Page 1

Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
Software Release 5.2
November 2008
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-17037-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network
are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To
You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems,
Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing,
FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace,
MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet,
Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.
and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0809R)
Copyright © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface xxiii
Audience xxiv
Purpose xxiv
Organization xxiv
Conventions xxv
Related Publications xxvii
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request xxvii
CHAPTER
1 Overview 1-1
Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Overview 1-2
Single-Controller Deployments 1-3
Multiple-Controller Deployments 1-4
Operating System Software 1-4
Operating System Security 1-5
Cisco WLAN Solution Wired Security 1-5
Layer 2 and Layer 3 Operation 1-6
Operational Requirements 1-6
Configuration Requirements 1-6
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers 1-6
Client Location 1-7
Controller Platforms 1-7
Cisco 2100 Series Controllers 1-8
Cisco 4400 Series Controllers 1-8
Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module 1-9
Cisco 7600 Series Router Wireless Services Module 1-10
Cisco 28/37/38xx Series Integrated Services Router 1-11
Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch 1-11
Features Not Supported 1-8
OL-17037-01
Cisco UWN Solution Wired Connections 1-12
Cisco UWN Solution WLANs 1-12
Identity Networking 1-13
Enhanced Integration with Cisco Secure ACS 1-13
File Transfers 1-14
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
Power over Ethernet 1-14
Startup Wizard 1-15
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Memory 1-15
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Failover Protection 1-16
Network Connections to Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers 1-17
Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controllers 1-17
Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controllers 1-18
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces 2-1
Using the Web-Browser Interface 2-2
Guidelines for Using the GUI 2-2
Opening the GUI 2-2
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes 2-2
Using the GUI to Enable Web and Secure Web Modes 2-3
Using the CLI to Enable Web and Secure Web Modes 2-4
Loading an Externally Generated SSL Certificate 2-5
Using the CLI 2-7
Logging into the CLI 2-7
Using a Local Serial Connection 2-8
Using a Remote Ethernet Connection 2-8
Logging Out of the CLI 2-9
Navigating the CLI 2-9
Enabling Wireless Connections to the Web-Browser and
CLI Interfaces
3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces 3-1
2-9
iv
Overview of Ports and Interfaces 3-2
Ports 3-2
Distribution System Ports 3-4
Service Port 3-5
Interfaces 3-6
Management Interface 3-6
AP-Manager Interface 3-6
Virtual Interface 3-7
Service-Port Interface 3-8
Dynamic Interface 3-8
WLANs 3-9
Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces 3-10
Using the GUI to Configure the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces 3-11
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 5

Contents
Using the CLI to Configure the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces 3-13
Using the CLI to Configure the Management Interface 3-13
Using the CLI to Configure the AP-Manager Interface 3-14
Using the CLI to Configure the Virtual Interface 3-14
Using the CLI to Configure the Service-Port Interface 3-15
Configuring Dynamic Interfaces 3-16
Using the GUI to Configure Dynamic Interfaces 3-16
Using the CLI to Configure Dynamic Interfaces 3-18
Configuring Ports 3-19
Configuring Port Mirroring 3-22
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol 3-23
Using the GUI to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol 3-24
Using the CLI to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol 3-28
Enabling Link Aggregation 3-29
Link Aggregation Guidelines 3-32
Using the GUI to Enable Link Aggregation 3-33
Using the CLI to Enable Link Aggregation 3-34
Using the CLI to Verify Link Aggregation Settings 3-34
Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support LAG 3-34
CHAPTER
Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points 3-34
Using Link Aggregation 3-35
Using Multiple AP-Manager Interfaces 3-35
4 Configuring Controller SettingsWireless Device Access 4-1
Using the Configuration Wizard 4-2
Before You Start 4-2
Resetting the Device to Default Settings 4-3
Resetting to Default Settings Using the CLI 4-3
Resetting to Default Settings Using the GUI 4-3
Running the Configuration Wizard on the CLI 4-4
Using the AutoInstall Feature for Controllers Without a Configuration 4-6
Overview of AutoInstall 4-6
Obtaining an IP Address Through DHCP and Downloading a Configuration File from a TFTP
Server
4-7
Selecting a Configuration File 4-8
Example of AutoInstall Operation 4-9
Managing the System Date and Time 4-10
Configuring an NTP Server to Obtain the Date and Time 4-10
Configuring the Date and Time Manually 4-10
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
Using the GUI to Configure the Date and Time 4-10
Using the CLI to Configure the Date and Time 4-11
Configuring 802.11 Bands 4-14
Using the GUI to Configure 802.11 Bands 4-14
Using the CLI to Configure 802.11 Bands 4-15
Configuring 802.11n Parameters 4-17
Using the GUI to Configure 802.11n Parameters 4-17
Using the CLI to Configure 802.11n Parameters 4-19
Configuring DHCP Proxy 4-22
Using the GUI to Configure DHCP Proxy 4-22
Using the CLI to Configure DHCP Proxy 4-23
Configuring Administrator Usernames and Passwords 4-23
Configuring Usernames and Passwords 4-23
Restoring Passwords 4-24
Configuring SNMP 4-24
Changing the Default Values of SNMP Community Strings 4-25
Using the GUI to Change the SNMP Community String Default Values 4-25
Using the CLI to Change the SNMP Community String Default Values 4-27
Changing the Default Values for SNMP v3 Users 4-27
Using the GUI to Change the SNMP v3 User Default Values 4-27
Using the CLI to Change the SNMP v3 User Default Values 4-29
Configuring Aggressive Load Balancing 4-29
Using the GUI to Configure Aggressive Load Balancing 4-30
Using the CLI to Configure Aggressive Load Balancing 4-30
Configuring Fast SSID Changing 4-31
Using the GUI to Configure Fast SSID Changing 4-31
Using the CLI to Configure Fast SSID Changing 4-31
Enabling 802.3X Flow Control 4-31
Configuring 802.3 Bridging 4-32
Using the GUI to Configure 802.3 Bridging 4-32
Using the CLI to Configure 802.3 Bridging 4-33
Configuring Multicast Mode 4-34
Understanding Multicast Mode 4-34
Guidelines for Using Multicast Mode 4-35
Using the GUI to Enable Multicast Mode 4-36
Using the GUI to View Multicast Groups 4-37
Using the CLI to Enable Multicast Mode 4-38
Using the CLI to View Multicast Groups 4-39
vi
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 7

Using the CLI to View an Access Point’s Multicast Client Table 4-39
Configuring Client Roaming 4-40
Intra-Controller Roaming 4-40
Inter-Controller Roaming 4-40
Inter-Subnet Roaming 4-40
Voice-over-IP Telephone Roaming 4-40
CCX Layer 2 Client Roaming 4-41
Using the GUI to Configure CCX Client Roaming Parameters 4-42
Using the CLI to Configure CCX Client Roaming Parameters 4-43
Using the CLI to Obtain CCX Client Roaming Information 4-43
Using the CLI to Debug CCX Client Roaming Issues 4-44
Configuring IP-MAC Address Binding 4-44
Configuring Quality of Service 4-45
Configuring Quality of Service Profiles 4-45
Using the GUI to Configure QoS Profiles 4-45
Using the CLI to Configure QoS Profiles 4-47
Configuring Quality of Service Roles 4-48
Using the GUI to Configure QoS Roles 4-48
Using the CLI to Configure QoS Roles 4-50
Contents
Configuring Voice and Video Parameters 4-52
Call Admission Control 4-52
Bandwidth-Based CAC 4-52
Load-Based CAC 4-52
Expedited Bandwidth Requests 4-53
U-APSD 4-54
Traffic Stream Metrics 4-54
Using the GUI to Configure Voice Parameters 4-54
Using the GUI to Configure Video Parameters 4-56
Using the GUI to View Voice and Video Settings 4-57
Using the CLI to Configure Voice Parameters 4-62
Using the CLI to Configure Video Parameters 4-63
Using the CLI to View Voice and Video Settings 4-64
Configuring EDCA Parameters 4-67
Using the GUI to Configure EDCA Parameters 4-67
Using the CLI to Configure EDCA Parameters 4-68
Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol 4-69
Using the GUI to Configure Cisco Discovery Protocol 4-72
Using the GUI to View Cisco Discovery Protocol Information 4-73
Using the CLI to Configure Cisco Discovery Protocol 4-77
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
vii
Page 8

Contents
Using the CLI to View Cisco Discovery Protocol Information 4-78
Configuring RFID Tag Tracking 4-79
Using the CLI to Configure RFID Tag Tracking 4-81
Using the CLI to View RFID Tag Tracking Information 4-82
Using the CLI to Debug RFID Tag Tracking Issues 4-83
Configuring and Viewing Location Settings 4-84
Installing the Location Appliance Certificate 4-84
Modifying the NMSP Notification Interval for Clients, RFID Tags, and Rogues 4-85
Synchronizing the Controller and Location Appliance 4-86
Using the CLI to View Location Settings 4-86
Configuring the Supervisor 720 to Support the WiSM 4-89
General WiSM Guidelines 4-90
Configuring the Supervisor 4-90
Using the Wireless LAN Controller Network Module 4-91
CHAPTER
5 Configuring Security Solutions 5-1
Cisco UWN Solution Security 5-2
Security Overview 5-2
Layer 1 Solutions 5-2
Layer 2 Solutions 5-2
Layer 3 Solutions 5-3
Integrated Security Solutions 5-3
Configuring RADIUS 5-3
Configuring RADIUS on the ACS 5-4
Using the GUI to Configure RADIUS 5-6
Using the CLI to Configure RADIUS 5-11
RADIUS Authentication Attributes Sent by the Access Point 5-15
RADIUS Accounting Attributes 5-17
Configuring TACACS+ 5-18
Configuring TACACS+ on the ACS 5-19
Using the GUI to Configure TACACS+ 5-23
Using the CLI to Configure TACACS+ 5-25
Viewing the TACACS+ Administration Server Logs 5-27
viii
Configuring Local Network Users 5-29
Using the GUI to Configure Local Network Users 5-30
Using the CLI to Configure Local Network Users 5-32
Configuring LDAP 5-33
Using the GUI to Configure LDAP 5-33
Using the CLI to Configure LDAP 5-36
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 9

Configuring Local EAP 5-38
Using the GUI to Configure Local EAP 5-40
Using the CLI to Configure Local EAP 5-45
Configuring the System for SpectraLink NetLink Telephones 5-50
Using the GUI to Enable Long Preambles 5-50
Using the CLI to Enable Long Preambles 5-51
Using the CLI to Configure Enhanced Distributed Channel Access 5-52
Using Management over Wireless 5-52
Using the GUI to Enable Management over Wireless 5-52
Using the CLI to Enable Management over Wireless 5-52
Configuring DHCP Option 82 5-53
Configuring and Applying Access Control Lists 5-54
Using the GUI to Configure Access Control Lists 5-55
Using the GUI to Apply Access Control Lists 5-59
Applying an Access Control List to an Interface 5-59
Applying an Access Control List to the Controller CPU 5-60
Applying an Access Control List to a WLAN 5-61
Applying a Preauthentication Access Control List to a WLAN 5-62
Using the CLI to Configure Access Control Lists 5-63
Using the CLI to Apply Access Control Lists 5-65
Contents
Configuring Management Frame Protection 5-66
Guidelines for Using MFP 5-67
Using the GUI to Configure MFP 5-68
Using the GUI to View MFP Settings 5-69
Using the CLI to Configure MFP 5-70
Using the CLI to View MFP Settings 5-71
Using the CLI to Debug MFP Issues 5-73
Configuring Client Exclusion Policies 5-73
Configuring Identity Networking 5-74
Identity Networking Overview 5-74
RADIUS Attributes Used in Identity Networking 5-75
QoS-Level 5-75
ACL-Name 5-75
Interface-Name 5-76
VLAN-Tag 5-76
Tunnel Attributes 5-77
Configuring AAA Override 5-78
Updating the RADIUS Server Dictionary File for Proper QoS Values 5-78
Using the GUI to Configure AAA Override 5-79
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
ix
Page 10

Contents
Using the CLI to Configure AAA Override 5-80
Managing Rogue Devices 5-80
Challenges 5-80
Detecting Rogue Devices 5-81
Classifying Rogue Access Points 5-81
WCS Interaction 5-84
Configuring RLDP 5-84
Using the GUI to Configure RLDP 5-84
Using the CLI to Configure RLDP 5-85
Configuring Rogue Classification Rules 5-87
Using the GUI to Configure Rogue Classification Rules 5-87
Using the CLI to Configure Rogue Classification Rules 5-90
Viewing and Classifying Rogue Devices 5-93
Using the GUI to View and Classify Rogue Devices 5-93
Using the CLI to View and Classify Rogue Devices 5-98
CHAPTER
Configuring IDS 5-103
Configuring IDS Sensors 5-103
Using the GUI to Configure IDS Sensors 5-103
Using the CLI to Configure IDS Sensors 5-105
Viewing Shunned Clients 5-106
Configuring IDS Signatures 5-107
Using the GUI to Configure IDS Signatures 5-109
Using the CLI to Configure IDS Signatures 5-115
Using the CLI to View IDS Signature Events 5-117
Configuring wIPS 5-119
Configuring wIPS on an Access Point 5-119
Viewing wIPS Information 5-120
Detecting Active Exploits 5-122
Configuring Maximum Local Database Entries 5-122
Using the GUI to Configure Maximum Local Database Entries 5-122
Using the CLI to Specify the Maximum Number of Local Database Entries 5-122
6 Configuring WLANsWireless Device Access 6-1
WLAN Overview 6-2
Configuring WLANs 6-2
Creating WLANs 6-3
Using the GUI to Create WLANs 6-3
Using the CLI to Create WLANs 6-5
Searching WLANs 6-7
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
x
OL-17037-01
Page 11

Configuring DHCP 6-8
Internal DHCP Server 6-8
External DHCP Servers 6-8
DHCP Assignment 6-8
Security Considerations 6-9
Using the GUI to Configure DHCP 6-9
Using the CLI to Configure DHCP 6-10
Using the CLI to Debug DHCP 6-11
Configuring DHCP Scopes 6-11
Configuring MAC Filtering for WLANs 6-14
Enabling MAC Filtering 6-15
Creating a Local MAC Filter 6-15
Configuring a Timeout for Disabled Clients 6-15
Assigning WLANs to Interfaces 6-15
Configuring the DTIM Period 6-16
Using the GUI to Configure the DTIM Period 6-16
Using the CLI to Configure the DTIM Period 6-17
Configuring Peer-to-Peer Blocking 6-18
Guidelines for Using Peer-to-Peer Blocking 6-19
Using the GUI to Configure Peer-to-Peer Blocking 6-19
Using the CLI to Configure Peer-to-Peer Blocking 6-20
Configuring Layer 2 Security 6-20
Static WEP Keys 6-21
Dynamic 802.1X Keys and Authorization 6-21
Configuring a WLAN for Both Static and Dynamic WEP 6-22
WPA1 and WPA2 6-22
CKIP 6-25
Configuring a Session Timeout 6-27
Using the GUI to Configure a Session Timeout 6-27
Using the CLI to Configure a Session Timeout 6-28
Configuring Layer 3 Security 6-28
VPN Passthrough 6-29
Web Authentication 6-29
Assigning a QoS Profile to a WLAN 6-30
Using the GUI to Assign a QoS Profile to a WLAN 6-31
Using the CLI to Assign a QoS Profile to a WLAN 6-32
Configuring QoS Enhanced BSS 6-32
Guidelines for Configuring QBSS 6-34
Additional Guidelines for Using 7921 and 7920 Wireless IP Phones 6-34
Using the GUI to Configure QBSS 6-35
Contents
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xi
Page 12

Contents
Using the CLI to Configure QBSS 6-36
Configuring IPv6 Bridging 6-36
Guidelines for Using IPv6 Bridging 6-37
Using the GUI to Configure IPv6 Bridging 6-38
Using the CLI to Configure IPv6 Bridging 6-39
Configuring Cisco Client Extensions 6-39
Using the GUI to Configure CCX Aironet IEs 6-40
Using the GUI to View a Client’s CCX Version 6-40
Using the CLI to Configure CCX Aironet IEs 6-42
Using the CLI to View a Client’s CCX Version 6-42
Configuring Access Point Groups 6-42
Creating Access Point Groups 6-44
Configuring Web Redirect with 802.1X Authentication 6-49
Conditional Web Redirect 6-49
Splash Page Web Redirect 6-50
Configuring the RADIUS Server 6-50
Using the GUI to Configure Web Redirect 6-51
Using the CLI to Configure Web Redirect 6-52
Disabling Accounting Servers per WLAN 6-53
Disabling Coverage Hole Detection per WLAN 6-54
Using the GUI to Disable Coverage Hole Detection on a WLAN 6-54
Using the CLI to Disable Coverage Hole Detection on a WLAN 6-55
Configuring NAC Out-of-Band Integration 6-55
Guidelines for Using NAC Out-of-Band Integration 6-56
Using the GUI to Configure NAC Out-of-Band Integration 6-57
Using the CLI to Configure NAC Out-of-Band Integration 6-60
CHAPTER
xii
7 Controlling Lightweight Access Points 7-1
Access Point Communication Protocols 7-2
Guidelines for Using CAPWAP 7-2
The Controller Discovery Process 7-2
Verifying that Access Points Join the Controller 7-4
Using the GUI to Verify that Access Points Join the Controller 7-4
Using the CLI to Verify that Access Points Join the Controller 7-4
Viewing CAPWAP MTU Information 7-5
Debugging CAPWAP 7-5
Configuring Global Credentials for Access Points 7-5
Using the GUI to Configure Global Credentials for Access Points 7-6
Using the CLI to Configure Global Credentials for Access Points 7-8
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 13

Contents
Configuring Authentication for Access Points 7-9
Using the GUI to Configure Authentication for Access Points 7-10
Using the CLI to Configure Authentication for Access Points 7-12
Configuring the Switch for Authentication 7-14
Embedded Access Points 7-14
Autonomous Access Points Converted to Lightweight Mode 7-16
Guidelines for Using Access Points Converted to Lightweight Mode 7-16
Reverting from Lightweight Mode to Autonomous Mode 7-17
Using a Controller to Return to a Previous Release 7-17
Using the MODE Button and a TFTP Server to Return to a Previous Release 7-17
Authorizing Access Points 7-18
Authorizing Access Points Using SSCs 7-18
Authorizing Access Points Using MICs 7-18
Authorizing Access Points Using LSCs 7-19
Using the GUI to Authorize Access Points 7-22
Using the CLI to Authorize Access Points 7-23
Using DHCP Option 43 and DHCP Option 60 7-24
Troubleshooting the Access Point Join Process 7-24
Configuring the Syslog Server for Access Points 7-26
Viewing Access Point Join Information 7-26
Using a Controller to Send Debug Commands to Access Points Converted to Lightweight Mode 7-28
Converted Access Points Send Crash Information to Controller 7-28
Converted Access Points Send Radio Core Dumps to Controller 7-28
Using the CLI to Retrieve Radio Core Dumps 7-29
Using the GUI to Upload Radio Core Dumps 7-29
Using the CLI to Upload Radio Core Dumps 7-30
Uploading Memory Core Dumps from Converted Access Points 7-31
Using the GUI to Upload Access Point Core Dumps 7-31
Using the CLI to Upload Access Point Core Dumps 7-32
Display of MAC Addresses for Converted Access Points 7-32
Disabling the Reset Button on Access Points Converted to Lightweight Mode 7-33
Configuring a Static IP Address on an Access Point Converted to Lightweight Mode 7-33
Supporting Oversized Access Point Images 7-33
OL-17037-01
Cisco Workgroup Bridges 7-34
Guidelines for Using WGBs 7-35
Sample WGB Configuration 7-37
Using the GUI to View the Status of Workgroup Bridges 7-37
Using the CLI to View the Status of Workgroup Bridges 7-40
Using the CLI to Debug WGB Issues 7-40
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xiii
Page 14

