Page 1

CHAPTER
6
Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
The Cisco Wireless Mobile Interface Card (WMIC) is a Cisco 3200 Series router interface card in a
standard PC/104-Plus form factor.
It is one component of the Cisco 3200 Series routers and provides a wireless interface:
• 2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) – Cisco 3201
• 4.9 GHz (public safety) – Cisco 3202
• 5.0 GHz (802.11h) – Cisco 3205 (The C3205WMIC-K9 and C3205WMIC-TP-K9 WMICs are
available only in the European Telecommunications Standards Institute [ETSI] domain.)
Caution The 4.9 GHz (public safety) radio requires an operators license and can only be operated by US Public
Safety operators who meet the requirements specified under FCC Part 90.20.
This chapterprovidesbasic information about the WMIC hardware for the purpose of performing simple
troubleshooting, such as reconnecting a loose cable. To solve more difficult problems, please contact
your vendor.
WMIC Component Systems
The ISA buses and PCI buses on the Cisco 3200 Series router cards provide power to the components
on the cards. The WMIC does not receive or transmit communications signals on either bus, but it will
pass signals through the bus to a card above or below the WMIC. Both buses comply with the
PC/104-Plus standard.
The PCI bus signals allow the Cisco cards to communicate. Non-Cisco cards cannot communicate with
the Cisco 3200 Series Router cards over the PCI bus.
Caution If you add non-Cisco cards that generates signals on the PCI bus, the router might shut down. Please do
not add non-Cisco cards that generate signals on the PCI bus.
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-1
Page 2
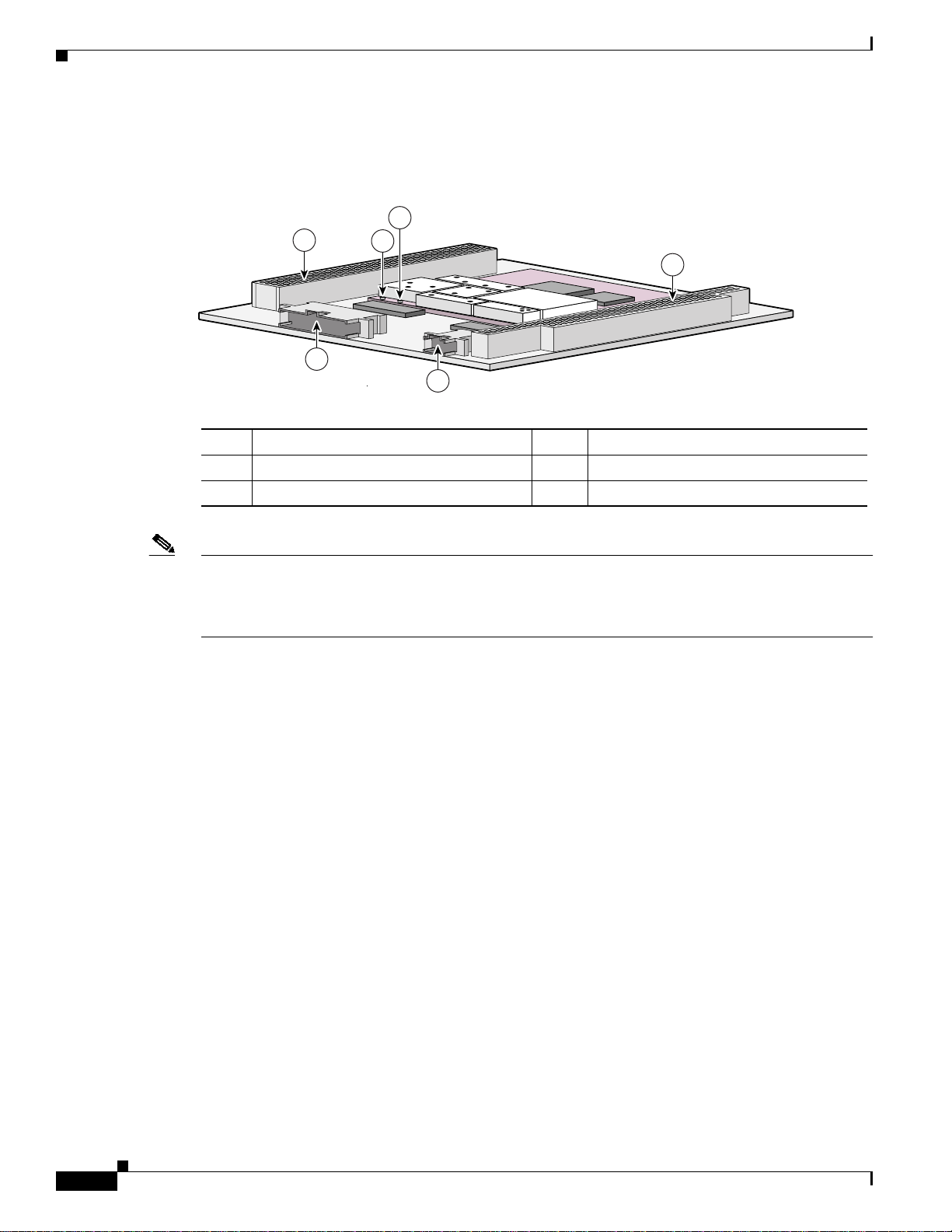
Figure 6-1 shows the WMIC header and bus locations.
