Page 1

Quick Start Guide
Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller
INCLUDING LICENSE AND WARRANTY
1 About this Guide
2 Unpacking and Preparing the Controller for Operation
3 Connecting the Network
4 Obtaining Documentation and Service Request
5 Translated Warnings
1 About this Guide
This guide is designed to help you install and minimally configure your Cisco
2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller.
Page 2
2
FCC Safety Compliance Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio
or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on.
Try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help. (cfr reference 15.105)
Safety Information
Safety warnings appear throughout this guide in procedures that may harm you if performed
incorrectly. A warning symbol precedes each warning statement. The warnings below are general
warnings that are applicable to the entire guide. Translated versions of the safety warnings in this guide
are provided in the “Translated Warnings” section on page 21.
Warning
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury.
Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical
circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the
statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate its translation in the
translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.
Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Warning
There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery
only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of
used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statement 1015
Page 3

3
Warning
This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the
equipment in the absence of a suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the
appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that
suitable grounding is available.
Statement 1024
Warning
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and
regulations.
Statement 1040
Safety Considerations
• Verify that the ambient temperature remains between 32 to 104° F (0 to 40° C), taking into
account the elevated temperatures when installed in a rack or enclosed space.
• When multiple Cisco 2100 series controllers are mounted in an equipment rack, be sure that the
power source is sufficiently rated to safely run all the equipment in the rack (input: 100–240VAC,
50/60 Hz, output: 48VDC, 2.08A per controller).
• Verify the integrity of the electrical ground before installing the controller.
Introduction to the Controller
The Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller works in conjunction with Cisco lightweight access
points and the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS) to provide system-wide wireless LAN functions.
As a component of the Cisco Unified Wireless Network, the Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN
Controller presents network administrators with the visibility and control necessary to effectively and
securely manage business-class WLANs and mobility services such as voice, guest access, and location
services.
Cisco 2100 series controllers have eight 10/100 copper Ethernet distribution system ports through
which the controller can support up to 6, 12, or 25 access points (2106, 2112, or 2125 models).
In order to best use this guide, you should have already designed the wireless topology of your network
and have a working knowledge of how controllers function in a wireless LAN network.
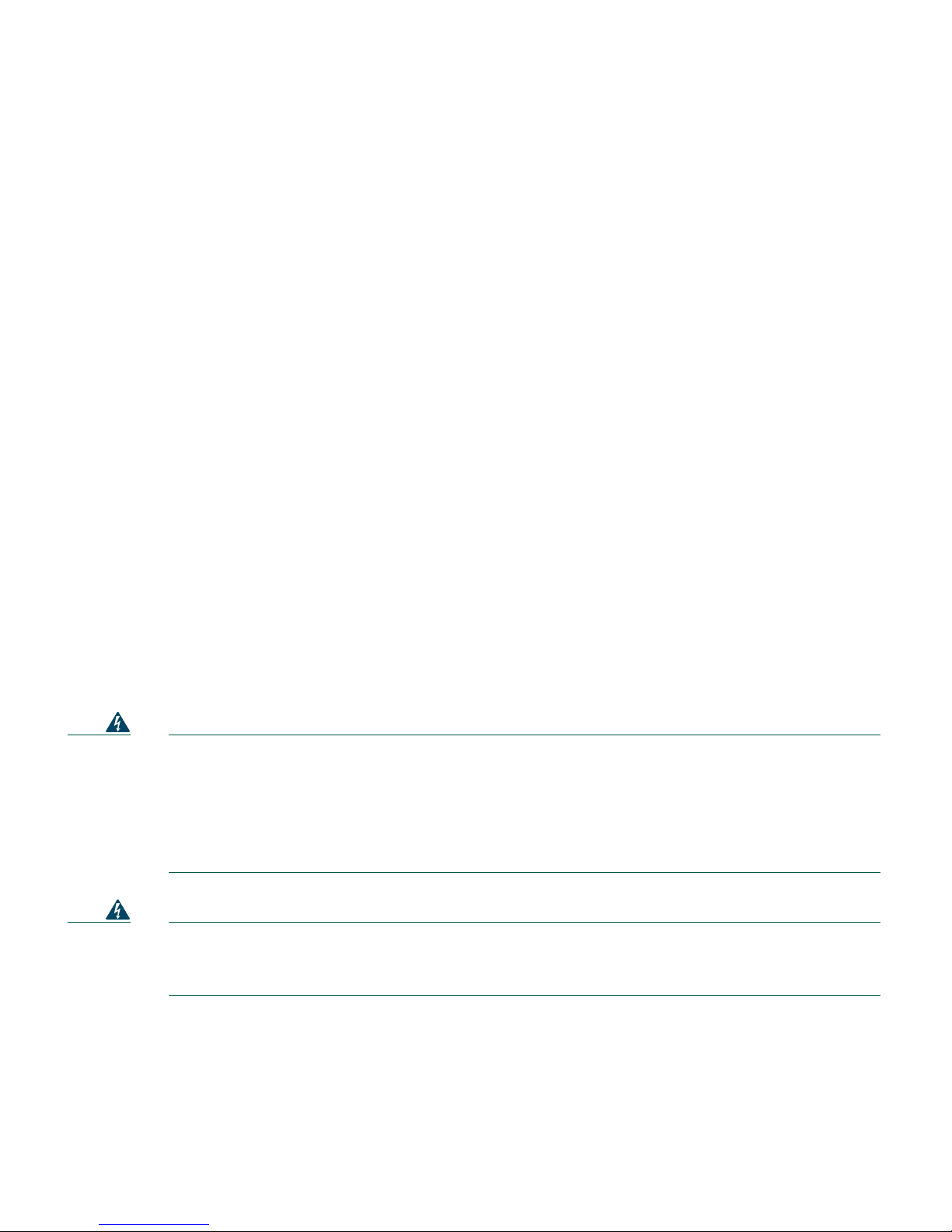
Figure 1 shows a typical Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller network topology and network
connections, showing the medium dependent interface (MDI) Ethernet cables required. The controller
has an auto MDI feature, so you can use straight-through or crossover cables.
Page 4
4
Figure 1 Typical Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller Topology and Network Connections
135755
10/100BASE-T
MDI cables
10/100BASE-T
MDI cable
Network
Distribution
system
connection
