Page 1

Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide
for Cisco CallManager 3.2
Cisco IP Phones 7960, 7940, and 7910
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Customer Order Number: DOC-7810453=
Text Part Number: 78-10453-04
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT
NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT
ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR
THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE
INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU
ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A
COPY.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: The equipment described in this manual generates and may radiate
radio-frequency energy. If it is not installed in accordance with Cisco’s installation instructions, it may cause interference with radio and television
reception. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in
part 15 of the FCC rules. These specifications are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
Modifying the equipment without Cisco’s written authorization may result in the equipment no longer complying with FCC requirements for Class
A or Class B digital devices. In that event, your right to use the equipment may be limited by FCC regulations, and you may be required to correct
any interference to radio or television communications at your own expense.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the Cisco
equipment or one of its peripheral devices. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the interference by
using one or more of the following measures:
• Turn the television or radio antenna until the interference stops.
• Move the equipment to one side or the other of the television or radio.
• Move the equipment farther away from the television or radio.
• Plug the equipment into an outlet that is on a different circuit from the television or radio. (That is, make certain the equipment and the television
or radio are on circuits controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.)
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco Systems, Inc. could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as
part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE
PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR
INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
CCIP, the Cisco Powered Network mark, the Cisco Systems Verified logo, Cisco Unity, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, Internet
Quotient, iQ Breakthrough, iQ Expertise, iQ FastTrack, the iQ Logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, Networking Academy, ScriptShare, SMARTnet,
TransPath, and Voice LAN are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Discover All That’s Possible,
The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst,
CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Press, Cisco
Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch,
GigaStack, IOS, IP/TV, LightStream, MGX, MICA, the Networkers logo, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, RateMUX,
Registrar, SlideCast, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its
affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Web site are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply
a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0201R)
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960, 7940, and 7910
Copyright © 2000-2002, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Page 3

About This Guide ix
Overview ix
Audience ix
Objectives x
Organization x
Related Documentation xi
Obtaining Documentation xii
World Wide Web xii
Documentation CD-ROM xii
Ordering Documentation xiii
Documentation Feedback xiii
Obtaining Technical Assistance xiv
Cisco.com xiv
Technical Assistance Center xiv
Cisco TAC Web Site xv
Cisco TAC Escalation Center xvi
CONTENTS
CHAPTER
78-10453-04
Document Conventions xvi
1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone 1-1
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940 1-2
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone 7910 1-5
What Networking Protocols Are Used? 1-7
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
iii
Page 4

Contents
What Features are Supported on the Cisco IP Phone? 1-9
Feature Overview 1-10
Configuring Telephony Features Using Cisco CallManager
Administration
Configuring Network Features Using the IP Phone 1-11
Providing Users with Feature Information 1-11
Understanding the Requirements for Installing and Configuring the
Cisco IP Phone
1-10
1-12
CHAPTER
2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network 2-1
Understanding Interactions with Other Cisco IP Telephony Products 2-1
Understanding How the Cisco IP Phone Interacts with
Cisco CallManager
2-2
Understanding How the Cisco IP Phone Interacts with the Cisco Catalyst
Family of Switches
2-2
Understanding the Phone Startup Process 2-3
Obtaining Power from the Switch 2-4
Loading the Stored Phone Image 2-4
Configuring VLAN 2-4
Obtaining an IP Address 2-4
Accessing TFTP Server 2-5
Requesting the Configuration File 2-5
Contacting Cisco CallManager 2-5
Guidelines for Configuring Ports on Cisco IP Phones 2-6
Connecting to the Network 2-6
Using the Network Port 2-6
Using the Access Port 2-7
Providing Power to the Cisco IP Phone 2-7
Power Source Design 2-7
Redundancy Feature 2-8
iv
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 5

Contents
Configuring the Handset, Headset, and Speakerphone 2-8
Connecting a Handset to a Cisco IP Phone 2-9
Connecting a Headset to a Cisco IP Phone 2-9
Disabling the Speakerphone Feature 2-10
Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database 2-10
Using Auto-Registration 2-11
Adding Phones Manually 2-12
Adding Phones Manually Using DHCP 2-12
Assigning Static IP Addresses 2-13
Using the Bulk Administration Tool 2-15
Configuring the Cisco IP Phone 7960 to Support the 7914 Expansion Module 2-15
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone 3-1
Before You Begin 3-1
Network Requirements 3-2
Cisco CallManager Configuration 3-2
Safety 3-3
Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network 3-4
Adjusting Placement of the Cisco IP Phone 3-7
Adjusting Cisco IP Phone Placement on the Desktop 3-7
Mounting the Phone to the Wall 3-7
Verifying the Phone Startup Process 3-9
Configuring Startup Network Settings 3-10
4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module 4-1
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module 4-2
Before You Begin 4-2
Package List 4-2
Footstand Kits 4-2
78-10453-04
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
v
Page 6

Contents
Additional Equipment 4-3
Safety Notices 4-3
Connecting the 7914 Expansion Module 4-4
Removing the Footstand from the Cisco IP Phone 7960 4-5
Connecting the Support Bar to the Cisco IP Phone 7960 4-6
Connecting the 7914 Expansion Module to the Support Bar 4-7
Connecting the RS 232 Cable 4-9
Connecting the Power Supply 4-11
Connecting the Footstand 4-12
Start Up Sequence 4-14
CHAPTER
5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone 5-1
Accessing the Network Configuration Settings 5-2
Verifying Network Settings 5-3
Modifying DHCP Settings 5-9
Enabling DHCP 5-10
Disabling DHCP 5-11
Releasing a DHCP Address 5-12
Configuring IP Settings 5-14
Assigning an IP Address 5-14
Assigning Default Router 5-15
Assigning Subnet Mask 5-17
Assigning Domain Name 5-18
Assigning DNS Servers 5-19
Configuring VLAN Settings 5-20
Configuring TFTP Options 5-21
Assigning a TFTP Sever 5-21
Using an Alternate TFTP Server 5-23
Assigning a Backup TFTP Server 5-24
vi
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 7

Configuring Ports 5-25
Configuring the SW Port 5-26
Configuring the PC Port 5-27
Contents
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
6 Configuring Cisco IP Phones, Users, and Features in Cisco CallManager 6-1
Configuring Cisco IP Phones in Cisco CallManager 6-2
Adding Users to Cisco CallManager 6-5
Modifying Phone Button Templates 6-5
Possible Phone Button Template Configurations 6-6
Updating Button Labels 6-7
Configuring Corporate Directories 6-8
Setting Up User Services 6-8
Providing Information to End Users 6-9
7 Troubleshooting the Cisco IP Phone 6-1
Obtaining Status, Model, and Version Information 6-1
Displaying Statistics for Current Call 6-2
Viewing Status Messages 6-3
Displaying Network Statistics 6-8
Verifying Model and Serial Number 6-10
Verifying Firmware Version 6-11
Resetting the Cisco IP Phone 6-12
78-10453-04
Erasing Local Configuration 6-13
Updating Firmware Version 6-14
Resolving Startup Problems 6-15
Symptom: Cisco IP Phone Does Not Start Up and LCD Screen Does Not
Display
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
6-16
vii
Page 8

Contents
Symptom: Cisco IP Phone Not Registering with Cisco CallManager 6-17
Identifying Error Messages 6-17
Registering the Phone with Cisco CallManager 6-18
Checking Network Connectivity 6-18
Verifying TFTP Server Settings 6-18
Verifying IP Addressing and Routing 6-19
Verifying DNS Settings 6-19
Verifying Cisco CallManager Settings 6-20
Cisco CallManager and TFTP Services Are Not Running 6-20
Creating a New Configuration File 6-21
Symptom: Cisco IP Phone Resetting 6-21
Verifying Physical Connection 6-22
Identifying Intermittent Network Outages 6-22
Verifying DHCP Settings 6-23
Checking Static IP Address Settings 6-23
Verifying Voice VLAN Configuration 6-23
Verifying that the Phones Have Not Been Intentionally Reset 6-23
Eliminating DNS or Other Connectivity Errors 6-24
I
NDEX
viii
Resolving Known Issues 6-25
Technical Specifications A-1
Physical and Operating Environment Specifications A-1
Cable Specifications A-2
Network and Access Port Pinouts A-2
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 9

Overview
Audience
About This Guide
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2,
Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910 provides the information you need to
understand, install, configure, and manage a Cisco IP Phone on your network.
78-10453-04
Network engineers, system administrators, or telecom engineers should review
this guide to learn the steps required to properly set up the Cisco IP Phone on the
network.
The tasks described are considered to be administration-level tasks and are not
intended for end-users of the phones. Many of the tasks involve configuring
network settings and affect the phone’s ability to function in the network.
Because of the close interaction between the Cisco IP Phone and
Cisco CallManager, these tasks require familiarity with Cisco CallManager.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
ix
Page 10
About This Guide
Objectives
Objectives
This guide provides the required steps to get the Cisco IP Phone up and running
on a Voice-over-IP (VoIP) network. Because of the complexity of an IP telephony
network, this guide does not provide complete and detailed information for
procedures that you need to perform on the Cisco CallManager application or
other network devices.
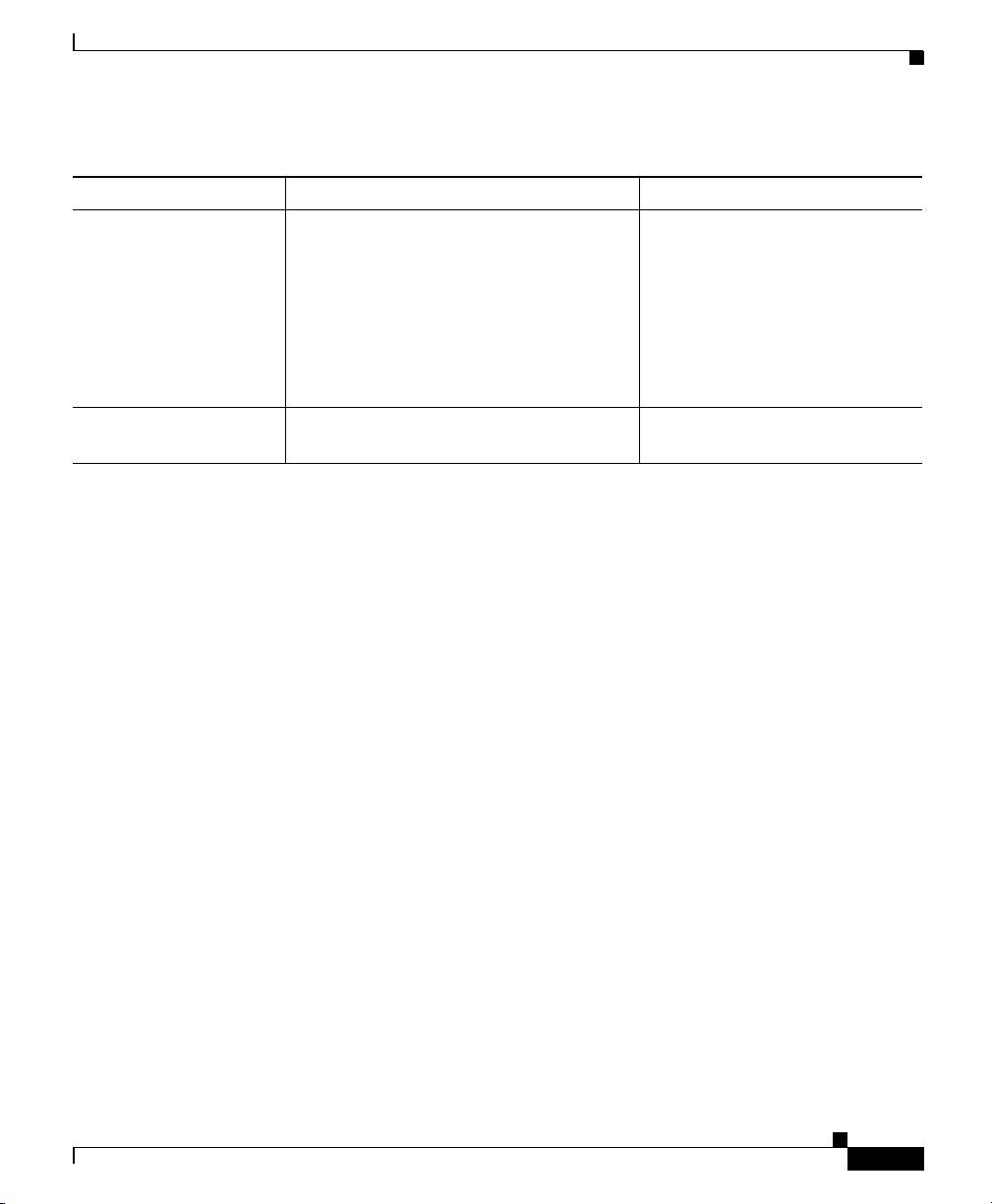
Organization
Table 1 provides an overview of the organization of this guide.
Table 1 Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide Organization
Chapter Description
Chapter 1, “An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone” Provides a conceptual overview and description of
the Cisco IP Phone.
Chapter 2, “Preparing to Install the
Cisco IP Phone on Your Network”
Chapter 3, “Installing the Cisco IP Phone” Describes how to properly and safely install and
Chapter 4, “Installing the
7914 Expansion Module”
Chapter 5, “Configuring Network Settings on the
Cisco IP Phone”
Chapter 6, “Configuring Cisco IP Phones, Users,
and Features in Cisco CallManager”
Chapter 7, “Troubleshooting the Cisco IP Phone” Provides tips for troubleshooting the
Describes how the IP Phone interacts with other
key IP telephony components, and provides an
overview of the tasks required prior to installation.
configure the Cisco IP Phone on your network.
Describes how to install and connect one or two
Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Modules on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960.
Describes how to configure network settings,
verify status, and make global changes to the
Cisco IP Phone.
Provides an overview of procedures for adding
users to the network, configuring corporate
directories, and setting up web information
services.
Cisco IP Phones and the Expansion Module.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
x
78-10453-04
Page 11
About This Guide
Related Documentation
Table 1 Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide Organization (continued)
Chapter Description
Appendix A, “Technical Specifications” Provides a reference of the detailed technical
specifications of the Cisco IP Phone.
Index Provides reference information.
Related Documentation
For more information about Cisco IP Phones or Cisco CallManager, refer to these
publications, which are available at the following location:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/index.htm
Cisco IP Phone Models 7960, 7940, and 7910
• Find Your Phone Guide on the Web
• At a Glance Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940
• Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940 User Guide
78-10453-04
• Quick Reference Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
• Release Notes for the IP Phone 7960/7940/7910
• Getting Started with the Cisco IP Phone 7910
• Cisco IP Phone 7910 Quick Reference Card
Cisco CallManager Administration
• Cisco CallManager Administration Guide
• Cisco CallManager System Guide
• Cisco CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide
• Cisco CallManager Serviceability System Guide
• Bulk Administration Tool User Guide
Cisco IP Phones Services and Features
• Personal Directory Configuration Guide
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xi
Page 12

