Page 1

Administrator Guide
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
Revised: April 2006
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Text Part Number: OL-6571-02
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCIP, CCSP, the Cisco Arrow logo, the Cisco Powered Network mark, Cisco Unity, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.;
Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE,
CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems
logo, Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, GigaStack, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ
Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, MGX, MICA, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, RateMUX,
Registrar, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, and VCO
are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0401R)
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Copyright © 2005-2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
CHAPTER
1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 1-1
Audience 1-1
Scope 1-1
Naming Conventions Used in This Guide 1-2
New Features in This Release 1-2
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Components
1-3
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace System 1-3
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 1-4
Standards That are Supported by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
1-4
Protocols That Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Uses
1-5
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency Support by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
Software Release 5.2.1
1-5
Audio Quality During a Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Meeting 1-6
Endpoints That are Supported by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
1-6
How PSTN and Cisco IP Phones Communicate by Using Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
1-7
How H.323 Clients and Cisco SIP IP Phones Communicate by Using Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
1-9
CHAPTER
OL-6571-02
Additional References 1-10
2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 2-1
How to Complete Prerequisites for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 Installation or Upgrade
2-1
How to Configure Cisco Unified CallManager for Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
2-2
Adding the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Server to the
Cisco Unified CallManager Configuration Database
2-2
Assigning a Cisco Unified CallManager Route Pattern to Point to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Release Release 5.2.1 Server
2-4
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
2-5
Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 2-6
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323 SIP/IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
iii
Page 4

Contents
Upgrading to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IPGW Software Release 5.2.1 From
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Release 5.x
2-6
Upgrading to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 From
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Release 4.x
2-7
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM 2-7
Changing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM Settings 2-8
Uninstalling Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 2-9
CHAPTER
3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 3-1
Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release
5.2.1
3-1
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 3-3
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use With
Cisco Unified CallManager
3-4
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use With
Cisco SIP Proxy Server
3-4
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use With
an H.323 Gatekeeper
3-5
Verifying MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Configuration 3-6
Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
for Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
3-7
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use With
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
3-7
Assigning the Primary IP Address 3-7
Information About Configuring Multiple Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 Servers for Load Balancing and Redundancy
3-8
Information About Configuring a Dialing Group 3-8
CHAPTER
iv
How to Configure a Dialing Group 3-8
Configuring a Dialing Group Example 3-9
Information About Reservationless Single Number Access Configuration 3-9
Information About Reverse Connection to the MeetingPlace Audio Server System Configuration 3-10
4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 4-1
Troubleshooting Network Connectivity 4-1
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity 4-2
Unable to Make Calls From a Cisco IP Phone 4-2
Unable to Call a PSTN Telephone From a Cisco IP Phone or Vice Versa 4-2
Dead Air Heard When Using an H.323 Device 4-3
Dead Air Heard When Using a Cisco IP Phone 4-3
Fast Busy Signal Heard When Using a Cisco IP Phone 4-3
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323 SIP/IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 5

Contents
Unable to Make Dial-Pad Key Selections When Using an H.323 Device 4-3
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When IP Ports Do Not Answer 4-4
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Server
When IP Ports Do Not Answer
4-4
Checking Cisco Unified CallManager When IP Ports Do Not Answer 4-5
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When IP Calls Connect But No Audio
Is Heard
4-5
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 When IP
Calls Connect But No Audio Is Heard
4-6
Checking the Cisco IP Phone When IP Calls Connect But No Audio Is Heard 4-6
Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports 4-6
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When Unable to Dial Out on IP
Ports
4-7
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Server
When Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports
4-7
Checking Cisco Unified CallManager When Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports 4-8
APPENDIX
I
NDEX
Troubleshooting Audio Problems 4-8
Poor or Low-Audio Quality 4-8
Echo 4-9
A Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation
Worksheets
A-1
Information About the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Installation Worksheet
A-1
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation
Worksheet
A-1
Information About the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial
A-2
Plan
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial Plan
Worksheet
A-3
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323 SIP/IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
v
Page 6

Contents
vi
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323 SIP/IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 7

CHA P TER
1
Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Audience, page 1-1
• Scope, page 1-1
• Naming Conventions Used in This Guide, page 1-2
• New Features in This Release, page 1-2
• Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Components, page 1-3
• Additional References, page 1-10
Note In this guide, Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 is referred to
as Release 5.2.1.
Audience
Scope
OL-6571-02
This guide is for network and telephony system administrators who are responsible for installing and
configuring Release 5.2.1 for use with the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
provides information about Release 5.2.1 that enables you to perform the following actions:
• Understand the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system and related IP telephony components.
• Install and configure Release 5.2.1.
• Configure Cisco Unified CallManager to route IP calls to the IP-gateway server.
• Use Release 5.2.1 with IP PBX systems that are running standard H.323 or SIP call control—such
as Avaya, Nortel, Alcatel, and Pingtel systems.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
1-1
Page 8
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Naming Conventions Used in This Guide
This guide does not provide information about configuring third-party, call-control applications. If you
are using an IP PBX that runs standard H.323 or SIP call control, see the “Information About
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1” section on
page 3-1 for required system settings and see your IP PBX documentation for information about how to
configure those settings.
Additionally, this guide does not provide information about installing Multi Access (MA) blades or
configuring the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system for IP; for more information about
these topics, see the “Additional References” section on page 1-10.
Naming Conventions Used in This Guide
The following naming conventions are used in this guide:
Product Naming Convention
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server release
and hardware upon which the release is installed
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server with
any possible combinations of integration
applications
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway System
Integrity Manager
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1—the hardware
upon which Release 5.2.1 is installed
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system
Gateway SIM
Release 5.2.1
IP-gateway server
New Features in This Release
Release 5.2.1 includes the following new features:
Feature Description
Dialing Group Configuration Dialing group configuration customizes the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system by presenting specific voice
prompts to callers who dial in to a meeting by using a particular IP
phone number.
Improved Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Gateway SIM
Installation
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
1-2
During Release 5.2.1 installation, the Gateway SIM installs or
upgrades automatically if an earlier Gateway SIM release is detected.
OL-6571-02
Page 9
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
Supporting up to 960 IP connections, Release 5.2.1 works with the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio
Server system to provide meeting access to callers. The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server
system supports connections from up to sixteen IP-gateway servers; this multigateway support provides
network load balancing and system redundancy.
To deploy Release 5.2.1, your network must have following system components:
• Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system to provide conferencing functionality.
• Release 5.2.1 to perform IP call setup and tear down for the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio
Server system.
• Endpoints that are supported by Release 5.2.1 to connect callers to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Audio Server system.
• One of the following applications to route IP calls to the IP-gateway server:
–
Cisco Unified CallManager
–
Cisco SIP Proxy Server
–
Cisco Gateway
Note If you are using an IP PBX that runs standard H.323 or SIP call control, see the “Information About
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1” section on
page 3-1 for the required system settings and see your IP PBX documentation for information about how
to configure these settings.
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace System
Consisting of the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system and a variety of integration
applications, the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system is an integrated communication and productivity
tool that is deployed on a corporate network behind the firewall. With the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
system, users in different locations can collaborate in real time by sharing documents over personal
computers and discussing content over telephones.
Access to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system is easy through end-user desktop applications, such
as web browsers and instant messaging clients. The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system also integrates
with groupware clients and PSTN and IP-based telephones. Because of this access and integration, users
can quickly schedule and attend Cisco Unified MeetingPlace meetings from any location by using their
preferred interfaces.
For additional information about the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system, see the Installation Planning
Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace 5.3 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/prod_installation_guides_list.html
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
1-3
Page 10

Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
IP telephony uses your data network infrastructure to transmit voice packets. The underlying technology
that is used by IP telephony applications is Voice over IP (VoIP), which enables different types of
endpoints—IP phones, PSTN phones, and H.323 clients, for example—to communicate over your
network.
The following sections provide information about VoIP concepts and how they relate to Release 5.2.1:
• Standards That are Supported by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1, page 1-4
• Protocols That Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Uses,
page 1-5
• Dual Tone Multi-Frequency Support by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
Software Release 5.2.1, page 1-5
• Audio Quality During a Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Meeting, page 1-6
Standards That are Supported by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
Release 5.2.1 supports the following networking and telephony standards:
• H.323
• SIP
• RTP
• Codec G.711 alaw and ulaw (64 kbps) and G.729a (8 kbps)
Note By default, G.729a is not enabled, and G711 codec calls are negotiated first. For more
information about assigning codec preferences, see the Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/products_installation_and_configura
tion_guides_list.html
1-4
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 11

Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
Protocols That Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Uses
Protocols are rules that endpoints follow for sending and receiving messages, checking errors, and
compressing data. Release 5.2.1 uses the following protocols to transmit data throughout the
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system:
Protocol Description
H.323 The protocol that is responsible for communication between
Cisco Unified CallManager and Release 5.2.1. The protocol suite,
which extends H.225 for call signaling and H.245 for data transfer, is
used in the successful acceptance and media exchange of data.
Session Initiation Protocol
(SIP)
Real-Time Transport
Protocol (RTP)
Skinny Station Protocol
(SSP)
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Gateway System Integrity
Manager (SIM)
A call-control protocol that supports all existing functionality that is
available to a Cisco IP phone. Release 5.2.1 complies with RFC 3261
and RFC 3515 specifications and interoperates with the following
endpoints:
• Cisco SIP Proxy Server environment
• Cisco 7960 and Cisco 7940 SIP IP phones
• Cisco IP/Videoconferencing Multipoint Control Unit
(IP/VC MCU)
• Microsoft Real-Time Communications (RTC) Server for
integration with Windows XP Messenger
An Internet protocol responsible for the transmission of real-time data,
such as video and audio. Generally, RTP runs on top of User Datagram
Protocol (UDP) but can also be supported by other transport protocols.
For Release 5.2.1, RTP is responsible for carrying the G.711 and
G.729a encoded data. G.711 is a standard 64 kbps codec, and G.729a is
an 8 kbps codec. Both codecs offer quality audio transmission over
high-speed connections.
A protocol that is used to establish connections, locate resources,
forward data, and handle flow control and error recovery, which enable
a Cisco IP phone to notify Cisco Unified CallManager of its ability to
place and receive calls.
A messaging service that enables NT services on the IP-gateway server
to communicate directly with the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system.
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency Support by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) is a signaling method that allocates a specific pair of frequencies
to each key on a touch-tone telephone. Various Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system
functions are invoked when callers press touch-tone keys in certain combinations. For example, the #5
key combination enables callers to mute and unmute their phones during a meeting.
PSTN phones use in-band DTMF, which embeds the tone in the audio stream. Although in-band DTMF
is efficient, it cannot carry DTMF signals reliably when a voice compression codec is used.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
1-5
Page 12
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
H.323 clients can use out-of-band DTMF, which carries digitized information on a separate data channel
and sends this information directly to Release 5.2.1. Because out-of-band DTMF does not require that
the tone be deciphered, distortion and signal loss are minimal.
The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system also supports RFC 2833: DTMF signals can be sent in the RTP
stream by using packets designed to carry the signal characteristics. The DTMF signal is not embedded
in the media and, therefore, does not suffer signal loss due to audio compression.
Release 5.2.1 handles both in-band and out-of-band DTMF.
Note Release 5.2.1 does not support out-of-band digit detection with SIP.
Audio Quality During a Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Meeting
The audio quality during a meeting depends upon the architecture of your network. Severe demands on
bandwidth, overloading, and latency cause dropped packets, resulting in broken audio, congestion, and
disruption of service.
In general, a switched-100 Mbps network handles VoIP traffic efficiently. To alleviate potentially
disruptive service and to improve audio quality, consider implementing class of service (CoS) and
quality of service (QoS).
When the server handles over 400 ports of IP calls, voice quality degradation can occur because of
network congestion. CoS is a technology that helps manage network traffic by assigning a class to
similar types of traffic and assigning a priority to each class. Typically in a VoIP environment, voice
traffic is set to a high priority while data traffic is set to a low priority, and CoS makes a best effort to
provide QoS by managing traffic based upon the assigned class and priority.
Release 5.2.1 implements IP Precedence Level 5 CoS for voice traffic. If your network is set to use this
CoS, the resulting QoS maximizes audio quality during your meetings.
Note Release 5.2.1 does not support sending Layer 2 QoS or CoS; therefore, you cannot set priorities at the
Layer 2 switch level.
Endpoints That are Supported by Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Release 5.2.1 integrates easily with existing networks to host Cisco Unified MeetingPlace meetings for
users through the following supported endpoints:
• Cisco IP Phones
• Cisco SIP IP Phones
• H.323 clients, such as Microsoft NetMeeting
• PSTN phones through a voice gateway
1-6
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 13
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
How PSTN and Cisco IP Phones Communicate by Using Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
When a call is placed from a PSTN phone to a Cisco IP phone, the call is routed through a voice gateway,
which is the demarcation point where the circuit-switched voice network meets the packet-switched data
network. The primary responsibility of the voice gateway is to ensure that PSTN voice traffic reaches
the data network and vice versa. You can use the voice gateway to forward an IP or PSTN call to its
opposing network through Cisco Unified CallManager or a PBX.
When a call is placed from an Cisco IP phone, it is routed to Cisco Unified CallManager, which is
responsible for setting up the call, directing the call to the called device, and sending network
information— such as the IP address, UDP port number, and communication capabilities of the called
device—to the Cisco IP phone. After receiving the information, the Cisco IP phone sends its digitized
voice traffic directly to the called device.
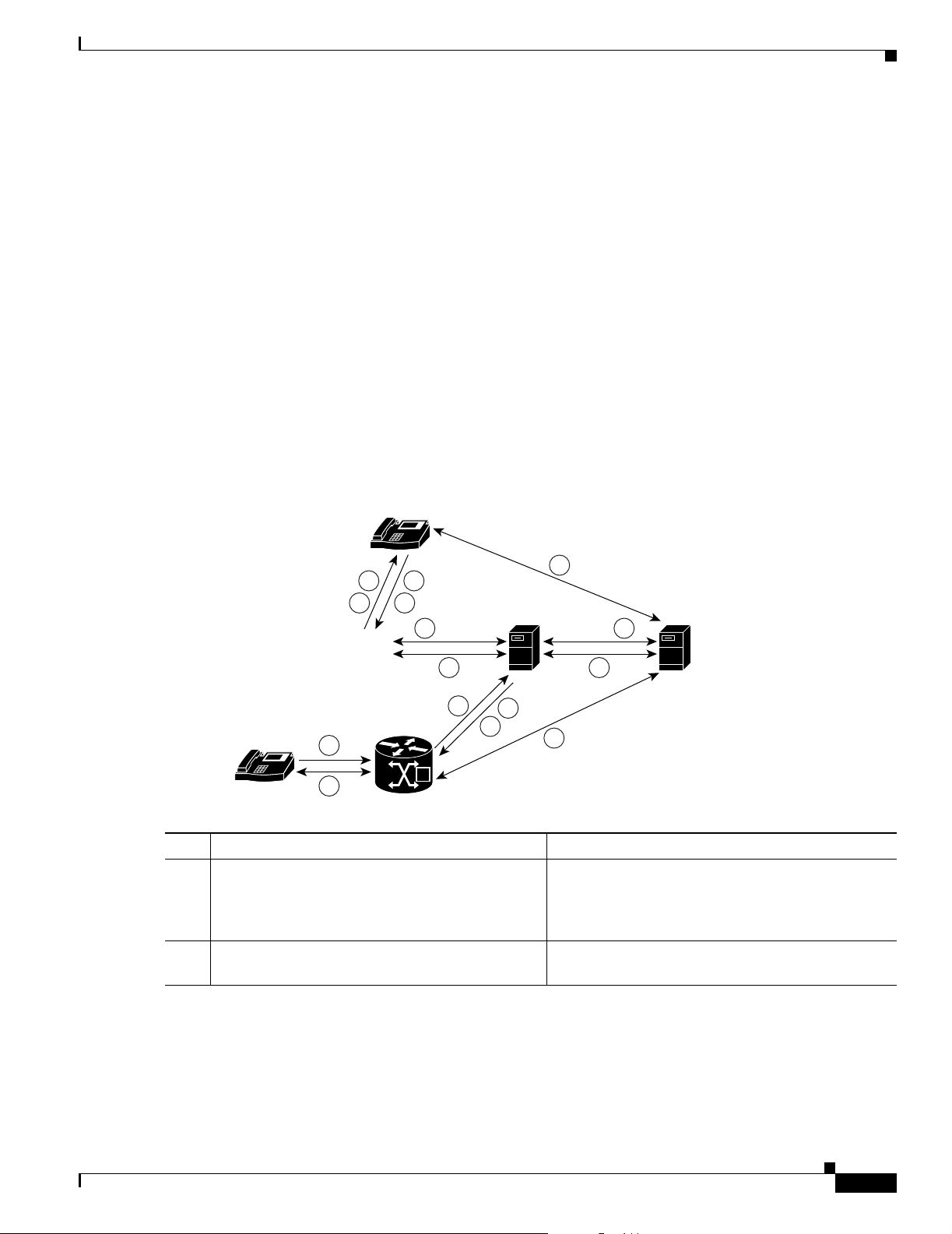
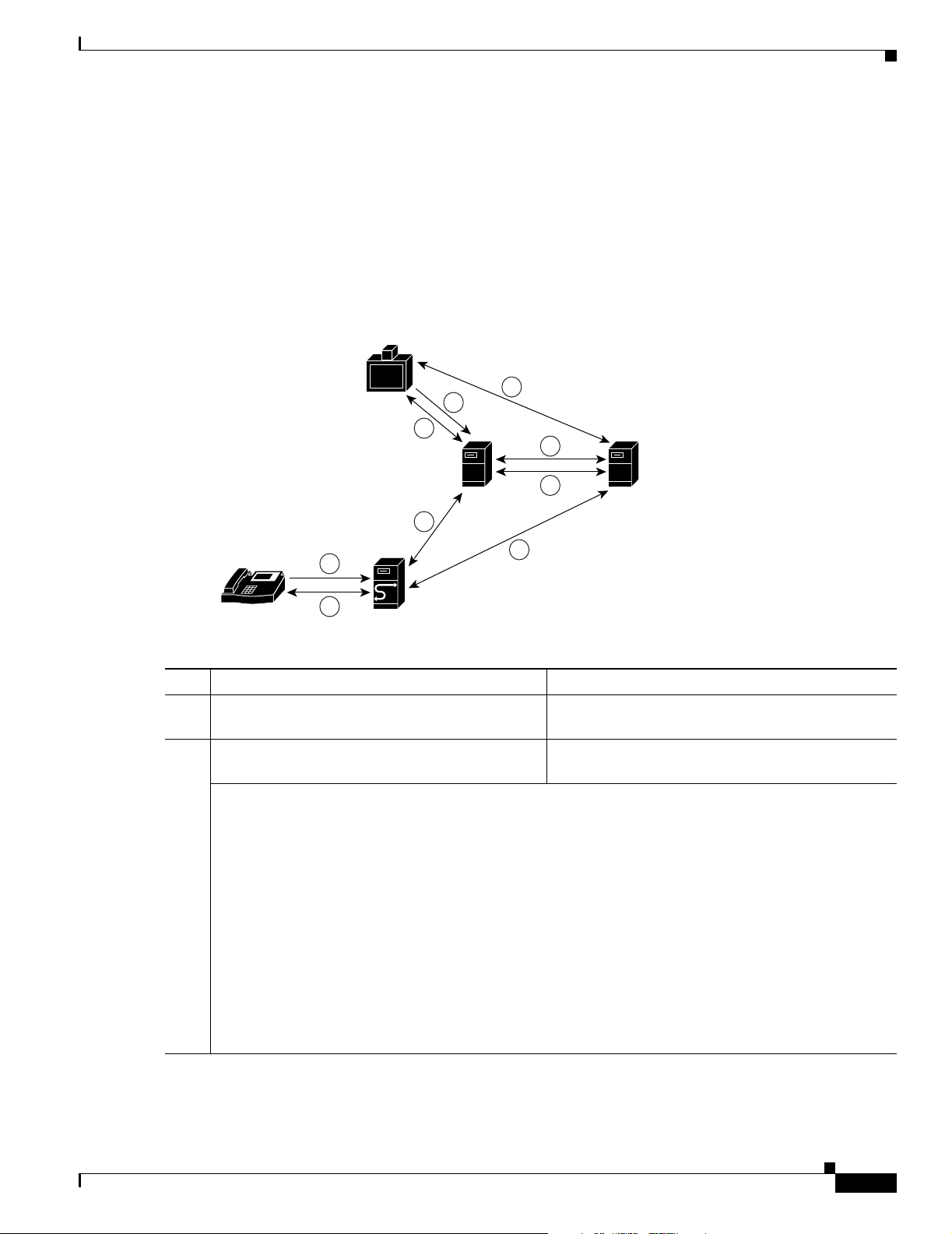
The following steps describe how Cisco IP phones and PSTN phones use Release 5.2.1 to access the
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 Cisco IP Phones and PSTN Phones Using Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software to Access the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System
Cisco IP phone
IP
5
1
3
2
4
Cisco CallManager
1
IP
PSTN phone
.
5
Voice gateway
Cisco MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway
3
4
2
V
4
3
3
4
5
Cisco
MeetingPlace
Audio Server
121557
Step Cisco IP Phone Description PSTN Phone Description
1. On the Cisco IP phone dial pad, the caller enters a
dialable number to the Cisco Unified
By using a PSTN phone, the caller dials the number
to the voice gateway.
MeetingPlace Audio Server system that will host
the meeting.
2. The call is immediately routed by using SSP to
Cisco Unified CallManager.
The voice gateway routes the call to Cisco Unified
CallManager.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
1-7
Page 14
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
Step Cisco IP Phone Description PSTN Phone Description
3. Cisco Unified CallManager and Release 5.2.1
communicate by using H.323. This
communication process involves H.225 for call
signaling and H.245 for media exchange.
a. Cisco Unified CallManager and Release 5.2.1 use H.225 to determine if the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system can accept the call. By using Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
GWSIM, Release 5.2.1 communicates directly with the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio
Server system to determine its availability.
b. If the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system is unavailable, Release 5.2.1 informs
Cisco Unified CallManager, and the caller hears a fast busy signal.
c. If the call is accepted, Cisco Unified CallManager and Release 5.2.1 use H.245 to negotiate
which codec will carry the voice activity. Release 5.2.1 uses G.711 or G.729a to carry the
encoded speech.
Cisco Unified CallManager examines its routing
table to resolve the dialed number with the IP
address of the IP-gateway server.
Cisco Unified CallManager and Release 5.2.1
communicate by using H.323. This communication
process involves H.225 for call signaling and H.245
for media exchange.
d. Once codec negotiation is complete, Release 5.2.1 uses the Gateway SIM to retrieve an IP
address and UDP port number from the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system. This
IP address and UDP port number provide access to the meeting.
4. Cisco Unified CallManager and Release 5.2.1 exchange the IP address and UDP port number of the
Cisco IP phone or voice gateway and the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system
a. Cisco Unified CallManager sends the IP address and UDP port number of the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system to the Cisco IP phone or voice gateway.
b. Release 5.2.1 sends the IP address and UDP port number of the Cisco IP phone or voice gateway
to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
5. After codec information, IP address, and UDP port number are received, the Cisco IP phone or voice
gateway uses the information to send voice traffic directly to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio
Server system. The Cisco IP phone or voice gateway is connected to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Audio Server system after each device exchanges data.
1-8
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 15
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Components
How H.323 Clients and Cisco SIP IP Phones Communicate by Using Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
H.323 clients and Cisco SIP IP phones—which can be simultaneously deployed—communicate with
Release 5.2.1 and provide another option to join a Cisco Unified MeetingPlace meeting.
The following steps describe how H.323 devices and Cisco SIP IP phones access the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system by using Release 5.2.1.
Figure 1-2 H.323 Device and Cisco SIP IP Phone Using Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software to Access the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System
H.323 device
Cisco MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway
1
IP
Cisco SIP
IP phone
.
4
IP
Cisco SIP
proxy server
1
2
2
4
2
3
4
Cisco
MeetingPlace
Audio Server
121556
Step H.323 Device Description Cisco SIP IP Phone Description
1. A caller places a call from an H.323 device
A caller places a call from a Cisco SIP IP phone.
interface.
2. The H.323 device and Release 5.2.1 communicate
by using H.323.
a. The H.323 device or Cisco SIP IP phone and Release 5.2.1 determine if the Cisco Unified
The Cisco SIP IP phone through Cisco SIP Proxy
Server and Release 5.2.1 communicate by using SIP.
MeetingPlace Audio Server system can accept the call. By using the Gateway SIM, the
Release 5.2.1 communicates directly with the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system
to determine its availability.
b. If the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system is unavailable, Release 5.2.1 informs
the H.323 device or Cisco SIP IP phone, and depending upon system configuration, callers may
hear a message informing them that the call cannot be accepted.
OL-6571-02
c. If the call is accepted, the H.323 device or Cisco SIP IP phone and Release 5.2.1 negotiate
which codec will carry the voice activity. Release 5.2.1 uses G.711 or G.729a to carry the
encoded speech.
d. Once codec negotiation is complete, Release 5.2.1 retrieves an IP address and UDP port number
from the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system by using Gateway SIM. This IP
address and UDP port number provide access to the meeting.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
1-9
Page 16

