Cisco 7246VXR - uBR Router, UBR7223 - uBR 7223 Modular Expansion Base, uBR7200 Series Software Configuration Manual
Page 1

Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal
Broadband Router Software
Configuration Guide
Cisco IOS® Software 12.3 BC, 12.2 BC, 12.2CX, 12.1 EC
May 2009
Text Part Number: OL-2239-05
Page 2

CCDE, CCSI, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, the Cisco logo, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco Nurse Connect, Cisco Stackpower, Cisco StadiumVision,
Cisco
TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are
service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the
Cisco
Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without
Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study,
IronPort, the IronPort
logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar,
PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath,
WebEx, and the WebEx
logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0903R)
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2004–2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

3
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
CONTENTS
Preface 11
Document Revision History 1-11
Document Objectives 1-11
Audience 1-12
Document Organization 1-12
Conventions 1-13
Terms and Acronyms 1-14
Related Documentation 1-17
Cisco uBR7200 Series Documentation 1-17
Cisco Cable Modem Termination System Reference Documentation 1-18
Related Cisco IOS Release Documentation 1-18
CHAPTER
1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software 1-1
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series 1-2
Determining Your Cisco IOS Software Release 1-2
Upgrading to a New Software Release 1-2
12.3 BC Release Train Images and Requirements 1-3
12.2 BC Release Train Images and Requirements 1-4
12.2 CX Images and Requirements 1-5
12.1 EC Images and Requirements 1-7
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview 1-8
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Routers 1-9
Supported Hardware on the Cisco uBR7200 Series 1-11
System Interoperability 1-14
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview 1-15
Port Adapter and Line Card Slot and Logical Interface Numbering 1-15
MAC-Layer Addressing 1-17
Cable Interface Line Cards 1-17
Cable Interface Line Card Slots 1-19
Interfaces and Physical Ports 1-20
Port Adapter Slots 1-20
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series 1-22
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Features and Cisco IOS Releases 1-22
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Tools 1-31
Page 4

Contents
4
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Bandwidth Management Features 1-33
Cisco IOS Command-Line Enhancements 1-33
Cisco Quality of Service Features 1-45
DHCP Servers and Feature Support 1-47
DOCSIS 1.0 Feature Support 1-49
DOCSIS 1.0+ Feature Support 1-56
DOCSIS 1.1 Feature Support 1-57
DOCSIS 2.0 Feature Support 1-67
High Availability Features 1-68
Intercept Features 1-72
IP Broadcast and Multicast Features 1-79
IP Routing Features 1-80
Management Features 1-86
Multicast Features 1-96
PacketCable and Voice Support Features 1-101
Security Features 1-102
SNMP Features and Enhancements 1-109
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management Features 1-119
Testing, Troubleshooting and Diagnostic Features 1-123
Virtual Interfaces 1-125
VLAN Features 1-126
VPN and Layer 2 Tunneling Features 1-126
WAN Optimization and Services Features 1-131
DOCSIS and CMTS Interoperability 1-137
DOCSIS NTSC Cable Plants 1-137
EuroDOCSIS Cable Plants 1-138
DOCSIS-Compliant Downstream Signals 1-139
DOCSIS-Compliant Upstream Signals 1-140
Traffic Engineering 1-142
CHAPTER
2 Configuring the Cable Modem Termination System for the First Time 2-1
Configuration Fundamentals for the Cisco uBR7200 Series 2-2
Preconfiguring the Cisco uBR7200 Series 2-2
Booting and Logging onto the Cisco uBR7200 Series 2-5
Setting Password Protection on the Cisco uBR7200 Series 2-5
Recovering Passwords on the Cisco uBR7200 Series 2-6
Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series Using AutoInstall 2-10
Autoinstall Requirements 2-10
Understanding AutoInstall 2-11
Page 5

Contents
5
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preparing for the AutoInstall Process 2-11
Performing the AutoInstall Procedure 2-12
Setting Up the TFTP Server for Autoinstall 2-15
Setting Up the BOOTP or RARP Server for Autoinstall 2-16
Connecting the New Router to the Network 2-16
Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series Using the Setup Facility 2-17
Introduction to the Setup Facility 2-17
Configuring Global Parameters with the Setup Facility 2-18
Configuring Upstream Frequencies with the Setup Facility 2-21
Configuring Interfaces with the Setup Facility 2-22
Configuring the Cable Interface with the Extended Setup Facility 2-25
Identifying the Cable Interface Line Card 2-25
Configuring Global Parameters in Extended Setup 2-26
Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series Manually Using Configuration Mode 2-27
Saving Your Configuration Settings 2-29
Reviewing Your Settings and Configurations 2-29
Viewing Sample Configuration Files 2-29
CHAPTER
3 Configuring Cable Modem Interface Features 3-1
Configuring the Downstream Cable Modem Interface 3-2
Activating Downstream Cable Address Resolution Protocol Requests 3-2
Activating Downstream Ports 3-3
Setting the Integrated Upconverter 3-4
Assigning the Downstream Channel ID 3-5
Configuring Downstream Rate Limiting and Traffic Shaping 3-6
Setting the Downstream Helper Address 3-7
Setting the Downstream Interleave Depth 3-8
Setting the Downstream Modulation 3-8
Setting the Downstream MPEG Framing Format 3-9
Setting Downstream Traffic Shaping 3-10
Configuring the Upstream Cable Modem Interface 3-11
Activating Upstream Admission Control 3-12
Activating Upstream Differential Encoding 3-13
Activating Upstream Forward Error Correction 3-14
Activating the Upstream Ports 3-15
Activating Upstream Frequency Adjustment 3-15
Activating Upstream Power Adjustment 3-16
Activating the Upstream Scrambler 3-17
Activating Upstream Timing Adjustment 3-17
Page 6

Contents
6
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Configuring Upstream Rate Limiting and Traffic Shaping 3-18
Setting Upstream Backoff Values 3-19
Setting the Upstream Channel Width 3-21
Setting the Upstream Frequency 3-22
Setting the Upstream Input Power Level 3-24
Specifying Upstream Minislot Size 3-25
Setting Upstream Traffic Shaping 3-26
Configuring Optional Cable Modem Interface Features 3-28
Activating Host-to-Host Communication (Proxy ARP) 3-28
Activating Packet Intercept Capabilities 3-29
Configuring Cable Subinterfaces 3-29
Configuring and Monitoring Cable Interface Bundling 3-30
Configuring Payload Header Suppression and Restoration 3-33
Setting Optional IP Parameters (Broadcast and Multicast Echo) 3-33
Activating IP Multicast Echo 3-33
Activating IP Broadcast Echo 3-34
CHAPTER
4 Configuring DOCSIS Baseline Privacy Interface on the Cisco uBR7200 Series 4-1
Baseline Privacy Interface Overview 4-1
BPI Key Management 4-2
Differentiating Traffic Streams 4-3
CM Communication with BPI 4-3
Enabling DOCSIS BPI 4-3
DOCSIS 1.1 Baseline Privacy Interface Plus Overview 4-4
CHAPTER
5 Managing Cable Modems on the Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial Network 5-1
Activating Cable Modem Authentication 5-2
Activating Cable Modem Insertion Interval 5-3
Activating Cable Modem Upstream Address Verification 5-4
Clearing Cable Modem Counters 5-5
Clearing Cable Modem Reset 5-5
Configuring Cable Modem Registration Timeout 5-6
Configuring Dynamic Contention Algorithms (Cable Insertion Interval, Range, and Data Backoff) 5-6
cable insertion-interval Command Examples 5-6
Configuring the Dynamic Map Advance Algorithm 5-7
Configuring Maximum Hosts Attached to a Cable Modem 5-8
Configuring Per-Modem Filters 5-8
Page 7

Contents
7
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Configuring Sync Message Interval 5-9
CHAPTER
6 Configuring Basic Broadband Internet Access 6-1
Overview of Basic Broadband Internet Access 6-1
Recommended Basic Configuration for High-Speed Internet Access 6-2
Basic Internet Access Sample Configuration File 6-3
CHAPTER
7 Overview of the Cisco Network Registrar for the Cisco uBR7200 Series 7-1
Cisco Network Registrar Description 7-1
Cable Modem DHCP Response Fields 7-2
DOCSIS DHCP Fields 7-2
DHCP Relay Option (DOCSIS Option 82) 7-2
Overview of Scripts 7-3
Two-way Cable Modem Scripts 7-3
Telco Return Cable Modem Scripts 7-3
Placement of Scripts 7-3
Windows NT 7-3
Solaris 7-3
Activate Scripts in Cisco Network Registrar 7-4
Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series to Use Scripts 7-4
Configure the System Default Policy 7-5
Cable Modems 7-5
PCs 7-5
Create Selection Tag Scopes 7-5
General 7-5
Telco Return 7-6
Create Network Scopes 7-6
Create Policies for Class of Service or for Upgrading Cable Modem Cisco IOS Images 7-7
CNR Steps to Support Subinterfaces 7-7
CHAPTER
8 Troubleshooting the System 8-1
Understanding show Command Responses 8-2
Using a Headend Cable Modem to Verify Downstream Signals 8-6
Performing Amplitude Averaging 8-7
Enabling or Disabling Power Adjustment 8-7
Setting Downstream Test Signals 8-9
Configuring Unmodulated Test Signals 8-9
Page 8

Contents
8
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Configuring PRBS Test Signals 8-10
Verifying Test Signal Output 8-10
Pinging Unresponsive Cable Modems 8-10
Pinging a Cable Modem 8-10
Verifying the Ping 8-10
Using Cable Interface debug Commands 8-11
debug cable arp 8-11
debug cable error (for MAC Protocol Errors) 8-11
debug cable keyman (for Baseline Privacy Activity) 8-12
debug cable mac-messages 8-12
debug cable map 8-12
debug cable phy 8-12
debug cable privacy (for Baseline Privacy) 8-13
debug cable qos 8-13
debug cable range (for Ranging Messages) 8-13
debug cable receive (for Upstream Messages) 8-13
debug cable reg (for Modem Registration Requests) 8-14
debug cable reset (for Reset Messages) 8-14
debug cable specmgmt (for Spectrum Management) 8-14
debug cable startalloc (for Channel Allocations) 8-14
debug cable transmit (for CMTS Transmissions) 8-15
debug cable ucc (for Upstream Channel Change Messages) 8-15
debug cable ucd (for Upstream Channel Description Messages) 8-15
APPENDIX
A Installing or Upgrading Cisco IOS Software A-1
Introduction A-1
Before You Begin A-1
Installing or Upgrading Cisco IOS Software A-2
Sample Output—Cisco uBR7200 Series Router A-3
Related Information A-3
Copying a System Image from One Device to Another A-4
Copying from Device to Device Inside the Same Router A-4
Copying from One Router to Another A-4
APPENDIX
B Resolving Common Image Installation Problems B-1
Before You Begin B-1
Resolving Default Gateway Issues B-1
Troubleshooting Problems During Software Transfer B-3
Troubleshooting Problems by Verifying the Software Image B-5
Page 9

Contents
9
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
APPENDIX
C Viewing Sample Configuration Files C-1
Basic Internet Access Examples C-1
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Example C-9
IP Telephony Example C-12
Telco Return Example C-14
APPENDIX
D Frequency Allocation for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Routers D-1
APPENDIX
E Configuration Register Information for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband
Routers E-1
Configuration Bit Meanings E-1
Bits 0–3 E-2
Bit 6 E-3
Bit 7 E-3
Bit 8 E-3
Bit 10 and Bit 14 E-4
Bit 11 and Bit 12 E-4
Bit 13 E-5
Bit 15 E-5
Displaying the Configuration Register While Running Cisco IOS E-5
Displaying the Configuration Register While Running ROM Monitor E-6
Setting the Configuration Register While Running Cisco IOS E-6
Setting the Configuration Register While Running ROM Monitor E-7
I
NDEX
Page 10

Contents
10
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Page 11

11
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
This preface describes the objectives, intended audience, organization and terminology of this
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide. The
Cisco
uBR7200 series CMTS and this guide support the following Cisco IOS release trains:
• 12.3 BC
• 12.2 BC
• 12.1 EC
• 12.0 SC
For additional supported Cisco IOS release trains, refer to Cisco uBR7200 Series Software Release Notes on
Cisco.com.
Document Revision History
The Document Revision History table below records technical changes to this document.
Ta b l e 1 Document Revision History
Document Objectives
This guide describes configuring, maintaining, and troubleshooting the Cisco uBR7200 series universal
broadband routers: the Cisco uBR7223, Cisco uBR7246, and Cisco
uBR7246 VXR. Cisco’s Cable
Modem Termination System (CMTS) solutions allow cable companies, Internet service providers (ISPs),
and others to allocate channel capacity for Internet access, Virtual Private Network (VPN), and Voice
over IP (VoIP) services using a broadband radio frequency (RF) cable plant.
The Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers sustain downstream and upstream traffic to and
from two-way Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS)-based cable modems (CMs)
that support 6 MHz National Television Systems Committee (NTSC) operations. For NTSC cable plants
not upgraded for full two-way operations, the routers also support DOCSIS-compliant telco-return CMs.
For international cable companies using 8 MHz channel widths, the Cisco
uBR7200 series equipment
supports Phase Alternating Line (PAL) and Systeme Electronique Couleur Avec Memoire (SECAM)
channel plans to operate with EuroDOCSIS-based CMs and set
top box (STB) units with integrated
EuroDOCSIS modems.
Document
Revision
Date Change Summary
OL-2239-04 September 30, 2005 Incorporated new features and enhancements introduced in
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC. Added Document
Revision History table.
Page 12

12
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
Audience
Audience
This guide is intended for system administrators and support engineers who configure and maintain the
Cisco
uBR7200 series. Many different delivery models exist for Cisco uBR7200 series equipment:
• In smaller networks, a single service provider manages all equipment and infrastructure.
• In larger networks, multiple service operators (MSOs) and ISPs share responsibility for provisioning
and managing the cable plant and IP network.
The MSO and ISP divide responsibilities according to the service model. In some cases, the MSO
maintains and operates the cable plant and attached CMs and STBs, whereas the ISP owns, operates, and
maintains the regional network and IP infrastructure beyond the cable distribution hub. In other cases,
the CMTS and RF customer premises equipment (CPE) are viewed as part of the networking
infrastructure, and the ISP maintains control for provisioning and managing DOCSIS functionality.
Note This guide considers the MSO and ISP as a single service principle with responsibility to provision and
manage DOCSIS-based cable modems and set-top boxes (STBs). This guide assumes that administrators
are familiar with Cisco
uBR7200 series hardware, DOCSIS or EuroDOCSIS requirements, and
networking.
Document Organization
This guide focuses on configuration of Cisco IOS software for the Cisco uBR7200 series. Tab l e 2
summarizes the chapters and procedures in this guide.
Ta b l e 2 Guide Contents and Organization
Title Description
Chapter 1, “Overview of Cisco uBR7200
Series Software”
Acquaints you with the supported Cisco IOS features and configuration.
Chapter 2, “Configuring the Cable Modem
Termination System for the First Time”
Provides instructions to make basic configurations to the Cisco uBR7200 series
cable modem termination system (CMTS) using AutoInstall, the Setup facility,
Extended Setup, or manual configuration mode. Includes sample
Cisco
uBR7200 series software configurations.
Note Complete the configurations in this chapter prior to attempting additional
configurations later in this guide or elsewhere.
Chapter 3, “Configuring Cable Modem
Interface Features”
Provides instructions for required cable modem interface configurations for
upstream and downstream interfaces.
Chapter 4, “Configuring DOCSIS Baseline
Privacy Interface on the Cisco uBR7200
Series”
Provides an overview of DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy Interface (BPI),
instructions for enabling BPI, and an introduction to DOCSIS 1.1 BPI+ features.
Chapter 5, “Managing Cable Modems on the
Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial Network”
After completing upstream and downstream cable modem interface
configurations, this chapter provides a number of procedures that you can
implement in order to manage operations of your cable modems in the hybrid
fiber-coaxial network.
Chapter 6, “Configuring Basic Broadband
Internet Access”
Provides a recommended basic configuration for high-speed Internet access and
a basic Internet access sample configuration file.
Page 13

13
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
Conventions
Conventions
This guide uses the following conventions for command syntax descriptions and textual emphasis:
Chapter 7, “Overview of the Cisco Network
Registrar for the Cisco uBR7200 Series”
Supplements the Cisco Network Registrar (CNR) documentation by providing
additional cable-specific instructions that are pertinent to the
Cisco
uBR7200 series and CMTS management.
Chapter 8, “Troubleshooting the System” Provides troubleshooting instructions for the configuration of the
Cisco
uBR7200 series CMTS.
Appendix A, “Installing or Upgrading Cisco
IOS Software”
Explains how to install Cisco IOS software onto "Run from RAM" Cisco routers
using a TFTP server or remote copy protocol (rcp) server application.
Appendix B, “Resolving Common Image
Installation Problems”
Explains the resolution to common installation problems when installing images
using TFTP or an rcp server.
Appendix C, “Viewing Sample
Configuration Files”
Provides examples of Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband router
configuration files.
Appendix D, “Frequency Allocation for the
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband
Routers”
Provides information on NTSC 6-MHz, Phase Alternating Line (PAL) and
Systeme Electronique Couleur Avec Memoire (SECAM) 8-MHz channel
bands.
Appendix E, “Configuration Register
Information for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Universal Broadband Routers”
Provides information about the functions and configuration of bits in the
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Register.
Index Index for the entire manual.
Table 2 Guide Contents and Organization (continued)
Title Description
Ta b l e 3 Command Syntax and Emphasis Conventions
Convention Description
boldface font Commands and keywords are in boldface.
italic font Arguments for which you supply values are in italics.
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional.
{x | y | z} Alternative, mutually exclusive, keywords are grouped in braces and
separated by vertical bars.
[x | y | z] Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars.
string A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string
or the string will include the quotation marks.
screen font Terminal sessions and information the system displays are in screen font.
boldface screen font Information you must enter is in boldface screen font.
italic screen font Arguments for which you supply values are in italic screen font.
^ The symbol ^ represents the key labeled Control—for example, the key
combination ^D in a screen display means hold down the Control key while
you press the D key.
Page 14

14
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
Terms and Acronyms
Note This symbol means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not
covered in the publication.
Tip This symbol means the following are useful tips.
Timesaver This symbol means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action
described in the paragraph.
Caution This symbol means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in
equipment damage or loss of data.
Terms and Acronyms
A complete list of terms and acronyms is available in the Internetworking Terms and Acronyms guide,
available on the Documentation CD-ROM.
To fully understand the content of this guide, you should be familiar with the following terms and
acronyms.
• A/D—analog to digital (conversion)
• ABR—available bit rate
• AAL5—ATM adaptation layer 5
• AGC—automatic gain control
• AM-VSB—Amplitude Modulation - Vestigial Side Band (Modulation scheme)
• ASIC—Application Specific Integrated Circuit
• AWG—American wire gauge
• BGP—Border Gateway Protocol
• BPI—Baseline Privacy Interface
• CATV—cable television
• CM—cable modem
• CMTS—cable modem termination system (headend)
• CoS—class of service
< > Nonprinting characters, such as passwords, are in angle brackets in contexts
where italics are not available.
[ ] Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets.
!, # An exclamation point ( ! ) or a pound sign ( # ) at the beginning of a line of
code indicates a comment line.
Table 3 Command Syntax and Emphasis Conventions (continued)
Convention Description
Page 15

15
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
Terms and Acronyms
• CPE—customer premises equipment
• CPR—Centralized Priority Reservation
• CRC—cyclic redundancy check
• CSU—channel service unit
• CTS—Clear To Send
• D/A—digital to analog (conversion)
• DAVIC —Digital Audio-Visual Council
• DCD—Data Carrier Detect
• DCE—data communications equipment
• DDS—Direct Digital Synthesis
• DES—Data Encryption Standard
• DHCP—Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
• DOCSIS—Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specification
• DVB—Digital Video Broadcasting
• DIMM—dual in-line memory module
• DSR—data set ready
• DSU—data service unit
• DTE—data terminal equipment
• DTR—data terminal ready
• ESP—Electronic Systems Products
• EMC—electromagnetic compliance
• EMI—electromagnetic interference
• ESD—electrostatic discharge
• EuroDOCSIS—European DOCSIS (Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specification)
• FCS—Frame Check Sequence; First Customer Shipment
• FDR—Final Design Review
• FEC—Forward Error Correction
• FRU—field-replaceable unit (router components that do not require replacement by a service
provider certified by Cisco)
• FTP—foil twisted-pair
• HCCP—Hot Standby CMTS-to-CMTS Protocol
• HDLC—High-Level Data Link Control
• HEAD—Head-end Modulator and Demodulator
• HEM—Head End Modem
• HFC—Hybrid Fiber Coax
• HOME—Subscriber Unit
• HS—Head-end Shelf
• HSRP—Hot-Standby Router Protocol
• IP—Internet Protocol
• IPSec—IP Security Protocol
• ISL—Inter-Switch Link protocol
• ISS—Instruction Set Simulator
• Kbps—kilo-bits per second
Page 16

16
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
Terms and Acronyms
• LAN—local area network
• LCN—logical channel number
• LED—light emitting diode
• LLC—logical link control
• MAC—Media Access Control
• MB—megabyte
• Mbps—mega-bits per second
• MM—multimode
• MODEM—modulator/demodulator
• MPEG-2—Moving Picture Experts Group (Specification 2)
• MPEG-2-TS—MPEG-2 Transport Stream
• MSN—manufacturer serial number
• MSO—multiple systems operator
• NIU/STB—network interface unit/set-top box
• nrt-VBR—non-real-time variable bit rate
• NTSC—National Television Standards Committee
• NVRAM—nonvolatile random-access memory
• OAM AIS—Operation, Administration, and Maintenance alarm indication signal
• OAM&P—Operations, Administration, Maintenance and Provisioning
• OC3—Optical Carrier Level 3
• OIR—online insertion and removal
• PCI—Peripheral Component Interconnect
• PCMCIA—Personal Computer Memory Card International Association
• PDD—Project Design Document
• PHY—Physical Layer Interface
• PID—Packet Identifier
• PLL—Phase Locked Loop
• PPP—Point-to-Point Protocol
• QAM—Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
• QoS—quality of service
• QPSK—Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
• rcp—remote copy protocol
• RFI—radio frequency interference
• RIP—Routing Information Protocol
• RISC—Reduced Instruction Set Computer
• RTP—Real-Time Transport Protocol
• RTS—Request To Send
• SDRAM—synchronous dynamic random-access memory
• SIMM—single in-line memory module
• SM—Subscriber Modem or Spectrum Manager
• SMI—single-mode intermediate reach
• SNMP—Simple Network Management Protocol
Page 17

17
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
Related Documentation
• SU—Subscriber Unit
• TCP/IP—Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
• TDE/C—Transmit Data Encoder/Controller
• TDM—time-division multiplexing
• TDMA—Time Division Multiple Access
• TFTP—Trivial File Transfer Protocol
• UBR—unspecified bit rate
• UDP—User Datagram Protocol
• UNI—User-Network Interface
• UTOPIA—Universal Test and Operation Physical Interface for ATM
• UTP—unshielded twisted-pair
• VC—virtual circuit
• VCI—Virtual Channel Identifier
• VCPU—Virtual CPU
• VP—Virtual Path
• VPI—Virtual Path Identifier
• VPN—Virtual Private Network
Related Documentation
Cisco uBR7200 Series Documentation
The procedures in this guide assume that site preparation and hardware setup are complete. Refer to the
documentation page for
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Routers for these and additional
document links:
Note If the hypertext link to any external document does not operate, you can access the desired document by
typing or pasting the full document title in the Search field of the Cisco.com home page. Click Go.
Document Title Online Location
Release Notes for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
(multiple release trains)
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/
product/cable/cab_rout/ub7200rn/index.htm
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router
Hardware Installation Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/u
br7200/installation/guide/ub72khig.html
Cisco uBR7200 Series Software Features http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/u
br7200/configuration/guide/cr72scg.html
Page 18

18
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-04
Preface
Related Documentation
• For information about installing and replacing field-replaceable units (FRUs), such as memory, on
Cisco
uBR7200 series routers, refer to the document that ships with each FRU.
• For information on the modular port adapter installed in your router (if present), refer to the
individual documents that ship with each port adapter.
• For international agency compliance, safety, and statutory information for WAN interfaces for
Cisco
uBR7200 series routers, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
document that shipped with your router.
Cisco Cable Modem Termination System Reference Documentation
Related Cisco IOS Release Documentation
For detailed Cisco IOS software configuration information and support, refer to the configuration and
command reference publications on these web pages:
• Cisco IOS Release 12.1 Documentation
• Cisco IOS Release 12.2 Documentation
• To query Cisco IOS releases according to feature or release number, refer to the Cisco IOS Feature
Navigator (Cisco.com login ID and password required). Obtaining Documentation and Submitting
a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s
New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and
revised Cisco
technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS
Ve r si o n 2.0.
Document Title Online Location
Cable DOCSIS 1.1 FAQs http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk168/te
chnologies_q_and_a_item09186a0080174789.s
html
Cisco Cable Modem Termination System Feature
Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/f
eature/guide/cmtsfg.html
Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/co
mmand/reference/cbl_book.html
Cisco IOS Multiservice Applications Configuration
Guide:
• Configuring Headend Broadband Access Router
Features
• Configuring Subscriber-End Broadband
Access Router Features
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1/mu
ltiserv/configuration/guide/multi_c.html
DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal
Broadband Routers
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/f
eature/DOCSIS11.html
Page 19