Obtaining Documentation
Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
• Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module Quick Start Guide
Cisco Customer Response Applications 2.2
• Cisco CallManager Extended Services Administrator's Guide
You can find these publications on the Web from links at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/index.htm
Obtaining Documentation
The following sections explain how to obtain documentation from Cisco Systems.
World Wide Web
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at
the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com
About This Guide
Translated documentation is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Documentation CD-ROM
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a Cisco
Documentation CD-ROM package, which is shipped with your product. The
Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than
printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or
through an annual subscription.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xii
78-10453-04
Page 13

About This Guide
Ordering Documentation
Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
• Registered Cisco Direct Customers can order Cisco product documentation
from the Networking Products MarketPlace:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/order/order_root.pl
• Registered Cisco.com users can order the Documentation CD-ROM through
the online Subscription Store:
http://www.cisco.com/go/subscription
• Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local
account representative by calling Cisco corporate headquarters (California,
USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in North America, by calling 800
553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
Obtaining Documentation
78-10453-04
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on Cisco.com, you can submit
technical comments electronically. Click Leave Feedback at the bottom of the
Cisco Documentation home page. After you complete the form, print it out and
fax it to Cisco at 408 527-0730.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover
of your document, or write to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Document Resource Connection
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xiii
Page 14

Obtaining Technical Assistance
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance.
Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and
sample configurations from online tools by using the Cisco Technical Assistance
Center (TAC) Web Site. Cisco.com registered users have complete access to the
technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco.com
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that
provides immediate, open access to Cisco information, networking solutions,
services, programs, and resources at any time, from anywhere in the world.
Cisco.com is a highly integrated Internet application and a powerful, easy-to-use
tool that provides a broad range of features and services to help you to
• Streamline business processes and improve productivity
• Resolve technical issues with online support
About This Guide
• Download and test software packages
• Order Cisco learning materials and merchandise
• Register for online skill assessment, training, and certification programs
You can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain customized information and service.
To access Cisco.com, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com
Technical Assistance Center
The Cisco TAC is available to all customers who need technical assistance with
a Cisco product, technology, or solution. Two types of support are available
through the Cisco TAC: the Cisco TAC Web Site and the Cisco TAC Escalation
Center.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xiv
78-10453-04
Page 15

About This Guide
Inquiries to Cisco TAC are categorized according to the urgency of the issue:
• Priority level 4 (P4)—You need information or assistance concerning Cisco
• Priority level 3 (P3)—Your network performance is degraded. Network
• Priority level 2 (P2)—Your production network is severely degraded,
• Priority level 1 (P1)—Your production network is down, and a critical impact
Which Cisco TAC resource you choose is based on the priority of the problem and
the conditions of service contracts, when applicable.
Cisco TAC Web Site
The Cisco TAC Web Site allows you to resolve P3 and P4 issues yourself, saving
both cost and time. The site provides around-the-clock access to online tools,
knowledge bases, and software. To access the Cisco TAC Web Site, go to the
following URL:
Obtaining Technical Assistance
product capabilities, product installation, or basic product configuration.
functionality is noticeably impaired, but most business operations continue.
affecting significant aspects of business operations. No workaround is
available.
to business operations will occur if service is not restored quickly. No
workaround is available.
78-10453-04
http://www.cisco.com/tac
All customers, partners, and resellers who have a valid Cisco services contract
have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web
Site. The Cisco TAC Web Site requires a Cisco.com login ID and password. If
you have a valid service contract but do not have a login ID or password, go to
the following URL to register:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issues by using the Cisco TAC Web Site, and
you are a Cisco.com registered user, you can open a case online by using the TAC
Case Open tool at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have Internet access, it is recommended that you open P3 and P4 cases
through the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xv
Page 16
Document Conventions
Cisco TAC Escalation Center
The Cisco TAC Escalation Center addresses issues that are classified as priority
level 1 or priority level 2; these classifications are assigned when severe network
degradation significantly impacts business operations. When you contact the TAC
Escalation Center with a P1 or P2 problem, a Cisco TAC engineer will
automatically open a case.
To obtain a directory of toll-free Cisco TAC telephone numbers for your country,
go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Before calling, please check with your network operations center to determine the
level of Cisco support services to which your company is entitled; for example,
SMARTnet, SMARTnet Onsite, or Network Supported Accounts (NSA). In
addition, please have available your service agreement number and your product
serial number.
Document Conventions
About This Guide
This document uses the following conventions:
Convention Description
boldface font Commands and keywords are in boldface.
italic font Arguments for which you supply values are in italics.
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional.
{ x | y | z } Alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars.
[ x | y | z ] Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars.
string A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string
or the string will include the quotation marks.
screen font Terminal sessions and information the system displays are in screen font.
boldface screen font Information you must enter is in boldface screen font.
italic screen font Arguments for which you supply values are in italic screen font.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xvi
78-10453-04
Page 17
About This Guide
Document Conventions
Convention Description
^ The symbol ^ represents the key labeled Control—for example, the key
combination ^D in a screen display means hold down the Control key while
you press the D key.
< > Nonprinting characters, such as passwords are in angle brackets.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to
material not covered in the publication.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could
result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warnings use the following conventions:
Warning
Waarschuwing
78-10453-04
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that
could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be
aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be
familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. To see
translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer
to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document
that accompanied this device.
Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een
situatie die lichamelijk letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan
enige apparatuur gaat werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de
bij elektrische schakelingen betrokken risico's en dient u op de
hoogte te zijn van standaard maatregelen om ongelukken te
voorkomen. Voor vertalingen van de waarschuwingen die in
deze publicatie verschijnen, kunt u het document Regulatory
Compliance and Safety Information (Informatie over naleving van
veiligheids- en andere voorschriften) raadplegen dat bij dit
toestel is ingesloten.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xvii
Page 18

Document Conventions
About This Guide
Varoitus
Attention
Warnung
Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi
johtaa ruumiinvammaan. Ennen kuin työskentelet minkään
laitteiston parissa, ota selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä
vaaroista ja tavanomaisista onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista.
Tässä julkaisussa esiintyvien varoitusten käännökset löydät
laitteen mukana olevasta Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information -kirjasesta (määräysten noudattaminen ja tietoa
turvallisuudesta).
Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous
trouvez dans une situation pouvant causer des blessures ou des
dommages corporels. Avant de travailler sur un équipement,
soyez conscient des dangers posés par les circuits électriques et
familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment utilisées
pour éviter les accidents. Pour prendre connaissance des
traductions d’avertissements figurant dans cette publication,
consultez le document Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information (Conformité aux règlements et consignes de
sécurité) qui accompagne cet appareil.
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer
Situation, die zu einer Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie
mit der Arbeit an irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie sich der
mit elektrischen Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der
Standardpraktiken zur Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt.
Übersetzungen der in dieser Veröffentlichung enthaltenen
Warnhinweise finden Sie im Dokument Regulatory Compliance
and Safety Information (Informationen zu behördlichen
Vorschriften und Sicherheit), das zusammen mit diesem Gerät
geliefert wurde.
xviii
Avvertenza
Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione
potrebbe causare infortuni alle persone. Prima di lavorare su
qualsiasi apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi
ai circuiti elettrici ed essere al corrente delle pratiche standard
per la prevenzione di incidenti. La traduzione delle avvertenze
riportate in questa pubblicazione si trova nel documento
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Conformità alle
norme e informazioni sulla sicurezza) che accompagna questo
dispositivo.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 19

About This Guide
Document Conventions
Advarsel
Aviso
¡Advertencia!
Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon
som kan føre til personskade. Før du utfører arbeid på utstyr, må
du vare oppmerksom på de faremomentene som elektriske
kretser innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med vanlig praksis når
det gjelder å unngå ulykker. Hvis du vil se oversettelser av de
advarslene som finnes i denne publikasjonen, kan du se i
dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
(Overholdelse av forskrifter og sikkerhetsinformasjon) som ble
levert med denne enheten.
Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação
que lhe poderá causar danos físicos. Antes de começar a
trabalhar com qualquer equipamento, familiarize-se com os
perigos relacionados com circuitos eléctricos, e com quaisquer
práticas comuns que possam prevenir possíveis acidentes. Para
ver as traduções dos avisos que constam desta publicação,
consulte o documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information (Informação de Segurança e Disposições
Reguladoras) que acompanha este dispositivo.
Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su
integridad física. Antes de manipular cualquier equipo,
considerar los riesgos que entraña la corriente eléctrica y
familiarizarse con los procedimientos estándar de prevención de
accidentes. Para ver una traducción de las advertencias que
aparecen en esta publicación, consultar el documento titulado
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Información
sobre seguridad y conformidad con las disposiciones
reglamentarias) que se acompaña con este dispositivo.
78-10453-04
Varning!
Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en
situation som kan leda till personskada. Innan du utför arbete på
någon utrustning måste du vara medveten om farorna med
elkretsar och känna till vanligt förfarande för att förebygga
skador. Se förklaringar av de varningar som förkommer i denna
publikation i dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information (Efterrättelse av föreskrifter och
säkerhetsinformation), vilket medföljer denna anordning.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
xix
Page 20

Document Conventions
About This Guide
xx
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 21

CHAPTER
1
An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
The Cisco IP Phone provides functionality similar to that of a traditional analog
phone, but must be configured and managed like other network devices.
You can choose among three models of Cisco IP Phones—Cisco IP Phone 7960,
Cisco IP Phone 7940, and Cisco IP Phone 7910. Each Cisco IP Phone supports
G.711, G.729, G.729a, G.729b, and G.729ab audio compression.
This section covers the following topics:
• Understanding the Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940, page 1-2
• Understanding the Cisco IP Phone 7910, page 1-5
• What Networking Protocols Are Used?, page 1-7
• What Features are Supported on the Cisco IP Phone?, page 1-9
• Understanding the Requirements for Installing and Configuring the
Cisco IP Phone, page 1-12
78-10453-04
Caution Using a cell phone or mobile phone in close proximity to a Cisco IP Phone might
cause interference.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
1-1
Page 22

Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone Models
7960 and 7940
The Cisco IP Phone models 7960 and 7940 are full-featured, multiline telephones
that provide voice communication over an IP network. These phones function as
managerial-level office telephones, replacing traditional analog telephones in an IP
telephony network.
The Cisco IP Phone model 7960 and 7940 differ only in the number of available
line or speed dial buttons. The Cisco IP Phone 7940 has two lines, and the 7960
has six lines.
The main components of both models are illustrated in and Figure 1-1 and
Figure 1-2, and defined in the table that follows.
Figure 1-1 Cisco IP Phone 7960
2
1
1617
15
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
121314
1011
68561
1-2
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 23

Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
Figure 1-2 Cisco IP Phone 7940
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940
2
3
4
1
5
6
7
8
9
1
Handset with
indicator light
10111617 12131415
Functions like a traditional handset. The light strip at the
top of the handset blinks when the phone rings and
68562
remains lit to indicate a new voice mail message.
2
LCD screen Displays features such as the time, date, phone number,
caller ID, line/call status and soft key tabs.
3
Cisco IP Phone
Indicates Cisco IP Phone model.
model type
4
Line or speed
dial button
Opens a new line, speed dials the number on the LCD
screen, or ends a call. The Cisco IP Phone 7960 has six
line or speed dial buttons and the 7940 has two.
78-10453-04
5
Footstand
Allows you to adjust the angle of the phone base.
adjustment
6
Directories
Provides access to call histories and directories.
button
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
1-3
Page 24
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940
7
? button Displays help on LCD screen for a phone button or
8
Settings button Provides access to phone settings such as contrast and
9
Speaker button Toggles the speaker on or off.
10
Mute button Toggles the mute on or off.
11
Headset button Toggles the headset on or off.
12
Volume button Increases or decreases volume for the handset, headset,
13
Services button Provides access to phone services (if available).
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
function and provides status information about the
current call.
ring sound, network configuration, and status
information.
or speakerphone (depending upon which is currently
active). Also controls the ringer volume (if on-hook),
and the LCD contrast.
1-4
14
Messages button Provides access to a message system (if available).
15
Navigation
button
16
Dial pad Works exactly like the dial pad on a traditional
Enables you to scroll through text and select features
displayed on the LCD screen.
telephone.
17
Soft keys Enable you to engage any of the functions displayed on
the corresponding LCD tabs. Soft keys point to feature
options displayed along the bottom of the LCD screen.
Soft keys change depending on the status of the phone.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 25

Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
Understanding the Cisco IPPhone 7910
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone 7910
The Cisco IP Phone 7910 is designed primarily for common-use areas that require
basic features, such as lobbies, break rooms, and hallways.
The Cisco IP Phone 7910 is available in two configurations:
• Cisco IP Phone 7910—includes a single 10-BaseT connection
• Cisco IP Phone 7910+SW—includes an optional internal 3-port switch that
allows a 100-Mbps connection
The main components of the Cisco IP Phone 7910 are illustrated in Figure 1-3
and defined in the table that follows.
Figure 1-3 Cisco IP Phone 7910 Features
1
2
3 4 5 7
6
78-10453-04
LINE HOLD TRANSFER SETTINGS
8
messages conf froward
speed 1 speed 2 redial
9
10
11
12
131516 14
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
68563
1-5
Page 26
Understanding the Cisco IP Phone 7910
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
1 Handset with
Functions like a traditional handset.
indicator light
2 LCD screen Displays features such as time, date, directory number,
caller ID, and line/call status.
3 Line button Opens a new line.
4 Hold button Puts a current call on hold or takes a call off hold.
5 Transfer button Transfers the current caller to a different phone number.
6 Settings button Adjust handset, speaker, and ringer volume, the ringer
type, and contrast on the LCD screen.
7 Footstand
Allows you to adjust the angle of the phone base.
adjustment
8 Messages
button
Programmable with Cisco CallManager to suit the needs
of your company. See the “Modifying Phone Button
Templates” section on page 6-5 for additional
information. The default setting for this button allows
you to access voice mail message.
9 Conference
button
Programmable with Cisco CallManager to suit the needs
of your company. See the “Modifying Phone Button
Templates” section on page 6-5 for additional
information. The default setting for this button allows
you to initiate a conference call.
10 Forward button Programmable with Cisco CallManager to suit the needs
of your company. See the “Modifying Phone Button
Templates” section on page 6-5 for additional
information. The default setting for this button allows
you to redirect calls to another number.
11 Redial button Programmable with Cisco CallManager to suit the needs
of your company. See the “Modifying Phone Button
Templates” section on page 6-5 for additional
information. The default setting for this button allows
you to dial the last number called.
12 Speaker button Toggles the speaker on or off.
1-6
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 27
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
What Networking Protocols Are Used?
13 Mute button Toggles the Mute on or off.
14 Volume button Increases or decreases the volume for the handset or
speaker. Also controls the ringer volume and the LCD
contrast.
15 Speed dials Programmable with Cisco CallManager to suit the needs
of your company. See the “Modifying Phone Button
Templates” section on page 6-5 for additional
information. The default setting for this button allows
you to quickly call a frequently dialed number.
16 Dialing pad Functions like a traditional telephone dialing pad.
What Networking Protocols Are Used?
Cisco IP Phones support several industry-standard and Cisco networking
protocols required for voice communication. See Table 1 - 1 for an overview of the
supported networking protocols.
Table 1-1 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco IP Phone
Networking Protocol Purpose Usage Notes
Bootstrap Protocol
(BootP)
Cisco Discovery
Protocol (CDP)
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
BootP enables a network device such as
the Cisco IP Phone to discover certain
startup information, such as its IP
address.
CDP is a device-discovery protocol that
runs on all Cisco-manufactured
equipment.
Using CDP, a device can advertise its
existence to other devices and receive
information about other devices in the
network.
If you are using BootP to assign
IP addresses to the
Cisco IP Phone, this is displayed
in the network configuration
settings on the phone.
The Cisco IP Phone uses CDP to
communicate information such as
auxiliary VLAN ID, per port
power management details, and
Quality of Service (QoS)
configuration information with the
Cisco Catalyst switch.
1-7
Page 28
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
What Networking Protocols Are Used?
Table 1-1 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco IP Phone (continued)
Networking Protocol Purpose Usage Notes
Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol
(DHCP)
DHCP dynamically allocates and assigns
an IP address to network devices.
DHCP enables you to connect the IP
phone into the network and become
operational without manually assigning
an IP address or configuring additional
required network parameters.
Internet Protocol (IP) IP is a messaging protocol that addresses
and sends packets across the network.
DHCP is enabled by default. If
disabled, you must manually
configure the IP address, subnet
mask, gateway, and an TFTP
server on each phone locally.
Cisco recommends that you use
DHCP custom option 150. With
this method, you configure the
TFTP server IP address as the
option value. For additional
supported DCHP configurations,
see the Cisco CallManager
System Guide.
To communicate using IP,
network devices must have an
assigned IP address, subnet, and
gateway.
Real-Time Transport
(RTP)
Transmission Control
Protocol (TCP)
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
1-8
RTP is a standard for transporting
real-time data, such as interactive voice
and video over data networks.
TCP is a a connection-oriented transport
protocol.
IP addresses, subnets, and
gateways identifications are
automatically assigned if you are
using the Cisco IP Phone with
Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP). If you are not
using DHCP, you must manually
assign these properties to each
phone locally.
Cisco IP Phones use the RTP
protocol to send and receive
real-time voice traffic from other
phones and gateways.
Cisco IP Phones use TCP to
connect to Cisco CallManager
and to access XML services.
78-10453-04
Page 29
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
What Features are Supported on the Cisco IP Phone?
Table 1-1 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco IP Phone (continued)
Networking Protocol Purpose Usage Notes
Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP)
User Datagram Protocol
(UDP)
TFTP allows you to transfer files over the
network.
On the Cisco IP Phone, TFTP enables
you to obtain a configuration file specific
to the phone type.
UDP is a connectionless messaging
protocol for delivery of data packets.
TFTP requires a TFTP server in
your network, which can be
automatically identified from the
DHCP server. If more than one
TFTP server is running in your
network, you must manually
assign a TFTP server to each
phone locally.
Cisco IP Phones receive and
process UDP messages.
What Features are Supported on the Cisco IP Phone?
The Cisco IP Phone functions much like a traditional analog phone, allowing you
to place and receive telephone calls.
78-10453-04
In addition to these traditional telephony features, the Cisco IP Phone includes
features that enable you to administer and monitor the phone as an IP networking
device.
This section covers the following topics:
• Feature Overview, page 1-10
• Configuring Telephony Features Using Cisco CallManager Administration,
page 1-10
• Configuring Network Features Using the IP Phone, page 1-11
• Providing Users with Feature Information, page 1-11
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
1-9
Page 30

What Features are Supported on the Cisco IP Phone?
Feature Overview
Cisco IP Phones provide traditional telephony functionality, such as call
forwarding and transferring, redialing, speed dialing, conference calling, and
voice mail access. For an overview of all the supported telephony features and tips
on configuring them, see the “Configuring Cisco IP Phones in
Cisco CallManager” section on page 6-2.
Because the Cisco IP Phones are connected to the rest of your IP network, they
can interact with other services and devices to provide enhanced functionality. For
example, you can integrate the Cisco IP Phones with the corporate Lightweight
Directory Access Protocol 3 (LDAP3) standard directory to enable users to search
for co-workers contact information directly from their IP phone. Or, you can use
XML to enable users to access information such as weather, stocks, quote of the
day or other Web-based information. For information about configuring these
services, see the “Configuring Corporate Directories” section on page 6-8 and the
“Setting Up User Services” section on page 6-8.
Finally, because the Cisco IP Phone is a network device, you can obtain detailed
status information from it directly. This information can assist you in
troubleshooting any problems users might encounter when using their IP phones.
See Chapter 7, “Troubleshooting the Cisco IP Phone” for tips on using this
information.
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
Configuring Telephony Features Using Cisco CallManager Administration
You can modify additional settings from the Cisco CallManager Administration
application. Use this web-based application to set up phone registration criteria
and calling search spaces, configure corporate directories and services, and
modify phone button templates, among other tasks. See the “Configuring Cisco IP
Phones in Cisco CallManager” section on page 6-2 and the Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide for additional information.
If you are not familiar with the Cisco CallManager Administration application,
use the context-sensitive help available within the application for guidance. You
can access context-sensitive help by choosing Help > For this screen from the
main menu bar.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
1-10
78-10453-04
Page 31

Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
What Features are Supported on the Cisco IP Phone?
This guide provides partial instructions for procedures that involve
Cisco CallManager Administration. These instructions are intended to point you
to the appropriate window in the Cisco CallManager application and to provide
some initial guidance.
For detailed information about using Cisco CallManager, refer to the
Cisco CallManager documentation suite available at this location:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_callmg/index.htm
Configuring Network Features Using the IP Phone
You can locally configure features such as DHCP, TFTP, and IP settings on the
phone, itself. You can also obtain statistics about a current call or firmware
versions on the phone.
For more information about configuring features and viewing statistics from the
phone, see Chapter 5, “Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone” and
Chapter 7, “Troubleshooting the Cisco IP Phone.”
Providing Users with Feature Information
If you are a system administrator, you are likely the primary source of information
for Cisco IP Phone users in your network or company. To ensure that you
distribute the most current feature and procedural information, familiarize
yourself with Cisco IP Phone documentation. Be sure to visit the Cisco IP Phone
web site:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_ipphon/index.htm.
From this site, you can view and order various user guides, including wallet cards.
For complete ordering information, see the “Obtaining Documentation” section
on page -xii.
In addition to providing documentation, it is important to inform users of
available Cisco IP Phone features—including those specific to your company or
network—and how to access and customize those features, if appropriate.
For a summary of some of the key information that phone users need their system
administrators to provide, see the “Providing Information to End Users” section
on page 6-9.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
1-11
Page 32

Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
Understanding the Requirements for Installing and Configuring the Cisco IP Phone
Understanding the Requirements for Installing and
Configuring the Cisco IP Phone
To install and configure the Cisco IP Phone, you must configure some network
settings, set up Cisco CallManager, and make changes locally on the phone.
Refer to Table 1 -2 for an overview of required procedures. For detailed
information about these steps, refer to the referenced sources.
Table 1-2 Overview of Configuration Procedures for the Cisco IP Phone
Required Task Purpose For More Information
1. Gather the following information
about the phone:
–
Model
–
MAC address
–
Physical location of the phone
–
Cisco CallManager user to
associate with the phone
–
Partition, calling search space,
and location information, if
used
–
Number of lines and
associated directory numbers
to assign to the phone
Required to configure
Cisco CallManager to support
the Cisco IP Phones.
See the following:
• “Adding Phones to the
Cisco CallManager
Database” section on
page 2-10
• “Configuring Cisco IP
Phones in
Cisco CallManager”
section on page 6-2
• Cisco CallManager
System Guide
• Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide.
–
Features to be added and
configured to the phone
2. Configure routers, gateways, and
switches to handle voice
communication.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
1-12
Establishes the infrastructure
for the IP telephony network.
See the “Understanding
How the Cisco IP Phone
Interacts with the
Cisco Catalyst Family of
Switches” section on
page 2-2 and the
documentation included
with these devices.
78-10453-04
Page 33

Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
Understanding the Requirements for Installing and Configuring the Cisco IP Phone
Table 1-2 Overview of Configuration Procedures for the Cisco IP Phone (continued)
Required Task Purpose For More Information
3. Add the phone to
Cisco CallManager.
4. Choose to auto-register phones,
add them to the Cisco CallManager
database manually, or use Bulk
Administration (BAT) to add many
phones to the database
simultaneously.
5. Choose to power through the
Cisco AC adapter or
Cisco Catalyst switch.
6. Install the phone in the network. Adds the phone to the
7. Add a 7914 Expansion Module. Extends functionality to the
8. Configure network settings on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960.
Provides call processing in the
IP telephony network.
Determines how the phone is
added to Cisco CallManager
and how the directory number
is assigned.
Determines whether the phone
receives power from an
external power source over a
power cord or from the in-line
power source over the
Ethernet cable.
network.
Cisco IP Phone 7960 by
adding 14 line appearances
and/or speed dial numbers.
Sets IP settings (if not using
DHCP in the network) and
assigns a TFTP server.
See the “Adding Phones to
the Cisco CallManager
Database” section on
page 2-10 and the
Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide.
See the “Adding Phones to
the Cisco CallManager
Database” section on
page 2-10 and the
Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide.
See the “Providing Power to
the Cisco IP Phone” section
on page 2-7 or the
documentation included
with the Cisco Catalyst
switch.
See Chapter 3, “Installing
the Cisco IP Phone”.
See the “Adding the
Cisco IP Phone 7914
Expansion Module” section
on page 4-1.
See the “Configuring IP
Settings” section on
page 5-14 and the
“Configuring TFTP
Options” section on
page 5-21.
78-10453-04
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
1-13
Page 34

Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco IP Phone
Understanding the Requirements for Installing and Configuring the Cisco IP Phone
Table 1-2 Overview of Configuration Procedures for the Cisco IP Phone (continued)
Required Task Purpose For More Information
9. Configure the phone features such
as call waiting, call forward, call
park, and call pickup.
10. Modify button templates. Provides customized phone
11. Configure Cisco IP phone
services.
12. Configure corporate directories. Integrates with a LDAP3
13. Add users to Cisco CallManager. Associates a user with a
14. Provide information to end users
about how to user their phone and
how to configure their phone
options.
Provides enhanced telephony
functionality.
buttons.
Allows users to quickly access
information such as weather,
stocks, quote of the day or any
Web-based information using
extensible markup language
(XML).
standard directory, enabling
users to search through a
corporate directory.
phone, enabling access to the
User Options web-based
application where users set up
features such as call
forwarding and speed dial, and
subscribe to services.
Ensures users have adequate
information to successfully
use their Cisco IP Phone.
See the “Configuring Cisco
IP Phones in
Cisco CallManager” section
on page 6-2 and the
Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide.
See the “Modifying Phone
Button Templates” section
on page 6-5.
See the “Setting Up User
Services” section on
page 6-8 or the
Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide.
See the “Configuring
Corporate Directories”
section on page 6-8 or the
Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide.
See Chapter 6, “Configuring
Cisco IP Phones, Users, and
Features in
Cisco CallManager” and the
Cisco CallManager
Administration Guide or
context-sensitive help.
See the “Setting Up User
Services” section on
page 6-8.
1-14
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 35

CHAPTER
2
Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone
on Your Network
Cisco IP Phones enable you to communicate using voice over a data network. To
do this, the IP Phones depend upon and interact with several other key
Cisco IP Telephony components, including Cisco CallManager.
These sections provide you with an important overview of the interaction between
Cisco IP Phones and other key components of the Voice over IP (VoIP) network:
• Understanding Interactions with Other Cisco IP Telephony Products,
page 2-1
• Understanding the Phone Startup Process, page 2-3
• Guidelines for Configuring Ports on Cisco IP Phones, page 2-6
• Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database, page 2-10
• Configuring the Cisco IP Phone 7960 to Support the
7914 Expansion Module, page 2-15
Understanding Interactions with Other
Cisco IP Telephony Products
To function in the IP telephony network, the Cisco IP Phone must be connected
to a networking device, such as a Cisco Catalyst switch. You must also register
the Cisco IP Phone with a Cisco CallManager system in order to send and receive
calls.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
2-1
Page 36

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Understanding Interactions with Other Cisco IP Telephony Products
This section covers the following topics:
• Understanding How the Cisco IP Phone Interacts with Cisco CallManager,
page 2-2
• Understanding How the Cisco IP Phone Interacts with the Cisco Catalyst
Family of Switches, page 2-2
Understanding How the Cisco IP Phone Interacts with
Cisco CallManager
Cisco CallManager is an open and industry-standard call processing system.
Cisco CallManager software runs on a Windows 2000 server and sets up and tears
down calls between phones, integrating traditional PBX functionality with the
corporate IP network. Cisco CallManager manages the components of the IP
telephony system—the phones, access gateways, and the resources necessary for
such features as call conferencing and route planning.
For information about configuring Cisco CallManager to work with the IP
devices described in this chapter, refer to the Cisco CallManager Administration
Guide and the Cisco CallManager System Guide.
Understanding How the Cisco IP Phone Interacts with the
Cisco Catalyst Family of Switches
Cisco IP Phones have an internal Ethernet switch, enabling them to switch
incoming traffic to the phone, the access port, or to the network port (see the
“Connecting to the Network” section on page 2-6 for details).
If a computer is connected to the access port, data packets traveling to and from
the computer, and to and from the phone, share the same physical link to the
switch and the same port on the switch.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-2
78-10453-04
Page 37

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
This shared physical link has the following implications for the VLAN
configuration on the network:
• The current VLANs might be configured on an IP subnet basis. However,
additional IP addresses might not be available to assign the phone to the same
subnet as other devices connected to the same port.
• Data traffic present on the VLAN supporting phones might reduce the quality
of Voice-over-IP traffic.
You can resolve these issues by isolating the voice traffic onto a separate VLAN
on each of the ports connected to a phone. The switch port configured for
connecting a phone would have separate VLANs configured for carrying:
• Voice traffic to and from the IP phone (auxiliary VLAN)
• Data traffic to and from the PC connected to the switch through the access
port of the IP phone (native VLAN)
Isolating the phones on a separate, auxiliary VLAN increases the quality of the
voice traffic and allows a large number of phones to be added to an existing
network where there are not enough IP addresses.
For more information, refer to the documentation included with the
Cisco Catalyst switch.
Understanding the Phone Startup Process
Note The Cisco IP Phone 7910 does not have an access port. If you require an access
port on this phone model, use the Cisco IP Phone 7910+SW instead.
Understanding the Phone Startup Process
When connecting to the VoIP network, the Cisco IP Phone goes through a
standard startup process comprised of seven steps. Some of these steps might not
occur, depending on the configuration of your specific network.
Each of these steps is described in the sections that follow:
• Obtaining Power from the Switch, page 2-4
• Loading the Stored Phone Image, page 2-4
• Configuring VLAN, page 2-4
• Obtaining an IP Address, page 2-4
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
2-3
Page 38

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Understanding the Phone Startup Process
• Accessing TFTP Server, page 2-5
• Requesting the Configuration File, page 2-5
• Contacting Cisco CallManager, page 2-5
Obtaining Power from the Switch
You can connect the Cisco IP Phone to a Cisco Catalyst switch with one of the
modules that provides power to the phone (WS-X6348-RJ45V). See the
“Providing Power to the Cisco IP Phone” section on page 2-7 for details.
If you use this optional configuration, the phone receives phantom power and
powers up when you connect the Cisco IP Phone to the switch. The phone then
sends Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) notifications to the switch indicating it is
ready to receive CDP packets and indicating the power requirement for the phone.
The switch allocates power and sends it over the network cable.
Loading the Stored Phone Image
The Cisco IP Phone has non-volatile Flash memory in which it stores firmware
images and user-defined preferences. At startup, the phone runs a bootstrap loader
that loads a phone image stored in Flash memory. Using this image, the phone
initializes its software and hardware.
Configuring VLAN
If the Cisco IP Phone is connected to a Cisco Catalyst switch, the switch next
informs the phone of the voice VLAN defined on the switch. The phone needs to
know its VLAN membership before it can proceed with the Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request for an IP address.
Obtaining an IP Address
If the Cisco IP Phone is using DHCP to obtain an IP address, the phone queries
the DHCP server to obtain one. If you are not using DHCP in your network, you
must assign static IP addresses to each phone locally.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-4
78-10453-04
Page 39

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Accessing TFTP Server
In addition to assigning an IP address, the DHCP server also directs the
Cisco IP Phone to a TFTP Server. If the phone has a statically defined IP address,
you must configure the TFTP server locally on the phone; the phone then goes to
the TFTP server directly.
Requesting the Configuration File
The TFTP server has configuration files (.cnf file format) for telephony devices,
which define parameters for connecting to Cisco CallManager. In general, any
time you make a change in Cisco CallManager that requires the phone (device) to
be reset, a change has been made to the phone's configuration file.
If a phone has an XML-compatible load, it requests a .XMLDefault.cnf.xml
format configuration file; otherwise, it requests a .cnf file.
If you have enabled auto-registration in Cisco CallManager, the phones access a
default configuration file (sepdefault.cnf.xml) from the TFTP server. If you have
manually entered the phones into the Cisco CallManager database, the phone
accesses a .cnf.xml file corresponding to its device name.
The .cnf.xml file also contains the information telling the phone which image load
it should be running. If this image load differs from the one currently loaded on
the phone, the phone contacts the TFTP server to request the new image file,
which is stored as a .bin file.
Understanding the Phone Startup Process
Contacting Cisco CallManager
The configuration file defines how the Cisco IP Phone communicates with
Cisco CallManager. After obtaining the file from the TFTP server, the phone next
attempts to make a TCP connection to the highest priority Cisco CallManager on
the list.
If the phone was manually added to the database, Cisco CallManager identifies
the phone. If the phone was not manually added to the database and
auto-registration is enabled in Cisco CallManager, the phone attempts to
auto-register itself in the Cisco CallManager database.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
2-5
Page 40

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Guidelines for Configuring Ports on Cisco IP Phones
Cisco CallManager informs devices using .cnf format configuration files of their
load ID. Devices using .xml format configuration files receive the load ID in the
configuration file.
Guidelines for Configuring Ports on Cisco IP Phones
Cisco IP Phones include ports for connecting the phones to the network, for
providing power to the phones, and for adding headsets to the phones. These
sections provide tips for configuring these ports:
• Connecting to the Network, page 2-6
• Providing Power to the Cisco IP Phone, page 2-7
• Configuring the Handset, Headset, and Speakerphone, page 2-8
Connecting to the Network
The Cisco IP Phones have two RJ-45 ports labelled “network” and “access.” Each
supports 10/100 Mbps half- or full-duplex connections to external devices. You
can use either Category 3 or 5 cabling for 10-Mbps connections, but you must use
Category 5 for 100 Mbps connections. On both the network port and access port,
use full-duplex mode to avoid collisions.
Note The Cisco IP Phone 7910 does not have an access port. If you require an access
port on this phone model, use the Cisco IP Phone 7910+SW instead.
Refer to Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 to see the connection ports available on the
back of the Cisco IP Phone models 7960/7940 and 7910.
Using the Network Port
Use the network port to connect the phone to the network. You must use a
straight-through cable on this port. The phone can also obtain inline power from
the Cisco Catalyst switch over this connection. See the “Providing Power to the
Cisco IP Phone” section on page 2-7 for details.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-6
78-10453-04
Page 41

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Guidelines for Configuring Ports on Cisco IP Phones
Using the Access Port
Use the access port to connect a network device, such as a computer, to the phone.
You must use a straight-through cable on this port.
Providing Power to the Cisco IP Phone
You can power a Cisco IP Phone from an external power supply, from a switch
port, or from a power source between the phone and the switch.
The Cisco IP Phone can be powered by the following sources:
• External power source—optional Cisco AC adapter and power cord for
connecting to a standard wall receptacle.
• WS-X6348-RJ45V 10/100 switching module—inline power provider to the
Cisco IP Phone when connected to a Catalyst 6000 family 10/100BaseTX
switching module.
This module sends power on pins 1 & 2 and 3 & 6, which are also used to
transmit Ethernet signals. Before the switch sends power, it tests for the
presence of a Cisco IP Phone, avoiding damage to other Ethernet devices.
• WS-PWR-PANEL—power patch panel that allows the Cisco IP Phone to be
Power Source Design
The phone and switch automatically determine which power source the phone
uses. If the power has to be switched to a different source, the phone user will
experience different results based on which power source is being used by the
phone.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Note Only the network port supports inline power from the Cisco
Catalyst switches.
connected to existing Catalyst 4000, 5000, and 6000 family 10/100BaseTX
switching modules.
This module sends power on pins 4, 5, 7, & 8, which are not used for Ethernet
signaling. Like the inline power, the power patch panel also attempts to verify
that the attached device is a Cisco IP Phone before providing power.
2-7
Page 42