Additional References
Step H.323 Device Description Cisco SIP IP Phone Description
3. The H.323 device or Cisco SIP IP phone and Release 5.2.1 exchange IP addresses and UDP port
numbers.
a. Release 5.2.1 sends the IP address and UDP port number of the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Audio Server system to the H.323 device or Cisco SIP IP phone.
b. Release 5.2.1 sends the IP address and UDP port number of the H.323 device or Cisco SIP IP
phone to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
4. After codec information, IP address, and UDP port number of the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio
Server system are received, the H.323 device or Cisco SIP IP phone uses the information to send voice
traffic directly to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system. The H.323 device or
Cisco SIP IP phone is connected to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system after each
device exchanges data.
Additional References
See to the following documents for additional information:
Chapter 1 Introducing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
• Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html
• Cisco Unified CallManager documentation for your release
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_callmg/index.htm
• Cisco SIP Proxy Server documentation for your release
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/sipproxy/index.htm
• Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/products_installation_and_configuration
_guides_list.html
• Guide to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Conferencing Documentation and Support
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/products_documentation_roadmaps_list.
html
• Installation Planning Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/prod_installation_guides_list.html
• Release Notes for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/prod_release_notes_list.html
• Release Notes for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/prod_release_notes_list.html
1-10
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 17

CHA P TER
2
Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP
IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
To install Release 5.2.1, perform the following procedures in this order:
• How to Complete Prerequisites for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 Installation or Upgrade, page 2-1
• How to Configure Cisco Unified CallManager for Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP
IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1, page 2-2
• How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1, page 2-5
How to Complete Prerequisites for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation or
Upgrade
• Verify that your system meets the requirements listed in the Release Notes for Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1.
• Complete the “Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Installation Worksheet” section on page A-1 and “Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial Plan Worksheet” section on page A-3.
These worksheets identify the required information that you need to install and configure Release
5.2.1 to work with VoIP devices.
• By following the instructions in the “How to Configure Cisco Unified CallManager for Use With
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1” section on page 2-2,
configure Cisco Unified CallManager for your network.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
2-1
Page 18