Access
point
connections
WAN or LAN
connection to
main office
Cisco Access Points
Null modem serial
cable (DB-9 -> RJ-45)
to console connection
LAN link for
management software
connections
Console emulator
for initial boot-up
Cisco WCS software,
web user interface
Page 5
5
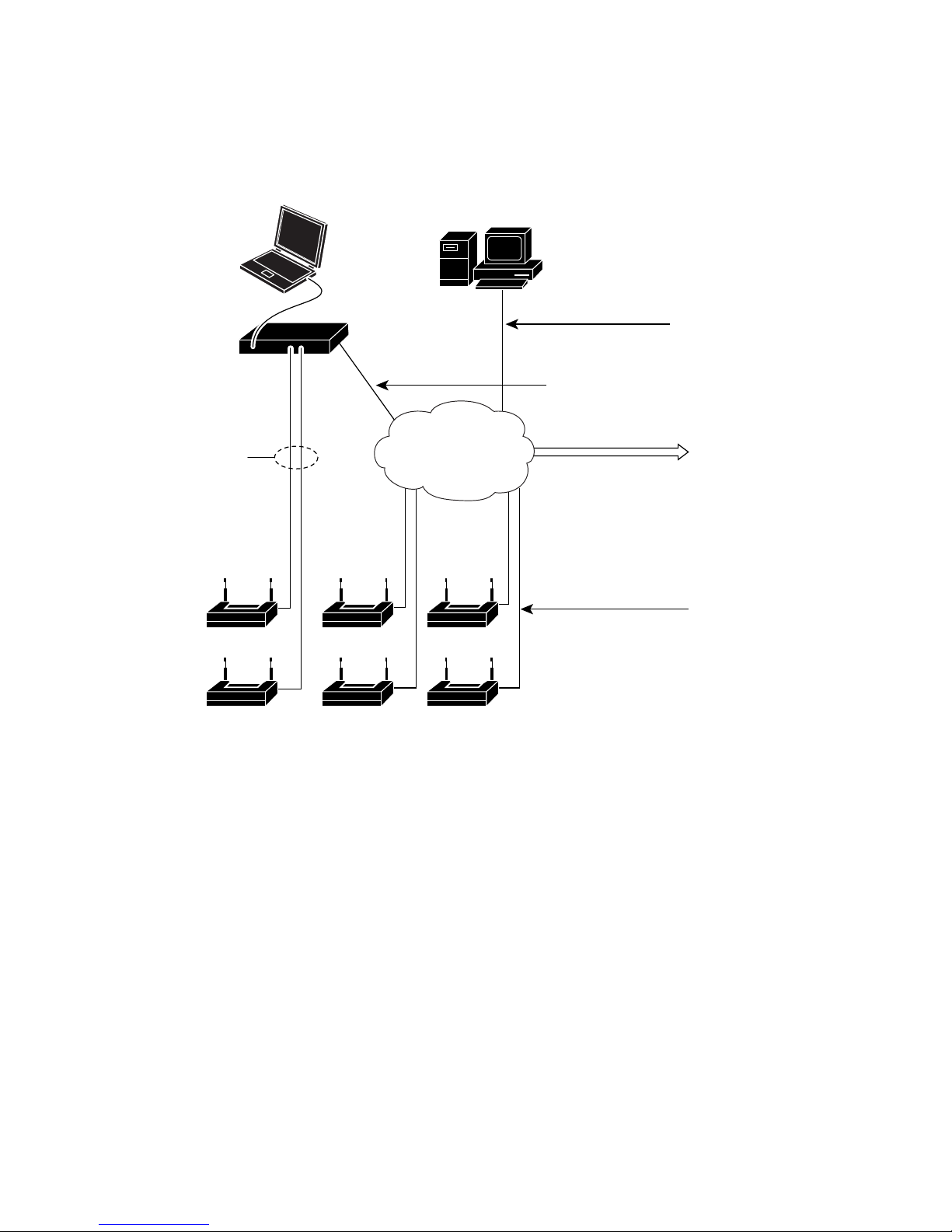
Figure 2 shows the front panel and describes the LEDs for the 2100 series controller.
Figure 2 Front Panel and LEDs
Component/LED State and Description
1
USB port Not used, reserved for future use.
2
Speed indicators (ports 1–8) Off—Network traffic flowing at 10 Mbps.
Green—Network traffic flowing at 100 Mbps.
3
Link activity indicators (ports 1–8) Green—Physical link established.
Flashing green—Network activity.
4
Power LED Green—Controller powered on.
Off—Controller is powered off.
5
Status LED Flashing green—Power-up diagnostics/booting.
Green—Controller is operational.
Amber—Problem encountered during boot.
6
Alarm LED Green—Not used.
Amber—An outstanding alarm exists.
7
AP LED Green—At least one access point has joined.
Off—No access points joined.
170956
Cisco 2100
SERIES
Wireless LAN Controller
1
LINK/ACT
100 MBPS
2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Power Status Alarm AP
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Page 6
6
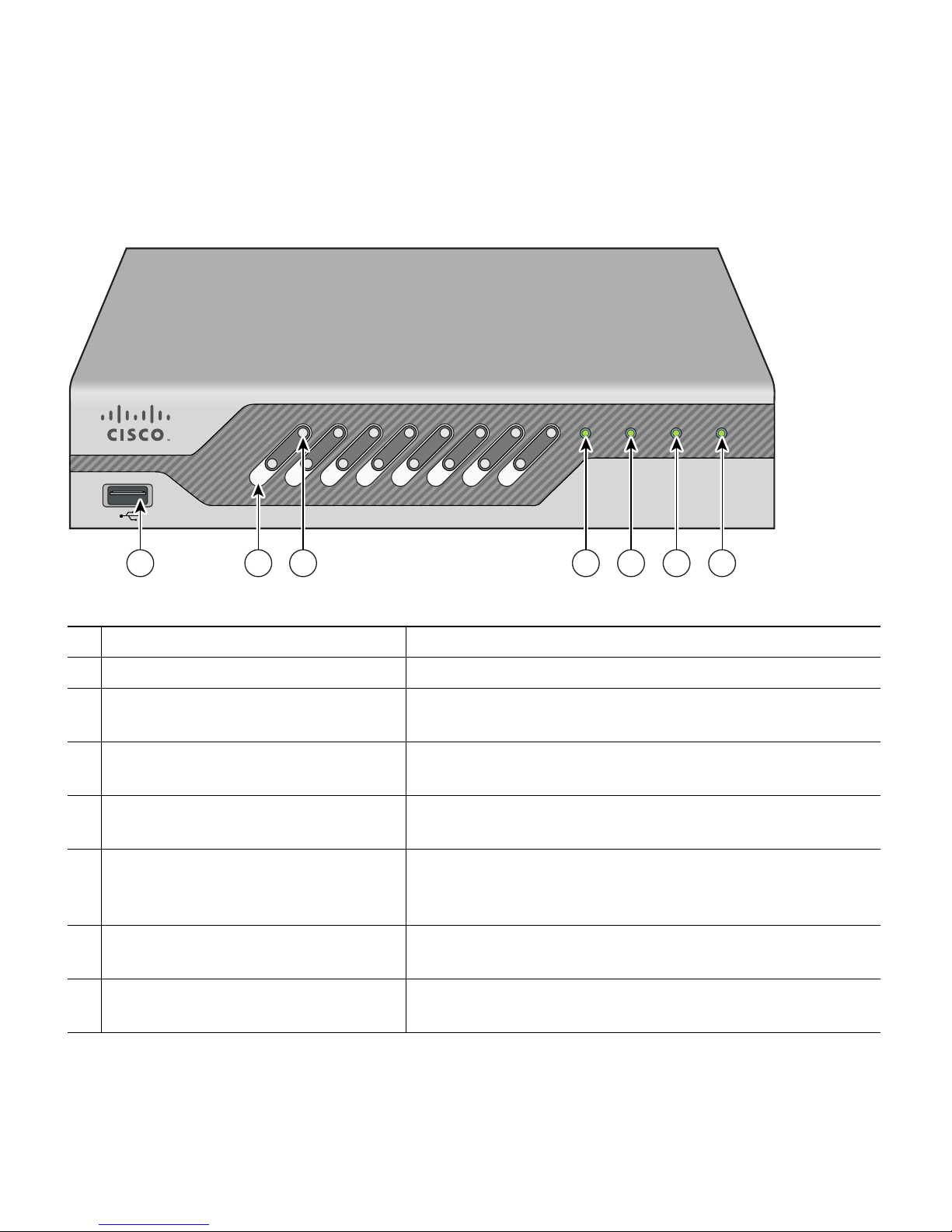
Figure 3 shows the back panel and identifies its components.
Figure 3 Back Panel and Components
Caution Do not connect a Power over Ethernet (PoE) cable to the console port. Doing so will
damage the controller.
Note Wait at least 20 seconds before reconnecting an access point to the controller. Otherwise, the
controller may fail to detect the device.
Note Direct connection is not supported; therefore ports 7 and 8 must not be used.
1
Power plug
5
Reset button
2
Power over Ethernet enabled ports (7 & 8)
6
Cable lock slot
3
Distribution ports (1–6)
7
Console port
4
USB ports (reserved for future use)
8
Security service card (SSC) slot (reserved for
future use)
78 6
43221 5
Page 7

