Page 1

CHAPTER
7
MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
This chapter describes how to recognize and troubleshoot problems you might encounter when
deploying MPLS VPN Solution services.
General Topics
1. Question: I executed an Add VPN Service to CE followed by a Deploy Service Requests, then I
selected Gener ate A udit Reports. Ho we v er , the All VPN Service Requests Report indicates that the
service request is not in either a Deployed or Functional state. Where do I look?
Answer: If the service request is in the Requested, Invalid, or the Failed Deploy state, refer to the
“Provisioning Problems” section on page 7-3. However, if the service request is stuck in Pending,
refer to the “Auditing Problems” section on page 7-10.
2. Question: What are the service deployment states? What do they mean?
Answer: Table 7-1 describes the VPN service request deployment states.
Table 7-1 Summary of MPLS VPN Service Request Types
Service Request Type Description
Broken While the router is correctly configured, the service is unavailable (due to a
broken cable or Layer 2 problem, fo r example). A service req uest moves to
Broken if the Auditor finds the routing and forwarding tables for this service,
but they do not match the service intent.
Closed A service request moves to Closed if the service request should no longer be
used during the provisioning or auditing process. A service request mo ves to
the Closed state only upon a successful audit of a remove request. MPLS
VPN Solution does not remove a service request from the database to allow
for extended auditing. Only a specific administrator action results i n service
requests being removed.
Deployed A service request moves to Deployed if the configlet commands have been
verified as found in t he router confi guration f ile. Deplo yed indicates t hat the
configuration file has been downloaded to the router, and the intent of the
request has been verified at the configuration level.
78-10548-02
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
7-1
Page 2
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
Table 7-1 Summary of MPLS VPN Service Request Types (continued)
Service Request Type Description
Failed Deploy After provisioning occurred, the ser vice req uest failed t o download the
configlets to the router. A service request moves to Failed Deploy if an err or
was detected during the deployment proce ss by the Cisco IP Manager
(CIPM). If CIPM is not being used to download configlets, and the product
is simply exporting configlets to a directory, there is no way to distinguish
between a service request in the Failed Deploy and Pending states. There are
two causes for Failed Deploy status:
• CIPM reports to VPIM that the download failed (lost connection, bad
password, etc.).
• The object could not establish configuration-level verification of intent.
If the configlets are exported to a directory, th e service request cannot mo v e
into a Failed Deploy state.
Functional A service request moves to Functional whe n the Aud itor finds the VPN
routing and forwarding tables (VRF) for this service and they match with the
service intent. This state requires configuration-level verification.
Invalid Indicates that the service request information is incorrect in some way. A
service request moves to Invalid if the request was either internally
inconsistent or not consistent with the rest of the existing network/router
configurations (for example, no more interfaces were available on the
router). The VPN Provisioning Inventory Manager (VPIM) server cannot
generate configlets to service this request.
Lost A service request moves to Lost when the Auditor can not find a
configuration-level verification of intent in the router configuration files.
The service request was deployed, but now some or all router configuration
information is missing. A service request can move to the Lost state only
when the service request had been Deployed or Functional.
Pending A service request moves to Pending when the VPN Provisioning Inventory
Manager (VPIM) server determines that the request looks consistent and w as
able to generate the required configlets for this request. Pending indicates
that the service request has generated the configlets and the configlets are
successfully downloaded to the routers.
The Auditor regards pending service requ ests as ne w requests and begins the
audit. If the service has been freshly provisioned and not yet audited, it is not
an error (pending audit). However, if an audit is done and the service is still
pending, it is in an error state.
Requested If the service is newly entered and not yet deployed, it is not an error.
However, if a Deploy is done and it remains Requested, the service is in an
error state.
7-2
3. Question: Which of the error states are due to provisioning and which are due to auditing?
Answer: Requested (after provisioning), Invalid, and Failed Deploy are due to error conditions in
provisioning. Pending (after auditing), Lost, and Broken are due to error conditions in auditing.
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
78-10548-02
Page 3

Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
Provisioning Problems
The MPLS VPN Solution provisioning system has the following functions:
1. Collect the PE router configuration files (PE-upload)
2. Collect the CE router configuration files (CE-upload)
3. Provisioning
4. Write the changed configuration information to the PE (PE-DownLoad)
5. Write the changed configuration information to the CE (CE-DownLoad)
Functions 1, 2, 4, and 5 are executed by a server called the Download to IPM (DIPM) server. For more
information on the DIPM Server, see “The Download to IPM (DIPM) Server” section on page A-1.
