Page 1

CHAPTER
Voice Health Monitor Overview
These topics provide an overview of the VHM application:
• Overview of VHM, page 1-2
• How VHM Integrates with Third-Party NMSs, page 1-9
• Device Types that VHM Manages, page 1-9
• VHM Support for Cisco CallManager, page 1-11
• Locating the Supported Device List, page 1-13
• How VHM Works with the CiscoWorks2000 Server, page 1-13
• Starting the VHM Application, page 1-14
• Getting Started with VHM, page 1-14
1
78-11324-02
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
1-1
Page 2

Overview of VHM
Overview of VHM
VHM helps network administrators and network operators determine and
maintain the stability of the VoIP network within their enterprise. VHM achieves
this goal by using:
• A series of availability and health checks on the VoIP equipment in the
network.
• A fault detection and escalation system to notify the users of any faults or
exceptions detected.
VHM integrates with network management systems (NMSs) such as HP
OpenView Network Node Manager.
With VHM, you can:
• Discover VoIP network devices and applications on a user-entered schedule
• Monitor faults in voice and data networks
• Run synthetic transaction tests, to check Cisco CallManager functions
• Check the availability and health of VoIP equipment and applications
• Obtain the status of each voice device group, such as Voice Cluster, Voice
Gateway, Phone Access Switches, and Work Flow Applications
• Discover and manage Ethernet ports that have IP Phones connected to them
• Monitor IP phones in the network
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
How VHM Works
VHM manages the voice-specific devices in the network by polling information
from managed devices, as well as processing SNMP Traps generated by the
devices. VHM relies on DFM to receive the SNMP Traps. VHM does not
duplicate queries for information collection, but shares the information collected
by DFM.
Any polling analysis done in DFM can be leveraged by VHM. When polling
devices, DFM monitors generic parameters, while VHM monitors voice-specific
parameters. When VHM is used in conjunction with DFM, users can detect
generic faults that are causing VoIP disruptions.
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
1-2
78-11324-02
Page 3

Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
VHM correlates the collected information and generates events on voice
components that can be viewed in the Monitoring Console or on the Real-Time
Dashboard. Users can also view device level faults in the DFM Monitoring
Console. Alarms for both VHM and DFM can be seen from the Monitoring
Console.
VHM and DFM share many features as well as some components of their
architectures. VHM and its commonality with DFM are described in more detail
in the “VHM and DFM Interdependencies” section on page 1-4.
Event Correlation in VHM
Two types of events are generated by VHM: Compounds and Symptoms. One or
more Symptoms generate Compound or aggregated events. Symptoms are faults,
such as Power Supply Down or Temperature Too High, which generate
EnvironmentExceptions.Events are generated when fault conditions are detected
and the event correlation cycle is reached. The event correlation cycle in VHM
occurs every 30 seconds.
An example of an event correlation in VHM is TooManyInActivePhones. This
eventis generated when phones registered with call managers in a cluster become
inactive and cross the InActivePhoneThreshold over a number of active phones.
In this event, all the call managers in the cluster are monitored to find out the total
number of phones that became inactive and compare that number with the total
number of active phones in the cluster.
Overview of VHM
78-11324-02
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
1-3
Page 4

