Page 1

Cisco TelePresence
ISDN Gateway
Version 2.1
Online help (printable format )
D14659.03
March 2011
Page 2

Contents
Contents
Contents ................................................................................................................................... 2
Logging into the web interface ............................................................................................... 7
Failing to log into the web interface ....................................................................................... 8
Invalid passwords .......................................................................................................................................... 8
Getting started with the ........................................................................................................... 9
Making calls with the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway ...................................................11
ISDN to IP calls ........................................................................................................................................... 11
IP to ISDN calls ........................................................................................................................................... 11
Using the auto attendant ........................................................................................................12
Using the Far End Camera Control ..................................................................................................... 12
Using the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway for voice-only calls .....................................13
Configuring the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway as a voice-only gateway .......................................... 13
Dial plan configuration ................................................................................................................................. 14
Calling a PSTN telephone from an MCU ............................................................................................. 14
Displaying ISDN port utilization .............................................................................................15
Displaying the ISDN calls list .................................................................................................16
Disconnecting and deleting calls ................................................................................................................. 16
Diagnostic controls ...................................................................................................................................... 16
Displaying detailed call information ......................................................................................17
Understanding the dial plan ...................................................................................................19
Rules ........................................................................................................................................................... 19
Using rules .................................................................................................................................................. 20
Rule ordering ............................................................................................................................................... 20
Displaying and testing the dial plan ......................................................................................21
Displaying the rules list ............................................................................................................................... 21
Modifying the rules list ................................................................................................................................. 23
Testing the dial plan .................................................................................................................................... 23
Adding dial plan rules .............................................................................................................24
Adding and updating dial plan rules......................................................................................25
Adding dial plan rules .................................................................................................................................. 25
Updating dial plan rules ............................................................................................................................... 29
Adding and updating dial plan rules in leased line mode ....................................................30
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 2 of 135
Page 3

Contents
Adding dial plan rules .................................................................................................................................. 30
Updating dial plan rules ............................................................................................................................... 33
Example dial plan rules ..........................................................................................................34
Allocating bandwidth using rules for IP to ISDN calls ................................................................................. 34
Allocating bandwidth using rules for ISDN to IP calls ................................................................................. 35
Forwarding ISDN calls to an operator or a conference ............................................................................... 35
Specifying voice-only IP to ISDN telephone calls ....................................................................................... 36
Setting up dial plan rules when using TCS-4 .............................................................................................. 37
ISDN to IP calls .................................................................................................................................... 37
IP > ISDN > ISDN > IP calls ................................................................................................................ 38
Dial plan examples in leased line mode ...................................................................................................... 39
ISDN to IP dial plan (leased line mode) ............................................................................................... 39
IP to ISDN dial plan (leased line mode) ............................................................................................... 40
Dial plan syntax .......................................................................................................................41
Syntax for conditions (Called number matches) ......................................................................................... 41
Syntax for actions (Call this number) .......................................................................................................... 42
Displaying the built-in gatekeeper registration list ...............................................................44
Configuring the built-in gatekeeper ............................................................................................................. 44
Configuring neighboring gatekeepers .................................................................................................. 44
Gatekeeper status ....................................................................................................................................... 46
ID view ................................................................................................................................................. 46
Registration view .................................................................................................................................. 47
Displaying the user list ...........................................................................................................48
Deleting users ............................................................................................................................................. 48
Adding and updating users ....................................................................................................49
Adding a user .............................................................................................................................................. 49
Updating a user ........................................................................................................................................... 49
Updating your user profile .....................................................................................................52
Changing your password .......................................................................................................53
Configuring network settings ................................................................................................54
IP configuration settings .............................................................................................................................. 54
IP status ...................................................................................................................................................... 55
Ethernet configuration ................................................................................................................................. 56
Ethernet status ............................................................................................................................................ 56
Automatic IPv6 address preferences ................................................................................................... 58
DNS settings............................................................................................................................59
Configuring DNS settings ............................................................................................................................ 59
Viewing DNS status .................................................................................................................................... 60
Configuring IP routes settings ...............................................................................................61
Port preferences .......................................................................................................................................... 61
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 3 of 135
Page 4

Contents
IP routes configuration ................................................................................................................................ 62
Adding a new IP route .......................................................................................................................... 62
Viewing and deleting existing IP routes ............................................................................................... 63
Routes behavior with disabled por ts .................................................................................................... 63
Current IP status ......................................................................................................................................... 63
Configuring IP services ..........................................................................................................64
Configuring SNMP settings ....................................................................................................66
System information ..................................................................................................................................... 66
Configured trap receivers ............................................................................................................................ 67
Access control ............................................................................................................................................. 67
Configuring QoS settings .......................................................................................................68
About QoS configuration settings ............................................................................................................... 68
ToS configuration ........................................................................................................................................ 69
DiffServ configuration .................................................................................................................................. 69
Default settings ........................................................................................................................................... 69
Network connectivity testing .................................................................................................70
Configuring general ISDN settings ........................................................................................71
Basic settings .............................................................................................................................................. 71
ISDN advanced settings .............................................................................................................................. 73
ISDN codec settings .................................................................................................................................... 75
ISDN multipoint settings .............................................................................................................................. 76
Configuring ISDN ports settings ............................................................................................77
Configuring ISDN ports settings (non-leased line mode) ............................................................................ 77
Port settings ......................................................................................................................................... 77
Configuring ISDN ports settings in leased line mode ................................................................................. 80
Port settings ......................................................................................................................................... 80
Configuring H.323 gatekeeper settings .................................................................................81
Gatekeeper settings .................................................................................................................................... 81
Gatekeeper status ....................................................................................................................................... 84
Configuring encryption settings ............................................................................................86
Displaying and resetting system time ...................................................................................87
System time................................................................................................................................................. 87
NTP ............................................................................................................................................................. 87
Using NTP over NAT (Network Address Translation) ......................................................................... 87
Configuring security settings ................................................................................................88
Advanced security mode ............................................................................................................................. 88
Hashing passwords .............................................................................................................................. 89
Password format .................................................................................................................................. 90
Expiring passwords .............................................................................................................................. 90
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 4 of 135
Page 5

Contents
Upgrading and backing up the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway....................................91
Upgrading the main ISDN Gateway software image .................................................................................. 91
Upgrading the loader software image ......................................................................................................... 91
Backing up and restoring the configuration................................................................................................. 92
Enabling ISDN Gateway features ............................................................................................................... 92
Shutting down and restarting the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway ...............................94
Displaying general status .......................................................................................................95
Displaying ISDN status ...........................................................................................................96
Displaying hardware health status ........................................................................................97
Displaying security status ......................................................................................................98
Working with the event logs ...................................................................................................99
Event log ..................................................................................................................................................... 99
Event capture filter ............................................................................................................................... 99
Event display filter ................................................................................................................................ 99
Syslog .................................................................................................................................................. 99
H.323 ......................................................................................................................................................... 100
Audit log .................................................................................................................................................... 100
Call Detail Records ................................................................................................................................... 100
Working with the audit logs ................................................................................................. 101
Audit log .................................................................................................................................................... 101
Understanding security warnings ........................................................................................ 102
Logging using syslog ........................................................................................................... 106
Syslog settings .......................................................................................................................................... 106
Using syslog .............................................................................................................................................. 107
Working with Call Detail Records ........................................................................................ 108
Call Detail Record log controls .................................................................................................................. 108
Call Detail Record log ............................................................................................................................... 108
Downloading and clearing the log ...................................................................................................... 109
CDR log display ................................................................................................................................. 110
Further information about CDR time field .......................................................................................... 110
Customizing the user interface ............................................................................................ 111
Configuring user interface settings ........................................................................................................... 111
Controlling the auto-refreshing of status pages on the ISDN Gateway ............................................. 111
Configuring welcome messages for the Login and Home pages ............................................................. 112
Customizing voice prompts on the ISDN Gateway ................................................................................... 112
Using default English voice prompts .................................................................................................. 112
Uploading a customization pac kage .................................................................................................. 113
Viewing the available voice prompts .................................................................................................. 113
Uploading and downloading customized voice prompts .................................................................... 114
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 5 of 135
Page 6

Contents
Downloading individual voice prompts ............................................................................................... 115
Deleting customized voice prompts ................................................................................................... 115
Voice prompt specification ........................................................................................................................ 116
Making the best possible recordings ................................................................................................. 116
Customization: More information ........................................................................................ 117
Precedence ............................................................................................................................................... 117
The factory default file set ......................................................................................................................... 117
Localization files ........................................................................................................................................ 117
Customization files .................................................................................................................................... 117
Backing up and restoring the configuration using FTP ..................................................... 118
Configuring SSL certificates ................................................................................................ 119
Contact details and license information .............................................................................. 121
TANDBERG .............................................................................................................................................. 121
Software licenses ...................................................................................................................................... 121
AVC VIDEO........................................................................................................................................ 122
RSA Data Security Inc. ...................................................................................................................... 122
The Internet Society ........................................................................................................................... 122
NetBSD .............................................................................................................................................. 122
Info-ZIP .............................................................................................................................................. 123
Independent JPEG Group's JPEG software ...................................................................................... 124
The OpenSSL Project ........................................................................................................................ 125
N.A.T. GmbH...................................................................................................................................... 126
Spirit Corporation ............................................................................................................................... 127
AES License....................................................................................................................................... 127
HMAC License ................................................................................................................................... 127
SHA1 License .................................................................................................................................... 128
Lua ..................................................................................................................................................... 128
Telenetworks ...................................................................................................................................... 129
Regents of the University of California .............................................................................................. 129
DHCP ................................................................................................................................................. 129
Net-SNMP .......................................................................................................................................... 129
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 6 of 135
Page 7

Logging into the web interface
Logging into the web interface
The Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway (ISDN Gateway) web interface is used for administering the
Cisco TelePresence ISDN GW 3241 and 3200 Series units and the ISDN GW MSE 8321 and ISDN GW
MSE 8310 blades, monitoring the progress of active and completed calls, managing dial plans and users,
and for obtaining event logging information for reference or for troubleshooting complex issues.
When connecting to the ISDN Gateway web interface, you must log in so that the ISDN Gateway can
associate the session with your configured user and a set of access privileges. The ISDN Gateway has a
set of configured users, and each user has a username and password that are used for logging in.
1. Using a web browser, enter the host name or IP address of the ISDN Gateway.
2. To log in as the administrator, click Log in and enter your assigned Username and Password.
3. Click OK
The main menu appears, offering options based on your access privileges.
The Login page of the ISDN Gateway displays a welcome banner which administrators can configure to
display text relevant to your organization. For more information, refer to
Customizing the user interface.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 7 of 135
Page 8

Failing to log into the web interface
Failing to log into the web interface
When connecting to the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway web interface, you must log in so that the
ISDN Gateway can associate the session with your configured user and a set of access privileges. The
ISDN Gateway has a set of configured users, and each user has an ID and password that are used for
logging in.
If you see the Access denied page, you have not been able to log in for one of the following reasons:
Invalid username/password: you have typed the incorrect username and/or password.
If Advanced account security mode is enabled and you incorrectly type the username and/or
password three times and if this is an admin account, it is disabled for 30 minutes; for any other
account, it is disabled indefinitely (or until you, the administrator, re-enable the account from the
User page)
No free sessions: the maximum number of sessions allowed simultaneously on the ISDN
Gateway has been exceeded
Your IP address does not match that of the browser cookie you supplied: try deleting your
cookies and log in again
You do not have access rights to view this page: you do not have the access rights necessary
to view the page that you attempted to see
Page expired: the Change password page can expire if the ISDN Gateway is not entirely happy
that the user who requested to change password, is actually the user submitting the change
password request. (This may happen if you use a new browser tab to submit the request.)
Invalid passwords
If Advanced account security mode has been enabled, the ISDN Gateway will disable a user's account if
that user incorrectly enters a password three times consecutively. If this is an admin account, it is
disabled for 30 minutes; for any other account, it is disabled indefinitely (or until you, the administrator, reenable the account from the Users page).
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 8 of 135
Page 9

Failing to log into the web interface
Getting started with the Cisco TelePresen ce
ISDN Gateway
Ensure you have correctly completed the physical setup of the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway (ISDN
Gateway) following the instructions in the Getting Started Guide that accompanied it. You must also
ensure that your endpoints and MCU are correctly configured to operate with the ISDN Gateway.
Before you can make calls using the ISDN Gateway, you need to complete its setup using the web
interface as follows:
1. Log into the ISDN Gateway: Use your browser to navigate to the IP address of the ISDN
Gateway. Click Change log in and enter the user name 'admin' with no password. We
recommend that you change the admin user account to use a password as soon as possible.
2. Set up the ISDN interfaces:
a. Go to Settings > ISDN.
b. Select the ISDN interface type to match that of your installation: E1 is typically used in
the UK and mainline Europe, and T1 in North America. Use T1 (Japan) in Japan.
c. You may need to set other advanced ISDN settings. Only change these settings if you
know of a specific requirement to do so.
d. Click Apply changes.
e. If you made any changes on this page, you must restart the ISDN Gateway before they
will take effect. Go to Settings > Shutdown and click Shut down ISDN GW.
3. Configure ISDN ports: Go to Settings > ISDN ports:
a. Set low and high channels:
i. If you have a fully-populated PRI (this is the normal case) set Low channel to '1'
for all network types and High channel to Max.
ii. If you have a fractional PRI, where your provider offers a reduced number of B-
channels, enter alternative values as appropriate.
b. Set the Channel search order: When making calls, the ISDN Gateway examines which
B-channels are free before placing a call. This search can be performed starting with the
high channel and working down, or starting with the low channel and working up. Your
ISDN provider will be able to advise which scheme to use, but the choice is not critical.
c. Click Apply changes and then, if required, repeat the above steps to configure further
ISDN ports. Select which port you want to configure using the numbered links at the top
right of the page.
4. Configure the dial plan: The default behavior of the ISDN Gateway is to reject all calls. You
must configure a dial plan to allow permitted calls to be placed. The simplest configuration is to
create a dial plan that will connect any 'IP to ISDN' call that has been routed to the ISDN Gateway
to the number that the caller has dialed (using any free enabled port) and that will connect any
'ISDN to IP' call to the auto attendant of your MCU:
a. Go to Dial plan > IP to ISDN and click Add rule.
b. For Rule name, type in a name for the new rule.
c. For Condition, select Match any called number.
d. For Action, select Call with the original called number.
e. Leave the other values unchanged. Cl ic k Add rule to add the rule to the dial plan.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 9 of 135
Page 10

