Page 1

CHA PTER
Configuring the Client Adapter
This chapter explains how to set the configuration parameters for a specific profile.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
• Overview, page 5-2
• Setting System Parameters, page 5-3
• Setting RF Network Parameters, page 5-7
• Setting Advanced Infrastructure Parameters, page 5-14
• Setting Advanced Ad Hoc Parameters, page 5-18
• Setting Network Security Parameters, page 5-21
5
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-1
Page 2

Overview
Overview
Note If you do not change any of the configuration parameters, the default values are used.
Note If you are planning to set parameters on more than one of the Properties screens, wait until you are
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
When you choose to create a new profile or edit an existing profile on the Profile Manager screen, the
Properties screens appear with the name of your profile in parentheses. These screens enable you to set
the configuration parameters for that profile.
finished with all of the screens before clicking OK. When you click OK, you are returned to the Profile
Manager screen.
Each of the Properties screens (listed below) contains parameters that affect a specific aspect of the client
adapter:
• System Parameters—Prepares the client adapter for use in a wireless network
• RF Network—Controls how the client adapter transmits and receives data
• Advanced (Infrastructure)—Controls how the client adapter operates within an infrastructure
network
• Advanced (Ad Hoc)—Controls how the client adapter operates within an ad hoc (peer-to-peer)
network
• Network Security—Controls how a client adapter associates to an access point, authenticates to the
wireless network, and encrypts and decrypts data
Table 5-1 enables you to quickly locate the instructions for setting each Properties screen’s parameters.
Table 5-1 Locating Configuration Instructions
Parameter Category Page Number
System page 5-3
RF network page 5-7
Advanced infrastructure page 5-14
Advanced ad hoc page 5-18
Network security page 5-21
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-2
OL-1394-08
Page 3

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Setting System Parameters
The System Parameters screen (see Figure 5-1) enables you to set parameters that prepare the client
adapter for use in a wireless network. This screen appears after you create and save a new profile or click
Edit on the Profile Manager screen.
Figure 5-1 System Parameters Screen
Setting System Parameters
Table 5-2 lists and describes the client adapter’s system parameters. Follow the instructions in the table
to change any parameters.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-3
Page 4

Setting System Parameters
Table 5-2 System Parameters
Parameter Description
Client Name A logical name for your workstation. It allows an administrator to
SSID1 The service set identifier (SSID) identifies the specific wireless
SSID2 An optional SSID that identifies a second distinct network and enables
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
determine which devices are connected to the access point without
having to memorize every MAC address. This name is included in the
access point’s list of connected devices.
Range: You can key in up to 16 ASCII characters
Default: A blank field
Note Each computer on the network should have a unique client
name.
network that you want to access.
Range: You can key in up to 32 ASCII characters (case sensitive)
Default: A blank field
Note If you leave this parameter blank, your client adapter can
associate to any access point on the network that is configured
to allow broadcast SSIDs (see the AP Radio Hardware page in
the access point management system). If the access point with
which the client adapter is to communicate is not configured to
allow broadcast SSIDs, the value of this parameter must match
the SSID of the access point. Otherwise, the client adapter is
unable to access the network.
you to roam to that network without having to reconfigure your client
adapter.
Range: You can key in up to 32 ASCII characters (case sensitive)
5-4
Default: A blank field
Note If a profile specifies more than one SSID, it cannot be included
in auto profile selection.
Note This field is unavailable for any profiles that are included in
auto profile selection.
SSID3 An optional SSID that identifies a third distinct network and enables
you to roam to that network without having to reconfigure your client
adapter.
Range: You can key in up to 32 ASCII characters (case sensitive)
Default: A blank field
Note If a profile specifies more than one SSID, it cannot be included
in auto profile selection.
Note This field is unavailable for any profiles that are included in
auto profile selection.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
Page 5

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-2 System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Power Save Mode Sets your client adapter to its optimum power consumption setting.
Options: CAM, Max PSP, or Fast PSP
Default: CAM (Constantly Awake Mode)
Power Save Mode Description
CAM (Constantly Awake
Mode)
Max PSP (Max Power
Savings)
Fast PSP (Power Save
Mode)
Keeps the client adapter powered up
continuously so there is little lag in
message response time.
Consumes the most power but offers the
highest throughput. Is recommended for
desktop computers and devices that use
AC power.
Causes the access point to buffer incoming
messages for the client adapter, which
wakes up periodically and polls the access
point to see if any buffered messages are
waiting for it. The adapter can request
each message and then go back to sleep.
Conserves the most power but offers the
lowest throughput. Is recommended for
devices for which power consumption is
the ultimate concern (such as small
battery-powered devices).
Note When you set Max PSP mode and
close ACU, the following message
appears the next time you open
ACU: “Maximum Power Save
Mode will be temporarily disabled
while you are running this
application.” While ACU is open,
Fast PSP mode is active. When
you close ACU, the card returns to
Max PSP mode.
Switches between PSP mode and CAM
mode, depending on network traffic. This
mode switches to CAM when retrieving a
large number of packets and switches back
to PSP after the packets have been
retrieved.
Is recommended when power consumption
is a concern but you need greater
throughput than that allowed by Max PSP.
Setting System Parameters
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-5
Page 6

Setting System Parameters
Table 5-2 System Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Network Type Specifies the type of network in which your client adapter is installed.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Options: Ad Hoc or Infrastructure
Default: Infrastructure
Network Type Description
Ad Hoc Often referred to as peer to peer. Indicates
that your wireless network consists of a
few wireless devices that are not
connected to a wired Ethernet network
through an access point. For example, an
ad hoc network can be set up between
computers in a conference room so users
can share information in a meeting.
Infrastructure Indicates that your wireless network is
connected to a wired Ethernet network
through an access point.
Go to the next section to set additional parameters or click OK to return to the Profile Manager screen.
On the Profile Manager screen, click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-6
OL-1394-08
Page 7

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Setting RF Network Parameters
The RF Network screen (see Figure 5-2) enables you to set parameters that control how and when the
client adapter transmits and receives data. To access this screen, choose the RF Network tab from the
Properties screens.
Figure 5-2 RF Network Screen
Setting RF Network Parameters
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-7
Page 8

Setting RF Network Parameters
Table 5-3 lists and describes the client adapter’s RF network parameters. Follow the instructions in the
table to change any parameters.
Table 5-3 RF Network Parameters
Parameter Description
Data Rate Specifies the rate at which your client adapter should transmit or
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
receive packets to or from access points (in infrastructure mode) or
other clients (in ad hoc mode).
Auto Rate Selection is recommended for infrastructure mode; setting a
specific data rate is recommended for ad hoc mode.
Options: Auto Rate Selection, 1 Mbps Only, 2 Mbps Only, 5.5 Mbps
Only, or 11 Mbps Only (2.4-GHz client adapters);
Auto Rate Selection, 6 Mbps Only, 9 Mbps Only, 12 Mbps
Only, 18 Mbps Only, 24 Mbps Only, 36 Mbps Only, 48 Mbps
Only, or 54 Mbps Only (5-GHz client adapters)
Default: Auto Rate Selection
Data Rate
2.4-GHz Client
Adapters
Auto Rate
Selection
5-GHz Client
Adapters
Auto Rate
Selection
Description
Uses the 11-Mbps (for 2.4-GHz client
adapters) or 54-Mbps (for 5-GHz client
adapters) data rate when possible but
drops to lower rates when necessary.
1 Mbps
Only
2 Mbps
Only and
5.5 Mbps
Only
11 Mbps
Only
Note Your client adapter’s data rate must be set to Auto Rate
6 Mbps
Only
9 Mbps
Only to 48
Mbps Only
54 Mbps
Only
Offers the greatest range but the lowest
throughput.
Progressively offers less range but greater
throughput than the 1 Mbps Only (for
2.4-GHz client adapters) or 6 Mbps Only
(for 5-GHz client adapters) option.
Offers the greatest throughput but the
lowest range.
Selection or must match the data rate of the access point (in
infrastructure mode) or the other clients (in ad hoc mode) with
which it is to communicate. Otherwise, your client adapter may
not be able to associate to them.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-8
OL-1394-08
Page 9

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-3 RF Network Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Use Short Radio Headers Checking this check box sets your client adapter to use short radio
World Mode Checking this check box enables the client adapter to adopt the
Setting RF Network Parameters
headers. However, the adapter can use short radio headers only if the
access point is also configured to support them and is using them. If any
clients associated to an access point are using long headers, then all
clients in that cell must also use long headers, even if both this client
and the access point have short radio headers enabled.
Short radio headers improve throughput performance; long radio
headers ensure compatibility with clients and access points that do not
support short radio headers.
Default: Checked
Note This parameter is available only for 2.4-GHz client adapters.
Note This parameter is referred to as Preambles on the access point
screens.
maximum transmit power level and the frequency range of the access
point to which it is associated, provided the access point is also
configured for world mode. This parameter is available only in
infrastructure mode and is designed for users who travel between
countries and want their client adapters to associate to access points in
different regulatory domains.
Default: Unchecked
Scan For A Better Access
Point
Note This parameter is available only for 2.4-GHz client adapters.
Note When World Mode is enabled, the client adapter is limited to
the maximum transmit power level allowed by the country of
operation’s regulatory agency.
Checking this check box causes the client to look for a better access
point if the signal strength of its associated access point is less than the
specified value after the specified time and to switch associations if it
finds one.
Example: If the default values of 20 seconds and 50% are used, the
client begins monitoring the strength of the signal received
from its associated access point 20 seconds after becoming
associated. The monitoring continues once per second. If
the client detects a signal strength reading below 50%, it
scans for a better access point.
Range: 5 to 255 seconds; 0 to 75% signal strength
Defaults:Checked, 20 seconds, 50% signal strength
Note The ability to specify the time and signal strength is available
in ACU version 6.1 or later, which is included in Install Wizard
version 1.1 or later.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-9
Page 10

Setting RF Network Parameters
Table 5-3 RF Network Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Channel Specifies the frequency that your client adapter will use as the channel
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
for communications. These channels conform to the IEEE 802.11
Standard for your regulatory domain.
• In infrastructure mode, this parameter is set automatically and
cannot be changed. The client adapter listens to the entire
spectrum, selects the best access point to associate to, and uses the
same frequency as that access point.
• In ad hoc mode, the channel of the client adapter must be set to
match the channel used by the other clients in the wireless network.
If the client adapter does not find any other ad hoc adapters, this
parameter specifies the channel with which the adapter will start its
cell.
Range: Dependent on client adapter radio and regulatory domain
Example for 2.4-GHz client adapters:
1 to 11 (2412 to 2462 MHz) in North America
Example for 5-GHz client adapters:
36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60, and 64 (5180, 5200, 5220, 5240,
5260, 5280, 5300, and 5320 MHz) in North America
Default: Dependent on client adapter radio and regulatory domain
Example for 2.4-GHz client adapters:
6 (2437 MHz) in North America
Example for 5-GHz client adapters:
36 (5180 MHz) in North America
Note Refer to Appendix D for a list of channel identifiers, channel
center frequencies, and regulatory domains for each channel.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-10
OL-1394-08
Page 11

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-3 RF Network Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Transmit Power Defines the power level at which your client adapter transmits. This
Setting RF Network Parameters
value must not be higher than that allowed by your country’s regulatory
agency (FCC in the U.S., DOC in Canada, ETSI in Europe, MKK in
Japan, etc.).
Options: Dependent on the power table programmed into the client
adapter; see the table below
Default: The maximum power level programmed into the client
adapter and allowed by your country’s regulatory agency
Possible Power Levels Client Adapter Type
30 mW or 1 mW 340 series PC cards
30 mW, 15 mW, 5 mW, or
1 mW
100 mW, 50 mW, 30 mW,
20 mW, 5 mW, or 1 mW
20 mW, 10 mW, or 5 mW PC-Cardbus card
Note Reducing the transmit power level conserves battery power but
decreases radio range.
340 series LM cards and PCI cards
350 series client adapters
Note When World Mode is enabled, the client adapter is limited to
the maximum transmit power level allowed by the country of
operation’s regulatory agency.
Note If you are using an older version of a 340 or 350 series client
adapter, your power level options may be different than those
listed here.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-11
Page 12

