Page 1

Cisco Unified IP Phone Services
Application Development Notes
Supporting XML Applications
Release 7.1(3)
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-20949-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPON SIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICA TION OF ANY PRODUCT S.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORM ATION PACKET THAT
S
HIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCAT E THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP head er compressi on is an adap tation of a program developed by the Universi ty of Ca lifornia, Berk
domain version of the UNIX operatin g system. All rights reserved . Copyri ght © 1981 , Rege nts of the Uni versity of Califor nia.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AN D SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPP LIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
AL
L FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EX PRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
L
IMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONIN FRINGEMENT OR ARIS ING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUP PLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGE S, INCL UDI NG,
WI
THOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES .
CCDE, CCENT, CCSI, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, Cisco IronPort, the Cisco logo, Cisco Nurse Connect, Cisco Pulse, Cisco SensorBase, Cisco StackPower,
Ci
sco StadiumVision , Cisc o TelePresence, Cisco Unified Computing System, Cisco W ebEx , DCE, Fl ip Chann els , Flip fo r Good , Flip Mino, Flip shar e (Des ign), Flip Ultr a,
F
lip Video, Flip Video (Design), Instant Broadband, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Cisco Capital,
Ci
sco Capital (Design), Ci s co:Financed (Stylized), Cisco Store, Flip Gift Card, and One Million Acts of Green are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet , All Touch,
Asy
ncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo,
Ci
sco IOS, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collabo rat ion Wi thout L imita tion ,
C
ontinuum, EtherFast, EtherSwi tch, E vent Center, Explorer, Follow Me Br ows in g, GainM aker, iLYNX, IOS, iPhone, Iron Por t, the IronPort logo, Laser L ink, LightStream,
Linksys, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, PCNow, PIX, PowerKEY, PowerP anels, Pow erTV, Pow erTV (Design) ,
PowerVu, Prisma, ProConnect, ROSA, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.
and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countri es.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partn
between Cisco and any other company. (0910 R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display ou
document are shown for illustrative pur poses onl y. Any use of act ual IP addr ess es in ill ustr ativ e conte nt is uninte ntio nal and coincident al.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Ser vices Application Development N o tes
Copyright © 2004-2009 Cisco S ystems, I nc. All right s reserv ed.
eley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
er does not imply a partnership relationship
tput, and figures included in the
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface vii
Overview vii
Revision History vii
Audience vii
Cisco Developer Support Program vii
Organization viii
Related Documentation ix
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request i-ix
Cisco Product Security Overview x
Document Conventions x
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
1 Overview 1-1
2 New and Changed Information 2-1
New Information for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 7.1(3) 2-1
3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects 3-1
Understanding Object Behavior 3-1
XML Object Definitions 3-3
CiscoIPPhoneMenu 3-3
CiscoIPPhoneText 3-4
CiscoIPPhoneInput 3-5
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory 3-6
Custom Directories 3-7
CiscoIPPhoneImage 3-7
CiscoIPPhoneImageFile 3-9
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu 3-11
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu 3-11
CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu 3-12
CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu 3-14
CiscoIPPhoneStatus 3-14
CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile 3-17
CiscoIPPhoneExecute 3-18
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
iii
Page 4

Contents
CiscoIPPhoneResponse 3-19
CiscoIPPhoneError 3-19
Custom Softkeys 3-19
XML Considerations 3-20
Mandatory Escape Sequences 3-21
XML Encoding 3-21
Application Event Handlers 3-22
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
4 Component APIs 4-1
Application Management API 4-1
RTP Streaming API 4-1
Interaction Rules with Legacy RTP URI Streams 4-2
RTP Streaming Schema 4-2
Error Schema 4-4
Examples 4-5
Errors and Responses 4-5
5 Internal URI Features 5-1
Supported URIs by Phone Model 5-1
Device Control URIs 5-2
Key 5-2
Unsupported Key URIs and Alternate Options 5-4
Display 5-5
XML Displayable Object URIs 5-6
SoftKey 5-6
QueryStringParam 5-7
iv
Multimedia URIs 5-9
RTP Streaming 5-9
RTPRx 5-10
RTPTx 5-11
RTPMRx 5-11
RTPMTx 5-11
Play 5-12
Vibrate 5-12
Telephony URIs 5-13
Dial 5-13
EditDial 5-14
SendDigits 5-14
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 5
Application Management URIs 5-16
Init 5-16
Notify 5-16
Application 5-18
Contents
CHAPTER
6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings 6-1
HTTP Client Requests (HTTP GET) 6-1
HTTP Server Requests (HTTP POST) 6-1
HTTP Header Settings 6-2
HTTP Refresh Setting 6-3
MIME Type and Other HTTP Headers 6-4
Audio Clips 6-4
Content Expiration Header Setting 6-4
Set-Cookie Header Setting 6-5
HTTP Encoding Header Setting 6-6
HTTP Response Headers: Content-Type 6-6
Identifying the Capabilities of IP Phone Clients 6-7
x-CiscoIPPhoneModelName 6-7
x-CiscoIPPhoneDisplay 6-7
x-CiscoIPPhoneSDKVersion 6-8
Accept Header 6-8
Accessing IP Phone Information 6-9
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
OL-20949-01
7 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified IP Phone
Service Applications
7-1
Troubleshooting Tips 7-1
XML Parsing Errors 7-1
Error Messages 7-2
8 Cisco IP Phone Services
Software Development Kit (SDK)
8-1
SDK Components 8-1
Sample Services Requirements 8-3
9 IP Phone Service Administration and Subscription 9-1
Accessing Phone Service Administration 9-1
Adding a Phone Service 9-2
Defining IP Phone Service Parameters 9-3
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
v
Page 6

Contents
User Service Subscription 9-4
CHAPTER
APPENDIX
10 DeviceListX Report 10-1
Benefits 10-2
Restrictions 10-2
Integration Considerations and Interoperability 10-2
Performance and Scalability 10-2
Security 10-3
Related Features and Technologies 10-3
Supported Platforms 10-3
Prerequisites 10-3
Message and Interface Definitions 10-3
DeviceList XML Object 10-3
Troubleshooting DeviceListX Reports 10-4
Error Codes 10-4
Determining Problems With the Interface 10-5
A CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference A-1
APPENDIX
I
NDEX
B Cisco Unified IP Phone Services
XML Schema File
B-1
Updated XML Parser and Schema Enforcement B-1
CiscoIPPhone.xsd B-2
vi
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 7

Overview
Preface
Use this document with Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Release 7.1(3) to develop and deploy
customized client services for the Cisco Unified IP Phones that su ppo rt C isco Uni fied Phone se rvice s.
Because of the complexity of a Unified Communications network, this guide does not provide complete
d detailed inform at ion f or pro ce du res t hat y ou need to pe rf orm i n Cisc o Unified Communications
an
anager or other ne twor k d evices. See the “R ela ted D oc umen tat ion” sec tio n on pa ge ix for a list of
M
related documentat ion.
Revision History
Date Updates
September 29, 2009 Initial release.
November 23, 20 09 Upd ate d the do cume nt w it h in for mat ion o n the Ci sco U nified I P Pho ne s 99 71,
951, and 8961 m ode ls. See , New Informa tion for Cisco Un ified
9
Communications Ma nager 7.1 (3), page 1.
December 10, 2009 Corrected the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7925G resolution from 176 x 220 to 176
140. See, Table 3-2 on page 9
x
Audience
This document p rovides t he i nf orm ati on nee de d for e Xte nsib le Ma rk up Lang uag e (XM L) a nd X /Op en
System Interface (XSI) pro gramme rs and system administr ators to develop and deploy new services.
Cisco Developer Support Program
The Cisco Developer Network (CDN) portal provides access to multiple Cisco technology d eveloper
interfaces and collaborative support communities. CDN also provides formalized support services for
these interfaces to enable developers, customers, and partners to accelerate their development. The
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
vii
Page 8
Preface
formalized process provides acce ss to CDN Engin eers who are a n extension of the prod uct techn ology
engineering team s. CDN En gine ers have access to t he resou rc es nec essar y to provide expert supp ort in
a timely manner.
The Cisco Developer Network Program is designed for businesses (IHV's and ISV's) interested in going
market with Cisco. The CDN Program enables members to develop compelling solutions that unify
to
data, voice, video, an d m obile com mun icat ions on Cisc o's powerful com muni cati ons plat form. T he
program also all ows membe rs t o ta ke advantage of Cisco' s br an d, m arket leade rs hip p osi tion, a nd
installed base to help drive positive business results for themselves and their customers.
For additional information about the CDN Program and CDN support services go to
http://develop er.cisco.com/web/devserv i ces
Note The Cisco TAC does NOT provide support fo r th is AP I/i nte rface un der s ta nd ard h ar dware o r s oftwa re
support agreements. All technical support for this API/interface, from initial development assistance
through API troubleshooting/bugs in final production apps, is provided by Cisco Developer Support and
requires a separate Developer Support contra ct. Whe n opening case s, a Developer Support contrac t
number must be provided to rece ive support.
Organization
This docu me n t c om p ri se s th e fo ll owin g se c ti on s:
Chapter Description
Chapter 1, “Overview” Provi des an ove r v i ew o f t he Ci sc o Unified IP Phone
Chapter 2, “New and Changed Informat ion” Provides details on the new and changed information in
Chapter 3, “CiscoIPPhone XML Objects” Describes the general behavior and usage of each XML
Chapter 4, “Component APIs” Describes additional APIs available to the
Chapter 5, “Inter nal UR I Fe atur es ” Describes how to implement embe dded feat ures on
Chapter 6, “HTTP Requests and Header
Settings”
Chapter 7, “Troubleshooting
Cisco Unified IP Phon e Serv ice
Applications”
Chapter 8, “Cisco IP Phone Services
Software Development Kit (SDK)”
ervices for developers.
s
e XML service interface for the latest release of Cisco
th
Unified Communicatio n Ma nage r.
ject.
ob
sco Unified IP Phones.
Ci
sco Unified IP Phones.
Ci
Provides a p rocedure on handling HTTP client r equests,
efinitions for HTTP header elements, identifies the
d
capabilities of the requesting IP phone client, and
defines the Accept header.
Provides troubleshooting tips, XML par sing erro rs, and
rror messages.
e
Provides a list of the components used in the
Ci
sco Unified IP Services Software Development Kit
SDK) and the sample services requirements.
(
viii
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 9

Preface
Chapter Description
Chapter 9, “IP Phone Service Administration
and Subscription”
Chapter 10, “DeviceListX Report” Describes how the report provides a list of the
Appendix A, “Ci scoI PPhon e XML Obje ct
Quick Reference”
Appendix B, “Cisco Unified IP Phone
Services XML Schema File”
Related Documentation
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Describes how to add an d a dmi nist er
sco Unified IP Phone Services through
Ci
sco Unified Communications Manager
Ci
dministration.
A
ervices-capable devices along with basic information
s
about the de vice to identify or classify the devi ces based
on specific criteria.
Provides a quick reference of the CiscoIPPhon e XML
jects and the de fin itions that a re asso ciated wi th each.
ob
Provides the CiscoIPPhone XML Schema.
For more information about Cisco U nified IP Phones or Cisco Unified Communications Mana ger, refer
to the following publications:
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7900 Series
These publications are available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/phones/ps379/tsd _produ cts_support_se ries_home .html
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
Related publications are available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition
Related publications are available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps7273/tsd_
products_support_series_home .html
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining docume ntatio n, submit ting a servi ce request , and gatheri ng additi onal
information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation,
revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
which also lists all new and
OL-20949-01
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the Wh
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
at’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
ix
Page 10
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Cisco Product Security Overview
This product co nt ain s c ryp togr ap hic fe atu res a nd is subj ect to Un ite d Sta tes an d loca l c ou ntry laws
governing import, export, tran sfer a nd use. De livery of Cisc o crypt o graph ic pro duc ts d oes no t i mp ly
third-party author ity to impo rt, export, dis tribute or use encry ption. Importer s, exporters , distributors
and users are responsible fo r compl ianc e with U.S. and l ocal co untry laws. By us ing this produ ct you
agree to comply with applicab le laws and regulat ions. If you a re unable to comply with U.S. and l ocal
laws, return this product immediately.
Further information regarding U.S. export regulations may be found at
http://www.access.gpo.gov/bis/ear/ear_data.html
Document Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
Convention Indication
bold fo
italic f
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional.
{x | y | z } Required alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by
[ x | y | z ] Optional al ternat ive keywords are grouped in brackets an d separ ated by
string A nonquoted set of char acte rs. Do not use qu otat ion mar ks around the string or
courier font Terminal sessions and information the system displays appear in cour ier fo nt .
< > Nonprinting characters such as passwords are in angle brackets.
[ ] Default responses to sy stem pr om pts are in sq uare br ackets .
!, # An exclamation poi nt (!) o r a pou nd si gn (#) a t t he b eginni ng of a li ne o f cod e
nt Commands and keywords and use r-enter ed text a ppea r in bold fon t.
ont Document titles, new or emphasized terms, and ar guments for which you su pply
values are in italic font.
ertical bars.
v
ertical bars.
v
e string will include the quotation marks.
th
dicates a comment line.
in
Preface
Note Means reader take note.
Tip Means the following information will help you solve a problem.
Caution Means rea de r be care ful. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
x
OL-20949-01
Page 11

Preface
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Timesaver Means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action described in
the paragraph.
Warning
Means reader be warned. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in
bodily injury.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
xi
Page 12

Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Preface
xii
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 13

CHA PTER
1
Overview
You can use Cisco Unified IP Phones to deploy customi zed c lient servi ces with w hich u sers can inter act
via the keypad and display. Services deploy using the HTTP protocol from stan dard web servers.
Users acces s t h ese fe at ur es usi ng th e s
varies by phone model). When a user presses the services button (or chooses the serv ic e s menu item), a
menu of configured services displays. The user then chooses a service from the list, and the phone
displays the service.
The following list gives ty pical services that might be supplied to a phone:
• Weather
• Stock information
• Contact information
• Company news
• To-do list s
• Daily schedule
ervices and directories buttons or menu options (availability
Figure 1-1 sh
Figure 1-1 Cisc o Unified IP Phone Text Menu Sample
Cisco Unified IP Phones can also display graphic menus, as shown in Figure 1-2.
ows a sample text menu.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
1-1
Page 14

Chapter 1 Overview
Figure 1-2 Graphic Menu on a Cisco Unified IP Phone Sample
Phone users can navigate a text menu by using the Navigation button followed by the Select softkey, or
by using the numeric keypad to e nter a se le ction di rec tly. Graphic menus c urren t ly do n ot su ppo rt
cursor-based navigation; users simply enter a numb er usi ng the DTMF keypad.
When a menu selection is made, the Cisco Unified IP Phone acts on it by using its HTTP client to load
specific URL. The return type from this URL can be plain text or one of the CiscoIPPhone XML
a
objects. The object loads and the user interacts with the object.
Figure 1-3 a
stock quote that was gene rated usi ng pl ai n text, and Figure 1-4 displays a gr ap hic i mage .
nd Figure 1-4 show typical displays that result from selecting a serv ice . Figure 1-3 shows a
Figure 1-3 Plain Text Display Example
Figure 1-4 Graphic Image Display Example
Cisco Unified Communications M anage r li mits Cisc o Unified IP Phone service activity to a specific
Services pane in the Cisco Unified IP Phone display. A service cannot modify the top line of the phone
isplay , which contains the time, date , and primary extens ion. A service cannot ov erwrite the bottom line
d
of the display, which contains softkey definitions. The pane tha t dis play s th e ser vice sit s flush with the
left side of the display, and enough of the right side of the display remains intact to ensure that users can
see the statu s of phone l ines.
1-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 15

Chapter 1 Overview
Note HTML Disclaimer: Phone service developers must take int o con si der ation t hat th e p hone i s no t a web
browser and cannot pars e H TML . Alt ho ugh c onte nt is de livered to th e phone thr oug h HT TP messa ges
by using a web serv e r, keep in mind that the content is not HTML. Al l conte nt comes eithe r as plain tex t
or packaged in propr i etary X ML w r ap pers .
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
1-3
Page 16

Chapter 1 Overview
1-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 17

CHA PTER
2
New and Changed Information
This chapter gi ves details on t he new and changed informat ion in the XML servic e interface fo r the latest
releases of Cisco Unified Communication Manager.
New Information for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
7.1(3)
The following are the updates made in the XML service interface for Cisco Unified Communication
manager 7.1(3):
• Support for t he late st 99 71, 9951, a nd 89 61 seri es Cisc o IP p hon es. For more infor mat ion see
Table 3-1 on page 3-2
• The 9971, 99 51, 8 961 seri es I P ph one s doe s n ot su ppo rt t he C isco IPPho neSta tus an d
CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile XM L objects . For m ore in forma tion see , Table 3-1 on page 3-2.
• Key URIs supported in 9971, 9951, and 8961 series IP phones and alternate options for unsupported
Key URIs. For more informat ion see, “Key” section on page 5-2.
OL-20949-01
• Changes in softkey position, behavior, and design. For more information see, “SoftKey” section on
page 5-6.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
2-1
Page 18

New Information for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 7.1(3)
Chapter 2 New and Changed Information
2-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 19

CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
The following sections descri be the ge neral behavior an d use of XML obj ects:
• Understandin g Obj ec t Behavio r
• XML Object Definitions
• Custom Softkeys
• XML Considerat ions
• Application Event Handlers
Understanding Object Behavior
Creating interactive service applications is relatively easy when you understand the XML objects that
are defined for Cisc o Unified IP Phones and the behavior that e ach objec t ge nerat es.
CHA PTER
3
Regarding services, the phone doe s not have any concept of a state when it loads an XM L page.
o Unified IP Phones can use HTTP to loa d a page of content in many dif ferent pla ces, st arting whe n
Cisc
e services button is pressed. Regardless of w ha t c ause s the p hon e t o lo ad a page , the phon e always
th
behaves appropriately after it loads a page.
Appropriate behavior depe nds solely o n the type of d ata tha t h as been d elivered in the pag e. T he we b
ver must deliver the XML pages with a MIME type of text/xml. However, the exact mechanism
ser
required v ari es accord ing to th e type of web serve r that y ou are u sing an d the ser ver side mechanis m that
you are using to create your pages (for example, static files, JavaScript, CGI, and so on). See Chapter 6,
“HTTP Reques ts a nd H ead er S et tin gs” for mor e info rmati on.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-1
Page 20
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Understanding Object Behavior
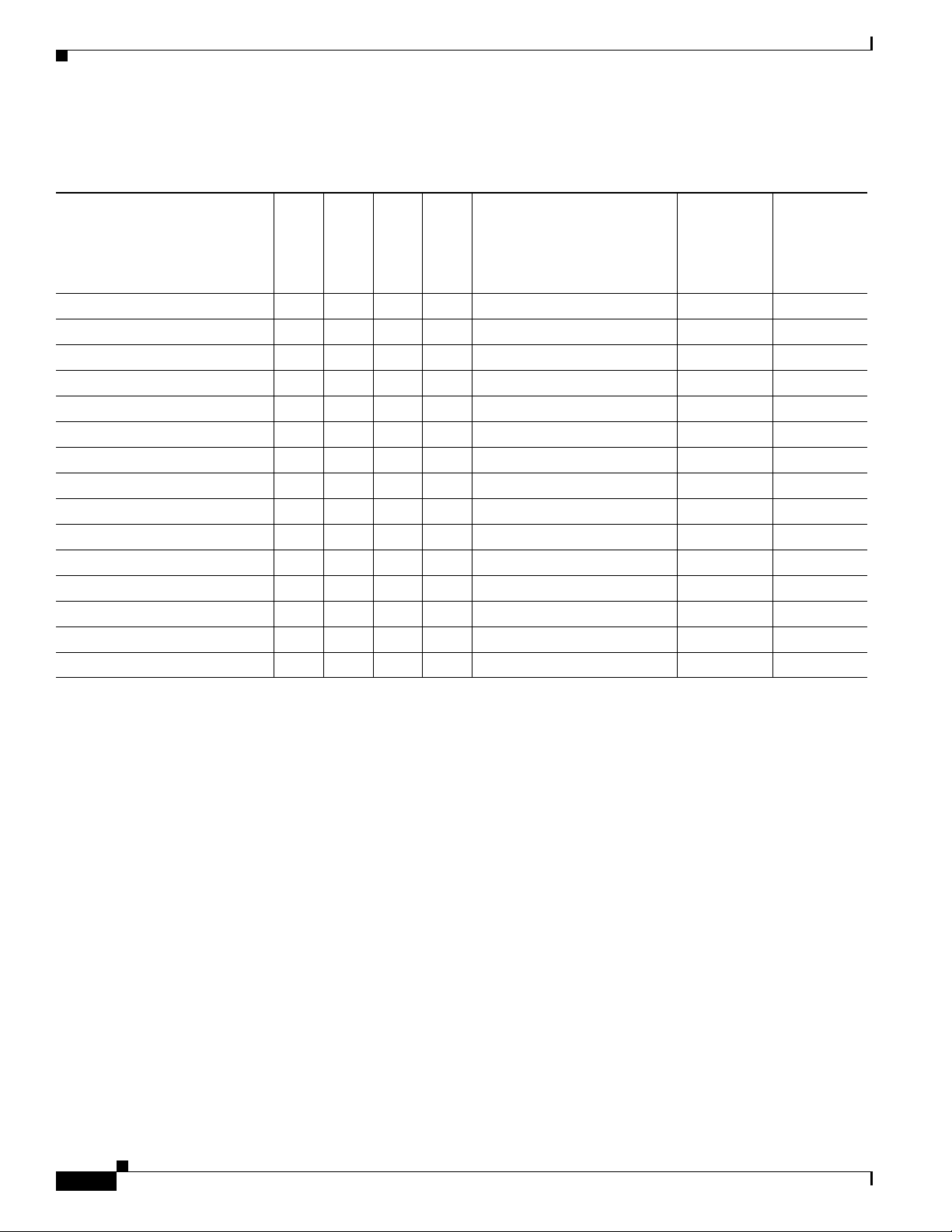
Table 3-1 shows the supported XML objects for this release.
Ta b l e 3-1 XML Objects Supported for Release 7.1(3) Cisco Unified IP Phone Services SDK
Phone Model XML Object
7905G
7906G
7911G
7912G
7931G 7920G
7921G
7925G
7940G
7960G
7941G/7941G-GE, 7942G,
945G, 7961G/7961G-GE,
7
7962G, 7965G, 7970G/
7971G-GE, 7975G, IP
Communicator
6921, 6941,
61
69
9971, 9951,
8961
CiscoIPPhoneMenu X X X X X X X
CiscoIPPhoneText X X X X X X X
CiscoIPPhoneInput X X X X X X X
CiscoIPPhoneDirect ory X X X X X X X
1
CiscoIPPhoneImage — X
X X X —
CiscoIPPhoneImageFi le — — X — X —
1
CiscoIPPhoneGraphi cMenu — X
X X X —
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFil eMenu — — X — X —
3
CiscoIPPhoneIco nMen u X
CiscoIPPhoneIconFi leMe nu — — X — X
X X X X X
5
2
2
2
2
4
4
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CiscoIPPhoneStatus — — — X X — —
CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile — — — — X
6
CiscoIPPhoneExecute X X
X X X X X
5
— —
CiscoIPPhoneResponse X X X X X X X
CiscoIPPhoneError X X X X X X X
1. The C i s c o Unified IP Phone 7920G has only a 128-by-59 display with 2 grayscale images clipping the graphic equally on both sides and providing
vertical scrolling. When an image with 4 grayscale settings occurs (<Depth>2</Depth>), the phone equally splits them into 2 grayscale settings (0-1 get
treated as 0 and 2-3 get treated as 1).
2. The C i s c o Unified IP Phones 6921, 6941, and 6961 do not support CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu, CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu,
CiscoIPPhoneImageFile, and CiscoIPPhoneImage
3. The C i s c o Unified IP Phones 7905G and 7912G do not support CIP images; therefore, all icons get ignored and does not display.
4. The C i s c o Unified IP Phones 6921, 6941, and 6961 do not support icons; therefore, all icons are ignored and does not display.
5. The C i s c o Unified IP Phones 7970G and 7971G-GE require firmware version 7.1(2) or higher to support this object, and Cisco IP Communicator
requires software version 2.01 or higher.
6. The Cisco Unified IP Phone 7920G does not support Priority 1 when on a call.
because these phones use monochrome LCD.
3-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 21

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
XML Object Definitions
The following sections provide definitions and descriptions of each CiscoIPPhone XML object:
• CiscoIPPhoneMenu
• CiscoIPPhoneText
• CiscoIPPhoneInput
• CiscoIPPhoneDirector y
• CiscoIPPhoneIm age
• CiscoIPPhoneIm ageFil e
• CiscoIPPhoneGraphic Menu
• CiscoIPPhoneGraphi cFileM enu
• CiscoIPPhoneIconM enu
• CiscoIPPhoneIconFil eMenu
• CiscoIPPhoneStatus
XML Object Definitions
• CiscoIPPhoneStatusFil e
• CiscoIPPhoneExecute
• CiscoIPPhoneRespon se
• CiscoIPPhoneError
CiscoIPPhoneMenu
A menu on the phone comprises a list of text items, one per line. Users choose individual menu items by
using the same mechanisms that are used for built-in menus in th e phone as described in Chapter 1,
“Overview”.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
Note • Th e Name field un der th e <MenuI tem > suppo rts a maximu m of 64 chara cters. Thi s field can also
accept two carriage returns to allow the MenuItem name to span three lines on the display.
• The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time. If
both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then these phones display only the Prompt
field.
OL-20949-01
The XML format allo ws you to specif y a t itle a nd p rompt th at are use d fo r the entire menu, followed b y
a sequence of
MenuItem includes a Name and an associated URL.
MenuItem objects. Cisco Unified IP Ph ones allow a maximu m of 100 MenuItems. Each
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-3
Page 22
XML Object Definitions
When a menu is loaded, th e phone behaves the same as for built-in phone menus. The user navigates
through the list of menu items and eventually chooses one by using either the Select softkey or the DTMF
keys.
After the user chooses a me nu optio n, the phone ge ne rat es an HT TP requ est for the pa ge with th e URL
r executes the uniform resource identifiers (URIs) that are associated with the menu item.
o
CiscoIPPhoneText
The CiscoIPPhoneText XML object displays ordinary 8-bit ASCII text on the phone display. The <Text>
message must not c onta in any c ontr ol cha ract ers, excep t fo r ca rri age re turn s, lin e fe ed s, an d t abs. T he
Cisco Unified IP Phone firmware controls all othe r pagina tion and wordw rap issues.
Note Cisco Unified IP Phones support the full ISO 8859-1 (Latin 1) and Shift_JIS character sets.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneText>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>The prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<Text>The text to be displayed as the message body goes here</Text>
</CiscoIPPhoneText>
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then t hes e phon es d isp lay only the
Prompt field.
Two optional fields can appear in the XML message:
• The first optional field, Title, defines text that displays at th e top of the displ ay page . If a Title is
not specified, the
• The second opt ional field, Prompt, defines text th at di spla ys at the bot tom of the displa y p age. If a
Prompt is not specified, Cisco Unified Communications Manager c lea rs the prom pt are a of the
Name field of the last chosen MenuItem displays in the Title fiel d .
display pane.
Many XML objects that are described in this document also have
Title and Prompt fields. These fields
normally behave identically to behavior described in this section.
Note Non-XML Text: This document only describes the supported CiscoIPPhone XML objects. Y ou can also
deliver plain text via HTTP . P ages that are delivered as MIME type text/html behave exactly the same as
XML pages of type
CiscoIPPhoneText. One important difference is that you cannot include a title or
prompt.
Note Keypad navigation: Cisco Unified IP Phones allow navigation to a specific line in a menu by pressing
numeric DTMF key s. When a menu is on the display, the number for selecting the menu is on the left.
When normal text displays, the numbers do not display on the left side of the screen, but the navigation
capability still exists. So, a carefully written text service display can take advantage of this capability.
3-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 23

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
CiscoIPPhoneInput
When a Cisco Unified IP Phone receives an XML object of type CiscoIPPhoneInput, it constructs an
input form and display s it. T he user then enters data in to each input item an d send s the parameter s to t he
target URL. Figure 3-1 shows a sample display that is receiving input fro m a user.
Figure 3-1 Sample User Input Display
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneInput>
<Title>Directory title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<URL>The target URL for the completed input goes here</URL>
<InputItem>
<DisplayName>Name of the input field to display</DisplayName>
<QueryStringParam>The parameter to be added to the target URL</QueryStringParam>
<DefaultValue>The default display name</DefaultValue>
<InputFlags>The flag specifying the type of allowable input</InputFlags>
</InputItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneInput>
XML Object Definitions
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then the se p hon es d ispl ay onl y the
Prompt field.
The Title and Prompt tags in the object delimit text are used in the sam e way as the identical fields in
the other CiscoIPPhone XML obj ects.
URL tag delimits the URL to which the input results are sent. The actual HTTP request sent to this
The
server specifies the URL with a list of parameters that are appended to it as a query string. The
parameters includ e Name/Value pairs, one for each input item.
Note CiscoIPPhoneInput objects do not use the HTTP POST method.
The
InputItem tag delimits each item in the list. The number of InputItems must not exceed five. Each
input item includes a
item. Each item als o has a
DisplayName, which is the prompt that is written to the display for that particular
QueryStringParam, which is the name of the parameter that is append ed to the
URL when it is sent out after input is co mplete. Each input ite m can al so use t he
the default value to be displayed.
The final attribute for each input item comprises a set o f
InputFlags. The following table describes the
input types that are cu rrentl y defined .
DefaultValue tag to set
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-5
Page 24

XML Object Definitions
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
InputFlag Description
A Plain ASCII text—use the DTMF keypad to enter text that consists
uppercase and l owe rcase l etters, numbe rs, and sp ecial c haracters .
of
T Telephone number—enter o nly DTMF digits for this field. The
cceptable input inc lude s numbe rs, #, a nd *.
a
N Numeric—enter numbers as the only acceptable input.
E Equation—enter numbers and special math symbols.
U Uppercase—enter uppercase letters as the only acceptable input.
L Lowercase—enter lowercase letters as the only acceptable input.
P Password field—enter individual characters using the standard
eypad-repeat entry mode. The system automatically converts
k
accepted characters into an asterisk, keeping the entered value
private.
Note P specifies the only InputFlag that works as a modifier. For
example, specify a value of “AP” in the
use plain ASCII as the input type and to mask the input as a
password by using an asterisk (* ).
InputFlag field t o
During text entry, Cisco Unified IP Phones display softkeys to assist users with text entry. Users can
navigate between fields with the vertical scroll button that is used to navigate men us, and so on.
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory
The phone ori gina lly i ncor por at ed th e CiscoIPPhoneDirectory X ML obj ect to su pport the Dir ectory
operation of Cisco Unified IP Phones, but it is a v ailable for y our development purposes also. Figure 3-2
shows how an XML
Figure 3-2 CiscoIPPhoneDirectory Object Display Sample
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneDirectory>
<Title>Directory title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<DirectoryEntry>
<Name>The name of the directory entry</Name>
<Telephone>The telephone number for the entry</Telephone>
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory object displays on the phone.
3-6
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 25

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
</DirectoryEntry>
</CiscoIPPhoneDirectory>
Note For the directory listing, the Cisco Unified IP Phone displays th e approp riate sof tke ys that ar e needed to
dial the numbers that are listed on the display. The softkeys include the Edit Dial softkey, which allows
users to insert access codes or other nece ssary item s before dial ing.
The Title and Prompt tags in t he XML ob ject have the usu al sem antic s. A sing le
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory object can conta in a m aximu m o f 32 DirectoryEntry ob jects. If mo re than 32
entries must be returned, use multiple
Note The 6900 series IP phones do es not display th e Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time. If both
Title and Prompt fields are defined at th e sam e t ime , t he n the se phon es displ ay onl y t he P rompt fie l d .
Custom Directories
You can use the Cisco Unified Communications Manager enterprise parameter, “URL Directories” a nd
CiscoIPPhone XML objects t o display custom directories. The “URL Directories” poi nts to a URL that
returns a
must return a valid
XML Object Definitions
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory objects in subsequent HTTP requests.
CiscoIPPhoneMenu object that extends the directories menu. The request fo r “URL Directori es”
CiscoIPPhoneMenu object, even if has n o DirectoryEntry objects.
To create a custom directory, use the following optional objects in the order in which they are listed:
1. Use the CiscoIPPhoneInput XML object to collect search criteria.
2. Use the CiscoIPPhoneText XML object to display status messages or errors.
3. Use the CiscoIPPhoneDirectory XML object to return a list of directory entries that can be dialed.
You can omit th e
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory objects by specifying an HTTP r efresh header that points to the URL of the n ext
individual directory object, which t he user accesses by pressing the Next softkey on the pho ne.
CiscoIPPhoneImage
The CiscoIPPhoneImage provides a bitmap display with a 133 x 65 pixel pane that is available to access
services. Each pixel includes four grayscale settings. A value of three (3) displays as black, and a value
of zero (0) displays as white.
Note The phone uses an LC D d ispl ay, which inverts the palette.
The
CiscoIPPhoneImage XML type lets you use the Cisco Unified IP Phone display to pres ent graphics
to the user.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneImage>
<Title>Image title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Position information of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Position information of graphic</LocationY>
<Width>Size information for the graphic</Width>
<Height>Size information for the graphic</Height>
CiscoIPPhoneInput or CiscoIPPhoneText objects. You can display multiple
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-7
Page 26
XML Object Definitions
Pixel values original sequence 1320
Pixel values converted to 2-bit
binary pairs
01 001011
Re-ordered binary pairs
2D
1-byte packed hexadecimal value
00 0110 11
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
<Depth>Number of bits per pixel</Depth>
<Data>Packed Pixel Data</Data>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Name of the softkey</Name>
<URL>URL of softkey</URL>
<Position>Numerical position of the softkey</Position>
</SoftKeyItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneImage>
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then t hes e phon es d isp lay only the
Prompt field.
The CiscoIPPhoneImage object definition includes two familiar elements: Title and Prompt. These
elements serve the same purp ose as the y do in the other CiscoI PPhone XML objects. Th e
at the top of the page, and the
LocationX and LocationY to position the graphic on the phone display. Position the upper, left corner
Use
Prompt displays at the bottom.
of the graphic at the pixel defined by these two parameters. Setting the X and Y location values to (0, 0)
positions the graphic at the upper, left corner of the display. Setting the X and Y location values to (-1,
-1) centers the graphic in the services pane of the phone display.
Title displays
Width and Height to size the graphic. If the values do not match with the pixel stream specified in
Use
Data field, results will be unpredictable incorrect.
the
Depth specifies the number of bits per pixel. Cisco Unified IP Phones support a maximum value of 2. A
bit depth of 1 is blac k an d wh ite .
Data tag delimits a string of hexadecimal digits that contain the packed value of the pixels in the
The
display. In the Cisco Unified IP Phone, each pixel has only four po ssibl e values, whi ch me ans tha t yo u
n pack four pixels into a single byte. A pa ir of hexadeci mal digi ts represe nts eac h byte.
ca
Figure 3-3 p
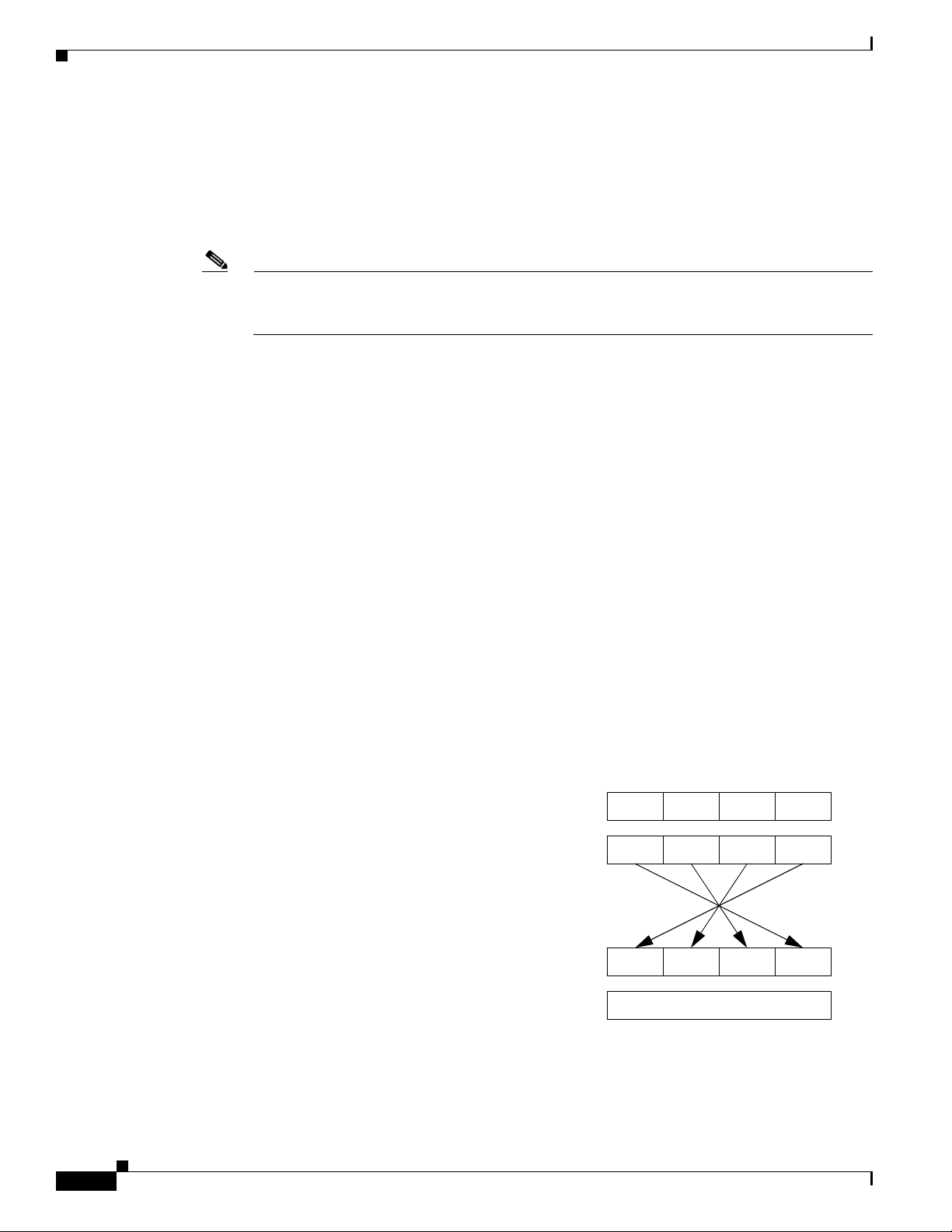
rovides an example o f t h e me ch an ics of pixel pa c king. Sca nning f rom le ft to r ight in the
display, the illustration shows the process for packing consecutive pixel values of 1, 3, 2, and 0. First,
e pixels get converted to 2-bit binary numbers. Then, the binary pairs get re-ordered in sets of four to
th
create a single re-orde red byte, wh ich two hexadecima l digits re presen t.
Figure 3-3 Packed Pixel Translation Example
3-8
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 27
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Example
The following XML code defines a CiscoIPPhoneImage object that displays the sequence of pixels shown
in Figure 3-3 as a graphic positioned at the center of the phone display:
<CiscoIPPhoneImage>
<Title/>
<LocationX>-1</LocationX>
<LocationY>-1</LocationY>
<Width>4</Width>
<Height>1</Height>
<Depth>2</Depth>
<Data>2D</Data>
<Prompt/>
</CiscoIPPhoneImage>
The graphic display com pris es a contiguo us stream of hexadecima l digits, w ith no spac es or other
separators. If the numbe r of pixels to be displaye d does not re present an even multiple of four, pad the
end of the pixel data with blank (zero value) pixels, so the data is packed correctly. The phone ignores
the padded data .
Tip Before displaying a graphic im age on a Cisc o Unified IP Phone, the software clears the pane dedicated
to services. If a service has te xt or other informa tion that must be preser ved (inc luding the title area), the
information must get redra wn as p art of th e grap hic. If th e title is to be hidde n, the gr aphic m ust be la r ge
enough to cover it.
XML Object Definitions
CiscoIPPhoneImageFile
The latest generation of Cisco Unified IP Phones have higher-resolution displays with more color depth.
The Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G, for example, has a disp lay area of 298 x168 pi xels available to the
vices pane and renders im ages in 12-b it col or.
Ser
To s upport these m ore ad vanced di sp lays, a new XML o bj ect al lows the u se of c olor PNG ima ge s in
ddition to the grayscale
a
CiscoIPPhoneImage object, except for the image data. In stead of using the <Data> tag to embed the
the
image data, the
<URL> tag points to the PNG image file.
The web server must del iver the PNG imag e to the pho ne wi th an ap propria te M IME Con tent- Type
ader, such as image/png, so the phone recognizes the content as a compressed, binary PNG image. The
he
PNG image can be either palettized or RGB, and the maximum image size and color depth are model
dependent (see Table 3-2).
Ta b l e 3-2 Cisco Unified IP Phones Display Image Sizes and Color Depths
Model
Cisco Unified IP Phones 7905G, 7906G,
2
7911G, 7912G
, 7931G
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7920 128 x 59 Grayscale 1
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7921G, 7925G 176 x 140 Color 16
Cisco Unified IP Phones 7940G/60G 133 x 65 Grayscale 2
Cisco Unified IP Phones 7941G, 7941G-GE ,
942G, 7961G, 7961 G-GE, 7 962G
7
CiscoIPPhoneImage objects. The CiscoIPPhoneIm age Fil e object behave s li k e
Resolution
(width x height)
1
Color/Grayscale
/
Monochrome Color Depth (bits)
N/A Grayscale 1
298 x 144 Grayscale 4
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-9
Page 28

