPA. Enter a string of at
least 8 characters to a maximum of 63 characters.
• Show Password: Check to show the pre-shared
key in plaintext.
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
• Encryption Algorithm: Choose either AES or
TKIP+AES as the encryption algorithm for data
encryption. The default is TKIP+AES.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 50
Page 54

Port Management
Configuring WLAN
4
Security Mode Configuration
WPA2-Personal WPA2 provides the best security for wireless
transmissions. This method implements the security
standards specified in the final version of 802.11i. WPA2Personal always uses AES encryption mechanism for data
encryption.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Pre-Shared Key: The Pre-shared Key (PSK) is
the shared secret key for WPA. Enter a string of at
least 8 characters to a maximum of 63 characters.
• Show Password: Check to show the pre-shared
key in plaintext.
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
• Encryption Algorithm: Choose either AES or
TKIP+AES as the encryption algorithm for data
encryption. The default is AES.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 51
Page 55

Port Management
Configuring WLAN
4
Security Mode Configuration
WPA-Enterprise WPA-Enterprise uses WPA with RADIUS authentication.
This mode supports TKIP and AES encryption
mechanisms (default is TKIP+AES) and requires the use of
a RADIUS server to authenticate users.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
• Encryption Algorithm: Choose either AES or
TKIP+AES as the encryption algorithm for data
encryption. The default is TKIP+AES.
• RADIUS Server IP Address: Enter the IP address
of the RADIUS server.
• RADIUS Server Port: Enter the port number of the
primary RADIUS server. The default value is 1812.
• RADIUS Server Key: Enter the key for
authentication used by the RADIUS server and the
RV315W.
• Show Password: Check to show the key in
plaintext.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 52
Page 56

Port Management
Configuring 3G Wireless Connection
Security Mode Configuration
WPA2-Enterprise WPA2-Enterprise uses WPA2 with RADIUS authentication.
4
This mode always uses AES encryption mechanism for
data encryption and requires the use of a RADIUS server
to authenticate users.
If you choose this option, enter the following information:
• WPA Key Renewal Timeout: Enter a value to set
the interval at which the key is refreshed for clients
associated to this SSID. A value of zero (0) indicates
that the key is not refreshed. The default value is
3600 seconds.
• Encryption Algorithm: Choose either AES or
TKIP+AES as the encryption algorithm for data
encryption. The default is AES.
• RADIUS Server IP Address: Enter the IP address
of the RADIUS server.
• RADIUS Server Port: Enter the port number of the
primary RADIUS server. The default value is 1812.
• RADIUS Server Key: Enter the key for
authentication used by the RADIUS server and the
RV315W.
• Show Password: Check to show the key in
plaintext.
STEP 6 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring 3G Wireless Connection
To connect the RV315W to a 3G wireless network, you should first insert an
applicable 3G USB dongle into the 3G interface on the back panel of the RV315W
and then configure the 3G wireless network settings on the RV315W.
To obtain the list of 3G USB dongle models supported by the RV315W, see
www.cisco.com/go/rv315w.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 53
Page 57

Port Management
Configuring 3G Wireless Connection
To configure the 3G wireless network settings:
STEP 1 Click Port Settings > 3G Interface Settings. The 3G Interface Settings page
opens.
STEP 2 Enter the following information:
• Current 3G Network: Displays whether the RV315W is detected a 3G USB
• Configure Mode: Choose Auto to automatically detect the settings of the
4
dongle. The 3G USB dongle should be inserted into the 3G USB port on the
back panel.
3G USB dongle, or choose Manual to manually specify the following settings
of the 3G USB dongle:
- APN: Enter the APN provided by the 3G wireless network service
provider.
- Username: Enter the username provided by the 3G wireless network
service provider.
- Password: Enter the password provided by the 3G wireless network
service provider.
- Dial String: Enter the dial string provided by the 3G wireless network
service provider.
• Connect Mode: Choose either Auto or Manual to dial in the 3G wireless
network.
• Keep Alive: If the dial method is set to Auto, choose one of the following
options:
- Keep Alive: Keep the connection always on, regardless of the level of
activity. This option is recommended if you pay a flat fee for your Internet
service. You can specify the interval to automatically re-dial in the 3G
wireless network after the connection is down. The default is 30 seconds.
- Connect on Demand: Let the RV315W disconnect from the 3G wireless
network after a specified period of inactivity (Idle Time). This option is
recommended if your ISP fees are based on the time that you spend
online. Enter the idle time in the Maximum Idle Time field. The default is
5 seconds.
• Manual Dial Up: If the dial method is set to Manual, specify how to manually
dial in the 3G wireless network from the drop-down menu.
- To manually connect to the 3G wireless network, click Connect.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 54
Page 58

Port Management
Configuring 3G Wireless Connection
• Service Type: If your ISP supports both 3G wireless network and 4G
• Status: Shows whether the RV315W is connected to a 3G wireless network
4
- To manually terminate the 3G wireless connection, click Disconnect.
wireless network, choose one of the following options to dial in the wireless
network:
- Auto: Automatically dial in the 3G wireless network or 4G wireless
network.
- 3G Only: Only dial in the 3G wireless network.
- 4G Only: Only dial in the 4G wireless network.
NOTE You should first check the types of wireless network supported by
your 3G USB dongle, and then determine which wireless network you
want to dial in.
or not.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 55
Page 59

Networking
This chapter describes how to configure other network settings of the RV315W.
Refer to the following sections:
5
• Configuring DDNS
• Configuring Port Forwarding
• Configuring Port Triggering
• Configuring DMZ
• Configuring UPnP
• Configuring Port Mirroring
• Configuring Routing
• Configuring IGMP
Configuring DDNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is an Internet service that allows routers with varying public
IP addresses to be located using Internet domain names. If your ISP has not
provided you with a static IP and your WAN connection is configured to use DHCP
to obtain an IP address dynamically, then DDNS provides the domain name to map
the dynamic IP address for your website. To use DDNS, you must set up an
account with a DDNS provider such as DynDNS.org or TZO.
To configure a DDNS service:
STEP 1 Click Networking > Dynamic DNS. The Dynamic DNS page opens.
STEP 2 In the DDNS Settings area, click Add to add a DDNS service.
STEP 3 Enter the following information:
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 56
Page 60

Networking
Configuring Port Forwarding
• DDNS Service: Specify the provider for your DDNS service. You can choose
either DynDNS.org or TZO.
• Domain Name: Enter the complete domain name of the DDNS service.
• Username: Enter the username of the account that you registered in the
DDNS provider.
• Password: Enter the password of the account that you registered in the
DDNS provider.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring Port Forwarding
5
Port forwarding forwards a TCP/IP packet traversing a Network Address
Translator (NAT) gateway to a predetermined network port on a host within a
NAT-masqueraded, typically private network based on the port number on which
it was received at the gateway from the originating host.
Configuring Single Port Forwarding
To add a single port forwarding rule:
STEP 1 Click Networking > Port Forwarding > Single Port Forwarding. The Single Port
Forwarding page opens.
STEP 2 Enter the following information:
• Interface: Choose a WAN interface or the 3G interface for this single port
forwarding rule.
• Protocol: Choose either TCP or UDP protocol for this single port forwarding
rule.
• External Port: Specify the port number that triggers this rule when a
connection request from outgoing traffic is made. You can choose a
predefined option (such as Finger, FTP, NNTP, POP3, SMTP, Telnet, or HTTP)
to use its default port value or choose Other to manually specify the external
port used by the application.
• Internal IP Address: Enter the IP address of the internal server.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 57
Page 61