Setting RF Network Parameters
Table 5-3 RF Network Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Clear Channel Assessment Specifies the method that determines whether the channel on which
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
your client adapter will operate is clear prior to the transmission of
data.
Options: Firmware Default (XXX), Carrier/Correlation (Car/Cor),
Energy Detect (ED), or ED or Car/Cor
Default: Firmware Default (XXX)
Method Description
Firmware Default (XXX) The Clear Channel Assessment (CCA)
mechanism will report that the channel is
busy based on the default value of the
client adapter’s firmware. The firmware’s
CCA default value is shown in
parentheses.
Note The CCA default value for PCM,
LMC, and PCI card firmware is
Car/Cor; the default value for mini
PCI card firmware is ED.
Carrier/Correlation
(Car/Cor)
Energy Detect (ED) The CCA mechanism will report that the
ED or Car/Cor The CCA mechanism will report that the
Note This parameter is available only for 2.4-GHz client adapters.
The CCA mechanism will report that the
channel is busy upon detection of a
direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS)
signal. This signal may be above or below
the ED threshold.
channel is busy upon detection of any
energy above the ED threshold.
channel is busy upon detection of a DSSS
signal or any energy above the ED
threshold.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-12
OL-1394-08
Page 13

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-3 RF Network Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Data Retries Defines the number of times a packet is resent if the initial transmission
Fragment Threshold Defines the threshold above which an RF data packet is split up or
Setting RF Network Parameters
is unsuccessful.
Range: 1 to 128
Default: 16 (2.4-GHz client adapters) or 32 (5-GHz client adapters)
Note If your network protocol performs its own retries, set this to a
smaller value than the default. This way notification of a “bad”
packet is sent up the protocol stack quickly so the application
can retransmit the packet if necessary.
fragmented. If one of those fragmented packets experiences
interference during transmission, only that specific packet would need
to be resent.
Throughput is generally lower for fragmented packets because the fixed
packet overhead consumes a higher portion of the RF bandwidth.
Range: 256 to 2312
Default: 2312
Go to the next section to set additional parameters or click OK to return to the Profile Manager screen.
On the Profile Manager screen, click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-13
Page 14

Setting Advanced Infrastructure Parameters
Setting Advanced Infrastructure Parameters
Note You can set advanced infrastructure parameters only if your client adapter has been set to
operate in an infrastructure network. See the Network Type parameter in Table 5-2.
The Advanced (Infrastructure) screen (see Figure 5-3) enables you to set parameters that control how the
client adapter operates within an infrastructure network. To access this screen, choose the Advanced
(Infrastructure) tab from the Properties screens.
Figure 5-3 Advanced (Infrastructure) Screen
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-14
OL-1394-08
Page 15

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-4 lists and describes the client adapter’s advanced infrastructure parameters. Follow the
instructions in the table to change any parameters.
Table 5-4 Advanced (Infrastructure) Parameters
Parameter Description
Antenna Mode (Receive) Specifies the antenna that your client adapter uses to receive data.
Setting Advanced Infrastructure Parameters
• PC card—The PC card’s integrated, permanently attached
antenna operates best when used in diversity mode. Diversity
mode allows the card to use the better signal from its two antenna
ports.
Options: Diversity (Both), Primary Antenna Only, Secondary
Antenna Only
Default: Diversity (Both)
• LM card—The LM card is shipped without an antenna; however,
an antenna can be connected through the card’s external
connector. If a snap-on antenna is used, diversity mode is
recommended. Otherwise, choose the mode that corresponds to
the antenna port to which the antenna is connected.
Options: Diversity (Both), Primary Antenna Only, Secondary
Antenna Only
Default: Diversity (Both)
• PCI card—The PCI card must use the Primary Antenna Only
option.
Default: Primary Antenna Only
• Mini PCI card—The mini PCI card, which can be used with one
or two antennas, operates best in diversity mode. Diversity mode
allows the card to use the better signal from its two antenna
connectors.
Options: Diversity (Both), Primary Antenna Only, Secondary
Antenna Only
Default: Diversity (Both)
Note This parameter is available only for 2.4-GHz client adapters.
Note The Primary Antenna Only and Secondary Antenna Only
options were formerly named Right Antenna Only and Left
Antenna Only, respectively.
Antenna Mode (Transmit) Specifies the antenna that your client adapter uses to transmit data.
See the Antenna Mode (Receive) parameter above for information on
the options available for your client adapter.
Note This parameter is available only for 2.4-GHz client adapters.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-15
Page 16

Setting Advanced Infrastructure Parameters
Table 5-4 Advanced (Infrastructure) Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Specified Access Point 1- 4 Specifies the MAC addresses of up to four preferred access points
RTS Threshold Specifies the size of the data packet that the low-level RF protocol
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
with which the client adapter can associate. If the specified access
points are not found or the client adapter roams out of range, the
adapter may associate to another access point.
You can enter the MAC addresses of the access points in the edit boxes
or choose not to specify access points by leaving the boxes blank.
Default: Blank fields
Note This parameter should be used only for access points that are
in repeater mode. For normal operation, leave these fields
blank because specifying an access point slows down the
roaming process.
issues to a request-to-send (RTS) packet.
Setting this parameter to a small value causes RTS packets to be sent
more often. When this occurs, more of the available bandwidth is
consumed and the throughput of other network packets is reduced, but
the system is able to recover faster from interference or collisions,
which may be caused from a high multipath environment
characterized by obstructions or metallic surfaces.
Range: 0 to 2312
Default: 2312
Note Refer to the IEEE 802.11 Standard for more information on
the RTS/CTS mechanism.
RTS Retry Limit Specifies the number of times the client adapter resends a
request-to-send (RTS) packet if it does not receive a clear-to-send
(CTS) packet from the previously sent RTS packet.
Setting this parameter to a large value decreases the available
bandwidth whenever interference is encountered but makes the system
more immune to interference and collisions, which may be caused
from a high multipath environment characterized by obstructions or
metallic surfaces.
Range: 1 to 128
Default: 16 (2.4-GHz client adapters) or 32 (5-GHz client adapters)
Note Refer to the IEEE 802.11 Standard for more information on
the RTS/CTS mechanism.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-16
OL-1394-08
Page 17

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-4 Advanced (Infrastructure) Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Enable Radio Management
Support
Setting Advanced Infrastructure Parameters
Checking this check box enables the access point to which the client
adapter is associated to control the use of radio management (RM),
provided RM is enabled on the access point. RM is a system-wide
feature that involves multiple infrastructure nodes. The RM feature on
the access point acts on radio measurement requests from other
network devices to instruct the access point and its associated clients
to perform required radio measurements and then report them.
Default: Checked
Note This parameter is available in Install Wizard version 1.2 or
later for 350 series cards and Install Wizard version 1.3 or
later for CB20A cards.
Note Access points must use Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)JA or later
to enable RM. Refer to the documentation for your access
point for instructions on enabling this feature.
Go to the next section to set additional parameters or click OK to return to the Profile Manager screen.
On the Profile Manager screen, click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-17
Page 18

Setting Advanced Ad Hoc Parameters
Setting Advanced Ad Hoc Parameters
Note You can set advanced ad hoc parameters only if your client adapter has been set to operate in an ad hoc
network. See the Network Type parameter in Tabl e 5-2.
The Advanced (Ad Hoc) screen (see Figure 5-4) enables you to set parameters that control how the client
adapter operates within an ad hoc network. To access this screen, choose the Advanced (Ad Hoc) tab
from the Properties screens.
Figure 5-4 Advanced (Ad Hoc) Screen
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-18
OL-1394-08
Page 19

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-5 lists and describes the client adapter’s advanced ad hoc parameters. Follow the instructions in
the table to change any parameters.
Table 5-5 Advanced (Ad Hoc) Parameters
Parameter Description
Antenna Mode (Receive) Specifies the antenna that your client adapter uses to receive data.
Setting Advanced Ad Hoc Parameters
• PC card—The PC card’s integrated, permanently attached
antenna operates best when used in diversity mode. Diversity
mode allows the card to use the better signal from its two antenna
ports.
Options: Diversity (Both), Primary Antenna Only, Secondary
Antenna Only
Default: Diversity (Both)
• LM card—The LM card is shipped without an antenna; however,
an antenna can be connected through the card’s external
connector. If a snap-on antenna is used, diversity mode is
recommended. Otherwise, choose the mode that corresponds to
the antenna port to which the antenna is connected.
Options: Diversity (Both), Primary Antenna Only, Secondary
Antenna Only
Default: Diversity (Both)
• PCI card—The PCI card must use the Primary Antenna Only
option.
Default: Primary Antenna Only
• Mini PCI card—The mini PCI card, which can be used with one
or two antennas, operates best in diversity mode. Diversity mode
allows the card to use the better signal from its two antenna
connectors.
Options: Diversity (Both), Primary Antenna Only, Secondary
Antenna Only
Default: Diversity (Both)
Note This parameter is available only for 2.4-GHz client adapters.
Note The Primary Antenna Only and Secondary Antenna Only
options were formerly named Right Antenna Only and Left
Antenna Only, respectively.
Antenna Mode (Transmit) Specifies the antenna that your client adapter uses to transmit data.
See the Antenna Mode (Receive) parameter above for information on
the options available for your client adapter.
Note This parameter is available only for 2.4-GHz client adapters.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-19
Page 20
Setting Advanced Ad Hoc Parameters
Table 5-5 Advanced (Ad Hoc) Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
RTS Threshold Specifies the size of the data packet that the low-level RF protocol
RTS Retry Limit Specifies the number of times the client adapter resends a
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
issues to a request-to-send (RTS) packet.
Setting this parameter to a small value causes RTS packets to be sent
more often. When this occurs, more of the available bandwidth is
consumed and the throughput of other network packets is reduced, but
the system is able to recover faster from interference or collisions,
which may be caused from a high multipath environment
characterized by obstructions or metallic surfaces.
Range: 0 to 2312
Default: 2312
Note Refer to the IEEE 802.11 Standard for more information on
the RTS/CTS mechanism.
request-to-send (RTS) packet if it does not receive a clear-to-send
(CTS) packet from the previously sent RTS packet.
Setting this parameter to a large value decreases the available
bandwidth whenever interference is encountered but makes the system
more immune to interference and collisions, which may be caused
from a high multipath environment characterized by obstructions or
metallic surfaces.
Range: 1 to 128
Default: 16 (2.4-GHz client adapters) or 32 (5-GHz client adapters)
Note Refer to the IEEE 802.11 Standard for more information on
the RTS/CTS mechanism.
Wake Duration (Kμs) Specifies the amount of time following a beacon that the client adapter
stays awake to receive announcement traffic indication message
(ATIM) packets, which are sent to the adapter to keep it awake until
the next beacon.
Refer to the Power Save Mode parameter in Table 5-2.
Range: 0 Kμs (in CAM mode); 5 to 60 Kμs (in Max PSP or Fast PSP
mode)
Default: 5 Kμs
Note If your client adapter is set to CAM mode, you must set the
wake duration to 0 Kμs. If your client adapter is set to Max PSP
or Fast PSP mode, you must set the wake duration to a minimum
of 5 Kμs.
Note Kμs is a unit of measurement in software terms. K = 1024,
μ = 10
-6
, and s = seconds, so Kμs = .001024 seconds, 1.024
milliseconds, or 1024 microseconds.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-20
OL-1394-08
Page 21

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-5 Advanced (Ad Hoc) Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Beacon Period (Kμs) Specifies the duration between beacon packets, which are used to help
clients find each other in ad hoc mode.
Range: 20 to 976 Kμs
Default: 100 Kμs
Go to the next section to set additional parameters or click OK to return to the Profile Manager screen.
On the Profile Manager screen, click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Setting Network Security Parameters
The Network Security screen (see Figure 5-5) enables you to set parameters that control how the client
adapter associates to an access point, authenticates to the wireless network, and encrypts and decrypts
data. To access this screen, choose the Network Security tab from the Properties screens.
Setting Network Security Parameters
Figure 5-5 Network Security Screen
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-21
Page 22

