Cisco 2431 - IAD Router, IAD2431-16FXS, IAD2432-24FXS, IAD2430 Series Software Configuration Manual
Page 1

Cisco IAD2430 Series
Integrated Access Devices
Software Configuration Guide
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO
CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS
MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY
PRODUCTS.
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-4306-03
Page 2

THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network
are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To
You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco
Cisco
Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing,
FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort
MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet,
Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx
and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0809R)
Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems,
logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace,
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2003 - 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Preface vii
To Access Online User Documentation (PDF and HTML Formats) iii-viii
CONTENTS
CHAPTER
1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics 1-1
Identifying Cisco IAD2430 Models 1-1
Cisco IAD2430-24FXS IAD 1-1
Cisco IAD2431-8FXS IAD 1-2
Cisco IAD2431-16FXS IAD 1-3
Cisco IAD2431-1T1E1 IAD 1-3
Cisco IAD2432-24FXS IAD 1-4
Cisco IAD2435-8FXS IAD 1-4
Port Numbering Conventions 1-5
Understanding Cisco IOS Software Basics 1-5
Getting Help 1-6
Command Modes 1-7
Undoing a Command or Feature 1-8
Saving Configuration Changes 1-8
Upgrading to a New Cisco IOS Release 1-8
Cisco IAD2430 Series Deployment Scenarios 1-9
Where to Go Next 1-10
CHAPTER
2 Using the setup Command Facility 2-1
Before Powering On Your Cisco IAD 2-1
The setup Command Facility 2-2
Configuring Global Parameters 2-2
Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters 2-5
Configuring Controller Parameters 2-5
Configuring Fast Ethernet and Serial Interface Parameters 2-5
Fast Ethernet WAN Interface Configuration 2-6
Serial Interface Configuration 2-7
T1/E1 Channelized Mode 2-9
Configuring a 1-Port, 4-Wire 56-kbps DSU/CSU Card 2-11
Choosing Circuit-Switched or Dedicated-Line Service 2-11
Switched Mode 2-12
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
Dedicated Mode 2-12
Completing the Configuration 2-13
CHAPTER
3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface 3-1
Configuring the Hostname and Password 3-2
Verifying the Hostname and Password 3-3
Configuring Fast Ethernet Interfaces 3-4
Configuring Network Clock 3-5
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces 3-7
Configuring Channel Groups on T1/E1 to Support Data 3-8
Configuring Channel Groups on T1/E1 to Support Data Under SHDSL Controller 3-10
Configuring Digital Voice on T1/E1 3-11
Configuring Switch Types for ISDN PRI Q.931 Support 3-12
Configuring DS0 Groups for CAS 3-14
Configuring TDM Cross-Connect 3-16
Configuring TDM to TDM 3-17
Configuring TDM to Analog Voice Port 3-18
Configuring TDM to Physical Serial Interface 3-18
Configuring a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 Serial WAN Interface Card 3-20
Configuring a WIC-1T or WIC-2T Serial WAN Interface Card 3-24
Configuring a VIC2-2FXO or VIC2-4FXO Voice Interface Card 3-24
CHAPTER
Configuring a VIC2-2FXS or VIC2-4FXS Voice Interface Card 3-26
Configuring ATM T1-WAN Ports 3-28
Verifying Your ATM Interface Configuration 3-31
Configuring 1-Port ADSL/SHDSL WAN Interface Card 3-32
Configuration Tasks 3-32
Configuring the ADSL/SHDSL Port on the ADSL and SHDSL WAN Interface Card 3-32
Verifying ATM Configuration 3-35
Configuring a VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE Card 3-36
Saving Configuration Changes 3-38
4 Configuring Voice over IP 4-1
Prerequisites 4-1
Configuring the Voice Interface 4-2
VoIP Configuration Examples 4-4
FXS-to-FXS Connection 4-4
Configuration for IAD-1 4-5
Configuration for Router RLB-w 4-5
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
iv
OL-4306-03
Page 5

Configuration for Router R12-e 4-5
Configuration for IAD-2 4-6
Linking PBX Users with Digital E&M Trunk Lines over T1/E1 CAS 4-6
IAD SJ Configuration 4-7
IAD SLC Configuration 4-7
PSTN Gateway Access Using an FXO Connection 4-8
IAD SJ Configuration 4-8
IAD SLC Configuration 4-9
PSTN Gateway Access Using an FXO Connection in PLAR Mode 4-9
IAD SJ Configuration 4-9
IAD SLC Configuration 4-10
Contents
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples A-1
Sample Configuration: Cisco IAD2435-8FXS A-1
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2430-24FXS A-3
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2431-1T1/E1 with WIC-2T A-6
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO
and QoS A-8
B Formatting the Flash Memory B-1
Formatting Procedures for Flash Memory B-1
Formatting Procedures B-1
Determining the File System on Flash Memory B-1
Formatting Flash Memory as a Class B Flash File System B-3
Formatting Flash Memory as a Class C File System B-4
File and Directory Operations B-5
Operations for Use with Class B Flash File System B-5
Operations for Use with Class C Flash File System B-7
File Operations for Class C Flash File System B-8
Directory Operations for Class C Flash File System B-10
APPENDIX
C Using the ROM Monitor C-1
Entering the ROM Monitor Mode C-1
ROM Monitor Commands C-2
Command Descriptions C-3
Recovering Boot and System Images C-4
Using the xmodem Command C-4
Using the tftpdnld -r Command C-5
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
v
Page 6

I
NDEX
Contents
Configuration Register C-6
Changing the Configuration Register Manually C-6
Changing the Configuration Register Using Prompts C-6
Console Download C-7
Command Description C-7
Error Reporting C-8
Debug Commands C-8
Exiting the ROM Monitor C-9
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
vi
OL-4306-03
Page 7

Preface
This preface describes the objectives, audience, organization, and conventions of this software
configuration guide, and where to get the latest version of this guide.
This preface presents the following major topics:
• Objectives, page vii
• Audience, page vii
• Document Organization, page viii
• Related and Referenced Documents, page viii
Objectives
Audience
• Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page ix
After installing the router, use this guide to complete a basic router configuration using the setup
command facility. This guide also contains information on using the Cisco
other configuration tasks, such as configuring a VoIP interface and other features.
This guide does not provide complete configuration instructions. See the Cisco IOS configuration guides
and command references for detailed configuration instructions.
This publication is designed for the person who will be responsible for configuring your router. This
guide is intended primarily for the following audiences:
• Customers with technical networking background and experience
• System administrators who are familiar with the fundamentals of router-based internetworking, but
who might not be familiar with Cisco
• System administrators who are responsible for installing and configuring internetworking
equipment, and who are familiar with Cisco
IOS software
IOS software
IOS software to perform
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
vii
Page 8
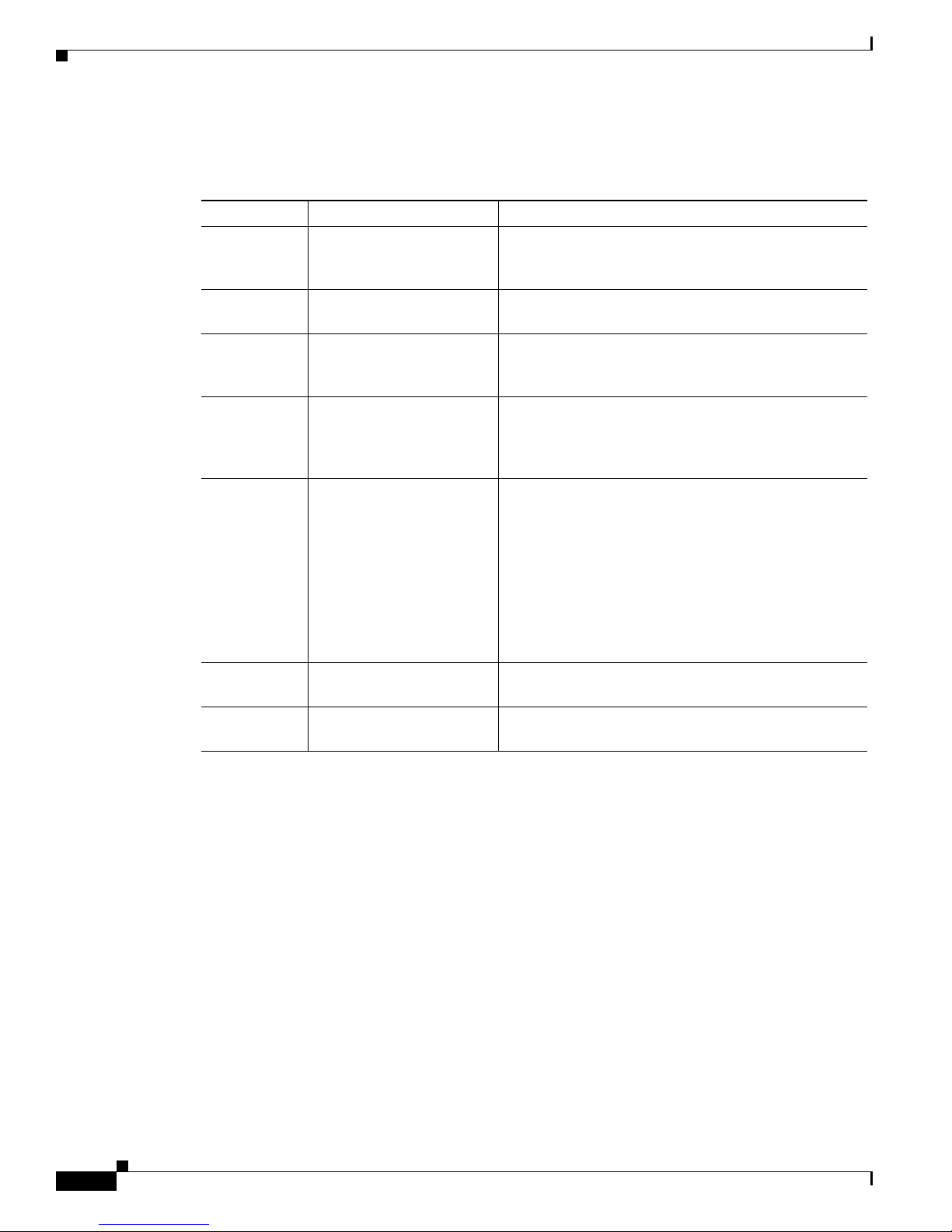
Document Organization
The following table summarizes the major sections of this document.
Chapter Title Description
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface
Numbering and Cisco IOS
Software Basics
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command
Facility
Chapter 3 Configuring with the
Command-Line Interface
Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP Describes how to configure voice network modules
Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series
Configuration Examples
Preface
Provides an overview of the interface numbering
conventions for the Cisco IAD2430 series IADs. Also
provides a basic understanding of Cisco IOS software.
Describes how to use the setup command facility to
configure your router.
Describes how to use the Cisco IOS software
command-line interface (CLI) to configure basic router
functionality.
with digital recEive and transMit (E&M) over T1/E1
CAS, foreign exchange office (FXO), and foreign
exchange station (FXS) interfaces for your router.
Provides a variety of configuration examples:
• Cisco IAD2431-8FXS
• Cisco IAD2431-16FXS
• Cisco IAD2430-24FXS
• Cisco IAD 2431-1T1/E1 with WIC-2T
• Cisco IAD2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO and QoS
• Cisco IAD2435-8FXS
Appendix B Formatting the Flash
Memory
Appendix C Using the ROM Monitor Describes how the ROM monitor works in the
Provides configuration information for the flash
memory.
Cisco
IAD2430 series IAD.
Related and Referenced Documents
The documents described here are available online. To be sure of obtaining the latest information, you
should access the online documentation.
To print a document in its original page format, access the online document, and click the PDF icon.
You can also order printed copies of documents. See the “Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a
Service Request” section on page ix.
To Access Online User Documentation (PDF and HTML Formats)
From Cisco.com at http://www.cisco.com, choose Documentation, > Voice and Unified
Communications, > Voi c e G a te w ay, > Cisco IAD2400 Series Integrated Access Devices.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
viii
OL-4306-03
Page 9

Preface
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s
revised Cisco
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
technical documentation, at:
New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
ix
Page 10

Preface
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
x
OL-4306-03
Page 11

CHAP T E R
1
Understanding Interface Numbering and
Cisco IOS Software Basics
This chapter provides an overview of interface numbering in the Cisco IAD2430 series integrated access
devices (IADs). It also describes how to use the Cisco IOS software commands.
This chapter presents the following major topics:
• Identifying Cisco IAD2430 Models, page 1-1
• Port Numbering Conventions, page 1-5
• Understanding Cisco IOS Software Basics, page 1-5
• Upgrading to a New Cisco IOS Release, page 1-8
• Cisco IAD2430 Series Deployment Scenarios, page 1-9
• Where to Go Next, page 1-10
Identifying Cisco IAD2430 Models
Figure 1-1 shows the front panel of the Cisco IAD2430 series IAD. Figure 1-2 shows the front panel of
the Cisco IAD2435 IAD.
Cisco IAD2430-24FXS IAD
The Cisco IAD2430-24FXS provides 24 analog foreign exchange station (FXS) ports with two
10/100BASE-T ports. The chassis has the following interfaces:
• RJ-21 analog voice interface
• Two 10/100BASE-T ports
• External flash memory
• AC and DC power inputs
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-1
Page 12

Identifying Cisco IAD2430 Models
Figure 1-1 Cisco IAD2430-24FXS Chassis—Front Panel
Figure 1-2 Cisco IAD2435-8FXS Chassis—Front Panel
OK
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
CISCO IAD2400
88839
FE
0/0
0/1
T1/E1
CD
AL
2/0 2/1
2/2
FXS
2/3 2/4 2/5
2/6 2/7
Cisco IAD2431-8FXS IAD
The Cisco IAD2431-8FXS provides eight analog FXS ports, two 10/100BASE-T ports, and one T1/E1
WAN port. The chassis has the following interfaces (see
• RJ-21 analog voice interface
• One T1/E1 port
• One 10/100BASE-T port
• One WIC/VIC slot
• External flash memory
• AC and DC power adapter
Figure 1-3 Cisco IAD2431-8FXS Chassis—Back Panel
Cisco IAD2400 SERIES
231872
Figure 1-3):
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-2
IAD2431-8FXS
88825
OL-4306-03
Page 13

Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
Cisco IAD2431-16FXS IAD
The Cisco IAD2431-16FXS provides 16 analog FXS ports with two 10/100BASE-T ports and one T1/E1
WAN ports. The chassis has the following interfaces (see
• RJ-21 analog voice interface
• One T1/E1 port
• Two 10/100BASE-T ports
• One WIC/VIC slot
• External flash memory
• AC and DC power inputs
Figure 1-4 Cisco IAD2431-16FXS Chassis—Back Panel
Identifying Cisco IAD2430 Models
Figure 1-4):
Cisco IAD2431-1T1E1 IAD
The Cisco IAD2431-1T1E1 provides one T1/E1 connection to a PBX, one T1/E1 WAN port, and two
10/100BASE-T ports. The chassis has the following interfaces (see
• One T1/E1 ports
• Two 10/100BASE-T ports
• One WIC/VIC slot
• External flash memory
• AC and DC power inputs
Figure 1-5 Cisco IAD2431-1T1E1 Chassis—Back Panel
IA
D
2
4
3
1
-16FXS
88826
Figure 1-5):
OL-4306-03
IAD2431-1T1E
1
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
88827
1-3
Page 14

Identifying Cisco IAD2430 Models
Cisco IAD2432-24FXS IAD
The Cisco IAD2432-24FXS provides 24 analog FXS ports, two 10/100BASE-T ports, and two T1/E1
WAN ports. The chassis has the following interfaces (see
• RJ-21 analog voice interface
• Two T1/E1 ports
• Two 10/100BASE-T ports
• One WIC/VIC slot
• External flash memory
• AC and DC power inputs
Figure 1-6 Cisco IAD2432-24FXS Chassis—Back Panel
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
Figure 1-6):
Cisco IAD2435-8FXS IAD
The Cisco IAD2435-8FXS provides eight analog FXS ports, two Fast Ethernet ports, and one T1/E1
WAN port. The chassis has the following interfaces (see
• RJ-21 analog voice interface
• One T1/E1 port
• Two Fast Ethernet ports
• AC and DC power inputs
Figure 1-7 Cisco IAD2435-8FXS Chassis—Back Panel
FXS
WAN
T1
/E
1
IAD2435-8FXS
FastEthernet
0
/1
0
/0
CONSOLE
AU
X
88824
Figure 1-7):
12V
DC
SA
231873
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-4
OL-4306-03
Page 15

Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
Port Numbering Conventions
Figure 1-8 shows the port numbers of the Cisco IAD2432-24FXS IAD. The figure is provided to show
an example of the port numbering conventions.
Figure 1-8 Analog FXS User Interfaces with Metro Ethernet Interface
1
2
3
4
Port Numbering Conventions
5
7
6
8
9
95001
1 RJ-21 connector 4 Flash memory port 7 Fast Ethernet port 0
2 T1/E1 port 0 5 WIC/VIC slot 8 AUX por t
3 T1/E1 port 1 6 Fast Ethernet port 1 9 Console port
Port numbering conventions for all the Cisco IAD2430 series IADs are as follows:
• Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) voice port numbering begins at 2/0 and extends to 2/7, 2/15, or
2/23, depending on the number of voice ports.
• T1/E1 ports are numbered T1 or E1 1/0 and T1 or E1 1/1, from right to left.
• The external flash memory port is numbered CF 0.
• The slot for WAN interface cards (WICs) and voice interface cards (VICs) is numbered slot 0. WIC
and VIC interfaces are numbered by interface with this slot number and an interface number,
beginning with 0, and running from right to left.
• 10/100BASE-T Fast Ethernet ports are numbered Fast Ethernet 0/0 and Fast Ethernet 0/1, from right
to left.
Understanding Cisco IOS Software Basics
This section describes what you need to know about the Cisco IOS software before you configure the
router by using the command-line interface (CLI). This chapter includes the following:
• Getting Help, page 1-6
• Command Modes, page 1-7
• Undoing a Command or Feature, page 1-8
• Saving Configuration Changes, page 1-8
• Where to Go Next, page 1-10
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-5
Page 16