Networking
Configuring Port Forwarding
STEP 3 Click Add.
5
• Internal Port: Specify the port number used by the remote system to
respond to the request that it receives. You can choose a predefined option
(such as Finger, FTP, NNTP, POP3, SMTP, Telnet, or HTTP) to use its default
port value or choose Other to manually specify the internal port used by the
application.
• Status: Click Enable to enable this single port forwarding rule, or click
Disable to disable this rule.
Configuring Port Range Forwarding
To add a port range forwarding rule:
STEP 1 Click Networking > Port Forwarding > Port Range Forwarding. The Port Range
Forwarding page opens.
STEP 2 Enter the following information:
• Interface: Choose a WAN interface or the 3G interface for this port range
forwarding rule.
• Protocol: Choose either TCP or UDP protocol for this port range forwarding
rule.
• Port Range: Specify the starting port and ending port to forward.
• Internal IP Address: Enter the IP address of the internal server.
• Status: Click Enable to enable this port range forwarding rule, or click
Disable to disable this rule.
STEP 3 Click Add.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 58
Page 62

Networking
Configuring Port Triggering
Configuring Port Triggering
Port triggering allows devices on the LAN or DMZ to request one or more ports to
be forwarded to them. Port triggering waits for an outbound request from the LAN
or DMZ on one of the defined outgoing ports, and then opens an incoming port for
that specified type of traffic.
Port triggering is a form of dynamic port forwarding while an application is
transmitting data over the opened outgoing or incoming ports. Port triggering
opens an incoming port for a specific type of traffic on a defined outgoing port.
Port triggering is more flexible than static port forwarding (available when
configuring firewall rules) because a rule does not have to reference a specific
LAN IP or IP range. Ports are also not left open when not in use, which provides a
level of security that port forwarding does not offer.
To add a port triggering rule:
5
STEP 1 Click Networking > Port Triggering. The Port Triggering page opens.
STEP 2 Enter the following information:
• WAN Port: Choose the WAN interface for this port triggering rule.
• LAN Port: Choose the LAN port for this port triggering rule.
• Protocol: Choose either TCP or UDP protocol.
• Triggering Range: Enter the port number or a range of port numbers that will
trigger this rule when a connection request from outgoing traffic is made. If
the outgoing connection uses only one port, enter the same port number in
both fields.
• Forwarding Range: Enter the port number or a range of port numbers used
by the remote system to respond to the request that it receives. If the
incoming connection uses only one port, then specify the same port number
in both fields.
• Status: Click Enable to enable the port triggering rule, or click Disable to
disable this rule.
STEP 3 Click Add.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 59
Page 63

Networking
Configuring DMZ
Configuring DMZ
A DMZ (Demarcation Zone or Demilitarized Zone) is a sub-network that is behind
the firewall but that is open to the public. By placing your public services on a
DMZ, you can add an additional layer of security to the LAN. The public can
connect to the services on the DMZ but cannot penetrate the LAN. You should
configure your DMZ to include any hosts that must be exposed to the WAN (such
as web or email servers).
The RV315W supports the software DMZ and hardware DMZ features. The
software DMZ allows you to expose an internal host (such as the web or email
server) to the WAN. The hardware DMZ sets the LAN8 port on the back panel to a
DMZ port. This feature is only available when you use Static IP or DHCP to connect
to the Internet.
5
Configuring Software DMZ
To configure software DMZ:
STEP 1 Click Networking > DMZ > Software DMZ. The Software DMZ page opens.
STEP 2 To create a DMZ rule, enter the following information:
• DMZ Status: Click Enable to enable this DMZ rule, or click Disable to disable
this DMZ rule.
• External Address: Enter the external IP address.
• Internal Address: Enter the IP address of the internal server in the DMZ
network.
• Binding Interface: Choose an interface for this DMZ rule.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 60
Page 64

Networking
Configuring UPnP
5
Configuring Hardware DMZ
To configure the hardware DMZ:
STEP 1 Click Networking > DMZ > Hardware DMZ. The Hardware DMZ page opens.
STEP 2 In the Hardware DMZ area, click Enable to enable the hardware DMZ feature and
set the LAN8 part on the back panel to a DMZ port.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
STEP 4 If you enable the hardware DMZ feature, click Add to create a hardware DMZ rule.
STEP 5 Enter the following information:
• Status: Click Enable to enable this DMZ rule, or click Disable to disable this
DMZ rule.
• Public IP: Enter the public IP address.
• WAN Port: Choose a WAN interface for this DMZ rule.
STEP 6 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring UPnP
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) allows for automatic discovery of devices that can
communicate with your RV315W.
To enable or disable UPnP on the RV315W:
STEP 1 Click Networking > UPnP. The UPnP page opens.
STEP 2 Click Enable to enable UPnP, or click Disable to disable UPnP. If UPnP is disabled,
the RV315W will not allow for automatic device configuration.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 61
Page 65

Networking
Configuring Port Mirroring
Configuring Port Mirroring
Port Mirroring allows traffic on one port to be visible on other ports. This feature is
useful for debugging or traffic monitoring.
To configure port mirroring:
STEP 1 Click Networking > Port Mirroring. The Port Mirroring page opens.
STEP 2 In the Port Mirroring area, click Enable to enable the Port Mirroring feature, or
click Disable to disable this feature.
STEP 3 If Port Mirroring is enabled, enter the following information:
• Mirror Destination Port: Choose the port that monitors the transmitted (TX)
or received (RX) traffic for other ports.
5
• Mirror Source Port: Check the ports that are monitored. The port that you
set as a TX destination port cannot be selected as a monitored port.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring Routing
This section provides information on configuring the routing mode between WAN
and LAN, viewing the routing table, and configuring the static routing, dynamic
routing, and policy-based routing settings.
Configuring Basic Routing Settings
Depending on the requirements of your ISP, you can configure the RV315W to
operate in NAT mode or Router mode. By default, NAT mode is enabled.
Configuring Routing Mode
To configure the routing mode:
STEP 1 Click Networking > Routing > Basic Routing. The Basic Routing page opens.
STEP 2 In the Routing Mode area, configure the routing mode between WAN and LAN.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 62
Page 66

Networking
Configuring Routing
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
STEP 1 Click Networking > Routing > Basic Routing. The Basic Routing page opens.
STEP 2 In the Inter-VLAN Routing area, click Enable to enable inter-VLAN routing.
5
• If your ISP assigns an IP address for each computer that you use, click
Router to enable the Router mode.
• If you are sharing IP addresses across several devices such as your LAN,
and are using other dedicated devices for the DMZ, click Gateway to enable
the Gateway mode.
Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
To configure inter-VLAN routing:
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring Static Routing
To configure static routes, specify the IP address and related information for the
destination.
STEP 1 Click Networking > Routing > Basic Routing. The Basic Routing page opens.
STEP 2 In the Static Routes area, click Add to add a new static route.
STEP 3 Enter the following information:
• Destination Address: Enter the IP address for the host or for the network
that the route leads to.
• Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask of the destination network.
• Next Hop: Enter the IP address of the gateway through which the destination
host or network can be reached.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 63
Page 67