Contents
Configuring Backup Controllers 7-41
Using the GUI to Configure Backup Controllers 7-42
Using the CLI to Configure Backup Controllers 7-44
Configuring Failover Priority for Access Points 7-46
Using the GUI to Configure Failover Priority for Access Points 7-46
Using the CLI to Configure Failover Priority for Access Points 7-48
Using the CLI to View Failover Priority Settings 7-48
Configuring Country Codes 7-49
Guidelines for Configuring Multiple Country Codes 7-49
Using the GUI to Configure Country Codes 7-50
Using the CLI to Configure Country Codes 7-52
Migrating Access Points from the -J Regulatory Domain to the -U Regulatory Domain 7-55
Guidelines for Migration 7-56
Migrating Access Points to the -U Regulatory Domain 7-56
Using the W56 Band in Japan 7-58
Dynamic Frequency Selection 7-58
Optimizing RFID Tracking on Access Points 7-59
Using the GUI to Optimize RFID Tracking on Access Points 7-59
Using the CLI to Optimize RFID Tracking on Access Points 7-61
Configuring Probe Request Forwarding 7-62
Retrieving the Unique Device Identifier on Controllers and Access Points 7-63
Using the GUI to Retrieve the Unique Device Identifier on Controllers and Access Points 7-63
Using the CLI to Retrieve the Unique Device Identifier on Controllers and Access Points 7-64
Performing a Link Test 7-64
Using the GUI to Perform a Link Test 7-65
Using the CLI to Perform a Link Test 7-67
Configuring Link Latency 7-67
Using the GUI to Configure Link Latency 7-68
Using the CLI to Configure Link Latency 7-69
Configuring Power over Ethernet 7-70
Using the GUI to Configure Power over Ethernet 7-71
Using the CLI to Configure Power over Ethernet 7-73
Configuring Flashing LEDs 7-74
xiv
Viewing Clients 7-74
Using the GUI to View Clients 7-74
Using the CLI to View Clients 7-78
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 15

Contents
CHAPTER
8 Controlling Mesh Access Points 8-1
Cisco Aironet Mesh Access Points 8-2
Access Point Roles 8-2
Network Access 8-3
Deployment Modes 8-4
Cisco Wireless Mesh Network 8-4
Wireless Backhaul 8-4
Point-to-Point Wireless Bridging 8-5
Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Bridging 8-5
Architecture Overview 8-6
CAPWAP 8-6
Cisco Adaptive Wireless Path Protocol Wireless Mesh Routing 8-6
Mesh Neighbors, Parents, and Children 8-7
Wireless Mesh Constraints 8-7
Adding Mesh Access Points to the Mesh Network 8-10
Adding MAC Addresses of Mesh Access Points to the Controller Filter List 8-10
Configuring External Authentication and Authorization Using a RADIUS Server 8-13
Defining the Mesh Access Point Role 8-16
Configuring Global Mesh Parameters 8-16
Configuring Local Mesh Parameters 8-22
Client Roaming 8-24
Configuring Ethernet Bridging and Ethernet VLAN Tagging 8-25
Configuring Advanced Features 8-32
Configuring Voice Parameters in Mesh Networks 8-32
CAC 8-32
QoS and DSCP Marking 8-32
Guidelines for Using Voice on the Mesh Network 8-33
Voice Call Support in a Mesh Network 8-34
Using the CLI to View Voice Details for Mesh Networks 8-34
Enabling Mesh Multicast Containment for Video 8-37
Backhaul Client Access (Universal Access) for Indoor and Outdoor Mesh Access Points 8-39
Viewing Mesh Statistics and Reports 8-39
Viewing Mesh Statistics for an Access Point 8-39
Using the GUI to View Mesh Statistics for an Access Point 8-39
Using the CLI to View Mesh Statistics for an Access Point 8-43
Viewing Neighbor Statistics for an Access Point 8-44
Using the GUI to View Neighbor Statistics for an Access Point 8-44
Using the CLI to View Neighbor Statistics for an Access Point 8-47
Converting Indoor Access Points to Mesh Access Points (1130AG, 1240AG) 8-48
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xv
Page 16

Contents
Changing MAP and RAP Roles for Indoor Mesh Access Points (1130AG, 1240AG) 8-49
Using the GUI to Change MAP and RAP Roles for Indoor Mesh Access Points 8-49
Using the CLI to Change MAP and RAP Roles for Indoor Mesh Access Points 8-49
Converting Indoor Mesh Access Points to Non-Mesh Lightweight Access Points (1130AG, 1240AG) 8-50
Configuring Mesh Access Points to Operate with Cisco 3200 Series Mobile Access Routers 8-51
Configuration Guidelines 8-51
Using the GUI to Enable Mesh Access Points to Operate with Cisco 3200 Series Mobile Access
Routers
Using the CLI to Enable Mesh Access Points to Operate with Cisco 3200 Series Mobile Access
Routers
8-52
8-53
CHAPTER
9 Managing Controller Software and Configurations 9-1
Upgrading Controller Software 9-2
Guidelines for Upgrading Controller Software 9-2
Guidelines for Upgrading to Controller Software 5.2 in Mesh Networks 9-3
Mandatory Boot Variable Update for Networks with 1522 Access Points 9-4
Upgrade Compatibility Matrix 9-6
Using the GUI to Upgrade Controller Software 9-8
Using the CLI to Upgrade Controller Software 9-10
Transferring Files to and from a Controller 9-13
Downloading Device Certificates 9-13
Using the GUI to Download Device Certificates 9-14
Using the CLI to Download Device Certificates 9-15
Downloading CA Certificates 9-16
Using the GUI to Download CA Certificates 9-16
Using the CLI to Download CA Certificates 9-17
Uploading PACs 9-19
Using the GUI to Upload PACs 9-19
Using the CLI to Upload PACs 9-20
Uploading and Downloading Configuration Files 9-21
Uploading Configuration Files 9-21
Downloading Configuration Files 9-23
xvi
Saving Configurations 9-26
Editing Configuration Files 9-27
Clearing the Controller Configuration 9-28
Erasing the Controller Configuration 9-28
Resetting the Controller 9-28
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 17

Contents
CHAPTER
10 Managing User Accounts 10-1
Creating Guest User Accounts 10-2
Creating a Lobby Ambassador Account 10-2
Using the GUI to Create a Lobby Ambassador Account 10-2
Using the CLI to Create a Lobby Ambassador Account 10-3
Creating Guest User Accounts as a Lobby Ambassador 10-4
Viewing Guest User Accounts 10-6
Using the GUI to View Guest Accounts 10-6
Using the CLI to View Guest Accounts 10-7
Web Authentication Process 10-7
Choosing the Web Authentication Login Page 10-9
Choosing the Default Web Authentication Login Page 10-10
Using the GUI to Choose the Default Web Authentication Login Page 10-10
Using the CLI to Choose the Default Web Authentication Login Page 10-11
Modified Default Web Authentication Login Page Example 10-13
Creating a Customized Web Authentication Login Page 10-14
Using a Customized Web Authentication Login Page from an External Web Server 10-16
Using the GUI to Choose a Customized Web Authentication Login Page from an External Web
Server
10-16
Using the CLI to Choose a Customized Web Authentication Login Page from an External Web
Server
10-17
Downloading a Customized Web Authentication Login Page 10-17
Using the GUI to Download a Customized Web Authentication Login Page 10-18
Using the CLI to Download a Customized Web Authentication Login Page 10-19
Customized Web Authentication Login Page Example 10-20
Using the CLI to Verify the Web Authentication Login Page Settings 10-20
Assigning Login, Login Failure, and Logout Pages per WLAN 10-21
Using the GUI to Assign Login, Login Failure, and Logout Pages per WLAN 10-21
Using the CLI to Assign Login, Login Failure, and Logout Pages per WLAN 10-22
CHAPTER
OL-17037-01
Configuring Wired Guest Access 10-23
Configuration Overview 10-25
Configuration Guidelines 10-25
Using the GUI to Configure Wired Guest Access 10-25
Using the CLI to Configure Wired Guest Access 10-29
11 Configuring Radio Resource ManagementWireless Device Access 11-1
Overview of Radio Resource Management 11-2
Radio Resource Monitoring 11-2
Transmit Power Control 11-2
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xvii
Page 18

Contents
Dynamic Channel Assignment 11-3
Coverage Hole Detection and Correction 11-4
RRM Benefits 11-5
Overview of RF Groups 11-5
RF Group Leader 11-6
RF Group Name 11-6
Configuring an RF Group 11-6
Using the GUI to Configure an RF Group 11-7
Using the CLI to Configure RF Groups 11-7
Viewing RF Group Status 11-8
Using the GUI to View RF Group Status 11-8
Using the CLI to View RF Group Status 11-9
Configuring RRM 11-9
Using the GUI to Configure RRM 11-9
Using the GUI to Configure RF Group Mode 11-10
Using the GUI to Configure Transmit Power Control 11-10
Using the GUI to Configure Dynamic Channel Assignment 11-12
Using the GUI to Configure Coverage Hole Detection 11-15
Using the GUI to Configure RRM Profile Thresholds, Monitoring Channels, and Monitor
Intervals
Using the CLI to Configure RRM 11-19
Using the CLI to View RRM Settings 11-23
Using the CLI to Debug RRM Issues 11-25
11-17
xviii
Overriding RRM 11-25
Statically Assigning Channel and Transmit Power Settings to Access Point Radios 11-26
Using the GUI to Statically Assign Channel and Transmit Power Settings 11-26
Using the CLI to Statically Assign Channel and Transmit Power Settings 11-30
Disabling Dynamic Channel and Power Assignment Globally for a Controller 11-33
Using the GUI to Disable Dynamic Channel and Power Assignment 11-33
Using the CLI to Disable Dynamic Channel and Power Assignment 11-33
Enabling Rogue Access Point Detection in RF Groups 11-34
Using the GUI to Enable Rogue Access Point Detection in RF Groups 11-34
Using the CLI to Enable Rogue Access Point Detection in RF Groups 11-36
Configuring CCX Radio Management Features 11-36
Radio Measurement Requests 11-37
Location Calibration 11-37
Using the GUI to Configure CCX Radio Management 11-37
Using the CLI to Configure CCX Radio Management 11-39
Using the CLI to Obtain CCX Radio Management Information 11-39
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 19

Using the CLI to Debug CCX Radio Management Issues 11-41
Configuring Pico Cell Mode 11-41
Guidelines for Using Pico Cell Mode 11-42
Using the GUI to Configure Pico Cell Mode 11-42
Using the CLI to Configure Pico Cell Mode 11-44
Using the CLI to Debug Pico Cell Mode Issues 11-45
Contents
CHAPTER
12 Configuring Mobility GroupsWireless Device Access 12-1
Overview of Mobility 12-2
Overview of Mobility Groups 12-5
Determining When to Include Controllers in a Mobility Group 12-7
Messaging among Mobility Groups 12-7
Using Mobility Groups with NAT Devices 12-8
Configuring Mobility Groups 12-9
Prerequisites 12-9
Using the GUI to Configure Mobility Groups 12-11
Using the CLI to Configure Mobility Groups 12-14
Viewing Mobility Group Statistics 12-16
Using the GUI to View Mobility Group Statistics 12-16
Using the CLI to View Mobility Group Statistics 12-19
Configuring Auto-Anchor Mobility 12-20
Guidelines for Using Auto-Anchor Mobility 12-21
Using the GUI to Configure Auto-Anchor Mobility 12-21
Using the CLI to Configure Auto-Anchor Mobility 12-23
WLAN Mobility Security Values 12-25
CHAPTER
OL-17037-01
Using Symmetric Mobility Tunneling 12-26
Running Mobility Ping Tests 12-28
13 Configuring Hybrid REAPWireless Device Access 13-1
Overview of Hybrid REAP 13-2
Hybrid-REAP Authentication Process 13-2
Hybrid REAP Guidelines 13-4
Configuring Hybrid REAP 13-5
Configuring the Switch at the Remote Site 13-5
Configuring the Controller for Hybrid REAP 13-6
Using the GUI to Configure the Controller for Hybrid REAP 13-7
Using the CLI to Configure the Controller for Hybrid REAP 13-11
Configuring an Access Point for Hybrid REAP 13-11
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xix
Page 20

Contents
Using the GUI to Configure an Access Point for Hybrid REAP 13-11
Using the CLI to Configure an Access Point for Hybrid REAP 13-14
Connecting Client Devices to the WLANs 13-15
Configuring Hybrid-REAP Groups 13-15
Hybrid-REAP Groups and Backup RADIUS Servers 13-16
Hybrid-REAP Groups and CCKM 13-16
Hybrid-REAP Groups and Local Authentication 13-17
Using the GUI to Configure Hybrid-REAP Groups 13-17
Using the CLI to Configure Hybrid-REAP Groups 13-22
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
A Safety Considerations and
Translated Safety Warnings
A-1
Safety Considerations A-2
Warning Definition A-2
Class 1 Laser Product Warning A-5
Ground Conductor Warning A-7
Chassis Warning for Rack-Mounting and Servicing A-9
Battery Handling Warning for 4400 Series Controllers A-18
Equipment Installation Warning A-20
More Than One Power Supply Warning for 4400 Series Controllers A-23
B Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information B-1
Regulatory Information for Lightweight Access Points B-2
Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement B-2
Department of Communications—Canada B-3
Canadian Compliance Statement B-3
European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein B-4
Declaration of Conformity with Regard to the R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC B-4
Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure B-5
Guidelines for Operating Controllers in Japan B-6
VCCI Class A Warning for 4400 Series Controllers in Japan B-6
VCCI Class B Warning for 2100 Series Controllers in Japan B-6
Power Cable and AC Adapter Warning for Japan B-7
Guidelines for Operating Controllers and Access Points in Japan B-7
Administrative Rules for Cisco Aironet Access Points in Taiwan B-8
Access Points with IEEE 802.11a Radios B-8
All Access Points B-9
Declaration of Conformity Statements B-10
xx
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 21

FCC Statement for Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controllers B-10
FCC Statement for 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controllers B-10
Contents
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
C End User License and Warranty C-1
End User License Agreement C-2
Limited Warranty C-4
Disclaimer of Warranty C-5
General Terms Applicable to the Limited Warranty Statement and End User License Agreement C-6
Notices C-6
OpenSSL/Open SSL Project C-6
License Issues C-7
D Troubleshooting D-1
Interpreting LEDs D-2
Interpreting Controller LEDs D-2
Interpreting Lightweight Access Point LEDs D-2
System Messages D-2
Using the CLI to Troubleshoot Problems D-5
Configuring System and Message Logging D-6
Using the GUI to Configure System and Message Logging D-7
Using the GUI to View Message Logs D-9
Using the CLI to Configure System and Message Logging D-10
Using the CLI to View System and Message Logs D-12
OL-17037-01
Viewing Access Point Event Logs D-13
Uploading Logs and Crash Files D-14
Using the GUI to Upload Logs and Crash Files D-14
Using the CLI to Upload Logs and Crash Files D-15
Uploading Core Dumps from the Controller D-17
Using the CLI to Upload Controller Core Dumps D-17
Monitoring Memory Leaks D-17
Troubleshooting CCXv5 Client Devices D-19
Diagnostic Channel D-19
Client Reporting D-19
Roaming and Real-Time Diagnostics D-20
Using the GUI to Configure the Diagnostic Channel D-20
Using the CLI to Configure the Diagnostic Channel D-21
Using the GUI to Configure Client Reporting D-25
Using the CLI to Configure Client Reporting D-28
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xxi
Page 22

Contents
Using the CLI to Configure Roaming and Real-Time Diagnostics D-31
Using the Debug Facility D-34
Configuring Wireless Sniffing D-39
Prerequisites for Wireless Sniffing D-39
Using the GUI to Configure Sniffing on an Access Point D-39
Using the CLI to Configure Sniffing on an Access Point D-41
Troubleshooting Access Points Using Telnet or SSH D-42
Debugging the Access Point Monitor Service D-43
Using the CLI to Debug Access Point Monitor Service Issues D-43
APPENDIX
I
NDEX
E Logical Connectivity Diagrams E-1
Cisco WiSM E-2
Cisco 28/37/38xx Integrated Services Router E-3
Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch E-4
xxii
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 23

Preface
This preface provides an overview of the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release
5.2, references related publications, and explains how to obtain other documentation and technical
assistance, if necessary. It contains these sections:
• Audience, page xxiv
• Purpose, page xxiv
• Organization, page xxiv
• Conventions, page xxv
• Related Publications, page xxvii
• Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page xxvii
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xxiii
Page 24

Audience
This guide describes Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Cisco Lightweight Access Points. This guide
is for the networking professional who installs and manages these devices. To use this guide, you should
be familiar with the concepts and terminology of wireless LANs.
Purpose
This guide provides the information you need to set up and configure wireless LAN controllers.
Note This version of the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide pertains specifically to
controller software release 5.2. If you are using an earlier version of software, you will notice differences
in features, functionality, and GUI pages.
Organization
Preface
This guide is organized into these chapters:
Chapter 1, “Overview,” provides an overview of the network roles and features of wireless LAN
controllers.
Chapter 2, “Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces,” describes how to use the controller GUI and
CLI.
Chapter 3, “Configuring Ports and Interfaces,” describes the controller’s physical ports and interfaces
and provides instructions for configuring them.
Chapter 4, “Configuring Controller SettingsWireless Device Access,” describes how to configure
settings on the controllers.
Chapter 5, “Configuring Security Solutions,” describes application-specific solutions for wireless
LANs.
Chapter 6, “Configuring WLANsWireless Device Access,” describes how to configure wireless LANs
and SSIDs on your system.
Chapter 7, “Controlling Lightweight Access Points,” explains how to connect lightweight access points
to the controller and manage access point settings.
Chapter 8, “Controlling Mesh Access Points,” explains how to connect mesh access points to the
controller and manage access point settings.
Chapter 9, “Managing Controller Software and Configurations,” describes how to upgrade and manage
controller software and configurations.
Chapter 10, “Managing User Accounts,” explains how to create and manage guest user accounts,
describes the web authentication process, and provides instructions for customizing the web
authentication login.
Chapter 11, “Configuring Radio Resource ManagementWireless Device Access,” describes radio
resource management (RRM) and explains how to configure it on the controllers.
xxiv
Chapter 12, “Configuring Mobility GroupsWireless Device Access,” describes mobility groups and
explains how to configure them on the controllers.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 25

Preface
Chapter 13, “Configuring Hybrid REAPWireless Device Access,” describes hybrid REAP and explains
how to configure this feature on controllers and access points.
Appendix A, “Safety Considerations and Translated Safety Warnings,” lists safety considerations and
translations of the safety warnings that apply to the Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution products.
Appendix B, “Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information,” provides declarations of
conformity and regulatory information for the products in the Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution.
Appendix C, “End User License and Warranty,” describes the end user license and warranty that apply
to the Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution products.
Appendix D, “Troubleshooting,” describes the LED patterns on controllers and lightweight access
points, lists system messages that can appear on the Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution interfaces,
and provides CLI commands that can be used to troubleshoot problems on the controller.
Appendix E, “Logical Connectivity Diagrams,”provides logical connectivity diagrams and related
software commands for controllers that are integrated into other Cisco products.
Conventions
This publication uses these conventions to convey instructions and information:
Command descriptions use these conventions:
• Commands and keywords are in boldface text.
• Arguments for which you supply values are in italic.
• Square brackets ([ ]) mean optional elements.
• Braces ({ }) group required choices, and vertical bars ( | ) separate the alternative elements.
• Braces and vertical bars within square brackets ([{ | }]) mean a required choice within an optional
element.
Interactive examples use these conventions:
• Terminal sessions and system displays are in screen font.
• Information you enter is in boldface.
• Nonprinting characters, such as passwords or tabs, are in angle brackets (< >).
Notes, cautions, and timesavers use these conventions and symbols:
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to materials not contained in
this manual.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result equipment damage
or loss of data.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xxv
Page 26