Understanding Cisco IOS Software Basics
Understanding these concepts will save time as you begin to use the CLI. If you have never used
Cisco
to the next chapter.
Note For a comprehensive view of Cisco IOS configuration fundamentals, see the Cisco IOS Configuration
Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 12.4 document.
If you are already familiar with Cisco IOS software, proceed to Chapter 2, “Using the setup Command
Facility.”
Getting Help
Use the question mark (?) and arrow keys to help you enter commands:
• For a list of available commands, enter a question mark:
Router> ?
• To complete a command, enter a few known characters followed by a question mark (with no space):
Router> s?
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
IOS software or if you need a refresher, take a few minutes to read this chapter before you proceed
• For a list of command variables, enter the command followed by a space and a question mark:
Router> show ?
• To redisplay a command you previously entered, press the Up arrow key. You can continue to press
the Up arrow key for more commands.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-6
OL-4306-03
Page 17
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
Command Modes
The Cisco IOS user interface involves different modes. Each command mode permits you to configure
different components on your router. The commands available at any given time depend on which mode
you are currently in. Entering a question mark (?) at the prompt displays a list of commands available
for each command mode.
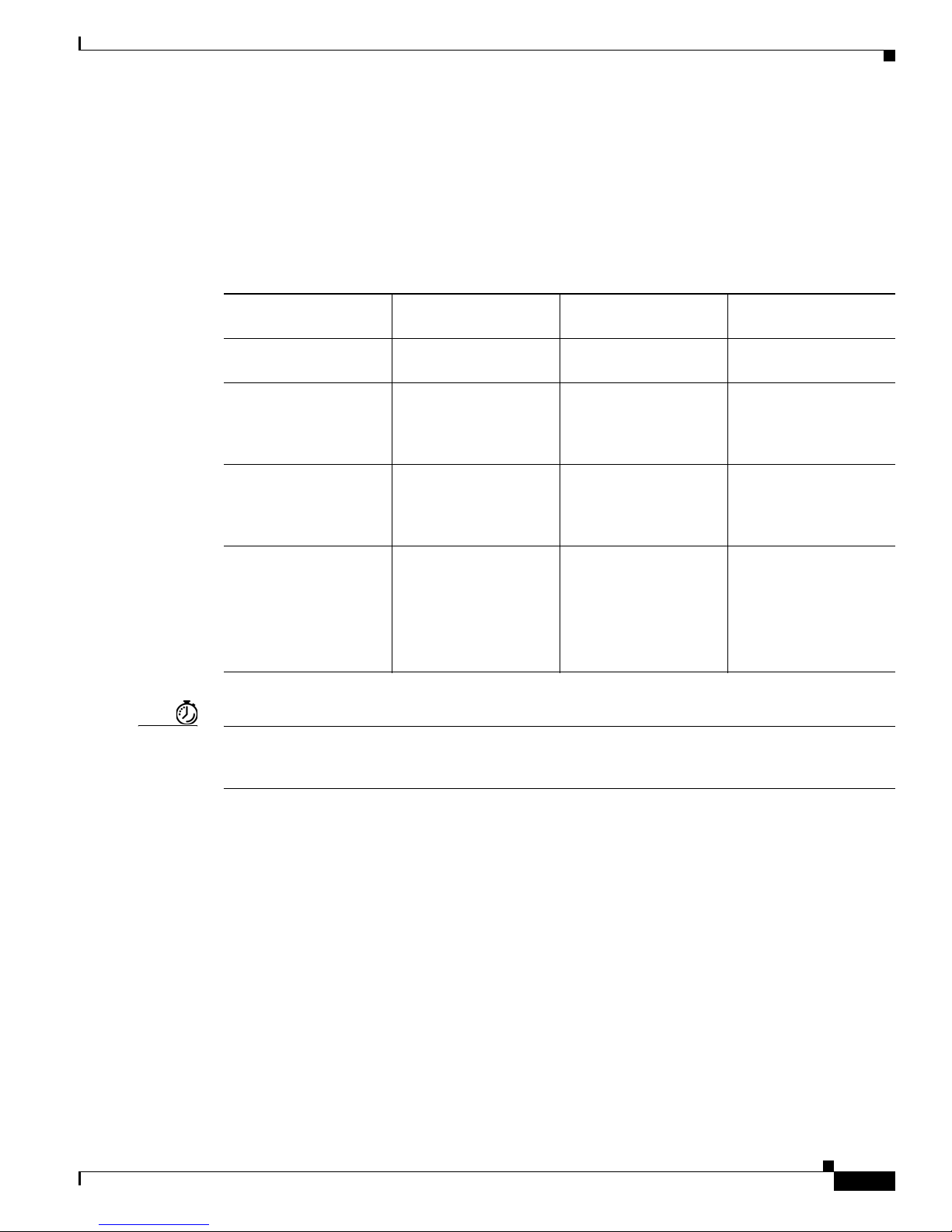
Ta b l e 1-1 Common Command Modes
Command Mode Access Method
User EXEC Log in. Router> Use the logout
Privileged EXEC From user EXEC mode,
Global configuration From the privileged
Interface configuration From the global
Table 1-1 lists the most common command modes.
enter the enable
command.
EXEC mode, enter the
configure terminal
command.
configuration mode,
enter the interface type
number command, such
as interface
serial 0/0.
Understanding Cisco IOS Software Basics
Router Prompt
Displayed
Exit Method
command.
Router# To exit to user EXEC
mode, use the disable,
exit, or logout
command.
Router (config)# To exit to privileged
EXEC mode, use the
exit or end command,
or press Ctrl-Z.
Router (config-if)# To exit to global
configuration mode, use
the exit command.
To exit directly to
privileged EXEC mode,
press Ctrl-Z.
Timesaver Each command mode restricts you to a subset of commands. If you are having trouble entering a
command, check the prompt, and enter the question mark (?) for a list of available commands. You might
be in the wrong command mode or using the wrong syntax.
In the following example, notice how the prompt changes after each command to indicate a new
command mode:
Router> enable
Password:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface serial 0/0
Router(config-if)# line 0
Router(config-line)# controller T1/E1 slot/port <---See second Note below
Router(config-controller)# exit
Router(config)# exit
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
<enable password>
The last message is normal and does not indicate an error. Press Enter to get the Router# prompt.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
OL-4306-03
1-7
Page 18

Upgrading to a New Cisco IOS Release
Note You can press Ctrl-Z in any mode to immediately return to enable mode (Router#), instead of entering
exit, which returns you to the previous mode.
Note In the Cisco IAD2430 series IADs, the controller port syntax is x/y, where
slot can be 0 (where 0 is the T1/E1 controller on a VWIC) or 1 (the onboard T1/E1), and
port can be 0 (the first port) or 1 (the second port).
See the “Port Numbering Conventions” section on page 1-5.
Undoing a Command or Feature
If you want to undo a command you entered or disable a feature, enter the keyword no before most
commands; for example, no ip routing.
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
Saving Configuration Changes
You need to enter the copy running-config startup-config command to save your configuration
changes to NVRAM, so the changes are not lost if there is a system reload or power outage. For example:
Router# copy running-config startup-config
Building configuration...
It might take a minute or two to save the configuration to NVRAM. After the configuration has been
saved, the following appears:
[OK]
Router#
Upgrading to a New Cisco IOS Release
To install or upgrade to a new Cisco IOS release, see Appendix B, “Formatting the Flash Memory.”
Note To simplify network operations and management of Cisco IOS software migration, see the Basics of a
Successful Cisco IOS Software Migration document.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-8
OL-4306-03
Page 19
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
Cisco IAD2430 Series Deployment Scenarios
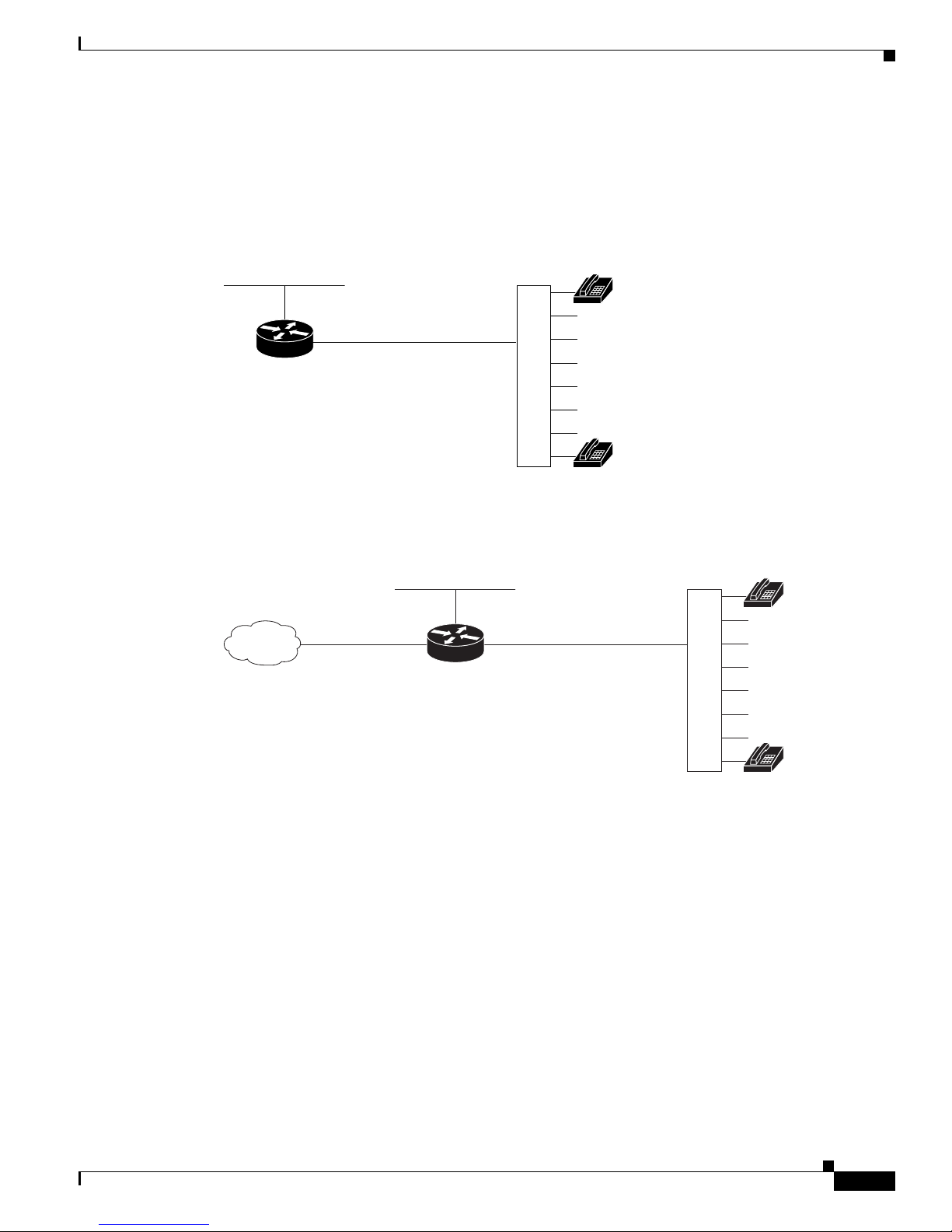
Cisco IAD2430 Series Deployment Scenarios
Figure 1-9 through Figure 1-9 on page 1-9 show some typical deployment scenarios for Cisco IAD2430
series IADs.
Figure 1-9 Analog FXS User Interface with Metro Ethernet Interface
Ethernet
RJ-21
IAD
Cisco IAD model number:
IAD2430-24FXS
Distribution
panel
Analog
telephones
88997
Figure 1-10 T1/E1 WAN Interface with Analog FXS User Interface
Ethernet
WAN
Cisco IAD model number:
IAD2431-8FXS
IAD2431-16FXS
IAD2432-24FXS
IAD2435-8FXS
T1 RJ-21
IAD
Distribution
panel
Analog
telephones
88998
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-9
Page 20
Where to Go Next
Chapter 1 Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
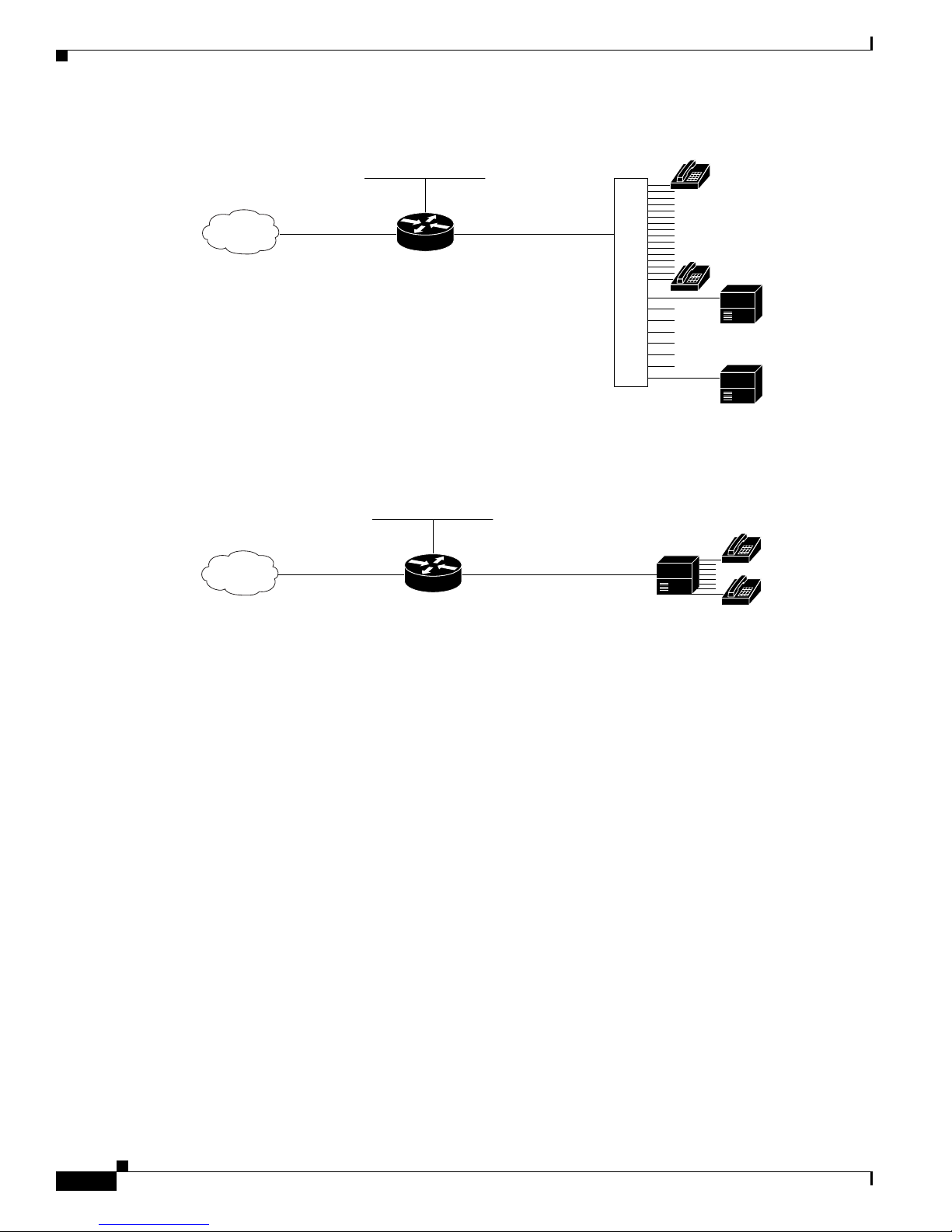
Figure 1-11 T1/E1 WAN Interface with Analog FXS and FXO User Interfaces
Ethernet
WAN
Cisco IAD model number:
Cisco IAD2432-24FXS
with
Cisco VIC2-4FXO interface card
Figure 1-12 T1/E1 WAN Interface with T1 Interface to PBX User Interface
WAN
T1 Multiple FXS and FXO
IAD
Distribution
panel
Ethernet
T1 T1
IAD
24 FXS
voice ports
4 FXO
voice ports
PBX
Analog
telephones
PBX
PBX
88996
Cisco IAD model number:
IAD2431-1T1E1
Where to Go Next
Now that you have learned some Cisco IOS software basics and seen some typical deployment scenarios,
you can begin to configure the router by using the command-line interface (CLI).
Remember that:
• You can use the question mark (?) and arrow keys to help you enter commands.
• Each command mode restricts you to a set of commands. If you have difficulty entering a command,
check the prompt and then enter the question mark (?) for a list of available commands. You might
be in the wrong command mode or be using the wrong syntax.
• To disable a feature, generally enter the keyword no before the command; for example, no ip
routing.
• You need to save your configuration changes to NVRAM so that the changes are not lost if there is
a system reload or power outage.
Go to Chapter 2, “Using the setup Command Facility,” to begin configuring the router.
88995
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
1-10
OL-4306-03
Page 21