7
2 Unpacking and Preparing the Controller for Operation
Follow these steps to unpack the controller and prepare it for operation:
Step 1 Open the shipping container and carefully remove the contents.
Step 2 Return all packing materials to the shipping container and save it.
Step 3 Ensure that all items listed in the “Package Contents” section are included in the shipment.
Check each item for damage. If any item is damaged or missing, notify your authorized Cisco
sales representative.
Package Contents
Each 2100 series controller package contains the following items:
• One Cisco 2100 series wireless LAN controller
• One Power supply and power cord
• One Ethernet cable (RJ45 to RJ45)
• One Console cable (RJ45 to DB9)
• This guide
• Cisco product registration card
Note The controller ships with controller software loaded. When upgrading software, do not
upgrade to any release earlier than release 4.0.197.0
Required Tools and Information
You will need the following tools and information before you can install the controller:
• Wireless LAN controller hardware
–
Controller with factory-supplied power cord and mounting hardware
–
Network, operating system service network, and access point cables as required
• Command-line interface (CLI) console
–
VT-100 terminal emulator on CLI console (PC, laptop, or palmtop)
–
Null modem serial cable to connect CLI console and controller
Page 8

8
• Local TFTP server (required for downloading operating system software updates). Cisco uses an
integral TFTP server. This means that third-party TFTP servers cannot run on the same
workstation as the Cisco WCS because Cisco WCS and third-party TFTP servers use the same
communication port.
Initial System Configuration Information
Obtain the following initial configuration parameters from your wireless LAN or network
administrator:
• A system (controller name), such as controller. The system name can contain up to 32 printable
ASCII characters.
• An administrative username and password, which can contain up to 24 printable ASCII
characters. If you do not specify a username and password, the defaults admin and admin are used.
• A management interface (DS Port or network interface port) IP address, such as 10.40.0.4.
• A management interface netmask address, such as 255.255.255.0.
• A management interface default router IP address, such as 10.40.0.5.
• A VLAN identifier if the management interface is assigned to a VLAN, such as 40 or 0 for an
untagged VLAN.
• A management interface port, such as 1.
• A management interface DHCP server IP address, such as 10.40.0.6 (the IP address of the default
DHCP server that will supply IP addresses to clients and the management interface.
• An access point manager interface IP address, such as 10.40.0.7.
• A virtual gateway IP address (a fictitious, unassigned IP address, such as 1.1.1.1, used by all Cisco
wireless LAN controller Layer 3 security and mobility managers).
• A Cisco wireless LAN controller mobility or RF group name, such as rfgrp40 if required. An RF
group name can contain up to 19 printable ASCII characters.
• An 802.11 network name (SSID), such as wlan1. An SSID can contain up to 32 printable,
case-sensitive ASCII characters.
• Whether or not to allow static IP addresses from clients, either Yes or No.
–
Yes is more convenient, but has lower security (session can be hijacked).
–
No is less convenient, but has higher security and works well for Windows XP devices.
• RADIUS server IP address, communications port, and secret if you are configuring a RADIUS
server, such as 10.40.0.3, 1812, and mysecretcode.
• The country code for this installation. Enter help to see a list or refer to the Cisco Wireless LAN
Controller Configuration Guide for country code information. This guide is available at
cisco.com.
Page 9

9
• Status of the 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g networks, either enabled or disabled.
• Status of radio resource management (RRM), either enabled or disabled.
Choosing a Physical Location
You can install the controller almost anywhere, but it is more secure and reliable if you install it in a
secure equipment room or wiring closet. For maximum reliability, mount the controller while
following these guidelines:
• Make sure you can reach the controller and all cables attached to it.
• Make sure that water or excessive moisture cannot get into the controller.
• Make sure that airflow through the controller is not obstructed. Leave at least 4 in. (10 cm) clear
on both sides of the controller.
• Verify that the ambient temperature remains between 32 to 104° F (0 to 40° C).
• Make sure that the controller is within 328 ft. (100 m) of equipment connected to the
10/100BASE-T ports.
• Make sure that the power cord can reach a 100 to 240 VAC grounded electrical outlet.
Connecting the Controller’s Console Port
Caution Do not connect a Power over Ethernet (PoE) cable to the console port. Doing so will
damage the controller.
Before you can configure the controller for basic operations, you need to connect it to a PC that uses
a VT-100 terminal emulator (such as HyperTerminal, ProComm, Minicom, or Tip). Follow these steps
to connect the PC to the controller’s console port:
Step 1 Plug the RJ-45 connector on a null-modem serial cable into the controller’s console port and
the other end of the cable into the PC’s serial port.
Step 2 Start the PC’s terminal emulation program.
Page 10

10
Step 3 Configure the terminal emulation program for the following parameters:
• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• No flow control
• 1 stop bit
• No parity
Running the Bootup Script and Power-On Self Test
When you plug the controller into an AC power source, the bootup script initializes the system, verifies
the hardware configuration, loads its microcode into memory, verifies its operating system software
load, and initializes itself with its stored configurations. Before performing this test, you should have
connected your PC to the controller’s CLI console as described in the “Connecting the Controller’s
Console Port” section on page 9. Follow these steps to run the bootup script and conduct the power-on
self test (POST).
Step 1 Plug the external power supply into the Power jack on the back of the controller.
Step 2 Plug a country-specific power cord into the external power supply, then plug the other end
into a grounded 100–240 VAC, 50/60 Hz electrical outlet.
Note If you wish to run a previous release of the controller code, press Esc when the boot
loader prompt appears. The Bootloader Options menu appears.
Note When the controller receives power, the green front panel Power LED lights. If the
Power LED does not light, make sure that the electrical outlet is supplying power and
that the power connections to the controller are correct.
Page 11

11
Step 3 Observe the bootup using the CLI screen.
The bootup script displays operating system software initialization (code download and POST
verification) and basic configuration as shown in the following bootup display example:
CISCO SYSTEMS
Embedded BIOS Version 1.0(12)6 08/21/06 17:26:53.43
Low Memory: 632 KB
High Memory: 251 MB
PCI Device Table.
Bus Dev Func VendID DevID Class Irq
00 01 00 1022 2080 Host Bridge
00 01 02 1022 2082 Chipset En/Decrypt 11
00 0C 00 1148 4320 Ethernet 11
00 0D 00 177D 0003 Network En/Decrypt 10
00 0F 00 1022 2090 ISA Bridge
00 0F 02 1022 2092 IDE Controller
00 0F 03 1022 2093 Audio 10
00 0F 04 1022 2094 Serial Bus 9
00 0F 05 1022 2095 Serial Bus 9
Evaluating BIOS Options ...
Launch BIOS Extension to setup ROMMON
Cisco Systems ROMMON Version (1.0(12)7) #2: Fri Oct 13 10:52:36 MDT 2006
Platform AIR-WLC2106-K9
Launching BootLoader...
Cisco Bootloader (Version 4.0.197.0)
.o88b. d888888b .d8888. .o88b. .d88b.
d8P Y8 `88' 88' YP d8P Y8 .8P Y8.
8P 88 `8bo. 8P 88 88
8b 88 `Y8b. 8b 88 88
Y8b d8 .88. db 8D Y8b d8 `8b d8'
`Y88P' Y888888P `8888Y' `Y88P' `Y88P'
Booting Primary Image...
Press <ESC> now for additional boot options...
Step 4 If desired, press Break or Ctrl-R to interrupt the boot process and access the rommon prompt
or or press Space to stop the countdown timer and boot immediately.
Page 12