Failing to log into the web interface
f. Now go to Dial plan > ISDN to IP, and click Add rule.
g. For Rule name, type in a name for the new rule.
h. For Condition, select Match any called number.
i. For Action, select Call this number and enter the IP address of your MCU.
j. Lea ve the other va lues unc hang ed. Cl ic k Add rule to add the rule to the dial plan.
For more information about dial plans, refer to
Understanding the dial pl an.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 10 of 135
Page 11
Making calls with the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway
Making calls with the Cisco TelePresence ISDN
Gateway
The Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway allows:
users with ISDN endpoints to place calls to users with IP endpoints
users with IP endpoints to place calls to users with ISDN endpoints
When configured correctly, the ISDN Gateway is transparent to users; they will require minimal
assistance and training to place calls through the ISDN Gateway successfully.
One training consideration for users making ISDN calls which is not usually present for IP calls is that of
cost; you may want to educate users that ISDN calls escalate in cost with increased bandwidth and
duration. You may also want to configure the ISDN Gateway to limit these values if required (for more
information, refer to
For information about setting up the ISDN Gateway, refer to:
the Getting Started Guide.
Understanding the dial plan).
Getting started with the ISDN Gateway.
When you have the ISDN Gateway and associated devices (for example, the MCU) correctly configured,
with an appropriate dial plan in place, calls can be placed through the ISDN Gateway.
ISDN to IP calls
If you have configured the dial plan as in Getting started with the ISDN Gateway, endpoints calling the
phone number of the ISDN Gateway will, after the call is completely established, be forwarded to the auto
attendant of the MCU. From here they may use the Far End Camera Controls (FECC) of their endpoint to
navigate the menus and join conferences as normal.
IP to ISDN calls
An IP to ISDN caller needs to know the number of the ISDN user whom they are calling. However, if the
call will be placed via an MCU, the ISDN user's number can be incorporated into the configured endpoint
details stored on the MCU.
You can configure the ISDN Gateway to allow calls to a single ISDN number. In this case, a single rule in
the dial plan will suffice, matching all numbers and calling out to a single phone number.
If you want users to be able to call any number, set the ISDN Gateway up as a 'H.323 gateway' on your
MCU and direct calls to ISDN numbers via that. Alternatively, if you are using a gatek eeper on your IP
network, you can register a prefix with which users may prefix the ISDN number they want to call (this is
similar to dialing a '9' for an external line on many telephone systems).
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 11 of 135
Page 12

Using the auto attendant
Using the auto attendant
You can use the auto attendant on the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway to enter the number you want
to call directly from your endpoint. If you are calling from an IP endpoint, you should enter a phone
number. If you are calling from an ISDN endpoint you should enter an IP address (optionally followed by
an extension number or phone number).
If your administrator has set up calls to be directed to the auto attendant, then you will see the instruction:
"Enter the number you wish to call", and hear an audio prompt. (Users of audio-only endpoints can use
the auto attendant even though they can only hear the audio prompt.)
When you dial, you can use the following:
Digits 0 to 9
* (asterisk or star), which is interpreted as a dot for ISDN to IP calls
** interpreted as a : and used as an extension separator for ISDN to IP calls
# (hash), to indicate that you have completed the number and to start dialing
To call a specific extension, separate the number/address from the extension by typing a colon (:). For
example, to call the MCU with IP "10.2.1.33", and try to join a conference with numeric identifier "00000",
you need to enter 10.2.1.33 : 00000 so you should type 10*2*1*33 ** 00000#
Note that if you do not include the #, the ISDN Gateway will dial after 20 seconds anyway. Equally, if you
do not enter any numbers but leave the auto attendant idle, the ISDN Gateway will hang up the call after
60 seconds.
Using the Far End Camera Control
If FECC is enabled on your endpoint, use the Left arrow to delete the last character and the Right to start
dialing
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 12 of 135
Page 13

Using the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway for voice-only calls
Using the Cisco TelePresence I SDN Gateway for
voice-only calls
The Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway can be used to forward voice-only IP calls to the ISDN network
(the PSTN); likewise, it can be used to forward voice-only ISDN calls from the PSTN to IP telephones on
the IP network. If you want to use the ISDN Gateway to forward voice-only calls, there are two ways to
configure this feature:
globally: either
o entirely as a voice-only gateway: where all IP calls and all ISDN calls are forwarded as
voice-only calls, or
o partly as a voice-only gateway: where incoming ISDN video-conferencing calls are
allowed, but outgoing ISDN calls are voice only (or vice versa)
dial plan configuration: where particular calls (ingoing and outgoing) are allowed to be video
conferencing calls, and where particular calls are restricted to voice-only
IP to ISDN calls: IP endpoints often do not allow the caller to specify the type of call being made. For
example, a caller may want to make a telephone call (that is, voice only), but are unable to specify that
this is a telephone call. To overcome this problem, for IP data calls, if required, the ISDN Gateway can
extract the voice part of the call and forward it to the ISDN network as a voice-only call. For IP to ISDN
calls, if the ISDN Gateway receives a video conferencing call that has been restricted to being a voiceonly call (due to the settings on the ISDN Gateway), the unit will forward it as a voice-only call (the call will
not be dropped). If the IP endpoint does allow the call type to be specified, an IP telephone call will
always be placed as such.
ISDN to IP calls: ISDN endpoints usually allow a caller to specify the type of call being made. This is
important, because with ISDN calls the voice part of the call cannot be separated from the video part.
Therefore, if the ISDN Gateway receives a video-conferencing call and the dial plan restricts the ISDN
Gateway to voice-only calls, the unit will drop the call. Voice-only telephone calls will always be accepted
by the ISDN Gateway.
Configuring the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway as a voiceonly gateway
1. Go to Settings > ISDN.
a. To configure the ISDN Gateway to restrict incoming ISDN calls to voice-only calls, set the
Max incoming ISDN call rate to Telephone.
b. To configure the ISDN Gateway to restrict outgoing ISDN calls to voice-only calls, set the
Max outgoing ISDN call rate to Telephone.
2. Complete the other ISDN settings as per your requirements. For more information about the
ISDN settings page, refer to
Note: You can set both the incoming and outgoing maximum call rates to Telephone to use the ISDN
Gateway entirely as a voice-only gateway.
Configuring general ISDN Settings.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 13 of 135
Page 14
Using the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway for voice-only calls
Dial plan configuration
You can configure the dial plan to restrict particular called numbers to voice-only calls. In this way, you
can configure the ISDN Gateway to allow particular outgoing/incoming ISDN calls to be videoconferencing calls. Using the dial plan therefore allows you greater flexibility (if you need it) than using the
global settings on the ISDN settings page.
You can use the dial plan to place a call where the ISDN Gateway will start sending DTMF tones after a
telephone call has connected. This is useful if there is a call through the ISDN Gateway to a device which
is perhaps behind another gateway which only supports DTMF to decide how to route the calls. The caller
is not required to additionally enter the DTMF codes manually on the telephone keypad but instead can
have the call re-routed automatically using the dial plan of the ISDN Gateway.
For more information about configuring the dial plan, refer to
Understanding the dial plan, Adding and
updating dial plan rules, and Example dial plan rules.
Calling a PSTN telephone from an MCU
If you want to call someone on a regular land-line telephone into a conference on the MCU, you must add
the ISDN Gateway as a participant, using one of the following methods:
specify it as a gateway with an extension.
call a particular number registered to a common gatekeeper.
call the ISDN Gateway by IP and let the ISDN Gatewa y its elf work out which number to call
based on dial plan rules.
Whichever method you use, you must have a dial plan configured such that a rule is invoked that has
"Telephone" bandwidth specified for the call. Then the call will be established correctly.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 14 of 135
Page 15
Using the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway for voice-only calls
#
Activity
Whether or not this channel on this port is currently active. Activity is one of:
Direction
If the channel is active, the direction of the call is displayed. Either:
Calling party
The identity of the endpoint that initiated the call (depending on what that endpoint
Called party
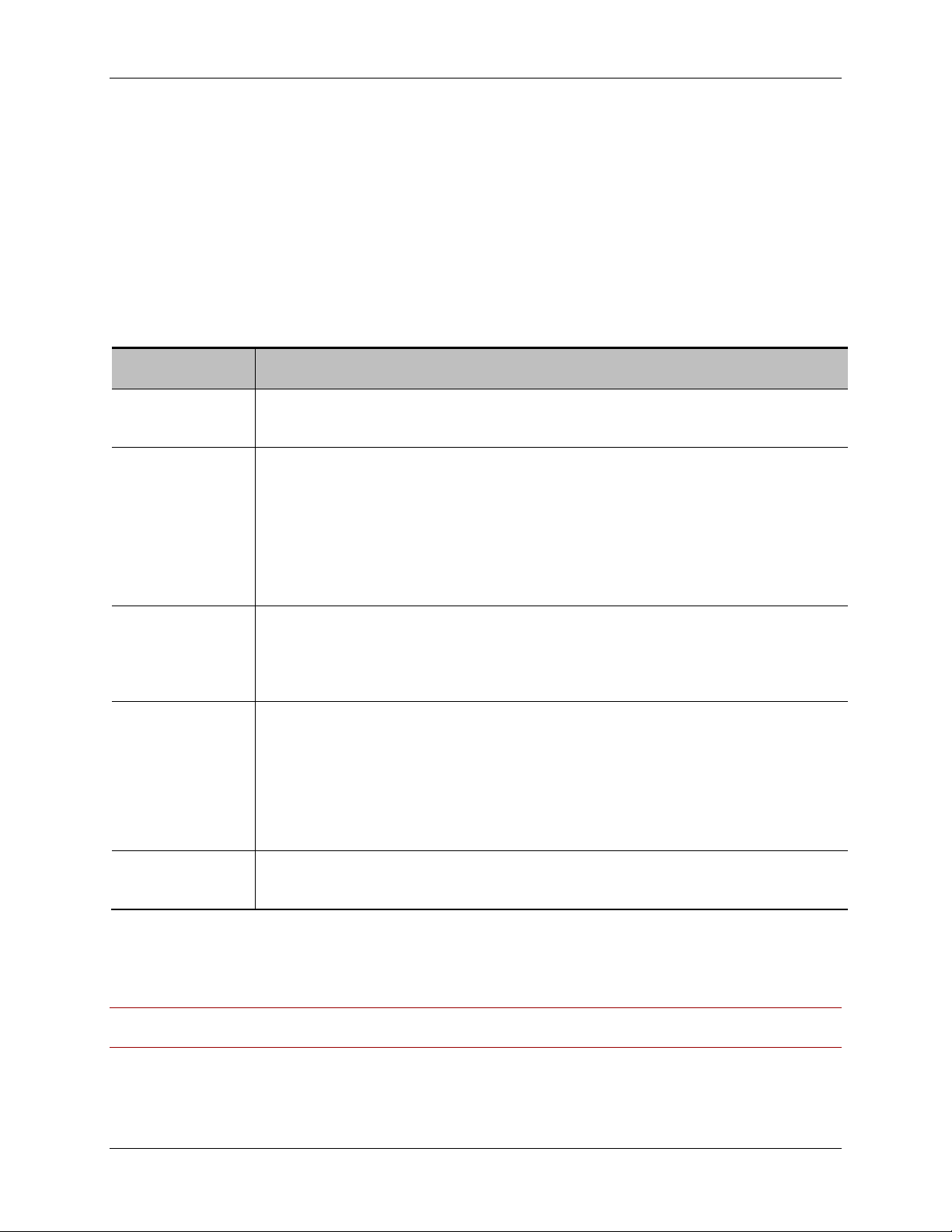
Displaying ISDN port utilization
For each ISDN port, you can view details of any port activity for each ISDN channel. To display ISDN port
utilization details, go to ISDN > ISDN ports.
A message shows the status of ISDN layers 1 (physical) and 2 (D-channel). The same information is
shown in the ISDN Status page.
Note that if the ISDN Gateway is in leased line mode, there will be no status for layer 2.
The following information is displayed for each channel of every ISDN port:
Field
Field description
The ISDN channel number.
inactive: not in use.
active (data): in use. A voice and video call is taking place and is using this
channel.
active (voice): in use. An audi o-only call is taking place and is using this
channel.
inbound: for calls to the ISDN endpoint.
outbound: for calls from the ISDN endpoint.
has provided):
for IP-ISDN calls (that is, outbound calls), this is the name of the H.323
device, the telephone number, or "Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway".
for ISDN-IP calls (that is, inbound calls), this is the telephone number of the
endpoint that made the call.
The number that was dialed by the calling party. Note that if the ISDN Gateway is in
leased line mode, there will be no called part number available.
For each port there is an Activate D-channel now button that is only active if layer 1 is up and layer 2 (Dchannel) is not. If neither or both are up for a port, the button is disabled for that port. Click the button to
bring up the D-channel.
Note: Typically, you need never do this because the ISDN Gateway automatically tries to bring up the Dchannel periodically. Also clicking the button is not guaranteed to work.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 15 of 135
Page 16
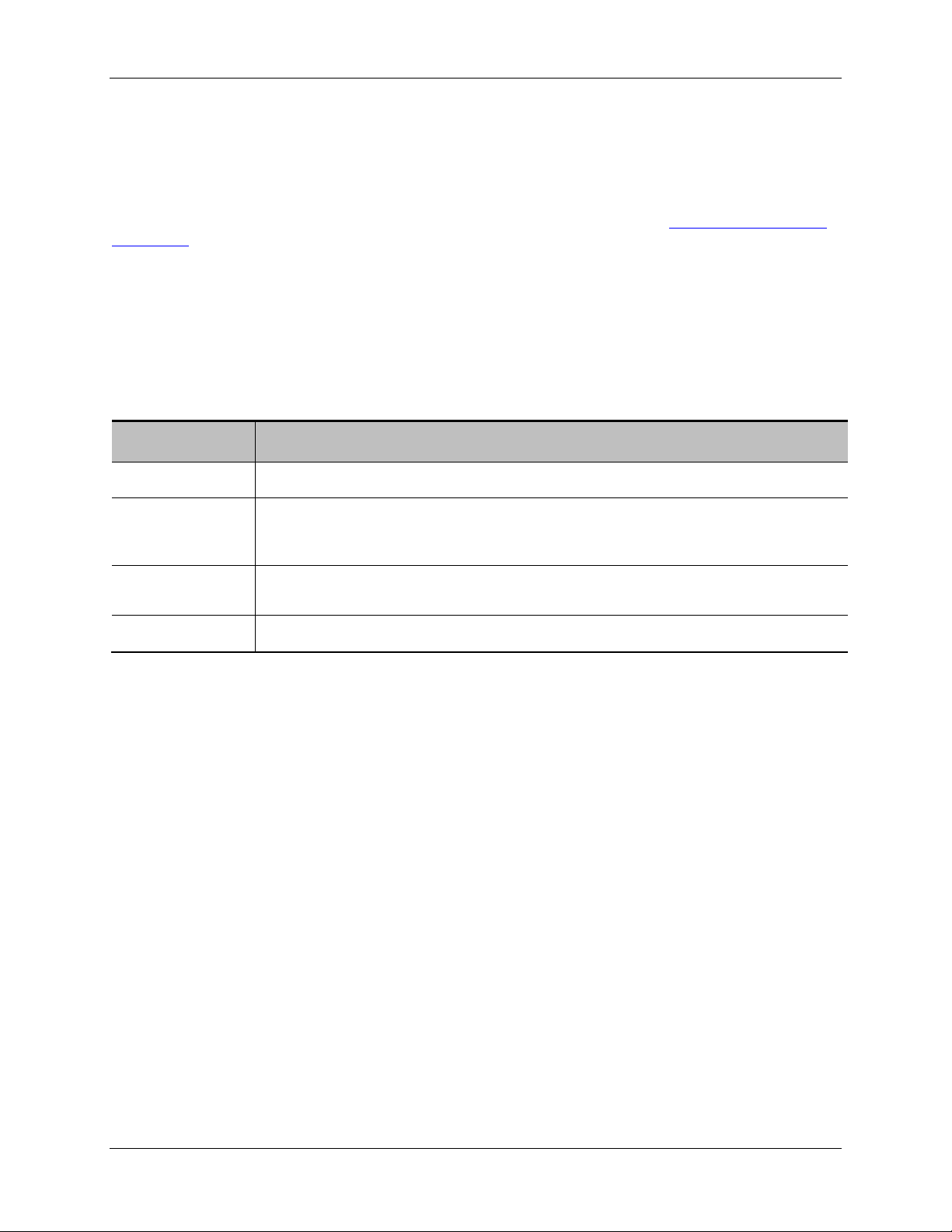
Displaying the ISDN calls list
Type
The type of call, which will be IP to ISDN or ISDN to IP.
Participants
"<none>" if this information is not supplied by your ISDN network.
Details
For example, the time that the call started, its duration and whether encryption is
used.
Progress
Progress is indicated for active calls only.
Displaying the ISDN calls list
The ISDN Calls List displays both active calls and completed calls on the Cisco TelePresence ISDN
Gateway together with their basic settings. The list enables you to disconnect active calls and to delete
completed calls from the list. For active calls, you can display further details (see
information).
Active calls are those calls that are taking place now. The active calls list shows all calls that are currently
taking place. The maximum number of calls that can take place simultaneously is constrained by the
ISDN bandwidth available to the ISDN Gateway. Completed calls are calls that have ended. The
completed calls list shows only the most recent calls (up to 20 calls). Older calls are automatically deleted
from the list.
To display the ISDN Calls List go to ISDN > ISDN calls.
Displaying detailed call
Field
Field description
The participants in the call. An IP participant will be listed by IP address, E164
number or H.323 ID. An ISDN participant will be listed by Calling Party Number or
Disconnecting and deleti ng c alls
To disconnect active calls, go to ISDN > ISDN Calls:
To disconnect particular calls, select the calls you want to disconnect and click Disconnect
selected.
To disconnect all active calls, click Disconnect all.
To delete calls from the list of completed calls, go to ISDN > ISDN calls:
To delete particular calls from the list, select the calls you want to delete and click Purge
selected.
To delete all completed calls, click Purge all.
Diagnostic controls
By default diagnostic logging is disabled. This feature is for use by Cisco customer support and we
suggest that you do not change the setting unless instructed to do so.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 16 of 135
Page 17
Displaying the ISDN calls list
Field
Started at
For IP to ISDN calls, this is the time at which the call was received by the ISDN
Call progress
The status of the call, which will be one of:
Unique index
A unique numeric identifier given by the ISDN Gateway to this part of the call.
Name
The name the caller provided when the call was initiated.
E.164
The telephone number of the participant.
Call type
The participant's call type: either H.320 (ISDN caller) or H.323 (IP caller).
FECC
Whether Far-End Camera Control has been established or not.
Progress
The status of the participant's side of the call, which will be one of:
Displaying detailed call information
Active calls are listed along with some basic details in the ISDN Calls List (see Displaying the ISDN Calls
List). To view additional details about an active call, go to ISDN > ISDN Calls and click more for the call
about which you want more information.
On the Call details page, the call for which more details are provided is displayed with a number
(example: "Call 15 details"). This number is generated by the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway
(numerically, starting from zero since the last reboot) for the purposes of internal identif ic at ion .
Field description
Gateway.
For ISDN to IP calls, this is the time at which all the channels comprising the call
connected and bonded.
Initial: an IP or ISDN call has just come in, and the ISDN Gateway is
determining if it is allowed and where to direct it.
Calling out: the ISDN Gateway is trying to make contact with the other side
Connected: the call is in progress between and IP and ISDN endpoints.
Dying: Displayed briefly while a call is terminated, either by one of the
Call progress also lists the caller's number, the number that was called and the
destination, including the IP address for an IP destination.
Participant details
Initial: the call is just starting.
Proceeding: trying to make contact with the other side of the call.
Alerting: the other side of the call is ringing (you might not see this state).
of the call.
participants or via the web interface.
Connected: the call is in progress.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 17 of 135
Disconnecting: the call is in the process of going down.
Page 18
Finished: the call is disconnected (you might not see this state).
Encryption
This field tells you whether encryption is active and if so, whether all or only some
Channel
Only for ISDN participants: The numbers of the ISDN channels that are in use for
Channel rate
Only for ISDN participants: Whether or not restricted 56k mode is in use for the
of the media channels are encrypted.
Displaying the ISDN calls list
bonding map
this call.
received (rx) and/or transmitted (tx) part of an ISDN call. For unrestricted calls (rx
and/or tx), the channel rate will be 64kbps.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 18 of 135
Page 19