CHAP T E R
1-1
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
1
Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
The Cisco uBR7200 series uses Cisco IOS® software to offer enhanced stability, features, performance
and investment protection. This chapter summarizes system and software features of the Cisco uBR7200
series Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS). This chapter contains the following sections:
Section Purpose
“Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the
Cisco uBR7200 Series,” page 2
Describes the supported Cisco IOS release trains, associated
features, and latest Cisco IOS images for each recently
supported train.
One early step in CMTS feature configuration is to verify
your Cisco IOS release train, the associated image and
feature set. This section guides you in determining such
information.
“Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis
Overview,” page 8
Describes the Cisco uBR7200 series routers, and their
supported hardware features and interoperability.
“Cisco uBR7200 Series Router
Configuration Overview,” page 15
Provides an overview of the hardware and interfaces that
typically require configuration through Cisco IOS software.
“Supported Software Features for the
Cisco uBR7200 Series,” page 22
Describes the features and configuration utilities that are
available on the Cisco
uBR7200 series.
“DOCSIS and CMTS Interoperability,”
page 137
Provides an overview of DOCSIS NTSC and EuroDOCSIS
cable plants, DOCSIS-compliant signals, and traffic
engineering.
Page 20

1-2
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
This section describes the supported releases, latest images, memory requirements, and major software
features for the following Cisco IOS software:
• Determining Your Cisco IOS Software Release
• Upgrading to a New Software Release
• 12.3 BC Release Train Images and Requirements
• 12.2 BC Release Train Images and Requirements
• 12.2 CX Images and Requirements
• 12.1 EC Images and Requirements
To configure the CMTS for the first time, refer to Chapter 2, “Configuring the Cable Modem
Termination System for the First Time.”
For additional release information, refer to the Cisco uBR7200 Series Software Release Notes on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/ubr7200/release/notes/12_3bc/123BCu72.html
Determining Your Cisco IOS Software Release
To determine the version of Cisco IOS software running on the Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband
router, log in to the router and enter the show version command in User or privileged EXEC mode.
Router> show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) Cisco IOS 12.2 BC Software (ubr7200-is-mz), Version Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1,
RELEASE SOFTWARE
Note Your display may vary according to your release and image.
Upgrading to a New Software Release
An upgrade is an order placed for a Cisco IOS feature set that contains more functionality than the
feature set that you are replacing. An upgrade is not an “update.” An update consists of installing a more
recent version of the same feature set.
• Exception—If a feature set has been made obsolete, the next closest feature set on a more recent
release is considered an update.
For general information about upgrading to a new software release, refer to the Cisco IOS Upgrade
Ordering Instructions on Cisco.com. Also refer to Appendix A, “Installing or Upgrading Cisco IOS
Software.”
Page 21
1-3
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
12.3 BC Release Train Images and Requirements
The Cisco 12.3 BC release train is the latest Cisco IOS release train to support the Cisco uBR7200
Series, and emphasizes additional features and performance specifically for the Cisco uBR7246VXR
universal broadband router.
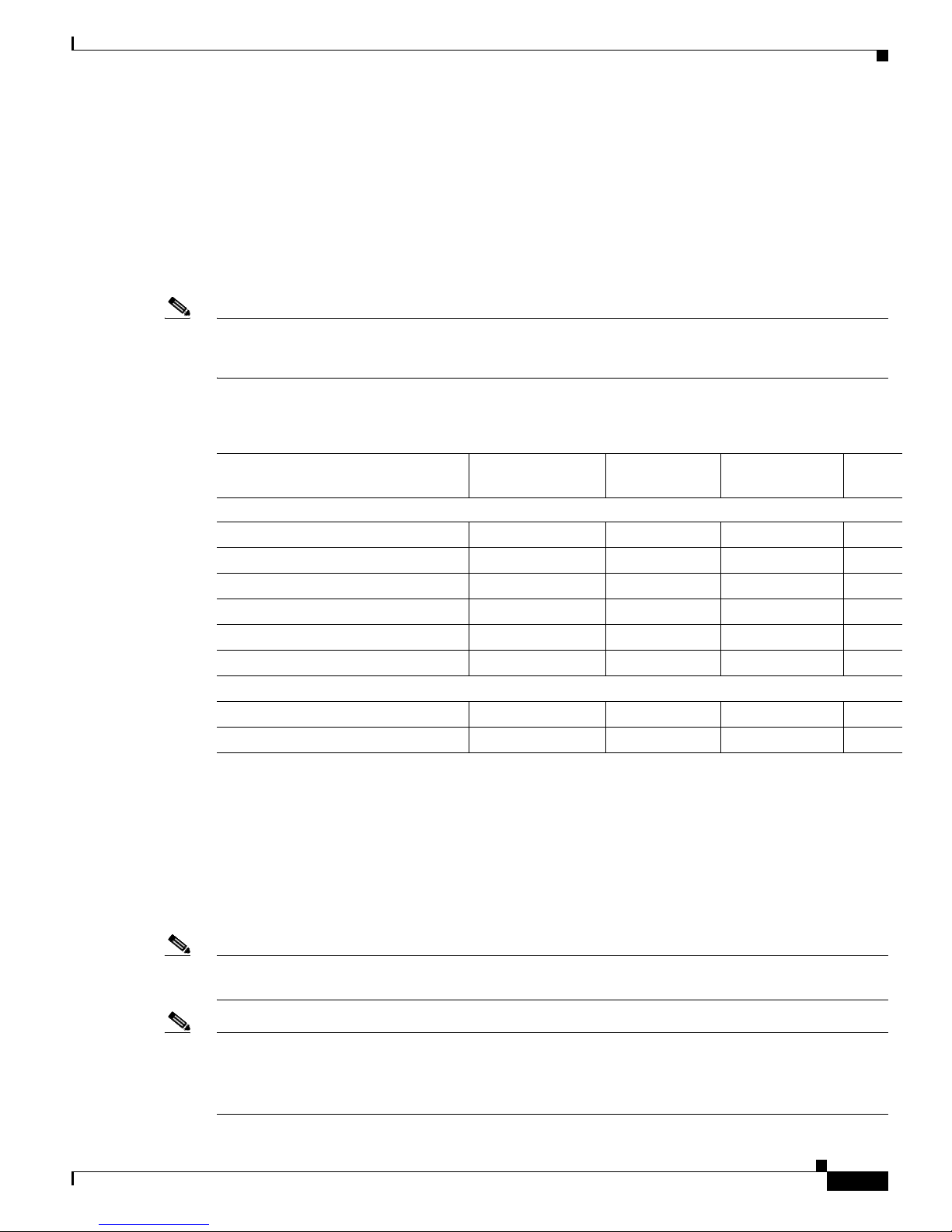
Table 1-2 displays the memory recommendations of the Cisco IOS feature sets for the
Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers for Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC.
Cisco
uBR7200 series routers are only available with a 48 MB or 128 MB of Flash disk memory on the
I/O Controller cards. The UBR7200-NPE-G1 uses compact Flash disk only.
Note Flash disks, an alternative to linear Flash memory, are Flash memory-based devices that can be used as
file storage media in the PCMCIA card slots of the I/O Controllers. Each I/O Controller has two
PCMCIA slots and can be configured with up to 256 MB of Flash disk memory.
The image subset legend for Tab l e 1-2 is as follows:
• i = IP routing, MPLS-VPN support, and non-cable interface bridging, including Network Address
Translation (NAT)
• k8 = DOCSIS Baseline Privacy
• p = IP routing with Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) and Border Gateway
Protocol (BGP); MPLS-VPN support; no bridging and no NAT
• s = “Plus” features: NAT and Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
• k9 = 3DES level of encryption
Note All images support all of the hardware listed in the “Supported Hardware on the Cisco uBR7200 Series”
section on page 1-11, unless otherwise indicated.
Note A Cisco uBR7200 series router requires 256 MB of DRAM memory on the NPE processor card when
HCCP redundancy is configured and the router is supporting more than 3,000 cable modems. Using less
memory in these conditions results in temporary out-of-memory situations and incomplete
synchronization between the Working and Protect interfaces.
Ta b l e 1 Memory Recommendations for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers,
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC Feature Sets
Feature Set Software Image
Recommended
Flash Memory
Recommended
DRAM Memory
Runs
From
Two-Way Data/VoIP Images
DOCSIS Two-Way ubr7200-p-mz 32 MB Flash 256 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus ubr7200-is-mz 32 MB Flash 256 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way with BPI ubr7200-k8p-mz 32 MB Flash 256 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus with BPI ubr7200-ik8s-mz 32 MB Flash 256 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way 3DES ubr7200-k9p-mz 32 MB Flash 256 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way 3DES IP Plus ubr7200-ik9s-mz 32 MB Flash 256 MB DRAM RAM
Boot Image
UBR7200 Boot Image ubr7200-kboot-mz None None —
UBR7200 Boot Image ubr7200-boot-mz None None —
Page 22

1-4
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
12.2 BC Release Train Images and Requirements
Note Cisco IOS release 12.2(4)BC1 offers certified DOCSIS 1.1 support on the Cisco uBR7246 VXR router.
The 12.2 BC train is an interim release train that provides certified DOCSIS 1.1 two-way support on the Cisco
uBR7246 VXR universal broadband router, along with support for selected new features. The latest release
in this train, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1, provides a migration path from the earlier Cisco IOS 12.2 XF
releases, which included a subset of the features supported in these Cisco IOS release trains:
• Cisco IOS Release 12.0 SC
• Cisco IOS Release 12.1 EC
• Cisco IOS Release 12.1 CX1
Table 1-2 displays the memory recommendations of the Cisco IOS feature sets for the
Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and
12.2(15)BC2a. Cisco
uBR7200 series routers are available with 48 MB or 128 MB of Flash disk memory
on the I/O Controller cards. The UBR7200-NPE-G1 uses compact Flash disk only.
Note Flash disks, an alternative to linear Flash memory, are Flash memory-based devices that can be used
as file storage media in the PCMCIA card slots of the I/O Controllers. Each I/O Controller has two
PCMCIA slots and can be configured with up to 256 MB of Flash disk memory.
Note Cisco IOS release 12.2(4)BC1and later BC releases offer certified DOCSIS 1.1 support on the Cisco
uBR7246 VXR router.
Ta b l e 1-2 Memory Recommendations for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers,
Cisco
IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1 and 12.2(15)BC2a Feature Sets
Feature Set Software Image
Recommended
Flash Memory
Recommended
DRAM Memory
Runs
From
Two-Way Data/VoIP Images
DOCSIS Two-Way ubr7200-p-mz 16 MB Flash
32 MB Flash
1
1. 32 MB of Flash is required for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2a and later releases in the Cisco IOS BC train.
128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus ubr7200-is-mz 16 MB Flash
32 MB Flash
1
128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way with BPI ubr7200-k8p-mz 16 MB Flash
32 MB Flash
1
128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus
with BPI
ubr7200-ik8s-mz 16 MB Flash
32 MB Flash
1
128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way 3DES ubr7200-k9p-mz 16 MB Flash
32 MB Flash
1
128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way 3DES IP
Plus
ubr7200-ik9s-mz 16 MB Flash
32 MB Flash
1
128 MB DRAM RAM
Boot Image
UBR7200 Boot Image ubr7200-kboot-mz None None —
UBR7200 Boot Image ubr7200-boot-mz None None —
Page 23

1-5
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
The image subset legend for Tab l e 1-2 is as follows:
• i = IP routing, MPLS-VPN support, and non-cable interface bridging, including Network Address
Translation (NAT)
• k8 = DOCSIS Baseline Privacy
• p = IP routing with Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) and Border Gateway
Protocol (BGP); MPLS-VPN support; no bridging and no NAT
• s = “Plus” features: NAT and Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
• k9 = 3DES level of encryption
Note All images support all of the hardware listed in the “Supported Hardware on the Cisco uBR7200
Series” section on page 1-11, unless otherwise indicated.
Note A Cisco uBR7200 series router requires 256 MB of DRAM memory on the NPE processor card when
HCCP redundancy is configured and the router is supporting more than 3,000 cable modems. Using
less memory in these conditions results in temporary out-of-memory situations and incomplete
synchronization between the Working and Protect interfaces.
12.2 CX Images and Requirements
The 12.2 CX releases are based on Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC1, which is a child of Cisco IOS
Release
12.2(15)T. The 12.2 BC train is an interim release train that provides DOCSIS 1.1 two-way
support, along with fixes for software caveats and support for selected new features.
The latest image in the 12.2 CX release train, Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)CX1, provides two different boot
images for the Cisco uBR7200 series routers:
• ubr7200-kboot-mz.122-15.CX.bin
The "kboot" version of the boot image is a new version of the boot image software that can run only
on the Cisco uBR7200-NPE-G1 processor and the UBR7200-I/O-2FE/E I/O controller, because it is
too large to load on the other I/O controllers. This image contains support for almost all supported
port adapters, allowing the Cisco uBR7246VXR router to boot over almost any type of WAN
interface.
• ubr7200-boot-mz.122-15.CX.bin
The "boot" version of the boot image is small enough to be loaded on I/O controllers with 4MB of
Flash memory, but it supports only Ethernet, FastEthernet, Gigabit Ethernet, OC POS, and a limited
number of ATM port adapters. If you are using a serial port adapter or most ATM port adapters, you
will not be able to boot over the WAN interface.
This difference in boot images affects only the ability of the Cisco uBR7246VXR router to boot over the
WAN interface. When the router has successfully loaded the Cisco IOS software, it has connectivity over
all of the port adapters that this particular version of Cisco IOS software supports.
Table 1-3 displays the memory recommendations of the Cisco IOS feature sets for the Cisco uBR7200
series universal broadband routers for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)CX1. Cisco uBR7200 series routers
are only available with a 48 MB or 128 MB of Flash disk memory on the I/O Controller cards. The
UBR7200-NPE-G1 uses only compact Flash disk.
Page 24

1-6
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Flash disks, an alternative to linear Flash memory, are Flash memory-based devices that can be used as
file storage media in the PCMCIA card slots of the I/O Controllers. Each I/O Controller has two
PCMCIA slots and can be configured with up to 256 MB of Flash disk memory.
The image subset legend for Tab l e 1-3 is as follows:
• i = IP routing, MPLS-VPN support, and non-cable interface bridging, including Network Address
Translation (NAT)
• k8 = DOCSIS Baseline Privacy
• p = IP routing with Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) and Border Gateway
Protocol (BGP); MPLS-VPN support; no bridging and no NAT
• s = "Plus" features: NAT and Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
• k9 = 3DES level of encryption
Ta b l e 1-3 Memory Recommendations for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers,
Cisco
Release 12.2(15)CX1 Feature Sets
Feature Set Software Image
Recommended
Flash Disk
Memory
Recommended
DRAM
Memory
Runs
From
Two-Way Data/VoIP Images
DOCSIS Two-Way ubr7200-p-mz 48 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus ubr7200-is-mz 48 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way with BPI ubr7200-k8p-mz 48 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus with BPI ubr7200-ik8s-mz 48 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way 3DES ubr7200-k9p-mz 48 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM
DOCSIS Two-Way 3DES IP Plus ubr7200-ik9s-mz 48 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM
Page 25

1-7
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco IOS Releases and Images for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
12.1 EC Images and Requirements
The 12.1 EC train is the Cisco cable-specific early deployment release train that introduces several new
feature sets, support for the Cisco uBR-MC28C cable interface line card, and several new software features.
Table 4 displays the memory recommendations of the Cisco IOS feature sets for the
Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers for the latest Cisco IOS Release 12.1(20)EC1.
Cisco
uBR7200 series routers support a 16-MB or 20-MB Type II PCMCIA Flash memory card.
The image subset legend for Tab l e 4 is as follows:
• i = IP routing, MPLS-VPN support, and non-cable interface bridging, including Network Address
Translation (NAT)
• k1 = DOCSIS Baseline Privacy and MPLS-VPN support
• p = IP routing with Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) and Border Gateway
Protocol (BGP); MPLS-VPN support; no bridging and no NAT
• s = “Plus” features: NAT and Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
• t = DOCSIS telco return
Note All images support all of the hardware listed in the section “Supported Hardware on the
Cisco uBR7200 Series” section on page 1-11, unless otherwise indicated.
Ta b l e 4 Memory Recommendations for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers,
Cisco Release 12.1(20)EC1 Feature Sets
Feature Set Software Image
Recommended
Flash
Memory
Recommended
DRAM
Memory
Runs
From
Two-Way Data/VoIP Images
DOCSIS Two-Way ubr7200-p-mz 16 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus ubr7200-is-mz 16 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way with BPI ubr7200-k1p-mz 16 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS Two-Way IP Plus
with BPI
ubr7200-ik1s-mz 16 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
Telco-Return Images
DOCSIS IP Plus Telco Return ubr7200-ist-mz 16 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
DOCSIS IP Plus Telco Return
with BPI
ubr7200-ik1st-mz 16 MB Flash 128 MB DRAM RAM
Boot Image
UBR7200 Boot Image
1
1. The 12.1 EC UBR7200 boot image is provided for the IUBR7200-I/O-2FE/E input/output controller, which must use the
Cisco
IOS 12.1(10)EC1 or later 12.1 EC release boot image. This image cannot be used on any other I/O controllers.
ubr7200-boot-mz None None —
Page 26

1-8
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
The Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers allow high-speed data services to be packaged
similar to cable TV service or video fare. Cisco uBR7200 Series equipment supports data and digitized
voice connectivity between Internet Protocol (IP) hosts and connected subscribers using a bidirectional
cable TV and IP backbone.
Note For 6 MHz National Television Systems Committee (NTSC) cable plants not fully upgraded to two-way
transmission, the equipment works with dial-up access products to support upstream traffic from
Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS)-based telco-return cable
interfaces.
For international cable plants that use 8-MHz Phase Alternating Line (PAL) or Systeme Electronique
Couleur Avec Memoire (SECAM) channel plans, Cisco uBR7200 Series equipment supports
bidirectional transfer of traffic between the Cable
Modem Termination System (CMTS) and
EuroDOCSIS-based CMs or set top box (STB) units with integrated EuroDOCSIS modems.
Cable companies and Internet service providers (ISPs) can allocate radio frequency (RF) channel
capacity for Internet access, Virtual Private Network (VPN), or Voice over IP (VoIP) services using a
hybrid fiber/coax (HFC) or all-coax cable
plant. Cisco currently provides three router-based DOCSIS
CMTS solutions that offer a wider feature set and better manageability than bridge-based systems.
• Cisco uBR7246 VXR Universal Broadband Router—Supports higher density and broad media
configurations; the chassis contains up to two single-width IP backbone interfaces, up to four cable
TV RF interfaces, up to two power supplies, an optional clock interface that enables the router to
synchronize to an external timing reference, a faster processor, and higher bus bandwidth.
• Cisco uBR7246 Universal Broadband Router—Supports large cable installations; the chassis
contains up to two single-width IP backbone interfaces, up to four cable TV RF interfaces, and up
to two power supplies.
• Cisco uBR7223 Universal Broadband Router—Supports small-to-medium cable installations; the
chassis contains one single-width IP backbone interface and up to two cable TV RF interfaces.
Note This guide focuses on Cisco uBR7200 Series software. For detailed descriptions of Cisco uBR7200
Series chassis and components, refer to the
Cisco uBR7200 Series Hardware Installation Guide and
appropriate field replaceable unit (FRU) documents on Cisco.com.
Cisco cable interface line cards serve as the RF cable TV interfaces, supporting downstream and
upstream signal combining and splitting arrangements. The cards currently require external upconverters
to connect to the cable system. Cisco port adapters connect to the IP backbone and external networks.
Your cable plant, combined with your planned and installed subscriber base, service offering, and
external network connections, determine the Cisco uBR7200 Series chassis, cable interface line cards,
port adapters, and other components you use.
Data is modulated or demodulated using either of the following two methods:
• Downstream 6 MHz channels in the 54-to-860 MHz range with upstream ranges of 5 to 42 MHz.
Cisco MC11 FPGA, MC11C, MC12C, MC14C, MC16B, MC16C, and MC16S cable interface line
cards support NTSC channel operation, using standard (STD), Harmonic Related Carrier (HRC), or
Incremental Related Carrier (IRC) frequency plans conforming to EIA-S542.
NTSC uses a 6 MHz-wide modulated signal with an interlaced format of 25 frames per second and
525 lines per frame. NTSC is compatible with CCIR Standard M.
PAL, used in West Germany,
England, Holland, Australia, and several other countries.
Page 27

1-9
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
Note Cisco 6 MHz products can be used in 8 MHz cable plants. The products, however, operate at a
maximum downstream bandwidth of 27 Mbps, ignoring 2 MHz of available channel width, and
limiting upstream channel choices to the range below 42 MHz.
• Downstream 8 MHz channels in the 85-to-860 MHz range with an upstream range of 5 to 65 MHz.
The Cisco MC16E cable interface line card supports PAL and SECAM channel plans using an
8
MHz modulated signal.
PAL uses a 625-line scan picture delivered at 25 frames per second where the color carrier phase
definition changes in alternate scan lines. SECAM uses an 819 line scan picture that provides better
resolution than PAL's 625-line and NTSC's 525-line.
The MC16E uses the EuroDOCSIS J.112 (Annex A) standard, CableLabs ECR RFI-R-98036, which
is similar to the Digital Audio Video Council/Digital Video Broadcast (DAVIC/DVB) ITU
J.83
Annex
A physical layer. Cable companies can support data, voice, and video services with
DOCSIS-based CMs or set top boxes (STBs) that contain integrated EuroDOCSIS modems.
Caution The MC16E supports only Annex A operation and should not be used in production cable plants that
support a 6 MHz channel plan.
Note The difference between DOCSIS and EuroDOCSIS is at the physical layer. EuroDOCSIS support
requires the Cisco MC16E cable interface line card, appropriate upconverters that support an 8
MHz
PAL or SECAM channel plan, appropriate diplex filters, and EuroDOCSIS-based CMs or STBs.
The DOCSIS Radio Frequency (RF) specification defines the RF communication paths between the
CMTS and CMs (or CMs in STBs). The DOCSIS RF specification defines the physical, link, and
network layer aspects of the communication interfaces. It includes specifications for power level,
frequency, modulation, coding, multiplexing, and contention control. Cisco offers products that support
all DOCSIS error correction encoding and modulation types and formats, and that support DOCSIS
Annex B or EuroDOCSIS Annex A operations.
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Routers
The Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers are based on the Data-over-Cable Service
Interface Specification (DOCSIS) standards. Each is designed to be installed at a cable operator's
headend facility or distribution hub and to function as the cable modem termination system (CMTS) for
subscriber-end devices such as the Cisco uBR905 and Cisco uBR925 cable access routers, and other
DOCSIS-compliant CMs and set-top boxes (STBs).
Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers allow two-way transmission of digital data and Voice
over IP (VoIP) traffic over a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) network. For cable plants not fully upgraded to
support two-way cable transmission, the routers support DOCSIS-compliant telco return, where the
cable modem's return path to the CMTS uses a dial-up telephone line connection instead of an upstream
channel over the coaxial cable. The telco-return delivery mechanism enables cable operators to
accelerate deployment of high-speed data services before the cable systems are upgraded to two-way
plants.
The Cisco uBR7200 series routers support IP routing with a wide variety of protocols and combinations
of Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, serial, High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI), Packet over
SONET (POS) OC-3 and OC-12c, and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) media.
Page 28

1-10
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
Cisco uBR7246 VXR Universal Broadband Router
The Cisco uBR7246VXR offers an industry-proven CMTS and carrier-class router in a scalable platform
with a high-performance network processing engine to support data, voice, and video services for
medium to large network installations.
The Cisco uBR7246 VXR provides the following major hardware features:
• High-performance network processing engine or network services engine
• I/O controller
• Up to two network interface port adapters
• Up to four cable interface line cards
• Up to two removable power supplies providing load-sharing and redundancy capabilities
• Two Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA) slots that allow for
software upgrades through the use of Flash memory cards
Note The Cisco uBR7246 VXR chassis does not support the MC11-FPGA cable interface line card.
Cisco uBR7246 Universal Broadband Router
The Cisco uBR7246 offers an industry-proven CMTS and carrier-class router in a scalable platform to
support data, voice, and video services for medium to large network installations. The Cisco uBR7246
provides the following major hardware features:
• Network processing engine
• I/O controller
• Up to two network interface port adapters
• Up to four cable interface line cards
• Up to two removable power supplies providing load-sharing and redundancy capabilities
• Two PCMCIA slots that allow for software upgrades through the use of Flash memory cards
Cisco uBR7223 Universal Broadband Router
The Cisco uBR7223 is a cost-effective, scalable interface between subscriber CMs and the backbone
data network, and is designed specifically for small to medium network installations.
The Cisco uBR7223 provides the following major hardware features:
• Network processing engine
• I/O controller
• One network interface port adapter
• Up to two cable interface line cards
• One removable power supply (The Cisco uBR7223 does not feature load-sharing and redundant
power supply capability like the Cisco uBR7246 VXR and Cisco uBR7246.)
• Two PCMCIA slots that allow for software upgrades through the use of Flash memory cards
Page 29