Networking
Configuring Routing
STEP 1 Click Networking > Routing > Policy-based Routing. The Policy-based Routing
STEP 2 Click Add to create a policy-based routing rule.
5
Configuring Policy-based Routing
Policy-based routing allows users to specify the internal IP and/or service going
through a specified WAN port to provide more flexible and granular traffic
handling capabilities.
This feature can be used to segregate traffic between links that are not of the
same speed. High volume traffic can be routed through the port connected to a
high-speed link and low-volume traffic can be routed through the port connected
to the slow link.
To configure policy-based routing:
page opens.
STEP 3 Enter the following information:
• Policy-based Routing Rule Name: Enter a unique name of the policy-based
routing rule for identification.
• Interface: Choose an interface for the policy-based routing rule.
• Source IP Address: Enter the source IP address for outbound traffic.
• Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask of the source network.
• Destination IP Address: Enter the destination IP address for outbound
traffic.
• Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask of the destination network.
• Port: Specify the port number that the policy-based routing sends out the
packages. Choose one of the following options:
- Any: Automatically select a routing port.
- Single: Manually set the port number.
- Range: Manually set a port range.
• Protocol: Choose Any, or choose either TCP or UDP.
• DSCP: Enter the value of DSCP.
• Next Hop: Choose one of the following options as the next hop:
- IPsec Tunnel: Use an IPsec VPN tunnel as the next hop.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 64
Page 68

Networking
Configuring Routing
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
5
- Interface: Use a WAN interface as the next hop.
- Disable this rule if the interface is down: Check to disable this rule
when the selected WAN interface is down.
Configuring Dynamic Routing
Dynamic routing is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) that is commonly used in
internal networks. It allows a router to exchange its routing information
automatically with other routers, and allows it to dynamically adjust its routing
tables and adapt to changes in the network.
Dynamic routing enables the RV315W to automatically adjust to physical changes
in the network's layout and exchange routing tables with the other routers.
The RV315W determines the network packets’ route based on the fewest number
of hops between the source and the destination.
To configure dynamic routing:
STEP 1 Click Networking > Routing > RIP. The RIP page opens.
STEP 2 In the RIP Basic Settings area, enter the following information:
• RIP Status: Click Enable to enable RIP, or click Disable to disable it. By
default, RIP is disabled.
• RIP Version: Specify the RIP version. The RV315W supports RIPv1 and
RIPv2.
• RIP Timer: Enter the values for the RIP refresh time, RIP timeout, and Flush
time.
• RIP Advertisement By: Choose either an interface or a RIP network for
routing.
STEP 3 If you choose an interface for routing in the RIP Advertisement By area, specify
the RIP interface settings in the RIP Members area.
• Check Enable RIP to enable RIP on an interface.
• Click Edit to specify the following RIP settings for an interface:
- RIP: Displays whether RIP is enabled or disabled on this interface.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 65
Page 69

Networking
Configuring Routing
STEP 4 If you choose Network for routing in the RIP Advertisement By area, you can
5
- Passive Interface: Determines how the RV315W receives RIP packets.
Click Enable to enable this feature on the port, or click Disable to disable
this feature.
- Authentication: Specify the authentication method for the port.
None: Choose this option to invalidate the authentication.
Simple Password Authentication: Choose this option to validate the
simple password authentication. Enter the password in the field.
MD5 Authentication: Choose this option to validate the MD5
authentication.
manually add RIP networks in the RIP Networks area. Click Add to add a new RIP
network.
STEP 5 Enter the IP address of the RIP network in the Network Address field.
STEP 6 Click Save to save your settings.
Viewing the Routing Table
To open the Routing Table page, click Networking > Routing > Routing Table. The
following information is displayed:
• Destination LAN IP: The IP address of the host or the network that the
route leads to.
• Subnet Mask: The subnet mask of the destination network.
• Gateway: The IP address of the gateway through which the destination
host or network can be reached.
• Interface and Tunnel: The physical port or VPN tunnel through which this
route is accessible.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 66
Page 70

Networking
Configuring IGMP
Configuring IGMP
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is a communication protocol used by
hosts and adjacent routers on IP networks to establish multicast group
memberships. IGMP can be used for online streaming video and gaming, and can
allow more efficient use of resources when supporting these types of
applications.
IGMP Proxy enables hosts that are not directly connected to a downstream router
to join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network. IGMP Snooping
constrains IPv4 multicast traffic at Layer 2 by configuring Layer 2 LAN ports
dynamically to forward IPv4 multicast traffic only to those ports that want to
receive it.
To configure IGMP:
5
STEP 1 Click Networking > IGMP. The IGMP page opens.
STEP 2 Enter the following information:
• IGMP Version: Choose either IGMP v1 or IGMP v2.
• IGMP Proxy: Click Enable to enable IGMP Proxy so that the RV315W can
act as a proxy for all IGMP requests and communicate with the IGMP servers
of the ISP, or click Disable to disable it.
• IGMP Snooping: You can use IGMP Snooping in subnets that receive IGMP
queries from either IGMP or IGMP Snooping querier. Click Enable to enable
IGMP Snooping, or click Disable to disable it.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 67
Page 71

VPN
6
The RV315W supports the IPsec Virtual Private Network (VPN) feature to set up a
single gateway-to-gateway VPN tunnel or a client-to-gateway VPN tunnel. In this
configuration, the RV315W creates a secure VPN connection to another VPNenabled router or a remote PC that installs third-party VPN client software. For
example, you can configure the RV315W at a branch site to connect to the VPN
router at the corporate site so that the branch site can securely access the
corporate network.
This chapter describes how to configure IPsec VPN that allows remote workers to
access your network resources. Refer to the following sections:
• Viewing IPsec VPN Status
• Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
Viewing IPsec VPN Status
Use the IPsec VPN page to view the status of all IPsec VPN connections.
To view information for an IPsec VPN connection:
STEP 1 Click VPN > IPsec VPN. The IPsec VPN page opens.
The IPsec VPN Connections area displays the following information for all
existing IPsec VPN policies specified on the RV315W:
• Policy Name: Name of the IPsec VPN policy.
• Status: Shows whether the IPsec VPN policy is enabled or disabled.
• Interface: Interface used for the IPsec VPN policy.
• Connection Type: VPN connection type, such as Site-to-Site or PC-to-Site.
- Site-to-Site VPN: A secure VPN tunnel between the RV315W and a
remote VPN router.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 68
Page 72

VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
6
- PC-to-Site VPN: A secure VPN tunnel between the RV315W and a
remote PC that installs a third-party client software.
• Remote Gateway Address/Hostname: IP address or hostname of the
remote network.
- For a Site-to-Site VPN, the IP address or hostname of the remote gateway
is displayed.
- For a PC-to-Site VPN, the IP address or hostname of the remote PC is
displayed. Separate multiple IP addresses with commas (,).
• Local Gateway Address: IP address of the local network.
• Authentication Method: Authentication method used by the IPsec VPN
policy.
• Connection Status: Shows whether the IPsec VPN tunnel is connected or
disconnected.
STEP 2 Click Add to add an IPsec VPN policy or click Edit to edit the settings of an existing
IPsec VPN policy. See Configuring IPsec VPN Policies.
STEP 3 Click Delete to delete an existing IPsec VPN policy.
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
An IPsec VPN policy is used to establish a VPN connection between two peers.
Up to 50 IPsec VPN policies can be configured on the RV315W.
Setting Up a Site-to-Site VPN
A Site-to-Site VPN policy is used to create a new tunnel between two VPN
devices, such as a Cisco RV315W router at your office and a Cisco RV315W
router at a remote office.
To create a Site-to-Site (gateway-to-gateway) VPN policy:
STEP 1 Click VPN > IPsec VPN. The IPsec VPN page opens.
STEP 2 Click Add.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 69
Page 73

VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
STEP 3 In the IPsec VPN Policy area, specify the IPsec VPN policy name and
identification:
STEP 4 In the Gateway Information area, specify the local and remote gateway settings:
6
• Status: Click Enable to enable the IPsec VPN policy, or click Disable to
disable the policy.
•Policy Number: Choose the identification for the IPsec VPN policy.
• IPsec VPN Policy Name: Enter a unique name for the IPsec VPN policy.
• VPN Failover: Click Enable to enable the VPN Failover feature, or click
Disable to disable this feature.
• Interface: If VPN Failover is disabled on your RV315W, choose a WAN
interface that traffic passes through over the IPsec VPN tunnel.
• Connection Type: Choose Site-to-Site as the type of the VPN connection.
• VPN Redundant: VPN Redundant allows the backup connection to be active
automatically when the connection of the remote gateway fails. Click Enable
to enable this feature and enter the following information:
- Primary: Enter the IP address or hostname of the primary remote
gateway.
- Backup: Enter the IP address or hostname of the secondary remote
gateway.
- Switch from backup to primary: Click Enable to enable this feature, or
click Disable to disable it. Enabling this feature allows the primary VPN
connection to be active automatically when the primary connection is
recovered. If you disable this feature, the backup connection still
becomes active even though the primary connection is recovered.
• Local Gateway Address: Displays the IP address of the local network. In
general, the local gateway address is the public IP address obtained by the
selected WAN interface.
• Local Gateway ID: Choose how to specify your local gateway ID.
- Auto: Automatically obtain the local gateway ID.
- Manual: Manually enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name
• Remote Gateway ID: Choose how to specify the primary remote gateway
ID.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 70
(FQDN) of the local gateway ID.
Page 74

VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
6
- Auto: Automatically obtain the primary remote gateway ID.
- Manual: Manually enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name
(FQDN) of the primary remote gateway ID.
• Backup Remote Gateway ID: Choose how to specify the secondary remote
gateway ID.
- Auto: Automatically obtain the secondary remote gateway ID.
- Manual: Manually enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name
(FQDN) of the secondary remote gateway ID.
• Authentication Method: The IPsec VPN uses a simple, password-based
key to authenticate. Enter the desired value that the peer device must
provide to establish a connection in the Pre-shared Key field. The preshared key must be entered exactly the same here and on the remote peer.
• Show Password: Check to show the pre-shared key in plaintext.
STEP 5 In the Interest Traffic area, choose one of the following methods:
• Route: If you choose this option, enter the IP address and subnet mask
protected by the IPsec VPN.
• Flow-based: If you choose this option, enter the source IP address/wildcard
and destination IP address/wildcard.
STEP 6 In the Advanced VPN Settings area, specify advanced VPN settings of the IPsec
VPN policy.
• 1st Phase: Enter the following information:
- Exchange Mode: Choose either Main Mode or Aggressive Mode. The
main mode has a higher priority than the aggressive mode.
- Authentication Algorithm: Specify the authentication algorithm for the
VPN header. There are two hash algorithms supported by the RV315W:
SHA1 and MD5. The default is SHA1.
- Encryption Algorithm: Choose the algorithm used to negotiate the
security association. The encryption standard supports DES, 3DES, AES128, AES-192, and AES-256. The default is AES-256.
- DH Group: Choose the Diffie-Hellman (DH) group identifier, which the
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 71
two IPsec peers use to derive a shared secret without transmitting it to
each other. The DH group sets the strength of the algorithm in bits. The
lower the DH group number, the less CPU time it requires to be executed.
The higher the DH group number, the greater the security.
Page 75

VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
6
- SA Lifetime: Enter the lifetime of the IPsec Security Association (SA).
The IPsec SA lifetime represents the interval after which the IPsec SA
becomes invalid. The IPsec SA is renegotiated after this interval. The
default value is 86400 seconds.
• 2rd Phase: Enter the following information:
- ESP Authentication Algorithm: Choose either SHA1 or MD5 as the ESP
authentication algorithm. The default is SHA1.
- ESP Encryption Algorithm: Choose the symmetric encryption algorithm
that protects data transmission between two IPsec peers. The advanced
encryption standard supports DES, 3DES, AES-128, AES-192, and AES-
256. The default is AES-256.
- PFS: Choose Enable to enable Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) to
improve security, or choose Disable to disable it. If you enable PFS, a DH
exchange is performed for every phase-2 negotiation. PFS is desired on
the keying channel of the VPN connection.
- SA Lifetime: Enter the values for the time-based SA lifetime and the flow-
based SA lifetime.
- DPD: Click Enable to enable Dead Peer Detection (DPD), or click Disable
to disable it. DPD is a method of detecting a dead Internet Key Exchange
(IKE) peer. This method uses IPsec traffic patterns to minimize the
number of messages required to confirm the availability of a peer. DPD is
used to reclaim the lost resources in case a peer is found dead and it is
also used to perform IKE peer failover. If you enable DPD, specify the
delay time and DPD timeout.
DPD Delay Time: Enter the value of delay time in seconds between
consecutive DPD R-U-THERE messages. DPD R-U-THERE messages are
sent only when IPsec traffic is idle.
DPD Timeout: Enter the value of detection timeout in seconds. If there
are no responses and no traffic over the timeout, declare the peer dead.
STEP 7 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 72
Page 76

VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
Setting Up a PC-to-Site VPN
A PC-to-Site VPN policy is used to create a VPN tunnel to allow teleworkers and
business travelers to access to your network by using third-party VPN client
software, such as TheGreenBow IPsec VPN client 5.1 and Shrewsoft VPN client
2.17.
To create a PC-to-Site (client-to-gateway) VPN policy:
STEP 1 Click VPN > IPsec VPN. The IPsec VPN page opens.
STEP 2 Click Add.
STEP 3 In the IPsec VPN Policy area, specify the IPsec VPN policy name and
identification:
6
• Status: Click Enable to enable the IPsec VPN policy, or click Disable to
disable the policy.
• Policy Number: Choose the identification for the IPsec VPN policy.
• IPsec VPN Policy Name: Enter a unique name for the IPsec VPN policy.
STEP 4 In the Gateway Information area, specify the local and remote gateway settings:
• VPN Failover: Click Enable to enable the VPN Failover feature, or click
Disable to disable this feature.
• Interface: If VPN Failover is disabled on your RV315W, choose a WAN
interface that traffic passes through over the IPsec VPN tunnel.
• Connection Type: Choose PC-to-Site as the type of the VPN connection.
• Local Gateway Address: Displays the IP address of the local network. In
general, the local gateway address is the public IP address obtained by the
selected WAN interface.
• Local Gateway ID: Choose how to specify your local gateway ID.
- Auto: Automatically obtain the local gateway ID.
- Manual: Manually enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name
(FQDN) of the local gateway ID.
• Remote Gateway ID: Choose how to specify the primary remote gateway
ID.
- Auto: Automatically obtain the primary remote gateway ID.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 73
Page 77

VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
6
- Manual: Manually enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name
(FQDN) of the primary remote gateway ID.
• Backup Remote Gateway ID: Choose how to specify the secondary remote
gateway ID.
- Auto: Automatically obtain the secondary remote gateway ID.
- Manual: Manually enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name
(FQDN) of the secondary remote gateway ID.
• Authentication Method: The IPsec VPN uses a simple, password-based
key to authenticate. Enter the desired value that the peer device must
provide to establish a connection in the Pre-shared Key field. The preshared key must be entered exactly the same here and on the remote peer.
• Show Password: Check to show the pre-shared key in plaintext.
STEP 5 In the Advanced VPN Settings area, specify advanced VPN settings of the IPsec
VPN policy:
• 1st Phase: Enter the following information:
- Exchange Mode: Choose either Main Mode or Aggressive Mode. The
main mode has a higher priority than the aggressive mode.
- Authentication Algorithm: Specify the authentication algorithm for the
VPN header. There are two hash algorithms supported by the RV315W:
SHA1 and MD5. The default is SHA1.
- Encryption Algorithm: Choose the algorithm used to negotiate the
security association. The encryption standard supports DES, 3DES, AES128, AES-192, and AES-256. The default is AES-256.
- DH Group: Choose the DH group identifier, which the two IPsec peers
use to derive a shared secret without transmitting it to each other. The DH
Group sets the strength of the algorithm in bits. The lower the DH group
number, the less CPU time it requires to be executed. The higher the
Diffie-Hellman group number, the greater the security.
- SA Lifetime: Enter the lifetime of the IPsec SA. The IPsec SA lifetime
represents the interval after which the IPsec SA becomes invalid. The
IPsec SA is renegotiated after this interval. The default value is 86400
seconds.
• 2rd Phase: Enter the following information:
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 74
Page 78

VPN
Configuring IPsec VPN Policies
6
- ESP Authentication Algorithm: Choose either SHA1 or MD5 as the ESP
authentication algorithm. The default is SH1.
- ESP Encryption Algorithm: Choose the symmetric encryption algorithm
that protects data transmission between two IPsec peers. The advanced
encryption standard supports DES, 3DES, AES-128, AES-192, and AES-
256. The default is AES-256.
- PFS: Click Enable to enable PFS to improve security, or click Disable to
disable it. If you enable PFS, a DH exchange is performed for every
phase-2 negotiation. PFS is desired on the keying channel of the VPN
connection.
- SA Lifetime: Enter the values for the time-based SA lifetime and the flow-
based SA lifetime.
- DPD: Click Enable to enable DPD, or click Disable to disable it. DPD is a
method of detecting a dead IKE peer. This method uses IPsec traffic
patterns to minimize the number of messages required to confirm the
availability of a peer. DPD is used to reclaim the lost resources in case a
peer is found dead and it is also used to perform IKE peer failover. If you
enable DPD, specify the delay time and DPD timeout.
DPD Delay Time: Enter the value of delay time in seconds between
consecutive DPD R-U-THERE messages. DPD R-U-THERE messages are
sent only when IPsec traffic is idle.
DPD Timeout: Enter the value of detection timeout in seconds. If there
are no responses and no traffic over the timeout, declare the peer dead.
STEP 6 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 75
Page 79

Quality of Service (QoS)
This chapter describes how to configure the quality of service (QoS) features.
Refer to the following sections:
• Configuring Bandwidth Management
• Configuring Flow Control Policies
• Configuring Session Limits
Configuring Bandwidth Management
7
Use the Bandwidth Control page to specify the maximum bandwidth for upstream
traffic allowed on each WAN interface, including the 3G WAN interfaces.
To set the upstream bandwidth:
STEP 1 Click QoS > Bandwidth Control. The Bandwidth Control page opens.
STEP 2 Check Enable to limit the upstream bandwidth on the WAN interface.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
STEP 4 Click Edit to modify the rate limit settings for that WAN interface.
STEP 5 In the Rate Limit field, enter the amount of maximum bandwidth in Kbps for
upstream traffic allowed on the WAN interface. The values range from 64 to
100,000 Kbps.
STEP 6 In the Interface Queue Settings area, specify the amount of minimum and
maximum upstream bandwidths for each interface queue.
• Queue Name: Name of the queue.
• Strict Priority Queue: Enter the amount of minimum bandwidth in Kbps for
upstream traffic allowed on the strict priority queue.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 76
Page 80

Quality of Service (QoS)
Configuring Flow Control Policies
• Guaranteed Rate: Enter the amount of minimum bandwidth in Kbps for
upstream traffic allowed on other queues.
• Maximum Rate: Enter the amount of maximum bandwidth in Kbps for
upstream traffic allowed on other queues.
STEP 7 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring Flow Control Policies
Use the Flow Control Policies page to configure the flow control policies. A flow
control policy is used to classify network traffic and prioritize traffic by using the
specified CoS or DSCP remarking value. Up to 25 flow control policies can be
configured on the RV315W.
7
To create a flow control policy:
STEP 1 Click QoS > Flow Control Policies. The Flow Control Policies page opens.
STEP 2 Click Add to create a new flow control policy. The Flow Control Policy Settings
page opens.
STEP 3 Enter the following information:
• Policy Name: Enter a unique name for the flow control policy.
• Policy Type: Choose one of the following options for flow control:
- Destination Port: Controls flow based on the specified destination port.
If you choose this option, specify the values in the Application Protocol,
LAN Interface, and Destination Port fields. You can choose a
predefined application that specifies the destination port, or manually
specify the application protocol and port range.
- MAC Address: Controls flow based on the specified MAC address. If you
choose this option, specify the values in the MAC Address and LAN
Interface fields.
- Physical Port: Controls flow based on the specified physical port. If you
choose this option, specify the values in the LAN Interface and Physical
Port fields.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 77
Page 81

Quality of Service (QoS)
Configuring Flow Control Policies
7
- VLAN: Controls flow based on the specified VLAN. If you choose this
option, choose a VLAN from the VLAN drop-down menu.
- Source IP Address: Controls flow based on the specified IP addresses
of the source hosts. If you choose this option, enter the starting and
ending IP addresses in the Start Address and End Address fields and
choose a LAN interface from the LAN Interface drop-down menu.
- Destination IP Address: Controls flow based on the specified IP
addresses of the destination hosts. If you choose this option, enter the
starting and ending IP addresses in the Start Address and End Address
fields and choose a LAN interface from the LAN Interface drop-down
menu.
• Application Queue: Choose an interface queue to which this flow control
policy applies.
• Enable Tag: Click Enable to prioritize network traffic, or click Disable to
disable this feature.
• Tag Va lue : Choose one of the following options to prioritize network traffic:
- CoS: Class of service (CoS) prioritizes network traffic by using the
specified CoS remarking value. If you choose this option, enter the CoS
remarking value in the field.
- DSCP: Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) prioritizes network
traffic by using the specified DSCP remarking value. If you choose this
option, enter the DSCP remarking value in the field.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 78
Page 82