Understanding the dial plan
Understanding the dial plan
The Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway uses the dial plan to determine how to route calls between IP
and ISDN networks. When the ISDN Gateway receives a request to initiate a new IP to ISDN or ISDN to
IP call, it examines the called number (if available), and uses the dial plan to determine whether to reject
the call, find out which number should be called to initiate the outgoing part of the call, and to check the
allowed call bandwidth.
There are a number of different ways in which you can use the dial plan. For example, you can use the
dial plan to enable callers to use a particular bandwidth for an IP to ISDN call. You can also use the dial
plan to enable the ISDN Gateway to join incoming ISDN calls to the correct conference on an MCU. (For
example dial plans, refer to
The dial plan is actually divided into two; an IP to ISDN dial plan and an ISDN to IP dial plan. If the
incoming part of a connection is from an IP endpoint, the IP to ISDN dial plan is used; if it is from an ISDN
endpoint, the ISDN to IP dial plan is used. The behavior of the two dial plans is nearly identical, and the
sections below only make a distinction between the two where differences exist.
The maximum number of rules that can be added to each dial plan is 200.
Note that if you have configured the ISDN Gateway to use leased line mode, then the options available
on the dial plan are different to those available in non-leased line mode. For information about configuring
dial plans in leased line mode, refer to
Example dial plan rules.)
Adding and updating dial plan rules in leased line mode.
Refer to the sections below for more information about the use and administration of dial plans:
Rules
Using rules
Rule ordering
Rules
Dial plans are administered using rules. Rules and their addition and control are nearly identical for the IP
to ISDN and ISDN to IP dial plans.
Each rule has a name and comprises:
a Condition that must be matched for the rule to be invoked
The condition can be set to match any called number, to match a call that has no called number,
or can specify the called number by specific number or pattern.
an Action that is carried out if the rule is invoked
The action can be to reject the call, enter the auto attendant, enter the auto attendant and use a
TCS-4 extension (ISDN to IP only), to place the call using the original dialed number, or to
specify the number/address to call.
a set of Additional parameters that modify the action:
o Call type: specifies whether the call is a normal video call, a telephone call, or a video
call that supports legacy ISDN endpoints that use n x 64kbps or n x 56kbps
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 19 of 135
Page 20

Understanding the dial plan
o Restrict (56k): whether a call will use 56kbps. Note that if 56k is specified for a rule, but
the endpoint only supports 64kbps, then the call will be terminated rather than use
56kbps
o Maximum bandwidth: used to limit the bandwidth available to for calls to particular
numbers, or to allow users to select their own bandwidth (for more information, see
Adding and updating dial plan rules)
o Encryption se ttings: whether transparent encryption is to be used and if not, whether
encryption is Optional or Required for the IP and ISDN parts of the call
o Place/Receive call on: the port(s) to use if you need to bond channels to complete
subsequent calls from the calling endpoint
a choice of allowed codecs
Using rules
Each dial plan comprises a set of rules. When the ISDN Gateway receives a new incoming call, it selects
the appropriate dial plan, then compares the called number (if available) to the condition of each rule in
that dial plan until a match is found. When a match is found, no more rules are checked, and the action of
the matching rule is used to determine what should be done next; typically the outgoing part of the
connection will be initiated - calling a number specified by the action, the auto attendant is displayed or
the connection will be rejected and the incoming part terminated.
If a dial plan contains no rules, or if no rule's condition matches the called number, calls are rejected by
default.
For more information on adding and modifying dial plan rules, see
Adding and updating dial plan rules.
Rule ordering
Rules are always checked in the same order for each incoming call. This means that a dial plan can be
designed to handle specific calling cases first, then general calls if no specific cases match. For example,
a dial plan might be set up to call a particular endpoint if an incoming call is received to a specific number,
but all other incoming calls get connected to an operator. Such a dial plan might look like this:
1. Condition: Called number is "6056" / Action: Call with the original called number.
2. Condition: Match any called number / Action: Call this number "1000"
Clearly rule ordering is important to achieve this functionality. You can view and test the rule list
comprising a dial plan, and modify the ordering of the rules by dragging and dropping as required. (You
can also use the up and down links to reorder.) For more information, see
plan.
Displaying and testing the dial
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 20 of 135
Page 21
Displaying and testing the dial plan
Field
More information
Name
Condition
Which called numbers will cause this
Possible conditions include:
Displaying and testing the dial plan
The dial plan is actually made up of two, separate dial plans: one for IP to ISDN calls and one for ISDN to
IP calls. Refer to the sections below for more information.
To display or modify the IP to ISDN dial plan, go to Dial plan > IP to ISDN. To display or modify the ISDN
to IP dial plan, go to Dial plan > ISDN to IP.
Note that if you have configured the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway to use leased line mode, then
the options available on the dial plan are different to those available in non-leased line mode. For
information about configuring dial plans in leased line mode, refer to
in leased line mode.
Displaying the rules list
Modifying rules list
Testing the dial plan
Displaying the rules lis t
Adding and updating dial plan rules
As described above, the dial plan comprises a set of rules that are followed in response to the incoming
part of a connection in order to determine how to proceed with the outgoing part of the connection.
You can view the set of rules comprising a dial plan as a list, with rules checked from top to bottom. Refer
to the table below for details of the fields displayed.
Field description
The unique number assigned to this
rule and the rule's name.
rule to be invoked.
Click on a number or name to view and modify
rule details (see
Adding and updating dial plan
rules).
Called number is "1025" meaning this
rule is invoked if the called number is
exactly as stated
No called number meaning this rule is
invoked if the incoming part of the call
has no called number available
Match port <port number> leased line
group <group number>: meaning this
rule is invoked if the incoming part of the
call is using the port number and leased
line group as stated in the rule
Match any called number meaning this
rule is always invoked if checked
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 21 of 135
Page 22

Displaying and testing the dial plan
Action
What will happen if this rule is
Possible actions include:
Bandwidth
The maximum ISDN bandwidth that
The value will be one of:
invoked.
Reject the call: if this rule is invoked the
call will be terminated and the outgoing
part of the call will not be established
Enter the auto attendant : the call will be
connected to the auto attendant
Enter the auto attendant + TCS-4: the call
will be connected to the auto attendant
and an extension accepted
Call this number "xxx": where xxx
represents what is displayed:
o for IP to ISDN calls: a number or
a pattern
o for ISDN to IP calls: a pattern, a
hostname, or an IP address
meaning that "xxx" will be called if this
rule is invoked.
Call with the original called number: the
original called number will be used to
place the outgoing part of the call
Call these numbers: meaning that this is
a video call using N x 64kbps or N x
56kbps (for legacy ISDN endpoints only).
The first two numbers to be called are
listed here; click the dial plan number to
view the complete list of numbers
included in this rule
will be used for the call if this rule is
invoked.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 22 of 135
Call port <x> leased line group <x>: if the
ISDN Gateway is using leased line mode,
this action indicates on which port the call
will be made and using which leased line
group
• Telephone: the call will be restricted to
voice-only.
• <default>: the default maximum
bandwidth setting is used. To configure
the default bandwidth go to Home >
Settings > ISDN
• Number of kbps: the maximum
bandwidth allowed for calls matching this
rule
• N x 64kbps: the call is a video call using
N x 64kbps (for legacy ISDN endpoints
only)
Page 23

Displaying and testing the dial plan
Ports
Codecs
UID
* (asterisk)
• N x 56kbps: the call is a video call using
N x 56kbps (for legacy ISDN endpoints
only)
The ISDN port(s) on which the call
may be placed.
Shows the choice made when adding
the dial plan rule.
The unique identifier for the dial plan
rule.
Identifies the rule you have just
moved.
One of Default, Custom or Safe. (See Adding and
updating dial plan rules for more details.)
Each rule in the dial plan is assigned a unique ID
number generated by the ISDN Gateway. This
UID uniquely identifies the dial plan rule when it is
referenced in the audit log.
If you have just moved a rule in the list, it will be
marked with an asterisk (*). This is to help you
see the changes you have made.
Modifying the rules lis t
To change the order of rules, drag and drop the rule that you want to move or use the up and down links.
To add a rule, click Add rule (see
To remove a rule, select one (or more) and click Delete selected rules.
Adding and updating dial plan rules).
Testing the dial plan
It may take some experimentation to create the dial plan that you require. The ISDN Gateway provides a
facility to test the dial plan to see how your set of rules acts on a particular number.
To test the dial plan:
1. Go to Dial plan.
2. If you want to test how the dial plan acts
o on a particular number or address for an ISDN to IP connection, ensure you are on the
ISDN to IP dial plan tab
o on a particular number for an IP to ISDN connection, ensure you are on the IP to ISDN
dial plan tab
3. In the Test dial plan section, enter the number to test and click Test number.
The ISDN Gateway displays the number that you have tested, the rule that the condition matched, the
outcome (that is, whether the call was rejected or the number that has been dialed in response) and the
bandwidth.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 23 of 135
Page 24