CHAP T E R
2
Using the setup Command Facility
This chapter describes how to use the setup command facility to configure your Cisco integrated access
device (IAD). The setup command facility prompts you to enter information needed to start a router
functioning quickly. The facility steps you through a basic configuration, including LAN and WAN
interfaces.
This chapter presents the following major topics:
• Before Powering On Your Cisco IAD, page 2-1
• The setup Command Facility, page 2-2
• Configuring Global Parameters, page 2-2
• Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters, page 2-5
• Completing the Configuration, page 2-13
If you prefer to configure the router manually or if you wish to configure a module or interface that is
not included in the setup command facility, proceed to “
Command-Line Interface,” for step-by-step instructions.
If you prefer to configure the router by using AutoInstall, see the Using AutoInstall to Remotely
Configure Cisco Networking Devices document.
Chapter 3, “Configuring with the
Before Powering On Your Cisco IAD
Before you power on your Cisco IAD and begin to use the setup command facility, follow these steps:
Step 1 Set up the hardware as described in the hardware installation documents for your Cisco IAD.
Step 2 Configure your PC terminal emulation program for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
Step 3 Determine which network protocols you are supporting.
Step 4 Determine the following for each network protocol:
• Addressing plan
• Which WAN protocols you will run on each interface (for example, Frame Relay [FR], High-Level
Data Link Control [HDLC], X.25, and so on)
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-1
Page 22

The setup Command Facility
The setup Command Facility
The setup command facility is displayed in your PC terminal emulation program window.
To create a basic configuration for your Cisco IAD, do the following:
• Complete the steps in the “Configuring Global Parameters” section on page 2-2.
• Complete the steps in the “Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters” section on page 2-5
that apply to your Cisco IAD and network.
• Complete the steps in the “Completing the Configuration” section on page 2-13.
Note If you make a mistake while using the setup command facility, you can exit and run the facility again.
Press Ctrl-C, and enter setup at the enable mode prompt (Router#).
Configuring Global Parameters
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
Step 1 Power on the Cisco IAD.
Note To power on the Cisco IAD2435 IAD, plug in the external power supply.
Messages begin to appear in your terminal emulation program window.
Caution Do not press any keys on the keyboard until the messages stop. Any keys pressed during this time are
interpreted as the first command typed when the messages stop, which might cause the Cisco IAD to
power off and start over. It takes a few minutes for the messages to stop.
The messages look similar to the following example.
Note Much of the following example is largely for a Cisco IAD2431-1T1E1 IAD. The messages vary,
depending on the Cisco
IOS software release, the interface modules in your Cisco IAD, and the
feature set you select. In addition, the word “Router” is the default prompt, and may appear
elsewhere; interpret this word as meaning “Cisco IAD.” The screen displays in this section are
for reference only and might not exactly match the messages on your console.
Also, although you see the interfaces of onboard and installed T1 controllers and installed serial
interface cards (such as the WIC-2T), you do not see the interfaces of installed voice interface
cards.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
System Bootstrap, Version 12.4(20080418:075150)
[BLD-iad.IAD_APRIL18_POST_SYNC_BUILD_UBLDIT-for_gopasaha 102], DEVELOPMENT SOFTWARE
Copyright (c) 1994-2008 by cisco Systems, Inc.
C2431 platform with 262144 Kbytes of main memory
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-2
OL-4306-03
Page 23

Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
Upgrade ROMMON initialized
program load complete, entry point: 0x80020000, size: 0x18d54b8
Self decompressing the image :
##########################################################################################
##########################################################################################
################################# [OK]
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is
subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c) of the Commercial Computer Software - Restricted
Rights clause at FAR sec. 52.227-19 and subparagraph
(c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer
Software clause at DFARS sec. 252.227-7013.
cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, California 95134-1706
Cisco IOS Software, C2435 Software (C2435-ADVIPSERVICESK9-M), Version
12.4(IAD_APRIL18_POST_SYNC_BUILD.2008-04-17) UBUILDIT Image, CISCO DEVELOPMENT TEST
VERSION
Copyright (c) 1986-2008 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Fri 18-Apr-08 01:58 by gopasaha
Configuring Global Parameters
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United
States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and
use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply
third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption.
Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for
compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you
agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable
to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.
A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at:
http://www.cisco.com/wwl/export/crypto/tool/stqrg.html
If you require further assistance please contact us by sending email to
export@cisco.com.
Cisco IAD2435 (MPC8323E) processor (revision 0x100) with 249856K/12288K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FOC11375MBF
MPC8300 CPU Rev: Part Number 0x8062, Revision ID 0x11
2 FastEthernet interfaces
8 Voice FXS interfaces
256K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
126000K bytes of ATA Flash (Read/Write)
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: y
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-3
Page 24

Configuring Global Parameters
Step 2 When the following message appears, enter yes to begin the initial configuration dialog:
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]:
Note If you answer no to this message, you are prompted to terminate AutoInstall. AutoInstall is a
Note The number of interfaces shown depends on the Cisco IAD2430 series model.
Step 3 When the following message appears, press Enter to see the current interface summary:
First, would you like to see the current interface summary? [yes]:
Any interface listed with OK? value “NO” does not have a valid configuration
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned NO unset up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned NO unset up down
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
procedure that configures a new Cisco IAD based on the configuration of an existing
Cisco IAD.
If you terminate AutoInstall, you enter the Cisco IOS software CLI.
Step 4 Enter a hostname for the Cisco IAD:
Configuring global parameters:
Enter hostname [Router]: IAD2435
The enable secret is a password used to protect access to privileged EXEC and
configuration modes. This password, after entered, becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Step 5 Enter an enable secret password. This password is encrypted (more secure) and cannot be seen when
viewing the configuration:
Enter enable secret:
The enable password is used when you do not specify an enable secret password, with some
older software versions, and some boot images.
Step 6 Enter an enable password that is different from the enable secret password. This password is not
xxxx
encrypted (less secure) and can be seen when viewing the configuration:
Enter enable password:
The virtual terminal password is used to protect access to the router over a network
interface.
Step 7 Enter the virtual terminal password, which prevents unauthenticated access to the router through ports
guessme
other than the console port:
Enter virtual terminal password:
guessagain
Step 8 Respond to the following prompts as appropriate for your network:
Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]: n
Configure bridging? [no]:
Configure IP? [yes]:
Configure RIP routing? [yes]: n
Configure CLNS? [no]:
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-4
OL-4306-03
Page 25

Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
Note If you answer no to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP), you are prompted to configure
Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
From this point on in the setup process, the prompts you see vary, depending on the interface cards
installed in your Cisco IAD.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
The following sections provide examples of the setup steps for cards. See the sections appropriate to
your Cisco IAD.
Configuration examples include the following:
• Configuring Controller Parameters, page 2-5
• Configuring Fast Ethernet and Serial Interface Parameters, page 2-5
• Configuring a 1-Port, 4-Wire 56-kbps DSU/CSU Card, page 2-11
When you complete the setup steps for your interface modules, go to the “Completing the
Configuration” section on page 2-13 for directions on saving your configuration.
Configuring Controller Parameters
Controllers can be either built in or on an interface module.
Configuring controller parameters. Controllers are hardware on the router
that you connect directly to a T1 or E1 line from your Telco. Configure
controllers for such purposes as Primary Rate ISDN(PRI) and/or
Channelized T1 or Channelized E1.
Note: J1 controllers are not configurable in setup mode.
Configuring controller T1 1/0 in pri or channelized mode
Do you want to configure this controller ? [yes]: no
Configuring Fast Ethernet and Serial Interface Parameters
This section provides examples for the following:
• Fast Ethernet WAN Interface Configuration
• Serial Interface Configuration
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-5
Page 26

Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
Fast Ethernet WAN Interface Configuration
This section provides sample steps and configuration for the Fast Ethernet WAN interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface type/number
4. ip address ip address/subnet mask
5. no shutdown
6. end
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Example:
Router# enable
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
interface
type/number
Example:
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 2
Router(config-if)#
ip address
ip address/subnet mask
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.12.2
255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters the configuration mode for a Fast Ethernet WAN
interface on the router.
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the specified Fast
Ethernet interface.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-6
OL-4306-03
Page 27
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
no shutdown
Example:
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
Enables the Fast Ethernet interface, changing its state
from administratively down to administratively up.
Step 6
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Router(config)#
Serial Interface Configuration
This section provides a sample configuration for the 1- or 2-port serial interface on a WAN interface
card (WIC) when it is installed. Enter the values appropriate for your interface card and network.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
The messages you see may vary.
Do you want to configure Serial0/0 interface? [yes]:
Some encapsulations supported are
ppp/hdlc/frame-relay/lapb/atm-dxi/smds/x25
Choose encapsulation type [ppp]:
The “Frame Relay Encapsulation” section on page 2-8 through “SMDS Encapsulation” section on
page 2-9 show the prompts for each encapsulation type. For PPP and High-Level Data Link Control
(HDLC) encapsulation, no further configuration is needed.
No serial cable seen.
Choose mode from (dce/dte) [dte]:
Exits configuration mode for the Fast Ethernet interface
and returns to global configuration mode.
If no cable is plugged into your interface card, you must indicate whether the interface is to be used as
DTE or DCE. If a cable is present, the setup command facility determines the DTE/DCE status. If the
serial cable is DCE, you see the following prompt:
Serial interface needs clock rate to be set in dce mode.
The following clock rates are supported on the serial interface.
0
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
56000, 64000, 72000, 125000, 148000, 500000
800000, 1000000, 1300000, 2000000, 4000000, 8000000
Choose clock rate from above: [2000000]:
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface: 2.0.0.1
Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0] : 255.255.255.0
Class A network is 9.0.0.0, 24 subnet bits; mask is /24
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-7
Page 28

Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
Sample configurations for the following encapsulation types are provided in this section:
• Frame Relay Encapsulation
• LAPB Encapsulation
• X.25 Encapsulation
• SMDS Encapsulation
Frame Relay Encapsulation
The following is an example of a typical Frame Relay encapsulation configuration:
The following lmi-types are available to be set,
when connected to a frame relay switch
[0] none
[1] ansi
[2] cisco
[3] q933a
Enter lmi-type [2]:
Note The setup command facility prompts for the data-link connection identifier (DLCI) number only if you
specify none for the Local Management Interface (LMI) type. If you accept the default or specify
another LMI type, the DLCI number is provided by the specified protocol.
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
LAPB Encapsulation
Enter the DLCI number for this interface [16]:
Do you want to map a remote machine’s IP address to dlci? [yes]:
IP address for the remote interface: 2.0.0.2
Do you want to map a remote machine’s IPX address to dlci? [yes]:
IPX address for the remote interface: 40.1234.5678
Serial interface needs clock rate to be set in dce mode.
The following clock rates are supported on the serial interface.
0
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
56000, 64000, 72000, 125000, 148000, 500000
800000, 1000000, 1300000, 2000000, 4000000, 8000000
choose speed from above: [2000000]: 1200
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface: 2.0.0.1
Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0]:
Class A network is 2.0.0.0, 8 subnet bits; mask is /8
The following is an example of a typical LAPB configuration:
lapb circuit can be either in dce/dte mode.
Choose either from (dce/dte) [dte]:
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-8
OL-4306-03
Page 29

Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
X.25 Encapsulation
The following is an example of a typical X.25 encapsulation configuration:
x25 circuit can be either in dce/dte mode.
Choose from either dce/dte [dte]:
Enter local x25 address: 1234
We will need to map the remote x.25 station’s x25 address
to the remote stations IP/IPX address
Enter remote x25 address: 4321
Do you want to map the remote machine’s x25 address to IP address? [yes]:
IP address for the remote interface: 2.0.0.2
Do you want to map the remote machine’s x25 address to IPX address? [yes]:
IPX address for the remote interface: 40.1234.5678
Enter lowest 2-way channel [1]:
Enter highest 2-way channel [64]:
Enter frame window (K) [7]:
Enter Packet window (W) [2]:
Enter Packet size (must be powers of 2) [128]:
Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
SMDS Encapsulation
The following is an example of a typical SMDS configuration:
Enter smds address for the local interface: c141.5556.1415
We will need to map the remote smds station’s address
to the remote stations IP/IPX address
Enter smds address for the remote interface: c141.5556.1414
Do you want to map the remote machine’s smds address to IP address? [yes]:
IP address for the remote interface: 2.0.0.2
Do you want to map the remote machine’s smds address to IPX address? [yes]:
IPX address for the remote interface: 40.1234.5678
Serial Cisco IOS Commands Generated
The following is an example of the Cisco IOS commands generated by a typical serial configuration:
interface Serial0/0
encapsulation ppp
clock rate 2000000
ip address 2.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
T1/E1 Channelized Mode
The following is an example of a T1 channelized mode configuration using the setup command facility:
The following framing types are available:
esf | sf
Enter the framing type [esf]:
The following linecode types are available:
ami | b8zs
Enter the line code type [b8zs]:
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-9
Page 30
Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
T1 is capable of being configured for channel 1-24
Enter number of time slots [24]: 3
Configure more channel groups? [no]: y
Enter number of time slots [21]: 3
Configure more channel groups? [no]: y
Enter number of time slots [18]: 3
Configure more channel groups? [no]: y
Enter number of time slots [15]:
Configure more channel groups? [no]:
The “PPP Encapsulation” section on page 2-10 through the “SMDS Encapsulation” section on page 2-11
show the prompts and provide examples for configuring each encapsulation type. No further
configuration is needed for HDLC encapsulation.
Sample configuration for the following encapsulation types are provided in this section:
• PPP Encapsulation
• Frame Relay Encapsulation
• LAPB Encapsulation
• SMDS Encapsulation
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
PPP Encapsulation
The following is an example of a typical PPP encapsulation configuration:
Would you like to enable multilink PPP [yes]:
Enter a remote hostname for PPP authentication [Router]:
Enter a password for PPP authentication:
Note The password, which is used by the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
authentication process, is case sensitive and must exactly match the remote router’s password.
Frame Relay Encapsulation
The following is an example of a typical Frame Relay encapsulation configuration:
The following lmi-types are available to be set,
when connected to a frame relay switch
[0] none
[1] ansi
[2] cisco
[3] q933a
Enter lmi-type [2]:
Note The setup command facility prompts for the data-link connection identifier (DLCI) number only if you
specify none for the Local Management Interface (LMI) type. If you accept the default or specify
another LMI type, the DLCI number is provided by the specified protocol.
Enter the DLCI number for this interface [16]:
Do you want to map a remote machine’s IP address to dlci? [yes]:
IP address for the remote interface: 2.0.0.2
Do you want to map a remote machine’s IPX address to dlci? [yes]:
IPX address for the remote interface: 40.1234.5678
Serial interface needs clock rate to be set in dce mode.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-10
OL-4306-03
Page 31

Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
The following clock rates are supported on the serial interface.
0
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
56000, 64000, 72000, 125000, 148000, 500000
800000, 1000000, 1300000, 2000000, 4000000, 8000000
choose speed from above: [2000000]: 1200
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface: 2.0.0.1
Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0]:
Class A network is 2.0.0.0, 8 subnet bits; mask is /8
LAPB Encapsulation
The following is an example of a typical LAPB encapsulation configuration:
lapb circuit can be either in dce/dte mode
Choose either from (dce/dte) [dte]:
SMDS Encapsulation
Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
The following is an example of a typical SMDS encapsulation configuration:
Enter smds address for the local interface: c141.5556.1415
We will need to map the remote smds station's address to the remote stations IP address
Enter smds address for the remote interface: c141.5556.1414
Do you want to map the remote machine's smds address to IP address? [yes]:
IP address for the remote interface: 2.0.0.1
Do you want to map the remote machine's smds address to IP address? [yes]:
IPX address for the remote interface: 40.0060.34c6.90ed
Configuring a 1-Port, 4-Wire 56-kbps DSU/CSU Card
This section describes using the setup command facility to configure a 1-port, 4-wire 56-kbps DSU/CSU
WAN interface card (for example, the WIC-1DSU-T1/E1).
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
Choosing Circuit-Switched or Dedicated-Line Service
The switched-56 WAN interface card is configured for dedicated, or leased-line, service by default, but
it can also be configured for circuit-switched service. Depending on the type of data transmissions you
typically use, you can configure the switched-56 WAN interface card for circuit-switched or
dedicated-line service.
Generally, circuit-switched service is ideal for short-duration data transmissions or as an alternative
route if a dedicated line fails. For example, circuit-switched service is ideal for sending electronic mail
messages or doing such tasks as updating inventory and ordering records from one network database to
another at the end of each day.
Dedicated service is ideal for heavy network traffic. Dedicated service is ideal if you need a constant
network connection or you need connection for more than eight hours per day.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-11
Page 32