12
Step 5 Continue booting the controller or press Esc to access the following menu:
1. Run primary image (active)
2. Run backup image (Version x.x.x.x)
3. Manual upgrade primary image
4. Change active boot image
5. Clear configuration
Please enter your choice:
If you did not press Esc, the boot process continues and takes two to three minutes. Do not
reboot the controller until the user login prompt appears.
Detecting hardware . . . .
Cisco is a trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc.
Software Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco AireOS Version 4.0.197.0
Initializing OS Services: ok
Initializing Serial Services: ok
Initializing Network Services: ok
Starting ARP Services: ok
Starting Trap Manager: ok
Starting Network Interface Management Services: ok
Starting System Services: ok
Starting Fast Path Hardware Acceleration: ok
Starting Switching Services: ok
Starting QoS Services: ok
Starting FIPS Features: Not enabled
Starting Policy Manager: ok
Starting Data Transport Link Layer: ok
Starting Access Control List Services: ok
Starting System Interfaces: ok
Starting Management Frame Protection: ok
Starting LWAPP: ok
Starting Crypto Accelerator: Not Present
Starting Certificate Database: ok
Starting VPN Services: ok
Starting Security Services: ok
Starting Policy Manager: ok
Starting Authentication Engine: ok
Starting Mobility Management: ok
Starting Virtual AP Services: ok
Starting AireWave Director: ok
Starting Network Time Services: ok
Starting Cisco Discovery Protocol: ok
Starting Broadcast Services: ok
Starting Power Over Ethernet Services: ok
Page 13

13
Starting Logging Services: ok
Starting DHCP Server: ok
Starting IDS Signature Manager: ok
Starting RFID Tag Tracking: ok
starting TSM: ok
Starting CIDS Services: ok
Starting Ethernet-over-IP: ok
Starting Management Services:
Web Server: ok
CLI: ok
Secure Web: ok
Step 6 If the controller passes the POST, the bootup script runs the Startup Wizard, which prompts
you for basic configuration information.
Welcome to the Cisco Wizard Configuration Tool
Use the '-' character to backup
System Name [Cisco_bc:d0:40]:
Note The startup wizard runs the first time that you power up the controller. The second
time you power it up, the controller prompts you for a login ID and password.
Using the Startup Wizard
Before you can use the startup wizard, you must obtain the information discussed in the “Required
Tools and Information” section on page 7. Table 1 contains startup wizard information you can use
to configure your controller for basic operation.
Note The available options appear in brackets after each configuration parameter. The default value
appears in all uppercase letters.
Note If you enter an incorrect response, the controller provides you with an appropriate error
message such as invalid response, and returns to the wizard prompt.
Page 14

14
Note Press the hyphen key if you need to return to the previous command line.
Table 1 Startup Wizard Information
Wizard Setting Action
System Name Enter the system name, which is the name you
want to assign to the controller. You can enter up
to 32 ASCII characters.
Administrative user name Enter the administrative username and password
to be assigned to this controller. You can enter up
to 24 ASCII characters for each.
The default administrative username and
password are both admin and admin.
Administrative user password
Management Interface IP Address Enter the IP address of the management interface.
The management interface is the default interface
for in-band management of the controller and
connectivity to enterprise services such as AAA
servers.
You can access the controller’s GUI interface
using this address.
Management Interface Netmask Enter the IP address of the management interface
netmask.
Management Interface Default Router Enter the IP address of the default router.
Management Interface VLAN Identifier Enter the VLAN identifier of the management
interface (a valid VLAN identifier or 0 for an
untagged VLAN).
The VLAN identifier should be set to match the
switch interface configuration.
Management Interface Port Number Enter the port number of the access point
manager interface.
Management Interface DHCP Server IP Address Enter the management interface DHCP server IP
address.
Page 15
15
AP Manager Interface IP Address Enter the IP address of the access point manager
interface.
The AP manager interface manages all Layer 3
communications between the controller and
lightweight access points after the access points
have joined the controller.
Virtual Gateway IP Address Enter the IP address of the controller’s virtual
interface. You should enter a fictitious,
unassigned IP address, such as 1.1.1.1.
The virtual interface is used to support mobility
management, DHCP relay, and embedded Layer
3 security such as guest web authentication and
VPN termination. All controllers within a
mobility group must be configured with the same
virtual interface IP address.
Mobility/RF Group Name If desired, enter the name of the mobility
group/RF group to which you want the controller
to belong.
Although the name that you enter here is assigned
to both the mobility group and the RF group,
these groups are not identical. Both groups define
clusters of controllers, but they have different
purposes. All of the controllers in an RF group
are usually also in the same mobility group and
vice versa. However, a mobility group facilitates
scalable, system-wide mobility and controller
redundancy while an RF group facilitates
scalable, system-wide dynamic RF management.
Network Name (SSID) Enter the network name, or service set identifier
(SSID). This is the default SSID that the access
points use when they join a controller.
Allow Static IP Addresses Enter YES to allow clients to assign their own IP
address or no to make clients request an IP
address from a DHCP server. The default setting
is YES.
Table 1 Startup Wizard Information (continued)
Wizard Setting Action
Page 16

16
The controller saves your configuration, reboots, and prompts you to log in.
Logging into the Controller
Follow these steps to log into the controller.
Step 1 Enter a valid username and password to log into the controller CLI.
Note The administrative username and password you created in the startup wizard are case
sensitive.
Configure a RADIUS Server Now? [YES] [no] If you select YES, you are prompted to enter the
following:
• RADIUS server IP address
• RADIUS server port (default port is 1812)
• RADIUS server secret
If you select no, the following message appears:
Warning! The default WLAN security policy
requires a RADIUS server. Please see
documentation for more details.
Enter Country Code Enter the two letter country code. The default
country code is the United States (US). Enter help
to see a list of countries.
Enable 802.11b Network Choose YES to enable or no to disable the
802.11b radio network. The default is YES.
Enable 802.11a Network Choose YES to enable or no to disable the
802.11a radio network. The default is YES.
Enable 802.11g Network Choose YES to enable or no disable the 802.11g
radio network. The default is YES.
Enable Auto-RF Choose YES to enable or no to disable radio
resource management. The default is YES.
Table 1 Startup Wizard Information (continued)
Wizard Setting Action
Page 17

