Page 1
EP9315 Data Sheet
FEATURES
• 200-MHz ARM920T Processor
• 16-kbyte Instruction Cache
• 16-kbyte Data Cache
• Linux
• 100-MHz System Bus
• MaverickCrunch
• Floating Point, Integer, and Signal Processing
• Optimized for digital music compression and
• Hardware interlocks allow in-line coding.
• MaverickKey
• 32-bit Unique ID can be used for DRM-compliant
• Integrated Peripheral Interfaces
• 32-bit SDRAM Interface (up to 4 Banks)
• 32-/16-bit SRAM / FLASH / ROM
• Serial EEPROM Interface
• EIDE (up to 2 devices)
• 1/10/100-Mbps Ethernet MAC
• Three UARTs
• Three-port USB 2.0 Full-speed Host (OHCI)
• LCD and Raster Interface with Graphics
®
, Microsoft® Windows® CE-enabled MMU
™
Math Engine
Instructions
decompression algorithms.
™
IDs
128-bit random ID.
(12 Mbits per second)
Accelerator
Enhanced Universal Platform
System-on-Chip Processor
• IrDA Interface
• PCMCIA Interface
• Touchscreen Interface with ADC
• 8 x 8 Keypad Scanner
• One Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI
• 6-channel or 2-channel Serial Audio Interface (I
• 2-channel, Low-cost Serial Audio Interface (AC'97)
• 2 High-resolution PWMs (16 bits each)
• Internal Peripherals
• 12 Direct Memory Access (DMA) Channels
• Real-time Clock with Software Trim
• Dual PLL controls all clock domains.
• Watchdog Timer
• Two General-purpose 16-bit Timers
• One General-purpose 32-bit Timer
• One 40-bit Debug Timer
• Interrupt Controller
•Boot ROM
• Package
• 352-pin PBGA
™
) Port
2
S)
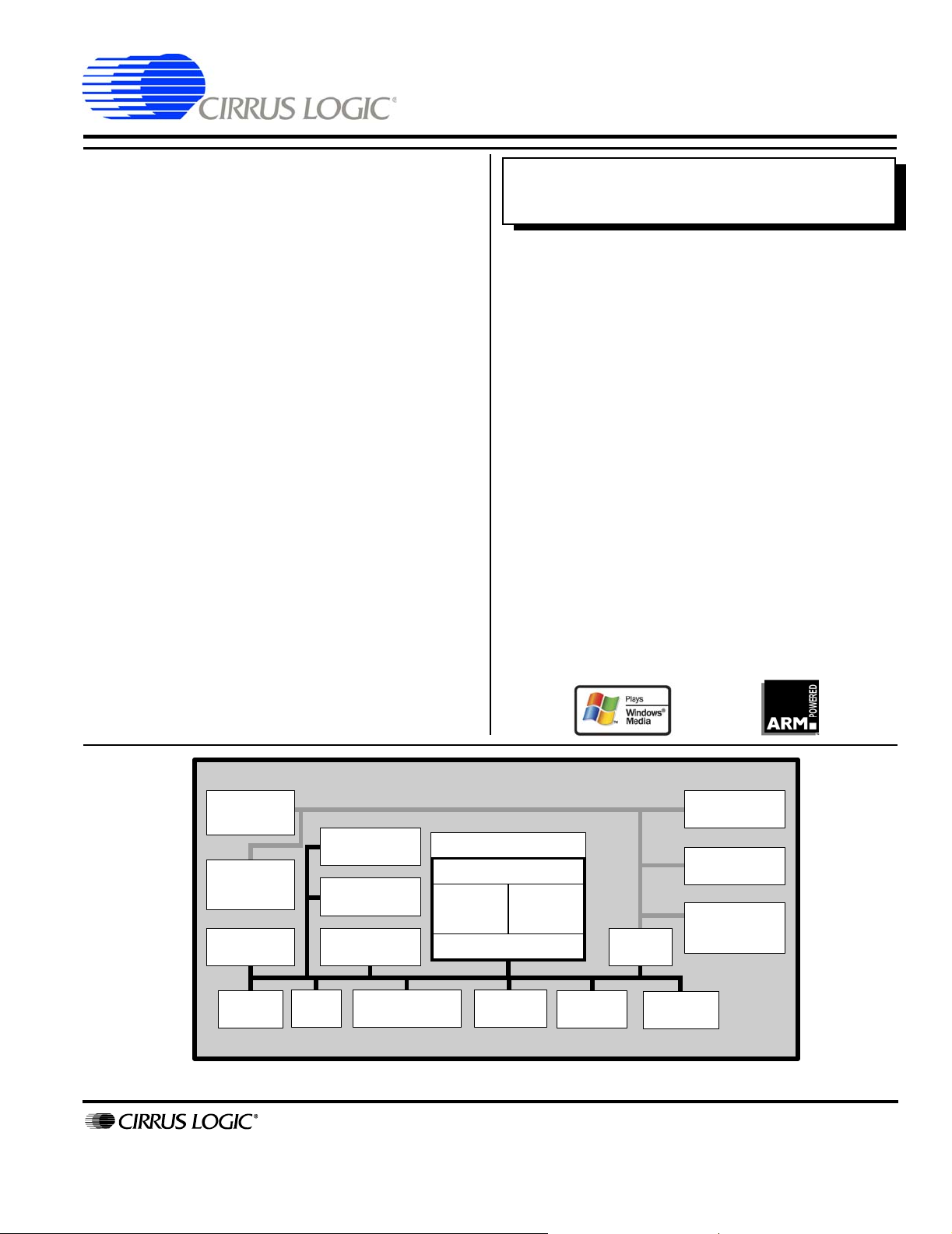
COMMUNICATIONS PORTS
http://www.cirrus.com
Serial
Audio
Interface
(3) UARTs
w/
IrDA
(3) USB
Hosts
Ethernet
MAC
12-channel DMA
MaverickKey
EIDE
I/F
TM
Boot
ROM
SRAM & Flash I/F
PCMCIA
Peripheral Bus
MaverickCrunch
ARM920T
D-Cache
16KB
I-Cache
16KB
MMU
Unified
SDRAM I/F
TM
Video/LCD
Controller
Bus
Bridge
Graphics
Accelerator
Clocks &
Timers
Interrupts
& GPIO
Keypad &
Touch
Screen I/F
Processor Bus
USER INTERFACE
MEMORY AND STORAGE
©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) MAR ‘05
DS638PP4
1
Page 2

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
OVERVIEW
The EP9315 is an ARM920T-based system-on-a-chip
design with a large peripheral set targeted to a variety of
applications:
• Thin Client Computers for Business and Home
• Internet Radio
• Internet Access Devices
• Industrial Computers
• Specialized Terminals
• Point-of-sale Terminals
• Test and Measurement Equipment
The ARM920T microprocessor core with separate
16-kbyte, 64-way set-associative instruction and data
caches is augmented by the MaverickCrunch™ coprocessor, enabling high-speed floating point
calculations.
MaverickKey
solution to the growing concern o ver sec ure web conten t
and commerce. With Internet security playing an
important role in the delivery of digital media such as
™
unique hardware programmed IDs are a
books or music, traditional software methods are quickly
becoming unreliable. The MaverickKey unique IDs
provide OEMs with a method of utilizing specific
hardware IDs such as those assigned for SDMI (Secure
Digital Music Initiative) or any other authentication
mechanism.
A high-performance 1/10/100-Mbps Ethernet media
access controller (EMAC) is included along with external
interfaces to SPI, I
2
S audio, Raster/LCD, IDE storage
peripherals, keypad, and touchscreen. A three-port USB
2.0 Full Speed Host (OHCI) (12 Mbits per second) and
three UARTs are included as well.
The EP9315 is a high-performance, low-power, RISCbased, single-chip computer built around an ARM920T
microprocessor core with a maximum operating clock
rate of 200 MHz (184 MHz for industrial conditions). The
ARM core operates from a 1.8 V supply, while the I/O
operates at 3.3 V with power usage between 100 mW
and 750 mW (dependent on speed).
Table A. Change History
Revision Date Changes
PP1 January 2004 Initial Release.
PP2 July 2004
PP3 Febuary 2005 Update electrical characteristics based upon more complete characterization data.
PP4 March 2005 Minor correction to block diagram on page 1. DD7 changed to pull down.
Update AC data.
Add ADC data.