1-11
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
Supported Hardware on the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Tabl e 1-5 provides a quick overview of the major hardware features of the Cisco uBR7200 series routers.
Note Earlier release notes stated that the NPE-175 was also supported on the Cisco uBR7200 series routers.
Because the NPE-175 has reached its end of life and was never made available for order on the Cisco
uBR7200 series routers, it has been removed from the table.
The UBR7200-NPE-G1 does not require that an I/O controller be installed. Refer to the Cisco uBR7200
Series Software Release Notes on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/ubr7200/release/notes/12_3bc/123BCu72.html
Network Processing Engines
The Cisco uBR7246 VXR supports the following Network Processing Engines (NPEs):
• UBR7200-NPE-G1
• NPE-225
• NPE-300
• NPE-400
The Cisco uBR7223 and the Cisco uBR7246 support the following Network Processing Engines (NPE) :
• NPE-150
• NPE-200
• NPE-225
Note The NPE-300 and NPE-400 are not supported on the Cisco uBR7223 and the Cisco uBR7246. The
NPE-150 and NPE-200 are not supported on the Cisco uBR7246 VXR.
Ta b l e 1-5 Cisco uBR7200 Series Hardware Overview
Supported Hardware Cisco uBR7246 VXR Cisco uBR7246 Cisco uBR7223
Network Processing Engines One of the following:
• UBR7200-NPE-G1
• NPE-225
• NPE-300
• NPE-400
One of the following:
• NPE-150
• NPE-200
• NPE-225
One of the following:
• NPE-150
• NPE-200
• NPE-225
I/O Controllers One of the following:
• UBR7200-I/O
• UBR7200-I/O-FE
• UBR7200-I/O-2FE/E
One of the following:
• UBR7200-I/O
• UBR7200-I/O-FE
One of the following:
• UBR7200-I/O
• UBR7200-I/O-FE
Network Interface Port Adapters Up to two Up to two One
Cable Interface Line Cards Up to four Up to four Up to four
Removable Power Supplies Up to two Up to two One
PCMCIA Slots Two Two Two
Page 30

1-12
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
For more information, refer to the following resources on Cisco.com:
• Network Processing Engine and Network Services Engine Installation and Configuration Guide
• Memory Replacement Instructions for the Network Processing Engine or Network Services Engine and
Input/Output Controller
I/O Controllers
The Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers support the following input/output (I/O)
controllers:
• UBR7200-I/O-2FE/E input/output controller
–
Features two Fast Ethernet ports and one Ethernet port.
–
Equipped with 2 RJ-45 receptacles for 10/100 Mbps operation.
–
Supported for the Cisco uBR7246VXR router.
–
The Cisco IOS Release 12.1(10)EC boot helper image [ubr7200-boot-mz.12.1-10.EC] must be
used on this controlle.r
• UBR7200-I/O-FE
–
Features one Fast Ethernet port.
–
Equipped with an MII receptacle and an RJ-45 receptacle for use at 100 Mbps full-duplex or
half-duplex operation.
–
Only one receptacle can be configured for use at a time.
–
Supported for Cisco uBR7223, Cisco uBR7246, and Cisco uBR7246 VXR routers.
–
The 12.0(15)SC [ubr7200-boot-mz.12.0-15.SC] boot helper image is recommended for this
controller.
• UBR7200-I/O
–
Has no Fast Ethernet port.
–
Supported for Cisco uBR7223, Cisco uBR7246, and Cisco uBR7246 VXR routers.
–
The 12.0(15)SC [ubr7200-boot-mz.12.0-15.SC] boot helper image is recommended for this
controller.
Note The Single-Port Fast Ethernet I/O Controller (UBR7200-I/O-FE) reached its End of Sale (EOS) point
on June 30, 2003. For details, see the Addendum to Product Bulletin, No. 1725, available at the
following location on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/cable/ps2217/prod_eol_notice09186a00800a470d.html
Note Do not use the 12.1(10)EC boot helper image with the UBR7200-I/O-FE and UBR7200-I/O
controllers.
Page 31

1-13
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
Network Interface Port Adapters
The Cisco uBR7200 series routers support multiple port adaptors with Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet and
Serial versions. Enhancements and options are available in multiple Cisco IOS Software release trains.
For the latest information about supported port adaptors, refer to Cisco uBR7200 Series Software Release
Notes on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/ubr7200/release/notes/12_3bc/123BCu72.html
Note Not all Cisco uBR7200 series routers support all port adapters. Some port adapters must be at certain
revision levels to be used in the Cisco uBR7246 VXR router.
Note Cisco recommends using the most current release in a release train if possible.
Cable Interface Line Cards
The Cisco uBR7200 series supports the following cable interface line cards, all of which provide
connection to the hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) network.
Table 1-6 provides a quick overview of the cable interface line cards that are supported with Cisco
uBR7200 series routers.
For the latest information about supported cable interface line cards, refer to Cisco uBR7200 Series
Software Release Notes on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/ubr7200/release/notes/12_3bc/123BCu72.html
Ta b l e 1-6 Cisco uBR7200 Series Cable Interface Line Cards
Cable Interface
Line Card
Upstream
Ports
Downstream
Ports
Additional Features
MC11C 1 1
MC12C 2 1
MC14C 4 1
MC16C 6 1
MC16E 6 1 EuroDOCSIS (Annex A) Support
MC16S 6 1 Enhanced software- and hardware-based Spectrum
Management Support
MC28C 8 2
MC28C-BNC 8 2 BNC connectors instead of F-connectors
Page 32

1-14
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Chassis Overview
System Interoperability
This section describes guidelines about the interoperability of certain features in the
Cisco
uBR7200 series universal broadband routers. Additional DOCSIS interoperability is described in
the
“Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series” section on page 1-22.
Cable Modem Interoperability
The Cisco uBR7200 series interoperates with the following cable modems:
• DOCSIS-based two-way cable modems that support basic Internet access, VoIP, or Virtual Private
Networks (VPNs).
• Telco-return Cable modems
To support telco return, use a Cisco uBR7200 series software image that contains “t” in its file name.
The telco-return cable modem must be DOCSIS-based or compliant and must be configured to
support telco return.
Note Some third-party telco-return CMs cannot receive traffic over the same downstream
channel as CMs operating on a two-way data system. In these instances, segment your
cable plant to allow more than one downstream channel.
• EuroDOCSIS cable modems or STBs with integrated EuroDOCSIS CMs using Cisco MC16E cable
interface line cards and Cisco
IOS Release 12.1(2)EC1 or higher.
EuroDOCSIS operation support includes 8-MHz Phase Alternating Line (PAL) or Systeme
Electronique Couleur Avec Memoire (SECAM) channel plans.
Clock Synchronization
The Cisco uBR7200 series support clock hardware and software to enable high-quality delivery of IP
telephony services through synchronized data transmissions. To support the clock feature set, a
Cisco
uBR7246 VXR chassis must be used. The Cisco uBR7246 VXR must contain a clock card and an
MC16S, MC16E, or MC28C cable interface line card. Only the MC16S, MC16E, and MC28C cable
interface line cards support the external clock reference from the clock card to distribute that signal to
CMs or STBs attached to the specific network segments. A chassis configured with an MC16S or
MC16E cable interface line card must be running Cisco
IOS Release 12.1(2)EC1 or higher. A chassis
configured with an MC28C cable interface line card must be running Cisco
IOS Release 12.1(3a)EC1 or
higher.
Each cable modem must also support VoIP applications and the clock reference feature set to enable
synchronized timing. The Cisco
uBR924 cable access router, running Cisco IOS Release 12.0(7)T or
later, supports the clock reference feature set automatically.
Page 33

1-15
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
This section describes Cisco uBR7200 series router features that require software configuration, and
summarizes these features of the Cisco
uBR7200 series router:
• Port Adapter and Line Card Slot and Logical Interface Numbering, page 1-15
• MAC-Layer Addressing, page 1-17
• Cable Interface Line Cards, page 1-17
• Cable Interface Line Card Slots, page 1-19
• Interfaces and Physical Ports, page 1-20
• Port Adapter Slots, page 1-20
Refer to the “Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Tools” section on page 1-31 for additional
configuration utilities.
Port Adapter and Line Card Slot and Logical Interface Numbering
For Cisco uBR7200 series components, the slot number is the chassis slot in which a port adapter or a
cable
interface card is installed. The logical interface number is the physical location of the interface
port on a port adapter. Numbers on a Cisco uBR7200 series router begin with 0. Using a Cisco uBR7246
to illustrate, slot/port positioning is as follows:
• Slot 0—I/O controller
• Slot 1-2—Cisco port adapters
• Slot 3-6—Cisco cable interface line cards; the upstream ports on the card start with port 0.
To configure the system, define the Cisco uBR7200 series interfaces, using the interface type slot/port
commands:
• Type—Cable
• Slot—Slot number in chassis. Slot numbers begin with 0.
• Port—Port number on a cable interface line card slot. Port numbers begin with a 0.
Configuring Cisco cable interface line cards is particularly important because these components serve
as the cable TV RF interfaces. Configuration involves the following tasks for each interface:
• Setting the downstream center frequency for the card to reflect the digital carrier frequency of the
downstream RF carrier (the channel) for that downstream port. To do this, enter the fixed center
frequency for your downstream RF carrier in Hz:
Router (config-int)# cable downstream frequency down-freq-hz
Note This command has no effect on the external upconverter, which actually sets the downstream
frequency. Noting the correct value for the cable interface line card, however, provides useful
information for troubleshooting.
The digital carrier frequency is specified to be the center of a 6 or 8 MHz channel based on your
channel plan. To illustrate for NTSC channel plans, EIA channel 95 spans 90.00 to 96.00 MHz. The
center frequency is 93.000 MHz which is the digital carrier frequency that should be configured as
the downstream frequency.
Page 34

1-16
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
Tip The digital carrier frequency is not the same as the video carrier frequency. For EIA channel 95, the
video carrier frequency is 91.250 MHz which is 1.75 MHz below the center frequency.
• Activating the downstream port on the cable interface line card for data transmission over the HFC
network, using the following command:
Router (config-int)# no shutdown
The particular downstream port LED should light.
• Setting the upstream frequency of your RF output to comply with the expected input frequency of
your Cisco cable interface line card.
Tip The valid range for a fixed upstream frequency is 5,000,000 Hz to 65,000,000 Hz for the MC16E cable
interface line card. The valid range for all other cable interface line cards that support NTSC operations
is 5,000,000 Hz to 42,000,000 Hz.
The cable interface will not operate until you either set a fixed upstream frequency or create and
configure a spectrum group. Enter the fixed center frequency for your upstream RF carrier in Hz and
specify a port number from 0 to 5:
Router (config-int)# cable upstream port frequency up-freq-hz
Note Make sure that the selected upstream frequency does not interfere with the frequencies used for
any other upstream applications in your cable plant.
• Entering an upstream RF carrier frequency for each upstream port on a cable modem.
• Activating the RF carrier on each upstream port to support data from CMs or set top boxes on your
network to the Cisco uBR7200 series router. Enable upstream data traffic, using the following
command:
Router (config-int)# no cable upstream port shutdown
The specified upstream port LED lights.
Repeat the above for each upstream port to activate.
• Verifying your settings using the following command:
Router# show running-config
• Saving the configuration to nonvolatile random access memory (NVRAM) so that your settings are
retained after a power cycle:
Router# copy running start
• Verifying the upstream frequency, using the show controllers cable slot/port upstream command
for the upstream port you just configured.
• Verifying the downstream center frequency, using the show controllers cable slot/port downstream
command for the downstream port you just configured.
Page 35

1-17
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
MAC-Layer Addressing
The Media Access Control (MAC)-layer or hardware address is a standardized data link layer address
required for certain network interface types. These addresses are not used by other devices in the
network; they are specific and unique to each port. The Cisco
uBR7200 series uses a specific method to
assign and control the MAC-layer addresses for port adapters.
All LAN interfaces (ports) require unique MAC-layer addresses, also known as hardware addresses.
Typically, the MAC address of an interface is stored on a memory component that resides directly on the
interface circuitry; however, the online insertion and removal (OIR) feature requires a different method.
The OIR feature lets you remove a port adapter or cable
interface card and replace it with another
identically configured one. If the new port adapter or cable
interface card matches the port adapter or
cable
interface card you removed, the system immediately brings it online.
To support OIR, an address allocator with a unique MAC address is stored in an EEPROM on the
universal broadband router midplane. Each address is reserved for a specific port and slot in the router
regardless of whether a port adapter or a cable
interface card resides in that slot.
Note Port adapter and cable interface card slots maintain the same slot number regardless of whether other port
adapters or cable
interface cards are installed or removed. However, when you move a port adapter or
cable interface card to a different slot, the logical interface number changes to reflect the new slot number.
Caution When “hot swapping” a port adapter or cable interface line card with a different type of component (for
example, an MC11 FPGA with an MC11C, or an MC16B with an MC16C), you might have to
reconfigure the interfaces. Refer to the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Hardware
Installation Guide or appropriate FRU document for more specific information regarding online
insertion and removal (OIR).
The MAC addresses are assigned to the slots in sequence. The first addresses are assigned to port adapter
slot
0 and slot 1, and the next addresses are assigned to port adapter slot 2 through cable interface card
slot
6. This address scheme allows you to remove port adapters or cable interface cards and insert them
into other universal broadband routers without causing the MAC addresses to move around the network
or be assigned to multiple devices.
Storing the MAC addresses for every slot in one central location means the addresses stay with the
memory device on which they are stored.
Cable Interface Line Cards
As of the date of this publication, the following Cisco cable interface cards can be installed in a
Cisco
uBR7200 series router:
• MC11 with one downstream modulator and one upstream demodulator. Two different revisions exist
for this card:
–
The FPGA version of the card supports the following defaults: Quadrature Amplitude
Modulation (QAM)-64 at 27
Mbps downstream, and Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) at
1.280 kbps upstream. The card outputs +32 dBmV and +/- 2 dBmV.
–
The C version of the card supports the following defaults: QAM-256 at 40 Mbps downstream
and QAM-16 at 5
Mbps upstream. The card supports upstream channel widths of 200 kHz,
400
kHz, 800 kHz, 1.6 MHz, and 3.2 MHz. The card outputs +42 dBmV and +/- 2 dBmV.
Page 36

1-18
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
Note All C version cards support all DOCSIS modulation and symbol rates. Refer to
Table 1-7Table 1-6 for a list of DOCSIS supported data rates and modulation schemes.
Because the FPGA version of the MC11 card supports only one upstream modulation and
channel width, you cannot define an upstream modulation profile for the card. The default
modulation profile 1 cannot be changed when using the FPGA version of the MC11 card.
• MC12C with one downstream modulator and two upstream demodulators: The card supports the
following defaults: QAM-256 at 40
Mbps downstream and QAM-16 at 5 Mbps upstream. The card
supports upstream channel widths of 200
kHz, 400 kHz, 800 kHz, 1.6 MHz, and 3.2 MHz.The card
outputs +42 dBmV and +/- 2
dBmV.
• MC14C with one downstream modulator and four upstream demodulators: The card supports the
following defaults: QAM-256 at 40
Mbps downstream and QAM-16 at 5 Mbps upstream. The card
supports upstream channel widths of 200
kHz, 400 kHz, 800 kHz, 1.6 MHz, and 3.2 MHz. The card
outputs +42 dBmV and +/- 2
dBmV.
• MC16 with one downstream modulator and six upstream demodulators. Two different revisions
exist for this card:
–
The B version of the card supports the following defaults: QAM-64 at 27 Mbps downstream and
QPSK at 2.56
Mbps upstream. The card supports channel widths of 200 kHz, 400 kHz, 800 kHz,
1.6 MHz, and 3.2 MHz. The card outputs +32 dBmV and +/- 2 dBmV.
Note The B version card excludes support of QAM-256 downstream and QAM-16 upstream
support at two of the five DOCSIS upstream symbol rates—2.56 M and 1.28 M. Refer to
Table 1-7Ta bl e 1-6 for Tab l e 1-6a list of DOCSIS supported data rates and modulation
schemes.
–
The C version of the card supports the following defaults: QAM-256 at 40 Mbps downstream
and QAM-16 at 5
Mbps upstream. The card supports upstream channel widths of 200 kHz,
400
kHz, 800 kHz, 1.6 MHz, and 3.2 MHz. The card outputs +42 dBmV and +/- 2 dBmV.
• MC16S with one downstream modulator and six upstream demodulators. The card supports the
following defaults: QAM-256 at 40
Mbps downstream and QAM-16 at 5 Mbps upstream. The card
supports upstream channel widths of 200
kHz, 400 kHz, 800 kHz, 1.6 MHz, and 3.2 MHz. The card
outputs +42 dBmV and +/-
2 dBmV.
The MC16S includes the ability to scan portions of the upstream spectrum for clean channels of varying
widths. A daughtercard on the MC16S samples the 5-to-42 MHz upstream spectrum and initiates a
frequency hop if an administrator-defined threshold value for offline CMs is met. The threshold value is
contained in the router’s configuration file. When the threshold value is reached, the spectrum
management daughtercard takes a snapshot of the available upstream spectrum and passes this
information to the Cisco IOS software where it is analyzed for indications of significant ingress or
impulse noise. From this analysis, the Cisco IOS software draws informed conclusions on the cleanest
portion(s) of the upstream frequency spectrum to switch to and initiates a frequency hop.
• MC16E with one downstream modulator and six upstream demodulators. The card supports the
following defaults: QAM-256 at 40
Mbps downstream and QAM-16 at 5 Mbps upstream. The card
supports EuroDOCSIS 8 MHz PAL and SECAM channel plans, supporting downstream rates of
85-to-860 MHz range with upstream ranges of 5-to-65 MHz. The card outputs +40
dBmV and +/- 2 dB.
Page 37

1-19
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
Note While most Cisco cable interface line cards transmit downstream signals to upconverters using a
44 MHz frequency, the MC16E transmits downstream IF signals to an upconverter using the
36.125 MHz frequency. Only the MC16E cable interface line card supports full 8 MHz operation.
The cable interface cards can be configured in a number of different upstream combinations based on
the card used, your cable network, and the anticipated subscription and service levels.
Table 1-7 shows
the DOCSIS and EuroDOCSIS data rates.
Cable Interface Line Card Slots
To display information about a specific cable interface card slot’s downstream channel, use the
show
interfaces cable command with the cable modem line card’s slot number and downstream port
number in the following format:
show interfaces cable slot/downstream-port [downstream]
Use the slot number and downstream port number to display information about a downstream interface.
You can abbreviate the command to sh
int c. The following example illustrates the display for
downstream channel port 0 in cable
interface slot 3 of a Cisco uBR7246:
Router# sh int c 3/0
Cable3/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is CMTS, address is 0009.0ed6.ee18 (bia 0009.0ed6.ee18
Internet address is 1.1.1.1/24
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 27000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
Encapsulation MCNS, loopback not set, keepalive not set
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 41000 bits/sec, 45 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 43000 bits/sec, 45 packets/sec
1616534 packets input, 184284660 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
1616534 packets output, 184284660 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Ta b l e 1-7 DOCSIS and EuroDOCSIS Data Rates
Upstream Channel Width Modulation Scheme Baud Rate Sym/sec Raw Bit Rate Mbit/sec
3.2 MHz QAM-16
QPSK
2.56 M 10.24
5.12
1.6 MHz QAM-16
QPSK
1.28 M 5.12
2.56
800 kHz QAM-16
QPSK
640 K 2.56
1.28
400 kHz QAM-16
QPSK
320 K 1.28
0.64
200 kHz QAM-16
QPSK
160 K 0.64
0.32
Page 38

1-20
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
To display information about a specific cable interface card slot’s upstream channel, use the
show
interfaces cable command with the cable modem card’s slot number, downstream port number,
and upstream port number in the format of show interfaces cable slot/downstream-port [upstream]
upstream-port. Use the slot number, downstream port number, and upstream port number to display
information about an upstream interface. You can abbreviate the command to sh
int c.
The following example shows the display for upstream channel port 0 in cable interface slot 3 of a
Cisco
uBR7246 that is turned up:
Router# sh int c 3/0 0
Cable6/0: Upstream 0 is up
Received 3699 broadcasts, 0 multicasts, 28586 unicasts
0 discards, 0 errors, 0 unknown protocol
21817 packets error-free, 2371 corrected, 8097 uncorrectable
0 noise, 0 microreflections
CBR_queue_depth: [not implemented], ABR_queue_depth: [not implemented],
UBR[1]_queue_depth: 0, UBR[2]_queue_depth: 0,
UBR[3]_queue_depth: 0, POLLS_queue_depth: [not implemented]
ADMIN_queue_depth: [not implemented]
Last Minislot Stamp (current_time_base):190026 FLAG:1
Last Minislot Stamp (scheduler_time_base):200706 FLAG:1
Interfaces and Physical Ports
Table 1-8 maps the cable interface card’s interfaces and physical ports. The cards can be configured in
a number of different upstream combinations.
Port Adapter Slots
You can display information on a specific port adapter or all port adapters in the Cisco uBR7200 series.
To display information about all port adapter slots, use the show interfaces command. To display
information about a specific port adapter slot, use the show interfaces command with the port adapter
type and slot number in the format of show interfaces [type slot/port].
Tip If you abbreviate the command (sh int) and do not specify the port adapter type and slot number (or
arguments), the system interprets the command as show interfaces. The system displays the status of all
port adapters, all cable interface cards, and all ports.
Ta b l e 1-8 Interface to Port Mapping
Cable Interface Line Card Interface Physical Ports
MC11 Cable N/0 DS, US0
MC12 Cable N/0 DS, US0, US1
MC14 Cable N/0 DS, US0, US1, US2, US3
MC16 Cable N/0 DS, US0, US1, US2, US3, US4, US5
Page 39

1-21
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Overview
The follow example illustrates the show interfaces command with status information (including the
physical port adapter number) for each port adapter and cable
interface card in the Cisco uBR7246 router:
Router# sh int
FastEthernet0/0 is administratively up, line protocol is up
Hardware is DEC21140, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)
Internet address is 1.1.1.3
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
(display text omitted)
Hssi1/0 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Hardware is MIF68840_MM, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)
Internet address is 1.1.1.0
MTU 4470 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
(display text omitted)
Ethernet2/0 is administratively up, line protocol is up
Hardware is AmdP2, address is 0000.0000.0000 (bia 0000.0000.0000)
Internet address is 1.1.1.7
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
(display text omitted)
Cable3/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is CMTS, address is 0009.0ed6.ee18 (bia 0009.0ed6.ee18)
Internet address is 1.1.1.1/24
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 27000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
(display text omitted)
You can also use arguments such as the interface type (Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, ATM, serial, HSSI,
Packet-over-SONET, and so forth) and the port address (slot/port) to display information about a specific
port adapter interface only. The following example shows such a display:
Router# sh int f1/0
FastEthernet1/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is AmdFE, address is 0030.7bfa.a81c (bia 0030.7bfa.a81c)
Internet address is 111.0.1.18/30
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, 100BaseTX/FX
ARP type:ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:01, output 00:00:02, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy:fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets put, 230925 bytes
Received 146107 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 watchdog
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
0 packets put, 284529 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 10 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Page 40

1-22
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
This section summarizes Cisco uBR7200 series router software features for all supported Cisco IOS
Release trains, and directs you to additional configuration information for each feature.
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Features and Cisco IOS Releases
Table 1-9 summarizes the software-related features and related Cisco IOS releases that support the
Cisco uBR7200 series router. Cisco IOS features indicate the first release in which the feature was
introduced. Unless otherwise noted, feature support continues in later releases of the same or related
Cisco IOS release train
Many additional features were introduced in release trains prior to those listed above, such as 12.0 T,
12.0
SC, 12.1 XF and other earlier releases that may no longer be supported on the Cisco uBR7200
Series. Refer to the release notes for your respective Cisco IOS release for additional feature support and
image information.
Ta b l e 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Tools
Autoinstall 12.0 T, 12.0 XR, 12.0 SC, 12.1 EC, 12.1 CX, 12.2 BC and 12.3
BC releases
Cable Interface Setup Facility 12.1 EC, 12.1 CX, 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Cable Interface Extended Setup
Facility
12.1(3a)EC1 and all later Cisco IOS releases supporting the
Cisco uBR7200 Series CMTS
Cisco Network Registrar 12.1 EC, 12.2 BC, 12.3 BC
Interface Range Specification 12.0 T, 12.0 XR, 12.0 SC, 12.1 EC, 12.1 CX, 12.2 BC and 12.3
BC releases
Internal Modem Configuration File
Editor
12.2(1)XF1 and later 12.2 XF, 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Manual Configuration Mode for the
Cisco uBR7200 Series CMTS
All Cisco IOS releases supporting the Cisco uBR7200 Series
CMTS
Virtual Interface Support and
Frequency Stacking Support
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Bandwidth Management Features
Load Balancing Support 12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Cisco IOS Command-Line Enhancements
exec prompt timestamp Command 12.1(12c)EC, 12.2(8)BC2 and later 12.1 EC, 12.2 BC and 12.3
BC releases
show Command Enhancements Multiple Cisco IOS software releases. Enhancements include:
• show cable qos
• show int cx/y sid
• show cable modem
• show cable modulation-profile
• show cable modem summary
Page 41