Adding dial plan rules
Adding dial plan rules
The options that are available to you when you are configuring dial plan rules depend on whether or not
the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway is in leased line mode. (Leased line mode is configured on the
Settings > ISDN page.)
Select the help topic that you need:
Adding and updating dial plan rules (non-leased line mode)
Adding dial plan rules in leased line mode
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 24 of 135
Page 25

Adding and updating dial plan rules
Adding and updating dial plan rules
This page describes how to add rules to the dial plan. It also tells you how to update rules.
Note that you may also find it helpful to refer to
Adding dial plan rules
To add a dial plan rule:
1. Go to Dial Plan. If you want to add an
o IP to ISDN rule, use the IP to ISDN page.
o ISDN to IP rule, use the ISDN to IP page.
2. Click Add rule.
3. Type a name for the rule.
4. For Condition choose one of :
o Match any called number: this condition matches any called number and also includes
calls where the called number is not known or unavailable. Generally, this kind of rule
should be used towards the bottom of the dial plan list to match numbers not recognized
by more specific rules higher up.
o No called number: this condition matches when the called number is not known or
unavailable for ISDN calls. For IP calls, this condition matches when the caller uses the
IP address or hostname of the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway.
o Called number matches:
Example dial plan rules.
To match a specific number, enter that specific number.
Example: to match calls to "001234", type 001234. The condition will match that
and only that number.
Use S to match * (asterisk) and use P to match # (pound/hash). Examples: to
match calls to "*234", type S234; to match calls to "#0987", type P0987
To match a more general number, use the wildcard character, D. This matches
any digit as well as # and *.
Example: to match any number that starts with "55" followed by exactly two more
digits, type 55DD. This condition will match "5500", "5523", "5555", "5599", etc.
but not "55" or "55233".
For more general matching, you may use one of the three repeat characters.
These modify the character immediately before, whether it is a specific digit or
the wildcard character. The repeat characters are:
? match once or zero times.
+ match once or more.
* match zero or more times.
For example, "5+" means " match at least one 5, but possibly more".
"D*" means "match any digit, any number of times". D matches any digit as well
as # and *.
Example: to match any number that starts with "01", has any amount of digits in
the middle, and ends with "5", type 01 D* 5.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 25 of 135
Page 26

Adding and updating dial plan rules
To include any of the incoming called digits in the outgoing called number,
enclose each substitution group in a set of parentheses. Note that if you want to
include the complete number, you do not need to enclose the whole expression
in parentheses.
Example: to match any number starting with "678", then followed by three or four
digits, and you want the final digits to form part of the called number, type the
expression: 678 (DDDD?). This will match "6780000", "678123", "6789999" etc.
but not "67822" or "775000".
5. For Action (that is, what happens to the outgoing part of the call if this rule is invoked) choose one
of:
o Reject the call: the call will be terminated and the outgoing part of the call will not be
established.
o Enter the auto attendant: the call will be connected to the auto attendant.
o Enter the auto attendant + TCS-4: the call enters the auto attendant and sends a TCS-4
request; when the auto attendant receives the reply, it dials out the TCS-4 extension.
Usually the TCS-4 reply is fast enough that the auto-attendant is not displayed; however,
you may see it briefly with the TCS-4 extension shown. (For more information about
using TCS-4 see
Example dial plan rules)
o Call with the original called number: (not valid if you are going to select Video using
H.221 aggregation (legacy) as the Call type in the Additional parameters section) the
outgoing part of the call will be placed to the number that was the original called number.
For example, an incoming ISDN call to "54321" will result in an outgoing call placed over
IP to "54321".
o Call this number: (not valid if you are going to select Video using H.221 aggregation
(legacy) as the Call type in the Additional parameters section) the outgoing call will be
placed to the number that is entered here. Type a number, or for ISDN to IP rules you
can also type an IP address or hostname.
To call a specific number (or for ISDN to IP calls, you can also specify an IP
address, hostname, or H.323 URI), type that number (or IP address, hostname,
or H.323 URI). IPv6 addresses must be enclosed in brackets [ ].
Example: to specify that when this rule is invoked, the MCU with hostnam e
my_mcu is called, type my_mcu.
Example: suppose the domain "cisco.com" has a H.323 service (SRV) record set
up. To call a H.323 video endpoint residing in that domain, e.g. with URI
example.person@cisco.com, set an action to call example.person@cisco.com.
For information about domain (DNS) SRV records, see RFC 2782.
To call a specific extension, separate the number/address from the extension by
typing an exclamation mark (!).
Example: to call the MCU with IP address "10.2.1. 33 ", and try to join a
conference with numeric identifier "00000", type 10.2.1.33 ! 00000
To include any of the digits from the incoming called number in the outgoing
number, specify a substitution, by typing the dollar sign ($) followed by a index.
Valid indices are:
A: substitute the entire incoming called number.
1..9: substitute the digits enclosed in the relevant set of parentheses of the
condition.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 26 of 135
Page 27

Example: for all calls matching the condition of "55 (DDDD)", set an action to call
the MCU with name "my_mcu" and join the call to the conference with identifier
that matches "(DDDD)". For this example, type the action of my_mcu ! 00 $1. In
this case, an incoming call to "551234" will attempt to join conference with
numeric identifier "001234" on the MCU with the name "my_mcu".
Example: in an IP to ISDN dial plan rule, for calls matching a condition (D*)P(D*),
setting an action to call $1!$2 will match any numbers which have a '#' in, using
the number before the '#' for the phone number and the number after the '#' as
the TCS-4 extension. (For more information about using TCS-4 see
plan rules)
o Call these numbers: this option only becomes available if you select Video using
H.221 aggregation (legacy) as the call type (for IP to ISDN calls) in the Additional
parameters section. Only use Video using H.221 aggregation ( legacy) if you are
supporting legacy ISDN endpoints that need this feature. You must ensure you enter
the correct number of telephone numbers. For example, if you select 3 x 64kbps as
the call bandwidth, you must enter three telephone numbers here. Note that you can
use the same scheme of substitutions as described for Call this number.
6. Complete the Additional parameters, if required:
o Call type: Specify the type of outgoing call:
Adding and updating dial plan rules
Example dial
Telephone: if the call is a voice-only telephone call.
Video using BONDING (default): a "t ypic al" video call.
Video using H.221 aggregation (legacy): only select this if you need to support
legacy ISDN endpoints that require n x 64kbps or n x 56kbps channels. This
option is only available for IP to ISDN calls
o Restrict (56k):(this is only for IP to ISDN dial plan rules) when selected, for calls
matching this dial plan rule the ISDN Gateway will make the outgoing ISDN call in
restricted 56k mode. Do not select this option unless your network requires it. Note that
for a call matching a rule that uses 56k mode, if the endpoint only supports 64k, the ISDN
Gateway will drop the call rather than use 64k.
o Maximum call bandwidth: optionally, select a maximum bandwidth for the ISDN part of
the call, which will otherwise be set to the default value. To view or edit the default value,
go to Settings > ISDN. The maximum bandwidth settings on the Settings > ISDN page
are global settings. Therefore, if you choose a greater setting in the dial plan than you
have as a global setting, the global setting will be used as the maximum value. For
example, if in the dial plan you choose to set 320kbps (5 x B channels) as the maximum
bandwidth and the global setting for maximum bandwidth for outgoing ISDN calls is
256kbps (4 x B channels), the maximum bandwidth available to the call will never be
more than 256kbps.
Note that if you have selected Telephone as the call type, this option is unavailable and
the bandwidth set automatically.
Note that if you have selected Video using H.221 aggregation (legacy) as the call type,
you must ensure you select a bandwidth that matches the number of telephone numbers
that you have entered.
o Encryption settings:
Use transparent encryption: whe n sel ected, t he ISD N G ate wa y will sim ulate
point-to-point encryption. That is, it will set the encryption state
(enabled/disabled) used on the received call as that to be used on the outgoing
call. That is, the ISDN Gateway will attempt to match the encryption state for the
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 27 of 135
Page 28

Adding and updating dial plan rules
outgoing call to that of the incoming call. This means that if the encryption state
changes on either the incoming or outgoing call, the ISDN Gateway will attempt
to change the encryption state on the other side of the call. This can be helpful if
a call starts as an encrypted call both sides of the ISDN Gateway and then the
incoming call stops being encrypted for some reason; the outgoing part of the call
will also drop the encryption and both callers will know that the call is no longer
encrypted.
Select Required in the appropriate checkbox(es) if you always want the IP and/or
ISDN part of a call to be encrypted or Optional if encryption is only to be used to
endpoints that support it. Note that:
Encryption must also be enabled globally in the Settings > Encryption
page.
If Required is selected and the endpoint does not support encryption, the
call will be disconnected. If the endpoint does support encryption, no
media is passed until encryption can be ensured. How ever if you selec t
Optional and the endpoint supports encryption, then a call to may start
even before encryption can be guaranteed but will use encryption as
soon as possible
If the Call type is Telephone, then ISDN encryption is Disabled
These settings for IP and ISDN encryption are not available if you have
selected to use transparent encryption for this dial plan rule
o Place call on: (IP to ISDN only) optionally, select the ISDN port(s) on which the call may
be placed. The selected ports will be used in ascending or descending order as specified
in the Port search order field in the Settings > ISDN page.
o Receive call on: (ISDN to IP only) select the port(s) to advertise to the calling endpoint.
These ports may be used to complete subsequent calls from the calling end. The
selected ports will be used in ascending or descending order as specified in the Port
search order field in the Settings > ISDN page.
7. For Codecs allowed select an option from the drop-down list: <use default choices>, Custom
codec choices or Safe codec choices. The last two options are provided for older endpoints that
you cannot connect to when some codecs are enabled (even if the endpoint supports those
codecs). We recommend that you only use these options when you experience a problem.
o When you select Custom codec choices, the screen refreshes and you can select the
audio, video and H.239 video codecs that are allowed with this dial plan
o Safe codec choices only allows G711 and H261
8. Click Add rule.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 28 of 135
Page 29

Updating dial plan rules
To update an existing dial plan rule:
1. Go to Dial plan and find the rule you want to modify.
2. Click on the number or name of the rule to view its details.
Adding and updating dial plan rules
3. Modify the rule details using the information listed above in
4. Click Update rule.
You may wish to create a new rule very similar to an existing rule. To do this, find the existing rule and
click on its name or number to view its details. Press Copy rule to create a new rule, initialized with the
existing parameters, then proceed as normal, pressing Add rule when you have finished
Adding dial plan rules to help you.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 29 of 135
Page 30

Adding and updating dial plan rules in leased line mode
Adding and updating dial plan rules in leased
line mode
This page describes how to add rules to the dial plan when the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway is in
leased line mode. It also tells you how to update rules.
When you use the ISDN Gateway in leased line mode, the options on the dial plan are different to those
in ‘non leased line mode’. This is because as there is no D-channel, no number is sent over the leased
line call; this necessarily affects the options available for the configuration of the dial plan.
Note that you may also find it helpful to refer to
Adding dial plan rules
To add a dial plan rule:
1. Go to Dial Plan. If you want to add an
o IP to ISDN rule, use the IP to ISDN page.
o ISDN to IP rule, use the ISDN to IP page.
2. Click Add rule.
3. Type a name for the rule.
4. For Condition choose one of :
o Match any incoming call : this condition matches any incoming call and also includes
calls where the called number is not known or unavailable. Generally, this kind of rule
should be used towards the bottom of the dial plan list to match numbers not recognized
by more specific rules higher up.
o No called number: (this is only for IP to ISDN dial plan rules) this condition matches
when the caller uses the IP address or hostname of the ISDN Gateway
o Called number matches: (this is only for IP to ISDN dial plan rules)
To match a specific number, enter that specific number.
Example dial plan rules.
Example: to match calls to "001234", type 001234. The condition will match that
and only that number.
Use S to match * (asterisk) and use P to match # (pound/hash). Examples: to
match calls to "*234", type S234; to match calls to "#0987", type P0987
To match a more general number, use the wildcard character, D. This matches
any digit as well as * and #.
Example: to match any number that starts with "55" followed by exactly two more
digits, type 55DD. This condition will match "5500", "5523", "5555", "5599", etc.
but not "55" or "55233".
For more general matching, you may use one of the three repeat characters.
These modify the character immediately before, whether it is a specific digit or
the wildcard character. The repeat characters are:
? match once or zero times.
+ match once or more.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 30 of 135
Page 31

Adding and updating dial plan rules in leased line mode
* match zero or more times.
For example, "5+" means " match at least one 5, but possibly more".
"D*" means "match any digit, any number of times". D matches any digit as well
as * and #
Example: to match any number that starts with "01", has any amount of digits in
the middle, and ends with "5", type 01 D* 5.
To include any of the incoming called digits as the port number, leased line
group, and optionally the TCS-4 extension for the outgoing call, enclose each
substitution group in a set of parentheses.
Example: For an incoming number that starts with "678", and is followed by two
digits, and where you want the penultimate digit to be used as the outgoing port
number and the final digit to be used as the outgoing leased line group, type the
expression: 678 (D)(D). This will match the incoming called digits: "67812". (For
more information about using substitution groups in leased line mode see
Example dial plan rules)
Example: For an incoming number that starts with 987 and that is followed by the
port number, the leased line group number, and a TCS-4 extension of four or
more digits, type the expression 987(D)(D)(DDDD+). This will match the
incoming digits: "987235678" and "98733456789. (For more information about
using substitution groups in leased line mode see
Example dial plan rules).
o Match calls incoming on port leased line group: (this is only for ISDN to IP dial plan
rules) this condition matches calls using the specified port number and leased line group
number. Note that you can specify Any for either/or both the port and the leased line
group.
5. For Action (that is, what happens to the outgoing part of the call if this rule is invoked) choose one
of:
o Reject the call: the call will be terminated and the outgoing part of the call will not be
established.
o Call port <X> leased line group <x>: (this is only for IP to ISDN dial plan rules)You can
select the port number and leased line group number for the outgoing ISDN call. You can
either specify these as digits or use substitution groups from the Called number matches
field in the condition of this dial plan rule (refer to the information above for more details
about using substitution groups in the Called number matches field).
o Enter the auto attendant: (this is only for ISDN to IP dial plan rules) the call will be
connected to the auto attendant. Note that the ISDN Gateway applies the dial plan to
numbers dialed in the auto attendant.
o Enter the auto attendant + TCS-4: (this is only for ISDN to IP dial plan rules) the call
enters the auto attendant and sends a TCS-4 request; when the auto attendant receives
the reply, it dials out the TCS-4 extension. Usually the TCS-4 reply is fast enough that the
auto-attendant is not displayed; however, you may see it briefly with the TCS-4 extension
shown. (For more information about using TCS-4 see
Example dial plan rules).
o Call this number: (this is only for ISDN to IP dial plan rules) the outgoing call will be
placed to the number that is entered here. Type a number, or you can also type an IP
address or hostname.
To call a specific number, IP address or hostname, type that number, IP address,
or hostname. IPv6 addresses must be enclosed in brackets [ ].
Example: to specify that when this rule is invoked, the Cisco TelePresence MCU
with hostname my_mcu is called, type my_mcu.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 31 of 135
Page 32