Configuring Controller and Interface Parameters
Switched Mode
The following is an example of a 1-port, 4-wire 56-kbps DSU/CSU switched-mode configuration using
the setup command facility:
Do you want to configure Serial0/0 interface? [yes]:
Some encapsulations supported are
ppp/hdlc/frame-relay/lapb/atm-dxi/smds/x25
Choose encapsulation type [ppp]:
Switched 56k interface may either be in switched/Dedicated mode
Choose from either (switched/dedicated) [switched]:
The following switched carrier types are to be set when in switched mode
(at&t, sprint or other)
Choose carrier (at&t/sprint/other) [other]:
Do you want to map the remote machine's ip address in dialer map? [yes]:
IP address for the remote interface : 1.0.0.2
Note The setup command facility asks for only one telephone number for both IP and IPX (if IPX is enabled).
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
Dedicated Mode
Note If internal is selected, speed cannot be set to “auto.” Autosensing is allowed only when the clock source
Please enter the phone number to call : 1234567890
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface: 1.0.0.1
Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0] :
Class A network is 1.0.0.0, 8 subnet bits; mask is /8
The following is an example of a 1-port, 4-wire 56-kbps DSU/CSU dedicated-mode configuration using
the setup command facility:
Do you want to configure Serial0/0 interface? [yes]:
Some encapsulations supported are
ppp/hdlc/frame-relay/lapb/atm-dxi/smds/x25
Choose encapsulation type [ppp]:
Switched 56k interface may either be in switched/Dedicated mode
Choose from either (switched/dedicated) [switched]: dedi
When in dds mode, the clock for sw56 module can either from line/internal.
Choose clock from (line/internal) [line]:
is line.
When in dds mode, the clock for sw56 module can either be from line/internal.
Choose clock from (line/internal) [line]: internal
Warning: internal can be choose only when connected back to back.
Serial interface needs clock rate to be set in dce mode.
The following clock rates are supported on the serial interface.
auto, 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 19.2, 38.4
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-12
OL-4306-03
Page 33

Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
56, 64
choose clock rate from above [56]:
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:
IP address for this interface: 1.0.0.1
Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0] :
Class A network is 1.0.0.0, 8 subnet bits; mask is /8
Completing the Configuration
When you have all the information that the setup command facility has prompted you for, the
configuration appears.
Note For sample configurations, see Appendix A, “Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples.”
To complete your configuration, follow these steps:
Step 1 A setup command facility prompt asks if you want to save this configuration, with the following options:
[0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.
[1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.
[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.
Completing the Configuration
If you answer 0, the configuration information you entered is not saved, and you return to the Cisco IAD
enable prompt (
Router#). Enter setup to return to the System Configuration Dialog.
If you answer 1, you return to setup without saving the configuration.
If you answer 2, the configuration is saved and you are returned to the user EXEC prompt (Router>).
Step 2 When the messages stop appearing on your screen, press Enter to get the Router> prompt.
Step 3 The Router> prompt indicates that you are now at the command-line interface (CLI) and you have just
completed a basic Cisco IAD configuration. However, this is not a complete configuration. At this point
you have two choices:
• Run the setup command facility again and create another configuration. Enter the following:
Router> enable
Password:
Router# setup
• Modify the existing configuration or configure additional features with the CLI as described in
password
Chapter 3, “Configuring with the Command-Line Interface.”
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-13
Page 34

Completing the Configuration
Chapter 2 Using the setup Command Facility
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
2-14
OL-4306-03
Page 35

CHAP T E R
3
Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
This chapter describes how to use the Cisco IOS software command-line interface (CLI) to configure
basic Cisco integrated access device (IAD) functionality.
This chapter presents the following major topics:
• Configuring the Hostname and Password, page 3-2
• Configuring Fast Ethernet Interfaces, page 3-4
• Configuring Network Clock, page 3-5
• Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces, page 3-7
• Configuring a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 Serial WAN Interface Card, page 3-20
• Configuring a WIC-1T or WIC-2T Serial WAN Interface Card, page 3-24
• Configuring a VIC2-2FXO or VIC2-4FXO Voice Interface Card, page 3-24
• Configuring a VIC2-2FXS or VIC2-4FXS Voice Interface Card, page 3-26
• Configuring ATM T1-WAN Ports, page 3-28
• Configuring 1-Port ADSL/SHDSL WAN Interface Card, page 3-32
OL-4306-03
• Configuring a VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE Card, page 3-36
• Saving Configuration Changes, page 3-38
Follow the procedures in this chapter to configure the Cisco IAD manually or, if you wish, to change the
configuration after you have run the setup command facility (see the
section on page 2-2).
This chapter does not describe every configuration possible—only a small portion of the most commonly
used configuration procedures. For advanced configuration topics, see the Cisco
guide and command reference publications. See the
Service Request” section on page -ix.
Note If you skipped Chapter 2, “Using the setup Command Facility,” and you have never configured a
Cisco IAD, return to Chapter 2, “Using the setup Command Facility,” and read it now. The chapter
contains important information that you need for configuring your Cisco IAD.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
“Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a
“The setup Command Facility”
IOS configuration
3-1
Page 36

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring the Hostname and Password
Configuring the Hostname and Password
One of the first configuration tasks is to configure the hostname and set an encrypted password.
Configuring a hostname allows you to distinguish multiple Cisco IADs and routers from each other.
Setting an encrypted password allows you to prevent unauthorized configuration changes.
Note A hostname can be specified only when the router has a DNS server available for hostname resolution.
To configure the hostname and password, perform the following steps.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. hostname
4. enable secret password
5. line-console
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
hostname
Example:
Router(config)# hostname IAD2430
Step 4
enable secret password
Example:
Router(config)# enable secret guessme
6. exec-timeout
7. exit
8. end
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Changes the name of the Cisco IAD to a meaningful
name.
Enters an enable secret password. This password
provides access to privileged EXEC mode. When you
press Enter at the user EXEC prompt
(Router>), you must enter the enable secret password to
gain access to configuration mode. Substitute your
enable secret password for
guessme.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-2
OL-4306-03
Page 37

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
line console
Example:
Router(config)# line console 0
Configuring the Hostname and Password
Enters line configuration mode to configure the console
port. When you enter line configuration mode, the
prompt changes to
Router(config-line)#.
Step 6
exec-timeout
Example:
Router(config-line)# exec-timeout 0 0
Step 7
exit
Example:
Router(config-line)# exit
Step 8
end
Example:
Router(config-if)# end
Verifying the Hostname and Password
To verify that you configured the correct hostname and password, follow these steps:
Step 1 Enter the show config command:
Router(config)# show config
If no input is detected during the interval, the EXEC
facility resumes the current connection. If no
connections exist, the EXEC facility returns the terminal
to the idle state and disconnects the incoming session.
Note To specify no timeout, enter the
exec-timeout
0 0 command.
Exits to global configuration mode.
Returns you to privileged EXEC mode.
OL-4306-03
Using 1888 out of 126968 bytes
!
version XX.X
.
.
.
!
hostname IAD2430
!
enable secret 5 $1$60L4$X2JYOwoDc0.kqa1loO/w8/
.
.
.
Check the hostname and encrypted password displayed near the top of the command output.
Step 2 Exit global configuration mode and attempt to reenter it, using the new enable password:
Router# exit
.
.
.
Router con0 is now available
Press RETURN to get started.
Router> enable
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-3
Page 38

Configuring Fast Ethernet Interfaces
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Password:
Router#
Tip If you are having trouble, ensure the following:
• Caps Lock is off.
• You entered the correct passwords. Passwords are case sensitive.
guessme
Configuring Fast Ethernet Interfaces
To configure a Fast Ethernet interface, use the configuration software provided with your Cisco IAD or
network module, if any. Otherwise, for greatest power and flexibility, use configuration mode (manual
configuration).
Note Before you begin, disconnect all WAN cables from the Cisco IAD to prevent it from running the
AutoInstall process. Whenever you power on the Cisco IAD, if there is a WAN connection on both ends
and the Cisco IAD does not have a valid configuration file stored in NVRAM (for instance, when you
add a new interface), the Cisco IAD tries to run AutoInstall. It can take several minutes for the Cisco
IAD to determine that AutoInstall is not connected to a remote TCP/IP host.
SUMMARY STEPS
This section describes basic Fast Ethernet interface configuration, including enabling the interface and
specifying IP routing. Depending on your own requirements and the protocols you plan to route, you
might also need to enter other configuration commands.
Before you begin configuring the interfaces, make sure to do the following:
• Connect a console to the Cisco IAD.
• Power on the Cisco IAD.
To configure Fast Ethernet interfaces, perform the following steps.
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. ip routing
4. interface type number
5. ip address ip address subnet mask
6. exit
7. Ctrl-z
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-4
OL-4306-03
Page 39

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
ip routing
Example:
Router(config)# ip routing
Step 4
interface
type number
Example:
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
Step 5
ip address
ip address subnet mask
Configuring Network Clock
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enables routing protocols as required for your global
configuration. This example uses IP routing.
Enters interface configuration mode. You have entered
interface configuration mode when the prompt changes
to
Router(config-if)#.
Assigns an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.74.3
255.255.255.0
Step 6
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Step 7
Ctrl-z
Example:
Router# Ctrl-z
Configuring Network Clock
At initialization, all controllers on the Cisco IAD2430 IAD, including onboard T1/E1 or VWIC T1/E1,
participate in the system clock domain. The default network clock algorithm selects one of the
controllers as a default network clock. The default network clock algorithm provides a best estimate of
the clocking system. This is mainly for voice applications to be configured easily after power up.
Cisco recommends that when you power up the system, make sure that network clocks are configured
properly for the applications to work, with consideration for the specific network system requirements.
To view the current primary clock, use the show network-clocks or show run command. Note that the
show network-clocks and show run commands do not display the default network clock, which is
selected by the default network clock algorithm.
Exits to global configuration mode.
Repeat Step 4 through Step 6 if your Cisco IAD has more
than one interface to configure.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring the
interfaces.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-5
Page 40

Configuring Network Clock
SUMMARY STEPS
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
To have the T1/E1 controller participate as a clock source for the Cisco IAD system clock domain and
to make sure it is available as a candidate for a clock selection algorithm, use the following CLI
configuration. If you have data applications that do not require clock participation, use the no form of
the commands.
To configure the network clock, perform the following steps.
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. network-clock-participate slot/port
4. controller {t1 | e1 | j1} slot/port
5. network-clock-participate slot/port
6. network-clock-select priority bri|atm|t1|e1 slot/port
7. network-clock-select priority serial slot/port
8. exit
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
network-clock-participate
Example:
Router(config)# network-clock-participate WIC 0
Step 4
controller t1
9. Ctrl-z
slot/port
slot/port
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters the controller into the system clock domain.
Note The IAD2435 IAD is configured with
network-clock-participate by default. You
cannot remove or configure this default
configuration.
Enters the first part of the VWIC controller at slot 0 into
the system clock domain.
Example:
Router(config)# controller t1 0/2
Step 5
network-clock-participate
slot/port
Example:
Router(config-controller)# controller t1 0/2
Router(config-controller)#
network-clock-participate wic 0
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-6
Enters both parts of the VWIC controller at slot 0 into the
system clock domain.
OL-4306-03
Page 41

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 6
network-clock-select
slot/port
priority
Example:
Router(config)# network-clock-select 1 T1 1/0
Step 7
network-clock-select
priority
Example:
Router(config)# network-clock-select 1 Serial 0/0
Step 8
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Step 9
Ctrl-z
{bri|atm|t1|e1}
serial
slot/port
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Selects the controller as a candidate for the clock
selection algorithm according to the priority entered. Use
either slots 1/0 or 0/0.
In case of a serial interface, selects the serial controller
as a candidate for the clock selection algorithm
according to the priority entered. This applies only when
the serial interface is used for time-division multiplexing
(TDM) connections.
Exits to global configuration mode.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring
interfaces.
Example:
Router#
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
To configure an ISDN PRI, channel-associated signaling (CAS) interface, or a T1/E1 multiflex trunk
interface, use the configuration software provided with your Cisco IAD or network module (if any).
Otherwise, for greatest power and flexibility, use configuration mode (manual configuration). In this
mode, you enter Cisco
This section covers the following topics:
• Configuring Channel Groups on T1/E1 to Support Data
• Configuring Channel Groups on T1/E1 to Support Data Under SHDSL Controller
• Configuring Digital Voice on T1/E1
• Configuring TDM Cross-Connect
Note Before you begin, disconnect all WAN cables from the Cisco IAD to prevent it from running the
AutoInstall process. Whenever you power on the Cisco IAD, if there is a WAN connection on both ends
and the Cisco IAD does not have a valid configuration file stored in NVRAM (for instance, when you
add a new interface), the Cisco IAD tries to run AutoInstall. It can take several minutes for the Cisco
IAD to determine that AutoInstall is not connected to a remote TCP/IP host.
IOS commands at the prompt.
This section describes basic configuration, including enabling the interface and specifying IP routing.
Depending on your own requirements and the protocols that you plan to route, you might need to enter
additional configuration commands.
Before you begin configuring the interfaces, make sure to do the following:
• Connect a console to the Cisco IAD.
• Power on the Cisco IAD.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-7
Page 42

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Configuring Channel Groups on T1/E1 to Support Data
To support data, use the following procedure to configure a new T1/E1 interface for channelized T1/E1
(CT1) or PRI, or to change the configuration of an existing interface.
To configure channel groups on T1/E1 to support data, perform the following steps.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. ip routing
4. controller t1 slot/port
5. clock source line
6. framing t1/e1 controller
7. framing t1/e1 controller
8. linecode {ami|b8zs|hdb3}
9. linecode {ami|b8zs|hdb3}
10. channel-group channel-group-number timeslots range
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
ip routing
Example:
Router(config)# ip routing
Step 4
controller t1
Example:
Router(config)# controller t1 0/2
11. interface type number
12. ip address ip address subnet mask
13. exit
14. Ctrl-z
slot/port
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enables routing protocols as required for your global
configuration. This example uses IP routing.
Selects the CT1, CE1, PRI interface to configure.
Controller numbers vary. See the
“Port Numbering
Conventions” section on page 1-5.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-8
OL-4306-03
Page 43

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
clock source line
Example:
Router(config-controller)# clock source line
Step 6
framing T1/E1 controller
Example:
Router(config-controller)# framing esf
Step 7
framing T1/E1 controller
Example:
Router(config-controller)# framing crc-4
Step 8
linecode {ami|b8zs|hdb3}
Example:
Router(config-controller)# linecode b8zs
Step 9
linecode {ami|b8zs|hdb3}
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Specifies which end of the circuit provides clocking. The
clock source should be set to use internal clocking only
for testing the network or if the full T1/E1 line is used as
the channel group. Only one end of the T1/E1 line should
be set to internal.
Specifies the framing type for T1.
Specifies the framing type for E1.
Specifies the line code format for E1 and the linecode
format for T1.
Specifies the line code format for E1 and the linecode
format for T1.
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Step 13
Step 14
Example:
Router(config-controller)# linecode hdb3
channel-group
range
channel-group-number
timeslots
Example:
Router(config-controller)# channel-group 0
timeslots 1,3-5,7
interface
type number
Example:
Router(config-controller)# interface serial 1/0:0
ip address
ip address subnet mask
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.15.1
255.255.255.0
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Ctrl-z
Specifies the channel group and time slots to be mapped.
For multiflex trunk interfaces, only channel 0 can be
configured.
Note Channel-group number should be different from
DS0-group number and TDM-group number
under the same controller.
Configures each channel group as a virtual serial
interface. Specifies the T1/E1 interface, the unit number,
and the channel group to modify.
Assigns an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
Exits to global configuration mode.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring
interfaces.
Example:
Router#
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-9
Page 44

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Configuring Channel Groups on T1/E1 to Support Data Under SHDSL Controller
To support data under symmetric high bit-rate digital subscriber line (SHDSL) controller, use the
following procedure either to configure a new T1/E1 interface for channelized T1/E1 (CT1) or PRI or
to change the configuration of an existing interface.
Perform the following steps to configure channel groups on T1/E1 to support data under SHDSL
controller.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. ip routing
4. controller dsl slot/port
5. mode {atm|t1|e1)
6. controller t1 slot/port
7. channel-group channel-group-number timeslots range
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
ip routing
Example:
Router(config)# ip routing
Step 4
controller dsl
Example:
Router(config)# controller dsl 2/4
8. interface type number
9. ip address ip address subnet mask
10. exit
11. Ctrl-z
slot/port
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enables routing protocols as required for your global
configuration. This example uses IP routing.
Selects the DSL interface to configure. Controller
numbers vary. See
Port Numbering Conventions,
page 1-5.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-10
OL-4306-03
Page 45

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
mode {atm|t1|e1}
Example:
Router(config-controller)# mode t1
Step 6
controller t1
slot/port
Example:
Router(config)# controller t1 0/2
Step 7
channel-group
range
channel-group-number
Example:
Router(config-controller)# channel-group 1
timeslots 1-24
Step 8
interface
type number
Example:
Router(config-controller)# interface serial 1/0:0
Step 9
ip address
ip address subnet mask
timeslots
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Specifies that the full T1/E1 line is used as the channel
group mode.
Specifies the T1 interface for control.
Specifies the channel group and time slots to be mapped.
Configures each channel group as a virtual serial
interface. Specifies the T1/E1 interface, unit number, and
channel group to modify.
Assigns an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.15.1
255.255.255.0
Step 10
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Step 11
Ctrl-z
Example:
Router#
Configuring Digital Voice on T1/E1
Digital voice is supported by both ISDN and PRI signaling. This section covers the following topics:
• Configuring Switch Types for ISDN PRI Q.931 Support
• Configuring DS0 Groups for CAS
For more information on configuring ISDN voice interfaces, see the Basic ISDN Voice-Interface
Configuration document.
Exits to global configuration mode.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring
interfaces.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-11
Page 46

Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Configuring Switch Types for ISDN PRI Q.931 Support
Perform the following steps to configure Q Signalling (QSIG) signaling support on Cisco IAD2430
series IADs.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. isdn switch-type primary
4. controller t1/e1 slot/port
5. pri-group timeslots range
6. isdn protocol-emulate {user|network}
7. no line-power
8. isdn incoming-voice voice
9. exit
10. Ctrl-z
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
isdn switch-type primary
Example:
Router(config)# isdn switch-type primary-net5
Step 4
controller t1/e1
Example:
Router(config)# controller t1 0/2
slot/port
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
(Optional; see note.) Selects a service provider switch
type that accommodates PRI.
Note You can configure the ISDN switch type in either
global or interface configuration mode.
If you configure the switch type here, specify the switch
type for all PRI ports.
If you configure the switch type on a single interface,
specify the switch type for that interface. The switch type
specified for any individual interface overrides the
globally specified switch type.
Enters controller configuration mode for the controller at
the specified slot/port location. Valid values for slot and
port are 0 and 1.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-12
OL-4306-03
Page 47

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
pri-group timeslots
range
Example:
Router(config-if)# pri-group timeslots 2-6
Step 6
isdn protocol-emulate {user|network}
Example:
Router(config-if)# isdn protocol-emulate network
Step 7
no line-power
Example:
Router(config-if)# no line-power
Step 8
isdn incoming-voice
voice
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Configures the PRI group for T1 to carry voice traffic.
For T1, available time slots are from 1 through 23.
You can configure the PRI group to include all available
time slots, or you can configure a select group of time
slots for the PRI group.
Note You can configure a maximum of 8 time slots in
a PRI group on the IAD2435 IAD.
Configures the ISDN interface to serve as either the
primary slave or the primary master. For this command,
user specifies slave, and network specifies master.
Turns on or turns off the power supplied from an
NT-configured port to a TE device. The default is no
line-power.
Routes incoming ISDN voice calls to the voice module.
Step 9
Step 10
Example
Example:
Router(config-if)# isdn incoming-voice voice
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Ctrl-z
Example:
Router#
The following example shows a typical ISDN PRI configuration:
controller T1 0/0
channel-group 0 timeslots 1-20 speed 64
pri-group timeslots 21-24
!
voice-port 0/0:23
!
voice-port 0/1/0 << FXS
!
dial-peer voice 1 pots
direct-inward-dial
description calls to PSTN - dial 9 from FXS
destination-pattern 9T
port 0/0:23
!
dial-peer voice 2 pots
direct-inward-dial
description calls to Analog phone from PSTN
destination-pattern 4083333333
port 0/1/0
Exits to global configuration mode.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring
interfaces.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-13
Page 48

Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Configuring DS0 Groups for CAS
The Cisco IAD2430 IAD supports as many as 24 voice lines (DS0s) for CAS, with controller:DS0-group
identification of 1:0 through 1:23.
Perform the following steps to configure the basic T1 controller and digital voice port settings.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. controller t1/e1 slot/port
4. mode css
5. ds0-group ds0-group-number timeslots timeslot-number
6. voice-port slot/port ds0-group-no
7. dial-type {pulse|dtmf}
8. compand-type {u-law|a-law}
9. no shutdown
10. exit
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
controller t1/e1
Example:
Router(config)# controller t1 0/2
Step 4
mode css
Example:
Router(config-controller)# mode css
11. Ctrl-z
slot/port
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters controller configuration mode for controller 1 (the
trunk controller for the T1-PBX port).
Note DS0-group number should be different from
channel-group number and TDM-group number
under the same controller.
Enters CAS configuration mode and configures the
T1/E1 trunk to support signaling that matches the PBX
signaling type:
• cas—Channel-associated signaling
• Common channel signaling cross-connect—CCS
cross-connect for bearer channels
• ccs frame-forwarding—CCS transparent signaling
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-14
OL-4306-03
Page 49

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
ds0-group
ds0-group-number
timeslots
timeslot-list
Example:
Router(config-controller-cas)# ds0-group 1
timeslots 1-4
Step 6
Repeat Step 3 for each additional DS0 group. After DS0
groups are defined, exit CAS configuration mode.
Step 7
voice-port
slot/port ds0-group-no
Example:
Router(config)# voice-port 1:D
Step 8
dial-type {pulse|dtmf}
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# dial-type dtmf
Step 9
compand-type {u-law|a-law}
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# compand-type a-law
Step 10
no shutdown
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Creates a DS0 group on the T1/E1 trunk. A DS0 group
can contain from 1 to 24 time slots numbered from 0 to
23 for T1, and 1 to 32 time slots numbered from 0 to 31
for E1.
Note The maximum number of time slots available in
a T1 DS0 group is 24. The maximum number of
time slots available in an E1 DS0 group is 32.
Note You can configure a maximum of 8 time slots in
a DS0 group on the IAD2435 IAD.
When configuring a DS0 group for a T1/E1 line to a
PBX, make sure that the time slot numbers match the
channels on the PBX. Contact the PBX administrator to
determine which channels to use.
Time slots with identical voice-port configuration can be
assigned to one DS0 group.
Time slots with nonidentical voice-port configurations
must be assigned to different DS0 groups.
Note The maximum number of time slots available in
a T1/E1 is 24. The time slots can be assigned to
one DS0 group, or they can be assigned to as
many as 24 DS0 groups within the T1/E1.
Configures additional DS0 groups on the T1/E1 interface
to the PBX.
Enters voice-port configuration mode, and specifies the
voice port that you want to configure. The logical slot for
these voice ports is the same as for the T1 controller. (See
Step 1). The logical port is 0 to 23 for T1 and 0 to 31 for E1,
corresponding to the DS0 group.
(FXO only) If this voice port supports rotary pulse
dialing, changes the transmit dial type to pulse. The
default is dtmf.
Changes the companding, if necessary. The default is
u-law (the North American mu-law ITU-T pulse code
modulation (PCM) encoding standard). Specify a-law to
use the European a-law ITU-T PCM encoding standard.
Activates the voice port. You should activate only the
voice ports that you plan to use.
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# no shutdown
Step 11
Exit voice-port configuration mode and repeat Step 5
through Step 8 for the remaining digital voice ports.
OL-4306-03
Configures any required digital voice ports.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-15
Page 50

Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Command or Action Purpose
Step 12
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Step 13
Ctrl-z
Example:
Router#
Example
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Exits to global configuration mode.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring
interfaces.
The following example shows typical DS0 groups configuration:
controller T1 0/0
channel-group 0 timeslots 1-20 speed 64
ds0-group 1 timeslots 21-24 type fxo-loopstart
!
voice-port 0/0:1
!
voice-port 0/1/0 << FXS
!
dial-peer voice 1 pots
description calls to PSTN - dial 9 from FXS
destination-pattern 9T
port 0/0:1
!
dial-peer voice 2 pots
description calls to Analog phone from PSTN
destination-pattern 4083333333
port 0/1/0
0
Configuring TDM Cross-Connect
For multiflex trunk interfaces using the time-division multiplexing (TDM) connect function, you can use
the connect command to cross-connect (1) two TDM groups from two controllers, or (2) an analog FXS
port and a DS0 group on a T1. Cross-connecting is done differently for data and voice, as shown in the
following procedures:
• Configuring TDM to TDM
• Configuring TDM to Analog Voice Port
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-16
OL-4306-03
Page 51

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring TDM to TDM
Perform the following steps to configure TDM connect for data (also referred to as pass-through).
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. controller t1/e1 slot/port
4. tdm-group tdm-group-no timeslot timeslot-list type
5. exit
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Router# enable
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
controller t1/e1
slot/port
Example:
Router(config)# controller t1 0/2
tdm-group
type
tdm-group-no
timeslot
timeslot-list
Example:
Router(config-controller)# tdm-group 1 timeslots
13-20
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters controller configuration mode for controller 1 (the
trunk controller for the T1-PBX port).
Note DS0-group number should be different from
channel-group number and TDM-group number
under the same controller.
Configures a TDM channel group for T1/E1. When
configuring cross-connect for data traffic only, do not
specify the type option. The type option applies only if
the mode cas command is enabled.
Note The TDM-group number should be different
from the DS0-group number and the
channel-group number under the same controller.
Exits to global configuration mode.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-17
Page 52

Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Configuring TDM to Analog Voice Port
Perform the following steps to configure TDM connect for voice between an onboard analog FXS port
and a DS0 group on a T1.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. ds0 ds0-group-number timeslots timeslot-list type
4. exit
5. connect
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Example:
Router# enable
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ds0-group
timeslot-list
[loop-start|ground-start]|fxo
[loop-start|ground-start]}
ds0-group-number
type {e&m|fxs
timeslots
Example:
Router(config-controller)# ds0-group 1 timeslots
1-10 type fxs-ground-start
Router(config-controller)# ds0-group 2 timeslots
11-24 type fxo-loop-start
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
connect id voice-port
ds0-group-id
voice-port
T1/E1
Enters global configuration mode.
Configures a DS0 group for T1. Use only one time slot to
map an analog port to a T1. Make sure that the signaling
type is fxo loop-start or fxo ground-start, depending on
the signaling type on the FXS port.
Exits to global configuration mode.
Configures cross-connect between the analog FXS port
and the DS0 group on the T1/E1.
Example:
Router(config)# connect
Configuring TDM to Physical Serial Interface
Perform the following steps to configure TDM connect for serial interface.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-18
OL-4306-03
Page 53

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Note The serial interface must be a DTE device.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. tdm-group tdm-group-no timeslot timeslot-list
4. exit
5. interface type number
6. no keepalive
7. exit
8. connect
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Command or Action Purpose
enable
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router# enable
configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
tdm-group
tdm-group-no
timeslot
timeslot-list
Configures a list of time slots for creating clear channel
groups (pass-through) for time-division multiplexing
Example:
Router(config-controller)# tdm-group 1 timeslot
13-20
exit
(TDM) cross-connect.
When configuring cross-connect for data traffic only, do
not specify the type option.
Exits to global controller mode.
Example:
Router(config-controller)# exit
interface
type number
Configures the serial interface.
Example:
Router(config-controller)# interface serial 1/0:0
no keepalive
Sets the no keepalive function.
Example:
Router(config-if)# no keepalive
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-19
Page 54

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 Serial WAN Interface Card
Command or Action Purpose
Step 7
exit
Exits serial interface mode.
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Step 8
connect id
serial-1 controller-2 tdm-group-no-2
Configures cross-connect pass-through between physical
serial interface and a controller.
Example:
Router(config)# connect
Configuring a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 Serial WAN Interface Card
You can manually configure the synchronous serial interfaces on a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 serial interface
card by entering Cisco IOS commands on the command line. This method, called configuration mode,
provides the greatest power and flexibility.
Note Before you begin, disconnect all WAN cables from the Cisco IAD to prevent it from running the
SUMMARY STEPS
AutoInstall process. Whenever you power on the Cisco IAD, if there is a WAN connection on both ends
and the Cisco IAD does not have a valid configuration file stored in NVRAM (for instance, when you
add a new interface), the Cisco IAD tries to run AutoInstall. It can take several minutes for the Cisco
IAD to determine that AutoInstall is not connected to a remote TCP/IP host.
Before you begin configuring the synchronous serial interface, make sure to do the following:
• Connect a console to the Cisco IAD.
• Power on the Cisco IAD.
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. ip routing
4. interface type number
5. ip address ip address subnet mask
6. half-duplex timer dcd-drop-delay value
7. clockrate value
8. dce-terminal-timing-enable
9. invert-txc
10. nrzi-encoding
11. exit
12. Ctrl-z
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-20
OL-4306-03
Page 55

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
ip routing
Example:
Router(config)# ip routing
Step 4
interface
type number
Example:
Router(config-controller)# interface serial 0/0
Step 5
ip address
ip address subnet mask
Configuring a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 Serial WAN Interface Card
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enables routing protocols as required for your global
configuration. This example uses IP routing.
Enters interface configuration mode. You have entered
interface configuration mode when the prompt changes
to
Router(config-if)#.
Assigns an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.74.1
255.255.255.0
half-duplex timer dcd-drop-delay
value
Example:
Router(config-if)# half-duplex timer
dcd-drop-delay 100
clockrate
value
Example:
Router(config-if)# clockrate 7200
dce-terminal-timing-enable
Example:
Router(config-if)# dce-terminal-timing-enable
Specifies the time that the interface waits in controlled
carrier mode. See
Table 3-1 for a list of half-duplex timer
commands.
To use a port in DCE mode, connect a DCE cable and set
the internal transmit clock signal (TXC) speed in bits per
second. See
Tabl e 3-2, Tabl e 3-3, and Tabl e 3-4 for lists
of clock rate settings for specific interfaces. (For ports
used in DTE mode, the Cisco IAD automatically uses the
external timing signal.)
When a port is operating in DCE mode, the default
operation is for the DCE to send serial clock transmit
(SCT) and serial clock receive (SCR) clock signals to the
DTE, and for the DTE to return a serial clock transmit
external (SCTE) signal to the DCE.
If the DTE does not return SCTE, enter this command to
configure the DCE port to use its own clock signal.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-21
Page 56

Configuring a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 Serial WAN Interface Card
Command or Action Purpose
Step 9
invert-txc
Example:
Router(config-if)# invert-txc
Step 10
nrzi-encoding
Example:
Router(config-if)# nrzi-encoding
Step 11
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Step 12
Ctrl-z
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Cisco IADs that use long cables might experience high
error rates when operating at higher transmission speeds,
because the clock and data signals can shift out of phase.
If a DCE port is reporting a high number of bad packets,
inverting the clock by means of this command can often
correct the shift.
All serial interfaces support both nonreturn to zero
(NRZ) and nonreturn to zero inverted (NRZI) formats.
NRZ is the default; NRZI is commonly used with
EIA/TIA-232 connections in IBM environments. To
enable NRZI encoding on an interface, enter this
command.
Exits to global configuration mode.
Repeat Step 4 through Step 12 if your Cisco IAD has
more than one serial interface that you need to configure.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring the
interfaces.
Example:
Router#
Ta b l e 3-1 Half-Duplex Timer Commands
Timer Syntax Default Setting (Milliseconds)
CTS delay
CTS drop timeout half-duplex timer
1
half-duplex timer cts-delay 100
5000
cts-drop-timeout
DCD drop delay
2
half-duplex timer
100
dcd-drop-delay
DCD transmission start delay half-duplex timer
100
dcd-txstart-delay
RTS3 drop delay
half-duplex timer
100
rts-drop-delay
RTS timeout half-duplex timer rts-timeout 2000
Transmit delay half-duplex timer
0
transmit-delay
1. CTS = Clear To Send.
2. DCD = Data carrier detect
3. RTS = Request To Send.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-22
OL-4306-03
Page 57

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Ta b l e 3-2 Clock Rate Settings for 1-Port/2-Port Serial WAN Interface Card in Synchronous
Mode
Configuring a WIC-1DSU-T1/E1 Serial WAN Interface Card
Timer (bits per
second)
Syntax (bits per
second)
Default Setting (bits
per second)
1200 38400 148000
2400 56000 500000
4800 57600 800000
9600 64000 1000000
14400 72000 1300000
19200 115200 2000000
28800 125000 4000000
32000 128000 148000
Ta b l e 3-3 Clock Rate Settings for 2-Port Synchronous Serial WAN Interface Card
Timer (bits per
second)
Syntax (bits per
second)
Default Setting (bits
per second)
1200 28800 72000
2400 32000 115200
4800 38400 125000
9600 56000 128000
14400 57600 —
19200 64000 —
OL-4306-03
Ta b l e 3-4 Clock Rate Settings for 4-Port Synchronous Serial Interface Card
Timer (bits per
second)
Syntax (bits per
second)
Default Setting (bits
per second)
300 19200 64000
1200 28800 72000
2400 32000 115200
4800 38400 128000
9600 56000 —
14400 57600 —
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-23
Page 58

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring a WIC-1T or WIC-2T Serial WAN Interface Card
Configuring a WIC-1T or WIC-2T Serial WAN Interface Card
The WIC-1T or WIC-2T serial interface cards include an integrated DSU/CSU and can be configured
either for full T1/E1 service at 1.544 Mb/s or for fractional T1/E1 service. You can configure the
interfaces on your T1/E1 WAN interface card manually by entering Cisco IOS commands on the
command line. This method, called configuration mode, provides the greatest power and flexibility.
Note Before you begin, disconnect all WAN cables from the Cisco IAD to prevent it from running the
AutoInstall process. Whenever you power on the Cisco IAD, if there is a WAN connection on both ends
and the Cisco IAD does not have a valid configuration file stored in NVRAM (for instance, when you
add a new interface), the Cisco IAD tries to run AutoInstall. It can take several minutes for the Cisco
IAD to determine that AutoInstall is not connected to a remote TCP/IP host.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
Before you begin configuring interfaces on a WIC-1T or WIC-2T serial WAN interface card, make sure
to do the following:
• Connect a console to the Cisco IAD.
• Power on the Cisco IAD.
Configuring a VIC2-2FXO or VIC2-4FXO Voice Interface Card
in most situations, the default voice-port values are adequate for FXO voice ports.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
If you need to change the default configuration for these voice ports, perform the following tasks. The
first two tasks are required; the third task is optional.
Step 1 Identify the voice port and enter voice-port configuration mode.
Step 2 Configure the following mandatory voice-port parameters:
a. Connection
b. Dial type
c. Signal type
d. Call progress tone
Step 3 (Optional) Configure a description.
Perform the following steps to configure FXO voice ports.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-24
OL-4306-03
Page 59

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. voice-port slot/port
4. connection
5. dial-type
6. signal
7. compand-type
8. cptone local
9. description string
10. exit
11. Ctrl-z
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a VIC2-2FXO or VIC2-4FXO Voice Interface Card
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Command or Action Purpose
enable
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router# enable
configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
voice-port
slot/port
Enters voice-port configuration mode. See Port
Numbering Conventions, page 1-5.
Example:
Router(config)# voice-port 0/1
connection {trunk|plar|tie-line|plar-opx}
string
Configures the voice-port connection mode type and the
destination telephone number.
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# connection tie-line
5550100
The plar value is used for private line automated
ringdown (PLAR) connections. The tie-line value is used
for a tie-line connection to a PBX. The plar-opx value,
for PLAR off-premises extension, allows the local voice
port to provide a local response before the remote voice
port receives an answer.
dial-type {pulse|dtmf|mf}
Configures the voice-port dial-type. The default is dtmf.
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# dial-type pulse
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-25
Page 60