Errors in functions 1 or 2 lead to functions 3, 4, and 5 being skipped. The two servers involved in
provisioning are CVPIM Server and CNGS Server. These are CORBA servers.
The provisioning engine has a model of the router. This router model is modified as necessary to
introduce attributes to support the service request.
1. Question: What is the flow of the provisioning operation?
Answer:
The program that runs all these functions is called VPIMDownLoadClient. VPIM Do wnLoad Client
is a client to the CVPIM server. VPIM DownLoad Client initializes the provisioning by making a
CORBA call to the CVPIM server.
Provisioning Problems
The CVPIM server calls the DIPM server to perform functions 1 and 2. After the product uploads
the fresh configuration files from the router, it provisions the service request and calls the CNGS
server for the changes.
After a successful operation to update the configlet with the necessary changes, the CVPIM server
calls the DIPM server to download the new configlets to the routers (that is, functions 4 and 5).
If functions 1 or 2 fail, the other functions are skipped, and the service request stays in the
Requested state.
If function 3 fails, the service request becomes Invalid.
If function 3 succeeds, but functions 4 or 5 fail, the service request moves to the Failed Deploy
state.
2. Question: Where can I see how the provisioning functions performed in my audit?
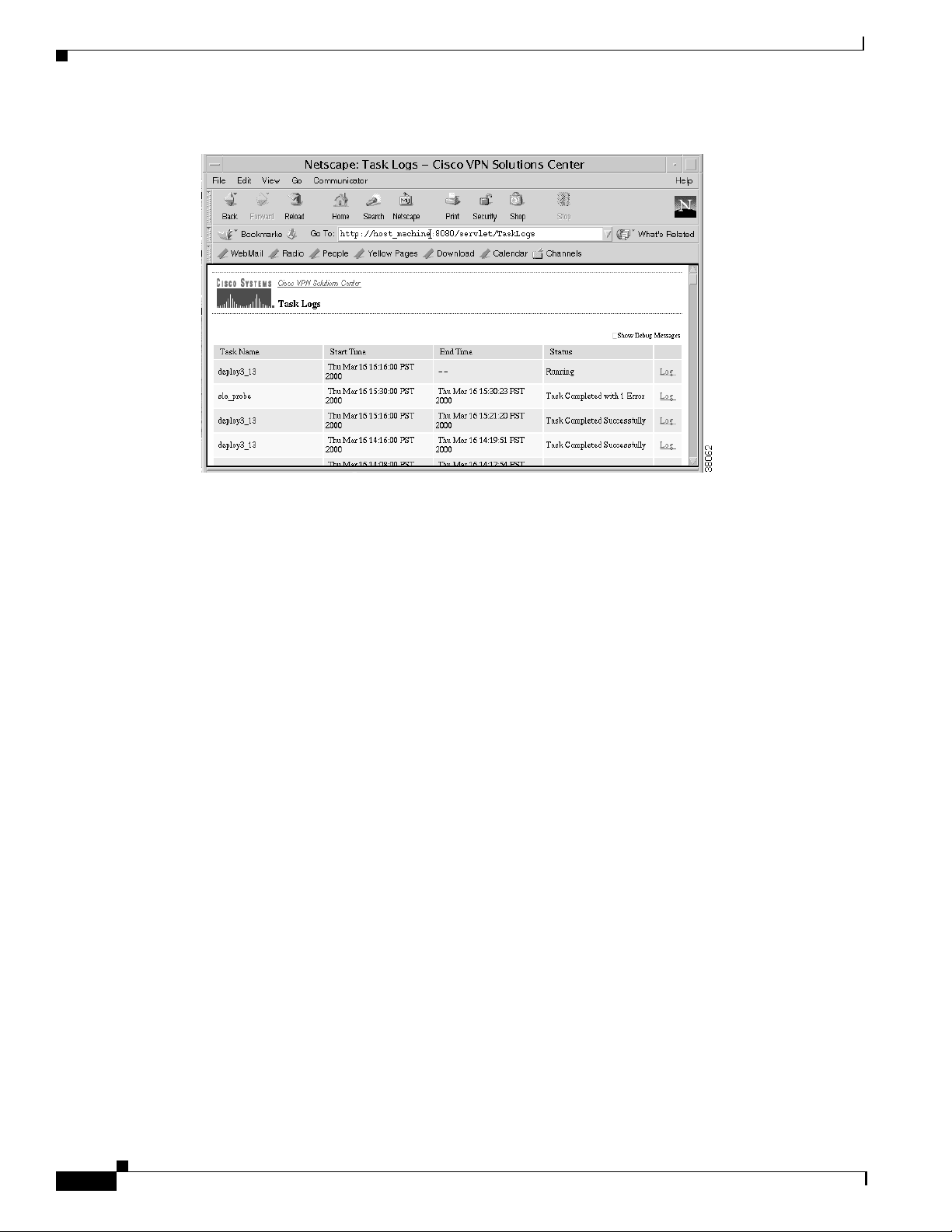
Answer: The first place to look at is in the Task Logs:
a. From the VPN Console, choose Tools > Task Logs.