17
Step 2 The CLI displays the root level system prompt:
#(system prompt)>
The system prompt can be any alphanumeric string up to 31 characters. You can change it by
entering the config prompt command. For example, to change the system prompt to Cisco
2112, enter config prompt “Cisco 2112” and press Enter. Make sure you enter the new
prompt using double quotation marks.
Note The CLI automatically logs out without saving any changes after 5 minutes of
inactivity. You can set the automatic logout from 0 (never log out) to 160 minutes
using the config serial timeout command.
3 Connecting the Network
Figure 4 shows the connection from the network (802.11 distribution system) to the controller. The
connection uses 10/100BASE-T Ethernet (RJ-45 physical port, UTP, Category-5 or higher cable).
Always use Category-5, Category-5e, Category-6, or Category-7 Ethernet cables to connect the office
network equipment to the controller.
Figure 4 External Network Equipment Connection to the Controller
135753
Network
Office
network
Firewall
Connection to
main office
10/100BASE-T
MDI cable
CLI console
Cisco Access Points
10/100BASE-T
MDI cable
Page 18

18
Note If the link does not activate, check the cable. When you are connecting to a hub or a switch,
use a straight-through cable.
Connecting Access Points
After you have configured the controller, use Category-5, Category-5e, Category-6, or Category-7
Ethernet cables to connect up to 6, 12, or 25 Cisco lightweight access points (on Cisco 2106, 2112, or
2125 Wireless LAN Controller) to the network (distribution system) as shown in Figure 5. The
controller has an auto MDI feature, so you can use an MDI-X or MDI cable (crossover or
straight-through) to make the connections.
As soon as the controller is operational, the controller is available to connect access that are scanning
for a controller. When it detects an access point, it records the access point MAC address in its
database. The controller radio resource management (RRM) feature automatically configures the
access point to start transmitting and allowing clients to associate.
You have prepared the controller for basic operation. Refer to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
Configuration Guide for information on configuring the controller to meet the specific needs of your
wireless network.
Page 19

19
Figure 5 Access Points Connected to a Controller
Checking the Controller LEDs
If your controller is not working properly, check the LEDs on the front panel of the unit. You can use
the LED indications to quickly assess the unit’s status. See Figure 2 on page 5 for a description of the
front panel LEDs.
The installation is complete. Refer to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide for
more information about configuring your controller. The guide is available on cisco.com.
Using the Reset Button
The Reset button on the controller’s back panel becomes active after the controller boots. Follow these
steps to reset the controller using the Reset button:
Step 1 Connect a PC to the controller console point.
Step 2 Press and hold the Reset button for at least 3 seconds using a pointed object, such as a ball
point pen, pencil, or paper clip.
135756
10/100BASE-T
MDI cables
10/100BASE-T
MDI cable
Cisco Access Points
Network
Cisco 2106 wireless
LAN controller
Page 20

20
Step 3 After the controller reboots, enter your username and password at the prompts.
If you have configured the controller, it reboots and loads the configuration. If you have not configured
the controller, the configuration wizard appears.
4 Obtaining Documentation and Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new
and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS)
feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds
are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
Page 21

21
5 Translated Warnings
Statement 1071—Warning Definition
Warning
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause
bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards
involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for
preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each
warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that
accompanied this device.
Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Waarschuwing
BELANGRIJKE VEILIGHEIDSINSTRUCTIES
Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die
lichamelijk letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat
werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij elektrische schakelingen
betrokken risico's en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van de standaard praktijken
om ongelukken te voorkomen. Gebruik het nummer van de verklaring
onderaan de waarschuwing als u een vertaling van de waarschuwing die bij
het apparaat wordt geleverd, wilt raadplegen.
BEWAAR DEZE INSTRUCTIES
Varoitus
TÄRKEITÄ TURVALLISUUSOHJEITA
Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Tilanne voi aiheuttaa ruumiillisia
vammoja. Ennen kuin käsittelet laitteistoa, huomioi sähköpiirien
käsittelemiseen liittyvät riskit ja tutustu onnettomuuksien yleisiin
ehkäisytapoihin. Turvallisuusvaroitusten käännökset löytyvät laitteen
mukana toimitettujen käännettyjen turvallisuusvaroitusten joukosta
varoitusten lopussa näkyvien lausuntonumeroiden avulla.
SÄILYTÄ NÄMÄ OHJEET
Page 22

22
Attention
IMPORTANTES INFORMATIONS DE SÉCURITÉ
Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une
situation pouvant entraîner des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant
de travailler sur un équipement, soyez conscient des dangers liés aux circuits
électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment utilisées
pour éviter les accidents. Pour prendre connaissance des traductions des
avertissements figurant dans les consignes de sécurité traduites qui
accompagnent cet appareil, référez-vous au numéro de l'instruction situé à la
fin de chaque avertissement.
CONSERVEZ CES INFORMATIONS
Warnung
WICHTIGE SICHERHEITSHINWEISE
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die
zu Verletzungen führen kann. Machen Sie sich vor der Arbeit mit Geräten mit
den Gefahren elektrischer Schaltungen und den üblichen Verfahren zur
Vorbeugung vor Unfällen vertraut. Suchen Sie mit der am Ende jeder Warnung
angegebenen Anweisungsnummer nach der jeweiligen Übersetzung in den
übersetzten Sicherheitshinweisen, die zusammen mit diesem Gerät
ausgeliefert wurden.
BEWAHREN SIE DIESE HINWEISE GUT AUF.
Avvertenza
IMPORTANTI ISTRUZIONI SULLA SICUREZZA
Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione potrebbe
causare infortuni alle persone. Prima di intervenire su qualsiasi
apparecchiatura, occorre essere al corrente dei pericoli relativi ai circuiti
elettrici e conoscere le procedure standard per la prevenzione di incidenti.
Utilizzare il numero di istruzione presente alla fine di ciascuna avvertenza per
individuare le traduzioni delle avvertenze riportate in questo documento.
CONSERVARE QUESTE ISTRUZIONI
Page 23