Preface
Warning
Waarschuwing
Varoitus
Attention
Warnung
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you
work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar
with standard practices for preventing accidents. (To see translations of the warnings that appear
in this publication, refer to the appendix “Translated Safety Warnings.”)
Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die lichamelijk letsel kan
veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij
elektrische schakelingen betrokken risico’s en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard
maatregelen om ongelukken te voorkomen. (Voor vertalingen van de waarschuwingen die in deze
publicatie verschijnen, kunt u het aanhangsel “Translated Safety Warnings” (Vertalingen van
veiligheidsvoorschriften) raadplegen.)
Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa ruumiinvammaan. Ennen
kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja
tavanomaisista onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista. (Tässä julkaisussa esiintyvien varoitusten
käännökset löydät liitteestä "Translated Safety Warnings" (käännetyt turvallisuutta koskevat
varoitukset).)
Ce symbole d’avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une situation pouvant
entraîner des blessures. Avant d’accéder à cet équipement, soyez conscient des dangers posés par
les circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures courantes de prévention des
accidents. Pour obtenir les traductions des mises en garde figurant dans cette publication, veuillez
consulter l’annexe intitulée « Translated Safety Warnings » (Traduction des avis de sécurité).
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die zu einer
Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie
sich der mit elektrischen Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur
Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt. (Übersetzungen der in dieser Veröffentlichung enthaltenen
Warnhinweise finden Sie im Anhang mit dem Titel “Translated Safety Warnings” (Übersetzung der
Warnhinweise).)
xxvi
Avvertenza
Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. Si è in una situazione che può causare infortuni.
Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai circuiti
elettrici ed essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti. La traduzione
delle avvertenze riportate in questa pubblicazione si trova nell’appendice, “Translated Safety
Warnings” (Traduzione delle avvertenze di sicurezza).
Advarsel
Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre til personskade. Før du
utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du være oppmerksom på de faremomentene som elektriske kretser
innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker. (Hvis du vil se
oversettelser av de advarslene som finnes i denne publikasjonen, kan du se i vedlegget "Translated
Safety Warnings" [Oversatte sikkerhetsadvarsler].)
Aviso
Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe poderá causar danos
fisicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos
relacionados com circuitos eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir
possíveis acidentes. (Para ver as traduções dos avisos que constam desta publicação, consulte o
apêndice “Translated Safety Warnings” - “Traduções dos Avisos de Segurança”).
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 27

Preface
¡Advertencia!
Varning!
Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física. Antes de manipular
cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que entraña la corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los
procedimientos estándar de prevención de accidentes. (Para ver traducciones de las advertencias
que aparecen en esta publicación, consultar el apéndice titulado “Translated Safety Warnings.”)
Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan leda till personskada.
Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara medveten om farorna med elkretsar och
känna till vanligt förfarande för att förebygga skador. (Se förklaringar av de varningar som
förekommer i denna publikation i appendix "Translated Safety Warnings" [Översatta
säkerhetsvarningar].)
Related Publications
These documents provide complete information about the Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution:
• Quick Start Guide: Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
• Quick Start Guide: Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Command Reference
• Cisco Wireless Control System Configuration Guide
• Quick Start Guide: Cisco Wireless Control System
• Quick start guide and hardware installation guide for your specific lightweight access point
Click this link to browse to user documentation for the Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/psa/default.html
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and
revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
xxvii
Page 28

Preface
xxviii
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 29

CHAP T E R
1
Overview
This chapter describes the controller components and features. Its contains these sections:
• Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Overview, page 1-2
• Operating System Software, page 1-5
• Operating System Security, page 1-5
• Layer 2 and Layer 3 Operation, page 1-6
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers, page 1-7
• Controller Platforms, page 1-8
• Cisco UWN Solution Wired Connections, page 1-12
• Cisco UWN Solution WLANs, page 1-13
• Identity Networking, page 1-13
• File Transfers, page 1-14
• Power over Ethernet, page 1-14
• Startup Wizard, page 1-15
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Memory, page 1-16
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Failover Protection, page 1-16
• Network Connections to Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers, page 1-17
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-1
Page 30

Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Overview
Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Overview
The Cisco Unified Wireless Network (Cisco UWN) Solution is designed to provide 802.11 wireless
networking solutions for enterprises and service providers. The Cisco UWN Solution simplifies
deploying and managing large-scale wireless LANs and enables a unique best-in-class security
infrastructure. The operating system manages all data client, communications, and system
administration functions, performs radio resource management (RRM) functions, manages system-wide
mobility policies using the operating system security solution, and coordinates all security functions
using the operating system security framework.
The Cisco UWN Solution consists of Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and their associated lightweight
access points controlled by the operating system, all concurrently managed by any or all of the operating
system user interfaces:
• An HTTP and/or HTTPS full-featured Web User Interface hosted by Cisco Wireless LAN
Controllers can be used to configure and monitor individual controllers. See Chapter 2.
• A full-featured command-line interface (CLI) can be used to configure and monitor individual Cisco
Wireless LAN Controllers. See Chapter 2.
• The Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), which you use to configure and monitor one or more
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and associated access points. WCS has tools to facilitate
large-system monitoring and control. WCS runs on Windows 2000, Windows 2003, and Red Hat
Enterprise Linux ES servers.
Chapter 1 Overview
Note WCS software release 5.2 must be used with controllers running controller software release
5.2. Do not attempt to use older versions of WCS software with controllers running
controller software release 5.2.
• An industry-standard SNMP V1, V2c, and V3 interface can be used with any SNMP-compliant
third-party network management system.
The Cisco UWN Solution supports client data services, client monitoring and control, and all rogue
access point detection, monitoring, and containment functions. It uses lightweight access points, Cisco
Wireless LAN Controllers, and the optional Cisco WCS to provide wireless services to enterprises and
service providers.
Note Unless otherwise noted, all of the Cisco wireless LAN controllers are hereafter referred to as controllers,
and all of the Cisco lightweight access points are hereafter referred to as access points.
Figure 1-1 shows the Cisco Wireless LAN Solution components, which can be simultaneously deployed
across multiple floors and buildings.
1-2
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 31

Chapter 1 Overview
Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Overview
Figure 1-1 Cisco UWN Solution Components
Single-Controller Deployments
A standalone controller can support lightweight access points across multiple floors and buildings
simultaneously, and supports the following features:
• Autodetecting and autoconfiguring lightweight access points as they are added to the network.
• Full control of lightweight access points.
• Lightweight access points connect to controllers through the network. The network equipment may
or may not provide Power over Ethernet to the access points.
Note that some controllers use redundant Gigabit Ethernet connections to bypass single network failures.
Note Some controllers can connect through multiple physical ports to multiple subnets in the network. This
feature can be helpful when operators want to confine multiple VLANs to separate subnets.
Figure 1-2 shows a typical single-controller deployment.
Figure 1-2 Single-Controller Deployment
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-3
Page 32

Operating System Software
Multiple-Controller Deployments
Each controller can support lightweight access points across multiple floors and buildings
simultaneously. However, full functionality of the Cisco Wireless LAN Solution is realized when it
includes multiple controllers. A multiple-controller system has the following additional features:
• Autodetecting and autoconfiguring RF parameters as the controllers are added to the network.
• Same-Subnet (Layer 2) Roaming and Inter-Subnet (Layer 3) Roaming.
• Automatic access point failover to any redundant controller with a reduced access point load (refer
to the “Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Failover Protection” section on page 1-16).
Figure 1-3 shows a typical multiple-controller deployment. The figure also shows an optional dedicated
Management Network and the three physical connection types between the network and the controllers.
Figure 1-3 Typical Multi-Controller Deployment
Chapter 1 Overview
Operating System Software
The operating system software controls controllers and lightweight access points. It includes full
operating system security and radio resource management (RRM) features.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-4
OL-17037-01
Page 33

Chapter 1 Overview
Operating System Security
Operating system security bundles Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3 security components into a simple,
Cisco WLAN Solution-wide policy manager that creates independent security policies for each of up to
16 wireless LANs. (Refer to the “Cisco UWN Solution WLANs” section on page 1-13.)
The 802.11 Static WEP weaknesses can be overcome using robust industry-standard security solutions,
such as:
• 802.1X dynamic keys with extensible authentication protocol (EAP).
• Wi-Fi protected access (WPA) dynamic keys. The Cisco WLAN Solution WPA implementation
includes:
–
Temporal key integrity protocol (TKIP) + message integrity code checksum (Michael) dynamic
keys, or
–
WEP keys, with or without Pre-Shared key Passphrase.
• RSN with or without Pre-Shared key.
• Optional MAC filtering.
The WEP problem can be further solved using industry-standard Layer 3 security solutions, such as:
Operating System Security
• Passthrough VPNs
• The Cisco Wireless LAN Solution supports local and RADIUS MAC address filtering.
• The Cisco Wireless LAN Solution supports local and RADIUS user/password authentication.
• The Cisco Wireless LAN Solution also uses manual and automated disabling to block access to
network services. In manual disabling, the operator blocks access using client MAC addresses. In
automated disabling, which is always active, the operating system software automatically blocks
access to network services for an operator-defined period of time when a client fails to authenticate
for a fixed number of consecutive attempts. This can be used to deter brute-force login attacks.
These and other security features use industry-standard authorization and authentication methods to
ensure the highest possible security for your business-critical wireless LAN traffic.
Cisco WLAN Solution Wired Security
Many traditional access point vendors concentrate on security for the Wireless interface similar to that
described in the “Operating System Security” section on page 1-5. However, for secure Cisco Wireless
LAN Controller Service Interfaces, Cisco Wireless LAN Controller to access point, and inter-Cisco
Wireless LAN Controller communications during device servicing and client roaming, the operating
system includes built-in security.
Each Cisco Wireless LAN Controller and lightweight access point is manufactured with a unique, signed
X.509 certificate. These signed certificates are used to verify downloaded code before it is loaded,
ensuring that hackers do not download malicious code into any Cisco Wireless LAN Controller or
lightweight access point.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and lightweight access points also use the signed certificates to verify
downloaded code before it is loaded, ensuring that hackers do not download malicious code into any
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller or lightweight access point.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-5
Page 34

Layer 2 and Layer 3 Operation
Layer 2 and Layer 3 Operation
Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) communications between the controller and lightweight
access points can be conducted at ISO Data Link Layer 2 or Network Layer 3. Control and Provisioning
of Wireless Access Points protocol (CAPWAP) communications between the controller and lightweight
access points are conducted at Network Layer 3. Layer 2 mode does not support CAPWAP.
Note Controller software release 5.2 or later supports only Layer 3 CAPWAP mode, controller software
releases 5.0 and 5.1 support only Layer 3 LWAPP mode, and controller software releases prior to 5.0
support Layer 2 or Layer 3 LWAPP mode.
Note The IPv4 network layer protocol is supported for transport through a CAPWAP or LWAPP controller
system. IPv6 (for clients only) and Appletalk are also supported but only on 4400 series controllers and
the Cisco WiSM. Other Layer 3 protocols (such as IPX, DECnet Phase IV, OSI CLNP, and so on) and
Layer 2 (bridged) protocols (such as LAT and NetBeui) are not supported.
Chapter 1 Overview
Operational Requirements
The requirement for Layer 3 LWAPP communications is that the controller and lightweight access points
can be connected through Layer 2 devices on the same subnet or connected through Layer 3 devices
across subnets. Another requirement is that the IP addresses of access points should be either statically
assigned or dynamically assigned through an external DHCP server.
The requirement for Layer 3 CAPWAP communications across subnets is that the controller and
lightweight access points are connected through Layer 3 devices. Another requirement is that the IP
addresses of access points should be either statically assigned or dynamically assigned through an
external DHCP server.
Configuration Requirements
When you are operating the Cisco Wireless LAN Solution in Layer 2 mode, you must configure a
management interface to control your Layer 2 communications.
When you are operating the Cisco Wireless LAN Solution in Layer 3 mode, you must configure an
AP-manager interface to control lightweight access points and a management interface as configured for
Layer 2 mode.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
1-6
When you are adding lightweight access points to a multiple Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
deployments network, it is convenient to have all lightweight access points associate with one master
controller on the same subnet. That way, the operator does not have to log into multiple controllers to
find out which controller newly-added lightweight access points associated with.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 35

Chapter 1 Overview
Note Lightweight access points without a primary, secondary, and tertiary controller assigned always search
Client Location
Controller Platforms
One controller in each subnet can be assigned as the master controller while adding lightweight access
points. As long as a master controller is active on the same subnet, all new access points without a
primary, secondary, and tertiary controller assigned automatically attempt to associate with the master
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller. This process is described in the “Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
Failover Protection” section on page 1-16.
The operator can monitor the master controller using the WCS Web User Interface and watch as access
points associate with the master controller. The operator can then verify access point configuration and
assign a primary, secondary, and tertiary controller to the access point, and reboot the access point so it
reassociates with its primary, secondary, or tertiary controller.
for a master controller first upon reboot. After adding lightweight access points through the master
controller, assign primary, secondary, and tertiary controllers to each access point. Cisco recommends
that you disable the master setting on all controllers after initial configuration.
When you use Cisco WCS in your Cisco Wireless LAN Solution, controllers periodically determine
client, rogue access point, rogue access point client, radio frequency ID (RFID) tag location and store
the locations in the Cisco WCS database. For more information on location solutions, refer to the Cisco
Wireless Control System Configuration Guide and the Cisco Location Appliance Configuration Guide at
these URLs:
Cisco Wireless Control System Configuration Guide:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6305/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.ht
ml
Cisco Location Appliance Configuration Guide:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6386/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.ht
ml
Controller Platforms
Controllers are enterprise-class high-performance wireless switching platforms that support 802.11a/n
and 802.11b/g/n protocols. They operate under control of the operating system, which includes the radio
resource management (RRM), creating a Cisco UWN Solution that can automatically adjust to real-time
changes in the 802.11 RF environment. The controllers are built around high-performance network and
security hardware, resulting in highly-reliable 802.11 enterprise networks with unparalleled security.
The following controllers are supported for use with software release 5.2:
• Cisco 2100 series controllers
• Cisco 4400 series controllers
OL-17037-01
• Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module (WiSM)
• Cisco 7600 Series Router Wireless Services Module (WiSM)
• Cisco 28/37/38xx Series Integrated Services Router with Controller Network Module
• Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-7
Page 36

Controller Platforms
The first three controllers are stand-alone platforms. The remaining four controllers are integrated into
Cisco switch and router products.
Cisco 2100 Series Controllers
The Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controllers work in conjunction with Cisco lightweight access
points and the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS) to provide system-wide wireless LAN functions.
Each 2100 series controller controls up to 6, 12, or 25 lightweight access points for multi-controller
architectures typical of enterprise branch deployments. It may also be used for single controller
deployments for small and medium-sized environments.
Caution Do not connect a power-over-Ethernet (PoE) cable to the controller’s console port. Doing so may damage
the controller.
Note Wait at least 20 seconds before reconnecting an access point to the controller. Otherwise, the controller
may fail to detect the device.
Chapter 1 Overview
Features Not Supported
This hardware feature is not supported on 2100 series controllers:
• Service port (separate out-of-band management 10/100-Mbps Ethernet interface)
These software features are not supported on 2100 series controllers:
• VPN termination (such as IPSec and L2TP)
• Termination of guest controller tunnels (origination of guest controller tunnels is supported)
• External web authentication web server list
• Spanning tree
• Port mirroring
• AppleTalk
• QoS per-user bandwidth contracts
• IPv6 pass-through
• Link aggregation (LAG)
• Multicast-unicast mode
Cisco 4400 Series Controllers
The Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controller is available in two models: 4402 and 4404. The 4402
supports up to 50 lightweight access points while the 4404 supports up to 100, making it ideal for
large-sized enterprises and large-density applications.
1-8
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 37

Chapter 1 Overview
Figure - Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controller
The Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controller can be factory-ordered with a VPN/Enhanced
Security Module (Crypto Card) to support VPN, IPSec and other processor-intensive tasks. The
VPN/Enhanced Security Module can also be installed in the field.
The 4400 series controller can be equipped with one or two Cisco 4400 series power supplies. When the
controller is equipped with two Cisco 4400 series power supplies, the power supplies are redundant, and
either power supply can continue to power the controller if the other power supply fails.
Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module
Controller Platforms
The Catalyst 6500 Series Wireless Services Module (WiSM) is an integrated Catalyst 6500 switch and
two Cisco 4404 controllers that supports up to 300 lightweight access points. The switch has eight
internal Gigabit Ethernet ports that connect the switch and the controller. The switch and the internal
controller run separate software versions, which must be upgraded separately.
Note Without any other service module installed, the Catalyst 6509 switch chassis can support up to seven
Cisco WiSMs, and the Catalyst 6506 with a Supervisor 720 can support up to four Cisco WiSMs. If one
or more service modules are installed, the chassis can support up to a maximum of four service modules
(WiSMs included). Redundant supervisors cannot be used with these maximum configurations.
Refer to the following documents for additional information:
• Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Installation Guide
• Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Wireless Services Module Installation and Configuration Note
• Release Notes for Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Wireless LAN Services Module
• Configuring a Cisco Wireless Services Module and Wireless Control System
• Catalyst 6500 Series Switch and Cisco 7600 Series Router Wireless Services Module Installation
and Verification Note
You can find these documents at these URLs:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/technology/wism/technical/reference/appnote.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/technology/wism/installation/note/78_17121.html
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-9
Page 38

Controller Platforms
Cisco 7600 Series Router Wireless Services Module
The Cisco 7600 Series Router Wireless Services Module (WiSM) is an integrated Cisco 7600 router and
two Cisco 4404 controllers that supports up to 300 lightweight access points. The router has eight
internal Gigabit Ethernet ports that connect the router and the controller. The router and the internal
controller run separate software versions, which must be upgraded separately.
Note The WiSM is supported on Cisco 7600 series routers running only Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SXF5 or
later.
Note Without any other service module installed, the Cisco 7609 router chassis can support up to seven Cisco
WiSMs, and any other Cisco 7600 series router chassis can support up to six Cisco WiSMs. If one or
more service modules are installed, the chassis can support up to a maximum of four service modules
(WiSMs included). Redundant supervisors cannot be used with these maximum configurations.
Chapter 1 Overview
1-10
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 39

Chapter 1 Overview
Refer to the following documents for additional information:
• Cisco 7600 Series Router Installation Guide
• Cisco 7600 Series Router Software Configuration Guide
• Cisco 7600 Series Router Command Reference
• Configuring a Cisco Wireless Services Module and Wireless Control System
• Catalyst 6500 Series Switch and Cisco 7600 Series Router Wireless Services Module Installation
and Verification Note
You can find these documents at these URLs:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/routers/ps368/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/technology/wism/technical/reference/appnote.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/technology/wism/installation/note/78_17121.html
Cisco 28/37/38xx Series Integrated Services Router
The Cisco 28/37/38xx Series Integrated Services Router is an integrated 28/37/38xx router and Cisco
controller network module that supports up to 6, 8, 12, or 25 lightweight access points, depending on the
version of the network module. The versions that support 8, 12, or 25 access points and the
NME-AIR-WLC6-K9 6-access-point version feature a high-speed processor and more on-board memory
than the NM-AIR-WLC6-K9 6-access-point version. An internal Fast Ethernet port (on the
NM-AIR-WLC6-K9 6-access-point version) or an internal Gigabit Ethernet port (on the 8-, 12-, and
25-access-point versions and on the NME-AIR-WLC6-K9 6-access-point version) connects the router
and the integrated controller. The router and the internal controller run separate software versions, which
must be upgraded separately. Refer to the following documents for additional information:
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Network Module Feature Guide
Controller Platforms
• Cisco 28/37/38xx Series Hardware Installation Guide
You can find these documents at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/index.html
Note The Cisco 2801 Integrated Services Router does not support the controller network module.
Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch
The Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch is an integrated Catalyst 3750 switch
and Cisco 4400 series controller that supports up to 25 or 50 lightweight access points. The switch has
two internal Gigabit Ethernet ports that connect the switch and the controller. The switch and the internal
controller run separate software versions, which must be upgraded separately. Refer to the following
documents for additional information:
• Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch Getting Started Guide
• Catalyst 3750 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Release Notes for the Catalyst 3750 Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch, Cisco IOS Release
12.2(25)FZ
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-11
Page 40