Adding and updating dial plan rules in leased line mode
To call a specific extension, separate the number/address from the extension by
typing an exclamation mark (!).
Example: to call the Cisco TelePresence MCU with IP address "10.2.1.33", and
try to join a conference with numeric identifier "00000", type 10.2.1 .33 ! 000 00
6. Complete the Additional parameters, if required:
o TCS-4 extension digits (optional):(this is only for IP to ISDN dial plan rules) specify the
TCS-4 extension to be used for calls matching this rule. Note that you can either type the
TCS-4 extension to be used, or you can specify a substitution group such that digits from
the original called number will be used as the TCS-4 extension.
Example: if you specify 99(D+) for the Called number matches field, and $1 for the
TCS-4 extension, then a call to 991234 will use "1234" as the TCS-4 extension.
o Restrict (56k):(this is only for IP to ISDN dial plan rules) when selected, for calls
matching this dial plan rule the ISDN Gateway will make the outgoing ISDN call in
restricted 56k mode. Do not select this option unless your network requires it. Note that
for a call matching a rule that uses 56k mode, if the endpoint only supports 64k, the ISDN
Gateway will drop the call rather than use 64k.
o Maximum call bandwidth:(this is only for ISDN to IP dial plan rules) optionally, select a
maximum bandwidth for the ISDN part of the call, which will otherwise be set to the
default value. To view or edit the default value, go to Settings > ISDN. The maximum
bandwidth settings on the Settings > ISDN page are global settings. Therefore, if you
choose a greater setting in the dial plan than you have as a global setting, the global
setting will be used as the maximum value. For example, if in the dial plan you choose to
set 320kbps (5 x B channels) as the maximum bandwidth and the global setting for
maximum bandwidth for outgoing ISDN calls is 256kbps (4 x B channels), the maximum
bandwidth available to the call will never be more than 256kbps.
o Encryption settings:
Use transparent encryption: whe n sel ected, t he ISD N G ate wa y will sim ulate
point-to-point encryption. That is, it will set the encryption state
(enabled/disabled) used on the received call as that to be used on the outgoing
call. That is, the ISDN Gateway will attempt to match the encryption state for the
outgoing call to that of the incoming call. This means that if the encryption state
changes on the incoming call, the ISDN Gateway will attempt to change the
encryption state on the outgoing call. This can be helpful if a call starts as an
encrypted call both sides of the ISDN Gateway and then the incoming call stops
being encrypted for some reason; the outgoing part of the call will also drop the
encryption and both callers will know that the call is no longer encrypted.
Select Required in the appropriate checkbox(es) if you always want the IP and/or
ISDN part of a call to be encrypted or Optional if encryption is only to be used to
endpoints that support it. Note that:
Encryption must also be enabled globally in the Settings > Encryption
page.
If Required is selected and the endpoint does not support encryption, the
call will be disconnected. If the endpoint does support encryption, no
media is passed until encryption can be ensur ed . However if you selec t
Optional and the endpoint supports encryption, then a call to may start
even before encryption can be guaranteed but will use encryption as
soon as possible
These settings for IP and ISDN encryption are not available if you have
selected to use transparent encryption for this dial plan rule
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 32 of 135
Page 33

Adding and updating dial plan rules in leased line mode
7. For Codecs allowed select an option from the drop-down list: <use default choices>, Custom
codec choices or Safe codec choices. The last two options are provided for older endpoints that
you cannot connect to when some codecs are enabled (even if the endpoint supports those
codecs). We recommend that you only use these options when you experience a problem.
o When you select Custom codec choices, the screen refreshes and you can select the
audio, video and H.239 video codecs that are allowed with this dial plan
o Safe codec choices only allows G.711 and H.261
8. Click Add rule.
Updating dial plan rules
To update an existing dial plan rule:
1. Go to Dial plan and find the rule you want to modify.
2. Click on the number or name of the rule to view its details.
3. Modify the rule details using the information listed above in
4. Click Update rule.
You may wish to create a new rule very similar to an existing rule. To do this, find the existing rule and
click on its name or number to view its details. Press Copy rule to create a new rule, initialized with the
existing parameters, then proceed as normal, pressing Add rule when you have finished.
Adding dial plan rules to help you.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 33 of 135
Page 34

Example dial plan rules
#
0
Called number
Call this
Video with
128Kbps
This rule allocates 128kbps (that is,
Example dial plan rules
Use the examples on this page to help you configure your own dial plan rules:
Allocating bandwidth using rules for IP to ISDN calls
•
•
Allocating bandwidth using rules for ISDN to IP calls
•
Forwarding ISDN calls to an operator or a conference
•
Specifying voice-only IP to ISDN telephone calls
•
Setting up dial plans rules when using T CS-4
Note these examples do not apply if the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway is in leased line mode. Refer
to the following example dial plan rules for leased line mode:
• Dial plan examples in leased line mode
Allocating bandwidth using rules for IP to ISDN c al ls
Using rules, it is possible to limit the bandwidth available for calls to particular numbers, or to allocate
more bandwidth to priority calls. For example, you may want to allocate maximum bandwidth to calls to
the chief executive of your company. In this case, set a Condition that matches calls to that specific
number, set the Action to call with the original called number, and set the Maximum call bandwidth to use
768kbps.
As cost is an issue with calls to the ISDN network, you may want to provide users with a list of prefixes
that they can use to control the bandwidth for the calls they make. In this way, rules enable you to allow
users to select their own appropriate bandwidth for a call. The table below shows some rules that you
could configure to set up different prefixes to represent the number of channels that will be available to
the call. It also shows how the IP to ISDN dial plan will remove those prefixes and dial the required
number.
Condition Action Call type Bandwidth Description
matches
"552 (D*)"
number "$1"
BONDING
two channels) to any call with prefix
552. The specified action means that
the dial plan removes the prefix and
dials the following group of
characters in the condition. For
example, an incoming call to
"55264321" will cause an outgoing
call allocated with two channels to be
placed to "64321".
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 34 of 135
Page 35

Example dial plan rules
1
Called number
Call this
Video with
192Kbps
This rule allocates 192kbps (that is,
2
Called number
Call this
Video with
512Kbps
This rule allocates 512kbps (that is,
#
matches
"553 (DDDD)"
matches
"558 (DDDD)"
number "$1"
number "$1"
BONDING
BONDING
three channels) to any call with prefix
553. The specified action means that
the dial plan removes the prefix and
dials the group of four characters
(containing 0 through 9 and # and *)
that match the four characters
represented by "(DDDD)" in the
condition. For example, an incoming
call to "5539876" will cause an
outgoing call allocated with three
channels to be placed to "9876".
eight channels) to any call with prefix
558. The specified action means that
the dial plan removes the prefix and
dials the group of four characters
(containing 0 through 9 and # and *)
that match the four characters
represented by "(DDDD)" in the
condition. For example, an incoming
call to "5585678" will cause an
outgoing call allocated with eight
channels to be placed to "5678".
In the above example, in the absence of any further rules, any calls that do not match the listed conditions
will be rejected because that is the default behavior of the dial plan.
Allocating bandwidth usi ng rules for ISDN to IP calls
Using rules, it is possible to limit the bandwidth available for incoming ISDN calls. This is useful where
you want to limit the network resources available to individual calls. In this way, you can prevent any one
call using the resources to the extent that other incoming calls are prevented.
Condition Action Call type Bandwidth Description
0 Match any
called number
Forwarding ISDN call s to an oper a tor or a conf erence
The dial plan below forwards any calls from the ISDN network ending in 0000 to an operator and forwards
any other dialed number of four digits or more to the MCU to join a conference where the conference
identifier is the last four numbers of the original dialed number.
Call with the
original
called
number
Video with
BONDING
384Kbps This rule forwards all calls to the
dialed number with a bandwidth of
384Kbps
The dial plan shown below is an ISDN to IP dial plan:
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 35 of 135
Page 36

#
0
Called number
Call this
Video with
384Kbps
This rule catches any number ending
1
Called number
Call this
Video with
384Kbps
This rule catches any set of four
#
Condition Action Call type Bandwidth Description
Example dial plan rules
matches
"D+ 0000"
matches
"D+(DDDD)"
number
"10.2.1.10"
number
"10.2.1.20 !
$1"
BONDING
BONDING
in 0000 and forwards it to, for
example an operator, at 10.2.1.10
characters or more and tries to join a
conference on the MCU at 10.2.1.20
with the numeric identifier that
matches the last four digits. Note
that although D matches ~ and * as
well as 0 through 9, the numeric
identifier of a conference can only be
a number.
Specifying voice-only IP to ISDN telephone calls
Use the following dial plan to specify how IP telephone calls (that is voice-only calls) will be forwarded to
the ISDN network.
IP endpoints sometimes do not allow users to specify the type of call being made. The following dial plan
shows that users can be told the prefix to dial, should their call be a telephone call rather than a video and
voice call.
This dial plan also includes an example of how you can use the dial plan to specify DTMF tones to be
dialed after the call has been answered.
The dial plan shown below is an IP to ISDN dial plan:
Condition Action Call type Bandwidth Description
0 Called
number
matches
"550 (D+)"
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 36 of 135
Call this number
"$1"
Telephone None This rule specifies a voice-only
call to any call with prefix 550.
The specified action means
that the dial plan removes the
prefix and dials the group of
numbers that match the
characters represented by
"(D+)" in the condition. For
example, an incoming call to
"5504321" will cause an
outgoing voice-only call to be
placed to "4321".
Page 37

Example dial plan rules
1
Called
Call this number
Telephone
None
This rule allows a caller to
2
Match any
Call with original
Video with
128Kbps
This rule catches any other
number
matches
"99555"
called
number
"01753
548333!555P,,888P
"
called number
BONDING
connect to a PIN protected
audio conference on an audio
bridge.
In this example, the audio
bridge will answer the call.
After a two second pause the
ISDN Gateway sends the
DTMF tones for the conference
ID (555); these are the digits
after the exclamation mark (!)
which indicates where the
number to dial ends and the
DTMF tones begin. There is a
four second pause
(represented by two commas)
and then the ISDN Gateway
sends the PIN (888). The audio
bridge requires a caller to press
pound/hash after the ID and
the PIN; these are represented
with ‘P’.
called number and will place it
as a video-conferencing call
(that is video and voice) using
the lowest bandwidth.
Setting up dial plan rules whe n usi ng TCS-4
TCS-4 is a protocol that only applies to H.320 video calls and is a method of signaling an extension
number after an H.320 call has been established. By using a TCS-4 extension to pass the extra digits to
the ISDN Gateway, customers can dial from a predefined endpoint phone list, rather than entering the
extension using DTMF in the auto attendant.
ISDN to IP calls
There is a new Action in the ISDN to IP dial plan: Enter the auto attendant + TCS-4. When used, the call
enters the auto attendant and sends a TCS-4 request; when the auto attendant receives the reply, it dials
out the TCS-4 extension. Usually the TCS-4 reply is fast enough that the ISDN Gateway auto-attendant is
not displayed; however, you may see it briefly with the TCS-4 extension shown.
To send a TCS-4 extension:
from an ISDN-capable Cisco TelePresence endpoint, dial the ISDN number followed by a * and
then enter the TCS-4 extension. For example, if the ISDN Gateway TCS-4 dial plan incoming
number match is 1234 and the required TCS-4 extension is 5678, dial 1234*5678 from your
endpoint. The ISDN Gateway will then connect to the TCS-4 dial plan and dial out 5678 from the
ISDN Gateway auto attendant without you having to enter the extension via DTMF
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 37 of 135
Page 38

Example dial plan rules
from a Polycom endpoint, replace the * with ##
from LifeSize and Sony endpoints, replace the * with #. For other endpoints, please refer to the
user manual.
It is possible to send an alphanumeric H.323 ID as a TCS-4 extension from most endpoints. For example,
you can dial 1234*MCU, where MCU is the registered H.323 ID with the gatekeeper (usually case
sensitive).
It is also possible to send an IP address as a TCS-4 extension from ISDN-capable Cisco TelePresence
endpoints.
IP > ISDN > ISDN > IP calls
When using TCS-4 in an "ISDN bridge between IP islands" (in which two IP endpoints/MCUs
communicate traversing an ISDN link), two ISDN Gateways are required. The first ISDN Gateway (for the
IP to ISDN conversion) cannot do TCS-4 because TCS-4 functionality only works in ISDN to IP direction.
However, the second ISDN Gateway will be able to process a TCS-4 request and therefore needs to be
set up with the TCS-4 dial plan as discussed above.
The first ISDN Gateway needs to forward a number to the second ISDN Gateway in the same format as a
TCS-4 request received from any other ISDN endpoint. That is why, even though the first ISDN Gateway
does not perform TCS-4 extension dialing, it should be set up so that it can call out with a number that is
same as sending a TCS-4 request to the second ISDN Gateway. This new functionality has been
implemented for the IP to ISDN dial plan on the ISDN Gateway, as described below.
When you dial from the calling IP endpoint, you need to send both the dial plan call-in match parameters
of the two ISDN Gateways as well as the required TCS-4 extension. Assume that:
the first ISDN Gateway dial plan call-in number match is 123
the second ISDN Ga teway TCS -4 dial plan call-in number match is 456
the TCS-4 extension required to dial the called IP endpoint is 789
Dial the full number 123456#789 from the calling IP endpoint separating the 789 portion with the
appropriate * or # mark to indicate that this is the TCS-4 extension. The first ISDN Gateway strips the 123
portion from this number and sends the rest of the number 456789 to the second ISDN Gateway in such
a format that the second ISDN Gateway understands that the 456 portion is the dial plan match number
and the 789 is the TCS-4 extension. The second ISDN Gateway then dials the TCS-4 extension using its
TCS-4 dial plan.
To set up the first ISDN Gateway to send a number string that matches a TCS-4 request, a new
delimiter ! has been introduced. This delimiter is used to split the Call this number field, where
the part before the ! is the ISDN number to call, and the rest (after !) is the extension address to
respond to a TCS-4 request. Therefore, in the Call this number field, enter <ISDN number of
second GW>!<the TCS-4 extension used by the second ISDN Gateway>
To dial 123456#789 from an IP endpoint, set up the first ISDN Gateway with an IP to ISDN dial plan:
o Called number match : 123(D*)P(D*)
o Action: Call out number: $1 ! $2
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 38 of 135
Page 39