2 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 3

Page 4

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
List of Figures
Figure 1. Timing Diagram Drawing Key .................................................................................14
Figure 2. SDRAM Load Mode Register Cycle Timing Measurement .....................................15
Figure 3. SDRAM Burst Read Cycle Timing Measurement ...................................................16
Figure 4. SDRAM Burst Write Cycle Timing Measurement ...................................................17
Figure 5. SDRAM Auto Refresh Cycle Timing Measurement ................................................ 18
Figure 6. Static Memory Single Word Read Cycle Timing Measurement ..............................19
Figure 7. Static Memory Single Word Write Cycle Timing Measurement ..............................20
Figure 8. Static Memory Multiple Word Read 8-bit Cycle Timing Measurement ....................21
Figure 9. Static Memory Multiple Word Write 8-bit Cycle Timing Measurement ....... .... ... ... ...22
Figure 10. Static Memory Multiple Word Read 16-bit Cycle Timing Measurement ................23
Figure 11. Static Memory Multiple Word Write 16-bit Cycle Timing Measurement ................24
Figure 12. Static Memory Burst Read Cycle Timing Measurement .......................................25
Figure 13. Static Memory Burst Write Cycle Timing Measurement .......................................26
Figure 14. Static Memory Single Read Wait Cycle Timing Measurement .............................27
Figure 15. Static Memory Single Write Wait Cycle Timing Measurement ..............................28
Figure 16. Static Memory Turnaround Cycle Timing Measurement .......................................29
Figure 17. PCMCIA Read Cycle Timing Measurement .................... ...... .......... ......... .......... ...30
Figure 18. PCMCIA Write Cycle Timing Measurement ................................ ..........................31
Figure 19. Register Transfer to/from Device ................................................................. .........33
Figure 20. PIO Data Transfer to/from Device ............... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ...35
Figure 21. Initiating an Ultra DMA data-in Burst ..................... ... ... ....................................... ...37
Figure 22. Sustained Ultra DMA data-in Burst .......................................................................38
Figure 23. Host Pausing an Ultra DMA data-in Burst ................... .... ... ... ................................38
Figure 24. Device Terminating an Ultra DMA data-in Burst ...................................................39
Figure 25. Host Terminating an Ultra DMA data-in Burst .......................................................40
Figure 26. Initiating an Ultra DMA data-out Burst ..... ... ... ....................................... ... .... .........41
Figure 27. Sustained Ultra DMA data-out Burst .....................................................................42
Figure 28. Device Pausing an Ultra DMA data-out Burst ....... ....................................... ......... 42
Figure 29. Host Terminating an Ultra DMA data-out Burst ....................................................43
Figure 30. Device Terminating an Ultra DMA data-out Burst .................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ......44
Figure 31. Ethernet MAC Timing Measurement .....................................................................46
Figure 32. TI Single Transfer Timing Measurement ............................ ... ...... ....... ...... ....... ......48
Figure 33. Microwire Frame Format, Single Transfer ......... ... ... ... .... ... ... ................................48
Figure 34. SPI Format with SPH=1 Timing Measurement .....................................................49
Figure 35. Inter-IC Sound (I2S) Timing Measurement ...........................................................50
Figure 36. AC ‘97 Configuration Timing Measurement .................... ...................................... 51
Figure 37. LCD Timing Measurement ....................................................................................52
Figure 38. ADC Transfer Function .........................................................................................53
Figure 39. JTAG Timing Measurement .................. ................................................................ 54
Figure 40. 352 Pin PBGA Pin Diagram ..................................................................................55
Figure 40. 352 PIN BGA PINOUT .........................................................................................57
4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 5

List of Tables
Table A. Change History ..................................... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ................. 2
Table B. General Purpose Memory Interface Pin Assignments ................................ .............. 6
Table C.IDE Interface Pin Assignments .................................................................................. 7
Table D.Ethernet Media Access Controller Pin Assignments ................................................. 7
Table E. Audio Interfaces Pin Assignment .............................................................................. 7
Table F. LCD Interface Pin Assignments . ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ...... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... . 8
Table G.Touch Screen Interface with 12-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter Pin Assignments ... 8
Table H.64-Key Keypad Interface Pin Assignments ............................................................... 8
Table I. Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters Pin Assignments ............................ 9
Table J. Triple Port USB Host Pin Assignments ..................................................................... 9
Table K. Two-Wire Port with EEPROM Support Pin Assignments .......................................... 9
Table L. Real-Time Clock with Pin Assignments ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... ...... 10
Table M. PLL and Clocking Pin Assignments ............................ ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...... ... 10
Table N.External Interrupt Pin Assignment ........................................................................... 10
Table O.Dual LED Pin Assignments ......................................... ... ... ...................................... 10
Table P. General Purpose Input/Output Pin Assignment ...................................................... 11
Table Q.Reset and Power Management Pin Assignments ................................................... 11
Table R.Hardware Debug Interface ...................................................................................... 11
Table S. PCMCIA Interface ......................... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... ................... 11
Table R.352 Pin Diagram Dimensions .................................................................................. 56
Table S. Pin Descriptions ..................................... ... ....................................... ... .... ............... 60
Table T. Pin Multiplex Usage Information ............................................................................. 62
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 5
Page 6

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Processor Core - ARM920T
The ARM920T is a Harvard architecture processor with
separate 16-kbyte instruction and data caches with an 8word line length but a unified memory. The processor
utilizes a five-stage pipeline consisting of fetch, decode,
execute, memory, and write stages. Key features include:
• ARM (32-bit) and Thumb (16-bit compressed)
Instruction Sets
• 32-bit Advanced Micro-Controller Bus Architecture
(AMBA)
• 16-kbyte Instruction Cache with Lockdown
• 16-kbyte Data Cache (pro grammable write-throu gh or
write-back) with Lockdown
• MMU for Linux
®
, Microsoft® Windows® CE and Other
Operating Systems
• Translation Look Aside Buffers with 64 Data and 64
Instruction Entries
• Programmable Page Sizes of 1 Mbyte, 64 kbyte,
4 kbyte, and 1 kbyte
• Independent Lockdown of TLB Entries
MaverickCrunch™ Math Engine
The MaverickCrunch Engine is a mixed-mode
coprocessor designed primarily to accelerate the math
processing required to rapidly encode digital audio
formats. It accelerates single and double precision
integer and floating point operations plus an integer
multiply-accumulate (MAC) instruction that is
considerably faster than the ARM920T's native MAC
instruction. The ARM920T coprocessor interface is
utilized thereby sharing its memory interface and
instruction stream. Hardware forwarding and interlock
allows the ARM to handle looping and addressing while
MaverickCrunch handles computation. Features include:
• IEEE-754 single and double precision floating point
• 32 / 64-bit integer
• Add / multiply / compare
• Integer MAC 32-bit input with 72-bit accumulate
• Integer Shifts
• Floating point to/from integer conversion
• Sixteen 64-bit register files
• Four 72-bit accumulators
MaverickKey™ Unique ID
MaverickKey unique hardware programmed IDs are a
solution to the growing concern over secure web content
and commerce. With Internet security playing an
important role in the delivery of digital media such as
books or music, traditional software methods are quick ly
becoming unreliable. The MaverickKey unique IDs
provide OEMs with a method of utilizing specific
hardware IDs such as those assigned for SDMI (Secure
Digital Music Initiative) or any other authentication
mechanism.
Both a specific 32-bit ID as well as a 128-bit random ID is
programmed into the EP9315 through the use of laser
probing technology. These IDs can then be used to
match secure copyrighted content with the ID of the
target device the EP9315 is powering, and then deliver
the copyrighted information over a secure connection. In
addition, secure transactions can benefit by also
matching device IDs to server IDs. MaverickKey IDs
provide a level of hardware security required for today’s
Internet appliances.
General Purpose Memory Interface (SDRAM, SRAM, ROM, FLASH)
The EP9315 features a unified memory address model
where all memory devices are accessed over a common
address/data bus. A separate internal po rt is dedicated to
the read-only Raster/LCD refresh engine, while the rest
of the memory accesses are performed via the Processor
bus. The SRAM memory controller supports 8, 16 and
32-bit devices and accommodates an internal boot ROM
concurrently with 32-bit SDRAM memory.
• 1-4 banks of 32-bit 66 or 100 MHz SDRAM
• One internal port dedicated to the Raster/LCD
Refresh Engine (Read Only)
• Address and data bus shared between SDRAM,
SRAM, ROM, and FLASH memory
• NOR FLASH memory supported
Table B. General Purpose Memory Interface Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Description
SDCLK SDRAM Clock
SDCLKEN SDRAM Clock Enable
SDCSn[3:0] SDRAM Chip Selects 3-0
RASn SDRAM RAS
CASn SDRAM CAS
SDWEn SDRAM Write Enable
CSn[7:6] and CSn[3:0] Chip Selects 7, 6, 3, 2, 1, 0
AD[25:0] Address Bus 25-0
DA[31:0] Data Bus 31-0
DQMn[3:0] SDRAM Output Enables / Data Masks
WRn SRAM Write Strobe
RDn SRAM Read / OE Strobe
WAITn SRAM Wait Input
6 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 7
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
IDE Interface
The IDE Interface provides an industry-standard
connection to two AT Advanced Packet Interface (ATAPI)
compliant devices. The IDE port will attach to a master
and a slave device. The internal DMA controller performs
all data transfers using the Ultra DMA modes. The
interface supports the following operating modes:
• PIO Mode 0 thru 4
• Ultra DMA Modes 0 thru 3
Table C. IDE Interface Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Description
DD[15-0] IDE Data bus
IDEDA[2-0] IDE Device address
IDECSn[0,1] IDE Chip Select 0 and 1
DIORn IDE Read Strobe
DIOWn IDE Write Strobe
DMACKn IDE DMA acknowledge
Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC)
The MAC subsystem is compliant with the ISO/TEC
802.3 topology for a single shared medium with several
stations. Multiple MII-compliant PHYs are supported.