Cisco UWN Solution Wired Connections
You can find these documents at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps5023/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Cisco UWN Solution Wired Connections
The Cisco UWN Solution components communicate with each other using industry-standard Ethernet
cables and connectors. The following paragraphs contain details of the wired connections.
• The 2100 series controller connects to the network using from one to six 10/100BASE-T Ethernet
cables.
• The 4402 controller connects to the network using one or two fiber-optic Gigabit Ethernet cables,
and the 4404 controller connects to the network using up to four fiber-optic Gigabit Ethernet cables:
two redundant Gigabit Ethernet connections to bypass single network failures.
• The controllers in the Wireless Services Module (WiSM), installed in a Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series
Switch or a Cisco 7600 Series Router, connect to the network through ports on the switch or router.
• The Wireless LAN Controller Network Module, installed in a Cisco Integrated Services Router,
connects to the network through the ports on the router.
• The controller in the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch connects to the
network through the ports on the switch.
Chapter 1 Overview
• Cisco lightweight access points connects to the network using 10/100BASE-T Ethernet cables. The
standard CAT-5 cable can also be used to conduct power for the lightweight access points from a
network device equipped with Power over Ethernet (PoE) capability. This power distribution plan
can be used to reduce the cost of individual AP power supplies and related cabling.
Cisco UWN Solution WLANs
The Cisco UWN Solution can control up to 16 WLANs for lightweight access points. Each WLAN has
a separate WLAN ID (1 through 16), a separate WLAN SSID (WLAN name), and can be assigned unique
security policies. Using software release 3.2 and later, you can configure both static and dynamic WEP
on the same WLAN.
The lightweight access points broadcast all active Cisco UWN Solution WLAN SSIDs and enforce the
policies defined for each WLAN.
Note Cisco recommends that you assign one set of VLANs for WLANs and a different set of VLANs for
management interfaces to ensure that controllers operate with optimum performance and ease of
management.
If management over wireless is enabled across the Cisco UWN Solution, the operator can manage the
system across the enabled WLAN using CLI and Telnet, http/https, and SNMP.
To configure WLANs, refer to Chapter 6.
1-12
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 41

Chapter 1 Overview
Identity Networking
Controllers can have the following parameters applied to all clients associating with a particular wireless
LAN: QoS, global or Interface-specific DHCP server, Layer 2 and Layer 3 Security Policies, and default
Interface (which includes physical port, VLAN and ACL assignments).
However, the controllers can also have individual clients (MAC addresses) override the preset wireless
LAN parameters by using MAC Filtering or by Allowing AAA Override parameters. This configuration
can be used, for example, to have all company clients log into the corporate wireless LAN, and then have
clients connect using different QoS, DHCP server, Layer 2 and Layer 3 Security Policies, and Interface
(which includes physical port, VLAN and ACL assignments) settings on a per-MAC Address basis.
When Cisco UWN Solution operators configure MAC Filtering for a client, they can assign a different
VLAN to the MAC Address, which can be used to have operating system automatically reroute the client
to the management interface or any of the operator-defined interfaces, each of which have their own
VLAN, access control list (ACL), DHCP server, and physical port assignments. This MAC Filtering can
be used as a coarse version of AAA Override, and normally takes precedence over any AAA (RADIUS
or other) Override.
However, when Allow AAA Override is enabled, the RADIUS (or other AAA) server can alternatively
be configured to return QoS
Allow AAA Override gives the AAA Override precedence over the MAC Filtering parameters set in the
controller; if there are no AAA Overrides available for a given MAC Address, the operating system uses
the MAC Filtering parameters already in the controller. This AAA (RADIUS or other) Override can be
used as a finer version of AAA Override, but only takes precedence over MAC Filtering when Allow
AAA Override is enabled.
Note that in all cases, the Override parameters (Operator-Defined Interface and QoS, for example) must
already be defined in the controller configuration.
In all cases, the operating system will use QoS
by the AAA server or MAC Filtering regardless of the Layer 2 and/or Layer 3 authentication used.
Identity Networking
, DSCP, 802.1p priority tag values and ACL on a per-MAC Address basis.
, DSCP, 802.1p priority tag values and ACL provided
Also note that the operating system only moves clients from the default Cisco UWN Solution WLAN
VLAN to a different VLAN when configured for MAC filtering, 802.1X, and/or WPA Layer 2
authentication. To configure WLANs, refer to Chapter 6.
Enhanced Integration with Cisco Secure ACS
The identity-based networking feature uses authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA)
override. When the following vendor-specific attributes are present in the RADIUS access accept
message, the values override those present in the wireless LAN profile:
• QoS level
• 802.1p value
• VLAN interface name
• Access control list (ACL) name
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-13
Page 42

File Transfers
In this release, support is being added for the AAA server to return the VLAN number or name using the
standard “RADIUS assigned VLAN name/number” feature defined in IETF RFC 2868 (RADIUS
Attributes for Tunnel Protocol Support). To assign a wireless client to a particular VLAN, the AAA
server sends the following attributes to the controller in the access accept message:
• IETF 64 (Tunnel Type): VLAN
• IETF 65 (Tunnel Medium Type): 802
• IETF 81 (Tunnel Private Group ID): VLAN # or VLAN Name String
This enables Cisco Secure ACS to communicate a VLAN change that may be a result of a posture
analysis. Benefits of this new feature include:
• Integration with Cisco Secure ACS reduces installation and setup time
• Cisco Secure ACS operates smoothly across both wired and wireless networks
This feature supports 2100 and 4400 series controllers and 1130 and 1200 series lightweight access
points.
File Transfers
Chapter 1 Overview
The Cisco UWN Solution operator can upload and download operating system code, configuration, and
certificate files to and from controller using the GUI, CLI commands, or Cisco WCS.
• To use CLI commands, refer to the “Transferring Files to and from a Controller” section on
page 8-7.
• To use Cisco WCS to upgrade software, refer to the Cisco Wireless Control System Configuration
Guide. Click this URL to browse to this document:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6305/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_lis
t.html
Power over Ethernet
Lightweight access points can receive power via their Ethernet cables from 802.3af-compatible Power
over Ethernet (PoE) devices, which can reduce the cost of discrete power supplies, additional wiring,
conduits, outlets, and installer time. PoE also frees installers from having to mount Cisco 1000 series
lightweight access points or other powered equipment near AC outlets, providing greater flexibility in
positioning Cisco 1000 series lightweight access points for maximum coverage.
When you are using PoE, the installer runs a single CAT-5 cable from each lightweight access point to
PoE-equipped network elements, such as a PoE power hub or a Cisco WLAN Solution Single-Line PoE
Injector. When the PoE equipment determines that the lightweight access point is PoE-enabled, it sends
48 VDC over the unused pairs in the Ethernet cable to power the lightweight access point.
The PoE cable length is limited by the 100BASE-T or 10BASE-T specification to 100 m or 200 m,
respectively.
Lightweight access points can receive power from an 802.3af-compliant device or from the external
power supply.
1-14
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 43

Chapter 1 Overview
Startup Wizard
When a controller is powered up with a new factory operating system software load or after being reset
to factory defaults, the bootup script runs the Startup Wizard, which prompts the installer for initial
configuration. The Startup Wizard:
• Ensures that the controller has a System Name, up to 32 characters.
• Adds an Administrative username and password, each up to 24 characters.
• Ensures that the controller can communicate with the GUI, CLI, or Cisco WCS (either directly or
indirectly) through the service port by accepting a valid IP configuration protocol (none or DHCP),
and if none, IP Address and netmask. If you do not want to use the service port, enter 0.0.0.0 for the
IP Address and netmask.
• Ensures that the controller can communicate with the network (802.11 Distribution System) through
the management interface by collecting a valid static IP Address, netmask, default router IP address,
VLAN identifier, and physical port assignment.
• Prompts for the IP address of the DHCP server used to supply IP addresses to clients, the controller
management interface, and optionally to the service port interface.
• Collects the Virtual Gateway IP Address; any fictitious, unassigned IP address (such as 1.1.1.1) to
be used by Layer 3 Security and Mobility managers.
• Allows you to enter the Mobility Group (RF Group) Name.
• Collects the wireless LAN 1 802.11 SSID, or Network Name.
Startup Wizard
• Asks you to define whether or not clients can use static IP addresses. Yes = more convenient, but
lower security (session can be hijacked), clients can supply their own IP Address, better for devices
that cannot use DHCP. No = less convenient, higher security, clients must DHCP for an IP Address,
works well for s XP devices.
• If you want to configure a RADIUS server from the Startup Wizard, the RADIUS server IP address,
communication port, and Secret.
• Collects the Country Code.
• Enables or disables the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n lightweight access point networks.
• Enables or disables radio resource management (RRM).
To use the Startup Wizard, refer to the “Using the Configuration Wizard” section on page 4-2.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Memory
The controller contains two kinds of memory: volatile RAM, which holds the current, active controller
configuration, and NVRAM (non-volatile RAM), which holds the reboot configuration. When you are
configuring the operating system in controller, you are modifying volatile RAM; you must save the
configuration from the volatile RAM to the NVRAM to ensure that the controller reboots in the current
configuration.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-15
Page 44

Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Failover Protection
Knowing which memory you are modifying is important when you are:
• Using the Configuration Wizard
• Clearing the Controller Configuration
• Saving Configurations
• Resetting the Controller
• Logging Out of the CLI
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Failover Protection
Each controller has a defined number of communication ports for lightweight access points. This means
that when multiple controllers with unused access point ports are deployed on the same network, if one
controller fails, the dropped access points automatically poll for unused controller ports and associate
with them.
During installation, Cisco recommends that you connect all lightweight access points to a dedicated
controller, and configure each lightweight access point for final operation. This step configures each
lightweight access point for a primary, secondary, and tertiary controller and allows it to store the
configured mobility group information.
Chapter 1 Overview
During failover recovery, the configured lightweight access points obtain an IP address from the local
DHCP server (only in Layer 3 operation), attempt to contact their primary, secondary, and tertiary
controllers, and then attempt to contact the IP addresses of the other controllers in the Mobility group.
This prevents the access points from spending time sending out blind polling messages, resulting in a
faster recovery period.
In multiple-controller deployments, this means that if one controller fails, its dropped access points
reboot and do the following under direction of the radio resource management (RRM):
• Obtain an IP address from a local DHCP server (one on the local subnet).
• If the lightweight access point has a primary, secondary, and tertiary controller assigned, it attempts
to associate with that controller.
• If the access point has no primary, secondary, or tertiary controllers assigned or if its primary,
secondary, or tertiary controllers are unavailable, it attempts to associate with a master controller on
the same subnet.
• If the access point finds no master controller on the same subnet, it attempts to contact stored
mobility group members by IP address.
• Should none of the mobility group members be available, and if the lightweight access point has no
primary, secondary, and tertiary controllers assigned and there is no master controller active, it
attempts to associate with the least-loaded controller on the same subnet to respond to its discovery
messages with unused ports.
This means that when sufficient controllers are deployed, should one controller fail, active access point
client sessions are momentarily dropped while the dropped access point associates with an unused port
on another controller, allowing the client device to immediately reassociate and reauthenticate.
1-16
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 45

Chapter 1 Overview
Network Connections to Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Network Connections to Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Regardless of operating mode, all controllers use the network as an 802.11 distribution system.
Regardless of the Ethernet port type or speed, each controller monitors and communicates with its
related controllers across the network. The following sections give details of these network connections:
• Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controllers, page 1-17
• Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controllers, page 1-18
Note Chapter 3 provides information on configuring the controller’s ports and assigning interfaces to them.
Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 2100 series controllers can communicate with the network through any one of their physical data
ports, as the logical management interface can be assigned to one of the ports. The physical port
description is as follows:
• Up to six 10/100BASE-T cables can plug into the six back-panel data ports on the 2100 series
controller chassis. The 2100 series also has two PoE ports (ports 7 and 8).
Figure 1-4 shows connections to the 2100 series controllers.
Figure 1-4 Physical Network Connections to the 2100 Series Controller
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
1-17
Page 46

Network Connections to Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 4400 series controllers can communicate with the network through one or two pairs of physical
data ports, and the logical management interface can be assigned to the ports. The physical port
descriptions follows:
• For the 4402 controller, up to two of the following connections are supported in any combination:
–
1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet, front panel, RJ-45 physical port, UTP cable).
–
1000BASE-SX (Gigabit Ethernet, front panel, LC physical port, multi-mode 850nM (SX)
fiber-optic links using LC physical connectors).
–
1000BASE-LX (Gigabit Ethernet, front panel, LC physical port, multi-mode 1300nM (LX/LH)
fiber-optic links using LC physical connectors).
• For the 4404 controller, up to four of the following connections are supported in any combination:
–
1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet, front panel, RJ-45 physical port, UTP cable).
–
1000BASE-SX (Gigabit Ethernet, front panel, LC physical port, multi-mode 850nM (SX)
fiber-optic links using LC physical connectors).
–
1000BASE-LX (Gigabit Ethernet, front panel, LX physical port, multi-mode 1300nM (LX/LH)
fiber-optic links using LC physical connectors).
Figure 1-5 shows connections to the 4400 series controller.
Chapter 1 Overview
Figure 1-5 Physical Network Connections to 4402 and 4404 Series Controllers
1-18
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 47

CHAP T E R
2
Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
This chapter describes the web-browser and CLI interfaces that you use to configure the controller.
It contains these sections:
• Using the Web-Browser Interface, page 2-2
• Using the CLI, page 2-7
• Enabling Wireless Connections to the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces, page 2-9
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
2-1
Page 48

Using the Web-Browser Interface
Using the Web-Browser Interface
The web-browser interface (hereafter called the GUI) is built into each controller. It allows up to five
users to simultaneously browse into the controller HTTP or HTTPS (HTTP + SSL) management pages
to configure parameters and monitor operational status for the controller and its associated access points.
Note Cisco recommends that you enable the HTTPS interface and disable the HTTP interface to ensure more
robust security for your Cisco UWN Solution.
Guidelines for Using the GUI
Keep these guidelines in mind when using the GUI:
• The GUI must be used on a PC running Windows XP SP1 (or later) or Windows 2000 SP4 (or later).
• The GUI is fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0 SP1 (or later) or Mozilla
Firefox 2.0.0.11 (or later).
Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Note Opera and Netscape are not supported.
Note Internet Explorer 6.0 SP1 (or later) and Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.11 (or later) are the only
browsers supported for accessing the controller GUI and for using web authentication.
• You can use either the service port interface or the management interface to access the GUI. Cisco
recommends that you use the service-port interface. Refer to Chapter 3 for instructions on
configuring the service port interface.
• Click Help at the top of any page in the GUI to display online help. You might need to disable your
browser’s pop-up blocker to view the online help.
Opening the GUI
To open the GUI, enter the controller IP address in the browser’s address line. For a secure connection,
enter https://ip-address. For a less secure connection, enter http://ip-address. See the “Using the GUI
to Enable Web and Secure Web Modes” section on page 2-3 for instructions on setting up HTTPS.
Enabling Web and Secure Web Modes
This section provides instructions for enabling the distribution system port as a web port (using HTTP)
or as a secure web port (using HTTPS). You can protect communication with the GUI by enabling
HTTPS. HTTPS protects HTTP browser sessions by using the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol.
When you enable HTTPS, the controller generates its own local web administration SSL certificate and
automatically applies it to the GUI. You also have the option of downloading an externally generated
certificate.
You can configure web and secure web mode using the controller GUI or CLI.
2-2
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 49

Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Using the GUI to Enable Web and Secure Web Modes
Follow these steps to enable web mode, secure web mode, or both using the controller GUI.
Step 1 Click Management > HTTP to open the HTTP Configuration page (see Figure 2-1).
Figure 2-1 HTTP Configuration Page
Using the Web-Browser Interface
Step 2
To enable web mode, which allows users to access the controller GUI using “http://ip-address,” choose
Enabled from the HTTP Access drop-down box. Otherwise, choose Disabled. The default value is
Disabled. Web mode is not a secure connection.
Step 3 To enable secure web mode, which allows users to access the controller GUI using “https://ip-address,”
choose Enabled from the HTTPS Access drop-down box. Otherwise, choose Disabled. The default
value is Enabled. Secure web mode is a secure connection.
Step 4 In the Web Session Timeout field, enter the amount of time (in minutes) before the web session times
out due to inactivity. You can enter a value between 30 and 160 minutes (inclusive), and the default value
is 30 minutes.
Step 5 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 6 If you enabled secure web mode in Step 3, the controller generates a local web administration SSL
certificate and automatically applies it to the GUI. The details of the current certificate appear in the
middle of the HTTP Configuration page (see Figure 2-1).
Note If you want to download your own SSL certificate to the controller, follow the instructions in the
“Loading an Externally Generated SSL Certificate” section on page 2-5.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
2-3
Page 50

Using the Web-Browser Interface
Note If desired, you can delete the current certificate by clicking Delete Certificate and have the
controller generate a new certificate by clicking Regenerate Certificate.
Step 7 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Using the CLI to Enable Web and Secure Web Modes
Follow these steps to enable web mode, secure web mode, or both using the controller CLI.
Step 1 To enable or disable web mode, enter this command:
config network webmode {enable | disable}
This command allows users to access the controller GUI using “http://ip-address.” The default value is
disabled. Web mode is not a secure connection.
Step 2 To enable or disable secure web mode, enter this command:
config network secureweb {enable | disable}
Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
This command allows users to access the controller GUI using “https://ip-address.” The default value is
enabled. Secure web mode is a secure connection.
Step 3 To enable or disable secure web mode with increased security, enter this command:
config network secureweb cipher-option high {enable | disable}
This command allows users to access the controller GUI using “https://ip-address” but only from
browsers that support 128-bit (or larger) ciphers. The default value is disabled.
Step 4 To enable or disable SSLv2 for web administration, enter this command:
config network secureweb cipher-option sslv2 {enable | disable}
If you disable SSLv2, users cannot connect using a browser configured with SSLv2 only. They must use
a browser that is configured to use a more secure protocol such as SSLv3 or later. The default value is
enabled.
Step 5 To verify that the controller has generated a certificate, enter this command:
show certificate summary
Information similar to the following appears:
Web Administration Certificate................. Locally Generated
Web Authentication Certificate................. Locally Generated
Certificate compatibility mode:................ off
Note If you want to download your own SSL certificate to the controller, follow the instructions in the
“Loading an Externally Generated SSL Certificate” section on page 2-5.
2-4
Step 6 (Optional) If you need to generate a new certificate, enter this command:
config certificate generate webadmin
After a few seconds, the controller verifies that the certificate has been generated.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 51
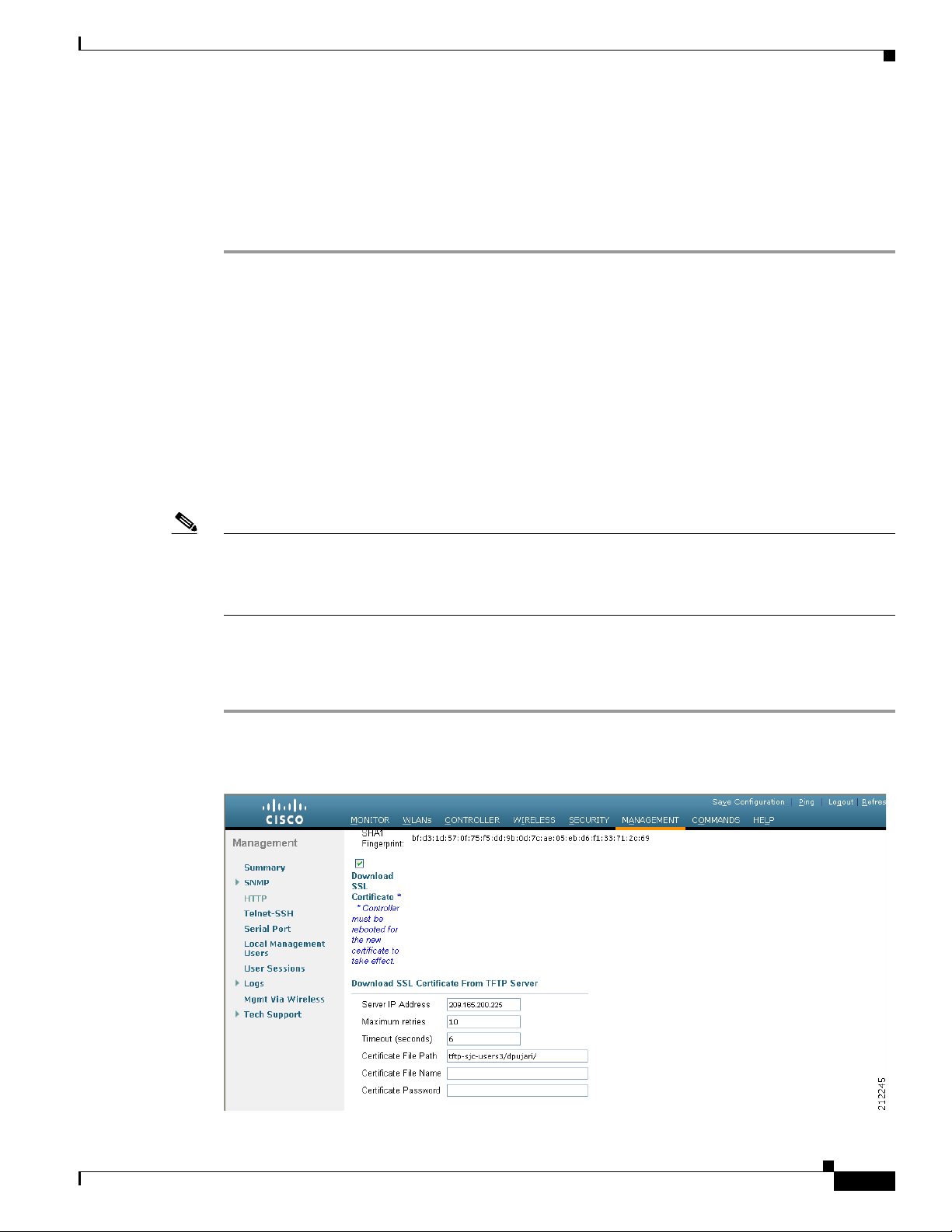
Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Step 7 To save the SSL certificate, key, and secure web password to non-volatile RAM (NVRAM) so that your
changes are retained across reboots, enter this command:
save config
Step 8 To reboot the controller, enter this command:
reset system
Loading an Externally Generated SSL Certificate
You can use a TFTP server to download an externally generated SSL certificate to the controller. Follow
these guidelines for using TFTP:
• If you load the certificate through the service port, the TFTP server must be on the same subnet as
the controller because the service port is not routable, or you must create static routes on the
controller. Also, if you load the certificate through the distribution system network port, the TFTP
server can be on any subnet.
• A third-party TFTP server cannot run on the same computer as the Cisco WCS because the WCS
built-in TFTP server and the third-party TFTP server require the same communication port.
Using the Web-Browser Interface
Note Every HTTPS certificate contains an embedded RSA key. The length of the key can vary from 512 bits,
which is relatively insecure, to thousands of bits, which is very secure. When you obtain a new certificate
from a Certificate Authority, make sure that the RSA key embedded in the certificate is at least 768 bits
long.
Using the GUI to Load an SSL Certificate
Follow these steps to load an externally generated SSL certificate using the controller GUI.
Step 1 On the HTTP Configuration page, check the Download SSL Certificate check box (see Figure 2-2).
Figure 2-2 HTTP Configuration Page
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
2-5
Page 52