Example dial plan rules
The first (D*) group matches the numbers before the Pound (hash) sign and the second (D*) group
matches the number after the Pound sign. Therefore in the Call out number field, $1 will replace the first
(D*) group, $2 will replace the second (D*) group after the # sign (the TCS-4 extension) and the ! sign will
indicate to the second ISDN Gateway that the first part is an ISDN number and the second portion is the
TCS-4 extension. In this example, the first ISDN Gateway will call out 456!789 to the second ISDN
Gateway which will receive it as a TCS-4 request (see below)
Set up the second ISDN Gateway with an ISDN to IP dial plan:
o Called number match: 456
o Action: Enter the auto attendant + TCS-4
The second ISDN Gateway treats 456!789 as a TCS-4 request and any digits after “!” as the TCS-4
extension. It matches 456 to this dial plan and calls the TCS-4 extension 789 to connect to the IP
endpoint
For the ISDN to IP TCS-4 dialing rule, you have to use *, # or ## to separate the ISDN number and the
TCS-4 extension depending on the ISDN endpoint manufacturer. However, in this case, when you are
dialing from the IP endpoint to the first ISDN Gateway, you can either use * or # irrespective of the
endpoint you’re using. For example, when you dial 123456#789 from the IP endpoint, you could also dial
123456*789. In the latter case, simply change the Called number match of the first ISDN Gateway from
123(D*)P(D*) to 123(D*)S(D*) (S denotes *).
Notes:
It is not possible to send alphanumeric characters as a TCS-4 extension from the IP side. That is,
you cannot dial 123456*MCU or 123456#MCU from an IP endpoint because the extension
number (after the * or #) is parsed by the dial plan and there is no way to match letters in the
Called number matches field. Therefore the $1 and $2 groups on the dial plan of the first ISDN
Gateway would only match numbers and not characters.
It is not possible to send an IP address as a TCS-4 extension from the IP endpoint to the first
ISDN Gateway.
Dial plan examples in leased line mode
ISDN to IP dial plan (leased line mode)
The dial plan rule below forwards any some calls from the ISDN network to an auto attendant on the
Cisco TelePresence MCU. It allows for some calls to arrive with a TCS-4 extension. It has a catch all rule
that forwards other calls to an operator.
The dial plan shown below is the ISDN to IP dial plan:
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 39 of 135
Page 40

Example dial plan rules
Maximum call
bandwidth
0
Match calls
Call this number
<use default
This rule matches any call arriving
1
Match calls
Enter the auto
<use default
This rule matches any call arriving
2
Match calls
Call this number
<use default
This rule matches any call arriving
#
0
Called number
Call port $1
$3
This rule matches any call to a four-
1
Match any
Call port "2"
This rule matches any call that does
#
Condition Action
Description
incoming on port
"1" leased line
group "2"
incoming on port
"2" leased line
group "1"
incoming on port
"Any" leased
line group "Any"
"10.2.1.12 ! 555"
attendant + TCS4
"10.2.1.10"
value>
value>
value>
IP to ISDN dial plan (leased line mode)
The dial plan shown below is the IP to ISDN dial plan:
from the ISDN network using leased
line group 2 on ISDN port 1 and
forwards it to the auto attendant on
the MCU at 10.2.1.12. (The MCU's
auto attendant is configured with
Numeric ID 555.)
from the ISDN network using leased
line group 1 on ISDN port 2 and
forwards it to the auto attendant
which dials out using the TCS-4
extension.
from the ISDN network (that has not
matched either of the above two
rules) and forwards it to, for example
an operator, at 10.2.1.10
Condition Action TCS-4 extension Description
matches
"98(D)(D)(D+)"
incoming call
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 40 of 135
leased line group
$2
leased line
group"3"
digit number beginning 98. The
dialed digits also provide the ISDN
port number, the leased line group,
and the TCS-4 extension. For
example, if the called number is
9812777, the call will be made on
ISDN port 1 using leased line group
2, with TCS-4 extension 777.
not match the first rule in the dial
plan. In this example, calls to port 2
leased line group 3 will be answered
by an operator.
Page 41

Dial plan syntax
Syntax
Example
Numbers 0
To match a specific number, enter that
Example: to match calls to "001234",
P
To match a # (known as a pound or hash),
Example: to match calls to "#1234", type
To match once or zero times, use ?
include any of the incoming called digits in the
with "678", then followed by a number of
Dial plan syntax
This page describes the syntax that you can use when adding dial plans.
Note: All IPv6 address fields in the ISDN Gateway require the IPv6 address to be enclosed in square
brackets [ ].
Syntax for conditions (Called number matches)
When you configure the Condition for a dial plan rule, you may want to specify a pattern for the called
number rather than specifying any of: match any called number, no called number or the exact called
number.
The table below describes the syntax you can use to express a pattern for the Called number matc hes
field in the condition of a rule:
Description
to 9
S To match an * (known as an asterisk or star),
D To match any digit, # (known as a pound or
?
+
number.
enter an S.
enter a P.
hash), and/or * (known as an asterisk or star)
use the wildcard character D
To match once or more, use + Example: "5+" means "match at least
type 001234. The condition will match
that and only that number.
Example: to match calls to "**1234",
type SS1234. The condition will match
that and only that number.
P1234. The condition will match that and
only that number.
Example: to match any number that
starts with "623" followed by exact l y two
more digits, type 623DD. This condition
will match "62300", "62323", "62355",
"62399" "623*#", etc. but not "623" or
"623233".
Example: "6?" means match one 6 or no
6s, and is useful when used with the
wildcard "D" where you do not know how
long a number will be. The expression:
"67800D?" will match "67800" and
"678004" but not "67800666".
one 5, but possibly more".
*
() Parentheses indicate substitution groups. To
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 41 of 135
To match zero or more times, use *. This is
useful when used with the wildcard: "D*"
means "match any digit, any number of times".
Example: to match any number that
starts with "01", has any amount of digits
in the middle, and ends with "5", type 01
D* 5.
Example: to match any number starting
Page 42

Dial plan syntax
Syntax
Letters and
To call a specific number (or for ISDN to
Example: to specify that when this rule is
To call a specific extension, separate the
Example: to call the Cisco TelePresence
To call a specific extension, separate the
Example: to call the MCU with IP
$
To include any of the digits from the
Example: for all calls matching the
Note that if the substitution creates an
outgoing called number, enclose them in
parentheses. Note that if you wish to include
the complete number, you do not need to
enclose the whole expression in parentheses.
other digits, and you want the final digits
to form part of the called number, type
the expression: 678 (D*). This will match
"6780000", "678123", "6789999" etc. but
not "775000".
Syntax for actions (Call this num ber)
When you configure the Action for a dial plan rule, you may want to specify a pattern for the number to
call, rather than specifying any of: call original called number, reject the call, or the exact number to call.
The table below describes the syntax you can use to express a pattern for the Call this number field in the
action of a rule:
Field description Example
numbers for
address
IP calls, you can also specify an IP
address, hostname, or H.323 URI), type
that number (or IP address, hostname, or
H.323 URI).
IPv6 addresses must be enclosed in
brackets [ ].
invoked, the MCU with hostname my_mcu
is called, type my_mcu.
Example: Suppose the domain “
cisco.com” has a H.323 service (SRV)
record set up. To call a H.323 video
endpoint residing in that domain, e.g. with
URI example.person@cisco.com, set an
action to call
example.person@cisco.com. For
information about domain (DNS) SRV
records, see RFC 2782.
:
number/address from the extension by
typing a colon (
!
number/address from the extension by
typing an exclamation mark (!).
incoming called number in the outgoing
number, specify a substitution, by typing
the dollar sign ($), followed by a index.
Valid indices are:
A: substitute the entire incoming called
number.
1 to 9 : substitute the digits enclosed in
the nth set of parentheses of the
condition.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 42 of 135
:).
MCU with IP "10.2.1.33", and try to join a
conference with numeric identifier "00000",
type 10.2.1.33 : 00000.
"10.2.1.33", and try to join a conference
with numeric identifier "00000", type
10.2.1.33 ! 00000.
condition of "55 (DDDD)", set an action to
call the MCU with name "my_mcu" and join
the call to the confer enc e w ith ide ntif ier that
matches "(DDDD)". For this example, type
the action of my_mcu ! 00 $1. In this case,
an incoming call to "551234" will attempt to
join conference with numeric identifier
"001234" on the MCU with the name
"my_mcu".
Page 43

Dial plan syntax
This delimiter is only for use in an "ISDN
extension..
This feature is for IP to ISDN telephone
the DTMF extension after it.
Pauses are useful where there are more
empty number, the call will be rejected; in
the above example, an incoming call to 55
would result in an empty substitution.
bridge between IP islands" when you want
to use TCS-4 extensions. In this case use
!
the ! before TCS-4 extension in the dial
plan for the first ISDN Gateway so that it
is passed to the second ISDN Gateway in
A detailed example and further explanation
of TCS-4 is provided in
Example dial plan
rules.
a format recognized as a TCS-4
calls. It allows you to configure the dial plan
to start sending DTMF tones after a
telephone call has connected. This is
useful if there is a call through the ISDN
Gateway to a device which is perhaps
behind another gatewa y which onl y
This is a delimiter that can be used for
!
telephone calls where there is a number
to dial which must be followed by DTMF
tones.
supports DTMF to decide how to route the
calls. The caller is not required to
additionally enter the DTMF codes
manually on the telephone keypad but
instead can have the call re-routed
automatically using the dial plan of the
ISDN GW.
When sending DTMF tones in a telephone
call, a comma indicates a two second
,
pause. Two commas (,,) indicate a four
second pause. You can insert as many
two second pauses as you want.
To do this, when completing the Call this
number field, first type the number to call
then type an exclamation mark (!) and type
than one set of DTMF tones to enter. For
example, if the call is answered by an
automated operator system which requires
that the caller chooses an option from a
menu and is then transferred to an audio
conferencing system (for example) and
then is asked to enter the conference ID.
Refer to the section "Specifying voice-only
IP to ISDN telephone calls" in
Example dial
plan rules.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 43 of 135
Page 44
Displaying the built-in gatekeeper registration list
Field
Status
Enables or disables the built-in gatekeeper.
To use the built-in gatekeeper, you
Neighbor
Enter the IP address(es), or hostname(s) (or
These are the gatekeepers to which
Displaying the built-in gatekeeper registrati on
list
The Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway contains a built-in gatekeeper with which dev ic es can re gister
multiple IDs. IDs can be numbers, H.323 IDs (e.g. Fredsendpoint) or prefixes.
Up to 25 devices can be registered without a feature key. Feature keys can be purchased to increase this
number.
Note: The ISDN Gateway can register with its own built-in gatekeeper. The ISDN Gateway then counts
as one registered device. See Configuring H.323 gatekeeper settings.
Configuring the built-in gatekeeper
To start the gatekeeper:
1. Go to Network > Services and select H.323 gatekeeper to open a port for the gatekeeper. (On
the ISDN Gateway, ports are not open by default for security reasons.)
2. Go to Gatekeeper, select Enabled in the Status field and click Apply changes. If you attempt to
enable the built-in gatekeeper without opening the port, an error message is displayed.
Configuring neighboring gatekeepers
You can optionally configure the built-in gatekeeper with up to two neighboring gatekeepers. This means
that if the built-in gatekeeper receives a request (known as an Admission Request or ARQ) to resolve an
ID to an IP address and that ID is not currently registered with it then it will for ward that reques t to its
neighbor gatekeeper(s), as a Location Request (LRQ). The built-in gat ekeeper will then use the
information received from the neighbor(s) to reply to the original request.
You can also configure the behavior of the built-in gatekeeper on receipt of LRQs from another
gatekeeper. It can:
• send LRQs regarding unknown IDs to its neighbor(s)
• reply to LRQs from other gatekeepers
• accept LCFs (Locations Confirms) from non-neighboring gatekeepers
Refer to this table for assistance when configuring the built-in gatekeeper:
Field description Usage tips
must enable it here.
gatekeeper
1 and 2
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 44 of 135
<host>:<port number> to specify a port other
than the default of 1719 on the neighboring
gatekeeper), of the neighboring gatekeeper(s).
the built-in gatekeeper will send an
LRQ if it has received an ARQ to
resolve an ID which it does not
Page 45

Displaying the built-in gatekeeper registration list
Accept
Configures the built-in gatekeeper to reply to
These requests can come from any
Forward
Configures the built-in gatekeeper to send (or not
Unless you have selected to Accept
Accept
This setting enables the built-in gatekeeper to
This setting is for use in
currently have registered. The builtin gatekeeper will then use the
information received from the
neighbor(s) to reply to the original
request.
LRQs
LRQs for
unknown
IDs
LRQs from other gatekeepers.
to send) LRQs regarding unknown IDs to its
neighbor(s). Choose from the options:
Disabled: The ISDN Gateway will on ly
respond to LRQs about IDs registered
with itself. It will not forward LRQs about
IDs that are not registered with itself to
neighboring gatekeepers.
Enabled, using local return address: The
ISDN Gateway will put, in the LRQ, its
own address as the return address for
the LCF.
Enabled, using received return address:
The ISDN Gateway will put, in the LRQ,
the address of the gatekeeper that
originated the request as the return
address for the LCF. Use this option only
if you are configuring the ISDN Gateway
to operate in an environment with a
multiple-level gatekeeper hierarchy. For
example, the 'received address' is
required by the national gatekeepers
connected to the Global Dialing Scheme
(GDS).
gatekeeper which has the ISDN
Gateway's built-in gatek eep er
configured as one of its neighbors.
LRQs, you cannot configure the
ISDN Gateway to forward any
LRQs.
Enabling using received return
address can be a significant security
risk. Only use this setting with
proper cause.
LCFs from
non-
accept LCF message responses from any IP
address.
neighbors
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 45 of 135
environments with a multiple-level
gatekeeper hierarchy. For example,
this feature is required by the
national gatekeepers connected to
the Global Dialing Scheme (GDS).
Enabling this setting can be a
significant security risk. Only use
this setting with proper cause.
Page 46