XML Object Definitions
Table 3-2 Cisco Unified IP Phones Display Image Sizes and Color Depths (continued)
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
1
Color/Grayscale
/Monochrome Color Depth (bits)
Model
Resolution
(width x height)
Cisco Unified IP Phones 7945G, 7965G 298 x 156 Color 16
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G/797 1G 298 x 168 Color 12
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7975G 298 x 168 Color 16
Cisco IP Communicator 298 x 168 Color 24
Cisco Unified IP Phones 6921, 69 61 396 x 81 Monochrome —
Cisco Unified IP Phone 6941 396 x162 Monochrome —
Cisco Unified IP Phones 9971, 99 51, 8 961 498x289 Color 24
1. Represents the size of the display that is accessible by Services—not the full resolution of the physical display.
2. The C i s c o Unified IP Phones 7905 and 7912 have pixel-based displays, but they do not support XML images.
If the number of colors in the image is not reduced to match the phone capabilities, the image will be
dithered by the phone and yield less than desirable results in most cases. To reduce the number of colors
in a graphics editing program, such as Adobe Photoshop, use the “Posterize” command. The “Posterize”
command takes one value as input for the number of color tones per color channel. For example, using
the value of 16 (4-bits per channel = 16 tones per channel) will correctly dither the color palette of the
image for the best display resu lts on the Cisc o Unified IP Phone 7970 G.
Figure 3-4
shows a CiscoIPPhoneImageFile object on a Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G display.
Figure 3-4 Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G Image File Display
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneImageFile>
<Title>Image Title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Horizontal position of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical position of graphic</LocationY>
<URL>Points to the PNG image</URL>
</CiscoIPPhoneImageFile>
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then t hes e phon es d isp lay only the
Prompt field.
3-10
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 29
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu
Graphic menus serve the sa me purpo se as text menus: they allow a user to select a URL from a list. Use
graphic menus in situations when the items may not be easy to display in a text list.
For example, users might prefer to have their choices presented in a non-ASCII character set such as
nji or Arabic. W hen us ing n on- ASC II character sets, the system presents th e in f orm atio n as a bitmap
Ka
graphic. To select a menu, the user enters a number from 1 to 12 usi ng the numeric keypad (* and # are
not active).
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu>
<Title>Menu title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Position information of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Position information of graphic</LocationY>
<Width>Size information for the graphic</Width>
<Height>Size information for the graphic</Height>
<Depth>Number of bits per pixel</Depth>
<Data>Packed Pixel Data</Data>
<MenuItem>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu>
XML Object Definitions
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then the se p hon es d ispl ay onl y the
Prompt field.
Menu items in the graphic menu have a name, like the text menu counterparts. Although the name does
not display to the user, it still performs a function. The name of the menu item provides the default title
that is used when th e URL for the chosen item is loaded. If the loaded page has a title of its own, the
phone uses that title instead.
The XML tags in
GraphicMenu use the tag definitions for CiscoIPPhoneImage and CiscoIPPhoneMenu.
Although the semantic s of the tags are identic al, you ca n have only 12
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu object. See “CiscoIPPhoneMenu” and “CiscoIPPhoneImage ” for detailed
descriptions.
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu
Some of the Cisco Unified IP Phone models, such as the Cisco Unified IP Phon e 7970G and
Cisco IP Communicato r, have pointer devices. The Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G us es a t ou chs cree n
verlay on the display, and the PC-based Cisco IP Communi cator u ses the st anda rd Windows mouse
o
nter.
poi
Because these devices can receive and process “pointer” events, a
object exposes the capability to application developers. The CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu behaves
similar to the CiscoIPPhoneGra phicM enu, in that a gr oup of opti ons are prese nted by an image. Whe n
one of those objects is selected, a UR L action ini tiates. However, the new FileMenu does not use the
keypad, but uses rectangular touch areas. This rectangular touch area,
coordinates relative to the upper-left corner of the Services display. The (X1,Y1) points specify the
upper-left co rner of the
<TouchArea>, and (X2,Y2) specify the lower-right corner of the <TouchArea>.
MenuItem objects in a
CiscoIPPhoneGraph icFile Menu
<TouchArea>, is defined by
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-11
Page 30

XML Object Definitions
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Figure 3-5 shows the display of the CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu.
Figure 3-5 CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu
If the coordinates that are supplied in <TouchArea> tag exceed the dimensions of the phone display, the
<TouchArea> rectangle will be “cli pped” t o f it. See Table 3-2 , “Cisco Unified IP Phones Display Image
Sizes and Color Depths” for a listing of u sab le displa y r esolut ions for ea ch ph one mod el.
<TouchArea> rectangles are allowed to overlap, and the first match is always taken. This allows a
The
sense of Z-order for images w here smal ler touc hable obj ects c an be overlaid on top of larger ones. In
this case, the smaller object
<CiscoIPPhoneGraphi cFileM enu > object.
The requiremen ts f or th e P NG ima ge r e fere nc ed by the
<MenuItem> must appear before the larger one in the
<URL> tag match t hose t h at the
CiscoIPPhoneImageFile ob ject uses.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu>
<Title>Image Title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Horizontal position of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical position of graphic</LocationY>
<URL>Points to the PNG background image</URL>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Same as CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu</Name>
<URL>Invoked when the TouchArea is touched</URL>
<TouchArea X1="left edge" Y1="top edge" X2="right edge" Y2="bottom edge"/>
</MenuItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu>
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then t hes e phon es d isp lay only the
Prompt field.
CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu
Icon menus serve the same p urpose as tex t menus: the y allo w a user to selec t a URL from a list. Use icon
menus in situations when you want to provide additional visual information to the user to show the state
or category of an item. For example, y ou inclu de a read an d unread icon in a mail viewer. You can use
the icons can to convey the message sta te.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-12
OL-20949-01
Page 31

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Icons in the CiscoIPPhoneMenu object have a maximum width of 16 pixels and a maximum height of 10
pixels.
XML Object Definitions
Figure 3-6
shows an IconMenu on a Cisco Unified IP Ph one.
Figure 3-6 IconMenu on a Cisco Unified IP Phone Sample
The system presents the information as a bitmap graphic to the left of the menu item text. The user
selects menu items in the same way as a
CiscoIPPhoneMenu object.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<IconIndex>Indicates what IconItem to display</IconIndex>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Name of softkey</Name>
<URL>URL or URI of softkey</URL>
<Position>Position information of the softkey</Position>
</SoftKeyItem>
<IconItem>
<Index>A unique index from 0 to 9</Index>
<Height>Size information for the icon</Height>
<Width>Size information for the icon</Width>
<Depth>Number of bits per pixel</Depth>
<Data>Packed Pixel Data</Data>
</IconItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu>
OL-20949-01
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then the se p hon es d ispl ay onl y the
Prompt field.
The XML tags in IconMenu use t he tag definitions fo r CiscoIPPho neImage and CiscoI PPhoneMe nu.
Although the semantic s of the tags are identic al, you ca n have only 32 MenuIte m objects in a
CiscoIPPhoneIconMen u obje ct. See “C isco IP Pho n eMe nu” an d “CiscoIPPhoneImage” for detailed
descriptions.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-13
Page 32

XML Object Definitions
CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu
This icon menu is similar to CiscoIPPhoneMenu, but it uses color PNG icons rather than grayscale CIP
icons. Use icon menus i n situa tio ns wh en you want t o provide addi tion al visu al info rm ati on to th e use r
to show the state or c ategory of an it em. For exam ple , y ou c an use icon s to indi cat e p rior ity (see
Figure 3-7).
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Icons in the
height of 18 pixels. Instead of using the
this object uses a
Figure 3-7 CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu Object Display Sample
CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu object have a maximum width of 18 pixels and a ma ximum
<Data> tag to embed the image data into the <IconItem> tag,
<URL> tag to point to the PNG image file to be used for that icon.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<IconIndex>Indicates what IconItem to display</IconIndex>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
<IconItem>
<Index>A unique index from 0 to 9</Index>
<URL>location of the PNG icon image</URL>
</IconItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu>
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then t hes e phon es d isp lay only the
Prompt field.
CiscoIPPhoneStatus
The CiscoIPPhoneStatus object is also a displayable object, but differs from the preceding objects in that
it displays on the Call plane of the phone rather than the Services plane. The CiscoIPPhoneStatus object
“hovers” above the Call plane and is typically used in conjunction with CTI applications to present
application status to th e user.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-14
OL-20949-01
Page 33

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
The Status object cannot be closed or cleared by the user (for example, by pressing Services) because
the Status object is only prese nt on the Ca ll plane. In or der to clea r the obje ct, the pho ne must execute
the Init:AppStatus URI. This would typically occur as the result of an application server pushing an
Execute object to the phone that contains the Init:AppStatus URI.
Note The CiscoIPPhoneStat us ob jec t c an on ly b e push ed (HT TP PO ST) to the phone ; i t ca nno t be pul led
(HTTP GET).
The CiscoIPPhoneStat us object ca n be refresh ed or replac ed at any time. It is not nec essary to clear an
existing Status object before sending a new Status object. The new object simply replaces the old object.
Figure 3-8 sh
• 106 x 21 gr ap hic s are a fo r displa ying CIP ima ges ( sam e image f orma t a s Cisc oI PPhoneI ma ge)
• Seedable, fr ee-runn ing tim er (optiona l)
• Single-line text area (optional)
Figure 3-8 IconMenu on a CiscoIPPhoneStatus Sample
XML Object Definitions
ows the CiscoIPPhoneStatus object that contains the following visual elements:
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneStatus>
<Text>This is the text area</Text>
<Timer>Timer seed value in seconds</Timer>
<LocationX>Horizontal alignment</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical alignment</LocationY>
<Width>Pixel width of graphic</Width>
<Height>Pixel height of graphic</Height>
<Depth>Color depth in bits</Depth>
<Data>Hex binary image data</Data>
</CiscoIPPhoneStatus>
Note The 6900 series IP phones does not displa y the Title and Prompt menu fields at the same time.
If both Title and Prompt fields are defined at the same time, then the se p hon es d ispl ay onl y the
Prompt field.
Dynamic Sizing of the Application Status Window
You can enab le appl icatio ns to dynamic ally ad just their w indow sizes based on t he displaye d conte nt.
The minimum size requirements limit the windows size so that it is a large enough size to stand out from
the Overvie w co ntent. For ex ample, u sing a s maller windo w f or an a pplicati on allo ws more c ontent from
the Overview to be displayed. Sizing the window occurs upon the reception of a CiscoIPPhoneStatus or
CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile object with its associated PNG file.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-15
Page 34

XML Object Definitions
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
The Application Status window conta ins three ma in area s: (see Figure 3-9):
• Te xt A rea
• Ti me r A re a
• Image Are a
Figure 3-9 Elements of Application Status Window
Note Self-terminatin g XML elemen ts, non-dec lared or missing e lements, an d element s with the default v alue s
are all considered non-configured elements.
T o al low dynam ic sizing , do not conf igur e the Text and Tim er areas with an y v alue othe r than the d efau lt
used by the XML parser. If both elements ar e not configur ed, you can procee d, but must follow these
rules:
• Do not display the Text Area and Timer Area sections of the Application Status window.
• If the LocationX element is not configured or is set to cent ered , a nd th e imag e provided is less than
the maximum width allowed, the Image Area can be resized.
• If the im ag e provi ded i s smal ler tha n the min im um w idt h, t he m i nimu m all owed wind ow width
should be used.
• If the width of t he image provided is between the minimum and maximum sizes of the window, the
window should be sized to display the image as w ell as the stan dard sur rounding border s.
• The image height should never change.
ble 3-3 for an overview of the maxi mum and m ini mum i m age ar e a si zes by p hone model . M ost
See Ta
phone models support all siz es between th e minimu m and maximu m. An excepti on is allowed for the
sco Unified IP Phones 7 940G/79 60G due to re sourc e c onstr aints. For t hese phone s, you sh oul d
Ci
implement both the maximum size and minimum size windows ignoring all of the intermediate sizes.
Ta b l e 3-3 Application Status Window Allowable Image Sizes
Phone Models
Maximum Image
A
rea Width
Minimum Image
Area Width
7940G, 7960G 106 21 21
7941G/7941G-GE, 7942G, 7945G, 7961G/7961G-GE,
, 7965G
7962G
252 50 50
7970G/7971G-GE, 7975G, IP Communicator 262 50 50
Maximum Image
Area Height
3-16
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 35

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Note The Cisco IP Phone mode ls 9951 , 997 1, and 896 1 d oes no t suppor t Ci scoI PPhoneSt atu s o bject . See
Table 3-1 on page 3-2 for information on X ML objects supporte d on various phone models .
See Ta
ble 3-4 for an overview of the text and ti mer ar ea size s by p hone mod el .
Ta b l e 3-4 Application Status Window Allowable Text and Timer Sizes
XML Object Definitions
Phone Models
7940G, 7960G 76x11 30x11 106x11
7941G/7941G-GE, 7942G, 7945G, 7961G/7961G-GE,
, 7965G,
7962G
7970G / 7971G-GE, 7975G, IP Communicator 202x20 60x20 262x20
CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile
The behavior of this objec t is iden tical to the CiscoI PPh oneS tatus object, except it uses a color PNG
image instead of a grayscale CIP image for the graphics area.
The maximum image size is 262 x 50 pixels for the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G, but differs for other
ne models. See “Dynamic Sizing of the Application Status Window” section on page 3-15 for details.
pho
Note The Cisco IP Phone models 9951, 9971, and 8961 does not support CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile object. See
Table 3-1 on page 3-2 for information on X ML objects supporte d on various phone models .
Figure 3-10 sho
Figure 3-10 CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile Object Display Sample
Text Area Size
(WxH)
Timer Area Size
(WxH)
192x20 60x20 252x20
ws how an XML CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile object displays on a pho ne.
Text Area Size
No Timer (WxH)
OL-20949-01
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile>
<Text>This is the text area</Text>
<Timer>Timer seed value in seconds</Timer>
<LocationX>Horizontal alignment</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical alignment</LocationY>
<URL>location of the PNG image</URL>
</CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile>
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-17
Page 36

XML Object Definitions
Note that instead of using t he <Data> tag to embed the image data, this object uses a <URL> tag to point
to the PNG image file to be used for the graphics area.
CiscoIPPhoneExecute
The CiscoIPPhone Exec ute object differs from the other CiscoIPPhone objects. It is not a displayable
object for prov iding user interaction. The purpose of this object is to deliver (potentially multiple)
execution requests to the p hon e.
Like the other XML objects, the CiscoIPPho neExecu te can be eith er pushed (H TTP POST) or pu lled
TTP GET). Upon receiving a Cisco IPPhoneExecu te object, the phone w ill begin executing the
(H
specified Exec uteItems. Order of exec ution is not guarantee d, so Execute Items will likely not e xecu te in
the order in whic h th ey are l isted in the Cisc oIPPh oneE xecute ob jec t.
Note Limit the requests to three ExecuteItems: only one can be a URL and two URIs per
CiscoIPPhoneExecute objec t, or you ca n send three UR Is with no U RL.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneExecute>
<ExecuteItem URL=”the URL or URI to be executed”/>
</CiscoIPPhoneExecute>
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
The <ExecuteItem > tag of t he CiscoIPP hon eExecut e object includes an optional attribute called
Priority. The Priority attribute is used to inform the phone of the urgency of the execute request and to
indicate whether the ph one shoul d be in terr upte d to p erfor m the requ est. T he Pr iorit y levels determine
whether the phone must be idle to perform the requested action. The Idle Timer (along with an optional
Idle URL) is defined global ly in the Cisco Unified Commu nication s Mana ger Admi nistra tion E nterpr ise
arameters and can be overridden o n a p er phon e basi s in th e Ci sco Unified Communications Mana ger
P
evice configuration.
D
The following table lists the Priority levels and their behavior.
Behavior Description
0 = Execute Immediately The URL executes regardless of the state of the phone. If the Priority
ttribute does not get specified in the
a
<ExecuteItem>, the default
priority gets set to zero for backward compatibility.
1 = Execute When Idle The URL gets delayed until the phone goes idle, then it executes.
2 = Execute If Id le The URL executes on an idle phone; otherwise, it does not get
xecuted (it does not get delayed).
e
Note The Priority attr ibute is only used for HTTP URLs. Internal URIs always execute immediately.
Example
The following CiscoIPPhoneExecute object results in the phone playing an aler t “c hime,” regard les s o f
the state of the phone, but waits until the phone goes idle before displaying the specified XML page:
<CiscoIPPhoneExecute>
<ExecuteItem Priority=”0” URL=”Play:chime.raw”/>
3-18
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 37

