Page 1

Administrator’s Guide for
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Release 5.3
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Text Part Number: OL-6280-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCSP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Cisco Unity, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work,
Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco,
the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Empowering the Internet Generation,
Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net
Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing,
ProConnect, RateMUX, Registrar, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient,
TransPath, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0406R)
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
Copyright © 2004-2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
1 Introducing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3 1-1
Audience 1-1
Scope 1-1
Naming Conventions Used in This Guide 1-2
Overview of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 1-2
Features and Benefits of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 1-3
Additional References 1-4
2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process 2-1
Overview of Components 2-1
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace System Configurations 2-4
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process 2-4
How Video Conferences Are Scheduled 2-5
How Video Conferences Start 2-6
How Video Conferences Run 2-8
About Displaying the Status and Options of Video Participants in the Meeting Room 2-8
How Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Tracks Port Availability 2-8
How Video Conferences End 2-9
CHAPTER
OL-6280-01
3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 3-1
Before You Install 3-1
Making Sure Component Systems Are Up and Running 3-1
Verifying your Video-Conferencing License 3-2
About Configuring the Cisco IPVC MCU to Use Cisco MeetingPlace 3-2
Configuring the Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server 3-11
Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway 3-12
Configuring Load-Balancing Configurations for Video Conferencing 3-12
About Installing and Configuring Video Endpoints 3-13
(Optional) Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook 3-14
(Optional) Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes 3-14
Configuring Cisco CallManager 3-14
Preparing to Install the Video Integration with DMZ Configurations 3-17
Gathering Installation Values 3-18
Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 3-18
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
i
Page 4

Contents
Uninstalling Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 3-19
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 4-1
About the Cisco MeetingPlace MeetingTime Software Application 4-1
About Video-Conferencing Access Information 4-1
About Changing System Configuration Settings 4-2
Changing Values Entered During Installation of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 4-3
Changing Settings in Other Components 4-3
About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources 4-4
About Configuring Port Parameters 4-7
About Managing User Profiles for Video Use 4-10
Important Information About DMZ Configurations and Video Conferencing 4-12
About Video-Conferencing Bandwidth 4-12
Specifying User and Group Profile Information 4-13
About Video-Conferencing Statistics 4-13
Viewing Video-Conferencing Statistics 4-14
5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing 5-1
Supported Meeting Types 5-1
About Setting Up End Users for Video Conferencing in Cisco MeetingPlace 5-2
About Scheduling Video Conferences 5-3
Who Can Schedule Video Conferences 5-3
When Video Conferences Can Be Scheduled 5-3
How Users Schedule Video Conferences 5-3
About Rescheduling Video Conferences 5-4
About Attending Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferences 5-4
How Users Join A Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conference 5-5
Video Features and Functions in the Meeting Room During the Conference 5-7
About Modifying the Video Transmission 5-8
About Modifying the Video Transmission of Other Participants 5-9
About Recording a Video-Conferencing Session 5-9
About Entering a Breakout Session 5-9
About Participating in Lecture Style Meetings 5-9
About Extending a Video Conference 5-10
About Leaving a Video Conference 5-10
About Ending a Video Conference 5-10
Information for End Users 5-10
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
ii
OL-6280-01
Page 5

Contents
CHAPTER
I
NDEX
6 Troubleshooting 6-1
Viewing the Eventlog 6-1
Setting the Level of Logging Detail 6-1
General Troubleshooting Guidelines 6-2
Problems Configuring and Initiating Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 6-2
Problems Scheduling a Video Conference 6-5
Problems Joining a Video Conference 6-5
Problems During a Video Conference 6-7
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
iii
Page 6

Contents
iv
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 7

CHAPTER
Introducing
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Release 5.3
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3 describes
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
This chapter contains the following topics:
• Audience, page 1-1
• Scope, page 1-1
• Naming Conventions Used in This Guide, page 1-2
• Overview of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, page 1-2
• Features and Benefits of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, page 1-3
1
Audience
Scope
• Additional References, page 1-4
This guide is intended for Cisco MeetingPlace system administrators who are familiar with the following
products, which are prerequisites for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration:
• Cisco MeetingPlace 8100 Series servers and the Cisco MeetingPlace MeetingTime software
application
• Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
• Other Cisco MeetingPlace integration products that are part of the Cisco MeetingPlace system
• Cisco CallManager (if your environment includes this product)
• Cisco IPVC MCU 3.5plus and its required components
This guide describes how to install, configure, manage, and troubleshoot the
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. This guide does not describe in detail how to set up
Cisco MeetingPlace audio and web conferencing, nor does it describe how to set up or configure the
Cisco IPVC MCU or any of its components, including H.323 gatekeepers, video endpoints, or gateways.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
1-1
Page 8
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
Naming Conventions Used in This Guide
This guide also does not describe in detail how to configure Cisco CallManager. Cisco IPVC video
conferencing, Cisco CallManager, and Cisco MeetingPlace audio and web-conferencing systems must
be up and running before you install Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
For information on any of the preceding systems, see the documents listed in Additional References,
page 1-4.
Naming Conventions Used in This Guide
The following products and components appear frequently in this guide.
Official Name Abbreviation
Cisco MeetingPlace 8100 Series server with
Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3
software
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
Release 5.3
Cisco MeetingPlace MeetingTime Release 5.3 MeetingTime
Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes Release 5.3 Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes
Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook Release 5.3 Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook
Cisco IPVC MCU 3.5plus Cisco IPVC MCU
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
Overview of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is a separately-licensed add-on to Cisco MeetingPlace
conferencing that integrates the voice and web-conferencing capabilities of Cisco MeetingPlace with the
video-conferencing functionality provided by the Cisco IPVC Multipoint Control Unit (MCU). Voice,
web, and video conference participants interact seamlessly in a single rich-media conference.
The visual channel of the video-conferencing medium is handled entirely by the Cisco IPVC MCU and
runs parallel to the voice and web conference. All media (video, voice, and data) are linked but
independent, so that each stream maintains its full feature set and functional richness.
The following steps provide a simplified overview of how the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
solution works (in a system that includes e-mail notifications):
1. You set up user profiles in Cisco MeetingPlace that control who can schedule video conferences.
2. Users whose profile authorizes them to schedule video conferences submit a single
Cisco MeetingPlace form to schedule a meeting that includes video, voice, and web-conferencing
functionality. Users can require passwords, or specify that only profiled or invited users can attend.
3. Cisco MeetingPlace keeps track of available conferencing resources, including resources available
on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and video resources on the Cisco IPVC MCU. If there are
sufficient resources on both systems to accommodate a scheduler’s request, Cisco MeetingPlace
schedules the meeting and sends notifications to the invitees. These notifications include the
information participants need in order to access all conference media.
1-2
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 9

Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4. At the scheduled meeting time, invitees use the information in the meeting notification to join each
aspect of the conference: the Cisco MeetingPlace web and voice conferences and the video
conference hosted on the Cisco IPVC MCU. Video participants attend the video aspect of the
conference via a room-based video system or via IP video cameras on their desktop, such as
Cisco VT Advantage. Participants can join the different media using any of several methods.
5. Cisco MeetingPlace initiates the voice conference on the Cisco MeetingPlace system and the video
conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU, and establishes the link that joins the audio of the video
conference with the audio of the voice conference.
6. After participants are in the integrated conference, audio-only and video participants can converse
seamlessly with each other. Video participants can control their audio and video transmission and
display from within the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room.
7. If the conference needs to continue past the time it was scheduled to end, Cisco MeetingPlace
evaluates whether conferencing resources are available on both the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server
and on the Cisco IPVC MCU, then determines whether the conference can be extended.
Video conferences can also be added to an existing Cisco MeetingPlace conference on an ad-hoc basis,
if resources are available.
For details about the end user experience and process for using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration,
see Chapter 5, “Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing” and Chapter 2,
“Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process.”
Features and Benefits of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Features and Benefits of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration offers the following features:
• Enhances meeting effectiveness by bringing together multiple media to create a rich-media
conferencing environment.
• Offers a solution that integrates readily into existing networks and IP infrastructure.
• Includes tools to manage video-conferencing resources for optimal availability.
• Simplifies the processes of scheduling, distributing notifications, attending, and participating in
multiple media for end users.
• Leverages the existing video-conferencing capability of the Cisco IPVC MCU and networking and
telephony infrastructure, such as Cisco CallManager, to provide a complete and unified multipoint
conferencing solution for Cisco customers.
• Extends important resource management tools from Cisco MeetingPlace to the Cisco IPVC MCU,
allowing you to plan, allocate, and measure resource use, and thus to maximize the utility of
video-conferencing resources.
• Resource management features include the following:
–
The ability to schedule video-conferencing resources in advance. Cisco MeetingPlace manages
the scheduling of video-conferencing resources on the Cisco IPVC MCU, which does not have
built-in scheduling functionality.
–
Floater and overbook ports to optimize port availability and minimize waste of conference ports.
This increases the availability of conference ports for ad-hoc video conferences.
–
User profiles to limit use of conferencing resources to designated meeting schedulers and
groups.
OL-6280-01
–
Statistics on video usage that are included in standard Cisco MeetingPlace reports, so you can
easily evaluate needs and manage all resources.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
1-3
Page 10

Additional References
• Ease-of-use features that simplify the rich-media conferencing process for users include the
following:
–
Unified scheduling, which allows users to coordinate all conferencing resources from a single
point. Scheduling is done through familiar desktop applications such as Microsoft Outlook,
Lotus Notes, or a web browser.
–
Notifications for each meeting that include the links and instructions to access all conference
media for that meeting.
–
Users can initiate or join a video conference on an ad-hoc basis, as long as video-conferencing
resources are available.
–
Preference information in user profiles, which automates parts of the attend process.
–
Video controls in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room, which allow users
to control all aspects of their conferencing experience from a single interface.
Additional References
Cisco MeetingPlace products
Guide to Cisco Conferencing Documentation and Support
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/roadmap.htm
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/video/53/index.htm
Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/audio/53/index.htm
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/web/53/index.htm
Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Release 5.2.1
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/ipgw/ip521/index.htm
Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/outlook/mpol53/index.htm
Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/notes/notes53/index.htm
Cisco IPVC products
All Cisco IPVC products and components
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/ipvc/index.htm
Cisco IOS H.323 Gatekeeper
Cisco IOS H.323 Configuration Guide
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios123/123cgcr/vvfax_c/callc_c/h323_
c/323confg/5gkconf.htm
1-4
Or look for the link on the following page:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios123/123cgcr/vcl.htm
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 11

Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
Cisco CallManager
Release 4.1 documentation
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_callmg/4_1/index.htm
Release 4.0 documentation
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_callmg/4_0/index.htm
Cisco IP Video Telephony Solution Reference Network Design (SRND) for Cisco CallManager
Release 4.0
http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/netsol/ns268/c649/ccmigration_09186a008026c
609.pdf
Cisco VT Advantage
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_ipphon/english/ipcvl/index.htm
Additional References
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
1-5
Page 12

Additional References
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
1-6
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 13

Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Components and Process
This chapter describes the components that are required for the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
solution:
• Overview of Components, page 2-1
• Supported Cisco MeetingPlace System Configurations, page 2-4
• About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process, page 2-4
Overview of Components
The components shown in Figure 2-1 and described in Tab l e 2-1 work together to provide video
conferences that are integrated with Cisco MeetingPlace voice and web conferences.
In the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration solution, Cisco MeetingPlace components provide audio
conferencing and web conferencing data collaboration, and the Cisco IPVC MCU and its associated
components provide video conferencing. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration integrates the two
solutions to provide integrated voice, data, and video conferencing.
CHAPTER
2
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
2-1
Page 14
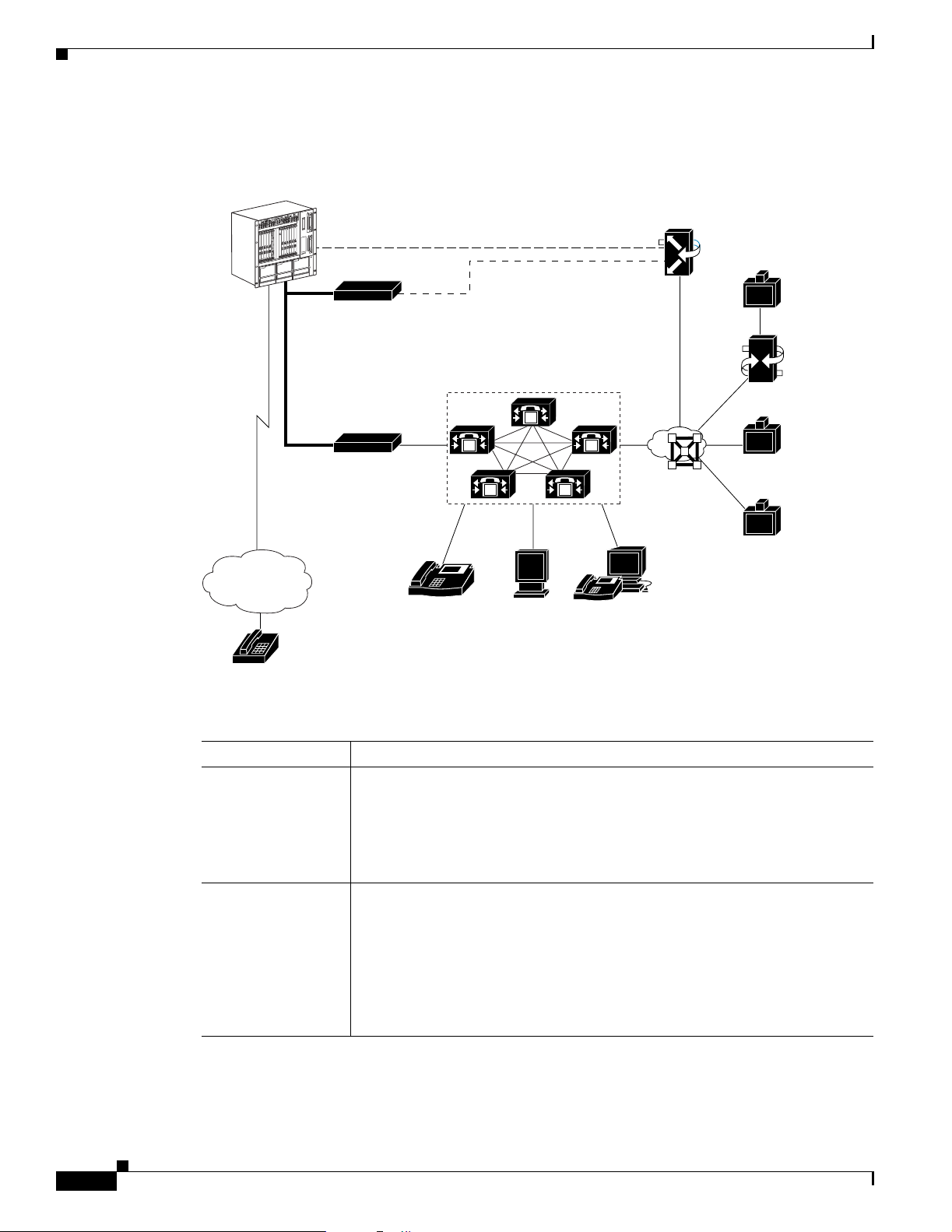
Overview of Components
Figure 2-1
Cisco
MeetingPlace
audio server
Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
Cisco
IP/VC MCU
RTP
XML
Cisco MeetingPlace
Web Conferencing
Cisco MeetingPlace
Video Integration
Cisco MeetingPlace
for Outlook (optional)
M M
Cisco MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway
PSTN
Phone
Table 2-1 Components Needed to Integrate Video Conferencing in Cisco MeetingPlace
IP
Cisco
IP Phone
Cisco
CallManager
M
M
SCCP
video
endpoint
M
IP
Cisco
VT Advantage
video endpoint
Cisco
IOS H.323
Gatekeeper
H.320
video
endpoint
Cisco
IP/VC
PRI
Gateway
H.323
video
endpoint
H.323
video
endpoint
92342
2-2
Component Functions
Cisco MeetingPlace
audio server
• Handles the audio conference.
• Schedules the video conference port resources for the Cisco IPVC MCU.
• Sets the parameters that are interpreted by
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, which uses these parameters to
control conference resources.
Cisco MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP
Gateways
• Allows the Cisco MeetingPlace system to communicate with IP telephony
devices.
• Connects the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server to the network and to
Cisco CallManager or the H.323 gatekeeper.
• Establishes the link between the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and the
Cisco IPVC MCU to enable video and audio participants to hear and speak
to each other.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 15
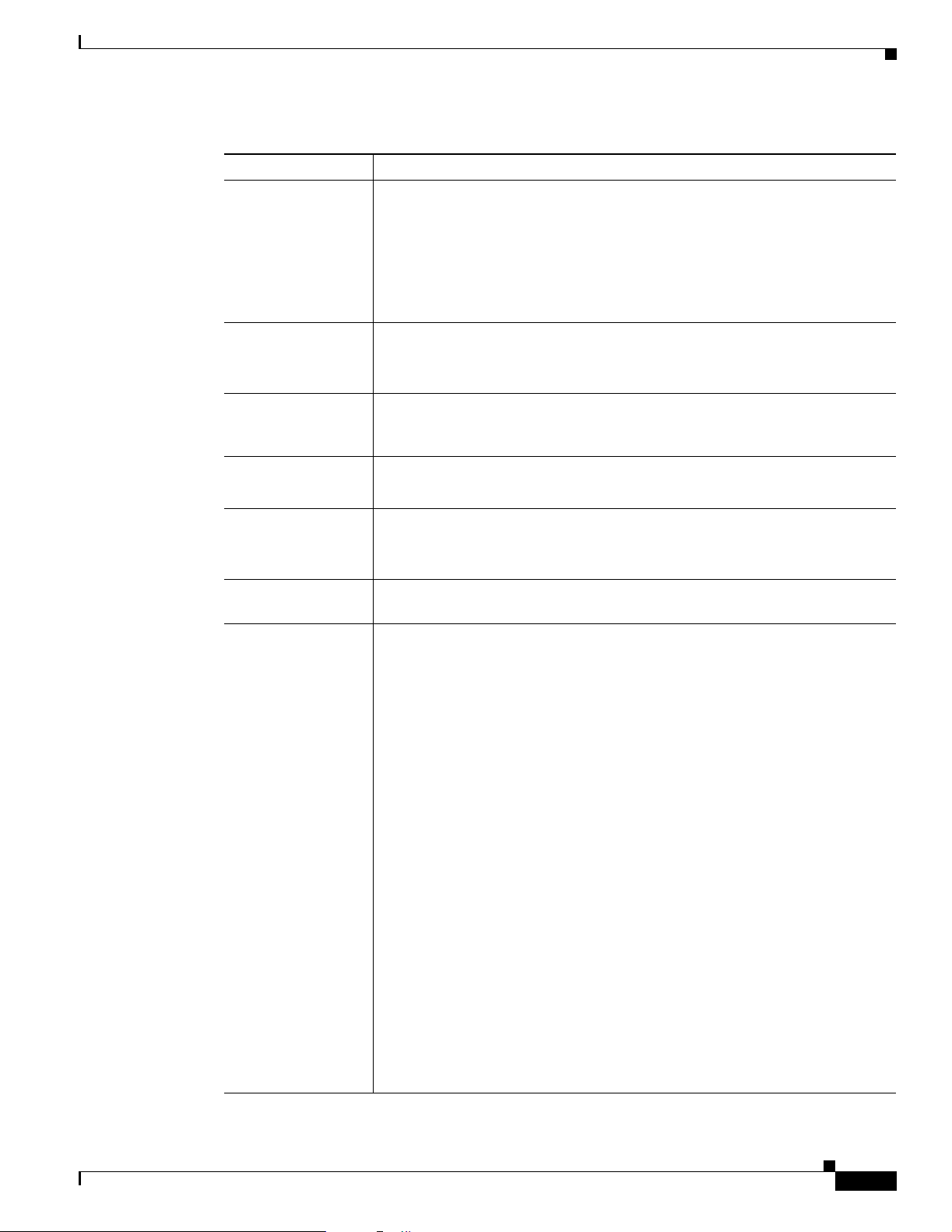
Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
Table 2-1 Components Needed to Integrate Video Conferencing in Cisco MeetingPlace (continued)
Component Functions
Cisco MeetingPlace
Web Conferencing
• Displays a user interface to schedule and attend meetings.
• Displays video participant status.
• Provides the web-conferencing meeting room from which users can join
and control video conferences.
• Includes components that enable the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server to
communicate with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
Cisco MeetingPlace
for Outlook
(Optional)
Cisco MeetingPlace
for Lotus Notes
• Presents a convenient scheduling interface to end users.
• Provides meeting notifications that offer users two ways to “click to attend”
video, voice, and web conferences.
• Schedule and attend Cisco MeetingPlace meetings that include video
directly from the Lotus Notes environment.
(Optional)
Cisco IPVC MCU
• Processes the video streams to provide the video capability of the system.
Overview of Components
H.323 gatekeeper
Cisco IPVC PRI
Gateway (Optional)
Cisco MeetingPlace
Video Integration
• Communicates with the video endpoints.
• Routes calls between the video endpoints and the Cisco IPVC MCU, based
on the number dialed.
• Handles the IP protocol signaling.
• Enables H.320 video endpoints to participate in video conferences on the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
• Monitors the configuration of the Cisco IPVC MCU and passes current
status to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
• Authorizes the Cisco IPVC MCU to create and initiate video conferences.
• Initiates the creation of the audio channel between the Cisco IPVC MCU
and the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
• Passes information between the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
• Coordinates capacity by transmitting meeting scheduling, initiation, and
termination information between the various components.
• Controls the behavior of the Cisco IPVC MCU based on meeting type and
requests placed via the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting
room.
• Controls entry of participants into video conferences, based on the number
of video ports scheduled on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server for the
conference, plus available video floater and video overbook ports, if any.
• Tells the Cisco IPVC MCU when to terminate conferences.
OL-6280-01
• Keeps track of information for all conference participants in the
Cisco IPVC MCU and their corresponding participant IDs assigned by the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
• Monitors the link between the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and the
Cisco IPVC MCU and supports recovery if the connection is lost.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
2-3
Page 16
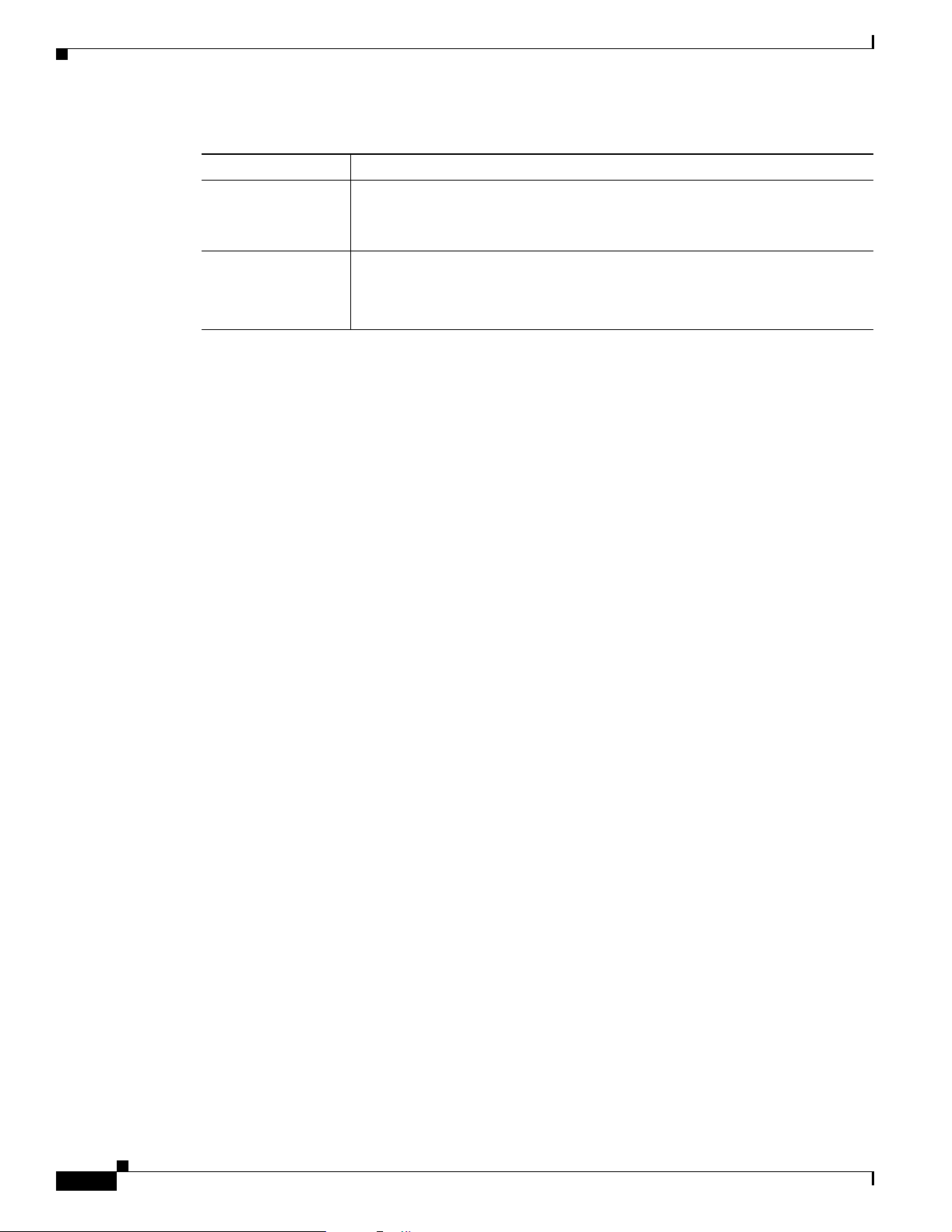
Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace System Configurations
Table 2-1 Components Needed to Integrate Video Conferencing in Cisco MeetingPlace (continued)
Component Functions
Video endpoints
Cisco CallManager
(Optional)
• Capture and transmit video images and audio from each user or location.
• Receive and display video images and audio from other video-conference
participants to the user or location.
On networks configured with Cisco CallManager:
• Allows SCCP endpoints to participate in Cisco MeetingPlace conferences.
• Routes traffic.
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace System Configurations
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace system configurations include the following. Complete system
requirements and a Cisco MeetingPlace version compatibility matrix are in the Release Note for
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3:
• One Cisco MeetingPlace 8100 series server.
• One or more Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway servers.
• Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing servers in any configuration that is supported in
Release 5.3. However, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration can be installed only on a single
Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing server.
• Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration installed on a Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing server.
If your system has a DMZ configuration, see Preparing to Install the Video Integration with DMZ
Configurations, page 3-17 for important considerations before installing
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. A DMZ configuration includes one or more servers in a
DMZ outside the corporate firewall.
• (Optional) Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook.
• (Optional) Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes.
• (Optional) Cisco MeetingPlace SMTP E-Mail Gateway.
The following additional components are also supported:
• One Cisco IPVC MCU with all components including an H.323 gatekeeper.
• (Optional) Cisco CallManager.
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
2-4
The process of creating, running, and terminating an integrated video, audio, and web conference is
described in this section.
Participants who are using audio-only devices connect to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
Participants with video equipment connect to the Cisco IPVC MCU, which processes both the video and
the audio channel of the video endpoints. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration mixes the audio streams
from both systems to allow all participants to hear and speak to each other. Figure 2-2 shows this process.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 17
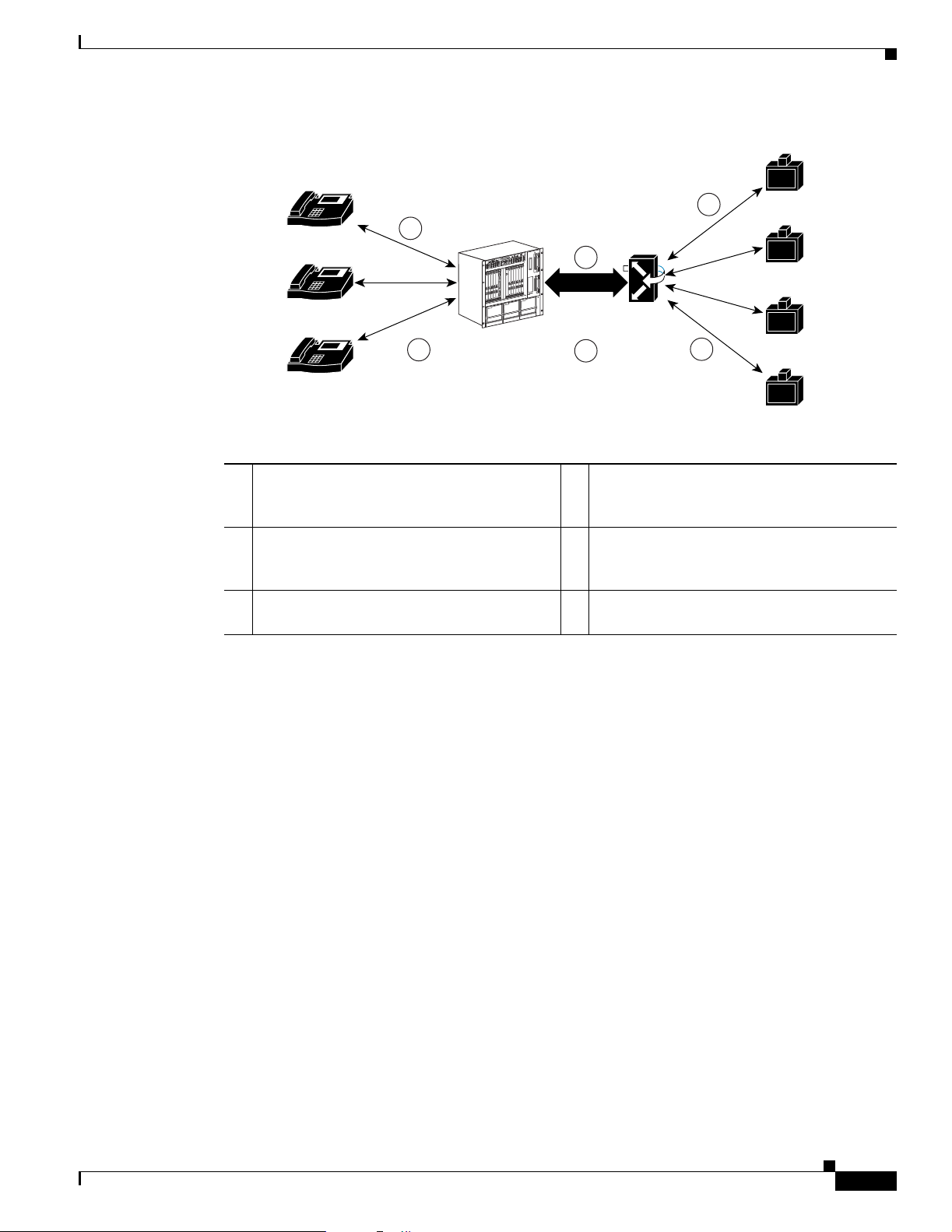
Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
Figure 2-2
Cisco
IP Phone
Cisco
IP Phone
Cisco
IP Phone
IP
IP
IP
1
MeetingPlace
audio server
6
Cisco
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
Video
endpoint
Cisco
IP/VC
MCU
2
5
3
Video
endpoint
Video
endpoint
4
Video
endpoint
92341
1 The audio of the telephone participants is
processed by the Cisco MeetingPlace audio
server.
2 The audio channels from telephone
participants are sent to join the audio on the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
3 Video participants hear the audio from
telephone participants.
How Video Conferences Are Scheduled
A user fills in a standard Cisco MeetingPlace conference scheduling form in Microsoft Outlook, Lotus
Notes, Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, or MeetingTime; then the user submits that form to
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. If the user has indicated that the conference will include video
participants, the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server verifies that resources are available, and if so,
schedules the requested number of video ports and (depending on system configuration) notifies
invitees.
About the Minimum Number of Video Ports Scheduled
In order to prevent more video conferences from being scheduled than the Cisco IPVC MCU can support
at one time, Cisco MeetingPlace may schedule more video ports than the meeting scheduler specifies for
a conference. The minimum number of ports that Cisco MeetingPlace schedules for each conference is
determined by the formula [(Total number of video conference ports - Number of video floater ports +
Number of video overbook ports)/ Total number of video conferences available]. If a user does not
schedule fewer ports than the number of ports resulting from this calculation, Cisco MeetingPlace
schedules the number of ports that the scheduler specifies. Floater and overbook ports are defined in
About Configuring Port Parameters, page 4-7.
4 The audio and video channels of the video
endpoints are processed by the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
5 The audio channels of the video endpoints are
sent to join the audio in Cisco MeetingPlace
audio conferencing.
6 Telephone participants hear the audio from
video endpoints.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
2-5
Page 18

About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
How Video Conferences Start
The Cisco IPVC MCU is configured to allow Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to control all H.323
video-conferencing resources and meeting operations on the Cisco IPVC MCU, including initiating
meetings. Cisco MeetingPlace does not control SCCP resources on the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Before a video conference can be started on the Cisco IPVC MCU, a Cisco MeetingPlace meeting must
exist on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. However, the meeting does not need to be scheduled in
advance; it can be scheduled as an immediate or reservationless meeting, as long as video ports and video
conferences are available at the time of the request.
The first Cisco MeetingPlace conference participant who joins the video conference initiates the creation
of the video conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration verifies that
the conference is currently in session or within the guard times of the existing meeting, then tells the
Cisco IPVC MCU to immediately create a video conference with the Meeting ID.
The Meeting ID for the video conference includes the MeetingPlace service prefix that identifies
Cisco MeetingPlace conferences on the Cisco IPVC MCU, plus the standard Cisco MeetingPlace
Meeting ID for that conference. This Meeting ID is used by the gatekeeper or Cisco CallManager to
route incoming calls for this conference over the network to the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Conferences cannot be created by dialing in to the Cisco IPVC MCU unless the meeting has been
scheduled on Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. If a participant dials in to the Cisco IPVC MCU to start
a conference, the Cisco IPVC MCU sends information about the new video conference to
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. If the conference has not been scheduled in Cisco MeetingPlace,
is not currently in session, or is outside the guard times of a scheduled meeting,
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tells the Cisco IPVC MCU not to create the conference.
Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
How the Link Between the Cisco IPVC MCU and the Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Is
Established
When the first video participant joins an authorized video conference, either by outdialing from the
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing meeting room or by dialing in to the Cisco IPVC MCU,
Cisco MeetingPlace creates the link that connects the audio channel of the video conference and the
audio channel of the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
To initiate this link, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tells the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server to
outdial to the Cisco IPVC MCU; the call is routed through the
Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway to Cisco CallManager or to the H.323 gatekeeper, either of
which has been configured to route the call to the Cisco IPVC MCU. Either the gatekeeper or the
Cisco IPVC MCU can route the call to the correct conference. The routing pattern (outdialed number)
for this transaction is composed of the service prefix that identifies Cisco MeetingPlace conferences on
the Cisco IPVC MCU (and also is unique among the routing patterns configured on the gatekeeper and
CallManager) plus the Cisco MeetingPlace Meeting ID of the conference.
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tries three times to establish this link.
After the link is established, the entire audio channel of the video conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU
becomes a participant in the Cisco MeetingPlace audio conference and vice versa.
Note The video link appears as a named participant in the in-session tab in MeetingTime, but not in the
Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. It also is included in some reports, but not all. See
About Video-Conferencing Statistics, page 4-13.
2-6
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 19

Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
After the link is established, all further communication between the Cisco IPVC MCU and the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server is handled through the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
component, which communicates with the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server through MPAgent.
MPAgent is a component of Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, which is a prerequisite to
installation of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
communicates with the Cisco IPVC MCU using proprietary XML messaging.
If the link between Cisco MeetingPlace and the Cisco IPVC MCU is disconnected,
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration attempts to reestablish it three times, checking every minute, or
when another participant joins the conference.
How Video Conference Participants Join Meetings
There are several ways additional participants can join the video conference. The process of adding
participants to the conference depends on how they enter the meeting.
If a Participant Joins a Scheduled Video Conference by Outdialing From the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Meeting
Room
When a participant clicks Connect from within Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, or in a calendar
entry in Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes, or in the MeetingPlace tab of a meeting notification in
Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration sends a message to the
Cisco IPVC MCU to outdial to the endpoint of the participant. When the participant has successfully
joined the video conference, the Cisco IPVC MCU notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, and
the status of the participant is recorded in the participant list that is displayed in the meeting room of
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing.
If a Participant Joins a Scheduled Video Conference by Dialing in to the Cisco IPVC MCU
Participants dial in to the conference from their video endpoint by using the number provided in the
Connect dialog box in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. This number is the
service prefix on the Cisco IPVC MCU that identifies Cisco MeetingPlace conferences, plus the
Cisco MeetingPlace Meeting ID. Cisco CallManager or the gatekeeper routes all incoming H.323 calls
that begin with the specified service prefix to the Cisco IPVC MCU, which routes each call to the correct
video conference based on the Cisco MeetingPlace meeting ID number portion of the number that was
dialed.
When participants attempt to join the video conference by dialing in from their video endpoint, the
Cisco IPVC MCU accepts the call only if the conference is not restricted to profiled or invited users and
does not require a password. (This is because the Cisco IPVC MCU cannot authenticate dial-in
participants.) If the participant is granted access, the Cisco IPVC MCU checks with
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to see if the meeting is in session and within the guard times. If
so, the Cisco IPVC MCU admits the participant to the video conference and notifies
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration that the participant has joined the conference.
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing and the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server of the status of the participant.
If a Participant Joins a Video Conference on an Ad-Hoc Basis
If all scheduled video-conferencing ports for a meeting that is already in progress are already in use and
an additional participant attempts to join the video conference, the user may be able to join on an ad-hoc
basis. In this case, the Cisco IPVC MCU polls Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to see if
video-conferencing ports are available, and if they are, the Cisco IPVC MCU allows the participant to
join the conference.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
2-7
Page 20

About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
How Video Conferences Run
About the Video Images
The visual stream to and from the video endpoints is entirely processed by the Cisco IPVC MCU. After
the call is connected, the media stream is routed from the video endpoint, through the Cisco IPVC MCU
for processing into a unified video stream, and back to the video endpoints for display to the users.
However, users control the status of the transmission (for example, started, paused, or terminated) from
within the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. See About Displaying the Status and
Options of Video Participants in the Meeting Room, page 2-8.
About the Audio Channel
The audio streams of the Cisco IPVC MCU and Cisco MeetingPlace are mixed to allow audio and
video-conferencing participants to hear and speak to each other. The audio channel from each video
endpoint is routed to the Cisco IPVC MCU, then passed through the video link to the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server, where it is mixed with the audio from audio-only endpoints and sent
back to all users, to form a seamless audio experience for participants on both video and audio-only
endpoints.
Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
About Displaying the Status and Options of Video Participants in the Meeting Room
When the Cisco IPVC MCU admits a participant to a video conference, the Cisco IPVC MCU notifies
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, which notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing.
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing identifies the participant as a video participant in the participant
list in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. The participant name displayed comes
from the participant’s profile or guest information if they outdialed from Cisco MeetingPlace, and from
the gatekeeper if they dialed in to the video conference. When a participant mutes, pauses, changes the
view of, or terminates their video connection, Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing registers this
change in the meeting room user interface and passes the request to
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, which passes the request to the Cisco IPVC MCU where it is
performed. If the user terminates the connection by hanging up the video endpoint, the
Cisco IPVC MCU notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, which then notifies
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing so that the status of that participant can be updated.
When a video participant speaks, the Now Speaking display shows “Video Participant.”
How Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Tracks Port Availability
The number of available ports and conferences is determined by the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration polls the Cisco IPVC MCU every 30 minutes for this information
and passes it to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server, which displays it in MeetingTime.
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration uses this information to regulate the creation of and entry to video
conferences.
2-8
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 21

Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
How Video Conferences End
The video conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU ends when the Cisco MeetingPlace conference ends,
according to the standard rules for ending conferences on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. At this
time, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tells the Cisco IPVC MCU to terminate the video
conference.
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
2-9
Page 22

About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
Chapter 2 Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
2-10
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 23

Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Perform the following tasks to set up Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration:
• Before You Install, page 3-1
• Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, page 3-18
• Uninstalling Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, page 3-19
Before You Install
Complete the following tasks in order before you run the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
installer:
• Making Sure Component Systems Are Up and Running, page 3-1
• Verifying your Video-Conferencing License, page 3-2
CHAPTER
3
• About Configuring the Cisco IPVC MCU to Use Cisco MeetingPlace, page 3-2
• Configuring the Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server, page 3-11
• Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway, page 3-12
• Configuring Load-Balancing Configurations for Video Conferencing, page 3-12
• About Installing and Configuring Video Endpoints, page 3-13
• (Optional) Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook, page 3-14
• (Optional) Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes, page 3-14
• Configuring Cisco CallManager, page 3-14
• Preparing to Install the Video Integration with DMZ Configurations, page 3-17
• Gathering Installation Values, page 3-18
Making Sure Component Systems Are Up and Running
Several component systems must be working independently before you prepare to install
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
Step 1 Make sure that the following are true:
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-1
Page 24

Before You Install
• Release 5.3 of the Cisco MeetingPlace system is up and running, including Cisco MeetingPlace
audio server and Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing.
• All video endpoints that your organization supports (H.323, SCCP, and ISDN) can successfully
participate in video conferences on the Cisco IPVC MCU. Endpoints must be able to join both by
dialing in and by having the Cisco IPVC MCU call the endpoint.
Verifying your Video-Conferencing License
Make sure your Cisco MeetingPlace system is licensed for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
The Cisco MeetingPlace MeetingTime utility is fully documented in the Administrator’s Guide for
Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3.
Step 1 In MeetingTime, click the Configure tab, then click System Options.
Step 2 Click Query.
Step 3 Click the > button until you see Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 4 Number of licenses should be 1. If it is 0 (zero) contact your Cisco technical support representative. See
the Guide to Cisco Conferencing Documentation and Support.
About Configuring the Cisco IPVC MCU to Use Cisco MeetingPlace
Before you configure the Cisco IPVC MCU for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, make sure that
the Cisco IPVC MCU is working independently of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration and can host
and manage video conferences.
For detailed information about video-conferencing parameters, see the Cisco IPVC MCU
documentation, including the Release Notes: Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU
Module Administrator Guide, Version 3.2 and Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU
Module Release Notes for Release 3.5.
All H.323 resources on the Cisco IPVC MCU are dedicated to a single Cisco MeetingPlace service, and
Cisco MeetingPlace controls all H.323 resources on the Cisco IPVC MCU. However, conferences can
be created using SCCP (SKINNY protocol), and Cisco MeetingPlace does not control those conferences.
Cisco IPVC MCU resources will be shared between the Cisco MeetingPlace service and any SCCP
services.
The unique service prefix associated with the Cisco MeetingPlace service will be used to route callers
to the Cisco IPVC MCU and must not conflict with other routing patterns in the gatekeeper or
Cisco CallManager.
3-2
The following optional cards for the Cisco IPVC MCU are not supported:
• Rate Matching card
• Data Conferencing card
If your Cisco MeetingPlace audio server is configured to use only G.729, make sure the
Cisco IPVC MCU is configured to support G.729. A transcoder card may be needed. For information
about specifying an audio codec, see the online help for the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 25

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
We do not recommend changing settings in the Cisco IPVC MCU after users have begun to schedule
conferences via Cisco MeetingPlace if such changes reduce the number of available video conferences
or ports. Before changing the settings in the Cisco IPVC MCU, see Changing Settings in Other
Components, page 4-3.
To configure your Cisco IPVC MCU to provide video content for Cisco MeetingPlace conferences, you
must do the following in this order:
Step 1 Verify that all video endpoints can connect to a conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU, and that the
Cisco IPVC MCU can call out to all video endpoints.
Step 2 Create a Cisco IPVC MCU user for Cisco MeetingPlace.
Step 3 Set Cisco IPVC MCU management parameters that are required to support Cisco MeetingPlace:
–
Reserve ports for Cisco MeetingPlace conferences.
–
Specify that only authorized users can use the Cisco IPVC MCU to create video conferences.
In this case, only Cisco MeetingPlace will be authorized to create video conferences.
–
Enable the Cisco IPVC MCU to generate an announcement for the Cisco MeetingPlace Waiting
Room.
Step 4 Create a Cisco IPVC MCU service for Cisco MeetingPlace.
Before You Install
Note You cannot stack embedded Cisco IPVC media processors to use with Cisco MeetingPlace.
Verifying that Video Endpoints Can Connect to the Cisco IPVC MCU
Endpoints must be able to join video conferences on the Cisco IPVC MCU before
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration can run.
If you have questions about routing calls through the gatekeeper and you use a Cisco IOS H.323
Gatekeeper, see the Cisco IOS H.323 Configuration Guide.
Step 1 Follow the instructions in the documentation for your Cisco IPVC MCU to have each video endpoint dial
in to a video conference.
Step 2 Follow the instructions in the documentation for your Cisco IPVC MCU to have the Cisco IPVC MCU
call each video endpoint.
Creating a Cisco IPVC MCU User for Cisco MeetingPlace
Create a username and password that Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration will use to log in to the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
Step 1 Log in to the Cisco IP/VC Administrator of the Cisco IPVC MCU that you want Cisco MeetingPlace to
use.
OL-6280-01
Step 2 Click Board or Device on the sidebar.
Step 3 Click the Users tab.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-3
Page 26

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Before You Install
Step 4 Click the Add button.
The Add User dialog box appears.
Step 5 In the “User name” field, enter the name that you want the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
server to use to log in to the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Step 6 In the “Access level” field, click Administrator or Operator.
Step 7 In the Password field, enter the password that you want this user to have.
Step 8 In the “Confirm Password” field, enter the password that you want Cisco MeetingPlace to use.
Step 9 To disable the ability of this user to telnet into the Cisco IPVC MCU, uncheck Enable for Telnet / FTP.
Step 10 To save this user profile, click Upload.
Setting Cisco IPVC MCU Parameters Required to Support Cisco MeetingPlace
To use your Cisco IPVC MCU with Cisco MeetingPlace, you must configure certain Cisco IPVC MCU
parameters to provide video for Cisco MeetingPlace conferences.
For more information about configuring the Cisco IPVC MCU for operation, see Cisco IP/VC 3511
MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Administrator Guide, Version 3.2.
Step 1 Log in to the Cisco IP/VC Administrator of the Cisco IPVC MCU that you want the Cisco MeetingPlace
server to use.
Step 2 Choose MCU > Settings > Basics.
Step 3 In the MCU field, click MCU.
Step 4 In the “Number of SCCP ports” field, select a value for the number of ports that you want
Cisco CallManager to use that leaves ports available for Cisco MeetingPlace.
For example, for a 60-port Cisco IPVC MCU select 0, 15, 30, or 45.
Step 5 Click the Conference Mgmt button.
Step 6 Set the following parameters in the Conference Mgmt page:
a. In the “External conference authorization policy” field, click Authorize.
b. In the “Allow conference creation using” field, click Scheduler, Web, Control API and dial-in.
c. In the “Allow conference joining using” field, click Invite and dial-in.
d. In the “Dial-in conference terminates when” field, click Last participant leaves.
Step 7 Click the Advance button.
Step 8 We recommend that you check Disconnect participants on communications (ICMP) failure and click
Audio failure in the “Disconnect on” field.
Step 9 To save these settings to memory, click Upload.
3-4
Setting the Audio Indication Interval (Optional)
If video participants join a conference that has not yet started, they must wait in the waiting room. To
play an announcement while participants wait, set the following parameter:
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 27

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 1 Click MCU, then click Settings.
Step 2 Click the Advanced button.
Step 3 Click the Commands button.
The Advanced Command dialog box appears.
Step 4 In the Advanced Command dialog box, do the following:
a. In the Available commands window, click Audio indication interval.
Your selection appears in the Command field.
b. In the Parameter field, enter the value in milliseconds that you want Cisco MeetingPlace to
announce to video participants that they are in the waiting room and that the conference has not
formally started.
Tip We recommend entering 1500 to establish an interval of 15 seconds.
c. Click Send, then click Close.
Before You Install
Creating a Service for Cisco MeetingPlace
You must create a Cisco IPVC MCU service for Cisco MeetingPlace. Before you create a service in the
Cisco IPVC MCU make sure that the media processor (MP) that the Cisco IPVC MCU uses supports
Cisco MeetingPlace.
Table 3 -1 provides information about which Cisco IPVC media processors support Cisco MeetingPlace.
Table 3-1 Media Processors That Support Video in Cisco MeetingPlace, Release 5.3
Cisco IPVC Media Processor
Local Cisco IPVC MCU media
processor
Cisco IPVC EMP Release 2.0.11 or later releases
Cisco IPVC Rate Matching module Does not support Cisco MeetingPlace
Data Conferencing Card Does not support Cisco MeetingPlace.
You can use one of the preconfigured Cisco MeetingPlace service templates or manually create a
Cisco MeetingPlace service.
Using Preconfigured Service Templates
Software Supporting
Cisco MeetingPlace
Release 3.5.24 or later releases
OL-6280-01
Cisco IPVC MCU, Release 3.5.24 includes three preconfigured services that are designed for Cisco
MeetingPlace.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-5
Page 28

Before You Install
Note The Cisco MeetingPlace service prefixes appear automatically on the IP/VC Administrator Services
Step 1 Run the Cisco IPVC MCU installer.
Step 2 At the first install screen, click Customize.
Step 3 Check the MCU Config File check box.
Step 4 Continue with the installation.
Step 5 After installation, log in to the Cisco IPVC MCU as administrator.
Step 6 Click MCU on the sidebar and click the Services tab.
Step 7 In the Services tab, choose the appropriate template for your needs. Voice Activated allows participants
Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
page for new Cisco IPVC MCUs. However, these services do not appear when you upgrade your
Cisco IPVC MCU to Release 3.5.24. To display these services, you must use the restore factory defaults
option. In doing so, you will lose your current configuration.
To install the Cisco MeetingPlace service templates on an existing Cisco IPVC MCU installation and
erase existing services:
to View Active Speaker, while Continuous Presence allows participants to View Multiple People. These
settings are available to participants in the web-conferencing meeting room:
Service Prefix Supported Views
887 Voice Activated and
888 Voice Activated SCCP,
889 Voice Activated and
Step 8 Review the remaining topics in About Configuring the Cisco IPVC MCU to Use Cisco MeetingPlace
and make additional configurations as required for your needs.
Creating a Service Manually
To create a Cisco IPVC MCU service for Cisco MeetingPlace, do the following tasks:
• Setting the Core Service Parameters, page 3-7
• Setting Audio Indications, page 3-7
• Making Sure that a Conference Password Is Not Required, page 3-8
• Setting Conference View Parameters, page 3-8
Continuous Presence
Continuous Presence
Supported
Endpoints
Processors
Required Format
Allow Dynamic
Scheme
H.323 MP H.261 Unchecked
MP H.263 Checked
H.323
SCCP,
H.323
MP and
EMP
H.263 Checked for both
views
3-6
• Setting Video Schemes Parameters, page 3-10
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 29

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Setting the Core Service Parameters
Step 1 Click MCU on the sidebar and click the Services tab.
Step 2 Click the Add button.
The Select Service dialog box appears.
Step 3 To create a new service, click OK.
The Add Service dialog box appears.
Step 4 In the “Service prefix” field, enter the value that you want to use for the Cisco MeetingPlace service.
Step 5 Uncheck the SCCP Service check box. Users of SCCP endpoints can still attend Cisco MeetingPlace
conferences.
Step 6 In the “Service description,” enter the description for this service that you want to appear on the Create
Conference page.
Step 7 In the “Media types” section, check Video.
Note Cisco MeetingPlace provides data collaboration in conferences. Disable data collaboration in
the Cisco IPVC MCU if it is currently enabled.
Before You Install
Step 8 Specify the number of ports that you want the Cisco IPVC MCU to reserve for each conference as
follows:
a. In the “Reserved number of parties” field, enter 2.
Tip You can ascertain the maximum number of ports this service can support by entering 200 in the
b. In the “Maximum number of parties” field, enter the total number of Cisco IPVC MCU ports that
Setting Audio Indications
We recommend that you enable all audio-indication parameters.
Step 1 Click the Indications button.
Note One of these ports is reserved for the Cisco MeetingPlace server.
“Maximum number of parties” field and choosing OK at the bottom of the page. The error
message that appears indicates the maximum number of ports the current configuration allows
based on the video bandwidth value specified in the Conference Views section.
are available for conferences.
OL-6280-01
The Indications Settings dialog box appears.
Step 2 Make sure that all parameters are checked.
Step 3 Click OK.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-7
Page 30