Figure 6-1 WMIC Header and Bus Locations
3
1
2
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
4
1 PCI bus 2 Left antenna connector (J2)
3 Right antenna connector (J1) 4 ISA bus
5 10-pin Fast Ethernet header 6 24-pin multifunction header
Note The PC/104-Plus standard requires that the PCI bus and the ISA bus utilize keying features in the
standard stacking headers to guarantee proper module installation. On the PCI bus, pin D30 is removed
and the D30 opening is plugged. On the ISA bus, pin C19 and pin B10 are removed, and the C19 and
B10 openings are plugged.
Antenna Connector
On the radio card, there are two ultra-miniature coaxial connectors (U.FL connector) that are used to
connect the coax cables between the WMIC and the external antenna connectors. Two connectors are
used to support antenna diversity.
The cable should be as short as possible to minimize the loss in strength of the radio frequency (RF)
signal. The cable carries the RF signal from the antenna to the low noise amplifier (LNA)on the receiver
and transmits the RF signal from power amplifier (PA) to the antenna that radiates the RF signal.
There are many antenna connector families. The Cisco RP-TNC antenna connector can be used to
support standard antennas.
6
5
103981
WMIC Console and Fast Ethernet Ports
Cisco 3200 Series router cards do not support any ISA bus signals. The PCI bus connector supports
communication between Cisco 3200 Series router card and the Fast Ethernet Switch Mobile Interface
Card (FESMIC) and Serial Mobile Interface Card (SMIC).
In a Cisco rugged enclosure, the WMIC communicates with the router through the WMIC Fast Ethernet
interface. The WMIC Fast Ethernet ports are connected internally to Fast Ethernet ports that provide a
communications link with the router.
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-2
OL-5816-09
Page 3
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
The WMIC interfaces are configured through a WMIC console port. In contrast, the Serial Mobile
Interface Card (SMIC) and FESMIC communicate with the router through the PC/104-Plus bus. The
interfaces are configuredthrough the router console port, and all of the router and FESMIC Fast Ethernet
ports are identified by using the slot/port format.
The WMIC runs an independent IOS image and when it is configured, the link between the WMIC and
the router forms an internal LAN. In standard configurations, a WMIC Fast Ethernet port is never
brought out to the end cap.
The WMIC console port is brought out to the corresponding RJ-45 port on the I/O end cap, replacing a
Fast Ethernet port. If the router includes one WMIC, the RS-232 WMIC console port replaces a Fast
Ethernet port on the end cap. If the router includes two WMICs, two WMIC RS-232 console ports
replace two Fast Ethernet ports on the end cap.
Note Currently, even if the router contains zero WMICs, in standard configurations a maximum of three Fast
Ethernet ports are brought out to the end cap. Unused RS-232 ports are sealed.
Fast Ethernet Signals on the WMIC
The Fast Ethernet signals are delivered through a 10-pin header. LED signals and RS-232 console signals
are provided through the 24-pin multifunction header.