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
<ExecuteItem Priority=”1” URL=”http://server/textmessage.xml”/>
</CiscoIPPhoneExecute>
CiscoIPPhoneResponse
The CiscoIPPhone Resp onse obj ect items pr ovide messages and in formatio n resulting fro m
CiscoIPPhoneExecute . As a result, a ResponseIt em exists for each ExecuteItems that you send. The
order differs based o n com pl etio n t ime , a nd the execution or der i s not gua rant ee d.
The URL attribute specifies the URL or URI that was sent with the request. The Data attribute contains
ny special data for the item. The Status attribute specifies a status code. Zero indicates that no error
a
occurred during proc essing o f the ExecuteI tem. If an error occurre d, the phone returns a
CiscoIPPhoneError obje ct.
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneResponse>
<ResponseItem Status=”the success or failure of the action”
Data=”the information returned with the response”
URL=”the URL or URI specified in the Execute object”/>
</CiscoIPPhoneResponse>
Custom Softkeys
CiscoIPPhoneError
The following list gives possible C iscoI PPhoneE rr or c odes:
• Error 1 = Err or parsi ng C iscoIPP hon eExecu te obj ect
• Error 2 = E rro r fr am ing Cis coI PPhoneR esp ons e object
• Error 3 = Internal file error
• Error 4 = Authentication error
Definition
<CiscoIPPhoneError Number=”x”/> optional error message <CiscoIPPhoneError>
The text value of the CiscoIPP hon eError ob jec t m ay cont ai n an opt ion al er ror m essag e to fu rth er
describe the nat ure of the er ror c ondi tio n.
Custom Softkeys
Cisco Unified IP Phones can use custom softkeys with any of the displayable CiscoIPPhone XML
objects, excluding the
CiscoIPPhoneExecute o bject w hic h is no t di splaya ble .
Softkeys can have either URL or URI “actions” associated with them. The
separate actions to b e taken whe n the sof tkey is pre ssed a nd rele ased. T he st and ard U I behavior is t o
execute an acti on whe n a key is released, and this action is defined by the
be taken when the softkey is initially pressed by including the optional
might use
and releasing the button stops it.
CiscoIPPhoneStatu s object whic h cannot con trol softkeys and the
SoftkeyItem can define
<URL> tag. An action can also
<URLDown> tag. For example, you
<URLDown> for a press-to-talk application in which pressing the button starts audio streaming
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-19
Page 38

XML Considerations
Note The <URLDown> tag can only contain Internal URIs—it cannot contain an HTTP URL. The “URL” in
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
the name “URLD own” does no t si gnif y th at an H TTP URL c an b e used.
Definition
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Displayed sofkey label</Name>
<URL>URL or URI action for softkey RELEASE event</URL>
<URLDown>URL or URI action for softkey PRESS event</URLDown>
<Position>position of softkey</Position>
</SoftKeyItem>
Example
In this example, a CiscoIPPhoneText object has a single custom softkey defined:
<CiscoIPPhoneText>
<Text>This object has one softkey named "Custom"</Text>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Custom</Name>
<URL>http://someserver/somepage</URL>
<Position>4</Position>
</SoftKeyItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneText>
If any custom softkeys a re d efined in t he X M L ob jec t, t h en al l de fault s oft keys are re moved from t hat
object. To retain default softkey behavior, then you must explicitly define it in the XML object using a
<SoftKeyItem>
tag. The internal Softk ey URIs can be us ed in the <URL> tag of <SoftKeyItem> to invoke
default softkey actions from custom softkeys. See Chapte r 5, “Internal U RI Fe atu re s” for mor e
information on invoking internal so ftkey feat ur es .
Note If there are no custom softkeys and there is no de fault softkey placed in position 1 , either a Next or
Update softkey is assigned automati cally. If the URL is a Refresh URL, the softkey will be “Next.” If
not, the Update softkey is assigned.
Example
The following softke y def initions w ould pro vide the custom softk ey, without losing the default “Select”
behavior:
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Select</Name>
<URL>SoftKey:Select</URL>
<Position>1</Position>
</SoftKeyItem>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Custom</Name>
<URL>http://someserver/somepage</URL>
<Position>4</Position>
</SoftKeyItem>
XML Considerations
The XML p ars er in C is co Unified IP Phones does not function as a fully capable XML parser. Do not
include any tags other tha n those defined in yo ur XML di splay definiti ons.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-20
OL-20949-01
Page 39

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Note All CiscoIPPho ne elem ent name s and at tribute name s are ca se sens itive.
Mandatory Escape Sequences
By XML convention, the XML parser also requires that you provide escape values for a few special
characters . Table 3-5 lists characters and their escape values.
.
Ta b l e 3-5 Escape Sequences for Special Characters
Character Name Escape Sequence
&
“
'
<
>
Ampersand &
Quote "
Apostrophe '
Left angle bracket <
Right angle bracket >
XML Considerations
XML Encoding
Note This behavior is NOT compliant with XML standards, which specify UTF-8 as the default encoding, so
Escaping text can be tedious, but some authorin g tools or script ing langua ges can automate this task.
Because the phone firmware can support multiple encodings, the XML encoding should always be set in
the XML head er.
If the XML encoding header is not specified, the phone will default to the encoding specified by the
rrent user loc ale.
cu
any UTF-8 encoded XML object must have the encoding explicitly set for the phone to parse it correctly.
The encoding value specified in the XML header must match one of the encodings provid ed by the IP
Phone in its Accept-Char set HTTP re quest he ader, as shown in the example below.
Example
The following examples illustrate UTF-8 and ISO-8859-1 encoding, respectively:
<?xml version="1.0" encod ing ="ut f-8" ? >
<?xml version="1.0" encod ing ="is o-8859 -1" ?>
For details on setting HTT P header en coding sett ings, see the “HTT P Enco ding Heade r Setting ” sect ion
on page 6-6.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-21
Page 40

Application Event Handlers
Application Event Handlers
The Application Manager API (see “Application” sect ion on page 5-18) includes an Ap pl ica t io n
Management Event Handler which is suppor ted by any displayable object , which are not ed in the
ollowing table. The unsupported objects are not contained in a standard application context and are
f
handled differently by the Applicat ion Mana ger API :
Supported Unsupported
CiscoIPPhoneMenu CiscoIPPhoneStatus
CiscoIPPhoneText CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile
CiscoIPPhoneInput
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory
CiscoIPPhoneImage
CiscoIPPhoneImageFile
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu
CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu
CiscoIPPhoneIconFil eMenu
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Note Support for the Applic ation Ev ent Handle rs requires an upda ted XML P arser ( see “U pdat ed XML P ars er
and Schema Enforcement ” sectio n on page B-1 for details).
Attributes
The Application Event Handlers can be attached to a supported object by specifying the attributes:
Note An Application URI with Priority=0 is not allowed in the Application Ev ent Handlers (see “Application”
section on page 5-18).
3-22
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 41

Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
Attribute Description
appID Identifies the application to which this displayable XSI
onAppFocusLost Invoked when the application loses focus, if:
onAppFocusGained Invoked when the application gains focus, if:
bject belongs. The format of the appID attribute should
o
be in the format
but this syntax is not enforced, and the application can
assign any unique identifier.
• The application’s context has lost focus, or
• The applicat ion was navigated away from, eit her
directly by the user, or programmatically by a refresh
header or HTTP push.
Note If a Notify URI is used as the event handler, a
notification is sent with this default data:
<notifyApplicationEv ent ap pId ="ap pId"
type="focusLost"/>
• The application is Active and the application’s
context has gained f ocus, or
vendor/product, suc h as Cisco/ Uni ty,
Application Event Handlers
• The applicat ion was navigated to, eith er direc tly by
the user, or by a refresh header or HTTP push.
Note If a Notify URI is used as the event handler, a
notification is sent with this default data:
<notifyApplicationEv ent ap pId ="ap pId"
type="focusGained"/>
onAppMinimized Invoked when the applica tion is min imize d.
An application can only be minimized programmatically
y a call to App:Minimize, but this in v ocation cou ld occur
b
by direct action of the user (from a softkey invocation, for
example) or from the application via a push request.
<notifyApplicatio nEvent ap pId ="appId "
type="minimized"/ >
onAppClosed Invoked whenever the application closes, if:
• The application's context is closed which will, in turn,
close all applications in its stack, or
• The application no longer exists on the conte xt’ s URL
stack because it was navigated out of, o r be cause it
was pruned fr om the URL st ack (stack siz e exceed ed).
Note This event handler cannot contain HTTP or
HTTPS URLs.
OL-20949-01
Note If a Notify URI is used as the event handler, a
notification is sent with this default data:
<notifyApplicationEv ent ap pId ="ap pId"
type="closed"/>
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
3-23
Page 42

Application Event Handlers
Event Handler Schema
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDe
<xs:element name="notifyApplicationEvent">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="appId" use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:minLength value="1"/>
<xs:maxLength value="64"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="closed"/>
<xs:enumeration value="minimized"/>
<xs:enumeration value="focusLost"/>
<xs:enumeration value="focusGained"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
Chapter 3 CiscoIPPhone XML Objects
fault="unqualified">
Example
<CiscoIPPhoneImage appId="Cisco/Unity"
onAppFocusLost="RTPRx:Stop; RTPTx:Stop; Notify:http:server:80:path"
onAppFocusGained="http://server/mainpage/updateUI"
onAppClosed="Notify:http:server:80:eventlistener/appClosed">
...
</CiscoIPPhoneImage>
3-24
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 43

Component APIs
In addition to the prim ary phone XSI API, two additional component APIs are available:
• Application M anagem ent API, page 4-1
• RTP Streaming API, page 4-1
Application Management API
To address the limited application management, the Applicatio n Management API provides a smoother
hand-off be twee n the call mode and the a ppli cation mode. Th e Appli cati on API co nsist s of two primary
components:
• Application URI—see the “Application” section on page 5-18
• Application Event Handlers—see the “Application Event Handlers” section on page 3-22
CHA PTER
4
Note Support for the Application Ma nagement API require s an updated X ML Parser (see “Updated XML
Parser and Schema Enforcem ent” sect ion on page B-1 for details).
RTP Streaming API
This XML-based RTP Streaming API allows app lica tions t o in itiat e an d ob ser ve RTP audio streams. It
extends capabilities beyond the legacy RTP streaming URIs by providing support for stream start/stop
event listeners and the ability to specify other exten ded stream attributes, such as codec type.
Note Support for the RTP Streaming API requires an updated XML Parser (see “Updated XML Parser and
Schema Enforcemen t” sect ion on page B- 1 for details).
The event handlers typically use the stand ard No tification fr amework (see “
page 5-16), but they can also invoke most other URIs, with the exception of HTTP URLs.
Notify” section on
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
4-1
Page 44

RTP Streaming API
Interaction Rules with Legacy RTP URI Streams
The RTP Streaming API allows a full-duplex stream (mode=sendReceive) to be setup as a single stream
request which simplifies the usage of the API. Ho wev er, in some cases, th is creates some inter operability
issues with the le g ac y RTP URIs because the legac y RTP URIs send and recei v e stream s sep arate ly. The
interaction rules between legacy RTP URI streams and the new RTP Streaming API are as follows:
• If an RTP Stop URI is invoked, and an RTP Streaming API stream is currently streaming in that same
direction, then the entir e RTP Streaming API stream is stopped.
For example, if a full-dupl ex stream is setup through the RTP Streaming API (mode=sendRec eive)
d then an RTPTx:Stop URI is invoked, the stream will be stopped in both the send and rec eive
an
directions (and the onStopped event handler will be called, if present).
• If the stopMedia request (from the RTP Streaming API) does not specify a stream ID, then the
request will stop all services RTP streams, in any direction (send or receive) and of any type
(multicast and un icast). This all ows ap plications usin g the R TP Stream ing API to stop media streams
which may have been started by the legacy RTP URIs or by other applications for which a stream
ID is not known.
Chapter 4 Component APIs
RTP Streaming Schema
Note The port number parameter of the startMe dia requ es t is op t iona l a nd i f it is no t spe cified, th e ph one
selects an available port and returns it in the
specified, must be an even number in the range of 20480-32768.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- edited with XML Spy v4.4 U (http://www.xmlspy.com) by Cisco Systems, Inc. (Cisco
Systems, Inc.)
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDe
<xs:element name="startMedia">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="mediaStream" type="mediaStream"/>
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="stopMedia">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="mediaStream">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:string" use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="startMediaResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="mediaStream" type="mediaStream"/>
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="notifyMediaEvent">
startMediaRespons e object. The port parameter, if
-->
fault="unqualified">
4-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 45

Chapter 4 Component APIs
<xs:complexType>
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="mediaStream">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:all>
<xs:attribute name="origin" use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="user"/>
<xs:enumeration value="application"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="stopped"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="mediaStream">
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="type">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="audio"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="codec">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="G.711"/>
<xs:enumeration value="G.722"/>
<xs:enumeration value="G.723"/>
<xs:enumeration value="G.728"/>
<xs:enumeration value="G.729"/>
<xs:enumeration value="GSM"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Wideband"/>
<xs:enumeration value="iLBC"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="mode">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="send"/>
<xs:enumeration value="receive"/>
<xs:enumeration value="sendReceive"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="address">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:minLength value="7"/>
<xs:maxLength value="15"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
RTP Streaming API
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
4-3
Page 46

RTP Streaming API
Chapter 4 Component APIs
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="port" minOccurs="0">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:unsignedShort">
<xs:minInclusive value="20480"/>
<xs:maxInclusive value="32768"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
</xs:all>
<xs:attribute name="onStopped" use="optional">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:minLength value="1"/>
<xs:maxLength value="256"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="receiveVolume" use="optional">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:integer">
<xs:minInclusive value="0"/>
<xs:maxInclusive value="100"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
Error Schema
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDe
<xs:element name="errorResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="type">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="InvalidURL"/>
<xs:enumeration value="InvalidResource"/>
<xs:enumeration value="InvalidResourceID"/>
<xs:enumeration value="UnavailableResource"/>
<xs:enumeration value="InvalidXML"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="data" nillable="true">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
fault="unqualified">
4-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 47

Chapter 4 Component APIs
Examples
RTP Streaming API
Start Media
• Request
HTTP POST /CGI/Exec ute
<startMedia>
<mediaStream
onStopped=”No tify:h ttp :ser ver:80 :pa th/page ”
receiveVolume =”50”>
<type>audio </type >
<codec>G.72 9</cod ec>
<mode>sendR eceive </m ode>
<address>23 9.1.2. 3</ addr ess>
<port>20480 </port >
</mediaStream>
</startMedia>
• Response
HTTP200 OK
<mediaStream id=”ab c123”/ >
Stop Media
• Request
HTTP POST CGI/Execu te
<stopMedia>
<mediaStream id=” abc123 ”/>
</stopMedia>
• Response
HTTP 200 OK
If the user te rm inate s t h e me dia stre a m by p lac ing the act ive audio pa th on- hoo k, t he fol lowing
notification is sent:
HTTP POST /server/p ath/pa ge
DATA=<notifyMediaEv ent ty pe= ”sto pped” ori gin=”us er” >
<mediaStream id =”abc1 23” />
</notifyMediaEvent>
Errors and Responses
Error conditions and response s for the RTP Streaming API include:
Applicable
Condition
Authorization failed all 401 (Authorizati on Failed) N/A N/A
Me
thods HTTP Result Code Ty pe Data
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
4-5
Page 48

RTP Streaming API
Condition
Request object does
not comply with the
API’s XML schema
Media cannot be
st
arted because no
DSP resources is
available to handle
the media
Media cannot be
opped because the
st
specified stream ID
does not exist
plicable
Ap
Methods HTTP Result Code Type Data
all 400 (BadRequest) InfalidXML <parser error
description>
startMedia 4 00 (BadR eque st) Unavailable
source
Re
stopMedia 400 (B adReq uest) InvalidResourceID Unknown Media
No Media
Resource
Available
eam ID:
Str
<streamID>
Chapter 4 Component APIs
4-6
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 49

Internal URI Features
Internal uniform resource identifiers (URIs) provide access to embedded phone features such as placing
calls, playing audio files, and invoking built-in object features.
These sections prov ide details about the available internal URIs:
• Supported URIs by Phone Mo del
• Device Control UR Is
• XML Displayable Object URIs
• Multimedia URIs
• Telephony URIs
• Application Management URIs
Supported URIs by Phone Model
CHA PTER
5
Table 5-1 lists the URIs that are supported for Release 7.1(3).
Ta b l e 5-1 URIs Supported for Release Cisco Unified IP Phone Services SDK
7941G/7941G-GE,
61G/7961G-GE,
79
7942G, 7962G,
7906G
7905G
URI
Key X X X X X X X X X
Softkey X X X X X X X X X
Init X X X X X X X X X
Dial, EditDial X X X X X X X X X
Play X X X X X X X X X
QueryStringParam X X X X X X X X X
Unicast RTP X X X
Multicast RTP X
Display — — — — — — X — X
7912G
7911G
7931G 7920G
2
X X X X X X X X
7921G
7925G
X X X X X X
7940G
796
7945G, 7965G,
IP
0G
Co
mmunicator
7970G
797
1G-GE
7975G
6921,
6941,
6961
9971,
9951,
8961
1
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-1
Page 50

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Device Control URIs
Table 5-1 URIs Supported for Release Cisco Unified IP Phone Services SDK (continued)
7941G/7941G-GE,
7961G/7961G-GE,
7942G, 7962G,
7906G
URI
7905G
7912G
7911G
7931G 7920G
7921G
7925G
7940G
7960G
Vibrate — — X X — — — — —
3
Notify
SendDigits
Application
1. Key:Info, Key:Ser vices, Key:Directories, Key:Settings, Key:App Menu, and Key:Hold are not supp orted by 9971, 9951, and 8961 models.
2. Only supports one incoming and one outgoing unicast stream and does not support the Volume parameter for RTP Receive streams.
3. Requires Cisco Unified IP Phone firmware version 8.3(2) or later, which contains an updated XML parser. See the “Updated XML Parser and
Schema Enforcement” section on page B-1.
3
3
— X — X — X X — X
— X — X — X X — X
— X — X — X X — X
7945G, 7965G,
IP
Communicator
7970G
7971G-GE
7975G
6921,
6941,
6961
9971,
9951,
8961
Device Control URIs
These sections de scr ibe t he d evice cont rol URI s:
• Key
• Display
Key
The Key URI allows a programmer to send an ev ent that a ke y has been p ressed. The syste m initiat es the
event as if the button was physically pressed.
Note that when buttons are pressed with this method, if the button is not present on the phone (hard
utton) or not available (softkey) when the URI is processed, the event is discarded.
b
If the softkey set is c hangi ng a nd disa bled w hil e the event is being pro cessed, the r eque st i s d iscard ed .
URI Format
Key:n
Where
a Key name.
n =
5-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 51

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Device Control URIs
Table 5-2 lists the Key URIs and the phone models in which these are supported.
Ta b l e 5-2 Key URIs With Supported Phone Models
7941G/7941G-GE,
61G/7961G-GE,
79
7942G, 7962G,
Key URIs
Key:Line1 to
ey:Line120
K
Key:KeyPad0 to
K
ey:KeyPad9
Key:S o f t 1 to
Ke
y:Soft5
7906G
7905G
7912G
7911G
7931G 7920G
7921G
7925G
7940G
796
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
7945G, 7965G,
IP
0G
Co
mmunicator
Key:KeyPadStar Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:KeyPadPoundYes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
7970G
797
1G-GE
7975G
6921,
6941,
6961
9971,
9951,
8961
Key:VolDwn Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:VolUp Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:Headset Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:Speaker Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:Mute Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:NavLeft Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:NavRight Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:NavSelect Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:I nfo Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Key:Messages Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:Services Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Key:Directories
Key:Settings
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Key:NavUp Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:NavDwn Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:AppMenu Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Key:Hold Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Key:Feature1 to
ey:Feature120
K
Key:Session1 to
K
ey:Session6
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:Applications Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:Contacts Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-3
Page 52

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Device Control URIs
Table 5-2 Key URIs With Supported Phone Models
7941G/7941G-GE,
7961G/7961G-GE,
7942G, 7962G,
7906G
Key URIs
7905G
7912G
7911G
7931G 7920G
7921G
7925G
7940G
7960G
Key:FixedFeature1Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:FixedFeature2Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:FixedFeature3Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:NavBack Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Key:Release Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
7945G, 7965G,
IP
Communicator
7970G
7971G-GE
7975G
6921,
6941,
6961
9971,
9951,
8961
Unsupported Key URIs and Alternate Options
This section describes the unsupported Key URIs in the phone models and provides alternative options,
if any, for the unsupported UR Is.
Ta b l e 5-3 Unsupported Key URIs and Alternative Options
Phone
Models
9971, 9951,
961
8
9971, 9951,
961
8
9971, 9951,
961
8
9971, 9951,
961
8
Unsupported
URI Description and Alternatives
Key:Services The 8900 and 9900 series IP phones does not have a services button.
Key:Info The 8900 and 9900 series IP phones does not have a standalone help
Key:Directories In the 8900 and 9900 series IP phones the Key:Contacts URI replaces
Key:Settings The 8900 and 9900 se ries IP phone s d oes no t have a si ngle
As such, the “Key:Services” URI is not supported in these phones.
The application has to use the “Init:Services” URI and the
“ App :Close” URI to cl ose th e last X SI appl icatio n launch ed from the
application. If t here is no a ppli cat ion op en , then the r eque st ha s no
effect.
Additionally, the Exit softkey takes the application to the previous
reen, and if the application is at the top level, it closes the
sc
application.
application. Help is provided within the context of each application.
the Key:Directories URI. You can use Key:Contacts to invoke the
new contacts applica tio n in the se ph ones.
monolithic settings application . As suc h th e Key:Settings URI is not
supported in these ph one s.
5-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 53