Quality of Service (QoS)
Configuring Session Limits
Configuring Session Limits
Use the Session Limits page to limit the maximum number of connection sessions
for the complete system, for a range of IP addresses, or for each physical port.
When the connection table is full, the new sessions that access the RV315W are
dropped.
To limit the maximum number of connection sessions:
STEP 1 Click QoS > Session Limits. The Session Limits page opens.
STEP 2 Click Enable to limit the number of connection sessions, or click Disable to disable
this feature.
STEP 3 If you enable this feature, enter the following information:
7
• IP-based Limit: Limits the sessions based on IP address. If you choose this
option, enter the maximum number of connection sessions allowed on each
IP address and/or the range of IP addresses.
• Port-based Limit: Limits the sessions based on the physical ports. If you
choose this option, enter the maximum number of connection sessions
allowed on each physical port.
• Maximum Sessions: Enter the maximum number of connection sessions
allowed on the complete system.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 79
Page 83

Security
8
This chapter describes how to configure the firewall, content filtering, access
control, and other security features. Refer to the following sections:
• Configuring the Firewall
• Configuring DoS Protection
• Configuring Content Filtering
• Configuring Access Control
• Configuring MAC Address Filtering
• Preventing ARP Attacks
• Configuring ALG
Configuring the Firewall
To configure basic firewall settings:
STEP 1 Click Security > Firewall. The Firewall page opens.
STEP 2 In the Firewall area, click Enable to enable the firewall feature (recommended), or
click Disable to disable this feature.
STEP 3 In the Block Proxy area, check to block proxy servers.
A proxy server (or proxy) allows computers to route the connections to other
computers through the proxy, thus circumventing certain firewall rules.
For example, if the connections to a specific IP address are blocked by a firewall
rule, the requests can be routed through a proxy that is not blocked by the rule,
rendering the restriction ineffective.
STEP 4 In the Block Java area, check to block Java applets.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 80
Page 84

Security
Configuring DoS Protection
STEP 5 In the Block ActiveX area, check to block ActiveX content.
STEP 6 In the Block Cookies area, check to block cookies.
8
Java applets are small programs embedded in web pages that enable dynamic
functionality of the page. A malicious applet can be used to compromise or infect
computers.
Similar to Java applets, ActiveX controls are installed on a Windows computer
while running Internet Explorer. A malicious ActiveX control can be used to
compromise or infect computers.
Cookies are used to store session information by websites that usually require
login. However, several websites use cookies to store tracking information and
browsing habits.
Many websites require that cookies be accepted in order for the site to be
accessed properly. Blocking cookies can cause many websites to not function
properly.
STEP 7 In the Filter Port field, enter the port number that is used for filtering HTTP traffic.
The firewall only monitors and controls the website visits through this HTTP port..
STEP 8 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring DoS Protection
Use the DoS Protection page to specify how to protect your network against
common types of Deny of Service (DoS) attacks.
To configure DoS protection:
STEP 1 Click Security > DoS Protection. The DoS Protection page opens.
STEP 2 In the DoS Protection area, click Enable to enable the DoS protection on your
RV315W, or click Disable to disable this feature.
STEP 3 The RV315W can prevent three types of DoS attacks: SYN Flood, UDP Flood, and
ICMP Flood. If you enable DoS protection, check Enable to enable the protection
for that DoS attack, or click Disable to disable it.
STEP 4 Specify the threshold of DoS attacks to trigger the protection. The default is 1000
attacks per second.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 81
Page 85

Security
Configuring Content Filtering
STEP 5 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring Content Filtering
Content filtering blocks or allows HTTP access to websites containing specific
keywords or domains. It controls access to certain Internet sites based on analysis
of its content (domain), rather than its source or other criteria. It is most widely
used on the Internet to filter web access.
Use the Content Filtering page to define the type of content filtering, configure the
content filtering rules, export the content filtering rules to your local PC, and import
the content filtering rules from a file.
8
To configure the content filtering settings:
STEP 1 Click Security > Content Filtering. The Content Filtering page opens.
STEP 2 Specify the type of filtering:
• Blacklist: Select this option to block HTTP access to websites in the
blacklist and allow HTTP access for other websites.
• Whitelist: Select this option to allow HTTP access to websites in the
whitelist and block HTTP access for other websites.
STEP 3 To add a content filtering rule, enter the following information:
• URL/Keyword: Enter the domain name or a keyword of a website that you
want to permit or block. If you enter a keyword, HTTP access to a website
that contains this keyword can be blocked or allowed.
• File Type: Choose the type of files that you want to permit or block.
STEP 4 Click Add.
STEP 5 To delete a content filtering rule, select it and click Delete.
STEP 6 To export the content filtering rules to your local PC, select the content filtering
rules that you want to export and click Export.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 82
Page 86

Security
Configuring Access Control
STEP 7 In the Import Content Filtering Rules area, you can import a mass of content
filtering rules from your local PC. Click Browse to locate and select the file, and
then click Import.
Configuring Access Control
Access Control permits or blocks access to a specific destination on schedule.
Use the Access Control page to enable or disable the Access Control feature on
the RV315W and configure the access control policies.
To configure the access control settings:
8
STEP 1 Click Security > Access Control. The Access Control
STEP 2 In the Control Type area, choose one of the following access control options:
• Blacklist: Permits all traffic from LAN to WAN and only blocks traffic that
matches the access control policies.
• Whitelist: Blocks all traffic from LAN to WAN and only permits traffic that
matches the access control policies.
STEP 3 In the Access Control Policies area, click Add to create a new access control
policy. The Access Control Policy Settings page opens.
STEP 4 Enter the following information:
• Time Range: Enter the starting time and ending time to keep the access
control policy active at specific times.
• Week: Check the days to keep the access control policy active at specific
days.
• Protocol: Choose the protocol to which the access control policy applies, or
choose All Traffic.
page opens.
• Physical Port: Choose a physical port to which the access control policy
applies, or choose Any.
• Source IP Address: Choose one of the following options to specify the
traffic source:
- Any: Controls traffic from any source IP address.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 83
Page 87

Security
Configuring MAC Address Filtering
• Destination IP Address: Choose one of the following options as the traffic
• Action: Click Enable to enable this policy, or click Disable to disable this
STEP 5 Click Save to save your settings.
8
- Single IP Address: Controls traffic from a specific source IP address.
- IP Address Range: Controls traffic from a specific range of source IP
addresses.
destination:
- Any: Controls traffic to any destination IP address.
- Single IP Address: Controls traffic to a specific destination IP address.
- IP Address Range: Controls traffic to a specific range of destination IP
addresses.
policy.
Configuring MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering permits and blocks network access from specific devices
through the use of MAC address list.
To configure MAC address filtering:
STEP 1 Click Security > MAC Address Filtering. The MAC Address Filtering page opens.
STEP 2 In the Filter Policy area, choose one of the following filtering policies:
• Deny Network Access: The MAC addresses in the list are denied and all
other MAC addresses not included in the list are permitted.
• Permit Network Access: Only the MAC addresses in the list are permitted
and all other MAC addresses not included in the list are denied.
STEP 3 In the MAC Address Filtering Policies area, specify the list of MAC addresses.
Click Add to add a MAC address. The MAC Address Filtering Policy page opens.
NOTE Up to 20 MAC addresses can be configured on the RV315W.
STEP 4 Enter the following information:
• MAC Address: Enter the MAC address that you want to filter.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 84
Page 88