Setting Network Security Parameters
This screen is different from the other Properties screens in that it presents several security features, each
of which involves a number of steps. In addition, the security features themselves are complex and need
to be understood before they are implemented. Therefore, this section provides an overview of the
security features as well as procedures for using them.
However, before you determine the appropriate security settings for your client adapter, you must decide
how to set the Allow Association to Mixed Cells parameter, which appears at the bottom of the Network
Security screen and is not associated to any of the security features. See the “Setting the Allow
Association to Mixed Cells Parameter” section below.
Setting the Allow Association to Mixed Cells Parameter
The Allow Association to Mixed Cells parameter indicates whether the client adapter can associate to
an access point that allows both WEP and non-WEP associations. Follow these steps to set this
parameter.
Note This parameter is unavailable if the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) check box is checked.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 1 Perform one of the following:
• Check the Allow Association to Mixed Cells check box if the access point with which the client
adapter is to associate has WEP set to Optional and WEP is enabled on the client adapter. Otherwise,
the client is unable to establish a connection with the access point.
• Uncheck the Allow Association to Mixed Cells check box if the access point with which the client
adapter is to associate does not have WEP set to Optional. This is the default setting.
Note For security reasons, Cisco recommends that WEP-enabled and WEP-disabled clients not be
allowed in the same cell because broadcast packets are sent unencrypted, even to clients running
WEP.
Step 2 Perform one of the following:
• If you do not want to change any other parameters on the Network Security screen, click OK to
return to the Profile Manager screen; then click OK or Apply to save your changes
• If you want to change some of the other parameters on the Network Security screen, go to the next
section.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-22
OL-1394-08
Page 23

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Overview of Security Features
You can protect your data as it is transmitted through your wireless network by encrypting it through the
use of wired equivalent privacy (WEP) encryption keys. With WEP encryption, the transmitting device
encrypts each packet with a WEP key, and the receiving device uses that same key to decrypt each
packet.
The WEP keys used to encrypt and decrypt transmitted data can be statically associated with your
adapter or dynamically created as part of the EAP authentication process. The information in the “Static
WEP Keys” and “EAP (with Dynamic WEP Keys)” sections below can help you to decide which type
of WEP keys you want to use. Dynamic WEP keys with EAP offer a higher degree of security than static
WEP keys.
WEP keys, whether static or dynamic, are either 40 or 128 bits in length. 128-bit WEP keys offer a
greater level of security than 40-bit WEP keys.
Note Refer to the “Additional WEP Key Security Features” section on page 5-29 for information on three
security features that can make your WEP keys even more secure.
Setting Network Security Parameters
Static WEP Keys
Each device (or profile) within your wireless network can be assigned up to four static WEP keys. If a
device receives a packet that is not encrypted with the appropriate key (as the WEP keys of all devices
that are to communicate with each other must match), the device discards the packet and never delivers
it to the intended receiver.
Static WEP keys are write-only and temporary; therefore, they cannot be read back from the client
adapter, and they are lost when power to the adapter is removed or the Windows device is rebooted.
Although the keys are temporary, you do not need to re-enter them each time the client adapter is inserted
or the Windows device is rebooted. This is because the keys are stored (in an encrypted format for
security reasons) in the registry of the Windows device. When the driver loads and reads the client
adapter’s registry parameters, it also finds the static WEP keys, unencrypts them, and stores them in
volatile memory on the adapter.
The Network Security screen enables you to view the current WEP key settings for the client adapter and
then to assign new WEP keys or overwrite existing WEP keys as well as to enable or disable static WEP.
Refer to the “Using Static WEP” section on page 5-35 for instructions.
EAP (with Dynamic WEP Keys)
The new standard for wireless LAN security, as defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers (IEEE), is called 802.1X for 802.11, or simply 802.1X. An access point that supports 802.1X
and its protocol, Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP), acts as the interface between a wireless
client and an authentication server, such as a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)
server, to which the access point communicates over the wired network.
Three 802.1X authentication types can be selected in ACU for use with Windows operating systems:
• EAP-Cisco Wireless (or LEAP)—This authentication type is available for Windows 98, 98 SE, NT,
2000, Me, and XP, as well as non-Windows systems. Support for LEAP is provided not in the
Windows operating system but in your client adapter’s firmware and the Cisco software that
supports it. RADIUS servers that support LEAP include Cisco Secure ACS version 2.6 and later,
Cisco Access Registrar version 1.7 and later, and Funk Software’s Steel-Belted RADIUS version 3.0
and later.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-23
Page 24

Setting Network Security Parameters
LEAP is enabled or disabled for a specific profile through ACU, provided the LEAP security module
was selected during installation. After LEAP is enabled, a variety of configuration options are
available, including how and when a username and password are entered to begin the authentication
process.
The username and password are used by the client adapter to perform mutual authentication with the
RADIUS server through the access point. The username and password need to be re-entered each
time the client adapter is inserted or the Windows device is rebooted, unless you configure your
adapter to use saved LEAP credentials.
Note If the LEAP security module was not selected during installation, the LEAP option is
• EAP-FAST—This authentication type (Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling) is available
for 350 series and CB20A cards on computers running Windows 2000 or XP. EAP-FAST uses a
three-phased tunneled authentication process to provide advanced 802.1X EAP mutual
authentication.
–
Phase 0 enables the client to dynamically provision a protected access credentials (PAC) when
necessary. During this phase, a PAC is generated securely between the user and the network.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
unavailable in ACU. If you want to be able to enable and disable LEAP, you must run the
installation program again and choose LEAP.
–
Phase 1 uses the PAC to establish a mutually authenticated and secure tunnel between the client
and the RADIUS server. RADIUS servers that support EAP-FAST include Cisco Secure ACS
version 3.2.3 and later.
–
Phase 2 performs client authentication in the established tunnel.
EAP-FAST is enabled or disabled for a specific profile through ACU, provided the EAP-FAST
security module was selected during installation. After EAP-FAST is enabled, a variety of
configuration options are available, including how and when a username and password are entered
to begin the authentication process and whether automatic or manual PAC provisioning is used.
The client adapter uses the username, password, and PAC to perform mutual authentication with the
RADIUS server through the access point. The username and password need to be re-entered each
time the client adapter is inserted or the Windows device is rebooted, unless you configure your
adapter to use saved EAP-FAST credentials.
PACs are created by Cisco Secure ACS and are identified by an ID. The user obtains his or her own
copy of the PAC from the server, and the ID links the PAC to the profile created in ACU. When
manual PAC provisioning is enabled, the PAC file is manually copied from the server and imported
onto the client device. The following rules govern PAC storage:
–
In most cases PACs are provisioned and stored separately for each Windows logon user. These
per-user PACs are not viewable by other users.
–
If a profile is configured to use manual provisioning, each user must manually provision his or
her own PAC for that profile.
–
PAC files can be added or replaced using the import feature, but they cannot be removed or
exported.
–
For profiles configured with saved EAP-FAST usernames and passwords, the PACs are not
stored per user but in a global PAC area shared by all users. Global PACs are also enabled when
the No Network Connection Unless User Is Logged In check box is unchecked. These global
PACs can be imported and used by all users.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-24
OL-1394-08
Page 25

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Note PACs are also stored globally on computers that use the Novell Network login prompt
EAP-FAST authentication is designed to support the following user databases over a wireless LAN:
–
Cisco Secure ACS internal user database
–
Cisco Secure ACS ODBC user database
–
Windows NT/2000/2003 domain user database
–
LDAP user database
LDAP user databases (such as NDS) support only manual PAC provisioning while the other three
user databases support both automatic and manual PAC provisioning.
Note If the EAP-FAST security module was not selected during installation, the EAP-FAST
Setting Network Security Parameters
or any other third-party login application that does not share its credentials with the
EAP-FAST supplicant.
option is unavailable in ACU. If you want to be able to enable and disable EAP-FAST, you
must run the installation program again and choose EAP-FAST. EAP-FAST is supported in
Install Wizard version 1.3 and later.
• Host Based EAP—Choosing this option enables you to use any 802.1X authentication type for
which your operating system has support. For example, if your operating system uses the Microsoft
802.1X supplicant, it provides native support for EAP-TLS authentication and general support for
PEAP and EAP-SIM authentication.
Note To use EAP-TLS, PEAP, or EAP-SIM authentication, you must install the Microsoft 802.1X
supplicant, ACU, and the PEAP or EAP-SIM supplicant; configure your client adapter using
ACU; enable the authentication type in Windows; and enable Network-EAP on the access
point.
–
EAP-TLS—EAP-TLS is enabled or disabled through the operating system and uses a dynamic
session-based WEP key, which is derived from the client adapter and RADIUS server, to encrypt
data. Once enabled, a few configuration parameters must be set within the operating system.
RADIUS servers that support EAP-TLS authentication include Cisco Secure ACS version 3.0
or later and Cisco Access Registrar version 1.8 or later.
Note EAP-TLS requires the use of a certificate. Refer to Microsoft’s documentation for
information on downloading and installing the certificate.
–
Protected EAP (or PEAP)—PEAP authentication is designed to support One-Time Password
(OTP), Windows NT or 2000 domain, and LDAP user databases over a wireless LAN. It is based
on EAP-TLS authentication but uses a password or PIN instead of a client certificate for
authentication. PEAP is enabled or disabled through the operating system and uses a dynamic
session-based WEP key, which is derived from the client adapter and RADIUS server, to encrypt
data. If your network uses an OTP user database, PEAP requires you to enter either a hardware
token password or a software token PIN to start the EAP authentication process and gain access
to the network. If your network uses a Windows NT or 2000 domain user database or an LDAP
user database (such as NDS), PEAP requires you to enter your username, password, and domain
name in order to start the authentication process.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-25
Page 26

Setting Network Security Parameters
RADIUS servers that support PEAP authentication include Cisco Secure ACS version 3.1 or
later and Cisco Access Registrar version 3.5 or later.
Note Windows XP Service Pack 1 and the Microsoft 802.1X supplicant for Windows 2000
–
EAP-SIM—EAP-SIM authentication is designed for use in public wireless LANs and requires
clients equipped with PCSC-compliant smartcard readers. The EAP-SIM supplicant included in
the Install Wizard file supports only Gemplus SIM+ cards; however, an updated supplicant is
available that supports standard GSM-SIM cards as well as more recent versions of the
EAP-SIM protocol. The new supplicant is available for download from Cisco.com at the
following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/access-registrar-encrypted
Please note that the above requirements are necessary but not sufficient to successfully perform
EAP-SIM authentication. Typically, you are also required to enter into a service contract with
a WLAN service provider, who must support EAP-SIM authentication in its network. Also,
while your PCSC smartcard reader may be able to read standard GSM-SIM cards or chips,
EAP-SIM authentication usually requires your GSM cell phone account to be provisioned for
WLAN service by your service provider.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
include Microsoft’s PEAP supplicant, which supports a Windows username and
password only and does not interoperate with Cisco’s PEAP supplicant. To use Cisco’s
PEAP supplicant, install the Install Wizard file after Windows XP Service Pack 1 or the
Microsoft 802.1X supplicant for Windows 2000. Otherwise, Cisco’s PEAP supplicant
is overwritten by Microsoft’s PEAP supplicant.
EAP-SIM is enabled or disabled through the operating system and uses a dynamic session-based
WEP key, which is derived from the client adapter and RADIUS server, to encrypt data.
EAP-SIM requires you to enter a user verification code, or PIN, for communication with the
SIM card. You can choose to have the PIN stored in your computer or to be prompted to enter
it after a reboot or prior to every authentication attempt.
RADIUS servers that support EAP-SIM include Cisco Access Registrar version 3.0 or later.
Note Because EAP-TLS, PEAP, and EAP-SIM authentication are enabled in the operating system
and not in ACU, you cannot switch between these authentication types simply by switching
profiles in ACU. You can create a profile in ACU that uses host-based EAP, but you must
enable the specific authentication type in Windows (provided Windows uses the Microsoft
802.1X supplicant). In addition, Windows can be set for only one authentication type at a
time; therefore, if you have more than one profile in ACU that uses host-based EAP and you
want to use another authentication type, you must change authentication types in Windows
after switching profiles in ACU.
When you enable Network-EAP or EAP on your access point and configure your client adapter for
LEAP, EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS, PEAP, or EAP-SIM, authentication to the network occurs in the following
sequence:
1. The client associates to an access point and begins the authentication process.
Note The client does not gain full access to the network until authentication between the client
and the RADIUS server is successful.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-26
OL-1394-08
Page 27

