Page 1

User Guide for Cisco Digital Media
Encoder
October 9, 2008
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
2200
Text Part Number: OL-17938-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the
document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopied, recorded, or
otherwise without prior written permission from Cisco Systems, Inc. ViewCast
SimulStream
Inc. Microsoft
Linus Torvalds. RealNetworks
of RealNetworks, Inc. Flash
Corporation. Indeo
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
®
and Osprey® are trademarks or registered trademarks of ViewCast Corporation or its subsidiaries. Macintosh® is a registered trademark of Apple Computer,
®
, Windows®, Windows® XP, Windows Media® and DirectDraw® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Linux® is a registered trademark of
®
®
, RealAudio®, RealVideo®, RealMedia®, RealPlayer®, RealProducer®, Helix® and SureStream are the trademarks or registered trademarks
®
is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/or other countries. Intel® is a registered trademark of Intel
is a registered trademark of Ligos Corporation.
®
, the ViewCast logo, Niagara®, the Niagara logo, GoStream, Niagara SCX® , EZ Stream and
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
Page 3

CONTENTS
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 1-1
Foreword 1-1
Safety Instructions 1-2
Warnings 1-2
Warranty 1-3
Package Contents 1-3
Installation 1-3
Connecting the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 1-4
Connecting to an Electrical Power Source 1-4
Rear Panel Diagram 1-4
Front Panel Diagram 1-6
Configuring the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 1-7
Completing First Start Setup 1-8
Configuring the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 to Connect to an IP Network 1-9
Changing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Network Settings 1-10
2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 2-1
Introduction 2-1
What is Streaming Media? 2-1
Streaming Infrastructure 2-2
Simple Guide to Streaming Audio and Video Types 2-3
Tutorial 2-3
OL-17938-01
Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel 2-4
Startup 2-4
Shutdown 2-5
Alternate Shutdown Method 2-5
Starting an Encoding Session 2-6
Checking CPU Usage 2-7
Stopping an Encoding Session 2-8
Connecting an External Storage Device 2-8
Exporting Captured Video Files 2-8
DME Security Best Practices 2-10
Factory-Defined Login Credentials 2-11
Changing Factory-Defined Login Credentials 2-11
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
i
Page 4

Contents
Other Required Password Maintenance (Only When Autologon Is Configured) 2-13
Tasks to Complete After Changing DME Login Passwords 2-14
Disabling Unneeded Services 2-14
After a Live Event Is Finished, Remove Its Encoded Video Files from the DME File Share 2-15
Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface 2-15
Accessing the Web Interface 2-15
Starting an Encoding Session 2-17
Stopping an Encoding Session 2-18
Viewing the Activity Log 2-19
Configuring the EZStream Buttons 2-20
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C) 2-21
Select Encoder 2-21
View All Encoders 2-22
Edit Preset Encoder Profile 2-22
AVI Encoder Properties 2-23
Flash Encoder Properties 2-23
MPEG-4 Encoder Properties 2-24
Real Encoder Properties (Helix) 2-25
Windows Media Encoder Properties 2-26
Editing an Encoder Profile 2-26
Video & Audio Settings 2-27
Streaming Properties 2-29
Advanced Streaming Settings 2-29
AVI Encoder Settings 2-32
Flash Encoder Settings 2-32
MPEG-4 Encoder Settings 2-33
Encoder Settings Web Interface 2-33
Real Encoder Settings (Helix) 2-39
Windows Media Encoder Settings 2-42
Deleting an Encoder Profile 2-43
My Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 2-44
Computer Name 2-45
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Properties 2-46
Changing the Login Password from the Factory Default 2-46
Restoring the Login Password to the Factory Default 2-47
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Alerts 2-47
Email Alert 2-48
Alarm Light 2-48
Edit Alert Settings 2-48
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
ii
OL-17938-01
Page 5

Network Properties 2-48
Network Card(s) 2-49
Advanced Settings (Network) 2-49
System Configuration Settings 2-50
Restore Factory Defaults 2-51
Email Settings 2-52
Idle Screen Information 2-53
Default Directory Setting 2-53
High Temperature Alert 2-54
Contents
CHAPTER
3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface 3-1
EASE Menu (LCD Display) 3-1
Encode Menu 3-2
Encode Start 3-2
Encode Stop 3-3
Encode Status 3-3
Access Health Menu 3-3
CPU Status 3-3
Memory Available 3-4
Temperature Status 3-4
Setup System Menu 3-5
Network Link Status 3-5
Network MAC Address 3-6
View Network Settings 3-7
Enable DHCP 3-8
Set Static IP Addresses 3-9
Set Gateway Address 3-11
Set Date & Time 3-12
Setting Temperature Alarm 3-13
Factory Restore 3-14
Export to USB Drive 3-16
Shutdown Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 3-16
OL-17938-01
Niagara SCX Web Interface 3-16
Log In 3-17
Home Page 3-18
Menu Bar 3-18
Home 3-18
Encoders 3-18
Configuration 3-18
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
iii
Page 6

Contents
Status 3-19
Log Out 3-19
All Encoders 3-19
Start Encoder 3-20
Stop Encoder 3-21
Edit Encoder 3-22
AVI Encoder Settings 3-27
Flash Encoder Settings 3-27
MPEG-4 Encoder Settings 3-28
Real Encoder Settings (Helix) 3-34
Windows Media Encoder Settings 3-37
Digital Rights Management (DRM) for Windows Media 3-39
Delete an Existing Encoder 3-44
Create an Encoder 3-44
Encoder Preset (A, B, & C) 3-45
Select Encoder 3-46
View All Encoders 3-47
Edit Preset Encoder Profile 3-47
My Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 3-47
Computer Name 3-48
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Properties 3-49
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Alerts 3-51
Email Alert 3-51
Alarm Light 3-51
Edit Alert Settings 3-52
Network Properties 3-52
Network Card(s) 3-53
Advanced Settings (Network) 3-54
System Configuration Settings 3-54
Restore Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Factory Defaults 3-55
Email Settings 3-56
Idle Screen Information 3-57
Default Directory Setting 3-57
High Temperature Alert 3-58
View Activity Log 3-58
View Alerts 3-59
The Help, or “i” Button, the Niagara SCX Web Interface, and Their Alert Settings 3-59
iv
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 7

Foreword
CHA PTER
1
Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Revised: October 9, 2008, OL-17938-01
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Foreword, page 1-1
• Safety Instructions, page 1-2
• Package Contents, page 1-3
• Installation, page 1-3
• Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page 1-12
Congratulations on the purchase of your Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200! You are the fortunate owner
of a state-of-the-art streaming media system. Now you can capture and stream your audio and video
content over the Internet or any local or wide area IP network. All you need is your audio and video
source, such as a camera or deck, a streaming media server or hosting provider, and an IP connection to
your viewing audience.
Throughout this document, Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 will be referred to generically as an
encoder or device.
OL-17938-01
Warning
For a complete overview on streaming audio and video over an IP network, go to the “Streaming
Infrastructure” section on page 2-2. This section will explain how streaming media works.
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 is an easy-to-use streaming device. You simply connect your audio
and video source to the encoder, select your target playback device, enter your streaming server
information, and press the Stream button. You’re streaming live!
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 can be configured and used straight out of the box for most streaming
uses. For more advanced settings or controlling your encoder from another networked computer, you will
use Niagara SCX Web Interface.
The front panel of your encoder can be customized by using the Configuration Web Browser Interface.
This configuration tool also provides the ability to set many other system parameters for your device.
We hope you enjoy your Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200!
Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power source.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
1-1
Page 8

Safety Instructions
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
Safety Instructions
This section includes the following topics:
• Warnings, page 1-2
• Warr a nty, p age 1-3
Warnings
Before installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200, read and comply with the following safety
warnings to ensure that you do not damage the equipment or cause personal injury.
Warning
Warning
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes.
Read the installation instructions before connecting the system to the power source.
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
This product requires short-circuit (overcurrent) protection, to be provided as part of the building
installation. Install only in accordance with national and local wiring regulations.
The power supply must be placed indoors.
The plug-socket combination must be accessible at all times, because it serves as the main
disconnecting device.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to telephone-network
voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits, and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some
LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables.
1-2
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 9
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Warranty
For complete warranty details, refer to the specific warranty included with each product.
Package Contents
Completely unpack all of the contents from the box, inspect each item for damage, and ensure that you
have all of the following components:
• Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
• Power Cable
• BNC-to-RCA Converter, Male-to-Female (8)
• 75 OHM BNC Terminator
• 1 Pair Rack Slide Rails
• 2 Rack Handles
• Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Documentation CD
If any of these components are missing or damaged, do not continue with the installation. Contact the
Cisco reseller from which you purchased your encoder system for assistance in obtaining any missing
parts or for parts replacement.
Package Contents
Warning
Installation
The encoder’s serial number is located on the right side of the chassis.
Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes.
This section will guide you through the physical connection and setup of your Cisco Digital Media
Encoder
There are two parts to the complete installation of the encoder, as follows:
1. Connecting the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2. Configuring the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Most of the basic operations you will routinely use are performed from the front panel of the encoder,
shown in
There are advanced setup and operations you may wish to access and to do so you will need to access
the SCX Web Interface from a computer that resides on the same network as the encoder.
Although these advanced operations are not required for most streaming applications, you may want to
customize your encoding settings and assign specific encoding profiles to the EZStream® ABC buttons
on the front panel. The SCX Web Interface provides the ability to remote control your encoder from a
computer that could be rooms or continents away from the system provided that both your encoder and
the computer have Internet access to communicate with each other.
First, you need to connect the encoder. See the “Connecting the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200”
section for connection information.
2200 system.
Figure 1-2.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
1-3
Page 10
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Installation
Connecting the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Although it has many features and capabilities, the encoder at its most basic function takes analog audio
and video input and processes the signals and then encodes them into digital IP video formats. Then, the
encoder delivers the IP audio and video content to a storage device or streams it over an IP network.
There are four requirements for setting up the encoder for streaming or capturing video, as follows:
• AC power source (100-240v)
• Audio/Video source (camera, video player, or other A/V output device)
• IP network and/or Internet connection
• A streaming media server for streaming your content to many viewers
Connecting to an Electrical Power Source
The appropriate power cable is specified when your unit is ordered. Attach the block end to the power
input located on the upper corner on the rear panel of the encoder (
Plug the other end into a wall outlet or surge protection enabled power strip that is connected to wall
outlet or other common power source.
Figure 1-1).
Warning
Warning
The plug-socket combination must be accessible at all times because it serves as the main
disconnecting device.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
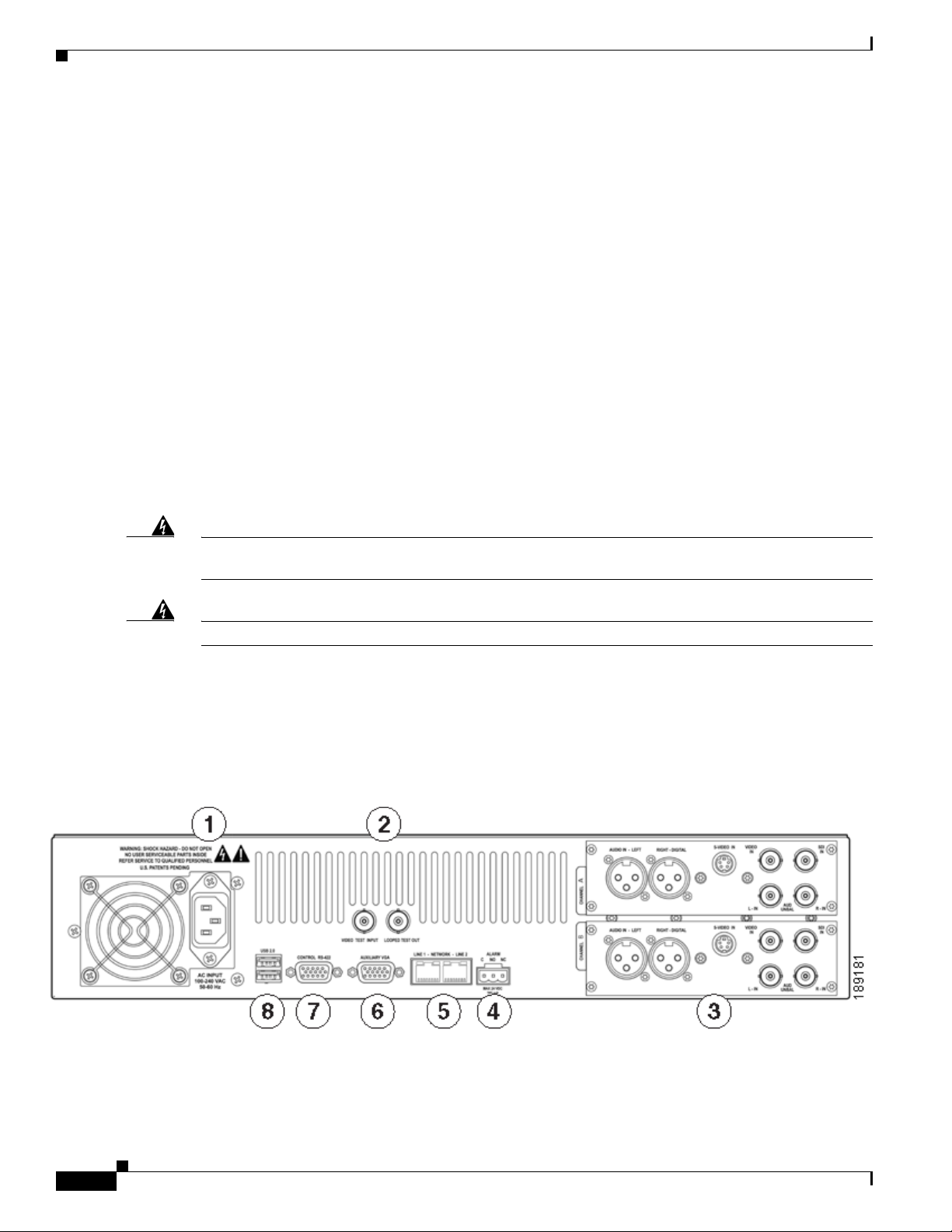
Rear Panel Diagram
The diagram in Figure 1-1 and Tab le 1-1 illustrate all of the connectors and other components of the
encoder rear panel.
Figure 1-1 Rear Panel Diag ra m
1-4
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 11
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Installation
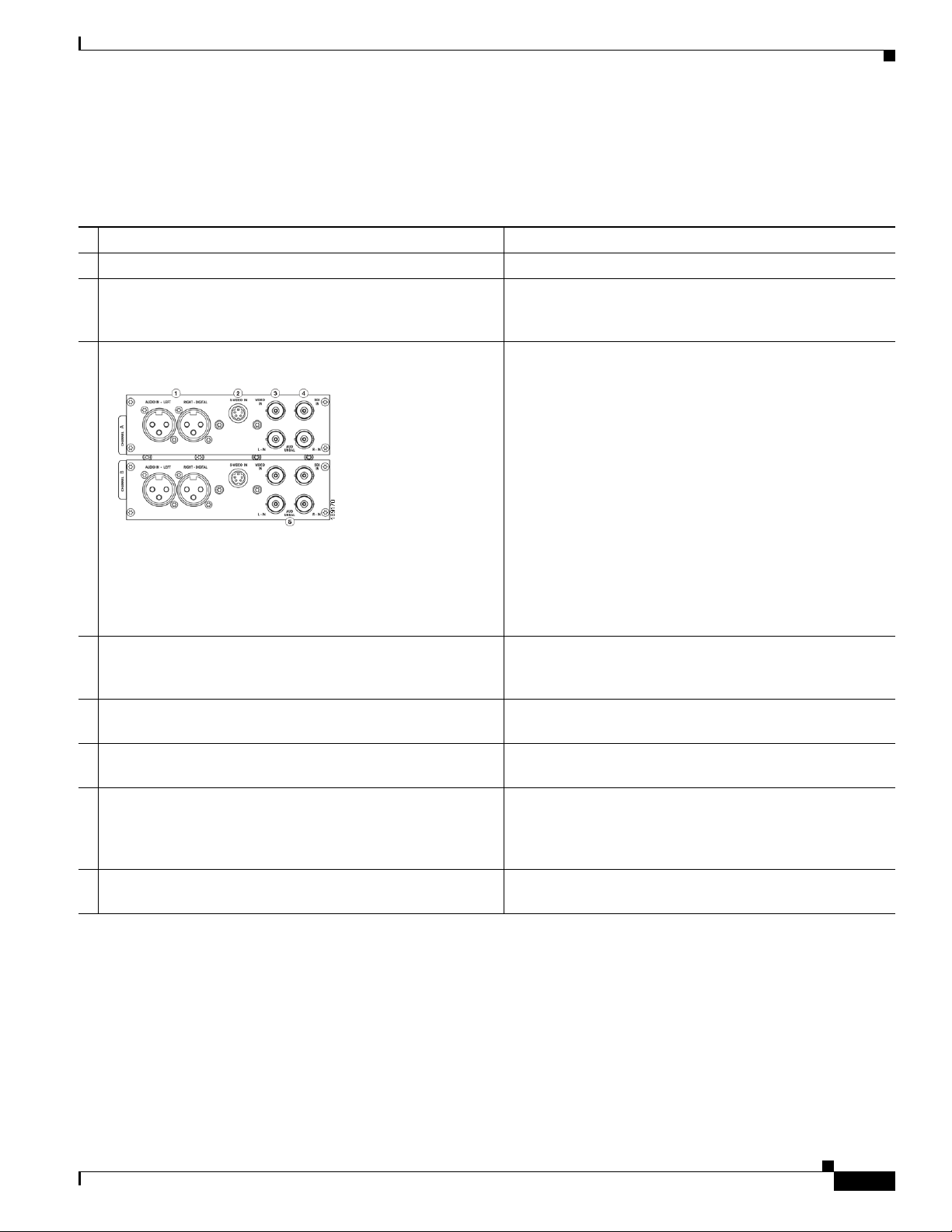
Figure 1-1 shows the rear panel of the encoder. Using the reference chart and images in Tab le 1-1, you
can connect the appropriate device and power to the encoder.
Ta b l e 1-1 Rear Panel Reference
— Port Description
1 AC Power Input Provides system power.
2 Video Test Ports BNC connector for composite video IN/OUT. Allows you
to connect a video test signal, such as a color bar generator,
to calibrate the video settings for video capture sessions.
3 Channel A & B AV Inputs Each AV Input channel provides the following input ports:
1. Left/Right XLR connector for balanced audio sources;
right XLR connector for AES/EBU audio
2. Mini-DIN connector for S-Video sources
3. BNC connector for composite video sources
4. BNC connector for SDI Video Sources with embedded
SDI audio
5. Left/Right BNC connectors for unbalanced audio
sources
4 Alarm Relay Connector Use this port to connect an external device (such as an
audible bell or buzzer) so that, if the system fails, it will
trigger an external audible sound.
5 Network Ports (Line 1 & 2) Dual Ethernet ports provide redundant connections to your
network.
6 Auxiliary VGA Connector Use this port to connect an external VGA monitor so that
you can view the Operating System Interface.
7 Control RS-422 Connector (FUTURE) 9-pin D connector. Allows you to control the
encoder via RS-422 protocols, providing integration into a
broadcast studio master control center. This is a standard
RS-422 port that can be used with deck control software.
8 USB 2.0 Connectors Use these ports to connect USB control devices, such as a
keyboard and mouse or USB memory devices.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
1-5
Page 12