Features include:
• Supports 1/10/100 Mbps transfer rates for home /
small-business / large-business applications
• Interfaces to an off-chip PHY through industry
standard Media Independent Interface (MII)
Table D. Ethernet Media Access Controller Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Description
MDC Management Data Clock
MDIO Management Data I/O
RXCLK Receive Clock
MIIRXD[3:0] Receive Data
RXDVAL Receive Data Valid
RXERR Receive Data Error
TXCLK Transmit Clock
MIITXD[3:0] Transmit Data
TXEN Transmit Enable
TXERR Transmit Error
CRS Carrier Sense
CLD Collision Detect
Serial Interfaces (SPI, I2S and AC ’97)
The SPI port can be configured as a master or a slave,
®
supporting the National Semi conductor
®
Texas Instruments
signaling protocols.
, Motorola® and
The AC'97 port supports multiple codecs for multicha nnel
audio output with a single stereo input. Three I
2
S ports
can be configured to support six channel 24-bit audio.
These ports are multiplexed so that I
2
S port 0 will take
over either the AC'97 pins or the SPI pins. The second
and third I2S ports' serial input and serial output pins are
multiplexed with EGPIO[4,5,6,13]. The clocks supplied in
the first I2S port are also used for the second and third
I2S ports.
• Normal Mode: One SPI Port and one AC’97 Port
2
•I
S on SSP Mode: One AC’97 Port and up to three I2S
Ports
2
•I
S on AC’97 Mode: One SPI Port and up to three I2S
Ports
Table E. Audio Interfaces Pin Assignment
Normal Mode
Pin
Name
SCLK1 SPI Bit Clock I2S Serial Clock SPI Bit Clock
SFRM1 SPI Frame Clock I2S Frame Clock SPI Frame Clock
SSPRX1 SPI Serial Input I2S Serial Input SPI Serial Input
SSPTX1
ARSTn AC'97 Reset AC'97 Reset I2S Master Clock
ABITCLK AC'97 Bit Clock AC'97 Bit Clock I2S Serial Clock
ASYNC
ASDI
ASDO
Pin
Description
SPI Serial
Output
AC'97 Frame
Clock
AC'97 Serial
Input
AC'97 Serial
Output
I2S on SSP
Mode
Pin Description Pin Description
I2S Serial Output SPI Serial Output
(No I2S Master
Clock)
AC'97 Frame
Clock
AC'97 Serial Input I2S Serial Input
AC'97 Serial
Output
I2S on AC'97
Mode
I2S Frame Clock
I2S Serial Output
Raster / LCD Interface
The Raster / LCD interface provides data and interface
signals for a variety of display types. It features fully
programmable video interface timing for non-interlaced
flat panel or dual scan displays. Resolutions up to
1024 x 768 are supported from a unified SDRAM based
frame buffer. A 16-bit PWM provides control for LCD
panel contrast. LCD specific features include:
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 7
Page 8
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
• Timing and interface signals for digital LCD and TFT
displays
• Full programmability for either non-interlaced or dualscan color and grayscale flat panel displays
• Dedicated data path to SDRAM controller for
improved system performance
• Pixel depths of 4, 8, 16, or 24 bits per pixel or 256
levels of grayscale
• Hardware Cursor up to 64 x 64 pixels
• 256 x 18 Color Lookup Table
• Hardware Blinking
• 8-bit interface to low end panel
Table F. LCD Interface Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Description
SPCLK Pixel Clock
P[17:0] Pixel Data Bus [17:0]
HSYNC / LP
VCSYNC / FP
BLANK Composite Blank
BRIGHT Pulse Width Modulated Brightness
Horizontal
Synchronization / Line Pulse
Vertical or Composite
Synchronization / Frame Pulse
Graphics Accelerator
The EP9315 contains a hardware graphics acceleration
engine that improves graphic performance by handling
block copy, block fill and hardware line draw operations.
The Graphics Accelerator is used in the system to offload graphics operations from the processor.
Pixel depths supported by the Graphics Accelerator are
4, 8, 16 or 24 bits per pixel. The 24 bits per pixel mode
can be operated as packed (4 pixels every 3 words) or
unpacked (1 pixel per word with the high byte unused.)
The block copy operations of the Graphics Accelerator
are similar to a DMA (Direct Memory Access) transfer
that understands pixel organization, block width,
transparency, and transformation from 1bpp to higher 4,
8, 16 or 24bpp.
The line draw operations also allow for solid lines or
dashed lines. The colors for line drawing can be either
foreground color and background color or foreground
color with the background being transparent.
only interrupts the processor when a meaningful change
occurs. The touch screen hardware may be disabled and
the switch matrix and ADC controlled directly if desired.
Features include:
• Support for 4-, 5-, 7-, or 8-wire analog resistive touch
screens.
• Flexibility - unused lines may be used for temperature
sensing or other functions.
• Touch screen interrupt function.
Table G. Touch Screen Interface with 12-bit Analog-to-Digital
Converter Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Description
Xp, Xm Touch screen ADC X Axis
Yp, Ym Touch screen ADC Y Axis
SXp, SXm
SYp, SYm
Touch screen ADC X Axis
Voltage Feedback
Touch screen ADC Y Axis
Voltage Feedback
64-Key Keypad Interface
The keypad circuitry scans an 8 x 8 array of 64 normally
open, single-pole switches. Any one or two keys
depressed will be de-bounced and decoded. An interrupt
is generated whenever a stable set of depressed keys is
detected. If the keypad is not utilized, the 16 column/row
pins may be used as general purpose I/O. The Keypad
interface:
• Provides scanning, debounce, and decoding for a 64key switch array.
• Scans an 8-row by 8-column matrix.
• May decode 2 keys at once.
• Generates an interrupt when a new stable key is
determined.
• Also generates a 3-key reset interrupt.
Table H. 64-Key Keypad Interface Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic
COL[7:0]
ROW[7:0]
Pin
Description
Key Matrix Column
Inputs
Key Matrix Row
Inputs
Alternative Usage
General Purpose I/O
General Purpose I/O
Touch Screen Interface with 12-bit Analogto-digital Converter (ADC)
The touch screen interface performs all sampling,
averaging, ADC range checking, and control for a wide
variety of analog resistive touch screens. This controller
8 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 9
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/T ransmitters (UARTs)
Three 16550-compatible UARTs are supplied. Two
provide asynchronous HDLC (High-level Data Link
Control) protocol support for full-duplex transmit and
receive. The HDLC receiver handles framing, address
matching, CRC checking, control-octet transparency, and
optionally passes the CRC to the host at the end of the
packet. The HDLC transmitter handles framing, CRC
generation, and control-octet transparency. The host
must assemble the frame in memory before
transmission. The HDLC receiver and transmitter use the
UART FIFOs to buffer the data streams. A third IrDA
compatible UART is also supplied.
• UART1 supports modem bit rates up to 115.2 Kbps,
supports HDLC and includes a 16-byte FIFO for
receive and a 16-byte FIFO for transmit. Interrupts are
generated on Rx, Tx, and modem status change.
• UART2 contains an IrDA encoder operating at eith er
the slow (up to 115 Kbps), medium (0.576 or 1.152
Mbps), or fast (4 Mbps) IR data rates. It also has a 16byte FIFO for receive and a 16-byte FIFO for transmit.
• UART3 supports HDLC and includes a 16-byte FIFO
for receive and a 16-byte FIFO for transmit. Interrupts
are generated on Rx and Tx.
®
Triple Port USB Host
The USB Open Host Controller Interface (Open HCI)
provides full speed serial communications ports at a
baud rate of 12 Mbits/sec. Up to 127 USB devices
(printer, mouse, camera, keyboard, etc.) and USB hubs
can be connected to the USB host in the USB “tieredstart” topology.