There is one set of fixed Fast Ethernet signals on the WMIC. The Fast Ethernet port signals are in
compliance with IEEE 802.3. They are provided through the Ethernet headers, which support the
following:
• Auto-negotiation for 10/100BASE-TX connection
• Full-duplex and half-duplex modes
• Low-power sleep mode
• 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX using a single Ethernet connection
• Robust baseline wander correction performance
• Standard carrier signal multiple access collision detect (CSMA/CD) or full-duplex operation
• Integrated LED drivers
Note If Auto-MDIX is disabled, when connecting to Ethernet switches or repeaters a straight-through cable
can be used. When connecting to compatible workstations, servers, and routers, a crossover cable should
be used. If Auto-MDIX is enabled, either a straight-through or crossover cable can be used can be used
to make the connection, as the router automatically changes the signals on the pins to compensate.
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-3
Page 4
LED Behavior
During normal operations, the indicator signals on the wireless device have the following meanings.
• The status indicator signals operational status. Steady green indicates that the wireless device is
• The radio indicator blinks green to indicate radio traffic activity. The light is normally off, but it
• The Ethernet indicator signals traffic on the wired LAN. This indicator is normally green when an
Table 6-1 shows the details of LED behavior.
Table 6-1 Indicator Signals
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
associated with at least one wireless client. Blinking green indicates that the wireless device is
operating normally but is not associated with any wireless devices.
blinks whenever a packet is received or transmitted over the radio.
Ethernet cable is connected, and blinks green when a packet is received or transmitted over the
Ethernet infrastructure. The indicator is off when the Ethernet cable is not connected.
Message
type
Boot loader
status
Association
status
Operating
status
Boot Loader
Errors
Ethernet
indicator
Green – Green DRAM memory test.
– Amber Red Board initialization test.
– Blinking
Amber Green – Ethernet initialization test.
Green Green Green Starting Cisco IOS software.
– Green – At least one wireless client device is
– Blinking
– Green Blinking
Green – – Ethernet link is operational.
Blinking
green
Red – Red DRAM memory test failure.
– Red Red File system failure.
Red Red – Ethernet failure during image recovery.
Amber Green Amber Boot environment error.
Red Green Red No Cisco IOS image file.
Amber Amber Amber Boot failure.
Status
indicator
green
green
– – Transmitting/receiving Ethernet packets.
Radio
indicator
Blinking
green
– No client devices are associated; check the
green
Meaning
Flash memory test.
associated with the unit.
wireless device SSID and WEP settings.
Transmitting/receiving radio packets.
6-4
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
Page 5
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-1 Indicator Signals (continued)
Message
type
Operation
Errors
Configuration
Reset
Failures Red Red Red Firmware failure; try disconnecting and
Firmware
Upgrade
Key Features
The key features of the Cisco wireless devices are listed in Table 6-2.
Ethernet
indicator
– Green Blinking
Blinking
Status
indicator
Radio
indicator
Meaning
Maximum retries or bufferfull occurred on
amber
the radio.
– – Transmit/receive Ethernet errors.
amber
– Blinking
– General warning.
amber
– Amber – Resetting the configuration options to
factory defaults.
reconnecting unit power.
Blinking red – – Hardware failure. The wireless device
must be replaced.
– Red – Loading new firmware image.
Table 6-2 Key Features
Feature Description
Wireless Medium
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Radio Media Access
Protocol
SNMP Compliance
Encryption Key Length
Quality of Service
(QoS) Support
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA)
MIB I and MIB II
128-bit
Prioritization of traffic for different requirements, such as voice and video.
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-5
Page 6
Table 6-2 Key Features (continued)
Feature Description
Security
Cisco Wireless Security Suite:
Authentication:
• 802.1X support including LEAP, PEAP, EAP-TLS, and EAP-SIM to
yield mutual authentication and dynamic, per-user, per-session WEP
keys
• MAC address and by standard 802.11 authentication mechanisms
Encryption:
• Static and dynamic IEEE 802.11 WEP keys of 40 bits and 128 bits
• 802.11i/WPAv2 Advanced Encryption Standard-Counter Mode with
Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol
(AES-CCMP); 128-bit key length
• Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) WEP enhancements: key
hashing (per-packet keying), message integrity check (MIC), and
broadcast key rotation by using WPA TKIP
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Status Indicators
Memory
Automatic Configuration
Support
Remote Configuration
Support
Uplink
Local Configuration
All WMICs in Root Mode:
PEAP, EAP-TTLS, LEAP, EAP-TLS, EAP-FAST, and EAP-SIM.
