Page 1

Cisco Small Business 200 Series Advanced Smart
Switch Command Line Reference
ADMINISTRATION
GUIDE
Page 2
Contents
Chapter 1: Using the Command Line Interface 14
Command Syntax 15
Command Conventions 16
Interface Naming Convention 17
Using the No Form of a Command 17
Using a Space in a Command 18
Command Modes 18
Command Completion and Abbreviation 20
CLI Error Messages 20
Using CLI Help 20
Command Organization in this Document 21
Chapter 2: Administration 22
Control Packet Handling 23
protocol cdp 23
protocol {lldp | dot1x} 23
show protocol 24
Auto Configuration 25
boot autoinstall 25
boot autoinstall backup-bootfile 26
boot autoinstall backup-tftp 27
boot autoinstall default-config 28
show autoinstall 29
Bonjour 30
bonjour run 30
show bonjour 31
Port Mirroring 32
monitor session 33
show monitor session 34
Cable Diagnostics 35
PoE 38
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 2
show cablestatus 35
show fiber-ports optical-transceiver 37
Page 3
lldp med transmit-tlv 38
lldp med transmit-tlv all 40
poe 41
poe power limit 42
poe power management 44
poe powered-device describe 46
poe priority 47
poe reset 48
poe usagethreshold 49
show poe 50
show poe port configuration 51
show poe port info 52
show poe port statistics 54
Contents
Switch Management Access Control 55
Authentication Methods 55
ip http authentication 55
login authentication 57
show authentication methods 58
User Logins and Passwords 59
password 59
passwords aging 59
passwords min-length 60
passwords strength-check 61
passwords strength check-username 62
passwords strength exclude-keyword 63
passwords strength maximum repeated-characters 64
show loginsession 65
show passwords configuration 66
show user accounts 67
show users 68
show users login-history 69
username 70
Management Access—General 72
network mgmt_vlan 72
show network 72
HTTP Access 73
ip http port 73
ip http server 74
ip http session soft-timeout 75
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 3
Page 4
show ip http 75
Contents
Telnet Access 76
ip telnet server enable 76
telnet 77
telnetcon timeout 78
show telnetcon 79
SSH Access 80
copy nvram:sshkey-dsa 80
copy nvram:sshkey-rsa1 80
copy nvram:sshkey-rsa2 81
crypto key generate dsa 81
crypto key generate rsa 82
ip ssh protocol 83
ip ssh server enable 83
sshcon maxsessions 84
sshcon timeout 85
show ip ssh 86
Console Access 86
line console 86
serial baudrate 87
serial databits 88
serial parity 88
serial stopbits 89
serial timeout 90
show serial 90
Management Access Lists 91
deny 91
management access-class 93
management access-list 94
permit 95
show management access-list 96
show management access-class 97
SNTP and Time Settings 98
Clock Commands 98
clock date 98
clock summer-time 99
clock summertime date 99
clock summertime recurring 101
clock timezone 102
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 4
Page 5
clock timezone config dhcp 103
show clock 104
Contents
SNTP Commands 105
sntp authenticate 105
sntp authentication-key 106
sntp broadcast client poll interval 107
sntp client mode 108
sntp client port 109
sntp server 110
sntp trusted-key 111
sntp unicast client poll-interval 112
show sntp 113
show sntp client 114
show sntp configuration 115
show sntp server 116
System Software and Configuration Management 117
copy 117
delete 121
set contact 122
set hostname 122
set location 123
reload 124
reset factory default 125
write memory 125
show config-file 126
show config-file list 127
show running-config 128
show language-packs detail 130
show language-packs summary 131
show sysinfo 132
Syslog 134
clear logging buffered 134
clear logging persistent 135
copy 135
logging aggregation enable 137
logging aggregation maxtime 137
logging buffered enable 138
logging buffered severity 139
logging console enable 140
logging console severity 140
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 5
Page 6
logging host 141
logging host remove 143
logging persistent enable 144
logging persistent severity 144
logging persistent size 146
logging syslog enable 146
logging syslog facility 147
logging syslog port 148
show logging 149
show logging buffered 151
show logging hosts 151
show logging persistent 152
show logging traplogs 154
Contents
RMON 155
rmon alarm 155
rmon collection history 157
rmon event 159
show environment 160
show process cpu 161
show rmon alarm 162
show rmon alarm-table 163
show rmon collection history 164
show rmon events 165
show rmon history 166
show rmon log 169
show rmon statistics 170
Chapter 3: Port Management 173
Switch Ports 173
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 6
auto-negotiate 173
auto-negotiate all 174
mtu 175
shutdown 176
shutdown all 176
speed 177
speed all 178
show interface advertise 179
show interface ethernet 180
show port 183
Page 7
Contents
Green Ethernet 185
green-mode energy-detect 185
show green-mode 186
Flow Control and Storm Control 188
storm-control broadcast 188
storm-control broadcast level 189
storm-control broadcast rate 190
storm-control flowcontrol 191
storm-control multicast 192
storm-control multicast rate 193
storm-control multicast level 194
storm-control unicast 195
storm-control unicast level 196
storm-control unicast rate 197
show storm-control 198
Link Aggregation 199
addport 200
deleteport (Interface Config) 200
deleteport (Global Config) 201
port lacpmode 202
port lacpmode all 203
port lacptimeout (Interface Config) 203
port lacptimeout (Global Config) 204
port-channel adminmode 205
port-channel load-balance 206
port-channel static 208
show lacp actor 208
show lacp partner 211
show port-channel 213
show port-channel brief 214
show port-channel system priority 215
Chapter 4: VLAN Management 217
VLAN 217
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 7
vlan 217
vlan database 218
vlan default 218
vlan priority 219
switchport access vlan 220
Page 8
switchport general acceptable-frame-type tagged-only 220
switchport general allowed vlan 221
switchport general pvid 222
switchport general ingress-filtering disable 223
switchport trunk allowed vlan 223
switchport mode 224
switchport trunk native-vlan 226
show interfaces switchport 226
Contents
LLDP-MED 228
lldp med 228
lldp med all 228
lldp med confignotification 229
lldp med confignotification all 229
lldp med inventory-tlv asset-id 230
lldp med location-tlv co-ordinate 231
lldp med location-tlv civic-addr 231
lldp med location-tlv elin-addr 233
lldp med location-tlv type 234
lldp med transmit-tlv 235
lldp med transmit-tlv all 236
show lldp med 237
show lldp med location-tlv 237
show lldp med local-device detail 238
show lldp med remote-device 240
show lldp med remote-device detail 241
Auto-VoIP 242
Media VLAN 252
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 8
auto-voip oui 243
auto-voip oui-based 243
auto-voip oui-based all 244
auto-voip oui-priority 245
auto-voip oui-vlan 246
auto-voip protocol-based 247
auto-voip protocol-based all 247
show auto-voip oui-based interface 248
show auto-voip oui-table 249
show auto-voip protocol-based interface 250
show auto-voip sessions 251
media-vlan (Global Config) 252
Page 9
media-vlan (Interface Config) 253
show media-vlan 255
Contents
Chapter 5: Spanning Tree Protocol 257
spanning-tree 257
spanning tree auto edge 258
spanning-tree bpdufilter 258
spanning-tree bpdufilter default 259
spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck 260
spanning-tree bpdu flood 260
spanning-tree bpdu flooding 261
spanning-tree configuration name 262
spanning-tree configuration revision 263
spanning-tree edgeport 264
spanning-tree forward-time 265
spanning-tree max-age 266
spanning-tree mode 267
spanning-tree mst 267
spanning-tree mst instance 270
spanning-tree mst priority 271
spanning-tree mst vlan 272
spanning-tree port mode 273
spanning-tree port mode all 274
spanning-tree priority 274
show spanning-tree 275
show spanning-tree brief 276
show spanning-tree interface 277
show spanning-tree mst port detailed 278
show spanning-tree mst port summary 280
show spanning-tree mst summary 282
show spanning-tree vlan 283
Chapter 6: MAC Address Tables 285
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 9
bridge address 285
bridge aging-time 286
clear mac-addr-table 287
show mac-addr-table 287
show mac-addr-table dynamic 290
show mac-addr-table static 291
Page 10
Contents
Chapter 7: Multicast 293
Multicast Forwarding and MAC Filtering 293
macfilter 293
macfilter adddest 294
macfilter adddest all 295
set multicast filter-unregistered 296
set multicast forward-all 297
set multicast forward-unregistered 298
show mac-address-table multicast 299
show mac-address-table staticfiltering 300
show multicast filtering 301
IGMP Snooping 302
set igmp 302
set igmp fast-leave 303
set igmp groupmembership-interval 304
set igmp maxresponse 305
set igmp mcrtrexpiretime 306
set igmp mrouter 307
set igmp mrouter interface 308
show igmpsnooping 308
show igmpsnooping mrouter interface 311
show igmpsnooping mrouter vlan 311
show mac-address-table igmpsnooping 312
MLD Snooping 314
set mld 314
set mld fast-leave 315
set mld groupmembership-interval 316
set mld maxresponse 316
set mld mcrtrexpiretime 317
set mld mrouter 318
set mld mrouter interface 319
show mac-address-table mldsnooping 320
show mldsnooping 321
show mldsnooping mrouter interface 323
show mldsnooping mrouter vlan 324
Chapter 8: Security 326
General 326
show net connections 326
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 10
Page 11
Contents
RADIUS 327
radius server attribute nas-ip-addr 327
radius server deadtime 328
radius server host 329
radius server key 331
radius server msgauth 332
radius server priority 333
radius server retransmit 334
radius server timeout 335
show radius 336
show radius servers 337
show radius statistics 340
Dot1x 342
authentication dot1x 343
clear dot1x statistics 343
dot1x pae 344
dot1x port-control 345
dot1x port-control all 346
dot1x re-authentication 348
dot1x supplicant portcontrol 348
dot1x supplicant user 349
dot1x system-auth-control 350
dot1x timeout quiet-period 351
dot1x timeout reauth-period 352
dot1x timeout server-timeout 353
dot1x timeout supp-timeout 354
dot1x timeout tx-period 355
dot1x user 356
show dot1x 357
show dot1x clients 362
show dot1x users 363
MAC Based Port Security 364
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 11
port-security 364
port-security mac-address move 365
port-security max-dynamic 365
port-security max-static 366
port-security reset port 367
port-security violation action 367
show port-security 369
Page 12
Contents
Chapter 9: Quality of Service 371
Rate Limit Profile Commands 371
rate-limit profile (Global) 371
rate-limit profile (Interface) 373
show rate-limit 373
show rate-limit profile 374
Class of Service Commands 376
classofservice dot1p-mapping 376
classofservice ip-dscp-mapping 377
classofservice ip-precedence-mapping 377
classofservice trust 378
cos-queue min-bandwidth 380
cos-queue wrr 381
traffic-shape 382
show classofservice dot1p-mapping 383
show classofservice ip-dscp mapping 384
show classofservice ip-precedence-mapping 385
show classofservice trust 386
show interfaces cos-queue 387
Chapter 10: IP Configuration 389
IP Addresses 389
clear arp-switch 389
clear network ipv6 dhcp statistics 390
dhcp client vendor-id-option 390
dhcp client vendor-id-option-string 391
network ipv6 address 392
network ipv6 enable 393
network ipv6 gateway 394
network ipv6 neighbor 394
network parms 395
network protocol 396
ping 397
ping ipv6 398
renew dhcp network-port 400
show arp switch 400
show dhcp client vendor-id-option 401
show dhcp client timezone-option 402
show network 402
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 12
Page 13
show network ipv6 dhcp statistics 403
show network ndp 405
Contents
DNS 406
clear host 407
ip domain lookup 407
ip domain name 408
ip domain retry 409
ip domain timeout 410
ip host 410
ip name server 411
ipv6 host 412
show hosts 413
Chapter 11: SNMP 415
snmp-server community 415
snmp-server enable 416
snmp-server enable traps authentication 416
snmp-server enable traps linkmode 417
snmp-server enable traps multiusers 418
snmp-server enable traps stpmode 418
snmp-server host traps 419
show snmp 420
snmp-server engineID local 420
snmp-server user 421
snmp-server v3-host 423
snmp trap link-status all 424
snmp trap link-status 424
show snmp engineid 425
show snmp users 425
show trapflags 427
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 13
Page 14