The browser opens and displays the MPLS VPN Solution Task Logs, as shown in Figure 7-1.
78-10548-02
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
7-3
Page 4
Provisioning Problems
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
Figure 7-1 MPLS VPN Solution Task Logs Browser
b.
Choose the task that was run for this deployment .
The task name is the name you assigned. The tasks are listed in reverse chronological order
(with the latest one first).
c. Click the Log link (in the rightmost column).
Summary information appears in the left pane.
7-4
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
78-10548-02
Page 5
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
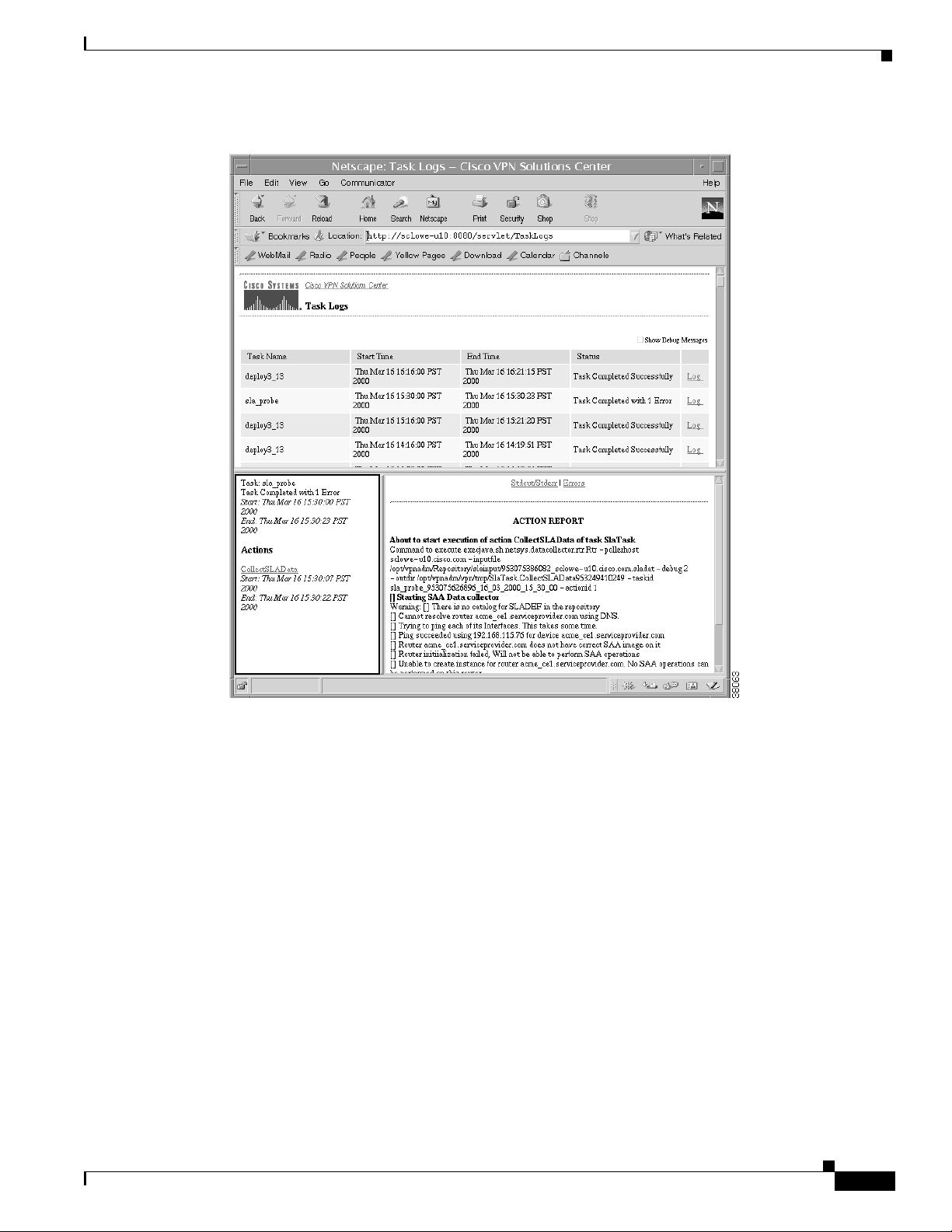
Figure 7-2 Task Log Summary Information and Action Report
Provisioning Problems
78-10548-02
d. To see the Action Report, click the link under the Actions heading.