Cisco 3201 WMICs in Client Mode:
LEAP, EAP-TLS & EAP-FAST
Cisco 3202 and Cisco 3205 WMICs in Client Mode:
LEAP
LEDs provide information concerning association status, operation,
error/warning, firmware upgrade, and configuration, network/modem, and
radio status
8 MB Flash
32 MB DRAM
BOOTP and DHCP
Telnet, HTTP, FTP, TFTP, and SNMP
Auto-sensing 10/100BaseT Ethernet
Console port
6-6
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
Page 7

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
MAC Address Allocation
The WMIC stores one unique MAC address for the BVI interface.
WMIC Power Requirement
In a typical Cisco 3200 Series router configuration, the WMIC draws power from the PCI and the ISA
connectors. Table 6-3 shows the estimated power consumption. Note that these are theoretical maximum
wattages.
Table 6-3 WMIC Power Requirement
Voltage Current Draw Power Source
+5.0 V 0.4 amps 2.0 W ISA and PCI connectors
+3.3 V 1.7 amps 5.6 W PCI connectors
Mean Time Between Failure
The calculated Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) in excess of 1,190,136 hours.
Differences Between WMICs
Table 6-4 Differences between WMICs
Feature 2.4GHz (802.11b/g) 4.9 GHz (public safety) 5.0 GHz (802.11h) Comment
Cisco IOS image
release
Cookie and banner
Frequency
Power
power client Command
Transmission Power
Control (TPC)
12.3(8) JK 12.3.(2) JK 12.3.(2) JL
C3201 C3202 C3205
2.4 GHz 4.9 GHz 5.0 GHz
Maximum OFDM power
level is 15dbm (30mw),
but the power level might
vary by country.
Supported Not supported. (Use the
Not supported Not supported Supported for ETSI. TPC limits the
Maximum OFDM power
level is 17dbm (50mw).
power local command.)
The power levels can be
definedas4 dBm, 7 dBm,
10 dBm, 13 dBm, or
16 dBm.
Not supported. (Use the
power local command.)
transmitted power to
the minimum power
levelneeded to reach
the furthest user.
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-7
Page 8

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-4 Differences between WMICs (continued)
Feature 2.4GHz (802.11b/g) 4.9 GHz (public safety) 5.0 GHz (802.11h) Comment
Dynamic Frequency
Selection (DFS)
NA NA Supported for ETSI. DFSselectsthe radio
channel most likely
to minimize
interference with
military radar.
Channelization
Statically declared as
defined by IEEE
802.11b/g.
Channel spacing selected
by using the CLI.
Statically declared as
definedbyIEEE 802.11h.
(Available only in
Europe.)
Concatenation
Fragmentation
Supported. Not supported. Not supported.
Maximum threshold is
4000 bytes.
Maximum threshold is
2346 bytes.
Supported Fragment counter is
in units of
fragmented packets.
distance Command
Autonomous Modes
Supported
World Mode
Supported up to 99
kilometers.
Work Group Bridge
(WGB), Non Root Bridge
(NRB), Root Bridge
(RB), Repeater, and
Access Point (AP)
Supported up to 3
kilometers (1.8 miles).
Work Group Bridge
(WGB), Non Root Bridge
(NRB), Root Bridge
(RB), Repeater, and
Access Point (AP)
Supported. Supported only if the
wireless device is in root
access point or root
bridge mode. Not
supported in client
modes.
Supported up to 99
kilometers.
Work Group Bridge
(WGB), Non Root Bridge
(NRB), Root Bridge
(RB), and Access Point
(AP)
Supported only if the
wireless device is in root
access point or root
bridge mode. Not
supported in client
modes.
Minimizes delay
propagation.