Using the Command Line Interface
The command-line interface (CLI) provides a text-based way to manage and
monitor the system. You can access the CLI using a physical serial connection or a
remote logical connection with telnet.
This chapter describes the CLI syntax, conventions, and modes. It contains the
following sections:
• Command Syntax
• Command Conventions
• Interface Naming Convention
• Using the No Form of a Command
1
• Command Modes
• Command Completion and Abbreviation
• CLI Error Messages
• Command Organization in this Document
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 14
Page 15
Using the Command Line Interface
Command Syntax
Command Syntax
A command is one or more words that might include one or more parameters.
Parameters might be required or optional values.
1
Some commands, such as
Other commands, such as
command. You must type the parameter values in a specific order. Optional
parameters follow required parameters. The following example describes the
network parms command syntax:
network parms ip-address netmask [gateway]
• network parms is the command name.
ip-address and netmask are mandatory parameters that you must replace with
•
the actual value.
gateway is an optional parameter that you can replace with text.
•
This reference lists each command by the command name and provides the
following information where applicable:
• Syntax Descriptions—describes each keyword and parameter.
• Defaults—describe any default values for the command parameters.
• Command Modes—identifies the CLI command modes in which you can
execute the command.
show network or clear vlan, do not require parameters.
network parms, require that you supply a value after the
• Examples—one or more examples of the command string, the output, and
descriptions of the output fields, if applicable.
• Related Commands—other commands you can use in conjunction with the
primary command.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 15
Page 16
Using the Command Line Interface
Command Conventions
Command Conventions
In this document the command elements include command key words and
parameters. Key words are entered as shown in the command. Parameters are
shown in italics and represent variable text. You must replace the parameter name
with an appropriate value, which might be an alphabetic, numeric, or alphanumeric
value. Parameters are order-dependent.
Keywords and parameters could be mandatory or optional, and might be one of
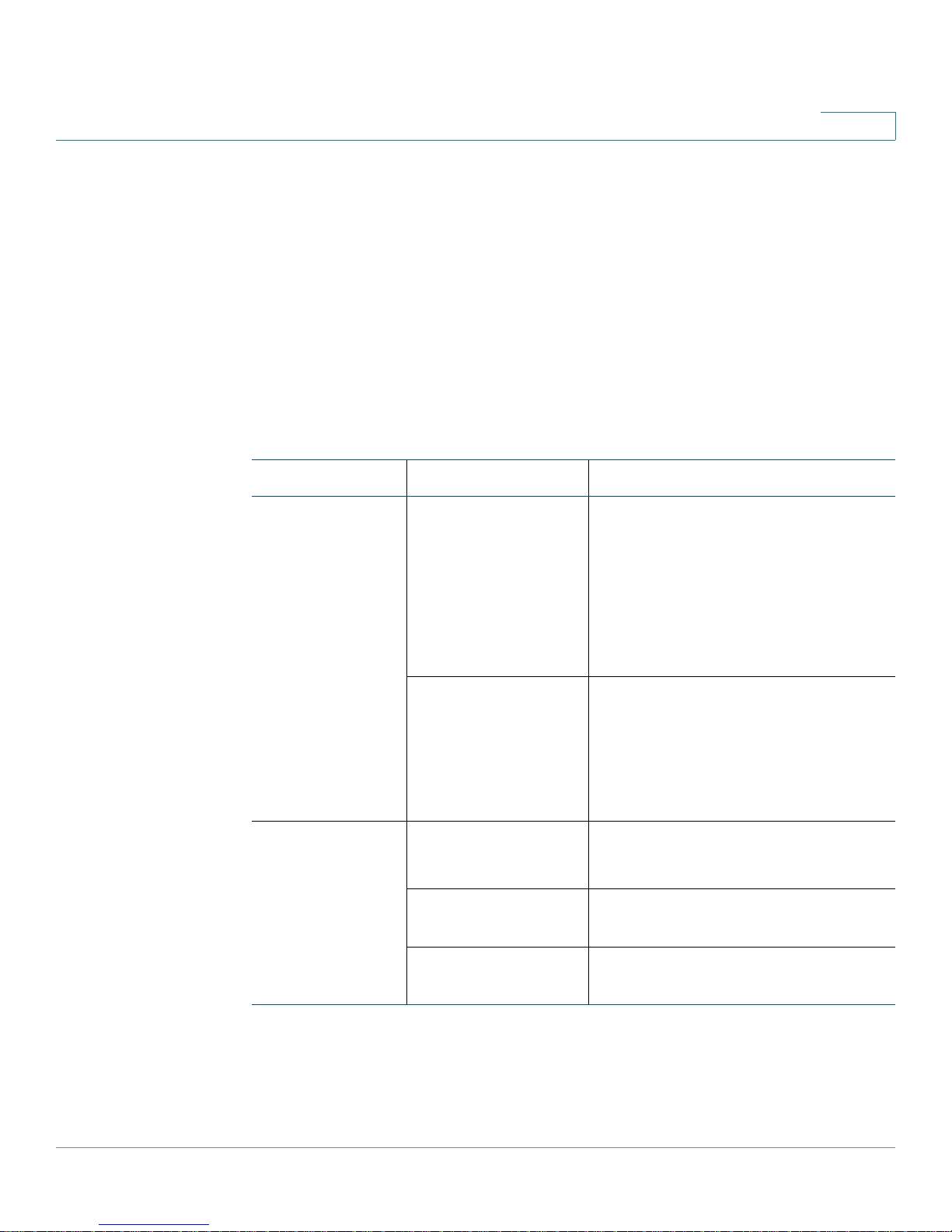
several choices. The following table describes the conventions this document
uses to distinguish command elements.
Symbol Examples Description
1
No brackets spanning-tree
ip-address
[ ] square brackets [encrypted]
[ip-address]
[level 0-100]
Mandatory parameter that is not in
italics. The command element is a
keyword. Enter it as shown.
When in italics, the command
element is a variable (placeholder
text). Enter your own text to replace
it.
A parameter in italics is a variable
(placeholder text). Enter the
command, replacing the variable in
the command with a value. For
example, the
be replaced by
Optional parameter entered as
show.
Optional variable that can be
replaced by a value.
Optional parameter with a range of
values.
ip-address variable might
192.168.10.254.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 16
Page 17
Using the Command Line Interface
Interface Naming Convention
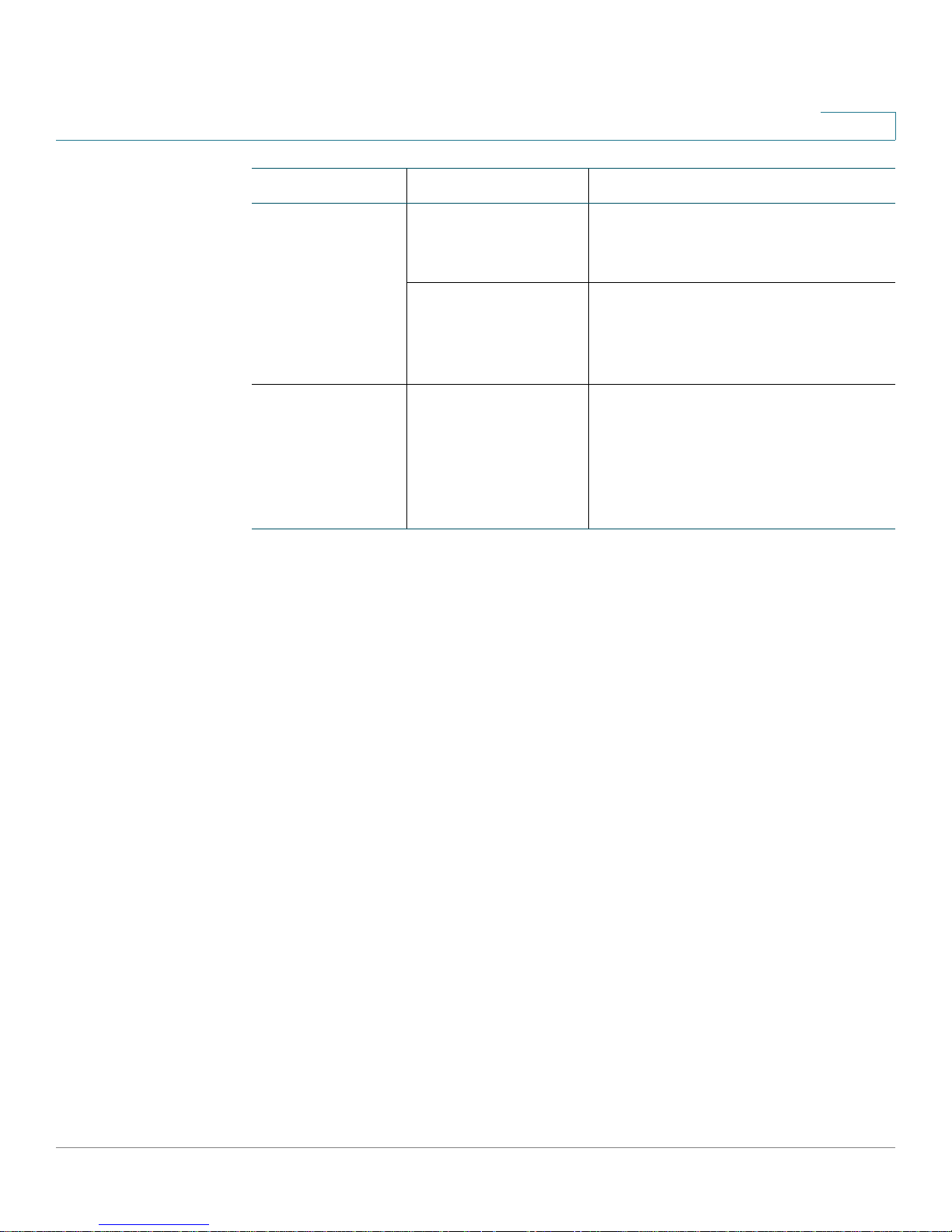
Symbol Examples Description
1
{} curly braces {drop | forward}
{ip-address | hostname}
[{}] Braces within
square brackets
{source interface
interface [{rx | tx}]
Interface Naming Convention
Fast Ethernet switch ports are represented in the CLI as e1 for port 1, e2 for port 2,
e3 for port 3, and so forth.
A list of parameter choices, each
separated by a vertical bar, to be
entered as shown.
A list of parameter choices, each
separated by a vertical bar. The
chosen variable is replaced by the
appropriate value.
A required choice within an optional
element. In the example, if you chose
to enter
enter a value for the
parameter, and you can optionally
chose the
source interface, you must
interface
rx or the tx parameter.
The gigabit Ethernet switch ports are represented as g1 and g2.
Link aggregation groups (LAGs) are configurable as logical interfaces and are
represented in the CLI as ch1, ch2, ch3, and so forth.
Using the No Form of a Command
The no keyword is a specific form of an existing configuration command and does
not represent a new or distinct command. Almost every configuration command
has a no form. In general, use the no form of the command to reverse the action of
a command or reset it to the default value. Example:
#no shutdown
Reverses the shutdown command to bring up the interface.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 17
Page 18