1-23
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Enhancements
12.3(9a) enhancements to or introductions of the following
commands:
• cable logging layer2events
• cable source-verify
• show cable tech-support
• show controllers cable
• show tech-support
Cisco Quality of Service Features
Cisco Network-Based Application
Recognition (NBAR)
12.1(10)EC, 12.2 BC and later releases
RTP Heade r Compressio n 11.3(11)NA, 12.0 T and later releases
DHCP Servers and Feature Support
Configurable Leasequery Server 12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
DHCP MAC Address Exclusion List
for cable-source verify dhcp
Command
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
See the “DOCSIS 1.1 Feature Support” section on page 1-57 for
additional DHCP features.
DOCSIS 1.0 Feature Support
DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy 12.0(6)SC, 12.1 EC and later releases
DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy
Interface Encryption and Encrypted
Key Exchange
12.0 SC and later releases in multiple release trains
DOCSIS 1.0 Concatenation Override
Featurette
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
DOCSIS 1.0 Extensions 12.0(16)SC3, 12.1 EC, 12.2 CX, 12.2 BC, and 12.3 BC
DOCSIS 1.0 Quality of Service 12.1 EC, 12.2 CX, 12.2 BC, and 12.3 BC
Several additional DOCSIS 1.0 QoS enhancements for the Cisco
uBR7200 Series are described in release notes for earlier
releases.
DOCSIS Quality of Service
Enhancements Prior to DOCSIS 1.1
DOCSIS quality of service (QoS) enhancements added to Cisco
IOS Release 12.1(1a)T1 and continue with later releases in
multiple trains.
DOCSIS 1.0 ToS Overwrite 12.3(17a)BC2 and later 12.3 BC releases.
DOCSIS Customer Premises
Equipment Configurator
DOCSIS CPE Configurator V2.0.4 and V 3.2 supported in
multiple Cisco IOS releases.
Enhanced Rate Bandwidth
Allocation (ERBA) Support for
DOCSIS 1.0 Cable Modems
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 42

1-24
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
DOCSIS 1.0+ Feature Support
Concatenation for DOCSIS 1.0+ 12.1(1)T and later releases in multiple trains support
DOCSIS
1.0+ on the Cisco uBR7200 Series.
Dynamic MAC messages
Multiple SIDs per Cable Modem
Separate Downstream Rates
Unsolicited Grant Service
(CBR-scheduling) on the Upstream
DOCSIS 1.1 Feature Support
Baseline Privacy Interface Plus
(BPI+)
12.2(4)BC1 and later 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Burst Profile Configuration 12.2(4)BC1 and later 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Cable Modulation Profile Default
Templates
12.1(3a)EC1 and later 12.1 EC releases
DHCP Cable Modem Host ID 12.0(4)T, with additional enhancements and support in 12.0 (6)
SC, 12.1(2) EC1, 12.1(3a)EC, 12.2(15)BC2 and later releases
DHCP Client ID/Remote ID Options 12.0(16)SC3 and later releases in multiple release trains
DHCP, Time of Day (ToD) and TFTP
Servers
Multiple releases in multiple release trains beginning with 12.0
early deployment releases
DOCSIS 1.1 Quality of Service
Features
12.2 BC and 12.3 BC release trains, with additional DOCSIS 1.1
features supported in certain earlier Cisco IOS 12.1 EC and 12.0
SC release trains. Includes:
• Concatenation for DOCSIS 1.1
• DOCSIS 1.0 and 1.0+ Cable Modem Support
• DOCSIS 1.1 Service Flow Model
• Downstream QoS Handling Supported
• Dynamic MAC Messages
• Dynamic Map-Advance
• Dynamic SID Support
• Fragmentation (Layer 2)
• Multiple SID Support
• Payload Header Suppression (PHS)
• QoS Configuration
• QoS Profile Enforcement
• Time-of-Day Server
• Trivial File Transfer Protocol Server
• Type/Length/Value Parser and Encoder
• UpstreamAddress Verification
• Upstream QoS Improvements
• Upstream QoS Models Supported
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 43

1-25
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
DOCSIS 1.1 Two-way
Transmission (Cisco
uBR7246VXR Router)
12.2 BC, 12.3 BC
Downstream Channel ID 12.0(4)T and later releases in multiple trains
Downstream Frequency Override 12.0(6)SC, 12.1 EC and later releases supporting the Cisco
uBR7200 series
Downstream Packet Classifier 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC release trains
Downstream Packet Scheduler 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC release trains
Downstream Rate Shaping with
IP Type of Service Bits
11.3NA, 12.0(5)T and later releases in multiple release trains.
Downstream Traffic Shaping 11.3(6) NA, with additional enhancements and support in
12.0(4)XI, 12.0(5)T1, 12.1(1)EC1, 12.2(4)BC1 and later
releases.
Optional Upstream Scheduler Modes 12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
DOCSIS 2.0 Feature Support
DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support 12.2(15)CX and continues with later 12.2 CX, 12.2 BC and
12.3
BC releases
High Availability Features
Cisco DDC (Dual DOCSIS Channel) 12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
DSX Messages and Synchronized
PHS Information
12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
HCCP Support for the Cisco
uBR-MC16S Cable Interface Line
Card
12.1(7)EC and later releases in multiple release trains
HCCP N+1 Redundancy 12.1(10)EC, with additional enhancements and support in
12.2(4)XF1, 12.2(4)BC1, 12.2(8)BC2, 12.2(11)BC1,
12.2(15)BC1, 12.2(15)BC2a and later releases in multiple trains
High Availability Features in
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Hot-Standby 1+1 Redundancy 12.1(3a)EC and later releases in multiple release trains
IF Muting for HCCP N+1
Redundancy
12.2(15)BC2a and later 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Intercept Features
Access Control List Support for
COPS Intercept
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Cable Monitor Enhancements 12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
COPS TCP Support for the Cisco
Cable Modem Termination System
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Service Independent Intercept (SII)
Support on the Cisco uBR7200
Series
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 44

1-26
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
IP Broadcast and Multicast Features
Multicast QoS Support on the Cisco
uBR7246VXR CMTS
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
IP Routing Features
Cable ARP Filter Enhancement 12.2(15)BC2b and later 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Cable Interface Bundling and Cable
Subinterfaces
12.0 SC, 12.1 EC, 12.2 BC and later BC releases
Configurable Alternate Termination
System Information Messages
12.1(2)EC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Easy IP (Phase 1) 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Fast-Switched Policy Routing 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
HSRP over ISL in Virtual LAN
Configurations
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
IP Enhanced IGRP Route
Authentication
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
IP Network Address Translation/Port
Address Translation
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
NAT—Support for NetMeeting
Directory (Internet Locator
Service—ILS)
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Router-Port Group Management
Protocol
12.1 T and later releases in this and additional release trains
Supported Protocols on the
Cisco uBR7200 Series
Multiple protocols are supported in all release trains that support
the Cisco uBR7200 Series.
Management Features
Admission Control for the Cisco
CMTS
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Cable ARP and Proxy ARP (cable
arp and cable proxy arp commands)
12.1T , 12.0(6)SC , 12.1(2) EC1, 12.2(8)BC1, and later releases
in respective release trains
cable map-advance Command
Enhancements
12.1 EC and later releases in multiple release trains
cable monitor Command 12.0(6)EC with additional enhancements and support in later
releases in multiple release trains
cable intercept Command 12.0(5)T1, 12.0(6)SC, 12.1(2)EC, 12.2(4)BC1 and later releases
in respective release trains
DOCSIS 2.0 SAMIS ECR Data Set 12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Downstream Load Balancing
Distribution with Upstream Load
Balancing
12.3(17b)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Dynamic Channel Change (DCC) for
Loadbalancing
12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 45

1-27
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Dynamic Ranging Support 12.1 EC and later releases in this and multiple release trains
Load Balancing for the Cisco CMTS 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases in the 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC
release trains
Management Information Base
(MIB) Changes and Enhancements
12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
MAX-CPE Override for Cable
Modems
12.1(2)EC1 and later releases or release trains
Per-Modem Error Counter
Enhancements
12.1(4)CX, 12.2(1)XF, and 12.2(4)BC1 and later releases in
these release trains
Pre-equalization Control for Cable
Modems
12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Subscriber Traffic Management
(STM) Version 1.1
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Usage Based Billing (SAMIS) 12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Multicast Features
Bidirectional PIM 12.1 EC, 12.2 BC
DOCSIS Set-top Gateway (DSG) 1.0 12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Advanced-mode DOCSIS Set-Top
Gateway Issue 1.1
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Advanced-mode DOCSIS Set-Top
Gateway Issue 1.2
12.3(17a)BC2 and later 12.3 BC releases
IGMP Version 3 12.1(3)T and later releases in multiple release trains
IP Multicast Load Splitting across
Equal-Cost Paths
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
IP Multicast over ATM
Point-to-Multipoint Virtual Circuits
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
IP Multicast over Token Ring LANs 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Source Specific Multicast 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Stub IP Multicast Routing 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
PacketCable and Voice Support
Features
PacketCable 1.0 With CALEA 12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Security Features
Access Control Lists 12.2(4)XF1 and later XF and BC releases
12.2(10)EC and later EC releases
Automated Double Authentication 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Cable Modem and Multicast
Authentication Using RADIUS
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Cable Source Verification (cable
source-verify Command)
11.3 XA with additional support and enhancements in later
releases in additional release trains
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 46

1-28
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cisco IOS Firewall Feature Set 12.0(1)T and later releases in this and additional release trains
Cisco IOS Firewall Feature
Enhancements
12.1 XM and later releases in this and additional release trains
Dynamic Mobile Hosts 12.1 CX, 12.2(4)XF and later releases in this and additional
release trains
Dynamic Shared Secret for DOCSIS 12.2(15)BC1 and later releases in the 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC
release trains
Dynamic Shared Secret (DMIC) with
OUI Exclusion for DOCSIS
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
HTTP Security 12.2(4)BC1 and later releases in this and additional release trains
Named Method Lists for AAA
Authorization & Accounting
12.0 T, 12.0 CX, and later releases in these and additional
release trains
Per-Modem Filters (Per-Modem and
Per-Host Access Lists)
12.0(5)T1, 12.0(6)SC, and later releases in these and additional
release trains
Per-User Configuration 12.0 T and later releases in this and additional release trains
Redirect-Number Support for
RADIUS and TACACS+ Servers
12.0(4)XI with additional support and enhancements in later
releases in additional release trains
Reflexive Access Lists 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Secure Shell (SSH) Supported in
"k1" Images for Cisco uBR7200
12.1(1)T, 12.2(2)XA, 12.2 CX and later releases in this and
additional release trains
Turbo Access Control Lists
12.1 EC, 12.2 CX, 12.2(4)XF1 and later releases in these and
additional release trains
Vendor-Proprietary RADIUS
Attributes
11.3(11)NA, 12.0 T and later releases in these and additional
release trains
SNMP Features and Enhancements
Individual SNMP Trap Support 12.1(3)T and later releases in this and additional release trains
LinkUp/Down Traps Support
(RFC 2233)
12.1 EC and later releases in this and additional release trains
SNMPv2C 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
SNMPv3 12.0 T and later releases in this and additional release trains
SNMP Cable Modem Remote Query 12.1 EC and later releases in this and additional release trains
SNMP Management Information
Base (MIB) Enhancements
Multiple Cisco IOS releases and release trains
SNMP MIBs Changes and Updates in
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
SNMP Warm Start Trap 12.1 CX, 12.1 EC and later releases in these and additional
release trains
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management Features
Advanced Spectrum Management 12.1 CX and later releases in this and additional release trains
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 47

1-29
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cable Modulation Profile Default
Templates
12.1 EC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Downstream Traffic Shaping 12.0(7)XR2, 12.2(2)XF1 and later releases in these and
additional release trains
Dynamic Upstream Modulation 12.1(3)EC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Guided and Scheduled Spectrum
Management
Refer to the following features:
• Traffic Shaping (Downstream or Upstream)
• Frequency Hopping Capabilities
• Dynamic Upstream Modulation (SNR-based)
• Input Power Levels
Input Power Levels 11.3 NA, with additional enhancements in 12.0(7)XR2,
12.0(13)SC, 12.1(4)EC, 12.2(4)BC1 and later releases in these
release trains
Spectrum Management
Enhancements in Cisco IOS Release
12.3(9a)BC
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Upstream Traffic Shaping 11.3(9)NA and later releases in this and additional release trains
Testing, Troubleshooting and Diagnostic Features
Cable Downstream Frequency
Override
12.0 SC, 12.1 EC, 12.1T and 12.2BC release trains
Cable Flap List 11.3 NA, 12.0(4)XA, 12.0(7)XR, 12.1(2)EC, 12.1(5)EC,
12.1(7)CX, 12.2(4)BC1 and later releases in these and
additional release trains
Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter
(CBT) 3.2
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Cisco CMTS Static CPE Override 12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Fast Fault Detection 12.2(15)BC1 and later 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Virtual Interfaces
Virtual Interface Bundling on the
Cisco uBR-MC28/U BPE
VPN and Layer 2 Tunneling Features
Dynamic SID/VRF Mapping Support 12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
NAT—Support for NetMeeting
Directory (Internet Locator
Service—ILS)
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
IPv6 over L2VPN 12.3(17a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Mapping Service Flows to
MPLS-VPN
12.2(11)BC2 and later 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
MPLS VPN Support for
Subinterfaces and Cable Interface
Bundles
12.1 CX, 12.1 EC and later releases in these and additional
release trains
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 48

1-30
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
For feature comparisons between multiple releases, refer to the corresponding release notes, or to the
Cisco IOS Feature Navigator on Cisco.com (registration required).
Overlapping Subinterface IP
Addresses
12.1(3)EC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Transparent LAN Services (TLS) and
L2 Tunneling ATM/SIDs
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
Transparent LAN Services (TLS) and
L2 Virtual Private Networks
12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
VLAN Features
HSRP over ISL in Virtual LAN
Configurations
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
WAN Optimization and Services Features
Bandwidth Allocation Control
Protocol (BACP)
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Closed User Group Selection Facility
Suppress Option
12.1 T, 12.1 XM and later releases in these and additional release
trains
Enhanced Local Management
Interface (ELMI)
11.3(11)T, 12.0 XC and later releases in these and additional
release trains
Frame Relay Enhancements 12.2(4)BC1 and later 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC releases
Frame Relay MIB Extensions 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Frame Relay Router ForeSight 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
ISDN Advice of Charge 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
ISDN Caller ID Callback 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
ISDN Multiple Switch Types 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
ISDN NFAS 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
Microsoft Point-to-Point
Compression (MPPC)
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
MLPPP Support 12.3(13a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
National ISDN Switch Types for BRI
and PRI
12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
PAD Subaddressing 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
PPPoE Termination Support on
Cable Interfaces
12.1(5)T and later releases in this and additional release trains
Transparent LAN Services (TLS) and
L2 Tunneling ATM/SIDs
12.3(9a)BC and later 12.3 BC releases
VPDN MIB and Syslog Facility 12.0 XC and later releases in this and additional release trains
X.25 Enhancements 11.3(11)NA and later releases in additional release trains
X.25 Switching Between PVCs and
SVCs
11.3(11)NA and later releases in additional release trains
Table 1-9 Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers Features by Cisco IOS Release (continued)
Feature Supporting Cisco IOS Releases
Page 49

1-31
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cisco uBR7200 Series Router Configuration Tools
The Cisco uBR7200 series router provides you with the following configuration tools, allowing you
flexibility in choosing your configuration method:
• Autoinstall, page 1-31
• Cable Interface Setup Facility, page 1-31
• Cable Interface Extended Setup Facility, page 1-31
• Cisco Network Registrar, page 1-32
• Interface Range Specification, page 1-32
• Internal Modem Configuration File Editor, page 1-32
• Manual Configuration Mode for the Cisco uBR7200 Series CMTS, page 1-32
• Virtual Interface Support and Frequency Stacking Support, page 1-32
Autoinstall
The AutoInstall Using DHCP for LAN Interfaces feature replaces the use of the Bootstrap Protocol
(BOOTP) with the use of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for Cisco IOS AutoInstall
over LAN interfaces. AutoInstall is a Cisco IOS software feature that provides for the configuration of
a new routing device automatically when the device is initialized. DHCP (defined in RFC 2131) is based
on the Bootstrap Protocol, which provides the framework for passing configuration information to hosts
on a TCP/IP network. DHCP adds the capability of automatic allocation of reusable network addresses
and additional configuration options.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.1(5)T, the IP address procurement phase of the AutoInstall process is now
accomplished using DHCP for Ethernet, Token Ring, and FDDI interfaces. Before this release, IP
addresses for LAN interfaces were obtained using BOOTP during the AutoInstall process. The
AutoInstall Using DHCP for LAN Interfaces feature also allows the routing device to recognize IP
address allocation messages coming from regular BOOTP servers, providing a seamless transition for
those devices already using BOOTP servers for AutoInstall. Additionally, this feature allows for the
uploading of configuration files using unicast Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
Use the Autoinstall facility to configure the Cisco uBR7200 series router automatically after connection
to your WAN. For further details, refer to these sections or documents:
• “Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series Using AutoInstall” section on page 2-10
• Autoinstall Using DHCP for LAN Interfaces on Cisco.com
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1t/12_1t5/feature/guide/dt_dhcpa.html
Cable Interface Setup Facility
Use the Setup facility prior to completing a WAN or LAN connection to your router. The Setup facility
supports a number of functions so that cable interfaces and cable interface line cards are fully operational
after initial setup. Refer to the
“Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series Using the Setup Facility” section
on page 2-17.
Cable Interface Extended Setup Facility
The Extended Setup facility enhances the Setup Facility by prompting you to configure each interface on
the system as you progress through the CMTS configuration. The Configuration mode allows you to
configure the Cisco
uBR7200 series router manually if you prefer not to use Autoinstall or the Setup
Facility. Refer to the
“Configuring the Cable Interface with the Extended Setup Facility” section on
page 2-25.
Page 50

1-32
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cisco Network Registrar
The Cisco Network Registrar (CNR) is a configuration tool that automates dynamic IP address allocation
to cable
interfaces, PCs, and other devices on the broadband network. CNR allows you to track serial
numbers and MAC addresses for each cable
interface on your network, and reduces customer service
involvement when tracking subscriber CPE equipment.
Cisco provides the CNR with each Cisco uBR7200 series router. CNR dramatically improves the
reliability of naming and addressing services for enterprise and service provider networks. CNR
provides scalable Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
services and forms the basis of a DOCSIS cable modem provisioning system.
For additional information about configuring or using CNR, refer to the document titled Cisco Network
Registrar for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Routers:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/ubr7200/feature/guide/6126inst.html
Interface Range Specification
The Interface Range Specification feature allows specification of a range of interfaces to which
subsequent commands are applied and supports definition of macros that contain an interface range.
Implement the Interface Range Specification feature with the range keyword, which is used with the
interface command. In the interface configuration mode with the range keyword, all entered commands
are applied to all interfaces within the range until you exit interface configuration mode.
For additional command information, refer to the Interface Range Specification feature module on
Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1t/12_1t4/feature/guide/range.html
Internal Modem Configuration File Editor
This feature adds support for internal DOCSIS cable modem configuration file storage and generation.
The cable modem configuration file is generated and stored as part of the Cisco IOS configuration file.
The DOCSIS configuration files are not stored in Flash memory but are automatically generated when
requested for TFTP downloads to cable modems.
For the latest additional information about DOCSIS configuration files, refer to the document titled
Internal
DOCSIS Configurator File Generator for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufgCFile.html
Manual Configuration Mode for the Cisco uBR7200 Series CMTS
The Configuration mode allows you to configure the Cisco uBR7200 series router manually if you prefer
not to use Autoinstall or the Setup Facility. Refer to the
“Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Manually Using Configuration Mode” section on page 2-27.
Virtual Interface Support and Frequency Stacking Support
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC supports virtual interfaces and frequency stacking on the Cisco
uBR7246VXR router. Virtual interfaces allows a DS interface to be configured with up to eight upstream
channels. Frequency stacking allows two frequencies to be configured on one physical connector.
For additional information about frequency stacking and virtual interfaces on the Cisco uBR7246VXR
router, refer to the following document on Cisco.com:
• Virtual Interfaces and Frequency Stacking Configuration on MC5x20S and MC28U Linecards
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk804/technologies_white_paper09186a0080232b49.shtml
Page 51

1-33
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Bandwidth Management Features
This section describes the following bandwidth management feature available on the Cisco uBR7200
Series:
• Load Balancing Support, page 1-33
Load Balancing Support
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC introduces support for Load Balancing on the Cisco uBR7246VXR
router. The Load Balancing feature allows system operators to distribute cable modems across radio
frequency (RF) downstreams and upstreams, to maximize bandwidth and usage of the cable plant.
The Load Balancing feature allows service providers to optimally use both downstream and upstream
bandwidth, enabling the deployment of new, high-speed services such as voice and video services. This
feature also can help reduce network congestion due to the uneven distribution of cable modems across
the cable network and due to different usage patterns of individual customers.
By default, the Cisco CMTS platforms use a form of load balancing that attempts to equally distribute
the cable modems to different upstreams when the cable modems register. You can refine this form of
load balancing by imposing a limit on the number of cable modems that can register on any particular
upstream, using the cable upstream admission-control command.
However, this default form of load balancing affects the cable modems only when they initially register
with the Cisco CMTS. It does not dynamically rebalance the cable modems at later times, such as when
they might change upstream channels in response to RF noise problems, or when bandwidth conditions
change rapidly because of real-time traffic such as Voice over IP (VoIP) and video services. It also does
not affect how the cable modems are distributed among downstream channels.
For additional information about configuring Load Balancing on the Cisco CMTS, refer to the following
document on Cisco.com:
• Configuring Load Balancing for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/troubleshooting_batch9/cmtslbg.html
Cisco IOS Command-Line Enhancements
In addition to new or enhanced commands that tie to a specific feature, this section describes general
enhancements to Cisco IOS Software commands that support the Cisco uBR7200 series.
• exec prompt timestamp Command, page 1-33
• parser cache Command, page 1-34
• show Command Enhancements, page 1-35
• Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC Command-Line Interface (CLI) Enhancements, page 1-36
In some cases, additional feature descriptions that relate to these commands are available elsewhere in
this chapter.
exec prompt timestamp Command
Cisco IOS Release 12.1(12c)EC and 12.2(8)BC2 add a new command, exec prompt timestamp. This
command adds load information and a timestamp to all show commands. This can be useful for
troubleshooting and system analysis.
Page 52

1-34
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
The exec prompt timestamp command has the following syntax in line configuration mode:
Router(config-line)# [no] exec prompt timestamp
The command has the following syntax in User EXEC mode, so that users who do not know the enable
password can also timestamp their show commands:
Router> terminal [no] exec prompt timestamp
The following example illustrates how to enable and disable the timestamp for the console connection:
Router# config t
Router(config)# line console 0
Router(config-line)# exec prompt timestamp
Router(config-line)# no exec prompt timestamp
The following example illustrates how to enable and disable the timestamp for the first five telnet
connections:
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)# exec prompt timestamp
Router(config-line)# no exec prompt timestamp
The following example illustrates how to enable and disable the timestamp when logged into User EXEC
mode:
Router> terminal exec prompt timestamp
Router> terminal no exec prompt timestamp
parser cache Command
A new global configuration command, [no] parser cache, allows you to enable or disable the parser
cache feature on the Cisco uBR7200 series.The parser cache feature is enabled by default on all
platforms using Cisco IOS Release 12.1(5)T or later.
The parser cache feature optimizes the parsing (translation) of Cisco IOS software configuration
command lines by remembering how to parse recently encountered command lines. This feature
improves the scalability of the Cisco IOS software command-line interface (CLI) parser when
processing large configuration files.
This improvement is especially useful for those cases in which thousands of virtual circuits must be
configured for interfaces, or hundreds of access control lists (ACLs) are required. The parser chain cache
can rapidly recognize and translate configuration lines that differ slightly from previously used
configuration lines (for example, pvc 0/100, pvc 0/101, and so on).
Note Testing indicates an improvement to load time of between 30% and 36% for large configuration files
when using the parser cache.
For additional information, refer to the Parser C a che feature module on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1t/12_1t5/feature/guide/dt5parse.html
Page 53

1-35
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
show Command Enhancements
The Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers contain the following additional or changed
show commands.
show cable qos
The show cable qos command is changed to show cable qos profile n command, where the optional
argument n can be used to display a specific profile.
Note The release notes up to and including Cisco IOS Release 12.0(12)SC stated that the show cable qos
command was changed to show cable qos-profile n command, with a hyphen between “qos” and
“profile”. This was incorrect.
show int cx/y sid
The show int cx/y sid command displays more complete Service ID (SID) status information.
show cable modem
The show cable modem command displays a list of options for a single modem to be specified by
entering either the cable modem's IP address or MAC address.
show cable modulation-profile
The show cable burst-profile command has been removed. Its functions have been incorporated into the
show cable modulation-profile command, which includes an added option number that displays the
modulation profile number.
show cable modem summary
Commencing with Cisco IOS Release 12.1(6) EC, the show cable modem summary command is
enhanced with the following options to display per-card and per-port totals:
• show cable modem summary total—Displays a summary and a total for all modems on the chassis.
• show cable modem summary cable x/0 total—Displays a summary of modems on a specified card.
• show cable modem summary cable x/0 upstream port1 port2 total—Displays a summary of
modems on the specified card and specified range of ports.
• show cable modem summary cable x/0 cable y/0 total—Displays a summary of modems on the
specified range of cards.
• show cable modem summary cable x/0 cable y/0 upstream port1 port2 total—Displays a
summary of modems on the specified range of ports on the specified range of cards.
For additional command information, refer to the Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
Page 54