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Table 5-3 Unsupported Key URIs and Alternative Options
Device Control URIs
Display
Phone
Models
9971, 9951,
8
961
Unsupported
URI Description and Alternatives
Key:AppMenu The 8900 and 9900 se ries IP phone s d oes no t sup por t t he
Key:AppMenu URI. All appl ic atio ns are ac cesse d v ia thei r
individual Key URIs like Applications, C ont acts, a nd M essage s.
9971, 9951,
961
8
Key:Hold The 8900 a nd 99 00 se ries IP pho nes d oes not suppor t t he Key:Hold
URI.
The Key URI equivalents for invoking the standard fixed features are
s follows:
a
• To invoke transfer use Key:FixedFeature1
• To invoke conference use Key:FixedFeature2
• To invoke hold use Key:FixedFeature3
The Display URI is available only on those Cisco Unified IP Phones that have a color backlight on the
phone display, including the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7970G and 7971G-GE. Using the Display URI, you
can control how long the backligh t remains on or off.
Note, however, that other administr ator-control led or user-indic ated displa y settings t ake precede nce
ver the Display U RI. A s suc h, variou s phon e st ate s (s uch as pho ne st art up, i n comi ng and ac tive calls,
o
or other user input states) override the Display URI settings.
URI Format
Display:State:Interval
Where
= whether the phone display is turned on or off or set to default to return the display to its specified
State
state.
Interval =
duration (in minutes) in wh ich th e phone state r emains i n the sp ecif ied state ( unless ac ti v at ed
by automated or user input). Value must be an integer ranging from 0-1440 minutes. If the value is set
to 0, the display rema ins in t he indica ted sta te inde f initel y (unless activated by automated or user input).
For example:
• Display:Off: 60 tu rns t he ph one di spla y off for 1 h our (60 mi nutes ).
• Display:On:1 0 tur ns the ph one d isplay on for 10 min utes.
• Display:Off: 0 turns off the display off until activated.
• Display:Defa ult returns the display to its specified state for that time.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-5
Page 54

XML Displayable Object URIs
XML Displayable Object URIs
These sections de scr ibe the XM L di spla yabl e ob jec t U RIs :
• SoftKey
• QueryStringParam
SoftKey
You can execute native softkey functionality when the phone executes a Softkey URI. The SoftKey URI
allows developers to customize softkey names and layout in the Services and Directories windows while
retaining the functionality that the softkeys provide.
Softkey URIs wor k in menu items a nd in softke y item s in the XML ob jects for which they nat iv ely occ ur
he phone.
on t
Note The Softkey URI is not supported in the Execute object.
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
URI Format
SoftKey:n
Where
e of the following softkey names:
n = on
• Back
• Cancel
• Exit
• Next
• Search
• Select
• Submit
• Update
• Dial
• EditDi a l
• <<
Table 5-4
contains valid softkey actions for each XSI object type follow. The URI invo kes the native
functionality that each key possesses in the given object context.
Ta b l e 5-4 Valid Softkey Actions for CiscoIPPhoneObject Types
IPPhoneObject
1
Select Exit Update Submit Search << Cancel Next Dial
CiscoIPPhoneMenu X X
CiscoIPPhoneIco nMen u X X
CiscoIPPhoneText X X
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-6
Edit
Dial
OL-20949-01
Page 55

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Table 5-4 Valid Softkey Actions for CiscoIPPhoneObject Types (continued)
XML Displayable Object URIs
IPPhoneObject
1
Select Exit Update Submit Search << Cancel Next Dial
Dial
CiscoIPPhoneImage X X
CiscoIPPhoneGraphi cMenu X X
Edit
CiscoIPPhoneInput X X
2
CiscoIPPhoneDirect ory X X X
1. The SoftKey URI is not allowed in an Execute object.
2. Only when used under the Directories button.
3. The SoftKey:Dial and SoftKey:Ed itDial URIs ca n be used only for Dir ectory object s, but t he Dial:xxx and EditDial:x xx URIs
can be used as the URL of any SoftKeyItem or MenuItem. For more details, see the
X X
3
3
X
“Telephony URIs” section on page 5-13.
The new generation 8900 / 9900 series IP phon es have the following enhance ments to the ir display :
• The positions of the sofkeys have been changed. Moving from left to right, the Exit is the first
softkey followed by the Submit/Select/Update/Next softkey, and finally the Delete softkey.
• In the submenu screens, the b ack arro w icon ( ) replaces the << or Exit softke ys, and it is place d
in the first (extreme left) position.
• The phone disp lays error me ssages, like X ML Parse error or HT TP failures, i n a new window.
QueryStringParam
The QueryStringParam URI allows an application developer to collect more information from the user
with less interaction. When the user performs an action with a softkey, you can either append a query
string parameter to the URL of the highlighted MenuItem or append the query string parameter from the
MenuItem to the URL of the softkey.
URI Format
QueryStringParam:d
Where
the data to b e appe nde d to a cor res pon ding UR L.
d =
Example 5-1 QueryStringParam URI in a CiscoIPPhoneMenu object
<CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
<Title>Message List</Title>
<Prompt>Two Messages</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Message One</Name>
<URL>QueryStringParam:message=1</URL>
</MenuItem>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Message Two</Name>
<URL>QueryStringParam:message=2</URL>
</MenuItem>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Read</Name>
<URL>http://server/read.asp</URL>
</SoftKeyItem>
<SoftKeyItem>
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-7
Page 56

XML Displayable Object URIs
</CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
Example 5- 1 shows how to use the QueryStringParam URI in a CiscoIPPhoneMenu obj ec t. Th e
CiscoIPPhoneMenu object includes two MenuItems with QueryStringParam URIs. If the user chooses the
MenuItem(s) with the numeric keypad, the cursor moves to that entry, but nothing executes because the
values are QueryStringParam URIs.
If the user presses either custom softkey, the currently highlig hte d Me nuIt em URI value get s ap pe nded
o the softkey URL that was pressed and request ed from t he web server.
t
If you highlight the first MenuItem and press the Read softkey, the phone generates the following URL:
http://server//read.asp?message=1
Example 5-2 Selecting an Item with Numeric Keypad Calls the URL
<CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
</CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
<Name>Delete</Name>
<URL>http://server/delete.asp</URL>
</SoftKeyItem>
<Title>Message List</Title>
<Prompt>Two Messages</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Messae One</Name>
<URL>http://server/messages.asp?message=1</URL>
</MenuItem>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Messae Two</Name>
<URL>http://server/messages.asp?message=2</URL>
</MenuItem>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Read</Name>
<Position>1</Position><URL>QueryStringParam:action=read</URL>
</SoftKeyItem>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Delete</Name>
<Position>2</Position><URL>QueryStringParam:action=delete</URL>
</SoftKeyItem>
5-8
The Cisco Unified IP Phones allow you to implement the QueryStringParam URI in either manner
although Example 5-2 is not as efficient as Example 5- 1. Ch oose th e be st way t o pe rf or m th e act ion
based on your applications needs.
Example 5- 2
does have a slight advantag e in that if the user chooses an item with the numeric keypad,
the URL gets called. This would allow you to invoke some default behavior such as to read the message
the example. By highlighting the first message and pressing the Read softkey, the phone creates the
in
following URL: http://server/messages.asp?message=1&action=read
Using the QueryStrin gPar am UR I re du ces t he si ze of t he X ML ob je cts th at yo u ge nera te by not having
o repeat redund ant po rtions of a URL in every MenuI tem .
t
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 57

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Multimedia URIs
These sections describe the multimedia URIs:
• RTP Streaming
• Play
• Vibrate
RTP Streaming
You can invoke RTP streaming via URIs in services. You can instruct the phone to transmit or receive
an RTP stream with the following specifications:
• RTPRx
• RTPTx
• RTPMRx
• RTPMTx
Multimedia URIs
Note For some Cisco Unified IP Phone models, the RTP Streaming URIs have been deprecated by the RTP
Streaming API. See the “RTP Stream ing API” sect ion on page 4-1.
The supported format of th e RTP stream is as follows:
• The codec i s G.711 mu -Law.
• The packet si ze is 20 ms.
The following list gives these possi ble CiscoI PPhon eE rror co des:
• Error 1 = Err or parsi ng C iscoIPP hon eExecu te obj ect
• Error 2 = E rro r fr am ing Cis coI PPhoneR esp ons e object
• Error 3 = Internal file error
• Error 4 = Authentication error
Interaction with Call Streaming
• Existing Tx URI streams will be terminated if a new call begins or an existing call is resumed
• Tx URI stream requests received when a call is active will be rejected with an errorNo=4
unauthorized
. If a call is in a He ld state ( connected b ut not act i v ely strea ming), th e Tx URI reque st
will be accepted, but will be terminated if the call is resumed.
Note Returning errorNo=4 allows the applicatio n to distinguish this error from the normal errorNo=1
busy response.
OL-20949-01
• Existing Rx URI streams will be terminated if a new call begins or an existing call is resumed.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-9
Page 58

Multimedia URIs
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
The user has no explicit mechanism for terminating the Rx URI stream independent of the call.
Thus, if the Rx stream is not terminat ed automatica lly , it w ould continu e to play . For e xample, a user
is listening to Internet radio feed and gets an incom in g call. T he user an swer s the call, whic h ei ther
closes or minim ize s t he I nt erne t r adio X SI ap plica tio n. Ot herw is e, t he us er ha s n o in tu itive way to
stop the music stream.
• New Rx URI stream requests received during an active call will be accepted (whisper), but the
volume parameter of the URI will be ignored.
If the Rx URI request was done via push, then the associated application is responsible for using
Priority attributes and fo r s toppi ng a nd sta rting the stre am.
push
If the user initiates the Rx URI via an application, then the user likely is not concerned about having
he audio mixed with the current call. However, they should also be presented with an option to stop
t
the application, when needed.
• For the Rx URI, the Mute indicator light is only lit when both these conditions are met:
–
There are no active transmit streams from either a call or an XML services stream, and
–
There is at le as t one ac t ive receive stre am
For example, if an active call is ended or put on hold while a Rx URI stream is active, the Mute
dicator will light.
in
RTPRx
• If a Rx or Tx URI request is received and there is already an active XML services stream in that
direction, then a resp onse wi th
errorNo=1 Tx/Rx is already active will be returned. The prev ious
stream must be terminated (either by the user or by an RTP Stop URI) before a new stream can be
started.
This response provides visibility to the application if the phone is currently busy. It then allows the
pplication to decide whether or not to terminat e the existin g stream and start a ne w one, rather than
a
being controlled by the phone firmware.
The RTPRx URI instructs the phone to receive a Unicast RTP stream or to stop receiving Unicast or
Multicast RTP streams.
URI Formats
RTPRx:i:p:v
RTPRx:Stop
Where
e IP Address from which the stream is coming.
i = th
the UDP port on which to recei v e the RTP stream. Ensure that this is an ev en p ort number within th e
p =
decimal range of 20480 t o 32768. If no p ort is specified, the phone ch ooses a port a nd return s it when
initiated by a push request.
the parameter that will stop any active RTP stream from being received on channel one
Stop =
5-10
he optional volume setting that control s the volume of stream playout . The suppli ed value is a
v = t
percentage of the max imu m volum e level of th e device a nd m ust b e in th e ra nge 0-1 00. The ph one
converts the specified percentage into the closest device-supported volume level setting and uses it. After
the initial volume level gets set and the stream starts, you can manually change the volume level as
needed. If the optional volume parameter does not get included, the current volume setting on the phone
gets used as the default.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 59

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
RTPTx
RTPMRx
Multimedia URIs
Use the RTPTx URI to instruct the phone to transmit a Unicast RTP stream or to stop transmitting
Unicast or Multicast RTP streams.
URI Formats
RTPTx:i:p
RTPTx:Stop
Where
e IP Address to which an RTP stream is transmit ed.
i = th
e UDP port on which to transmit the RTP stream. Ensure that this is an even port number within
p = th
the decimal range of 20480 t o 32768.
the parameter that will stop any active RTP stream from being transmitted on ch anne l one.
Stop =
The RTPMRx URI instructs the phone to receive a Multicast RTP.
RTPMTx
URI Format
RTPMRx:i:p:v
Where
= the Multicast IP Address from which to receive an RTP stream.
i
e Multicast UDP port from which to receive the RTP stream. Ensure that this is an even port
p = th
number within the d ecima l r an ge of 2 0480 to 32 768.
he optional volume setting that control s the volume of stream playout . The suppli ed value is a
v = t
percentage of the max imu m volum e level of th e device a nd m ust b e in th e ra nge 0-1 00. The ph one
converts the specified percentage into the closest device-supported volume level setting and uses it. After
the initial volume level gets set and the stream starts, you can manually change the volume level as
needed. If the optional volume parameter does not get included, the current volume setting on the phone
gets used as the default.
The RTPMTx URI instructs the phone to transmit a Multicast RTP stream.
URI Formats
RTPTx:i:p
Where
= the Multicast IP Address to which an RTP stream is transmitted.
i
e Multicast UDP port on which to transmit the R T P stream. Ensure tha t this is an e ven por t number
p = th
within the decima l r ange of 2048 0 t o 32 768 .
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-11
Page 60

Multimedia URIs
Play
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
The Play URI downloads an au dio file from the TFTP server and play s through the phone speaker. This
same mechanism also plays ring files, an d the format of the f iles is the same. You could use the Play URI
to play files th at are in th e Ringlist .xml or tho se that ar e not. If t he phone is equipped w ith an MWI light,
it will be flashing while the audio file is playing, providing a visual alert as well.
Note The Play URI is a s ynchr onou s r eque st . If the re quest is pu she d to the p hon e via HTT P, the HTTP
response (CiscoIPPhoneResponse object) is not returned until after the playback has completed.
Interaction with Incoming Calls
The Play URI and incoming calls (rin ging) have equal priority ac cess to the D SP ringer res ources
resulting in the following interactions:
• If a Play URI is currently playing, an incoming call (ringing) will not preempt the Play URI; the
Play URI will finish playing first.
• If the phon e is rin ging a nd a Pl ay URI re qu est is se nt t o the p hone, the executi on of t h e Play U RI
defers until the phone stops ringing (the DSP ringer resource becomes available) and then the Play
URI will play.
Vibrate
URI Format
Play:f
Where
he filename of a raw audio file in the TFTP path (such as Play:Classic2.raw).
f = t
The audio files for the rings must meet the following requirements for proper playback on Cisco Unified
IP Phon
• Raw PCM (no header)
• 8000 samples per se cond
• 8 bits per sample
• uLaw compression
• Maximum rin g siz e—1 608 0 sam ples
• Minimum ring size—240 sa mples
• Number of samp les in the ring is evenly divisible by 240.
• Ring starts and ends at the zero cr ossing.
es:
To cr eat e PCM files for c usto m p hon e ring s, you can u se any sta nda rd a ud io e di ting pa ck ages t hat
ort these file format requir ement s.
supp
5-12
The Vibrate URI is available on the Cisco Unified IP Phones 7920G, 7921G, and 7925G wireless phone
models, and it enables third-party applications to invoke the phone’s vibration capabilities for silent
alerts, similar to the way in which the Play URI plays audible alerts. If the Vibrate parameters are not
specified or if the device is unable to support custom Vibrate sequences, the device will execute its
default vibrate se quenc e.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 61

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
URI Format
Vibrate:vibrateDuration:silenceDuration:count
Where
Telephony URIs
vibrateDuration
integer ranging from 0-6553 6 millisec onds.
silenceDuration
integer ranging from 0-65536 mi llisec onds.
count = num
For example:
• Vibrate:1000 :0:1 initiates a single vibrate for 1 second.
• Vibrate:500: 1500 :5i nitiates five vibrations each lasting for 500 ms. followed by 1500 ms of
silence.
Telephony URIs
These sections de scr ibe the tel ephony URIs :
• Dial
• EditDi a l
• SendDigits
Dial
= duration (in milliseconds) in which the vibrate state remains on. Value must be an
= duration (in milliseconds) in which the vibrate state remains off. Va lue must be an
ber of times to repeat the vibrate on an d off sequence.
The Dial URI initiates a new call to a specified number. The Dial URI invokes when it is contained in a
menu item, the menu it em i s high lig ht ed, an d th e device is t aken o ff hook.
Activate the Dial URI by one of the following:
• Line button
• Speaker button
• Headset button
• Handset hook switch
• Normal menu i tem
• Softkey item selection
URI Format
Dial:{dialSequence}[:{useAppUI}:{applicationId}[:audibleFeedback]]
Where
dialSequence = Th
e sequence of DTMF digits to be dialed. Com mas re present 1 second pause s.
Value Type: String
Values: m inLe ng th=0 , no ma xLen gt h, c an o nl y con t ain 012 345 6789#* AB CD,
Default value: N/A
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-13
Page 62

Telephony URIs
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
useAppUI = Specifies whether or not this application will be used as the user interface for this call. A
value of true will cause the application to keep UI focus when the call is made instead of switching to
the Call UI application. The ap pId must be sp ecif ied o r this param will ha v e no effect – it will always be
false.
Value Type: boolean
Values: 0 or 1 (0=fa lse 1=true )
Default value: 0
EditDial
applicationId =
The unique name of the XSI web application requesting this call
Value Type: String
Values: min Length =1, no maxL ength, cannot co ntain semicolons – shou ld be in the for mat
pany/Product.
Com
Default value: Nil which means this dial request will not be associated with any application
audibleFeedback =
Whether or not to pr ovide au di ble fe ed back t o the use r w he n th e DT MF dig its ar e
dialed.
Value Type: Boolean
Values: 0, 1 (0=false 1=true)
Default value: 1
The EditDial URI initiates a new call to a specified number. The EditDial URI invokes when it is
contained in a menu item and the menu item is highlighted.
Activate the EditDial URI by one of the following:
• Line button
• Speaker button
• Headset button
• Handset hook switch
SendDigits
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-14
• Normal menu i tem
• Softkey item selection
URI Format
EditDial:n
Where
= the number dialed (suc h as EditDial: 1000).
n
The SendDigits URI instructs the phone to send a specified sequence of DTMF digits in-band with in the
media stream of the current active (streaming) call.
OL-20949-01
Page 63