This includes the following features:
• Compliance with the USB 2.0 specification
• Compliance with the Open HCI Rev 1.0 specification
• Supports both low speed (1.5 Mbp s) and full speed
-
(12 Mbps) USB device connections
• Root HUB integrated with 3 downstream USB ports
• Transceiver buff ers integrated, over-current protection
on ports
• Supports power management
• Operates as a master on the bus
The Open HCI host controller initializes the master DMA
transfer with the AHB bus:
• Fetches endpoint descriptors and transfer descriptors
• Accesses endpoint data from system memory
• Accesses the HC communication area
• Writes status and retire transfer descriptor
Table I. Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters Pin
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
TXD0 UART1 Transmit
RXD0 UART1 Receive
CTSn
DSRn / DCDn
DTRn UART1 Data Terminal Ready
RTSn UART1 Ready To Send
EGPIO[0] / RI UART1 Ring Indicator
TXD1 / SIROUT
RXD1 / SIRIN UART2 Receive / IrDA Input
TXD2 UART3 Transmit
RXD2 UART3 Receive
EGPIO[3] / TENn HDLC3 Transmit Enable
Assignments
UART1 Clear To Send /
Transmit Enable
UART1 Data Set Ready /
Data Carrier Detect
UART2 Transmit /
IrDA Output
Table J. Triple Port USB Host Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
USBp[2:0] USB Positive signals
USBm[2:0] USB Negative Signals
Two-wire Interface
The two-wire interface provides communication and
control for synchronous-serial-driven devices.
Table K. Two-Wire Port with EEPROM Support Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
EECLK Two-Wire Interface Clock
EEDATA Two-Wire Interface Data
Alternative
Usage
General
Purpose I/O
General
Purpose I/O
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 9
Page 10
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Real-Time Clock with Software Trim
The software trim feature on the real time clock (RTC)
provides software controlled digital compensation of the
32.768 kHz input clock. This compensation is accurate to
± 1.24 sec/month.
Note: A real time clock must be connected to RTCXTALI or
the EP9315 device will not boot.
Table L. Real-Time Clock with Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
RTCXTALI Real-Time Clock Oscillator Input
RTCXTALO Real-Time Clock Oscillator Output
PLL and Clocking
The processor and the peripheral clocks operate from a
single 14.7456 MHz crystal.
The real time clock operates from a 32.768 kHz external
oscillator.
Table M. PLL and Clocking Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
XTALI Main Oscillator Input
XTALO Main Oscillator Output
VDD_PLL Main Oscillator Power
GND_PLL Main Oscillator Ground
Timers
low, level-sensitive inputs. GPIO may be programmed as
active-high level-sensitive, active-low level-sensitive,
rising-edge-triggered, falling-edge-triggered, or combined
rising/falling-edge-triggered.
• Supports 64 interrupts from a variety of sources (such
as UARTs, GPIO, and key matrix)
• Routes interrupt sources to either the ARM920T’s
IRQ or FIQ (Fast IRQ) inputs
• Four dedicated off-chip interrupt lines INT[3:0]
operate as active-high, level-sensitive interrupts
• Any of the 16 GPIO lines maybe configured to
generate interrupts
• Software supported priority mask for all FIQs and
IRQs
Table N. External Interrupt Pin Assignment
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
INT[3:0] External Interrupt 3-0
Dual LED Drivers
Two pins are assigned specifically to drive external
LEDs.
Table O. Dual LED Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic
GRLED Green LED General Purpose I/O
REDLED Red LED General Purpose I/O
Pin Name -
Description
Alternative Usage
The Watchdog Timer insures proper operation by
requiring periodic attention to prevent a reset-on-timeout.
General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
The 16 EGPIO pins may each be configured individually
as an output, an input, or an interrupt input. Port F may
Two 16-bit timers operate as free running down-counters
or as periodic timers for fixed interval interrupts and have
a range of 0.03 ms to 4.27 seconds.
One 32-bit timer, plus a 6-bit prescale counter, has a
range of 0.03 µs to 73.3 hours.
One 40-bit debug timer , plu s 6-bit prescale co unter, has a
range of 1.0 µs to 12.7 days.
Interrupt Controller
The interrupt controller allows up to 64 interrupts to
generate an Interrupt Request (IRQ) or Fast Interrupt
Request (FIQ) signal to the processor core. Thirty-two
hardware priority assignments are provided fo r assisting
be configured as GPIO. Each Port F pin may be
configured individually as an output, input or an interrupt
input.
There are 23 pins that may be used as alternate input s or
outputs, but do not support interrupts. These pins are:
• Key Matrix ROW[7:0], COL[7:0]
• Ethernet MDIO
• Both LED Outputs
• Two-wire Clock and Data
• SLA [1:0]
6 pins may alternatively be used as inputs only:
• CTSn, DSRn / DCDn
• 4 Interrupt Lines
IRQ vectoring, and two levels are provided for FIQ
vectoring. This allows time critical interrupts to be
processed in the shortest time possible. Internal
interrupts may be programmed as active-high or active-
10 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
2 pins may alternatively be used as outputs only:
•RTSn
•ARSTn
Page 11
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Table P. General Purpose Input/Output Pin Assignment
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
EGPIO[15:0]
FGPIO[7:0]
Note: Port F defaults as PCMCIA pins. Port F must be
configured by software to be used as GPIO.
Expanded General Purpose Input / Output
Pins with Interrupts
Expanded General Purpose Input / Output
Pins with Interrupts
Reset and Power Management
The chip may be reset through the PRSTn pin or through
the open drain common reset pin, RSTOn.
Clocks are managed on a peripheral-by-peripheral basis
and may be turned off to conserve power.
The processor clock is dynamically adjustable from 0 to
200 MHz (184 MHz for industrial conditions).
Table Q. Reset and Power Management Pin Assignments
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
PRSTn Power On Reset
RSTOn
User Reset In/Out – Open Drain –
Preserves Real Time Clock value
Hardware Debug Interface
The JTAG interface allows use of ARM’s Multi-ICE or
other in-circuit emulators.
Note: The JTAG interface does not support boundary scan.
Table R. Hardware Debug Interface
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
TCK JTAG Clock
TDI JTAG Data In
TDO JTAG Data Out
TMS JTAG Test Mode Select
TRSTn JTAG Port Reset
Internal Boot ROM
12-channel DMA Controller
The DMA module contains 12 separate DMA channels.
Ten of these may be used for peripheral-to-memory or
memory-to-peripheral access. Two of these are
dedicated to memory-to-memory transfers. Each DMA
channel is connected to the 16-bit DMA request bus.
The request bus is a collection of requests, Serial Audio,
and UARTs. Each DMA channel can be used
independently or dedicated to any request signal. For
each DMA channel, source and destination addressing
can be independently programmed to increment,
decrement, or stay at the same value. All DMA
addresses are physical, not virtual addresses.
PCMCIA Interface
The EP9315 has a single PCMCIA port which can be
used to access either 8 or 16-bit devices.
Table S. PCMCIA Interface
Pin Mnemonic Pin Name - Description
VS1 Voltage sense
VS2 Voltage sense
MCD1 Card detect
MCD2 Card detect
MCBVD1 Voltage detection / status change
MCBVD2 Voltage detection
MCDIR Data transceiver direction control
MCDAENn Data bus transceiver enable
MCADENn Address bus transceiver enable
MCREGn Memory card register
MCEHn Memory card high byte select
MCELn Memory card low byte select
IORDn I/O card read
IOWRn I/O card write
MCRDn Memory card read
MCWRn Memory card write
READY Ready / interrupt
WP Write protect
MCWAITn Wait Input
MCRESETn Card reset
The Internal 16-kbyte ROM allows booting from FLASH
memory, SPI or UART. Consult the EP93xx User’s
Manual for operational details
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 11
Page 12
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Electrical Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(All grounds = 0 V, all voltages with respect to 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
RVDD
Power Supplies
Total Power Dissipation (Note 1) - 2 W
Input Current per Pin, DC (Except supply pins) - ±10 mA
Output current per pin, DC -±50mA
Digital Input voltage (Note 2) -0.3 RVDD+0.3 V
Storage temperature -40 +125 °C
Note: 1. Includes all power generated due to AC and/or DC output loading.
2. The power supply pins are at recommended maximum values.
3. At ambient temperatures above 70° C, total power dissipation must be limited to less than 2.5 Watts.
CVDD
VDD_PLL
VDD_ADC
-
-
-
-
3.96
2.16
2.16
3.96
V
V
V
V
WARNING: Operation beyond these limits may result in permanent damage to the device.
Normal operation is not guaranteed at these extremes.