Guidelines for Configuring Ports on Cisco IP Phones
Use the following information to choose a power source for the phone:
• If you plug a phone into the optional power supply before plugging it into the
network, the phone is powered by the power supply.
• If you then unplug the phone from the power supply, the phone resets. If the
switch port is configured for 10/100 Mbps, the switch recognizes the loss of
power and brings the phone back up.
• If the switch port is configured for 10 Mbps only, then you must unplug the
network connection and plug it back into the phone for the switch to
recognize the phone’s loss of power.
• If, however, you plugged the network connection into the phone before you
plugged in the power cord, the phone receives power through the switch, and
unplugging the power cord will not bring down the phone. If the switch
reboots, the phone will then be powered by the power cord.
Redundancy Feature
For redundancy, you can use the Cisco AC adapter even if you are using inline
power from the Cisco Catalyst switches. The Cisco IP Phone can share the power
load being used from the inline power and external power source. If either the
inline power or the external power goes down, the phone can switch entirely to
the other power source.
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
To use this redundancy feature:
1. Set the inline power mode to auto on the Cisco Catalyst switch.
2. Connect the unpowered Cisco IP Phone to the network.
3. Connect the external power supply to the phone after the phone powers up.
Configuring the Handset, Headset, and Speakerphone
Cisco IP Phones enable you to connect a headset to them or use the built-in
speakerphone to make calls rather than the standard handset. These sections
provide you with additional information about configuring these options:
• Connecting a Handset to a Cisco IP Phone, page 2-9
• Connecting a Headset to a Cisco IP Phone, page 2-9
• Disabling the Speakerphone Feature, page 2-10
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-8
78-10453-04
Page 43

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Connecting a Handset to a Cisco IP Phone
All Cisco IP Phones include a handset designed especially for use with a
Cisco IP Phone. These handsets are interchangeable among Cisco IP Phone
models. The handsets include a light strip used to indicate voice mail messages.
To place and answer calls using a handset, plug the included handset into the back
of the phone base (see the “Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network”
section on page 3-4 for details) and pick up the handset.
Connecting a Headset to a Cisco IP Phone
You can use a headset with any Cisco IP Phone. These sections help you
determine the headset supported by a particular Cisco IP Phone:
• Using a Headset with a Cisco IP Phone Model 7960 or 7940, page 2-9
• Using a Headset with a Cisco IP Phone 7910, page 2-10
Using a Headset with a Cisco IP Phone Model 7960 or 7940
Guidelines for Configuring Ports on Cisco IP Phones
78-10453-04
To place and answer calls using a headset, plug an approved headset into the back
of the phone base (see the “Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network”
section on page 3-4 for details) and press the Headset button on the front of your
phone.
You can use the headset in conjunction with all of the features on your
Cisco IP Phone, including the Volume and Mute buttons. Use these buttons to
adjust the ear piece volume and to mute the speech path from the headset
microphone.
The Cisco IP Phone models 7960 and 7940 support four- or six-wire headset
jacks. For information on the exact models supported, see the following URLs:
• http://cisco.getheadsets.com
• http://vxicorp.com/cisco
To disable the headset on these models, choose Device > Phone from the Cisco
CallManager Administration application and locate the phone you want to
modify. Check the Disable Speakerphone and Headset check box to disable the
speakerphone for the phone you have selected.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-9
Page 44

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database
Using a Headset with a Cisco IP Phone 7910
The Cisco IP Phone 7910 does not have a separate headset jack. However, you can
use a headset in place of the handset. You can use industry-standard headsets,
such as Plantronics M-12 amplified headsets or other headsets that provide switch
capability between the headset and handset.
Disabling the Speakerphone Feature
By default, the speakerphone is enabled on Cisco IP Phones. However, you can
disable it on Cisco IP Phone models 7960 and 7940.
To disable the speakerphone on these models, choose Device > Phone from the
Cisco CallManager Administration application and locate the phone you want to
modify. Check the Disable Speakerphone check box to disable the speakerphone
for the phone you have selected.
Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database
2-10
Before installing any Cisco IP phones, you must make decisions about how you
want the phones to be added to the Cisco CallManager database. Because
Cisco CallManager handles call processing in the network, this is a critical step.
You can add phones to the Cisco CallManager database automatically using
auto-registration, manually using the Cisco CallManager Administration
application, or in groups with the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).
Once you add a Cisco IP phone using the Cisco CallManager Administration
application, the Phone Configuration Window in the application displays the
device name, registration status, and the IP address of the Cisco CallManager to
which the device is registered.
This section covers the following topics:
• Using Auto-Registration, page 2-11
• Adding Phones Manually, page 2-12
• Using the Bulk Administration Tool, page 2-15
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 45

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Tip To get help using the Cisco CallManager application, access context-sensitive
help by choosing Help > For this screen from the main menu bar. For
complete instructions and conceptual information, refer to the
Cisco CallManager Administration Guide and the Cisco CallManager System
Guide.
Using Auto-Registration
Use auto-registration if you want Cisco CallManager to assign directory numbers
automatically to new phones as they connect to the IP telephony network. Once a
phone has auto-registered, you can move it to a new location and assign it to a
different device pool without affecting its directory number.
With auto-registration enabled, Cisco CallManager begins the automatic startup
process to obtain a directory number as soon as you connect the Cisco IP Phone
to the network. During auto-registration, Cisco CallManager automatically
assigns the next available sequential directory number to the phone.
Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database
78-10453-04
Use auto-registration to quickly get all phones into the Cisco CallManager
database. You can then modify any settings, such as the directory numbers, from
Cisco CallManager. If you do not use auto-registration, you must manually add
phones to the Cisco CallManager database or use the Bulk Administration Tool
(BAT).
Use the following procedure as a starting point to enable auto-registration using
the Cisco CallManager Administration application. For additional information,
access context-sensitive help from the application or refer to Cisco CallManager
documentation.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the Cisco CallManager Administration application.
Step 2 From the menu bar, choose System > Cisco CallManager.
The Cisco CallManager Configuration window appears.
Step 3 Verify that the “Auto-registration disabled on this Cisco CallManager” setting is
not checked. Cisco CallManager disables the auto-registration by default to
prevent unauthorized connections to the network.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-11
Page 46

Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database
Step 4 To modify phone settings, choose Device > Phone. Use the Find and List Phones
window to enter search criteria for each phone.
Step 5 Install the phone by following the instructions in Chapter 3, “Installing the
Cisco IP Phone.”
Step 6 To configure additional phone features, see the “Configuring Cisco IP Phones in
Cisco CallManager” section on page 6-2 for details.
Adding Phones Manually
If you want to assign specific directory numbers to a specific Cisco IP Phone
without using auto-registration, you can manually add each phone to the
Cisco CallManager database or use the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).
If you want to add phones manually, and are not using Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) in your network, then you must configure the IP
settings and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server locally on each phone.
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Alternatively, if you use DHCP, but want to manually set the TFTP server, then
allow the phone to start up, using DHCP, before re-assigning the TFTP server.
Refer to these topics for more information:
• Adding Phones Manually Using DHCP, page 2-12
• Assigning Static IP Addresses, page 2-13
Adding Phones Manually Using DHCP
If you are using DHCP in your network, but you are not using auto-registration,
you can manually add a phone to the Cisco CallManager database. If you are
using DHCP, you do not need to assign IP addresses or TFTP servers.
Use the following procedure as a starting point to add phones manually using the
Cisco CallManager Administration application.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-12
78-10453-04
Page 47

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the Cisco CallManager Administration application.
Step 2 From the menu bar, choose Device > Add a New Device.
The Add a New Device window appears.
Step 3 Select Phone from the Device Type drop-down menu and click Next.
The Add a New Phone window appears.
Step 4 Select a phone type from the drop-down menu and click Next.
The Phone Configuration window appears. The fields displayed in this window
depend upon the phone type selected.
Step 5 In the Phone Configuration window, you must enter information in the following
three fields:
• MAC Address
• Device Pool
• Phone Button Template
Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database
Step 6 Click Insert.
The Cisco CallManager Administration application asks if you want to assign a
directory number.
Step 7 To configure additional phone features, see the “Configuring Cisco IP Phones in
Cisco CallManager” section on page 6-2 for details.
For additional information, access context-sensitive help from the application or
refer to Cisco CallManager documentation.
Assigning Static IP Addresses
If you do not use DHCP in your network, you must assign static IP addresses to
each phone. You must configure each phone locally.
Use the following procedure as a starting point to add phones manually using the
Cisco CallManager Administration application.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
2-13
Page 48

Adding Phones to the Cisco CallManager Database
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the Cisco CallManager Administration application.
Step 2 From the menu bar, choose Device > Add a New Device.
The Add a New Device window appears.
Step 3 Select Phone from the Device Type drop-down menu and click Next.
The Add a New Phone window appears.
Step 4 Select a phone type from the drop-down menu and click Next.
The Phone Configuration window appears. The fields displayed in this window
depend upon the phone type selected.
Step 5 In the Phone Configuration window, you must enter information in the following
three fields:
• MAC Address
• Device Pool
• Phone Button Template
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
2-14
Step 6 Click Insert.
The Cisco CallManager Administration application asks if you want to assign a
directory number.
Step 7 Enter the required fields.
Step 8 Install the phone by following the instructions in the Chapter 3, “Installing the
Cisco IP Phone.”
Step 9 Configure the IP settings by following the instructions in the “Configuring IP
Settings” section on page 5-14.
Step 10 Configure the TFTP server by following the instructions in the “Configuring
TFTP Options” section on page 5-21.
Step 11 To configure additional phone features, see the “Configuring Cisco IP Phones in
Cisco CallManager” section on page 6-2 for details.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 49

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Configuring the Cisco IP Phone 7960 to Support the 7914 Expansion Module
Using the Bulk Administration Tool
The Cisco Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) is a plug-in application for
Cisco CallManager that enables system administrators to perform batch
operations, including registration, on large numbers of Cisco IP Phones.
Refer to the Bulk Administration Tool Guide for Cisco CallManager for
information about using BAT in your network.
Configuring the Cisco IP Phone 7960 to Support the
7914 Expansion Module
The Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module attaches to a Cisco IP Phone 7960
to extend the number or line appearances and/or speed dial buttons.
Before the 7914 Expansion Module can be used, you must access the
Cisco CallManager Administration application. Use the application to perform
the tasks detailed in the following sections:
78-10453-04
Follow these steps to configure the Cisco IP Phone 7960 to support the
7914 Expansion Module.
Before You Begin
You might also want to customize the button templates for the
7914 Expansion Module. See the “Modifying Phone Button Templates” section
on page 6-5 for details.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the Cisco CallManager Administration application.
The Cisco CallManager Administration page appears.
Step 2 From the menu, choose Device > Phone.
The Find and List Phone page appears. You can search for one or more phones
that you want to configure for the 7914 Expansion Module.
Step 3 Select and enter your search criteria and click Find.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
2-15
Page 50

Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on Your Network
Configuring the Cisco IP Phone 7960 to Support the 7914 Expansion Module
The Find and List Phone page re-displays showing a list of the phones matching
your search criteria.
Step 4 Click on the IP Phone that you want to configure for the 7914 Expansion Module.
The Phone Configuration page appears.
Step 5 Scroll down to the Phone Button and Expansion Module Template Information
section of the page.
Step 6 To add support for one Expansion Module, in the Expansion Module 1 field,
select Default 7914.
To add support for a second Expansion Module, in the Expansion Module 2 field,
select Default 7914.
In the Firmware Load Information section of the page, there are two fields for
specifying the firmware load for Expansion Modules 1 and 2. You can leave these
fields blank to use the default firmware load.
Step 7 Scroll back to the top of the page and click Update.
A message displays asking you to reset the phone for the changes to take effect.
Click OK.
2-16
Step 8 Click Reset Phone for the changes to take effect.
Note Make sure you tell your users how to access their IP Phone User Options
application Web pages so that they can subscribe to the Speed Dial Service and
set up the speed dial buttons on their Expansion Modules. See the “Providing
Information to End Users” section on page 6-9 for more details.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 51

CHAPTER
3
Installing the Cisco IP Phone
These topics help you install the Cisco IP Phone on an IP telephony network:
• Before You Begin, page 3-1
• Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network, page 3-4
• Adjusting Placement of the Cisco IP Phone, page 3-7
• Verifying the Phone Startup Process, page 3-9
• Configuring Startup Network Settings, page 3-10
Note For each Cisco IP phone that you install in your network, you must first make
some critical decisions about how to configure the phone in your network. You
can then safely install the phone and verify its functionality. For information on
preparing to install, see Chapter 2, “Preparing to Install the Cisco IP Phone on
Your Network.”.
Before You Begin
Before installing a Cisco IP Phone, verify that your network meets the
requirements and that Cisco CallManager is properly configured. Most
importantly, review the safety precautions. See the “Safety” section on page 3-3
for more details.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
3-1
Page 52