World Mode on the
client side updates a
client with the
channels of the
specified domain.
The Cisco 3200
Series router is
limited to fixed
channels, so
world-mode is not
available on the
client side.
Universal Workgroup
Bridge Mode
Supported Not supported Not supported Enables operation
with non-Cisco
access points.
Multiple Client Profiles
Supported Not supported Not supported Support is enabled
only when universal
workgroup bridge
mode is enabled.
Multiple Basic SSIDs
VLANs
Supported Not supported Not supported
16 unencrypted VLANs,
16 static key VLANs, or
16 dynamic key VLANs,
16 unencrypted VLANs,
1 static key VLAN, or 4
dynamic key VLANs.
16 unencrypted VLANs,
1 static key VLAN, or 4
dynamic key VLANs.
6-8
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
Page 9

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-4 Differences between WMICs (continued)
Feature 2.4GHz (802.11b/g) 4.9 GHz (public safety) 5.0 GHz (802.11h) Comment
Wireless
encryption/cipher
suites
Max Number of
Stations with WEP
Max Number of
Stations with TKIP
Max Number of
Stations with
AES-CCM
WDS Server
WDS Client
EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS
EAP-FAST
WDS Server Related
MIBS
WEP-40, WEP-128,
TKIP, CKIP, CMIC and
WEP-40, WEP-128,
TKIP, and AES-CCM
WEP-40, WEP-128,
TKIP, and AES-CCM
CKIP-CMIC
255 116 116
256 26 26
256 116 116
Not supported. Supported Supported
Can auto discover and
work with a subnet WDS
server.
EAP-TLS is supported.
EAP-TTLS is supported
on root devices only.
Supported on root and
non-root devices.
Can auto discover and
work with a WDS server
on the same subnet as the
WMIC. If the IP address
of a WDS server is
anywhere on the network
and the IP address is
statically configured on a
WMIC acting as root
device, the WMIC can
work with the WDS
server.
EAP-TLS is supported in
client mode. EAP-TTLS
is not supported.
Can auto discover and
work with a WDS server
on the same subnet as the
WMIC. If the IP address
of a WDS server is
anywhere on the network
and the IP address is
statically configured on a
WMIC acting as root
device, the WMIC can
work with the WDS
server.
EAP-TLS is supported in
client mode. EAP-TTLS
is not supported.
Not supported Supported on root and
non-root devices.
N/A Supported Supported
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-9
Page 10

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-4 Differences between WMICs (continued)
Feature 2.4GHz (802.11b/g) 4.9 GHz (public safety) 5.0 GHz (802.11h) Comment
Fast Roaming
Scanning
Enhancements
All scanning
enhancements for faster
roaming are available.
All scanning
enhancements for faster
roaming are available
except “Use First Better
Access Point.”
All scanning
enhancements for faster
roaming are available
except “Use First Better
Access Point.”
• Synthesizer
tuning time
• Start on current
channel
• Only probe
current SSID
• Shorten wait
time for probe
response
• Automatically
limiting
frequencies
scanned
• Time out the
scan
• Use first better
access point
• Save best probe
response
CCXv4 features
802.11e MMN QoS
Simple Network
Management Protocol
(SNMP) MIB IDs
Dot11 MIB parameters
Supported Not supported Supported
Supported Not supported Supported
Supported Supported for new values Supported The
Supported The dot11 parameters are
returned through the
dot11 MIB interface.
2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) WMIC Features
The key features of the 2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) WMIC are listed below.
Data Rates Supported
Network Standard
1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 Mbps
IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g
platform-dependent
SNMP code was
modified to return
new values
(entPhysicalVendorT
ype, System OID,
and Chassis ID).