Recommended Operating Conditions
(All grounds = 0 V, all voltages with respect to 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
RVDD
Power Supplies
Operating Ambient Temperature - Commercial
Operating Ambient Temperature - Industrial
Processor Clock Speed - Commercial FCLK - - 200 MHz
Processor Clock Speed - Industrial FCLK - - 184 MHz
System Clock Speed - Commercial HCLK - - 100 MHz
System Clock Speed - Industrial HCLK - - 92 MHz
CVDD
VDD_PLL
VDD_ADC
T
A
T
A
3.0
1.65
1.65
3.0
0+25+70°C
-40 +25 +85 °C
3.3
1.80
1.80
3.3
3.6
1.94
1.94
3.6
V
V
V
V
12 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 13

DC Characteristics
(TA = 0 to 70° C; CVDD = VDD_PLL = 1.8; RVDD = 3.3 V;
All grounds = 0 V; all voltages with respect to 0 V unless otherwise noted)
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
High level output voltage Iout = -4 mA (Note 4)
Low level output voltage Iout = 4 mA
High level input voltage (Note 5)
Low level input voltage (Note 5)
High level leakage current Vin = 3.3 V (Note 5)
Low level leakage current Vin = 0 (Note 5)
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
V
oh
V
ol
V
ih
V
il
I
ih
I
il
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
0.85 × RVDD - V
- 0.15 × RVDD V
0.65 × RVDD VDD + 0.3 V
-0.3 0.35 × RVDD V
-10 µA
--10 µA
Power Supply Pins (Outputs Unloaded), 25
Power Supply Current: CVDD / VDD_PLL Total
Low-Power Mode Supply Current CVDD / VDD_PLL Total
Note: 4. For open drain pins, high level output voltage is dependent on the external load.
5. All inputs that do not include internal pull-ups or pull-downs, must be externally driven for proper operation (See Table S on
page 60). If an input is not driven, it should be tied to power or ground, depending on the particular function. If an I/O pin is not
driven and programmed as an input, it should be tied to power or ground through its own resistor.
° C
RVDD
RVDD
-
-
-
-
190
45
2
1
240
80
3.5
2
mA
mA
mA
mA
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 13
Page 14
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Timings
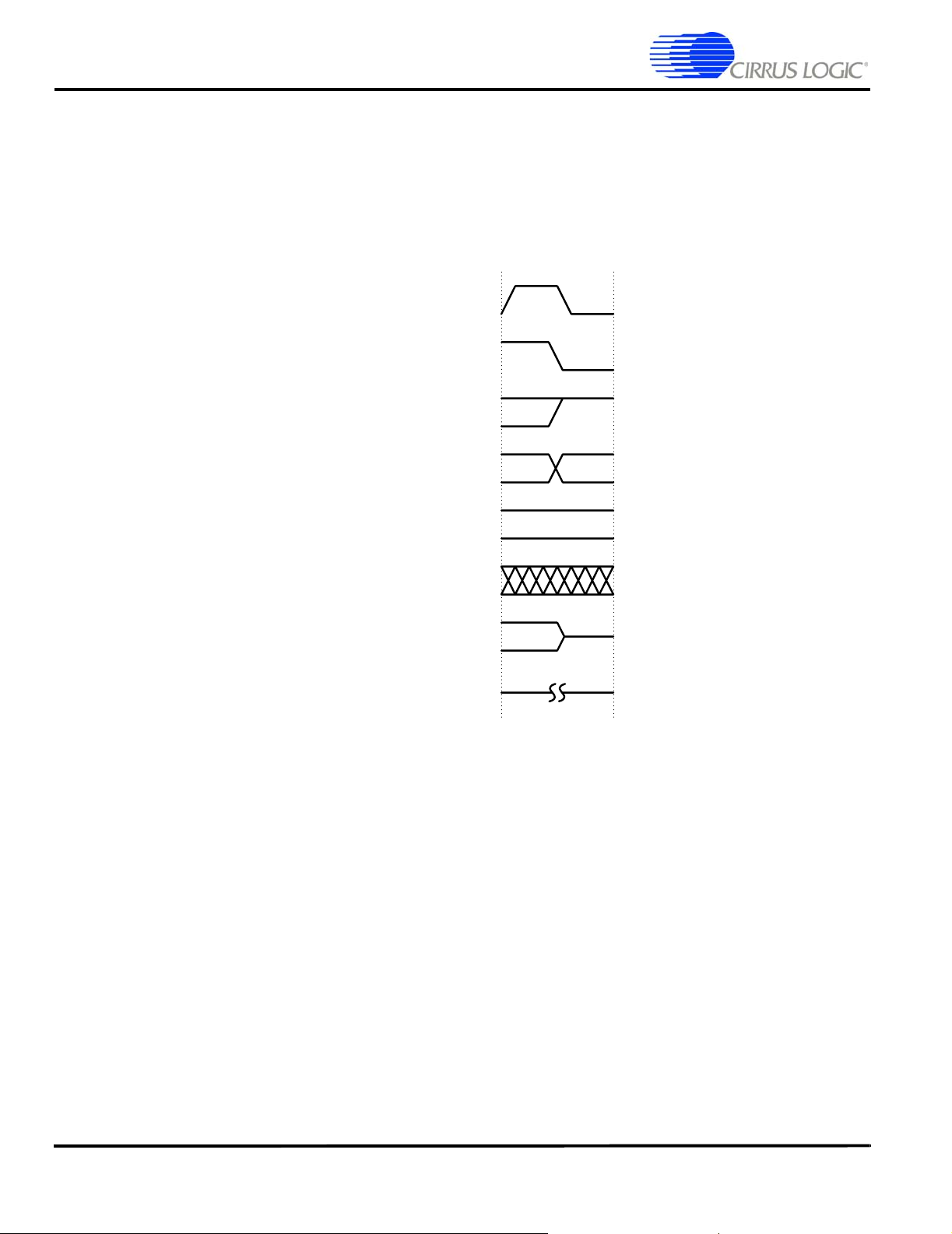
Timing Diagram Conventions
This data sheet contains one or more timing diagrams. The following key explains the components used in these
diagrams. Any variations are clearly labe lled when they occur. Therefore, no additional meaning should be attached
unless specifically stated.
Clock
High to Low
High/Low to High
Bus Change
Bus Valid
Undefined/Invalid
Valid Bus to Tristate
Bus/Signal Omission
Figure 1. Timing Diagram Drawing Key
Timing Conditions
Unless specified otherwise, the following conditions are true for all timing measurem e nts.
•T
= 0 to 70° C
A
• CVDD = VDD_PLL = 1.8V
•RVDD = 3.3V
• All grounds = 0 V
• Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = 3.3 V
• Output loading = 50 pF
• Timing reference levels = 1.5 V
• The Processor Bus Clock (HCLK) is programmable and is set by the user. The frequen cy is typica lly between