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
2. Communicating through the access point, the client and RADIUS server complete the authentication
process, with the password (LEAP and PEAP), password and PAC (EAP-FAST), certificate
(EAP-TLS), or internal key stored on the SIM card and in the service provider’s Authentication
Center (EAP-SIM) being the shared secret for authentication. The password, PAC, or internal key is
never transmitted during the process.
3. If authentication is successful, the client and RADIUS server derive a dynamic, session-based WEP
key that is unique to the client.
4. The RADIUS server transmits the key to the access point using a secure channel on the wired LAN.
5. For the length of a session, or time period, the access point and the client use this key to encrypt or
decrypt all unicast packets (and broadcast packets if the access point is set up to do so) that travel
between them.
Refer to one of these sections for instructions on enabling EAP authentication:
• Enabling LEAP, page 5-38
• Enabling EAP-FAST, page 5-42
• Enabling Host-Based EAP, page 5-49
Setting Network Security Parameters
Note Refer to the IEEE 802.11 Standard for more information on 802.1X authentication and to the following
URL for additional information on RADIUS servers:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios120/12cgcr/secur_c/scprt2/scrad.htm
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a standards-based, interoperable security enhancement that greatly
increases the level of data protection and access control for existing and future wireless LAN systems.
It is derived from and will be compatible with the upcoming IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA leverages
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and Michael message integrity check (MIC) for data protection
and 802.1X for authenticated key management.
WPA supports two mutually exclusive key management types: WPA and WPA-Pre-shared key
(WPA-PSK). Using WPA key management, clients and the authentication server authenticate to each
other using an EAP authentication method, and the client and server generate a pairwise master key
(PMK). The server generates the PMK dynamically and passes it to the access point. Using WPA-PSK
key management, however, you configure a pre-shared key on both the client and the access point, and
that pre-shared key is used as the PMK.
Only 350 series and CB20A cards that are installed on computers running Windows 2000 or XP and
running LEAP, EAP-FAST, or host-based EAP authentication can be used with WPA. Support for WPA
is available in the software components included in Install Wizard version 1.2 or later. However, if you
want to use host-based EAP authentication with WPA, you must install additional software with WPA
support. The following WPA software is recommended for use with Cisco Aironet client adapters:
• Funk Odyssey Client supplicant version 2.2 (for Windows 2000)
• Windows XP Service Pack 1 and Microsoft support patch 815485 (for Windows XP)
Note Meetinghouse AEGIS Client supplicant version 2.1 or later is also supported for use with
Windows 2000 and XP; however, it was not tested with this client adapter software release.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-27
Page 28

Setting Network Security Parameters
The software components included in Install Wizard version 1.3 or later automatically support WPA
migration mode. WPA migration mode is an access point setting that enables both WPA and non-WPA
clients to associate to the access point using the same SSID.
Refer to one of these sections for instructions on enabling EAP authentication with WPA:
• Enabling LEAP, page 5-38
• Enabling EAP-FAST, page 5-42
• Enabling Host-Based EAP, page 5-49
Note WPA must also be enabled on the access point. Access points must use Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)JA
or later to enable WPA. Refer to the documentation for your access point for instructions on enabling
this feature.
Fast Roaming (CCKM)
Some applications that run on a client device may require fast roaming between access points. Voice
applications, for example, require seamless roaming to prevent delays and gaps in conversation. Support
for fast roaming is available for LEAP-enabled clients in Install Wizard version 1.1 or later and
EAP-FAST-enabled clients in Install Wizard version 1.3 or later.
During normal operation, LEAP- or EAP-FAST-enabled clients mutually authenticate with a new access
point by performing a complete LEAP or EAP-FAST authentication, including communication with the
main RADIUS server. However, when you configure your wireless LAN for fast roaming, LEAP- or
EAP-FAST-enabled clients securely roam from one access point to another without the need to
reauthenticate with the RADIUS server. Using Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM), an access
point that is configured for wireless domain services (WDS) uses a fast rekeying technique that enables
client devices to roam from one access point to another in under 150 milliseconds (ms). Fast roaming
ensures that there is no perceptible delay in time-sensitive applications such as wireless Voice over IP
(VoIP), enterprise resource planning (ERP), or Citrix-based solutions.
This feature is enabled on the client adapter in two ways, depending on the software installed:
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
5-28
• If you are using ACU version 6.2 and client adapter firmware version 5.30.17 (which is included in
Install Wizard version 1.2) or later, you need to enable fast roaming in ACU. Refer to Step 10 in the
“Enabling LEAP” section or Step 12 in the “Enabling EAP-FAST” section for details.
• If you are using client adapter firmware version 5.20.17 (which is included in Install Wizard version
1.1), fast roaming is supported automatically.
Regardless of how fast roaming is enabled on the client adapter, it must also be enabled on the access
point.
Note Access points must use Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)JA or later to enable fast roaming. Refer to the
documentation for your access point for instructions on enabling this feature.
Note If the Microsoft 802.1X supplicant is installed on your computer, you must disable one or two Windows
parameters in order for this feature to operate correctly. Refer to Step 13 in the “Enabling LEAP” section
or Step 15 in the “Enabling EAP-FAST” section for details.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
Page 29

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Reporting Access Points that Fail LEAP or EAP-FAST Authentication
The following client adapter and access point firmware versions support a feature that is designed to
detect access points that fail LEAP or EAP-FAST authentication:
• Client adapter firmware version 5.02.20 or later (for LEAP)
• Client adapter firmware version 5.40.10 or later (for EAP-FAST)
• 12.00T or later (340, 350, and 1200 series access points)
• Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)JA or later (1100 series access points)
An access point running one of these firmware versions records a message in the system log when a
client running one of these firmware versions discovers and reports another access point in the wireless
network that has failed LEAP or EAP-FAST authentication.
The process takes place as follows:
1. A client with a LEAP or EAP-FAST profile attempts to associate to access point A.
2. Access point A does not handle LEAP or EAP-FAST authentication successfully, perhaps because
the access point does not understand LEAP or EAP-FAST or cannot communicate to a trusted LEAP
or EAP-FAST authentication server.
3. The client records the MAC address for access point A and the reason why the association failed.
Setting Network Security Parameters
4. The client associates successfully to access point B.
5. The client sends the MAC address of access point A and the reason code for the failure to access
point B.
6. Access point B logs the failure in the system log.
Note This feature does not need to be enabled on the client adapter or access point; it is supported
automatically in the firmware of both devices. However, both the client and access point must use these
firmware versions or later.
Additional WEP Key Security Features
The three security features discussed in this section (MIC, TKIP, and broadcast key rotation) are
designed to prevent sophisticated attacks on your wireless network’s WEP keys. These features do not
need to be enabled on the client adapter; they are supported automatically in the firmware and driver
versions included in the Install Wizard file. However, they must be enabled on the access point.
Note Access point firmware version 11.10T or later is required to enable these security features. Refer to the
documentation for your access point for instructions on enabling these security features.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-29
Page 30

Setting Network Security Parameters
Message Integrity Check (MIC)
MIC prevents bit-flip attacks on encrypted packets. During a bit-flip attack, an intruder intercepts an
encrypted message, alters it slightly, and retransmits it, and the receiver accepts the retransmitted
message as legitimate. The MIC adds a few bytes to each packet to make the packets tamper-proof.
The Status screen indicates if MIC is being used, and the Statistics screen provides MIC statistics.
Note If you enable MIC on the access point, your client adapter’s driver must support these features;
otherwise, the client cannot associate.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
This feature, also referred to as WEP key hashing, defends against an attack on WEP in which the
intruder uses the initialization vector (IV) in encrypted packets to calculate the WEP key. TKIP removes
the predictability that an intruder relies on to determine the WEP key by exploiting IVs. It protects both
unicast and broadcast WEP keys.
Note If you enable TKIP on the access point, your client adapter’s firmware must support these features;
otherwise, the client cannot associate.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Note TKIP is automatically enabled whenever WPA is enabled, and it is disabled whenever WPA is disabled.
Broadcast Key Rotation
EAP authentication provides dynamic unicast WEP keys for client devices but uses static broadcast, or
multicast, keys. When you enable broadcast WEP key rotation, the access point provides a dynamic
broadcast WEP key and changes it at the interval you choose. When you enable this feature, only
wireless client devices using LEAP, EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS, PEAP, or EAP-SIM authentication can
associate to the access point. Client devices using static WEP (with open or shared key authentication)
cannot associate.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-30
OL-1394-08
Page 31

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Synchronizing Security Features
In order to use any of the security features discussed in this section, both your client adapter and the
access point to which it will associate must be set appropriately. Table 5-6 indicates the client and access
point settings required for each security feature. This chapter provides specific instructions for enabling
the security features on your client adapter. Refer to the documentation for your access point for
instructions on enabling any of these features on the access point.
Table 5-6 Client and Access Point Security Settings
Security Feature Client Setting Access Point Setting
Static WEP with open
authentication
Static WEP with shared key
authentication
LEAP authentication Enable LEAP Set up and enable WEP and enable
LEAP authentication with
WPA
EAP-FAST authentication Enable EAP-FAST and enable
EAP-FAST authentication
with WPA
Disable Network Authentication,
enable Static WEP and Open
Authentication and create a WEP
key
Disable Network Authentication,
enable Static WEP and Shared Key
Authentication and create a WEP
key
Enable LEAP and Wi-Fi Protected
Access (WPA)
Note To allow the client to
associate to both WPA and
non-WPA access points,
enable Allow Association
to both WPA and non-WPA
authenticators.
automatic provisioning or import a
PAC fil e
Enable EAP-FAST and Wi-Fi
Protected Access (WPA) and
enable automatic provisioning or
import a PAC file
Note To allow the client to
associate to both WPA and
non-WPA access points,
enable Allow Association
to both WPA and non-WPA
authenticators.
Setting Network Security Parameters
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Open Authentication for the SSID
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Shared Key Authentication for the
SSID
Network-EAP for the SSID
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP, set up and enable WEP, and
enable Network-EAP and WPA for
the SSID
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Network-EAP for the SSID
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP, set up and enable WEP, and
enable Network-EAP and WPA for
the SSID
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-31
Page 32

Setting Network Security Parameters
Table 5-6 Client and Access Point Security Settings (continued)
Security Feature Client Setting Access Point Setting
EAP-TLS authentication
If using ACU to
configure card
If using Windows XP
to configure card
EAP-TLS authentication with WPA
If using ACU to
configure card
If using Windows XP
to configure card
Enable Host Based EAP (802.1x)
and Dynamic WEP in ACU and
select Enable network access
control using IEEE 802.1X (or
Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication
for this network) and Certificates
(or Smart Card or other Certificate)
as the EAP Type in Windows
Select Enable network access
control using IEEE 802.1X and
Smart Card or other Certificate as
the EAP Type
Enable Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA), Host Based EAP (WPA),
and Dynamic WEP in ACU and
enable WPA and select Enable
network access control using IEEE
802.1X and Certificates (or Smart
Card or Other Certificate) as the
EAP Type in Windows
Enable WPA and select Enable
network access control using IEEE
802.1X and Smart Card or other
Certificate as the EAP Type
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Open Authentication for the SSID
and specify the use of EAP
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Open Authentication for the SSID
and specify the use of EAP
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP; set up and enable WEP; and
enable WPA and Open
Authentication for the SSID and
specify the use of EAP
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP; set up and enable WEP; and
enable WPA and Open
Authentication for the SSID and
specify the use of EAP
5-32
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
PEAP authentication
If using ACU to
configure card
Enable Host Based EAP (802.1x)
and Dynamic WEP in ACU and
select Enable network access
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Open Authentication for the SSID
and specify the use of EAP
control using IEEE 802.1X (or
Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication
for this network) and PEAP as the
EAP Type in Windows
If using Windows XP
to configure card
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
Select Enable network access
control using IEEE 802.1X and
PEAP as the EAP Type
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Open Authentication for the SSID
and specify the use of EAP
OL-1394-08
Page 33