Using the Command Line Interface
Using a Space in a Command
Using a Space in a Command
To include a space in a string, enclose the string in quotes, such as "string space".
Example:
#set contact "Thom Dobro"
Command Modes
Modes group commands according to the function of each command. The
commands in a particular mode are not available until you change to that mode.
The command prompt changes in each command mode to identify the current
mode. The following table describes the command modes and the prompts for
that mode.
1
NOTE In the following table, the word switch in the prompt represents the switch
hostname. By default, the hostname is switch<
You can use the set hostname command to configure a different hostname that will
display in the CLI prompt.
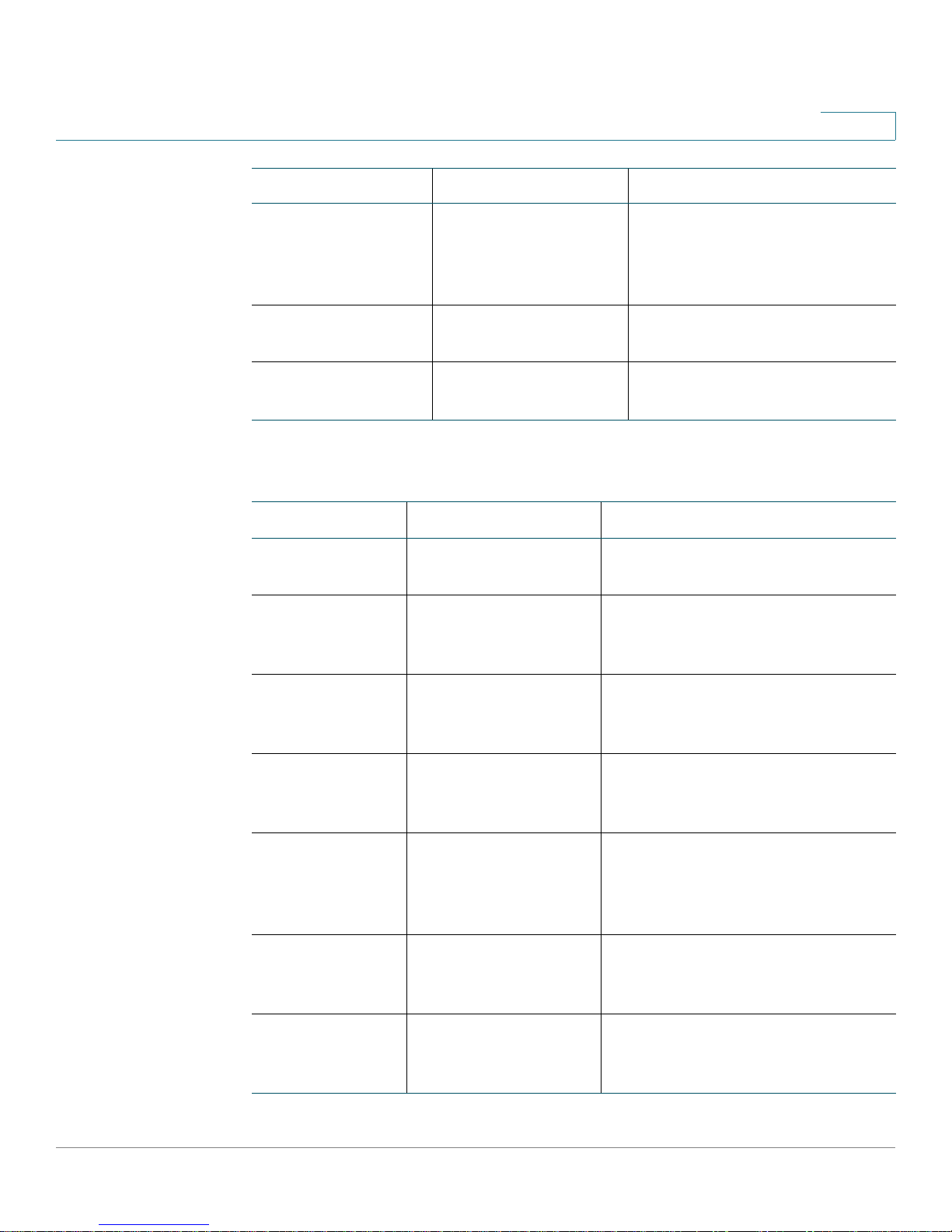
Command Mode Prompt Description
Privileged EXEC switch# The show commands that
Global Config switch (Config)# General setup commands and
VLAN Config switch (Vlan)# VLAN configuration commands.
Interface Config (switch) (Interface
interface)#
last three bytes of the MAC address>.
display status and statistics,
some configuration commands,
and access to the Global
Config and VLAN Config
modes.
modifications to the running
configuration.
Manage the interfaces.
Access List Config switch(config-macal)# Switch management access list
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 18
configuration commands.
Page 19
Using the Command Line Interface
Command Modes
Command Mode Prompt Description
1
Line Console
Config
Line SSH Config switch (config-ssh)# SSH login and authentication
Line Telnet Config switch (config-telnet)# Telnet login and authentication
The following table explains how to enter and exit each mode.
Mode To Enter To Exit
Privileged EXEC Users enter this mode
Global Config From the Privileged
switch (config-line)# Outbound telnet settings and
console interface settings,
including console login and
authentication information.
information.
information.
To log out of the CLI session, enter
when they log in.
EXEC mode, enter
configure or config.
quit.
To exit to the Privileged EXEC
mode, enter exit, or press Ctrl-Z.
VLAN Config From the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter
vlan database.
Interface Config From the Global
Config mode, enter
interface interface
Access List
Config
Line Console From the Global
Line SSH From the Global
From the Global
Config mode, enter
management
access-list listname
Config mode, enter
line console.
Config mode, enter
line ssh.
To exit to the Privileged EXEC
mode, enter exit or press Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 19
Page 20

Using the Command Line Interface
Command Completion and Abbreviation
Mode To Enter To Exit
1
Line telnet From the Global
Config mode, enter
line telnet.
Command Completion and Abbreviation
The command completion feature finishes spelling the keyword when you type
enough letters of a command to uniquely identify the command keyword. After
you have entered enough letters, press the spacebar or Tab key to complete the
keyword.
The command abbreviation feature allows you to execute a command when you
have entered enough letters to uniquely identify the command. You must enter all
of the required keywords and parameters, however.
CLI Error Messages
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Using CLI Help
If you enter a command and the system is unable to execute it, an error message
appears. The most common CLI error messages are:
• % Invalid input detected at '^' marker—You entered an
incorrect or unavailable command. The carat (^) shows where the invalid
text is detected. This message also appears if any of the parameters or
values are not recognized.
• Command not found / Incomplete command. Use ? to list
commands—You did not enter the required keywords or values.
• Ambiguous command—You did not enter enough letters to uniquely
identify the command.
Enter a question mark (?) at the command prompt to display the commands
available in the current mode.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 20
Page 21
Using the Command Line Interface
Command Organization in this Document
Command Organization in this Document
This document is divided into chapters, such as Administration and Port
Management chapters, based on general CLI functions. Chapters are divided into
sections, such as the Port Mirroring and Cable Diagnostics sections, where all
commands related to those features are listed. Commands that configure the
feature are listed first in each section, in alphabetical order, followed by
commands that display status and statistics information (show commands), in
alphabetical order.
1
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 21
Page 22

Administration
This chapter describes how to configure global system settings and perform
diagnostics.
It contains the following topics:
• Control Packet Handling
• Auto Configuration
• Bonjour
• Port Mirroring
• Cable Diagnostics
2
• PoE
• Switch Management Access Control
• SNTP and Time Settings
• System Software and Configuration Management
• Syslog
• RMON
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 22
Page 23

Administration
Control Packet Handling
Control Packet Handling
You can use the commands described in this section to control how the switch
handles packets of the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), Link Layer Discovery
Protocol (LLDP), or 802.1X protocol.
protocol cdp
Use this command to drop or forward Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) packets.
CDP enables directly connected devices to share information such as their IP
addresses, capabilities, and software versions. Although the switch does not use
CDP to share its own information, by default it forwards CDP packets on behalf of
connected devices within a VLAN.
protocol cdp {drop | forward}
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
drop The switch drops all CDP packets.
forward The switch forwards all CDP packets.
Default
CDP packets are forwarded.
Command Modes
Global Config
protocol {lldp | dot1x}
Use this command to drop, forward, or terminate Link Layer Discovery Protocol
(LLDP) or IEEE 802.1X Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPOL)
packets.
protocol {lldp | dot1x} {drop | forward | terminate}
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 23
Page 24

Administration
Control Packet Handling
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
lldp Specifies that the command applies to LLDP packets.
dot1x Specifies that the command applies to IEEE 802.1X
packets.
drop Drop all packets of the specified type.
forward Forwards all packets of the specified type to the VLAN.
terminate Process the packets.
Default
LLDP and 802.1X packets are terminated.
Command Modes
Global Config
Usage Guidelines
LLDP or 802.1X must be disabled globally before you can use this command to
configure the drop, forward, or terminate action for each protocol.
Related Commands
Command Description
[no] lldp med Enables and disables LLDP MED.
[no] dot1x portcontrol
show protocol Displays the drop, forward, or terminate state for the CPD,
Enables and disables the 802.1X operation on all ports.
LLDP, and Dot1X protocols.
show protocol
Use this command to display the drop, forward, or terminate state for the CPD,
LLDP, and Dot1X protocols.
show protocol
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 24
Page 25

Administration
Auto Configuration
2
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command:
(Switch) #show protocol
Protocol Mode
-------- ---cdp forward
dot1x terminate
lldp terminate
Related Commands
Command Description
protocol cpd Configures the switch to drop or forward CDP packets.
protocol {lldp |
dot1x}
Auto Configuration
The following commands configure the Auto Configuration file download feature.
When enabled, the switch automatically downloads a network configuration file if
no file is found in flash memory when the switch reboots. The switch uses
information obtained through DHCP to identify the TFTP server and file name to
use in the download.
boot autoinstall
Use this command to enable DHCP Auto Configuration on the switch. Use the no
form of the command to disable this feature.
Configures the switch to drop, forward, or terminate LLDP
or 802.1X packets.
boot autoinstall
no boot autoinstall
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 25
Page 26

Administration
Auto Configuration
2
Default
DHCP Auto Configuration is enabled.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Usage Guidelines
The Auto Configuration feature depends upon the proper configuration of other
devices in the network, including a DHCP or BOOTP server, a TFTP server, and, if
necessary, a DNS server.
Related Commands
Command Description
boot autoinstall
default-config
show autoinstall Displays Auto Configuration status information.
boot autoinstall
backup-tftp
boot autoinstall
backup-bootfile
Enables the switch to look for and download a default
network configuration file upon startup when no hostspecific configuration file is found.
Configures the address of a backup TFTP server to be
used when the Auto Configuration process cannot locate
the primary server or network configuration file name
provided by the DHCP server at startup.
Configures a backup configuration file name to be used
when the Auto Configuration process cannot locate the
primary server or network configuration file name
provided by the DHCP server at startup.
boot autoinstall backup-bootfile
Use this command to configure a backup configuration file name to be used when
the Auto Configuration process cannot locate the primary server or configuration
file name provided by a DHCP server at startup.
boot autoinstall backup-bootfile filename
no boot autoinstall backup-bootfile
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 26
Page 27

Administration
Auto Configuration
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
filename The name of the network configuration file on the backup
TFTP server.
Default
No backup file name is configured.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Related Commands
Command Description
boot autoinstall Enables or disables the Auto Configuration feature.
boot autoinstall
backup-tftp
show autoinstall Displays Auto Configuration status information.
Configures the address of a backup TFTP server to be
used when the Auto Configuration process cannot locate
the server or network configuration file name provided by
the DHCP server at startup.
boot autoinstall backup-tftp
Use this command to configure the address of a backup TFTP server to be used
when the Auto Configuration process cannot locate the primary server or
configuration file name provided by the DHCP server at startup. Use the no form of
this command to delete the backup server address.
boot autoinstall backup-tftp {server-ip | hostname}
no boot autoinstall backup-tftp
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 27
Page 28