Installation
Front Panel Diagram
You should familiarize yourself with the front panel controls for the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200.
Besides the basic buttons for power, start/stop, up/down and menu access, there are also several indicator
lights.
Figure 1-2 and Ta b l e 1-2 illustrate all buttons and lights, so you can review the front panel
functions and interface.
Figure 1-2 Front Panel Diagram
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Ta b l e 1-2 Front Panel Buttons and Lights
Item Description
Control Buttons
Power Pressing this button once will power up Niagara Pro II. When Niagara Pro II is powered up,
pressing this button once will power down the system. Pressing and holding for 5 seconds will
perform an immediate power off.
EZStream Buttons When an encoder profile is assigned to one of these buttons, pressing the assigned button and then
the Stream button will start the encoder. Pressing the assigned button and then the Stop button will
stop the encoder.
Alarm Information When the Alarm Light indicator is lit, pressing this button will provide a log of the most recent
alarms recorded. Pressing the Enter button will clear these alarms from the log.
Menu Pressing this button will activate the encoder menu on the LCD display.
Enter Pressing this button will enter or accept the menu choice highlighted on the LCD display. It is used
for menu operations.
Up/Down These buttons are used for menu navigation on the LCD display.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
1-6
OL-17938-01
Page 13

Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Installation
Table 1-2 Front Panel Buttons and Lights
Stream Pressing this button when an encoder profile is highlighted in the LCD display will start the
encoder.
Stop Pressing this button when an encoder profile is highlighted in the LCD display will stop the
encoder.
Alarm This light indicates that an application alert has occurred.
Remote Control This light indicates that another user is accessing the encoder across the network from a computer.
Audio Activity These lights indicate audio input presence.
Headphone Jack and
Vol u me B u t t o ns
The jack allows headphones to be connected to the encoder for audio monitoring. The Volume
Buttons control the audio level on the headphones.
USB Port The USB port allows the export of files to USB devices.
Configuring the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
This section includes the following topics:
• Completing First Start Setup, page 1-8
• Configuring the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 to Connect to an IP Network, page 1-9
• Changing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Network Settings, page 1-10
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
1-7
Page 14

Installation
Completing First Start Setup
The first time the encoder is powered, the LCD display will present a series of menus that will assist in
setting up the system clock, date, and video input format (NTSC [North America/Japan] or PAL).
1. To start the encoder, press the <POWER> button located on the front panel.
2. During the power up process, the encoder LCD readout displays the following message:
3. After the encoder powers up the first time, it displays the following message:
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
4. Press the <ENTER> button to begin the initial setup.
5. The encoder will now ask you to set the date.
6. To set the date, use the <UP> and <DOWN> arrow keys to increment the numerical value of the
month.
7. Once you set the numerical value for the month, press the <STREAM> button to move to the day
field.
8. Again, use the <UP> and <DOWN> arrow keys to increment the numerical value of the day.
1-8
9. Press <STREAM> to enter the value and move to the year field.
10. Use the same process for setting the month and day so that you may set the year.
11. If you want to change a previous setting, you can continue pressing the <STREAM> button until
the cursor cycles around to the month.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 15

Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
12. Once you are satisfied with your settings, you then press the <ENTER> button to accept the settings
and move to the next screen to set the system clock.
13. The encoder uses Military Time, which is a 24-hour clock format, for its system clock entries.
14. Use the <UP>, <DOWN>, <STREAM>, and <ENTER> buttons to set the hour and minute of the
system clock.
15. The last setting is the selection of the video input format that you will enter into the encoder.
16. You will see the following prompt message:
17. Press the <ENTER> button to continue.
Installation
18. Select your video source format from either NTSC or PAL.
19. Press the <ENTER> button to set the format, and the final screen will appear confirming that you
have successfully set up your encoder.
20. Press the <ENTER> button to exit the setup menu and begin using your encoder.
Configuring the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 to Connect to an IP Network
Note If you are not familiar with network protocols, please contact your network administrator for assistance.
The Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 network settings for its two 1,000 megabit network interfaces
default to dynamically obtain an IP address from a DHCP server on the network.
If a DHCP server is not available or cannot be found on the network, then the encoder will assign its own
IP address.
OL-17938-01
For most network environments, it will not be necessary to modify these default settings. However, if
you wish to assign a static IP address to the encoder’s Network Interface Cards (NICs), then you can
change the network setting using the encoder front panel menu.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
1-9
Page 16
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Installation
Changing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Network Settings
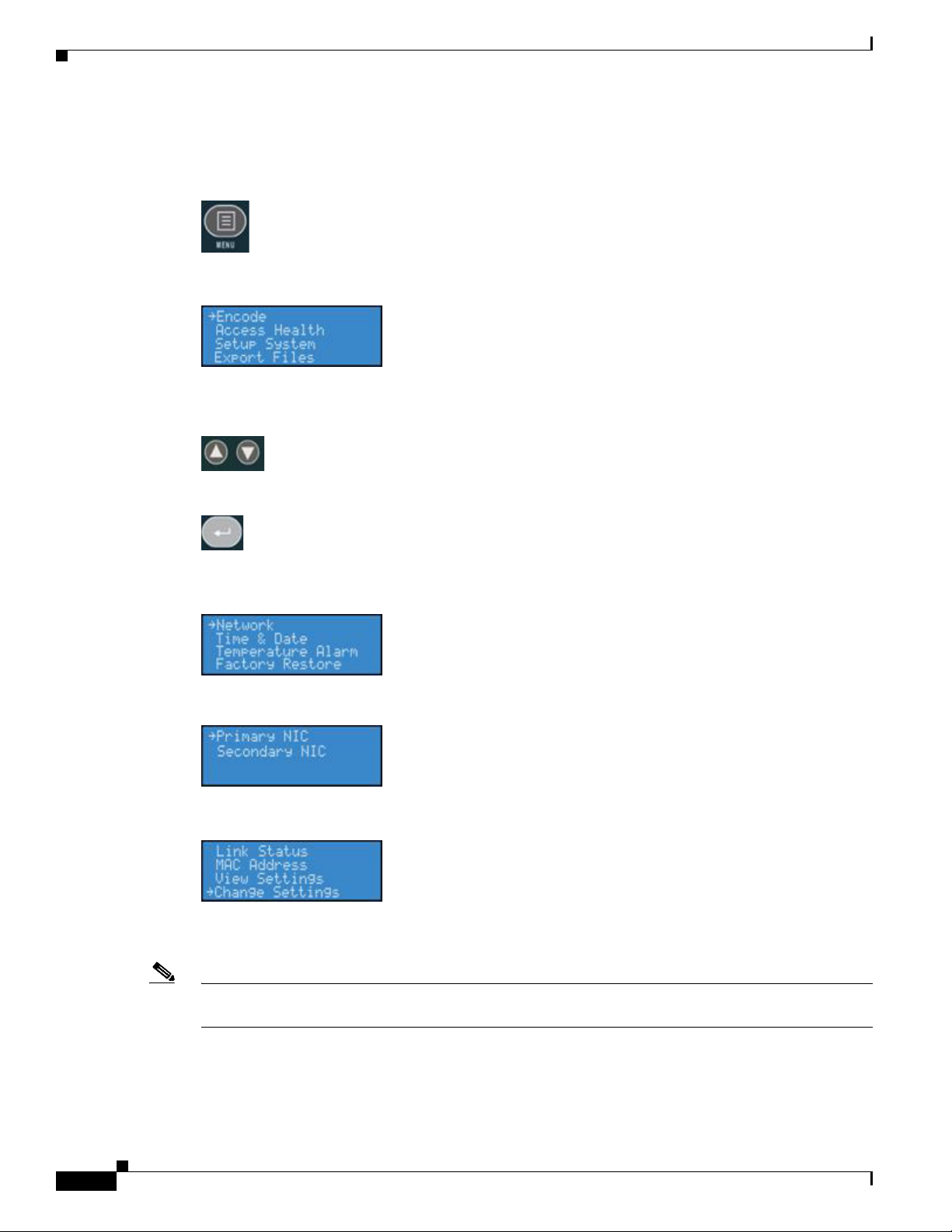
1. Press the Menu button to access the encoder’s EASE menu.
2. The EASE Menu options are the following:
3. Use the <UP> and <DOWN> buttons to move the select arrow in the menu until the arrow points to
Setup System option.
4. Now, press the <ENTER> button.
5. The encoder LCD readout will display the Setup menu. Using the <UP> and <DOWN> buttons,
select Network, and press the <ENTER> button.
6. Select the network interface you wish to modify, and then press <ENTER>.
7. Select Change Settings, and press the <ENTER> button.
The next menu presents the various network settings. Selecting one of these menu items allows you to
change these individual settings.
Note Once you modify these settings, the changes will be saved until you modify the settings again or you
restore the encoder back to its original factory settings.
1-10
8. Select DHCP On/Off, and then press the <ENTER> button. If you wish to cancel this process,
press the <MENU> button to return to the main menu.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 17

Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
9. The following buttons and their respective actions represent your choices:
• Press the <ENTER> button to select and continue.
• Press the Menu button to cancel and exit.
10. The next menu offers you the choice to enable DHCP for the network interface.
11. Using the <UP> and <DOWN> buttons, you can toggle the selection from the No to the Ye s option.
After you make your selection, press the <ENTER> button to input the change. The encoder will
confirm that you wish to change this setting.
Installation
12. Press <ENTER> to confirm your choice. The encoder will return to the menu to select another
individual setting to modify.
13. To input a static address for the IP address and/or Gateway, select either from the menu, and press
the <ENTER> button.
14. Using the <UP> and <DOWN> arrow keys to increment numerical value, enter a static IP address.
15. Press the <STREAM> button to move to the next field.
OL-17938-01
16. When you have correctly entered the IP address or Gateway address, press <ENTER> to input the
data into the encoder. When setting a static IP address, a screen will appear that will allow you to
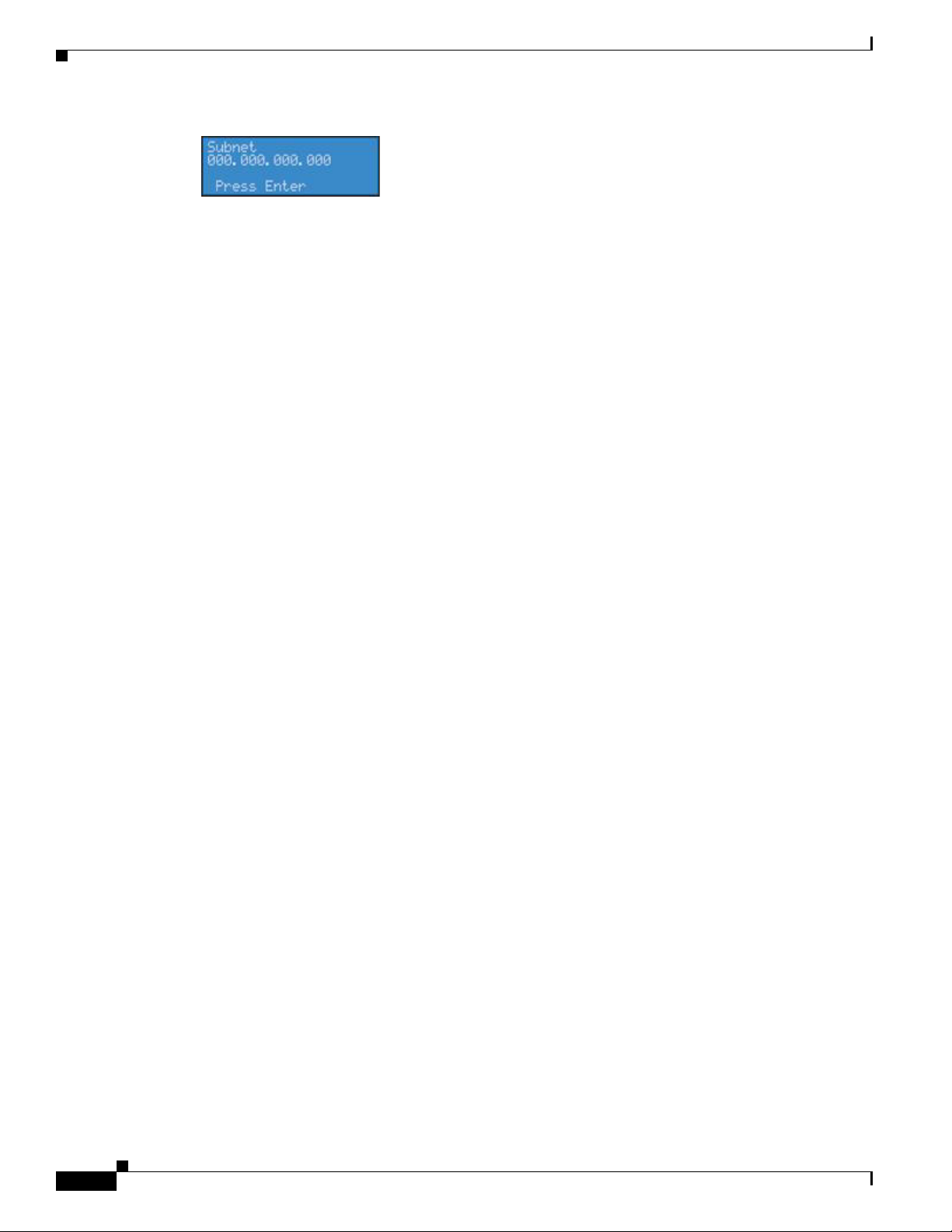
set the subnet address.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
1-11
Page 18
Chapter 1 Installing the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Installation
17. If you wish to remove a static IP address and/or Gateway previously set on the encoder, simply
enable DHCP by using the method described in Step
be removed.
10. Any previously entered static address will
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s
revised Cisco
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as an RSS feed and set content to be
delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service. Cisco currently
supports RSS
technical documentation, at:
Ve rs i on 2.0.
New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and
1-12
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 19