Configuring a VIC2-2FXS or VIC2-4FXS Voice Interface Card
Command or Action Purpose
Step 6
signal {groundstart|loopstart|live-feed}
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# signal groundstart
Step 7
compand-type {u-law|a-law}
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# compand-type a-law
Step 8
cptone
local
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configures the signaling type for analog FXO voice
ports. The default is loop-start.
Configures the companding standard used to convert
between analog and digital signals in PCM systems.
Configures the appropriate call progress tone for the
local region.
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# cptone ca
The default for this command is northamerica. For a list
of supported countries, see the Cisco Voice, Video, and
Fax Command Reference, Release 12.3(4)T.
Step 9
description
string
(Optional) Enters a string description for the voice port.
The string describes the voice port in displays. You can
use the description command to note the voice port
location or use.
Exits to voice-port mode.
Step 10
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)#
description
exit
purchasing_dept
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# exit
Step 11
Ctrl-z
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring the
interfaces.
Example:
Router#
Configuring a VIC2-2FXS or VIC2-4FXS Voice Interface Card
In most situations, the default voice-port values are adequate for FXS voice ports.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
If you need to change the default configuration for the FXS voice ports, perform the following tasks.
The first two tasks are required; the third task is optional.
Step 1 Identify the voice port and enter voice-port configuration mode.
Step 2 Configure the following mandatory voice-port parameters:
a. Connection
b. Dial type
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-26
OL-4306-03
Page 61

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
c. Signal type
d. Call progress tone
Step 3 (Optional) Configure a description.
Perform the following steps to configure FXS voice ports.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. voice-port slot/port
4. signal
5. compand-type
6. cptone local
7. description string
Configuring a VIC2-2FXS or VIC2-4FXS Voice Interface Card
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
voice-port
Example:
Router(config)# voice-port 0/1
Step 4
signal {groundstart|loopstart|live-feed}
8. exit
9. Ctrl-z
slot/port
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters voice-port configuration mode. See Port
Numbering Conventions, page 1-5.
Configures the signaling type for analog FXS voice
ports. The default is loop-start.
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# signal groundstart
Step 5
compand-type {u-law|a-law}
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# compand-type a-law
OL-4306-03
Configures the companding standard used to convert
between analog and digital signals in PCM systems.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-27
Page 62

Configuring ATM T1-WAN Ports
Command or Action Purpose
Step 6
cptone
local
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# cptone ca
Step 7
description
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)#
description
Step 8
exit
Example:
Router(config-voice-port)# exit
Step 9
Ctrl-z
string
purchasing_dept
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configures the appropriate call progress tone for the
local region.
The default for this command is northamerica. For a list
of supported countries, see the Cisco Voice, Video, and
Fax Command Reference, Release 12.3(4)T.
(Optional) Enters a string description for the voice port.
The string describes the voice port in displays. You can
use the description command to note the voice port
location or use.
Exits to voice-port mode.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring the
interfaces.
Example:
Router#
Configuring ATM T1-WAN Ports
If your Cisco IAD has a T1-WAN port, a default ATM configuration is automatically enabled when you
enter the mode atm controller command.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router does not support an ATM interface.
The default ATM configuration has the following operating parameters:
• Maximum virtual path identifiers (VPIs) per virtual channel identifier (VCI) (atm
vc-per-vc)—1024.
• No IP address.
• ATM User to Network Interface (UNI) Version 3.0 is assigned.
• ATM Integrated Local Management Interface (ILMI) keepalive is disabled.
• No ATM PVCs are configured.
To configure the ATM interface parameters for your application, you need the following information:
• IP addresses and subnet masks
• VPI/VCI numbers
• Any other information related to the routing protocol
Perform the following steps to enter an ATM configuration.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-28
OL-4306-03
Page 63

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. controller {t1|e1|j1} slot/port
4. mode {rpr|rpr-plus|sso}
5. exit
6. interface type number
7. ip address ip address subnet mask
8. atm uni-version version-number
9. atm ilmi-keepalive seconds
10. pvc name vpi/vci
11. protocol ipv6 ipv6-address
12. vbr-rt peak-rate average-rate burst
13. encapsulation {aal5ciscoppp|aal5mux|aal5nlpid|aal5snap}
Configuring ATM T1-WAN Ports
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
controller {t1|e1|j1}
14. vbr-rt peak-rate average-rate burst
15. exit
16. Repeat Step 8 through Step 12 for each additional ATM PVC to be configured.
17. no shutdown
18. exit
19. exit
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Enters global configuration mode.
slot/port
Enters controller configuration mode and specifies the
controller number.
Example:
Router(config)# controller t1 0
Step 4
mode {rpr|rpr-plus|sso}
Example:
Router(config-ctrl)# mode atm
OL-4306-03
Enables ATM encapsulation and creates logical ATM
interface 0. Controller framing is automatically set to
Extended SuperFrame (ESF). The linecode is
automatically set to binary 8-zero substitution (B8ZS).
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-29
Page 64

Configuring ATM T1-WAN Ports
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
exit
Example:
Router(config-ctrl)# exit
Step 6
interface
Example:
Router(config)# interface atm 0
Step 7
ip address
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.74.1
255.255.255.0
Step 8
atm uni-version
Example:
Router(config-if)# atm uni-version 3.1
Step 9
atm ilmi-keepalive
Example:
Router(config-if)# atm ilmi-keepalive
pvc
Step 10
name vpi/vci
Example:
Router(config-if)# pvc cisco 0/8
Step 11
protocol ipv6
type number
ip address subnet mask
version-number
seconds
ipv6-address
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Exits to controller mode.
Enters ATM configuration mode for interface ATM 0.
(Optional) Assigns an IP address to the asymmetric
digital subscriber line (ADSL) or symmetric high bit-rate
digital subscriber line (SHDSL) ATM interface.
(Optional) Specifies an ATM user network interface
(UNI) version number.
(Optional) Enables Integrated Local Management
Interface (ILMI) keepalives.
If you enable ILMI keepalives without specifying the
seconds, the default time interval is 3 seconds.
Enters atm-virtual-circuit (interface-atm-vc)
configuration mode, and configure a new ATM PVC by
assigning a name (optional) and VPI/VCI numbers.
The default traffic shaping is unspecified bit rate (UBR);
the default encapsulation is ATM adaption layer 5+
(AAL5+), Logical Link Control Protocol (LLC),
Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP).
(Optional) Enables IP connectivity and creates a
point-to-point IP address for the VC.
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# protocol ipv6 address
2001:0DB8:2222::72/32
Step 12
vbr-rt
peak-rate
average-rate
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# vbr-rt 640 320 80
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-30
burst
(Optional) Configures the PVC for real-time variable bit
rate (VBR), VBR-nrt (non-real time), unspecified bit rate
(UBR) UBR+, unspecified bit rate constant bit rate
(CBR), available bit rate (ABR) traffic shaping.
• Peak rate—peak information rate (PIR).
For SHDSL ports, set the peak rate for the trained
line rate minus 8
• Average rate—average information rate (AIR).
• Burst—burst size in cells.
kb/s.
OL-4306-03
Page 65

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 13
encapsulation
{aal5ciscoppp|aal5mux|aal5nlpid|aal5snap}
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# encapsulation aal5autoppp
virtual-template 1
Step 14
exit
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# exit
Step 15
Repeat Step 8 through Step 12 for each additional ATM
PVC to be configured.
Step 16
no shutdown
Configuring ATM T1-WAN Ports
(Optional) Configures the ATM adaptation layer (AAL)
and encapsulation type.
• aal5ciscoppp for Cisco PPP over AAL5
• aal5mux for AAL5+MUX (multiplexer)
• aal5nlpid for AAL5+NLPID (Network Layer
Protocol Identifier)
• aal5snap for AAL5+LLC/SNAP (the default)
Exits interface-atm-vc configuration mode.
Configures any additional ATM PVCs.
Activates the ATM interface.
Example:
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 17
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Step 18
exit
Example:
Router(config)# exit
Verifying Your ATM Interface Configuration
To verify the ATM interface configuration, enter the show interface atm 0 privileged EXEC command.
The following example shows typical output from the show interface atm
Router# show interface atm 0
ATM0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is PQUICC Atom1
MTU 1500 bytes, sub MTU 1500, BW 2304 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ATM, loopback not set
Keepalive not supported
Encapsulation(s):, PVC mode
512 maximum active VCs, 4 current VCCs
VC idle disconnect time:300 seconds
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue:0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops:0
Queueing strategy:None
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
20486 packets input, 368419 bytes, 0 no buffer
Exits ATM interface configuration mode.
Exits global configuration mode.
0 command:
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-31
Page 66

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring 1-Port ADSL/SHDSL WAN Interface Card
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Router#
Configuring 1-Port ADSL/SHDSL WAN Interface Card
The ADSL/SHDSL WAN interface card is a 1-port WAN interface card (WIC) for the Cisco IAD2430
Series IADs. The card provides asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) or symmetric high bit-rate
digital subscriber line (SHDSL) high-speed digital data transfer between a single customer premises
equipment (CPE) subscriber and the central office.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
Note ADSL/SHDSL is a last-mile access technology, which has an asymmetrical data rate running over a
single copper wire pair.
Note A 1-port ADSL/SHDSL WIC must be installed in the router to match the DSL service to be configured.
Configuration Tasks
See the following sections for configuration tasks for this feature. Each task in the list is identified as
either required or optional:
• Configuring the ADSL/SHDSL Port on the ADSL and SHDSL WAN Interface Card (required)
• Verifying ATM Configuration (optional)
Features used on the ADSL/SHDSL WAN interface card must also be configured on the digital
subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM). See the documentation for the specific DSLAM for
information about configuring features.
Configuring the ADSL/SHDSL Port on the ADSL and SHDSL WAN Interface Card
Perform the following steps to configure an ADSL/SHDSL port on the ADSL/SHDSL WAN interface
card.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. interface atm slot/port
4. ip address ip address subnet mask
5. pvc name vpi/vci
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-32
OL-4306-03
Page 67

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
6. protocol ipv6 ipv6-address
7. vbr-rt peak-rate average-rate burst
8. encapsulation {aal5ciscoppp|aal5mux|aal5nlpid|aal5snap}
9. exit
10. dsl operating-mode
11. no shutdown
12. exit
13. exit
14. show interface atm slot/port
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Configuring 1-Port ADSL/SHDSL WAN Interface Card
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Example:
Router# enable
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
interface atm
slot/port
Example:
Router(config)# interface atm 1/0
ip address
ip address subnet mask
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 172.16.74.3
255.255.255.0
pvc
name vpi/vci
Example:
Router(config-if)# pvc cisco 0/8
protocol ipv6
ipv6-address
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters ATM configuration mode for the ATM interface
in the specified slot and port.
Assigns an IP address to the ADSL/SHDSL ATM
interface.
Enters atm-virtual-circuit (interface-atm-vc)
configuration mode, and configure a new ATM PVC by
assigning a name (optional) and VPI/VCI numbers.
The default traffic shaping is unspecified bit rate (UBR);
the default encapsulation is ATM adaption layer 5+
(AAL5+), Logical Link Control Protocol (LLC),
Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP).
(Optional) Enables IP connectivity and creates a
point-to-point IP address for the VC.
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# protocol ipv6 address
2001:0DB8:2222::72/32
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-33
Page 68

Configuring 1-Port ADSL/SHDSL WAN Interface Card
Command or Action Purpose
Step 7
vbr-rt
peak-rate
average-rate
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# vbr-rt 640 320 80
Step 8
encapsulation
{aal5ciscoppp|aal5mux|aal5nlpid|aal5snap}
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# encapsulation aal5autoppp
virtual-template 1
Step 9
exit
burst
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
(Optional) Configures the PVC for real-time variable bit
rate (VBR), VBR-nrt (non-real time), unspecified bit rate
(UBR) UBR+, unspecified bit rate constant bit rate
(CBR), available bit rate (ABR) traffic shaping.
• Peak rate—peak information rate (PIR).
For SHDSL ports, set the peak rate for the trained
line rate minus 8
• Average rate—average information rate (AIR).
• Burst—burst size in cells.
(Optional) Configures the ATM adaptation layer (AAL)
and encapsulation type.
• aal5ciscoppp—Cisco PPP over AAL5
• aal5mux—AAL5+MUX
• aal5nlpid—AAL5+NLPID
• aal5snap—AAL5+LLC/SNAP (the default)
Exits interface-atm-vc configuration mode.
kb/s.
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Example:
Router(config-if-vc)# exit
dsl operating-mode {adsl2[annex a|annex m]|adsl2+
[annex a|annex m]|ansi-dmt|auto|itu-dmt}
Example:
Router(config-if)# dsl operating-mode adsl2+
annex m
no shutdown
Example:
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
exit
Configure the ADSL/SHDSL interface to operate in a
specified mode:
• ansi-dmt—ANSI full rate mode per T1.413 (ITU
G.DMT Issue 1)
• auto—Automatic detection mode
• itu-dmt—ITU full rate mode (ITU G.DMT Issue 1)
• splitterless—G.lite mode per ITU G.992.2
Caution This command is for testing or lab
environments only. Using a configuration
other than the default configuration for the
DSL operating mode can lead to unpredictable
behavior on the ADSL/SHDSL line.
Activates the ATM interface.
Exits from ATM interface configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-34
OL-4306-03
Page 69

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Command or Action Purpose
Step 13
exit
Example:
Router(config)# exit
Step 14
show interface atm
slot/port
Example:
Router> show interface atm 1/0
Verifying ATM Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the ATM configuration:
• To verify current configuration and to view the status for all controllers, use the show
running-config command.
• To view ATM controller statistics, use the show controllers atm slot/port command.
• To verify the PVC status, use the show atm vc command. Make sure that active PVCs are up.
• To help identify ATM-related events as they are generated, use the debug atm events command.
Configuring 1-Port ADSL/SHDSL WAN Interface Card
Exits from global configuration mode.
Verifies the ATM interface configuration.
• To indicate which interfaces are having trouble, use the debug atm errors command.
• To identify an entry for the ATM interface you configured and to show an entry for the ATM
slot/port that you configured, use the show ip route command.
• To display the configured list of ATM static maps to remote hosts on an ATM network, use the show
atm map command.
• To view the status of an ATM interface, use the show interface atm slot/port command. Make sure
that the ATM slot/port and line protocol are up, as shown in the following example:
Router# show interface atm1/0
ATM 1/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is DSLSAR (with Alcatel ADSL Module)
MTU 4470 bytes, sub MTU 4470, BW 800 Kbit, DLY 2560 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ATM, loopback not set
Keepalive not supported
Encapsulation(s):AAL5 PVC mode
24 maximum active VCs, 256 VCs per VP, 2 current VCCs
VC idle disconnect time:300 seconds
Last input never, output 00:00:01, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 03:16:00
Queueing strategy:fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
30 second input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
30 second output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
2527 packets input, 57116 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
10798 packets output, 892801 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Router# show atm vc
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-35
Page 70

Configuring a VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE Card
VCD / Peak Avg/Min Burst
Interface Name VPI VCI Type Encaps SC Kbps Kbps Cells Sts
1/0.3 2 9 36 PVC MUX UBR 800 UP
1/0.2 1 9 37 PVC SNAP UBR 800 UP
Router# show controllers atm 1/0
Interface ATM1/0 is up
Hardware is DSLSAR (with Alcatel ADSL Module)
IDB: 62586758 Instance:6258E054 reg_dslsar:3C810000 wic_regs:3C810080
PHY Inst:62588490 Ser0Inst:62573074 Ser1Inst: 6257CBD8 us_bwidth:800
Slot: 1 Unit: 1 Subunit: 0 pkt Size:4496
VCperVP:256 max_vp: 256 max_vc: 65536 total vc:2
rct_size:65536 vpivcibit:16 connTblVCI:8 vpi_bits:8
vpvc_sel:3 enabled: 0 throttled:0
WIC Register Value Notes
--------------- ---------- ---------FPGA Dev ID (LB) 0x44 'D'
FPGA Dev ID (UB) 0x53 'S'
FPGA Revision 0x99
WIC Config Reg 0x45 WIC / VIC select = WIC;
CTRLE addr bit 8 = 1;
OK LED on;
LOOPBACK LED off;
CD LED on;
WIC Config Reg2 0x07 Gen bus error on bad ADSL access
Int 0 Enable Reg 0x03 ADSL normal interrupt enabled
ADSL error interrupt enabled
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Configuring a VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE Card
ISDN BRI VICs provide digital connectivity for VoIP networks using the European
Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) Net3 switch type.
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
BRI VICs present an ISDN S/T physical interface that connects to a network termination (NT) or
terminal equipment (TE) device. With ISDN BRI VICs, you can connect a Cisco IAD2431 or IAD2432
series IAD to a private branch exchange (PBX) network in NT or TE mode or to a public switched
telephone network (PSTN) in TE mode.
Each of the two BRI ports can operate in NT mode because the clock source can operate in TE mode as
a clock slave.
Note When a VIC port operates in NT mode, it sources a clock to the BRI interface (a PBX trunk card, for
example) which is operating in TE mode. When a VIC port operates in TE mode, it receives a clock from
the BRI interface (a PBX line card, for example) which is operating in NT mode.
Perform the following steps to configure a VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE card.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-36
OL-4306-03
Page 71