Before You Install
Making Sure that a Conference Password Is Not Required
Step 1 Click the Management button.
The Management Settings dialog box appears.
Step 2 Make sure that password-related parameters are unchecked.
Step 3 Click OK.
The Add Services dialog box appears.
Setting Conference View Parameters
When you set view parameters, use the Cisco MeetingPlace service template as a model. The templates
are described in Using Preconfigured Service Templates, page 3-5. A Voice Activated view allows
participants to View Active Speaker, while a Continuous Presence view allows participants to View
Multiple People.
Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Note • One Voice Activated, 1-participant layout is required. A Continuous Presence view is optional, if
your hardware supports it.
• Do not create multiple identical views for a single service code. Each view must be unique.
General Instructions for Setting View Parameters
Step 1 Click the edit view icon.
The Edit View dialog box appears.
Step 2 In the “Use Processor” field, click the type of media processor that you want this service to use.
Note The MP and RM option does not support Cisco MeetingPlace.
• Click MP to specify that the service only uses the local media processor to process video conference
calls.
• Click EMP to specify that the service uses the Cisco IPVC Enhanced Media Processor (EMP)
register with the Cisco IPVC MCU to process video conference calls.
• Click Auto to allow the Cisco IPVC MCU to choose the media processor the Cisco IPVC MCU will
use to process a specific video conference.
3-8
Note See Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Administrator Guide,
Version 3.2 for information about registering a media processor with the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Step 3 In the “Video Picture Size” field, click the video format that you anticipate most endpoints will use.
Step 4 To enable the Cisco IPVC MCU to switch the video to the speaker who is speaking the loudest, check
Enable voice activate.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 31

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 5 In the “Voice activate method” field, we recommend that you click All see one to have all participants
see the current speaker.
Step 6 To disable automatic switching of nonspeaking participants, uncheck Enable auto-switch.
Step 7 To save these conference-view parameters and to close the Edit View dialog box, click OK.
Special Instructions for Accommodating SCCP Endpoints
Because SCCP endpoints require the H.263 format, special view settings are required. To set up views,
use the table in Using Preconfigured Service Templates, page 3-5 as a model for setting parameters, or
use the appropriate procedure from this section.
If your users will attend via SCCP endpoints and your Cisco IPVC MCU has only an MP card, only the
Voice Activated view can be used. In this case, all participants will be able to use only the View Active
Speaker option available in the Cisco MeetingPlace meeting room. They will not be able to view multiple
people simultaneously.
Creating a Single Voice Activated View
Before You Install
Step 1 The default view should have the correct parameter settings. Verify that the settings are as follows:
Parameter Value
Initial Layout 1-participant layout
Max Layout 1-participant layout
Use Processor MP
Format (in the Video Schemes Settings section) H.263
Other parameters As desired
Step 2 Click OK.
If your users will attend via SCCP endpoints and you have both an MP card and an EMP card, in order
for participants to be able to use both the View Active Speaker and the View Multiple People options
that are available in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room, both views are required.
The View Active Speaker option corresponds to the Voice Activated view, and View Multiple People
corresponds to the Continuous Presence view.
Creating Two Separate Views
OL-6280-01
Step 1 In the service, click the Views button to create the first view.
Step 2 Set the following parameters for this view:
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-9
Page 32

Before You Install
Step 3 Click OK.
Step 4 Check the Display all conference views check box.
Step 5 Click Add View.
Step 6 Set the following parameters for the second view:
Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Parameter Value
Initial Layout Desired multiple participant layout (for example,
4 participant)
Max Layout Desired multiple participant layout (for example,
4 participant)
Use Processor EMP
Format (in the Video Schemes Settings section) H.263
Other parameters As desired
Parameter Value
Initial Layout 1-participant layout
Max Layout 1-participant layout
Use Processor MP
Format (in the Video Schemes Settings section) H.263
Other parameters As desired
Step 7 Click OK.
Setting Video Schemes Parameters
Step 1 Select the “Video Settings Schemes” profile that you want to edit and click the Edit button.
The Edit Video Scheme dialog box appears.
Step 2 In the “Max bit rate” field, click the maximum video bandwidth that you want this service to support.
This number must be less than or equal to the bandwidth settings in Cisco MeetingPlace (and in
Cisco CallManager, if your network uses Cisco CallManager.)
Note Endpoints that are not capable of supporting this bandwidth receive only the conference audio
unless dynamic scheme is allowed.
3-10
Step 3 Check Allow dynamic scheme to enable the Cisco IPVC MCU to switch the conference video
bandwidth to a lower value when a less capable endpoint joins the conference.
• In the “Min bit rate” field, click the lowest bandwidth that you want this parameter to support.
Step 4 To save these Video Scheme changes and to close this dialog box, click OK.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 33

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 5 To save these conference-view parameters and to close the Edit View dialog box, click OK.
Saving Your Service
To save your service, click OK at the bottom of the Service page.
Configuring the Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server
Perform the following tasks before you install Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
Modifying the Translation Table
Step 1 If your Cisco MeetingPlace system supports IP phones only, you do not need to change the translation
table on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
If your Cisco MeetingPlace audio server is configured for both PSTN and IP interfaces, and your
organization does not have a certified Cisco MeetingPlace technician, contact Cisco MeetingPlace
Professional Services to modify the translation table in Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. For
information, contact your Cisco technical support representative. See the Guide to Cisco Conferencing
Documentation and Support.
Before You Install
About Setting the Audio Codec Negotiation Priority
Sound quality and bandwidth use are determined partly by the audio codec that the Cisco MeetingPlace
and Cisco IPVC systems use. The video endpoint’s video signal and its audio channel must share
available bandwidth. As a result, better picture quality may degrade audio quality or delay audio
transmission.
The Cisco MeetingPlace audio server supports the G.711 and G.729a compression codecs. To allocate
resources between audio and video to best meet your needs, specify a voice data compression protocol
in Cisco MeetingPlace audio server using the setipcodec command. For instructions, see the
Configuration Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3. Use the following guideline:
• To make more bandwidth available for video, assign G.729 the highest priority.
• For better audio sound quality, assign G.711 the highest priority.
Supporting G.729
Step 1 If Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server is configured to use only G.729, make sure the Cisco IPVC MCU
is configured to support G.729. A transcoder card may be needed.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-11
Page 34

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Before You Install
Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
The Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway connects the Cisco MeetingPlace system to the network.
Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway also initiates the call that connects the Cisco MeetingPlace
audio server with the Cisco IPVC MCU.
• If your MeetingPlace system currently supports Cisco IP telephony, you do not need to make further
changes to the Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway.
• If your network includes Cisco CallManager and you have not yet configured the Cisco
MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway and Cisco CallManager to route calls to each other, see
instructions in the Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
Release 5.2.1.
• If Cisco CallManager is not part of your network environment, MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
can register itself directly to the H.323 gatekeeper. For instructions on configuring the
Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway for use with an H.323 gatekeeper, see the
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Release 5.2.1. If it is
correctly configured, the H.323/SIP IP Gateway appears in the endpoint registration table in the
gatekeeper.
If your Cisco MeetingPlace system includes more than one Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway, and if the gateways are connecting to a gatekeeper, the E.164 number of each
MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway must be unique. (The E.164 numbers do not need to be unique
if they connect to Cisco CallManager.)
Step 1 If the Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway is not already connected to your network, use the
information in this section to configure all necessary components.
Configuring Load-Balancing Configurations for Video Conferencing
In Cisco MeetingPlace deployments for large numbers of users, multiple
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing servers can be configured in clusters, and meetings are
distributed among the servers in a cluster. However, you can install
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration on only one of those Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
servers, and meetings that include video conferencing must be held on that server.
Meetings that are scheduled with video ports are automatically held on the server that has
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration installed on it. However, in order to ensure that ad-hoc video
conferences can occur, configure Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing so that meetings that are
scheduled by users whose profiles allow them to schedule video conferences are always hosted on the
server that has Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration installed on it.
If your Cisco MeetingPlace system is configured for load balancing, set the system to allow ad-hoc video
conferencing.
Note Perform the following steps even if Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is not installed on a server in
a cluster that includes load balancing.
3-12
Step 1 Sign in to the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing interface using your System Manager password.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 35

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 2 Click Admin.
Step 3 Click Site Properties.
Step 4 On the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Administration page for your site, set Allow Web Load
Balancing in Ad Hoc Video Meetings to No.
How Load Balancing Works
If the server with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is not available at the start of a conference, the
meeting rolls to another server after 5 times the Load Stats Poll Period value on the
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Site Administration page. The Load Stats Poll Period
parameter defaults to 1 minute. In this situation, video conferencing is not possible, but data and voice
conferencing are available as usual.
If you do not set this option to No, all web conferences will be load-balanced. Video conferencing will
not be available to conferences that are held on web-conferencing servers other than the one on which
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is installed.
For general information about load-balancing configurations, see the Administrator’s Guide for
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Release 5.3.
Before You Install
About Installing and Configuring Video Endpoints
Video endpoints are the hardware and software that capture, send, receive, and display video images and
audio. They can be either of the following:
• Room-based video systems.
• Desktop video systems, for example, a digital camera that is attached to the computer or IP phone
of an individual user, and software to display images on the computer screen.
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration supports all video endpoints that are supported by
Cisco IPVC MCU version 3.5plus. SCCP video endpoints (such as Cisco VT Advantage) require
Cisco CallManager. ISDN video endpoints require a Cisco IPVC PRI Gateway as part of the
Cisco IPVC MCU configuration. All endpoints must be able to participate successfully in a video
conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU independently of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
If Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server is configured to use only G.729, make sure your Cisco IPVC MCU
supports this protocol.
If an endpoint is correctly configured to work with the Cisco IPVC MCU and configured to optimize
audio quality according to the documentation that came with the product, no additional configuration is
required for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. To optimize sound quality, see the tips in the
troubleshooting section on Problems During a Video Conference, page 6-7.
To set up Cisco VT Advantage endpoints, see the Cisco VT Advantage Administration Guide.
Because SCCP endpoints do not support the H.261 protocol, they support View Multiple People mode
only if the Cisco IPVC MCU has an EMP processor and you have configured views on the
Cisco IPVC MCU to support Continuous Presence according to instructions in Setting Conference View
Parameters, page 3-8.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-13
Page 36

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Before You Install
(Optional) Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook
If your Cisco MeetingPlace system includes Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook, perform the tasks in this
section. If not, skip this section.
Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook generates meeting notifications that users receive when they are invited
to a meeting. These notifications are generated from templates that you can optionally customize.
For complete information about customizing meeting notification templates, see the Administrator’s
Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook Release 5.3.
When the system includes Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, three video-specific templates are
used. By default, these templates include parameters for dial in numbers for IP and ISDN video
endpoints. They also direct users to join the web conference first, then join the video or voice conference.
(This is the preferred method. Users who join the video conference from within the web conference have
full access to the video controls and features in the web-conferencing meeting room.)
You can remove information that is not applicable, or add special instructions or other information that
your users can use to attend conferences that include video.
Step 1 Examine the three video-specific notification templates to determine whether they have by default the
information that your video users need.
Step 2 If not, customize the video-related meeting notifications.
(Optional) Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes
If your Cisco MeetingPlace system includes Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes, perform the tasks in
this section. If not, skip this section.
The following steps provide a general overview. For complete instructions, see the Administrator’s
Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes Release 5.3.
Step 1 Configure the video-related settings in the MeetingPlace Server Agent database (MPSA.nsf):
• MeetingPlace Functionality Settings
–
Hide # of Video Callers Field
–
Make Meetings Web Only
• MeetingPlace Scheduling Parameters
–
# of Video Ports to Schedule
Configuring Cisco CallManager
If your environment does not include Cisco CallManager, skip this section and follow instructions in
Configuring Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway, page 3-12 to route calls to and from
Cisco MeetingPlace via the H.323 gatekeeper.
If your environment includes Cisco CallManager, set up Cisco CallManager to route calls between the
components involved in integrating video conferencing with Cisco MeetingPlace.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-14
OL-6280-01
Page 37

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
There are many ways to set up Cisco CallManager to work with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
For example, you can use the guidelines in the Cisco IP Video Telephony Solution Reference Network
Design to set up Cisco CallManager to route all calls, or you can follow the example in this section to
have the gatekeeper route H.323 calls. The best solution will depend on your network environment and
requirements. Determining the best configuration of Cisco CallManager for your network is beyond the
scope of this document; see the documentation for Cisco CallManager or contact your Cisco technical
support representative. See the Guide to Cisco Conferencing Documentation and Support.
Note If your Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway is not yet configured for use with Cisco CallManager,
see the Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway, Release 5.2.1 for
configuration instructions.
To set up Cisco CallManager if you use a gatekeeper to route calls, perform the following general steps:
Step 1 Create a gatekeeper device that points to the gatekeeper associated with the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Step 2 Create an H.225 (Gatekeeper Controlled) trunk for the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Step 3 Create a route pattern to route calls to the H.225 (Gatekeeper Controlled) trunk for the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
Before You Install
Gathering Configuration Values
Step 1 Make a note of the following:
• The service code for Cisco MeetingPlace conferences that you specified in the Cisco IPVC MCU.
• The IP address or hostname of the Cisco IPVC MCU.
• The IP address or hostname of the H.323 gatekeeper.
Adding an H.323 Gatekeeper
Step 1 Launch and log in to the Cisco CallManager Administration interface.
Step 2 Choose Device > Gatekeeper.
Step 3 Click Add a New Gatekeeper.
Step 4 Enter options:
Field Value
Host Name / IP Address IP address of the gatekeeper that your
Description A name that identifies this gatekeeper.
Enable Device Check the check box.
Other options Values as appropriate for your environment.
Cisco IPVC MCU is registered to.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-15
Page 38

Before You Install
Step 5 Click Insert.
Creating an H.225 Trunk for the Cisco IPVC MCU
Step 1 From the Cisco CallManager Administration menu bar, choose Device > Trunk.
Step 2 Click Add a New Trunk.
Step 3 For Trunk Type, choose H.225 (Gatekeeper Controlled).
Step 4 Click Next.
Step 5 Enter options:
Field Value
Device Name The IP address of your Cisco IPVC MCU.
Description A name that identifies this trunk.
Retry Video Call as Audio Check the check box.
Wait for Far End H.245 Terminal Capability Set Check the check box.
Gatekeeper Name The IP address of the gatekeeper to which your
Terminal Type Gateway
Technology Prefix The prefix or pattern that will route calls to
Other parameters Values as appropriate for your environment.
Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Cisco IPVC MCU is registered.
Cisco CallManager.
Step 6 Click Insert.
Step 7 Click OK.
Step 8 Click Reset Trunk.
Adding the Route Pattern to Route Calls to the Cisco IPVC MCU
Step 1 From the Cisco CallManager Administration menu bar, do one of the following:
• In Cisco CallManager 4.0, choose Route Plan > Route Pattern/Hunt Pilot.
• In Cisco CallManager 4.1, choose Route Plan > Route /Hunt > Route Pattern.
Step 2 Click Add a New Route Pattern/Hunt Pilot.
Step 3 Enter options:
3-16
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 39

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Parameter Value
Route Pattern/Hunt Pilot The MeetingPlace service prefix you defined on
Description The MeetingPlace Service on the
Cisco CallManager 4.0:
Gateway or Route/Hunt List
Cisco CallManager 4.1:
Gateway or Route List
Provide Outside Dialtone Uncheck this check box.
Other parameters. Values as appropriate for your environment.
Step 4 Click Insert.
Before You Install
the Cisco IPVC MCU, followed by an
exclamation point (!).
Cisco IPVC MCU, or a different name that
describes this route pattern.
The IP address or hostname of the H225 Trunk
(Gatekeeper Controlled) that you created.
Preparing to Install the Video Integration with DMZ Configurations
A DMZ is an area on the corporate network that is outside the corporate firewall. In order to allow
external participants to attend Cisco MeetingPlace conferences without compromising security, one or
more Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing servers are deployed behind the firewall, and one or more
web-conferencing servers are deployed in a DMZ. These configurations are called “segmented meeting
access” (SMA) configurations; they are described fully in the Administrator’s Guide for
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Release 5.3.
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration must be installed on one and only one server on which
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing is installed:
• If it is installed behind the firewall, only internal participants can attend video conferences.
• If it is installed in the DMZ, external participants can also attend.
Note • If Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is installed in the DMZ, meeting schedulers must allow
Internet access for all conferences that will include video, even if only internal participants will
attend. The web and video conferences will be held on the server in the DMZ.
• If Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is installed behind the firewall in a DMZ configuration,
users cannot include video conferencing in a meeting that also includes web-conferencing
participants who are outside the firewall.
• Additional caveats apply. See Important Information About DMZ Configurations and Video
Conferencing, page 4-12.
OL-6280-01
Step 1 Use the information in this section to decide whether you will install
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration behind the firewall or in the DMZ.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-17
Page 40

Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 2 If you will install Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration in the DMZ, and if the Cisco IPVC MCU is
installed behind the firewall, open TCP port 3336 through the firewall to allow you to connect
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Gathering Installation Values
You need to know the following in order to install Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration:
Item Value
IP address or host name of the Cisco IPVC MCU.
The unique, dedicated service prefix that
identifies Cisco MeetingPlace conferences on the
Cisco IPVC MCU. This number must not
coincide with other routing patterns that are
registered with Cisco CallManager or the H.323
gatekeeper.
Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
The operator or administrator account user name
and password on the Cisco IPVC MCU that
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration will use to
control video conferences.
The E.164 number or numbers assigned to the
Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateways.
If more than one Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP
IP Gateway is connected to the same
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server, each IP
Gateway must have a unique E.164 number. List
up to five E.164 numbers, each separated by a
semicolon (;).
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 1 Make sure you have completed all prerequisite tasks documented in this chapter.
Step 2 Make sure Cisco MeetingPlace is not in use. The Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration installer will
stop the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing master service and all subordinate services.
Step 3 Make sure Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Release 5.3 is installed on the server on which you
will install Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
3-18
Step 4 Make sure that the Cisco IPVC MCU is available on the network (reachable via its IP address).
Step 5 Run the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Setup.exe and follow the prompts: Enter the values that
you collected in Gathering Installation Values, page 3-18.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 41

Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Step 6 All Cisco MeetingPlace services will restart automatically after the installation is complete. Click the
refresh button in the Services window to update the view.
Step 7 To see if your system is configured correctly, click the orange Cisco MeetingPlace icon in the system
tray at the bottom of the computer screen and choose Eventlog.
If the installation is configured properly, this message appears:
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration -> CConferenceTechnologyProvider::initialize()
STATUS: Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration READY to receive requests from MPAgent
Step 8 Configure the following parameters:
Parameter See
If your Cisco IPVC system supports ISDN
endpoints, configure the video phone number.
Floater and overbook ports. About Configuring Port Parameters, page 4-7
The maximum number of video ports that users
can schedule for a conference.
The default number of video ports to schedule for
each conference.
User profiles. About Managing User Profiles for Video Use,
Uninstalling Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
.
Tabl e 4- 1 , Video Conferencing Access
Information
Tabl e 4- 2 , Conference and Port Parameters
Tabl e 4- 2 , Conference and Port Parameters
page 4-10
Uninstalling Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
To uninstall Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, use Add/Remove Programs in the Control Panel, or
run the installer again.
The uninstall process will automatically stop the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing service and
other Cisco MeetingPlace services including the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration service.
If you plan to reinstall Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing and
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, uninstall Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration first; then
uninstall Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing.
All services will automatically start again when the uninstallation is complete.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
3-19
Page 42

Uninstalling Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Chapter 3 Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
3-20
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 43

CHAPTER
Configuring and Managing
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
This chapter contains the following information:
• About the Cisco MeetingPlace MeetingTime Software Application, page 4-1
• About Video-Conferencing Access Information, page 4-1
• About Changing System Configuration Settings, page 4-2
• About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources, page 4-4
• About Managing User Profiles for Video Use, page 4-10
• About Video-Conferencing Statistics, page 4-13
About the Cisco MeetingPlace MeetingTime Software
4
Application
Some parameters relevant to Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration can be viewed or modified in
Cisco MeetingPlace MeetingTime, the PC-based utility for the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. For
complete information about MeetingTime, see the Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Audio
Server Release 5.3.
Only parameters in MeetingTime that specify “video” apply to video conferencing.
About Video-Conferencing Access Information
Each video conference is identified by a code that is composed of two numbers:
• The service prefix of the service you defined on the Cisco IPVC MCU that is dedicated to
Cisco MeetingPlace conferences
• The Cisco MeetingPlace Meeting ID
For example, if the Cisco MeetingPlace service prefix is 67 and the Cisco MeetingPlace conference ID
of a conference is 1234, then the corresponding video conference is identified as 671234.
Cisco CallManager and the gatekeeper use this number to route participants through the network to the
Cisco IPVC MCU, and then the gatekeeper or the Cisco IPVC MCU uses the Meeting ID part of this
number to direct callers to the correct conference.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-1
Page 44

About Changing System Configuration Settings
Users of ISDN video endpoints dial in using an ordinary E.164 number, wait for an IVR prompt, then
enter the code for the conference they want to attend.
Table 4-1 Video Conferencing Access Information
Parameter Values Where Specified
Video Service Code The service prefix that is assigned
Main video phone
number
Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
to the dedicated MeetingPlace
service created on the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
The Video Service Code in
MeetingTime must match the
MeetingPlace service prefix
defined on the Cisco IPVC MCU.
If your Cisco IPVC MCU system
is configured to support ISDN
video endpoints, enter the
telephone number those endpoints
used to dial in to the
Cisco IPVC MCU. This is the DID
number assigned to the Cisco
IPVC PRI Gateway associated
with your Cisco IPVC MCU.
You specified the service prefix when
you installed
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
.
To view the service prefix:
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, look for the COMPANY
SPECIFIC INFORMATION
heading, click Usage Parameters,
then scroll down in the panel on the
right to the Video Service Code field.
This value will be updated
automatically in MeetingTime if you
change it on the Cisco IPVC MCU. It
is best not to make changes after
meetings are scheduled.
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, look for the SYSTEM
CONFIGRATION heading, click
Telephony Access, then scroll down in
the panel to the right to the Video
Information section.
For information, see the
documentation for your Cisco
IPVC PRI Gateway.
1st alternate video phone
number
2nd alternate video
phone number
Cisco MeetingPlace does not
currently use these fields.
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, look for the SYSTEM
CONFIGRATION heading, click
Telephony Access, then scroll down in
the panel to the right to the Video
Information section.
About Changing System Configuration Settings
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration components are configured to work together. Settings in each
component enable communication between the components. If you change settings in one component,
you must also change the corresponding setting you entered in other components.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-2
OL-6280-01
Page 45

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
If you need to change values that you entered during installation of
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, or change configuration settings in any of the other component
parts needed to make the system work, see the following sections.
Changing Values Entered During Installation of
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
When you installed Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, you specified settings for the components
needed to run Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
To change these settings, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Stop the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing master service. The Cisco MeetingPlace Video
service will automatically stop.
Step 2 In the Windows Control Panel, double-click MeetingPlace Gateways.
Step 3 Click the Video tab.
Step 4 Change any of the following settings:
• Service Code (the service prefix you specified on the Cisco IPVC MCU for MeetingPlace
conferences)
About Changing System Configuration Settings
• Tracing Level (logging verbosity)
• MCU IP Address
• MCU User Account (this can be an Operator- or Administrator-level account)
• MCU User Password (password for the user account)
• Voice Link E.164
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 Restart the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing master service. The Cisco MeetingPlace Video
service will automatically restart.
Changing Settings in Other Components
To change settings in other components that are required for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration,
such as the Cisco IPVC MCU or Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway, follow these general steps:
Step 1 Plan to make changes during a time when your system is not in use.
Step 2 If changes you make to settings in the Cisco IPVC MCU will reduce the number of conferences or ports
available, make sure that there are still enough resources to accommodate conferences that have already
been scheduled. See About Video-Conferencing Statistics, page 4-13.
OL-6280-01
Step 3 Stop the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing service, which will also stop the Video Integration
service.
Step 4 Make the changes in the other components according to the appropriate section in Chapter 3, “Installing
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration” and the documentation for those components.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-3
Page 46

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources
Step 5 If you change any of the following, make the corresponding changes in
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, as described in Changing Values Entered During Installation of
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, page 4-3:
• The service prefix you specified on the Cisco IPVC MCU that identifies Cisco MeetingPlace
conferences
• MCU IP Address
• MCU User Account
• MCU User Password (password for the user account)
• Voice Link E.164 number
Step 6 Restart the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing service. This will restart all necessary services.
About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources
Video-conferencing capacity (the number of video conferences and the total number of ports available
at one time) is determined by the Cisco IPVC MCU hardware and settings. For complete details about
these settings, see the Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Administrator
Guide, Version 3.2 and Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Release Notes for
Release 3.5.
Several factors affect video-conferencing resource availability. Manage the availability of ports and
conferences by doing one or more of the following:
• Configuring the MeetingPlace service on the Cisco IPVC MCU to use nonresource-intensive
features. For information, see the Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module
Administrator Guide, Version 3.2 and Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module
Release Notes for Release 3.5. For example, on the Settings > Basics page, set the Number of SCCP
ports to 0.
• Changing the number of video floater ports available. See About Configuring the Number of Video
Floater Ports, page 4-7.
• Changing the number of video overbook ports available. See (Optional) Configuring the Number of
Overbook Ports, page 4-8.
• Raising or lowering the default and maximum number of video ports users can schedule. See
Table 4-2 on page 4-5.
• Restricting user access to video-conferencing resources. See About Managing User Profiles for
Video Use, page 4-10.
• Modifying the default bandwidth of participant connections. See About Managing User Profiles for
Video Use, page 4-10.
Table 4 -2 contains conference and port parameters. For more information about MeetingTime, see the
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3.
4-4
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 47

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Table 4-2 Conference and Port Parameters
Parameter Values Where Specified
Maximum number of
simultaneous
conferences that are
This number depends on
settings in the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
possible
About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources
This number is dynamically taken from
the Cisco IPVC MCU and cannot be
changed in MeetingTime.
To view the value:
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, then Server Configuration, then
scroll down in the panel on the right to
Video conferences.
For information on Cisco IPVC MCU
hardware and configuration, see the
Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco
IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Administrator
Guide, Version 3.2 and Cisco IP/VC
3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU
Module Release Notes for Release 3.5.
Total number of ports
that are available to
Cisco MeetingPlace
video conferencing.
This value depends on
hardware and feature
configuration of the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
Choosing resource-intensive
features for the MeetingPlace
service on the
Cisco IPVC MCU may reduce
the number of
video-conferencing ports
available.
If you increase the number of available
video conferences by changing settings
on the Cisco IPVC MCU, the value for
this parameter may not update until all
meetings that were in session when you
made the change have terminated.
This number is dynamically taken from
the Cisco IPVC MCU and cannot be
changed in MeetingTime.
To view the value:
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, then Server Configuration, then
scroll down in the panel on the right to
Video conference ports.
For information on Cisco IPVC MCU
hardware and configuration, see the
Cisco IP/VC 3511 MCU and Cisco
IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Administrator
Guide, Version 3.2 and Cisco IP/VC
3511 MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU
Module Release Notes for Release 3.5.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-5
Page 48

About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources
Table 4-2 Conference and Port Parameters (continued)
Parameter Values Where Specified
Maximum number of
video ports that users can
schedule for a
conference.
Default number of video
ports to schedule for each
conference.
This number appears by
default in the # of video
callers field on the
scheduling form of users
whose profiles allow
them to schedule video
conferences. If users do
not change this value
when they schedule a
conference, this number
of video ports will be
scheduled for that
conference.
Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
2 to the maximum number of
ports that can be scheduled in
advance. The number of ports
that can be scheduled in
advance is the total number of
ports minus the number of ports
designated as floater ports, plus
the number of overbook ports.
Entering a large number into
this field may limit the
availability of ports and
simultaneous conferences.
Entering 0 means that video
conferences cannot be
scheduled.
0 (zero), or any number
between 2 and the maximum
number of video ports in the
system that can be scheduled.
The number of ports that can be
scheduled in advance is the
total number of ports minus the
number of ports designated as
floater ports, plus the number of
overbook ports.
By default, this parameter is set
to zero.
Do not enter 1; Cisco
MeetingPlace will not schedule
a conference that specifies a
single video port.
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, then Scheduling Parameters, then
scroll down in the panel on the right to
the Video meetings heading, Max ports
per meeting field.
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, then click Scheduling Parameters,
then scroll down in the panel on the right
to the Video meetings heading, Default
# of ports to schedule field.
4-6
Entering a large number into
this field may limit the
availability of ports and
simultaneous conferences.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 49

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Table 4-2 Conference and Port Parameters (continued)
Parameter Values Where Specified
Number of video floater
ports in the system.
Video-conferencing
floater ports differ from
audio floater ports and
are described in About
Configuring the Number
of Video Floater Ports,
page 4-7.
This number cannot be zero. It
is the total of the following:
• Minimum required number
of floater ports
• Number of floater ports
that you want.
See About Configuring the
Number of Video Floater Ports,
page 4-7.
Number of video
overbook ports in the
system.
Overbook ports are
described in (Optional)
Configuring the Number
of Overbook Ports, page
4-8.
By default, this value is 0.
If you want to adjust the
number of overbook ports, we
recommend using the formula
in (Optional) Configuring the
Number of Overbook Ports,
page 4-8 in order to optimize
your resources.
About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, then click Server Configuration,
then scroll down in the panel on the right
to Video floater ports.
In MeetingTime, click the Configure
tab, then click Server Configuration,
then scroll down in the panel on the right
to Video overbook ports.
About Configuring Port Parameters
After Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is up and running, configure the following before users
begin to schedule meetings that include video conferencing:
• Number of floater ports
• Number of overbook ports
To determine the optimal number of floater and overbook ports for your system, use the information in
the following subsections and the values in the preceding table.
About Configuring the Number of Video Floater Ports
Floater ports are ports that cannot be scheduled in advance. They are a configurable subset of the total
number of ports available on the system. Video floater ports are used differently than audio floater ports.
When Cisco MeetingPlace seeks available video ports to establish the link between the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and the Cisco IPVC MCU, or to accommodate unscheduled
conferences or participants, or to extend a meeting, it first uses available video-conferencing ports that
can be scheduled. If video-conferencing ports that can be scheduled are not available, or if additional
ports are required, Cisco MeetingPlace uses available video floater ports, if there are any.
The total number of video floater ports that you configure includes:
• The minimum number of video floater ports that Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration requires in
order to function
OL-6280-01
• An optional number of video floater ports that you make available to conference participants on a
first come, first served basis
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-7
Page 50

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources
Configuring the Required Minimum Number of Video Floater Ports
Each video conference requires one dedicated video port to link the audio stream of the video conference
to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio conference, and this port may be taken from the pool of video floater
ports. Therefore, the number of floater ports you allocate cannot be zero. The minimum number of
floater ports you allocate depends on the number of video conferences and ports available on your
system.
If your system has fewer video conferences than ports, the required minimum number of floater ports is
the lesser of the following values:
• The total number of video ports on your system, divided by 3, rounded up to the next whole number,
or
• The maximum number of video conferences available on the Cisco IPVC MCU.
For example, if your Cisco IPVC MCU provides 24 ports and 10 simultaneous conferences, then the
required minimum number of floater ports is 24/3, which totals 8, which is smaller than the maximum
number of video conferences, which is 10. Therefore, the required minimum number of ports is 8.
This calculation maximizes system flexibility while minimizing the chance that video conferencing will
be unavailable in a particular meeting.
The floater ports resulting from this calculation are not available to video-conference participants; for
standard floater-port functionality, add additional floater ports.
Step 1 Use the information in this section to calculate the required minimum number of video floater ports.
Step 2 Continue with the steps in the following section, Adding Optional Video Floater Ports.
Adding Optional Video Floater Ports
In addition to the required minimum number of video floater ports, you can include floater ports that are
available on a first-come, first-served basis to participants in conferences that are in session. These video
floater ports are analogous to floater ports in audio conferencing.
Add the number of floater ports you need to the minimum required number of floater ports. The total
number of video floater ports cannot be more than the total number of video ports available.
Step 1 Use the information in this section to calculate the total number of video floater ports.
Step 2 Enter the number of video floater ports in the Video floater ports field in MeetingTime: Click the
Configure tab, then click Server Configuration, then scroll down in the panel on the right to Video
floater ports.
Step 3 Continue with the steps in the following section, (Optional) Configuring the Number of Overbook Ports.
(Optional) Configuring the Number of Overbook Ports
Overbook ports allow users to schedule more participants for a meeting than the number of ports that are
actually available. Overbook ports are useful because typically not all invitees attend meetings, and
reserved ports would otherwise go to waste. Video overbook ports are analogous to but separate from
audio overbook ports. Determining the optimal number of video overbook ports requires a different
calculation than determining the optimal number of audio ports.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-8
OL-6280-01
Page 51

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
We recommend setting the number of video overbook ports to about 20% of the total number of video
conferencing ports available. To make optimal use of video conferences and ports that are available on
your system, determine the number of overbook ports according to the following formula:
Mod [(Total number of video ports available on the Cisco IPVC MCU - Total number of video floater
ports + Number of video overbook ports) /Total number of video conferences available on the
Cisco IPVC MCU]= 0
In other words, the total number of video ports available on the Cisco IPVC MCU, minus the total
number of floater ports you have specified, plus the number of overbook ports you choose, altogether
must be evenly divisible by the total number of conferences available on the Cisco IPVC MCU. If you
perform this calculation and the result is not a whole number, increase or decrease the number of
overbook ports until your result has no remainder.
For example, suppose your values are as indicated in Tab l e 4-3:
Table 4-3 Example Overbook Port Calculation Values
Variable Example 1 Example 2 Example 3
Total number of video ports available 24 24 24
Number of video floater ports (including
the required minimum number of video
floater ports plus optional additional
video floater ports)
Estimated number of video overbook
ports
Total number of video conferences
available
Calculation result is a whole number? No Yes Yes
Is this an optimal number of video
overbook ports?
About Managing Video-Conferencing Resources
8 8 8
6 4 14
10 10 10
No Yes Yes
OL-6280-01
The result of your calculation using the values in Example 1 would be (24-8+6)/10, or 2.2, so 6 is not an
optimal number of overbook ports. If you decrease the estimated number of overbook ports by 2, as in
Example 2, your result is 2, a whole number. Therefore, one optimal number of overbook ports is 6-2,
or 4. If you prefer more overbook ports, increase the estimated number of overbook ports by 8, as in
Example 3, so that your optimal number of overbook ports is 6+8, or 14. You can also modify the number
of floater ports, then try this calculation again.
If you change the number of floater ports, and you have set the number of overbook ports to maximize
video-conferencing resources as described in this section, recalculate the optimal number of overbook
ports.
If you specify more than zero video overbook ports, the system cannot guarantee that video ports will
be available at the time of the meeting, even if the meeting was successfully scheduled. However, this
situation is unlikely if you set the number of overbook ports using the formula in this section.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-9
Page 52

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
About Managing User Profiles for Video Use
Step 1 Use the information in this section to calculate the number of video overbook ports.
Step 2 Enter the number of video overbook ports in the Video overbook ports field in MeetingTime: Click the
Configure tab, then click Server Configuration, then scroll down in the panel on the right to Video
overbook ports.
About Managing User Profiles for Video Use
Use profile settings for users and groups to manage video-conferencing resources and simplify video
conferencing for users.
Users can be assigned to groups to simplify assigning privileges and parameters. Enter settings in the
MeetingTime application using the table in this section
Manage the use of video resources by doing the following:
• Controlling which users and groups can schedule video conferences. There are no restrictions on
attending video conferences.
• Prioritizing bandwidth use by assigning profiled users and groups default bandwidths.
By default, video conferencing is not enabled in user profiles, and video endpoint bandwidth is set to the
maximum, 384 kbps.
Table 4 -4 shows settings for groups; Ta ble 4- 5 shows settings for individual profiled users.
Table 4-4 Available Settings For Each Group
Item Values Where to Configure in MeetingTime
Allow Video Scheduling? No
Yes
Endpoint Bandwidth
This value is the default bandwidth
for the group to which a user has
been assigned.
For more information about
bandwidth use, see About
Video-Conferencing Bandwidth,
page 4-12.
128K
256K
384K (Default)
In the specific User Group profile, in
the Restrictions section.
In the specific User Group profile, in
the Video Meetings section.
4-10
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 53