Overview of VHM
VHM and DFM Interdependencies
Note For all DFM references in this guide, refer to the User Guide for Device Fault
Manager for more detailed information.
Device Fault Manager (DFM) and VHM both analyze Cisco device failures. The
two products often identify problems before users of network services realize that
a problem exists. Both VHM and DFM:
• Use a top-down approachthat starts with users identifying problems and their
symptoms:
–
Identify the problems affecting managed systems that are critical to
correlate.
–
Describe the symptoms, developing a “problem signature” that specifies
which conditions are present in a faulty element when the problem
occurs.
• Create a causality mapping between the problems and the symptoms.
Problems andsymptoms are coded in correlation models that VHM and DFM
use to:
–
Analyze network conditions.
–
Generate faults and exceptions.
The event information necessary to diagnose problems is present in the
correlation model. Therefore, VHM and DFM monitor only the events necessary
to diagnose problems.
Table 1-1 lists the interdependencies between VHM and DFM.
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
1-4
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
Page 5
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Overview of VHM
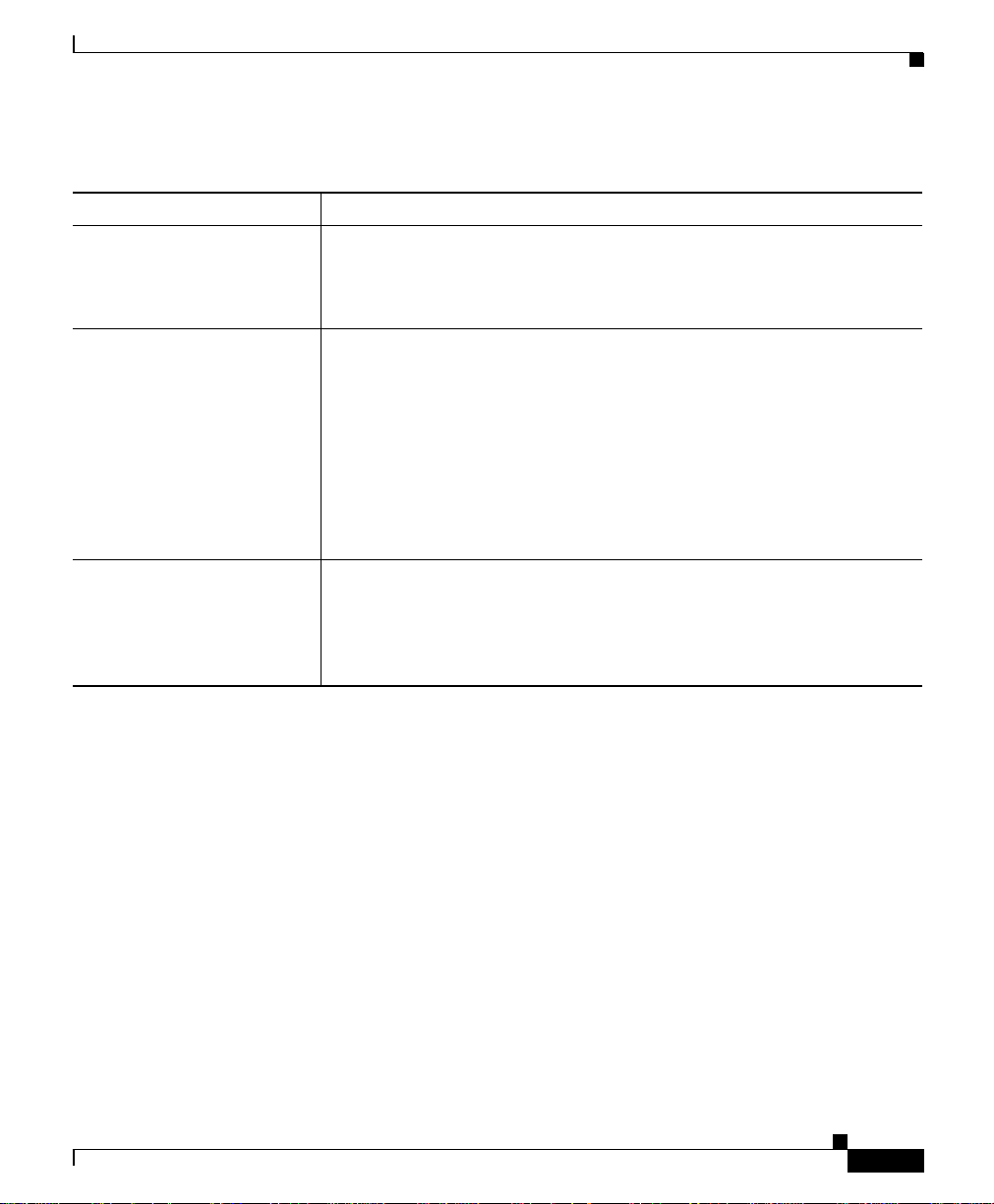
Table 1-1 Interdependencies between VHM and DFM
Component or Feature Description of Dependency
DFM Installation A DFM version, which is compatible with VHM, must be installed
either on the same system as VHM or on a remote system where it is
network accessible to VHM. See Installing and Setting Up VoiceHealth
Monitor on Windows 2000 for server system requirements.
DFM Broker The DFM Broker maintains a list of activedomain managers running on
the network and registered with the DFM Broker. Domain managers are
fault management server processes such as VHM and DFM. Each
domain manager is identified by name and the IP address and port the
domain manager is running on.
The VHM installation process can find the DFM Broker if it is installed
locally.If not, during installation, VHM prompts the user to enter the IP
address and port for the DFM Broker. VHM then registers the VHM
domain manager with the DFM broker.
SNMP Trap Receiving To receive SNMP traps for VoIP devices from DFM, VHM must update
the trap forwarding filter in DFM. When DFM receives a trap, it
forwards the trap based on the definition of the trap forwarding filter.
The VHM trap receiver receives the trap and analyzes it to generate an
event in VHM.
78-11324-02
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
1-5
Page 6

Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Overview of VHM
Table 1-1 Interdependencies between VHM and DFM (continued)
Component or Feature Description of Dependency
Inventory Collection Inventory Collection synchronizes the VHM device list with DFM;
during this process, voice-enabled devices that have been added to or
deleted from DFM inventory will also be added to or deleted from VHM
inventory.
When Inventory Collect All is triggered in VHM, it sends a rediscovery
trigger to DFM. After DFM completes rediscovery,VHM proceeds with
rediscovery, importing any newly installed voice cards, ports, or voice
applications.
If the link between the device and the DFM server is slow, DFM could
time out or markthe interface type as Generic. If the rediscovery process
times out and DFM does not discover an interface, VHM also will not
discover the interface.
VHM also registers with DFM to receivedevice list update events.If any
device is added or deleted, or becomes unresponsive, DFM sends an
event alarm to VHM. VHM can process the event by, for example,
starting to manage new voice-enabled devices.
Note If a device appears as Undiscovered in DFM, it also appears as
Undiscovered in VHM. If a device appears in a valid category
(for exampleHost, Switch, or Router) in DFM but does not have
a voice interface, it will be unsupported in VHM. If a device is
uncertified in DFM, it will not appear anywhere in VHM.
Alarm logs VHM generates voice faults and listens for element-level faults from
DFM. If VHM receives an alarm for a device it manages, it uses the
alarm in voice fault correlations. Alarms for devices that VHM does not
manage are dropped.
For more information about VHM fault browsers, see Chapter 2,
“Monitoring Voice Network Health.”
1-6
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
Page 7

Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Table 1-1 Interdependencies between VHM and DFM (continued)
Component or Feature Description of Dependency
Device classification
differences between VHM
and DFM
VHM and DFM classify devices differently. For example, Cisco routers
and Catalyst switches are managed by both VHM and DFM. However,
DFM classifies Cisco routers as Router class, while VHM classifies
routers as Voice Gateways.
Note VHM only manages Cisco routers and Catalyst switches that
have VoIP cards or ports. See the “Device Types that VHM
Manages” section on page 1-9 for more information.
Polling and threshold
parameters between VHM
and DFM
Threshold parameters for voice-enabled routers and switches must be
set in DFM. However, threshold parameters for media servers must be
set in VHM and are not shared with DFM.
Polling parameters are not shared between VHM and DFM. However,it
is best to synchronize them to avoid inconsistent polling of devices.
Therefore, it is recommended that you set polling intervals the same in
both VHM and DFM.
Overview of VHM
78-11324-02
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
1-7
Page 8

Overview of VHM
Figure 1-1 illustrates the architecture that VHM shares with DFM.
Figure 1-1 VHM Architecture
Monitoring
Real-Time
Console
Dashboard
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Adminstration
Console
DFM
consoles
VHM
server
SNMP/HTTP
polled info
Media
servers
Events generated by DFM
SNMP traps
DFM
broker
DFM
server
SNMP
traps
SNMP/HTTP
polled info
Managed network
IP
IP
IP
51198
1-8
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
Page 9

Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
How VHM Integrates with Third-Party NMSs
How VHM Integrates with Third-Party NMSs
VHM can be integrated with third-party vendors’ NMSs such as HP OpenView
Network Node Manager. VHM integrates with an NMS in two ways:
• Although VHM receives traps only from DFM, DFM can receive traps from
an NMS or directly from devices. As a result, the traps DFM forwards to
VHM may have come from an NMS or from a device.
See Installing and Setting Up the Device Fault Manager on Solaris for the
default port numbers used by DFM and NMS and for example configuration
scenarios to help you understand how DFM and NMSs can work together.
• VHM provides a trap notifier that allows you to:
–
Configurethe port and IP address of the NMS that the trap notifiersends
SNMP trap messages to.
–
Forward event notifications in the form of an SNMP trap to an NMS,
when the NMS has been configured to listen on that port.
Device Types that VHM Manages
The voice-specific devices managed by VHM are categorized by voice device
group. Table 1-2 lists the voice device groups and their descriptions.
Table 1-2 Voice Device Groups
Group Description
VC (voice cluster) All CallManagers in a voice cluster,
and all the devices with voice cards
that register with any CallManager in a
cluster (including Voice Gateways and
Digital Voice Gateways).
VoiceServices Media servers that may be running
workflow applications or Cisco voice
applications.
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
1-9
Page 10

Device Types that VHM Manages
Table 1-2 Voice Device Groups (continued)
Group Description
Phone Access Switch Catalyst switches with Ethernet ports
VoiceGateway These include:
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
that support IP phone connections and
can supply power to IP phones.
Note If a switch has both Ethernet
and Voice Gateway modules,
the switch will appear only
under VoiceGateway in the
Administration Console. In the
Real-Time Dashboard, it will
appear in both the
VoiceGateway and the Phone
Access Switch groups.
• Catalyst switches with:
–
Voice T1/E1
–
Transcoder
–
Conference bridge
–
Media termination points
(MTPs)
–
Voice FXS
• IOS routers with:
–
FXS
–
FXO
–
T1 PRI/E1 PRI
1-10
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
Page 11

Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Table 1-2 Voice Device Groups (continued)
Group Description
VoiceMailGateways Digital PBX Adapter (DPA) devices
MonitoredPhone Selected IP phones monitored. In the
For each voice device group, the following information is displayed on VHM
Real-Time Dashboard:
• Number of devices in the group
• Number of devices that have a Critical level fault
• Number of devices that have a Warning level fault
• Number of devices whose status is Indeterminate
For further information on the Real-Time Dashboard and the individual
information displayed for each voice device group, see the “Using the Real-Time
Dashboard” section on page 2-1.
VHM Support for Cisco CallManager
that provide Octel Voice Mail
integration to Cisco CallManager. In
the Summary View,
VoiceMailGatewaysare summarized in
one row.
Summary View, all monitored phones
are summarized in one row.
VHM Support for Cisco CallManager
VHM supports Cisco CallManager Release 3.0(5) to 3.2. The functionality you
receive from VHM depends on the release of Cisco CallManager you are using.
Also, each release of Cisco CallManager displays certain information differently.
See the “Cisco CallManager Caveats” section on page 1-12.
The following lists describe the functionality you receive with each release.
Cisco CallManager Release 3.0
• Monitoring of Cisco CallManager run status
• Monitoring of other voice services on run status
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
1-11
Page 12

VHM Support for Cisco CallManager
• Configurationof synthetic transaction on Cisco CallManager,and monitoring
the transactions
• Monitoring of connectivity between Cisco CallManager and various voice
gateways (for example, digital voice gateway DT24+ and DE30+ running
skinny protocol, voice gateways having FXS and FXO )
Cisco CallManager Release 3.1
You receive all the functionality of Cisco CallManager 3.0(5) plus the following:
• Monitoring of Gatekeeper connectivity with a Cisco CallManager cluster
• Monitoring of IP phones
• The ability to identify the voice cluster for the Publisher Node Media Server
• Additional voice gateways:
–
–
–
–
–
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Catalyst 6000 with T1 port and FXS card
VG 200 with FXS, FXO and T1 running MGCP
Digital Voice Gateways DT24+ and DE30
Catalyst 4224 Access Gateway Switch with FXS, FXO and T1
Catalyst 4000 Access Gateway Module with FXS, FXO and T1
1-12
Cisco CallManager Release 3.2
You receive all the functionality of Cisco CallManager 3.1, plus the following.
• Suspect phone detection
• Cluster level information for total and active IP phones
There are also differences in the support for the two hardware platforms Cisco
CallManager uses. The voltage sensor trap is supported for the IBM system but
not for the Compaq system, and processor utilization is supported in the Compaq
system but not in the IBM system.
Cisco CallManager Caveats
• For Cisco CallManager 3.0, the Connectivity tabin the Real-TimeDashboard
DeviceDetail Viewdisplays multiplerows for a voicegatewayport registered
to the CallManager. The rows are empty; the Active CallManager and the
CallManager list do not populate the rows.
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
Page 13

Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
• For Cisco CallManager 3.1 and 3.2, the Connectivity tab in the Real-Time
Dashboard Device Detail View displays one row for a voice gateway port
registered to a Cisco CallManager Cluster. The Active CallManager and the
CallManager list populate the rows.
• For Cisco CallManager 3.0, the Real-Time Dashboard Device Detail View
displays a digital voice interface in the Interface tab. This displays the
D-Channel status. For Cisco CallManagers Release 3.1 and 3.2, the
D-Channel status is not displayed. For these releases, D-Channel is supported
by the ccmGatewayLayer2Change trap.
Locating the Supported Device List
Information about devices installed with VHM can be found at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cw2000/vhm/vhm1_
1/index.htm
Locating the Supported Device List
How VHM Works with the CiscoWorks2000 Server
VHM works in conjunction with the CiscoWorks2000 Server,which represents a
common management foundation, providing a set of management services shared
by multiple management applications. VHM uses these CiscoWorks2000
components:
• Desktop GUI
• Security
• Help Engine and Files
• Web Server/Servlet Engine
• User Accounts
• Widgets, Classes, and Libraries
• Java on SNMP Stack
• CMF Debugging Tools—LogMsg
• Process Management
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
1-13
Page 14

Starting the VHM Application
Starting the VHM Application
To start VHM from the CiscoWorks2000 desktop:
Step 1 Click the Voice Health Monitor drawer from the CiscoWorks2000 desktop.
The following applications and folders are displayed:
• Real-TimeDashboard—Provides a summarized status of the voice network,
grouping voice devices logically and allowing you to drill down into the
details of each device and device group. See the “Using the Real-Time
Dashboard” section on page 2-1.
• Monitoring Console—Allows you to view the alarm logs that VHM and
DFM have generated against devices. See the “Using the Monitoring
Console” section on page 2-17.
• Administration—Contains applications that are used to configure and
administer VHM. See Chapter 5, “Basic VHM Configuration.”
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Getting Started with VHM
Table 1-3 contains the tasks necessary to use VHM to discover VoIP network
devices and applications and to generate faults based on voice network events.
Table 1-3 Getting Started Tasks
Log in as this
CiscoWorks2000
To perform this task...
Import voice network devices into
VHM
Adjust polling intervals and fault
thresholds
Configure VHM notifiers Network Admin or
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
1-14
security role... Then see...
Network Admin or
Network Operator
Network Admin or
Network Operator
Network Operator
“Managing and Unmanaging Voice
Devices in VHM” section on page 5-4
“Configuring Polling and Thresholds”
section on page 5-10
“Configuring Fault Notification”
section on page 5-36
78-11324-02
Page 15

Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
Getting Started with VHM
Table 1-3 Getting Started Tasks (continued)
Log in as this
CiscoWorks2000
To perform this task...
Schedule inventory collection Network Admin or
Configure synthetic transactions
against CallManager
Examine a Real-Time Dashboard
Summary View of the voice
network
Use the Real-Time Dashboard
Status View for a voice device
group
Obtaindevice-specificinformation
from the Real-Time Dashboard
security role... Then see...
“Scheduling Inventory Collection”
Network Operator
Network Admin or
Network Operator
Users in all five security
roles may execute these
section on page 5-27
“Synthetic Transaction Overview”
section on page 6-1
“Using the Real-Time Dashboard”
section on page 2-1
tasks
Users in all five security
roles may execute these
“Using the Status View” section on
page 2-9
tasks
Users in all five security
roles may execute these
“Using the Device Detail View”
section on page 2-15
tasks
View and respond to alarms Users in all five security
roles may execute these
“Using the Monitoring Console”
section on page 2-17
tasks
Add and monitor specific IP
Phones
Network Admin “Setting Up Phone Monitoring”
section on page 5-24
Managing Ethernet voice ports Network Admin “Managing Ethernet Voice Ports”
section on page 5-8
78-11324-02
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
1-15
Page 16

Getting Started with VHM
Chapter 1 Voice Health Monitor Overview
1-16
User Guide for Voice Health Monitor
78-11324-02
 Loading...
Loading...