Displaying the built-in gatekeeper registration list
Field
ID
The ID which the registrant has registered
IDs can be numbers, H.323 IDs or
Type
The type of registration.
One of: E.164 (digits), H.323 ID or Prefix.
Index
This registrations index within the tota l
In the format X / Y where Y is the number
Registrant
The IP address of the device that this
If the remote device has indicated via the
Gatekeeper status
The number of registered devices is shown in the format X / Y where Y is the number of registered
devices that your built-in gatekeeper is licensed for. Equally, the total number of registered IDs is shown
as Z / 1000, where 1000 is the maximum number of registrations allowed over all registered devices.
Below these summary figures is a table showing individual registrations. Registrations can be viewed by
registered ID (the "ID view") or by device (the "Registration view"), giving complete and easily searchable
lists. Switch between the views by clicking on the appropriate button.
The Registration view shows the summary per device (also known as the registrant), while the ID view
shows individual registrations. This means that registrations from the same device are not necessarily
listed together in the ID view but the view can be sorted by Registrant or Index to help you identify IDs
belonging to the same registrant.
ID view
Field description Usage tips
with the gatekeeper.
number of registrations that this registrant
has made with the gatekeeper.
registration was made from.
prefixes.
of registrations that this registrant has
made with the built-in gatekeeper, and X
is this particular registration's position
within the total. Therefore, if a device
registered 3 IDs with the gatekeeper and
this was the second registration to be
made, the Index would be 2 / 3.
RAI (Resource Availability Indication)
mechanism that it is close to its resource
limit, the Registrant will be labeled as
"almost out of resources".
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 46 of 135
Page 47

Displaying the built-in gatekeeper registration list
Field
Registrant
The IP address of the device.
If the remote device has indicated via the RAI
H.323 ID
The registered H.323 ID of the
To help identify registering devices, if the
Registered
The number of registrations that this
Click (view) to display individual registrations for
Registration
The time today or date and time of
Registration view
This view shows a one-line summary for each device registered with the built-in gatekeeper.
To deregister one or more devices (and all registrations for these devices), select the check boxes for the
appropriate entries and then click Deregister selected.
Field description Usage tips
(Resource Availability Indication) mechanism
that it is close to its resource limit, the
Registrant will be labeled as "almost out of
resources".
IDs
time
device.
device has made with the built-in
gatekeeper.
the last registration.
registrant has registered a H.323 ID (which will
typically be its device name) that H.323 ID is
shown here. If the device has registered
multiple H.323 IDs, only the first is displayed.
the selected device. (The format is the same as
the ID view, but the table only includes entries
for one device.)
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 47 of 135
Page 48

Displaying the user list
Field
User ID
The user name that the user needs to access the web interface of the ISDN Gateway.
Name
Privilege
Access privileges associated with this user.
Displaying the user list
The User list gives you a quick overview of all configured users on the Cisco TelePresence ISDN
Gateway and provides a summary of some of their settings. To view the User list page, go to Users.
Refer to the table below for assistance.
Field description
Although you can enter text in whichever character set you require, note that some
browsers and FTP clients do not support Unicode characters.
Click on a name for further details (see Updating a user).
The full name of the user.
An administrator can change any ISDN Gateway configuration, and view all status
information. A user with the list only privilege can only view basic details about active
calls.
Deleting users
To delete a user, select the user you want to delete and click Delete selected users. You can not delet e
the admin and guest users.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 48 of 135
Page 49

Adding and updating users
Field
User ID
Identifies the log-in name that the
Although you can enter text in whichever
unknown
Password
Adding and updating users
You can add users to and update users on the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway. Although most
information is identical for both tasks, some fields differ.
Adding a user
To add a user:
1. Go to the Users page.
2. Click Add user.
3. Complete the fields referring to the table below to determine the most appropriate settings for the
user.
4. After entering the settings, click Add user.
Updating a user
To update an existing user:
1. Go to Users.
2. Click a user name.
3. Edit the fields as required referring to the table below to determine the most appropriate settings
for the user.
4. After entering the settings, click Update user settings.
Field description Usage tips
user will use to access the ISDN
Gateway web browser.
character set you require, note that some
browsers and FTP clients do not support
Unicode characters.
The following user ids are reserved and cannot
be added:
admin
guest
invalid
system
The required password, if any. Although you can enter text in whichever
character set you require, note that some
browsers and FTP clients do not support
Unicode characters.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 49 of 135
Page 50

Adding and updating users
Re-enter
Verifies the required password.
Disable user
Select to disable this account.
This can be useful if you want to keep an
it. To re-enable a disabled account, clear this
In advanced security mode (configured on the
Settings > Security page), passwords must
have:
at least fifteen characters
at least two uppercase alphabetic
characters
at least two lowercase alphabetic
characters
at least two numeric characters
at least two non-alphanumeric (special)
characters
not more than two consecutive
repeating characters. That is, two
repeating characters are allowed, three
are not
In advanced security mode, a password must
be different from the previous ten used with that
account. Also, a password will expire if it is not
changed within 60 days.
If the ISDN Gateway is not using advanced
security mode, any password can be used.
Note that passwords are stored in the
configuration.xml file as plain text unless the
ISDN Gateway is configured (or has ever been
configured) to use advanced security mode. For
more information, refer to
Configuring security
settings.
Note that this field is only active when adding a
new user. If you are updating an existing user
and want to change that user's password, click
Change password control instead.
password
account
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 50 of 135
account's details, but do not want anyone to be
able to use it at the moment.
You cannot disable the system-created admin
account.
The system-created guest account is disabled
by default. If you enable it, the ISDN Gateway
will create a security warning.
In advanced account security mode, a nonadmin account will expire after 30 days of
inactivity; that is, the ISDN Gateway will disable
Page 51
Adding and updating users
Lock password
Prevents user from changing
This is useful where you want multiple users to
Force user to
Select this option to force a user
This option is enabled by default for a newly
Privilege level
The access privileges to be
An administrator can change any ISDN
option.
For more information about advanced security
mode, refer to
Configuring security settings.
change
password on
next login
password.
to change their pass word. N ext
time this user attempts to log in to
the ISDN Gateway, a change
password prompt will appear .
granted to this user.
be able to use the same user ID. The systemcreated guest account has Lock password
enabled by default.
created account. It is a good idea for new users
to set their own secure passwords.
This option is not available for accounts where
Lock password is selected.
When the user changes his password, the ISDN
Gateway clears this check box automatically.
Gateway configuration, and view all status
information; a user with the list only privilege
can only view basic details about active calls.
The system-created gues t ac count is fix ed with
privilege level of list only.
All users can view the online help
documentation.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 51 of 135
Page 52

Updating your user profile
Field
Current
Type your current
Password
Type your new password.
In advanced security mode, passwords must have:
Re-enter
Verify your new password.
Updating your user profile
You can make some changes to your user profile. To do this, go to User profile. Refer to the table below
for tips.
Field description More information
password
password
password.
at least fifteen characters
at least two uppercase alphabetic characters
at least two lowercase alphabetic characters
at least two numeric characters
at least two non-alphanumeric (special)
characters
not more than two consecutive repeating
characters. That is, two repeating characters are
allowed, three are not
In advanced security mode, a new password must be
different to the previous 10 passwords that have been
used with an account.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 52 of 135
Page 53

Changing your password
Changing your password
In advanced security mode, passwords must have:
at least fifteen characters
at least two uppercase alphabetic characters
at least two lowercase alphabetic characters
at least two numeric characters
at least two non-alphanumeric (special) characters
not more than two consecutive repeating characters. That is, two repeating characters are
allowed, three are not
In advanced account security mode, a new password must be different to the previous 10 passwords that
have been used with an account.
In advanced account security mode, if a user logs in with a correct but expired password the Cisco
TelePresence ISDN Gateway asks that user to change the password. If the user chooses not to change
it, that user is allowed two more login attempts to change the password before the account gets disabled.
In advanced account security mode, users other than administrator users are not allowed to change their
password more than once in a 24 hour period.
If the ISDN Gateway is not in advanced account security mode, there are no criteria for password
selection.
If the ISDN Gateway is in advanced account security mode, the above criteria for passwords are
displayed on the Change password page.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 53 of 135
Page 54

Configuring network settings
Field
IPv4 configuration
IP
Specifies whether the port should be
Manual configuration
IP address
The dot-separated IPv4 address for this
You only need to specify this option if you
Subnet mask
address you wish to use, for example
Configuring network settings
To configure the network settings on the Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway and check the network
status, go to Network > Port A or Network > Port B.
The ISDN Gateway has two Ethernet interfaces, Port A and Port B. The configuration pages for the two
interfaces look and behave similarly, and so are described together. Differences will be noted as
appropriate.
Port A and Port B can be configured to be allocated their IP address by DHCP (IPv4) or SLAAC/DHCPv6
(IPv6). Connect Port A to your local network and connect Port B to a second subnet or the internet
depending on your application of the ISDN Gateway.
In this section:
IP configuration settings
IP status
Ethernet configuration
Ethernet status
IP configuration setti ngs
These settings determine the IP configuration for the appropriate Ethernet port of the ISDN Gateway.
When you have finished, click Update IP configuration and then reboot the ISDN Gateway.
Field description Usage tips
configuration
configured manually or automatically. If
set to Automatic via DHCP the ISDN
Gateway obtains its own IP address for
this port automatically via DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). If
set to Manual the ISDN Gateway will use
the values that you specify in the Manual
configuration fields below.
port, for example 192.168.4.45.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 54 of 135
The subnet mask required for the IP
have chosen Manual IP configuration, as
described above.
If IP configuration is set to Automatic by
DHCP this setting will be ignored.
Page 55

255.255.255.0
Default
The IP address of the default gateway on
IPv6 configuration
IP
Specifies whether the port should be
Manual configuration
IPv6 address
The hexadecimal colon-separated global
Only specify this option if IP configuration is
Prefix length
The decimal prefix length value for the
Default
Optionally, specifies the IPv6 address of
The address can be global or link-local.
Configuring network settings
gateway
configuration
this subnet, for example 192.168.4.1
configured manually or automatically. If
set to Automatic via SLAAC/DHCPv6 the
ISDN Gateway obtains an IP address for
the port automatically. The protocol used
will be SLAAC, Stateful DHCPv6, or
Stateless DHCPv6 as indicated b y the
ICMPv6 Router Advertisement (RA)
messages (for details see
Automatic
IPv6 address preferences below). If set
to Manual the ISDN Gateway will use the
values that you specify in the Manual
configuration fields below.
IPv6 address for this port. For example
[2001:DB8::1]
set to Manual.
If IP configuration is set to Automatic via
SLAAC/DHCPv6 this setting is ignored.
global IPv6 address for this port.
gateway
the default gateway on this subnet.
IP status
Use the IP Status fields to verify the current IP settings for the appropriate Ethernet port of the ISDN
Gateway, which were obtained using DHCP or configured manually (see
including:
DHCP
IP address
Subnet mask (IPv4)
Default gateway
Link-local address (IPv6)
When you enter an IPv6 address anywhere
in the user interface, the address must be
enclosed in square brackets [ ].
IP configuration settings)
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 55 of 135
Page 56

Configuring network settings
Ethernet
Specify whether you want this Ethernet port to
It is important that your Ethernet
Speed
Identifies the connection speed: 10 Mbit/s or 100
The connection speed must match
settings, as described above.
Duplex
Identifies the connection duplex mode:
The duplex setting must match that
Link status
Indicates whether this Ethernet port is connected
to or disconnected from the network.
Speed
The speed (10/100/10 00 M bit/s ) of the network
This value is negotiated with the
configuration selected above.
Duplex
The duplex mode (full duplex or half duplex) of
This value is negotiated with the
connected or based on your Manual
Ethernet configurati on
These settings determine the Ethernet settings for the appropriate port of the ISDN Gateway. Refer to the
table for assistance with these settings. When you have finished, click Update Ethernet configuration.
Field Field description Usage tips
settings
Manual configuration
automatically negotiate its Ether net set tings with
the device it is connected to, or if it should use
the values that you specify in the Manual
configuration fields below.
Mbit/s. Use automatic negotiation if a connection
speed of 1000 Mbit/s is required.
Full duplex
Half duplex
Both devices can send data to each
other at the same time
Only one device can send to the other at
a time
settings match those of the device to
which this port is connected. For
example, both devices must be
configured to use automatic
negotiation, or both configured with
fixed and matching speed and
duplex settings (see below).
that of the device to which this port
is connected.
You only need to select this option if
you have chosen manual Ethernet
of the device to which this port is
connected.
You only need to select this option if
you have chosen manual Ethernet
settings, as described above.
Ethernet status
Field Field description Usage tips
connection to the ISDN Gateway on this port.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 56 of 135
the network connection to this port.
device to which this port is
connected or based on your Manual
device to which this port is
Page 57

Configuring network settings
MAC
address
address of this port.
for information only.
Packets
network.
Packets
Displays a count of the total number of packets
When troubleshooting connectivity
receiving packets from the network.
Statistics
The fields display further statistics for this port.
Use these fields for advanced
configuration selected above.
sent
received
The fixed hardware MAC (Media Access Control)
Displays a count of the total number of packets
sent from this port by the ISDN Gateway. This
includes all TCP and UDP traffic.
received by this port of the ISDN Gateway. This
includes all TCP and UDP traffic.
Multicast packets sent
Multicast packets received
Total bytes sent
Total bytes received
Receive queue drops
Collisions
Transmit errors
Receive error s
This value cannot be changed and is
When troubleshooting connectivity
issues, this information can help you
confirm that the ISDN Gateway is
transmitting packets into the
issues, this information can help you
confirm that the ISDN Gateway is
network diagnostics, such as
resolution of problems with Ethernet
link speed and duplex negotiation.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 57 of 135
Page 58