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Table 4-5 Configure For Each User
Item Values Where to Configure
Allow video scheduling?
Users who are allowed to schedule
meetings will see the video scheduling
option when they schedule a meeting.
Otherwise, the video scheduling option will
not appear on the scheduling form.
Endpoint Bandwidth
The default video endpoint bandwidth of
this user.
For more information about bandwidth use,
see About Video-Conferencing Bandwidth,
page 4-12.
No
Ye s
Group Dflt (Group Default)
• 128 kbps
• 256 kbps
• 384 kbps
• Group Dflt (Group
Default: the bandwidth
set for the group to
which this user is
assigned)
About Managing User Profiles for Video Use
In the profile of the user,
in the Restrictions
section
In the profile of the user,
in the Video Meetings
section.
Endpoint Address
Default video endpoint address that Cisco
MeetingPlace outdials to bring the user into
the video conference.
Entering a value for this parameter
simplifies for users the process of attending
video conferences.
The default bandwidth is
384kbps.
For H.323 or SCCP
endpoints:
Enter the E.164 phone
number of the endpoint of
the user.
For ISDN endpoints:
Precede the E.164 phone
number of the video
endpoint with the service
code of the Cisco IPVC PRI
Gateway. For example, if the
phone number of the ISDN
video endpoint is
1-800-555-0101, and the
service prefix for the type of
call that is appropriate for
that endpoint is 89, enter
8918005550101. For
information, see the
documentation for your
Cisco IPVC PRI Gateway.
In the profile of the user,
in the Video Meetings
section.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-11
Page 54

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
About Managing User Profiles for Video Use
Important Information About DMZ Configurations and Video Conferencing
When users schedule immediate or reservationless meetings, their profile settings determine whether or
not the meeting allows Internet access to the web conference. Because video conferences must be held
on the server on which Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is installed, this profile setting therefore
also determines whether a user’s immediate or reservationless meetings can include video conferencing
and who can attend the video and web conferences.
Use the following table to determine the appropriate setting for the Allow Internet Access profile
parameter for users who are allowed to schedule video conferences:
And the Allow
Internet Access
Parameter In The
If
Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration Is Installed
Behind the firewall No Video conferencing for
Behind the firewall Yes Web-conferencing
In the DMZ No — Any video
In the DMZ Yes All video- and
Profile of the
Meeting Scheduler
is Set To
Then That Scheduler Can
Initiate Immediate or
Reservationless Meetings
That Include
internal participants and
participants with ISDN
video endpoints
participants who are
outside the firewall
web-conferencing
participants
But That Scheduler
Cannot Initiate
Immediate or
Reservationless
Meetings That Include
Web- conferencing
participants or
IP-based
video-conferencing
participants who are
outside the firewall
Any video
conferencing
conferencing, or
web-conferencing
participants who are
outside the firewall
—
Note Users can work around the limitations in this section by scheduling standard scheduled meetings that
start as soon as they are scheduled, instead of scheduling immediate or reservationless meetings. They
must include a meeting ID that is different from their profile ID when they schedule the meeting.
About Video-Conferencing Bandwidth
The default bandwidth for video conferencing when users outdial to their video endpoint from
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing is set in the profile for each user, or for the group that each user
is assigned to.
Users can change their bandwidth setting at any time. Changes take effect if they rejoin the web
conference, or the next time they join a web conference. When participants dial in, the endpoint and the
Cisco IPVC MCU negotiate to determine the minimum usable bandwidth.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-12
OL-6280-01
Page 55

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Users can change their video connection bandwidth via the Account Basics page in
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, or in MeetingTime.
If the endpoint does not support the specified bandwidth, participants will have only voice capability. If
the Cisco IPVC MCU has an MP card, viewing multiple participants (continuous presence mode)
requires more bandwidth than viewing only the active speaker. For details, see the Cisco IP/VC 3511
MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Administrator Guide, Version 3.2.
Specifying User and Group Profile Information
Step 1 Use the information in this section, About Managing User Profiles for Video Use, including the
information about DMZ configurations, to specify user and group profile parameters for video
conferencing.
About Video-Conferencing Statistics
About Video-Conferencing Statistics
Use the tools described in this section to monitor video-conferencing usage. The reports indicated in the
table include nonvideo statistics in addition to video-conferencing statistics. Reports in MeetingTime
that are not listed in the table do not include video-conferencing statistics.
Complete information about reporting in MeetingTime is available in the Administrator’s Guide for
Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-13
Page 56

About Video-Conferencing Statistics
Viewing Video-Conferencing Statistics
Step 1 Use the information in Table 4 -6 to view video-conferencing statistics.
Table 4-6 Video-Conferencing Statistics
Statistic To View This Information
For each meeting or instance of a recurring
meeting, you can view the following values:
• The scheduled number of video locations.
• The actual number of video locations that
attended the meeting.
This number includes the link between the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
• The bandwidth used for that conference
For each conference in the range of dates you
choose, view or save the following
video-conferencing statistics:
• The number of video ports scheduled
(nVideoPortsReq.)
• The number of video ports actually used
(ActNumVideoPorts.)
• The total number of seconds of video
attended by all video participants in that
conference (TotVideoPortSecs.)
For each conference in the range of dates you
choose, view or save the following
video-conferencing statistic:
• The length of the video conference.
Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
In MeetingTime, click the Review tab. Search for
the meeting or meetings you are interested in. In the
window on the left, click a meeting. View
information about that meeting in the window on
the right.
Information in the Review tab is best for onscreen
viewing. For statistics that you can save and
manipulate in other applications, use the Report
tab and the information in the remaining rows of
this table.
In MeetingTime, click the Report tab, then click
Raw Meeting Details Info in the panel on the left.
In the window on the right, in the Val ue s column,
click an option such as the start date for your report,
then enter a value and click OK. Choose a value for
each option you desire. You cannot change items
that appear in italics. Finally, click Generate
Report.
Statistics in this report do not include the link
between the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and
the Cisco IPVC MCU.
In MeetingTime, click the Report tab, then click
Raw Mtg Participant Info in the panel on the left.
In the window on the right, in the Val ue s column,
click an option such as the start date for your report,
then enter a value and click OK. You cannot change
items that appear in italics. Choose a value for each
option you desire. Finally, click Generate Report.
4-14
Look for videolink in the uid column for the
conferences (confnum) that you are interested in;
the value in the nVSecInConf column for the
videolink row for that conference is the length in
seconds of the video conference, from the time the
first video participant entered the conference to the
time the last video participant left, plus 5 minutes.
Statistics in this report include the link between the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and the
Cisco IPVC MCU. This link is called videolink.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 57

Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Table 4-6 Video-Conferencing Statistics
Statistic To View This Information
For the range of dates you choose, which
unidentified participants attended meetings via
video endpoint, and when each participant
entered and left the video conference.
About Video-Conferencing Statistics
In MeetingTime, click the Report tab, then click
Raw Participant Join Leave Info in the panel on
the left. In the window on the right, in the Valu es
column, click an option such as the start date or end
date for your report, then enter a value and click
OK. You cannot change items that are written in
italics. Choose a value for each option you desire.
Finally, click Generate Report.
Each line in this report represents one participant in
one conference. A conference is listed as many
times as there were participants in that conference.
In the Device column, number 4084 indicates a
video endpoint. Therefore, if 4 lines for a particular
conference list 4084 in the Device column, then 4
participants attended that conference via video
endpoint.
A summary of profile information includes the
following video-related fields:
• Allow Video Scheduling.
• Video Endpoint Bandwidth.
• Video Endpoint Address.
A summary of group information includes the
following video-related fields:
• Allow Video Scheduling.
• Video Endpoint Bandwidth.
Statistics in this report do not include the link
between the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server and
the Cisco IPVC MCU.
In MeetingTime, click the Report tab, then click
Raw Profile Info in the panel on the left. In the
window on the right, in the Va lu es column, choose
a value for each option. You cannot change items
that are written in italics. Finally, click Generate
Report.
In this report, gd represents Group Default.
In MeetingTime, click the Report tab, then click
Raw Group Info in the panel on the left. In the
window on the right, in the Va lu es column, choose
a value for each option. You cannot change items
that are written in italics. Finally, click Generate
Report.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
4-15
Page 58

About Video-Conferencing Statistics
Chapter 4 Configuring and Managing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
4-16
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 59

CHAPTER
5
Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
This chapter contains a detailed description of Cisco MeetingPlace video-conferencing from a
nontechnical perspective. It assumes all necessary hardware and software are up and running.
Specific information includes:
• Supported Meeting Types, page 5-1
• About Setting Up End Users for Video Conferencing in Cisco MeetingPlace, page 5-2
• About Scheduling Video Conferences, page 5-3
• About Attending Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferences, page 5-4
• Video Features and Functions in the Meeting Room During the Conference, page 5-7
• Information for End Users, page 5-10
Supported Meeting Types
Cisco MeetingPlace video capability is available for the meeting types listed in Table 5-1; for more
information about these meeting types see the Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Audio
Server Release 5.3.
Table 5-1 Supported Meeting Types
Meeting Type Video-Conferencing Behavior
Standard scheduled meetings As described in this document.
Recurring meetings As described in this document.
Immediate meetings Video conferences are not scheduled with
immediate meetings but can be created and
attended on an ad-hoc basis. See About Attending
Ad-Hoc Video Conferences, page 5-6 for
requirements. Other behavior is as described in
this document.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
5-1
Page 60

About Setting Up End Users for Video Conferencing in Cisco MeetingPlace
Meeting Type Video-Conferencing Behavior
Reservationless meetings (not all
Cisco MeetingPlace systems have this
functionality)
Continuous meetings The video conference begins when the first
Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
Video conferences are not scheduled with
reservationless meetings but can be created and
attended on an ad-hoc basis when users join the
conference or during the conference. See About
Attending Ad-Hoc Video Conferences, page 5-6
for requirements.
As with audio conferences, participants who join
the meeting before the scheduler arrives will wait
in the waiting room until the scheduler starts the
video conference.
Other behavior is as described in this document.
attendee joins the video conference, and continues
until it is terminated in Cisco MeetingPlace. If the
video conference is terminated for any reason, it
will resume as soon as a participant joins again.
Other behavior is as described in this document.
Lecture-style meetings (excluding Q and A mode,
which is not enabled for video conferencing in
Release 5.3, but which is available for audio-only
conferences)
See About Participating in Lecture Style
Meetings, page 5-9.
About Setting Up End Users for Video Conferencing in
Cisco MeetingPlace
After end-users’ desktop or room-based video equipment is installed and running, set the
Cisco MeetingPlace profiles of designated users to allow them to schedule meetings that include video
conferencing. See About Managing User Profiles for Video Use, page 4-10.
Users see video options when they schedule meetings only if their Cisco MeetingPlace profiles are
enabled for video conferencing. Users without Cisco MeetingPlace profiles cannot schedule video
conferences. Users do not need a Cisco MeetingPlace profile to attend video conferences.
In MeetingTime, you can set or change the video-conferencing bandwidth for groups and individual
users, and set or change the default video-conferencing endpoint address for each user.
Users can set or change their video-conferencing bandwidth and default endpoint address in
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing on the Account Basics page (if the optional Account link is
displayed, allowing access to that page).
5-2
The endpoint address can be a phone number or an H.323 endpoint address. The endpoint address must
be less than 128 digits; however, some endpoints require fewer than 128 digits.
For details about administrative functions in MeetingTime and Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing,
see the Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3 and the Administrator’s
Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Release 5.3.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 61

Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
About Scheduling Video Conferences
All aspects of Cisco MeetingPlace conferences (data, voice, and video) must be scheduled on the
Cisco MeetingPlace audio server before anyone can attend them. However, they do not need to be
scheduled in advance; they can be scheduled as immediate or reservationless meetings.
Who Can Schedule Video Conferences
Only profiled users whose profiles allow video conference scheduling can schedule video conferences.
Users who cannot schedule video conferences do not see video conference options when they schedule
meetings.
When Video Conferences Can Be Scheduled
Video conferences can be scheduled with the other aspects of the Cisco MeetingPlace conference in
advance of the meeting, or they can be initiated at the beginning of a reservationless or immediate
meeting, or in the middle of any Cisco MeetingPlace meeting (see About Attending Ad-Hoc Video
Conferences, page 5-6.)
About Scheduling Video Conferences
In either case, video-conferencing resources must be available and the meeting must be scheduled by a
user whose profile is enabled for scheduling video conferencing.
How Users Schedule Video Conferences
Users schedule video-conferencing functionality when they schedule a Cisco MeetingPlace voice or web
conference via the standard Cisco MeetingPlace scheduling interfaces in Release 5.3 of
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook, Cisco MeetingPlace for
Lotus Notes, and MeetingTime. Video conferencing cannot be scheduled via the telephone user interface
(TUI) / Voice user interface (VUI).
For step-by-step instructions on scheduling video conferences in MeetingTime,
Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook, Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes, and
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, see the see the Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace
Audio Server Release 5.3, or the online help for Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook,
Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes, or Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing.
The following caveats apply to scheduling video conferences:
• To schedule a video conference, the meeting scheduler must include at least 2 video callers on the
scheduling form. If the necessary number of video or audio ports is unavailable, Cisco MeetingPlace
will not schedule the meeting.
• The number of ports reserved for a video conference cannot be changed while the meeting is in
session, although it may be possible for additional participants to join the video conference on an
ad-hoc basis. See About Attending Ad-Hoc Video Conferences, page 5-6.
OL-6280-01
• Users of Cisco MeetingPlace clients earlier than Release 5.3 cannot schedule conferences that
include video capability. However, they may be able to attend video conferences. See About
Attending Ad-Hoc Video Conferences, page 5-6.
• Cisco MeetingPlace cannot reserve video ports when an immediate or reservationless meeting is
scheduled. However, it may be possible for participants to initiate video conferencing on an ad-hoc
basis. See About Attending Ad-Hoc Video Conferences, page 5-6.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
5-3
Page 62

About Attending Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferences
• Passwords are never required to attend an immediate or reservationless meeting, even if meeting
schedulers enter a password when they schedule a meeting. To schedule a meeting that has password
protection, schedulers can include a Meeting ID that is different from their profile ID when they
schedule the meeting.
• For scheduled meetings that include both video conferencing and external access:
–
If Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is deployed in the DMZ to allow attendees outside the
firewall to participate in video conferences, meeting schedulers must set the Allow Internet
Access option to Yes each time they schedule video ports, whether or not external participants
will attend.
–
If Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is deployed behind the firewall, people who are
outside the firewall cannot attend video conferences via IP-based endpoints, and meeting
schedulers must set Allow Internet Access to No if they want to enable video conferencing for
internal users with IP-based endpoints. In this case, people who are outside the firewall cannot
attend the web conference. If meeting schedulers want to allow participants outside the firewall
to attend the web conference, they must set Allow Internet Access to Yes , and video
conferencing will not be available for this conference. External users of ISDN video endpoints
can join the video conference even if Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is installed behind
the firewall.
• When users schedule immediate or reservationless meetings in configurations that include both
video conferencing and external access, the profile settings of each user for the Allow Internet
Access parameter may affect their ability to schedule video conferences and their ability to include
web-conferencing participants who are outside the firewall. See Important Information About DMZ
Configurations and Video Conferencing, page 4-12. Users can choose which functionality they want
for each meeting by scheduling scheduled meetings that start as soon as they are scheduled (rather
than immediate or reservationless meetings.) In order to do this, they must include a meeting ID that
is different from their profile ID.
Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
• Cisco MeetingPlace may schedule more video ports than the scheduler specified. This is because the
number of video conferences is limited; Cisco MeetingPlace determines the average number of
video ports available to each video conference and automatically distributes “extra” ports if the
scheduler included fewer ports than the average.
• The Meeting ID becomes part of the dial string that video endpoints use if they dial in to attend the
conference. Some endpoints can accommodate only relatively short dial strings, we recommend that
you determine the number of digits your endpoints can accommodate and recommend that your
users keep their Meeting IDs short enough to work with that limit.
About Rescheduling Video Conferences
Meeting schedulers can reschedule meetings that include video capability in the same way they
reschedule meetings that do not include video conferencing.
Required conditions for scheduling video conferences also apply to rescheduling them.
About Attending Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferences
A Cisco MeetingPlace conference must exist before a user can initiate the associated video conference.
The Cisco MeetingPlace conference can be scheduled in advance or started as an immediate or
reservationless meeting.
5-4
The video conference starts as soon as one person joins the video conference.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 63

Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
About Attending Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferences
For participants who attend via a desktop video endpoint, the video image appears separately in the
window of their desktop video endpoint, not in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room
window.
Profiled users connect with the bandwidth specified in their profile or with the default bandwidth if their
profile does not specify a bandwidth. Guest connections enter with the default bandwidth you specified
in MeetingTime.
About Attending Reservationless Meetings
If the meeting is reservationless and the organizer has not yet started the conference at the time a
participant joins the video conference, video participants will stay in the video waiting room until the
organizer starts the voice or web conference. As with data and voice conferencing, no in-meeting
functionality is available to conference participants in the waiting room.
How Users Join A Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conference
Participants should always start their video endpoints before attempting to join the Cisco MeetingPlace
video conference.
Users of Apple computers should always dial in from their video endpoints.
If participants join a single conference with both an audio-only device and a video endpoint, they should
mute one or the other.
Participants can join the video conference in any of several ways described in the following sections.
About Attending Video Conferences by Outdialing from Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
In Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, users can join the video conference in several ways:
• From the Current Meeting page by clicking the Connect button
• From the meeting room by clicking the Connect button
• From the meeting room by choosing Connect from the Personal menu
In each case, users enter the number for their video endpoint if it is not automatically entered, then click
Connect. For users of ISDN endpoints, the number of their video endpoint must be preceded by the
appropriate service prefix defined on the Cisco IPVC PRI Gateway. For information, see the Cisco IP/VC
3526 PRI Gateway and Cisco IP/VC 3540 PRI Gateway Module Administrator Guide, 2.0.
About Attending Video Conferences Via Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook
If video conference resources were scheduled with the Cisco MeetingPlace conference, users can click
the MeetingPlace tab of a notification they have received in Microsoft Outlook, then click the Connect
Me button to have Cisco MeetingPlace dial their video endpoint and connect them to the video
conference. They can also dial in from their video endpoint using the dial-in number provided in the text
of the meeting notification. If the meeting requires a password or is restricted to profiled or invited users,
participants must join the video conference by clicking the Connect Me button in the notification, or
from within the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
5-5
Page 64

Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
About Attending Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferences
About Attending Video Conferences Via SMTP E-mail Clients
Cisco MeetingPlace SMTP E-Mail Gateway provides Cisco MeetingPlace meeting notifications to users
of SMTP e-mail applications. SMTP notifications include instructions for attending a video conference
and a hypertext link to bring up the Current Meeting page in Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing,
from which participants can have the conference outdial to their video endpoint. For meetings that
require a password or are restricted to profiled or invited users, users can attend only by having the
system outdial to their endpoint.
About Attending Video Conferences Via Cisco VT Advantage Video Endpoints
Cisco VT Advantage consists of the Cisco VT Advantage software application and a Cisco VT Camera,
a video telephony USB camera. These work with a Cisco IP phone to provide video conferencing.
To attend a Cisco MeetingPlace video conference via a Cisco VT Advantage video endpoint, users can
plug in their desktop endpoint, launch their Cisco VT Advantage software, and join via one of the
following methods:
• Outdial to their Cisco VT Advantage endpoints by clicking Connect and entering the number for
their VT Advantage endpoint, if this number is not already entered in to their profile.
• Dial the number for the conference on their IP telephone keypad. The number to dial is shown when
users click the Connect button in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room, and in
e-mailed meeting notifications if the scheduler included video conferencing with the meeting. There
may be a delay while the call is connected. This is normal. Users cannot dial in if the meeting has
attendance restrictions.
Users cannot attend a video conference via Cisco VT Advantage if they are using VPN software to
access the network.
About Attending Video Conferences By Dialing In
If a video conference does not have password or profile access restrictions, participants can dial in to the
conference from their endpoint. The number to enter in to their endpoint is shown on the Current
Meeting page in Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing and at the bottom of the dialog box that comes
up if a user clicks Connect in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. This number is
also included in the text of e-mailed meeting notifications if the scheduler included video conferencing.
All users who dial in from an endpoint participate in the video conference as guests, and their video
endpoint is listed separately from their web presence in the participant list in the meeting room.
Instructions for dialing a number via the endpoint are in the documentation for the endpoint or its
software. There may be a delay before the call is connected to the meeting.
Anyone who has the access information can dial in to the conference. If access to the meeting is
restricted, participants who try to dial in with their video endpoints may not receive an error message,
but they will not be connected to the meeting.
Users who dial in from an ISDN endpoint must dial the number provided for ISDN endpoints; at the IVR
prompt, they enter the remaining digits provided.
About Attending Ad-Hoc Video Conferences
If a meeting scheduler did not or could not schedule video-conferencing ports with the meeting, it may
still be possible for video callers to participate.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
5-6
OL-6280-01
Page 65

Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
Ad-hoc video conferencing is convenient in situations like these:
• The meeting is an immediate or reservationless meeting.
• The conference scheduler did not schedule video resources with the meeting.
• The conference was scheduled via the TUI (Telephone User Interface, formerly called the VUI, or
voice user interface.)
• The conference was scheduled with a release of Cisco MeetingPlace that is earlier than Release 5.3.
• More participants need to join the video conference than the scheduler included on the scheduling
form.
Ad-hoc video conferences can occur only if the following conditions are met:
• The profile of the meeting scheduler is enabled for video.
• The meeting has been scheduled on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. This includes
reservationless and immediate meetings.
• The meeting is in session, or a user is trying to initiate the ad-hoc conference within the guard times
of a scheduled meeting.
• The maximum number of video conferences has not been reached.
Video Features and Functions in the Meeting Room During the Conference
• The minimum number of ports that can be scheduled for a video conference is available.
A participant can join an existing video conference on an ad-hoc basis if one video-conferencing port is
available.
Participants join ad-hoc video conferences the same way they join scheduled video conferences.
About Attending Password-Protected Meetings
If a scheduler schedules a Cisco MeetingPlace conference that requires a password for entry, all
participants must enter the video conference by outdialing from Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
or from the MeetingPlace tab in a Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook notification.
About Attending Invitation-Only or Profiled-User-Only Meetings
If a meeting is not a public meeting (attendance is by invitation only, or is only available to profiled
users), then only recipients of the meeting notification, attendees of the voice or web conference who
outdial to a video endpoint, or profiled users can attend the video conference. Participants cannot dial in
to these video conferences.
Note Cisco MeetingPlace cannot authenticate an endpoint that is outdialed to. It is assumed that users are
familiar with and authorized to include the number they are outdialing to.
Video Features and Functions in the Meeting Room During the
Conference
After participants join the video conference, their video image appears on the video monitor in a
room-based system, or in a separate window on the desktop of participants who are using a
computer-based video endpoint.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
5-7
Page 66

Video Features and Functions in the Meeting Room During the Conference
The video image can be the active speaker only (or the room the active speaker is in, in the case of
room-based systems), or multiple people (or rooms) including the active speaker (or the room the active
speaker is in, in the case of room-based systems.) If multiple images are displayed, participants do not
control which participants are shown. If an audio-only participant is the active speaker, the last active
video speaker continues to display until another video participant speaks.
When video participants are speaking through their video endpoint, the Now Speaking feature in the
Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room displays Video Participant. When an audio
participant speaks, the name or Guest ID of that participant is displayed.
In the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room, video-conference participants are identified
in the participant list by icons for a video camera and a microphone. Status information about the video
transmission, such as whether a participant is muted or paused, is also indicated in the participant list.
The video link does not appear in the participant list in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing
meeting room, but it displays as a telephone in MeetingTime.
The following sections describe the video-related functionality available to video participants in the
meeting room.
All voice (telephone) and web-conferencing features are available as usual to all participants.
Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
Note Telephone User Interface (TUI) commands (formerly called Voice User Interface or VUI commands)
that are available to audio conference participants are not available to video conference participants
because they are not connected directly to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. For example, the #5
telephone key combination that mutes an audio endpoint does not affect the audio transmission of a video
endpoint.
About Modifying the Video Transmission
Participants can control certain aspects of their video transmission from within the Cisco MeetingPlace
web-conferencing meeting room. Video participants who are accustomed to controlling their video
options through the IPVC interface can also do that.
At any time during a Cisco MeetingPlace conference, participants can modify their own video
transmission, via the Personal menu in the web conference meeting room:
• Connect to or disconnect from the video conference while remaining in the data and voice
conference.
• Pause or play (resume) video transmission of their own image from their video endpoint. If
transmissions from multiple endpoints are displayed, the image from the camera of a paused
participant is omitted from the display rotation. If only the active speaker is showing and the paused
participant is the current speaker, the video image of the user or room freezes at the last image sent,
without hanging up the video call. Pausing video transmission does not affect the audio channel of
the video transmission.
5-8
• Mute or unmute all audio sources the user has (video microphone, telephone, etc.) To mute the audio
in their video transmission without affecting their audio-only connection, participants must mute the
endpoint using the hardware or software of the endpoint. Muting the audio channel of the video
transmission does not affect transmission of the visual image from that endpoint. Voice conferencing
keystrokes such as #5 do not apply to video endpoints, because they are not connected directly to
the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 67

Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
Video Features and Functions in the Meeting Room During the Conference
• View only the active speaker (or the room the speaker is in) or view multiple participants (or the
rooms they are in).
The participant list indicates when a video participant joins or leaves, mutes or unmutes, or pauses or
resumes their video transmission.
About Modifying the Video Transmission of Other Participants
Any profiled user can do the following to any video participant by clicking the name or Guest ID of that
person in the participant list:
• Pause or play (resume) the video transmission of that participant.
• Disconnect another video participant from the video conference. This action does not remove the
participant from the voice or web conference.
• Eject a participant from all media used in the meeting (video, voice, and web conferencing.)
About Recording a Video-Conferencing Session
When video-conferencing participants are present in a Cisco MeetingPlace meeting that is recorded, the
audio channel of their video transmission is recorded. The visual image of a video transmission is not
recorded.
About Entering a Breakout Session
Breakout sessions are only available to audio participants. Video endpoints cannot enter a breakout
session. If a video user attempts to enter a breakout session, the audio channel of the video transmission
of that participant, and the focus of the web conference, remain in the main meeting room.
In order to participate in a breakout session, video participants must also join the Cisco MeetingPlace
conference via an audio device (such as a telephone or speaker phone) and must manually mute the audio
channel of their video endpoint from the video endpoint (not by using the meeting room interface, which
mutes all audio channels) before exiting the main meeting room.
About Participating in Lecture Style Meetings
Lecture style meetings have one or more presenters, and all other participants are the audience. The
audience can be granted speaking privileges. For general information about lecture-style meetings, see
the Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3.
In a lecture-style meeting, standard rules apply to video attendees, except that:
• If the floor is closed, all video participants are muted (including the presenter) but can see each
other. The presenters must join the audio conference with a standard audio device in order to speak.
Any participant can speak via a standard audio connection, subject to the rules that govern
lecture-style meetings in audio conferences.
OL-6280-01
• If the floor is open, all video participants can speak and see each other.
• It is not possible for the speaker to mute or unmute the endpoints of individual video participants.
However, participants in an open-floor meeting can mute and unmute themselves.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
5-9
Page 68

Information for End Users
• If participants are in the waiting room, they can neither speak to nor see each other.
The meeting scheduler determines whether all invitees enter as audience or all invitees enter an
"open-floor" meeting and can speak.
About Extending a Video Conference
A conference will be extended only if enough video and audio ports are available to accommodate all
participants.
About Leaving a Video Conference
Participants can leave the video conference while remaining in the Web conference by performing one
of the following actions:
• Disconnecting their video by choosing Disconnect my video in the meeting room.
• Hanging up their video endpoint.
Chapter 5 Using Cisco MeetingPlace Video Conferencing
About Ending a Video Conference
A video conference continues as long as the Cisco MeetingPlace web conference continues and at least
two video participants or one audio and one video participant are present.
The Cisco MeetingPlace web conference ends if one of the following occurs:
• All participants close the meeting room window to exit the Cisco MeetingPlace web conference, or
choose Personal > Leave Meeting.
• The meeting scheduler chooses End Meeting from the Meeting menu in the Cisco MeetingPlace
web-conferencing meeting room.
Information for End Users
A Quick Start Guide with step-by-step instructions is available for video-conferencing users at
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/video/53/index.htm.
Step by step instructions for end users that includes video-conferencing functionality are also in the
online help for Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook, and
Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes.
5-10
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 69

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting topics are divided into the following areas:
• Viewing the Eventlog, page 6-1
• General Troubleshooting Guidelines, page 6-2
• Problems Configuring and Initiating Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, page 6-2
• Problems Scheduling a Video Conference, page 6-5
• Problems Joining a Video Conference, page 6-5
• Problems During a Video Conference, page 6-7
Viewing the Eventlog
All Cisco MeetingPlace logging is made to the Gateway SIM eventlog.
To view the event log, right-click the Cisco MeetingPlace icon (the orange door) in the system tray and
choose Eventlog.
CHAPTER
6
Setting the Level of Logging Detail
Step 1 In the Windows Control Panel, double-click MeetingPlace Gateways.
Step 2 Click the Video tab.
Step 3 In the Tracing Level field, type a value from the following table. All entries are case-sensitive.
For This Level of Detail
Minimal logging information, including error and
video conference status from
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Set the Tracing
Level To
Retail.
This is the default
value.
6-1
Page 70

General Troubleshooting Guidelines
For This Level of Detail
More detailed logging than the Retail setting, less
detailed than the Detail setting.
Detailed data for debugging purposes.
Set the key for this level only when needed,
because this setting quickly fills the log.
Step 4 Click OK. This change may take up to one minute to take effect.
General Troubleshooting Guidelines
The items in this section are general things to check if you are experiencing problems with your system.
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
Set the Tracing
Level To
Mid.
Detail.
Note The Cisco MeetingPlace system and the Cisco IPVC video-conferencing system must each be running
successfully in order for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to work. If you have problems, first
verify that each of these systems is working correctly, independently of the
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration:
• Create and attend an audio and web conference in Cisco MeetingPlace.
• Create and attend a video conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU. If you have already configured the
Cisco IPVC MCU to allow Cisco MeetingPlace to control its resources, you cannot test the
independent video-conferencing functionality until you disable the authorization you set in the
External conference authorization policy field on the Cisco IPVC MCU.
• Check to be sure all components are configured correctly for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration,
according to the instructions in Chapter 3, “Installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration.”
• Check the eventlog for errors and warnings.
• Use the gwcptrace CLI command for Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server to look for items related to
the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. These items are identified by MPVidSvc.
Problems Configuring and Initiating
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
6-2
Problem Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration failed to initialize.
Solution Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration was unable to do at least one of the following, and will
continue to attempt to initialize until it is successful or the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration service
is stopped. Specific error messages for each follow this Problem/Solution list:
• Connect to the Cisco IPVC MCU.
• Register as authorizer to the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 71

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: Failed to invoke
MPCGICOM.\n");
Solution
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: XmlMsgHandler failed to
initialize: %d\n", ret);
Solution Contact your Cisco technical support representative. See the Guide to Cisco Conferencing
Documentation and Support.
Problems Configuring and Initiating Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
• Retrieve system resource data from the Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server.
• Verify the existence on the Cisco IPVC MCU of the service prefix entered during installation.
• Verify the existence on the Cisco IPVC MCU of the required Voice Activated conference view.
• Synchronize with the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server the status of an existing conference on the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
•
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is unable to establish a connection with
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing. Allow it to try again; if it continues to be unsuccessful,
restart the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing service.
• Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing is not running.
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: XmlSocket failed to
initialize: %d\n", ret);
Solution Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is unable to establish a connection to the
Cisco IPVC MCU. Ping the Cisco IPVC MCU to check the connectivity.
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: CmdHandler failed to
initialize.\n");
Solution Contact your Cisco technical support representative. See the Guide to Cisco Conferencing
Documentation and Support.
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: Failed to verify designated
service code from MCU\n");
Solution Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is unable to determine the existence of the designated
service prefix for the MeetingPlace service on the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: Repeatedly failed to send
resource info to MP Server. \n");
Solution
•
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing is still starting up or is not running.
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration will try three times at 15-second intervals to connect to
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing. Wait for Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing to
initialize.
OL-6280-01
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: Failed to verify resources
in MCU\n");
Solution Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is unable to receive the resource data from the
Cisco IPVC MCU that it needs in order to calculate the number of available video ports and conferences.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
6-3
Page 72

Problems Configuring and Initiating Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: Failed to register MPVideo
as authorizer.\n");
Solution
•
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is unable to register itself as the authorizer on the
Cisco IPVC MCU. Check the authorization settings on the Cisco IPVC MCU. See Setting
Cisco IPVC MCU Parameters Required to Support Cisco MeetingPlace, page 3-4.
• Check if another application has previously declared itself as the authorizer on the
Cisco IPVC MCU. If necessary, reboot the Cisco IPVC MCU to disconnect all applications.
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: Failed to get Video
Information from the MCU unit.\n")
Solution Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is unable to get video conference view settings, or the
current view settings do not fulfill the requirements. Check the previous entry in the eventlog for
explanation.
Problem Error message in Eventlog: "CMcuController::initialize(), ERROR: Failed to register MPVideo
for Notifications.\n")
Solution
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
•
Wait a few moments to allow Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to try again to reinitialize.
• If this error continues to appear, contact your Cisco technical support representative. See the Guide
to Cisco Conferencing Documentation and Support.
Problem Error in Eventlog after installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration: Conference
Technology Provider Initialization Failed, MCU Controller initialization failed
Solution Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration and Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing are not yet
ready to establish the connection. Wait a few minutes; Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration will try
again to establish the connection.
Problem Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration does not seem to be running.
Solution Verify that Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is running:
• Check the eventlog. You should see this message: STATUS:
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration READY to receive requests from MPAgent
• From the Cisco MeetingPlace command-line interface (CLI), type gwstatus. If it is running
.
correctly, its status will be OK.
Problem The Eventlog shows socket failure during Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration initiation, and
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is unable to communicate with the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Solution
• The Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration may be on a different network domain than the
Cisco IPVC MCU and an IP port between the two has not been opened. Open port 3336.
6-4
• The Cisco IPVC MCU is down.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 73