Administration
Auto Configuration
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
server ip The IP address of a TFTP server.
hostname The hostname of the backup TFTP server. The switch must
be configured to use a DNS server if a hostname is
specified.
Default
No backup TFTP server address is configured.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Related Commands
Command Description
boot autoinstall Enables and disables the Auto Configuration feature.
boot autoinstall
backup-bootfile
show autoinstall Displays Auto Configuration status information.
Configures a backup configuration file name to be used
when the Auto Configuration process cannot locate the
server or network configuration file name provided by the
DHCP server at startup.
boot autoinstall default-config
Use this command to enable the switch to attempt to download a default network
configuration file when no host-specific configuration file is found during bootup.
Use the no form of this command to disable it.
boot autoinstall default-config
no boot autoinstall default-config
Default
This feature is enabled.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 28
Page 29

Administration
Auto Configuration
2
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Usage Guidelines
The Auto Configuration feature must be enabled on the switch for this feature to be
operational. See the boot autoinstall command.
Related Commands
Command Description
boot autoinstall Enables and disables the Auto Configuration feature.
show autoinstall Displays Auto Configuration status information.
show autoinstall
Use this command to display the status of the Auto Configuration feature.
show autoinstall
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command:
(Switch) #show autoinstall
AutoInstall Mode............................... Started
AutoInstall default-config Mode................ Disabled
AutoInstall Backup TFTP Server Address......... Not configured
AutoInstall Backup Boot Filename............... Not configured
AutoInstall State.............................. Waiting for boot options
Related Commands
Command Description
boot autoinstall Enables and disables the autoinstall feature.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 29
Page 30

Administration
Bonjour
2
Command Description
Bonjour
boot autoinstall
default-config
boot autoinstall
backup-tftp
boot autoinstall
backup-bootfile
Bonjour enables the switch and its services to be discovered by using multicast
DNS (mDNS). Bonjour advertises switch services to the network and answers
queries for service types it supports, simplifying network configuration in small
business environments.
Enables the switch to look for and download a default
network configuration file upon startup when no hostspecific configuration file is found.
Configures the address of a backup TFTP server to be
used when the Auto Configuration process cannot locate
the server or network configuration file name provided by
the DHCP server at startup.
Configures a backup configuration file name to be used
when the Auto Configuration process cannot locate the
server or network configuration file name provided by the
DHCP server at startup.
bonjour run
Use this command to enable Bonjour on the switch. Use the no form of the
command to disable it.
bonjour run
no bonjour run
Default
Bonjour is enabled.
Command Modes
Global Config
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 30
Page 31

Administration
Bonjour
2
Usage Guidelines
When bonjour is enabled, the switch advertises the following service types:
• Cisco-specific device description (csco-sb)—This service enables clients to
discover Cisco switches and other products deployed in small business
networks.
• Management user interfaces—This service identifies the management
interfaces available on the switch (HTTP, Telnet, or SSH).
When a Bonjour-enabled switch is attached to a network, any Bonjour client can
discover and get access to the management interface without prior configuration.
A system administrator can use an installed Internet Explorer plug-in to discover
the switch. The web-based interface for this switch shows up as a tab in the
browser.
Bonjour works in both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
Related Commands
Command Description
show bonjour Displays Bonjour configuration details.
show bonjour
Use this command to show all the info related to Bonjour like on/off Bonjour, RR
TTL, and all the available service types.
show bonjour
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following example shows the output of the show bonjour command.
User:cisco
Password:**********
(Switch) #show bonjour
Bonjour Administration Mode: Enabled
Published Services:
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 31
Page 32

Administration
Port Mirroring
# Service Name Type Domain Port TXT data
--- ----------------- --------------- ------------ ------ -----------------------1 switchEC38FE _csco-sb._tcp. local. 80 deviceType=Switch
deviceDescr=Emulation,
0.0.0.0, Linux 2.6.23.17-
88.fc7
fmVersion=0.0.0.0
hdVersion=1.0
hostname=switchEC38FE
MACAddress=00:02:BC:EC:38:
FE
model=Emulation
serialNo=none
Related Commands
Command Description
2
Port Mirroring
bonjour run Enables Bonjour on the switch.
Port Mirroring enables you to monitor and analyze network traffic on a port or
VLAN by using a network analyzer.
A mirroring session consist of a destination probe port and at least one source
port or VLAN. The external network analyzer can use any of the Ethernet ports as a
probe port. The probe port transmits a mirror copy of the probed traffic to the
network analyzer.
A port configured as a destination port acts as a mirroring port when the session
is operationally active. When the session is not active, the port acts as a normal
port with respect to transmitting traffic.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 32
Page 33

Administration
Port Mirroring
2
monitor session
This command adds a mirrored port (source port) or probe port (destination port)
to a mirroring session. This command can also be used to disable the
administrative mode of the session. The no form of this command removes all the
configuration of this session, including the source and destinations interfaces and
VLAN.
monitor session 1-4 {source interface interface [{rx | tx}] | vlan vlan-id |
destination interface interface | mode}
no monitor session session-id {source interface interface | vlan vlan-id |
destination interface interface | mode}
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
1- 4 Four port mirroring sessions can be configured, numbered
1 to 4.
source interface The port or LAG to be mirrored.
rx | tx If the source interface parameter is specified, option rx
can be used to monitor only ingress packets. Option tx can
be used to monitor only egress packets. If no option is
specified, both ingress and egress packets are monitored.
vlan-id The VLAN ID of the traffic to be monitored.
destination
interface
mode Enables the mirroring session. Use the no form of the
Default
No port is configured to perform mirroring.
The port where data from the monitored port will be
copied to.
command with the mode keyword to disable the session
while leaving all other configured values intact.
Command Modes
Global Config
Usage Guidelines
VLAN mirroring mirrors only the ingress (Rx) traffic only.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 33
Page 34

Administration
Port Mirroring
2
Examples
The following commands configure a mirroring session that copies VLAN 30 traffic
received on port e7 to port e8:
(Switch) (Config)#monitor session 1 source interface e7 rx
(Switch) (Config)#monitor session 1 vlan 30
(Switch) (Config)#monitor session 1 destination interface e8
The following command administratively enables mirroring session 1:
(Switch) (Config)#monitor session 1 mode
Related Commands
Command Description
show monitor
session
Displays the port monitoring information for a particular
mirroring session.
show monitor session
This command displays the port and vlan mirroring information for a particular
mirroring session.
show monitor session session-id
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
session-id A unique number assigned to the mirroring session when it
was configured.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 34
Page 35

Administration
Cable Diagnostics
2
Examples
The following example shows the output of this command when no VLAN is
specified.
(Switch) #show monitor session 1
Port Mirroring is enabled on Following VLAN: None
Session ID Admin Mode Probe Port Mirrored Port Type
---------- ----------- ----------- -------------- ------1 Enable e1 e2 Rx,Tx
e3 Rx,Tx
The following example shows the output of this command when a VLAN is
specified.
(Switch) #show monitor session 2
Port Mirroring is enabled on Following VLAN: 10
Session ID Admin Mode Probe Port Mirrored Port Type
---------- ---------- ---------- ------------- ------1 Enable e4 e5 Rx
Related Commands
Command Description
monitor session Adds a mirrored port (source port) or probe port
Cable Diagnostics
The commands in this section enable you to run hardware diagnostic tests on
ports and view the results.
show cablestatus
(destination port) to a mirroring session and enables the
administrative mode of the session.
Use this command to display the cable connection status on a selected port.
show cablestatus interface
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 35
Page 36

Administration
Cable Diagnostics
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
interface The port number.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following example shows sample command output.
(switch) #show cablestatus e1
Cable Status................................... Normal
Cable Length................................... 0m - 10m
(switch) #show cablestatus e2
Cable Status................................... Open
Failure Location............................... 1m
Cable Status One of the following states is returned:
• Normal—The cable is working correctly.
• Open—The cable is disconnected or there is a faulty
connector.
• Short—There is an electrical short in the cable.
• Cable Test Failed—The cable status could not be
determined. The cable might be working.
Cable Length If this feature is supported by the PHY for the current link
speed, the cable length is displayed as a range between
the shortest estimated length and the longest estimated
length. Note that if the link is down and a cable is attached to
a 10/100 Ethernet adapter, the cable status might display as
Open or Short because some Ethernet adapters leave
unused wire pairs unterminated or grounded. Unknown is
displayed if the cable length could not be determined.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 36
Page 37

Administration
Cable Diagnostics
2
Failure Location The estimated distance in meters from end of the cable to
the failure location. The failure location is valid only if the
cable status is Open or Short.
Related Commands
Command Description
show fiber-ports
Displays diagnostic information for optical transceivers.
optical
transceiver
show fiber-ports optical-transceiver
Use this command to display diagnostics for optical transceivers.
show fiber-ports optical-transceiver [interface]
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
interface The port number.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following example shows output for the command when no port is specified.
Output Input
Port Temp Voltage Current Power Power TX LOS
------- ---- ------- ------- ------- ------- ----- --g1 0.4 0.000 3081249.3 54.887 50.502 Yes No
g2 0.9 0.000 3081249.3 54.887 50.502 Yes No
Temp - Internally measured transceiver temperatures.
Voltage - Internally measured supply voltage.
Current - Measured TX bias current.
Output Power - Measured optical output power relative to 1mW.
Input Power - Measured optical power received relative to 1mW.
TX Fault - Transmitter fault.
LOS - Loss of signal.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 37
[C] [Volt] [mA] [dBm] [dBm] Fault
Page 38

Administration
PoE
2
TEMP Internally measured transceiver temperature.
Voltage Internally measured supply voltage.
Current Measured TX bias current.
Output Power Measured TX output power in milliwatts.
Input Power Measured RX received power in milliwatts.
TX Fault Transmitter fault.
LOS Loss of signal.
Related Commands
PoE
Command Description
show cablestatus Displays the cable connection status on a selected port.
The following commands configure the Power-over-Ethernet functionality on the
switch.
NOTE These commands are valid only for the SF 200E-24P and SF 200E-48P switches.
lldp med transmit-tlv
Use this command to specify the optional Type Length Values (TLVs) in the LLDP
MED set transmitted in the Link Layer Discovery Protocol Data Units (LLDPDUs) on
a specific port. Use the no form of the command to exclude the specified TLV for
the specified port.
lldp med transmit-tlv [capabilities] [ex-pse] [inventory] [location] [network-policy]
no lldp med transmit-tlv [capabilities] [ex-pse] [inventory] [location] [network-
policy]
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 38
Page 39

Administration
PoE
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
capabilities Includes the switch capabilities TLV in LLDP
advertisements.
ex-pse Includes the extended power sourcing equipment TLV in
LLDP advertisements. This keyword is available only on
switches that support PoE.
inventory Includes the switch inventory TLV in LLDP advertisements.
location Includes the switch location TLV in LLDP advertisements.
network-policy Includes the switch network policy TLV in LLDP
advertisements.
Default
No LLDP capabilities are advertised.
Command Modes
Interface Config
Examples
The following example includes the network policy TLV in LLDP advertisements on
port e7.
(Switch) (Interface e7)#lldp med transmit-tlv network-policy
Related Commands
Command Description
lldp med
transmit-tlv
Specifies the optional Type Length Values (TLVs) in the
LLDP MED set that are transmitted in the Link Layer
Discovery Protocol Data Units (LLDPDUs) on all ports.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 39
Page 40