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Audible feedback to the user can be enabled or disabled and an optional application ID can be specified
to ensure that the DTMF digits will only be sent to the call which is associated with a specific
application.
URI Format
SendDigits:dtmfSequ ence:a udi bleF eedbac k:: applica tio nId
Where
Telephony URIs
dtmfSequence
audibleFeedback =
= the sequence of DTMF digits to be sent. V alue must contain only 0123456789#*ABCD
indicates whether to provide audible feedback to the user as the DTMF digits are
entered. Values can be 0 (false) or 1 (true).
applicationId =
optional identifier of the application associated with the call which must receive the
DTMF digits. Value must be 0-64 and cannot contain colons. The default value is null indicating that the
active call should receive the DTMF digit s, r egardle ss o f any a pplic ation a ssociat ion.
For example:
• Make a call using a calling card service that implements these steps:
1. Connects to a 8 00 ca lli ng ca rd se rvic e ( using t he D ial U RI)
2. Application waits to give call time to connect
3. Dials the destination number, ensuring that the digits can only be dialed from this application.
4. Pauses 2 seconds
5. Dials the call ing card number
6. Pauses 1 second
7. Dials the pin number
<CiscoIPPhoneExecut e>
<ExecuteItem URL= "Dial: 918 0055 51212: 1:C isco/Di ale r"/ >
</CiscoIPPhoneExecu te>
<CiscoIPPhoneExecut e>
<ExecuteItem URL= "SendD igi ts:6 185551 212 ,,98765 432 1,1 234:1: Cisc o/Dial er" />
</CiscoIPPhoneExecu te>
Error and Response
When the SendDigits URI is in v ok ed via an Ex ecu te objec t, it will u se t he standard URI Status a nd Data
values in Respons eIte m s:
Condition Status Data
Executed successfully 0 (Success) Success
URI syntax is invalid 1 (Parse error) Invalid URI
URI is not supported 6 (Internal er ror) URI not found
Unable to execute URI because there currently is no
ve (streaming) call
acti
Unable to execute URI because the curren t active
(s
treaming) call is not associated with the specified
6 (Internal er ror) No Active Call
6 (Internal er ror) No Active Call for
Application
application
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
5-15
Page 64

Application Management URIs
Condition Status Data
Phone is temporarily unable to execute URI due to
me other transient issue
so
6 (Internal er ror) <Failure>
Application Management URIs
These sections describe the application management URIs:
• Init
• Notify
• Application
Init
The Init URI allows an application to initialize a feature or data with the argument that is passed with
the URI.
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Notify
URI Format
Init:o
Where
the Object name.
o =
Valid object name:
CallHistory—When the phon e encount ers an Init:C allHi story URI, it cle ars the in ternal call history
logs that are stored in the phone. This action initializes Missed Calls, Received Calls, and Placed Calls.
Services—When the phone encounters an Init:SERVICES URI, it closes the Services application. If
Services is not currently open, it has no effect.
Messages—When the phone encounters an Init:Messages URI, it closes the Messages application. If
Messages is not currently open, it has no effect.
Directories—When the phone encounters an Init:Directories URI, it clo ses the Directorie s application.
If Directories is not currently open, it has no effect.
The Notify URI generates network notifications to back-end applications. This feature is most useful for
XSI objects that support act ion handle rs (such as displaya ble XSI obje cts and RTP streams). For
example, use the Notify URI to deliver notifications to back-end applications when an XSI application
is closed or when an RTP stream is terminated.
5-16
You can also specify the N otify UR I in plac e of mo st fi elds th at accep t a gene ric URI, in cludin g softk ey s
d menu items. For example , yo u can ca ll the Not ify UR I f rom a so ft key or me nu it em t o t rigg er a
an
back-end event that does not require an interface change, such as manipulating the state of audio streams
or other non-vis ual re sourc es. T he Not ify URI a lso wo rks in co njunc tion w ith the Que ry Stri ngParam
URI, such that the exact contents of the QueryStringParam data will be used as the Notify URI data.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 65

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
The Notify URI is not made in the context of an XSI application session and does not contain any HTTP
cookie or session informatio n. Thus, the b ack-en d application ca nnot rely on HTT P cookies or se ssion
information to uniqu ely ident ify the cl ient or appl icati on. Instead, the appl icati on must embe d any
necessary information in the Notify path and data fields, or leave the data field empty and rely on any
default information provided by the specific event handler.
Note The Notify URI is not suppor ted in the Exec ute objec t.
URI Format
Notify:protocol:host:port:path:credentials:data
Where
Application Management URIs
protocol =
host =
network protocol to use f or th e N oti fy c onn ect ion; ht tp i s the only sup por ted pr otoc ol.
network host desig nate d t o r ece ive the notificat ion. Value must be entered as a ho st name or IP
address.
= network port to use for th e N oti fy c on nect ion. Value must be a number fro m 1-6 553 5.
port
protocol-specific informat ion. Value cannot contain colons or semicolons.
path =
credentials = o
a base64-enco ded versio n o f
ptional protoc ol-specific credentials used to au th en tica t e to th e ser ver. For HTTP, this is
userid:password. Value cannot contain colors or semicolons. If the
credentials parameter is not specified or if it is null, no Authorization header will be included in the
request. The HTTP notif ication service will retry the request 3 times before fail in g and lo ggi ng an er r or
message.
data = o
ptional application-specific event data. Value cannot contain semicolons.
For example:
• Called from RTP onStreamStopped Event Handler, no credentials, with da ta:
Notify:http:myserver:8080:path/streamhandler?event=stopped:
:myStreamStoppedData
HTTP POST /path/streamhandler?event=stopped HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=”UTF-8”
Host: myserver:8080
Content-Length: 23
DATA=myStreamStoppedData
OL-20949-01
• Called from RTP onStreamStopped Event Handler, no credentials, no data :
Notify:http:server:8080:path/streamhandler?event=stopped
HTTP POST /path/streamhandler?event=stopped HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=”UTF-8”
Host: myserver:8080
Content-Length: 40
DATA=<notifyStreamStopped id=”stream1”/>
• Called from SoftKey, with credentials, with data:
Notify:http:myserver:8080:path/streamhandler?event=stopped:
8fh4hf7s7dhf :myStreamStoppedData
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-17
Page 66

Application Management URIs
• Called from SoftKey, no credentials, no data
• Called from SoftKey with QueryStringParam URI:
<CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Voicemail1</Name>
<URL>QueryStringParam:id=1</URL>
</MenuItem>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Voicemail2</Name>
<URL>QueryStringParam:id=2</URL>
</MenuItem>
<SoftKeyItem>
<Name>Play</Name>
<URL>Notify:http:vmailSrvr:8080:path/play</URL>
</SoftKeyItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
HTTP POST /path/streamhandler?event=stopped HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Authorization: Basic 8fh4hf7s7dhf
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=”UTF-8”
Host: myserver:8080
Content-Length: 23
Notify:http:server:8080:path/streamhandler?event=stopped
HTTP POST /path/streamhandler?event=stopped HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=”UTF-8”
Host: myserver:8080
Content-Length: 5
Application
Note The other component of the Appli cation M anagem ent API is the Appl ication Ma nageme nt Event
If the Voicemail2 menu item was selected when the Play softkey was pressed, the following
notification would be sent:
HTTP POST /path/play HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=”UTF-8”
Host: vmailSrvr:8080
Content-Length: 9
DATA=id=2
The Application URI is a co mpone nt of th e Ap pl icat ion M an agem ent API , wh ich p rovides an improved
hand-off between call mode and application mode. The Application URI allows applications to request
changes to their application or window state. Applications can request to change focus, to be minimized,
or to be closed.
Handler, see the “Application Event Handlers” sect ion on page 3-22 for details.
When an Application URI request is made, it has a specific application associated with it (not just the
a
pplication context) and that action can only be taken on that specific application. The Application
specified in the appId parameter (of the displayable XML object) must be active at the time the action
is requested, or an error will be returned.
5-18
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 67

Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
This preven ts open, b ut not acti ve, applicatio ns which are b uried on th e application “ stack” from clo sing
the entire application context which would also close the active application, potentially disrupting the
user’s interaction with the application. This also means that if an application closes or becomes
non-active (for example, i f us er n avigates o ut o f an a ppli cat ion, or a new appl icat ion is pu shed to t he
context) any pending A pp lica tio n URI r eq ues ts a re i m medi ate ly canc ell ed.
Note The 6900 series IP phones ca nnot add phone service under application due to hardkey mapping.
URI Format
App:action:priority:idleTimer:applicationId
Where
Application Management URIs
action =
• RequestFocus—Makes a requ est to the ap plication ma nager to bring the applic ation cont ext
action to be taken with the application. Values include:
(window) containing this application into focus (maximize). This is a request, not a demand, as
higher priority appl ications ma y prevent the applica tion fro m actua lly gaining foc us. Appl icatio ns
must use onAppFocusGained event handlers (see the “Application Event Handlers” section on
page 3-22) to know when focus is actually gained.
–
If the requested applica tion is Open, but not currently Acti ve, this req uest will not succeed (err or
response).
–
If the application already has focus, the request has no effect.
• ReleaseFocus—Makes a request to the application manager to relinquish focus to another
application context (essentially, a “move-to-back” request). Applications must use onAppFocusLost
event handler s to know when focus is actually lost (se e the “Application Event Handlers” section on
page 3-22).
–
If the application does not have focus, the request has no effect.
–
If there are no other applications open (available to receive focus) then this application will
retain focus.
• Minimize —Makes a reques t to the ap plicat ion mana ger to mi nimize t he applic ation c ontext
containing this application. This request always results in the application (eve ntually) being
minimized. If the applicatio n has focu s when th is URI ex ec utes, t he onApp Focu sLost e v e nt handler
will be invo ked first, then the onAppMinimize handler (see the “Application Event Handlers”
section on page 3-22).
–
If the requested applica tion is Open, but not currently Acti ve, this req uest will not succeed (err or
response).
OL-20949-01
–
If the applica tion i s alr eady mi nim ize d, the re que st h as no effec t.
• Close—Makes a request to the application manager to close the app lication context containing this
application.
–
If the requested applic ation is open, b ut n ot cur rently ac ti v e, this r equest w ill not succeed (error
response). This request will result in the application context (and all applications within that
context) being closed.
–
If the application has focus when this URI executes, the onAppFocusLost event handler will be
invoked prior to the onAppClosed even t handler (which will always be invoked).
priority = p
riority at which the action should be take. Values include:
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
5-19
Page 68

Application Management URIs
• 0—Do immediately, even if user is interacting with the phone. This priority is unavailable if the
• 1—Do when us er is done int eracti ng with the phone.
• 2—Do only if the user is not interacting with the phone.
idleTimer =
be taken. Values mus t range fro m 10-864 00 (seconds ); defau lt is 60 second s. The idl eTimer value has
no effect on priority=0 requests. Any pending timers are automatically cancelled wh en the displayable
object changes for an application context.
Chapter 5 Internal URI Features
Application URI is c onta ine d within a n App lic at ion M ana geme nt E vent Ha ndle r (se e the
“Application Event Handlers” section on page 3-22).
duration of time (in seconds) the phone or application must be idle before the action should
applicationId = o
ptional identifier of the application on which the action should be taken. Values must
range in length from 1-64 stri ng chara cters and ca nnot contain colo ns. The de fault value is the
application of the displayable object in which the URI is defined.
Note If the Applica tion U RI is use d in a n Execut eIt em, you m ust sp ec ify the appl ic ati on Id be cause
the application cont ext of the re que st ca nno t be inf erre d.
Error and Response
All Application URI requests are asynchronous, so the only return value indicates that the URI was
successfully parsed and that the specified application was valid and currently active in its context. The
application is no t ified of the a ctua l st at e ch an ge async hr ono usly via the event hand ler s.
Condition Status Data
Executed successfully 0 (Success) Success
URI syntax is invalid 1 (Parse error) Invalid URI
Unknown application ID 6 (Internal er ror) Unknown Application ID
Request made to change state of an application that is
t current active
no
6 (Internal er ror) Application is not Active
5-20
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 69

CHA PTER
6
HTTP Requests and Header Settings
Cisco Unified IP Phones use HTTP to communicate to external applications. The phone firmware
includes both an HTTP client for making requests, and an HTTP server for receiving requests. This
chapter describes the capabilities of the HTTP interface.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• HTTP Client Requests (HTTP GET)
• HTTP Server Requests (HTTP POST)
• HTTP Header Settings
• Identifying the Capabilities of IP Phone Clients
• Accept Header
• Accessing IP Phone Inform ation
HTTP Client Requests (HTTP GET)
The following descri ption de sign ate s h ow HTTP cl ien t re qu ests ar e hand led:
1. The Cisco Unified IP Phone HTTP client performs an HTTP GET for a specified URL.
2. The HTTP server processes request and returns an XML object or plain text.
3. The phone proc esses the sup port ed H TTP h ea ders.
4. The phone parses the XML object if Content Type is text/xml.
5. The phone presents da ta and option s to the user, or in the case of a CiscoIPPh oneExecute object,
begins executing the URIs.
HTTP Server Requests (HTTP POST)
The following descri ption de sign ate s h ow an HT TP server re quest is ma de t o t he ph one v ia an HT TP
POST operation:
1. The server performs an HTTP POST in response to a case-sensitive URL of the phone with this
format: http://x.x.x.x/CGI/Execute, where x.x.x.x represents the IP address of the destination
Cisco Unified IP Phone.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
6-1
Page 70

HTTP Header Settings
Tip Any HTTP POST object is limited to 512 bytes in size. Larger objects (such as images) can only be
Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
The form that is posted should have a case-sensitive form field name called “XML” that contains
the desired XML object. For any HTTP POST operation, the server must provide basic HTTP
authentication information with the POST. The provided credentials must be of a user in the global
directory with a device a ssoci ation w it h the ta rget p hone.
If the credentials are invalid, or the Authentication URL is not set properly in the
o Unified Communications M a nage r Ad mi nistra ti on, t he phon e w ill retu rn a
Cisc
IPPhoneError with a value of 4 (Authentication Error) and processing will stop.
Cisco
2. The phone proc esses the sup port ed H TTP hea ders
3. The phone parses an d validates the XM L objec t
4. The phone presents da ta and option s to the user, or in the case of a CiscoIPPh oneExecute object,
begins executing the URIs.
delivered to the phone via HTTP GET. So, to push large objects to the phone, the server application must
take an indirect approa ch. To do this, push an Execute object to the phone that contains an ExecuteItem
pointing to the URL of the large object.
Note JTAPI al so can push an XML object dir ectly to an IP phone, wit h the added be nefit of not requiri ng
authentication (since the JTAPI connection itself is already authenticated). This option works
particularly well for adding XML services interfaces to existing CTI applications (where the overhead
of the CTI connection is already a requirement). Objects pushed via JTAPI are also limited to a
maximum size of 512 bytes. See th e Cisco Unified Communications Manager JTAPI Developer Guide
for more informa ti on.
HTTP Header Settings
The following list provides definitions for HTTP header elements for Cisco Unified IP Phone Services:
• “Refresh”—sets the refresh time (in seconds) and URL
–
If no time is set or it is zero, the refresh gets set to manual.
–
If no URL is set, the current URL gets used.
See the “
• ContentType —notifies the phone of the MIME type that was sent. See the “MIME Type and Other
HTTP Headers” sect ion on page 6-4 section.
• “Expires”—sets the Date/Time in GMT when the page is to expire.
Pages that have expired before being loaded do not ge t added to the URL stack in the phone. The
hone does not cache content. See “Content Expiration Header Setting” section on page 6-4 for
p
more information.
HTTP Refresh Setting” section on page 6-3 section.
6-2
• “Set Cookie” - see “Set-Cookie Header Setting” section on page 6-5
• “HTTP Encoding Header Setting” section on page 6-6
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 71

Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
HTTP Refresh Setting
The HTTP headers that ar e se n t wi th an y page from an HTTP server can include a Refres h s ett ing . This
setting comprises two parameters: a time in seconds and a URL. These two parameters direct the
recipient to wait the tim e given in the seconds parameter and then get the data to which the URL points.
The Cisco Unified IP Phone HT TP client pr oper ly suppor ts this setting, which gives a great deal of
ower to service developers. It means that a new page can replace any XML object that displays after a
p
fixed time.
Figure 6-1
current value of Cisco stock.
1. A splash screen t hat disp lays the Yahoo logo.
2. After a very short time, it displays the nume ric Cisco stock paramete rs.
3. Finally, it shows a graph of Cisco intraday stoc k perf orm ance . T he di spla y t hen r epea te dly cycles
Figure 6-1 Refresh Display Sample
shows an example of how to use the refresh setting. This sampl e page shows the user th e
between the final two views.
HTTP Header Settings
OL-20949-01
Refreshing the display can occur without user intervention, because the display automatically cycles if
a timer paramete r is s pecified. On any gi v en screen, however, the user can for ce an im me diate reload by
pressing the Update softkey. Also, if a timer parameter of 0 was sent in the heade r, the page never
automatically reloads. In this c ase, the display will mov e to th e ne x t p age only w hen th e U pdate so ftk ey
is pressed. If no refresh URL is specified, the current page gets reloaded.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
6-3
Page 72

HTTP Header Settings
MIME Type and Other HTTP Headers
Although delivering pages with the proper MIME type and other formatting items is not difficult, it
requires moderately in depth knowledge of your web server. The following code excerpt, written in
JavaScript and used with Microsoft IIS and ASP, s ets these values in a few lines:
<%@ Language=JavaScript %>
<%
Response.AddHeader( "Refresh",
"3; url=http://services.cisco.com/s/q.asp");
Response.ContentType = "text/xml";
//
// Additional page content here
//
%>
Usually, you can set the MIME type for pages in any web server by simply performing an association to
the .xml file extension. Your web server documentatio n s hould expla in h ow to acc omp lish this . T his
action allows you to serve static pages without the need for writing script.
If you want to d eliver dynam ic con t en t by usi ng t he oth er su ppo rted H T TP he ad er s, you w ill ne ed t o
erstand how to genera te the H TTP h ea ders by usi ng the desi red pr ogram mi n g la nguag e an d have
und
common gateway interface (CGI) or script acc ess on the target web server.
Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
Audio Clips
You can serve audio clips to the phone from a web server by using the “audio/basic” MIME type setting.
When this MIME type is used, the body of the response should contain raw audio data in the same format
that is used for custom Cisco Unified IP Phone rings. Ref er to the chapter on “Cus tom Phone Rings” in
e Cisco Unified Communications Manager Syste m Gui de (
th
Note The audio file should not be longe r than five seconds.
Use the following ASP sample script to set the MIME type and to serve the file that is specified in the
#i
nclude command:
<%@ Language=JavaScript%>
<%
Response.ContentType = "audio/basic";
%><!--#include file="filename.raw" --><% Response.End();%>
Using script to generate the MIME header when playing a sound provides an advantage because you may
also include a refresh header to take the phone to a subsequent URL. Usually, you can set the MIME type
for pages in any web server by simply performing an association to the .xml or .raw file extension. Y our
web server documentation should explain how to accomplish this. This action allows you to serve static
pages without the need for writing script.
also available in the online help).
Content Expiration Header Setting
The expiration header can control which URLs are added to the phone URL history. This behavior differs
slightly from traditional web browsers but is implemented to perform the same function. Disable the
back button functio nality to avoid calling a URL twice.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
6-4
OL-20949-01
Page 73

Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
This functiona lity allows you t o make the co nte nt of a ny page th at is sen t t o the ph one expi re. Wh en a
user presses the Exit softkey, the user goes back to the last URL that did not expire when it was loaded.
This differs from trad itio nal browsers by no t consi der ing t h e curre nt fr esh ness of t he da ta but the
freshness of the da ta when t he U RL was reque ste d. Th is re qu ire s yo u to have a page expire when i t is
first loaded and to not set a time and date in the future.
The following example sh ows how to have content o n IIS expire by usin g A ct ive Server Page (ASP):
<%@ Language=JavaScript %>
<%
Response.ContentType = "text/xml";
Response.Expires = -1;
%>
The “Expires” property specifies the number of minutes to wait for the content to expire. Setting this
value to -1 subtracts 1 minute from the request time and returns a date and time that have already passed.
Set-Cookie Header Setting
A “cookie” is a term for a mec hanism that the Web server uses to gi v e the c lient a piece of data and h a v e
the client return the data with each request. The two traditional uses for cookies are:
HTTP Header Settings
• For Web sites to store a unique identifier and/or other information on the client's file system. The
information is available to the Web server on subsequent visits.
• To track a unique identifier for state management. The client returns the cookie with each request
and the server uses this identifier to index information about the current session. The identifier is
commonly referred to as a session ID. Most Web servers have a built-in session management layer
that uses this second type of co okie, wh ich is com monly re ferred t o as a sessio n cookie .
The following example sh ows the Set -C ookie hea der tha t i s r eturne d to the browser whe n a re quest
thod is used:
me
Set-Cookie: ASPSESSIONIDGQGQGRLS=OCPNMLFDBJIPNIOOKFNFMOAL; path=/
The Cisco Unified IP Phone can receive and use a total of four cookies per host per session and can store
information for up t o ei ght s essi ons a t onc e . Ea ch cooki e c an be u p t o 2 55 bytes in si ze. T hes e co oki es
are available until the server terminates the session or the client session has been idle for more than 30
minutes. On the la test g en eration ph one s wh ich are cap abl e of ru nning m ultip le appl icat ions
concurrently (Cisco Unified IP Phones 7970G, 7971G, 7961G, 7941G, 7911G), the session state is also
eared whenever the applicati on window closes. This beh avior is consi stent with PC-bas ed browsers
cl
and provides better security since anyone attempting to reopen a secure application would be forced to
authenticate. If the client is connecting to a new server and all session resources are in use, the client
clears and reuses the session with the longest inactivity time.
When using ASP on IIS t he de fau lt ser ver con figurati on au to matic ally gene rate s a session c ook ie an d
ds it to the client using the Set-Cookie header. This enables you to utilize the Session object from
sen
within ASP to store and retrieve data spanning multiple requests for the life of the session. When using
JSP on Tomcat, the default configuration generates and issues a session cookie.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
6-5
Page 74