CHA PTER
2
Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Revised: November 9, 2009, OL-17938-01
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Introduction, page 2-1
• Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel, page 2-4
• DME Security Best Practices, page 2-10
• Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface, page 2-15
• Encoder Preset (A, B, and C), page 2-21
• Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Alerts, page 2-47
• Network Properties, page 2-48
• System Configuration Settings, page 2-50
Introduction
• What is Streaming Media?, page 2-1
• Streaming Infrastructure, page 2-2
• Simple Guide to Streaming Audio and Video Types, page 2-3
• Tutorial, page 2-3
What is Streaming Media?
Streaming media is media that is consumed (read, heard, viewed) while it is being delivered. Streaming
is more a property of the delivery system than the media itself. The distinction is usually applied to media
that is distributed over computer networks; most other delivery systems are either inherently streaming
(radio, television, Internet TV) or inherently non-streaming (books, video cassettes, audio CDs).
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 is designed specifically for streaming audio and video media over an
IP network.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-1
Page 20
Introduction
Streaming Infrastructure
Before setting up your new Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200, it is useful to understand the complete
overview of live streaming video—from video capture to streaming video playback.
There are many applications for capturing video into the computer environment that can range from
DVD authoring to live webcasting. Regardless of the final use of the video, all can be categorized into
three main workflow processes:
• Single video/session capture (one-off file capture for non-real time delivery)
–
Typically the captured file is then processed and/or authored into its final form for delivery
• Batch video/session capture (archiving, scheduling and storage)
–
Multiple source content is to be digitalized
–
Device control is needed for unattended source
–
Ability to schedule sessions is needed to capture timed events
• Live video capture, processing and delivery (webcasting)
–
Can be single or multiple sources
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
–
Live event at a specific time
–
Can be a remote or local capture
–
Final content is delivered in real time to viewers
Each category has its unique set of requirements that also dictates different user interfaces, functionality
and experiences. The Cisco
Digital Media Encoder 2200 is designed for live video capture, processing
and delivery.
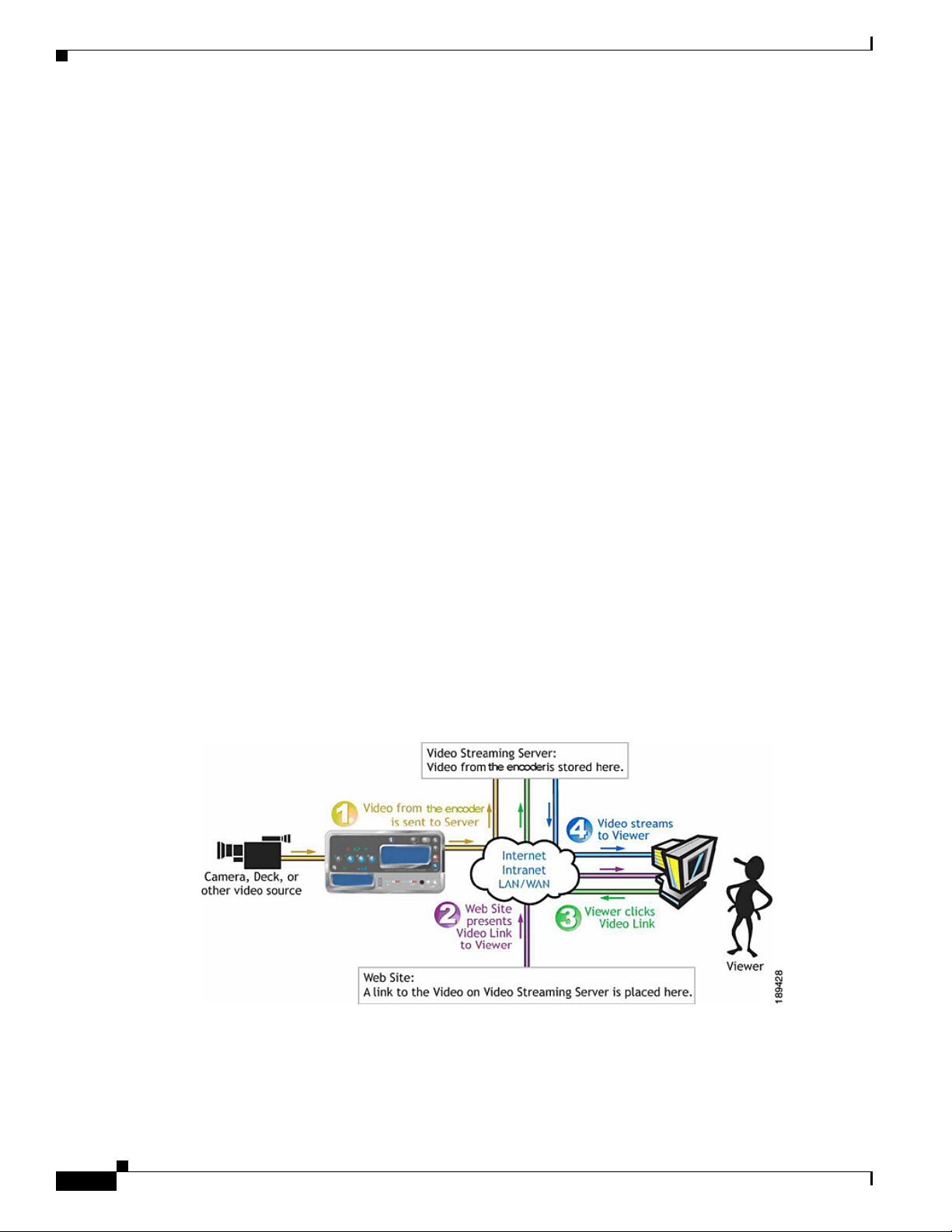
Figure 2-1 is a diagram illustrating the video path starting with the source, like a camera or video player,
going through the encoder, to the server, across an IP network, to a software player and displayed on a
monitor for audience viewing.
Figure 2-1 Video Path
2-2
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 21
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Simple Guide to Streaming Audio and Video Types
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 can create several different types of audio and video streams.
Although all are a type of IP video format, each has certain properties that make it more attuned to a
specific streaming video application. Cisco
content in a reduced resolution to allow the content to be streamed across the Internet to be played back
on a computer or a handheld mobile device.
Table 2-1 lists all formats supported by Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 with suggested application
uses. All of these formats can be used for many different applications.
Ta b l e 2-1 IP Video Compression for Streaming in Full Resolution or Lower
Format Description
Windows Media
RealVideo®/Helix
®
®
MPEG-4 Handheld devices and mobile phones
Digital Media Encoder 2200 was designed for creating video
Streaming Internet video and mobile devices
Streaming Internet video and mobile devices
Introduction
Tutorial
In choosing the right streaming format for your needs, you should first consider the audience to which
you will be sending your content. What is the most common player that they will have available to watch
your content? This will determine the format of the stream that you will create for your audience.
To determine the data rate that you will stream your content, you will need to determine the IP bandwidth
to which your audience has access. For example, if the access method uses an ISDN connection or less,
then you would stream your video and/or audio at a low data rate such as QCIF at 56kbps. If the access
is much greater like a cable modem or DSL connection, then you can provide a higher quality stream at
full resolution at 2 Mbps.
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 provides preconfigured encoding profiles for different bandwidth
connections. The profiles loaded will depend upon how you configure your encoder on its initial startup.
There are two interfaces for operation of your Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200: the encoder front
panel LCD display and buttons and the Niagara SCX Web Interface. This tutorial is divided into the
following two parts:
1. Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel, page 2-4
2. Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface, page 2-15
Note To access the Niagara SCX Web Interface or the Niagara SCX Encoder Explorer Software, you will
need a computer with a current web browser installed that has an IP connection to the encoder via a local
network on which both the encoder and the computer reside or through a direct IP connection by using
the included RJ-45 cable to connect directly from the encoder to a computer.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-3
Page 22
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel
Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel
Note For information about the front panel buttons, see the “Front Panel Diagram” section on page 1-6.
This section includes the following topics:
• Startup, page 2-4
• Shutdown, page 2-5
• Alternate Shutdown Method, page 2-5
• Starting an Encoding Session, page 2-6
• Checking CPU Usage, page 2-7
• Stopping an Encoding Session, page 2-8
• Connecting an External Storage Device, page 2-8
• Exporting Captured Video Files, page 2-8
Startup
Note If this is the first time that the encoder has been started, read the “Completing First Start Setup” section
on page 1-8 before continuing.
To start your encoder, press the <POWER> button on the front panel.
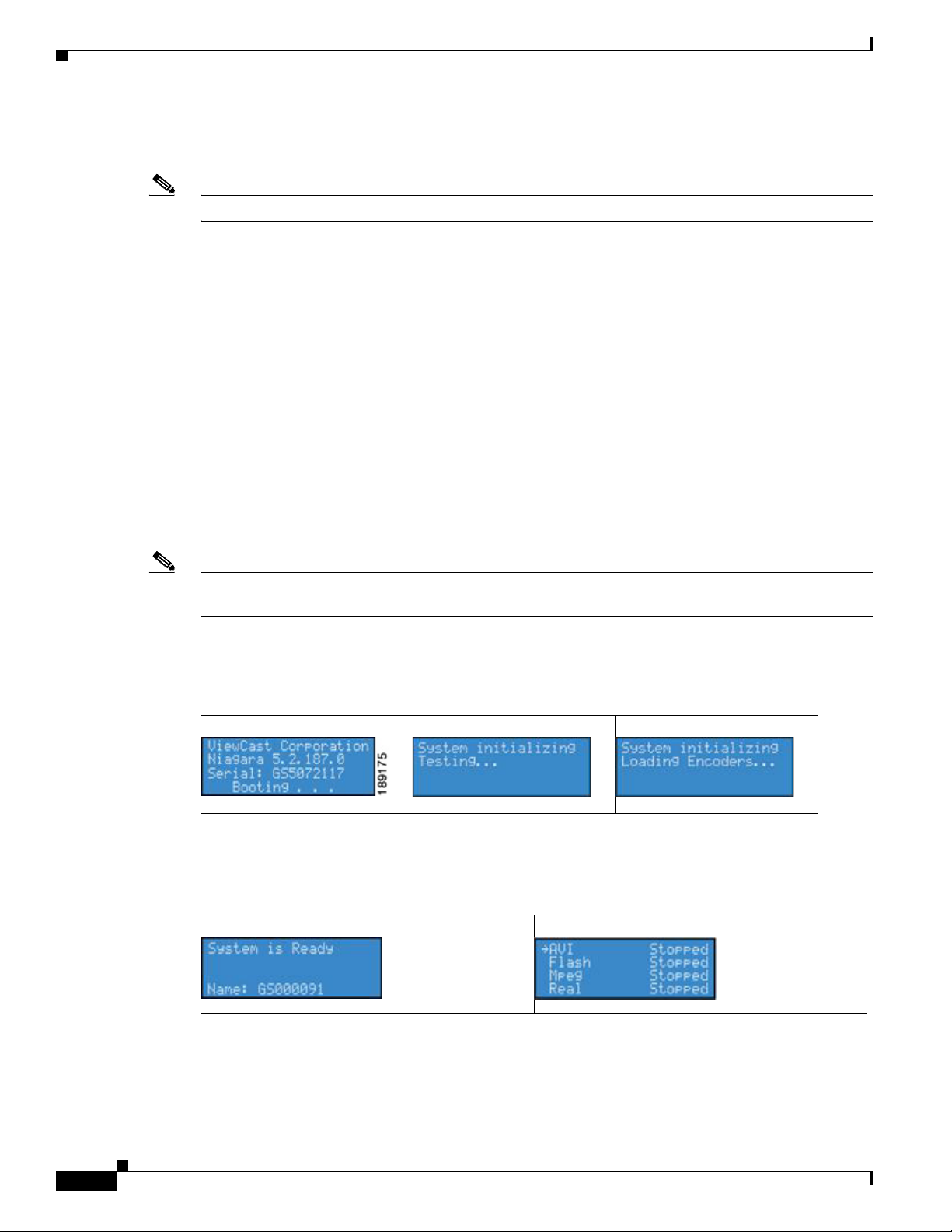
While powering up, the encoder LCD readout will display the following series of messages:
When System is Ready for operation, the encoder LCD display will alternate between status readouts that
are similar to the following:
2-4
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 23
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
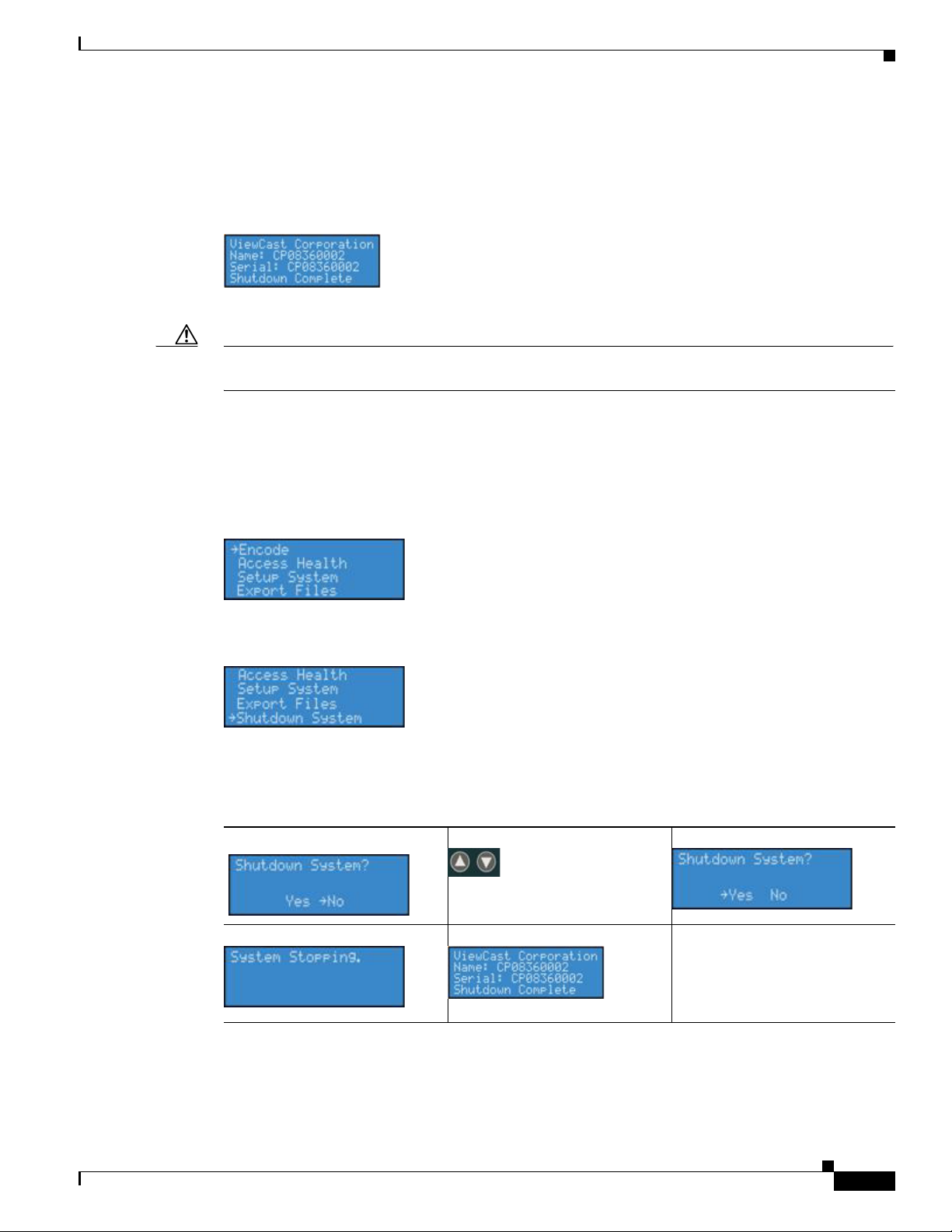
Shutdown
To shutdown the encoder, briefly press the <POWER> button on the front panel.
The encoder LCD readout will display the following messages:
After a few seconds, the encoder will power off.
Caution Allow the encoder to power down normally. If you force the system to shutdown improperly, data can
be corrupted. If so, the next time the system is started it can take several minutes to complete startup.
Alternate Shutdown Method
Alternatively, you can shut down the encoder by using the EASE menu.
Press the <MENU> button to display the EASE menu.
Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel
Using the <UP> and <DOWN> arrow buttons, scroll down until Shutdown System is displayed and
selected.
Press <ENTER>.
Then, confirm that you wish to shut down the system using the <UP> and <DOWN> buttons to select
either Ye s or No. Press <ENTER>.
.
—
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-5
Page 24

Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel
Starting an Encoding Session
The encoder LCD readout will display a list of available encoder profiles that can be used together with
the current status of each.
Note The name of each encoder profile is abbreviated to display the first 10 characters. When creating names
for custom profiles, be sure to create unique names that will be distinguishable by the first ten characters.
Use the <UP> and <DOWN> buttons to move the select arrow to point to the encoder profile that you
want the encoder to use for this encoding session.
Once you select the encoder profile you need, press the <STREAM> button again to start the encoder.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The encoder LCD readout then displays messages about the encoder start process.
After the encoder session has successfully begun, the encoder LCD readout returns to the previous
display of available encoders. The screen will indicate that the encoder profile you selected has begun
encoding.
If the encoder you started was assigned to one of the EZStream ABC buttons, the corresponding button
flashes and steady illuminates during and after the starting process.
By repeating this method, you can quickly start multiple encoders at the same time.
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 is a two-channel encoder, which means you can connect and stream
up to two audio and video sources at any given time. However, you can stream the same audio and video
at multiple data rates and multiple formats to provide the best user experience for different viewing
audiences.
2-6
For example, you can stream Windows Media at full resolution at 1 Mbps and the same time stream
RealVideo at CIF resolution at 300kbps.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 25
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel
Warning
There are limitations to the number of streams that you can capture simultaneously. If you attempt to
capture more streams than the encoder is capable of processing simultaneously, the streams will
drop frames and the video will appear to stutter resulting in a poor viewer experience. If the number
of sessions is not reduced in order to reduce CPU load, all encoding sessions could self-terminate
without warning.
Checking CPU Usage
Since you are able to start multiple streams, understanding how much of the processing power of the
encoder is being used is invaluable. If you are using less than 50%, then you should be able to start
another encoding session without adversely affecting system performance.
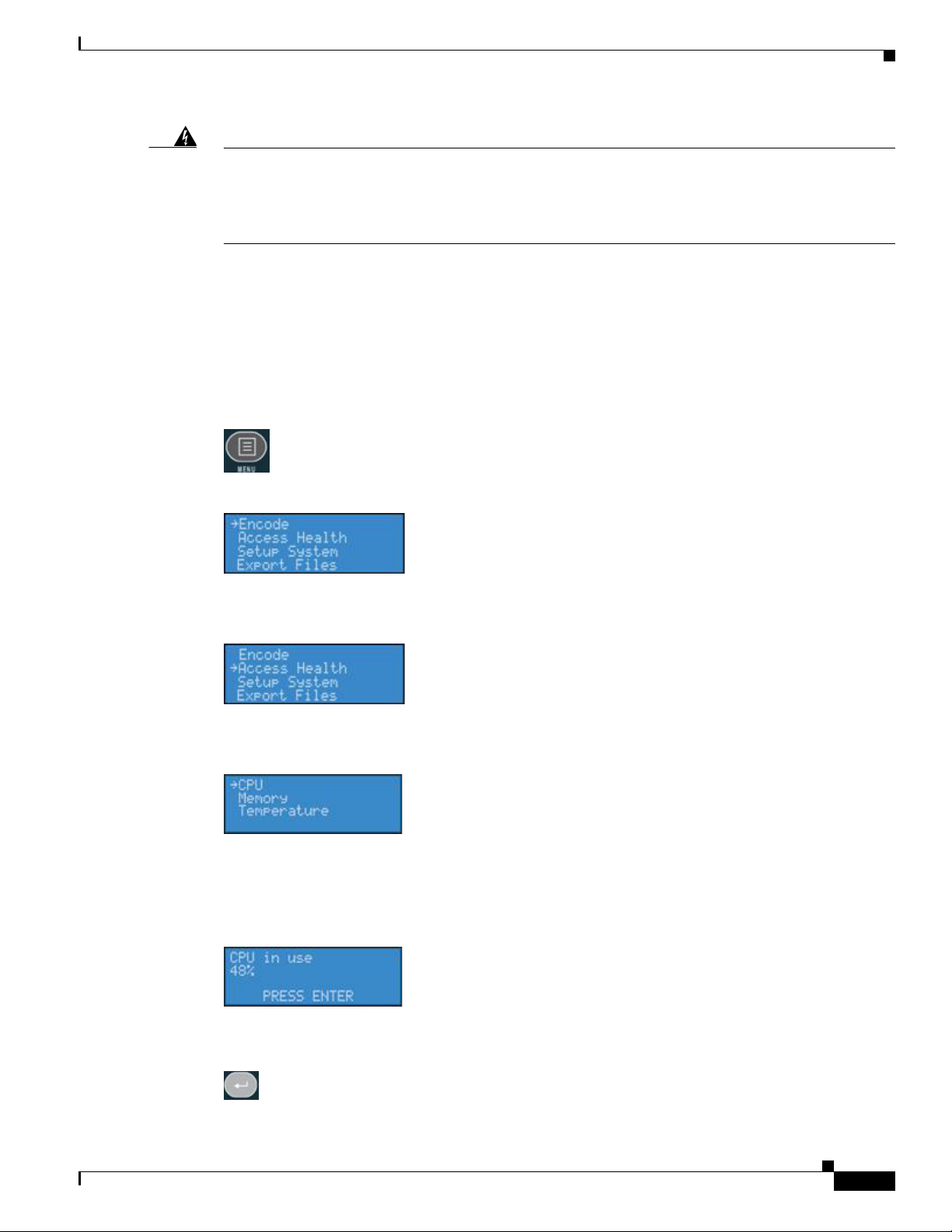
Press the <MENU> button to display the main menu on the encoder LCD readout.
The LCD readout will display the following menu choices:
Using the <UP> and <DOWN> buttons, move the arrow until it is next to the menu item Access and then
press the <ENTER> button.
OL-17938-01
The LCD readout will display the Access menu choices. Press the <ENTER> button with CPU menu
item selected.
The encoder LCD readout displays the amount of CPU cycles in use. When the encoder is idle (no
encoder sessions running), the CPU percent displayed should be 4% or less. If one or more encoder
sessions are running, then the percent displayed will be much higher and will fluctuate in a range of +/10 percentage points.
Press the <ENTER> button to return to the previous menu.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-7
Page 26

Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel
Stopping an Encoding Session
To stop an encoder, press the <STOP> button.
The encoder LCD readout displays the list of encoding and shows the current status of each session.
Using the <UP> and <DOWN> buttons, move the pointer to the position next to the encoding session
you want to terminate.
Press the <STOP> button again, and the encoder session selected will terminate.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
To return to the main menu, press the <MENU> button.
Connecting an External Storage Device
The Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 rear panel provides two USB ports, and the front panel provides
one. You can connect almost any standard USB flash drive to one or both of these ports. This allows you
to export any AV files you may have created on the encoder’s local storage drive. The local storage drive
is the D drive when you use the Save to File setting while you employ the Niagara SCX Web Interface.
When you insert a USB flash drive in one of the USB ports on the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200,
the encoder automatically detects the removable storage device and assigns a random drive letter to the
device. This device can capture files directly or can be employed to use the encoder Export File
function, which is available for access when using the front panel menu.
Exporting Captured Video Files
You can export your captured video files to an external USB drive.
2-8
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 27
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Note To export files to a USB device from Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200, you must set a default location
for the captured video files via the SCX Web Interface, and place those files in that default location. This
can be done on the System Configuration page of the web interface at the *Default AV Folder box. By
default, this folder is set to D:\AVFiles. After you input the preferred default location in the *Default AV
Folder box, you can begin exporting your files from the encoder.
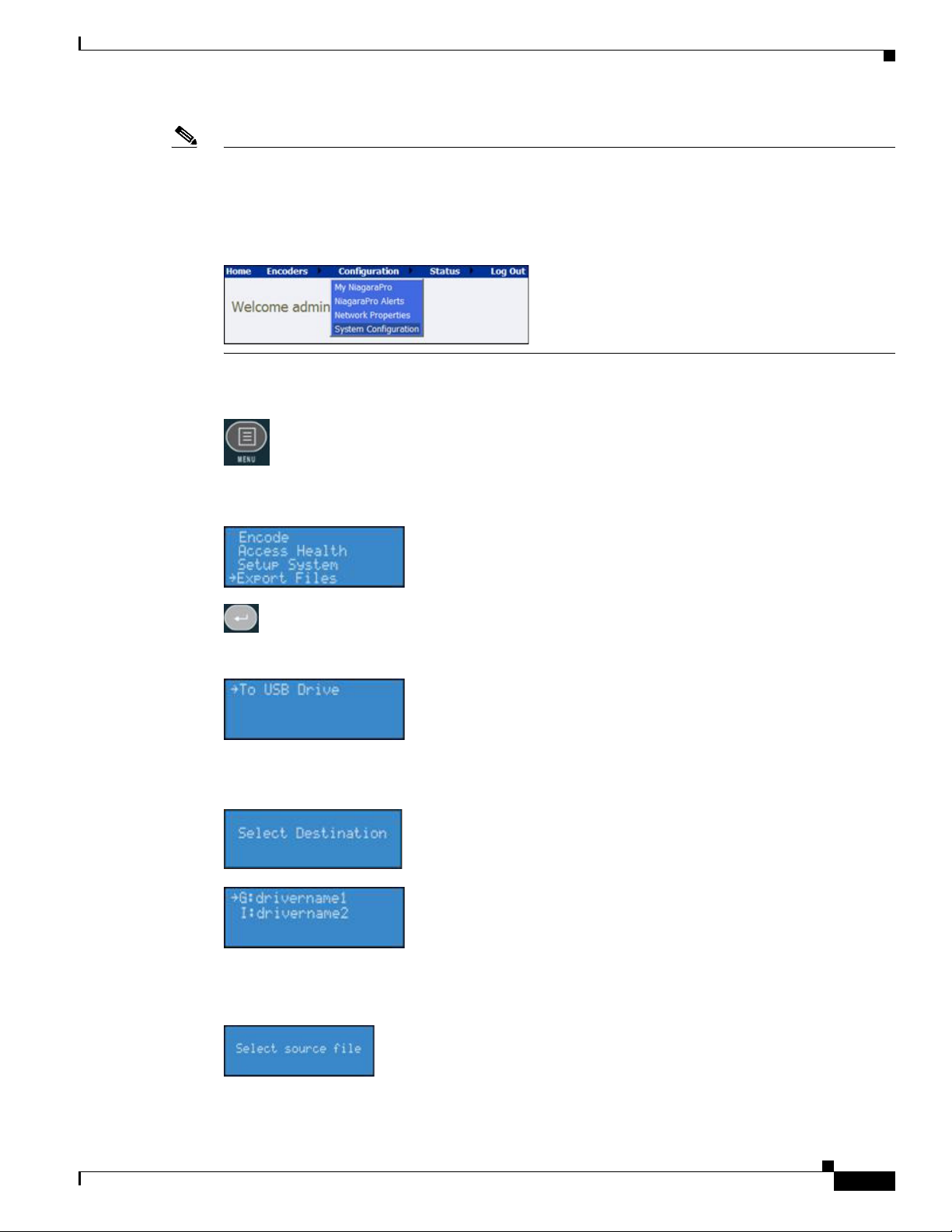
Press the <Menu> button to access the encoder menu.
Using the <UP> and <DOWN> arrow buttons, highlight the Export Files option, and press the <Enter>
button.
Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel
Then, select the To USB Drive option, and press <ENTER>.
The next screen will ask you to select the drive destination and provide a list of active USB drives
connect to the encoder.
Select the USB drive to which you wish to export, and press <ENTER>.
The next screen will ask you to select a source file, i.e., the file you want to export to the USB device.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-9
Page 28

DME Security Best Practices
Your source file should appear on the following screen.
Note The file name on this screen is for instructional purposes only.
Upon seeing the name of the file you wish to export on the screen, press <ENTER>. You will then see
the following screens.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Once the encoder is finished exporting the file, you can remove the USB device.
DME Security Best Practices
We wrote topics in this section to answer and expand upon these customer questions about
DME
security:
• CSCsz67661 — How do I change the factory-default password for Windows?
• CSCta04924 — How do I disable unneeded Windows services, such as NNTP, SMTP, and SNMP?
• CSCsz67661 — How do I safeguard my encoded files on the DME file share?
Warning
Factory-defined passwords exist by default on all new and newly restored DMEs. These credentials
persist until you change them. Because they are well-known, these credentials are a security
vulnerability in your network. Therefore, we recommend very strongly that you change
each time that you start to configure a DME.
In addition, some services are enabled by default that you might never use. We recommend that you
disable all unneeded services.
• Factory-Defined Login Credentials, page 2-11
• Changing Factory-Defined Login Credentials, page 2-11
them promptly
2-10
• Other Required Password Maintenance (Only When Autologon Is Configured), page 2-13
• Tasks to Complete After Changing DME Login Passwords, page 2-14
• Disabling Unneeded Services, page 2-14
• After a Live Event Is Finished, Remove Its Encoded Video Files from the DME File Share,
page 2-15
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 29
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Factory-Defined Login Credentials
Table 2-2 lists login credentials that are predefined on DMEs.
Ta b l e 2-2 Factory-Defined User Accounts and Passwords
DME Model
DME Security Best Practices
Username Password
User Accounts for Microsoft Windows — See Harden Windows, page 2-12.
GoStream password
1
DMS-DME 2200
DMS-DME 2000
— — — X
Niagara password X X X —
DMS-DME 1100
Notes
DMS-DME 1000
Warning
Never configure a DME to log in automatically. Doing so
prevents true security in your network.
If — despite our recommendation — you configure a DME to log into
Windows automatically, password management becomes far more
complex. Thus, any time that you neglect to change an auto-logon
password specifically, you will prevent your DME from working as
designed. See
Other Required Password Maintenance (Only When
Autologon Is Configured), page 2-13.
SCXUser viewcast X X X X Used for the Niagara SCX service as well as the web service. This is not
the user account that is used to log-in to Niagara SCX.
User Accounts for the Niagara SCX Web Interface — See Harden the web interface, page 2-13.
admin admin X X X X Used for the web-based administrative console on DMEs.
Login is possible only through a system from which your DME is
reachable. Its connection to your DME might be either direct
or
networked.
1. In 5.2.187 and later releases on a DME 1000.
Changing Factory-Defined Login Credentials
Warning
OL-17938-01
Be very careful as you complete this workflow. Any mistakes that you make might prevent your DME
from booting correctly or functioning correctly.
Before You Begin
• This workflow uses the instance of Microsoft Windows that runs on your DME. Even though a
remote management connection might be sufficient, we recommend instead that you connect a
keyboard, a mouse, and a monitor to your DME directly and use them to control Windows.
• From Step 1, this workflow assumes that your DME is either new or in a factory-restored condition.
If this is not true, or if you are not sure, we recommend very strongly that you perform a factory
restore operation now.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-11
Page 30
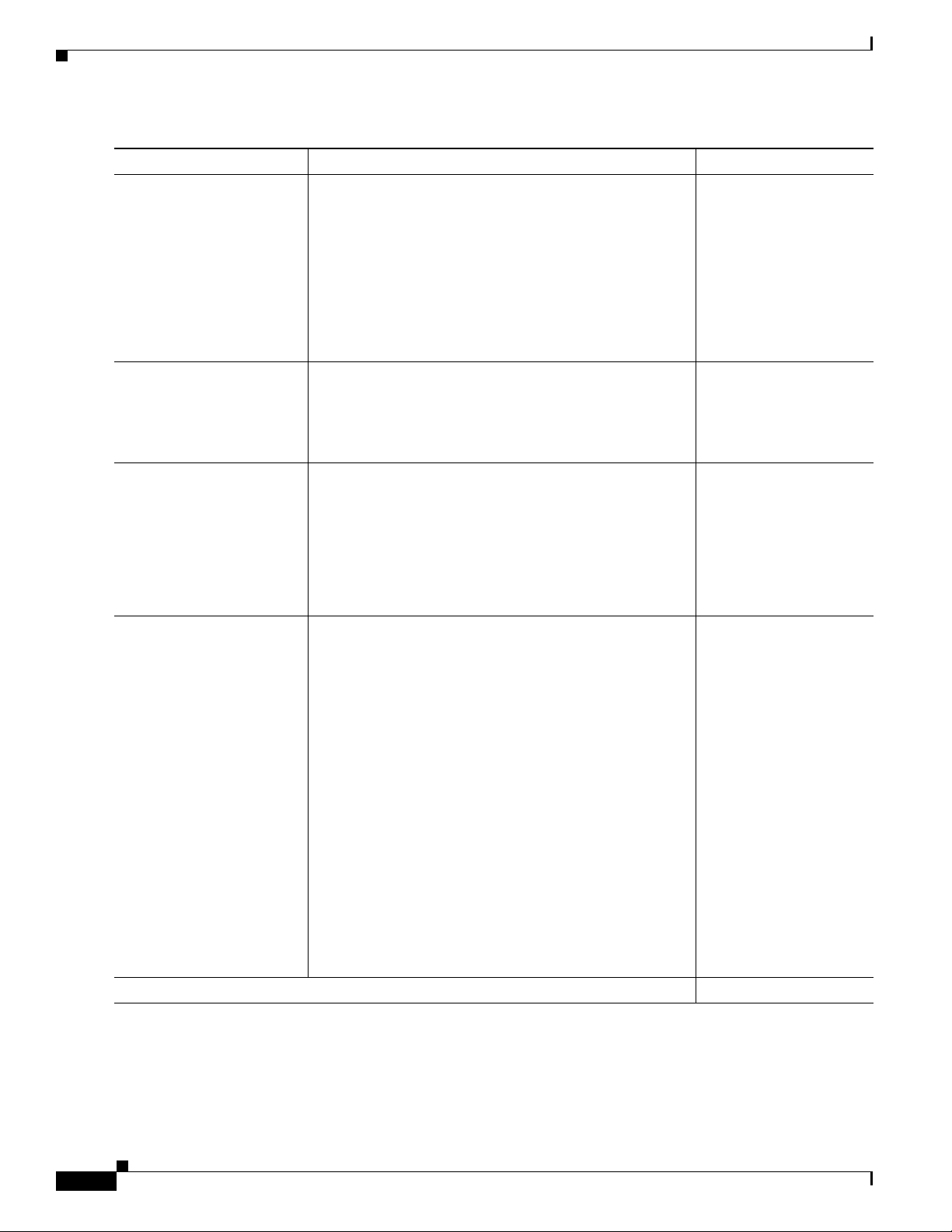
DME Security Best Practices
Tas k Steps Notes
Step 1
Harden Windows
Change the Windows
password for the main
account.
Step 2
Harden Niagara SCX
Change the password for the
SCXUser account, which
you use to log in to Niagara
SCX Encoder Explorer.
Step 3
Stop agent services
Procedure
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
a. Choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > User
Accounts, and then:
• If you have a DME 1000, choose GoStream >
Change my password.
• Otherwise, choose Niagara > Change my
password.
b. Change the password as desired.
c. Click Change Password.
a. Choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > User
Accounts
b. Change the password as desired.
c. Click Change Password.
a. Do either of the following:
> SCXUser > Change my password.
Depending on your DME
model type, the username
is either Niagara or
GoStream. See
Table 2-2
on page 2-11.
—
—
Step 4
Update web.config to use the
new password
Edit the web.config file.
• Choose Start > Run. Type system32 and press
Enter. Double-click
GoStreamStopServices.bat.
• Choose Start > All Programs > Viewcast >
Niagrara SCX
> Niagara SCX Agent, and then
click Stop.
a. Use Windows Explorer to browse to
\inetpub\wwwroot\encoderswebservice.
OR
Browse instead to one of the following:
• For a DMS-DME 1000,
\inetpub\wwwroot\GoStream.
• Otherwise, \inetpub\wwwroot\Niagara.
b. Open the web.config file in a text editor, such as
Notepad.exe.
c. Locate the line of text that looks like this:
<identity impersonate="true"
userName="scxuser" password="viewcast"/>
d. Edit the password string in this line of text.
—
Step 5
2-12
e. Save your work and exit the text editor.
Restart your DME
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
—
OL-17938-01
Page 31