Administration
PoE
2
lldp med transmit-tlv all
Use this command to specify the optional Type Length Values (TLVs) in the LLDP
MED set transmitted in the Link Layer Discovery Protocol Data Units (LLDPDUs) for
all ports. Use the no form of the command to exclude the specified TLV for all the
ports.
lldp med transmit-tlv all [capabilities] [ex-pse] [inventory] [location] [network-
policy]
no lldp med transmit-tlv all [capabilities] [ex-pse] [inventory] [location] [network-
policy]
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
capabilities Includes the switch capabilities TLV in LLDP
advertisements.
ex-pse Includes the extended power sourcing equipment TLV in
LLDP advertisements. This keyword is available only on
switches that support PoE.
inventory Includes the switch inventory TLV in LLDP advertisements.
location Includes the switch location TLV in LLDP advertisements.
network-policy Includes the switch network policy TLV in LLDP
advertisements.
Default
No LLDP capabilities are advertised.
Command Modes
Global Config
Examples
The following example includes the network policy TLV in LLDP advertisements on
all ports.
(Switch) (Config)#lldp med transmit-tlv all network-policy
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 40
Page 41

Administration
PoE
2
Related Commands
Command Description
lldp med
transmit-tlv
show lldp med Displays a summary of the current LLDP-MED
Specifies the optional TLVs in the LLDP MED set
transmitted in the Link Layer Discovery Protocol Data Units
(LLDPDUs) on a specific port.
configuration.
poe
Use this command to configure the port as a Power-Sourcing Equipment (PSE)capable interface. Use the no form of the command to configure as a non-PSE
interface.
poe
no poe
Default
PoE is enabled on PoE-capable ports (not applicable to non-PoE ports).
Command Modes
Global Config
Interface Config
Usage Guidelines
Use the command in Global Config mode to enable PSE functionality on all PSEcapable ports. Use the command in Interface Config mode to configure PSE
functionality on a specific port.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 41
Page 42

Administration
PoE
2
Related Commands
Command Description
lldp med
transmit-tlv
lldp med
transmit-tlv all
poe power
management
poe power limit Sets the method for power management.
poe priority Configures the port priority level for the delivery of power
poe
usagethreshold
poe reset Configures the PoE functionality to reinitialize
poe powereddevice describe
Specifies the TLVs in the LLDP MED set transmitted in the
Link Layer Discovery Protocol Data Units (LLDPDUs) on a
specific port or on all ports.
Sets the power management as dynamic or static.
to an attached device.
Configures the system power usage threshold level at
which a trap is generated and a message is logged.
automatically on encountering a fault condition.
Adds a comment or description of the powered device
type to enable the operator to remember what is attached
to the interface.
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
show poe port
configuration
show poe port Displays per-port PoE status.
Displays per-port PoE configuration.
poe power limit
Use this command to set the power management method. Use the no form of the
command to reset the method to the default.
poe power limit {{dot3af | user-def 3000-16200}} | [lldp-med]}
no poe power limit
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 42
Page 43

Administration
PoE
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
dot3af The maximum power that can be delivered by the PSE
port is limited by the detected IEEE 802.3af class.
user-def The maximum power that can be delivered by the PSE
port is specified by the user. The value can be in the range
of 3W (3000) to 16.2W (16200).
lldp-med The maximum power that can be delivered by the PSE
port is limited by the value in LLDP-MED TLVs received
from a powered device. The value specified by the
powered device should be in the range of 3–16.2 watts. If
it is not in the range, then the default value of 16.2 watts is
configured, unless the dot3af is specified or a different
user-defined value is configured.
Modes
Global Config
Interface Config
Default
PoE power is limit by the port. The value is 16.2 watts.
Usage Guidelines
The keywords lldp-med and dot3af, and the keywords lldp-med and user-def,
can be enabled simultaneously. If an LLDP-MED TLV is received from the powered
device, that value is given priority over a dot3af or user-defined value.
If only lldp-med is enabled, and no LLDP-MED TLV is received from the powered
device, then the default value of 16.2 watts is configured.
Related Commands
Command Description
poe power
management
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 43
Sets the power management as dynamic or static.
Page 44

Administration
PoE
2
Command Description
poe power limit Sets the method for power management.
poe priority Configures the port priority level for the delivery of power
to an attached device.
poe
usagethreshold
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
show poe port
configuration
show poe port Displays per-port PoE status.
Configures the system power usage threshold level at
which a trap is generated and a message is logged.
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
Displays per-port PoE configuration.
poe power management
Use this command to set the power management as dynamic or static. Use the no
form of the command to reset it to its default value.
poe power management {dynamic-with-priority | static- with-priority}
no poe power management
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
dynamic-withpriority
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 44
Power management is done by the PoE controller. Power
is supplied to devices as long as the consumption is within
the configured limit and priority. There is no pre-allocation
of power. A port with a higher port priority is given
preference when the switch supplies power to multiple
ports. If two or more port priorities are equal, the port with
the lower port number is given preference.
Page 45

Administration
PoE
2
Parameter Description
static-withpriority
Default
Dynamic-with-priority power management is enabled.
Command Modes
Global Config
Interface Config
Related Commands
Command Description
Power management is done by the PoE controller. The
switch pre-allocates power based on the configured
power limit and the priority of the port. A port with a higher
port priority is given preference when the switch supplies
power to multiple ports. If two or more port priorities are
equal, the port with the lower port number is given
preference.
poe power limit Sets the method for power management.
poe priority Configures the port priority level for the delivery of power
to an attached device.
poe
usagethreshold
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
show poe port
configuration
show poe port Displays per-port PoE status.
Configures the system power usage threshold level at
which a trap is generated and a message is logged.
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
Displays per-port PoE configuration.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 45
Page 46

Administration
PoE
2
poe powered-device describe
Use this command to add a comment or description of the powered device type
to enable the operator to remember what is attached to the interface. To remove
the description, use the no form of this command. This is applicable to powered
devices attached to the PSE ports on the switch.
NOTE The command can be used in Global Config mode to configure all ports and can be
used in Interface mode to configure a specific port.
poe powered-device describe pd-type
no poe powered-device describe
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
pd-type The type of powered device attached to the interface. The
range is 1–24 characters.
Modes
Global Config
Interface Config
Examples
The following example shows entering into Interface Config mode and adding a
description for port e1.
switch(config)#interface ethernet e1
switch(interface e1)#poe powered-device describe IP-phone
Command Description
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
show poe port
configuration
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 46
Displays per-port PoE configuration.
Page 47

Administration
PoE
2
poe priority
The switch might not be able to supply power to all connected PoE devices. Port
priority determines which ports supply power when adequate power capacity is
not available for all enabled ports. Use this command to configure the port priority
level for the delivery of power to an attached device. Use the no form of the
command to reset the priority value to the default.
NOTE The command can be used in Global Config mode to configure all ports and can be
used in Interface mode to configure a specific port.
poe priority {critical | high | low}
no poe priority
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
critical The port is assigned the highest prioritized when PoE
power requests exceed the available supply.
high The port is assigned a high priority when PoE power
requests exceed the available supply.
low The port is assigned a low priority when PoE power
requests exceed the available supply.
Command Modes
Global Config
Interface Config
Usage Guidelines
For ports that have the same priority level, the lower-numbered port is given
higher priority. For a system delivering peak power to a certain number of devices,
if a new device is attached on a higher-priority port, power to a device on a lowerpriority port is shut down.
Default
All ports are configured with low priority.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 47
Page 48

Administration
PoE
2
Command Description
poe power
management
poe power limit Sets the method for power management.
poe priority Configures the port priority level for the delivery of power
poe
usagethreshold
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
show poe port
configuration
show poe port Displays per-port PoE status.
Sets the power management as dynamic or static.
to an attached device.
Configures the system power usage threshold level at
which a trap is generated and a message is logged.
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
Displays per-port PoE configuration.
poe reset
Use this command to enable PoE to reinitialize automatically upon encountering a
fault condition. If this is disabled, then administrator intervention is required to
reinitialize the port. A fault condition is reported by the PoE controller in PSE Port
Detection Status parameter. The possible fault conditions are Fault and Other
Fault. Use the no form of the command to remove automatic reinitialization on a
port.
NOTE The command can be used in Global Config mode to configure all ports and can be
used in Interface mode to configure a specific port.
poe reset
no poe reset
Modes
Global Config
Interface Config
Default
PoE auto-reset is enabled.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 48
Page 49

Administration
PoE
2
Command Description
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
show poe port
configuration
show poe port Displays per-port PoE status.
Displays per-port PoE configuration.
poe usagethreshold
Use this command to configure the system power usage threshold level at which a
trap is generated and a message is logged.
poe usagethreshold 1-100
no poe usagethreshold
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
1-100 The power threshold percentage of total available system
power.
Default
• PoE usage threshold level is 95%
Command Modes
Global Config
Related Commands
Command Description
poe power
management
poe power limit Sets the method for power management.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 49
Sets the power management as dynamic or static.
Page 50

Administration
PoE
2
Command Description
poe threshold Configures the system power usage threshold level at
which a trap is generated and a message is logged.
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
show poe port
Displays per-port PoE configuration.
configuration
show poe port Displays per-port PoE status.
show poe
Use this command to display the global configuration of the switch, and
information about each device connected to the PSE port(s).
show poe
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(switch) #show poe
Nominal Power.................................. 180
Threshold Power................................ 162
Total Power Consumed........................... 0
Usage Threshold................................ 90
Power Management Mode.......................... dynamic-with-priority
Port Configuration
Intf Description
------ -----------------------e1 IP Phone
e2
e3
e4
e5
e6
e13
e14 Wireless AP
e15
e16
e17
e18
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 50
Page 51

Administration
PoE
2
Related Commands
Command Description
show poe port
configuration
show poe port
info
show poe port
statistics
Displays PoE configuration for a port or all ports.
Displays PoE status for a port or all ports.
Displays PoE statistics for a port or all ports.
show poe port configuration
Use this command to display PoE configuration for a port or all ports.
show poe port configuration {all | interface}
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
all Displays PoE configuration for all ports.
interface Displays PoE configuration for the specified port.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for all ports on which PoE operation is
available.
(switch1) #show poe port configuration all
Admin Priority Power Power Port Detection
Intf Mode Limit Limit pair Type
---- ------- --------- -------- ----------------- ----- ----------------e1 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e2 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e3 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 51
(W) Type
Page 52

Administration
PoE
2
e4 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e5 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e6 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e13 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e14 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e15 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e16 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e17 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
e18 Enable low 15.400 class alt-a 4ptdot3af
The following shows sample output for a specific port.
(switch1) #show poe port configuration e1
Interface...................................... e1
Description....................................
Admin Mode..................................... Enable
Priority....................................... low
Power Limit(W)................................. 15.400
Power Limit Type............................... class
Port Pair...................................... alt-a
Detection Type................................. 4ptdot3af
Related Commands
Command Description
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
show poe port
Displays PoE status for a port or all ports.
info
show poe port
Displays PoE statistics for a port or all ports.
statistics
show poe port info
Use this command to display PoE status for a port or all ports.
show poe port info {all | interface}
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 52
Page 53

Administration
PoE
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
all Displays PoE status for all ports.
interface Displays PoE status for the specified port.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(switch) #show poe port info all
Output Output
Intf Class Power Current Voltage Temperature Status
(mW) (mA) (volt) (C)
------ ------ -------- -------- -------- ------------- -----------e1 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e2 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e3 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e4 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e5 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e6 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e13 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e14 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e15 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e16 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e17 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
e18 0 00000 0000 00 0 Searching
Related Commands
Command Description
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
show poe port
configuration
show poe port
statistics
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 53
Displays PoE configuration for a port or all ports.
Displays PoE statistics for a port or all ports.
Page 54

Administration
PoE
2
show poe port statistics
Use this command to display PoE statistics for an interface or all interfaces.
show poe port statistics {all | interface}
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
all Displays PoE statistics for all ports.
interface Displays PoE statistics for the specified port.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(switch) #show poe port statistics all
MPS Power Over Invalid
Intf Absent Denied Load Short Signature
------ -------- -------- -------- -------- -----------e1 00001583117
e2 00001583110
e3 00001572025
e4 00001572172
e5 00001541835
e6 00001541945
e1300001583102
e1400001583067
e1500001572154
e1600001572088
e1700001541959
e1800001541924
Related Commands
Command Description
show poe Displays the global configuration, and information about
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 54
each device connected to the PSE port(s).
Page 55