1-36
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC Command-Line Interface (CLI) Enhancements
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC supports the following new or enhanced command-line interface:
• cable logging layer2events, page 1-36
• cable source-verify, page 1-37
• show cable tech-support, page 1-41
• show controllers cable, page 1-42
• show tech-support, page 1-44
For additional information about these command changes, refer to this document on Cisco.com:
• CiscoIOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
cable logging layer2events
To save DOCSIS events that are specified in Cable Device MIB to the cable logging buffer (instead of
to the general logging buffer), use the cable
logging layer2events command in global configuration
mode. To disable the logging of DOCSIS events to the cable logging buffer, use the no form of this
command.
cable logging layer2events
no cable logging layer2events
Syntax Description This command has no additional arguments or keywords.
Defaults DOCSIS events are saved to the general logging buffer on the Cisco CMTS by default.
Command Modes Global configuration mode
Command History
Usage Guidelines Use the show cable logging command to check whether the logging feature is enabled and the status of
the logging buffer.
Examples The following example shows how to clear the log buffer that contains a bad IP source address error
messages:
Router# show cable logging summary
Cable logging: BADIPSOURCE Enabled
Total buffer size (bytes): 1000000
Release Modification
12.3(9a)BC This command was introduced on the Cisco uBR10012 and
Cisco
uBR7246VXR universal broadband routers.
Page 55

1-37
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Used buffer size (bytes) : 36968
Logged messages : 231
Router# clear cable logging badipsource
Router# show cable logging summary
Cable logging: BADIPSOURCE Enabled
Total buffer size (bytes): 1000000
Used buffer size (bytes) : 0
Logged messages : 0
Related Commands
For additional information about logging events on the Cisco CMTS, refer to the following document on
Cisco.com:
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
cable source-verify
To enable verification of IP addresses or service IDs (SIDs) for CMs and CPE devices on the upstream,
use the cable source-verify command in global configuration, cable interface configuration or
subinterface configuration modes. To disable verification, use the no form of this command.
Cable Interface and Subinterface Configuration Modes
cable source-verify [dhcp | leasetimer value | leasequery-filter upstream query-num interval]
no cable source-verify
Global Configuration Mode
cable source-verify leasequery-filter downstream query-num interval
no cable source-verify
Command Description
cable logging badipsource Logs error messages about bad IP source addresses on the cable
interfaces to a separate log buffer,
show cable logging Indicates whether the logging feature is enabled and the status of the
logging buffer.
Page 56

1-38
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Syntax Description
Defaults Disabled. When the dhcp option is specified, the leasetimer option is set by default to 60 minutes.
Command Modes Global configuration, Cable interface configuration or subinterface configuration
Note Configuring the cable source-verify command on the master interface of a bundle will
configure it for all of the slave interfaces in the bundle as well.
Command History
dhcp (Optional) Specifies that queries will be sent to verify unknown source IP
addresses in upstream data packets.
Note Do not enable the local DHCP server on the Cisco CMTS and
configure local DHCP address pools, using the ip dhcp pool
command, when using this option, because this prevents DHCP
address validation.
leasetimer value (Optional) Specifies the time, in minutes, for how often the router should
check its internal CPE database for IP addresses whose lease times have
expired. The valid range for value is 1 to 240 minutes, with a default of
60
minutes.
Note The leasetimer option takes effect only when the dhcp option is
also used on an interface. Also, this option is supported only on the
master interface and cannot be configured on subinterfaces.
Configuring it for a master interface automatically applies it to all
subinterfaces.
leasequery-filter
upstream query-num
interval
(Optional) Enables upstream lease queries to be defined on a per-SID basis
to reduce the chance of Denial of Service attacks.
• query-num— Number of leased queries per SID.
• interval—Size of timer window in seconds.
leasequery-filter
downstream
query-num interval
(Optional) Enables downstream lease queries to be defined on a per-SID
basis to reduce the chance of Denial of Service attacks.
• query-num— Number of leased queries for an unknown SID.
• interval—Size of timer window in seconds.
Release Modification
11.3 XA This command was introduced.
12.0(7)T The dhcp keyword was added.
12.0(10)SC, 12.1(2)EC Support was added for these trains.
12.1(3a)EC Subinterface support was added.
12.1(13)EC,
12.2(11)BC1
The leasetimer keyword was added.
12.2(15)BC1 The verification of CPE devices was changed when using the dhcp keyword.
Page 57

1-39
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
For additional information about this and other commands, refer to the following document on
Cisco.com:
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
cable submgmt default
To enable the Cisco CMTS Static CPE Override feature on the Cisco CMTS, use the cable submgmt
default command in global configuration mode. This command enables field technicians to add a
temporary CPE device behind the subscriber’s cable modem. The temporary CPE device shares the same
SID settings as the original CPE device, even though the temporary CPE device has a different MAC
address. The original CPE device automatically changes from dhcp cpe to static cpe in the CMTS host
routing tables, and the CPE device continues to receive service with the same SID. To disable Cisco
CMTS Static CPE Override on the Cisco CMTS, use the no form of this command. This automatically
updates the routing tables and enables the MAC address from the technician’s laptop for a future field
service connection at a different location.
cable submgmt default {active | filter-group {cm | cpe} | learnable | max-cpe}
no cable submgmt default
Syntax Description
12.2(15)BC2 Support for verifying CMs and CPE devices that are on a different subnet
than the cable interface was enhanced to use Reverse Path Forwarding
(RFP).
12.3(9a)BC In order to protect the Cisco CMTS from denial of service attacks, Cisco IOS
Release 12.3(9a)BC adds the option of using a per SID basis for deriving
lease queries from CPE devices. This release also introduces a global rate
limit for lease queries initiated by downstream traffic. These enhancements
reduce the CPU utilization of DHCP Receive and ISR processes when the
Cisco CMTS is configured with the cable source-verify dhcp and no cable
arp commands.
Release Modification
active Keyword enables Cisco CMTS Static CPE Override, granting local CPE
control for subscriber management filtering (as defined by existing SID
settings).
filter-group {cm | cpe} Keyword enables one ore more temporary CPE devices to inherit the
characteristics of an existing filter group, either on the downstream or the
upstream of the cable modem (cm) or the CPE device (cpe).
• filter-group cm {downstream | upstream}—This keyword
combination enables one or more temporary CPE devices to inherit and
filter by the default downstream cable modem group, or by the default
upstream cable modem group.
• filter-group cpe {downstream | upstream}—This keyword
combination enables one or more temporary CPE devices to inherit and
filter by the default downstream CPE group, or by the default upstream
CPE group.
Page 58

1-40
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Defaults This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes Global configuration mode
Command History
Usage Guidelines Prior to using this command, the first (existing) DHCP CPE device maintains its DHCP dynamic MAC
address behind the cable modem. The SID is assigned to this IP address.
However, by enabling Static CPE override, you gain the following states and options on two CPE devices
behind the cable modem.
• The SID definition on the first CPE device is assigned a different static IP address. This enables you
to change the existing (dynamic) DHCP IP address to a static IP address without first clearing the
DHCP CPE host entries from the Cisco CMTS. The CPE IP state changes from dhcp to static cpe.
• This static override allows a second CPE device with a second MAC address behind the same cable
modem with SID1 to be assigned same IP address as the first CPE device.
Note The second CPE device changes from dhcp cpe to static CPE in the CMTS host tables.
Examples The following example enables Cisco CMTS Static CPE Override in the field, enabling more or more
additional CPE devices to be added behind a subscriber’s cable modem:
Router(config)# cable submgmt default active
The following example configures the Cisco CMTS to accept a temporary CPE device, which inherits
and filters by the subscriber’s default downstream cable modem group:
Router(config)# cable submgmt default filter-group cm downstream
The following example configures the Cisco CMTS to accept a temporary CPE device, and to update the
temporary CPE device with the current routing table from the Cisco CMTS:
Router(config)# cable submgmt default learnable
learnable Keyword automatically enables one or more temporary CPE devices to
learn and to operate within the CPE IP address(es) in the Cisco CMTS
routing table.
max-cpe Keyword sets the maximum number of IP addresses to be permitted behind
a cable modem while the Cisco CMTS Static CPE Override feature is
enabled. This keyword enables multiple temporary CPE devices in the
range of 0 to 1024.
Release Modification
12.3(9a)BC This feature was introduced on Cisco uBR10012 and Cisco uBR7200 series
universal broadband routers.
Page 59

1-41
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
The following example configures the Cisco CMTS to accept a maximum of five temporary CPE devices
behind a subscriber’s cable modem:
Router(config)# cable submgmt default max-cpe 5
Related Commands
show cable tech-support
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC introduces changes to the output of the show cable tech-support
command. This change allows users with large numbers of online cable modems to collect the necessary
information without consuming the console session for a long period of time.
To display general information about the router when reporting a problem, use the show cable
tech-support command in privileged EXEC mode.
show cable tech-support
Syntax Description This command has no additional arguments or keywords.
Defaults This command has no default behavior or values.
Command Modes Privileged EXEC
Command History
Examples The following example illustrates the cable modem and interface information from a Cisco
uBR7246VXR router on which Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC is installed.
Router# show cable tech-support
Command Description
show cable host Displays the CPE devices (hosts) residing behind a specified cable modem
(MAC address).
Release Modification
11.2 This command was introduced.
12.1(1a)T1 This command was modified to include information about the cable clock
card.
12.2(15)BC2 This command added several show pxf commands to the display on the
Cisco
uBR10012 router.
12.3(9a)BC The output of the command was significantly shortened by moving a
number of show commands (the ones that display information about
individual cable modems) to the show tech-support command. This release
also adds support for an option to display information about only one
specific cable interface.
Page 60

1-42
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
For additional information about this and other commands, refer to the following document on
Cisco.com:
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
show controllers cable
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC removes the tech-support keyword from the show controllers cable
command. This change allows users with large numbers of online cable modems to collect the necessary
information without consuming the console session for a long period of time.
Additional and related improvements are also available for the show tech-support command.
To display information about the interface controllers for a cable interface on the Cisco CMTS router,
use the show controllers cable command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show controllers cable {slot/port | slot/subslot/port} [downstream | upstream [port] | [mem-stat]
[memory] [proc-cpu]] [tech-support]
Syntax Description slot/port Identifies the cable interface and downstream port on the
Cisco
uBR7100 series and Cisco uBR7200 series routers.
On the Cisco uBR7100 series router, the only valid value is 1/0. On the
Cisco
uBR7200 series router, slot can range from 3 to 6, and port can
be 0 or 1, depending on the cable interface.
slot/port Identifies the cable interface on the Cisco uBR7246VXR router.
Th syntax for the Cisco uBR10012 router is slot/subslot/port, where
the following are the valid values:
• slot = 5 to 8
• subslot = 0 or 1
• port = 0 to 4 (depending on the cable interface)
downstream (Optional) Displays downstream interface status.
upstream (Optional) Displays upstream interface status.
port (Optional) Specifies the desired upstream port. Valid values start with
0 for the first upstream port on the cable interface line card.
mem-stat (Optional) Displays the output from the show memory statistics
command to display a summary of memory statistics for a Broadband
Processing Engine (BPE) cable interface line card.
memory (Optional) Displays the output from the show memory command to
display a summary of memory statistics, including the memory as it is
allocated per process, for a Broadband Processing Engine (BPE) cable
interface line card.
proc-cpu (Optional) Displays the output from the show processes cpu command
to display the processor status for a Broadband Processing Engine
(BPE) cable interface line card.
tech-support (Optional) Displays information from a number of different show
commands for technical support purposes. The exact output depends
on the platform, configuration, and type of protocols being used
Page 61

1-43
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Command Modes User EXEC, Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines The mem-stat, memory, and proc-cpu keywords execute the related command on the processor that
runs on added to obtain the relevant information from the onboard processor on Broadband Processing
Engine (BPE) cable interface line cards, such as the Cisco
uBR-MC16U/X, Cisco uBR-MC28U/X, and
Cisco
uBR-MC5X20S/U cards. This allows you to obtain information that is specific for that particular
cable interface card, as opposed to having to run these commands on the entire router.
Note The mem-stat, memory, and proc-cpu options are not available for cable interface line cards that do not
contain an onboard processor (for example, the Cisco uBR-MC16C card).
Examples The following is sample output for the downstream connection for slot 3 on port 0 on Cisco CMTS router
from the show controllers cable downstream command:
CMTS01# show controllers cable 3/0 downstream
Cable 3/0 Downstream is up
Frequency not set, Channel Width 6 MHz, 64-QAM, Symbol Rate 5.056941 Msps
FEC ITU-T J.83 Annex A, R/S Interleave I=12, J=17
Release Modification
11.3 NA This command was introduced.
12.0(2)XC This command was modified to show a number of additional fields.
12.1(5)EC1 Support was added for the Cisco uBR7100 series router, including
information about the Cisco
uBR7100 series integrated upconverter.
12.2(1)XF1 Support was added for the Cisco uBR10012 router.
12.0(16)SC2,
12.1(10)EC1,
12.2(4)BC1b
The algorithm for calculating the SNR value was enhanced for a more
accurate value.
12.2(15)CX Support was added for the Cisco uBR-MC28U/X cable interface line card,
including the display of the number of packets dropped because they were
for a Service Flow ID (SFID) of 0.
12.2(15)BC2b The mem-stat, memory, and proc-cpu options were added to obtain
processor information from the onboard processor on Broadband Processing
Engine (BPE) cable interface line cards, such as the Cisco
uBR-MC16U/X,
Cisco
uBR-MC28U/X, and Cisco uBR-MC5X20S/U cards.
12.3(9a)BC Adds the tech-support option to improve information required during
technical support.
Page 62

1-44
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Table 10 describes the fields displayed by the show controllers cable downstream command.
The following example illustrates the information from the show controllers cable command on a Cisco
uBR7246VXR router on which Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC is installed.
Router# show controllers cable x/y
For additional information about this and other commands, refer to the following document on
Cisco.com:
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
show tech-support
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC shortens the output of the show tech-support command on the Cisco
uBR10012 and the Cisco uBR7246VXR routers. This change allows users with large numbers of online
cable modems to collect information without consuming the console session for a long period of time.
To display general information about the Cisco CMTS router when reporting a problem to Cisco
technical support, use the show tech-support command in privileged EXEC mode.
show tech-support [page] [password] [cef | ipc | ipmulticast | isis | mpls | ospf | rsvp]
Note The show tech-support command automatically displays the output of a number of different show
commands. The exact output depends on the platform, configuration, and type of protocols being used.
Note The show tech-support includes most of the information shown in the show cable tech-support
command.
Ta b l e 10 show controllers cable downstream Field Descriptions
Field Description
Cable Slot number/port number indicating the location of the Cisco cable
interface line card.
Downstream is up Indicates that the RF downstream interface is enabled.
Frequency Transmission frequency of the RF downstream. (This information
may not match the current transmission frequency, which is
external on CMTS platforms that use an external upconverter.)
Channel Width Indicates the width of the RF downstream channel.
QAM Indicates the modulation scheme.
Symbol Rate Indicates the transmission rate (in number of symbols per second).
FEC ITU-T Indicates the Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG) framing
standard.
R/S Interleave I/J Indicates Reed Solomon framing based on ITU S.83-B.
Page 63

1-45
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Syntax Description
For additional information about this and other commands, refer to the following document on
Cisco.com (updated through Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC):
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
Cisco Quality of Service Features
Networks must provide secure, predictable, measurable, and sometimes guaranteed services. Achieving
the required Quality of Service (QoS) by managing delay, delay variation (jitter), bandwidth, and packet
loss parameters on a network becomes the secret to a successful end-to-end business solution. Cisco QoS
is the set of techniques to manage network resources. The Cisco
uBR7200 series CMTS offers the
following Cisco QoS features, in addition to supporting additional DOCSIS QoS features.
• Cisco Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR), page 1-46
• RTP Header Compression, page 1-46
For additional information, refer to the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Web page on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/technologies/tk389/tk813/technologies_white_paper0900aecd802b68
b1_ps6558_Products_White_Paper.html
page (Optional) Causes the output to display a page of information at a time. Use the
Return key to display the next line of output or use the space bar to display the next
page of information. If not used, the output scrolls (that is, does not stop for page
breaks).
password (Optional) Leaves passwords and other security information in the output. If not used,
passwords and other security-sensitive information in the output are replaced with the
label "<removed>" (this is the default).
cef (Optional) Displays information about the Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) protocol
configuration and status.
ipc (Optional) Displays information about interprocess communications on the Cisco
router.
ipmulticast (Optional) Displays information about the IP multicast configuration and status.
isis (Optional) Displays information about the Connectionless Network Service (CLNS)
and Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) routing protocol
configuration and status.
Note IS-IS support is provided only on CMTS platforms running Cisco IOS images
that have a “-p-” as part of the image name.
mpls (Optional) Displays information about Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on the
Cisco router, which instructs the routers and the switches in the network on where to
forward the packets based on preestablished IP routing information.
ospf (Optional) Displays information about the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing
algorithm and status on the Cisco router.
rsvp (Optional) Displays information about the IP Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
configuration and status.
Page 64

1-46
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Cisco Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR)
Cisco IOS Release 12.1(10)EC added support for Cisco IOS Network-Based Application Recognition
(NBAR). The NBAR feature is a new classification engine that can recognize a wide variety of network
applications, including Web-based applications, client/server applications, and other difficult-to-classify
protocols that dynamically assign TCP or UDP port numbers.
NBAR enhances existing methods of application-recognition by adding several new classification features:
• Classification of applications that use statically assigned TCP/UDP port numbers, that use
dynamically assigned TCP/UDP port numbers, or that use protocols other than TCP and UDP
• Classification of HTTP traffic by URL, host, or MIME type
• Classification of Citrix ICA traffic by application name
• Classification of application traffic using subport information
NBAR can also classify static port protocols. Although access control lists (ACLs) can also be used for
this purpose, NBAR is easier to configure and can provide other options and classification statistics that
are not available when using ACLs.
After NBAR recognizes an application, the Cisco uBR7200 series router can invoke specific services
appropriate for that application. These services can provide QoS features such as:
• Guaranteed bandwidth
• Bandwidth limits
• Traffic shaping
• Packet coloring
The Cisco IOS NBAR feature can also be used to detect and respond to denial-of-service and other types
of network attacks. Cisco IOS NBAR uses a protocol description language module (PDLM) to define the
rules by which the NBAR processes recognize an application. New PDLM definitions can usually be
loaded without the need for a Cisco IOS software upgrade or a router reboot, allowing for a rapid
response to discovered attacks.
Note For basic information on configuring and using the Cisco IOS NBAR feature, see the Network-Based
Application Recognition feature module.
For information on configuring NBAR for Quality of Service (QoS) control, see the “Configuring
Network-Based Application Recognition” chapter of theCisco IOS Release 12.2 Quality of Service
Solutions Configuration Guide.
These documents are available on Cisco.com and the Customer Documentation CD-ROM.
Tip Cisco.com also contains a technical note, Using Network-Based Application Recognition and Access
Control Lists for Blocking the Code Red Worm, that provides information on using NBAR to block
denial-of-service attacks. Registration and login is required to view this document.
RTP Header Compression
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) is the Internet Standard (RFC 1889) protocol for the transport of
real-time data. It is intended to provide end-to-end network transport functions for applications that
support audio, video, or simulation data over multicast or unicast network services.
RTP provides support for real-time conferencing of groups of any size within the Internet. This support
includes source identification and support for gateways such as audio and video bridges as well as
multicast-to-unicast translators. RTP offers QoS feedback from receivers to the multicast group, and
support for the synchronization of different media streams.
Page 65

1-47
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
RTP includes a data portion and a header portion. The data portion of RTP is a thin protocol that provides
support for the real-time properties of applications, such as continuous media, including timing
reconstruction, loss detection, and content identification.
The header portion of RTP is considerably large. As shown in Figure 16, the minimal 12 bytes of the
RTP header, combined with 20 bytes of IP header (IPH) and 8 bytes of UDP header, create a 40-byte
IP/UDP/RTP header. For compressed-payload audio applications, the RTP packet typically has a 20-byte
to 160-byte payload. Given the size of the IP/UDP/RTP header combinations, it is inefficient to send the
IP/UDP/RTP header without compressing it.
To avoid the unnecessary consumption of available bandwidth, the RTP header compression
feature—referred to as CRTP—is used on a link-by-link basis.
For configuration information and additional explanation, refer to the Link Efficiency Mechanisms”
chapters of the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 on Cisco.com.
DHCP Servers and Feature Support
Cisco IOS software supports multiple DHCP features and server functions on the network for the
Cisco
uBR7200 series.
• Configurable Leasequery Server, page 1-47
• DHCP MAC Address Exclusion List for cable-source verify dhcp Command, page 1-48
• See the “DOCSIS 1.1 Feature Support” section on page 1-57 for additional DHCP features.
Configurable Leasequery Server
Previously, lease query requests could only be sent to the DHCP server. Beginning with Cisco IOS
Release 12.3(17a)BC, an alternate server may be configured to receive the requests.
There are a few restrictions:
• Lease queries are sent to the DHCP server unless an alternate server is configured.
• Only one alternate server may be configured.
• Users are responsible for the synchronization of the DHCP server and configured alternate server.
• If the configured alternate server fails, lease query requests will not be diverted back to the DHCP
server.
Regardless of which server is configured (DHCP or alternate), unknown IP addresses that are found in
packets for customer premises equipment (CPE) devices that use the cable modems on the cable interface
are verified. The DHCP server or configured alternate server returns a DHCP ACK message with the
MAC address of the CPE device that has been assigned this IP address, if any.
To configure the Cisco CMTS router to send DHCP LEASEQUERY requests to an alternate server, use
the cable source-verify dhcp server ipaddress and no cable arp commands. (To configure the DHCP
server instead, use the cable source-verify dhcp and no cable arp commands.)
For additional information about this feature, refer to the following documents on Cisco.com:
• Filtering Cable DHCP Lease Queries on Cisco CMTS Routers
URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/cblsrcvy.html
Page 66

1-48
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
DHCP MAC Address Exclusion List for cable-source verify dhcp Command
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC introduces the ability to exclude trusted MAC addresses from standard
DHCP source verification checks, as supported in previous Cisco IOS releases for the Cisco CMTS. This
feature enables packets from trusted MAC addresses to pass when otherwise packets would be rejected
with standard DHCP source verification. This feature overrides the cable source-verify command on the
Cisco CMTS for the specified MAC address, yet maintains overall support for standard and enabled
DHCP source verification processes. This feature is supported on Performance Routing Engine 1 (PRE1)
and PRE2 modules on the Cisco uBR10012 router chassis.
To enable packets from trusted source MAC addresses in DHCP, use the cable trust command in global
configuration mode. To remove a trusted MAC address from the MAC exclusion list, use the no form of
this command. Removing a MAC address from the exclusion list subjects all packets from that source to
standard DHCP source verification.
cable trust mac-address
no cable trust mac-address
Syntax Description
Usage Guidelines This command and capability are only supported in circumstances in which the Cable Source Verify
feature is first enabled on the Cisco CMTS.
When this feature is enabled in addition to cable source verify, a packet’s source must belong to the MAC
Exclude list on the Cisco CMTS. If the packet succeeds this exclusionary check, then the source IP
address is verified against Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) tables as per normal and previously
supported source verification checks. The service ID (SID) and the source IP address of the packet must
match those in the ARP host database on the Cisco CMTS. If the packet check succeeds, the packet is
allowed to pass. Rejected packets are discarded in either of these two checks.
Any trusted source MAC address in the optional exclusion list may be removed at any time. Removal of
a MAC address returns previously trusted packets to non-trusted status, and subjects all packets to
standard source verification checks on the Cisco CMTS.
Note When the cable source-verify dhcp feature is enabled, and a statically-defined IP address has been
added to the CMTS for a CM using the cable trust command to override the cable source-verify dhcp
checks for this device, packets from this CM will continue to be dropped until an entry for this CM is
added to the ARP database of the CMTS. To achieve this, disable the cable source-verify dhcp feature,
ping the CMTS from the CM to add an entry to the ARP database, and re-enable the cable source-verify
dhcp feature.
For additional information about the enhanced Cable Source Verify DHCP feature, and general
guidelines for its use, refer to the following documents on Cisco.com:
• IP Address Verification for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Cable Router
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0t/12_0t7/feature/guide/sourcver.html
• Filtering Cable DHCP Lease Queries
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/cblsrcvy.html
• Cisco IOS CTMS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
mac-address The MAC address of a trusted DHCP source, and from which packets will
not be subject to standard DHCP source verification.
Page 67

1-49
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
• CABLE SECURITY, Cable Source-Verify and IP Address Security, White Paper
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk803/technologies_tech_note09186a00800a7828.shtml
DOCSIS 1.0 Feature Support
The Cisco uBR7200 series and associated Cisco IOS software support multiple DOCSIS 1.0
enhancements, extensions, and features.
• DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy, page 1-49
• DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy Interface Encryption and Encrypted Key Exchange, page 1-49
• DOCSIS 1.0 Concatenation Override Featurette, page 1-50
• DOCSIS 1.0 Extensions, page 1-51
• DOCSIS 1.0 Quality of Service, page 1-51
• DOCSIS Quality of Service Enhancements Prior to DOCSIS 1.1, page 1-52
• DOCSIS Customer Premises Equipment Configurator, page 1-53
• Enhanced Rate Bandwidth Allocation (ERBA) Support for DOCSIS 1.0 Cable Modems, page 1-54
DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy
DOCSIS baseline privacy interface (BPI) gives subscribers data privacy across the RF network, encrypting
traffic flows between the CMTS and cable modem. BPI ensures that a cable modem, uniquely identified by
its Media Access Control (MAC) address, can obtain keying material for services only it is authorized to
access.
To enable BPI, choose software at both the CMTS and cable modem that support the mode of operation.
For the Cisco
uBR7200 series software, choose an image with “k1” in its file name or BPI in the feature
set description.
The cable modem must also support BPI. CMs must have factory-installed RSA private/public key pairs
to support internal algorithms to generate key pairs prior to first BPI establishment. BPI must be enabled
using the DOCSIS configuration file.
Note RSA stands for Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman, inventors of a public-key cryptographic
system.
DOCSIS 1.0 Baseline Privacy Interface Encryption and Encrypted Key Exchange
The Cisco uBR7200 series supports full DOCSIS 1.0 BPI specifications. The BPI for DOCSIS 1.0 protects
user data privacy across the shared-medium cable network and prevents unauthorized access to
DOCSIS-based data transport services across the cable network. BPI encrypts traffic across the RF interface
between the cable modem and CMTS, and includes authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA)
features.
The level of data privacy is roughly equivalent to that provided by dedicated line network access services
such as analog modems or digital subscriber lines (DSL). BPI provides basic protection of service,
ensuring that a cable modem, uniquely identified by its MAC address, can obtain keying material for
services only when it is authorized to access.
Note Encryption and decryption are subject to export licensing controls.
Page 68