The Action Report appears.
3. Question: My service request is stuck in the Requested state. Where should I go to lo ok for errors?
Answer: In the Task Log Summary Ta ble, look at the PE-UpLoad and CE-Up Load information for
that service request. One or both of them should say “Fail.” This makes the rest of them “skipped.”
Thus, the service request remains in the Requested state.
4. Question: I tried the link to the Task Log Summary table, but the table isn’t displayed.
Answer: Check at the top of the frame for a set of links: Stdout/Stderr Errors. Std out/Stderr giv es
you the messages that were displayed to the terminal when the VPIMDownLoadClient program
runs. From this, you can see whether and how th e client application ran. Al l abnormal terminations
would be reported. Similarly, Errors lists the error messages reported by the client.
5. Question: When I try to access the Log Summary Table, I see a “Fatal Error” message displayed.
What happened?
Answer: Click the Stdout/Stderr link and view the output.
First, being a CORBA client, did it connect to the CORBA server?
If it did not, you see a number for “Retrying Co nnecti on” lines, follo wed by these lines (at the v ery
end):
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
7-5
Page 6

Provisioning Problems
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
Caught exception when pinging VPIMManager: SYSTEM_EXCEPTION:10085—Communication
failure—no server at host: your_host_name [Completion status: COMPLETED_NO]
This message means that the CVPIM Server is not running. Invoke wdgui and t ake the appropriate
actions:
a. If disabled, issue the following command:
wdclient start CVPIMServer.
b. If disabled-dependent, see which of the dependent server(s) are disabled.
c. If the lock_manager is not running, restart Watchdog.
6. Question: I do not see the task in the Task Log. What happened?
The typical reasons for this are as follows:
–
The Task Scheduler has crashed and it is disabled.
–
The Task Scheduler is malfunctioni ng
–
The Task Scheduler is “disabled-dependent.”
In each of these cases, the scheduled job does not run and no task log is produced.
a. Use wdgui to check the state of the Task Scheduler.
b. If the Task Scheduler is disabled, issue the following command:
wdclient start scheduler
c. If the Task Scheduler is “disabled-dependent,” some of the dependent servers (such as the
lock_manager and the EventServiceServer monitor poller) did not start. Start them by issuing
the command:
wdclient start server_name
If the dependent servers are started, then Task Scheduler starts automatically.
7. Question: I see in the wdlog that the Task Scheduler is up and running. Yet my scheduled task is
not running. What’s wrong?
Answer: When the Task Scheduler starts, it automatically picks up pending requests. However,
there are cases in which it may not. Watch the wdgui messages for the Task Scheduler for a few
minutes. If the Task Scheduler does not start after a few minutes, schedule the task again.
If the Task Scheduler is malfunctioning, do the following:
a. Check the wdgui information for the Task Scheduler. Does this show any abnormality?
b. If not, go to the Task dialog box and issue a refresh.
c. Does the task still show up as active?
d. Note the time it is supposed to start.
Has the time already passed (as shown by the system clock where the Task Scheduler is
running)?
e. In these cases, delete the earlier task and reschedule. After a few minutes, check the wdgui T ask
Scheduler information for any activity or messages.
f. If there are any abnormal error messages in the T ask Scheduler , read the messages and take the
recommended corrective action.
g. However, if there are no messages, or the messages are not understandable, delete the old task
from the task dialog box and restart the Task Scheduler by the command: wdclient restart Task
Scheduler.
h. When the Task Scheduler starts, reschedule the command.