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Table 5-6 Client and Access Point Security Settings (continued)
Security Feature Client Setting Access Point Setting
PEAP authentication with WPA
If using ACU to
configure card
If using Windows XP
to configure card
EAP-SIM authentication
If using ACU to
configure card
If using Windows XP
to configure card
Enable Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA), Host Based EAP (WPA),
and Dynamic WEP in ACU and
enable WPA and select Enable
network access control using IEEE
802.1X and PEAP as the EAP Type
in Windows
Enable WPA and select Enable
network access control using IEEE
802.1X and PEAP as the EAP Type
Enable Host Based EAP (802.1x)
and Dynamic WEP in ACU and
select Enable network access
control using IEEE 802.1X (or
Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication
for this network) and SIM
Authentication as the EAP Type in
Windows
Select Enable network access
control using IEEE 802.1X and
SIM Authentication as the EAP
Type
Setting Network Security Parameters
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP; set up and enable WEP; and
enable WPA and Open
Authentication for the SSID and
specify the use of EAP
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP; set up and enable WEP; and
enable WPA and Open
Authentication for the SSID and
specify the use of EAP
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Open Authentication for the SSID
and specify the use of EAP
Set up and enable WEP and enable
Open Authentication for the SSID
and specify the use of EAP
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-33
Page 34
Setting Network Security Parameters
Table 5-6 Client and Access Point Security Settings (continued)
Security Feature Client Setting Access Point Setting
EAP-SIM authentication with WPA
If using ACU to
configure card
If using Windows XP
to configure card
Fast roaming (CCKM) Enable LEAP or EAP-FAST and
Enable Wi-Fi Protected Access
(WPA), Host Based EAP (WPA),
and Dynamic WEP in ACU and
enable WPA and select Enable
network access control using IEEE
802.1X and SIM Authentication as
the EAP Type in Windows
Enable WPA and select Enable
network access control using IEEE
802.1X and SIM Authentication as
the EAP Type
select Allow Fast Roaming
(CCKM)
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP; set up and enable WEP; and
enable WPA and Open
Authentication for the SSID and
specify the use of EAP
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
Select a cipher suite that includes
TKIP; set up and enable WEP; and
enable WPA and Open
Authentication for the SSID and
specify the use of EAP
Note To allow both WPA and
non-WPA clients to use the
SSID, enable optional
WPA.
Use firmware version 12.2(11)JA
or later, select a cipher suite that is
compatible with CCKM, and
enable Network-EAP and CCKM
for the SSID
Reporting access points
that fail LEAP or
EAP-FAST authentication
No settings required; automatically
enabled in firmware version
5.02.20 or later (for LEAP) or
5.40.10 or later (for EAP-FAST)
MIC No settings required; automatically
enabled by the driver included in
the Install Wizard file
TKIP No settings required; automatically
enabled by the firmware included
in the Install Wizard file
Broadcast key rotation Enable LEAP, EAP-FAST,
EAP-TLS, PEAP, or EAP-SIM and
use the firmware included in the
Install Wizard file
Note To allow both 802.1X
clients and non-802.1X
clients to use the SSID,
enable optional CCKM.
No settings required; automatically
enabled in the following firmware
versions: 12.00T or later (340, 350,
and 1200 series access points) or
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)JA or
later (1100 series access points)
Set up and enable WEP with full
encryption, set MIC to MMH or
select Enable MIC check box, and
set Use Aironet Extensions to Yes
Set up and enable WEP, set TKIP to
Cisco or select Enable Per Packet
Keying check box, and set Use
Aironet Extensions to Yes
Set up and enable WEP and set
Broadcast WEP Key Rotation
Interval to any value other than
zero (0)
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-34
OL-1394-08
Page 35

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Using Static WEP
This section provides instructions for entering new static WEP keys or overwriting existing static WEP
keys.
Entering a New Static WEP Key
Follow these steps to enter a new static WEP key for this profile.
Step 1 Choose None under Network Authentication on the Network Security screen.
Step 2 Choose Static WEP under Data Encryption.
Step 3 Click the Static WEP Keys button. The Static WEP Keys screen appears (see Figure 5-6).
Figure 5-6 Static WEP Keys Screen
Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 4
Choose one of the following WEP key entry methods:
• Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F)—Specifies that the WEP key will be entered in hexadecimal characters,
which include 0-9, A-F, and a-f.
• ASCII Text—Specifies that the WEP key will be entered in ASCII text, which includes alpha
characters, numbers, and punctuation marks.
Note ASCII text WEP keys are not supported on the Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Points, so
you must choose the Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F) option if you are planning to use your client
adapter with these access points.
Step 5 For the static WEP key that you are entering (1, 2, 3, or 4), choose a WEP key size of 40 or 128 on the
right side of the screen. 128-bit client adapters can use 40- or 128-bit keys, but 40-bit adapters can use
only 40-bit keys. If 128 bit is not supported by the client adapter, this option is unavailable.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-35
Page 36

Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 6 Obtain the static WEP key from your system administrator and enter it in the blank field for the key you
are creating. Follow the guidelines below to enter a new static WEP key:
• WEP keys must contain the following number of characters:
–
10 hexadecimal characters or 5 ASCII text characters for 40-bit keys
Example: 5A5A313859 (hexadecimal) or ZZ18Y (ASCII)
–
26 hexadecimal characters or 13 ASCII text characters for 128-bit keys
Example: 5A583135333554595549333534 (hexadecimal) or ZX1535TYUI354 (ASCII)
Note You must enter hexadecimal characters for 5-GHz client adapters if these adapters will be
• Your client adapter’s WEP key must match the WEP key used by the access point (in infrastructure
mode) or clients (in ad hoc mode) with which you are planning to communicate.
• When setting more than one WEP key, the keys must be assigned to the same WEP key numbers for
all devices. For example, WEP key 2 must be WEP key number 2 on all devices. When multiple
WEP keys are set, they must be in the same order on all devices.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
used with Cisco Aironet 1200 Series Access Points.
Note After you enter a WEP key, you can write over it, but you cannot edit or delete it.
Step 7 Click the Tran sm it Key button to the left of the key you want to use to transmit packets. Only one WEP
key can be selected as the transmit key.
Step 8 Click OK to exit the Static WEP Keys screen and return to the Network Security screen.
Step 9 Choose one of the following access point authentication options, which defines how your client adapter
will attempt to authenticate to an access point:
• Open—Enables your client adapter, regardless of its WEP settings, to authenticate and attempt to
communicate with an access point. Open Authentication is the default setting.
• Shared Key—Enables your client adapter to communicate only with access points that have the
same WEP key. This option is available only if Use Static WEP Keys is selected.
In shared key authentication, the access point sends a known unencrypted “challenge packet” to the
client adapter, which encrypts the packet and sends it back to the access point. The access point
attempts to decrypt the encrypted packet and sends an authentication response packet indicating the
success or failure of the decryption back to the client adapter. If the packet is successfully
encrypted/decrypted, the user is considered to be authenticated.
Note Cisco recommends that shared key authentication not be used because it presents a security
risk.
Step 10 Click OK to return to the Profile Manager screen; then click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-36
OL-1394-08
Page 37

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Overwriting an Existing Static WEP Key
Follow these steps to overwrite an existing static WEP key.
Note You can overwrite existing WEP keys, but you cannot edit or delete them.
Step 1 Click the Static WEP Keys button on the Network Security screen. The Static WEP Keys screen appears
(see Figure 5-6).
Step 2 Look at the current WEP key settings in the middle of the screen. A check mark appears in the Already
Set? box for all existing static WEP keys.
Note For security reasons, the codes for existing static WEP keys do not appear on the screen.
Step 3 Decide which existing static WEP key you want to overwrite.
Step 4 Click within the blank field of that key.
Step 5 Enter a new key, following the guidelines outlined in Step 6 of the “Entering a New Static WEP Key”
section on page 5-35.
Step 6 Make sure the Tran smit Key button to the left of your key is selected, if you want this key to be used to
transmit packets.
Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 7 Click OK to exit the Static WEP Keys screen and return to the Network Security screen.
Step 8 Click OK to return to the Profile Manager screen; then click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Disabling Static WEP
If you ever need to disable static WEP for a particular profile, choose None under Data Encryption on
the Network Security screen, click OK, and click OK or Apply on the Profile Manager screen.
Note Choosing LEAP or EAP-FAST under Network Authentication on the Network Security screen disables
static WEP automatically.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-37
Page 38

Setting Network Security Parameters
Enabling LEAP
Before you can enable LEAP authentication, your network devices must meet the following
requirements:
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
• Client adapters must support WEP and use the firmware, drivers, utilities, and security modules
included in the Install Wizard file.
• To use WPA, 350 series and CB20A client adapters must use the software included in Install Wizard
version 1.2 or later on a computer running Windows 2000 or XP.
• Access points to which your client adapter may attempt to authenticate must use the following
firmware versions or later: 11.23T (340 and 350 series access points), 11.54T (1200 series access
points), or Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)JA (1100 series access points).
Note To use WPA or fast roaming (CCKM), access points must use Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)JA
or later. To use the Reporting Access Points That Fail LEAP or EAP-FAST Authentication
and Fast Roaming features, access points must use the firmware versions listed on page 5-31.
• All necessary infrastructure devices such as access points and servers must be properly configured
for LEAP authentication.
Note Cisco recommends the use of strong passwords for LEAP authentication in order to minimize the risk of
successful attacks by rogue access points. Refer to the “Creating Strong Passwords” section on
page 10-13 for tips on creating strong passwords.
Follow these steps to enable LEAP authentication for this profile.
Step 1 Check the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) check box under Network Authentication on the Network
Security screen if you want to enable WPA. This parameter enables the client adapter to associate to
access points using WPA.
Note WPA is not supported on Cisco Aironet 340 series client adapters.
Note Refer to the “Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)” section on page 5-27 for additional information.
Step 2 Choose LEAP or LEAP (WPA).
Note This option is available only if you chose the LEAP security module during installation.
Note When you choose this option, dynamic WEP (if WPA is disabled) or TKIP (if WPA is enabled)
is set automatically.
Step 3 Click the Configure button. The LEAP Settings screen appears (see Figure 5-7).
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-38
OL-1394-08
Page 39

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Figure 5-7 LEAP Settings Screen
Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 4
Choose one of the following LEAP username and password setting options:
• Use Temporary User Name and Password—Requires you to enter the LEAP username and
password each time the computer reboots in order to authenticate and gain access to the network.
• Use Saved User Name and Password—Does not require you to enter a LEAP username and
password each time the computer reboots. Authentication occurs automatically as needed using a
saved username and password (which are registered with the RADIUS server).
Note The Use Saved User Name and Password option is available only if the Allow Saved LEAP
User Name and Password option was enabled (set to Yes) during installation.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-39
Page 40

Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 5 Perform one of the following:
• If you selected Use Temporary User Name and Password in Step 4, choose one of the following
options:
–
Use Windows Logon User Name and Password—Causes your Windows username and
password to also serve as your LEAP username and password, giving you only one set of
credentials to remember. After you log in, the LEAP authentication process begins
automatically. This option is the default setting.
–
Automatically Prompt for User Name and Password—Requires you to enter a separate
LEAP username and password (which are registered with the RADIUS server) in addition to
your regular Windows login in order to start the LEAP authentication process.
–
Manually Prompt for User Name and Password—Requires you to manually invoke the LEAP
authentication process as needed using the Manual Login option from the Commands
drop-down menu. You are not prompted to enter a LEAP username and password during the
Windows login. This option might be used to support a software token one-time password
system or other systems that require additional software that is not available at login.
• If you selected Use Saved User Name and Password in Step 4, follow these steps:
a. Enter a username and password in the appropriate fields.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Note Usernames are limited to 64 ASCII characters in the software included in Install Wizard
version 1.3 or later and to 32 ASCII characters in previous Install Wizard versions.
Passwords are limited to 32 ASCII characters. However, if a domain name is entered in
the Domain field, the sum of the username and domain name is limited to 63 ASCII
characters in the software included in Install Wizard version 1.3 or later and to 31
characters in previous Install Wizard versions.
b. Re-enter the password in the Confirm Password field.
c. If you wish to specify a domain name that will be passed to the RADIUS server along with your
username, enter it in the Domain field.
Note If you are using the software included in Install Wizard version 1.3 or later, you can
include the domain name in the User Name field as follows: username@domain.com
(provided that your RADIUS server supports this format). A maximum of 64 ASCII
characters can be entered for the username@domain.com string. If you include the
domain name in the User Name field, the Domain field becomes disabled.
Step 6 If you work in an environment with multiple domains and, therefore, want your Windows login domain
to be passed to the RADIUS server along with your username, check the Include Windows Logon
Domain with User Name check box. The default setting is checked.
Note If you selected to use a saved username and password but do not check the Include Windows
Logon Domain with User Name check box, the Domain field becomes unavailable, and a
domain name is not passed to the RADIUS server.
Step 7 If you want to force the client adapter to disassociate after you log off so that another user cannot gain
access to the wireless network using your credentials, check the No Network Connection Unless User
Is Logged In check box. The default setting is checked.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-40
OL-1394-08
Page 41
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 8 In the Authentication Timeout Value field, enter the amount of time (in seconds) before a LEAP
authentication attempt is considered to be failed and an error message appears.
Range: 10 to 300 seconds
Default: 90 seconds
Step 9 Click OK to exit the LEAP Settings screen.
Step 10 Check the Allow Fast Roaming (CCKM) check box on the Network Security screen if you want to
enable fast roaming for your client adapter.
• Checking this check box enables the client adapter to use CCKM when associated to an access point
that uses CCKM or to associate to access points that are not using CCKM.
• Unchecking this check box prevents the client adapter from using CCKM even with access points
that use it.
Default: Unchecked
Note Refer to the “Fast Roaming (CCKM)” section on page 5-28 for additional information.
Step 11 Check the Allow Association to both WPA and non-WPA authenticators check box if you want to
allow the client adapter to associate to access points that are configured for LEAP authentication with:
• WPA enabled (associates with WPA security)
Setting Network Security Parameters
• WPA disabled or not supported (associates without WPA security)
• Cisco migration mode, where WPA is optional (associates without WPA security)
If this check box is not checked, the client adapter can associate only to access points that are configured
for LEAP authentication with WPA.
Default: Unchecked
Note This parameter is available only if you enable WPA.
Step 12 Click OK to exit the Network Security screen and return to the Profile Manager screen. On the Profile
Manager screen, click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Step 13 Follow these steps if the Microsoft 802.1X supplicant is installed on your computer and you want to take
advantage of the fast roaming feature:
a. Perform one of the following steps, depending on your computer’s operating system:
–
If your computer is running Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, or Me, run the Microsoft 802.1X
Authentication Client application. Then go to Step c.
–
If your computer is running Windows 2000, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and
Network and Dial-up Connections. Right-click Local Area Connection. Click Properties.
The Local Area Connection Properties screen appears.
–
If your computer is running Windows XP, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and
Network Connections. Right-click Wireless Network Connection. Click Properties. The
Wireless Network Connection Properties screen appears. Choose the Wireless Networks tab.
Uncheck the Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings check box unless you
are using Windows XP Service Pack 1.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-41
Page 42

Setting Network Security Parameters
b. Click the Authentication tab.
Note In Windows Service Pack 1, the Authentication tab has moved from its previous location. To
c. Uncheck the Enable network access control using IEEE 802.1X or Enable IEEE 802.1x
authentication for this network check box.
d. Click OK to save your settings.
e. If you are using Windows XP Service Pack 1, uncheck the Use Windows to configure my wireless
network settings check box on the Wireless Networks screen and click OK.
Step 14 Refer to Chapter 6 for instructions on authenticating using LEAP.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
access it, make sure the Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings check
box is checked. Click the SSID of the profile you are creating from the list of available
networks and click Configure. If your profile’s SSID is not listed, click Add, enter your
profile’s SSID in the Network name (SSID) field, and choose the Authentication tab.
Enabling EAP-FAST
Before you can enable EAP-FAST authentication, your network devices must meet the following
requirements:
• 350 series and CB20A client adapters must use the software included in Install Wizard version 1.3
or later on a computer running Windows 2000 or XP.
• Access points to which your client adapter may attempt to authenticate must use the following
firmware versions or later: 11.23T (340 and 350 series access points), 11.54T (1200 series access
points), or Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)JA (1100 series access points).
Note To use WPA or fast roaming (CCKM), access points must use Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)JA
• All necessary infrastructure devices such as access points, servers, gateways, and user databases
must be properly configured for EAP-FAST authentication.
Follow these steps to enable EAP-FAST authentication for this profile.
Step 1 Check the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) check box under Network Authentication on the Network
Security screen if you want to enable WPA. This parameter enables the client adapter to associate to
access points using WPA.
or later. To use the Reporting Access Points That Fail LEAP or EAP-FAST Authentication
and Fast Roaming features, access points must use the firmware versions listed on page 5-34.
Note Refer to the “Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)” section on page 5-27 for additional information.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-42
OL-1394-08
Page 43
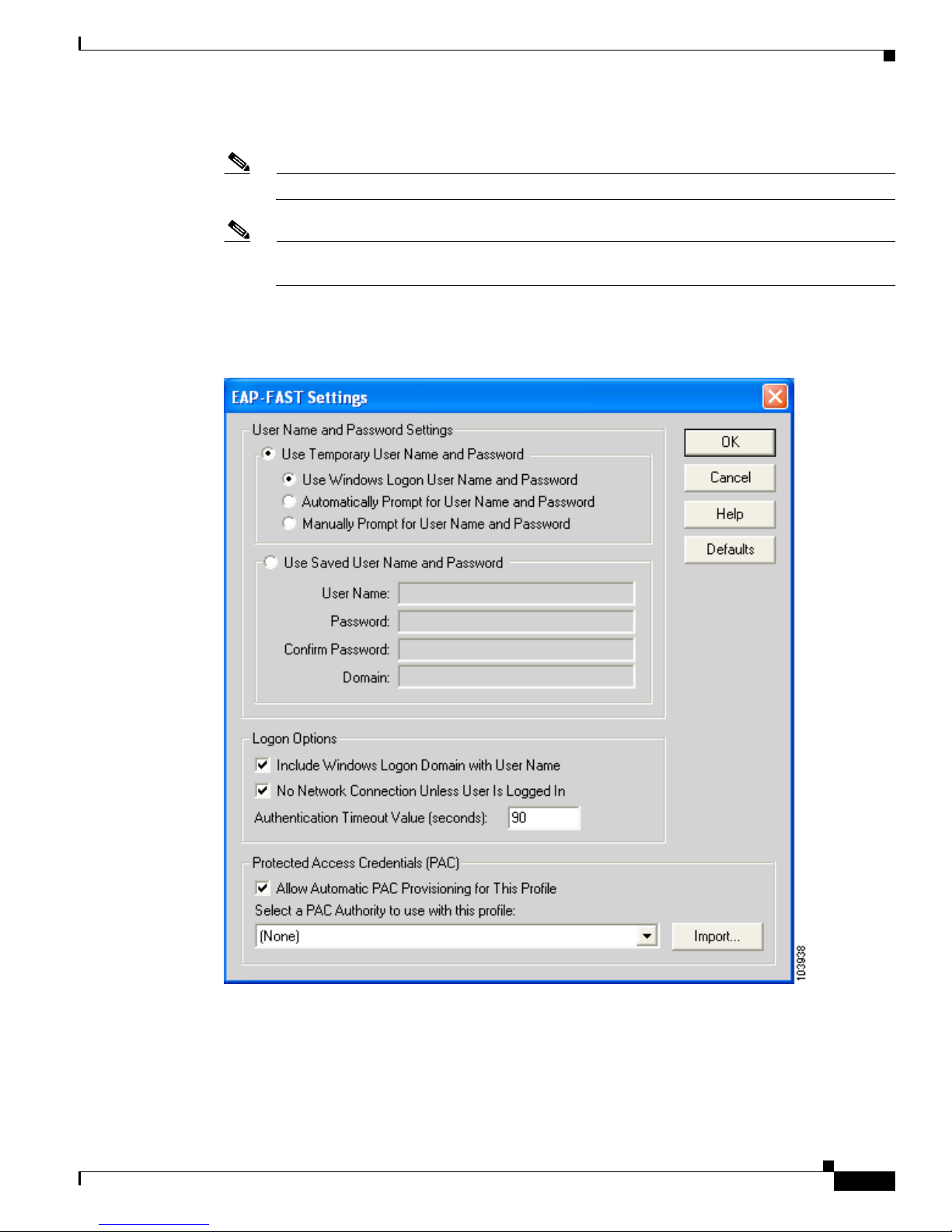
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 2 Choose EAP-FAST or EAP-FAST (WPA).
Note This option is available only if you selected the EAP-FAST security module during installation.
Note When you choose this option, dynamic WEP (if WPA is disabled) or TKIP (if WPA is enabled)
is set automatically.
Step 3 Click Configure. The EAP-FAST Settings screen appears (see Figure 5-8).
Figure 5-8 EAP-FAST Settings Screen
Setting Network Security Parameters
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-43
Page 44

Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 4 Choose one of the following EAP-FAST username and password setting options:
• Use Temporary User Name and Password—Requires you to enter the EAP-FAST username and
password each time the computer reboots in order to authenticate and gain access to the network.
• Use Saved User Name and Password—Does not require you to enter an EAP-FAST username and
password each time the computer reboots. Authentication occurs automatically as needed using a
saved username and password (which are registered with the RADIUS server).
Note The Use Saved User Name and Password option is available only if the Allow Saved
Step 5 Perform one of the following:
• If you selected Use Temporary User Name and Password in Step 4, choose one of the following
options:
–
Use Windows Logon User Name and Password—Causes your Windows username and
password to also serve as your EAP-FAST username and password, giving you only one set of
credentials to remember. After you log in, the EAP-FAST authentication process begins
automatically. This option is the default setting.
–
Automatically Prompt for User Name and Password—Requires you to enter a separate
EAP-FAST username and password (which are registered with the RADIUS server) in addition
to your regular Windows login in order to start the EAP-FAST authentication process.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
EAP-FAST User Name and Password option was enabled (set to Yes) during installation.
–
Manually Prompt for User Name and Password—Requires you to manually invoke the
EAP-FAST authentication process as needed using the Manual Login option from the
Commands drop-down menu. You are not prompted to enter an EAP-FAST username and
password during the Windows login. This option might be used to support a software token
one-time password system or other systems that require additional software that is not available
at login.
• If you selected Use Saved User Name and Password in Step 4, follow these steps:
a. Enter a username and password in the appropriate fields.
Note Usernames are limited to 64 ASCII characters, and passwords are limited to 32 ASCII
characters. However, if a domain name is entered in the Domain field, the sum of the
username and domain name is limited to 63 ASCII characters.
b. Re-enter the password in the Confirm Password field.
c. If you wish to specify a domain name that will be passed to the RADIUS server along with your
username, enter it in the Domain field or include it in the User Name field as follows:
username@domain.com. A maximum of 64 ASCII characters can be entered for the
username@domain.com string, and this format must be supported by your RADIUS server.
Note If you include the domain name in the User Name field, the Domain field becomes
disabled.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-44
OL-1394-08
Page 45