Before You Begin
Before installing the Cisco IP Phone, review the requirements in these sections:
• Network Requirements, page 3-2
• Cisco CallManager Configuration, page 3-2
• Safety, page 3-3
Network Requirements
For the Cisco IP Phone to successfully operate as a Cisco IP Phone endpoint in
your network, your network must meet the following requirements:
• Working VoIP Network
–
Voice over IP (VoIP) configured on your Cisco routers and gateways
–
Cisco CallManager Release 3.0 or higher installed in your network and
configured to handle call processing
• IP network that supports DHCP or manual assignment of IP address, gateway,
and subnet mask
Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco CallManager Configuration
The Cisco IP Phone requires Cisco CallManager to handle call processing. Refer
to the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide or context-sensitive help in the
Cisco CallManager application to ensure that Cisco CallManager is set up
properly to manage the phone and to properly route and process calls.
If you plan to use auto-registration, verify that it is enabled and properly
configured in Cisco CallManager before connecting any Cisco IP Phone to the
network. See the “Using Auto-Registration” section on page 2-11 for details.
In Cisco CallManager, you can add users to the database and associate them with
specific phones. By doing this, users gain access to web pages that allow them to
configure phone options such as call forwarding, speed dialing, and voice mail.
See the “Adding Users to Cisco CallManager” section on page 6-5 for details.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
3-2
78-10453-04
Page 53

Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
Safety
Review the following warnings before installing the Cisco IP Phone.
Before You Begin
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power
source.
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or
service this equipment.
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national
laws and regulations.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of
lightning activity.
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra low voltage (SELV) circuits
to telephone network voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits,
and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45
connectors. Use caution when connecting cables.
The following warning applies when you use an external power supply.
78-10453-04
Warning
Warning
This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent)
protection. Ensure that a fuse or circuit breaker no larger than 120 VAC, 15 A
U.S. (240 VAC, 10 A international) is used on the phase conductors (all
current-carrying conductors).
The device is designed to work with TN power systems.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
3-3
Page 54

Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network
Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
Warning
The plug-socket combination must be accessible at all times because it serves
as the main disconnecting device.
Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network
You must connect the Cisco IP Phone to the network and to a power source before
using it. Refer to Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 for graphical overviews of the
procedures that follow.
To install a Cisco IP Phone, perform these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Connect a Category 3 or 5 straight-through Ethernet cable from the switch to the
network port on the phone.
See the “Connecting to the Network” section on page 2-6 for guidelines. Each
Cisco IP Phone ships with one Ethernet cable in the box.
Step 2 Connect the handset and headset to their respective ports.
See the “Connecting a Headset to a Cisco IP Phone” section on page 2-9 for
supported headsets.
Step 3 Connect a Category 3 or 5 straight-through Ethernet cable from another network
device, such as a desktop computer, to the access port on the phone (optional).
See the “Connecting to the Network” section on page 2-6 for guidelines.
3-4
Note This option is not available on all Cisco IP Phone 7910 models. There are
two versions of this phone and their only distinction is whether the access
port is present. The Cisco IP Phone 7910+SW has an access port, and the
Cisco IP Phone 7910 does not.
Step 4 Connect the power plug to the Cisco AC Adapter port (optional).
See the “Providing Power to the Cisco IP Phone” section on page 2-7.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 55

Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
Figure 3-1 Cisco IP Phone Models 7960 and 7940 Cable Connections
Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network
1
78-10453-04
RS232
DC48V
2
10/100 SW 10/100 PC
+
7
6
3
5
4
58670
1 AC adapter port (DC48V) 5 Access port (10/100 PC)
2 Power supply with AC adapter port plug 6 Handset port
3 Power cable with wall socket plug 7 Headset port
4 Network port (10/100 SW)
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
3-5
Page 56

Connecting the Cisco IP Phone to the Network
Figure 3-2 Cisco IP Phone Model 7910 Cable Connections
Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
1
3-6
RS232
DC48V
10/100 SW 10/100 PC
+
6
2
3
5
4
1 AC adapter port (DC48V) 4 Network port (10/100 SW)
2 Power supply with AC adapter port plug 5 Access port (10/100 PC)
3 Power cable with wall socket plug 6 Handset port
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
63273
78-10453-04
Page 57

Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
Adjusting Placement of the Cisco IP Phone
Adjusting Placement of the Cisco IP Phone
The Cisco IP Phone includes an adjustable footstand. When placing the phone on
a desktop surface, you can adjust the tilt height to several different angles in 7.5
degree increments from flat to 60 degrees. You can also mount the phone to the
wall using the footstand or using the optional locking accessory.
Adjusting Cisco IP Phone Placement on the Desktop
Adjust the footstand to the height that provides optimum viewing of the LCD
screen.
Procedure
Step 1 Push in the footstand adjustment knob.
Step 2 Adjust the footstand to desired height.
Mounting the Phone to the Wall
You can mount the Cisco IP Phone on the wall using the footstand as a mounting
bracket, or you can use special brackets available in a Cisco IP Phone wall mount
kit. (A wall mount kit must be ordered separately from the phone.) If you attach
the Cisco IP Phone to a wall using the standard footstand and not the wall mount
kit, you need to supply the following tools and parts:
• Screwdriver
• Screws to secure the Cisco IP phone to the wall
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
3-7
Page 58

Adjusting Placement of the Cisco IP Phone
Use the following procedure to mount the phone on the wall using the standard
footstand. Refer to Figure 3-3 for a graphical overview of these procedures.
Before You Begin
To ensure that the handset attaches securely to a wall-mounted phone, remove the
handset wall hook from the handset rest, rotate the hook 180 degrees, and reinsert
the hook. Turning the hook exposes a lip on which the handset catches when the
phone is vertical. For an illustrated procedure, see Installing the Wall Mount Kit
for the Cisco IP Phone.
Procedure
Step 1 Push in the footstand adjustment knob.
Step 2 Adjust the footstand so it is flat against the back of the phone.
Step 3 Modify the handset rest so that the handset remains on the ear-piece rest when the
phone is vertically placed.
a. Remove the handset from the ear-piece rest.
b. Locate the tab (handset wall hook) at the base of the ear-piece rest.
c. Slide this tab out, rotate it 180 degrees (left to right), and reinsert it.
Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
3-8
d. Place the handset on the ear-piece rest.
Step 4 Insert two screws into a wall stud, matching them to the two screw holes on the
back of the footstand.
The keyholes fit standard phone jack mounts.
Step 5 Hang the phone on the wall.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 59

Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
Figure 3-3 Parts Used in Wall Mounting the Cisco IP Phone
Verifying the Phone Startup Process
1
2
2
3
63274
1 Footstand adjustment knob—Raises and lowers adjustment plate
2 Wall mounting screw holes
3 Adjustment plate—Raises and lowers phone vertically
Verifying the Phone Startup Process
After the Cisco IP Phone has power connected to it, the phone begins its startup
process by cycling through these steps:
1. These buttons flash on and off in sequence:
–
Headset (on Cisco IP Phone models 7960 and 7940 only)
–
Mute
–
Speaker
2. The LCD screen displays the Cisco Systems, Inc., copyright screen.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
3-9
Page 60

Configuring Startup Network Settings
3. These messages display as phone starts up:
–
–
–
–
–
–
4. The main LCD screen displays:
–
–
–
If the phone successfully passes through these stages, it has started up properly.
Otherwise, refer to the “Resolving Startup Problems” section on page 7-15.
Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco IP Phone
Configuring VLAN
Configuring IP
Configuring CM List
Connecting
Registering
Requesting Template
The date and time
Primary directory number
Soft keys (on Cisco IP Phone models 7960 and 7940 only)
Configuring Startup Network Settings
If you are not using DHCP in your network, you must configure these network
settings on the Cisco IP Phone after installing the phone on the network:
• IP address
• IP subnet mask
• Default gateway IP address
• Domain name
• DNS server IP address
• TFTP server IP address
Collect this information and follow the procedures defined in Chapter 5,
“Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone.”
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
3-10
78-10453-04
Page 61

CHAPTER
4
Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914
Expansion Module
The Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module attaches to the
Cisco IP Phone 7960 and extends its functionality by adding 14 line appearances
and/or speed dial numbers per module. One or two Expansion Modules can be
attached to your IP Phone. One Expansion Module provides a total of 20 line
and/or speed dial numbers. Two Expansion Modules provide a total of 34 line
and/or speed dial buttons, as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 Cisco IP Phone 7960 with Two Expansion Modules
78-10453-04
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-1
Page 62

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
These sections describe how to install the Expansion Module:
• Before You Begin, page 4-2
• Connecting the 7914 Expansion Module, page 4-4
• Start Up Sequence, page 4-14
Before You Begin
Before you begin the installation of the Cisco 7914 Expansion Module, read all
of the following topics in this section:
• Package List, page 4-2
• Footstand Kits, page 4-2
• Additional Equipment, page 4-3
• Safety Notices, page 4-3
Package List
Footstand Kits
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-2
Make sure that you have received all of the following parts in your package:
• One Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
• One RS 232 cable
• One Quick Start Guide
• One Warranty Card
In addition to the package list items, you will also need a Footstand Kit (separate
orderable item). If you are attaching one 7914 Expansion Module, you need to
have the single Footstand Kit. If you are attaching two 7914 Expansion Modules,
you need to have the double Footstand Kit.
78-10453-04
Page 63

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Each Footstand Kit contains:
• One support bar (single with one thumb screw, or double with two thumb
screws)
• One footstand
Additional Equipment
You will need to have the following additional equipment.
• Small flat head screwdriver—for use during the installation
• Power supply unit—depending on how many Expansion Modules you are
installing and how your Cisco IP Phone 7960 is powered, you will require
power supply unit(s) as follows:
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Power over the Ethernet to your
Cisco IP Phone 7960
Local power to your
Cisco IP Phone 7960
With one or two Expansion Modules, you need a power supply
unit (separate orderable item).
With one Expansion Module, no power supply unit needed.
With two Expansion Modules, you need a power supply unit
(separate orderable item).
Note Use of a non-Cisco certified power supply unit may not work and will void the
7914 Expansion Module product warranty.
Safety Notices
These are the safety considerations for using the 7914 Expansion Module. Read
these notices before you install or use the 7914 Expansion Module.
Warning
Warning
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause
bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards
involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for
preventing accidents.
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power
source.
78-10453-04
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-3
Page 64

Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national
laws and regulations.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of
lightning activity.
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra low voltage (SELV) circuits
to telephone network voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits,
and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some LAN and WAN ports use RJ-45
connectors. Use caution when connecting cables.
The following warnings apply when you use the external power supply with the
7914 Expansion Module:
This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (over current)
protection. Ensure that a fuse or circuit breaker no larger than 120 VAC, 15A U.S.
(240 VAC, 10A international) is used on the phase conductors (all
current-carrying conductors).
Warning
The device is designed to work with TN power systems.
Connecting the 7914 Expansion Module
To connect the 7914 Expansion Module, you need to perform the following
procedures. Each procedure corresponds to a section that contains detailed
instructions and illustrations:
• Removing the Footstand from the Cisco IP Phone 7960, page 4-5
• Connecting the Support Bar to the Cisco IP Phone 7960, page 4-6
• Connecting the 7914 Expansion Module to the Support Bar, page 4-7
• Connecting the RS 232 Cable, page 4-9
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-4
78-10453-04
Page 65

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
• Connecting the Power Supply, page 4-11
• Connecting the Footstand, page 4-12
Note To ensure a successful installation of the 7914 Expansion Module, make sure you
have read the entire “Before You Begin” section on page 4-2.
Removing the Footstand from the Cisco IP Phone 7960
To remove the footstand from the IP Phone 7960 to which you are attaching the
7914 Expansion Module, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Unplug the Cisco IP Phone 7960 network and power connections.
Step 2 Unplug the handset, and headset (if one is attached to the phone).
Step 3 Turn the Cisco IP Phone 7960 over and lay it on a protected flat surface to prevent
it from being scratched.
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
78-10453-04
Step 4 On the footstand, locate the two foot pins.
Step 5 Using a flat head screwdriver, carefully push away from your body on one of the
foot pins to release it. Then carefully push away from your body on the other foot
pin to release it. Push the pins as illustrated in Figure 4-2.
Note You may have to lift and hold the IP Phone to support it when pushing the
foot pins.
Step 6 Lift off the footstand and store it separately.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-5
Page 66

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Figure 4-2 Foot Pins on the Cisco IP Phone 7960
Connecting the Support Bar to the Cisco IP Phone 7960
63147
4-6
To connect the support bar to the Cisco IP Phone 7960, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Position the support bar on the back of the IP Phone so that it fits flush with the
phone.
Step 2 Locate the two connector pins, as illustrated in Figure 4-3.
Step 3 Using a flat head screwdriver, carefully push each of the connector pins so that
the support bar is firmly fastened to the IP Phone.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 67