7-6
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
78-10548-02
Page 7

Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
i. If the problem persists, stop the Watchdog.
j. Wait for two minutes, then restart the Watchdog with the startwd command.
Do not forget to delete the active task before restarting Watchdog. Wait until the servers stabilize
before you reschedule the task.
8. Question: My service request is in the Invalid state. How do I correct the problem?
Answer: Wh en a service request is in mo ved to In valid, it is because the request canno t be serviced.
Either something asked for in the service request cannot be serviced or there was an internal error.
a. Bring up is Task Log Summary table at the Task Logs browser page by choose Tools >
Task Logs.
You can also access this information from your browser by entering this URL:
http://vpn_host:8080/servlet/TaskLogs
Refer to the Questions 2 and 3 in this section for additional information.
b. In the Task Log Summary table, click Fail (under Provision).
This takes you to the description of what error condition was noticed during the provisioning.
In some cases, this may give a more detailed error message.
Provisioning Problems
Another place to find internal error information is from the VPN Console.
a. From the VPN Console, choose Provisioning > List all Service Requests.
The All VPN Service Requests Report appears. Notice that the service request is Invalid.
b. Click Request Details.
c. Scroll to the end where you wi ll find this line:
“Moved t o I nvalid by V PI M ,” foll owe d by t h e reason. In some cases , this may include a
summarized error message.
d. Read the error message and note the incorrect value(s) entered.
e. From the All VPN Service Request Report, click Provisioning and choose Modify VPN
Service (see the “Modifying an Existing Service” section on page 4-18).
f. Correct the errors in the modified request and redeploy the service request.
9. Question: What does the error code “10085—Communication failure” mean and how should I
respond to it?
Answer: This is the internal error discussed in Question 8.
The “Communication failure” message in dicates th at the CNGS Server is down or not working
properly.
a. If the CNGS Server is not running, issue the command:
wdclient start CNGSServer
b. If the CNGS Server is running, issue the command:
wdclient restart CNGSServer
After getting the CNGS Server running again, you need to force service deployment.
78-10548-02
c. To do this, choose Provisioning > List all Service Requests.
The All VPN Service Request Report appears.
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
7-7
Page 8

Provisioning Problems
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
Figure 7-3 All VPN Service Request Report
d.
Select the Invalid service request.
e. From the Provisioning drop-down menu, choose Deploy VPN Service.
f. If you have multiple Invalid requests, then either repeat this procedure for all service requests
or choose Provisioning > Deploy Service Requests.
g. Be sure to click the Deploy selected service requests radio button.
10. Question: My service request is in the Failed Deploy state. How should I address the problem?
Answer: Failed Deploy indicates that there is an error while downloading the changed configlets
back to the router (refer to Table 7-1 on page 7-1 for more information).
The procedure described for an Invalid request (see Question 8) pertains here as well. However, in
the Task Logs Summary table, look at the PE-Download or CE-Download information. That is
where the error is. Take the link from there.
The cause of the problem could be either one of two possibilities: 1) while the configuration
changes were downloading, the link to the rou ter(s) was dro pped or 2) a co nfiguration comm and
that was sent to a router invoked a warning or error message.
a. First, read the error message and try to understand it. Was it a communication error?
b. If so, Telnet to the router from the MPLS VPN Solution workstation. Get the communication
to work first.
c. Redeploy the service request by choosing Provisioning > List All Service Requests.
d. From the All VPN Service Requests Report, click Provisioning, and choose Deploy VPN
Services.
7-8
If the error was due to a command that generated a warning or error, the router may have
rejected the command because the version of the Cisco IOS on the router does not support it.
If the problem persists, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center and provide a) the
Command Rejected information, and b) the show version output from the router.
11. Question: I’ve received the error “CORBA generated exception.” Now even if I start the CNGS
Server and redeploy, I get this error and the service request is Invalid.
Answer: It is likely that the CNGS Server has crashed.