HTTP Header Settings
HTTP Encoding Header Setting
The encoding hea der cont rols lang uage and ch arac ter sett ings rel ated to loc aliza tion.
Accept-Language
Cisco Unified IP Phones populate the Accept-Language HTTP request header in compliance with the
HTTP specification.
For example, the Accept-Language value advertised by a phon e configured for the
nglish_United_States user locale would look like:
E
Accept-Language: en -US
Accept-Charset
As of this release, the phones are capable of handling UTF-8 encoding and, depending on phone model,
some degree of Unicode support.
The phone mode ls ( suc h as t he 7940, 7 960, 7905 a nd 79 12) c an ha nd le UTF-8 e ncodi n g, but w il l on ly
cognize characters which can be represented by the default encoding of the phone's current user locale.
re
For example, if the phone is currently configured to use the English_United_States locale, then it will
only be able to display UTF-8 characters which map to the ISO-8859-1 character set.
Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
The phone models (such as t he 7970, 7 971, 7941, 796 1, and 791 1) provide UTF-8 an d true Uni code
ort. These phones provide support for more multi-byte character sets and user locales like Japanese
supp
and Chinese.
In addition to the character set for the currently configured user locale, the new phone models will also
ort ISO-8859-1 char acters in their font files.
supp
All phones will advertise their supported encodings using the standard HTTP Accept-Charset header. Per
TTP standard, q-values are use d to speci fy prefer red en codings. The older phone mod els, wi th more
H
limited UTF-8 supp ort, w ill speci fy a lower q-value fo r UT F-8 tha n the de fault u ser lo ca le en codi ng.
For example, an older phone model configured wit h the Engli sh_Unite d_Stat es user locale would
clude an Accept-Charset header similar to the following:
in
Accept-Charset: iso-88 59-1, utf-8;q =0.8
A newer phone model with Unicode support would advertise an Accept-Charset similar to the following:
Accept-Charset: utf-8, iso-8859-1 ;q=0.8
HTTP Response Headers: Content-Type
Because the phones are capable of supporting multiple character encodings, HTTP responses returned
to the phones sh ould in clu de t he ' cha rse t' pa ra met er o n the HTTP Con ten t- Type header. Examples of
responses including the “c harset ” parame nt are shown below:
Content-Type: text/ xml; c har set= ISO-88 59- 1
Content-Type: text/ xml; c har set= UTF-8
Content-Type: text/ plain; ch arse t=Shif t_J IS
HTTP standards state that if the encoding is not explicitly specified, ISO-8859-1 is the
default.Cisco Unified IP Phones are typically compatible with this spec, but not fully compliant.
6-6
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 75

Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
Identifying the Capabilities of IP Phone Clients
If 'charset' is not specified, the phones will use the default encoding for the currently configured user
locale. So to avoid possible problems where the phone's default encoding may NOT be ISO-8859-1, the
web server should explic itly set the Conten t-Type charset (which must match one of the Accept-Charset
values specified by the phone).
Identifying the Capabilities of IP Phone Clients
XML services are su pported on many C isco Unified IP Phones, so web application servers must identify
the capabilities of the requesting IP phone to optimize the content returned to the phone. For example,
if the requesting phon e i s a Cisco Unified IP Phone 7960, which cannot support color PNG images, the
pplication server must be able to identify this and return a gray scale CIP image instead.
a
The IP phone client request to send the relevant informat ion from the IP phon e to the web ser ver
pplication includes three (3) HTTP headers:
a
• x-CiscoIPPhoneModelName
• x-CiscoIPPhoneDisplay
• x-CiscoIPPhoneSDKVersion
x-CiscoIPPhoneModelName
This Cisco-proprie tar y he ad er con t ains t he Cisco ma nufact ur ing Mo de l Na me of t he d evice, whi ch ca n
typically be foun d by goi ng t o Settings > Model Information, but varies between different models.
Some examples of manu facturing M odel N ame s are CP-7 960, CP-79 60G, CP-794 0G, CP-7 905G, and
CP-7970G.
x-CiscoIPPhoneDisplay
This Cisco-propri et ary h ead er co nta ins t he di spla y ca pab iliti es of th e re quest ing device with the
following four parameters (listed in the order in which they appear):
• Width (in pixels)
• Height (in pixels)
• Color depth (in bits)
• A single character indicating whether the display is color (''C'') or gray scale (''G'')
These parameter s ge t se pa rat ed by c om mas as s hown in the foll owing exampl e of a
o Unified IP Phone 7970 hea der:
Cisc
x-CiscoIPPhoneDispl ay: 29 8, 168, 12, C
Note The pixel resolutions advertise d by the device define the area of the disp lay accessib le by the phone
services; not the actual resolution of the display.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
6-7
Page 76

Accept Header
x-CiscoIPPhoneSDKVersion
This Cisco-proprietary header contains the version of the IP Phone Services SDK that the requesting
phone supports. Th e H TTP he ad er does n ot sp ecify w hic h URI s a re supp orte d. T he refor e, you mu st
check the “Supported URIs” matrix in the IP Phone Services SDK to determine which URIs are
orted based on the Phone Model Nam e and supporte d SDK version.
supp
ble 5-1 table to find which IP phone models supp ort the U RIs docum ented in this SDK.
See Ta
Note Beginning with the IP Ph one Ser vices SDK 3.3 (3) , t he SD K version n umb er m atc hes t he mini mum
Cisco Unified Communication s Ma nage r s oftwa re th at i s requi r ed t o supp ort it. For exa mple , SDK
version 3.3(4) gets supported only on Cisco Communications Man ager version 3. 3( 4) or l ater.
Accept Header
The Accept header represents a standard HTTP header that is used to inform web servers about the
content-handling capabilities of the client.
Cisco Unified IP Phones include prop rie tar y con t ent- type s to indi ca te wh ich XML o bje cts ar e
orted. These proprietary c ontent-typ es all begin with x-Cisc oIPPhone, to indicate
supp
Cisco Unified IP Phone XML objects, fol lo wed b y a s lash “ /”, f ollo w ed b y eit her a spec if ic XML objec t
r a “*” to indicate all objects.
o
Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
For example, x-CiscoIPPhone/* indicate s that all XML obj ects defined in the spec ified version of the
DK are support ed, and x-Cisc oIPPh one/ Menu speci fies th at the
S
supported.
As the example illustr ates, the name o f the XML object can be derived directly from the content-type by
pending the sub-type (the part after the slash) onto “CiscoIPPhone.” The content-type can also include
ap
an optional version to indi cat e su ppo rt f or a part ic ular SD K ver sio n of t ha t obje c t. I f a version is n ot
specified, then the x - Cisco IPPhone SDKVersion is implied. The syntax of the ve rsion num ber ma y vary,
but, in general, will be as follows:
<major version>.<minor version>.<maintenance version>
Here are some examples of typ ical cont ent-ty pes:
x-CiscoIPPhone/*;version= 3.3.3
x-CiscoIPPhone/Text
x-CiscoIPPhone/Menu;version=3.3.4
<CiscoIPPhoneMenu> ob ject get s
6-8
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 77

Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
Accessing IP Phone Information
Cisco Unified IP Phones have an embedded web server to pr ovide a programming interface for external
applications and a debugging and manageme nt inter face for system administr ators.
You can access the administrative pages using a standard web browser and pointing to the IP address of
e phone with: /http://<phoneIP>/, where phoneIP is the IP a ddres s of t he speci fic phone .
th
These device information pages are available in either HTML format, for manual debugging purposes,
in XML form at for aut om a tion p urp oses . Table 6-1 lists the available URLs and their purpose.
or
Ta b l e 6-1 Device Information URLs
HTML URL XML URL Description
/DeviceInformation /DeviceInformationX General device information
/NetworkConfiguration /NetworkConfigurationX Network configuration information
/EthernetInformation /EthernetInformationX Ethernet counte rs
/PortInformation?n /PortInformationX?n Detailed port information, where n is
model-specific ethernet port
a
identifier, typically in the range 1- 3.
/DeviceLog?n /DeviceLogX?n Device logging, debug, and error
ssages, where n is a
me
model-specific log numbe r , typically
in the range 0 - 2.
/StreamingStatistics?n /StreamingStatisticsX?n Current RTP streaming stats, where
n' is model-specific RTP stream
'
identifier, typically in the range 1-3.
/CGI/Execute
/CGI/Screenshot
1. Pa sswo rd-p r otect ed CG I sc ri pt
1
1
The target URL of a phon e pu sh
(HTTP POST) request.
Returns an exact snapshot of the
current phone display. The size and
format of the im ag e ret urn ed is
model-specific.
Accessing IP Phone Information
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
6-9
Page 78

Accessing IP Phone Information
Chapter 6 HTTP Requests and Header Settings
6-10
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 79

Troubleshooting Cisco Unified IP Phone
Service Applications
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Troubleshooting Tips
• XML Parsing E rro rs
• Error Messages
Troubleshooting Tips
The following tips apply to troubl eshoo ting Cisco Unified IP Phon e servic e applic ations:
• Microsoft Inte rnet Ex plore r 5 or higher can display the XML sou rce with its default style she et.
• Understand tha t standard IP troubles hooting technique s are impo rtant for H TTP errors.
CHA PTER
7
• Externally verify name resolut ion (Phone has DNS set).
• If DNS is suspected, use IP ad dresses in URLs.
• Browse the URL in question with Microsoft Internet Explorer or download and verify with another
web browser
• Use a logged telnet session to v erify that the de sired HTTP he aders are retu rned (T e lnet to the serv er
on port 80; the n, e nte r get /pa th/ page) .
XML Parsing Errors
The following tips ap pl y to tro ubl eshoo t ing XML parsi n g err or s in Cisc o Unified IP Phone services
applications:
• Verify the object tags (the object tag s are case sensitive).
• Verify that “&” and the other four special characters are used per the restrictions while inside the
XML objects. See Chapter 3, “CiscoIPPhone XML Objects” for more information.
• Vali date XML a pplic ation s developed prior to Cisc o Unified IP Ph one firmware re lea se 8 .3( 2)
against the more recent XML parser (see the “Updated XML Parser and Schema Enforcem ent”
section on page B-1 for detail s). Some of examples of the t ypes of error s you migh t encount er
include:
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
7-1
Page 80

Error Messages
–
–
–
–
Error Messages
The following error messa ge s may appe a r on th e pr omp t l ine of t he Ci sco Unified IP Phone display:
• XML Error[4] = X ML Par ser error (In val id Obj ect)
• XML Error[5] = U nsuppo rte d XML O bje ct (not s uppo rted b y t his pho ne mod el)
• HTTP Error[8 ] = Unknow n H TTP Err or
• HTTP Error[1 0] = HTTP Con nection Fa ile d
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified IP Phone Service Applications
CiscoIPPhoneMenu Object—If the field <Name> is missing for a < MenuIt em>, the original parser
would stop rendering fr om tha t
in the menu list and conti nue to render any subsequen t
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory Object—If the field <Name> is not present, the old original parser would
not display the directory entry, the new parser will display the directo r y entr y, but there will be
<Name> associated with it.
no
CiscoIPPhoneInput Object—The URL and QueryStringPa ram fields are mandatory. The original
parser would not re port an er ro r o n th e missi ng U RL and on sub mit r eq ues t wou ld d ispl ay a
“Host not Found: message. If the
report an error.
SoftKeyItem—The Position field is mandatory. If the Position field is not present, the updated
XML parser will report an error.
<MenuItem> onwards. The new parser will display a blank line
<MenuItem> definitions.
QueryStringParam field is missing, the updated parser will
7-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 81

Cisco IP Phone Services Software Development Kit (SDK)
The Cisco IP Phone Services Software Development Kit (SDK) contains everything that you require to
create XML appli cations, includin g necessar y documen tation an d sampl e applic ations . Contact Ci sco
Developer Services to obtain the SDK at:
http://developer.cisco.com/web/ipps
These sections describe the Cisco IP Phone Services SDK:
• SDK Component s
• Sample Services Requirements
SDK Components
The following list contains the components that are included in the SDK:
• Documentation
CHA PTER
8
OL-20949-01
–
Cisco IP Services Development Notes (PDF format)
–
Cisco URL Proxy Guide (Ric h Text Format)
–
Cisco LDAP Programming Guide (Mic rosoft Word format)
–
Cisco CIP Image Release Notes (Microsoft Word format)
–
Cisco IP Applications Samples (Microsoft Word format)
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
8-1
Page 82

SDK Components
• Development Tools
–
Cip.8bi—Adobe Photo shop plug-i n that allows .cip extensi ons to be viewed and saved.
–
Cip2Gif.exe—DOS-based program that converts .cip files to .gif.
–
Gif2Cip.exe—DOS-based program that converts .gif files to .cip.
–
ImageViewer.exe—Windows application that displays .cip graphic files.
–
Cisco CIPImage—used for converting images to and from CIP images (automatically installed)
–
Cisco URL Proxy—Proxy server that is needed to use the sample services (automatically
installed).
–
Cisco LDAP Search—Service that is installed to do LDAP searches (automatically installed).
–
Microsoft XML Parser (MX SML) 3.0— Used for parsing XML data (a utomat icall y installe d)
–
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services ASP/Javascript Library (automatically installed)
–
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Jav a Lib rary—Use d b y the JSP apps (m anua lly insta lled - see
JSP Install readme)
–
CallManager Simulato r — Used for d eveloping Phone Serv ices w it hout a Ci sco Uni fied
Communications Manager server
Chapter 8 Cisco IP Phone Services Software Development Kit (SDK)
–
Cisco Unified IP Phone XML Schema (.xsd) file—Used with an XML editor to validate XML
syntax
• Sample Services
–
Wea ther for ecast lookup for any city (ASP)
–
Currency Exchange Rates and Converter (ASP
–
UPS Rates & tracking (ASP)
–
Wo rld Clock (ASP)
–
Measurement conversions (ASP)
–
US White pages/Yellow Pages search (ASP)
–
Calendar (ASP)
–
Stock Ticker (ASP)
–
Stock Chart (ASP)
–
Push2Phone (ASP and JSP)
–
Click2Dial (ASP and JSP)
–
IdleURL (ASP) - Not suppo rt ed o n Cisco Uni fied IP Phon es 79 05G and 7 912G
–
MConference (J SP)
–
Hootie (ASP)
–
InterCom (ASP)
8-2
–
JPEGViewer (ASP)
–
Logo (ASP)
–
Clock (ASP)
–
Personal Service (ASP)
–
Wa terM ark (AS P)
–
Extension Mobility Controller (JSP)
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 83

Chapter 8 Cisco IP Phone Services Software Development Kit (SDK)
–
Speed Dials (JSP)
–
Group MWI (JSP)
–
AutoDialer (JSP)
–
PhotoDirectory (JSP)
–
CallerInfo (JSP)
–
PushAuthenticate (ASP)
–
ScreenShot (ASP)
–
Integrating RS-232 devices with IP Telephony Applications (OtherApps)
–
PNGViewer (ASP)
–
Keyboard (ASP)
–
MultiDirectory (ASP)
–
Phone Push Step and Subsystem (Cisco Un ified Contact Ce nter Expr ess / C RS)
Sample Services Requirements
Sample Services Requirements
The following list contains the items that are required for the sample services to work properly:
• Microsoft II S 4.0 or later (fo r ASP sa mple servi ces)
• Sun J2SE 1.4.2 or later and Tomcat 4.0 or later (for JSP sample services)
• Internet Conn ect ion to ext erna l w ebsi tes l ike Yahoo.com, Cnn.com etc .
• Cisco Unified Communic ation s M ana ger 4.1(2) or later.
• Cisco Unified IP Phones that supports XM L servic es
The setup program installs a CiscoServi ces web proje ct to c
:\CiscoIpServi c es di rector y. The sample
services are copied to c:\CiscoIpServic e s\ S ervic es subdirectory, and IIS and WSH example codes are
provided. The web server already senses these ser vices an d you do not requir e furthe r admini strati on.
You can view or edit all the source code with any text editor. For additional documentation, go to this
directory: c:\CiscoIpServices\Documentation. Find tools to help develop services i n
c:\CiscoIpServices\Tools.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
8-3
Page 84

Sample Services Requirements
Chapter 8 Cisco IP Phone Services Software Development Kit (SDK)
8-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 85

CHA PTER
9
IP Phone Service Administration and Subscription
Cisco Unified Communications Manager administrators maintain the list of services to which u sers can
subscribe. Administrators must use Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration to add and
dminister Cisco Unified IP Phone services.
a
Note This chapter p rovides just a b ri ef overvi ew about m a nagi ng IP Phon e ser vic es. For d eta iled up- to-d ate
instructio ns, refe r to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Guide availab le at the
following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
These sections provide an overview about admi nisteri ng Cisco Unified IP Phone Services using
Cisco Unified Communications M ana ger A d minist rat ion.
• Accessing Phone Ser vice Admini stration
• Adding a Phone Serv ice
• Defining IP Phone S ervic e Paramete rs
• User Service Subscription
Accessing Phone Service Administration
To acce ss phone service administration, op en Cisco Unified Communications Manage r Adm ini stra tion
and choose Device > D evice S ett in g s > Ph o n e S erv ic es :
• Phone servi ces can have any number of param eters as soci ated with th em.
• You ca n specif y phone ser vice para meter s as optiona l or require d, dep ending on how the phone
service application defines them.
• Users can subscribe to any service configured in their cluster, using their User Options web pages.
• Service subscr iptions cur rentl y occur on a device basis.
A URL constitutes the core of each service. When a service is chosen from the menu, the URL gets
equested via HTTP, and a server somewhere provides the content. The Service URL field shows this
r
URL entry. For the services to be available, the phones in the Cisco Unified Communications Ma nage r
uster must have network connectivity to the server.
cl
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
9-1
Page 86

Chapter 9 IP Phone Service Administration and Subscription
Adding a Phone Service
Example
http://<servername>/ccmuser/sample/sample.asp
Where
ervername> designates a fully qualified domain name or an IP address.
<s
Adding a Phone Service
To acce ss phone service administration, op en Cisco Unified Communications Manage r Adm ini stra tion
and choose Device > Dev ice Se tt in g s > Ph o ne S erv ice s:
The Cisco Unified Services Con figuration page in Cisco Unified Communications Ma nager
dministration contains the fiel ds as shown in Table 9-1.
A
Ta b l e 9-1 IP Phone Service Configuration Settings
Field Description
Service Information
Service Name Enter the name of the service as i t will display on the menu of av ailable
ervices in Cisco Unified CM User Options. Enter up to 32 characters
s
for the service name.
ASCII Service Name Enter the name of the service to display if the phone cannot display
icode.
Un
Service Description Enter a description of the content that the service provides.
Service URL Enter the URL of the server where the IP ph one ser vices application is
cated. Make sure that this server remains independent of the servers
lo
in your Cisco Un ified Comm unic atio ns M ana ger clust er. Do not
specify a Cisco Unified Communications Manager server or any server
that is associated with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (such
as a TFTP server or d ir ector y d ata base pu bli she r ser ver).
For the services to be available, the phones in the Cisco Unified
ommunications Manage r clus ter must have network conne ctivity to
C
the server.
Service Category Select a service application type.
Service Type Select whether the service will be provisioned to the Services,
ectories, or Messages button.
Dir
Service Vendor For XML services, you can leave this field blank.
Service Version You can leave this field blank for XML services.
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
9-2
OL-20949-01
Page 87