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Task Steps Notes
Step 6
Check for errors
Point the DME web browser at http://localhost/encoderswebservice/, and then verify
that the SCX service is available.
Step 7
Harden the web interface
a. Point your browser to the HTTP address of your DME.
b. Enter the username and the password, as prompted.
The factory default for each of these is admin.
c. Click Log In.
d. Choose Configuration > My NiagaraPro.
e. Click the username admin in the NiagaraPro
Properties area.
f. Enter the current password in the Password field.
g. Enter the new password identically in both of
these
• New Password
• Confirm New Password
DME Security Best Practices
—
—
fields:
h. Click Change Password.
The changed password takes effect immediately.
Tip Saved changes are lost each time that you perform a factory restore operation. Remember to repeat this
procedure any time that login credentials use factory-defined values.
What to Do Next
• If Windows is configured to allow automatic logins, see Other Required Password Maintenance
(Only When Autologon Is Configured), page 2-13.
• Otherwise, see Tasks to Complete After Changing DME Login Passwords, page 2-14.
Other Required Password Maintenance (Only When Autologon Is Configured)
Warning
Never configure Microsoft Windows on your DME to enter login passwords automatically. Doing so
creates a significant security vulnerability in your network.
If you disregard the warning against allowing automatic logins and you configure them nonetheless, you
must take additional steps to ensure that logins occur as expected after you change the encrypted
auto-logon password that Windows uses.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-13
Page 32

DME Security Best Practices
Procedure
Step 1 Search the DME hard drive for TweakUI.exe. In most cases, this file is in F:\Windows.
Alternatively, you can download this file as part of a Microsoft tools package at
http://www.microsoft.com/windowsxp/downloads/powertoys/xppowertoys.mspx.
Step 2 Open TweakUI, and then choose Logon > Autologon.
Step 3 Click Set Password.
Step 4 Enter the new password twice, as prompted. Be careful that the password matches exactly.
Step 5 Click OK to save your work and exit TweakUI.
Step 6 Restart your DME.
Step 7 Verify that login occurs automatically and that the Windows desktop loads.
Note If you disregard the warning against allowing automatic logins and configure them nonetheless,
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
ViewCast software will not work unless the Windows desktop loads correctly on your DME.
Tasks to Complete After Changing DME Login Passwords
Procedure
Tas k Notes
Step 1
Perform basic setup
See Basic Operation: Using the Front Panel, page 2-4.
functions via the front
panel.
Step 2
Test and validate that your
DME performs as expected.
Tip If your DME does not perform as expected, we recommend that you complete
a factory restore operation. In this case, the factory-defined login credentials
that you changed will become active again and might expose your network to
attack or other types of unauthorized use.
Disabling Unneeded Services
Caution Intuders might use exposed services as security attack vectors against your network.
If your DME enables and exposes any service that is not required, you can disable it. Possible examples
of such services include NNTP, SMTP, and SNMP.
2-14
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 33

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
Step 2 Double-click the name of a service that should be disabled.
Step 3 Click the Log On tab.
Step 4 Do one of the following:
• If only one hardware profile is listed, click it, and then click Disable.
• If multiple hardware profiles are listed, click one, then click Disable, and repeat as often as
necessary until you have disabled this service on each profile.
Step 5 Click Apply, and then click OK.
Step 6 Restart Windows.
After a Live Event Is Finished, Remove Its Encoded Video Files from the DME
Share
File
Caution We strongly recommend that you save copies of the encoded video files on your DME file share, and
then promptly delete the original filess from your DME.
The file share uses a factory-default username and password, which you cannot change. Anyone who
knows which network node is your DME and knows these login credentials can mount the file share and
manipulate its files.
Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface
This section includes the following topics:
• Accessing the Web Interface, page 2-15
• Starting an Encoding Session, page 2-17
• Stopping an Encoding Session, page 2-18
• Viewing the Activity Log, page 2-19
• Configuring the EZStream Buttons, page 2-20
Accessing the Web Interface
The Niagara SCX Web Interface does not require software and works with any computer that has a
current web browser, including Microsoft
Cisco
Digital Media Encoder 2200 system must either reside on a shared IP network with the computer
or can be directly connected to a Windows computer by using an Ethernet cable (RJ-45).
OL-17938-01
®
Windows®, Macintosh, and Linux® machines. The
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-15
Page 34

Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface
To access the Niagara SCX Web Interface, open the web browser on your computer and access the web
interface by typing in the encoder machine name. For example, you would type http://cp08360002. The
network name of the encoder is also its serial number and can be obtained from the LCD readout during
the power up process.
If the encoder is already powered up, the serial number can be obtained from the LCD display while the
system is idle.
At that time the encoder LCD display will alternate between readouts that are similar to the following
display:
If the name is not immediately displayed on the System is Ready window, press the <UP> and
<DOWN> arrow buttons to toggle through the system information until the name is displayed.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The serial number is also located on the bottom of the encoder.
Enter the encoder name in the web browser (as shown below), and press enter.
You will be prompted with a login screen that requires a user name and password. By default, the user
name and password are both admin.
After logging in, you will have access to all of the web-enabled functions, including encoder operations,
management, and system configuration tools.
Note If you cannot browse to the encoder by using its machine name, type in the encoder IP address instead.
This information is also available from the System is Ready window when the system is idle.
2-16
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 35

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Starting an Encoding Session
To start an encoding session, move the mouse pointer over Encoders in the menu bar, and click on All
Encoders in the drop-down menu.
All of the encoder profiles loaded on the encoder will be presented in a list indicating format and current
status.
Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface
Press the red Stream icon located in the right column of the encoder you wish to start.
The web page automatically updates with messages detailing the encoder start progress.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-17
Page 36

Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface
After the encoder has started successfully, the web page will return to the All Encoders page with the
encoder status updated to reflect the Started mode.
Stopping an Encoding Session
If you are not already on the All Encoders page, move your mouse over Encoders in the menu bar and
click All Encoders in the drop-down menu.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
This will bring you to a web page similar to the following.
Press the blue icon, which indicates it is a streaming encoder, located in the right column of the encoder
you wish to stop.
2-18
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 37

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The web page automatically updates with messages detailing the encoder stop progress.
After the encoder has stopped successfully, the web page will return to the All Encoders page with the
encoder status updated to reflect Stopped mode.
Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface
Viewing the Activity Log
The Activity Log records the Encoder Start and Stop events. To view the Activity Log, move the mouse
pointer over Status in the menu bar, and click on Activity Log in the drop-down menu.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-19
Page 38

Advanced Operation: Using the Niagara SCX Web Interface
The log is updated for every event on the encoder. The log now includes the starting and stopping events
for the encoder from the
Encoding Session” section on page 2-18.
Each event is date and time stamped. Pressing the Clear Activity Log button in the upper-right clears
all logged activities.
“Starting an Encoding Session” section on page 2-17 and “Stopping an
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Configuring the EZStream Buttons
The encoder provides one-button streaming via the EZStream buttons located on the front panel of the
system. By default, these buttons are not assigned to an encoder. The Niagara SCX Web Interface is
used to configure each button to a specific encoder.
You can assign a preset encoder using the Niagara SCX Web Interface by moving your mouse pointer
over Encoders in the menu bar and selecting Preset A, B, or C in the drop-down menu. A preset is a
quick way to select and assign a specific encoder to Preset A, B, or C.
2-20
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 39

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
When you access the Encoder Preset A page, you are presented with the configuration page for the
EZStream A button. This page contains a graphic representation of the front panel of the encoder. The
A button is highlighted on this graphic representing that you are actively assigning an encoder to this
corresponding EZStream button.
This page presents a Select Encoder field and a link at the bottom of the page to view the View All
Encoders page. If an encoder has been assigned to the Preset, then you will also be presented with an
Edit link next to the View All Encoders link.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Select Encoder
Click the drop-down list next to Select Encoder. This provides the complete list of encoders available
on the system.
Select the encoder you wish to assign, and click the Submit button.
The web page will update the preset A and provide a message reporting Encoder Preset: A updated
successfully.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-21
Page 40

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
By clicking on the B and C buttons on the encoder graphic, you can assign encoders to the EZStream
buttons in the same way, as shown in the following diagram.
Note It is not possible to assign the same encoder to two EZStream buttons simultaneously. If an encoder is
already assigned to a button and you assign it to another button, the encoder will remove the association
to the previous button in favor of the most current request.
View All Encoders
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
After assigning encoders to the A, B, and C buttons, the Presets column on the All Encoders page
updates to reflect these changes.
Edit Preset Encoder Profile
After assigning encoders to the EZStream buttons, you can access the encoder editing page by clicking
the button Edit Encoder link at the bottom of the Preset page.
The following sections show what each encoding format property page looks like. For more information
on setting up each type of encoder, see the
• AVI Encoder Properties, page 2-23
• Flash Encoder Properties, page 2-23
“Editing an Encoder Profile” section on page 2-26.
2-22
• MPEG-4 Encoder Properties, page 2-24
• Real Encoder Properties (Helix), page 2-25
• Windows Media Encoder Properties, page 2-26
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 41

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
AVI Encoder Properties
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Flash Encoder Properties
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-23
Page 42

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
MPEG-4 Encoder Properties
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-24
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 43

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Real Encoder Properties (Helix)
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-25
Page 44

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Windows Media Encoder Properties
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Editing an Encoder Profile
When you create a new encoder, the Encoder Properties page appears. You will be able to edit the new
profile provided by default to your specific encoder settings and requirements. The property windows
for editing a new encoder or an existing encoder are identical.
You can also edit an existing encoder profile by going to the All Encoders page.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-26
OL-17938-01
Page 45

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Click the Edit link next to the encoder whose properties you wish to modify.
The properties page for that encoder is then displayed.
Video & Audio Settings
Regardless of the encoder type, all types require that you set the audio and video properties. These values
are the same for all encoder types except for the added color space setting for AVI and MPEG-4.
You can enable or disable video and/or audio by clicking the check box next to Source under Video
Settings and/or Audio Settings. When enabled, the Input, Signal, Proportions, Size fields under Video
Settings, and the Input field under Audio Settings, as shown in the following screenshot.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
OL-17938-01
Although the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 is a single channel encoder, meaning you can capture
from two independent audio and video sources at any given time, you can capture multiple streaming
formats and resolutions simultaneously from the same video source. To accomplish this, the video source
is seen as multiple inputs denoted by incrementing decimal values. They appear in the following manner:
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-27
Page 46

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
The audio source settings include the choices set forth below.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Warning
Ensure that all of the encoders using the same video Proportion and Size settings also use the same
video and audio source settings. For example, all encoders capturing at Standard proportion and CIF
size are set to Osprey-5x0 Video Device 1.1 while encoders capturing at Standard proportion but QCIF
resolution are set to Osprey-5x0 Video Device 1.2.
Set Input for both video and audio to match the connectors on the back of the encoder to which you have
connected your video and audio source. This could be Composite or S-Video, or SD SDI for video input
and Unbalanced, XLR Balanced, XLR AES/EBU, or embedded SDI for audio input.
When you performed the First Start Setup, you determine if your video signal was NTSC or PAL. The
Signal field adds granularity for regional NTSC, PAL, and SECAM settings. If you are uncertain which
setting applies, refer to the owner’s manual for the video source you have connected to the encoder
hardware.
The Proportions setting uses the term Standard, meaning square pixels for a VGA monitor, and
CCIR-601, meaning elongated pixels for a TV monitor. Choose the setting that reflects the type of
display on which your content will be viewed. For example, if you will be streaming your video on the
Internet to be viewed on a computer monitor, select Standard. If the inaccurate setting is selected, your
streaming video will be distorted.
The Size field refers to the pixel size of the encoded video. The standard sizes are as follows:
• Full-size for full screen video
• CIF for video scaled from full-size to one-fourth size
• QCIF for video scaled from full-size to one-fourth of CIF size
You can also specify a custom size for your video. This is useful when capturing video to be played on
a mobile video device that requires a non-standard size for compatibility.
2-28
If you select Custom from the drop-down menu, two additional fields will appear allowing you to type
in the exact size you want the resulting video to be.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 47