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
Problems Scheduling a Video Conference
Problem A user attempted to schedule a video meeting but the meeting could not be scheduled.
Solution One of the following may be the cause:
• Insufficient video ports are available for the time specified. If this occurs often, consider reducing
the number of floater ports or increasing the number of overbook ports. See About Configuring Port
Parameters, page 4-7.
• No more video conferences may be available for the time specified.
• If the required minimum number of video ports per conference is not available, the meeting cannot
be scheduled. For information, see About the Minimum Number of Video Ports Scheduled, page
2-5. If this problem occurs frequently, adjust the number of overbook ports. See (Optional)
Configuring the Number of Overbook Ports, page 4-8.
Problem The system allocates more ports to a meeting than the user scheduled.
Solution This is normal. In order to prevent more conferences from being scheduled than the system can
accommodate, extra video ports are automatically allocated if a user schedules fewer video ports than
the average number of ports per conference available on the system. The formula that
Cisco MeetingPlace uses to determine the average number of conferences is: (Number of video ports –
number of video floater ports + number of video overbook ports) / Total number of video conferences.
Extra ports are more commonly allocated if the Cisco IPVC MCU uses an EMP card than if it uses an
MP card. To minimize the chances that this will happen, configure the IPVC according to the instructions
specific to Cisco MeetingPlace conferences. For details, see the IPVC release notes: Cisco IP/VC 3511
MCU and Cisco IP/VC 3540 MCU Module Release Notes for Release 3.5.
Problems Scheduling a Video Conference
Problems Joining a Video Conference
Problem Cisco MeetingPlace is unable to initiate the link connecting the audio channel of video
conferences on the Cisco IPVC MCU with the Cisco MeetingPlace audio conference.
Solution
•
Make sure the Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway is set correctly. To test this, create a
Cisco MeetingPlace audio conference and try outdialing to an IP phone. If the IP phone connects
successfully to the audio conference, the MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway is set correctly; check
your Cisco CallManager and MCU gatekeeper settings. If not, see the Administrator’s Guide for
Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway, Release 5.2.1.
• Check the connectivity to the Cisco IPVC MCU. To test that the routing is occurring correctly, try
outdialing from a Cisco MeetingPlace conference to the corresponding video conference on the
Cisco IPVC MCU.
• Check the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server to make sure the outdial actually occurred.
• It is possible but highly unlikely that no video port is available for the link.
• Check in MeetingTime to be sure your video license is activated.
Problem User is unable to initiate or connect to a video conference.
Solution
•
Make sure Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is running.
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
6-5
Page 74

Problems Joining a Video Conference
• If the participant is attempting to join on an ad-hoc basis, video resources cannot be guaranteed and
may not be available.
• It is possible, though highly unlikely, that video ports may be unavailable, even if video ports have
been scheduled in advance. If this problem occurs frequently, consider reducing the number of
overbook ports you have specified. To set an optimal number of overbook ports, see (Optional)
Configuring the Number of Overbook Ports, page 4-8.
• Verify that all connectivity is set correctly, all calls are routed to their intended destinations, and the
intended endpoint is reachable.
• Check the eventlog.
• See also other problem/solution sets in this section related to outdialing and dialing in.
Problem Cannot dial in to meeting from the video endpoint.
Solution Possible causes include the following:
• Any of the items in the previous problem/solution set.
• The problem may be temporary. Try again.
• It is not possible to create an ad-hoc conference simply by dialing in to the Cisco IPVC MCU from
a video endpoint. The meeting must first be either in progress or scheduled in Cisco MeetingPlace.
To start an ad-hoc conference in Cisco MeetingPlace, see About Attending Ad-Hoc Video
Conferences, page 5-6. After the Cisco MeetingPlace conference is in session, then initiate the video
conference.
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
• If the meeting requires a password, or is restricted to profiled or invited users, users must join the
meeting by outdialing from Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing or from a
Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook notification.
• The call may not have successfully reached its intended destination. Check your routing patterns.
For example, make sure the service prefix for Cisco MeetingPlace meetings is unique in the
Cisco IPVC MCU, and that the gatekeeper and Cisco CallManager have no initial strings that are
identical to or begin with this code. For example, if your service prefix is 87, make sure the
gatekeeper and Cisco CallManager do not have a routing instruction that routes all calls beginning
with 8* to an unintended destination.
• Some endpoints may have a maximum dial string length that is shorter than the dial-in number.
Problem Unable to outdial successfully to SCCP endpoints.
Solution Make sure the technology prefix is correctly set in Cisco CallManager.
Problem A user attempts to outdial to join the video conference but nothing happens, or an outdial failure
message appears.
Solution
•
The video endpoint must be running before the user attempts to join the video conference.
• Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration may be configured with the wrong E.164 number.
• There may be no more ports available on the system.
• The line to be outdialed to may be already in use (busy), not connected, nonexistent, entered
incorrectly, or configured incorrectly.
6-6
• See also the items in the problem/solution set related to initiating or joining conferences.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 75

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
Problem (For load-balancing configurations only) The voice and web conferences are up and running but
the video conference is unavailable.
Solution The Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing server on which
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is installed may have been down or unavailable at the start of a
conference. If this happens, the meeting rolls to a server on which Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
is not installed, and video conferencing is not possible for this conference. See Configuring
Load-Balancing Configurations for Video Conferencing, page 3-12.
Problem Error message when dialing out to a video endpoint: Error:[513] A video call is already in
progress. Please wait for the call to complete.
Solution The E.164 number that the user has specified in the Connect dialog box is associated with an
endpoint that is already participating in the video conference, or is currently being called.
Problem User trying to dial in to a conference hears a message that the call has been rejected.
Solution The video conference is not in session, or resources are not available to accommodate the
participant.
Problem The option to join the video conference is not available from within the web conference.
Solution In a DMZ or load-balancing configuration, if the conference is held on a server that
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration is not installed on, video conferencing is not available for that
conference.
Problems During a Video Conference
Problem No video-conferencing ports are available, but ports should be available.
Solution
•
Make sure SCCP services are not using ports you expect to be available to Cisco MeetingPlace.
SCCP and H.323 share the resources on the Cisco IPVC MCU.
• If this happens frequently, examine usage patterns using the reporting tools described in About
Video-Conferencing Statistics, page 4-13 and change the settings for floater and overbook ports
using the calculations in About Configuring Port Parameters, page 4-7.
Problems During a Video Conference
Problem Video participants can hear audio participants, but audio participants cannot hear video
participants.
Solution Make sure the audio codec priority settings on the Cisco IPVC MCU are consistent with the
settings on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
Problem The video image is transmitted, but no audio is transmitted.
Solution
• Make sure the video endpoint is not muted at the endpoint.
Problem The audio channel from the video endpoint is transmitted, but no video image is transmitted.
OL-6280-01
Solution
•
The conference may be set to a bandwidth that the endpoint does not support.
• The endpoint may not support the video format (codec) being used.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
6-7
Page 76

Problems During a Video Conference
Problem No video when joining a video meeting with Cisco VT Advantage.
Solution Make sure the video codecs match on the Cisco IPVC MCU and Cisco CallManager.
Problem Only View Active Speaker is available; users cannot choose to View Multiple People.
Solution
If the Cisco IPVC MCU has only an MP card and not an EMP card, and the MCU is configured to
•
allow SCCP endpoints to attend the conference, all participants can view only the current speaker.
• If the Cisco IPVC MCU has an EMP card, make sure the Continuous Presence view has been set
correctly. See Setting Conference View Parameters, page 3-8.
Problem Poor sound quality, static, or echo coming from the video endpoint.
Solution These issues are not related to Cisco MeetingPlace. Possible solutions:
• Minimize background noise by choosing a quiet location and using the most directional microphone
available.
• If connected via both a video endpoint with a microphone and a telephone, or more than one audio
device of any kind, mute or hang up all but one device.
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
• If your network uses Cisco CallManager, turn off silence suppression (the comfort noise) in
Cisco CallManager.
• Configure all endpoints to optimize sound quality, according to the documentation that came with
the endpoint. Cisco Systems cannot provide technical support for third-party endpoints.
• If other solutions do not solve the problem, try muting the audio channel of the video endpoint at
the endpoint, then connect to the conference via telephone.
For desktop video endpoints, try the following in addition to the previous items:
• Reduce the input gain (volume) of the endpoint that is generating unwanted noise.
• Increase the output volume of an endpoint that is not loud enough.
• The microphone built into most computers generally has poor sound quality. We recommend using
an external microphone instead.
• There may be multiple microphones sending signal from a single user. Check for a microphone on
the computer, a microphone on the video camera, and an external microphone plugged in to your
audio card. Turn off all but one.
• Use a headset with a directional microphone.
• Do not use a desktop video endpoint and a soft phone (such as Cisco VT Advantage and Cisco
Communicator) on the same system to attend a single conference.
• Software-based endpoints generally have lower sound quality than Hardware-based endpoints.
Problem The video image does not update to the current speaker.
Solution
6-8
•
The current speaker may not be video-enabled.
• Check settings in the Cisco IPVC MCU. The Voice Activated view should be set to All see one.
Problem Multiple video links are established.
Solution You have specified an incorrect E.164 address in Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. To
change the entry, see Changing Values Entered During Installation of
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, page 4-3.
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 77

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
Problem Telephone keypad commands do not work (for example, #5 to mute.)
Solution This is correct behavior. Video endpoints are connected to the Cisco IPVC MCU, not directly
to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server, so Cisco MeetingPlace key commands do not apply.
Problems During a Video Conference
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
6-9
Page 78

Problems During a Video Conference
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
6-10
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 79

INDEX
A
ad-hoc video conferencing
adding to existing conference
1-3
and load balancing 3-12
attending 5-6 to 5-7
initiating and joining 1-4
joining 2-7
scheduling 5-3
Allow Internet Access parameter
about
4-12, 5-4
attending meetings
dialing in
2-6, 2-7
outdialing 2-7
video conferences 1-3
attending video conferences
about
2-7, 5-4 to 5-7
ad-hoc 5-6 to 5-7
dialing in 5-6
outdialing 5-5
password-protected meetings 5-7
restricted meetings 5-7
troubleshooting 6-6
using Cisco VT Advantage 5-6
audio codecs
see codecs
B
bandwidth
changing in Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
modifying the default when using Cisco MeetingPlace
Video Integration
4-4
5-2
setting value for Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
4-10
breakout sessions
entering
5-9
C
changing settings
for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
in Cisco IPVC MCU 3-3
Cisco CallManager
configuring to work with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-12, 3-14 to 3-17
documentation 1-5
troubleshooting with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
6-6
used with SCCP video endpoints 3-13
using the service prefix 2-6
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 2-4
Cisco IPVC MCU
and video conferencing
2-6
changing settings 3-3
changing settings for Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
4-3
configuring for Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-2 to 3-11, 4-4
prerequisites before installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-2
resource control 3-2
service prefix used 4-2
troubleshooting with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
6-2, 6-5, 6-8
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 1-3,
2-3, 2-4, 2-5
working with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
1-2
4-2 to 4-4
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
IN-1
Page 80

Index
Cisco IPVC MCU cards
data conferencing card
3-2
rate matching card 3-2
Cisco IPVC PRI Gateway
DID number assigned to
4-2
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 2-3
Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server
configuring to work with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-11
prerequisites before installing Cisco MeetingPlace
Video Integration
3-2
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 2-2
Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes
using
with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
2-3, 2-4
Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook
attending video conferences
5-5
configuring
to work with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-14
using
with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
2-3, 2-4
Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
changing settings for Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
4-3
configuring
to work with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-12
troubleshooting with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
6-5
using with
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
2-2, 2-4
Cisco MeetingPlace SMTP E-Mail Gateway
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
using with video conferencing 5-6
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
about
1-2
prerequisites before installing 3-1
system configurations 2-4
uninstalling 3-19
2-4
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
installing
prerequisites for Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-2
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 2-3,
2-4
Cisco VT Advantage
as a video endpoint for Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-13
attending video conferences 5-6
documentation 1-5
troubleshooting with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
6-8
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 1-3
codecs
audio
3-11, 6-7
bandwidth 3-11
G.729 3-2, 3-13
negotiation priority 3-11
sound quality 3-11
conferences
control
2-6
conference views
continuous-presence
3-6
setting parameters 3-8 to 3-11
voice-activated 3-6
continuous meetings
and video conferencing
5-2
continuous-presence conference views 3-6
D
data conferencing card 3-2
DMZ
configurations
configurations for scheduling video conferences 5-4
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 3-17,
4-12
2-4, 3-17, 4-12, 6-7
IN-2
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 81

Index
E
E.164 number installation value
about
and endpoint address 4-11
and troubleshooting video conferences 6-7
ejecting a participant 5-9
e-mail notifications
using with video conferencing
EMP processor 3-6
ending
video conferences
endpoints
setting address for video conferencing
eventlog
viewing
extending
video conferences
3-18
1-2, 1-4, 5-5
5-10
6-1
1-3, 5-10
5-2
using the service prefix 2-6
using with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
2-3, 2-4
video endpoints 3-2, 3-6, 4-11
I
immediate meetings
and video conferencing
5-1, 5-3
ISDN video endpoints 3-2, 3-13, 3-14, 3-19, 4-2, 4-11, 4-12
IVR prompts 4-2
J
joining meetings with Cisco MeetingPlace Web
Conferencing
see also attending meetings
F
firewall
see also DMZ configurations
floater ports
see also video floater ports
G
G.729 codec 3-2
H
H.225 trunk, creating for Cisco IPVC MCU 3-16
H.320 video endpoints 2-3
H.323
Gatekeeper
about
configuring to work with Cisco MeetingPlace Video
3-2
Integration
3-12
L
leaving video conferences 5-10
lecture-style meetings
and video conferencing
5-2
attending 5-9
licenses
for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
3-2
load balancing
configurations, and video conferencing
3-12
troubleshooting video conferencing 6-7
M
MCU 1-2
meeting room
and video conferencing
and video controls 1-4
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing 5-7 to 5-10
MeetingTime
2-8
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
IN-3
Page 82

Index
using to configure Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
4-1
MP processor 3-6
Multipoint Control Unit
see MCU
muting
audio transmission
5-8
N
negotiation priority for codecs 3-11
now speaking feature 5-8
O
overbook ports
see also video overbook ports
recurring meetings
and video conferencing
5-1
reports
using to troubleshoot Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
6-7
rescheduling
video conferences
5-4
reservationless meetings
and video conferencing
5-2, 5-5
scheduling video conferences 5-3
resources
control
4-4
control of H.323 3-2
maximum number of video conferences 4-5
maximum number of video ports 4-5
tracking availability 2-8
restricted meetings 1-2, 5-7
routing pattern 2-6, 3-2, 3-16
P
participants
showing when a participant leaves
5-9
status in video conferences 2-8
passwords
needed to attend video conferences
5-7
requiring for video conferences 1-2
used for scheduling video conferences 5-4
pause video transmission 5-8, 5-9
ports
tracking availability in Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
2-8
processors supported in Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-6
R
rate matching card 3-2
recording meetings
video conferences
5-9
S
SCCP video endpoints 3-2, 3-6, 3-13, 4-11, 6-6
scheduling
video conferences
scheduling meetings
video conferences
about 1-2, 2-5
minimum number of ports 2-5
service prefix 2-6, 2-7, 3-2, 4-1
service templates for Cisco MeetingPlace 3-5
setting up
end-users
5-2
sound quality
troubleshooting
starting
video conferences
system configuration
for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
1-4
5-3 to 5-4
6-8
1-3, 2-6
2-4
IN-4
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
Page 83

Index
T
terminating video conferences 2-9, 5-10
translation tables
modifying for Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
3-11
troubleshooting
attending video conferences
6-5 to 6-7
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration 6-1
configuring Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
6-2 to 6-4
scheduling
video conferences
6-5
video conferencing
no video image
6-7, 6-8
poor sound quality 6-8
reports 6-7
using Cisco VT Advantage 6-8
with DMZ configurations 6-7
video link problems 6-5
U
uninstalling
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration
usage statistics
see reports
user profiles
managing for video use
4-10 to 4-13
used to schedule video conferences 5-2
video conferencing 1-2
V
video conferencing
ad-hoc
Allow Internet Access parameter 4-12
attending 5-4 to 5-7
attending lecture-style meetings 5-9
1-3, 1-4, 2-7, 3-12
3-19
attending meetings 1-3
bandwidth 4-12
breakout sessions 5-9
components 2-1
continuous meetings 5-2
displaying participant status 2-8
E.164 number 3-18, 4-11
ejecting a participant 5-9
ending 2-9
extending 1-3
extending meetings 5-10
immediate meetings 5-1
leaving a meeting 5-10
lecture-style meetings 5-2
license 3-2
load-balancing configurations 3-12
muting audio transmission 5-8
now speaking feature 5-8
participant list 5-9
pausing video transmission 5-8, 5-9
prerequisites 3-1
recording 5-9
recurring meetings 5-1
reports 1-3, 4-13 to 4-15
rescheduling 5-4
reservationless meetings 5-2
restricted meetings 1-2
scheduling 1-2, 1-4, 2-5, 5-3 to 5-4
sending e-mail notifications 1-2
setting up end-users 5-2
starting 1-3
terminating 5-10
tracking available ports 2-8
troubleshooting 6-1, 6-2 to 6-4
troubleshooting dialing in 6-6
troubleshooting load-balancing configurations 6-7
troubleshooting outdialing 6-6
troubleshooting scheduling 6-5
troubleshooting with E.164 number 6-7
OL-6280-01
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
IN-5
Page 84

Index
using a video link 2-6 to 2-7
video controls 1-4
video floater ports 1-3
video overbook ports 1-3
views
view active speaker
5-8, 5-9
view multiple people 5-8, 5-9
video controls 1-4
video endpoints
about
1-3
address 4-11
functions of 2-4
H.323 3-2, 3-6, 4-11
illustration 2-5
installing 3-13
ISDN 3-2, 3-13, 3-14, 3-19, 4-2, 4-11, 4-12
prerequisites before installing Cisco MeetingPlace
Video Integration
3-2
SCCP 3-2, 3-6, 3-13, 4-11, 6-6
setting up 5-2
verifying connection to Cisco IPVC MCU 3-3
video floater ports 1-3, 2-5
video link
about
2-2
displaying in video conferencing 5-8
function of 2-3
in video conferences 1-3
problems 6-5
video overbook ports 1-3, 2-5
video phone numbers 4-2
video ports
changing settings
4-9
configuring video floater ports 4-7 to 4-8
default number scheduled 4-4, 4-6
floater 4-4, 4-7
maximum number of schedulable 4-4, 4-6
overbook 4-4, 4-7, 4-8 to 4-10
used when scheduling video conferences 2-5
video service code 4-2
visual images in Cisco MeetingPlace Video
Integration
2-8
voice-activated conference views 3-6
IN-6
Administrator’s Guide for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3
OL-6280-01
 Loading...
Loading...