Using the Web-Browser Interface
Step 2 In the Server IP Address field, enter the IP address of the TFTP server.
Step 3 In the Maximum Retries field, enter the maximum number of times that the TFTP server attempts to
download the certificate.
Step 4 In the Timeout field, enter the amount of time (in seconds) that the TFTP server attempts to download
the certificate.
Step 5 In the Certificate File Path field, enter the directory path of the certificate.
Step 6 In the Certificate File Name field, enter the name of the certificate (webadmincert_name.pem).
Step 7 (Optional) In the Certificate Password field, enter a password to encrypt the certificate.
Step 8 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 9 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Step 10 To reboot the controller for your changes to take effect, click Commands > Reboot > Reboot > Save
and Reboot.
Using the CLI to Load an SSL Certificate
Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Follow these steps to load an externally generated SSL certificate using the controller CLI.
Step 1 Use a password to encrypt the HTTPS certificate in a .PEM-encoded file. The PEM-encoded file is called
a web administration certificate file (webadmincert_name.pem).
Step 2 Move the webadmincert_name.pem file to the default directory on your TFTP server.
Step 3 To view the current download settings, enter this command and answer n to the prompt:
transfer download start
Information similar to the following appears:
Mode........................................... TFTP
Data Type...................................... Admin Cert
TFTP Server IP................................. xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
TFTP Path...................................... <directory path>
TFTP Filename..................................
Are you sure you want to start? (y/n) n
Transfer Canceled
Step 4 Use these commands to change the download settings:
transfer download mode tftp
transfer download datatype webauthcert
transfer download serverip TFTP_server IP_address
transfer download path absolute_TFTP_server_path_to_the_update_file
2-6
transfer download filename webadmincert_name.pem
Step 5 To set the password for the .PEM file so that the operating system can decrypt the web administration
SSL key and certificate, enter this command:
transfer download certpassword private_key_password
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 53

Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Step 6 To confirm the current download settings and start the certificate and key download, enter this command
and answer y to the prompt:
transfer download start
Information similar to the following appears:
Mode........................................... TFTP
Data Type...................................... Site Cert
TFTP Server IP................................. xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
TFTP Path...................................... directory path
TFTP Filename.................................. webadmincert_name
Are you sure you want to start? (y/n) y
TFTP Webadmin cert transfer starting.
Certificate installed.
Please restart the switch (reset system) to use the new certificate.
Step 7 To save the SSL certificate, key, and secure web password to NVRAM so that your changes are retained
across reboots, enter this command:
save config
Step 8 To reboot the controller, enter this command:
reset system
Using the CLI
Using the CLI
The Cisco UWN Solution command line interface (CLI) is built into each controller. The CLI allows you
to use a VT-100 emulator to locally or remotely configure, monitor, and control individual controllers
and its associated lightweight access points. The CLI is a simple text-based, tree-structured interface that
allows up to five users with Telnet-capable terminal emulators to access the controller.
Note Refer to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Command Reference for information on specific commands.
Note If you want to input any strings from the XML configuration into CLI commands, you must enclose the
strings in quotation marks.
Logging into the CLI
You access the CLI using one of two methods:
• A direct ASCII serial connection to the controller console port
• A remote console session over Ethernet through the pre-configured service port or the distribution
system ports
Before you log into the CLI, configure your connectivity and environment variables based on the type
of connection you use.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
2-7
Page 54

Using the CLI
Using a Local Serial Connection
You need these items to connect to the serial port:
• A computer that has a DB-9 serial port and is running a terminal emulation program
• A DB-9 male-to-female null-modem serial cable
Follow these steps to log into the CLI through the serial port.
Step 1 Connect your computer to the controller using the DB-9 null-modem serial cable.
Step 2 Open a terminal emulator session using these settings:
• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
• No parity
• No hardware flow control
Step 3 At the prompt, log into the CLI. The default username is admin, and the default password is admin.
Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Note The controller serial port is set for a 9600 baud rate and a short timeout. If you would like to
change either of these values, enter config serial baudrate baudrate and config serial timeout
timeout to make your changes. If you enter config serial timeout 0, serial sessions never time
out.
Using a Remote Ethernet Connection
You need these items to connect to a controller remotely:
• A computer with access to the controller over the Ethernet network
• The IP address of the controller
• A terminal emulation program or a DOS shell for the Telnet session
Note By default, controllers block Telnet sessions. You must use a local connection to the serial port to enable
Telnet sessions.
Follow these steps to log into the CLI through a remote Ethernet connection.
Step 1 Verify that your terminal emulator or DOS shell interface is configured with these parameters:
2-8
• Ethernet address
• Port 23
Step 2 Use the controller IP address to Telnet to the CLI.
Step 3 At the prompt, log into the CLI. The default username is admin, and the default password is admin.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 55

Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Logging Out of the CLI
When you finish using the CLI, navigate to the root level and enter logout. The system prompts you to
save any changes you made to the volatile RAM.
Navigating the CLI
The CLI is organized around five levels:
Root Level
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Level 5
When you log into the CLI, you are at the root level. From the root level, you can enter any full command
without first navigating to the correct command level. Tabl e 2-1 lists commands you use to navigate the
CLI and to perform common tasks.
Enabling Wireless Connections to the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Table 2-1 Commands for CLI Navigation and Common Tasks
Command Action
help At the root level, view systemwide navigation
commands
? View commands available at the current level
command ? View parameters for a specific command
exit Move down one level
Ctrl-Z Return from any level to the root level
save config At the root level, save configuration changes from
active working RAM to non-volatile RAM
(NVRAM) so they are retained after reboot
reset system At the root level, reset the controller without
logging out
Enabling Wireless Connections to the Web-Browser and
CLI Interfaces
You can monitor and configure controllers using a wireless client. This feature is supported for all
management tasks except uploads from and downloads to the controller.
Before you can open the GUI or the CLI from a wireless client device, you must configure the controller
to allow the connection. Follow these steps to enable wireless connections to the GUI or CLI.
OL-17037-01
Step 1 Log into the CLI.
Step 2 Enter config network mgmt-via-wireless enable.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
2-9
Page 56

Enabling Wireless Connections to the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
Step 3 Use a wireless client to associate to a lightweight access point connected to the controller.
Step 4 On the wireless client, open a Telnet session to the controller, or browse to the controller GUI.
Tip To use the controller GUI to enable wireless connections, click Management > Mgmt Via Wireless
page and check the Enable Controller Management to be accessible from Wireless Clients check
box.
Chapter 2 Using the Web-Browser and CLI Interfaces
2-10
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 57

CHAP T E R
3
Configuring Ports and Interfaces
This chapter describes the controller’s physical ports and interfaces and provides instructions for
configuring them. It contains these sections:
• Overview of Ports and Interfaces, page 3-2
• Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces, page 3-10
• Configuring Dynamic Interfaces, page 3-16
• Configuring Ports, page 3-19
• Enabling Link Aggregation, page 3-29
• Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points, page 3-34
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-1
Page 58

Overview of Ports and Interfaces
230622
Console port
Distribution system
ports 1-6
PoE-enabled
ports 7 and 8
146999
STATUS
ALARM
LINK
SERVICE
CONSOLE
LINK
ACT
LINK
ACT
UTILITY
1
PS1
PS2
ACT
LINK
ACT
2 3 4
Distribution system
ports 1-4
Service
port
Serial
console port
Overview of Ports and Interfaces
Three concepts are key to understanding how controllers connect to a wireless network: ports, interfaces,
and WLANs.
Ports
A port is a physical entity that is used for connections on the controller platform. Controllers have two
types of ports: distribution system ports and a service port. The following figures show the ports
available on each controller.
Note The controller in a Cisco Integrated Services Router and the controllers on the Cisco WiSM do not have
external physical ports. They connect to the network through ports on the router or switch.
Figure 3-1 Ports on the Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
3-2
Figure 3-2 Ports on the Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Note Figure 3-2 shows a Cisco 4404 controller. The Cisco 4402 controller is similar but has only two
distribution system ports. The utility port, which is the unlabeled port in Figure 3-2, is currently not
operational.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 59
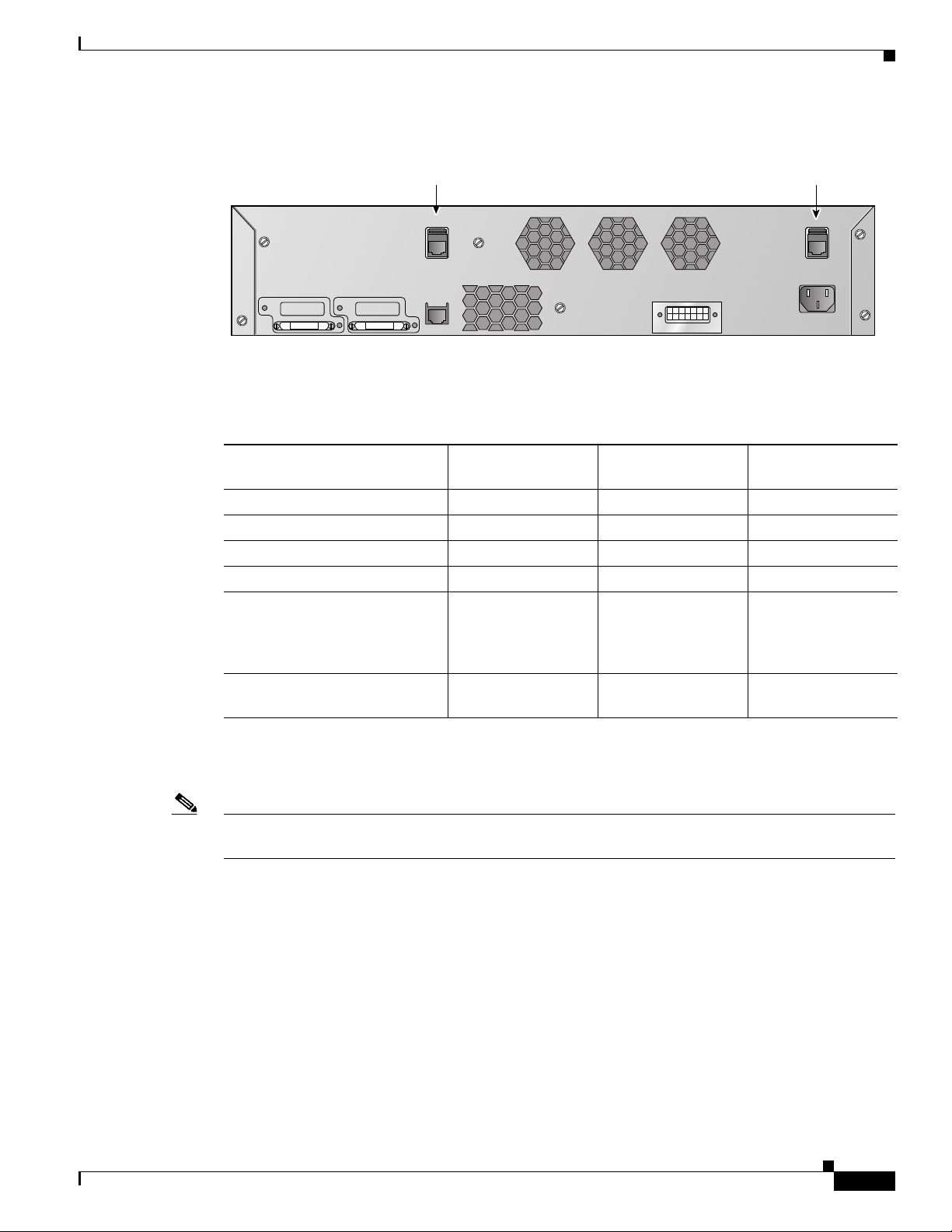
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
155755
Controller console
port
Service
port
STACK1 STACK2
SWITCH
CONSOLE
CONTROLLER
CONSOLE
SERVICE
Figure 3-3 Ports on the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch
Table 3 -1 provides a list of ports per controller.
Table 3-1 Controller Ports
Controller Service Ports
2100 series None 8 (6 + 2 PoE ports) 1
4402 1 2 1
4404 1 4 1
Cisco WiSM 2 (ports 9 and 10) 8 (ports 1-8) 2
Controller Network Module
within the Cisco 28/37/38xx
Series Integrated Services
Routers
Catalyst 3750G Integrated
Wireless LAN Controller Switch
1. The baud rate for the Gigabit Ethernet version of the controller network module is limited to 9600 bps while the baud rate for
the Fast Ethernet version supports up to 57600 bps.
Overview of Ports and Interfaces
Distribution System
Ethernet Ports Serial Console Port
None 1 1
1 2 (ports 27 and 28) 1
1
OL-17037-01
Note Appendix E provides logical connectivity diagrams and related software commands for the integrated
controllers.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-3
Page 60

Overview of Ports and Interfaces
Distribution System Ports
A distribution system port connects the controller to a neighbor switch and serves as the data path
between these two devices.
• Cisco 2100 series controllers have eight 10/100 copper Ethernet distribution system ports through
which the controller can support up to 6, 12, or 25 access points. Two of these ports (7 and 8) are
power-over-Ethernet (PoE) enabled and can be used to provide power directly to access points that
are connected to these ports.
Note All client connections to the 2100 series controllers are limited to the 10/100 Ethernet uplink
• Cisco 4402 controllers have two Gigabit Ethernet distribution system ports, each of which is capable
of managing up to 48 access points. However, Cisco recommends no more than 25 access points per
port due to bandwidth constraints. The 4402-25 and 4402-50 models allow a total of 25 or 50 access
points to join the controller.
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
port connection between the switch and the controller, even though their connection speeds
might be higher. The exception is for access points running in local hybrid-REAP mode
because this traffic is switched at the access point level and not forwarded back to the
controller.
• Cisco 4404 controllers have four Gigabit Ethernet distribution system ports, each of which is
capable of managing up to 48 access points. However, Cisco recommends no more than 25 access
points per port due to bandwidth constraints. The 4404-25, 4404-50, and 4404-100 models allow a
total of 25, 50, or 100 access points to join the controller.
Note The Gigabit Ethernet ports on the 4402 and 4404 controllers accept these SX/LC/T small
form-factor plug-in (SFP) modules:
- 1000BASE-SX SFP modules, which provide a 1000-Mbps wired connection to a network
through an 850nM (SX) fiber-optic link using an LC physical connector
- 1000BASE-LX SFP modules, which provide a 1000-Mbps wired connection to a network
through a 1300nM (LX/LH) fiber-optic link using an LC physical connector
- 1000BASE-T SFP modules, which provide a 1000-Mbps wired connection to a network
through a copper link using an RJ-45 physical connector
• The Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Wireless Services Module (WiSM) and the Cisco 7600
Series Router Wireless Services Module (WiSM) have eight internal Gigabit Ethernet distribution
system ports (ports 1 through 8) that connect the switch or router and the integrated controller. These
internal ports are located on the backplane of the switch or router and are not visible on the front
panel. Through these ports, the controller can support up to 300 access points.
• The controller network module within the Cisco 28/37/38xx Series Integrated Services Router can
support up to 6, 8, 12, or 25 access points (and up to 256, 256, 350, or 350 clients, respectively),
depending on the version of the network module. The network module supports these access points
through a Fast Ethernet distribution system port (on the NM-AIR-WLC6-K9 6-access-point version)
or a Gigabit Ethernet distribution system port (on the 8-, 12-, and 25-access-point versions and on
the NME-AIR-WLC6-K9 6-access-point version) that connects the router and the integrated
controller. This port is located on the router backplane and is not visible on the front panel. The Fast
Ethernet port operates at speeds up to 100 Mbps, and the Gigabit Ethernet port operates at speeds
up to 1 Gbps.
3-4
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 61

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
• The Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch has two internal Gigabit Ethernet
distribution system ports (ports 27 and 28) that connect the switch and the integrated controller.
These internal ports are located on the switch backplane and are not visible on the front panel. Each
port is capable of managing up to 48 access points. However, Cisco recommends no more than 25
access points per port due to bandwidth constraints. The -S25 and -S50 models allow a total of 25
or 50 access points to join the controller.
Note Refer to the “Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points” section on
page 3-34 if you want to configure your Cisco 4400 series controller to support more than 48 access
points.
Each distribution system port is, by default, an 802.1Q VLAN trunk port. The VLAN trunking
characteristics of the port are not configurable.
Note Some controllers support link aggregation (LAG), which bundles all of the controller’s distribution
system ports into a single 802.3ad port channel. Cisco 4400 series controllers support LAG in software
release 3.2 and higher, and LAG is enabled automatically on the Cisco WiSM controllers. Refer to the
“Enabling Link Aggregation” section on page 3-29 for more information.
Overview of Ports and Interfaces
Service Port
Cisco 4400 series controllers also have a 10/100 copper Ethernet service port. The service port is
controlled by the service-port interface and is reserved for out-of-band management of the controller and
system recovery and maintenance in the event of a network failure. It is also the only port that is active
when the controller is in boot mode. The service port is not capable of carrying 802.1Q tags, so it must
be connected to an access port on the neighbor switch. Use of the service port is optional.
Note The Cisco WiSM’s controllers use the service port for internal protocol communication between the
controllers and the Supervisor 720.
Note The Cisco 2100 series controllers and the controller in the Cisco Integrated Services Router do not have
a service port.
Note The service port is not auto-sensing. You must use the correct straight-through or crossover Ethernet
cable to communicate with the service port.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-5
Page 62