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Figure 4-3 Connector Pins on the Support Bar
Connecting the 7914 Expansion Module to the Support Bar
78-10453-04
To connect the Expansion Module to the support bar, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Position the phone so that the front of the phone is facing up.
Step 2 Line up the two open slots on the bottom of the 7914 Expansion Module with the
two hooks on the support bar. Insert the hooks into the slots and then rotate the
top of the 7914 Expansion Module into the support bar so that it rests flush with
the bar.
Step 3 Tighten the thumb screw on the back of the 7914 Expansion Module.
Note If you are installing two Expansion Modules, repeat Steps 2 and 3 for the second
Expansion Module.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-7
Page 68

Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Figure 4-4 Part Connections on the Expansion Module and Support Bar
Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
4-8
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 69

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Figure 4-5 Thumb Screw Connections
1 Slots on the 7914 Expansion Module
2 Hooks on the support bar
3 Insert and rotate the Expansion Module into the support bar
4 Tighten the thumb screws
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Connecting the RS 232 Cable
To connect the RS 232 cable, follow these steps, and refer to the following table,
which depicts the “in” and “out” icons on the RS 232 jacks.
In icon Out icon
Procedure
Step 1 Plug one end of the RS 232 cable into the jack labeled RS 232 on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960, as shown in Figure 4-6.
Step 2 Plug the other end of the RS 232 cable into the RS 232 jack with the “in” icon
underneath on the 7914 Expansion Module.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
4-9
Page 70

Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Note If you are installing a second 7914 Expansion Module, continue with Steps 3 and
4. Otherwise go to the “Connecting the Power Supply” section on page 4-11.
Refer to Figure 4-6 for an illustration of cable connections.
Step 3 Plug one end of the second RS 232 cable into the RS 232 jack with the “out” icon
underneath on the 1st Expansion Module.
Step 4 Plug the other end of the second RS 232 cable into the RS 232 jack with the “in”
icon underneath on the 2nd Expansion Module.
Figure 4-6 Cable Connections with Two Expansion Modules
Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
4-10
1 RS 232 cable connection to the RS 232 jack on the IP Phone
2 RS 232 cable connection to the RS 232 jack on Expansion Module 1
3 2nd RS 232 cable connection to the RS 232 jack on Expansion Module 1
4 2nd RS 232 cable connection to the RS 232 jack on Expansion Module 2
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 71

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Connecting the Power Supply
To connect the power supply, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Depending on how your Cisco IP Phone 7960 is powered, perform one of the
following actions:
• If your Cisco IP Phone 7960 is powered over the Ethernet and:
–
you have one Expansion Module, then connect the power supply unit to
the AC adaptor port on the Expansion Module and plug the other end into
a standard electrical power outlet in the wall.
or
–
you have two Expansion Modules, then connect the power supply unit to
the AC adaptor port on the Expansion Module closest to the IP Phone
and plug the other end into a standard electrical power outlet in the wall.
• If your Cisco IP Phone 7960 is powered with a power supply unit and:
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
78-10453-04
–
you have one Expansion Module, then reconnect the original IP Phone
power supply unit to the AC adaptor port on the IP Phone and plug the
other end into a standard electrical power outlet in the wall.
or
–
you have two Expansion Modules, then connect a second power supply
unit to the AC adaptor port on the Expansion Module closest to the
IP Phone and plug the other end into a standard electrical power outlet in
the wall.
Step 2 Reconnect the Cisco IP Phone 7960 handset and network connections.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-11
Page 72

Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Figure 4-7 Power Supply Connector Port
Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
1 Power supply connector plugged in to the power supply
port on the back of the Expansion Module
Connecting the Footstand
To connect the footstand to the support bar, follow these steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Locate the three hooks on the footstand.
Step 2 Position the hooks so that they align with the two open slots on the support bar.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-12
78-10453-04
Page 73

Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
Note Note: There are four positions in each of the three sets of open slots on the support
bar. This lets you choose the angle of the footstand.
Step 3 Insert the footstand hooks into the support bar and push in slightly to make the
connection.
Figure 4-8 Part Connections on the Footstand and Support Bar
Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
78-10453-04
1 Slots on the support bar
2 Hooks on the footstand
3 Insert and rotate footstand to connect to support bar
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
4-13
Page 74

Installing the 7914 Expansion Module
Start Up Sequence
After the 7914 Expansion Module is installed, upon startup the lighted buttons are
all steady red. Then the LCD screen refreshes and the lighted buttons are all off
and any line appearances are displayed in the LCD screen. You can then start
using the Expansion Module.
Chapter 4 Adding the Cisco IP Phone 7914 Expansion Module
4-14
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 75

CHAPTER
5
Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Because the Cisco IP Phone is a network device, it includes many configurable
network settings. You must configure many of these options before the phone is
accessible and functional for your users.
The following sections provide details about configuring and verifying these
network settings:
• Accessing the Network Configuration Settings, page 5-2
• Verifying Network Settings, page 5-3
• Modifying DHCP Settings, page 5-9
• Configuring IP Settings, page 5-14
• Configuring VLAN Settings, page 5-20
78-10453-04
• Configuring TFTP Options, page 5-21
• Configuring Ports, page 5-25
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-1
Page 76

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Accessing the Network Configuration Settings
Accessing the Network Configuration Settings
By default, the network configuration options are locked to prevent users from
making changes that could impact their network connectivity. You must unlock
the network configuration options before you can configure them.
The unlocked padlock icon, shown below, appears in the margins of this chapter
to indicate procedures that require you to unlock settings before modifying them.
The padlock icon also appears in the Network Configuration area of the
Cisco IP Phone LCD screen to indicate that settings are unlocked and accessible
for modification.
When settings are inaccessible, you can see an image of a locked padlock on the
LCD screen. After you make the necessary changes to the network configuration
settings, be sure to lock the settings again to prevent users from modifying them.
Follow these steps to view the padlock icon and to modify network settings:
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press **#
This step either locks or unlocks the options, depending on the previous state.
Continue with Step 2 to view the padlock icon.
Step 2 Press settings.
Step 3 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 4 Press the Select soft key.
Step 5 Look at the upper-right portion of your LCD.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-2
• Locked—The icon displays a locked padlock.
• Unlocked—The icon displays an unlocked padlock.
78-10453-04
Page 77

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Procedure
Step 1 Press **#
This step either locks or unlocks the options, depending on the previous state.
Continue with Step 2 to view the padlock icon.
Step 2 Press settings.
Step 3 Select 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 4 Look at the upper-right portion of your LCD.
• Locked—The icon displays a locked padlock.
• Unlocked—The icon displays an unlocked padlock.
Verifying Network Settings
Verifying Network Settings
The Cisco IP Phone displays detailed information about its current network
settings. Use this information to troubleshoot or to make modifications.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll through the options to display the settings described in Tabl e 5 -1 .
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
5-3
Page 78

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Verifying Network Settings
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 3 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Scroll through the options to display the settings described in Tabl e 5 -1 .
If the Cisco IP Phone 7910 is locked, only the configured options in Ta ble 5 - 1
appear. When the phone is unlocked, all options display.
Table 5-1 Network Settings
Network Setting Description Usage Notes
DHCP Server Displays IP address of the Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server that the phone used to obtain IP
address.
BootP Server Indicates whether the phone obtained its
IP configuration from a Bootstrap
Protocol (BootP) server rather than a
DHCP server.
MAC Address Identifies the unique Media Access
Control (MAC) address of the phone.
Host Name Identifies the unique host name assigned
to the phone.
Domain Name Identifies the name of the Domain Name
System (DNS) domain in which the
phone resides.
IP Address Indicates the Internet Protocol (IP)
address of the phone.
Subnet Mask Indicates the subnet mask used by the
phone.
See the “Modifying DHCP
Settings” section on page 5-9.
• Displays Ye s or No.
• Cannot be configured.
Cannot configure.
Obtained from the DHCP server.
See the “Assigning Domain
Name” section on page 5-18.
See the “Assigning an IP Address”
section on page 5-14.
See the “Assigning Subnet Mask”
section on page 5-17.
5-4
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 79

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Table 5-1 Network Settings (continued)
Network Setting Description Usage Notes
TFTP Server 1 Indicates the primary Trivial File
Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server used by
the phone to obtain configuration files.
Default Routers 1-5 Identifies the default gateway used by
the phone.
DNS Servers 1-5 Indicates the Domain Name System
(DNS) server used by the phone to
resolve the host name of the TFTP
server, Cisco CallManager system and
web server host names.
Operational VLAN Indicates the auxiliary Virtual Local
Area Network (VLAN) configured on a
Cisco Catalyst switch in which the
phone is a member.
If the phone has not received an
auxiliary VLAN, then the operational
VLAN reflects the Administrative
VLAN.
See the “Assigning a TFTP Sever”
section on page 5-21.
See the “Assigning Default
Router” section on page 5-15.
See the “Assigning DNS Servers”
section on page 5-19.
Obtained via Cisco Discovery
Protocol (CDP) from the switch to
which the phone is attached.
Verifying Network Settings
If neither the auxiliary VLAN nor the
Administrative VLAN are configured,
then the Operational VLAN field is
blank.
Administrative VLAN Indicates the auxiliary VLAN in which
the phone is a member.
Used only if the phone does not receive
an auxiliary VLAN from the switch.
The Administrative VLAN is ignored if
an auxiliary VLAN is obtained from the
switch.
CallManager 1-5 Identifies the Cisco CallManager
systems that are available for processing
calls from this phone.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
See the “Configuring VLAN
Settings” section on page 5-20.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
5-5
Page 80

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Verifying Network Settings
Table 5-1 Network Settings (continued)
Network Setting Description Usage Notes
Information URL Specifies the location (UL) of the help
text for the information (?) button.
Directories URL Specifies the server from which the
phone obtains directory information.
Messages URL Specifies the message services URL. Available only on the
Services URL Specifies the location (URL) for
Cisco IP Phone Services.
Available only on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Available only on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Available only on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
DHCP Enabled Indicates whether DHCP is being used
by the phone.
DHCP Address
Released
Allows the IP-address assigned by
DHCP to be released.
Alternative TFTP Indicates whether the phone is using an
alternative TFTP server.
Erase configuration Allows you to erase all locally-assigned
settings on the phone and reset values to
the default settings.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-6
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
See the “Modifying DHCP
Settings” section on page 5-9.
See the “Releasing a DHCP
Address” section on page 5-12.
See the “Using an Alternate TFTP
Server” section on page 5-23.
See the “Erasing Local
Configuration” section on
page 7-13.
78-10453-04
Page 81

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Table 5-1 Network Settings (continued)
Network Setting Description Usage Notes
Forwarding Delay Indicates whether the internal switch
begins forwarding packets between the
PC port and switch (SW) port on your
phone when your the PC port becomes
active.
Idle URL Specifies the URL that the phone
displays when the phone has not been
used for the time specified in Idle URL
Timer setting. For example, your
administrator can display a logo on the
LCD when the phone has not been used
for 5 minutes.
Idle URL Time Displays the amount of time (in
seconds) that elapses before the URL
specified in the Idle URL setting
displays.
Authentication URL Displays the URL that the phone uses to
validate requests made to the phone web
server.
Proxy Server URL Specifies the host and port used to proxy
HTTP requests for access to non-local
host addresses from the phone HTTP
client.
Displays Ye s or No.
When set to No, the internal
switch begins forwarding packets
immediately. When set to Yes, the
internal switch waits 8 seconds
before forwarding packets
between the PC Port and the SW
Port.
Set the Forwarding Delay to Yes
if you connect both ports to
switches for redundant uplinks or
daisy chain phones together.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Available only on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Available only on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Available only on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Available only on the
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Verifying Network Settings
78-10453-04
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-7
Page 82

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Verifying Network Settings
Table 5-1 Network Settings (continued)
Network Setting Description Usage Notes
PC Port Disabled Indicates whether the PC port on the
phone is enabled or disabled. The port is
labeled “10/100 PC” on the back of the
phone and is used to connect a PC or
workstation to the phone so that they can
share a single network connection.
SW Port Configuration Indicates the speed and duplex of the
switch port. Valid values are: A (auto
negotiate), 10H (10BASE-T/half
duplex), 10F (10BASE-T /full duplex),
100H (100BASE-T /half duplex), or
100F (100BASE-T /full duplex).
PC Port Configuration Indicates the speed and duplex of the PC
port. Valid values are: A (auto
negotiate), 10H (10BASE-T /half
duplex), 10F (10BASE-T /full duplex),
100H (100BASE-T/half duplex), or
100F (100BASE-T/full duplex).
TFTP Server 2 Displays the IP address of the backup
TFTP server. This server is used to
obtain configuration files and software
upgrades if the primary TFTP server is
unavailable.
User Locale Identifies the locale associated with the
phone user. The user locale identifies a
set of detailed information to support
users, including language, font, date and
time formatting, and alphanumeric
keyboard text information.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
This parameter is configured at
the phone. See “Configuring the
SW Port” section on page 5-26.
This parameter is configured at
the phone. See “Configuring the
PC Port” section on page 5-27.
See the “Assigning a Backup
TFTP Server” section on
page 5-24.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
5-8
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 83