33 MHz and 100 MHz (92 MHz for industrial conditions).
14 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 15
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Memory Interface
Figure 2 through Figure 5 define the timings associated with all phases of the SDRAM. The following table contains the
values for the timings of each of the SDRAM modes.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
SDCLK high time
SDCLK low time
SDCLK rise/fall time
Signal delay from SDCLK rising edge time
Signal hold from SDCLK rising edge time
DQMn delay from SDCLK rising edge time
DQMn hold from SDCLK rising edge time
DA valid setup to SDCLK rising edge time
DA valid hold from SDCLK rising edge time
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
t
clkrf
t
d
t
h
t
DQd
t
DQh
t
DAs
t
DAh
-
-
-24ns
--8ns
1--ns
--8ns
1--ns
2--ns
3--ns
(t
(t
HCLK
HCLK
) / 2
) / 2
-ns
-ns
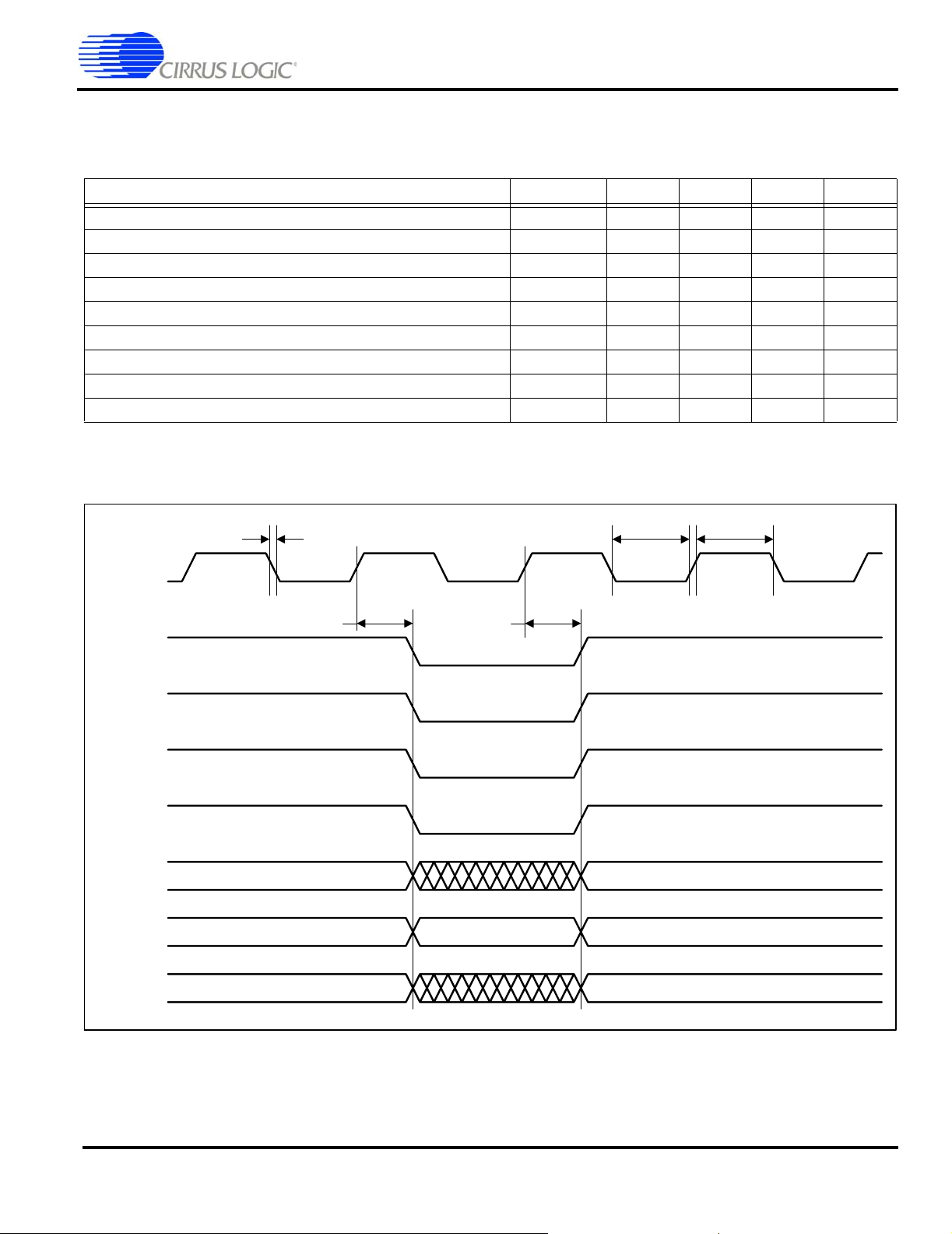
SDRAM Load Mode Register Cycle
SDCLK
SDCSn
RASn
CASn
SDWEn
DQMn
AD
t
clkrf
t
clk_low
t
d
t
h
t
clk_high
OP-Code
DA
Figure 2. SDRAM Load Mode Register Cycle Timing Measurement
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 15
Page 16
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
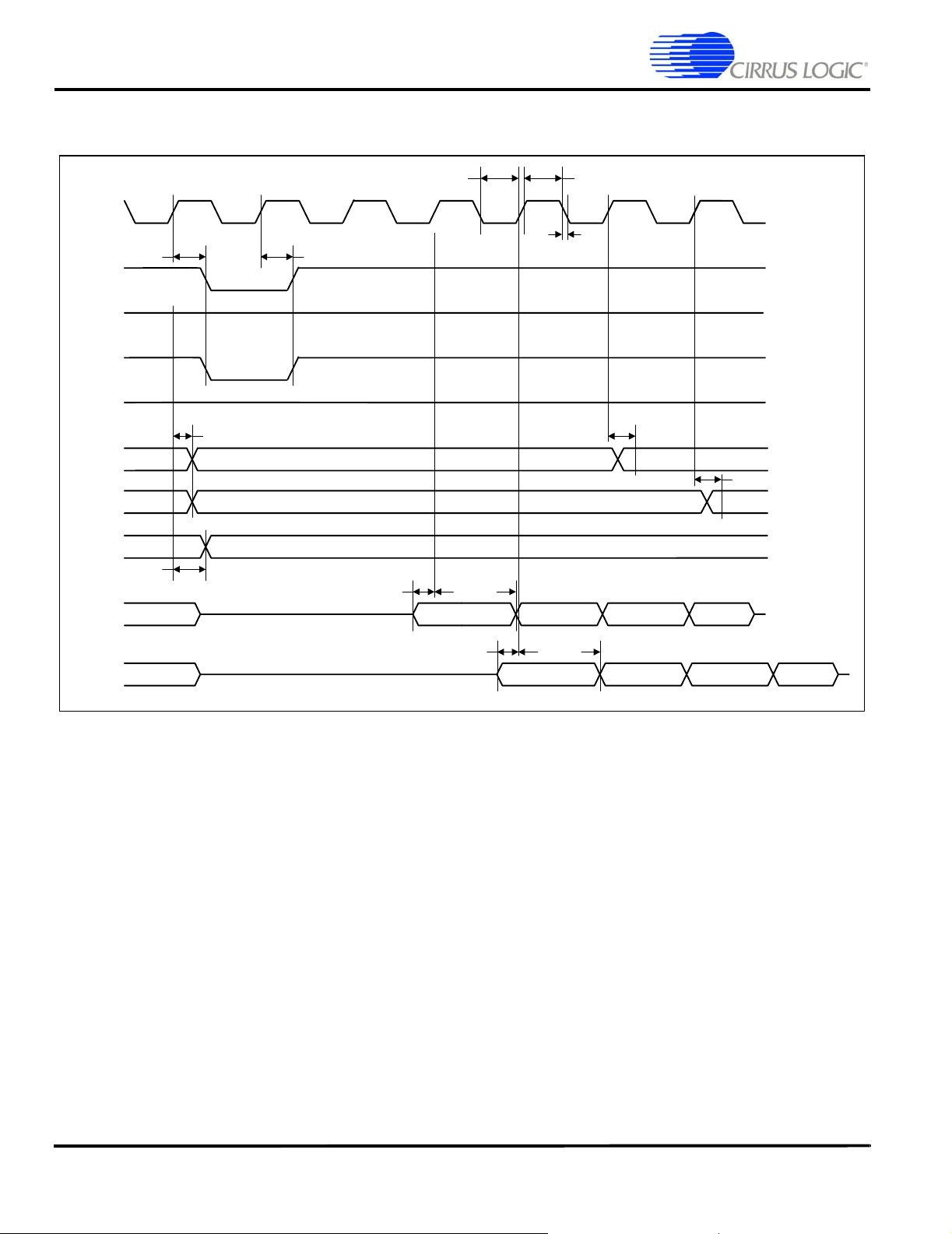
SDRAM Burst Read Cycle
SDCLK
SDCSn
RASn
CASn
SDWEn
DQMn
CL = 2
DQMn
CL = 3
AD
DA
CL = 2
t
clk_low
t