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 6 If you work in an environment with multiple domains and therefore want your Windows login domain
to be passed to the RADIUS server along with your username, check the Include Windows Logon
Domain with User Name check box. The default setting is checked.
Note If you chose to use a saved username and password but do not check the Include Windows
Logon Domain with User Name check box, the Domain field becomes unavailable, and a
domain name is not passed to the RADIUS server.
Step 7 If you want to force the client adapter to disassociate after you log off so that another user cannot gain
access to the wireless network using your credentials, check the No Network Connection Unless User
Is Logged In check box. The default setting is checked.
Step 8 In the Authentication Timeout Value field, enter the amount of time (in seconds) before an EAP-FAST
authentication attempt is considered to be failed and an error message appears.
Range: 10 to 300 seconds
Default: 90 seconds
Step 9 Perform one of the following:
• If you want to enable automatic PAC provisioning, check the Allow Automatic PAC Provisioning
for This Profile check box. A protected access credentials (PAC) file is obtained automatically as
needed (for instance, when a PAC expires, when the client adapter accesses a different server, when
the EAP-FAST username cannot be matched to a previously provisioned PAC, etc.). This is the
default setting. If you choose this option, go to Step 11.
Setting Network Security Parameters
• If you want to enable manual PAC provisioning, uncheck the Allow Automatic PAC Provisioning
for This Profile check box. You must choose a PAC authority or manually import a PAC file. If you
choose this option, go to Step 10.
Note The Allow Automatic PAC Provisioning for This Profile option is available only if the Allow
Auto-Provisioning? option was enabled (set to Yes) during installation. If this option is not
available, you must enable manual PAC provisioning.
Note LDAP user databases support only manual PAC provisioning while Cisco Secure ACS internal,
Cisco Secure ODBC, and Windows NT/2000/2003 domain user databases support both
automatic and manual PAC provisioning.
Note Provisioning occurs only upon initial negotiation of the PAC or upon PAC expiration. After the
PAC is provisioned, it serves as the per-user key by which authentication transactions are
secured.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-45
Page 46

Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 10 Perform one of the following to enable manual PAC provisioning:
• From the Select a PAC Authority To Use with This Profile drop-down list, select the PAC authority
that is associated with the network defined by the profile’s SSID. The list contains the names of all
the PAC authorities from which you have previously provisioned a PAC.
• If the PAC authority drop-down list is empty or does not contain the name of a desired PAC authority,
follow these steps to import a PAC file:
a. Click the Import button. The Import Protected Access Credentials (PAC) File screen appears
(see Figure 5-9).
Figure 5-9 Import Protected Access Credentials (PAC) File Screen
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
5-46
b.
Find the location of the PAC file in the Look in box. The default location is My Documents.
Note If you browse to a different location to obtain the PAC, the new location becomes the
default location going forward.
c. Click the PAC file (*.pac) so that it appears in the File name box at the bottom of the screen.
Note The filename and extension of PAC files is determined by the PAC authority that issues
them, but the standard file extension is pac.
d. Click the Open button.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
Page 47

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
e. If a message appears indicating that the PAC file you are about to import will be made accessible
to all users of your system, click Yes . If you click No, the PAC file is not imported.
Note The PAC file you are about to import will be made accessible to all users of your system
Note If you try to import a PAC file with the same PAC ID as a previously imported PAC file,
f. If the Enter PAC File Password screen appears (see Figure 5-10), enter the PAC file password
and click OK.
Setting Network Security Parameters
if your profile is configured for global PACs. Global PACs are enabled when you choose
the Use Saved User Name and Password option, uncheck the No Network Connection
Unless User Is Logged In check box on the EAP-FAST Settings screen, or use the Novell
Network login prompt or any other third-party login application that does not share its
credentials with the EAP-FAST supplicant.
you are asked if you want to overwrite the existing PAC. If you click Ye s, the existing
PAC is replaced by the new one from the imported file.
Figure 5-10 Enter PAC File Password Screen
Note PAC file passwords are optional. The PAC authority determines whether to issue PAC
files that require user-supplied passwords. Nevertheless, all PAC files (even those
without passwords) are encrypted and protected. PAC file passwords are different from
EAP-FAST passwords and need to be entered only once, at the time a PAC is imported.
g. The PAC file is imported and added to your PAC database, and the name of the PAC authority
that issued the PAC file is added to the PAC authority drop-down list on the EAP-FAST Settings
screen. Choose the desired PAC authority from the list.
Step 11 Click OK to exit the EAP-FAST Settings screen.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-47
Page 48

Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 12 Check the Allow Fast Roaming (CCKM) check box on the Network Security screen if you want to
enable fast roaming for your client adapter.
• Checking this check box enables the client adapter to use CCKM when associated to an access point
that uses CCKM or to associate to access points that are not using CCKM.
• Unchecking this check box prevents the client adapter from using CCKM even with access points
that use it.
Default: Unchecked
Note Refer to the “Fast Roaming (CCKM)” section on page 5-28 for additional information.
Step 13 Check the Allow Association to both WPA and non-WPA authenticators check box if you want to
allow the client adapter to associate to access points that are configured for EAP-FAST authentication
with:
• WPA enabled (associates with WPA security)
• WPA disabled or not supported (associates without WPA security)
• Cisco migration mode, where WPA is optional (associates without WPA security)
If this check box is not checked, the client adapter can associate only to access points that are configured
for EAP-FAST authentication with WPA.
Default: Unchecked
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Note This parameter is available only if you enable WPA.
Step 14 Click OK to exit the Network Security screen and return to the Profile Manager screen. On the Profile
Manager screen, click OK or Apply to save your changes.
Step 15 Follow these steps if the Microsoft 802.1X supplicant is installed on your computer and you want to take
advantage of the fast roaming feature:
a. Perform one of the following steps, depending on your computer’s operating system:
–
If your computer is running Windows 2000, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and
Network and Dial-up Connections. Right-click Local Area Connection. Click Properties.
The Local Area Connection Properties screen appears.
–
If your computer is running Windows XP, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and
Network Connections. Right-click Wireless Network Connection. Click Properties. The
Wireless Network Connection Properties screen appears. Choose the Wireless Networks tab.
Uncheck the Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings check box unless you
are using Windows XP Service Pack 1.
b. Click the Authentication tab.
Note In Windows Service Pack 1, the Authentication tab has moved from its previous location. To
access it, make sure the Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings check
box is checked. Click the SSID of the profile you are creating from the list of available
networks and click Configure. If your profile’s SSID is not listed, click Add, enter your
profile’s SSID in the Network name (SSID) field, and choose the Authentication tab.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-48
OL-1394-08
Page 49

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
c. Uncheck the Enable network access control using IEEE 802.1X or Enable IEEE 802.1x
authentication for this network check box.
d. Click OK to save your settings.
e. If you are using Windows XP Service Pack 1, uncheck the Use Windows to configure my wireless
network settings check box on the Wireless Networks screen and click OK.
Step 16 If you imported a PAC file in Step 10, you may want to consider deleting it from its original location,
depending on your organization’s policy. PAC files are similar to ID cards and should be protected from
unauthorized access. Such action would prevent exposure of the PAC by having multiple storage
locations. Contact your system administrator to determine your organization’s policy on PAC security.
Step 17 Refer to Chapter 6 for instructions on authenticating using EAP-FAST.
Enabling Host-Based EAP
Before you can enable host-based EAP authentication, your network devices must meet the following
requirements:
• Client adapters must support WEP and use the firmware, drivers, utilities, and security modules
included in the Install Wizard file.
• The Microsoft 802.1X supplicant must be installed on your Windows device.
Setting Network Security Parameters
• To use WPA, you must use a 350 series or CB20A client adapter with the software included in Install
Wizard version 1.2 or later on a computer running Windows 2000 or XP. Also, you must install
additional software with WPA support. You can download this software from the URLs provided:
–
Funk Odyssey Client supplicant version 2.2 (for Windows 2000)
http://www.funk.com/radius/wlan/wlan_c_radius.asp
–
Windows XP Service Pack 1 and Microsoft support patch 815485 (for Windows XP)
http://www.microsoft.com/WindowsXP/pro/downloads/servicepacks/sp1/default.asp
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=009d8425-ce2b-47a4-abec-274
845dc9e91&DisplayLang=en
Note Meetinghouse AEGIS Client supplicant version 2.1 or later is also supported for use with
Windows 2000 and XP; however, it was not tested with this client adapter software release.
You can download the Meetinghouse supplicant from the following URL:
http://www.mtghouse.com/support/downloads/index.shtml
• Access points to which your client adapter may attempt to authenticate must use the following
firmware versions or later: 12.00T (340, 350, and 1200 series access points) or Cisco IOS Release
12.2(4)JA (1100 series access points).
Note To use WPA or fast roaming, access points must use Cisco IOS Release 12.2(11)JA or later.
• All necessary infrastructure devices such as access points, servers, gateways, and user databases
must be properly configured for the authentication type you plan to enable on the client.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-49
Page 50

Setting Network Security Parameters
This section consists of the following three subsections. Follow the steps in each subsection to enable
host-based EAP authentication (EAP-TLS, PEAP, or EAP-SIM) for this profile.
• Enabling Host-Based EAP authentication in ACU
• Enabling WPA (an optional procedure for computers running Windows 2000 or XP)
• Enabling EAP authentication in Windows
Note Because EAP-TLS, PEAP, and EAP-SIM authentication are enabled in the operating system and not in
ACU, you cannot switch between these authentication types simply by switching profiles in ACU. You
can create a profile in ACU that uses host-based EAP, but you must enable the specific authentication
type in Windows (provided Windows uses the Microsoft 802.1X supplicant). In addition, Windows can
be set for only one authentication type at a time; therefore, if you have more than one profile in ACU
that uses host-based EAP and you want to use another authentication type, you must change
authentication types in Windows after switching profiles in ACU.
Enabling Host-Based EAP Authentication in ACU
Follow the steps in this section to set up host-based EAP authentication in ACU.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 1 Check the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) check box under Network Authentication on the Network
Security screen if you want to enable WPA. This parameter enables the client adapter to associate to
access points using WPA.
Note Refer to the “Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)” section on page 5-27 for additional information.
Step 2 Choose Host Based EAP (802.1x) or Host Based EAP (WPA).
Note If WPA is disabled, 802.1x appears in parentheses. If WPA is enabled, WPA appears in
parentheses.
Step 3 Choose Dynamic WEP under Data Encryption if WPA is not enabled.
Step 4 Click OK to return to the Profile Manager screen.
Step 5 Click OK or Apply on the Profile Manager screen to save your changes.
Step 6 Perform one of the following, depending on your computer’s operating system:
• If your computer is running Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, or Me, run the Microsoft 802.1X
Authentication Client application. Then go to Step 2 of the “Enabling EAP Authentication in
Windows” section on page 5-54.
• If your computer is running Windows 2000, perform one of the following:
–
If you want to enable WPA, go to the “Enabling WPA (Windows 2000 or XP Only - Optional)”
section below.
–
If you do not want to enable WPA, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and Network
and Dial-up Connections. Right-click Local Area Connection. Click Properties. The Local
Area Connection Properties screen appears. Go to the “Enabling EAP Authentication in
Windows” section on page 5-54.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-50
OL-1394-08
Page 51

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
• If your computer is running Windows XP, perform one of the following:
–
If you want to enable WPA, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and Network
Connections. Right-click Wireless Network Connection. Click Properties. The Wireless
Network Connection Properties screen appears. Go to the “Enabling WPA (Windows 2000 or
XP Only - Optional)” section below.
–
If you do not want to enable WPA, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and Network
Connections. Right-click Wireless Network Connection. Click Properties. The Wireless
Network Connection Properties screen appears. If you are using Windows XP Service Pack 1,
choose the Wireless Networks tab, make sure the Use Windows to configure my wireless
network settings check box is checked. Click the SSID of the profile you are creating from the
list of available networks and click Configure. If your profile’s SSID is not listed, click Add
and enter your profile’s SSID in the Network name (SSID) field. Go to the “Enabling EAP
Authentication in Windows” section on page 5-54.
Enabling WPA (Windows 2000 or XP Only - Optional)
Follow the steps in the corresponding section below if you want to enable WPA for this profile.
Instructions are different for computers running Windows 2000 and XP.
Setting Network Security Parameters
Windows 2000
Windows XP
Follow these steps to enable WPA in Funk Odyssey Client supplicant version 2.2 on a computer running
Windows 2000.
Step 1 Use your web browser to access the following URL:
http://www.funk.com/radius/enterprise/ent_solns.asp
Step 2 Under Manuals, click Odyssey Client User Guide.
Step 3 Follow the instructions in the user guide to enable WPA and EAP-TLS, PEAP, or EAP-SIM
authentication.
Follow these steps to enable WPA in Windows XP Service Pack 1 and Microsoft support patch 815485.
Step 1 Choose the Wireless Networks tab on the Wireless Network Connection Properties screen. The
following screen appears (see Figure 5-11).
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-51
Page 52