Chapter 9 IP Phone Service Administration and Subscription
Defining IP Phone Service Parameters
Table 9-1 IP Phone Service Configuration Settings (continued)
Field Description
Enable Select this check box to enable the service, or clear the check box to
d
isable the service wi thout delet ing it.
Note You ca nnot de lete defau lt ser vic es. U se thi s field i f a defa ult
service exists, but you do not want to make it available for
subscription.
Enterprise Subscriptions Select this check box to automatically provision the new service to all
evices in the enterprise without requiring individual subscription. If
d
this option is selected, the service automatically gets provisioned and
does not get presented for user subscription.
Note Be aware that this check box is available for selection only
when the service is created. You cannot modify it.
Defining IP Phone Service Parameters
Each service c an ha ve a list of para meters. You can use these para meters, w hich are appended t o the URL
when they are se nt to th e ser ver, to personalize a servi ce f o r an in d ividual user. Exam p les o f par am ete rs
include stock ticker symbols, city names, or user IDs. The service provider defines the semantics of a
parameter.
The Cisco Unified IP Phone Se rv ice Para meter Configurat ion page in Cisc o Unified Communications
anager Administration conta ins the fields as descri bed in Table 9-2.
M
Ta b l e 9-2 IP Phone Service Parameter Settings
Field Description
Service Parameter Information
Parameter Name Enter the exact query stri ng parame ter to use wh en you build the
bscription URL; for example, symbol.
su
Parameter Display Name Enter a descriptiv e parameter name to di splay to the user in Cisco Unif ied
M User Opti on s; fo r exam p le, Ticker Sy mbo l .
C
Default Value Enter the default value for the parameter. This value displays to the user
n a service is being subscribed to for the first time; for example,
whe
CSCO.
Parameter Description Enter a description of the parameter. The user can access the text that is
tered here while the user is subscribing to the service. The parameter
en
description should provide in forma tion or exampl es t o h elp use r s inp ut
the correct value for the parameter.
Parameter is Required If the user must enter data for this parameter before the subscription can
e saved, check the Parameter is Required check box.
b
Parameter is a Password
mask contents)
(
You can mask entries in Cisco Unified CM User Op tions, so asterisks
display rather than the actual user entry. You may want to do this for
parameters such as pa sswords t hat you d o no t want o thers to be ab le to
view . To mask parameter entry, select the Parameter is a P assword (mask
contents) check box in the Configure IP phone service Parameter window
in Cisco Unified Communications Mana ger Admini stration .
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
9-3
Page 88

User Service Subscription
Tip If you change the service URL, remove a Cisco Unified IP Phone service parameter, or change the
Parameter Name of a phone service parameter for a phone service to which users are already subscribed,
be sure to click Update Subscriptions to update all currently subscribed users with the changes. If you
do not do so, users must resubscribe to the service to rebuild the URL correctly.
User Service Subscription
End users can configure service subscriptions using the Cisco Unified CM User Options. After users log
in and choose a device, a list of ser vic es t hat are assi gned to t h e pho ne disp lays. The u ser ca n th en
configure these services, adding ad ditio nal ones or remov ing un-used services . These
password-protected win dows are authen ticat ed via the LDAP directory.
Users can persona li ze th ei r se rvic e s usin g t he Us er Opt ions page s to :
• Customi ze th e name of the s ervic e.
• Enter any available service parameters.
• Review the description of each parame ter.
After all the required fields are set, the user clicks Subscri
built and stored in the d atabase for t his subscr iption. The service then a ppears on t he de vice services list.
Chapter 9 IP Phone Service Administration and Subscription
be to add the services. A custom URL gets
9-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 89

CHA PTER
10
DeviceListX Report
The DeviceListX Report is no longer supported as of Cisco Unified Communicat ions Manager Release
5.0. Retrieving real-time information from Cisco Unified Communicatio ns Ma nage r is now sup por ted
ia the Cisco Unified Communications Manager AXL Serviceability API.
v
The DeviceListX Report provides a list of the services-capable devices along with basic information
bout the device to identify or classify the d evic es based on spec ific criteria. Th e report also includes the
a
current device status and the IP ad dress info rmati on that is obt ained fr om the Real -Time Information
Service.
These sections prov ide details about the DeviceListX Report:
• Benefits
• Restrictions
• Integration Considerations and Interoperability
• Performance and Scalability
• Security
• Related Features and Technologies
OL-20949-01
• Supported Platform s
• Prerequisites
• Message and I nterface Definitions
• DeviceList XML Object
• Troubleshooting DeviceListX Reports
Note DeviceListX does not sup por t a ll devices. If you have a device tha t y ou need t o supp ort, c onta ct Ci sco
Developer Support to verify whether it is suppo rted:
http://developer.cisco.com/web/ipps
When a third-party developer initiates an HTTP GET request for the DeviceList X.as p rep ort pa ge, th e
system retrieve s the following information about phones that are registered to a
Cisco Unified Communication s M ana ger s er ver f rom t he dat aba se:
• Device Type
• Device Name
• Device Description
• Calling Search Space
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
10-1
Page 90

Benefits
Benefits
Restrictions
Chapter 10 DeviceListX Report
• Device Pool
• IP Address
• Real-Time Information
The completed list of data gets formatted into a simple XML object and gets returned in the HTTP
onse to the developer.
Resp
DeviceListX provides access to critical real-time data that was previously unavailable to third-party
developers. In particular , the ability to list currently re gistered devic es along with their IP addr ess allows
developers to easily build push, broadcast, and CTI-type applications.
Only users with administrative privileges to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration can access the report.
Note To min imi ze pr oc essin g overhead on th e C isco Unified Communications Manager server, access to the
DeviceListX report gets rate-limited to once per minute. Any attempt to pull the report more frequently
will fail. In practice, the developer application should pull and cache the Devic eListX re port, refr eshing
only as often a s req uire d, typ ica lly every few hours or da il y.
Integration Considerations and Interoperability
The interface allows HTTP 1.1 or HTTP 1.0 GET requests for the report. The report returns data that is
encapsulated by u sing XM L versi on 1 .0.
Performance and Scalability
You can run this report on the largest supported Cisco Unified Communications Manager cluster size for
the targeted release without impacting core features, such as delaying dial tone. On multiserver
Cisco Unified Communications Manager clusters, the report can acc ess only from the publisher server.
large cluster s w he re th e pub li sh er i s not a Ci sco Unified Communications Manager server, no
In
ibility exists of impacting th e system pe rforman ce as pe rceived by a user.
poss
This report is not intended for use during real time, so this interface should provide a mechanism for
velopers to poll for the data o n a daily or hourly basis. Give consideration to the frequency of polli ng
de
and the time of day to prevent unnecessary burden on the system during peak usage times.
10-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 91

Chapter 10 DeviceListX Report
Security
This report, which is within the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, inherits its
security from that web site, so no security issues directly relate to this report. If the
Cisco Unified Communication s M ana ger A d mini stra tion ch an ge s how it i mpl em ents se cu rity w it h
ditions, such as SSL, thi s r ep ort bene fits fro m that enha nce men t.
ad
Related Features and Technologies
DeviceListX acts as an independent interface, which is a real-time complement to the XML-Layer
Database API (AXL), where AXL prov ides access to static, persisted data, and DeviceListX provides
access to dynamic, volatile information.
Supported Platforms
For the DeviceListX.asp page to function requires Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration repo rting infr astruc ture. Th e following rele ases supp ort DeviceListX.a sp:
Security
• Cisco C all M an ager Release 3.2(3)SPB
• Cisco Unified CallManager Release 4.0(1) and lat er
Prerequisites
You can access this feature when devicelistX.asp resides in the C:\ciscoWebs\Admin\reports directory
of the Cisco Unified Commu nications Ma nager pu blishe r server.
Message and Interface Definitions
Use the following URL to access the report via HTTP:
http://x.x.x.x/CCMAdmin/reports/devicelistx.asp
where
x.x.x.x can eit
that contains the report.
Note Beginning with Cisco Unified CallManager 4.1 release, the De viceList X report can o nly be accessed via
secure HTTP (HTTPS), so the URL must begin with “https:” rather than “http:”.
her be the IP address or hostname of the Cisco Unified CallManager system
DeviceList XML Object
Third-party applica tions th at reside elsewhere on the net work common ly use the interfac e. The
application makes an HTT P r eq ues t fo r the re port and ge ts a re sponse t hat cont ain s a DeviceL ist X M L
object. The XML object follows:
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
10-3
Page 92

Chapter 10 DeviceListX Report
Troubleshooting DeviceListX Reports
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>
<DeviceList>
<Device t="" n="" d="" c="" p="" i="" s="" />
</DeviceList>
Ta b l e 10-1 DeviceList XML Object Attributes
Attribute Name Field Name Description
t Device Type Numeric enumeration val ue that is specified in the
abase.
dat
n Device Name String value that specifies the device name.
d Device Description String value that is specified in the database.
c Devic e C all i ng Se ar ch S p ace String value that is specified in the database.
p Device Pool String value that is specified in the database.
i Device IP Address Last known IP address as reporte d by the
l-Time Information Se rvic e
Rea
"" = No known IP a dd re ss
"x.x.x.x" = Last known IP address
s Device Status Numeric enumer ation for t he current de vice st atus
s reported by the Real-Time Information Service
a
"" = Device not fou nd
"1" = Device registered
"2" = Device found but not currently registered
Example 10-1 DeviceList Object with Data
<?xml version="1" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>
<DeviceList>
<Device t="35" n="SEP000123456789" d="Auto 2010" c=”” p="Default" i="10.1.1.1" s="1"/>
</DeviceList>
Troubleshooting DeviceListX Reports
These sections can assist you in troublesh ooting DeviceListX Rep orts:
• Error Code s
• Deter min ing Prob le ms With the In terfa ce
Error Codes
The error codes that are specific to this report interface follow.
10-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 93

Chapter 10 DeviceListX Report
Error Message 1001 Too many simultaneous requests for Device List. Please wait at
least 60 seconds and try again.
Troubleshooting DeviceListX Reports
Explanation
When two or more clients attempt to get the list at the same time, or if the list is long,
overlapping requests can re sult ( first r equest is processing wh en the sec ond r eque st atte mp ts
processing).
Recommended Action Re qu est info rma tion onl y a s o ften as nec essar y.
Note Cisco recommend s tha t y ou wait lo nge r than 6 0 sec ond s b etwee n requ ests .
Error Message 1002 Too many consecutive requests for Device List. Please wait at
least 60 seconds and try again.
Explanation
Recommended Action Request informa tion only as ofte n as necessa ry. Because the real-time status o f
Because the system is busy, it cannot process a Device List.
every device gets checked, Device List represents a CPU-intensive process.
Note Cisco recommend s tha t y ou wait lo nge r than 6 0 sec ond s b etwee n requ ests .
Determining Problems With the Interface
Use the following p rocedure to determ ine whether a problem exists w ith the in terfa ce and d etermine th e
root cause of the prob l em.
Procedure
Step 1 Check the Windows NT Event Logs for error messag es th at pertain to the IIS ser ver and the SQL server .
Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Event Viewer
Step 2 Check for error messages or successful completion of a request in the IIS log files, which are typically
located in
C:\WINNT\System32\LogFiles\W3SVC1
The date of the log provide s part of the log name. All times in the log file s specify GMT for noted e ven ts.
e IIS logs appear in chronolo gical o rder and ca n easily be se arch ed by specific query event.
Th
Step 3 Use a web bro w ser, such as IE, to r eq uest t he UR L o f the d e vic eli stx .as p we b page . A su cces sf ul re qu est
yields a well-formed X ML obje ct of all the device infor mation.
Step 4 Use a Sniffer trace to view the HTT P GET reque st and respo nse trans actio n between the third- party
application and th e report .
Step 5 If you need further assistance, see the “Document Conventions” section on page x.
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
10-5
Page 94

Troubleshooting DeviceListX Reports
Chapter 10 DeviceListX Report
10-6
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 95

CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference
Table A- 1 provi des a qu i ck re f eren ce o f th e Cisc oIPPho ne XM L obje cts a nd the de finitio ns th at ar e
associated w it h ea ch .
Ta b l e A-1 CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference
Object Definition
CiscoIPPhoneMenu <CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
CiscoIPPhoneText <CiscoIPPhoneText>
CiscoIPPhoneInput <CiscoIPPhoneInput>
CiscoIPPhoneDirectory <CiscoIPPhoneDirectory>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneMenu>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>The prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<Text>Text to display as the message body goes here</Text>
</CiscoIPPhoneText>
<Title>Directory title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<URL>The target URL for the completed input goes here</URL>
<InputItem>
<DisplayName>Name of input field to display</DisplayName>
<QueryStringParam>The parameter to be added to the target
URL</QueryStringPara
<DefaultValue>Value</DefaultValue>
<InputFlags>The flag specifying the type of allowable
input</InputFlags>
</InputItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneInput>
<Title>Directory title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<DirectoryEntry>
<Name>The name of the directory entry</Name>
<Telephone>The telephone number for the entry</Telephone>
</DirectoryEntry>
</CiscoIPPhoneDirectory>
m>
APPENDIX
A
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
A-1
Page 96

Table A-1 CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference (continued)
Object Definition
CiscoIPPhoneImage <CiscoIPPhoneImage>
CiscoIPPhoneImageFile <CiscoIPPhoneImageFile>
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu <CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu>
CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu <CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu>
<Title>Image title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Position information of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Position information of graphic</LocationY>
<Width>Size information for the graphic</Width>
<Height>Size information for the graphic</Height>
<Depth>Number of bits per pixel</Depth>
<Data>Packed Pixel Data</Data>
</CiscoIPPhoneImage>
<Title>Image Title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Horizontal position of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical position of graphic</LocationY>
<URL>Points to the PNG image</URL>
</CiscoIPPhoneImageFile>
<Title>Menu title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Position information of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Position information of graphic</LocationY>
<Width>Size information for the graphic</Width>
<Height>Size information for the graphic</Height>
<Depth>Number of bits per pixel</Depth>
<Data>Packed Pixel Data</Data>
<MenuItem>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu>
<Title>Image Title goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<LocationX>Horizontal position of graphic</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical position of graphic</LocationY>
<URL>Points to the PNG background image</URL>
<MenuItem>
<Name>Same as CiscoIPPhoneGraphicMenu</Name>
<URL>Invoked when the TouchArea is touched</URL>
<TouchArea X1="left edge" Y1="top edge" X2="right
edge"Y2="bottom edge
</MenuItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneGraphicFileMenu>
"/>
Appendix A CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference
A-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 97

Appendix A CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference
Table A-1 CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference (continued)
Object Definition
CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu <CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu>
CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu <CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu>
CiscoIPPhoneStatus <CiscoIPPhoneStatus>
CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile <CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile>
CiscoIPPhoneExecute <CiscoIPPhoneExecute>
CiscoIPPhoneError <CiscoIPPhoneError Number=”x”/>
CiscoIPPhoneResponse <CiscoIPPhoneResponse>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<IconIndex>Indicates what IconItem to display</IconIndex>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
<IconItem>
<Index>A unique index from 0 to 9</Index>
<Height>Size information for the icon</Height>
<Width>Size information for the icon</Width>
<Depth>Number of bits per pixel</Depth>
<Data>Packed Pixel Data</Data>
</IconItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneIconMenu>
<Title>Title text goes here</Title>
<Prompt>Prompt text goes here</Prompt>
<MenuItem>
<IconIndex>Indicates what IconItem to display</IconIndex>
<Name>The name of each menu item</Name>
<URL>The URL associated with the menu item</URL>
</MenuItem>
<IconItem>
<Index>A unique index from 0 to 9</Index>
<URL>location of the PNG icon image</URL>
</IconItem>
</CiscoIPPhoneIconFileMenu>
<Text>This is the text area</Text>
<Timer>Timer seed value in seconds</Timer>
<LocationX>Horizontal alignment</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical alignment</LocationY>
<Width>Pixel width of graphic</Width>
<Height>Pixel height of graphic</Height>
<Depth>Color depth in bits</Depth>
<Data>Hex binary image data</Data>
</CiscoIPPhoneStatus>
<Text>This is the text area</Text>
<Timer>Timer seed value in seconds</Timer>
<LocationX>Horizontal alignment</LocationX>
<LocationY>Vertical alignment</LocationY>
<URL>location of the PNG image</URL>
</CiscoIPPhoneStatusFile>
<ExecuteItem URL=”The URL or URI to be executed”/>
</CiscoIPPhoneExecute>
<ResponseItem Status”the success or failure of the
action”Data=”the inf
URL=”the URL or URI specified in the Execute object”/>
</CiscoIPPhoneResponse>
ormation associated with the request”
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
A-3
Page 98

Appendix A CiscoIPPhone XML Object Quick Reference
A-4
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
Page 99

APPENDIX
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services XML Schema File
These sections provide details ab out the XML schema support ed on Cisco Unified IP Phone s:
• Updated X M L Pars er and Sch em a Enfo rc em en t
• CiscoIPPhone.xsd
Updated XML Parser and Schema Enforcement
In order to provide a st able and c on siste nt plat f orm u pon w hic h to build e nh ance ment s to I P ph one s
services, Cisco re lease d an up dated X ML p ars er b eginni ng w ith firmware rel ease 8.3( 2). As a re sult,
many Cisco Unified IP Phone s n ow contai n th is up da ted XML par ser whi ch provide s a more rigid
enforcement of the XML schema. This updated parser provides more error logging information when it
encounters XML schema violatio ns, an d it enab les developers to debug their applicati ons more
efficiently.
B
Cisco recommends that developers verify that their existing applications conform to the XML schema
avoid incompatibilities with any XML enhancements, particularly if you want to incorporate new
to
URIs.
The following Cisco Unified IP Phones implement this new XML parser: 7906G, 7911G, 7921G, 7925G,
1G, 7941G/7941G-GE 79 42G, 7945G, 7961G/79 61G-GE , 7962G, 796 5G, 7970G / 7971G-GE ,
793
7975G, 6921, 6941, 6 961
OL-20949-01
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
B-1
Page 100

CiscoIPPhone.xsd
CiscoIPPhone.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- edited with XML Spy v4.4 U (http://www.xmlspy.com) by Cisco Systems, Inc. (Cisco
Systems, Inc.)
<xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDe
<xsd:complexType name="CiscoIPPhoneExecuteItemType">
<xsd:attribute name="Priority" use="optional">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:unsignedByte">
<xsd:minInclusive value="0"/>
<xsd:maxInclusive value="2"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="URL" use="required">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:maxLength value="256"/>
<xsd:minLength value="1"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="CiscoIPPhoneResponseItemType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="Status" type="xsd:short"/>
<xsd:element name="Data">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:maxLength value="32"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="URL">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:maxLength value="256"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="CiscoIPPhoneTouchAreaMenuItemType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="Name" minOccurs="0">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:minLength value="0"/>
<xsd:maxLength value="32"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="URL" minOccurs="0">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:minLength value="0"/>
<xsd:maxLength value="256"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="TouchArea" type="CiscoIPPhoneTouchAreaType" minOccurs="0"/>
Appendix B Cisco Unified IP Phone Services XML Schema File
-->
fault="unqualified" version="3.3.4">
B-2
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services Application Development Notes
OL-20949-01
 Loading...
Loading...