Configuring network settings
*RA flags
Preferred address
a o m
1 1 0
Stateless DHCPv6
0 0 1
Stateful DHCPv6
1 0 1
Stateful DHCPv6
0 1 1
Stateful DHCPv6
1 1 1
Stateful DHCPv6
Automatic IPv6 address preferences
This table details the address assignment preferences that are applied for IPv6 addressing when port
configuration is set to Automatic.
0 0 0
1 0 0
0
1
0
NA
SLAAC
NA
*a: ICMPv6 prefix information, auto flag
*o: ICMPv6, other flag
*m, ICMPv6, managed flag
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 58 of 135
Page 59

DNS settings
DNS configuration
Name server
Select a DNS server preference from the list
The DNS settings of the preferred
Host name
Specifies a name for the ISDN Gateway.
Depending on your network
needing to know its IP address.
Name server
The IP address of the name server.
Secondary name
Identifies an optional second name server.
The secondary DNS server is only
DNS server will not be queried.
Domain name
Specifies an optional suffix to add when
This option can allow you to use
lookup endpoint.cisco.com.
DNS settings
This section describes how to configure and view DNS settings for the Cisco TelePresence ISDN
Gateway.
Configuring DNS settings
To configure DNS settings on the ISDN Gateway, go to Network > DNS. These settings determine the
DNS configuration for the ISDN Gateway.
Click Update DNS configuration after making any changes.
Field Field description Usage tips
(DNS)
preference
server
(DNS suffix)
or select Manual to specify DNS settings
manually.
performing DNS lookups.
DNS information source will only be
applied if the corresponding
interface address configuration
method is used. For example, to
apply IPv6 DNS information for Port
A requires the IPv6 address
configuration for Port A to be set to
Automatic.
configuration, you may be able to
use this host name to communicate
with the ISDN Gateway, without
used if the first is unavailable. If the
first server returns that it does not
know an address, the secondary
non-fully qualified host names when
referring to a device by host name
instead of IP address.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 59 of 135
For example, if the domain name is
set to cisco.com, then a request to
the name server to look up the IP
address of host endpoint will actua lly
Page 60

Viewing DNS status
Use the DNS status fields to verify the current DNS settings for the ISDN Gateway, including:
• Host name
• Name server
• Secondary name server
• Domain name (DNS suffix)
DNS settings
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 60 of 135
Page 61

Configuring IP routes settings
Field
IPv4 gateway
IPv6 gateway
The IPv6 address to which the ISDN
If Ethernet Port B is disabled, you
Configuring IP routes settings
You need to set up one or more routing settings to control how IP traffic flows in and out of the Cisco
TelePresence ISDN Gateway. It is important that these settings are configured correctly, or you may be
unable to make calls or access the web interface.
To configure the route settings, go to Network > Routes.
In this section:
Port preferences
IP routes configuration
Port preferences
If both Ethernet ports are enabled, it is necessary to specify which port is used in certain special
circumstances. Make the appropriate select ions des cr ibed below. Click Apply changes.
preference
preference
Field description Usage tips
The IPv4 address to which the ISDN
Gateway will send packets in the absence
of more specific routing (see
configuration).
Therefore, it only makes sense to have
precisely one default gateway, even though
different default gateways may have been
configured for Ports A and B. Use this
option to decide which port's default
gateway configuration to use as the ISDN
Gateway's default gateway.
Gateway will send packets in the absence
of more specific routing (see
configuration).
As in the IPv4 case, it only makes sense to
have precisely one default gateway, even
though different default gateways may have
been configured for Ports A and B. Use this
option to decide which port's default
gateway configuration to use as the ISDN
Gateway's default gateway.
IP routes
IP routes
If Ethernet Port B is disabled, you
cannot specify that port as the
default gateway preference.
Selecting Port B as default gateway
preference then disabling Port B will
cause the preference to revert to
Port A.
cannot specify that port as the
default gateway preference.
Selecting Port B as default gateway
preference then disabling Port B will
cause the preference to revert to
Port A.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 61 of 135
Page 62
Configuring IP routes settings
Field
IP address /
Use these fields to define the type of IP
To route all IPv4 addresses in the
Route
Use this field to control how packets destined
You may select Port A, Port B or
IP routes configuration
In this section you can control how IP packets should be directed out of the ISDN Gateway. You should
only change this configuration if you have a good understanding of the topology of the network(s) to
which the ISDN Gateway is connected.
Configuration of routes is divided into two sections: addition of new routes, and the display and removal of
existing routes.
Adding a new IP route
To add a new route, enter the details using the table below for reference. Click Add IP route to make the
addition. If the route already exists, or aliases (overlaps) an existing route, you will be prompted to correct
the problem and try again.
Field description Usage tips
mask length
addresses to which this route applies.
For IPv4 addressing, the IP address pattern
must be in the dot-separated IPv4 format, while
the mask length is chosen in the IP address /
mask length field. The mask field specifies
how many bits of the address are fixed; unfixed
bits must be set to zero in the address
specified.
For IPv6 addressing, the IP address pattern
must be in standard CIDR notation
(address/prefix length). IPv6 addresses must
be enclosed in square brackets [ ].
for addresses matching the specified pattern
are routed.
range 192.168.4.128 to
192.168.4.255 for example, specify
the IP address as 192.168.4.128
and the mask length as 25, to
indicate that all but the last seven
bits address are fixed.
Gateway. If Gateway is selected,
specify the IP address of the
gateway to which you want packets
to be directed.
Selecting Port A results in matching
packets being routed to Port A's
default gateway (see
network settings).
Configuring
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 62 of 135
Selecting Port B will cause matching
packets to be routed to Port B's
default gateway.
If Ethernet Port B is disabled, the
option to route packets to Port B will
be disabled.
Page 63

Configuring IP routes settings
Viewing and deleting existing IP routes
Configured routes are listed below the Add IP route controls. For each route, the following details are
shown:
The IP address pattern and mask
Where matching packets will be routed, with the possibilities being:
o Port A - meaning the default gateway configured for Port A
o Port B - meaning the default gateway configured for Port B
o <IP address> - a specific address has been chosen
Whether the route has been configured automatically as a consequence of other settings, or
added by the user as described above.
The default route is configured automatically in correspondence with the Default gateway preference field
Port preferences) and cannot be deleted. Any packets not covered by manually configured routes
(see
will be routed according to this route.
Manually configured routes may be deleted by selecting the appropriate checkbox and clicking Delete
selected.
Routes behavior with disabled ports
If the default gateway preference is set to Port B and that port is disabled, the default route will be
updated automatically to route packets not covered by any manually configured route via Port A.
If a manually configured route specifies Port B and that port is disabled, packets matching that route will
not be automatically routed via Port A, but discarded. You should take care to avoid this situation.
Current IP status
This table shows the current default gateway and name server(s) for Ethernet Ports A and B. No fields
can be changed, and are provided for reference when configuring the other parameters described in the
sections above.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 63 of 135
Page 64

Configuring IP services
Field
TCP service
Web
Enable/disable web access on the
Web access is required to view and change the
Secure web
Enable/disable secure (HTTPS) web
This field is only visible if the ISDN Gateway has
By default, the ISDN Gateway has its own SSL
Configuring IP services
To configure IP services, go to Network > Services.
Use this page to control the type of services that may be accessed via Ethernet Ports A and B. You might
want to configure the services that are available on each port if you want to use one port for management
and the other for calls, for example, by only allowing web access on Port B. The Cisco TelePresence
ISDN Gateway does not allow IP to IP calls (calls between Ethernet ports). Refer to the table below for
more details.
To prevent accidental lock-outs the system does not allow you to disable the service that is currently
being used to administer the ISDN Gateway. For example, if you are configuring the gateway over http
and coming in on Port A, then the option to change the http service for Port A will be unavailable in the
interface.
In addition to controlling the Ethernet interfaces over which a service operates, this page also allows an
administrator to specify the port number on which that service is provided. If the port number for a service
is changed, it is necessary to ensure that the new value chosen does not clash with the port number used
by any of the other services; it is not, however, normally necessary to use anything other than the preconfigured default values.
The settings on this page apply to both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. The page displays the IPv4 and/or
IPv6 values per port, depending on whether IPv4 and/or IPv6 are enabled for the port. When specifying
settings use the appropriate column for the required addressing scheme.
Note that by default SNMP Traps are sent to port UDP port 162 (on the destination network management
station); this is configurable. For more information, refer to
To reset all values back to their factory default settings, click Reset to default and then click Apply
changes.
Field description Usage tips
appropriate port.
Configuring SNMP settings
ISDN Gateway web pages and read onl in e help
files. If you disable web access on Port A you
will need to use the serial console interface to
re-enable it.
If you require advanced security for the ISDN
Gateway, disable web access .
If a port is disabled, this option will be
unavailable.
.
access on the appropriate port.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 64 of 135
the Secure management (HTTPS) feature key
or an Encryption feature key installed. For more
information about installing feature keys, refer to
Upgrading the firmware.
Page 65

Configuring IP services
Incoming
FTP
Enable/disable FTP access on the
FTP can be used to upload and download ISDN
UDP service
SNMP
Enable/disable the receiving of the
If a port is disabled, this option will be
H.323
Enable/disable access to the built-in
If a port is disabled, this option will be
certificate and private key. However, you can
upload a new private key and certificates if
required. For more information about SSL
certificates, refer to
Configuring SSL certificates.
If a port is disabled, this option will be
unavailable.
H.323
Enable/disable the ability to receive
incoming calls to the ISDN Gateway
using H.323 or change the port that
is used for this service.
specified interface or change the port
that is used for this service.
SNMP protocol on this port or
change the port that is used for this
service.
Disabling this option will not prevent outgoing
calls to H.323 devices being made by the ISDN
Gateway.
If a port is disabled, this option will be
unavailable.
Gateway configuration.
You should consider disabling FTP access on
any port that is outside your organization's
firewall.
If you require advanced security for the ISDN
Gateway, disable FTP access.
If a port is disabled, this option will be
unavailable.
unavailable.
You must use the same port number for both
Port A and Port B. The number is automatically
refreshed for Port B.
Note that by default SNMP Traps are sent to
port UDP port 162 (on the destination network
management station); this is configurable. For
more information, refer to
Configuring SNMP
settings.
If you require advanced security for the ISDN
Gateway, disable the SNMP service.
gatekeeper
H.323 gatekeeper or change the port
that is used for the built-in H.323
gatekeeper.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 65 of 135
unavailable.
You must use the same port number for both
Port A and Port B. The number is automatically
refreshed for Port B.
Page 66

Configuring SNMP settings
Field
Name
Location
The location that appears in the system
An optional field. It is useful where you
Contact
Description
A description that appears in the system
An optional field, by default this will indicate
Configuring SNMP settings
To configure monitoring using SNMP, go to Network > SNMP.
The Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway sends out an SNMP trap when the device is shut down or
started up. The SMNP page allows you to set various parameters; when you are satisfied with the
settings, click Update SNMP settings.
Note that:
The 'system up time' that appears in the trap is the time since SNMP was initialized on the ISDN
Gateway (and therefore will differ from the Up time reported by the ISDN Gateway on the Status
> General page).
The SNMP MIBs are read-only.
System information
Field description Usage tips
Identifies the ISDN Gateway in the SNMP
system MIB.
MIB.
The contact details that appear in the
system MIB.
MIB.
Usually you would give every device a
unique name. The default setting is:
Cisco ISDN GW
have more than one ISDN Gateway to
identify where the unit is located. The
default setting is:
Unknown
An optional field. The default setting is:
Unknown
Add the administrator’s email address or
name to identify who to contact when there
is a problem with the device. If SNMP is
enabled for a port on the public network,
take care with the details you provide here.
the model number of the unit. Can be used
to provide more information on the ISDN
Gateway.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 66 of 135
Page 67
Configured trap recei ver s
Field
Enable traps
Select this check box to enable the
If you do not check this box, no traps
Enable
Select this check box to enable
You cannot select this check box unless
Trap receiver
Field
RO community
RW community
Community string/password that gives
Trap community
Field description Usage tips
Configuring SNMP settings
authentication
failure trap
addresses 1 to 4
Access control
ISDN Gateway to send traps.
authentication failure traps.
Enter the IP address or hostname f or
up to four devices that will receive both
the general and the authentication
failure traps.
Field description Usage tips
Community string/password that gives
read-only access to all trap
information.
read/write access to all trap
information.
will be sent.
you have selected to Enable traps
above. Authentication failure traps are
generated and sent to the trap receivers
when someone tries to read or write a
MIB value with an incorrect community
string.
The traps that are sent by the ISDN
Gateway are all SNMP v1 traps. You
can configure trap receivers or you can
view the MIB using a MIB browser. You
can set the UDP port number for the
trap in the format <IP address>: <port
number>. By default the UDP port
number is 162.
Note that SNMP community strings are
not secure. They are sent in plain text
across the network.
It is advisable to change the community
strings before enabl ing SN MP as the
defaults are well known.
Community string/password that is
sent with all traps.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 67 of 135
Some trap receivers can filter on trap
community.
Page 68

Configuring QoS settings
Field
IPv4 configuration
Audio
Six bit binary field for prioritizing audio data
Do not alter these settings unless
Video
Six bit binary field for prioritizing video data
IPv6 configuration
Configuring QoS settings
To configure Quality of Service (QoS) on the ISDN Gateway for audio and video, go to Network > QoS.
QoS is a term that refers to a network's ability to customize the treatment of specific classes of data. For
example, QoS can be used to prioritize audio transmissions and video transmissions over HTTP traffic.
These settings affect all audio and video packets to H.323 endpoints. All other packets are sent with a
QoS of 0.
The ISDN Gateway allows you to set a six-bit value for Type of Service (IPv4) or Traffic Class (IPv6),
which can be interpreted by networks as either Type of Service (ToS) or Differentiated Services
(DiffServ).
Note: Do not alter the QoS settings unless you need to do so.
Further information about QoS, inc luding values for ToS and DiffServ, can be found in the following
RFCs, available on the Internet Engineering Task Force web site
RFC 791
www.ietf.org:
RFC 2474
RFC 2597
RFC 3246
In this section:
About QoS configuration settings
ToS configuration
DiffServ configuration
Default settings
About QoS configurati on s ett ings
The table below describes the settings on the Network > QoS page.
Field description Usage tips
packets on the network.
you need to.
packets on the network.
Cisco TelePresence ISDN Gateway 2.1 Online help (Printable format) 68 of 135
 Loading...
Loading...