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Configure Cisco Unified CallManager for Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
• If a firewall separates the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system from the IP-gateway
server, open port 5003.
Tip The Gateway SIM communicates with the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system through
port 5003. This port can be bidirectional or unidirectional and can be opened on either the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system or the IP-gateway server depending on your corporate security
needs.
• Stop all previously installed Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system services.
How to Configure Cisco Unified CallManager for Use With
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
When a caller dials a number from an IP phone, the call is first directed to Cisco Unified CallManager;
from there, Cisco Unified CallManager associates the dialed number with a route pattern that points to
the appropriate IP-gateway server.
Note Traffic must be allowed to pass through ports 1024-65535 because the IP-gateway server uses these
ports to send dynamic TCP and UDP traffic to Cisco Unified CallManager.
Before you can install and configure Release 5.2.1, you must configure Cisco Unified CallManager to
point to your IP-gateway server. To configure Cisco Unified CallManager, you must first add a gateway;
the, assign the gateway to a route pattern.
To configure Cisco Unified CallManager for use with Release 5.2.1, perform the following procedures
in this order:
• Adding the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Server to the
Cisco Unified CallManager Configuration Database, page 2-2
• Assigning a Cisco Unified CallManager Route Pattern to Point to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Release Release 5.2.1 Server, page 2-4
Adding the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 Server to the Cisco Unified CallManager Configuration Database
To enable Cisco Unified CallManager to route calls to IP-gateway servers in your network, you must first
add each IP-gateway server to the Cisco Unified CallManager configuration database.
Step 1 From the Cisco Unified CallManager server, choose Start > Programs > Cisco Unified CallManager
> CallManager Administration.
2-2
Step 2 Enter the user name and password in the appropriate fields and click OK.
Step 3 In the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration page, choose System > CallManager.
Step 4 To display the Find/List Gateways window, choose Device > Gateway.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 19

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Configure Cisco Unified CallManager for Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
Step 5 Click the Add a New Gateway link.
The Add a New Gateway window appears.
Step 6 From the Gateway drop-down menu, choose H.323 Gateway.
In the Device Protocol drop-down menu, the H.225 device protocol appears.
Step 7 Click Next.
The Gateway Configuration window appears.
Step 8 Enter information in each field of the Gateway Configuration window, as shown in Table 2-1.
Note Maintain the default setting for all other parameters
.
Table 2-1 Fields in the Gateway Configuration Window
Field Description Task
C.
Device Name Identifies the Cisco Unified CallManager
device.
Device Pool Specifies a collection of properties for this
device including Cisco Unified
CallManager Group, Date/Time Group,
Region, and Calling Search Space for
autoregistration of devices.
Locations Specifies the total bandwidth that is
available for calls to and from this
location. A location setting of None means
that the locations feature does not keep
track of the bandwidth that is consumed by
this device.
Calling Party
Selection
Sends directory number information for an
outbound call. Information in this field
determines which directory number is
sent. The following options specify which
directory number is sent:
• Originator—Sends the directory
number of the calling device.
• First Redirect Number—Sends the
directory number of the redirecting
device.
• Last Redirect Number—Sends the
directory number of the last device to
redirect the call.
Enter the hostname or IP address of the
IP-gateway server.
Choose Default.
If applicable, choose the location of the
IP-gateway server on your network.
Choose Originator.
OL-6571-02
Presentation
Bit
Determines whether the central office
Choose None.
transmits or blocks caller ID.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
2-3
Page 20

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Configure Cisco Unified CallManager for Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Table 2-1 Fields in the Gateway Configuration Window (continued)
Field Description Task
Gatekeeper
Registration
Media
Termination
Point (MTP)
Required
Step 9 Click Insert.
Provides address translation and controls
access to the LAN for connections
between H.323-compliant devices, such as
terminals and gateways.
Implements features that H.323 does not
support (such as hold and transfer) via
MTP. This check box is only for H.323
clients and H.323 devices that do not
support the H.245 Empty Capabilities Set
message.
Choose None.
Deselect this option.
Assigning a Cisco Unified CallManager Route Pattern to Point to the
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Release Release 5.2.1
Server
After adding the IP-gateway server to the Cisco Unified CallManager configuration database, you must
assign a route pattern, which comprises a string of digits (an address) and a set of associated digit
manipulations that can be assigned to the IP-gateway server. Route patterns work with route filters and
route lists to direct calls to the IP-gateway server and to include, exclude, or modify specific digit
patterns.
2-4
Tip Assigning 8XXX to a gateway routes all directory numbers 8000 to 8999 out the gateway. Similarly,
82XX routes directory numbers 8200 to 8299.
Step 1 If applicable, ensure that you have configured the following items in Cisco Unified CallManager:
• Gateway
• Route list
• Partition
• Route filter
Step 2 In the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration page, choose Route Plan > Route Pattern.
Step 3 Click Add a New Route Pattern.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 21

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Step 4 Enter the information in Tab le 2 -2 into the corresponding fields in the Route Pattern Configuration
window.
Table 2-2 Fields in the Route Pattern Configuration Window
Field Description
Route Pattern Enter the number for IP-gateway that you configured in “Adding the
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release
5.2.1 Server to the Cisco Unified CallManager Configuration
Database” section on page 2-2. This is the number that callers use to
connect to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Numbering Plan If applicable, choose the appropriate numbering-plan option.
Gateway/Route List Choose the host name or IP address of the IP-gateway server.
Route Option Choose Route this pattern and deselect the Provide Outside Dial
Tone box.
Step 5 To save your settings, click Insert.
Audio Server system.
Note Once you click Insert and the window refreshes, an (Edit) link appears in the window next to the
Gateway/Route List field. This link takes you to the Gateway Configuration or Route List Configuration
window for reference, depending upon whether the Gateway/Route List field contains a gateway or a
route list. You can see the route group that is included in that route list if the route group was specified.
If the route group was not specified, you see devices.
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Note You must configure Cisco Unified CallManager before you install Release 5.2.1.
This section includes the following procedures:
• Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1, page 2-6
• Upgrading to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IPGW Software Release 5.2.1 From
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Release 5.x, page 2-6
• Upgrading to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 From
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Release 4.x, page 2-7
OL-6571-02
• Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM, page 2-7
• (Optional) Changing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM Settings, page 2-8
• (Optional) Uninstalling Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1,
page 2-9
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
2-5
Page 22

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
Step 1 Complete the tasks in the “How to Complete Prerequisites for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP
IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation or Upgrade” section on page 2-1.
Step 2 To install the software by running the setup.exe file, insert the Release 5.2.1 CD-ROM into the
IP-gateway server CD-ROM drive.
Step 3 After the Welcome window appears, click Next.
The Installer window appears.
Step 4 (Optional) If the installation utility does not start, perform the following steps:
Caution Do not manually run the ISScript8.Msi file.
a. Choose Start > Run.
b. Enter X:\SETUP where X is the mapped CD-ROM drive.
c. Click OK.
Step 5 Choose Complete for setup type and click Next.
Step 6 Click Install.
The installation begins.
Step 7 If the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM InstallShield Wizard begins, install and configure
Gateway SIM by completing the steps in the “Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM”
section on page 2-7.
Step 8 To complete installation, click Finish.
Step 9 If prompted, reboot the IP-gateway server.
Step 10 If you plan to install Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system integration applications on the Release 5.2.1
IP-gateway server, install those applications now.
Note Before you install multiple Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system integration applications on the
IP-gateway server, ensure that your system meets the requirements for integration. For additional
information, see Important Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Products and Cisco Media
Convergence Servers at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/mpmcs.htm
Upgrading to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IPGW Software
Release 5.2.1 From Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Release 5.x
2-6
Step 1 Ensure that the tasks in “How to Complete Prerequisites for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation or Upgrade” section on page 2-1 have been completed and
that you have collected the configuration information for the currently installed Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace IP Gateway release.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 23

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Step 2 Install Release 5.2.1by using the procedures in the“How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1” section on page 2-5.
The configuration settings are imported during installation.
Upgrading to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 From Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Release 4.x
Step 1 Ensure that the tasks in “How to Complete Prerequisites for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation or Upgrade” section on page 2-1 have been completed and
that you have collected the configuration information for the currently installed Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace IP Gateway release.
Step 2 To uninstall Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway 4.x, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel >
Add/Remove Programs.
Step 3 Select MeetingPlace IP Gateway and click Remove.
Note Uninstalling Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway 4.x may also uninstall any previous
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace GWSIM release.
Step 4 Install Release 5.2.1 by using the procedures in “How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1” section on page 2-5.
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM
Gateway SIM enables Release 5.2.1 and other Cisco Unified MeetingPlace integration applications to
communicate with the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system. With Release 5.2.1, Gateway
SIM installs or upgrades automatically; perform the following steps to configure the settings:
Step 1 After the Welcome window appears, click Next.
Step 2 In the Choose Destination Location dialog box, click Next to begin installation.
Step 3 To complete installation, click Finish.
The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Server Entry dialog box appears.
Step 4 Enter the name of the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system and click Next.
The Installation Key Entry dialog box appears.
Step 5 If the Gateway SIM for this gateway has been previously configured in the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Audio Server system, enter the configured Ethernet address.
or
If the Gateway SIM for this gateway has not been previously configured, leave this field empty.
OL-6571-02
Step 6 Click Next.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
2-7
Page 24