1-50
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
BPI supports access control lists (ACLs), tunnels, filtering, protection against spoofing, and commands
to configure source IP filtering on RF subnets to prevent subscribers from using source IP addresses that
are not valid.
Baseline privacy extensions permit the encryption of data transferred between the cable modem and the
Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband router. The key management protocol defined by baseline
privacy allows Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers to provide two types of keys to cable
modems. The Key Exchange Key (KEK) decrypts the Traffic Exchange Keys (TEK). The TEK is the key
used to encrypt and decrypt data packets.
DOCSIS 1.0 Concatenation Override Featurette
Cisco IOS release 12.3(13a)BC introduces support for the DOCSIS 1.0 concatenation override feature
on the Cisco uBR10012 router. This feature provides the ability to disable concatenation on DOCSIS 1.0
cable modems, even in circumstances where concatenation is otherwise supported for the upstream
channel.
DOCSIS 1.0 concatenation allows the cable modem to make a single-time slice request for multiple
packets, and to send all packets in a single large burst on the upstream. Concatenation was introduced in
the upstream receive driver in the previous Cisco IOS releases that supported DOCSIS 1.0 +. Per-SID
counters were later added in Cisco IOS release 12.1(4)CX for debugging concatenation activity.
In some circumstances, overriding concatenation on DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems may be preferable, and
Cisco IOS release 12.3(13a)BC supports either option.
Note Even when DOCSIS 1.0 concatenation is disabled with this feature, concatenation remains enabled for
cable modems that are compliant with DOCSIS 1.1 or DOCSIS 2.0.
To enable DOCSIS 1.0 concatenation override with Cisco IOS release 12.3(13a)BC and later releases,
use the new docsis10 keyword with the previously supported cable upstream <n> concatenation
command in privileged EXEC mode:
cable upstream <n> concatenation docsis10
Syntax Description
Examples The following example illustrates DOCSIS 1.0 concatenation override on the Cisco uBR7246VXR
router:
Router# no cable upstream 0 concatenation docsis10
In this example, DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems are updated with REG-RSP so that they are not permitted
to use concatenation.
For additional information about this command, refer to the Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference
Guide on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
n Specifies the upstream port number. Valid values start with 0 for the first
upstream port on the cable interface line card.
Page 69

1-51
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
DOCSIS 1.0 Extensions
The Cisco uBR7200 series supports the following DOCSIS 1.0 Quality of Service (QoS) extensions:
• Multi-Service ID (SID) support, allowing the definition of multiple SIDs on the upstream—Voice
traffic can be designated on a higher QoS committed information rate (CIR) secondary SID, while
data traffic can be forwarded on a best-effort basis on a primary SID. Secondary SIDs are higher
QoS CIR-type classes that have a nonzero minimum reserved rate (CIR-type service). These SIDs
receive preferential treatment at the CMTS for grants over any tiered best-effort type data SID of
that upstream. Reliable operation with voice requires multiple SIDs—at least two per cable modem
to separate voice from data. In DOCSIS 1.0, SIDs are set up statically. When supporting DOCSIS
1.0 extensions, SIDs can be set up statically or dynamically. Both the CMTS and cable modem must
support this capability.
• Cable modem-initiated dynamic MAC messages—Dynamic Service Addition (DSA) and Dynamic
Service Deletion (DSD). These messages allow dynamic SIDs to be created and deleted at run-time
on a per-VoIP call basis.
• Unsolicited grant service (constant bit rate [CBR] scheduling) on the upstream—This helps provide
a higher-quality channel for upstream VoIP packets from an Integrated Telephony Cable Modem
(ITCM) such as the Cisco
uBR924 cable access router.
• Ability to provide separate downstream rates for any given ITCM, based on the IP-precedence value
in the packet—This helps separate voice signaling and data traffic that goes to the same ITCM to
address rate-shaping purposes.
–
Concatenation—To increase the per- cable modem upstream throughput in certain releases of
software, Cisco
uBR7200 series software supports a concatenated burst of multiple MAC
frames from a cable modem that supports concatenation.
Note All DOCSIS 1.0 extensions are activated only when a cable modem or Cisco uBR924 that
supports these extensions solicits services using dynamic MAC messages or the feature set.
If the CMs in your network are pure DOCSIS 1.0-based, they receive regular DOCSIS 1.0
treatment from the CMTS.
DOCSIS 1.0 Quality of Service
The Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers support quality of service (QoS) as defined by
the DOCSIS 1.0 specification. Service class profiles can be configured through the command-line
interface to support the QoS profile number, traffic priority, maximum upstream bandwidth, guaranteed
upstream bandwidth, maximum downstream bandwidth, maximum transmit burst length, baseline
privacy enable/disable, and type of service (ToS) overwrite byte.
QoS Profile Enforcement allows cable modem termination system (CMTS) operators to control the QoS
to eliminate any interference from improper local-rate limiting implemented on the cable modem. The
CMTS provisions a registering cable modem with a default DOCSIS 1.0 service class assigned by the
operator, overriding any service class that previously existed on the modem. This service class has no
upstream or downstream rate limits, so that the CMTS can do traffic shaping based on the QoS profile
enforced by the operator.
The following commands are available on Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers to update
the QoS table:
• create-snmp—Permits creation of QoS table entries by SNMP.
• modems—Permits creation of QoS table entries by modem registration requests.
• update-snmp—Permits dynamic update of QoS table entries by SNMP.
Page 70

1-52
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
DOCSIS Quality of Service Enhancements Prior to DOCSIS 1.1
A number of DOCSIS quality of service (QoS) enhancements were added to Cisco IOS Release
12.1(1a)T1 and continue with later releases; these features paralleled some of those that were expected
in the DOCSIS 1.1 specification prior to finalization.
For supported DOCSIS 1.1 QoS features, refer to the “DOCSIS 1.1 Quality of Service Features” section
on page 1-60.
Note These QoS enhancements are in addition to the currently existing QoS traffic shaping and tiered best
effort features.
Concatenation Support Prior to DOCSIS 1.1
DOCSIS Concatenation combines multiple upstream packets into one packet to reduce packet overhead
and overall latency, as well as increase transmission efficiency. Using concatenation, a DOCSIS cable
modem needs to make only one bandwidth request for a concatenated packet, as opposed to making a
different bandwidth request for each individual packet; this technique is especially effective for
burst-intensive real-time traffic, such as voice calls.
Concatenation is enabled by default for current cable modem cards (see the “Cable Modem Cards”
section), but can be disabled with the Cisco IOS command no cable upstream number concatenation
interface. The show controller command displays whether concatenation is enabled on an interface.
Note Concatenation is supported only with cable modems that support DOCSIS concatenation.
Embedded Client Signaling (dynamic SIDs)
Supports the dynamic creation, configuration, and deletion of Service Identifiers (SIDs) to accommodate
different classes of service. This allows cable modems to request high-priority or high-bandwidth data
streams as needed, such as when a VoIP call is made.
Note Dynamic SIDs can be used only with cable modems that also support this feature. Otherwise, cable
modems must use the static SIDs supported in previous releases.
IP Precedence-Based Rate Limiting
In addition to the currently supported traffic shaping techniques, Cisco IOS Release 12.1(1a)T1 supports
a new configuration field that associates a maximum bandwidth (in kbps) with a particular setting of the
IP type of service (ToS) bits. This can be used to ensure that certain traffic, such as data, does not exceed
a preset rate limit and thereby interfere with higher-priority real-time traffic, such as VoIP calls.
Support for Unsolicited Grants
New fields in the DOCSIS configuration file can be used so that when a cable modem requests a voice
or fax SID, the MAC scheduler on the Cisco uBR7200 series router schedules fixed periodic slots on the
upstream for that traffic flow. The cable modem does not have to contend for these slots, and because
the Cisco
uBR7200 series router controls the timing of the slots, it has a very precise control over
potential delay and jitter. This provides a Constant Bit Rate (CBR) traffic flow for real-time traffic such
as voice and fax calls.
Page 71

1-53
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
In addition, the Cisco uBR7200 series router can create QoS profiles for G.711 fax traffic and G.729
voice traffic. These profiles can be customized with the scheduling parameters required for the G.711
and G.729 CODECs being used at the subscriber's site.
DOCSIS 1.0 ToS Overwrite
Cisco IOS release 12.3(17a)BC2 introduces support for the DOCSIS 1.0 Type of Service (ToS)
Overwrite feature. Currently, ToS overwrite requires the creation of static cable QoS profiles, which are
then assigned to the ToS fields. This implementation works well if only a few different service types are
offered. However, scalability issues arise when large numbers of service types are presented; each
requiring a static QoS profile in order to perform ToS overwrite.
The Default DOCSIS 1.0 ToS Overwrite feature eliminates the need to create multiple QoS profiles in
order to perform type-of-service (ToS) overwrite by automatically bounding all DOCSIS 1.0 Cable
Modem (CM) created profiles to a default ToS overwrite.
DOCSIS Customer Premises Equipment Configurator
DOCSIS CPE Configurator V2.0.4
The DOCSIS specification requires that a DOCSIS-compliant modem download a DOCSIS
configuration file during its power-on or reset sequence. This file must be in the format described in the
DOCSIS Radio Frequency Specification (SP-RFI-IOS-991105).
The DOCSIS Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) Configurator V2.0.4 provides you with a Web-based
graphical user interface (GUI) that allows you to collect information needed to generate and download
configuration files for DOCSIS or EuroDOCSIS CMs and STBs.
There are two versions of the Cisco DOCSIS CPE Configurator V2.0.4:
• Cisco Connection Online (CCO) version (HTML-based). This Web-based, free-of-charge version
needs no installation at the customer site, and is viewable at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/netmgtsw/ps819/products_user_guide09186a008017472
6.html.
• Desktop (Java-based) version. This stand-alone, desktop version gives operators flexibility in
supporting NOC and remote subscriber site usage, and is viewable at this online location:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/cpe-conf.
Refer to the following document for additional information about CPE Configurator V2.0.4:
• CMTS Configuration FAQ, Document ID: 12180
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk804/technologies_q_and_a_item09186a00800a4ae5.shtm
l
DOCSIS CPE Configurator V3.2
Cisco has developed the DOCSIS CPE Configurator tool Version 3.2 that allows to configure
DOCSIS
1.1 specific features like upstream and downstream service flows, upstream and downstream
Packet Classification, and Payload Header Suppression.
If you are a registered user and are logged in to Cisco.com, you can download the stand-alone
DOCSIS
CPE Configurator tool Version 3.2 at this online location:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/cpe-conf.
Refer to the following document for additional information about the DOCSIS CPE Configurator V3.2,
which is available to
registered, logged in users only.
Page 72

1-54
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
• Building DOCSIS 1.0 Configuration Files Using Cisco DOCSIS Configurator, Document ID: 16480
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/customer/tech/tk86/tk168/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094d00.shtml
Enhanced Rate Bandwidth Allocation (ERBA) Support for DOCSIS 1.0 Cable Modems
Cisco IOS release 12.3(13a)BC introduces Enhanced Rate Bandwidth Allocation (ERBA) support for
DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems and the Cisco uBR7200 series router. ERBA allows DOCSIS1.0 modems to
burst their temporary transmission rate up to the full line rate for short durations of time. This capability
provides higher bandwidth for instantaneous bandwidth requests, such as those in Internet downloads,
without having to make changes to existing service levels in the QoS Profile.
This feature enables MSOs to set the DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems burst transmissions, with mapping to
overriding DOCSIS
1.1 QoS profile parameters on the Cisco CMTS. DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems require
DOCSIS 1.0 parameters when registering to a matching QoS profile. This feature enables maximum
downstream line rates, and the ERBA setting applies to all cable modems that register to the
corresponding QoS profile.
Note QoS definitions must previously exist on the Cisco CMTS headend to support this feature.
ERBA for DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems is supported with these new or enhanced commands or keywords
in Cisco IOS release 12.3(13a)BC:
• cable qos pro max-ds-burst burst-size
• show cable qos profile n [verbose]
To define ERBA on the downstream for DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems, use the cable qos promax-ds-burst
command in global configuration mode. To remove this ERBA setting from the QoS profile, use the no
form of this command.
cable qos pro max-ds-burst burst-size
no cable qos pro max-ds-burst
Syntax Description
To display ERBA settings as applied to DOCSIS 1.0 cable modems and QoS profiles on the Cisco
CMTS, use the show cable qos profile command in Privileged EXEC mode.
The following example of the cable qos profile command in global configuration mode illustrates
changes to the cable qos profile command. Fields relating to the ERBA feature are shown in bold for
illustration:
Router(config)# cable qos pro 10 ?
grant-interval Grant interval
grant-size Grant size
guaranteed-upstream Guaranteed Upstream
max-burst Max Upstream Tx Burst
max-ds-burst Max Downstream Tx burst (cisco specific)
max-downstream Max Downstream
max-upstream Max Upstream
name QoS Profile name string (cisco specific)
priority Priority
privacy Cable Baseline Privacy Enable
tos-overwrite Overwrite TOS byte by setting mask bits to value
burst-size The QoS profile’s downstream burst size in bytes.
Page 73

1-55
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
The following example of the show cable qos profile command illustrates that the maximum
downstream burst has been defined, and is a management-created QoS profile:
Router# show cable qos pro
ID Prio Max Guarantee Max Max TOS TOS Create B IP prec.
upstream upstream downstream tx mask value by priv rate
bandwidth bandwidth bandwidth burst enab enab
1 0 0 0 0 0 0xFF 0x0 cmts(r) no no
2 0 64000 0 1000000 0 0xFF 0x0 cmts(r) no no
3 7 31200 31200 0 0 0xFF 0x0 cmts yes no
4 7 87200 87200 0 0 0xFF 0x0 cmts yes no
6 1 90000 0 90000 1522 0xFF 0x0 mgmt yes no
10 1 90000 0 90000 1522 0x1 0xA0 mgmt no no
50 0 0 0 96000 0 0xFF 0x0 mgmt no no
51 0 0 0 97000 0 0xFF 0x0 mgmt no no
The following example illustrates the maximum downstream burst size in sample QoS profile 10 with
the show
cable qos prof verbose command in privileged EXEC mode:
Router# show cable qos pro 10 ver
Profile Index 10
Name
Upstream Traffic Priority 1
Upstream Maximum Rate (bps) 90000
Upstream Guaranteed Rate (bps) 0
Unsolicited Grant Size (bytes) 0
Unsolicited Grant Interval (usecs) 0
Upstream Maximum Transmit Burst (bytes) 1522
Downstreamam Maximum Transmit Burst (bytes) 100000
IP Type of Service Overwrite Mask 0x1
IP Type of Service Overwrite Value 0xA0
Downstream Maximum Rate (bps) 90000
Created By mgmt
Baseline Privacy Enabled no
Usage Guidelines If a cable modem registers with a QoS profile that matches one of the existing QoS profiles on the Cisco
CMTS, then the maximum downstream burst size, as defined for that profile, is used instead of the
default DOCSIS QoS profile of 1522.
For example, a DOCSIS 1.0 configuration that matches QoS profile 10 in the previous examples would
be as follows:
03 (Net Access Control) = 1
04 (Class of Service Encodings Block)
S01 (Class ID) = 1
S02 (Maximum DS rate) = 90000
S03 (Maximum US rate) = 90000
S06 (US burst) = 1522
S04 (US Channel Priority) = 1
S07 (Privacy Enable) = 0
The maximum downstream burst size (as well as the ToS overwrite values) are not explicitly defined in
the QoS configuration file because they are not defined in DOCSIS. However, because all other
parameters are a perfect match to profile 10 in this example, then any cable modem that registers with
these QoS parameters has a maximum downstream burst of 100000 bytes applied to it.
For further illustration, consider a scenario in which packets are set in lengths of 1000 bytes at 100
packets per second (pps). Therefore, the total rate is a multiplied total of 1000, 100, and 8, or 800kbps.
Page 74

1-56
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
To change these settings, two or more traffic profiles are defined, with differing downstream QoS
settings as desired.
Table 11 provides two examples of such QoS profiles for illustration:
In this scenario, both QoS profiles are identical except for the max-ds-burst size, which is set to 5000 in
QoS profile 101 and 5000 in QoS profile 102.
Optimal Settings for DOCSIS 1.0 Downstream Powerburst
DOCSIS allows the setting different token bucket parameters for each service flow, including the token
bucket burst size. When burst sizes are closer to 0, QoS is enforced in a stricter manner, allowing a more
predictable sharing of network resources, and as a result easier network planning.
When burst sizes are larger, individual flows can transmit information faster (lower latency), although
the latency variance can be larger as well.
For individual flows, a larger burst size is likely to be better. As long as the system is not congested, a large
burst size reduces the chances of two flows transmitting at the same time, because each burst is likely to take
less time to transmit. However, as channel bandwidth consumption increases, it is probably that large burst
traffic would exceed the thresholds of buffer depths, and latency is longer than with well shaped traffic.
For additional information about the cable qos profile command and configuring QoS profiles, refer to
the following documents on Cisco.com:
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
• DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_docs.html
DOCSIS 1.0+ Feature Support
In response to the limitations of DOCSIS 1.0 in handling real-time traffic, such as voice calls,
Cisco
created the DOCSIS 1.0+ extensions to provide the more important QoS enhancements that were
expected in DOCSIS 1.1. The main enhancements provide basic Voice-over IP (VoIP) service over the
DOCSIS link, support for dynamic creation and teardown of flows during voice calls, support for one
new unsolicited grant service (UGS) slot scheduling mechanism for voice slots, and per IP-precedence
rate shaping on the downstream. In particular, the Cisco
DOCSIS 1.0+ extensions include the
DOCSIS
1.1 features described in this section:
• Concatenation for DOCSIS 1.0+, page 1-57
• Dynamic MAC messages, page 1-57
• Multiple SIDs per Cable Modem, page 1-57
• Separate Downstream Rates, page 1-57
• Unsolicited Grant Service (CBR-scheduling) on the Upstream, page 1-57
Refer to the following online document for additional information about DOCSIS 1.0+ support on the
Cisco uBR7200 Series:
• Frequently Asked Questions on DOCSIS 1.0+
Ta b l e 11 Sample QoS Profiles with Differing ERBA (Maximum Downstream) Settings
QoS Profile Setting QoS Profile 101 QoS Profile 102
Maximum Downstream Transmit Burst (bytes) max-burst 4000 max-burst 4000
Maximum Downstream Burst (bps) max-ds-burst 20000 max-ds-burst 5000
Maximum Downstream Bandwidth max-downstream 100 max-downstream 100
Page 75

1-57
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk86/tk168/technologies_q_and_a_item09186a0080094eb2.sht
ml
Concatenation for DOCSIS 1.0+
Concatenation allows a cable modem to send several packets in one large burst, instead of having to
make a separate grant request for each.
Caution All DOCSIS 1.0 extensions are available only when using a cable modem (such as the Cisco uBR924
cable access router) and CMTS (such as the Cisco
uBR7200 series router) that support these extensions.
The cable modem activates the use of the extensions by sending a dynamic MAC message. DOCSIS 1.0
CMs continue to receive DOCSIS 1.0 treatment from the CMTS.
Dynamic MAC messages
The Dynamic Service Addition (DSA) and Dynamic Service Deletion (DSD) messages allow dynamic
SIDs to be created and deleted on demand so that the bandwidth required for a voice call can be allocated
at the time a call is placed and then freed up for other uses when the call is over.
Multiple SIDs per Cable Modem
This feature creates separate service flows for voice and data traffic. This allows the CMTS and cable
modem to give higher priority for voice traffic, preventing the data traffic from affecting the quality of
the voice calls.
Separate Downstream Rates
This feature provides an ability to provide separate downstream rates for any given cable modem, based
on the IP-precedence value in the packet—This helps separate voice signaling and data traffic that goes
to the same ITCM to address rate shaping purposes.
Unsolicited Grant Service (CBR-scheduling) on the Upstream
This feature helps provide a higher-quality channel for upstream VoIP packets from an Integrated
Telephony Cable Modem (ITCM) such as the Cisco
uBR924 cable access router.
DOCSIS 1.1 Feature Support
DOCSIS 1.1 is the first major revision of the initial DOCSIS 1.0 standard for cable networks. Although
the initial standard provided quality data traffic over the coaxial cable network, the demands of real-time
traffic such as voice and video required many changes to the DOCSIS specification.
This section describes the major enhancements supported on the Cisco uBR7200 series:
• Baseline Privacy Interface Plus (BPI+), page 1-58
• Burst Profile Configuration, page 1-58
• Cable Modulation Profile Default Templates, page 1-58
• DHCP Cable Modem Host ID, page 1-59
• DHCP Client ID/Remote ID Options, page 1-59
• DHCP, Time of Day (ToD) and TFTP Servers, page 1-60
• DOCSIS 1.1 Quality of Service Features, page 1-60
Page 76

1-58
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
• DOCSIS 1.1 Two-way Transmission (Cisco uBR7246VXR Router), page 1-65
• Downstream Channel ID, page 1-65
• Downstream Frequency Override, page 1-65
• Downstream Rate Shaping with IP Type of Service Bits, page 1-66
• Optional Upstream Scheduler Modes, page 1-66
Baseline Privacy Interface Plus (BPI+)
Baseline Privacy Interface Plus (BPI+) is available and supported on the Cisco uBR7200 series with
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)BC1 and subsequent BC1 releases.
DOCSIS 1.1 enhances these security features with Baseline Privacy Interface Plus (BPI+), which
includes the following enhancements:
• Digital certificates provide secure user identification and authentication.
• Key encryption uses 168-bit Triple DES (3DES) encryption that is suitable for the most sensitive
applications.
• 1024-bit public key with Pkcs#1 Version 2.0 encryption.
• Multicast support.
• Secure software download allows a service provider to upgrade a cable modem's software remotely,
without the threat of interception, interference, or alteration.
Additional feature information and configuration guidelines are provided in Configuring DOCSIS
Baseline Privacy Interface on the Cisco uBR7200 Series, available on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/ubr7200/configuration/guide/u72_bpi.html
Burst Profile Configuration
For each modulation/burst profile configuration, Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband routers
support burst profile number, burst profile interval usage code, burst type, preamble length and unique
word length, differential encoding enable/disable, forward error correction (FEC) correctable bytes
value, FEC code word length, scrambler seed value, maximum burst size, guard time size, last code word
shortened/lengthened, and scrambler enable/disable.
Note Multiple burst profiles are supported on the MC11C, MC12C, MC14C, MC16B, and MC16C cable
modem cards. Only one profile is supported on the original MC11-FPGA card.
Cable Modulation Profile Default Templates
Commencing with Release 12.1(3a)EC1 and later releases, the cable modulation-profile global
configuration command has been enhanced with three new options that enable you to quickly create
basic modulation profiles using the default values for each burst type.
To define the modulation profile, use the cable modulation-profile command in global configuration
mode. Use the no form of this command to remove the entire modulation profile or to reset a particular
burst to its default values.
cable modulation-profile profile {mix | qam-16 | qpsk}
no cable modulation-profile profile {mix | qam-16 | qpsk}
Page 77

1-59
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Syntax Description The syntax for the new options is as follows:
DHCP Cable Modem Host ID
This feature—also known as Cable Modem and Host Subnet Addressing—allows the Cisco uBR7200
series universal broadband router to set the GIADDR field of DHCPDISCOVER and DHCPREQUEST
packets with a Relay IP address to help automate the provisioning of cable modems on systems that use
multiple IP subnets.
To modify the GIADDR field of DHCPDISCOVER and DHCPREQUEST packets with a Relay IP
address before they are forwarded to the DHCP server, use the cable dhcp-giaddr command in cable
interface or subinterface configuration mode. To set the GIADDR field to its default, use the no form of
this command.
cable dhcp-giaddr [policy | primary]
no cable dhcp-giaddr
Syntax Description
For additional command information, refer to the Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
on Cisco.com.
DHCP Client ID/Remote ID Options
This feature—also known as the Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) Limitation—allows Cisco
uBR7200 series universal broadband routers to report and limit the number of CPEs that can use the
cable modem to access the cable network.
Note This feature is separate from the cable modem's ability to support multiple CPE devices. For example,
depending on the Cisco IOS software release being used, Cisco uBR900 series cable access routers can
support a maximum of either 3 or 254 CPE devices. Also, by default, a DOCSIS-based cable modem
supports one CPE device, but this can be changed by modifying the MAX CPE parameter in the modem's
DOCSIS configuration file.
profile Specifies the modulation profile number (1-8).
mix Creates a default QPSK/16-QAM mix modulation profile where short and long grant bursts
are sent using 16-QAM, while request, request data, initial ranging, and station maintenance
bursts are sent using QPSK). The burst parameters are set to their default values for each
burst type.
qam-16 Creates a default 16-QAM modulation profile, where all bursts are sent using 16-QAM. The
burst parameters are set to their default values for each burst type.
qpsk Creates a default QPSK modulation profile, where all bursts are sent using QPSK. The burst
parameters are set to their default values for each burst type.
policy (Optional) Selects the control policy, so the primary address is used for CMs and the
secondary addresses are used for hosts.
primary (Optional) Always selects the primary address to be used for the GIADDR field. Primarily
used for the MC16E card and Cisco uBR7100E series routers, for support of EuroDOCSIS.
Page 78