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. no isdn switch-type switch-type
4. tdm clock bri-auto, tdm clock bri slot/port export, tdm clock bri slot/port import
5. interface bri slot/port
6. no ip address
7. shutdown, isdn layer1-emulate {user|network}, no shutdown
8. line-power
9. isdn protocol-emulate {user|network}
10. exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a VIC2-2BRI-NT/TE Card
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Command or Action Purpose
enable
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router# enable
configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
no isdn switch-type
switch-type
Removes the ISDN switch type.
Example:
Router(config)# no isdn switch-type basic-net3
tdm clock bri-auto
or
tdm clock bri
and/or
tdm clock bri
{t1|e1|atm|bri|onboard}
slot/port
slot/port
export
import
Configures automatic TDM selection for the BRI VIC.
• Configures the BRI port that exports the TDM clock.
• Configures the BRI port(s) that import(s) the TDM
clock.
Example:
Router(config)# tdm clock bri-auto
interface bri
slot/port
Changes to interface configuration mode for port 0 in slot
0.
Example:
Router(config)# interface bri 0/0
Step 6
no ip address
Example:
Router(config-if)# no ip address
OL-4306-03
Specifies that there is no IP address for this interface.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-37
Page 72

Saving Configuration Changes
Command or Action Purpose
Step 7
shutdown
isdn layer1-emulate {user|network}
no shutdown
Example:
Router(config-if)# shutdown
Router(config-if)# isdn layer1-emulate user
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 8
line-power
Example:
Router(config-if)# line-power
Step 9
isdn protocol-emulate {user|network}
Example:
Router(config-if)# isdn protocol-emulate user
Step 10
exit
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Shuts down the interface.
Configures the Layer 1 port mode and clock settings:
• Enter user to configure the port as TE and to
function as a clock slave. This is the default.
• Enter network to configure the port as NT and to
function as a clock master.
Activates the interface after the port configuration.
(Optional only for NT-configured ports.) Turns on the
power supplied from the port to a TE device.
Configures the Layer 2 port protocol emulation:
• Enter user to configure the port as TE so that the
PBX is the master. This is the default.
• Enter network to configure the port as NT so that the
PBX is the slave.
Exits global configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Saving Configuration Changes
Perform the following steps to prevent loss of the Cisco IAD configuration.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. enable
2. copy running-config startup-config
3. Ctrl-z
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-38
OL-4306-03
Page 73

Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router# enable
Step 2
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
Router# copy running-config startup-config
Step 3
Ctrl-z
Example:
Router# Ctrl-z
Saving Configuration Changes
Enters privileged EXEC mode.
Saves the configuration changes to NVRAM so that they
are not lost during resets, power cycles, or power
outages.
Returns to enable mode when you finish configuring the
interfaces.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-39
Page 74

Saving Configuration Changes
Chapter 3 Configuring with the Command-Line Interface
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
3-40
OL-4306-03
Page 75

CHAP T E R
4
Configuring Voice over IP
This chapter explains how to configure voice interfaces and ports, which convert telephone voice signals
for transmission over an IP network.
This chapter presents the following major topics:
• Prerequisites, page 4-1
• Configuring the Voice Interface, page 4-2
• VoIP Configuration Examples, page 4-4
VoIP enables your Cisco IAD to carry live voice traffic (for example, telephone calls and faxes) over an
IP network. VoIP offers the following benefits:
• Toll bypass
• Remote PBX presence over WANs
• Unified voice and data trunking
• Plain old telephone service (POTS)–Internet telephony gateways
For more information on understanding and configuring VoIP, see the Configuring Voice over IP
document.
Prerequisites
Before you can configure your Cisco integrated access device (IAD) to use VoIP, you must first do the
following:
• Establish a working IP network.
Note For information applicable to the Cisco IAD2400 series, see “Voice over IP for the
Cisco 3600 Series Overview,” and references therein, at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios113ed/113t/113t_1/voip/
voipover.htm
See also Configuring Voice over IP for the Cisco 3600 Series at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios120/12cgcr/voice_c/vcprt1/
vcvoip.htm
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-1
Page 76
Configuring the Voice Interface
• Implement a dial plan, including the following tasks:
–
Complete your company’s dial plan. That is, decide what patterns of dialed numbers will access
what telephony endpoints.
–
Establish a working telephony network based on your company’s dial plan.
–
Integrate your dial plan and telephony network into your existing IP network topology.
Note To support FXO signaling, you must install a VIC2-4FXO interface card. For information on
connecting voice interface cards (VICs), see “Connecting Voice Network Modules” at the
following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/acs_mod/cis2600/hw_inst/nm_inst/
nm-doc/conntvoi.htm
Configuring the Voice Interface
Whenever you install a new interface or want to change the configuration of an existing interface, you
must configure the interface. If you replace a module that was already configured, the Cisco IAD
recognizes it and brings up the interface in the existing configuration.
Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
Note The Cisco IAD2435 router is a fixed-configuration router and does not support interface cards.
Before you configure an interface, have the following information available:
• Protocols you plan to route on the new interface
• IP addresses, subnet masks, network numbers, zones, or other information related to the routing
protocol
Timesaver Obtain this information from your system administrator or network plan before you begin configuring
your Cisco IAD.
To configure a voice interface, you must use configuration mode (manual configuration). In this mode,
you can enter Cisco
IOS commands through the command-line interface (CLI).
Before you begin, disconnect all WAN cables from the Cisco IAD to prevent it from running the
AutoInstall process. The Cisco IAD tries to run AutoInstall whenever you power it on if there is a WAN
connection on both ends and the Cisco IAD does not have a valid configuration file stored in NVRAM
(for instance, when you add a new interface). It can take several minutes for the Cisco IAD to determine
that AutoInstall is not connected to a remote TCP/IP host.
To configure the voice interface configuration mode, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect a console to the Cisco IAD. If you need instructions for connecting a console, see the
installation chapter of your Cisco IAD installation and configuration guide.
Step 2 Power on the Cisco IAD. If the current configuration is no longer valid, after about one minute you see
the following prompt:
Would you like to enter the initial dialog? [yes/no]:
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-2
OL-4306-03
Page 77

Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
Answer no. You now enter the normal operating mode of the Cisco IAD.
Note If the current configuration is valid, you enter the normal operating mode automatically.
Step 3 After a few seconds, you see the user EXEC prompt (Router>). Type enable and the password to enter
enable mode:
Router> enable
Password: <
The prompt changes to the privileged EXEC (enable) prompt (Router#):
Router#
Step 4 Enter the configure terminal command to enter global configuration mode:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)#
The Cisco IAD enters global configuration mode, indicated by the Router(config)# prompt.
Step 5 If you have not configured the Cisco IAD before, or you want to change the configuration, use Cisco
IOS commands to configure global parameters, passwords, network management, and routing protocols.
In this example, IP routing is enabled:
Router(config)# ip routing
password
Configuring the Voice Interface
>
For complete information about global configuration commands, see the Cisco IOS configuration guides
and command references.
Step 6 If you have not already done so, configure the network module or WAN interface card that you plan to
use for IP traffic. For instructions, see your Cisco IAD hardware installation and software configuration
guides or the configuration note for the network module or WAN interface card.
Step 7 To configure another interface, enter the exit command to return to the Router(config)# prompt.
Step 8 To configure the Cisco IAD for voice traffic, see the VoIP references in the “Prerequisites” section on
page 4-1.
Step 9 To exit configuration mode and return to the enable prompt, when you finish configuring interfaces,
press Ctrl-Z. To see the current operating configuration, including any changes you just made, enter the
show running-config command:
Router# show running-config
To see the configuration currently stored in NVRAM, enter the show startup-config command at the
enable prompt:
Router# show startup-config
Step 10 The results of the show running-config and show startup-config commands differ if you have made
changes to the configuration but have not yet written them to NVRAM. To write your changes to
NVRAM and make them permanent, enter the copy
running-config startup-config command at the
enable prompt:
Router# copy running-config startup-config
Building configuration. . .
[OK]
Router#
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-3
Page 78

VoIP Configuration Examples
The Cisco IAD is now configured to boot in the new configuration.
VoIP Configuration Examples
The actual VoIP configuration procedure you complete depends on the topology of your voice network.
The following configuration examples give you a starting point. Of course, you need to customize these
configuration examples for your own network topology.
Configuration procedures and examples are supplied for the following scenarios:
• FXS-to-FXS Connection
• Linking PBX Users with Digital E&M Trunk Lines over T1/E1 CAS
• PSTN Gateway Access Using an FXO Connection
• PSTN Gateway Access Using an FXO Connection in PLAR Mode
Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
FXS-to-FXS Connection
The following example shows how to configure VoIP for simple FXS-to-FXS connections over
channelized T1/E1s. In this example, a very small company, consisting of two offices, has decided to
integrate VoIP into its existing IP network. One basic telephony device is connected to IAD-1; therefore,
IAD-1 has been configured for one POTS peer and one VoIP peer. Routers RLB-w and R12-e establish
the WAN connection between the two offices. Because one POTS telephony device is connected to
IAD-2, that Cisco IAD has also been configured for only one POTS peer and one VoIP peer.
Figure 4-1 illustrates the topology of this FXS-to-FXS connection example.
Figure 4-1 Channelized T1/E1 FXS-to-FXS Connection
MLPPP over serial MLPPP over channelized T1
Voice port
2/0
Dial peer 1
POTS
Serial port
1/0 1/3
Router
RLB-w
Serial port
0/0
IAD IAD
IAD-1 IAD-2
IP cloud
128 kbps
Serial port
1/3 1/0
Router
R12-e
Serial port
1/0:0
Voice port
2/0
Dial peer 2
POTS
95107
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-4
OL-4306-03
Page 79

Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
Configuration for IAD-1
hostname iad-1
! Create voip dial-peer 10
dial-peer voice 10 voip
! Define its associated telephone number and IP address
destination-pattern +4152222222
session target ipv4:10.0.0.1
! Create pots dial-peer 1
dial-peer voice 1 pots
! Define its associated telephone number and voice port
destination-pattern +4081111111
port 2/0
!Configure serial interface 0/0
interface Serial0/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
no ip mroute-cache
! Configure RTP header compression
ip rtp header-compression
ip rtp compression-connections 25
fair-queue 64 256 36
router igrp 888
network 10.0.0.0
VoIP Configuration Examples
Configuration for Router RLB-w
hostname rlb-w
! Configure serial interface 1/0
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
! Configure RTP header compression
ip rtp header-compression
ip rtp compression-connections 25
fair-queue 64 256 3
! Configure serial interface 1/3
interface Serial1/3
ip address 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
! Configure RTP header compression
ip rtp header-compression
ip rtp compression-connections 25
fair-queue 64 256 3
! Configure IGRP
router igrp 888
network 10.0.0.0
network 20.0.0.0
Configuration for Router R12-e
hostname r12-e
! Configure serial interface 1/0
interface Serial1/0
ip address 40.0.0.2 25.0.0.0
! Configure RTP header compression
ip rtp header-compression
ip rtp compression-connections 25
fair-queue 64 256 3
! Configure serial interface 1/3
interface Serial1/3
ip address 20.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
! Configure RTP header compression
ip rtp header-compression
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-5
Page 80

VoIP Configuration Examples
ip rtp compression-connections 25
fair-queue 64 256 3
clockrate 128000
! Configure IGRP
router igrp 888
network 20.0.0.0
network 40.0.0.0
Configuration for IAD-2
hostname iad-2
! Create pots dial-peer 2
dial-peer voice 2 pots
! Define its associated telephone number and voice-port
destination-pattern +4152222222
port 2/0
! Create voip dial-peer 20
dial-peer voice 20 voip
!Define its associated telephone number and IP address
destination-pattern +4081111111
session target ipv4:40.0.0.1
! Configure channel group on T1/E1
controller T1 1/0
channel-group 0 timeslots 1-24
! Configure serial interface 1/0:0
interface Serial1/0:0
ip address 40.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
no ip mroute-cache
! Configure RTP header compression
ip rtp header-compression
ip rtp compression-connections 25
fair-queue 64 256 3
clockrate 64000
! Configure IGRP
router igrp 888
network 40.0.0.0
Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
Linking PBX Users with Digital E&M Trunk Lines over T1/E1 CAS
The following example shows how to configure VoIP to link PBX users with digital E&M trunk lines
over T1/E1 Channel-associated signalling (CAS). (See the
on page 3-14.)
In this example, a company wants to connect two offices: one in San Jose, California, and the other in
Salt Lake City, Utah. Each office has an internal telephone network using a PBX connected to the voice
network by an E&M interface. Both offices are using E&M Port Type II, with four-wire operation and
ImmediateStart signaling. Each E&M interface connects to the router by means of two voice interface
connections. Users in San Jose dial “8-569” and then the extension number to reach a destination at the
Salt Lake City office. Users in Salt Lake City dial “4-527” and then the extension number to reach a
destination in the San Jose office.
Figure 4-2 shows the topology of this connection example.
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-6
“Configuring DS0 Groups for CAS” section
OL-4306-03
Page 81

Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
Figure 4-2 Linking PBX Users with Digital E&M Trunk Lines over T1/E1 CAS
VoIP Configuration Examples
Note This example assumes that the company already has established a working IP connection between its
two remote offices.
IAD SJ Configuration
hostname sanjose
!Configure digital voice-ports
controller T1 1/0
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-24 type e&m-immediate-start
!Configure pots dial-peer 1
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern +527....
port 1/1:0
!Configure voip dial-peer 2
dial-peer voice 3 voip
destination-pattern +569....
session target ipv4:172.16.65.182
!Configure the fastethernet interface
interface fe 0/0
ip address 172.16.1.123
no shutdown
172.16.1.123
Dial peer
1 POTS
PBX PBX
Voice port
T1 1/1
1/1:0
IAD SJ
IAD IAD
Digital E&M with
T1 CAS
San Jose
(408)
172.16.65.182
IP cloud
FaE 0/0
Voice port
1/1:0
IAD SLC
Dial peer
1 POTS
T1 1/1
Digital E&M with
T1 CAS
Salt Lake City
(801)
95108
IAD SLC Configuration
hostname saltlake
!Configure digital voice-ports
controller T1 1/0
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-24 type e&m-immediate-start
!Configure pots dial-peer 1
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern +569....
port 1/1:0
!Configure voip dial-peer 2
dial-peer voice 3 voip
destination-pattern +527....
session target ipv4:172.16.65.123
!Configure the fastethernet interface
interface fe 0/0
ip address 172.16.1.182
no shutdown
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-7
Page 82

VoIP Configuration Examples
Note PBXs should be configured to pass all dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) signals to the Cisco IAD. We
recommend that you do not configure “store-and-forward” tone.
Note If you change the gain or the telephony port, make sure that the telephony port still accepts DTMF
signals.
PSTN Gateway Access Using an FXO Connection
The following example shows how to configure VoIP to link users with the PSTN gateway using a
Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) connection.
In this example, users connected to Router SJ in San Jose, California, can reach PSTN users in Salt Lake
City, Utah, using Router SLC. Router SLC in Salt Lake City is connected directly to the PSTN through
an FXO interface.
Figure 4-3 shows the topology of this connection example.
Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
Figure 4-3 PSTN Gateway Access Using FXO Connection Example
1(408) 555-4000
Note This example assumes that the company already has established a working IP connection between its
two remote offices.
IAD SJ Configuration
! Configure pots dial-peer 1
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern +14081111111
port 2/0
! Configure voip dial-peer 2
dial-peer voice 2 voip
destination-pattern +9...........
session target ipv4:172.16.65.182
! Configure the serial interface
interface serial 0/0
clock rate 2000000
ip address 172.16.1.123
no shutdown
FaE 0/0
IP cloud
Analog to FXS
San Jose Salt Lake City
Voice port
IAD SJ
IAD IAD
172.16.1.123 172.16.65.182
2/0
FaE 0/0
IAD SLC
FXO
Voice port
2/0
PSTN user
PSTN
cloud
95109
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-8
OL-4306-03
Page 83

Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
r
VoIP Configuration Examples
IAD SLC Configuration
! Configure pots dial-peer 1
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern +9...........
port 2/0
! Configure voip dial-peer 2
dial-peer voice 2 voip
destination-pattern +14081111111
session target ipv4:172.16.1.123
! Configure serial interface
interface serial 0/0
ip address 172.16.65.182
no shutdown
PSTN Gateway Access Using an FXO Connection in PLAR Mode
The following example shows how to configure VoIP to link users with the PSTN gateway using an
Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) connection in private line, automated ringdown (PLAR) mode.
In this example, PSTN users in Salt Lake City, Utah, can dial a local number and establish a private line
connection in a remote location. As in the previous example (that is, a PSTN gateway using an FXO
connection) Router SLC in Salt Lake City is connected directly to the PSTN through an FXO interface.
Figure 4-4 shows the topology of this connection example.
Figure 4-4 PSTN Gateway Access Using FXO Connection (PLAR Mode)
1(408) 555-4000
San Jose
Note This example assumes that the company already has established a working IP connection between its
two remote offices.
IAD SJ Configuration
! Configure pots dial-peer 1
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern +14081111111
port 2/0
! Configure voip dial-peer 2
dial-peer voice 2 voip
destination-pattern +9...........
session target ipv4:172.16.65.182
! Configure the serial interface
interface serial 0/0
IAD SJ
Voice port
2/0
PLAR connection
IP cloud
IAD SLC
172.16.1.123 172.16.65.182
IADIAD
Voice port
2/0
FXO
PSTN use
PSTN
cloud
Salt Lake City
95110
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-9
Page 84