Supported
6-10
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
Page 11

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Frequency Band
Modulation
Operating Channels
Receive Sensitivity
Transmit Power Settings
2.400 GHz to 2.497 GHz
BPSK 1 Mbps and 6 Mbps
QPSK 2 Mbps and 12 Mbps
CCK 5.5 Mbps
BPSK 9.6 Mbps
CCK2 11 Mbps
QPSK 18 Mbps
16 QAM 24 Mbps and 36 Mbps
64 QAM 48 Mbps and 54 Mbps
North America: 11; ETSI: 13; Japan: 14
1 Mbps: -94 dBm
2 Mbps: -91 dBm
5.5 Mbps: -89 dBm
11 Mbps: -85 dBm
100 mW (20 dBm)
50 mW (17 dBm)
30 mW (15 dBm)
20 mW (13 dBm)
5 mW (7 dBm)
1 mW (0 dBm)
Maximum power setting vary to comply with the regulatory domain.
Range (typical @ 100 mW
transmit power setting
with 6 dBi diversity dipole
antenna)
Outdoor:
0.5 mile (804 m) @ 45 Mbps
1 mile (1609 m) @ 11 Mbps
3 miles (4,827 m) @ 1 Mbps
Compliance
2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) operates license free under FCC Part 15 and complies
as a Class B device; complies with DOC regulations; complies with ETS
300.328, FTZ 2100, and MPT 1349 standards; rugged version complies with
UL 2043
The channel identifiers, channel center frequencies, and regulatory domains of each IEEE 802.11b/g
22-MHz-wide channel are shown in Table 6-5 .
Table 6-5 Channels for IEEE 802.11b/g
Regulatory Domains
Channel
Identifier
Center
Frequency
(MHz)
Americas (–A) EMEA (–E) Japan (–J)
CCK OFDM CCK OFDM CCK OFDM
1 2412 X X X X X X
2 2417 X X X X X X
3 2422 X X X X X X
4 2427 X X X X X X
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-11
Page 12

Table 6-5 Channels for IEEE 802.11b/g (continued)
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Center
Channel
Identifier
Frequency
(MHz)
5 2432 X X X X X X
6 2437 X X X X X X
7 2442 X X X X X X
8 2447 X X X X X X
9 2452 X X X X X X
10 2457 X X X X X X
11 2462 X X X X X X
12 2467 – – X X X X
13 2472 – – X X X X
14 2484 – – – – X –
Universal Workgroup Bridge Limitations
The following limitations and restrictions apply to universal workgroup bridges:
• A universal workgroup bridge can not associate with the Cisco WLAN AP with CKIP or CMIC
encryption configuration.
• If the universal workgroup bridge is associated with a Cisco AP or third party AP and if the user
issues the command show dot11 association all, the IP address and name information is not
available.
• Users should configure the static IP address on the BVI when it is in the universal workgroup bridge
mode, so that the WMIC is manageable from the MAR through the Mobile IP tunnel from the
infrastructure side.
• If the dynamic CCoA is used on the Cisco 3200 Series Wireless and Mobile Router, you should
configure the static IP address using the ip secondary address command.
• The universal workgroup bridge is not compatible with the Tropos version 3.1.1.2 AP.
• A universal workgroup bridge can not associate with the Cisco 1500 router when it is configured
with the Allow WPA2 TKIP Clients option.
Regulatory Domains
Americas (–A) EMEA (–E) Japan (–J)
CCK OFDM CCK OFDM CCK OFDM
6-12
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
Page 13

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
4.9 GHz (public safety) WMIC Features
The key features of the 4.9 GHz (public safety) WMIC are listed in Table 6-6.
Table 6-6 Key Features of the 4.9 GHz (public safety) WMIC
Feature Description
Data Rates Supported
Network Standard
Frequency Band
Available Transmit Power
Settings
Compliance
5 MHz channelization: 1.5, 2.25, 3, 4.5, 6, 9, 12, and 13.5 Mbps
10 MHz channelization: 3, 4.5, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, and 27 Mbps
20 MHz channelization: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 Mbps
Currently there is no IEEE 4.9 GHz (public safety) standard; however, it is
similar to the IEEE 802.11a standard.
4.940 GHz to 4.990 GHz
50 mW (17 dBm)
40 mW (16 dBm)
30 mW (15 dBm)
20 mW (13 dBm)
10 mW (10 dBm)
5 mW (7 dBm)
4.9 GHz (public safety):
• Operation restricted to operators meeting requirements of CFR47 Part
90.20 of the technical rules for qualification as a Public Safety operator.