1-60
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
DHCP, Time of Day (ToD) and TFTP Servers
The Cisco uBR7200 series routers support onboard Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
servers, Time of Day (ToD) and TFTP servers. This allows the Cisco uBR7200 series routers to provide
cable modems with IP address information, to supply an RFC 868-compliant time-of-day timestamp, and
to download a DOCSIS configuration file, without requiring separate and external servers.
A DOCSIS-compliant cable modem requires access to three types of servers in order to successfully
come online:
• The first is a DHCP server, which provides the cable modem with an IP address, a subnet mask and
other IP related parameters.
• The second is an RFC868 compliant Time-of-Day Server which lets the modem know what the
current time is. A cable modem needs to know the time in order to be able to properly add accurate
timestamps to its event log.
• The third is a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server from which a cable modem is able to
download a DOCSIS configuration file containing cable modem specific operational parameters.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management features that simplifies CMTS
provisioning. DHCP provides configuration parameters to Internet hosts. DHCP consists of two components:
• a protocol for delivering host-specific configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a host
• a mechanism for allocating network addresses to hosts
DHCP is built on a client/server model, where designated DHCP server hosts allocate network addresses
and deliver configuration parameters to dynamically configured hosts. DHCP supports three
mechanisms for IP address allocation:
• Automatic allocation—DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client.
• Dynamic allocation—DHCP assigns an IP address to a client for a limited period of time (or until
the client explicitly relinquishes the address).
• Manual allocation—The network administrator assigns an IP address to a client and DHCP is used
simply to convey the assigned address to the client.
The Cisco IOS DHCP server feature is a full DHCP server implementation that assigns and manages IP
addresses from specified address pools within the router to DHCP clients. If the Cisco IOS DHCP server
cannot satisfy a DHCP request from its own database, it can forward the request to one or more
secondary DHCP servers defined by the network administrator.
You can configure a DHCP server in the following ways:
• You can configure the DHCP server when using the Cable Interface Setup facility. For additional
information, refer to the
“Configuring the Cisco uBR7200 Series Using the Setup Facility” section
on page 2-17.
• You can configure DHCP services alone, or when configuring ToD and TFTP services. For
additional information, refer to the chapter titled “Configuring DHCP, ToD, and TFTP Services” in
the
Cisco Cable Modem Termination System Feature Guide on Cisco.com.
DOCSIS 1.1 Quality of Service Features
DOCSIS 1.1 modifies the DOCSIS 1.0 specification to provide better performance, in particular for
real-time traffic such as voice calls. The DOCSIS 1.1 specification provides several functional
enhancements over DOCSIS 1.0 coaxial cable networks.
DOCSIS 1.1 features are supported in the Cisco IOS 12.2 BC release train, with additional DOCSIS 1.1
features being supported in certain earlier Cisco IOS 12.1 EC and 12.0 SC release trains.
Page 79

1-61
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Concatenation for DOCSIS 1.1
Concatenation allows a cable modem to send multiple MAC frames in the same time slot, as opposed to
making an individual grant request for each frame. This avoids wasting upstream bandwidth when
sending a number of very small packets, such as TCP acknowledgement packets.
You can turn concatenation on or off. For information about configuring concatenation, refer to
Configuring Concatenation on the Cisco uBR7200 Series Cable Router on Cisco.com.
DOCSIS 1.0 and 1.0+ Cable Modem Support
DOCSIS 1.1 cable modems can coexist with DOCSIS 1.0 and 1.0+ cable modems in the same network—the
Cisco uBR7200 series provides the levels of service that are appropriate for each cable modem.
DOCSIS 1.1 Service Flow Model
DOCSIS 1.1 offers enhanced Quality of Service (QoS) features that give priority for real-time traffic
such as voice and video:
• The DOCSIS 1.0 QoS model (a Service IDs (SID) associated with a QoS profile) has been replaced
with a service flow model that allows greater flexibility in assigning QoS parameters to different
types of traffic and in responding to changing bandwidth conditions
• Multiple service flows per cable modem in either direction due to packet classifiers
• Support for multiple service flows per cable modem allowing a single cable modem to support a
combination of data, voice, and video traffic.
• Greater granularity in QoS per cable modem in either direction, using unidirectional service flows
• Dynamic MAC messages that can create, modify, and tear-down QoS service flows dynamically
when requested by a DOCSIS 1.1 cable modem
Downstream QoS Handling Supported
Downstream QoS handling is compliant with Multimedia Cable Network System (MCNS) requirements.
For additional downstream QoS feature configuration, refer to the DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco uBR7200
Series Universal Broadband Routers feature module on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/DOCSIS11.html
Dynamic MAC Messages
Dynamic Service MAC messages allow dynamic signaling of QoS between the cable modem and the
CMTS. These messages are DOCSIS link layer equivalents of the higher layer messages that create, tear
down, and modify a service flow. These messages are collectively known as DSX messages.
The DSX state machine module on the CMTS manages the several concurrent dynamic service
transactions between cable modems and the CMTS. It include state machine support for all three
DOCSIS1.1 DSX MAC messages:
• Dynamic Service Add (DSA)—This message is used to create a new service flow.
• Dynamic Service Change (DSC)—This message is used to change the attributes of an existing
service flow.
• Dynamic Service Deletion (DSD)—This message is used to delete an existing service flow.
For additional information, refer to the DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband
Routers feature module on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/DOCSIS11.html
Page 80

1-62
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Dynamic Map-Advance
A CMTS administrator can enhance the upstream throughput from a cable modem connected to the
Cisco Cisco
uBR7200 series CMTS. The system employs a new algorithm that automatically tunes the
lookahead time in MAPs, based on several input parameters for the corresponding upstream channel.
The use of dynamic and optimal lookahead time in MAPs significantly improves the per-modem
upstream throughput.
For configuration information, refer to “Configuring the Dynamic Map Advance Algorithm” section on
page 5-7.
Dynamic SID Support
For additional feature information, refer to the document titled Cisco uBR7200 - QoS/MAC
Enhancements for Voice and Fax Calls: DOCSIS 1.0+ on Cisco.com.
Fragmentation (Layer 2)
Layer 2 fragmentation on the upstream prevents large data packets from affecting real-time traffic, such
as voice and video. Large data packets are fragmented and then transmitted in the time slots that are
available between the time slots used for the real-time traffic.
Multiple SID Support
This feature consists of changes made to various show commands to expand service identifier (SID)
information.
• The show cable modem command has been changed to indicate that the SID shown is the primary
SID for each cable modem.
• The show interface cable command has been updated to include the secondary SIDs for each cable
modem.
For additional information, refer to Multiple Service ID Support for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Cable
Router on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0t/12_0t5/feature/guide/multisid.html
Payload Header Suppression (PHS)
Payload Header Suppression (PHS) conserves link-layer bandwidth by suppressing unnecessary packet
headers on both upstream and downstream traffic flows.
To configure PHS, refer to the “Configuring Payload Header Suppression and Restoration” section on
page 3-33. For additional information about configuring these and other DOCSIS features, refer to the
DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Routers feature module on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/DOCSIS11.html
QoS Configuration
QoS configuration information is now included in the Cable Modem Database Manager, which is
described further in the document titled DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband
Routers feature module on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/DOCSIS11.html
QoS Profile Enforcement
This feature allows CMTS operators to override the provisioned service class of a cable modem at the
time of registration with a CMTS local-static quality of service (QoS) profile. CMTS operators can
control the QoS from the CMTS and eliminate any interference from improper local-rate limiting
Page 81

1-63
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
implemented on the cable modem. The CMTS provisions a registering cable modem with a default
Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) 1.0 service class that is assigned by the
operator. This service class has no upstream or downstream rate limits.
When the modem sends data upstream, it makes bandwidth requests without throttling or dropping
packets because of its own rate-policing algorithm. The CMTS does traffic shaping based on the QoS
profile enforced by the operator.
For configuration information, refer to the document titled QoS Profile Enforcement for the Cisco
uBR7200 Series Router on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0t/12_0t4/feature/guide/qospr124.html
Time-of-Day Server
The Time-of-Day (ToD) server enables the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) to provide
a ToD server to the CMs and other customer premises equipment (CPE) devices connected to its cable
interfaces. The cable modem uses the ToD server to get the current date and time to accurately
time-stamp its Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) messages and error log entries.
The Data-over-Cable System Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) 1.0 and 1.1 specifications require that
a DOCSIS cable modem or other CPE device must specify the following time-related fields in the
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request it sends during its initial power-on provisioning:
• Time Offset (option 2)—Specifies the time zone for the cable modem or CPE device, as the number
of seconds that the device's time stamp is offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
• Time Server Option (option 4)—Specifies one or more IP addresses for a ToD server.
• During initial provisioning, a DOCSIS cable modem or CPE device attempts to contact the ToD
server. If successful, the cable device updates its onboard clock with the time offset and timestamp
received from the ToD server. If a ToD server cannot be reached or if it does not respond, the cable
device eventually times out and continues on with the initialization process.
For configuration information, refer to the chapter titled Time of Day Server” in the Cisco Cable Modem
Termination System Feature Guide on Cisco.com.
Trivial File Transfer Protocol Server
A DOCSIS-compliant cable modem requires access to three types of servers in order to successfully
come online:
• A DHCP, Time of Day (ToD) and TFTP Servers provides the cable modem with an IP address, a
subnet mask and other IP related parameters.
• A Time-of-Day Server which lets the modem know what the current time is. A cable modem needs
to know the time in order to be able to properly add accurate timestamps to its event log.
• A Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server from which a cable modem is able to download a
DOCSIS configuration file containing cable modem specific operational parameters. After a cable
modem has attempted to contact a ToD server, it contacts a TFTP server to download a DOCSIS
configuration file. If a binary DOCSIS configuration file can be copied to a Flash device on a Cisco
CMTS, then the router can act as a TFTP server for that file.
Type/Length/Value Parser and Encoder
The Type/Length/Value (TLV) parser and encoder is a new module that handles parsing and encoding
TLVs on the CMTS. All old DOCSIS1.0/1.0+ TLVs are supported. In addition, many new TLVs have
been added in DOCSIS1.1, such as service flow encodings, classifier encodings, and support for PHS
rules. The new TLV parser features are used by different MAC message modules.
Page 82

1-64
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
To display the Type/Length/Value (TLV) encodings parsed by the DOCSIS 1.1 TLV parser/encoder, use
the debug cable tlvs command in privileged EXEC mode. The no form of this command disables
debugging output.
debug cable tlvs
no debug cable tlvs
Refer to the following documents on Cisco.com for additional information about the TLV parser/encoder:
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
• DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Routers
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/DOCSIS11.html
• Cable DOCSIS 1.1 FAQs
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/109/cable_faq_docsis11.shtml
UpstreamAddress Verification
This feature prevents the spoofing of IP addresses. Using the CLI, administrators can determine the IP
and MAC address of a given cable interface, and the SID number that shows the IP and MAC addresses
of all devices learned in the cable interface’s MAC table.
The CMTS verifies the source IP address against the MAC address for the cable modem. Cable modem
and PC IP addresses are verified to ensure that SID and MAC addresses are consistent. A PC behind a
cable interface is assigned an IP address from the DHCP server. If a user on a second PC or cable
interface statically assigns the same IP address to a PC, the Cisco uBR7200 series CMTS reports this.
Using customer databases, administrators can cross-reference the spoofing cable modem and PC to
prevent further usage.
The cable source-verify [dhcp] command (for cable interfaces) specifies that DHCP lease query requests are
sent to verify any unknown source IP address found in upstream data packets. Upstream Address Verification
requires a DHCP server that supports the new LEASEQUERY message type.
Cisco Network Registrar
supports the LEASEQUERY message type in Cisco IOS Release 3.01(T) and later releases.
For configuration information, refer to the “Activating Cable Modem Upstream Address Verification”
section on page 5-4.
Upstream QoS Improvements
Supported QoS models for the upstream are:
• Best-effort—Data traffic sent on a non-guaranteed best-effort basis.
• Committed information rate (CIR)—Guaranteed minimum bandwidth for data traffic.
• Unsolicited grants (UGS)—Constant bit rate (CBR) traffic, such as voice, that is characterized by
fixed size packets at fixed intervals.
• Unsolicited grants with activity detection (USG-AD)—Combination of UGS and RTPS, to
accommodate real time traffic that might have periods of inactivity (such as voice using silence
suppression). The service flow uses UGS fixed grants while active, but switches to RTPS polling
during periods of inactivity to avoid wasting unused bandwidth.
For detailed information about QoS, refer to the DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal
Broadband Routers feature module on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/cmtsfg.html
Upstream QoS Models Supported
Supported QoS models for the upstream are as follows:
Page 83

1-65
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
• Best effort-Data traffic sent on a non-guaranteed best-effort basis
• Committed Information Rate (CIR)—Guaranteed minimum bandwidth for data traffic
• Unsolicited Grants (UGS)—Constant bit rate (CBR) traffic, such as voice, that is characterized by
fixed size packets at fixed intervals
• Real Time Polling (rtPS)—Real Time service flows, such as video, that produce unicast, variable
size packets at fixed intervals
• Unsolicited Grants with Activity Detection (USG-AD)—Combination of UGS and RTPS, to
accommodate real time traffic that might have periods of inactivity (such as voice using silence
suppression). The service flow uses UGS fixed grants while active, but switches to RTPS polling
during periods of inactivity to avoid wasting unused bandwidth.
• Enhanced time-slot scheduling mechanisms to support guaranteed delay/jitter sensitive traffic on the
shared multiple access upstream link
DOCSIS 1.1 Two-way Transmission (Cisco uBR7246VXR Router)
The Cisco uBR7200 series routers allow DOCSIS 1.1 two-way transmission of digital data and Voice
over IP (VoIP) traffic over a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) network. The Cisco
uBR7200 series support IP
routing with a wide variety of protocols and combinations of Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet,
serial, High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI), Packet over SONET (POS) OC-3 and OC-12c, and
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) media.
Downstream Channel ID
This feature allows all cable modems in an HFC network to identify themselves via unique downstream
channel IDs instead of their downstream frequencies.
To configure the downstream channel ID, use the cable downstream channel-id configuration
command. Use the no form of this command to set the downstream channel ID to its default value.
cable downstream channel-id id
no cable downstream channel-id
Syntax DescriptionS
For additional information, refer to the following documents on Cisco.com:
• Configuring Downstream Channel IDs
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0t/12_0t4/feature/guide/downchan.html
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
Downstream Frequency Override
Downstream frequency override allows the CMTS administrator to change the downstream frequency
assigned to a cable modem, overriding the frequency set in the cable modem DOCSIS configuration file.
To enable cable downstream frequency override, use the cable downstream override command in cable
interface configuration mode. To disable the override feature, use the no form of this command.
cable downstream override
no cable downstream override
For additional command information, refer to the following document on Cisco.com:
id Specifies a downstream channel ID. Valid values are from 1 to 255.
Page 84

1-66
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
• Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/cable/command/reference/cbl_book.html
Downstream Packet Classifier
This feature helps to map packets into DOCSIS service flows. The Cisco CMTS supports downstream
IP packet classifiers.
Downstream Packet Scheduler
This module controls all output packet queuing service on the downstream link of each cable interface.
Downstream Rate Shaping with IP Type of Service Bits
Cisco uBR7200 series routers support downstream data rate shaping on a per-modem basis. The Type of
Service (ToS) bits in the IP packet header can be set to specify that packet's class of service, allowing
packets for certain traffic flows (such as VoIP) to be given precedence over packets for other flows (such
as data).
Downstream rate shaping with ToS bits allows you to configure multiple data rates for a given modem.
Also, by specifying a maximum data rate for a particular ToS, you can override the common maximum
downstream data rate. Packets that contain ToS bytes that have not been configured for downstream data
rates continue to use the common data rate limits.
Prior releases set the ToS bits to zero; however, with the advent of virtual private network (VPN) and
QoS applications, it is desirable to copy the ToS bits when the router encapsulates the packets using
generic routing encapsulation (GRE). Thus, intermediate routers between tunnel endpoints can also take
advantage of QoS features such as weighted fair queuing (WFQ) and weighted random early detection
(WRED).
For additional information, refer to the following document on Cisco.com:
• Downstream Rate Shaping with TOS Bits for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Cable Router
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0t/12_0t5/feature/guide/tosbit.html
Optional Upstream Scheduler Modes
With this feature, the user is able to select either Unsolicited Grant Services (UGS) or Real Time Polling
Service (rtPS) scheduling types, as well as packet-based or TDM-based scheduling. Low latency
queueing (LLQ) emulates a packet-mode-like operation over the Time Division Multiplex (TDM)
infrastructure of DOCSIS. As such, the feature provides the typical trade-off between packets and TDM:
with LLQ, the user has more flexibility in defining service parameters for UGS or rtPS, but with no
guarantee (other than statistical distribution) regarding parameters such as delay and jitter.
Restrictions
• To ensure proper operation, Call Admission Control (CAC) must be enabled. When the Low Latency
Queueing (LLQ) option is enabled, it is possible for the upstream path to be filled with so many calls
that it becomes unusable, making voice quality unacceptable. CAC must be used to limit the number
of calls to ensure acceptable voice quality, as well as to ensure traffic other than voice traffic.
• Even if CAC is not enabled, the default (DOCSIS) scheduling mode blocks traffic after a certain
number of calls.
• Unsolicited Grant Services with Activity Detection (UGS-AD) and Non Real Time Polling Service
(nrtPS) are not supported.
Page 85

1-67
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
cable upstream n scheduling type
Use this new command to turn the various scheduling modes on or off, where n specifies the upstream port.
Router(config-if)# [no] cable upstream n scheduling type [ugs | rtps] mode [llq | docsis]
For additional information about scheduler enhancements on the Cisco CMTS, refer to the following
documents on Cisco.com:
• Cisco CMTS Feature Guide — Configuring Upstream Scheduler Modes on the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_schd.html
• DOCSIS 1.1 for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_docs.html
DOCSIS 2.0 Feature Support
This section describes DOCSIS 2.0 enhancements supported on the Cisco uBR7200 series:
• DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support, page 1-67
DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support
Support for DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA on the Cisco uBR7200 series commences with Cisco IOS Release
12.2(15)CX and continues with later releases in the 12.2 CX, 12.2 BC and 12.3 BC release trains.
The Cisco uBR-MC16U/X and Cisco uBR-MC28U/X cards improve the maximum upstream bandwidth
on existing DOCSIS 1.0 and DOCSIS 1.1 cable networks by providing a number of advanced PHY
capabilities that have been specified by the new DOCSIS 2.0 specifications.
The DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support feature incorporates the following advantages and improvements of
DOCSIS 2.0 networks:
• Builds on existing DOCSIS cable networks by providing full compatibility with existing DOCSIS
1.0 and DOCSIS 1.1 cable modems. (The registration response (REG-RSP) message contains the
DOCSIS version number to identify each cable modem's capabilities.)
• Upstreams can be configured for three different modes to support different mixes of cable modems:
–
An upstream can be configured for TDMA mode to support only DOCSIS 1.0 and DOCSIS 1.1
cable modems.
–
An upstream can be configured for A-TDMA mode to support only DOCSIS 2.0 cable modems.
–
An upstream can be configured for a mixed, TDMA/A-TDMA mode, to support both DOCSIS
1.0/DOCSIS 1.1 and DOCSIS 2.0 cable modems on the same upstream.
Note DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA cable modems will not register on a TDMA upstream if an A-TDMA or
mixed upstream exists in the same MAC domain, unless the CMTS explicitly switches the cable
modem to another upstream using an Upstream Channel Change (UCC) message. DOCSIS 1.0
and DOCSIS 1.1 cable modems cannot register on an A-TDMA only upstream.
• A-TDMA mode defines new interval usage codes (IUC) of A-TDMA short data grants, long data
grants, and Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS) grants (IUC 9, 10, and 11) to supplement the existing
DOCSIS 1.1 IUC types
• Increases the maximum channel capacity for A-TDMA upstreams to 30 Mbps per 6 MHz channel.
• A-TDMA and mixed modes of operation provide higher bandwidth on the upstream using new
32-QAM and 64-QAM modulation profiles. In addition, an 8-QAM modulation profile is supported.
Page 86

1-68
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
• Supports a minislot size of 1 tick for A-TDMA operations.
• Increases channel widths to 6.4 MHz (5.12 Msymbol rate).
For additional information on DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support on the Cisco uBR-MC16U/X card, refer
to the section, "DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support" in Configuring the Cisco uBR-MC16U/MC16X Cable
Interface Line Card on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/interfaces_modules/cable/line_cards/ubr16u_x/configuration/gu
ide/mc16uxfm.html#wp1153687
For additional information on DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support on the Cisco uBR-MC28U/X card, refer
to the section, "DOCSIS 2.0 A-TDMA Support" in Configuring the Cisco uBR-MC28U/MC28X Cable
Interface Line Card on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/interfaces_modules/cable/line_cards/ubr28u_x/configuration/gu
ide/mc28uxfm.html#wp1153687
High Availability Features
Several powerful High Availability features are supported on the Cisco uBR7200 series:
• Cisco DDC (Dual DOCSIS Channel), page 1-68
• DRP Server Agent, page 1-69
• DSX Messages and Synchronized PHS Information, page 1-69
• Globally Configured HCCP 4+1 Redundancy on the Cisco uBR7246VXR Router, page 1-69
• HCCP Support for the Cisco uBR-MC16S Cable Interface Line Card, page 1-70
• HCCP N+1 Redundancy, page 1-70
• High Availability Features in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC, page 1-71
• High Availability Support for Encrypted IP Multicast, page 1-71
• Hot-Standby 1+1 Redundancy, page 1-71
• IF Muting for HCCP N+1 Redundancy, page 1-72
Cisco DDC (Dual DOCSIS Channel)
The Cisco Dual DOCSIS Channel (DDC) feature provides redundancy to cable voice and data customers
by using two or three CMTSs with connected RF upstreams and downstreams. Redundancy is provided
by controlling each CMTS on which the cable modems register, and by allowing movement of the cable
modems between the Cisco CMTS systems.
Cisco DDC provides redundancy during planned downtime, especially during software upgrades, with
minimal configuration or control external to the Cisco CMTS.
For information about configuring, maintaining and troubleshooting DDC on the Cisco uBR7246VXR
router, refer to the section “Configuring Dual DOCSIS Channel on the Cisco uBR7246VXR Universal
Broadband Router” in the following document on Cisco.com:
• Cisco Dual DOCSIS Channel (DDC) on the Cisco uBR7246VXR Universal Broadband Router
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/docs_DDC.html
Page 87

1-69
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
DRP Server Agent
The Director Response Protocol (DRP) is a simple User Datagram Protocol (UDP)-based application
developed by Cisco Systems. It enables Cisco's DistributedDirector product to query routers (DRP
Server Agents) in the field for Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP)
routing table metrics between distributed servers and clients. DistributedDirector, a separate standalone
product, uses DRP to transparently redirect end-user service requests to the topologically closest
responsive server. DRP enables DistributedDirector to provide dynamic, scalable, and “network
intelligent” Internet traffic load distribution between multiple geographically dispersed servers.
DRP Server Agents are border routers (or peers to border routers) that support the geographically
distributed servers for which DistributedDirector service distribution is desired. Note that, because
DistributedDirector makes decisions based on BGP and IGP information, all DRP Server Agents must
have access to full BGP and IGP routing tables. For configuration information, refer to the section titled
“Configuring a DRP Server Agent” in the Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide, Release 12.2.
DSX Messages and Synchronized PHS Information
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(17a)BC introduces support for PHS rules in a High Availability environment.
In this release, and later releases, PHS rules synchronize and are supported during a switchover event of
these types:
• Route Processor Redundancy Plus (RPR+), with Active and Standby Performance Routing Engines
(PREs)
• HCCP N+1 Redundancy, with Working and Protect cable interface line cards
For additional information about these enhancements, and related High Availability features, refer to the
following documents on Cisco.com:
• N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/uFGnpls1.html
• Route Processor Redundancy Plus for the Cisco uBR10012 Router
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/cable/ps2209/products_feature_guide09186a00801a24e
0.html
Globally Configured HCCP 4+1 Redundancy on the Cisco uBR7246VXR Router
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(17a)BC introduces support for HCCP 4+1 Redundancy on the
Cisco
uBR7246VXR router. Global configuration makes this High Availability feature quick to
implement in the HCCP redundancy scheme.
In this High Availability configuration, four Working router chassis are supported with one Protect router
chassis. These five routers are further cabled and configured with two Cisco RF Switches in the same
rack using the Cisco Hot Standby Connection to Connection (HCCP) protocol.
HCCP 4+1 Redundancy is a global configuration for all the Cisco uBR7246VXR routers in the scheme.
HCCP 4+1 Redundancy supports the Cisco uBR-MC28U broadband processing engine (BPE),
configured in inter-chassis protection, where the Working and Protect cable interface line cards or BPEs
are operating in different router chassis. A switchover event applies to an entire cable interface line card.
Note 4+1 Redundancy on the Cisco uBR7246VXR router requires that all BPEs in the router be the same.
For additional information about HCCP 4+1 Redundancy, refer to the following document on
Cisco.com:
Page 88