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Note If you specify a video size that is not compatible with the color space of your source video, the encoder
will automatically correct the size to the closest compatible setting when you click the Submit button.
The color space format setting, entitled Format, is available only in AV I and MPEG-4 Encoder
Properties and appears as an additional field under the Size setting (see below).
Now that you have completed all of the Video and Audio settings, you can proceed to the encoder type
settings at the bottom of the page.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Streaming Properties
As previously stated, these settings will vary according to the encoder type. Please refer to each encoder
properties page setting in this document for further explanation and detail on the Streaming Properties
Settings and Advanced Streaming Settings sections of each encoder.
Advanced Streaming Settings
This section includes the following topics:
• SimulStream, page 2-29
• Deinterlace, page 2-31
SimulStream
SimulStream employs filters to change the appearance of an image or part of an image by altering the
shades and colors of the pixels in some manner. Filters are used to increase brightness and contrast as
well as to add a wide variety of textures, tones and special effects to a picture. SimulStream filters have
two interrelated purposes, as follows:
• They allow applications to enumerate and list video capture and preview pins or streams (each with
different settings) as named entries in their video device select lists. The video device driver can be
configured to show multiple filters per device. Each filter has one preview pin and one capture pin.
Standard applications have the capability to access a particular filter without any custom
programming specialized for Osprey devices.
OL-17938-01
• Each filter has independent settings for cropping, default output size, watermarks, and captions that
can be stored between sessions. Compared with the previous “pin-based” method, no requirements
are necessary for a particular startup order to associate settings with instantiations.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-29
Page 48

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Please see the Enable SimulStream dialog box below.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The checkbox next to Enable SimulStream at the top of the dialog box, when checked, enables
SimulStream to run for the currently selected encoder.
The encoder includes a full SimulStream license installed for each A/V channel, and this checkbox
controls full SimulStreaming.
Note When you change the Enable SimulStream status and click Submit, you must restart the appliance. If
you do not, SimulStream may become partially active, but the capture devices may be incorrectly named,
and their pins may be incorrect.
Show filters per device
With the Show filters per device control, you can set the device driver to expose multiple filters per
device for enumeration and selection by encoders. If, for example, 5 filters per device are chosen, device
lists in applications will show four entries for the currently chosen device. For device 1, they are
designated as 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5.
Note The number of filters you request will not display or work correctly until the system is restarted.
Note While it is possible to expose and enumerate multiple filters per device, the practical number of working
filters will be less. The practical number of filters depends on the capability of the appliance, the types
of filtering enabled, the types of scaling and color format conversions requested per encoder, and the
type of processing employed. If the appliance has multiple capture channels, the number of filters is the
total across all channels. In addition, some types of processing, such as deinterlacing and gamma
corrections, which are performed once per channel may, in this case, occur multiple times. In summary,
2-30
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 49

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
an appliance can support multiple concurrent filters on one device if the processing per filter is light.
However, only 2 or 3 simultaneously running filters can be supported if the processing load inside or
outside the driver is particularly heavy.
Deinterlace
The Deinterlace field has four drop-down choices. These choices are Off, Auto, Inverse Telecine, and
Motion Adaptive, as you can see below.
In further explanation of each choice, please see the following definitions.
• Off —Performs no deinterlacing of any kind.
• Aut o—Applies inverse telecine deinterlacing to all telecine video. Applies motion adaptive
deinterlacing to all video that is not telecine. Switches dynamically between the two modes as the
content changes. Available for NTSC video only.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
• Inverse Telecine—Applies inverse telecine deinterlacing to all telecine video. Performs no
deinterlacing of video that is not telecine. Available for NTSC video only.
• Motion Adaptive—Applies motion adaptive deinterlacing to all video.
Deinterlace settings are applied and stored per-device and are applied to all filters and pins associated
with a device.
Motion Adaptive Deinterlace
Motion adaptive deinterlace is an algorithm for deinterlacing pure video (non-telecine) content. It
detects which portions of the image are still, and which portions are in motion, and then applies different
processing to each scenario. Motion Adaptive Deinterlace is the only type of deinterlacing that uses
Motion Threshold under Advanced Streaming Settings—Simulstream.
Telecine and Inverse Telecine
Telecine video is NTSC video which was originally created on film at 24 frames per second. In the
telecine conversion process, certain fields are repeated in a regular, recurring sequence. If a telecined
sequence is viewed directly on a progressive screen, interlacing artifacts will be visible.
The process called “inverse telecine” is the reverse of “telecine” — inverse telecine drops the redundant
fields and reassembles the video in a 24 fps progressive format. Interlacing artifacts are 100 percent
removed. If the video is viewed at 24 fps, you will see the exact timing and sequencing that was on the
original film. If the video is viewed at 30 fps, every fifth frame will be repeated. However, there will be
no deinterlacing artifacts.
OL-17938-01
Telecine and inverse telecine only apply to NTSC video. They are not used for PAL and SECAM video.
The Aut o and Inverse Telecine button choices will be disabled when either PAL or SECAM is selected
as the video standard.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-31
Page 50

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Motion Threshold
Motion Threshold adjusts the threshold of difference from spatially- and temporally-related pixels,
which are judged to be “motion.” If you enter a higher value, the number of pixels in motion will be
greatly reduced. If you enter a lower value, the number of motion pixels greatly increases until the entire
screen, more or less, is considered in motion. The recommended default is 16.
Sharp and Smooth Motion
When the Sharp Motion radio button is selected, detail in motion areas will be sharper, but at the
expense of somewhat jagged diagonal edges.
When the Smooth Motion radio button is selected, more loss of detail will occur in motion areas, but
edges will be smoother.
Since the eye does not clearly see detail in areas of motion—and edge artifacts are highly intrusive—the
Smooth algorithm is preferred for most applications. The Smooth algorithm uses a bit more CPU.
Both algorithms treat still areas in the same fashion, and there should be no loss of detail in still areas.
AVI Encoder Settings
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
AVI is an uncompressed audio and video storage format and, therefore, only has the ability to save to a
file. You can type in a unique name for the generated AVI file and modify the directory path to the
location the file will be stored. Clicking the Default Folder link will insert the path of the default folder
for file storage on the encoder. By default the path is d:\AVFILES\.
Note It is not recommend that you store files in any other directory on the encoder.
Once you have saved your file to the encoder internal hard drive, we recommend that you move the drive
to another external storage device such as a USB drive or a network drive for backup purposes.
After you have input your settings, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page to save your
changes.
Warning
If you click away from the current page to another web page without clicking Submit, your changes
will be lost.
Flash Encoder Settings
2-32
The Flash Encoder Settings are similar to the AVI settings for saving the audio and video to a file.
However, Flash adds some additional frame and bit rate controls. The frame rate changes the frames per
second at which the video will be encoded. The audio format setting can be used to modify the audio
frequency and changes stereo to mono. The bit rate settings pertain to the amount of data per second the
audio and video are captured. Decreasing the bit rate for both or either will decrease the playback
viewing quality.
The Flash encoder creates a Flash format audio and video file. You can type in a unique name for the
Flash file (.flv).
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 51

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
After you have input your settings, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page to save your
changes.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Warning
If you click away to another web page without clicking Submit, your changes will be lost.
MPEG-4 Encoder Settings
This section includes the following topics:
• Encoder Settings Web Interface, page 2-33
• Real Encoder Settings (Helix), page 2-39
Encoder Settings Web Interface
The Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 software MPEG-4 compression engine provides (1) H.264,
MPEG-4, Part 10, (Baseline Profile) (2) MPEG-4, Part 2, (Simple Profile) and (3) H263 (Simple Profile)
encoding functionality. This product provides the capabilities to encode streams for Internet video,
mobile phones, set top boxes and create media files for other MPEG-4 compatible devices such as
®
iPods
.
The Niagara SCX Web Interface provides options for basic and advanced settings for the video and
audio options of MPEG-4 available with the encoder.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-33
Page 52

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
The following figure illustrates the screen you will see after creating an encoder through the Niagara
SCX Web Interface.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The Advanced MPEG Video Settings provide you with the ability to choose the MPEG Type required
for your output. These MPEG Types include the following:
• H.264–MP4: H.264, MPEG-4, Part 10, or AVC (Advanced Video Coding) was designed for very
high-data compression while maintain better quality than its predecessor, H.263. It was also created
to address a broad range of applications from low bit rate to high bit rate and from low resolution
such as cell phones to high resolution such as broadcast. The encoder’s H.264 is Baseline Profile.
• H.264–3G2: This setting will create an H.264 stream stored in a 3G2 container.
• H.264–3GP: This setting will create an H.264 stream stored in a 3GPP container.
• MPEG4–MP4: MPEG-4, Part 2, or H.263, is designed for situations where low bit rate and low
resolution are mandated by other conditions of the applications, like network bandwidth or device
size. Examples of video applications for H.263 are cell phones, some low end video conferencing
systems, and surveillance systems. H.263 is important for legacy handheld devices that do not
support H.264.
Note By default, the encoder’s H.263 uses Simple Profile unless you select the Enable B Frames
option. If B frames are enabled, then the resulting stream will be Advanced Simple Profile.
• MPEG4–3G2: This setting will create an H.263 stream stored in a 3G2 container.
2-34
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 53

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
• MPEG4–3GP: 3GP is a multimedia container format defined by the Third Generation Partnership
Project (3GPP) for use on 3G mobile phones. It stores video streams such as MPEG-4 or H.264 and
audio streams such as AMR or AAC. This setting will create an H.263 stream stored in a 3GPP
container. There are two defined standards for this format:
–
3GPP for GSM based mobile phones
–
3GPP2 for CDMA based mobile phones
• H263–MP4: MPEG-4, Part 2, or H.263, is designed for situations where low bit rate and low
resolution are mandated by other conditions of the applications, like network bandwidth or device
size. Examples of video applications for H.263 are cell phones, some low end video conferencing
systems, and surveillance systems. H.263 is important for legacy handheld devices that do not
support H.264.
Note By default, the encoder’s H.263 uses Simple Profile unless you select the Enable B Frames
option. If B frames are enabled, then the resulting stream will be Advanced Simple Profile.
• H263–3G2: This setting will create an H.263 stream stored in a 3G2 container.
• H263–3GP: This setting will create an H.263 stream stored in a 3GPP container.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Note The Encoder Quality setting is currently not active and will not affect the results of the encoding stream
or file.
Note Some players, such as Quicktime
®
player, are not compatible with streams that include B frames. If your
resulting stream has quality issues on playback, try disabling B frames to ensure compatibility with most
players.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-35
Page 54

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
The Advanced MPEG Audio Settings, provide you with several Audio Formats, Audio Types, Audio
Encoders, and Bitrates from which to choose. These choices include several options as to audio
sampling, and whether the audio is to be encoded monophonically (mono) or stereo.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The Audio Type setting is only related to AAC Encoding. If you select AMR in the Audio Encoder
field, this setting is not used. The Audio Type field provides you with a drop-down box, which includes
the following two choices:
• Main: This format is the same as Low Complexity, but adds backward prediction.
• Low Complexity (LC): The simplest and most widely used and support AAC audio format.
Note Depending on the player on which the resulting stream will be heard, either choice—Main or Low
Complexity—will use a specific set of tools to encode the audio stream. You should make your choice
based on the requirement of the playback software or device. The most widely supported format is LC
profile.
The Audio Encoder settings provides you with a drop-down box, which includes the following three
choices:
• AAC (Advanced Audio Coding): A standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for
digital audio. AAC achieves better audio quality than MP3 and has been named a standard by the
Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG)
• AMR-NB (Adaptive Multi-Rate Narrow-Band – 8 kHz): An audio data compression scheme
optimized for speech coding. AMR was adopted as the standard narrowband speech codec by 3GPP
and is widely used in GSM.
• AMR-WB (Adaptive Multi-Rate Wide-Band – 16 kHz): An audio data compression scheme
optimized for speech coding. AMR was adopted as the standard wideband speech codec by 3GPP
and is widely used in GSM.
2-36
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 55

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Note When you select AMR Encoder for audio, the audio will automatically be encoded using 8 kHz
mono for playback on cell phones. When you select AMR-WB for audio, you must change the
Audio Format to be 16 kHz, 16 bit, mono, for playback on cell phones.
The Audio Bitrate drop-down box provides you with several choices, ranging from 8 to 320.
The web interface for the encoder includes options for Streaming Properties and Advanced Streaming
Properties. As to the broadcast type you choose, you have the option to check the Enable Streaming
box. Please see the
“Real Encoder Properties (Helix)” section on page 2-25 for a more detailed
description of enabling pull. Another option provides you with the abilities to Save to Portable Media
and provide a Media Title.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
OL-17938-01
Under the Advanced Streaming Settings feature, you have the options to output to a file while
streaming, or only output to a file. You must type in a unique name and location for this file.
Check the Output to file box if you would like to save the encoded content to a file. Enter a file
destination in the field provided. By default, this folder is set to D:\AVFiles\Out.
Check the Save to Portable Media box if you would like to save the stream from portable media to a file.
Note Remember the file name is referenced to the encoder system not to the system running SCX Explorer.
When SCX Manager and SCX Explorer are not on the same computer, always start your browse for files
at My Network Places and work down or enter the entire file pathname beginning with the system name
(for example, \\fileserver\c\videos). If you simply enter a file name, you may inadvertently browse your
local computer when the media file resides on the remote computer.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-37
Page 56

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
To stream your MPEG-4 content, select Enable Streaming. Set the appropriate streaming properties.
Note Live streaming and streaming to a file cannot be accomplished at the same time. Only one box can be
checked at a time. To stream Live and to file at the same time, a separate profile must be set up.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Note The default settings will enable multicast streaming. If this is not desired, change the IP address for
Group to the IP address of the server to which you want to stream from the encoder.
The save SDP File field will require a name and destination path for the resulting SDP file created when
the stream is started. If you are streaming to a Helix
®
, a Quicktime, or a Darwin server, refer to its
respective documentation or online message boards for setup details specific for the individual streaming
server.
Note You can stream point-to-point by selecting a share destination directory for the saved SDP file.
Remember to disable multicasting by entering in the IP address of the PC to which you want to stream.
For example, if you want another PC to view the stream, save the SDP file to a share folder on the local
drive. The other PC can open the SDP file and the stream can be played in a Quicktime or other MPEG-4
compatible streaming player. Since MPEG-4 encoding can be CPU intensive, it is not recommend that
you view the stream on the same system as the encoder unless you have a very powerful system
(dual-core processors or better). Doing so may overtax the host CPU which will cause video quality
degradation and encode session failure.
After you have input your settings, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page to save your
settings.
Warning
If you click away to another web page without clicking Submit, your changes will be lost.
2-38
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 57

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Real Encoder Settings (Helix)
Real (Helix) is both a storage format and a streaming format. In addition to the ability to output to a file,
the Real Encoder can stream to a Helix Server. The settings for the Real Encoder include the ability to
adjust parameters for connecting and streaming to the server.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Broadcast Method: There are several different broadcast types for streaming Real format video to a
Helix Server, as follows:
• Push, Account-Based Login (Helix Server): Account-based, push broadcasting allows you to send
a stream to Helix Server version 9 or later. In this method, the encoder maintains a monitoring
connection to Helix Server. This connection allows it to pass a user name and password to
authenticate access to the server. Helix Server uses this connection to send statistics about the
broadcast stream back to the encoder.
• Push, Password-Only Login (Helix Server): Unlike account-based broadcasting, password-only
broadcasting does not establish a monitoring connection. Therefore, this type of broadcasting
requires less network overhead, but receives no feedback from Helix Server. This broadcast method
allows you to send a live stream to Helix Server version 9 or later. However, you must set up the
server as a receiver in a splitting arrangement. Please refer to Helix Server documentation for
details.
• Push, Multicast (Helix Server): In a multicast, the encoder can deliver the same broadcast stream
to any number of Helix Servers without increasing its outgoing bandwidth. The Helix Servers will
need to be pre-configured for a multicast from the encoder. Refer to your Helix Server
documentation for details.
• Pull (Helix Server): In pull broadcasting, the encoder begins to generate broadcast packets as soon
as you start the encoding. However, it does not deliver the broadcast stream until Helix Server
requests the stream, which occurs when the first RealPlayer
®
user requests the broadcast. In that
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-39
Page 58