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
78-10548-02
Page 9

Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
a. Check to see whether it is disabled or starting. Initially, the CNGS Server is running.
b. Redeploy the service without doing an audit (this skips automatic audit saving time and
complexity).
c. Find the state remaining in Invalid with 1) the error being “CORBA generated exception” and
2) CNGS Server is disabled or starting.
d. Go to the tmpdir (as given in netsys.tmpdir.unix in the csm.properties file) and see if you find
a core dump.
e. If so, preserve the core file and both the PE’s and CE’s configuration files.
f. Tar the Repository at this stage (including the PE CE configurations) and submit the tar file
along with the core fie to the Cisco Support Staff.
12. Question: When downloading router configuration files via C isco IP Manager, how can I see
exactly what is happening?
Answer: The best way is to turn on the Telnet trace for the Cisco IP Manager Network Element
Manager server, or nem_server. You can do this while the Cisco IP Manager system is running by
executing the following command (which is located on the Cisco IP Manager system in the Cisco
IP Manager SRVRS directory):
setTelnetTraceOn
The output is displayed in the terminal window where the Cisco IP Manager system was started.
You need to run this command only once. The command writes a trace flag into a configuration file
for the nem_server expect scripts. The Telnet trace can also be logged to a file.
Start the Cisco IP Manager system as follows:
ipmgr.launch -T trace_files_dir all
For detailed information on configuring and starting Cisco IP Manager, refer to Chapter 3,
“Installation and Configuration” in the Cisco IP Manager (Lite) User’s Guide, Version 2.0.
The Telnet trace is placed in the nem.trace file in the directory specified. On the MPLS VPN
Solution system, you can use the Watchdog GUI to check the DIPM Server log file to monitor the
uploading and downloading of router configuration files via the Cisco IP Manager nem_server. If
more detail is needed, you can enable additional logging information by setting the property
DIPMServer.debugLevel to 3 in the csm.properties file. For this to take effect, you must restart the
DIPM Server.
Provisioning Problems
78-10548-02
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
7-9
Page 10

Auditing Problems
Auditing Problems
Both the Audit new service requests and Audit existi ng servi ce requests audit types provide two tests: a
deployed test and—if specified by checking Use VPN routing information during audits in the task
window—a routing test.These tests are performed in that order. However, if the deployed test fails, the
routing test is not performed.
The deployed test tests whether the router configuration files reflect the service request intent. MPLS
VPN Solution takes the configuration files and builds a “model router” from the configuration
information. The deployed test builds a softw are model of the router and audits it. Hence this mak es our
audit “attribute based.”
However, the de ployed test cann ot determin e whether the service is actually running.The routing te st
(“audit routing”) tests whether the VPN routing tables indicate the service is present.
If the service request fails an Audi t New Service Request, it is kept in Pending. If the service request
passes this audit and audit routing is enabled (by checking Use VPN routi ng information during audits
in the task window), MPLS VPN Solution tests whether there is adequate data for audit routing. If the
audit does not have the data or the Use VPN routing information during audits is not checked, the
service request moves to Deployed.
If the routing test passes, the service request moves to Functional. If the routing test fails, the service
request is Broken.
The starting state for an Audit Existing Service Request can be Deployed, Lost, Functional, or Broken
(refer to Table 7-1 on page 7-1). In each case, the deployed and routing tests a re perform ed in order.
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
If the deployed test fails, the service request moves to (or remains in) the Lost state. If the routing test
fails, the service request moves to (or remains in) the Broken state. If the deployed test succeeds, the
service request moves to (or remains in) the Deployed state; if the ensuing routing test succeeds, the
service request moves to (or remains in) the Functional state.
1. Question: My service request is stuck in Pending or Lost. How do I find out what went wrong?
Answer:
a. For a service request stuck in Pending, generate a service request audit report and select the
Audit new service requests checkbox. In the report window, select Audit Details.
For a service request stuck in Lost, generate a service request audit report and select the Audi t
existing service requests checkbox. In the report window, s elect Audit Details.
This gives you the audit t race for bo th the PE and CE. There are tw o columns—one for the PE
and other for the CE.
b. Look in the “Audit Status” row.
For the audit to pass, both should say “Success.” However, as the service request is stuck in
Pending or Lost, one or both of them should say “Failure.”
c. Go to the column and read through the audit details.
One or both of the tests would fail and the audit details explains why it failed. (This is usually
reported in the next-to-last line.)
d. Read the error information.