• Requires a FCC license to operate under this part of the Part 90
Regulation
4.9 GHz Channels
Table 6-7 shows the channel options for the 4.94 GHz to 4.99 GHz band for the United States regulatory
domain.
Table 6-7 FCC 4.9 Operational Channels as per TIA TR-8 Specification
Operating Channel
Numbers
Channel Center 5 MHz
Channel Spacing
Channel Center 10 MHz
Channel Spacing
Channel Center 20 MHz
Channel Spacing
1
3
5 4942.5
7
9
10 4945.0
15 4947.5
20 4950.0 4950.0
25 4952.5
30 4955.0 4955.0
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-13
Page 14

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-7 FCC 4.9 Operational Channels as per TIA TR-8 Specification (continued)
Operating Channel
Numbers
Channel Center 5 MHz
Channel Spacing
Channel Center 10 MHz
Channel Spacing
Channel Center 20 MHz
Channel Spacing
35 4957.5
40 4960.0 4960.0
45 4962.5
50 4965.0 4965.0
55 4967.5
60 4970.0 4970.0
65 4972.5
70 4975.0 4975.0
75 4977.5
80 4980.0 4980.0
85 4982.5
90 4985.0
91
93
95 4987.5
97
99
Throughput
Modulation
Note Channel Center Frequencies (MHz) 1 MHz Channel Spacing is documented in the TIA TR-8
specification, but it is not supported by the 4.9 GHz (public safety) WMIC.
The throughput is a minimum of:
• 4 Mbps half-duplex at one mile line-of-sight for a 5 MHz-wide channel
• 8 Mbps half-duplex at one mile line-of-sight range for a 10 MHz-wide channel.
• 16 Mbps half-duplex at one mile line-of-sight range for a 20 MHz-wide channel.
Table 6-8 shows the modulation.
Table 6-8 Modulation
Modulation 5 Mbps 10 Mbps 20 Mbps
BPSK
QPSK
1.5 Mbps and 2.25 Mbps 3 Mbps and 4.5 Mbps 6 Mbps and 9 Mbps
3 Mbps and 4.5 Mbps 6 Mbps and 9 Mbps 12 Mbps and 18 Mbps
6-14
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
Page 15

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-8 Modulation (continued)
Modulation 5 Mbps 10 Mbps 20 Mbps
16 QAM
64 QAM
Receive Sensitivity
Table 6-9 shows the receive sensitivity.
Table 6-9 Receive Sensitivity
5 MHz 10 MHz 20 MHz
1.5 Mbps -89 dBm 3 Mbps -87 dBm 6 Mbps -85 dBm
2.25 Mbps -89 dBm 4.5 Mbps -87 dBm 9 Mbps -85 dBm
3 Mbps -89 dBm 6 Mbps -87 dBm 12 Mbps -85 dBm
4.5 Mbps -85 dBm 9 Mbps -87 dBm 18 Mbps -82 dBm
6 Mbps -82 dBm 12 Mbps -85 dBm 24 Mbps -79 dBm
9 Mbps -79 dBm 18 Mbps -79 dBm 36 Mbps -76 dBm
12 Mbps -74 dBm 24 Mbps -74 dBm 48 Mbps -71 dBm
13.5 Mbps -72 dBm 27 Mbps -72 dBm 54 Mbps -69 dBm
6 Mbps and 9 Mbps 12 Mbps and 18 Mbps 24 Mbps and 27 Mbps
12 Mbps and 13.5 Mbps 24 Mbps and 27 Mbps 48 Mbps and 54 Mbps
5.0-GHz (802.11h) Radio Features
The radio supports only 20-MHz channelization.
Note 802.11h is supported only in the ETSI regulatory domain.
Note By default, the C3205 WMIC uses the right antenna to receive and transmit data.