Overview of Ports and Interfaces
Interfaces
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
An interface is a logical entity on the controller. An interface has multiple parameters associated with it,
including an IP address, default-gateway (for the IP subnet), primary physical port, secondary physical
port, VLAN identifier, and DHCP server.
These five types of interfaces are available on the controller. Four of these are static and are configured
at setup time:
• Management interface (Static and configured at setup time; mandatory)
• AP-manager interface (Static and configured at setup time; mandatory)
• Virtual interface (Static and configured at setup time; mandatory)
• Service-port interface (Static and configured at setup time; optional)
• Dynamic interface (User-defined)
Each interface is mapped to at least one primary port, and some interfaces (management and dynamic)
can be mapped to an optional secondary (or backup) port. If the primary port for an interface fails, the
interface automatically moves to the backup port. In addition, multiple interfaces can be mapped to a
single controller port.
Note Refer to the “Enabling Link Aggregation” section on page 3-29 if you want to configure the controller
to dynamically map the interfaces to a single port channel rather than having to configure primary and
secondary ports for each interface.
Management Interface
The management interface is the default interface for in-band management of the controller and
connectivity to enterprise services such as AAA servers. The management interface has the only
consistently “pingable” in-band interface IP address on the controller. You can access the controller’s
GUI by entering the controller’s management interface IP address in Internet Explorer’s Address field.
For CAPWAP, the controller requires one management interface to control all inter-controller
communications and one AP-manager interface to control all controller-to-access point
communications, regardless of the number of ports.
Note If the service port is in use, the management interface must be on a different supernet from the
service-port interface.
AP-Manager Interface
A controller has one or more AP-manager interfaces, which are used for all Layer 3 communications
between the controller and lightweight access points after the access points have joined the controller.
The AP-manager IP address is used as the tunnel source for CAPWAP packets from the controller to the
access point and as the destination for CAPWAP packets from the access point to the controller.
For Cisco 4404 and WiSM controllers, configure the AP-manager interface on all distribution system
ports (1, 2, 3, and 4). For Cisco 4402 controllers, configure the AP-manager interface on distribution
system ports 1 and 2. In both cases, the static (or permanent) AP-manager interface is always assigned
3-6
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 63

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
to distribution system port 1 and given a unique IP address. Configuring the AP-manager interface on
the same VLAN or IP subnet as the management interface results in optimum access point association,
but this is not a requirement.
Note If LAG is enabled, there can be only one AP-manager interface. But when LAG is disabled, you must
assign an AP-manager interface to each port on the controller.
Note If only one distribution system port can be used, you should use distribution system port 1.
The AP-manager interface communicates through any distribution system port by listening across the
Layer 3 network for access point CAPWAP or LWAPP join messages to associate and communicate with
as many lightweight access points as possible.
Note Port redundancy for the AP-manager interface is not supported. You cannot map the AP-manager
interface to a backup port.
Overview of Ports and Interfaces
Note Refer to the “Using Multiple AP-Manager Interfaces” section on page 3-35 for information on creating
Virtual Interface
and using multiple AP-manager interfaces.
The virtual interface is used to support mobility management, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) relay, and embedded Layer 3 security such as guest web authentication. It also maintains the
DNS gateway host name used by Layer 3 security and mobility managers to verify the source of
certificates when Layer 3 web authorization is enabled.
Specifically, the virtual interface plays these two primary roles:
• Acts as the DHCP server placeholder for wireless clients that obtain their IP address from a DHCP
server.
• Serves as the redirect address for the web authentication login page.
Note See Chapter 5 for additional information on web authentication.
The virtual interface IP address is used only in communications between the controller and wireless
clients. It never appears as the source or destination address of a packet that goes out a distribution
system port and onto the switched network. For the system to operate correctly, the virtual interface IP
address must be set (it cannot be 0.0.0.0), and no other device on the network can have the same address
as the virtual interface. Therefore, the virtual interface must be configured with an unassigned and
unused gateway IP address, such as 1.1.1.1. The virtual interface IP address is not pingable and should
not exist in any routing table in your network. In addition, the virtual interface cannot be mapped to a
backup port.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-7
Page 64

Overview of Ports and Interfaces
Note All controllers within a mobility group must be configured with the same virtual interface IP address.
Otherwise, inter-controller roaming may appear to work, but the hand-off does not complete, and the
client loses connectivity for a period of time.
Service-Port Interface
The service-port interface controls communications through and is statically mapped by the system to
the service port. It must have an IP address on a different supernet from the management, AP-manager,
and any dynamic interfaces, and it cannot be mapped to a backup port. This configuration enables you
to manage the controller directly or through a dedicated operating system network, such as 10.1.2.x,
which can ensure service access during network downtime.
The service port can obtain an IP address using DHCP, or it can be assigned a static IP address, but a
default gateway cannot be assigned to the service-port interface. Static routes can be defined through the
controller for remote network access to the service port.
Note Only Cisco 4400 series controllers have a service-port interface.
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Note You must configure an IP address on the service-port interface of both Cisco WiSM controllers.
Dynamic Interface
Note Configuring a dynamic interface with a secondary subnet is not supported.
Note Cisco recommends using tagged VLANs for dynamic interfaces.
Otherwise, the neighbor switch is unable to check the status of each controller.
Dynamic interfaces, also known as VLAN interfaces, are created by users and designed to be analogous
to VLANs for wireless LAN clients. A controller can support up to 512 dynamic interfaces (VLANs).
Each dynamic interface is individually configured and allows separate communication streams to exist
on any or all of a controller’s distribution system ports. Each dynamic interface controls VLAN and other
communications between controllers and all other network devices, and each acts as a DHCP relay for
wireless clients associated to WLANs mapped to the interface. You can assign dynamic interfaces to
distribution system ports, WLANs, the Layer 2 management interface, and the Layer 3 AP-manager
interface, and you can map the dynamic interface to a backup port.
You can configure zero, one, or multiple dynamic interfaces on a distribution system port. However, all
dynamic interfaces must be on a different VLAN or IP subnet from all other interfaces configured on the
port. If the port is untagged, all dynamic interfaces must be on a different IP subnet from any other
interface configured on the port.
3-8
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 65

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
WLANs
A WLAN associates a service set identifier (SSID) to an interface. It is configured with security, quality
of service (QoS), radio policies, and other wireless network parameters. Up to 16 access point WLANs
can be configured per controller.
Note Chapter 6 provides instructions for configuring WLANs.
Figure 3-4 illustrates the relationship between ports, interfaces, and WLANs.
Figure 3-4 Ports, Interfaces, and WLANs
Overview of Ports and Interfaces
OL-17037-01
As shown in Figure 3-4, each controller port connection is an 802.1Q trunk and should be configured as
such on the neighbor switch. On Cisco switches, the native VLAN of an 802.1Q trunk is an untagged
VLAN. Therefore, if you configure an interface to use the native VLAN on a neighboring Cisco switch,
make sure you configure the interface on the controller to be untagged.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-9
Page 66

Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
Note A zero value for the VLAN identifier (on the Controller > Interfaces page) means that the interface is
untagged.
The default (untagged) native VLAN on Cisco switches is VLAN 1. When controller interfaces are
configured as tagged (meaning that the VLAN identifier is set to a non-zero value), the VLAN must be
allowed on the 802.1Q trunk configuration on the neighbor switch and not be the native untagged VLAN.
Cisco recommends that tagged VLANs be used on the controller. You should also allow only relevant
VLANs on the neighbor switch’s 802.1Q trunk connections to controller ports. All other VLANs should
be disallowed or pruned in the switch port trunk configuration. This practice is extremely important for
optimal performance of the controller.
Note Cisco recommends that you assign one set of VLANs for WLANs and a different set of VLANs for
management interfaces to ensure that controllers properly route VLAN traffic.
Follow the instructions on the pages indicated to configure your controller’s interfaces and ports:
• Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces, page 3-10
• Configuring Dynamic Interfaces, page 3-16
• Configuring Ports, page 3-19
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
• Enabling Link Aggregation, page 3-29
• Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points, page 3-34
Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and
Service-Port Interfaces
Typically, you define the management, AP-manager, virtual, and service-port interface parameters using
the Startup Wizard. However, you can display and configure interface parameters through either the GUI
or CLI after the controller is running.
Note When assigning a WLAN to a DHCP server, both should be on the same subnet. Otherwise, you need to
use a router to route traffic between the WLAN and the DHCP server.
3-10
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 67

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
Using the GUI to Configure the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
Follow these steps to display and configure the management, AP-manager, virtual, and service-port
interface parameters using the GUI.
Step 1 Click Controller > Interfaces to open the Interfaces page (see Figure 3-5).
Figure 3-5 Interfaces Page
This page shows the current controller interface settings.
Step 2 If you want to modify the settings of a particular interface, click the name of the interface. The Interfaces
> Edit page for that interface appears.
Step 3 Configure the following parameters for each interface type:
Management Interface
Note The management interface uses the controller’s factory-set distribution system MAC address.
• Quarantine and quarantine VLAN ID, if applicable
Note Check the Quarantine check box if you want to configure this VLAN as unhealthy or you
want to configure network access control (NAC) out-of-band integration. Doing so causes
the data traffic of any client that is assigned to this VLAN to pass through the controller. See
Chapter 6 for more information about NAC out-of-band integration.
• VLAN identifier
Note Enter 0 for an untagged VLAN or a non-zero value for a tagged VLAN. Cisco recommends
using tagged VLANs for the management interface.
OL-17037-01
• Fixed IP address, IP netmask, and default gateway
• Physical port assignment
• Primary and secondary DHCP servers
• Access control list (ACL) setting, if required
Note To create ACLs, follow the instructions in Chapter 5.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-11
Page 68

Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
AP-Manager Interface
• VLAN identifier
Note Enter 0 for an untagged VLAN or a non-zero value for a tagged VLAN. Cisco recommends
using tagged VLANs for the AP-manager interface.
• Fixed IP address, IP netmask, and default gateway
Note The AP-manager interface’s IP address must be different from the management interface’s
IP address and may or may not be on the same subnet as the management interface. However,
Cisco recommends that both interfaces be on the same subnet for optimum access point
association.
• Physical port assignment
• Primary and secondary DHCP servers
• Access control list (ACL) name, if required
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Note To create ACLs, follow the instructions in Chapter 5.
Virtual Interface
• Any fictitious, unassigned, and unused gateway IP address, such as 1.1.1.1
• DNS gateway host name
Note To ensure connectivity and web authentication, the DNS server should always point to the
virtual interface. If a DNS host name is configured for the virtual interface, then the same
DNS host name must be configured on the DNS server(s) used by the client.
Service-Port Interface
Note The service-port interface uses the controller’s factory-set service-port MAC address.
• DHCP protocol (enabled) or
• DHCP protocol (disabled) and IP address and IP netmask
Step 4 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Step 5 If you made any changes to the virtual interface, reboot the controller so your changes take effect.
3-12
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 69

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
Using the CLI to Configure the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
This section provides instructions for displaying and configuring the management, AP-manager, virtual,
and service-port interfaces using the CLI.
Using the CLI to Configure the Management Interface
Follow these steps to display and configure the management interface parameters using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter show interface detailed management to view the current management interface settings.
Note The management interface uses the controller’s factory-set distribution system MAC address.
Step 2 Enter config wlan disable wlan-number to disable each WLAN that uses the management interface for
distribution system communication.
Step 3 Enter these commands to define the management interface:
• config interface address management ip-addr ip-netmask gateway
• config interface quarantine vlan management vlan_id
Note Use this command to configure a quarantine VLAN on the management interface.
• config interface vlan management {vlan-id | 0}
Note Enter 0 for an untagged VLAN or a non-zero value for a tagged VLAN. Cisco recommends
using tagged VLANs for the management interface.
• config interface port management physical-ds-port-number
• config interface dhcp management ip-address-of-primary-dhcp-server
[ip-address-of-secondary-dhcp-server]
• config interface acl management access-control-list-name
Note See Chapter 5 for more information on ACLs.
Step 4 Enter save config to save your changes.
Step 5 Enter show interface detailed management to verify that your changes have been saved.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-13
Page 70

Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
Using the CLI to Configure the AP-Manager Interface
Follow these steps to display and configure the AP-manager interface parameters using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter show interface summary to view the current interfaces.
Note If the system is operating in Layer 2 mode, the AP-manager interface is not listed.
Step 2 Enter show interface detailed ap-manager to view the current AP-manager interface settings.
Step 3 Enter config wlan disable wlan-number to disable each WLAN that uses the AP-manager interface for
distribution system communication.
Step 4 Enter these commands to define the AP-manager interface:
• config interface address ap-manager ip-addr ip-netmask gateway
• config interface vlan ap-manager {vlan-id | 0}
Note Enter 0 for an untagged VLAN or a non-zero value for a tagged VLAN. Cisco recommends
using tagged VLANs for the AP-manager interface.
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
• config interface port ap-manager physical-ds-port-number
• config interface dhcp ap-manager ip-address-of-primary-dhcp-server
[ip-address-of-secondary-dhcp-server]
• config interface acl ap-manager access-control-list-name
Note See Chapter 5 for more information on ACLs.
Step 5 Enter save config to save your changes.
Step 6 Enter show interface detailed ap-manager to verify that your changes have been saved.
Using the CLI to Configure the Virtual Interface
Follow these steps to display and configure the virtual interface parameters using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter show interface detailed virtual to view the current virtual interface settings.
Step 2 Enter config wlan disable wlan-number to disable each WLAN that uses the virtual interface for
distribution system communication.
3-14
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 71

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Configuring the Management, AP-Manager, Virtual, and Service-Port Interfaces
Step 3 Enter these commands to define the virtual interface:
• config interface address virtual ip-address
Note For ip-address, enter any fictitious, unassigned, and unused gateway IP address, such as
1.1.1.1.
• config interface hostname virtual dns-host-name
Step 4 Enter reset system. At the confirmation prompt, enter Y to save your configuration changes to NVRAM.
The controller reboots.
Step 5 Enter show interface detailed virtual to verify that your changes have been saved.
Using the CLI to Configure the Service-Port Interface
Follow these steps to display and configure the service-port interface parameters using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter show interface detailed service-port to view the current service-port interface settings.
Note The service-port interface uses the controller’s factory-set service-port MAC address.
Step 2 Enter these commands to define the service-port interface:
• To configure the DHCP server: config interface dhcp service-port ip-address-of-primary-dhcp-
server [ip-address-of-secondary-dhcp-server]
• To disable the DHCP server: config interface dhcp service-port none
• To configure the IP address: config interface address service-port ip-addr ip-netmask
Step 3 The service port is used for out-of-band management of the controller. If the management workstation
is in a remote subnet, you may need to add a route on the controller in order to manage the controller
from that remote workstation. To do so, enter this command:
config route add network-ip-addr ip-netmask gateway
Step 4 Enter save config to save your changes.
Step 5 Enter show interface detailed service-port to verify that your changes have been saved.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-15
Page 72

Configuring Dynamic Interfaces
Configuring Dynamic Interfaces
This section provides instructions for configuring dynamic interfaces using either the GUI or CLI.
Using the GUI to Configure Dynamic Interfaces
Follow these steps to create new or edit existing dynamic interfaces using the GUI.
Step 1 Click Controller > Interfaces to open the Interfaces page (see Figure 3-5).
Step 2 Perform one of the following:
• To create a new dynamic interface, click New. The Interfaces > New page appears (see Figure 3-6).
Go to Step 3.
• To modify the settings of an existing dynamic interface, click the name of the interface. The
Interfaces > Edit page for that interface appears (see Figure 3-7). Go to Step 5.
• To delete an existing dynamic interface, hover your cursor over the blue drop-down arrow for the
desired interface and choose Remove.
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Figure 3-6 Interfaces > New Page
Step 3
Step 4 Click Apply to commit your changes. The Interfaces > Edit page appears (see Figure 3-7).
Enter an interface name and a VLAN identifier, as shown in Figure 3-6.
3-16
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 73

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Figure 3-7 Interfaces > Edit Page
Configuring Dynamic Interfaces
Step 5
Configure the following parameters:
• Guest LAN, if applicable
• Quarantine and quarantine VLAN ID, if applicable
Note Check the Quarantine check box if you want to configure this VLAN as unhealthy or you
want to configure network access control (NAC) out-of-band integration. Doing so causes
the data traffic of any client that is assigned to this VLAN to pass through the controller. See
Chapter 6 for more information about NAC out-of-band integration.
• Physical port assignment
• VLAN identifier
• Fixed IP address, IP netmask, and default gateway
• Primary and secondary DHCP servers
• Access control list (ACL) name, if required
Note See Chapter 5 for more information on ACLs.
Note To ensure proper operation, you must set the Port Number and Primary DHCP Server
parameters.
OL-17037-01
Step 6 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Step 7 Repeat this procedure for each dynamic interface that you want to create or edit.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-17
Page 74

Configuring Dynamic Interfaces
Using the CLI to Configure Dynamic Interfaces
Follow these steps to configure dynamic interfaces using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter show interface summary to view the current dynamic interfaces.
Step 2 To view the details of a specific dynamic interface, enter show interface detailed
operator_defined_interface_name.
Step 3 Enter config wlan disable wlan_id to disable each WLAN that uses the dynamic interface for
distribution system communication.
Step 4 Enter these commands to configure dynamic interfaces:
• config interface create operator_defined_interface_name {vlan_id | x}
• config interface address operator_defined_interface_name ip_addr ip_netmask [gateway]
• config interface vlan operator_defined_interface_name {vlan_id | 0}
• config interface port operator_defined_interface_name physical_ds_port_number
• config interface dhcp operator_defined_interface_name ip_address_of_primary_dhcp_server
[ip_address_of_secondary_dhcp_server]
• config interface quarantine vlan interface_name vlan_id
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Note Use this command to configure a quarantine VLAN on any interface.
• config interface acl operator_defined_interface_name access_control_list_name
Note See Chapter 5 for more information on ACLs.
Step 5 Enter config wlan enable wlan_id to re-enable each WLAN that uses the dynamic interface for
distribution system communication.
Step 6 Enter save config to save your changes.
Step 7 Enter show interface detailed operator_defined_interface_name and show interface summary to
verify that your changes have been saved.
Note If desired, you can enter config interface delete operator_defined_interface_name to delete a
dynamic interface.
3-18
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 75

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Configuring Ports
The controller’s ports are preconfigured with factory default settings designed to make the controllers’
ports operational without additional configuration. However, you can view the status of the controller’s
ports and edit their configuration parameters at any time.
Follow these steps to use the GUI to view the status of the controller’s ports and make any configuration
changes if necessary.
Step 1 Click Controller > Ports to open the Ports page (see Figure 3-8).
Figure 3-8 Ports Page
Configuring Ports
This page shows the current configuration for each of the controller’s ports.
Step 2 If you want to change the settings of any port, click the number for that specific port. The Port >
Configure page appears (see Figure 3-9).
Note If the management and AP-manager interfaces are mapped to the same port and are members of
the same VLAN, you must disable the WLAN before making a port-mapping change to either
interface. If the management and AP-manager interfaces are assigned to different VLANs, you
do not need to disable the WLAN.
Note The number of parameters available on the Port > Configure page depends on your controller
type. For instance, 2100 series controllers and the controller in a Cisco Integrated Services
Router have fewer configurable parameters than a 4400 series controller, which is shown in
Figure 3-9.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-19
Page 76

Configuring Ports
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Figure 3-9 Port > Configure Page
Table 3 -2 interprets the current status of the port.
Ta b le 3 - 2 P o r t S t a tu s
Parameter Description
Port Number The number of the current port.
Physical Status The data rate being used by the port. The available data rates vary based
on controller type.
Controller Available Data Rates
4400 series 1000 Mbps full duplex
2100 series 10 or 100 Mbps, half or full
duplex
WiSM 1000 Mbps full duplex
Controller network module 100 Mbps full duplex
Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless
1000 Mbps full duplex
LAN Controller Switch
Link Status The port’s link status.
Valu es: Link Up or Link Down
3-20
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 77