23
Advarsel
VIKTIGE SIKKERHETSINSTRUKSJONER
Dette advarselssymbolet betyr fare. Du er i en situasjon som kan føre til skade
på person. Før du begynner å arbeide med noe av utstyret, må du være
oppmerksom på farene forbundet med elektriske kretser, og kjenne til
standardprosedyrer for å forhindre ulykker. Bruk nummeret i slutten av hver
advarsel for å finne oversettelsen i de oversatte sikkerhetsadvarslene som
fulgte med denne enheten.
TA VARE PÅ DISSE INSTRUKSJONENE
Aviso
INSTRUÇÕES IMPORTANTES DE SEGURANÇA
Este símbolo de aviso significa perigo. Você está em uma situação que poderá
ser causadora de lesões corporais. Antes de iniciar a utilização de qualquer
equipamento, tenha conhecimento dos perigos envolvidos no manuseio de
circuitos elétricos e familiarize-se com as práticas habituais de prevenção de
acidentes. Utilize o número da instrução fornecido ao final de cada aviso para
localizar sua tradução nos avisos de segurança traduzidos que acompanham
este dispositivo.
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUÇÕES
¡Advertencia!
INSTRUCCIONES IMPORTANTES DE SEGURIDAD
Este símbolo de aviso indica peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física.
Antes de manipular cualquier equipo, considere los riesgos de la corriente
eléctrica y familiarícese con los procedimientos estándar de prevención de
accidentes. Al final de cada advertencia encontrará el número que le ayudará
a encontrar el texto traducido en el apartado de traducciones que acompaña
a este dispositivo.
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES
Page 24

24
Varning!
VIKTIGA SÄKERHETSANVISNINGAR
Denna varningssignal signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan
leda till personskada. Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara
medveten om farorna med elkretsar och känna till vanliga förfaranden för att
förebygga olyckor. Använd det nummer som finns i slutet av varje varning för
att hitta dess översättning i de översatta säkerhetsvarningar som medföljer
denna anordning.
SPARA DESSA ANVISNINGAR
Page 25

25
Page 26

26
Page 27

27
Page 28

28
Page 29

29
Page 30

30
Statement 1015—Battery Handling
Warning
There is the danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace
the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s
instructions.
Statement 1015
Waarschuwing
Er is ontploffingsgevaar als de batterij verkeerd vervangen wordt. Vervang de
batterij slechts met hetzelfde of een equivalent type dat door de fabrikant
aanbevolen is. Gebruikte batterijen dienen overeenkomstig
fabrieksvoorschriften weggeworpen te worden.
Varoitus
Räjähdyksen vaara, jos akku on vaihdettu väärään akkuun. Käytä
vaihtamiseen ainoastaan saman- tai vastaavantyyppistä akkua, joka on
valmistajan suosittelema. Hävitä käytetyt akut valmistajan ohjeiden mukaan.
Attention
Danger d'explosion si la pile n'est pas remplacée correctement. Ne la
remplacer que par une pile de type semblable ou équivalent, recommandée
par le fabricant. Jeter les piles usagées conformément aux instructions du
fabricant.
Warnung
Bei Einsetzen einer falschen Batterie besteht Explosionsgefahr. Ersetzen Sie
die Batterie nur durch den gleichen oder vom Hersteller empfohlenen
Batterietyp. Entsorgen Sie die benutzten Batterien nach den Anweisungen des
Herstellers.
Avvertenza
Pericolo di esplosione se la batteria non è installata correttamente. Sostituire
solo con una di tipo uguale o equivalente, consigliata dal produttore.
Eliminare le batterie usate secondo le istruzioni del produttore.
Advarsel
Det kan være fare for eksplosjon hvis batteriet skiftes på feil måte. Skift kun
med samme eller tilsvarende type som er anbefalt av produsenten. Kasser
brukte batterier i henhold til produsentens instruksjoner.
Aviso
Existe perigo de explosão se a bateria for substituída incorrectamente.
Substitua a bateria por uma bateria igual ou de um tipo equivalente
recomendado pelo fabricante. Destrua as baterias usadas conforme as
instruções do fabricante.
Page 31

31
¡Advertencia!
Existe peligro de explosión si la batería se reemplaza de manera incorrecta.
Reemplazar la batería exclusivamente con el mismo tipo o el equivalente
recomendado por el fabricante. Desechar las baterías gastadas según las
instrucciones del fabricante.
Varning!
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Ersätt endast batteriet med samma
batterityp som rekommenderas av tillverkaren eller motsvarande. Följ
tillverkarens anvisningar vid kassering av använda batterier.
Page 32