5.0-GHz (802.11h) Channels
The 5.0-GHz (802.11h) radio in the Cisco 3200 Series router (currently available as the Cisco 3205
WMIC) supports the following channels/frequencies in the ETSI regulatory domain:
• 5.250 GHz to 5.350 GHz: 5260 MHz (52), 5280 MHz (56), 5300 MHz (60), 5320 MHz (64),
• 5.470 GHz to 5.725 GHz: 5500 MHz (100), 5520 MHz (104), 5540 MHz (108), 5560 MHz (112),
5580 MHz (116), 5600 MHz (120), 5620 MHz (124), 5640 MHz (128), 5660 MHz (132),
5680 MHz (136), 5700 MHz (140). (Channels 52 through 140 are ETSI outdoor channels.)
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-15
Page 16

Throughput
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Note By default, the C3205 WMIC performs automatic channel selection on the radio interface. For more
information about configuring a channel on the radio interface of the C3205 WMIC using the
command-line interface (CLI), refer to the “Configuring the Radio Channel or Frequency for the C3205
WMIC” section in the Radio Channels and Transmit Frequenciesdocument. The show interface d0 dfs
command provides DFS statistics.
The throughput is a minimum of 16 Mbps half-duplex at one mile line-of-sight range for a
20 MHz-wide channel. The range performance is dependent on output power, antenna gain,
path loss, and other factors.
The following are range performance estimations:
• 6 Mbps at 10 kilometers (6 miles) at 30 dBm EIRP
• 1 Mbps at 30 kilometers (18 miles) at 30 dBm EIRP
Modulation
Table 6-10 shows the 5.0-GHz (802.11h) modulation.
Table 6-10 5.0-GHz (802.11h) Modulation
Receive Sensitivity
Table 6-11 shows the receive sensitivity for all locations.
Table 6-11 Receive Sensitivity for 5.0-GHz (802.11h) Radios
Modulation 20 Mbps
BPSK
QPSK
16 QAM
64 QAM
6 Mbps and 9 Mbps
12 Mbps and 18 Mbps
24 Mbps and 27 Mbps
48 Mbps and 54 Mbps
Data Rates 5.25 GHz to 5.35 GHz 5.47 GHz to 5.725 GHz 5.725 GHz to 5.825 GHz
6 Mbps -85 dBm -85 dBm -85 dBm
9 Mbps -85 dBm -85 dBm -85 dBm
12 Mbps -85 dBm -85 dBm -85 dBm
18 Mbps -82 dBm -82 dBm -82 dBm
24 Mbps -79 dBm -79 dBm -79 dBm
36 Mbps -76 dBm -76 dBm -76 dBm
48 Mbps -71 dBm -71 dBm -71 dBm
54 Mbps -69 dBm -69 dBm -69 dBm
1. The 5.725-GHz to 5.825-GHz range is not supported on European models.
1
6-16
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
Page 17

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Transmit Sensitivity
Table 6-12 shows the transmit sensitivity.
Table 6-12 Transmit Power Levels for the C3205 WMIC
Data Rates 5.25 GHz to 5.35 GHz 5.47 GHz to 5.725 GHz 5.725 GHz to 5.825 GHz
6 Mbps 16 dBm 16 dBm 16 dBm
9 Mbps 16 dBm 16 dBm 16 dBm
12 Mbps 16 dBm 16 dBm 16 dBm
18 Mbps 16 dBm 16 dBm 16 dBm
24 Mbps 16 dBm 16 dBm 16 dBm
36 Mbps 16 dBm 16 dBm 16 dBm
48 Mbps 14 dBm 14 dBm 14 dBm
54 Mbps 13 dBm 13 dBm 13 dBm
1. The 5.725-GHz to 5.825-GHz range is not supported on European models.
Additional cards and components provide power and link interfaces to the WMIC. The exact
configuration of your router will vary, depending on how it was configured by the vendor.
Related Documentation
These documents provide detailed information regarding the configuration of the wireless card:
• Cisco IOS Switching Services Configuration Guide. Click this link to browse to this document:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/122cgcr/fswtch_c/index.htm
• Cisco Internetwork Design Guide. Click this link to browse to this document:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/idg4/index.htm
• Cisco Internetworking Technology Handbook. Click this link to browse to this document:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/ito_doc/index.htm
• Cisco Internetworking Troubleshooting Guide. Click this link to browse to this document:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/itg_v1/index.htm
1
OL-5816-09
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-17
Page 18

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
6-18
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
OL-5816-09
 Loading...
Loading...