The problem is usually missing or wrong configuration information on the router. Has this
configuration command generated in the configlet? The configlet for the router is given below
in the same column.
e. See if the command is present, and if present, whether it is correct.
7-10
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
78-10548-02
Page 11

Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
f. If you feel that the command is incorrect and should be changed, contact Cisco Support for
help.
g. If the command is correct, press the corresponding router configuration button.
The router configuration on which the auditing was performed is shown.
h. Check the configuration command line in the configlet (the line that is apparently missing or
incorrect as discovered by the audit) and see if the command line is present in the router.
i. If it is removed or absent or incorrectly changed in the router, redeploy the service request to
get the corrections sent to the router.
j. However, if the configlet seems correct and the configuration commands are present in the
router, call Cisco Support for assistance.
k. You can continue troubleshooting by selecting Show Pr ocessed Config Text. This presents the
configuration file of the model router.
l. Check whether that command is also present in the configuration of the model router.
m. If it is absent or incorrectly modeled, be sure to inform Cisco Support.
2. Question: I have a service request in two VPNs called Red and Blue. I ran an aud it, bu t I don’ t f ind
my service request listed in the audit reports for the Red VPN.
Answer: The audit is for a service request that may or may not be in multiple VPNs. However,
MPLS VPN Solution runs an Audit VPN by V PN in alphabetical order. In case a service request is
in multiple VPNs, the software audits the service request only once. This takes place in the VPN
that comes up first in the alphabetical sequence, which in this case, is Blue. The software does not
audit the same service request in other VPNs because (a) it is already been audited a nd there is
nothing new to audit; (b) auditing is a costly process and auditing again for the sake of display in
audit reports is a waste of time; and (c) the service request information along with the audit run
information is already available in the VPN Console.
Auditing Problems
If you have a service request in multiple VPNs, lo ok for the audit report i n the VPN that comes first
in the alphabetical sequence.
3. Question: What is the Show Processed Config Text button? How does it differ from the
configuration file?
Answer: When performing a deployed test, MPLS VPN Solution software executes an “attribute
based” audit. This means that the Au ditor builds a softwar e model of the rou ter. To do this, th e
product takes all the relev ant conf i guration commands from th e router. Then the product builds the
software model. MPLS VPN Solution software runs the provisioning and auditing functions using
this software model as a basis.
The configuration text is the computed configuration file of the router’s software model. The
software model does not model all aspects of the router configuration, such as enable passwords
and clock commands, so the configuration text does not contain everything that the configuration
file contains. It does contain all the relevant information such as interface commands, routing
protocol commands, and their dependencies (such as access lists, route-map, and so forth).
4. Question: How do I move my service request to the Functional state?
Answer: When you are scheduling an audit task (by choosing Auditing > Generate Service
Request Audit Reports), you must check the check box, Use VPN routing information
during audits.
78-10548-02
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
7-11
Page 12

Auditing Problems
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
Figure 7-4 Audit Options Window
Also be sure to schedule data collection by choosing Monitoring > Collect VPN Routing
Information.
5. Question: I checked the “Use VPN routing info during audits” option, but I receive the message,
“No VPN routing information found.”
Answer: You must collect VPN routing info to use it. Schedule data collection by choosing
Monitoring > Collect VPN Routing Information.
6. Question: My service request is the Broken state. How do I address the problem?
Answer: While the router is correctly conf ig ured, the service is una vailable (due to a broken cable
or Layer 2 problem, for example). A service request moves to Broken if the Auditor finds the
routing and forwarding tables for this service, but they do not match the service intent.
There are three tests done for the routing test: 1) presence of routes toward the CE, 2) presence of
routes away from the CE, and 3) i f the CE is managed using the management VPN technique, routes
to at least one of the CEs in the management VPN.
All these tests are done for the VRF in w hich the se rvice request belongs. To test the presence of
routes toward the CE, the product looks for a route toward the CE’s provider facing IP address.
The test for routes away from the CE looks for routes toward the “other side of the VPN.” This test
checks the remote connectivity status If the service request is in a management VPN, the final test
checks for a route to the management CE (MCE).
If any of the tests fail, the service request is set to Broken. Since this audit is from the routing
information found on the PE, the routing test audit details are placed under the PE. Because the
routing test is a Layer 3 operational test, the product cannot know why things have gone wrong at
that layer—it could be a broken cable, lost Layer 2 connectivity, and so on.