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
• Legacy Push (8.x, 7.x, G2): The legacy push method is similar to the account-based push method.
Transport Protocol: When you use a push broadcast method, you specify whether to use UDP or TCP
upon delivering the broadcast stream to Helix Server. UDP is the preferred protocol due to the lower
network overhead. But you may want to use TCP when delivering the broadcast over a lossy
environment.
For the Server Address field, enter the IP address or DNS name of the Helix Server used for the
broadcast, such as 207.188.7.176 or helixserver.example.com.
For the Port/Port Range field, specify the HTTP port on Helix Server. The default value is port 80,
which is the server's default HTTP port. If multicasting, indicate the range of ports on the Helix Server
receivers where the broadcast packets will be sent. The encoder and Helix Server negotiate the actual
ports to use once the broadcast begins. The default range is from 30001 to 30020.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
way, Pull broadcasting saves bandwidth between the encoder and Helix Server when no one is
viewing the broadcast. This broadcast method allows you to send a stream to Helix Server version
9 or later.
However, the legacy push does not use a monitoring connection to provide server feedback and
statistics and is not as robust a broadcast method as an account-based push. Use this broadcasting
method only when sending a broadcast stream to a server that predates Helix Server version 9, such
as RealSystem Server G2, 7, or 8.
If using a Multicast Address, enter the multicast address for the broadcast stream in the Multicast
Address field. The Multicast Address must be in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
The Listen Address field is the IP address of your machine where Helix Producer will listen for resend
requests from the server.
The listen address sets the IP address that Helix Mobile Producer Live uses to listen for packet resend
requests from Helix Server. For the listen address, you can use one of the following possible values:
• Automatic: This is the safest setting, and will work with most firewall configurations
• System IP: The IP address of the machine
• System IP 2: The second IP of the machine is multi-homed
• An IP address typed in by the user
If your Helix Mobile Producer Live machine has multiple IP addresses, enter the IP address that Helix
Mobile Producer Live should use for communications from Helix Server. If you are broadcasting through
a firewall performing network address translation (NAT), set the listen address to the IP address of the
firewall or the value 0.0.0.0. The 0.0.0.0 value tells Helix Server to allow a Helix Mobile Producer Live
connection from any IP address. The connection still requires the valid password, however.
In the Stream Name field, enter a name for the broadcast stream. This name resembles a clip name and
should use the appropriate extension, either .rm for a constant bit rate stream or .rmvb for a variable bit
rate stream. This name appears in the broadcast URL.
The Path (optional) field specifies a virtual path, which can be used for archiving or splitting on Helix
Server. Use a simple name followed by a forward slash, such as news/.
2-40
In the User Name and Password fields, enter the User Name and Password defined in each Helix Server
receiver definition. The broadcast connection fails if the value is incorrect.
Frame Rate, or frame frequency, is the measurement of the frequency (rate) at which an imaging device
produces unique consecutive images called frames. The term applies equally well to computer graphics,
video cameras, film cameras, and motion capture systems. Frame rate is most often expressed in frames
per second (fps), or simply hertz (Hz).
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 59

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The next series of fields activate the Real Encoder’s filters to improve video and audio quality. These
filter settings will depend upon the type of content you are streaming and your subjective preference. It
is recommended you experiment with these settings and view their results on a test capture.
The Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 features integrated de-interlacing and inverse telecine filters that
automatically apply when needed. This allows the encoder to perform at maximum efficiency.
Note We recommend that you do not enable the Real Encoder de-interlace and inverse telecine filters since
applying filters multiple times can produce undesirable results and consume additional system resources.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Enable SureStream™: SureStream allows you to encode the broadcast stream for multiple audiences.
However, each primary stream or substream you choose increases the processor load during encoding
and adds to the outgoing bandwidth requirements. For example, with SureStream enabled, you can
choose the 56k Dial-up audience and the 128k Dual ISDN audience. In addition, with SureStream
enabled, the encoding might require twice as much processing power.
Regardless of whether or not you enable SureStream, you must choose at least one Audience Selection
for your stream.
You can also choose to output to a file while streaming or output only to a file. Type in a unique name
for the file.
Note If you use the same name as a current file, the current file will be overwritten.
After you have input your settings, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page to save your
changes.
Warning
If you click away to another web page without first clicking Submit, your changes will be lost.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-41
Page 60

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Windows Media Encoder Settings
Windows Media is both a storage format and a streaming format. In addition to the ability to output to a
file, the Windows Media encoder can stream to a Windows Media Server. The settings for Windows
Media encoder include the ability to set parameters for connecting and streaming to the server.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
First, select a Windows Media Capture Profile from the drop-down menu.
Note Some Windows Media Capture Profiles have pre-defined video resolutions and input selections. When
you select a Windows Media Capture Profile, verify that your current video and audio settings have not
been modified. If they have been modified, simply change these settings back to their previous settings
and click the Submit button.
When streaming audio and video, there are two methods of delivery, as follows:
• Pull: Using this method, the encoder begins to generate broadcast packets as soon as you start the
encoding. However, it does not deliver the broadcast stream until Windows Media Server requests
the stream. This method does not provide a secure connection to the server and should only be used
if the encoder and server reside within the same network firewall.
• Push: Using this method, the encoder maintains a secure connection to Windows Media Server. This
connection allows the encoder to pass a user name and password to authenticate access to the server.
To enable clients to pull the stream from Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200, you set up a session and
begin broadcasting directly from the encoder. Clients (Windows Media servers or players) can connect
to the stream at any time by using the following URL format:
• http://IP_address:port (for Internet connections)
• http://encoding_computer_name:port (for LAN connections)
By default, the encoder supports up to 50 direct connections during a broadcast.
2-42
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 61

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Note The greater the number of direct connections to the encoder, the more system resources are required. We
do not recommend having players connect directly to Cisco
servers should connect to the encoder and, in turn, players should connect to the servers.
Select the Enable Pull check box. Then, enter a port number that will be used by the server to pull the
stream from the encoder.
Note Be sure to enter a port number that is not already assigned to another encoder. If two encoders attempt
to use the same port number, one or both encoders will fail to start.
Select Enable Push and enter a port number that is not assigned to another encoder. Then, enter the
server name or IP address, Alias (optional), user name, and password.
You can also choose to output to file at the same time you are streaming to a server. However, you can
set the server to archive the file and streaming, allowing the encoder to reserve its system resources for
encoding. Refer to the Windows Media Server documentation for details.
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Digital Media Encoder 2200. Streaming
Warning
If you check Index the file, viewers will be able to direct access any point within the Windows Media®
file using the Windows Media player. Indexing is also required for editing the Windows Media file
using Microsoft Windows Media Utilities.
After you have input your settings, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page to save your
changes.
If you click away to another web page without first clicking Submit, your changes will be lost.
The Niagara SCX Web Interface will then display the All Encoders list.
Deleting an Encoder Profile
You can also delete encoder profiles from the encoder. It is valuable to remove encoders you will not
use, as every encoder profile, regardless if active or idle, uses active memory.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-43
Page 62

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Note Once you delete a custom profile, you cannot restore it. It must be recreated.
Note If you delete a default encoder profile, you can restore it by using the Restore Encoder Factory
Defaults function. Running the Restore Encoder Factory Defaults will remove any custom encoder
profiles you have created and load only the default encoder profiles.
To delete an encoder profile, you must access the All Encoders list in the Niagara SCX Web Interface.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
You can delete an encoder by clicking the Del link next to the encoder you wish to remove.
Alternatively, you can click the Edit link to view the encoder profile, verify that it is the encoder that
you wish to remove.
Then, click the Delete Encoder link at the bottom of the page once you have verified that it is the
encoder you want to delete.
My Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
To link to the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 page, go to Configuration on the menu at the top of
the web page, and click on My Niagara Pro II from the drop-down list.
2-44
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 63

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The My Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 page provides details on software versions, network name,
serial number, and hard drive configurations. Most of the data on this page is for informational purposes
and cannot be altered. However, the following two fields allow modifications:
• Computer Name
• Admin password
Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
Computer Name
The Computer Name field contains the current network name for the encoder. This is the same name
that you typed into a web browser to access the Niagara SCX Web Interface. You can change the
Computer Name by clicking the Click to change name link next to this field.
The screen will refresh and now the Computer Name field is an editable text field. Type in a new name
for the encoder.
Then, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-45
Page 64

Encoder Preset (A, B, and C)
The page will refresh and you will be prompted to reboot the encoder. Your changes will not take effect
until the system is restarted.
Click the Reboot Now link to restart the system and apply the Computer Name change.
While the encoder is restarting, the following message will appear in the web interface.
Note The restart process takes approximately two minutes to complete.
When encoder has restarted, you will be returned to the Login screen.
Note If you close your web browser and later want to log into the Niagara SCX Web Interface, you will need
to use the new computer name you created to access the encoder.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Properties
The encoder Properties section has two fields: User Name and Serial Number. Only the User Name
field allows modification, which changes the User Password from the factory default.
• Changing the Login Password from the Factory Default, page 2-46
• Restoring the Login Password to the Factory Default, page 2-47
Changing the Login Password from the Factory Default
Click the admin link in the User Name field. You will be presented with a new screen that allows you
to change your login password for the Niagara SCX Web Interface.
Note You cannot change the User Name for the Niagara SCX Web Interface.
2-46
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 65

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Type in your current password in the Password field and then type in the new password in both the New
Password and Confirm New Password fields.
Note The Niagara SCX Web Interface password is case sensitive.
Then, click the Change Password button. You will then be presented with the following results:
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Alerts
Note You will need to log back into the web interface with your new password.
Restoring the Login Password to the Factory Default
If you have forgotten or lost your password, you can restore the default password by running the Restore
Factory Defaults option. For more information, see the
page 2-51.
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Alerts
The Alerts page can be viewed by navigating to the Configuration link at the top of the web page and
clicking on the Alerts link.
“Restore Factory Defaults” section on
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-47
Page 66

Network Properties
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The following is a representation of a page that allows you to control how the encoder handles
application alerts that may occur during streaming or other operations. Cisco
Encoder
alarm light on the front panel of the encoder automatically lights when there is an alarm.
2200 can optionally send an email to multiple recipients should an alarm present itself. The
Digital Media
Email Alert
You can optionally send an email alert to specific email address in the event of an application alarm.
Checking Send Email will enable this feature. You must specify the email address to which an alert will
be sent, along with your email server user name, password, and server name. For more information about
configuring Cisco
Settings” section on page 2-50.
Alarm Light
Checking the Light Alarm box will instruct the encoder to light the front panel alarm light should an
alert become necessary.
Edit Alert Settings
To edit the settings for each alert listed, click the Edit link in the row of the alert you want to modify.
Note that at this juncture, you will be presented with two alternatives: to either update the alarm or cancel
the alarm.
Should you decide to update, once you have made your modifications to the alert settings, click the
Update link to enter your settings and return to the Alerts list.
Digital Media Encoder 2200 to send email alerts, see the “System Configuration
Network Properties
The Network Properties page can be viewed by navigating to the Configuration link at the top of the
web page and clicking on Network Properties.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-48
OL-17938-01
Page 67

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The Network Properties page provides detailed information on the encoder’s current network settings
for the Network Interface Card (NIC).
Network Properties
Network Card(s)
Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 has two 1,000 megabit network connections. To view the current
properties for each card, select the card you wish to view from the drop-down menu in the Network
Card(s) field.
Advanced Settings (Network)
Advanced Settings provides the encoder network name, MAC Address and server IP address settings.
The encoder network name is a link. If you click this link, you will be directed to the My Cisco Digital
Media Encoder
information, see the
2200 page. From this page you can change the encoders’s network name. For more
“Computer Name” section on page 2-45.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-49
Page 68

System Configuration Settings
The Active Network Link field uses two icons to indicate whether the network interface card selected
has a network connected.
Ta b l e 2-3 Network Link Icons and Descriptions
Icon Description
The network link is detected.
The network link is not detected.
System Configuration Settings
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
The System Configuration page can be viewed by navigating to the Configuration link at the top of the
web page and clicking on System Configuration.
The System Configuration Settings page allows you to modify your encoder default system settings.
You can configure email settings so that Cisco
predefined email addresses whenever the encoder encounters an alert condition. You can also customize
the information that the encoder displays on its front panel when the system is idle.
Digital Media Encoder 2200 can send an email to
2-50
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 69

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
This page also provides the ability to restore your encoder to its original factory disk image, returning
all of the system settings to their original state. Using the Restore Factory Defaults option will remove
all custom settings and takes approximately 10 minutes to complete.
System Configuration Settings
Restore Factory Defaults
Click the Restore Factory Defaults link to start the process.
The following screen gives details of the process that you are about to execute and allows you the
opportunity to cancel the process.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-51
Page 70

System Configuration Settings
Note Restore Factory Defaults rebuilds the encoder primary disk drive (C:) with the original system image.
All custom settings and any files saved to drive C: will be lost. This process cannot be reversed. However,
you can manually re-enter your custom settings once the encoder restore process is completed.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Note The default directory for saving your audio and video files is D:\AV Files\. When using the Restore
Email Settings
Factory Defaults option, only drive C: is re-imaged. All files and folders on drive D: are preserved. To
ensure your personal files are not removed, always use the default directory – drive D – for storage of
personal files.
If you are unfamiliar with setting up an SMTP email account for sending email, please contact your
network administrator for assistance.
To configure encoder Email Settings, you will need to enter the following information:
• The address to which to send the email (separate multiple email address with a comma)
• A valid email address from which the email comes
• A subject line for your email alert—required
• The SMTP (mail server) settings
–
User name for server access
–
Password (if required)
–
The name of the SMTP server
2-52
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 71

Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Note For security purposes, the password for your account will not be displayed once it has been
entered into the settings. However, although this field appears blank after you click the Submit
button, the password information has been retained.
Note If you change any information in this dialogue box, you will need to re-enter your SMTP
password before clicking the Submit button. Not doing so will overwrite the previously entered
password with a blank entry.
Once you have entered the information above, click the Submit button to save your changes.
You can test your settings by clicking the Save and Send Test Email link. The resulting page will report
if the email was successfully sent or there was a send failure.
Idle Screen Information
This section allows you to modify the information that is displayed in the encoder LCD display on its
front panel.
System Configuration Settings
Check the boxes next to the information you wish to be displayed. This information is cycled as the LCD
display alternates between status information and encoder information.
At the top of the LCD idle screen is the default message System is Ready. You can customize this
message.
Once you have entered the information above, click the Submit button to save your changes.
Default Directory Setting
Note We strongly recommend that you do not alter the default directory setting unless you understand the risk
of saving your files to a directory not located on drive D. If you save your files to another drive on the
encoder, these files could be deleted if you use the Restore Factory Defaults feature.
OL-17938-01
Note Only drive D on the encoder has available storage to save your files.
Note Drives C, E, and F are used strictly for encoder operational programs. Any modifications to these drives
can permanently damage your system and void your warranty.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
2-53
Page 72

System Configuration Settings
The Default AV Folder is the directory that the encoder stores AV files created whenever you select the
Save to File option in an encoder profile. Refer to the Save to File option under the
Properties, Flash Encoder Properties, MPEG-4 Encoder Properties, Real Encoder Properties (Helix), and
Windows Media Encoder Properties sections for information about setting an encoder profile to create
an AV file.
High Temperature Alert
The Alert Configuration links to the Alerts page. For information on setting the Alerts, refer to the
“Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Alerts” section on page 2-47.
You can enable an alert if the encoder reaches a predefined maximum temperature level. To set the level,
select from the High Temperature Alert drop-down menu.
Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
AVI Encoder
2-54
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 73

Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Revised: October 9, 2008, OL-17938-01
This chapter includes the following sections:
• EASE Menu (LCD Display), page 3-1
• Niagara SCX Web Interface, page 3-16
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
This section provides details about the LCD menu tree. It is intended to be a complete reference to all
levels and functions accessible by using the encoder front panel LCD display.
It is designed to be a visual reference of the LCD screen including the front panel button action to move
to the next screen.
CHA PTER
3
This section includes the following topics:
• Encode Menu, page 3-2
• Access Health Menu, page 3-3
• Setup System Menu, page 3-5
• Export to USB Drive, page 3-16
• Shutdown Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200, page 3-16
Note This section will use the following graphical icons for the various button actions:
Icon Description
Power On
Access Menu/Return to Previous
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-1
Page 74

EASE Menu (LCD Display)
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Icon Description
Enter/Execute Command
Move Pointer Up/Down
Start Encoder
Stop Encoder
Load Encoder
Encode Menu
Encode Start
This section includes the following topics:
• Encode Start, page 3-2
• Encode Stop, page 3-3
• Encode Status, page 3-3
3-2
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 75

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Encode Stop
Encode Status
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
Access Health Menu
This section includes the following topics:
• CPU Status, page 3-3
• Memory Available, page 3-4
• Temperature Status, page 3-4
CPU Status
—
—
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-3
Page 76