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Table 5-1 Network Settings (continued)
Network Setting Description Usage Notes
Network Locale Identifies the locale associate with the
phone. The network locale identifies a
set of detailed information to support the
hardware in a specific location. The
network locale contains a definition of
the tones and cadences used by the
phone in a specific geographic area.
Handset Only Mode Indicates that the headset and speaker
are disabled.
Cannot configure locally. Use
Cisco CallManager to modify.
Informational only. See the
“Configuring the Handset,
Headset, and Speakerphone”
section on page 2-8 for additional
information.
Modifying DHCP Settings
Modifying DHCP Settings
78-10453-04
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) automatically assigns IP
addresses to devices when you connect them to the network. This section provides
information about enabling DHCP and releasing a DHCP-assigned IP address in
the following topics:
• Enabling DHCP, page 5-10
• Disabling DHCP, page 5-11
• Releasing a DHCP Address, page 5-12
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-9
Page 84

Modifying DHCP Settings
Enabling DHCP
Cisco IP Phones enable DHCP by default, but you can reset the protocol if it
becomes disabled.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to DHCP Enabled.
If DHCP is disabled, the option displays as
DHCP Enabled NO
Step 5 Press the Ye s soft key to enable DHCP.
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Step 6 Press Save.
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 3 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select DHCP Enabled.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-10
Procedure
If DHCP is disabled, the option displays as
DHCP Enabled
NO
78-10453-04
Page 85

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Step 5 Use the down volume key to select Ye s.
Step 6 Press # to save.
Disabling DHCP
If you do not use DHCP in your network, use this procedure to disable DHCP
before manually assigning IP addresses to Cisco IP phones.
Note Procedures involved in configuring IP settings or TFTP options cannot be
completed when DHCP is enabled in your network.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Modifying DHCP Settings
78-10453-04
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select to Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to DHCP Enabled.
If DHCP is enabled, the option displays as
DHCP Enabled YES
Step 5 Press the No soft key to disable DHCP.
Step 6 Enter the IP settings as described in “Configuring IP Settings” section on
page 5-14.
Step 7 Press Save.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-11
Page 86

Modifying DHCP Settings
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select DHCP Enabled.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the down volume key to select No.
Step 6 Press # to save.
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Procedure
If DHCP is enabled, the option displays as
DHCP Enabled
YES
Releasing a DHCP Address
When moving the phone to a new network segment, you should first release the
DHCP address.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to DHCP Address Released.
If the DHCP address is currently assigned, the option displays as
DHCP Address Released No
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-12
78-10453-04
Page 87

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Step 5 Press the Ye s soft key to release the DHCP-assigned IP address.
Step 6 Press Save.
The phone remains in an idle state, without an IP address assigned, until you do
one of the following actions:
• Manually assign an IP address
• Set DHCP Address Released back to No.
• Power cycle the phone, which enables all default settings, including enabling
DHCP.
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Modifying DHCP Settings
78-10453-04
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select DHCP Address Released.
If the DHCP address is currently assigned, the option displays as
DHCP Address Released
NO
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the down volume key to select Ye s.
Step 6 Press # to save.
The phone remains in an idle state, without an IP address assigned, until you do
one of the following actions:
• Manually assign an IP address.
• Set DHCP Address Released back to No.
• Power cycle the phone, which enables all default settings, including enabling
DHCP.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-13
Page 88

Configuring IP Settings
Configuring IP Settings
Use these guidelines when manually configuring the IP settings:
• You can use 0.0.0.0 for the subnet mask only if the default gateway is also
0.0.0.0.
• Ensure TFTP server has an IP address.
• Ensure the default gateway IP address is on the same subnet as the host IP
address.
Note Procedures involved in configuring IP settings or TFTP options cannot be
completed when DHCP is enabled in your network.
This section covers the following topics:
• Assigning an IP Address, page 5-14
• Assigning Default Router, page 5-15
• Assigning Subnet Mask, page 5-17
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
• Assigning Domain Name, page 5-18
• Assigning DNS Servers, page 5-19
Assigning an IP Address
The IP address is the unique logical address identifying each host computer, or
node, on a TCP/IP network. An IP address is a 32-bit number expressed as four
decimal numbers from 0 to 255 separated by periods.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-14
78-10453-04
Page 89

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Step 4 Scroll to IP Address.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter a new IP address, using the * key on the
dial pad or the . soft key to enter periods.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Step 8 Press the Validate soft key.
Step 9 Press Save.
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select IP Address.
Configuring IP Settings
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter a new IP address, using the down arrow
to back space and the * key on the dial pad to enter periods.
Step 6 Press # to save.
Assigning Default Router
If you manually assign an IP address to the Cisco IP Phone, you must indicate the
default router to be used. The default router provides connectivity to the IP
network beyond the subnet to which the phone belongs.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
5-15
Page 90

Configuring IP Settings
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to Default Router 1.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new router IP address, using the * key
on the dial pad or the . soft key to enter periods.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Step 8 Press the Validate soft key.
Step 9 Scroll to Default Router 2-5 to add backup gateways.
Step 10 Press Save.
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select Default Router 1.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new router IP address, using the down
Step 6 Scroll to Default Router 2-5 to add backup gateways.
Step 7 Press # to Save.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-16
Procedure
arrow to backspace and the * key on the dial pad to enter periods.
78-10453-04
Page 91

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Assigning Subnet Mask
The subnet mask is used to partition the IP address into a network and a host
identifier. The subnet mask is used to mask a portion of the IP address so that
TCP/IP can distinguish the network ID from the host ID.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to Subnet Mask.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new subnet mask, using the * key on
the dial pad or the . soft key to enter periods.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Configuring IP Settings
Step 8 Press the Validate soft key.
Step 9 Press the Save soft key to save this change.
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select Subnet Mask.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Procedure
5-17
Page 92

Configuring IP Settings
Step 5 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new subnet mask, using the down
arrow to back space and the * key on the dial pad to enter periods.
Step 6 Press # to save.
Assigning Domain Name
The domain name is the name of the Domain Name System (DNS) domain in
which the phone is located. DNS is a hierarchical name for TCP/IP host
computers that provides standard naming conventions.
Before assigning a domain name, verify that you have a DNS in your network.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
5-18
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to Domain Name.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter a new domain name, using the 0 key on
the dial pad to enter periods.
To enter letters, use the numbers associated with a particular letter. For example,
the 2 key has the letters ABC. For a lower case “a,” press 2 once. Press the 2 key
repeatedly to scroll through the available letters and numbers. Pause after the
selected letter appears on the screen.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Step 8 Press the Validate soft key.
Step 9 Press the Save soft key to save this change.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
Page 93

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Changing the domain name on the Cisco IP Phone 7910 is not currently
supported.
Assigning DNS Servers
The DNS setting on the Cisco IP Phone allows users to specify remote computers
by host names, which are character strings with some mnemonic value, rather than
by using IP addresses, which are simply strings of numbers.
The phones use DNS to resolve the host name of TFTP servers,
Cisco CallManager systems, and web server host names when the system is
configured to use names rather than IP addresses.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Configuring IP Settings
78-10453-04
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to DNS Server 1.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter a new DNS server address, using the * key
on the dial pad or the . soft key to enter periods.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Step 8 Press the Validate soft key.
Step 9 Scroll to DNS Server 2-5 to add backup DNS server.
Step 10 Press Save.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-19
Page 94

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Configuring VLAN Settings
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select DNS server 1.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new DNS server address, using the
down arrow to back space and the * key on the dial pad to enter periods.
Step 6 Press # to save.
Configuring VLAN Settings
You can change the administrative VLAN used by the Cisco IP Phone. However,
if you have an auxiliary VLAN assigned on the Cisco Catalyst switch, that setting
overrides any changes made on the phone.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to Admin. VLAN Id.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new Admin VLAN setting.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-20
78-10453-04
Page 95

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Step 8 Press Validate.
Step 9 Press Save.
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select Admin VLAN ID setting.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new Admin VLAN ID, using the down
arrow to backspace.
Step 6 Press # to save.
Configuring TFTP Options
Configuring TFTP Options
If you do not use DHCP to direct the Cisco IP Phone 7960 to a TFTP server, you
must manually assign one. You can also assign an alternative TFTP server to use
instead of the one assigned by DHCP.
This section covers these topics:
• Assigning a TFTP Sever, page 5-21
• Using an Alternate TFTP Server, page 5-23
Assigning a TFTP Sever
The default TFTP server is set to CiscoCM1. If you are not using DHCP in your
network, and you want to change this setting, you must manually assign the TFTP
server to the phone.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
5-21
Page 96

Configuring TFTP Options
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to TFTP Server 1.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter a new TFTP server address, using the *
key on the dial pad or the . soft key to enter periods.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Step 8 Press Validate.
Step 9 Press Save.
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select TFTP Server 1 setting.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new TFTP server address, using the
Step 6 Press # to save.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-22
Procedure
down arrow to back space and the * key on the dial pad to enter periods.
78-10453-04
Page 97

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Using an Alternate TFTP Server
If you are using DHCP, but you want to override the TFTP address that the phone
received through DHCP, enable an alternate TFTP Server.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to Alternate TFTP Server.
If the phone is not using an alternative TFTP server, the option displays as
Alternate TFTP NO
Step 5 Press the Ye s soft key.
Step 6 Scroll to TFTP Server
Step 7 Press the Edit soft key.
Configuring TFTP Options
Step 8 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new Alternative TFTP Server address,
Step 9 Press the Ye s soft key to enable an alternative TFTP server.
Step 10 Press Validate.
Step 11 Press Save.
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select Alternate TFTP setting.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
using the * key on the dial pad or the . soft key to enter periods.
Procedure
5-23
Page 98

Configuring TFTP Options
If an alternate TFTP server is currently unassigned, the option displays as:
Alternate TFTP
NO
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the down volume key to select Ye s.
Step 6 Press # to save.
Step 7 Use the down volume key to select TFTP Server setting.
Step 8 Press * to edit.
Step 9 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the new TFTP server address, using the
down arrow to back space and the * key on the dial pad to enter periods.
Step 10 Press # to save.
Assigning a Backup TFTP Server
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
TFTP Server 2 displays the IP address of the backup TFTP server. This server is
used to obtain configuration files and software upgrades if the primary TFTP
server is unavailable.
Before You Begin
To assign a backup TFTP server, the Alternate TFTP setting must be set to Ye s
and TFTP Server 1 setting must contain a value.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to TFTP Server 2.
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
5-24
78-10453-04
Page 99

Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter a backup TFTP server address, using the
* key on the dial pad or the . soft key to enter periods.
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Step 8 Press Validate.
Step 9 Press Save.
Cisco IP Phone 7910
Procedure
Step 1 Press settings.
Step 2 Press 6 (Network Configuration).
Step 3 Use the down volume key to select TFTP Server 2 setting.
Step 4 Press * to edit.
Step 5 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the backup TFTP server address, using the
down arrow to back space and the * key on the dial pad to enter periods.
Configuring Ports
Step 6 Press # to save.
Configuring Ports
The PC and switch (SW) port configuration settings determine the speed and
duplex of the PC and network ports, respectively.
If you change the port configuration setting value for either the PC port or the SW
port, you must change the other to match or configure both to auto-negotiate.
If the phone is connected to a switch, you must configure the switch's port to the
same speed/duplex as the phone, or configure both to auto-negotiate.
The values for both are: A (auto-negotiate), 10H (10BaseT/Half Duplex), 10F
(10BaseT/Full Duplex), 100H (100BaseT/Half Duplex), or 100F (100BaseT/Full
Duplex). This setting is not case sensitive.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
5-25
Page 100

Configuring Ports
This section covers the following topics:
• Configuring the SW Port, page 5-26
• Configuring the PC Port, page 5-27
Configuring the SW Port
Follow these procedures to set the speed of the switch port on the Cisco IP Phone.
Cisco IP Phone 7960/7940
Procedure
Step 1 Press the Settings button.
Step 2 Use the Navigation button to select Network Configuration.
Step 3 Press the Select soft key.
Step 4 Scroll to SW Port Configuration.
Chapter 5 Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco IP Phone
5-26
Step 5 Press the Edit soft key.
Step 6 Use the buttons on the dial pad to enter the selected option.
To enter letters, use the numbers associated with a particular letter. For example,
the 2 key has the letters ABC. For a lower case “a,” press 2 once. Press the 2 key
repeatedly to scroll through the available letters and numbers. Pause after the
selected letter appears on the screen.
Valid values are as follows:
• A (auto negotiate)
• 10H (10basedT/half duplex)
• 10F (10basedT/full duplex)
• 100H (100basedT/half duplex)
• 100F (100basedT/full duplex)
Step 7 Use the << soft key to correct any mistakes.
Cisco IP Phone Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager 3.2, Cisco IP Phones 7960/7940/7910
78-10453-04
 Loading...
Loading...