d
t
DQd
t
d
t
h
t
DAs
t
DAh
n n + 1 n + 2 n + 3
t
clk_high
t
clkrf
t
DQh
t
DQh
DA
CL = 3
t
DAs
t
DAh
n n + 1 n + 2 n + 3
Figure 3. SDRAM Burst Read Cycle Timing Measurement
16 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 17
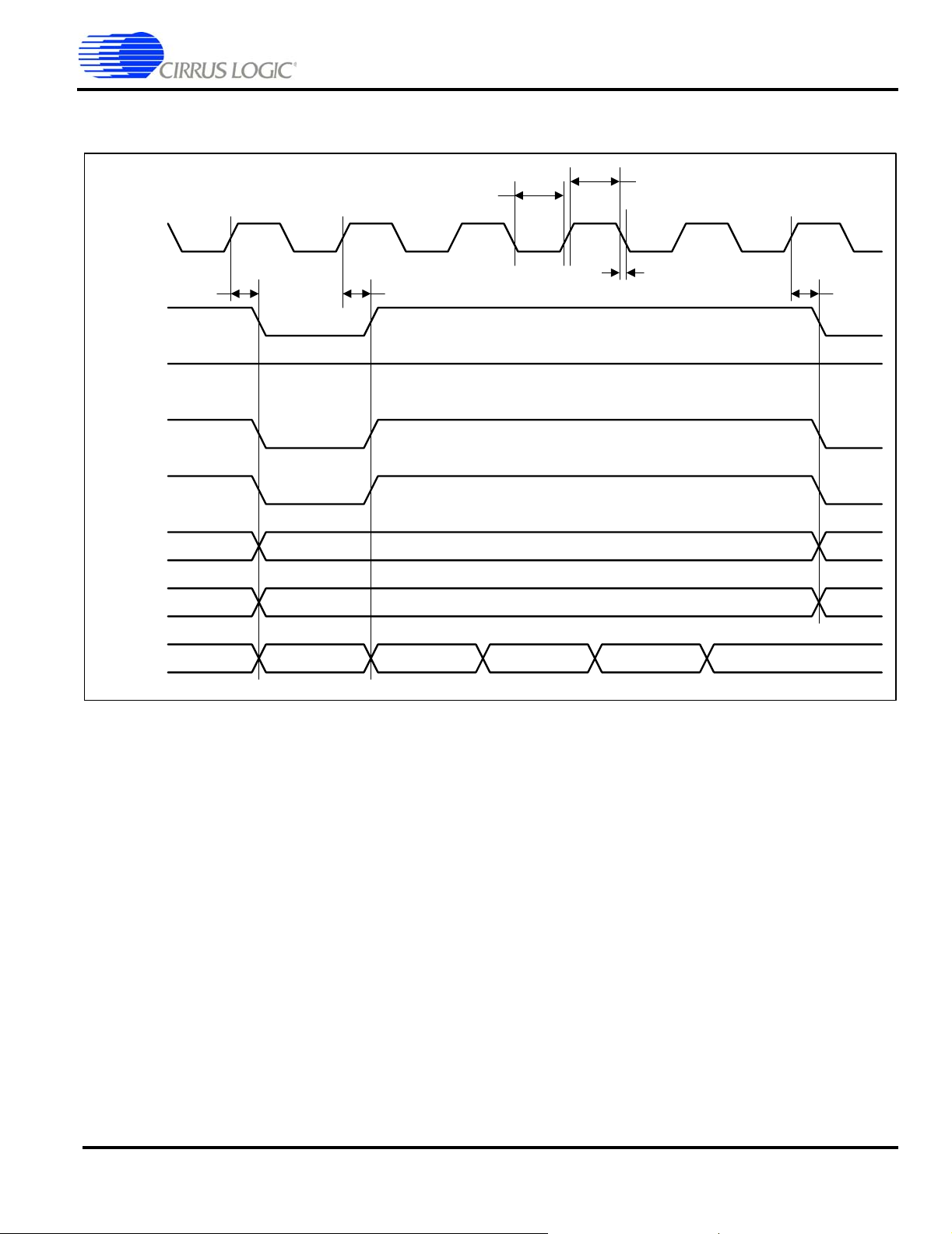
SDRAM Burst Write Cycle
SDCLK
t
d
SDCSn
RASn
CASn
SDWEn
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
t
clk_low
t
h
clk_high
t
clkrf
t
h
DQMn
AD
DA
n n +1 n + 2 n + 3
Figure 4. SDRAM Burst Write Cycle Timing Measurement
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 17
Page 18
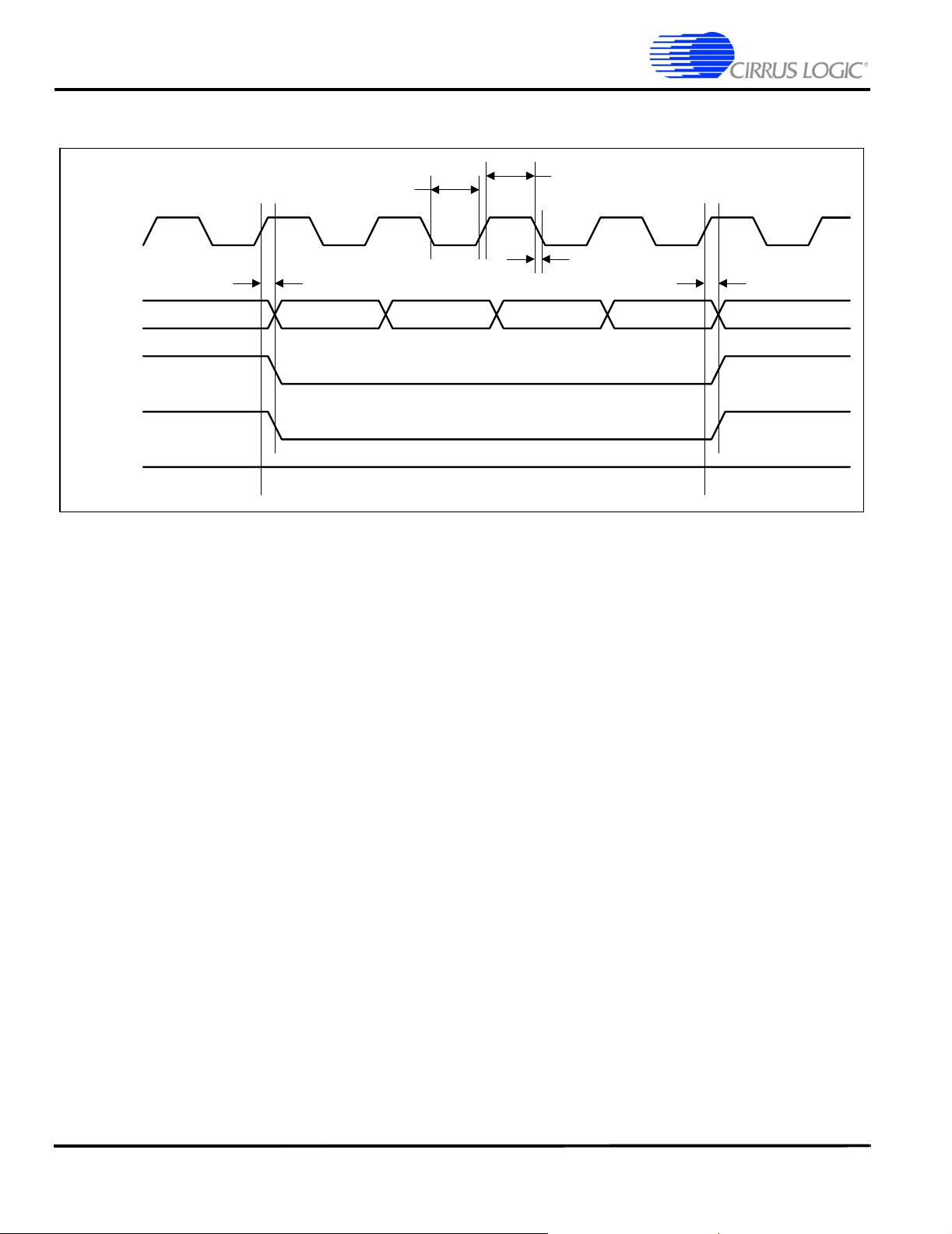
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
SDRAM Auto Refresh Cycle
SDCLK
t
d
SDCSn
RASn
CASn
SDWEn
7bde
t
clk_low
t
clk_high
t
clkrf
t
h
Note: Chip select shown as bus to illustrate multiple devices being put into auto refresh in one access
Figure 5. SDRAM Auto Refresh Cycle Timing Measurement
18 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 19
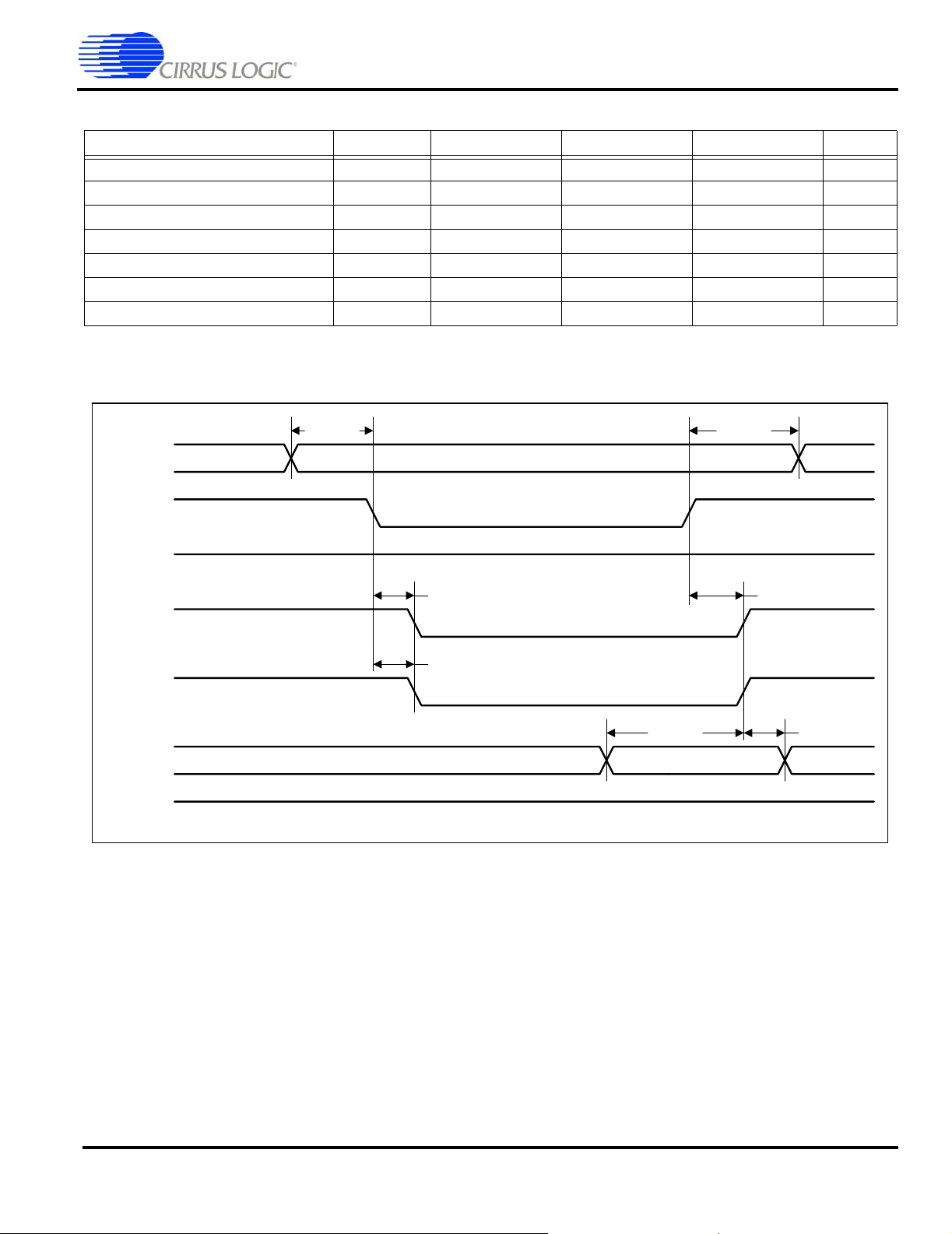
Static Memory Single Word Read Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AD setup to CSn assert time
AD hold from CSn deassert time
RDn assert time
CSn to RDn delay time
CSn assert to DQMn assert delay time
DA setup to RDn deassert time
DA hold from RDn deassert time
See “Timing Conditions” on page 14 for definition of HCLK.