Security
Preventing ARP Attacks
• Time Range: Enter the starting time and ending time to keep the MAC
address filtering rule active at specific times.
• Week: Check the days to keep the MAC address filtering rule active at
specific days.
STEP 5 Click Save to save your settings.
Preventing ARP Attacks
Use the ARP Attack Protection page to specify how to protect your network
against common types of ARP attacks and configure the IP&MAC binding rules.
8
IP&MAC Binding allows you to bind an IP address to a MAC address and vice
versa. It only allows traffic when the host IP address matches a specified MAC
address. By requiring the gateway to validate the source traffic’s IP address with
the unique MAC address of device, this ensures that traffic from the specified IP
address is not spoofed.
To prevent ARP attacks and configure the IP&MAC binding settings:
STEP 1 Click Security > ARP Attack Protection. The ARP Attack Protection page opens.
STEP 2 Enter the following information:
• ARP Attack Protection: Click Enable to enable ARP Attack Protection, or
click Disable to disable this feature.
• Enable Auto Learning: Click Enable to enable Auto Learning, or click
Disable to disable this feature. Enabling this feature allows the system to
determine whether the IP address and MAC address of the user are valid or
not.
• ARP Flooding Threshold: Enter the threshold value of ARP Flooding attacks.
This value determines the amount of ARP packets that the system allows to
receive per second. The greater value, the more ARP packets can be
allowed to receive.
• ARP Broadcast Interval: Enter the interval for ARP broadcasting. The value
of zero indicates that this feature is disabled.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 85
Page 89

Security
Configuring ALG
STEP 4 If you enable Auto Learning, you can manually configure the IP&MAC binding rules
in the IP&MAC Binding area. Click Add to create a new IP&MAC binding rule. The
Add IP&MAC Binding Rule page opens.
STEP 5 Enter the following information:
STEP 6 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring ALG
8
• IP Address: Enter the IP address that you want to bind with a MAC address.
• MAC Address: Enter the MAC address.
The RV315W can function as an Application Level Gateway (ALG) to allow certain
NAT incompatible applications to operate properly through the RV315W.
To configure ALG:
STEP 1 Click Security > Application Level Gateway. The Application Level Gateway
page opens.
STEP 2 Enable or disable the ALG support for these protocols: GRE, SIP, H.323, IPsec,
L2TP, RTSP, and IPsec NAT-T.
STEP 3 Click Save to save your settings.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 86
Page 90

System Management
This chapter describes the administration features of the RV315W, including user
management, remote management, system diagnostics and logs, system time
settings, and other settings. Refer to the following sections:
• Rebooting the RV315W
• Configuring Password Complexity
• Configuring User Accounts
• Restoring Factory Default Settings
• Managing System Configuration
• Upgrading the Firmware
9
• Using Diagnostic Utilities
• Configuring System Time
• Configuring TR-069 Settings
• Configuring SNMP
• Configuring Remote Management
• Log Management
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 87
Page 91

System Management
Rebooting the RV315W
Rebooting the RV315W
To reboot the RV315W, you can press and release the RESET button on the back
panel for less than 5 seconds, or perform the Reboot operation from web-based
Configuration Utility.
To reboot the RV315W through web-based Configuration Utility:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Reboot. The Reboot page opens.
STEP 2 Click Reboot.
STEP 3 Click OK to reboot the unit. Rebooting the unit will close all current sessions and
the system will be down for several seconds.
9
Configuring Password Complexity
The RV315W can enforce the minimum password complexity requirements for
password changes. Use the Password Complexity page to define the password
complexity settings on the RV315W.
To define the minimum password complexity settings:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Password Complexity. The Password Complexity
page opens.
STEP 2 In the Password Complexity Settings area, click Enable to enable the password
strength enforcement on the RV315W, or click Disable to disable this feature.
STEP 3 If you enable this feature, specify the following password complexity settings:
• Minimum password length: Enter the minimum password length (0 to 64
characters). The default is 8 characters.
• Minimum number of character classes: Enter a number representing one
of the following character classes:
- Uppercase letters
- Lowercase letters
- Numbers
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 88
Page 92

System Management
Configuring User Accounts
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
9
- Special characters available on a standard keyboard
By default, passwords must contain characters from at least three of these
classes.
• The new password must be different than the current one: Click Enable
to require that new passwords differ from the current password.
• Password Aging: Click Enable to expire passwords after a specified time,
or click Disable to always keep the passwords active.
• Password Aging Time: Enter the number of days after which the password
expires (1 to 365). The default is 180 days.
Configuring User Accounts
Use the User Management page to manage the user accounts. You can view
information of the users on the RV315W, change user’s password, and add or
delete normal users.
Viewing User Information
The RV315W predefines an administrative account (cisco) and a guest user
(guest). The usernames of the system administrator (cisco) and the guest user
(guest) cannot be modified, but their passwords can be changed. For security
purposes, we recommend that you change the default administrator password at
your first login.
To view user information, click System Management > User Management. The
User Management page opens.
All existing users are listed in the Local User List. The following information is
displayed:
• Username: Displays the name of the user account.
- cisco: Default system administrator. Its default password is cisco.
- guest: Default guest user. Its default password is guest.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 89
Page 93

System Management
Configuring User Accounts
STEP 1 Click System Management > User Management. The User Management page
9
• Privilege: Displays the privilege of the user account, such as Administrator
and Normal User. The administrator has full privilege to set the configuration
and read the system status. The normal users can only read the system
status after they login. They cannot edit any configuration.
Creating a New User
To create a normal user, you must log in to web-based Configuration Utility by
using the system administrator account. Up to 5 user accounts can be configured
on the RV315W, including the default system administrator and guest accounts.
To create a new user:
opens.
STEP 2 In the Add Local User area, enter the following information:
• Username: Enter the username for the user.
• Password: Enter the password for the user. Passwords are case sensitive.
By default, passwords should not contain dictionary words from any
language or be the default password. They should contain a mixture of
uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Passwords must
be at least 8 characters in length.
• Password Confirm: Enter the password again for confirmation.
STEP 3 Click Add. The new user is added in the Local User List.
Changing User Password
For security purposes, we recommend that you change the default administrator
password at the first login.
To change the password of a user:
STEP 1 Click System Management > User Management. The User Management page
opens.
STEP 2 In the Local User List area, check the corresponding user and click Change
Password.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 90
Page 94

System Management
!
Restoring Factory Default Settings
STEP 3 Enter the following information:
• Old Password: Enter the current administrator password.
• New Password: Enter a new administrator password. Passwords are case
• Password Confirm: Enter the password again for confirmation.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Deleting a Local User
The system administrator can remove a new added user from the local user
database.
9
sensitive.
To delete a user:
STEP 1 Click System Management > User Management. The User Management page
opens.
STEP 2 In the Local User List area, check the corresponding user and click Delete.
STEP 3 Click OK to delete it from the local user database.
Restoring Factory Default Settings
To restore the RV315W to the factory default settings, you can press and hold the
RESET button on the back panel for more than 5 seconds, or perform the Reset to
Factory Defaults operation from web-based Configuration Utility.
CAUTION During restoring to factory defaults, do NOT turn off the device, shut down the PC,
remove the cable, or interrupt the process in any way until the operation is
complete. This process should take several minutes including the reboot process.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 91
Page 95