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Step 7 In the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Client IP Address dialog box, enter the IP address of the IP-gateway
server where you are currently installing Gateway SIM and click Next.
Step 8 Click Finish.
Step 9 To complete Release 5.2.1 installation, go to the “Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1” section on page 2-6.
Changing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM Settings
You cannot modify Gateway SIM settings; to change these settings, you must perform the following
tasks:
• Delete the current Gateway SIM configuration
• Add a new Gateway SIM configuration
Step 1 To stop all Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system services, choose Start > Programs > Administrative
Too l s > S er v ic e s.
Step 2 Right-click each Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system service and choose Stop.
Step 3 Choose Start > Programs > MeetingPlace Applications > MeetingPlace Gateway Configuration.
The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway Configurations dialog box appears.
Step 4 From the list on the left, select the name of the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
Step 5 Click Delete.
Step 6 Click Add.
The MeetingPlace Server Entry dialog box appears.
Step 7 Enter the configuration information from Table 2-3 in to the corresponding fields.
Table 2-3 MeetingPlace Server Entry Dialog Box
Field Description
Server Name Enter the hostname of the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
Shadow Server Leave this field empty; it is not used by Release 5.2.1 but may be used by other
gateways.
Client IP Address Enter the IP address of the computer where the Gateway SIM is being installed.
Transfer
Destination
Leave this field empty; it is not used by Release 5.2.1 but may be used by other
gateways.
Link Encryption
Disabled
Note We do not recommend Link Encryption Disabled.
If you want to encrypt communications between the Gateway SIM and
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system, do not select this option.
Encryption uses a 56-bit Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm with a secret
key.
2-8
To send communications in clear text, click this option.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 25

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Step 8 Click OK.
Step 9 To apply the configuration settings, click OK again.
Step 10 To restart the Gateway SIM, choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
Step 11 Right-click MeetingPlace GWSIM and choose Start.
Uninstalling Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1
Caution Before you uninstall Release 5.2.1, ensure that you have configured Cisco Unified CallManager to route
calls to another IP gateway.
Step 1 To stop all Cisco Unified MeetingPlace services, choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools >
Services.
Step 2 Right-click on each Cisco Unified MeetingPlace service and choose Stop.
Step 3 Choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > Add/Remove Programs.
Step 4 Select MeetingPlace IP Gateway and click Remove.
Step 5 Restart the IP-gateway server.
Step 6 To verify that Release 5.2.1 was successfully uninstalled, review the list of programs in Add/Remove
Programs.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
2-9
Page 26

Chapter 2 Installing Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Install or Upgrade to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
2-10
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 27

CHA P TER
3
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
This chapter provides procedures for configuringRelease 5.2.1 and includes the following sections:
• Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1, page 3-1
• How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1, page
3-3
• Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 for Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, page 3-7
• How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for
Use With Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, page 3-7
• Information About Configuring Multiple Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
Software Release 5.2.1 Servers for Load Balancing and Redundancy, page 3-8
• Information About Configuring a Dialing Group, page 3-8
• How to Configure a Dialing Group, page 3-8
• Information About Reservationless Single Number Access Configuration, page 3-9
• Information About Reverse Connection to the MeetingPlace Audio Server System Configuration,
page 3-10
Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
After you install Release 5.2.1, you must configure it for use with one of the following servers:
• Cisco Unified CallManager
• Cisco SIP Proxy Server
• (Optional) H.323 gatekeeper
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
3-1
Page 28

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Note If you are using an IP PBX that runs standard H.323 or SIP call control, see the “How to Configure
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1” section on page 3-3 for the
required system settings and see your IP PBX documentation for information about how to configure
those settings.
Table 3 -1 describes the Release 5.2.1 Management Console fields and lists the default settings.
Table 3-1 Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Management
Console Fields and Default Settings
Setting Description Default
General Settings
Max Number of
Callers
Outdial Protocol Controls whether outdials from the IP-gateway server are
Maximum number of callers Release 5.2.1 will accept. This
maximum number can be a combination of H.323 and SIP
callers.
placed by using H.323 or SIP.
960
H.323
Note In mixed H.323-SIP, call-control environments, you
must select one protocol for outdials; otherwise, the
default protocol will be used.
Verbose Logging Sets the level of logging information. Normal
H.323 Settings
Enabled Enables or disables the H.323 protocol. Yes
Max Number of
Maximum number of H.323 callers Release 5.2.1 accepts. 960
Callers
E.164 Address A dialable number for the IP-gateway server. —
H323 ID Caller ID name that is used by Release 5.2.1. MeetingPlace
Gateway Address and
Gateway Port
IP address and port number of the server responsible for
routing H.323 calls. Outdials using H.323 are directed to this
IP address and port if an H.323 gatekeeper is not used.
Note You must enter this gateway information if you are
Address: —
Port: 1720
using H.323 without a gatekeeper.
Use Gatekeeper Enables the IP-gateway server to register with an H.323
No
gatekeeper.
Gatekeeper Address
and Gatekeeper Port
IP address and port number of the H.323 gatekeeper. If an
H.323 gatekeeper is used, Release 5.2.1 registers with the
server and directs H.323 outdials to the server.
Address: —
Port: 1719
3-2
Note If using an H.323 gatekeeper, ensure that your system
allows traffic to pass through ports 1024-65535
because MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IPGW uses these
ports for dynamic TCP and UDP traffic.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 29

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Table 3-1 Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Management
Console Fields and Default Settings
Setting Description Default
SIP Settings
Enabled Enables or disables the SIP protocol. Yes
Max Number of
Callers
Display Name Display name of the IP-gateway server that is used for SIP
User Name A dialable number for the IP-gateway server. <blank>
Session Name Session name used in Session Description Protocol (SDP)
Proxy Server Address
and Proxy Server Port
Maximum number of SIP callers Release 5.2.1 accepts. 960
messages.
body.
IP address and port number of the Cisco SIP Proxy Server.
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system outdials placed by using
SIP are directed to this IP address and port.
MeetingPlace
MeetingPlace
IP Call
Address: —
Port: 5060
Note If using Cisco SIP Proxy Server, ensure that your
system allows traffic to pass through ports
1024-65535 because Release 5.2.1 uses these ports for
dynamic TCP and UDP traffic.
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
You must configure Release 5.2.1 to dial out by using one of the following servers:
• Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use
With Cisco Unified CallManager, page 3-4
• Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use
With Cisco SIP Proxy Server, page 3-4
• (Optional) Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
for Use With an H.323 Gatekeeper, page 3-5
• (Optional) Verifying MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Configuration,
page 3-6
Note Release 5.2.1 supports concurrent incoming H.323 and SIP calls; however, you must configure the
Release 5.2.1 to use one protocol, either H.323 or SIP, to dial out.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
3-3
Page 30

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 for Use With Cisco Unified CallManager
Step 1 From the IP-gateway server, choose Start > Programs > MeetingPlace Applications > MeetingPlace
Management.
Step 2 Double-click the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway icon.
The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Management Console opens.
Tip You can also access Release 5.2.1 configuration settings through the Registry Editor by navigating to
\\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Latitude\MeetingPlace IP Gateway.
Use the settings in Tab le 3-2 to configure Release 5.2.1 for use with Cisco Unified CallManager.
Table 3-2 Release 5.2.1 Configuration Settings for Use With Cisco Unified CallManager
Field Name Setting
General Settings
Outdial Protocol H.323
H.323 Settings
Enabled Yes
E.164 Address Dialable number for the MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IPGW
H.323 ID MeetingPlace
Gateway Address IP address of Cisco Unified CallManager
Gateway Port 1720
Use Gatekeeper No
Step 3 To accept the settings, click Submit.
Step 4 Restart the IP-gateway server.
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 for Use With Cisco SIP Proxy Server
Note Release 5.2.1 does not support out-of-band digit detection with SIP.
Step 1 From the IP-gateway server, choose Start > Programs > MeetingPlace Applications > MeetingPlace
Management.
Step 2 Double-click the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway icon.
The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Management Console opens.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
3-4
OL-6571-02
Page 31