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Description
2
show poe port
configuration
show poe port
info
Displays PoE configuration for a specific port or all ports.
Displays PoE status for a specific port or all ports.
Switch Management Access Control
The following commands configure user login information and access settings for
the switch management interfaces. Switch management can be performed
through the web-based interface, a command line interface (CLI), or SNMP.
This section contains the following subsections:
• Authentication Methods
• User Logins and Passwords
• Management Access—General
• HTTP Access
• Telnet Access
• SSH Access
• Console Access
• Management Access Lists
Authentication Methods
ip http authentication
Use this command to specify authentication methods for HTTP server users. To
return to the default, use the no form of this command. The supported methods
are local or RADIUS.
ip http authentication method1 [method2]
no ip http authentication
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 55
Page 56

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
method1 The primary authentication method to use, local or
method2 The secondary authentication method to use if the primary
Default
method1—local authentication
Command Modes
2
RADIUS.
method returns an error, local or RADIUS.
Global Config
Examples
The following example configures HTTP authentication using a RADIUS server
and, if the RADIUS server is not available, using a locally administered user names
and passwords.
(switch) (Config)#ip http authentication radius
Related Commands
Command Description
radius server host Configures the IP address or DNS for a RADIUS server.
show
authentication
methods
Displays information about the authentication methods.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 56
Page 57

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
login authentication
Use this command to specify the login authentication method for a line (console
and Telnet) access mode. To return to the default list configuration, use the no form
of this command. The supported methods are local, RADIUS, or none.
If two methods of authentication are defined, then the second method is used only
if the first method returns an error—not if there is an authentication denial from the
first method.
login authentication method1 [method2]
no login authentication
Syntax Descriptions
2
Parameter Description
method1 The primary authentication method to use, which can be
local, RADIUS, or none.
method2 The secondary authentication method to use if the primary
method returns an error.
Default
method1—local authentication
Command Modes
Line Console Config
Line Telnet Config
Examples
The following example specifies the default authentication method for console
access.
(Switch) (config)#line console
(Switch) (config-line)#login authentication radius
The following example specifies the default authentication method for Telnet
access.
(Switch) (config)#line telnet
(Switch) (config-telnet)#login authentication radius
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 57
Page 58

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
2
ip http
authentication
radius server host Configures the IP address or DNS for a RADIUS server.
show
authentication
methods
Specifies authentication methods for HTTP server users.
Displays information about the authentication methods.
show authentication methods
Use this command to display information about the authentication methods.
show authentication methods
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(switch)#show authentication methods
Line Method
------- ----------------Console :local radius none
Telnet :radius
HTTP :local
DOT1X :
Related Commands
Command Description
ip http
authentication
login
authentication
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 58
Specifies authentication methods for HTTP server users.
Specifies the login authentication method list for a line
(console and Telnet) access mode.
Page 59

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
User Logins and Passwords
password
The currently logged-in user can use this command to change the password. This
command can be used after the password has aged-out or at any time to change
the user’s password. The user is prompted to enter the old password and the new
password. The change is effective upon the next log-in.
password
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Related Commands
2
Command Description
passwords minlength
passwords aging Implement aging on passwords for local users.
show passwords
configuration
Enforces a minimum password length for local users.
Displays the configured password management settings.
passwords aging
Use this command to implement aging on passwords for local users. When a
user's password expires, the user is prompted to change it before logging in again.
Use the no form of the command to reset it to the default value (180 days). If it is
set to 0, password aging is disabled.
passwords aging 0-365
no passwords aging
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
0-365 The number of days. The range is 0–365.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 59
Page 60

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Default
aging—180 days
Command Modes
Global Config
Related Commands
Command Description
2
passwords minlength
password Allows a user to change their password after it has
show passwords
configuration
Enforces a minimum password length for local users.
expired.
Displays the configured password management settings.
passwords min-length
Use this command to enforce a minimum password length for local users. Use the
no form of the command to reset it to its default value.
passwords min-length min-length
no passwords min-length
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
min-length The minimum number of characters that a password must
Default
min length—8 characters
Command Modes
Global Config
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 60
have. The range is 8-64.
Page 61

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
passwords aging Implement aging on passwords for local users.
password Allows a user to change their password after it has
2
expired.
show passwords
configuration
Displays the configured password management settings.
passwords strength-check
Use this command to enable the switch to perform the configured password
strength checks when users log in. The strength checks are configured separately
(see Related Commands). Use the no form of this command to disable password
strength checking.
passwords strength-check
no passwords strength-check
Default
This feature is enabled.
Command Modes
Global Config
Related Commands
Command Description
passwords
strength checkusername
passwords
strength excludekeyword
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 61
Configures the switch to prevent users from including their
user names in their passwords when they create or
change their password.
Configures the switch to check whether preconfigured
keywords are used in a password when a user attempts to
create or change the password.
Page 62

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Description
2
passwords
strength
maximum
repeatedcharacters
Configures the switch to check whether any character in
the password is repeated more that three consecutive
times.
passwords strength check-username
Use this command to prevent users from including their user names in their
passwords when they create or change them.
This security check is enforced only when the passwords strength check feature
is enabled (see the passwords strength-check command).
Use the no form of this command to disable checking for user names in
passwords.
passwords strength check-username
no password strength check-username
Default
This feature is enabled.
Command Modes
Global Config
Usage Guidelines
When you enable this feature, the following warning displays if one or more
currently configured users violates the user name condition.
Warning: Not all user(s) passwords comply with the current password strength
restriction(s).
Related Commands
Command Description
passwords
strength excludekeyword
Configures the switch to check whether preconfigured
keywords cisco and ocsic are used in a password
when a user attempts to create or change the password.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 62
Page 63

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Description
2
passwords
strength
maximum
repeatedcharacters
passwords
strength-check
Configures the switch to check whether any character in
the password is repeated consecutively more than three
times.
Enables the switch to perform the configured password
strength checks when users log in.
passwords strength exclude-keyword
Configures the switch to check whether preconfigured keywords are used in a
password when a user attempts to create or change the password. The
preconfigured keywords are cisco and ocsic.
This security check is enforced only when the passwords strength check feature
is enabled (see the passwords strength-check command).
Use the no form of this command to disable checking for keyword usage in
passwords.
password strength exclude-keyword
no password strength exclude-keyword
Default
This feature is disabled.
Command Modes
Global Config
Usage Guidelines
When you enable this feature, the following warning displays if one or more
currently configured users violates the keyword strength setting.
Warning: Not all user(s) passwords comply with the current password strength
restriction(s).
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 63
Page 64

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
2
passwords
strength checkusername
passwords
strength
maximum
repeatedcharacters
passwords
strength-check
Configures the switch to prevent users from including their
user names in their passwords when they create or
change them.
Configures the switch to check whether any character in
the password is repeated consecutively more than three
times.
Enables the switch to perform the configured password
strength checks when users log in.
passwords strength maximum repeated-characters
Use this command to configure the switch to check whether any character in the
password is repeated consecutively more than three times.
This security check is enforced only when the passwords strength check feature
is enabled (see the passwords strength-check command).
Use the no form of this command to disable checking for repeated characters in
passwords.
password strength maximum repeated-characters
no password strength maximum repeated-characters
Default
This feature is disabled.
Command Modes
Global Config
Usage Guidelines
When you enable this feature, the following warning displays if one or more
currently configured users violates the maximum repeated characters setting.
Warning: Not all user(s) passwords comply with the current password strength
restriction(s).
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 64
Page 65

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
2
passwords
strength checkusername
passwords
strength excludekeyword
passwords
strength-check
Configures the switch to prevent users from including their
user names in their passwords when they create or
change them.
Configures the switch to check whether preconfigured
keywords are used in a password when a user attempts to
create or change the password.
Enables the switch to perform the configured password
strength checks when users log in.
show loginsession
Use this command to display the current login sessions to the to the switch.
show loginsession {long}
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
long Use the long parameter to display full-length usernames.
Without this keyword, the usernames are truncated in the
output.
Command Modes
Global Config
Examples
In version 1.0.1.nn:
(switch121D4E) #show loginsession
ID User Name Connection From Idle Time Session Time Session Type
-- ------------- --------------------- ----------- ------------ -----------00 cisco EIA-232 00:00:00 00:03:49 Serial Port
In version 1.0.2.nn and higher:
(switch122D4E) #
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 65
Page 66

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
(switch122D4E) #show loginsession
ID User Name Connection From Idle Time Session Time Session Type Auth Method
-- ------------- --------------- --------- ------------ ------------ ----------00 cisco EIA-232 00:00:00 00:02:39 Serial Port Local
ID Login session ID.
System Name A name used to identify the switch. The factory default is
blank.
Username The name the user entered to log on to the system.
2
Connection
From
Idle Time Total time this session has been connected.
Session Type Type of session, such as HTTP, HTTPS, telnet, serial, or SSH.
Authentication
Method
Related Commands
Command Description
passwords minlength
passwords aging Implement aging on passwords for local users.
password Allows a user to change their password after it has
Time this session has been idle.
The authentication method can be Local or RADIUS.
Enforces a minimum password length for local users.
expired.
show users Displays the configured user names and their settings.
show passwords configuration
Use this command to display the configured password management settings.
show passwords configuration
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 66
Page 67

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
Switch) #show passwords configuration
Passwords Configuration
----------------------Password Strength Check Disabled
Minimum Password Length........................ 8
Maximum Password Repeated Characters........... Disabled
Minimum Password Character Classes............. Disabled
Password Exclude User Name..................... Disabled
Password Exclude Keywords...................... Disabled
Password History............................... 0
Password Aging (days).......................... 0
Related Commands
2
Command Description
passwords min-
Enforces a minimum password length for local users.
length
passwords aging Implements aging on passwords for local users.
show user accounts
This command displays the local user status with respect to user account lockout
and password aging.
show user accounts [long]
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
long Displays the complete user names. Without this keyword,
the long user names are truncated in the output.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 67
Page 68

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(switch) #show users accounts
UserName Privilege Password Password Lockout
-------------------- --------- ---------- --------------------- ------cisco 15 180 Jun 30 1970 00:00:43 False
jonstew 15 180 Jul 07 1970 08:32:36 False
User Name The local user account user name.
Privilege The privilege level of the users. All users are assigned the
Password Aging The number of days before the password expires.
2
Aging Expiry date
highest privilege level (15) by default.
Password
Expiry date
Lockout Indicates True if the user is currently locked out due to an
Related Commands
Command Description
show users Displays the configured user names and their settings.
The date when the password is scheduled to expire.
aged-out password or False if not locked out.
show users
Use this command to display the management users that are currently accessing
the switch through one of the user interfaces (serial console, Telnet, web, or
SNMP).
show users [long]
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 68
Page 69

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
long Displays the complete user names. Without this keyword,
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
Switch) #show users
2
the long user names are truncated in the output.
User Name Protocol Location
-------------------- ---------- ----------------------cisco Serial EIA-232
User Name The name the user enters to login using serial, port, Telnet,
web and SNMP.
Protocol Shows the protocol the user is using to access the switch.
Location Shows the IP address of the user system.
Related Commands
Command Description
show user
accounts
Displays the local user status with respect to user account
lockout and password aging.
show users login-history
Use this command to display information about the login history of users.
show users login-history
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 69
Page 70