VoIP Configuration Examples
clock rate 2000000
ip address 172.16.1.123
no shutdown
IAD SLC Configuration
! Configure pots dial-peer 1
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern +9...........
port 2/0
! Configure voip dial-peer 2
dial-peer voice 2 voip
destination-pattern +14081111111
session target ipv4:172.16.1.123
! Configure the voice port
voice port 2/0
connection plar 14081111111
! Configure the serial interface
interface serial 0/0
ip address 172.16.65.182
no shutdown
Chapter 4 Configuring Voice over IP
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
4-10
OL-4306-03
Page 85

APPENDIX
Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
This appendix presents the following sample configurations for the Cisco 2430 series IADs:
• Sample Configuration: Cisco IAD2435-8FXS, page A-1
• Sample Configuration: Cisco 2430-24FXS, page A-3
• Sample Configuration: Cisco 2431-1T1/E1 with WIC-2T, page A-6
• Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO and QoS, page A-8
Sample Configuration: Cisco IAD2435-8FXS
Current configuration : 1089 bytes
!
version 12.4(1)T
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname 2435-8FXS
!
logging queue-limit 100
!
ip subnet-zero
!
!
!
no voice hpi capture buffer
no voice hpi capture destination
!
!
mta receive maximum-recipients 0
!
!
controller T1 1/0
framing sf
linecode ami
channel-group 0 timeslots 1-24
!
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 1.3.21.53 255.255.0.0
no ip mroute-cache
duplex auto
speed auto
A
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-1
Page 86

Sample Configuration: Cisco IAD2435-8FXS
fair-queue
!
interface Serial1/0:0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.0.0
encapsulation ppp
!
ip http server
ip classless
!
!
!
call rsvp-sync
!
voice-port 2/0
!
voice-port 2/1
!
voice-port 2/2
!
voice-port 2/3
!
voice-port 2/4
!
voice-port 2/5
!
voice-port 2/6
!
voice-port 2/7
!
mgcp
mgcp call-agent 1.3.37.1 service-type mgcp version 1.0
!
mgcp profile default
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
!
!
dial-peer voice 1 pots
application mgcpapp
port 2/0
!
dial-peer voice 2 pots
application mgcpapp
port 2/1
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
speed 115200
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
!
end
Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-2
OL-4306-03
Page 87

Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2430-24FXS
Current configuration : 2612 bytes
!
version 12.4(1)T
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname swell-China
!
ip subnet-zero
!
!
no voice hpi capture buffer
no voice hpi capture destination
!
!
mta receive maximum-recipients 0
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 1.3.21.55 255.255.0.0
ip nat inside
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 1.2.111.1 255.255.0.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.2.0.1
!
!
call rsvp-sync
!
voice-port 2/0
disc_pi_off
input gain 10
output attenuation 10
playout-delay minimum low
cptone HK
timing digit 53
description cflow1
music-threshold -50
bearer-cap Speech
station-id name ashoowin
station-id number 1000
caller-id enable
ren 3
disconnect-ack
!
voice-port 2/1
disc_pi_off
input gain 10
output attenuation 10
playout-delay minimum low
cptone HK
timing digit 53
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2430-24FXS
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-3
Page 88

Sample Configuration: Cisco 2430-24FXS
description cflow1
music-threshold -50
bearer-cap Speech
station-id name ashwin
station-id number 1000
caller-id enable
ren 3
disconnect-ack
!
voice-port 2/2
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/3
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/4
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/5
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/6
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/7
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/8
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/9
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/10
cptone HK
!
voice-port 2/11
!
voice-port 2/12
!
voice-port 2/13
!
voice-port 2/14
!
voice-port 2/15
!
voice-port 2/16
!
voice-port 2/17
!
voice-port 2/18
!
voice-port 2/19
!
voice-port 2/20
!
voice-port 2/21
!
voice-port 2/22
!
voice-port 2/23
!
mgcp profile default
!
Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-4
OL-4306-03
Page 89

Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
dial-peer cor custom
!
!
dial-peer voice 1 pots
destination-pattern 1000
port 2/0
!
dial-peer voice 2 pots
destination-pattern 2000
port 2/1
!
dial-peer voice 3 pots
destination-pattern 1002
port 2/2
!
dial-peer voice 4 pots
destination-pattern 1003
port 2/3
!
dial-peer voice 5 pots
destination-pattern 1004
port 2/4
!
dial-peer voice 6 pots
destination-pattern 1005
port 2/5
!
dial-peer voice 10 voip
destination-pattern 2...
session target ipv4:1.2.125.57
codec g711ulaw
!
dial-peer voice 7 pots
destination-pattern 1006
port 2/6
!
dial-peer voice 8 pots
destination-pattern 1007
port 2/7
!
dial-peer voice 9 pots
destination-pattern 1008
port 2/8
!
dial-peer voice 11 pots
destination-pattern 1009
port 2/9
!
dial-peer voice 12 pots
destination-pattern 1010
port 2/10
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
speed 115200
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2430-24FXS
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-5
Page 90

Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2431-1T1/E1 with WIC-2T
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2431-1T1/E1 with WIC-2T
Current configuration : 1755 bytes
!
version 12.4(1)T
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname 2431-2T1/E1-1
!
logging queue-limit 100
logging buffered 10000000 debugging
no logging console
!
network-clock-select 1 T1 1/0
ip subnet-zero
!
!
!
backhaul-session-manager
set vsc1_set client nft
group vsc1_grp set vsc1_set
isdn switch-type primary-ni
!
!
!
no voice hpi capture buffer
no voice hpi capture destination
!
!
mta receive maximum-recipients 0
!
!
controller T1 1/0
shutdown
framing sf
linecode ami
channel-group 0 timeslots 1-24
!
controller T1 1/1
mode cas
framing esf
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-24 type e&m-wink-start
!
!
!
interface Multilink1
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.0.0
ppp multilink
multilink-group 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 1.3.21.56 255.255.0.0
duplex auto
speed auto
ip rsvp bandwidth 1 1
!
interface Serial0/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
clockrate 2000000
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-6
OL-4306-03
Page 91

Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
shutdown
clockrate 2000000
ppp multilink
multilink-group 1
!
interface Serial1/0:0
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
no logging event link-status
ppp multilink
multilink-group 1
!
ip http server
ip classless
ip route 223.255.254.254 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0
!
!
access-list 101 permit ip host 10.1.1.1 host 10.1.1.2
no cdp run
!
!
call rsvp-sync
!
voice-port 1/1:1
!
mgcp
mgcp call-agent 1.3.37.1 service-type sgcp version 1.5
mgcp quarantine mode process loop
mgcp timer receive-rtcp 2
!
mgcp profile default
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
!
!
dial-peer voice 1 voip
destination-pattern 408....
session target ipv4:1.3.21.54
!
dial-peer voice 2 pots
application mgcpapp
incoming called-number 408....
port 1/1:1
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
speed 115200
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2431-1T1/E1 with WIC-2T
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-7
Page 92

Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO and QoS
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO
and QoS
Current configuration : 3807 bytes
!
version 12.4(1)T
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname 2432-24-2T1/E1-2
!
logging queue-limit 100
logging buffered 5000 debugging
no logging console
!
ip subnet-zero
!
!
ip cef
no ip domain lookup
!
!
!
no voice hpi capture buffer
no voice hpi capture destination
!
!
mta receive maximum-recipients 0
!
!
controller T1 1/0
shutdown
framing sf
clock source internal
linecode ami
channel-group 1 timeslots 1-12 speed 64
!
controller T1 1/1
framing esf
clock source internal
linecode b8zs
channel-group 1 timeslots 1-12 speed 64
!
class-map match-all control
match ip dscp af31
class-map match-all voice
match ip dscp ef
!
!
policy-map CORP-POLICY
class voice
priority percent 45
class control
bandwidth percent 10
class class-default
fair-queue
!
!
!
interface Multilink1
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-8
OL-4306-03
Page 93

Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
ip address 12.12.0.1 255.255.0.0
service-policy output CORP-POLICY
ip tcp header-compression iphc-format
load-interval 30
no cdp enable
ppp multilink
ppp multilink fragment-delay 10
ppp multilink interleave
multilink-group 1
ip rtp header-compression iphc-format
ip rtp compression-connections 1000
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 1.3.21.57 255.255.0.0
load-interval 30
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial1/0:1
bandwidth 768
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
load-interval 30
ppp multilink
multilink-group 1
!
interface Serial1/1:1
bandwidth 768
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
load-interval 30
ppp multilink
multilink-group 1
!
ip http server
ip classless
ip route 1.3.0.0 255.255.255.0 FastEthernet0/0
ip route 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 Multilink1
ip route 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 12.12.0.2
!
!
!
call threshold global cpu-5sec low 80 high 90 treatment
call threshold global cpu-avg low 80 high 90 treatment
call threshold global total-mem low 80 high 90 treatment
call threshold global io-mem low 80 high 90 treatment
call threshold global proc-mem low 80 high 90 treatment
call threshold global total-calls low 10 high 12 treatment
call rsvp-sync
!
voice-port 0/0
battery-reversal answer
!
voice-port 0/1
battery-reversal answer
!
voice-port 0/2
battery-reversal answer
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO and QoS
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-9
Page 94

Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO and QoS
!
voice-port 0/3
battery-reversal answer
!
voice-port 2/0
!
voice-port 2/1
!
voice-port 2/2
!
voice-port 2/3
!
voice-port 2/4
!
voice-port 2/5
!
voice-port 2/6
!
voice-port 2/7
!
voice-port 2/8
!
voice-port 2/9
!
voice-port 2/10
!
voice-port 2/11
!
voice-port 2/12
!
voice-port 2/13
!
voice-port 2/14
!
voice-port 2/15
!
voice-port 2/16
!
voice-port 2/17
!
voice-port 2/18
!
voice-port 2/19
!
voice-port 2/20
!
voice-port 2/21
!
voice-port 2/22
!
voice-port 2/23
!
mgcp
mgcp call-agent 1.3.37.1 service-type mgcp version 1.0
mgcp src-cac
no mgcp piggyback message
!
mgcp profile default
!
dial-peer cor custom
!
!
!
dial-peer voice 1 voip
Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-10
OL-4306-03
Page 95

Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
incoming called-number 4088...
destination-pattern 4089...
session target ipv4:12.12.0.2
codec g711ulaw
no vad
!
dial-peer voice 2 pots
destination-pattern 4088001
port 2/0
!
dial-peer voice 3 pots
destination-pattern 4088002
port 2/1
!
dial-peer voice 4 pots
destination-pattern 4088003
port 2/2
!
dial-peer voice 5 pots
destination-pattern 4088004
port 2/3
!
dial-peer voice 6 pots
destination-pattern 4088005
port 2/4
!
dial-peer voice 7 pots
destination-pattern 4088006
port 2/5
!
dial-peer voice 8 pots
destination-pattern 4088007
port 2/6
!
dial-peer voice 9 pots
destination-pattern 4088008
port 2/7
!
dial-peer voice 10 pots
destination-pattern 4088009
port 2/8
!
dial-peer voice 11 pots
destination-pattern 4088010
port 2/9
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
speed 115200
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
login
!
!
end
Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO and QoS
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-11
Page 96

Sample Configuration: Cisco 2432-24FXS with VIC2-4FXO and QoS
Appendix A Cisco IAD2430 Series Configuration Examples
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
A-12
OL-4306-03
Page 97

APPENDIX
B
Formatting the Flash Memory
This appendix describes how to format the flash memory into a Class B flash file system, known as the
low-end file system (LEFS), or into a Class C flash file system, which is similar to the standard DOS
file system. It also describes how to perform file and directory operations in each file system.
Note The IAD2435 IAD does not support LEFS, but supports Disk Operating System Filing System (DOSFS)
and refers to internal compact flash as flash only.
This appendix presents the following major topics:
• Formatting Procedures for Flash Memory, page B-1
• File and Directory Operations, page B-5
For additional information on formatting flash memory, see the Maintaining System Memory section in
the
Cisco IOS Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 12.2 document.
Formatting Procedures for Flash Memory
The following sections show formatting procedures for internal and external flash memory.
Formatting Procedures
We recommend that you erase (Class B) or format (Class C) new flash memory to initialize them with
either a Class B or Class C flash file system. This ensures proper formatting and enables the ROM
monitor to recognize and boot the flash memory.
Note Flash memory that is formatted with the standard DOS file system does not support booting from the
ROM monitor.
Determining the File System on Flash Memory
To determine the file system of external flash memory, enter the show slot0: all command.
Note slot0 is not supported on the IAD2435 IAD.
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
B-1
Page 98

Formatting Procedures for Flash Memory
To determine the file system of internal flash memory, enter the show flash: all command.
• If geometry and format information is not displayed, the card is formatted with a Class B flash file
system.
• If geometry and format information is displayed, the card is formatted with a Class C flash file
system.
The following examples show sample outputs for Class B and Class C flash file systems:
External Card with Class B Flash File System
The geometry and format information is not displayed for this format:
Router# show slot0: all
Partition Size Used Free Bank-Size State Copy
Mode
1 31360K 6502K 24857K 0K Read/Write Direct
Slot0 Flash directory:
File Length Name/status
addr fcksum ccksum
1 6658376 c2430-is-mz
0x40 0xE0FF 0xE0FF
[6658440 bytes used, 25454200 available, 32112640 total]
31360K bytes of ATA Slot0 Flash (Read/Write)
Appendix B Formatting the Flash Memory
Chip information NOT available.
Note slot0 is not supported on the IAD2435 IAD.
External Card with Class C Flash File System
The geometry and format information is displayed in this format:
Router# show slot0: all
-#- --length-- -----date/time------ path
1 6658376 Mar 01 2008 04:27:46 c2430-is-mz
25268224 bytes available (6664192 bytes used)
******** ATA Flash Card Geometry/Format Info ********
ATA CARD GEOMETRY
Number of Heads: 4
Number of Cylinders 490
Sectors per Cylinder 32
Sector Size 512
Total Sectors 62720
ATA CARD FORMAT
Number of FAT Sectors 31
Sectors Per Cluster 8
Number of Clusters 7796
Number of Data Sectors 62560
Base Root Sector 155
Base FAT Sector 93
Base Data Sector 187
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
B-2
OL-4306-03
Page 99

Appendix B Formatting the Flash Memory
Note slot0 is not supported on the IAD2435 IAD.
Internal Card with Class B Flash File System
The geometry and format information is not displayed for this format:
Router# show flash: all
Partition Size Used Free Bank-Size State Copy
Mode
1 125184K 20390K 104793K 0K Read/Write
Direct
System Flash directory:
File Length Name/status
addr fcksum ccksum
1 6658376 c2430-is-mz
0x40 0xE0FF 0xE0FF
2 14221136 c2430-telcoent-mz
0x6599C8 0x5C3D 0x5C3D
[20879640 bytes used, 107308776 available, 128188416 total]
125184K bytes of ATA System Flash (Read/Write)
Formatting Procedures for Flash Memory
Chip information NOT available.
Internal Card with Class C Flash File System
The geometry and format information is displayed in this format:
11# show flash: all
-#- --length-- -----date/time------ path
1 6658376 Mar 01 2008 04:27:46 c2430-is-mz
25268224 bytes available (6664192 bytes used)
******** ATA Flash Card Geometry/Format Info ********
ATA CARD GEOMETRY
Number of Heads: 4
Number of Cylinders 490
Sectors per Cylinder 32
Sector Size 512
Total Sectors 62720
ATA CARD FORMAT
Number of FAT Sectors 31
Sectors Per Cluster 8
Number of Clusters 7796
Number of Data Sectors 62560
Base Root Sector 155
Base FAT Sector 93
Base Data Sector 187
Formatting Flash Memory as a Class B Flash File System
Use these formatting commands to:
• Format flash memory with a Class B flash file system (LEFS)
OL-4306-03
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
B-3
Page 100

Formatting Procedures for Flash Memory
• Remove the files from flash memory previously formatted with a Class B flash file system
For external flash memory, enter the erase slot0: command.
Note slot0 is not supported on the IAD2435 IAD.
Note The IAD2435 IAD supports the class C file system.
For internal flash memory, enter the erase flash: command.
The following example shows sample output for formatting an external flash memory with a Class B
flash file system:
Router# erase slot0:
Erasing the slot0 filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm]
Current DOS File System flash card in slot0: will be formatted into Low
End File System flash card! Continue? [confirm]
Erasing device...
eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee
eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee
eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee
...erased
Erase of slot0: complete
Appendix B Formatting the Flash Memory
Formatting Flash Memory as a Class C File System
Use these formatting commands to do the following:
• Format flash memory with a Class C flash file system
• Remove the files from flash memory previously formatted with a Class C flash file system
Note The IAD2435 IAD supports the class C file system.
For external flash memory, enter the format slot0: command.
Note slot0 is not supported on the IAD2435 IAD.
For internal flash memory, enter the format flash: command.
Note The IAD2435 IAD does not support LEFS, but supports Disk Operating System Filing System (DOSFS)
and refers to internal compact flash as flash only.
The following example shows sample output for formatting an internal flash memory with a Class C
flash file system:
Router# format flash:
Format operation may take a while. Continue? [confirm]
Format operation will destroy all data in "flash:". Continue? [confirm]
Enter volume ID (up to 64 chars)[default flash]:
Current Low End File System flash card in flash will be formatted into DOS
Cisco IAD2430 Series Integrated Access Devices Software Configuration Guide
B-4
OL-4306-03
 Loading...
Loading...