32
Statement 1024—Ground Conductor
Warning
This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or
operate the equipment in the absence of a suitably installed ground conductor.
Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you
are uncertain that suitable grounding is available.
Statement 1024
Waarschuwing
Deze apparatuur dient geaard te zijn. De aardingsleiding mag nooit buiten
werking worden gesteld en de apparatuur mag nooit bediend worden zonder
dat er een op de juiste wijze geïnstalleerde aardingsleiding aanwezig is.
Neem contact op met de bevoegde instantie voor elektrische inspecties of met
een elektricien als u er niet zeker van bent dat er voor passende aarding
gezorgd is.
Varoitus
Laitteiden on oltava maadoitettuja. Älä koskaan ohita maajohdinta tai käytä
laitteita ilman oikein asennettua maajohdinta. Ota yhteys
sähkötarkastusviranomaiseen tai sähköasentajaan, jos olet epävarma
maadoituksen sopivuudesta.
Attention
Cet équipement doit être mis à la masse. Ne jamais rendre inopérant le
conducteur de masse ni utiliser l'équipement sans un conducteur de masse
adéquatement installé. En cas de doute sur la mise à la masse appropriée
disponible, s'adresser à l'organisme responsable de la sécurité électrique ou
à un électricien.
Warnung
Dieses Gerät muss geerdet sein. Auf keinen Fall den Erdungsleiter unwirksam
machen oder das Gerät ohne einen sachgerecht installierten Erdungsleiter
verwenden. Wenn Sie sich nicht sicher sind, ob eine sachgerechte Erdung
vorhanden ist, wenden Sie sich an die zuständige Inspektionsbehörde oder
einen Elektriker.
Avvertenza
Questa apparecchiatura deve essere dotata di messa a terra. Non escludere
mai il conduttore di protezione né usare l'apparecchiatura in assenza di un
conduttore di protezione installato in modo corretto. Se non si è certi della
disponibilità di un adeguato collegamento di messa a terra, richiedere un
controllo elettrico presso le autorità competenti o rivolgersi a un elettricista.
Page 33

33
Advarsel
Dette utstyret må jordes. Omgå aldri jordingslederen og bruk aldri utstyret
uten riktig montert jordingsleder. Ta kontakt med fagfolk innen elektrisk
inspeksjon eller med en elektriker hvis du er usikker på om det finnes
velegnet jordning.
Aviso
Este equipamento deve ser aterrado. Nunca anule o fio terra nem opere o
equipamento sem um aterramento adequadamente instalado. Em caso de
dúvida com relação ao sistema de aterramento disponível, entre em contato
com os serviços locais de inspeção elétrica ou um eletricista qualificado.
¡Advertencia!
Este equipo debe estar conectado a tierra. No inhabilite el conductor de tierra
ni haga funcionar el equipo si no hay un conductor de tierra instalado
correctamente. Póngase en contacto con la autoridad correspondiente de
inspección eléctrica o con un electricista si no está seguro de que haya una
conexión a tierra adecuada.
Varning!
Denna utrustning måste jordas. Koppla aldrig från jordledningen och använd
aldrig utrustningen utan en på lämpligt sätt installerad jordledning. Om det
föreligger osäkerhet huruvida lämplig jordning finns skall elektrisk
besiktningsauktoritet eller elektriker kontaktas.
Page 34

34
Page 35

35
Statement 1040—Product Disposal
Warning
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national
laws and regulations.
Statement 1040
Waarschuwing
Het uiteindelijke wegruimen van dit product dient te geschieden in
overeenstemming met alle nationale wetten en reglementen.
Varoitus
Tämä tuote on hävitettävä kansallisten lakien ja määräysten mukaisesti.
Attention
La mise au rebut ou le recyclage de ce produit sont généralement soumis à des
lois et/ou directives de respect de l'environnement. Renseignez-vous auprès
de l'organisme compétent.
Warnung
Die Entsorgung dieses Produkts sollte gemäß allen Bestimmungen und
Gesetzen des Landes erfolgen.
Page 36

36
Avvertenza
Lo smaltimento di questo prodotto deve essere eseguito secondo le leggi e
regolazioni locali.
Advarsel
Endelig kassering av dette produktet skal være i henhold til alle relevante
nasjonale lover og bestemmelser.
Aviso
Deitar fora este produto em conformidade com todas as leis e regulamentos
nacionais.
¡Advertencia!
Al deshacerse por completo de este producto debe seguir todas las leyes y
reglamentos nacionales.
Varning!
Vid deponering hanteras produkten enligt gällande lagar och bestämmelser.
Page 37

37
Statement 371—Power Cable and AC Adapter
Page 38

38
Statement 157—VCCI Compliance for Class B Equipment
Warning
This is a Class B product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control
Council for Interference from Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this
is used near a radio or television receiver in a domestic environment, it may
cause radio interference. Install and use the equipment according to the
instruction manual.
Page 39

39
Page 40

40
Page 41

41
Page 42

42
Page 43

43
Page 44

44
Page 45

45
Page 46

46
Page 47

47
Page 48

Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
European Headquarters
Cisco Systems International BV
Haarlerbergpark
Haarlerbergweg 13-19
1101 CH Amsterdam
The Netherlands
www-europe.cisco.com
Tel: 31 0 20 357 1000
Fax: 31 0 20 357 1100
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-7660
Fax: 408 527-0883
Asia Pacific Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
168 Robinson Road
#28-01 Capital Tower
Singapore 068912
www.cisco.com
Tel: +65 6317 7777
Fax: +65 6317 7799
Cisco Systems has more than 200 offices in the following countries. Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers are listed on the
Cisco Website at www.cisco.com/go/offices
Argentina • Australia • Austria • Belgium • Brazil • Bulgaria • Canada • Chile • China PRC • Colombia • Costa Rica • Croatia • Cyprus • Czech Republic • Denmark • Dubai, UAE
Finland • France • Germany • Greece • Hong Kong SAR • Hungary • India • Indonesia • Ireland • Israel • Italy • Japan • Korea • Luxembourg • Malaysia • Mexico
The Netherlands • New Zealand • Norway • Peru • Philippines • Poland • Portugal • Puerto Rico • Romania • Russia • Saudi Arabia • Scotland • Singapore
Slovakia • Slovenia • South Africa • Spain • Sweden • Switzerland • Taiwan • Thailand • Turkey • Ukraine • United Kingdom • United States • Venezuela • Vietnam • Zimbabwe
CCCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco StadiumVision, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and
Learn is a service mark; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the
Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation,
Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQ
Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MGX, Networkers, Networking
Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your
Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0803R)
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Printed in the USA on recycled paper containing 10% postconsumer waste.
78-17875-04
DOC-7817875=
 Loading...
Loading...