EASE Menu (LCD Display)
Memory Available
Temperature Status
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
—
(X 2)
—
3-4
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 77

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Setup System Menu
This section includes the following topics:
• Network Link Status, page 3-5
• Network MAC Address, page 3-6
• View Network Settings, page 3-7
• Enable DHCP, page 3-8
• Set Static IP Addresses, page 3-9
• Set Gateway Address, page 3-11
• Set Date & Time, page 3-12
• Setting Temperature Alarm, page 3-13
• Factory Restore, page 3-14
Network Link Status
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
OL-17938-01
— — —
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-5
Page 78

EASE Menu (LCD Display)
Network MAC Address
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
— — —
3-6
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 79

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
View Network Settings
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-7
Page 80

EASE Menu (LCD Display)
Enable DHCP
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
— — —
3-8
— — —
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 81

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Set Static IP Addresses
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
(X 3)
(X 4)
(X 6)
(X 5)
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-9
Page 82

EASE Menu (LCD Display)
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
(X 3)
(X 4)
—
3-10
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 83

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Set Gateway Address
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
(X 2)
(X 1)
(X 9) (X 2)
(X 1)
(X 6)
(X 8)
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-11
Page 84

EASE Menu (LCD Display)
(X 1)
Set Date & Time
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
(X 1)
— —
3-12
(X 5)
(X 15)
(X 2)
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 85

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
(X 16)
(X 25)
Setting Temperature Alarm
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
(X 3)
(X 2)
(X 2)
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-13
Page 86

EASE Menu (LCD Display)
Factory Restore
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
(X 3)
(X 3)
3-14
— —
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 87

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
<10-minute delay>
EASE Menu (LCD Display)
(X 5)
(X 15)
(X 2)
(X 16)
(X 25)
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-15
Page 88

Niagara SCX Web Interface
Export to USB Drive
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Shutdown Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
(X 4)
— — —
Niagara SCX Web Interface
The Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 includes the Niagara SCX Web Interface, which allows you to
access the advanced system settings. The web interface also provides detailed settings and control over
the encoder profiles installed on the encoder. This section details each setting and page of the Niagara
SCX Web Interface.
3-16
• Log In, page 3-17
• Home Page, page 3-18
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 89

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
• All Encoders, page 3-19
• My Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200, page 3-47
• Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 Alerts, page 3-51
• Network Properties, page 3-52
• System Configuration Settings, page 3-54
• View Activity Log, page 3-58
• View Alerts, page 3-59
• The Help, or “i” Button, the Niagara SCX Web Interface, and Their Alert Settings, page 3-59
Log In
The Niagara SCX Web Interface does not require software and works with any computer that has a
current web browser and current operating software for Windows, Macintosh, and Linux machines. The
encoder system must either reside on a shared IP network with the computer or can be directly connected
to a Windows computer using an Ethernet cable (RJ-45).
Niagara SCX Web Interface
Open the web browser on your computer and access the web interface by typing in the encoder network
name. The network name of the encoder is also its serial number and can be obtained from the LCD
readout during the power-up process.
The serial number is also located on the right side of the encoder.
Enter the encoder name in the web browser (as shown below) and press enter.
You will be prompted with a login screen that requires a user name and password. By default, the user
name and password are both admin.
Note If you cannot browse to the encoder by using its machine name, type in the encoder IP address instead.
This information is available by accessing the LCD menus on the front panel of encoder.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-17
Page 90

Niagara SCX Web Interface
Home Page
Menu Bar
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
The Home page is the first page presented after you log into the Niagara SCX Web Interface. From this
page, you can access the different pages for configuring, controlling, and monitoring the activities and
alerts from the encoder.
The menu bar at the top of the Home page is consistent and available throughout the website.
Home
Encoders
With the exception of the Home and Log Out menu options in the menu bar at the top of the Home page,
the other options in the menu bar have drop-down menus. These drop-down menus appear within
Encoders, Configuration, and Status. Each drop-down menu provides a list of additional options
available.
The Home title is an active link. Clicking this link will direct you to the Home page of the website.
The Encoders drop-down menu provides access to the following web pages that provide the following
information:
• All Encoders: Lists all of the encoding profiles loaded on the encoder and provides management of
those profiles
• Preset A: Allows you to assign a loaded encoding profile to the A button on the front panel of the
encoder
• Preset B: Allows you to assign a loaded encoding profile to the B button on the front panel of the
encoder
• Preset C: Allows you to assign a loaded encoding profile to the C button on the front panel of the
encoder
Configuration
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-18
The Configuration drop-down menu provides access to the following:
• My Encoder: Provides details on the Machine Properties of the encoder, including the Network
Name, Serial Number, and all software versions installed
OL-17938-01
Page 91

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
• Encoder Alerts: Allows modification of the settings for each application alert that the encoder
could generate during normal operations
• Network Properties: Provides information on the encoder network properties and addresses for
both NIC ports and allows modification to these properties
• System Configuration: Allows modification of the system configuration including setup for email
alerts from the encoder whenever it encounters an operation error
Status
The Status drop-down menu provides access to the following:
• View Activity Log: A list of all encoder activities with date and timestamp on each event
Niagara SCX Web Interface
Log Out
All Encoders
• View Alert: A list of encoder alerts with date and timestamp on each alert
The Log Out option executes user log out from the encoder and returns you to the website Log In screen.
The All Encoders web page provides a list of all of the encoder profiles loaded on the encoder. On this
page, you can do the following:
• View all of the loaded and available encoder profiles
• Start and Stop each encoder individually
• Access the Editing page for an encoder
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-19
Page 92

Niagara SCX Web Interface
• Delete an encoder profile
• Create an encoder profile
The Encoders list has five titled columns, as follows:
• Name: Provides the name of the encoder profile (this name is displayed in the encoder front panel
• Description: Defines the type of encoder which are AVI, Flash, Helix Producer, and Windows
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
LCD display)
Media
Start Encoder
• Last Status: Provides the activity of the encoder when the information on this page was last
refreshed (for example, Encoder started or Encoder failed to start)
• Streaming: Provides a column of buttons that allow you to start or stop an encoder
• Preset: Provides information on the EZStream button assignment for each encoder (if this field is
blank then the encoder is not assigned to a EZStream button)
Enabling the Auto Refresh Page check box at the top of the page will execute a refresh of this page every
10 seconds. This is useful when you are monitoring the encoder while another user is operating it.
Press the red Stream icon located in the right column of the encoder you wish to start.
3-20
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 93

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
The web page will automatically update with messages detailing the encoder start progress.
After the encoder has started successfully, the web page will return to the All Encoders page with the
encoder status updated to reflect Started mode.
Niagara SCX Web Interface
Stop Encoder
OL-17938-01
Press the blue icon located in the right column of the encoder you wish to stop.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-21
Page 94

Niagara SCX Web Interface
The web page will automatically update with messages detailing the encoder stop progress.
After the encoder has successfully stopped, the web page will return to the All Encoders page with the
encoder status updated to reflect Stopped mode.
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Edit Encoder
To edit an encoder, click the Edit link in the first column.
The properties page for that encoder will be displayed.
3-22
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 95

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Video & Audio Settings
The properties page for each encoder type uses the same Video and Audio Settings except for the added
color space setting for AVI and MPEG-4.
You enable or disable video and/or audio by clicking the check box next to Source: When Source is
enabled, the Source, Input, Signal, Proportions, Size, Format, and Input fields can be edited.
Source: This field displays a drop-down list of devices available on the encoder. The Cisco Digital
Media Encoder
2200 is a two channel encoder, so there are two physical sets of audio and video inputs
can be used at any one time. However, you can capture multiple streaming formats and resolutions
simultaneously from this one set of video inputs. Video source is seen as multiple inputs denoted by
incrementing decimal values. They appear in this manner:
Niagara SCX Web Interface
• Osprey 5x0 Video Device 1.1
• Osprey 5x0 Video Device 1.2
• Osprey 5x0 Video Device 1.3
• Osprey 5x0 Video Device 1.4
Set Input for both video and audio to match the video and audio inputs on the back of the encoder to
which you connected your video and audio source. This would be either Composite, S-Video or SDI for
video input and Unbalanced, XLR Balanced, XLR AES/EBU or SDI for audio input.
When you performed the First Start Setup, you determined if your video signal was NTSC or PAL. The
Signal field adds granularity for regional NTSC, PAL, and SECAM settings. If you are uncertain which
setting applies, refer to the owner’s manual for the video source that you have connected to the encoder.
The proportion setting uses the term Standard, meaning square pixels for a VGA monitor, and
CCIR-601 meaning elongated pixels for a television monitor. Choose the setting that reflects the type
of display on which your content will be viewed. For example, if you will be streaming your video on
the Internet to be viewed on a computer monitor, select Standard. Selecting the incorrect setting can
make the streaming video appear distorted.
The Size field refers to the pixel size of the encoded video. The standard sizes are as follows:
• Full for full screen video
• CIF for video scaled from full size to ¼ size
• QCIF for video scaled from full size to ¼ of CIF size
You can also specify a custom size for your video. This is useful when capturing video to be played on
a mobile video device that requires a non-standard size for compatibility.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-23
Page 96

Niagara SCX Web Interface
If you select Custom from the drop-down menu, two additional fields will appear allowing you to type
in the exact size you want the resulting video to be.
Note If you specify a video size that is not compatible with the color space of your source video, the encoder
will automatically correct the size to the closest compatible setting when you click the Submit button.
The color space format setting is only available in AVI and Flash encoder properties and appears as an
additional field under the Size setting (see below).
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Now that you have completed all of the Video and Audio settings, you can proceed to the encoder type
settings at the bottom of the page. As previously stated, these settings will vary according to the encoder
type.
Advanced Streaming Settings
SimulStream and DirectShow Filters
SimulStream filters have two interrelated purposes, as follows:
• They allow applications to enumerate and list video capture and preview pins or streams (each with
different settings) as named entries in their video device select lists. The video device driver can be
configured to show multiple filters per device. Each filter has one preview pin and one capture pin.
Standard applications have the capability to access a particular filter without any custom
programming specialized for Osprey devices.
• Each filter has independent settings for cropping, default output size, watermarks, and captions that
can be stored between sessions. Compared with the previous “pin-based” method, no requirements
are necessary for a particular startup order to associate settings with instantiations.
3-24
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 97

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Please see the Enable SimulStream checkbox below.
The checkbox next to Enable SimulStream at the top of the dialog box, when checked, enables
SimulStream to run for the currently selected encoder.
The encoder includes a full SimulStream license installed for each A/V channel, and this checkbox
controls full SimulStreaming.
Niagara SCX Web Interface
Note When you change the Enable SimulStream status and click Submit, you must restart the appliance. If
you do not, SimulStream may become partially active, but the capture devices may be incorrectly named,
and their pins may be incorrect.
Show filters per device
With this control, you can set the device driver to expose 1 to 10 filters per device for enumeration and
selection by encoders. If, for example, 4 filters per device are chosen, device lists in applications will
show four entries for the currently chosen device. For device 1, they are designated as 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and
1.4.
Note The number of filters you request will not display or work correctly until the system is restarted.
Note While it is possible to expose and enumerate up to 10 filters per device, the practical number of working
filters will be less. The practical number of filters depends on the capability of the appliance, the types
of filtering enabled, the types of scaling and color format conversions requested per encoder, and the
type of processing being done. If the appliance has multiple capture channels, the number of filters is
the total across all channels. In addition, some types of processing, such as deinterlacing and gamma
corrections, which are performed once per channel may, in this case, occur multiple times. In summary,
an appliance can support 5, 6, or more concurrent filters on one device if the processing per filter is light.
However, only 2 or 3 simultaneously running filters can be supported if the processing load inside or
outside the driver is particularly heavy.
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-25
Page 98

Niagara SCX Web Interface
Deinterlace
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
The Deinterlace field has four drop-down choices. These choices are Off, Auto, Inverse Telecine, and
Motion Adaptive, as you can see below.
In further explanation of each choice, please see the following definitions.
• Off —Performs no deinterlacing of any kind.
• Aut o—Applies inverse telecine deinterlacing to all telecine video. Applies motion adaptive
deinterlacing to all video that is not telecine. Switches dynamically between the two modes as the
content changes. Available for NTSC video only.
• Inverse Telecine—Applies inverse telecine deinterlacing to all telecine video. Performs no
deinterlacing of video that is not telecine. Available for NTSC video only.
• Motion Adaptive—Applies motion adaptive deinterlacing to all video.
Deinterlace settings are applied and stored per-device and are applied to all filters and pins associated
with a device.
Motion Adaptive Deinterlace
Motion adaptive deinterlace is an algorithm for deinterlacing pure video (non-telecine) content. It
detects which portions of the image are still, and which portions are in motion, and then applies different
processing to each scenario.
Telecine and Inverse Telecine
Telecine video is NTSC video which was originally created on film at 24 frames per second. In the
telecine conversion process, certain fields are repeated in a regular, recurring sequence. If a telecined
sequence is viewed directly on a progressive screen, interlacing artifacts will be visible.
The process called Inverse Telecine is the reverse of Telecine — it drops the redundant fields and
reassembles the video in a 24 fps progressive format. Interlacing artifacts are 100% removed. If the
video is viewed at 24 fps, you will see the exact timing and sequencing that was on the original film. If
the video is viewed at 30 fps, every fifth frame will be repeated. However, there will be no deinterlacing
artifacts.
Telecine and inverse telecine only apply to NTSC video. They are not used for PAL and SECAM video.
The Auto and Inverse Telecine buttons will be disabled when either PAL or SECAM is selected as the
video standard.
Motion Threshold
Motion Threshold adjusts the threshold of difference from spatially- and temporally-related pixels,
which are judged to be “motion.” If you enter a higher value, the number of pixels in motion will be
greatly reduced. If you enter a lower value, the number of motion pixels greatly increases until the entire
screen, more or less, is considered in motion. The recommended default is 16.
Sharp and Smooth Motion
3-26
When the Sharp Motion radio button is selected, detail in motion areas will be sharper, but at the
expense of somewhat jagged diagonal edges.
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
Page 99

Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
When the Smooth Motion radio button is selected, more loss of detail will occur in motion areas, but
edges will be smoother.
Since the eye does not clearly see detail in areas of motion—and edge artifacts are highly intrusive—the
Smooth algorithm is preferred for most applications. The Smooth algorithm uses a bit more CPU.
Both algorithms treat still areas in the same fashion, and there should be no loss of detail in still areas.
AVI Encoder Settings
AVI is an uncompressed audio and video storage format and therefore has only the ability to save to a
file. You can type in a unique name for the generated AVI file and modify the directory path to where
the file will be stored. Clicking the Default Folder link will insert the path of the default folder for file
storage on the encoder. By default, the path is D:\AVFILES\.
Niagara SCX Web Interface
Note We do not recommend that you store files in any other directory on the encoder.
Once you save your file to the encoder’s internal hard drive, we recommend that you move it to another
external storage device such as a USB drive or a network drive.
After you have input your settings, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page to save your
changes.
Warning
If you click away to another web page without first clicking Submit, your changes will be lost.
Flash Encoder Settings
OL-17938-01
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
3-27
Page 100

Niagara SCX Web Interface
The Flash encoder settings are similar to the AVI settings for saving the audio and video to a file. To
enable streaming to file, ensure the Output to a File box is selected. Flash adds some additional frame
and bit rate controls. The frame rate changes the frames per second that the video will be encoded. The
audio format setting can be used to modify the audio frequency and changes stereo to mono. The bit rate
settings pertain to the amount of data per second the audio and video are captured. Decreasing the bit
rate for both or either will decrease the playback viewing quality.
The Flash encoder creates a Flash format audio and video file. You can type in a unique name for the
Flash file (.flv).
After you have input your settings, click the Submit button at the bottom of the page to save your
changes.
Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Warning
If you click away to another web page without clicking Submit, your changes will be lost.
MPEG-4 Encoder Settings
The encoder software MPEG-4 compression engine provides (1) H.264, MPEG-4, Part 10, (2) MPEG-4,
Part 2, and (3) H263 – MP4, Part 2 Baseline encoding functionality. Please see the figure below.
This product provides the capabilities to encode streams for Internet video, mobile phones, set top boxes
and create media files for other MPEG-4 compatible devices such as an iPod
The Niagara SCX Web Interface provides options for basic and advanced settings for the video and
audio options of MPEG-4 available with the encoder.
The following figure illustrates the screen you will see after creating an encoder through the Niagara
SCX Web Interface.
®
.
3-28
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
OL-17938-01
 Loading...
Loading...