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Tip You can also access Release 5.2.1 configuration settings through the Registry Editor by navigating to
\\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Latitude\MeetingPlace IP Gateway.
Step 3 Use the settings in Table 3-3 to configure Release 5.2.1 for use with Cisco SIP Proxy Server.
Table 3-3 Release 5.2.1 Configuration Settings for Use With Cisco SIP Proxy Server
Field Name Setting
General Settings
Outdial Protocol SIP
SIP Settings
Enabled Yes
Display Name MeetingPlace
User Name Dialable number for the MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IPGW
Session Name MeetingPlace IP Call
Proxy Server Address IP address of the Cisco SIP Proxy Server
Proxy Server Port 5060
Step 4 To accept the settings, click Submit.
Step 5 Restart the IP-gateway server.
Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 for Use With an H.323 Gatekeeper
Note Release 5.2.1 registers to the gatekeeper as a terminal device.
Step 1 From the IP-gateway server, choose Start > Programs > MeetingPlace Applications > MeetingPlace
Management.
Step 2 Double-click the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway icon.
The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway Management Console opens.
Tip You can also access Release 5.2.1 configuration settings through the Registry Editor by navigating to
\\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Latitude\MeetingPlace IP Gateway.
Step 3 Use the settings in Table 3-4 to configure Release 5.2.1for use with an H.323 gatekeeper.
Table 3-4 Release 5.2.1 Configuration Settings for Use With an H.323 Gatekeeper
OL-6571-02
Field Name Setting
General Settings
Outdial Protocol H.323
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
3-5
Page 32

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Table 3-4 Release 5.2.1 Configuration Settings for Use With an H.323 Gatekeeper
Field Name Setting
H.323 Settings
Enabled Yes
E.164 Address Dialable number for the MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IPGW
H.323 ID MeetingPlace
Gateway Port 1720
Gatekeeper Address IP address of the H.323 Gatekeeper
Gatekeeper Port 1719
Use Gatekeeper Yes
Step 4 To accept the settings, click Submit.
Step 5 Restart the IP-gateway server.
Verifying MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Configuration
Step 1 To verify that Release 5.2.1 services are running, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel from the
IP-gateway server; then, select Services.
Step 2 Make sure that the following services are running:
• Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM
• Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway
Step 3 To verify that the IP-gateway server is logging in, telnet to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server
system.
Step 4 To verify that the IP-gateway server status is OK, enter gwstatus.
Note It can take up to five minutes for gwstatus to update; therefore, any recent changes to the gateway may
not be reflected.
Step 5 Verify that you can access the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system by using a Cisco IP
Phone.
Step 6 Verify that you can access Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system by using a PSTN phone.
3-6
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 33

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use With
Information About Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use With
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
You can install Release 5.2.1 on either the same or separate server as Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Web Conferencing. If you install Release 5.2.1and Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing on
the same server, you must configure the server to include a primary and secondary IP address. Release
5.2.1 uses the primary address, and you must configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
to use the secondary address. If Release 5.2.1 is installed on a server with more than one IP address, you
must define a gateway for each IP address either in Cisco Unified CallManager, Cisco SIP Proxy server,
or H.323 Gatekeeper for outdials to work.
Note Before you install multiple Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system integration applications on the same
server, ensure that your system meets the requirements for integration. For additional information, see
Important Information About Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Products and Cisco Media Convergence
Servers at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/conf/mtgplace/mpmcs.htm
How to Configure Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 for Use With Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Web Conferencing
To configure Release 5.2.1 for use with Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, perform the
following procedure:
Assigning the Primary IP Address
Step 1 From the IP-gateway server desktop, right-click Network Neighborhood and choose Properties.
Step 2 In the Protocols tab, click TCP/IP Protocol and click Properties.
Step 3 In the TCP/IP Properties window, select the IP Address tab.
Step 4 Enter your system information into the corresponding fields shown in Table 3-5 .
Table 3-5 IP Address Tab Fields
Field Task
Adapter Choose the adapter that allows MeetingPlace IP Gateway to
communicate with the network.
Radio buttons Choose Specify an IP address.
IP Address Enter the primary address for the IP-gateway server
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask for the IP-gateway server.
Default Gateway Enter the default gateway for the IP-gateway server.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
3-7
Page 34

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Configuring Multiple Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Step 5 Click OK to apply your settings and return to the desktop.
Information About Configuring Multiple Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Servers for Load Balancing and Redundancy
If you have deployed multiple IP-gateway servers to route IP calls, you can configure Cisco Unified
CallManager or your IP PBX to load balance and to provide Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system
redundancy by creating route groups that send calls to other IP-gateway servers if gateway failure occurs.
A route group allows you to designate the order in which IP-gateway servers are selected and to prioritize
a list of IP-gateways and ports for outgoing trunk selection.
All IP-gateway servers actively handle calls, and calls are routed round-robin among the IP-gateway
servers. Therefore, in-session calls that are connected to a IP-gateway server that has failed are
disconnected, and those callers must call again to be reconnected to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Audio Server system. New callers, however, are routed to another IP-gateway server.
For information about configuring route groups, see to the Redundancy Chapter in the Cisco Unified
CallManager System Guide for your software release at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_callmg/index.htm
Information About Configuring a Dialing Group
Dialing groups customize the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system by presenting specific
voice prompts to callers who dial in to a meeting by using a particular IP phone number. For example,
you can configure a dialing group to immediately place callers who dial extension 2121 into meeting ID
656565.
You configure dialing groups by editing the dialgroups.txt file to include the dial pattern with which to
associate a specific dialing group; the application, or prompt, to play for the dialing group callers; and
the meeting number to present to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system. Entries in
dialgroups.txt are processed in order from top to bottom. If a match is not found, the caller is placed at
the CombinedAccess menu, and the dialed digits are presented to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio
Server system.
How to Configure a Dialing Group
Step 1 Open the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway folder on your IP-gateway server.
Step 2 By using a text editor, open the dialgroups.txt file.
Step 3 Read the comment lines that start with the # symbol.
Step 4 Enter the dial pattern that you want to customize; then, enter a space. Valid selections are the following:
• [0-9] [ A-D]—Presents the digits to the MeetingPlace audio server.
• [.]—Matches any valid digit.
3-8
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 35

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Reservationless Single Number Access Configuration
• [*]—Matches 0 or more occurrences of the preceding digit.
Step 5 Enter the type of prompt menu to play to the caller; then, enter a space. Valid selections are the
following:
• CombinedAccess—Selects the Main menu.
• DIDMeeting—Prompts the caller for the meeting ID to join. This option can be used to place the
caller directly into a meeting if the digits match an existing meeting ID on the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
• Profile—Prompts the caller for a profile number, which is not passed along to the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace server for user authentication.
• MeetingNotes—Prompts the caller to retrieve meeting notes.
Step 6 Enter the digits to present to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system. Valid selections are
the following:
• [0-9] [ A-D]—Presents the entered digits to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
• KEEP—Preserves the dialed digits.
• NONE—Presents no digits to the server.
Step 7 Repeat Step 4 through Step 6 until the file contains one line for each dialing group that you want to
configure.
Step 8 Save and close the dialgroups.txt file.
Step 9 Restart the IP-gateway server.
Configuring a Dialing Group Example
The following is a sample dialgroups.txt file that shows callers who dial extension 2121 are forwarded
to meeting ID 656565. Callers who dial any other valid number are prompted to enter a profile number,
and those digits are forwarded to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
2121 DIDMeeting 656565
.* Profile KEEP
Information About Reservationless Single Number Access
Configuration
With Reservationless Single Number Access (RSNA), profiled users who host or attend a reservationless
meeting as either profile users or guests can access their meetings by dialing the same phone number,
regardless of which Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system is hosting the meeting. With
RSNA, users always dial the number of their home server, which then transfers the call to the scheduler
or host’s home server.
For information about configuring Reservationless Single Number Access, see the Administrator Guide
for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3 at the following URL:
OL-6571-02
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
3-9
Page 36

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Information About Reverse Connection to the MeetingPlace Audio Server System Configuration
Note Gateways must support the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Refer Method, RFC 3515, to use the
Reservationless Single Number Access feature.
Information About Reverse Connection to the
MeetingPlace Audio Server System Configuration
The Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system can initiate a reverse connection, eliminating the
need for incoming port 5003 to be open on the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system. To
initiate the reverse connection, you must open port 5003 on the IP-gateway server.
3-10
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 37

Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
This chapter provides troubleshooting tips about the following topics for problems that can occur after
installing and configuring Release 5.2.1:
• Troubleshooting Network Connectivity, page 4-1
• Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity, page 4-2
• Troubleshooting Audio Problems, page 4-8
Troubleshooting Network Connectivity
If you experience a network connectivity problem, perform the following steps to make sure that the
IP-gateway server has not lost its connection to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
CHA P TER
4
Step 1 To verify that Release 5.2.1 services are running, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > Services
from the IP-gateway server.
Step 2 Make sure the following services are started:
–
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM
–
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace IP Gateway
Step 3 To verify that the IP-gateway server is logging in, telnet to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server
system.
Step 4 To verify that the IP-gateway server status is OK, enter gwstatus.
Step 5 Check the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System eventlog for any errors relating to the
IP-gateway server.
Step 6 Make sure that all cards are seated properly in the chassis.
Step 7 Check all cables and connections.
Step 8 Verify card configuration by entering the blade, dcard, and span commands.
Step 9 Verify port configuration by entering the port command.
Step 10 Check the error log by entering the errorlog command.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
4-1
Page 38