1-70
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
• N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/uFGnpls1.html
HCCP Support for the Cisco uBR-MC16S Cable Interface Line Card
Cisco IOS Release 12.1(7)EC adds support for the Cisco uBR-MC16S cable interface line card when
used in an HCCP 1+1 redundant configuration. Previously, the Cisco uBR-MC16S card could be used
in a redundant configuration only by first disabling its intelligent spectrum management features.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.1(7)EC and later releases, the Cisco uBR-MC16S card can be used as the
protect cable interface or working cable interface, with either another Cisco uBR-MC16S card or a Cisco
uBR-MC16C card. Table 9 shows how a switchover in each of these configurations affects the intelligent
spectrum management features of the Cisco uBR-MC16S card.
For additional information, refer to Advanced Spectrum Management Features for the Cisco
uBR-MC16S Spectrum Management Card on Cisco.com.
Note HCCP support for the Cisco uBR-MC16S card exists only in Cisco IOS Release 12.1(7)EC or later, so
you cannot use the advanced spectrum management features in Cisco IOS Release 12.1(7)CX with
HCCP 1+1 redundant configuration.
HCCP N+1 Redundancy
HCCP N+1 Redundancy is made possible with the addition of the Cisco RF Switch to your cable
headend network. Together with the Cisco uBR10012 and/or the Cisco uBR7246VXR routers, the Cisco
RF Switch provides a fully redundant system that enables cable operators to achieve PacketCable system
availability, minimize service disruptions, and simplify operations.
HCCP N+1 Redundancy is an important step toward high availability on CMTS and telecommunications
networks that use broadband media. HCCP N+1 Redundancy can help limit Customer Premises
Equipment (CPE) downtime by enabling robust automatic switchover and recovery in the event that there
is a localized system failure.
Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2, HCCP N+1 Redundancy adds synchronization
between HCCP Working interface configurations and those inherited upon switchover to HCCP Protect
interfaces. This makes the configuration of both easier and switchover times faster.
Ta b l e 1-12 Switchover Operation for a Cisco uBR-MC16C/Cisco uBR-MC16S Configuration
Working Cable Interface Protect Cable Interface Operation After Switchover
Cisco uBR-MC16C Cisco uBR-MC16S The protect card (Cisco uBR-MC16S) uses the
same upstream frequency as the working card, but
after the system stabilizes, the protect card begins
using the intelligent spectrum management
features of the Cisco uBR-MC16S card, as
configured on the protect CMTS.
Cisco uBR-MC16S Cisco uBR-MC16C The protect card (Cisco uBR-MC16C) uses the same
upstream frequency as the working card. If the
upstream becomes unstable, the Cisco uBR-MC16C
performs only blind frequency hopping.
Cisco uBR-MC16S Cisco uBR-MC16S The protect card initially uses the same upstream
frequency as the working card, but after the system
stabilizes, the protect card continues using the
intelligent spectrum management features of the
Cisco uBR-MC16S card.
Page 89

1-71
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
For additional configuration information about HCCP N+1 Redundancy, refer to HCCP N+1
Redundancy for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System on Cisco.com:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/uFGnpls1.html
High Availability Features in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC removes support for HCCP N+1 Redundancy on the Cisco uBR7200
series routers. Associated configuration, show, and debug commands are not supported in this release.
Note The latest release to support HCCP N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco uBR7200 Series is Cisco IOS release
12.3(9a)BC. When upgrading from this or earlier supporting Cisco IOS releases to Cisco IOS release
12.3(13a)BC, the HCCP configurations are discarded and not retained.
HCCP N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco CMTS is described for earlier releases in this and additional
documents on Cisco.com:
• N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/uFGnpls1.html
High Availability Support for Encrypted IP Multicast
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(17a)BC introduces support for IP Multicast streams during switchover events
in a High Availability environment. This feature is supported for Route Processor Redundancy Plus
(RPR+), N+1 Redundancy, and encrypted BPI+ streams.
For additional information about IP Multicast and High Availability, refer to these documents on
Cisco.com:
• Cisco CMTS Universal Broadband Router MIB Specifications Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/mib/reference/guide/ubrmibv5.html
• Dynamic Shared Secret for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/ubrdmic.html
• IP Multicast in Cable Networks, White Paper
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk828/technologies_case_study0900aecd802e2ce2.shtml
• N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/uFGnpls1.html
Hot-Standby 1+1 Redundancy
The Hot-Standby 1+1 Redundancy feature offers the ability to provide high system availability when
configuring a Cisco uBR7200 series universal broadband router to wait in hot-standby mode to protect
another Cisco uBR7200 series router in case of system failure.
The 1+1 redundancy feature is essential in a residential Voice over IP (VoIP) cable network, since it
provides a three- to five-second automatic system recovery time, thus helping to eliminate “call drops”
in the VoIP cable network. System failure in a non-redundancy (unprotected) deployment results in loss
of all voice calls in progress as well as all voice calls in “setup” phase, because the CMTS requires
human intervention to reconfigure and bring the CMTS back online.
Page 90

1-72
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Configuration for 1+1 redundancy takes place at the cable interface line card interface level. That is,
rather than assigning an entire Cisco uBR7200 series router to support another Cisco uBR7200 series
router, individual interfaces on one Cisco uBR7200 series router are configured to protect individual
interfaces installed in a different Cisco uBR7200 series router.
Note 1+1 redundancy protection takes place only on an inter chassis basis. That is, you cannot protect cable
interfaces on a particular CMTS with cable interfaces installed in the same chassis.
You can configure the system to switch over automatically when the interface state of a cable interface
line card interface moves from “up” to “down.” Alternatively, you can manually force a switch over.
Note Ensure that the same channel ID is configured for both the active and the standby cable router.
For more information on the 1+1 redundancy feature, including information on configuration tasks and
command reference, refer to the document on Cisco.com:
• Hot-Standby 1+1 Redundancy
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/HCCPfeat.html
IF Muting for HCCP N+1 Redundancy
Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2a, Cisco supports IF Muting with both SNMP and
non-SNMP-capable upconverters in HCCP N+1 Redundancy. IF Muting offers the following benefits:
• IF Muting for either type of upconverter significantly increases the N+1 protection schemes that are
available for Cisco CMTS headends.
• IF Muting offers the additional benefit of being faster than RF Muting.
• IF Muting is enabled by default. The Cisco CMTS automatically enjoys the benefits and availability
of IF Muting.
For additional information about IF Muting and configuring HCCP N+1 Redundancy, refer to the
following document on Cisco.com:
• HCCP N+1 Redundancy for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/uFGnpls1.html#wp1049303
Intercept Features
The Cisco uBR7200 Series supports several intercept features through multiple Cisco IOS release trains:
• Access Control List Support for COPS Intercept, page 1-72
• Cable Monitor Enhancements, page 1-73
• COPS TCP Support for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System, page 1-74
• Service Independent Intercept (SII) Support on the Cisco uBR7200 Series, page 1-78
Access Control List Support for COPS Intercept
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC introduces enhanced support for Access Control Lists (ACLs) and
associated commands for the Common Open Policy Service (COPS) feature.
Page 91

1-73
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
To configure access control lists (ACLs) for inbound connections to all COPS listener applications on
the Cisco CMTS, user the cops listeners access-list command in global configuration mode. To remove
this setting from the Cisco CMTS, us the no form of this command.
cops listeners access-list {acl-num | acl-name}
no cops listeners access-list {acl-num | acl-name}
Syntax Description
Additional Information
Refer also the Service Independent Intercept (SII) feature in this document. For additional information,
refer to the following documents on Cisco.com:
• Configuring COPS for RSVP, Cisco IOS Versions 12.2 and 12.3
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/qos/configuration/guide/qcfcops_ps1835_TSD_Produ
cts_Configuration_Guide_Chapter.html
• Cable Monitor and Intercept Features for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_cmon.html
• PacketCable and PacketCable Multimedia on the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_pkcb.html
• Cisco PacketCable Primer White Paper
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns341/ns121/ns342/ns343/networking_solutions_white_paper
09186a0080179138.shtml
Cable Monitor Enhancements
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(17a)BC introduces the following enhancements to the cable monitor feature:
• Access Control Lists are now supported on the Cisco uBR-MC5X20U/D and Cisco uBR-MC28U
cable interface line cards
• Unconditional downstream sniffing now enables downstream packets to be monitored, either for
MAC or data packets. This enhancement supports both DOCSIS and Ethernet packet encapsulation.
For additional information about this enhancements to the cable monitor feature, refer to the following
documents on Cisco.com:
• Cable Monitor and Intercept Features on the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_cmon.html
acl-num Alphanumeric identifier of up to 30 characters, beginning with a letter that
identifies the ACL to apply to the current interface.
acl-name Numeric identifier that identifies the access list to apply to the current
interface. For standard access lists, the valid range is 1 to 99; for extended
access lists, the valid range is 100 to 199.
Page 92

1-74
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
Supported Software Features for the Cisco uBR7200 Series
COPS TCP Support for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC introduces optimized support for the Common Open Policy Service
(COPS) feature for the Cisco uBR7200 series routers. This feature supports two new configuration
commands for enabling and setting COPS processes. The COPS feature in Cisco 12.3(13a)BC enables
the following COPS functions:
COPS DSCP Marking for the Cisco CMTS
This feature allows you to change the DSCP marking for COPS messages that are transmitted or received
by the Cisco router. Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) values are used in Quality of Service
(QoS) configurations on a Cisco router. DSCP summarizes the relationship between DSCP and IP
precedence.
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC supports this function with the cops ip dscp command in global
configuration mode.
COPS TCP Window Size for the Cisco CMTS
This feature allows you to override the default TCP receive window size that is used by COPS processes.
This setting can be used to prevent the COPS server from sending too much data at one time.
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC supports this function with the cops tcp window-size command in
global configuration mode.
Note These two commands affect all TCP connections with all COPS servers.
Page 93

1-75
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops ip dscp
cops ip dscp
To specify the marking for COPS messages that are transmitted by the Cisco router, use the cops ip dscp
command in global configuration mode. To remove this configuration, use the no form of this command.
cops ip dscp x
no cops ip dscp
Syntax Description
Defaults • For messages transmitted by the Cisco router, the default DSCP value is 0.
• For incoming connections to the Cisco router, by default, the COPS engine takes the DSCP value
used by the COPS server that initiates the TCP connection.
Usage Guidelines • The cops ip dscp command allows the Cisco router to re-mark the COPS packets for either incoming
or outbound connections.
• This command affects all TCP connections with all COPS servers.
• This command does not affect existing connections to COPS servers. Once you issue this command,
this function is supported only for new connections after that point in time.
x This value specifies the markings with which COPS messages are transmitted. The
following values are supported:
• 0-63—DSCP value ranging from 0-63.
• af11—Use AF11 dscp (001010)
• af12—Use AF12 dscp (001100)
• af13—Use AF13 dscp (001110)
• af21—Use AF21 dscp (010010)
• af22—Use AF22 dscp (010100)
• af23—Use AF23 dscp (010110)
• af31—Use AF31 dscp (011010)
• af32—Use AF32 dscp (011100)
• af33—Use AF33 dscp (011110)
• af41—Use AF41 dscp (100010)
• af42—Use AF42 dscp (100100)
• af43—Use AF43 dscp (100110)
• cs1—Use CS1 dscp (001000) [precedence 1]
• cs2—Use CS2 dscp (010000) [precedence 2]
• cs3—Use CS3 dscp (011000) [precedence 3]
• cs4—Use CS4 dscp (100000) [precedence 4]
• cs5—Use CS5 dscp (101000) [precedence 5]
• cs6—Use CS6 dscp (110000) [precedence 6]
• cs7—Use CS7 dscp (111000) [precedence 7]
• default—Use default dscp (000000)
• ef—Use EF dscp (101110)
Page 94

1-76
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops ip dscp
Examples The following example illustrates the cops ip dscp command with supported command variations:
Router(config)# cops ip dscp ?
<0-63> DSCP value
af11 Use AF11 dscp (001010)
af12 Use AF12 dscp (001100)
af13 Use AF13 dscp (001110)
af21 Use AF21 dscp (010010)
af22 Use AF22 dscp (010100)
af23 Use AF23 dscp (010110)
af31 Use AF31 dscp (011010)
af32 Use AF32 dscp (011100)
af33 Use AF33 dscp (011110)
af41 Use AF41 dscp (100010)
af42 Use AF42 dscp (100100)
af43 Use AF43 dscp (100110)
cs1 Use CS1 dscp (001000) [precedence 1]
cs2 Use CS2 dscp (010000) [precedence 2]
cs3 Use CS3 dscp (011000) [precedence 3]
cs4 Use CS4 dscp (100000) [precedence 4]
cs5 Use CS5 dscp (101000) [precedence 5]
cs6 Use CS6 dscp (110000) [precedence 6]
cs7 Use CS7 dscp (111000) [precedence 7]
default Use default dscp (000000)
ef Use EF dscp (101110)
Additional COPS Information
Cisco 12.3(13a)BC also supports Access Control Lists (ACLs) for use with COPS. Refer to the “Access
Control List Support for COPS Intercept” section on page 1-72.
For additional information about configuring COPS on the Cisco CMTS, refer to the following
documents on Cisco.com:
• Cable Monitor and Intercept Features for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_cmon.html
• Configuring COPS for RSVP
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/qos/configuration/guide/qcfcops_ps1835_TSD_Produ
cts_Configuration_Guide_Chapter.html
• COPS for RSVP
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1t/12_1t1/feature/guide/CopsRSVP.html
Page 95

1-77
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops tcp window-size
cops tcp window-size
To override the default TCP receive window size on the Cisco CMTS, use the cops tcp window-size
command in global configuration mode. This setting allows you to prevent the COPS server from
sending too much data at one time. To return the TCP window size to a default setting of 4K, use the no
form of this command.
cops tcp window-size bytes
no cops tcp window-size
Syntax Description
Defaults The default COPS TCP window size is 4000 bytes.
Usage Guidelines This command does not affect existing connections to COPS servers. Once you issue this command, this
function is supported only for new connections after that point in time.
Examples The following example configures the TCP window size to be 64000 bytes.
Router(config)# cops tcp window-size 64000
The following example illustrates online help for this command:
Router(config)# cops tcp window-size ?
<516-65535> Size in bytes
Additional COPS Information
Cisco 12.3(13a)BC also supports Access Control Lists (ACLs) for use with COPS. Refer to the “Access
Control List Support for COPS Intercept” section on page 1-72.
For additional information about configuring COPS on the Cisco CMTS, refer to the following
documents on Cisco.com:
• Cable Monitor and Intercept Features for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_cmon.html
• Configuring COPS for RSVP
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/qos/configuration/guide/qcfcops_ps1835_TSD_Produ
cts_Configuration_Guide_Chapter.html
• COPS for RSVP
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1t/12_1t1/feature/guide/CopsRSVP.html
bytes This is the TCP window size setting in bytes. This value can range from 516
to 65535 bytes.
Page 96

1-78
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops tcp window-size
Service Independent Intercept (SII) Support on the Cisco uBR7200 Series
The Cisco CMTS supports the Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act (CALEA) for
voice and data. Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC introduces support for Service Independent Intercept
(SII) on the Cisco uBR7200 CMTS. Cisco SII provides a more robust level of the lawful intercept (LI)
options offered in the Packet Intercept feature. Cisco SII is the next level of support for judicially
authorized electronic intercept, to include dial access, mobile wireless, tunneled traffic, and Resilient
Transport Protocol (RTP) for voice and data traffic on the Cisco CMTS.
SII on the Cisco CMTS in Cisco IOS release 12.3(13a)BC includes these functions:
• Packet intercept on specified or unspecified interfaces or ports, including port lists
• Packet intercept on virtual interface bundles
• Corresponding SNMP MIB enhancements for each of these functions, as intercept requests are
initiated a mediation device (MD) using SNMPv3
Note No new CLI commands are provided for this feature in Cisco IOS release 12.3(13a)BC.
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC enables full Multiple Service Operator (MSO) compliance with SII and
LI regulations. Service providers worldwide are legally required to allow government agencies to
conduct surveillance on the service provider's traditional telephony equipment. The objective of the SII
feature is to enable service providers with New World networks that legally allow government agencies
to conduct electronic network surveillance.
Lawful Intercept (LI) describes the process and judicial authority by which law enforcement agencies
conduct electronic surveillance of circuit and packet-mode communications. LI is autho rized by ju dicial
or administrative order and implemented for either voice or data traffic on the Cisco CMTS.
Table 13
lists the differences between packet intercept and SII features
Ta b l e 13 Differences Between Packet Intercept and SII Features
Feature Packet Intercept Service Independent Intercept
Interface Type Cable Any
IP Masks 255.255.255.255 or 0.0.0.0 Any
L4 Ports Any single port or 0-65535 Any port range
Protocol UDP Any
TOS/DSCP Not supported Supported
Page 97

1-79
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops tcp window-size
Additional Information
For additional information, refer to the following documents:
• Configuring COPS for RSVP, Cisco IOS Versions 12.2 and 12.3
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/qos/configuration/guide/qcfcops_ps1835_TSD_Produ
cts_Configuration_Guide_Chapter.html
• Cable Monitor and Intercept Features for the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_cmon.html
• PacketCable and PacketCable Multimedia on the Cisco CMTS
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_pkcb.html
• Cisco PacketCable Primer White Paper
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns341/ns121/ns342/ns343/networking_solutions_white_paper
09186a0080179138.shtml
IP Broadcast and Multicast Features
The Cisco uBR7200 Series supports the following IP broadcast and Multicast feature:
• Multicast QoS Support on the Cisco uBR7246VXR CMTS, page 1-79
Multicast QoS Support on the Cisco uBR7246VXR CMTS
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(13a)BC introduces support for Multicast downstream QoS feature. This feature
t provides the ability to assign static mapping to a multicast group. The Multicast downstream QoS
feature uses the existing infrastructure (DOCSIS 1.1 service flow) to assign a multicast service identifier
(SID) to a multicast group used in the Baseline Privacy Interface (BPI) encryption feature.
When disabled, the Multicast downstream QoS feature does not impact any other features. The multicast
packets to downstream cable interfaces are sent to the default service flow.
This feature is being implemented in response to CSCeg22989 which states, multicast traffic is not
classified to any service flow, and therefore ends up queued on the default service flow. The default
service flow has no specific QoS guarantees assigned to it. So once the interface approaches congestion
level, multicast packets may be dropped.
Restrictions
• The multicast definitions are per-bundle, not per interface. This means that all downstreams in a
bundle share the same multicast to QoS association. The downstreams will create their own service
flows according to the same QoS parameters.
• Multicast to QoS definitions can not be assigned per sub-interface
• Multicast SIDs are not deleted when a group becomes idle (no response to IGMP reports).
• The QoS assignments for a multicast group can not be changed dynamically. If the user wishes to
change them then a new “cable match” command must be configured.
• Multicast QoS is not supported on Multicast Echo on Cisco uBR10012 router.
Page 98

1-80
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops tcp window-size
New and Changed Commands
cable match address
Use the existing “cable match” command to assign QoS to a multicast group, with BPI either enabled or
disabled.
router# cable match address <number>|<name> [service-class <name> [bpi-enable]]
router# no cable match address [<number>|<name> [service-class <name> [bpi-enable]]]
debug cable mcast-qos
Use this command to turn on CMTS Multicast Qos debugging.
router# debug cable mcast-qos
IP Routing Features
The Cisco uBR7200 series router offers you several features to assist with IP routing configuration and
performance.
• Cable ARP Filter Enhancement, page 1-80
• cable intercept Command, page 1-81
• Cable Interface Bundling and Cable Subinterfaces, page 1-82
• Configurable Alternate Termination System Information Messages, page 1-83
• Easy IP (Phase 1), page 1-83
• Fast-Switched Policy Routing, page 1-83
• IP Enhanced IGRP Route Authentication, page 1-84
• IP Network Address Translation/Port Address Translation, page 1-84
• NAT—Support for NetMeeting Directory (Internet Locator Service—ILS), page 1-84
• Router-Port Group Management Protocol, page 1-85
• Supported Protocols on the Cisco uBR7200 Series, page 1-85
Cable ARP Filter Enhancement
The cable arp filter command, introduced with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)BC2b, enables service
providers to filter ARP request and reply packets. This prevents a large volume of such packets from
interfering with the other traffic on the cable network.
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC introduces enhanced command option syntax for the cable arp filter
command, where number and window-size values are optional for reply-accept and request-send
settings.
Page 99

1-81
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops tcp window-size
To control the number of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets that are allowable for each Service
ID (SID) on a cable interface, use the cable arp command in cable interface configuration mode. To stop
the filtering of ARP broadcasts for CMs, use the no form of this command.
cable arp filter {reply-accept number window-size | request-send number window-size}
no cable arp filter {reply-accept | request-send}
default cable arp filter {reply-accept | request-send}
Syntax Description
Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9a)BC also removes a prior caveat with HCCP Protect interfaces. Previously, in
the event of a revert-back HCCP N+1 switchover, manual removal of cable arp filter reply and
cable
arp filter request configurations may have been required afterward on Protect interfaces.
For more information about ARP Filtering, refer to the following document on Cisco.com:
• Cable ARP Filtering
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/cblarpfl.html
cable intercept Command
Use the cable intercept command in cable interface configuration mode to allow the CMTS to forward
all traffic to and from a particular cable modem to a data collector located at particular User Datagram
Protocol (UDP) port. To deactivate this function, use the no form of this command.
cable intercept mac-address ip-address udp-port
no cable intercept mac-address
reply-accept number
window-size
Configures the cable interface to accept only the specified number of ARP
reply packets every window-size seconds for each active Service ID (SID) on
that interface. The cable interface drops ARP reply packets for a SID that
would exceed this number.
• number = (Optional) Number of ARP reply packets that is allowed for
each SID within the window time period. The allowable range is 0 to 20
packets, with a default of 4 packets. If number is 0, the cable interface
drops all ARP reply packets. If not specified, this value uses default.
• window-size = (Optional) Size of the window time period, in seconds, in
which to monitor ARP replies. The valid range is 1 to 5 seconds, with a
default of 2 seconds.
request-send number
window-size
Configures the cable interface to send only the specified number of ARP
request packets every window-size seconds for each active SID on that
interface. The cable interface drops ARP requests for a SID that would
exceed this number.
• number = (Optional) Number of ARP request packets that is allowed for
each SID within the window time period. The allowable range is 0 to 20
packets, with a default of 4 packets. If number is 0, the cable interface
does not send any ARP request packets.
• window-size = (Optional) Size of the window time period, in seconds, in
which to monitor ARP requests. The valid range is 1 to 5 seconds, with
a default of 2 seconds.
Page 100

1-82
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-05
Chapter 1 Overview of Cisco uBR7200 Series Software
cops tcp window-size
The cable intercept command can be used to comply with the United States Federal Communications
Assistance for Law Enforcement Act (CALEA) and other law enforcement wiretap requirements for
voice communications.
Syntax Description
For additional command information, refer to the Cisco IOS CMTS Cable Command Reference Guide.
Cable Interface Bundling and Cable Subinterfaces
Support for cable interface bundling on the Cisco uBR7200 series commences with Cisco IOS Release
12.2(4)XF1 and continues with later Cisco 12.2 BC releases.
To reduce the number of subnets consumed per Cisco CMTS, cable interface bundling is used. Multiple
cable interfaces can share a single IP subnet. An IP subnet is required for each bundle. You can bundle
all cable interfaces on a Cisco CMTS into a single bundle.
Note Cable interface bundling is applicable only in two-way cable configurations. It is not supported in
telco-return configurations.
Using the CLI, first configure a master interface for a cable interface bundle. The master interface has
an IP address assigned and is visible for IP routing functionality. After you configure the master
interface, add additional cable interfaces to the same interface bundle. Those interfaces must not have
an IP address assigned. You can also configure multiple bundle interfaces.
Use the following commands to configure and view cable interface bundles:
[no] cable bundle n master
show cable bundle
Up to four interface bundles can be configured. In each bundle, specify exactly one interface as the
master interface, using the "master" keyword. In the case of a subinterface over a cable bundle, `x' is the
interface number of the bundle master [1]. The subinterface number starts from 1.
Caution Configure an IP address on the master interface only. An attempt to add an interface to a bundle will be
rejected if an IP address is configured and the interface is not specified as a master interface.
When bundling cable interfaces, only the interface configured to be the bundle master is allowed to have
subinterfaces. An interface that has subinterface(s) defined over it will not be allowed to be part of a
bundle. MIB objects on cable interface bundles are not supported as of the date of this publication.
For more information on cable bundling, refer to these documents on Cisco.com:
• Cable Interface Bundling for the Cisco uBR7200 Series Cable Router feature module:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/cable/cmts/feature/guide/ufg_bund.html
• Bundling Cable Interfaces Sample Configuration and Verification, TAC Document ID 44122
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/cable/ps2217/
products_configuration_example09186a00801ae255.shtml
mac-address Specifies the MAC address to be intercepted.
ip-address Specifies the IP address for the destination data collector.
udp-port Specifies the destination UDP port number for the intercept stream at the
data collector. Valid range is 0 to 65535.
 Loading...
Loading...