System Management
!
Managing System Configuration
CAUTION The Reset To Factory Defaults operation will wipe out the current settings used on
the RV315W. We recommend that you back up your current settings before
restoring the RV315W to the factory default settings.
To restore the RV315W to the factory default settings through the utility:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Reset To Factory Defaults. The Reset To Factory
Defaults page opens.
STEP 2 Click Reset to Factory Defaults.
STEP 3 Click OK. This operation reboots the unit and restores the RV315W to the factory
default settings. The settings that you have previously made to the RV315W are
lost.
9
Managing System Configuration
This section describes how to work with the configuration. You can perform the
following tasks to maintain system configuration:
• Back up the settings currently used on your RV315W.
• Restore your settings from a saved configuration file.
• Upload the configuration to an upper-level Network Management System
(NMS).
To manage system configuration:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Configuration Management. The Configuration
Management page opens.
STEP 2 To back up the settings currently used on your RV315W, click Backup
Configuration. Select where to locate the configuration file, and then click Save.
STEP 3 To restore your setting from a saved configuration file, click Browse to locate and
select a saved configuration file, and then click Import. The system will reboot
with the loaded configuration file.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 92
Page 96

System Management
!
Upgrading the Firmware
STEP 4 To upload the configuration to an upper-level Network Management System
(NMS), you must first configure the TR-069 settings on your RV315W (see
Configuring TR-069 Settings), and then click Upload Configuration.
The RV315W first sends a message to the upper-level NMS. The upper-level NMS
automatically gets the configuration file of the RV315W after the NMS receives the
requesting message.
Upgrading the Firmware
Use the Firmware Upgrade page to view information of the primary and
secondary firmware images used on the RV315W, download the latest firmware
image from a specific website, and upgrade your firmware to a newer version.
9
CAUTION During a firmware upgrade, do NOT turn off the device, shut down the PC, remove
the cable, or interrupt the process in any way until the operation is complete. This
process should take several minutes including the reboot process. Interrupting the
upgrade process at specific points when the flash is being written to can corrupt
the flash memory and render the RV315W unusable.
To upgrade the RV315W to a newer firmware:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Firmware Upgrade. The Firmware Upgrade page
opens.
The following information is displayed:
• Device Model: Displays the device model.
• PID VID: Displays the product ID and version ID.
• Primary Firmware Version: Displays the firmware version (primary
firmware) that the RV315W is currently using.
• Secondary Firmware Version: Displays the firmware version (secondary
firmware) that is used as a backup.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 93
Page 97

System Management
Using Diagnostic Utilities
STEP 2 In the Download the latest firmware area, click Download to download the latest
STEP 3 In the Locate & select the upgrade file area, click Browse to locate and select the
STEP 4 Click Upgrade.
9
When you upgrade the firmware to a newer version, the system first
overwrites the secondary firmware with the new version in the flash, and
then reboots with the new firmware. The new firmware becomes the
primary firmware and the previous primary firmware becomes the
secondary firmware.
version of the firmware from the specified website to your local PC. Make sure that
you have an active WAN connection.
downloaded firmware image from your local PC.
After the new firmware image is validated, the new image is written to flash and
the RV315W is automatically rebooted with the new firmware.
Using Diagnostic Utilities
Use the following diagnostic utilities to access configuration of the RV315W and to
monitor the overall network health:
Ping
Use the Ping page to test the connectivity between the RV315W and a connected
device on the network.
STEP 1 Click System Management > Diagnostic Utilities > Ping. The Ping page opens.
STEP 2 In the Destination IP Address or Hostname area, enter the IP address or domain
name to ping.
STEP 3 Click Start to ping the IP address or the domain name.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 94
Page 98

System Management
Using Diagnostic Utilities
STEP 1 Click System Management > Diagnostic Utilities > Traceroute. The Traceroute
STEP 2 Enter the IP address or URL of the destination.
STEP 3 Click Start to trace the route of the IP address or URL, or click Stop to stop tracing.
9
Traceroute
Use the Traceroute page to view the route between the RV315W and a
destination.
page opens.
HTTP Get
Use the HTTP Get page to query the URL information of a website.
STEP 1 Click System Management > Diagnostic Utilities > HTTP Get. The HTTP Get
page opens.
STEP 2 Enter the IP address or URL of the website.
STEP 3 Click Start.
DNS Query
Use the DNS Query page to retrieve the IP address of any server on the Internet.
STEP 1 Click System Management > Diagnostic Utilities > DNS Query. The DNS Query
page opens.
STEP 2 In the Domain Name field, enter the IP address or domain name that you want to
look up.
STEP 3 Click Run to query the server on the Internet. If the host or domain name exists,
you will see a response with the IP address.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 95
Page 99

System Management
Configuring System Time
Configuring System Time
Use the Time Settings page to manually configure the system time, or to
dynamically synchronize the system time with a Network Time Protocol (NTP)
server.
To configure the system time:
STEP 1 Click System Management > Time Settings. The Time Settings page opens.
The Current System Time field displays the current date and time.
STEP 2 In the Set System Time area, select the Manually radio button to manually set the
date and time. Enter the values in the Date and Time fields.
STEP 3 In the Set System Time area, select the Dynamically radio button to automatically
synchronize the date and time with the specified NTP servers, and then enter the
following information:
9
• NTP Server 1: Enter the IP address or domain name of the primary NTP
server.
• NTP Server 2: Enter the IP address or domain name of the secondary NTP
server.
STEP 4 Click Save to save your settings.
Configuring TR-069 Settings
TR-069 is a DSL Forum specification for CPE WAN Management Protocol (CWMP).
It defines an application layer protocol for remote management of end-user
devices. As a bidirectional SOAP/HTTP-based protocol, it provides the
communication between customer-premises equipment (CPE) and Auto
Configuration Servers (ACS).
To configure general TR-069 settings:
STEP 1 Click System Management > TR-069 Settings. The TR-069 Settings page
opens.
STEP 2 In the TR-069 Settings area, click Enable to enable the TR-069 server, or click
Disable to disable it.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 96
Page 100

System Management
Configuring TR-069 Settings
STEP 3 In the ACS area, specify the settings of the ACS remote management server:
STEP 4 In the CPE area, specify the CPE settings for TR-069 remote management:
9
• URL: Enter the URL of the ACS remote management server.
• Username: Enter the username to log in to the ACS remote management
server.
• Password: Enter the password to log in to the ACS remote management
server.
• Username: Enter the username of the remote management server in order
to send the connection requests to CPE.
• Password: Enter the password of the remote management server in order to
send the connection requests to CPE.
• Send Inform Packets: (Optional) Click Enable to enable the Send Inform
Packets feature, or click Disable to disable this feature.
• Send Interval: Enter the interval in seconds to send the inform packets. The
default is 43200 seconds.
• Request Connection Port: Enter the port number used to request the
connection to TR-069.
• Download Request: (Optional) Specify the type of download request and
then click Send to send the corresponding download request to the TR-069
server.
- Firmware: Request to download the firmware of the RV315W from the
TR-069 server.
- Vendor Configuration: Request to download the configuration file from
the TR-069 server.
• Upload Request: (Optional) Specify the type of upload request, and then
click Send to send the corresponding request to the TR-069 server.
- Configuration File: Request to upload the current configuration file of the
RV315W to the TR-069 server.
- Vendor Configuration: Request to upload the configuration file with the
factory default settings of the RV315W to the TR-069 server.
• Change Account Request: Click Send to send the request of changing the
administrative password of the RV315W to the TR-069 server.
Cisco RV315W Broadband Wireless VPN Router Administration Guide 97
 Loading...
Loading...