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity
• Unable to Make Calls From a Cisco IP Phone, page 4-2
• Unable to Call a PSTN Telephone From a Cisco IP Phone or Vice Versa, page 4-2
• Dead Air Heard When Using an H.323 Device, page 4-3
• Dead Air Heard When Using a Cisco IP Phone, page 4-3
• Fast Busy Signal Heard When Using a Cisco IP Phone, page 4-3
• Unable to Make Dial-Pad Key Selections When Using an H.323 Device, page 4-3
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When IP Ports Do Not Answer,
page 4-4
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Server
When IP Ports Do Not Answer, page 4-4
• Checking Cisco Unified CallManager When IP Ports Do Not Answer, page 4-5
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When IP Calls Connect But No
Audio Is Heard, page 4-5
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 When IP
Calls Connect But No Audio Is Heard, page 4-6
• Checking the Cisco IP Phone When IP Calls Connect But No Audio Is Heard, page 4-6
• Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports, page 4-6
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When Unable to Dial Out on IP
Ports, page 4-7
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Server
When Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports, page 4-7
• Checking Cisco Unified CallManager When Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports, page 4-8
Unable to Make Calls From a Cisco IP Phone
Possible Cause—The network may not be functioning properly.
Corrective Action—Verify your network access.
Possible Cause—Cisco Unified CallManager may not be configured correctly.
Corrective Action—Verify your Cisco Unified CallManager configuration.
Unable to Call a PSTN Telephone From a Cisco IP Phone or Vice Versa
4-2
Possible Cause—The voice gateway may not be functioning or configured properly.
Corrective Action—Verify your configuration settings.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 39

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Dead Air Heard When Using an H.323 Device
Possible Cause—Data packets transmitted across IP are at times inconsistently sized.
Corrective Action—Ensure that Cisco Unified CallManager, the IP-gateway server, and the
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system are all be set to handle the same size data packet.
Dead Air Heard When Using a Cisco IP Phone
Possible Cause—There may be a poor connection between the Cisco IP phone and the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
Corrective Action—Verify that all associated connections are secure.
Fast Busy Signal Heard When Using a Cisco IP Phone
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity
Possible Cause—The route pattern to IP-gateway server may not be configured properly in
Cisco Unified CallManager.
Corrective Action—To resolve a fast busy-signal problem, verify that the configuration information
that you entered in the “Assigning a Cisco Unified CallManager Route Pattern to Point to the
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Release Release 5.2.1 Server” section on page 2-4
is correct.
To verify the configuration, perform the following steps:
Step 1 In the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration page, choose Route Plan > Route Pattern.
Step 2 Verify that the settings are correct and make changes if necessary.
Step 3 When finished, click Insert.
Possible Cause—All IP ports on the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system are in use.
Corrective Action—Confirm that Cisco Unified CallManager and the voice gateway have been
configured to handle IP call overflow.
.
Unable to Make Dial-Pad Key Selections When Using an H.323 Device
OL-6571-02
Possible Cause—The audio compression setting of the H.323 device may be incorrect.
Corrective Action—Use CCITT u-Law, 8.000 kHz, 8 Bit Mono
Audio Server system with T1; use CCITT A-Law, 8.000 kHz, 8 Bit Mono for a Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system with E1.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
for a Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
4-3
Page 40

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When IP Ports
Do Not Answer
Step 1 Check that the Ethernet switch port or any other network devices to which the MA-16 blade connects
directly is set to fixed 100 Base-TX Full Duplex.
Step 2 Make sure that the IP ports on the server are configured and active by using the blade and portstat
commands.
Step 3 Check the port status by performing the following steps:
a. Log in to the CLI.
b. At the tech$ prompt, enter the tvportstat -all command and monitor the output.
c. Make a test call.
d. Verify that the incoming call is seen by the server.
Step 4 Trace a test call by performing the following steps:
a. At the tech$ prompt, enter the cptrace -T 5 command and monitor the output.
b. Make another test call.
c. Verify that the incoming call is seen by the server.
Step 5 Check for warnings and alarms, especially those that occur in “cpiphandler.cc” by performing the
following steps:
a. At the tech$ prompt, enter the viewexlog -s info -l | more command.
b. Scroll through the log by entering f.
Step 6 At the tech$ prompt, enter gwstatus to verify that both the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM
and IP-gateway server have a status of OK.
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 Server When IP Ports Do Not Answer
Step 1 To verify that both the Gateway SIM and IP-gateway server have a status of OK, enter gwstatus at the
tech$ prompt.
Step 2 Verify that the Release 5.2.1 configuration has the appropriate call control enabled—either H.323 or SIP.
Step 3 Open the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM eventlog.
Step 4 Make a test call.
Step 5 From the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM eventlog, verify that the test call is received by the
IP-gateway server and that the call-processing server is returning a response code of 0, as shown the
following example:
MP Resp. Msg=3 CPerr=0 SeqNum=0x16
4-4
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 41

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity
Step 6 Verify that soft phones are not running on the gateway.
Step 7 If Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing is on the same server as Release 5.2.1, make sure that
they are each assigned different IP addresses.
Checking Cisco Unified CallManager When IP Ports Do Not Answer
Step 1 Verify that an H.323 gateway has been created for the IP-gateway server and that a route pattern has
been assigned to it.
Step 2 Verify that the Cisco Unified CallManager server can ping the IP-gateway server and vice versa.
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When IP Calls
Connect But No Audio Is Heard
Step 1 Check that the Ethernet switch port or any other network devices to which the MA-16 connects directly
is set to fixed 100Base-TX Full Duplex.
Step 2 Verify that the subnet mask address is correct by entering the blade command. If it is not correct,
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system will not be able to send voice packets to the phone.
Restart the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system for any changes to take effect.
Step 3 At the tech$ prompt, enter tvportstat -all.
Step 4 While monitoring the output, make a test call to verify that the IP call is seen by the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
Step 5 At the tech$ prompt, enter cptrace -T 5.
Step 6 While monitoring the output of the trace command, make a test call to verify that the IP call is seen by
the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
Step 7 At the tech$ prompt, enter tvportstat number, where number is the port number that you used in Step 6.
Step 8 Look for the RTCP packets sent by far end message to verify that the phone is transmitting voice data
to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
If the message is present, there is a one-way connection.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
4-5
Page 42

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 When IP Calls Connect But No Audio Is Heard
Step 1 Open the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM eventlog and verify that the following log entries
have the correct IP address of the IP MA-16 blade:
MP RTP info. IP=10.10.10.1 Port=5010
MP RTCP info. IP=10.10.10.2 Port=5011
Step 2 From the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM eventlog, verify that the following log entries have
the correct IP address of the IP phone:
Remote RTP info. IP=10.10.10.3 Port=6510
Remote RTCP info. IP=10.10.10.4 Port=6511
Step 3 Ping the IP addresses of all MA-16 blades and of the IP phone.
Checking the Cisco IP Phone When IP Calls Connect But No Audio Is Heard
Step 1 Press the blue i button quickly twice.
Step 2 Verify that the phone is receiving and sending packets.
Step 3 Verify that the expected codec has been negotiated.
Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports
Possible Cause—Dialing out may be prevented because of information that is in the translation table.
Corrective Action—Verify that the table contains the necessary numbering plans to allow for dialing
out.
Note In a mixed IP-PSTN environment, the translation table must contain numbering plans for each type of
call.
4-6
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 43

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Troubleshooting Caller Connectivity
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When Unable
to Dial Out on IP Ports
Step 1 Verify that incoming calls to the server are connecting. If not, perform the following procedures:
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server System When IP Ports Do Not Answer,
page 4-4
• Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Server
When IP Ports Do Not Answer, page 4-4
• Checking Cisco Unified CallManager When IP Ports Do Not Answer, page 4-5
Step 2 Verify that the port group is enabled for outgoing calls by using the port command.
Step 3 Check the translation table to verify IP calls are being directed to a port group that is configured for IP.
Tip You can use the xltest utility to check which port group will be used for the dialed number. This is
especially important for mixed PSTN and IP systems.
Step 4 At the tech$ prompt, enter cptrace -T 5.
Step 5 While monitoring the output of the trace command, make a test call.
Step 6 At the tech$ prompt, enter viewexlog -s info -l | more.
Tip Enter f to move forward in the log.
Step 7 Check for warnings and alarms, especially those that occur in “cpiphandler.cc” and “cpplacecall.cc”.
Step 8 At the tech$ prompt, enter activity.
Step 9 Choose option 4 to make a test call.
Step 10 Test internal extensions and outside numbers to isolate the problem.
Checking the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software
Release 5.2.1 Server When Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports
Step 1 Open the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM eventlog and verify that the IP-gateway server
receives the outdial command from the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
Step 2 In the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM eventlog, verify that the correct phone number was
received by the IP-gateway server, as shown in the following example:
MeetingPlace IP outdial. Phone=651515 IRC=0 PSTN=46 Unit=0
OL-6571-02
Step 3 In the Release 5.2.1 configuration, verify that the outdial is sent by using the appropriate protocol.
Step 4 Verify that the gateway, gatekeeper, and proxy server addresses and ports are correct according to the
desired protocol.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
4-7
Page 44