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(switch)#show users login-history
Login Time Username Protocol Location
-------------------- --------- --------- --------------Jan 19 2005 08:23:48 Bob Serial
Jan 19 2005 08:29:29 Robert HTTP 172.16.0.8
Jan 19 2005 08:49:52 Betty Telnet 172.16.1.7
Login Time The date and time the user logged into switch.
Username User name.
Protocol Serial/Telnet/HTTP.
Location IP address for Telnet and HTTP.
2
Related Commands
Command Description
show users Displays the configured user names and their settings.
username
Use this command to add a new user to the local user database. Use the no form
of the command to remove the user.
username name {password password [encrypted] | no password} [override-
complexity check]
no username name
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
name The name of the user. The range is 1-32 characters.
password The authentication password for the user. The range is 8–
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 70
64 characters. This value can be zero if the no passwords
min-length command has been executed.
Page 71

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Parameter Description
encrypted The password as entered is an encrypted value, which has
nopassword Specifies that the user has no passwords.
2
been copied from another switch where it was encrypted.
overridecomplexity check
Defaults
• Default user: cisco
• Default password for cisco user: cisco
Command Modes
Global Config
Usage Guidelines
The cisco user can not be deleted.
Users created using this command have full administrative privileges.
Examples
The following example configures a user name and password with encryption.
Switch(config)#username "user1" password fb3604df5a109405b2d79ecb06c47ab5
encrypted
Specifies that the password will not be checked to meet
any password criteria configured using the passwords
strength-check commands.
Related Commands
Command Description
passwords minlength
passwords aging Implement aging on passwords for local users.
password Allows a user to change their password after it has
show users Displays the configured user names and their settings.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 71
Enforces a minimum password length for local users.
expired.
Page 72

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Management Access—General
network mgmt_vlan
Use this command to the configure management VLAN ID. Use the no form of the
command to reset it to the default value (VLAN 1).
network mgmt_vlan 1-4094
no network mgmt_vlan
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
1-4094 The VLAN ID. Access to the management interfaces is
2
restricted to the specified VLAN.
Default
The default VLAN ID for management access is1.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Related Commands
Command Description
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
switch's management interface.
show network
Use this command to display configuration settings associated with the switch
management interface.
show network
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 72
Page 73

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Usage Guidelines
The management interface is the logical interface used for in-band connectivity
with the switch via any of the front panel ports. The configuration parameters
associated with the switch management interface do not affect the configuration
of the front panel ports through which traffic is switched. The management
interface is always considered to be up, whether or not any member ports are up;
therefore, the show network command will always show Interface Status as Up.
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command
(switch) #show network
Interface Status............................... Always Up
IP Address..................................... 10.131.12.78
Subnet Mask.................................... 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway................................ 10.131.12.1
IPv6 Administrative Mode....................... Enabled
IPv6 Prefix is ................................ fe80::205:5ff:fe0a:201/64
Burned In MAC Address.......................... 00:05:05:0A:02:01
Configured IPv4 Protocol....................... DHCP
Configured IPv6 Protocol....................... None
IPv6 AutoConfig Mode........................... Disabled
Management VLAN ID............................. 1
2
HTTP Access
The following commands configure user access to the management interface
through HTTP.
ip http port
Use this command to specify the TCP port for use by a web browser to configure
the switch. To use the default TCP port, use the no form of this command.
ip http port 1025-65535
no ip http port
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
1025-65535 The HTTP protocol port number.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 73
Page 74

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Default
port—80
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Related Commands
Command Description
show ip http Displays the HTTP server configuration.
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
2
switch's management interface.
ip http server
Use this command to enable the switch to be configured, monitored, or modified
from a browser. To disable this function use the no form of this command.
ip http server
no ip http server
Default
HTTP access is enabled.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Related Commands
Command Description
show ip http Displays the HTTP server configuration.
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 74
switch's management interface.
Page 75

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
ip http session soft-timeout
Use this command to configure the soft timeout for HTTP sessions. When this
timeout expires the user will be forced to reauthenticate. This timer begins on
initiation of the web session and is restarted with each access to the switch. Use
the no form of this command to reset the timeout to the defaults.
ip http session soft-timeout 1-60
no ip http session soft-timeout
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
1- 60 The timeout in minutes.
2
Default
timeout—10 minutes
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Related Commands
Command Description
ip http server Enables the switch to be configured, monitored, or
modified from a browser.
show ip http Displays the HTTP server configuration.
show ip http
Use this command to display the HTTP server configuration.
show ip http
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 75
Page 76

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(Switch) #show ip http
HTTP Mode (Unsecure)................................. Enabled
HTTP Server Port......................................... 80
Maximum Allowable HTTP Sessions................ 5
HTTP Session Soft Timeout........................... 10 minutes
Related Commands
Command Description
ip http server Enables the switch to be configured, monitored, or
2
modified from a browser.
ip http session
soft-timeout
Configures the soft timeout for HTTP sessions.
Telnet Access
The following commands configure user access to the management interface and
outbound connections through Telnet.
ip telnet server enable
Use this command to enable the Telnet Server Admin Mode, in which the telnet
command can be used to establish a telnet connection to a remote host.
Use the no form of command to disable the Telnet Server Admin Mode and close
any existing telnet connections to remote hosts.
ip telnet server enable
no ip telnet server enable
Default
Telnet Server Admin Mode is disabled.
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 76
Page 77

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
telnet Establishes a new outbound Telnet connection to a remote
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
show telnetcon Displays Telnet configuration and status information.
telnet
Use this command to establish a new outbound Telnet connection to a remote
host.
2
host.
switch's management interface.
telnet {ip-address | hostname} port [debug] [line] [localecho]
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
ip address The IP address of the Telnet server.
hostname The hostname of the Telnet server. Ensure that a DNS
server is configured if a hostname is specified.
port The logical port number for Telnet communications in the
range of 1025 to 65535.
debug
line
localecho
Displays the currently enabled Telnet options.
Sets the outbound Telnet operational mode as line mode.
By default, the operational mode is character mode.
Enables keystrokes entered on the local device to be
echoed back to the screen immediately.
Defaults
• No ip address or hostname.
• Port—23
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 77
Page 78

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
• line—Character mode
• noecho—Disabled
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Related Commands
Command Description
2
ip telnet server
enable
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
show telnetcon Displays Telnet configuration and status information.
Enables Telnet connections to the system and enables the
Telnet Server Admin Mode.
switch's management interface.
telnetcon timeout
Use this command to set the Telnet connection session timeout value in minutes. A
session is active as long as the session has not been idle for the value set. Use the
no form of this command to reset the timeout to the default.
telnetcon timeout 1-160
no telnetcon timeout
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
1-160 The timeout value in minutes.
Default
timeout—5 minutes
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 78
Page 79

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Usage Guidelines
When the timeout value is changed, the new value is applied to all active and
inactive sessions immediately. Any sessions that have been idle longer than the
new timeout value are disconnected immediately.
Related Commands
Command Description
2
ip telnet server
enable
telnet Establishes a new outbound Telnet connection to a remote
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
show telnetcon Displays Telnet configuration and status information.
Enables Telnet connections to the system and enables the
Telnet Server Admin Mode.
host.
switch's management interface.
show telnetcon
Use this command to display Telnet configuration and status information, such as
the configured timeout, the number of allowed sessions, and the administrative
mode for making outbound Telnet connections from the switch.
show telnetcon
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(Switch) #show telnetcon
Remote Connection Login Timeout (minutes)...... 5
Maximum Number of Remote Connection Sessions... 2
Allow New Telnet Sessions...................... Yes
Telnet Server Admin Mode....................... Disable
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 79
Page 80

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
2
ip telnet server
enable
telnet Establishes a new outbound Telnet connection to a remote
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
Enables Telnet connections to the system and enables the
Telnet Server Admin Mode.
host.
switch's management interface.
SSH Access
The following commands configure user access to the management interface
through SSH.
copy nvram:sshkey-dsa
Use this command to download a DSA SSH host key. A key cannot be
downloaded while SSH is enabled or sessions are active.
copy url nvram:sshkey-dsa
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Related Commands
Command Description
crypto key
generate dsa
Generates a DSA key pair for SSH.
copy nvram:sshkey-rsa1
Use this command to download an RSA1 SSH host key. A key cannot be
downloaded while SSH is enabled or sessions are active.
copy url nvram:sshkey-rsa1
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 80
Page 81

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Related Commands
Command Description
2
copy
nvram:sshkeyrsa2
crypto key
generate rsa
Downloads an RSA2 SSH host key.
Generates an RSA key pair for SSH.
copy nvram:sshkey-rsa2
Use this command to download an RSA2 SSH host key. A key cannot be
downloaded while SSH is enabled or sessions are active.
copy url nvram:sshkey-rsa2
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Related Commands
Command Description
copy
nvram:sshkeyrsa1
crypto key
generate rsa
crypto key generate dsa
Use this command to generate a DSA key pair for SSH. The new key files
overwrite any existing generated or downloaded DSA key files. Use the no form of
this command to delete the DSA key files from the device.
crypto key generate dsa
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 81
Downloads an RSA1 SSH host key.
Generates an RSA key pair for SSH.
Page 82

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
no crypto key generate dsa
Command Modes
Global Config
Related Commands
Command Description
2
copy
nvram:sshkeydsa
Downloads a DSA SSH host key.
crypto key generate rsa
Use this command to generate an RSA key pair for SSH. The new key files
overwrite any existing generated or downloaded RSA key files. Use the no form of
the command to delete the RSA key files from the device.
crypto key generate rsa
no crypto key generate rsa
Command Modes
Global Config
Related Commands
Command Description
copy
nvram:sshkeyrsa1
copy
nvram:sshkeyrsa2
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 82
Downloads an RSA1 SSH host key.
Downloads an RSA2 SSH host key.
Page 83

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
ip ssh protocol
Use this command to set the available protocol levels (versions) for SSH. SSH
version 1, version 2, or both can be set. The specified level(s) are enabled and any
unspecified level is disabled.
ssh protocol {{1 | 2} | {1 2}}
Default
Version 1 and 2 are set.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Examples
The following example sets protocol level 1 (and unsets level 2 if it was previously
set).
2
(switch) #ip ssh protocol 1
The following example sets both levels:
(switch) #ip ssh protocol 1 2
Related Commands
Command Description
ip ssh server
enable
sshcon
maxsessions
sshcon timeout Configures the SSH Login Inactivity Timeout in minutes.
show ip ssh Shows SSH configuration information.
Enables management access through SSH.
Configures the number of remote SSH connections
allowed.
ip ssh server enable
Use this command to enable management access through SSH. Use the no form
of this command to disable access through SSH.
ip ssh server enable
no ip ssh server enable
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 83
Page 84

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Default
SSH access is disabled.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Related Commands
Command Description
ip ssh protocol Sets or removes protocol levels (versions) for SSH.
2
sshcon
maxsessions
sshcon timeout Configures the SSH Login Inactivity Timeout in minutes.
show ip ssh Shows SSH configuration information.
Configures the number of remote SSH connections
allowed.
sshcon maxsessions
Use this command to configure the number of remote SSH connections allowed.
Use the no form of the command to return the maximum to the default (2 sessions).
sshcon maxsessions 0-2
no sshcon maxsessions
Default
maxsessions—2
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Related Commands
Command Description
ip ssh server
enable
ip ssh protocol Sets or removes protocol levels (versions) for SSH.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 84
Enables management access through SSH.
Page 85

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Description
sshcon timeout Configures the SSH Login Inactivity Timeout in minutes.
show ip ssh Shows SSH configuration information.
sshcon timeout
Use this command to set the SSH connection timeout value in minutes. A session
is active as long as the session has not been idle for the value set. Use the no form
of this command to reset the timeout to the default.
sshcon timeout 1-160
no sshcon timeout
Syntax Descriptions
2
Parameter Description
1-160 The timeout value in minutes.
Default
timeout—10 minutes
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Usage Guidelines
When the timeout value is changed, the new value is applied to all active and
inactive sessions immediately. Any sessions that have been idle longer than the
new timeout value are disconnected immediately.
Related Commands
Command Description
ip ssh server
enable
ip ssh protocol Sets or removes protocol levels (versions) for SSH.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 85
Enables management access through SSH.
Page 86