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Table 3-2 Port Status (continued)
Parameter Description
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Determines if the connecting device is equipped to receive power
Step 3 Tabl e 3-3 lists and describes the port’s configurable parameters. Follow the instructions in the table to
make any desired changes.
Table 3-3 Port Parameters
Parameter Description
Admin Status Enables or disables the flow of traffic through the port.
Configuring Ports
through the Ethernet cable and if so provides -48 VDC.
Valu es: Enable or Disable
Note Some older Cisco access points do not draw PoE even if it is
enabled on the controller port. In such cases, contact the Cisco
Technical Assistance Center (TAC).
Note The controller in the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN
Controller Switch supports PoE on all ports.
Options: Enable or Disable
Default: Enable
Note Administratively disabling the port on a controller does not
affect the port’s link status. The link can be brought down only
by other Cisco devices. On other Cisco products, however,
administratively disabling a port brings the link down.
Physical Mode Determines whether the port’s data rate is set automatically or specified
by the user. The supported data rates vary based on controller type.
Default: Auto
Controller Supported Data Rates
4400 series Auto or 1000 Mbps full duplex
2100 series Auto or 10 or 100 Mbps, half or
full duplex
WiSM Auto or 1000 Mbps full duplex
Controller network module Auto or 100 Mbps full duplex
Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless
Auto or 1000 Mbps full duplex
LAN Controller Switch
Note Make sure that a duplex mismatch does not exist between a
2100 series controller and the Catalyst switch. A duplex
mismatch is a situation where the switch operates at full duplex
and the connected device operates at half duplex or vice versa.
The results of a duplex mismatch are extremely slow
performance, intermittent connectivity, and loss of connection.
Other possible causes of data link errors at full duplex are bad
cables, faulty switch ports, or client software or hardware
issues.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-21
Page 78
Configuring Ports
Step 4 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 5 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Step 6 Click Back to return to the Ports page and review your changes.
Step 7 Repeat this procedure for each additional port that you want to configure.
Step 8 Go to the following sections if you want to configure the controller’s ports for these advanced features:
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Table 3-3 Port Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
Link Trap Causes the port to send a trap when the port’s link status changes.
Options: Enable or Disable
Default: Enable
Multicast Appliance Mode Enables or disables the multicast appliance service for this port.
Options: Enable or Disable
Default: Enable
• Port mirroring, see below
• Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), page 3-23
Configuring Port Mirroring
Mirror mode enables you to duplicate to another port all of the traffic originating from or terminating at
a single client device or access point. It is useful in diagnosing specific network problems. Mirror mode
should be enabled only on an unused port as any connections to this port become unresponsive.
Note The 2100 series controllers, controller network modules, and Cisco WiSM controllers do not support
mirror mode. Also, a controller’s service port cannot be used as a mirrored port.
Note Port mirroring is not supported when link aggregation (LAG) is enabled on the controller.
Note Cisco recommends that you do not mirror traffic from one controller port to another as this setup could
cause network problems.
3-22
Follow these steps to enable port mirroring.
Step 1 Click Controller > Ports to open the Ports page (see Figure 3-8).
Step 2 Click the number of the unused port for which you want to enable mirror mode. The Port > Configure
page appears (see Figure 3-9).
Step 3 Set the Mirror Mode parameter to Enable.
Step 4 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 79

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Step 5 Perform one of the following:
• Follow these steps if you want to choose a specific client device that will mirror its traffic to the port
you selected on the controller:
a. Click Wireless > Clients to open the Clients page.
b. Click the MAC address of the client for which you want to enable mirror mode. The Clients >
Detail page appears.
c. Under Client Details, set the Mirror Mode parameter to Enable.
• Follow these steps if you want to choose an access point that will mirror its traffic to the port you
selected on the controller:
a. Click Wireless > Access Points > All APs to open the All APs page.
b. Click the name of the access point for which you want to enable mirror mode. The All APs >
Details page appears.
c. Click the Advanced tab.
d. Set the Mirror Mode parameter to Enable.
Step 6 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Configuring Ports
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 link management protocol that provides path redundancy
while preventing loops in the network. For a Layer 2 Ethernet network to function properly, only one
active path can exist between any two network devices. STP allows only one active path at a time
between network devices but establishes redundant links as a backup if the initial link should fail.
The spanning-tree algorithm calculates the best loop-free path throughout a Layer 2 network.
Infrastructure devices such as controllers and switches send and receive spanning-tree frames, called
bridge protocol data units (BPDUs), at regular intervals. The devices do not forward these frames but
use them to construct a loop-free path.
Multiple active paths among end stations cause loops in the network. If a loop exists in the network, end
stations might receive duplicate messages. Infrastructure devices might also learn end-station MAC
addresses on multiple Layer 2 interfaces. These conditions result in an unstable network.
STP defines a tree with a root bridge and a loop-free path from the root to all infrastructure devices in
the Layer 2 network.
Note STP discussions use the term root to describe two concepts: the controller on the network that serves as
a central point in the spanning tree is called the root bridge, and the port on each controller that provides
the most efficient path to the root bridge is called the root port. The root bridge in the spanning tree is
called the spanning-tree root.
STP forces redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. If a network segment in the spanning tree
fails and a redundant path exists, the spanning-tree algorithm recalculates the spanning-tree topology
and activates the standby path.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-23
Page 80
Configuring Ports
When two ports on a controller are part of a loop, the spanning-tree port priority and path cost settings
determine which port is put in the forwarding state and which is put in the blocking state. The port
priority value represents the location of a port in the network topology and how well it is located to pass
traffic. The path cost value represents media speed.
The controller maintains a separate spanning-tree instance for each active VLAN configured on it. A
bridge ID, consisting of the bridge priority and the controller’s MAC address, is associated with each
instance. For each VLAN, the controller with the lowest controller ID becomes the spanning-tree root
for that VLAN.
STP is disabled for the controller’s distribution system ports by default. The following sections provide
instructions for configuring STP for your controller using either the GUI or CLI.
Note STP cannot be configured for the controller in the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller
Switch.
Using the GUI to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol
Follow these steps to configure STP using the GUI.
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Step 1 Click Controller > Ports to open the Ports page (see Figure 3-8).
Step 2 Click the number of the port for which you want to configure STP. The Port > Configure page appears
(see Figure 3-9). This page shows the STP status of the port and enables you to configure STP
parameters.
Table 3 -4 interprets the current STP status of the port.
Table 3-4 Port Spanning Tree Status
Parameter Description
STP Port ID The number of the port for which STP is enabled or disabled.
STP State The port’s current STP state. It controls the action that a port takes upon
receiving a frame.
Valu es: Disabled, Blocking, Listening, Learning, Forwarding, and
Broken
STP State Description
Disabled The port is not participating in spanning tree because the
port is shut down, the link is down, or STP is not enabled
for this port.
Blocking The port does not participate in frame forwarding.
Listening The first transitional state after the blocking state when
STP determines that the port should participate in frame
forwarding.
Learning The port prepares to participate in frame forwarding.
Forwarding The port forwards frames.
Broken The port is malfunctioning.
STP Port Designated Root The unique identifier of the root bridge in the configuration BPDUs.
3-24
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 81

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Table 3-4 Port Spanning Tree Status (continued)
Parameter Description
STP Port Designated Cost The path cost of the designated port.
STP Port Designated Bridge The identifier of the bridge that the port considers to be the designated
STP Port Designated Port The port identifier on the designated bridge for this port.
STP Port Forward Transitions
Count
Step 3 Tab le 3 -5 lists and describes the port’s configurable STP parameters. Follow the instructions in the table
to make any desired changes.
Table 3-5 Port Spanning Tree Parameters
Parameter Description
STP Mode The STP administrative mode associated with this port.
Configuring Ports
bridge for this port.
The number of times that the port has transitioned from the learning
state to the forwarding state.
Options: Off, 802.1D, or Fast
Default: Off
STP Mode Description
Off Disables STP for this port.
802.1D Enables this port to participate in the
spanning tree and go through all of the
spanning tree states when the link state
transitions from down to up.
Fast Enables this port to participate in the
spanning tree and puts it in the forwarding
state when the link state transitions from
down to up more quickly than when the
STP mode is set to 802.1D.
Note In this state, the forwarding delay
timer is ignored on link up.
STP Port Priority The location of the port in the network topology and how well the port
is located to pass traffic.
Range: 0 to 255
Default: 128
STP Port Path Cost Mode Determines whether the STP port path cost is set automatically or
specified by the user. If you choose User Configured, you also need to
set a value for the STP Port Path Cost parameter.
Range: Auto or User Configured
OL-17037-01
Default: Auto
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-25
Page 82
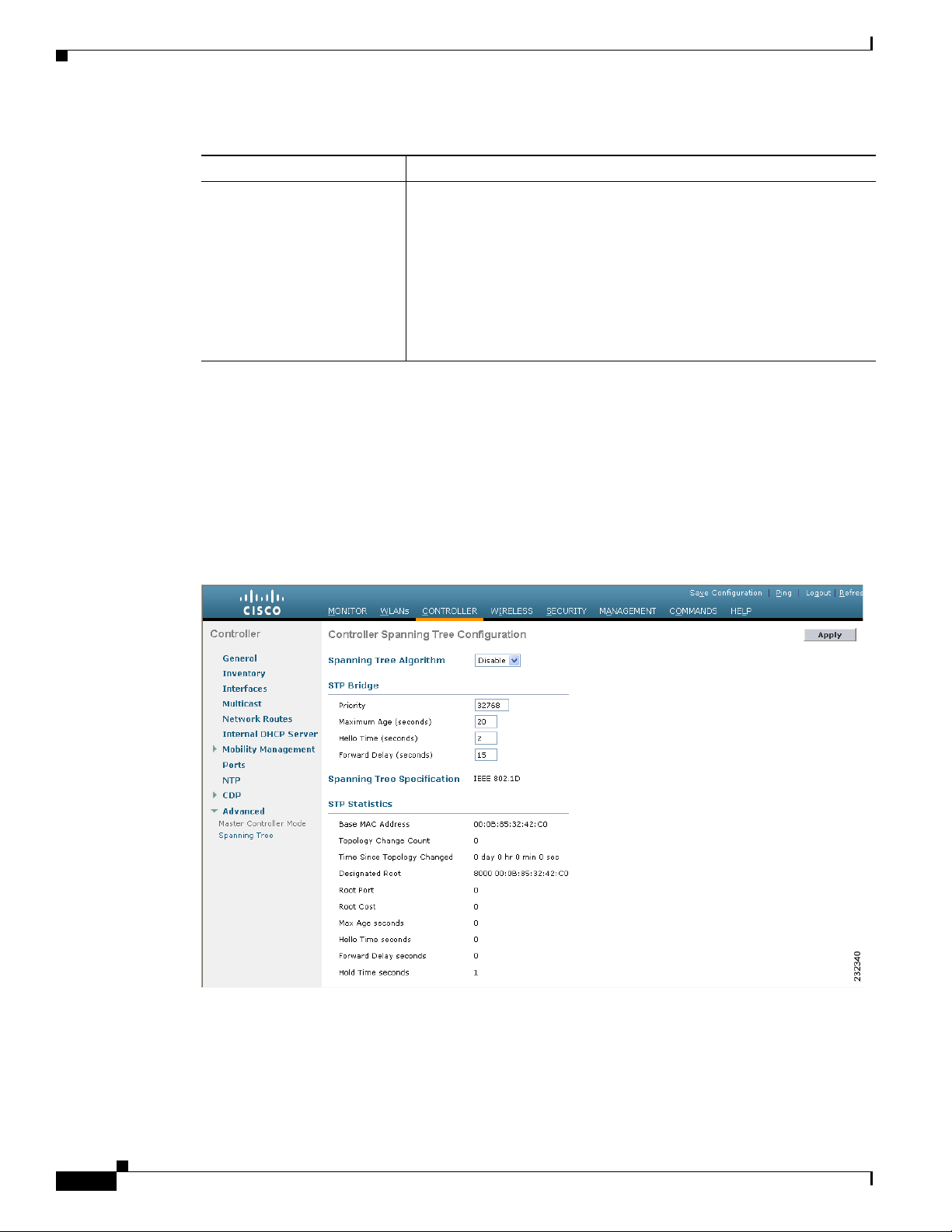
Configuring Ports
Step 4 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 5 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Step 6 Click Back to return to the Ports page.
Step 7 Repeat Step 2 through Step 6 for each port for which you want to enable STP.
Step 8 Click Controller > Advanced > Spanning Tree to open the Controller Spanning Tree Configuration
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Table 3-5 Port Spanning Tree Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
STP Port Path Cost The speed at which traffic is passed through the port. This parameter
must be set if the STP Port Path Cost Mode parameter is set to User
Configured.
Options: 0 to 65535
Default: 0, which causes the cost to be adjusted for the speed of the
port when the link comes up.
Note Typically, a value of 100 is used for 10-Mbps ports and 19 for
100-Mbps ports.
page (see Figure 3-10).
Figure 3-10 Controller Spanning Tree Configuration Page
3-26
This page allows you to enable or disable the spanning tree algorithm for the controller, modify its
characteristics, and view the STP status.Table 3 - 6 interprets the current STP status for the controller.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 83

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Table 3-6 Controller Spanning Tree Status
Parameter Description
Spanning Tree Specification The STP version being used by the controller. Currently, only an IEEE
Base MAC Address The MAC address used by this bridge when it must be referred to in a
Topology Change Count The total number of topology changes detected by this bridge since the
Time Since Topology
Changed
Designated Root The bridge identifier of the spanning tree root. This value is used as the
Root Port The number of the port that offers the lowest cost path from this bridge
Root Cost The cost of the path to the root as seen from this bridge.
Max Age (seconds) The maximum age of STP information learned from the network on any
Hello Time (seconds) The amount of time between the transmission of configuration BPDUs
Forward Delay (seconds) This value controls how fast a port changes its spanning tree state when
Hold Time (seconds) The minimum time period to elapse between the transmission of
Configuring Ports
802.1D implementation is available.
unique fashion. When it is concatenated with dot1dStpPriority, a
unique bridge identifier is formed that is used in STP.
management entity was last reset or initialized.
The time (in days, hours, minutes, and seconds) since a topology
change was detected by the bridge.
Root Identifier parameter in all configuration BPDUs originated by this
node.
to the root bridge.
port before it is discarded.
by this node on any port when it is the root of the spanning tree or trying
to become so. This is the actual value that this bridge is currently using.
moving toward the forwarding state. It determines how long the port
stays in each of the listening and learning states that precede the
forwarding state. This value is also used, when a topology change has
been detected and is underway, to age all dynamic entries in the
forwarding database.
Note This is the actual value that this bridge is currently using, in
contrast to Stp Bridge Forward Delay, which is the value that
this bridge and all others would start using if this bridge were
to become the root.
configuration BPDUs through a given LAN port.
Note At most, one configuration BPDU can be transmitted in any
hold time period.
OL-17037-01
Step 9 Tabl e 3-7 lists and describes the controller’s configurable STP parameters. Follow the instructions in the
table to make any desired changes.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-27
Page 84

Configuring Ports
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Table 3-7 Controller Spanning Tree Parameters
Parameter Description
Spanning Tree Algorithm Enables or disables STP for the controller.
Options: Enable or Disable
Default: Disable
Priority The location of the controller in the network topology and how well the
controller is located to pass traffic.
Range: 0 to 65535
Default: 32768
Maximum Age (seconds) The length of time that the controller stores protocol information
received on a port.
Range: 6 to 40 seconds
Default: 20 seconds
Hello Time (seconds) The length of time that the controller broadcasts hello messages to
other controllers.
Options: 1 to 10 seconds
Default: 2 seconds
Forward Delay (seconds) The length of time that each of the listening and learning states lasts
before the port begins forwarding.
Options: 4 to 30 seconds
Default: 15 seconds
Step 10 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 11 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Using the CLI to Configure Spanning Tree Protocol
Follow these steps to configure STP using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter show spanningtree port and show spanningtree switch to view the current STP status.
Step 2 If STP is enabled, you must disable it before you can change STP settings. Enter config spanningtree
switch mode disable to disable STP on all ports.
Step 3 Enter one of these commands to configure the STP port administrative mode:
• config spanningtree port mode 802.1d {port-number | all}
• config spanningtree port mode fast {port-number | all}
3-28
• config spanningtree port mode off {port-number | all}
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 85

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Step 4 Enter one of these commands to configure the STP port path cost on the STP ports:
• config spanningtree port pathcost 1-65535 {port-number | all}—Specifies a path cost from 1 to
65535 to the port.
• config spanningtree port mode pathcost auto {port-number | all}—Enables the STP algorithm to
automatically assign the path cost. This is the default setting.
Step 5 Enter config spanningtree port priority 0-255 port-number to configure the port priority on STP ports.
The default priority is 128.
Step 6 If necessary, enter config spanningtree switch bridgepriority 0-65535 to configure the controller’s
STP bridge priority. The default bridge priority is 32768.
Step 7 If necessary, enter config spanningtree switch forwarddelay 4-30 to configure the controller’s STP
forward delay in seconds. The default forward delay is 15 seconds.
Step 8 If necessary, enter config spanningtree switch hellotime 1-10 to configure the controller’s STP hello
time in seconds. The default hello time is 2 seconds.
Step 9 If necessary, enter config spanningtree switch maxage 6-40 to configure the controller’s STP maximum
age. The default maximum age is 20 seconds.
Step 10 After you configure STP settings for the ports, enter config spanningtree switch mode enable to enable
STP for the controller. The controller automatically detects logical network loops, places redundant
ports on standby, and builds a network with the most efficient pathways.
Step 11 Enter save config to save your settings.
Step 12 Enter show spanningtree port and show spanningtree switch to verify that your changes have been
saved.
Enabling Link Aggregation
Enabling Link Aggregation
Link aggregation (LAG) is a partial implementation of the 802.3ad port aggregation standard. It bundles
all of the controller’s distribution system ports into a single 802.3ad port channel, thereby reducing the
number of IP addresses needed to configure the ports on your controller. When LAG is enabled, the system
dynamically manages port redundancy and load balances access points transparently to the user.
Cisco 4400 series controllers support LAG in software release 3.2 and higher, and LAG is enabled
automatically on the controllers within the Cisco WiSM and the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless
LAN Controller Switch. Without LAG, each distribution system port on the controller supports up to 48
access points. With LAG enabled, a 4402 controller’s logical port supports up to 50 access points, a 4404
controller’s logical port supports up to 100 access points, and the logical port on each Cisco WiSM
controller supports up to 150 access points.
Note You can bundle all four ports on a 4404 controller (or two on a 4402 controller) into a single link.
Figure 3-11 illustrates LAG.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-29
Page 86

Enabling Link Aggregation
Figure 3-11 Link Aggregation
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
LAG simplifies controller configuration because you no longer need to configure primary and secondary
ports for each interface. If any of the controller ports fail, traffic is automatically migrated to one of the
other ports. As long as at least one controller port is functioning, the system continues to operate, access
points remain connected to the network, and wireless clients continue to send and receive data.
When configuring bundled ports on the controller, you may want to consider terminating on two different
modules within a modular switch such as the Catalyst 6500; however, Cisco does not recommend
connecting the LAG ports of a 4400 controller to multiple Catalyst 6500 or 3750G switches.
Terminating on two different modules within a single Catalyst 6500 switch provides redundancy and
ensures that connectivity between the switch and the controller is maintained when one module fails.
Figure 3-12 illustrates this use of redundant modules. A 4402-50 controller is connected to two different
Gigabit modules (slots 2 and 3) within the Catalyst 6500. The controller’s port 1 is connected to Gigabit
interface 3/1, and the controller’s port 2 is connected to Gigabit interface 2/1 on the Catalyst 6500. Both
switch ports are assigned to the same channel group.
When a 4404 controller or WiSM controller module LAG port is connected to a Catalyst 3750G or a 6500
or 7600 channel group employing load balancing, note the following:
• LAG requires the Etherchannel to be configured for the “on” mode on both the controller and the
Catalyst switch.
• Once the Etherchannel is configured as “on” at both ends of the link, it does not matter if the Catalyst
switch is configured for either Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) or Cisco proprietary Port
Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) because no channel negotiation is done between the controller and the
switch. Additionally, LACP and PAgP are not supported on the controller.
• The load-balancing method configured on the Catalyst switch must be a load-balancing method that
terminates all IP datagram fragments on a single controller port. Not following this recommendation
may result in problems with access point association.
• The recommended load-balancing method for Catalyst switches is src-dest-ip (CLI command:
port-channel load-balance src_dest_ip).
3-30
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 87