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Troubleshooting Audio Problems
Step 5 Verify that the E.164 Address and H.323 ID fields are correct for H.323 outdials.
Step 6 Verify that the Display Name, User Name, and Session Name fields are correct for SIP outdials.
Checking Cisco Unified CallManager When Unable to Dial Out on IP Ports
Step 1 If Release 5.2.1 is installed on a gateway with multiple IP addresses, verify that Cisco Unified
CallManager has an H.323 gateway configuration for each address.
Step 2 Verify that the gateway settings created for Release 5.2.1 allow dialing out.
Troubleshooting Audio Problems
See the following sections for information about troubleshooting audio problems:
• Poor or Low-Audio Quality, page 4-8
• Echo, page 4-9
Poor or Low-Audio Quality
Possible Cause—The caller is using a low-quality headset with the Cisco IP phone.
Corrective Action—Reduce the speaker volume to a volume that is comfortable but not loud enough to
cause feedback from the microphone back to the other end of the call.
Corrective Action—Use a headset that is approved by Cisco Systems.
Possible Cause—Cisco IP phone audio settings need adjustment.
Corrective Action—During a meeting, on a Cisco 7960, press the blue i button twice to obtain network
settings. The information that you receive provides statistics needed to optimize your network for VoIP.
Corrective Action—Lower the volume. Voice quality degrades if the volume on a Cisco IP phone is set
to maximum.
Possible Cause—Network settings may need to be modified.
Corrective Action—Consider the CoS/QoS setting on your network. If the CoS setting is IP Precedence
5, you should hear considerable improvement in audio quality.
Corrective Action—Establish locations on your network. Locations enable you to regulate voice
quality by limiting the amount of bandwidth that is available for calls.
For more information, refer to the Location Configuration section in the appropriate
Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide for your release.
4-8
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 45

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Echo
Possible Cause—The caller is using a low-quality headset with Cisco IP phone.
Corrective Action—Reduce the speaker volume to a volume that is comfortable but not loud enough to
cause feedback from the microphone back to the other end of the call.
Corrective Action—Use a headset that is approved by Cisco Systems.
Possible Cause—Cisco IP phone audio settings need adjustment.
Corrective Action—Lower the volume. Voice quality degrades if the volume on a Cisco IP phone is set
to maximum.
Troubleshooting Audio Problems
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
4-9
Page 46

Troubleshooting Audio Problems
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
4-10
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 47

APPENDIX
A
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation
Worksheets
Information About the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation Worksheet
Before you install Release 5.2.1, complete the following worksheet. You need to supply these values
when you install and configure Release 5.2.1.
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
Installation Worksheet
OL-6571-02
Description Value
1. Hostname or IP address of the IP-gateway
server.
2. Number of the IP-gateway server. dialable
3. Hostname of the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Audio Server system.
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
host name
IP address
number ____________________________
hostname
IP address
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
A-1
Page 48

Appendix A Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation Worksheets
Information About the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial Plan
Description Value
4. Additional IP addresses of the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
Up to four additional IP addresses are needed
for the Multi Access blade. If a TP1610 Multi
Access blade is in use but only 240 VoIP or
fewer are deployed, then you must specify the
lower address; the upper address can be set to
0.0.0.0. You must also set the Ethernet switch
port or any other network devices to which the
Multi Access blade connects directly to fixed
100Base-TX Full Duplex.
Note Do not set the lower address to 0.0.0.0.
hostname
IP address
hostname
IP address
hostname
IP address
hostname
IP address
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
5. Hostname or IP address of one of the
following:
• Cisco Unified CallManager server or
IP PBX that runs standard H.323 or SIP
call control
• Cisco SIP Proxy Server
6. Host name or IP address of the Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace Web Conferencing server if
running on the same server as Release 5.2.1.
Note If you use a hostname, DNS must be
enabled to resolve the hostname to an IP
address.
hostname
IP address
hostname
IP address
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
____________________________
Information About the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial Plan
A dial plan ensures that IP and PSTN calls to and from the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server
system are directed to the proper endpoints on their respective network. Each type of call has a dial
pattern that specifies its call flow to and from the MeetingPlace Audio Server system.
For example, if your Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system has both IP and PSTN interfaces,
you may want to configure their outdial patterns so that outdials to a PSTN phone will go through the
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system PSTN interface. This ensures an outdial to a PSTN
phone does not go through the IP network first and then to the PSTN.
A-2
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 49

Appendix A Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation Worksheets
Information About the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial Plan
For Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Servers systems that have both PSTN and IP interfaces, a dial
plan should account for rollover from PSTN to IP ports and vice versa. For example, if you have a
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server system with 96 IP user licenses and 192 PSTN user licenses,
the 97th caller to IP is automatically forwarded to a PSTN port by Cisco Unified CallManager through
a voice gateway, rather than producing a fast busy signal.
For additional information about mixed-mode configuration, see the Configuration Guide for
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Audio Server Release 5.3 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/ps5664/ps5669/products_installation_and_configuration_gui
des_list.html
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial
Plan Worksheet
Use the following worksheet to create a a dial plan.
MeetingPlace IP call flow Value
1. From an IP phone to the IP-gateway server.
dial pattern____________________
If the IP-gateway server is busy, Cisco Unified
CallManager can forward calls to Cisco Unified
MeetingPlace system PSTN through a voice gateway.
You must configure Cisco Unified CallManager and
the voice gateway to route this type of call.
2. From a PSTN phone to Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
system PSTN.
If Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system PSTN is busy,
the PBX or CO can forward calls to the IP-gateway
server through Cisco Unified CallManager. You must
configure the PBX or CO to route this type of call.
3. From Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system IP to an IP
phone.
4. From Cisco Unified MeetingPlace system PSTN to a
PSTN phone.
A 4-digit number that does not conflict
with a corporate phone extension number
scheme.
dial pattern____________________
A 7- or 10-digit phone number that does
not conflict with a corporate phone
numbering scheme.
dial pattern____________________
Typically, the last four digits of the phone
number.
dial pattern____________________
Typicall y 9, if needed for an outside line,
followed by either the 7- or 10-digit phone
number.
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
A-3
Page 50

Appendix A Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Installation Worksheets
Information About the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1 Dial Plan
A-4
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
Page 51

INDEX
A
audio quality
during a meeting
1-6
troubleshooting 4-8
C
call-control software
see Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
Cisco IP phones
about
communicating with Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Cisco Unified CallManager
adding a gateway
assigning a route pattern 2-4
Gateway Configuration window 2-3
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
about
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM
changing settings
installing with Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
about
components 1-3
configuring
installation 2-1
installation worksheet A-1
1-7
H.323/SIP IP Gateway
2-2
1-3
2-8
about
Gateway
1-1, 1-4
3-1
2-7
multiple servers 3-8
verifying 3-6
1-9
troubleshooting with Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
H.323/SIP IP Gateway
4-1
uninstalling 2-9
upgrading 2-6
using with
Cisco SIP Proxy Server
3-4
Cisco Unified CallManager 3-4
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Web Conferencing 3-7
H.323 clients and Cisco SIP phones 1-9
H.323 Gatekeeper 3-5
IP PBX 1-1
PSTN and Cisco IP phones 1-7
class of service
about
1-6
codecs
G.711 alaw and ulaw
1-4
G.729a 1-4
configuring
dialing group
3-8
multiple Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway servers
3-8
reverse connection to the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
Audio Server system
3-10
D
dead air, troubleshooting 4-3
dialing group
about
example 3-9
dial plan
about
worksheet A-2
DTMF
3-8
A-2
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
IN-1
Page 52

Index
in band 1-5
out of band 1-5
out of band and SIP 1-5
support for 1-5
dual tone multi-frequency
see DTMF
E
endpoints
supported
supported by SIP 1-5
1-6
F
fast busy signal, troubleshooting 4-3
G
G.711 codec
and Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
Software
G.729 codec, and Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP
IP Gateway Software
gateways
adding
configuring 2-4
2-2
1-4
1-4
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway 2-1
2-7
L
load balancing
with Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP
Gateway
3-8
M
MeetingPlace
see Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
P
protocols
about
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Gateway SIM 1-5
H.323 1-5
real-time transport protocol (RTP) 1-5
session initiation protocol (SIP) 1-5
skinny station protocol (SSP) 1-5
proxy server
configuring
PSTN 1-7
1-5
3-1
H
H.323
clients
Gatekeeper
configuring
protocol 1-5
I
installing
IN-2
Q
quality of service (QOS) 1-6
1-9
R
3-5
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
redundancy 3-8
RSNA
about
RTP protocol
see protocols
3-9
OL-6571-02
Page 53

S
SIP phones
see Cisco IP phones
SIP protocol
see protocols
SSP protocol
see protocols
T
telephony
standards supported
troubleshooting
audio problems
caller connectivity 4-2
Cisco IP phones 4-3
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway 4-1
dead air with Cisco IP phone 4-3
network connectivity 4-1
1-4
4-8
Index
U
uninstalling
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
upgrading
Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway
V
voice gateway 1-6
2-9
2-6
OL-6571-02
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
IN-3
Page 54

Index
IN-4
Administrator Guide for Cisco Unified MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway Software Release 5.2.1
OL-6571-02
 Loading...
Loading...