7. Question: I have a VPN with two CEs. One PE-CE Layer 2 connection is down and in a Brok en or
Lost state. Why does the other PE-CE pair’s service request also move to Broken?
Answer: The routing test checks whether the service request provides a routing level connection
of the site to the VPN. For a VPN to exist, there must be at least two sites. Hence, in a VPN with
two sites, if connectivity of one of the sites go down, the VPN no longer exists. Therefore, the
connectivity of the other site to the VPN also fails—there are no routes across the provider’s core
network.
8. Question: I just created a VPN and added my first site to it. I ran a VPN routing information
collection operation and selected “Use VPN routing information.” Why does the servic e request
move to B r ok e n?
7-12
Answer: First read the answer to the previous question (Question 7).
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
78-10548-02
Page 13

Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
Until you add at least two sites to the VPN, the VPN is not complete. The first site cannot
participate in a VPN because the VPN does not yet exist. Thus, the service request moves to
Broken. The service request moves to Functional when the second site is connected to the VPN,
assuming core network connectivity exists and is functional.
9. Question: What are the run_ngs.log and conn_solver.log files?
Answer: These files are found in repository_path/Baselines/baseline_name
where baseline_name is VPN_BS_vpn_name for a VPN and SP_BS_provider_name for a provider.
These files contains log information about how the audit proceeds from th e two processes that make
up the auditing system—run_ngs and conn_solver. Run_ngs is the initialization, reporting, and
finalization process. Conn_solver is the actual audit engine.
10. Question: I’ve scheduled an audit. But I do not see any audit reports. Has it run as yet?
Answer: First, is there a service request to audit? If not , no reports can be genera ted.
n. If a service request exists, start by going to the Task Logs (see Question 2 under “Provisioning
Problems” for information on accessing the Task Logs).
o. Click GenerateVPN AuditReports And Topologies.
p. Click Stdout/Stderr.
Detailed information is listed on the right pane.
Auditing Problems
q. Scroll down to the line “about to call run_ngs on baseline baseline_name.”
where baseline_name is VPN_BS_vpn_name for a VPN and SP_BS_provider_name for a
provider. Below that note a call to “run_ngs” made with n argument.
r. Look for a line such as “run_ngs for baseline VPN_BS_VPN failed with exit code n.”
s. Check the value of n.
If the value of n is 6, run_ngs may have crashed.
t. Check the core file in the tmpdir directory (as given in netsys.tmpdir.unix in csm.properties
file) and see if it belongs to run_ngs or conn_solver.
u. If the value of n is 1 or another number, go to the repository_path/Baselines/baseline_name
directory and read the file run_ngs.log.
The run_ngs.log file provides the reasons for the unexpected termination.
v. In any case, tar the Repository and save the core file (if any) and contact Cisco Support for
assistance.
If the run_ngs.log file says something like: “path/.dataroot pointed to by default.ddf does not
exist,” someone copied over the Repository. Read the next question for the solution for this.
11. Question: I copied my Repository to a new location on a new machine. Now I cannot run audits.
Answer: Go to repository_path/Baselines and issue this command:
rm -f VPN_BS_*/default.ddf SP_BS_*/default.ddf
Now the audits will run.
12. Question: The audit seems to have been performed (from List All Service Requests), b ut there are
no reports.
78-10548-02
Answer: This can occur if run_ngs crashed while conn_solver succeeded in writing out state
change and audit trail information to the Repository. If this is this case, you do not see any reports,
yet the job seems to be done. Be sure to send the core file and the Repository to Cisco Support.
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
7-13
Page 14

Auditing Problems
Chapter 7 MPLS VPN Solution Troubleshooting Guide
13. Question: The audit seems to have been performed (from audit reports), but the All VPN Service
Requests Report shows the service request is still in the prior state.
Answer: This is possible if the saving the state change and audit trail information to the Repository
failed. In such a case, observe that an extra row is present in the report: Repository Error. This
details the reasons for the failure to write to the Repository. If you see this, report it to the Cisco
Support.
14. Question: I see an extra row in the Audit Reports: Repository Error. What does this mean?
Answer: A read/write operation to the Repository failed. Report this error and send your current
Repository to Cisco Support.
7-14
Cisco VPN Solutions Center: MPLS Solution User Guide
78-10548-02
 Loading...
Loading...