Setting Network Security Parameters
Figure 5-11 Wireless Network Connection Properties Screen (Wireless Networks Tab)
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
5-52
Step 2
Step 3 Click the SSID of the profile you began setting up in ACU from the list of available networks and click
Make sure that the Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings check box is checked.
Configure. If your profile’s SSID is not listed, click Add. The Wireless Network Properties screen
appears (see Figure 5-12).
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
Page 53

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Figure 5-12 Wireless Network Properties Screen (Association Tab)
Setting Network Security Parameters
OL-1394-08
Step 4
Perform one of the following:
• If you selected an SSID from the list of available networks, make sure the SSID appears in the
Network name (SSID) field.
• If you clicked Add, enter the case-sensitive SSID of your profile in the Network name (SSID) field.
Step 5 Choose WPA from the Network Authentication drop-down list. This option enables your client adapter
to associate to access points using WPA.
Step 6 Choose TKIP from the Data encryption drop-down list.
Step 7 Go to the “Enabling EAP Authentication in Windows” section below to enable EAP authentication for
this profile.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-53
Page 54

Setting Network Security Parameters
Enabling EAP Authentication in Windows
Follow the steps in this section to enable EAP authentication in Windows for this profile.
Step 1 Click the Authentication tab. The following screen appears (see Figure 5-13).
Figure 5-13 Wireless Network Connection Properties Screen (Authentication Tab)
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Note The Authentication screen shown above appears on computers running Windows 2000 or XP.
The screen looks slightly different on computers running Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, or Me or
Windows XP Service Pack 1.
Step 2 Check the Enable network access control using IEEE 802.1X or Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication
for this network check box if you did not enable WPA.
Step 3 Perform one of the following, depending on the authentication type you want to use:
• If you are planning to use EAP-TLS, go to the “Enabling EAP-TLS” section on page 5-55.
• If you are planning to use PEAP, go to the “Enabling PEAP” section on page 5-58.
• If you are planning to use EAP-SIM, go to the “Enabling EAP-SIM” section on page 5-60.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-54
OL-1394-08
Page 55

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Enabling EAP-TLS
Follow these steps to enable EAP-TLS.
Step 1 For EAP type, choose Certificates (on Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, or Me) or Smart Card or other
Certificate (on Windows 2000 or XP).
Step 2 Click Properties. The Certificate Properties screen (see Figure 5-14) or the Smart Card or other
Certificate Properties screen appears (see Figure 5-15 and Figure 5-16).
Figure 5-14 Certificate Properties Screen - Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, and Me
Setting Network Security Parameters
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-55
Page 56

Setting Network Security Parameters
Figure 5-15 Smart Card or other Certificate Properties Screen - Windows 2000 and XP
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Figure 5-16 Smart Card or Other Certificate Properties Screen - Windows XP Service Pack 1
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-56
OL-1394-08
Page 57

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 3 Choose the Use a certificate on this computer option.
Step 4 If your computer is running Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, or Me or Windows XP Service Pack 1, make sure
the Use simple certificate selection (Recommended) check box is selected.
Step 5 Check the Validate server certificate check box if server certificate validation is required.
Step 6 If you want to specify the name of the server to connect to, check the Connect to these servers or
Connect only if server name ends with check box and enter the appropriate server name or se rv er na me
suffix in the field below.
Note If you enter a server name and the client adapter connects to a server that does not match the
name you entered, you are prompted to accept or cancel the connection during the authentication
process.
Note If you leave this field blank, the server name is not verified, and a connection is established as
long as the certificate is valid.
Step 7 Perform one of the following:
• If your computer is running Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, or Me, choose the certificate authority from
which the server certificate was downloaded in the Trusted Root Certification Authorities field.
Setting Network Security Parameters
• If your computer is running Windows 2000 or XP, make sure that the name of the certificate
authority from which the server certificate was downloaded appears in the Trusted root certificate
authority field.
• If your computer is running Windows XP Service Pack 1, check the check box beside the name of
the certificate authority from which the server certificate was downloaded in the Trusted Root
Certification Authorities field.
Note If you leave this field blank or all check boxes unchecked, you are prompted to accept a
connection to the root certification authority during the authentication process.
Step 8 Click OK two or three times to save your settings. The configuration is complete.
Step 9 Refer to Chapter 6 for instructions on authenticating using EAP-TLS.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-57
Page 58

Setting Network Security Parameters
Enabling PEAP
Follow these steps to enable PEAP.
Step 1 For EAP type, choose PEAP.
Step 2 Click Properties. The PEAP Properties screen appears (see Figure 5-17).
Figure 5-17 PEAP Properties Screen
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
5-58
Step 3
Check the Validate server certificate check box if server certificate validation is required
(recommended).
Step 4 If you want to specify the name of the server to connect to, check the Connect only if server name ends
with check box and enter the appropriate server name suffix in the field below.
Note If you enter a server name and the client adapter connects to a server that does not match the
name you entered, you are prompted to accept or cancel the connection during the authentication
process.
Note If you leave this field blank, the server name is not verified, and a connection is established as
long as the certificate is valid.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
Page 59

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 5 Make sure that the name of the certificate authority from which the server certificate was downloaded
appears in the Trusted root certificate authority (CA) field. If necessary, click the arrow on the
drop-down menu and choose the appropriate name.
Note If you leave this field blank, you are prompted to accept a connection to the root certification
authority during the authentication process.
Step 6 Check the Connect only if server is signed by specified trusted root CA check box if you want to
ensure that the certificate server uses the trusted root certificate specified in the field above. This
prevents the client from establishing connections to rogue access points.
Step 7 Perform one of the following:
• Check the Always try to resume secure session check box if you want the PEAP protocol to always
attempt to resume the previous session before prompting you to re-enter your credentials.
• Uncheck the Always try to resume secure session check box if you want to be prompted to re-enter
your username and password whenever your client adapter’s radio becomes disassociated (for
example, when the card is ejected, the radio is turned off, you wander out of range of an access point,
you switch profiles, and so on).
Setting Network Security Parameters
Note Checking this check box gives you the convenience of not having to re-enter your username and
password when your client adapter experiences momentary losses of association. The PEAP
Session Timeout setting on the Cisco Secure ACS System Configuration - Global Authentication
Setup screen controls how long the resume feature is active (that is, the amount of time during
which the PEAP session can be resumed without re-entering user credentials). If you leave your
device unattended during this timeout period, be aware that someone can resume your PEAP
session and access the network.
Step 8 Currently Generic Token Card is the only second phase EAP type available. Click Properties. The
Generic Token Card Properties screen appears (see Figure 5-18).
Figure 5-18 Generic Token Card Properties Screen
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-59
Page 60

Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 9 Choose either the Static Password (Windows NT/2000, LDAP) or the One Time Password option,
depending on your user database.
Step 10 Perform one of the following:
• If you selected the Static Password (Windows NT/2000, LDAP) option in Step 9, go to Step 11.
• If you selected the One Time Password option in Step 9, check one or both of the following check
boxes to specify the type of tokens that will be supported for one-time passwords:
–
Support Hardware Token—A hardware token device obtains the one-time password. You
must use your hardware token device to obtain the one-time password and enter the password
when prompted for your user credentials.
–
Support Software Token—The PEAP supplicant works with a software token program to
retrieve the one-time password. You have to enter only the PIN, not the one-time password. If
you check this check box, you must also select from the Supported Type drop-down box the
software token software that is installed on the client (such as Secure Computing SofToken
Version 1.3, Secure Computing SofToken II 2.0, or RSA SecurID Software Token v 2.5), and if
Secure Computing SofToken Version 1.3 is selected, you must locate the software program path
using the Browse button.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Step 11 Click OK three times to save your settings. The configuration is complete.
Step 12 Refer to Chapter 6 for instructions on authenticating using PEAP.
Enabling EAP-SIM
Step 1 For EAP type, choose SIM Authentication.
Step 2 Click Properties. The SIM Authentication Properties screen appears (see Figure 5-19).
Note The SofToken Program Path field is unavailable if a software token program other than
Secure Computing SofToken Version 1.3 is selected.
Follow these steps to enable EAP-SIM.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-60
OL-1394-08
Page 61

Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
Figure 5-19 SIM Authentication Properties Screen
Setting Network Security Parameters
Step 3
To access any resources (data or commands) on the SIM, the EAP-SIM supplicant must provide a valid
PIN to the SIM card, which must match the PIN stored on the SIM. Choose one of the following options
to specify how the EAP-SIM supplicant should handle the SIM card’s PIN:
• Ask for my PIN once after I turn my computer on (recommended)—The software does not
permanently store the PIN. It prompts you for the PIN once, on the first authentication of every
session, where a session is defined as the time between power-up and shutdown or reboot.
• Ask for my PIN every time the network asks for authentication—The software never stores the
PIN; it prompts you for the PIN every time an EAP-SIM authentication is performed. This option is
not recommended if your client will be roaming between access points or if session timeouts are
implemented (such as for accounting and security purposes).
• Let me give my PIN to the computer now and never ask me again; PIN will be encrypted and
stored on computer (not recommended)—You need to enter the PIN only once, in the Enter PIN
edit box below this option. The software stores the PIN in the registry and retrieves it from there
when required. If you choose this option, you must enter the PIN now. The PIN is validated when
an authentication attempt is made.
Note This option is not recommended because it enables others to use the SIM without knowing
the PIN.
Step 4 Click OK twice to save your settings. The configuration is complete.
Step 5 If you are prompted to restart your client adapter, turn off your client adapter’s radio, wait a few seconds,
and then turn the radio back on. Refer to the “Turning Your Client Adapter’s Radio On or Off” section
on page 9-16 for instructions.
Step 6 Refer to Chapter 6 for instructions on authenticating using EAP-SIM.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
OL-1394-08
5-61
Page 62

Setting Network Security Parameters
Disabling LEAP, EAP-FAST, or Host-Based EAP
If you ever need to disable LEAP, EAP-FAST, or host-based EAP for a particular profile, follow the
instructions below for your EAP authentication type.
Disabling LEAP or EAP-FAST
To disable LEAP or EAP-FAST for a particular profile, choose None under Network Authentication on
the Network Security screen in ACU, click OK, and click OK or Apply on the Profile Manager screen.
Disabling Host-Based EAP
To disable host-based EAP (EAP-TLS, PEAP, or EAP-SIM) for a particular profile, follow these steps:
Step 1 Choose None under Network Authentication on the Network Security screen in ACU and click OK.
Step 2 Click OK or Apply on the Profile Manager screen.
Step 3 Perform one of the following, depending on your computer’s operating system:
• If your computer is running Windows 98, 98 SE, NT, or Me, run the Microsoft 802.1X
Authentication Client application. Then go to Step 5.
• If your computer is running Windows 2000, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and
Network and Dial-up Connections. Right-click Local Area Connection. Click Properties. The
Local Area Connection Properties screen appears.
Chapter 5 Configuring the Client Adapter
• If your computer is running Windows XP, double-click My Computer, Control Panel, and
Network Connections. Right-click Wireless Network Connection. Click Properties. The
Wireless Network Connection Properties screen appears. If you are using Windows XP Service Pack
1, click the Wireless Networks tab, click the SSID of the profile for which you are disabling
host-based EAP in the Preferred networks list, and click Properties.
Step 4 Click the Authentication tab.
Step 5 Uncheck the Enable network access control using IEEE 802.1X or Enable IEEE 802.1x
authentication for this network check box.
Step 6 Click OK.
Cisco Aironet 340, 350, and CB20A Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for Windows
5-62
OL-1394-08
 Loading...
Loading...