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
• The Catalyst 6500 series switches running in PFC3 or PFC3CXL mode implement enhanced
EtherChannel load balancing. The enhanced EtherChannel load balancing adds the VLAN number
to the hash function, which is incompatible with LAG. From the 12.2(33)SXH and later releases,
Catalyst 6500 IOS software offers the exclude vlan keyword to the port-channel load-balance
command to implement src-dst-ip load distribution. See the Cisco IOS Interface and Hardware
Component Command Reference guide for more information.
• Enter the show platform hardware pfc mode command on the Catalyst 6500 switch to confirm the
PFC operating mode.
The following example shows a Catalyst 6500 series switch in PFC3B mode when you enter the
global configuration port-channel load-balance src-dst-ip command for proper LAG
functionality:
# show platform hardware pfc mode PFC operating mode
PFC operating mode : PFC3B
# show EtherChannel load-balance
EtherChannel Load-Balancing Configuration:
src-dst-ip
The following example shows Catalyst 6500 series switch in PFC3C mode when you enter the
exclude vlan keyword in the port-channel load- balance src-dst-ip exclude vlan command.
# show platform hardware pfc mode
PFC operating mode : PFC3C
# show EtherChannel load-balance
EtherChannel Load-Balancing Configuration:
src-ip enhanced
# mpls label-ip
Enabling Link Aggregation
• If the recommended load-balancing method cannot be configured on the Catalyst switch, then
configure the LAG connection as a single member link or disable LAG on the controller.
Figure 3-12 Link Aggregation with Catalyst 6500 Neighbor Switch
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-31
Page 88

Enabling Link Aggregation
Link Aggregation Guidelines
Keep these guidelines in mind when using LAG:
• You cannot configure the controller’s ports into separate LAG groups. Only one LAG group is
supported per controller. Therefore, you can connect a controller in LAG mode to only one neighbor
device.
Note The two internal Gigabit ports on the controller within the Catalyst 3750G Integrated
Wireless LAN Controller Switch are always assigned to the same LAG group.
• When you enable LAG or make any changes to the LAG configuration, you must immediately reboot
the controller.
• When you enable LAG, you can configure only one AP-manager interface because only one logical
port is needed. LAG removes the requirement for supporting multiple AP-manager interfaces.
• When you enable LAG, all dynamic AP-manager interfaces and untagged interfaces are deleted, and
all WLANs are disabled and mapped to the management interface. Also, the management, static
AP-manager, and VLAN-tagged dynamic interfaces are moved to the LAG port.
• Multiple untagged interfaces to the same port are not allowed.
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
• When you enable LAG, you cannot create interfaces with a primary port other than 29.
• When you enable LAG, all ports participate in LAG by default. Therefore, you must configure LAG
for all of the connected ports in the neighbor switch.
• When you enable LAG on the Cisco WiSM, you must enable port-channeling/Ether-channeling for
all of the controller’s ports on the switch.
• When you enable LAG, port mirroring is not supported.
• When you enable LAG, if any single link goes down, traffic migrates to the other links.
• When you enable LAG, only one functional physical port is needed for the controller to pass client
traffic.
• When you enable LAG, access points remain connected to the switch, and data service for users
continues uninterrupted.
• When you enable LAG, you eliminate the need to configure primary and secondary ports for each
interface.
• When you enable LAG, the controller sends packets out on the same port on which it received them.
If a CAPWAP packet from an access point enters the controller on physical port 1, the controller
removes the CAPWAP wrapper, processes the packet, and forwards it to the network on physical
port 1. This may not be the case if you disable LAG.
• When you disable LAG, the management, static AP-manager, and dynamic interfaces are moved to
port 1.
• When you disable LAG, you must configure primary and secondary ports for all interfaces.
3-32
• When you disable LAG, you must assign an AP-manager interface to each port on the controller.
Otherwise, access points are unable to join.
• Cisco 4400 series controllers support a single static link aggregation bundle.
• LAG is typically configured using the Startup Wizard, but you can enable or disable it at any time
through either the GUI or CLI.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 89

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Note LAG is enabled by default and is the only option on the WiSM controller and the controller
in the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch.
Using the GUI to Enable Link Aggregation
Follow these steps to enable LAG on your controller using the GUI.
Step 1 Click Controller > General to open the General page (see Figure 3-13).
Figure 3-13 General Page
Enabling Link Aggregation
OL-17037-01
Step 2
Set the LAG Mode on Next Reboot parameter to Enabled.
Note Choose Disabled if you want to disable LAG. LAG is disabled by default on the Cisco 4400
series controllers but enabled by default on the Cisco WiSM.
Step 3 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 4 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Step 5 Reboot the controller.
Step 6 Assign the WLAN to the appropriate VLAN.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-33
Page 90

Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points
Using the CLI to Enable Link Aggregation
Follow these steps to enable LAG on your controller using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter config lag enable to enable LAG.
Note Enter config lag disable if you want to disable LAG.
Step 2 Enter save config to save your settings.
Step 3 Reboot the controller.
Using the CLI to Verify Link Aggregation Settings
To verify your LAG settings, enter this command:
show lag summary
Information similar to the following appears:
LAG Enabled
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support LAG
The controller’s neighbor devices must also be properly configured to support LAG.
• Each neighbor port to which the controller is connected should be configured as follows:
interface GigabitEthernet <interface id>
switchport
channel-group <id> mode on
no shutdown
• The port channel on the neighbor switch should be configured as follows:
interface port-channel <id>
switchport
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport trunk native vlan <native vlan id>
switchport trunk allowed vlan <allowed vlans>
switchport mode trunk
no shutdown
Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48
Access Points
As noted earlier, 4400 series controllers can support up to 48 access points per port. However, you can
configure your 4400 series controller to support more access points using one of the following methods:
3-34
• Link aggregation, page 3-35
• Multiple AP-manager interfaces, page 3-35
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 91

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Follow the instructions on the page indicated for the method you want to use.
The following factors should help you decide which method to use if your controller is set for Layer 3
operation:
• With link aggregation, all of the controller ports need to connect to the same neighbor switch. If the
neighbor switch goes down, the controller loses connectivity.
• With multiple AP-manager interfaces, you can connect your ports to different neighbor devices. If
one of the neighbor switches goes down, the controller still has connectivity. However, using
multiple AP-manager interfaces presents certain challenges (as discussed in the “Using Multiple
AP-Manager Interfaces” section below) when port redundancy is a concern.
Using Link Aggregation
See the “Enabling Link Aggregation” section on page 3-29 for more information and instructions on
enabling link aggregation.
Note Link aggregation is the only method that can be used for the Cisco WiSM and Catalyst 3750G Integrated
Wireless LAN Controller Switch controllers.
Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points
Using Multiple AP-Manager Interfaces
Note This method can be used only with Cisco 4400 series stand-alone controllers.
When you create two or more AP-manager interfaces, each one is mapped to a different port (see
Figure 3-14). The ports should be configured in sequential order such that AP-manager interface 2 is on
port 2, AP-manager interface 3 is on port 3, and AP-manager interface 4 is on port 4.
Note AP-manager interfaces need not be on the same VLAN or IP subnet, and they may or may not be on the
same VLAN or IP subnet as the management interface. However, Cisco recommends that you configure
all AP-manager interfaces on the same VLAN or IP subnet.
Note You must assign an AP-manager interface to each port on the controller.
Before an access point joins a controller, it sends out a discovery request. From the discovery response
that it receives, the access point can tell the number of AP-manager interfaces on the controller and the
number of access points on each AP-manager interface. The access point generally joins the AP-manager
with the least number of access points. In this way, the access point load is dynamically distributed
across the multiple AP-manager interfaces.
OL-17037-01
Note Access points may not be distributed completely evenly across all of the AP-manager interfaces, but a
certain level of load balancing occurs.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-35
Page 92

Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points
Figure 3-14 Two AP-Manager Interfaces
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Before implementing multiple AP-manager interfaces, you should consider how they would impact your
controller’s port redundancy.
Examples:
1. The 4402-50 controller supports a maximum of 50 access points and has two ports. To support the
maximum number of access points, you would need to create two AP-manager interfaces (see
Figure 3-14) because a controller can support only 48 access points on one port.
2. The 4404-100 controller supports up to 100 access points and has four ports. To support the
maximum number of access points, you would need to create three (or more) AP-manager interfaces
(see Figure 3-15). If the port of one of the AP-manager interfaces fails, the controller clears the
access points’ state, and the access points must reboot to reestablish communication with the
controller using the normal controller join process. The controller no longer includes the failed
AP-manager interface in the CAPWAP or LWAPP discovery responses. The access points then
rejoin the controller and are load-balanced among the available AP-manager interfaces.
3-36
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 93

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Figure 3-15 Three AP-Manager Interfaces
Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points
Figure 3-16 illustrates the use of four AP-manager interfaces to support 100 access points.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-37
Page 94
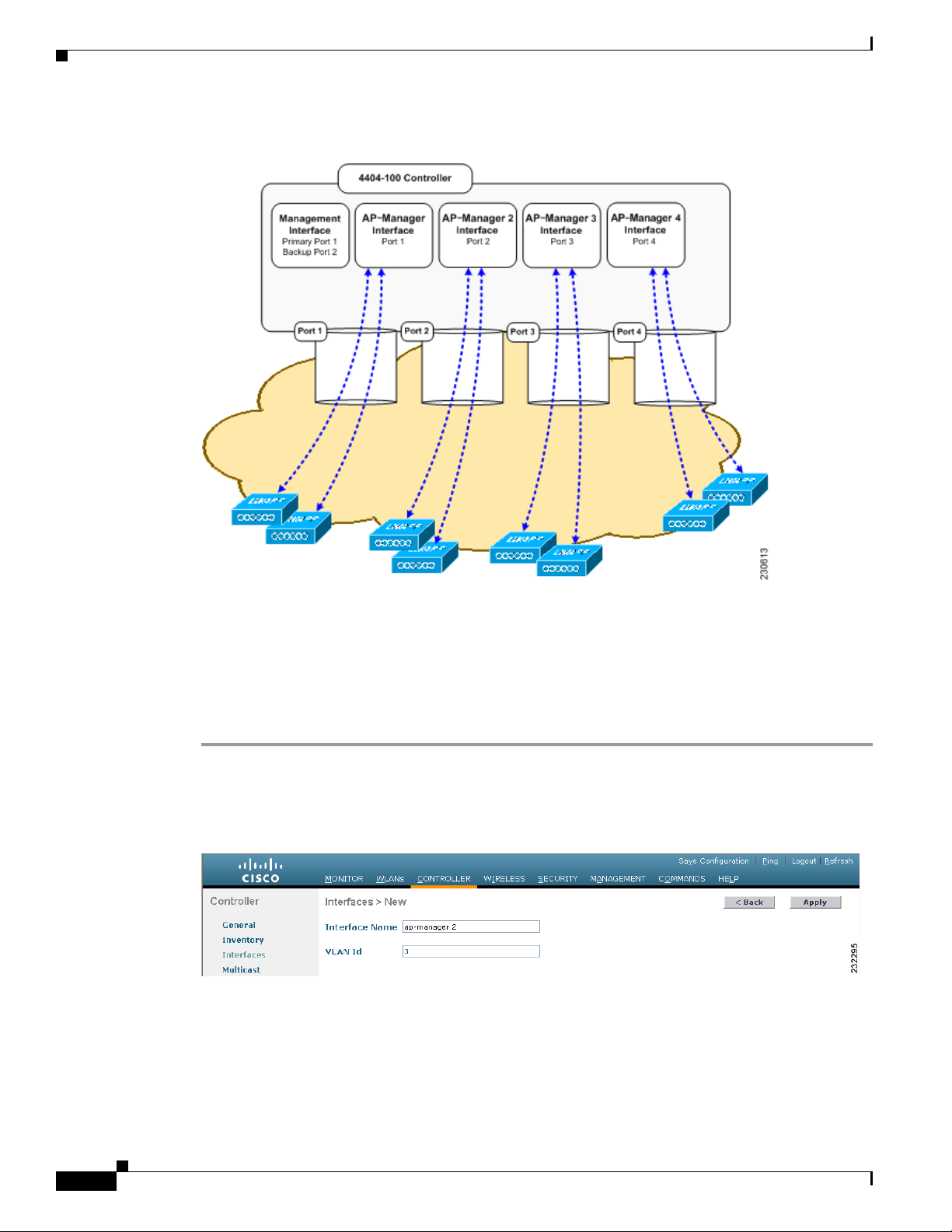
Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points
Figure 3-16 Four AP-Manager Interfaces
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
This configuration has the advantage of load-balancing all 100 access points evenly across all four
AP-manager interfaces. If one of the AP-manager interfaces fails, all of the access points connected
to the controller would be evenly distributed among the three available AP-manager interfaces. For
example, if AP-manager interface 2 fails, the remaining AP-manager interfaces (1, 3, and 4) would
each manage approximately 33 access points.
Follow these steps to create multiple AP-manager interfaces.
Step 1 Click Controller > Interfaces to open the Interfaces page.
Step 2 Click New. The Interfaces > New page appears (see Figure 3-18).
Figure 3-17 Interfaces > New Page
Step 3
Step 4 Click Apply to commit your changes. The Interfaces > Edit page appears (see Figure 3-18).
Enter an AP-manager interface name and a VLAN identifier, as shown above.
3-38
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 95

Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
Figure 3-18 Interfaces > Edit Page
Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points
Step 5
Enter the appropriate interface parameters.
Note Do not define a backup port for an AP-manager interface. Port redundancy is not supported for
AP-manager interfaces. If the AP-manager interface fails, all of the access points connected to
the controller through that interface are evenly distributed among the other configured
AP-manager interfaces.
Step 6 To make the interface an AP-manager interface, check the Enable Dynamic AP Management check
box.
Step 7 Click Save Configuration to save your settings.
Step 8 Repeat this procedure for each additional AP-manager interface that you want to create.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
3-39
Page 96

Configuring a 4400 Series Controller to Support More Than 48 Access Points
Chapter 3 Configuring Ports and Interfaces
3-40
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 97

CHAP T E R
4
Configuring Controller SettingsWireless Device Access
This chapter describes how to configure settings on the controllers. It contains these sections:
• Using the Configuration Wizard, page 4-2
• Using the AutoInstall Feature for Controllers Without a Configuration, page 4-6
• Managing the System Date and Time, page 4-10
• Configuring 802.11 Bands, page 4-14
• Configuring 802.11n Parameters, page 4-17
• Configuring DHCP Proxy, page 4-22
• Configuring Administrator Usernames and Passwords, page 4-23
• Configuring SNMP, page 4-24
• Changing the Default Values of SNMP Community Strings, page 4-25
• Changing the Default Values for SNMP v3 Users, page 4-27
OL-17037-01
• Configuring Aggressive Load Balancing, page 4-29
• Configuring Fast SSID Changing, page 4-31
• Enabling 802.3X Flow Control, page 4-31
• Configuring 802.3 Bridging, page 4-32
• Configuring Multicast Mode, page 4-34
• Configuring Client Roaming, page 4-40
• Configuring IP-MAC Address Binding, page 4-44
• Configuring Quality of Service, page 4-45
• Configuring Voice and Video Parameters, page 4-52
• Configuring EDCA Parameters, page 4-67
• Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol, page 4-69
• Configuring RFID Tag Tracking, page 4-79
• Configuring and Viewing Location Settings, page 4-84
• Configuring the Supervisor 720 to Support the WiSM, page 4-89
• Using the Wireless LAN Controller Network Module, page 4-91
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
4-1
Page 98

Using the Configuration Wizard
Using the Configuration Wizard
This section describes how to configure basic settings on a controller for the first time or after the
configuration has been reset to factory defaults. The contents of this chapter are similar to the
instructions in the quick start guide that shipped with your controller.
You use the configuration wizard to configure basic settings. You can run the wizard on the CLI or the
GUI. This section explains how to run the wizard on the CLI.
This section contains these sections:
• Before You Start, page 4-2
• Resetting the Device to Default Settings, page 4-3
• Running the Configuration Wizard on the CLI, page 4-4
Before You Start
You should collect these basic configuration parameters before configuring the controller:
Chapter 4 Configuring Controller SettingsWireless Device Access
• System name for the controller
• 802.11 protocols supported: 802.11a/n or 802.11b/g/n or both
• Administrator usernames and passwords (optional)
• Distribution system (network) port static IP address, netmask, and optional default gateway IP
address
• Service port static IP address and netmask (optional)
• Distribution system physical port (1000BASE-T, 1000BASE-SX, or 10/100BASE-T)
Note Each 1000BASE-SX connector provides a 100/1000-Mbps wired connection to a network
through an 850nM (SX) fiber-optic link using an LC physical connector.
• Distribution system port VALN assignment (optional)
• Distribution system port web and secure web mode settings: enabled or disabled
• Distribution system port Spanning Tree Protocol: enabled/disabled, 802.1D/fast/off mode per port,
path cost per port, priority per port, bridge priority, forward delay, hello time, maximum age
• WLAN configuration: SSID, VLAN assignments, Layer 2 security settings, Layer 3 security
settings, QoS assignments
• Mobility Settings: Mobility Group Name (optional)
• RADIUS Settings
• SNMP Settings
4-2
• NTP server settings (the wizard prompts you for NTP server settings when you run the wizard on a
wireless controller network module installed in a Cisco Integrated Services router)
• Other port and parameter settings: service port, Radio Resource Management (RRM), third-party
access points, console port, 802.3x flow control, and system logging
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Page 99

Chapter 4 Configuring Controller SettingsWireless Device Access
Resetting the Device to Default Settings
If you need to start over during the initial setup process, you can reset the controller to factory default
settings.
Note After resetting the configuration to defaults, you need a serial connection to the controller to use the
configuration wizard.
Resetting to Default Settings Using the CLI
Follow these steps to reset the configuration to factory default settings using the CLI.
Step 1 Enter reset system. At the prompt that asks whether you need to save changes to the configuration, enter
Y or N. The unit reboots.
Step 2 When you are prompted for a username, enter recover-config to restore the factory default
configuration. The controller reboots and displays this message:
Welcome to the Cisco WLAN Solution Wizard Configuration Tool
Using the Configuration Wizard
Step 3 Use the configuration wizard to enter configuration settings.
Resetting to Default Settings Using the GUI
Follow these steps to return to default settings using the GUI.
Step 1 Open your Internet browser. The GUI is fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0
or later on s platforms.
Step 2 Enter the controller IP address in the browser address line and press Enter. An Enter Network Password
s appears.
Step 3 Enter your username in the User Name field. The default username is admin.
Step 4 Enter the wireless device password in the Password field and press Enter. The default password is
admin.
Step 5 Browse to the Commands > Reset to Factory Defaults page.
Step 6 Click Reset. At the prompt, confirm the reset.
Step 7 Reboot the unit and do not save changes.
Step 8 Use the configuration wizard to enter configuration settings.
OL-17037-01
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
4-3
Page 100

Using the Configuration Wizard
Running the Configuration Wizard on the CLI
When the controller boots at factory defaults, the bootup script runs the configuration wizard, which
prompts the installer for initial configuration settings. Follow these steps to enter settings using the
wizard on the CLI.
Note To configure the controller in the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch, Cisco
recommends that you use the GUI configuration wizard that launches from the 3750 Device Manager.
Refer to the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch Getting Started Guide for
instructions.
Note The available options appear in brackets after each configuration parameter. The default value appears
in all uppercase letters.
Note If you enter an incorrect response, the controller provides you with an appropriate error message, such
as “Invalid Response,” and returns you to the wizard prompt.
Chapter 4 Configuring Controller SettingsWireless Device Access
Note Press the hyphen key if you ever need to return to the previous command line.
Step 1 Connect your computer to the controller using a DB-9 null-modem serial cable.
Step 2 Open a terminal emulator session using these settings:
• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
• no parity
• no hardware flow control
Step 3 At the prompt, log into the CLI. The default username is admin and the default password is admin.
Step 4 If necessary, enter reset system to reboot the unit and start the wizard.
Step 5 Enter the system name, which is the name you want to assign to the controller. You can enter up to 32
ASCII characters.
Step 6 Enter the administrative username and password to be assigned to this controller. You can enter up to 24
ASCII characters for each. The default administrative username and password are admin and admin,
respectively.
Step 7 Enter the service-port interface IP configuration protocol: none or DHCP. If you do not want to use the
service port or if you want to assign a static IP Address to the service port, enter none.
Step 8 If you entered none in step 7 and need to enter a static IP address for the service port, enter the
service-port interface IP address and netmask for the next two prompts.
4-4
Step 9 Enable or disable link aggregation (LAG) by choosing yes or NO. Refer to Chapter 3 for more
information on LAG.
Step 10 Enter the IP address of the management interface.
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
 Loading...
Loading...