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Description
2
sshcon
maxsessions
show ip ssh Shows SSH configuration information.
Configures the number of remote SSH connections
allowed.
show ip ssh
Use this command to display SSH settings.
show ip ssh
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command.
(Switch) #show ip ssh
SSH Configuration
Administrative Mode: .......................... Enabled
Protocol Levels: .............................. Versions 1 and 2
SSH Sessions Currently Active: ................ 0
Max SSH Sessions Allowed: ..................... 2
SSH Timeout: .................................. 5
Keys Present: ................................. DSA RSA
Key Generation In Progress: ................... None
Console Access
This section describes the commands you use to configure properties for the
console connection to the switch CLI.
line console
Use this command in Global Config mode to enter the Line (Console) Config Mode,
where you set properties of the console port.
line console
Command Modes
Global Mode
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 86
Page 87

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
serial baudrate Specifies the communication rate of the console port.
serial databits Specifies the number of data bits per character for the
serial parity Sets the parity for the console connection.
serial stopbits Sets the number of stop bits for the console connection.
show serial Displays serial port communication settings.
serial baudrate
2
console connection.
Use this command to specify the communication rate of the console port. The
supported rates are 9600, 38400, and 115200. Use the no form of the command to
reset it to the default value.
serial baudrate {9600 | 38400 | 115200}
no serial baudrate
Default
baud rate—115200
Command Modes
Line (Console) Config Mode
Related Commands
Command Description
serial databits Specifies the number of data bits per character for the
console connection.
serial parity Sets the parity for the console connection.
serial stopbits Sets the number of stop bits for the console connection.
show serial Displays serial port communication settings.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 87
Page 88

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
serial databits
Use this command to specify the number of data bits per character for the console
connection. Use the no form of the command to reset it to the default value.
serial databits {7 | 8}
no serial databits
Default
Eight data bits per character
Command Modes
Line (Console) Config Mode
Related Commands
2
Command Description
serial baudrate Specifies the communication rate of the console port.
serial parity Sets the parity for the console connection.
serial stopbits Sets the number of stop bits for the console connection.
show serial Displays serial port communication settings.
serial parity
Use this command to set the parity for the console connection. Use the no form of
the command to remove the parity setting.
serial parity {even | odd | none}
no serial parity
Default
parity bits—none
Command Modes
Line (Console) Config Mode
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 88
Page 89

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
serial databits Specifies the number of data bits per character for the
serial baudrate Specifies the communication rate of the console port.
serial stopbits Sets the number of stop bits for the console connection.
show serial Displays serial port communication settings.
serial stopbits
Use this command to set the number of stop bits for the console connection. Use
the no form of the command to reset it to its default value (1).
2
console connection.
serial stopbits {1 | 2}
no serial stopbits
Default
stop bits—1
Command Modes
Line (Console) Config Mode
Related Commands
Command Description
serial databits Specifies the number of data bits per character for the
console connection.
serial baudrate Specifies the communication rate of the console port.
serial parity Sets the parity for the console connection.
show serial Displays serial port communication settings.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 89
Page 90

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
serial timeout
Use this command to specify the maximum time (in minutes) the system waits for
without console activity. A value of 0 indicates that a console can be connected
indefinitely. Use the no form of this command to reset the timeout to the default.
serial timeout 0-160
no serial timeout
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
1-160 The timeout in minutes.
2
Default
timeout—5 minutes
Command Modes
Line Config
Related Commands
Command Description
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the switch
management interface.
show serial Displays serial port communication settings.
show serial
Use this command to display serial port communication settings.
show serial
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 90
Page 91

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Examples
The following shows sample output for the command:
switch#show serial
Serial Port Login Timeout (minutes)............ 5
Baud Rate (bps)................................ 115200
Character Size (bits).......................... 8
Stop Bits...................................... 1
Parity......................................... none
Related Commands
Command Description
show network Displays configuration settings associated with the
2
switch's management interface.
show serial Displays configuration settings associated with the
switch's serial console interface.
Management Access Lists
deny
Use this command in Management Access-List Config mode to set conditions for
the management access list. This command can take the following forms:
deny interface interface [service service] [priority priority]
deny ip-source ip-address [mask mask | prefix-length] [service service] [priority
priority]
deny user username [priority priority]
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
interface A port number.
service The service type: telnet, http, tftp, ssh, or snmp.
priority Priority for the rule. The range is 1–16.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 91
Page 92

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Parameter Description
ip-address The source IP address to deny.
mask The network mask of the source IP address.
prefix-length The number of bits that comprise the source IP address
username The name of a management user.
Default
No users are denied access.
Command Modes
2
prefix. The prefix length must be preceded by a forward
slash (/). The range is 0–32 bits.
Access List Config
User Guidelines
Management access must be retained on at least one interface; i.e., if you deny
management access to all but one interface, you cannot deny access on the last
interface.
Examples
The following example uses the command to allow management access on all the
interfaces except for e1 and e2:
switch(config)#management access-list mlist
switch(config-macal)#deny interface e1 priority <1-16>
switch(config-macal)#deny interface e2 priority <1-16>
switch(config-macal)#exit
switch(config)#management access-class mlist
Related Commands
Command Description
management
access-class
management
access-list
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 92
Restrict management connections.
Defines an access list for management and enters the
access-list configuration mode.
Page 93

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Description
permit Sets conditions for the management access list.
2
show
management
access-list
Displays information about the configured management
access list.
management access-class
Use this command in Global Config mode to restrict management connections. To
disable restriction, use the no form of this command.
NOTE Console access cannot be disabled.
management access-class {console-only | access-list-name}
no management access-class
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
console-only
Restricts management access to the serial (console)
interface.
access-list-name Restricts management access to the specified access list
name.
Default
Management access is not restricted.
Command Modes
Global Config
Examples
The following example uses the management access-class command to restrict
access to an access list named mlist after the access list has been defined:
switch(config)#management access-list mlist
switch(config-macal)#deny interface e1 priority <1-16
switch(config-macal)#deny interface e2 priority <1-16>
switch(config-macal)#permit priority <1-16>
switch(config-macal)#exit
switch(config) #management access-class mlist
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 93
Page 94

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Related Commands
Command Description
2
management
access-list
deny
permit
show
management
access-list
Defines an access list for management and enters the
access-list configuration mode.
Sets conditions for the management access list.
Displays information about the configured management
access list.
management access-list
Use this command to define an access list for management and to enter the
Access List Config mode. In Access List Config mode, you can configure the
denied or permitted access conditions using the deny and permit commands. To
remove an access list, use the no form of this command.
management access-list access-list-name
no management access-list
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
access-list-name The user-defined name of the access list.
Default
No access list.
Command Modes
Global Config
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 94
Page 95

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Usage Guidelines
This command enters the access-list configuration mode, where the denied or
permitted access conditions with the deny and permit commands must be
defined. If no match criteria are defined, the default is to permit access. If reentering to an access-list context, the new rules are entered at the end of the
access-list. Use the management access-class command to select the active
access-list. The active management list cannot be updated or removed.
Related Commands
Command Description
2
management
access-class
deny
permit
Restrict management connections.
Sets conditions for the management access list.
permit
Use this command in Management Access-List Configuration mode to set
conditions for the management access list.
permit interface interface [service service] [priority priority]
permit ip-source ip-address [mask mask | prefix-length] [service service] [priority
priority]
permit user username [priority priority]
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
interface A port number.
service The service type: telnet, http, tftp, ssh, or snmp.
priority Priority for the rule. The range is 1–16.
ip-address The source IP address to deny.
mask The network mask of the source IP address.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 95
Page 96

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Parameter Description
prefix-length The number of bits that comprise the source IP address
username The name of a management user.
Default
All users are permitted management access.
Command Modes
Management Access-list Configuration mode
Examples
2
prefix. The prefix length must be preceded by a forward
slash (/). The range is 0–32 bits.
The following example uses the permit command to allow access only to two
management interfaces, e1 and e2:
switch(config)#management access-list mlist
switch(config-macal)#permit interface e1 priority <1-16>
switch(config-macal)#permit interface e2 priority <1-16>
switch(config-macal)#deny priority <1-16>
switch(config-macal)#exit
switch(config)#management access-class mlist
Related Commands
Command Description
management
access-class
management
access-list
deny Sets conditions for the management access list.
Restrict management connections.
Defines an access list for management and enters the
access-list configuration mode.
show management access-list
Use this command to display information about the configured management
access list.
show management access-list
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 96
Page 97

Administration
Switch Management Access Control
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following example displays the active management access list.
switch#show management access-list a1
--deny interface e5 priority 1
! (Note: all other access implicitly permitted)
Related Commands
Command Description
2
management
access-list
Defines an access list for management and enters the
access-list configuration mode.
show management access-class
Use this command to display information about the active management access
list.
show management access-class
Command Modes
Privileged Exec
Examples
The following example displays the management access-list information.
switch#show management access-class
Management access-class is enabled, using access list mlist
Related Commands
Command Description
management
access-class
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 97
Restrict management connections.
Page 98

Administration
SNTP and Time Settings
SNTP and Time Settings
A system clock is used to provide a network-synchronized time-stamping service
for switch software events such as message logs. You can configure the system
clock manually or configure the switch as an SNTP client that obtains the clock
from a server. This section describes the SNTP and time commands.
This section contains the following subsections:
• Clock Commands
• SNTP Commands
Clock Commands
Use the commands described in this section to view and configure clock settings
when the SNTP feature is not used.
2
clock date
Use this command to set the date and time manually.
clock date dd/mm/yyyy time hh:mm:ss
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
dd/mm/yyyy The current date in day:month:year format.
hh:mm:ss The time in hours:minutes:seconds format.
Defaults
The switch clock initiates with the following values:
• date—01/01/1970
• time—00:00:00
Command Modes
Global Config
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 98
Page 99

Administration
SNTP and Time Settings
2
Related Commands
Command Description
clock timezone Sets the offset to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
show clock Displays the time and date from the system clock.
clock summer-time
Use this command to enable daylight savings time (DST). Use the no form of the
command to remove the DST configuration.
clock summer-time
no clock summer-time
Default
DST is not configured by default.
Command Modes
Global Config
Related Commands
Command Description
clock
summertime date
show clock Displays the time and date from the system clock.
Sets the summertime offset from the universal
coordinated time (UTC).
clock summertime date
Use this command to set the summertime offset to the UTC. Use the no form of the
command to delete the summertime configuration.
clock summer-time date start-date start-month start-year start-minutes end-date end-
month} end-year end-minutes [offset offset] [zone acronym]
no clock summer-time
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 99
Page 100

Administration
SNTP and Time Settings
2
Syntax Descriptions
Parameter Description
date The day of the month when DST begins. The range is 1–31.
month The month when DST begins, specified as the first three
letters by name. For example, enter jan for January.
year The current year. The range is 2000–2097.
hh:mm The time in hours and minutes. The range for hh is 0–23
and the range for mm is 0–59.
offset Number of minutes to add during the summertime. The
range is 1–1440 minutes.
zone acronym An acronym for the local timezone during DST, up to four
characters. The acronym is for display purposes only.
Default
No summertime offset is configured.
Command Modes
Global Config
Examples
The following example configures a summertime date starting on March 14, 2010
at 2:00 A.M, with an offset of 1 hour, ending on November 7, 2010 at 2:00 A.M. This
example also names this timezone EDT.
(Switch) (Config)#clock summer-time date 14 mar 2010 02:00 7 nov 2010 02:00
offset 60 zone EDT
Related Commands
Command Description
clock
summertime
recurring
show clock Displays the time and date from the system clock.
Cisco Small Business 200E Series Advanced Smart Switch Command Reference 100
Sets the summertime offset to UTC recursively every year.
 Loading...
Loading...