t
ADs
t
ADh
t
RDpw
t
RDd
t
DQMd
t
DAs
t
DAh
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
0--ns
t
HCLK
-
--3ns
--1ns
t
+ 12
HCLK
0--ns
t
HCLK
-
× (WST1 + 2)
--ns
-ns
-ns
AD
CSn
WRn
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
ADs
t
RDd
t
DQMd
t
DAs
Figure 6. Static Memory Single Word Read Cycle Timing Measurement
t
ADh
t
RDd
t
DAh
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 19
Page 20
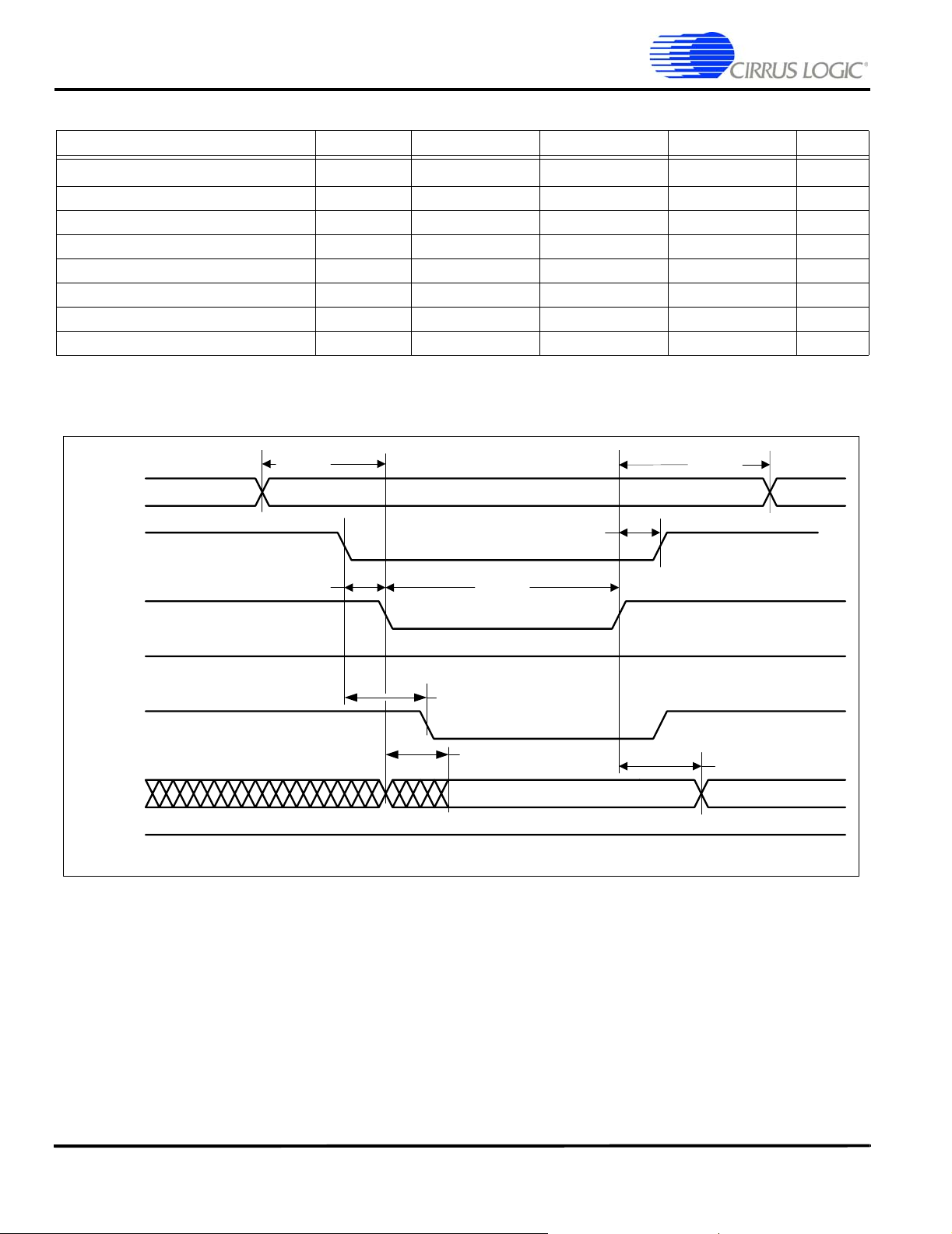
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Static Memory Single Word Write Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AD setup to WRn assert time
AD hold from WRn deassert time
WRn deassert to CSn deassert time
CSn to WRn assert delay time
WRn assert time
CSn to DQMn assert delay time
WRn deassert to DA transition time
WRn assert to DA valid
AD
CSn
WRn
t
ADs
t
WRd
t
ADs
t
ADh
t
CSh
t
WRd
t
WRpw
t
DQMd
t
DAh
t
DAV
t
- 3
HCLK
t
× 2
HCLK
7
--2ns
-
--1ns
t
HCLK
--8ns
t
WRpw
t
HCLK
-
--ns
-
× (WST1 + 1)
-
t
CSh
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
t
ADh
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
DQMd
t
DAV
Figure 7. Static Memory Single Word Write Cycle Timing Measurement
t
DAh
20 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 21

Static Memory 32-bit Read on 8-bit External Bus
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AD setup to CSn assert time
CSn assert to Address transition time
Address assert time
AD transition to CSn deassert time
AD hold from CSn deassert time
RDn assert time
CSn to RDn delay time
CSn assert to DQMn assert delay time
DA setup to AD transition time
DA setup to RDn deassert time
DA hold from AD transition time
DA hold from RDn deassert time
t
ADs
t
AD1
t
AD2
t
AD3
t
ADh
t
RDpwL
t
RDd
t
DQMd
t
DAs1
t
DAs2
t
DAh1
t
DAh2
t
HCLK
-
-
-
t
HCLK
-
-- 3ns
-- 1ns
15 - - ns
t
+ 12
HCLK
0- -ns
0- -ns
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
× (WST1 + 1)
t
HCLK
× (WST1 + 1)
t
HCLK
× (WST1 + 2)
t
HCLK
× (4 × WST1 + 5)
t
HCLK
-
--ns
--ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
EP9315
AD
CSn
WRn
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
ADs
t
DAs1
t
AD1
t
RDd
t
DQMd
t
AD2
t
DAh1
t
DAs1
t
AD2
t
DAh1
t
DAs1
t
AD3
t
DAh1
Figure 8. Static Memory Multiple Word Read 8-bit Cycle Timing Measurement
t
ADh
t
RDd
1
t
DAs2
t
DAh2
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 21
Page 22

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Static Memory 32-bit Write on 8-bit External Bus
Parameter Symbol Min Ty p Max Unit
AD setup to WRn assert time
WRn/DQMn deassert to AD transition time
AD hold from WRn deassert time
CSn hold from WRn deassert time
CSn to WRn assert delay time
WRn assert time
WRn deassert time
CSn to DQMn assert delay time
DQMn assert time
DQMn deassert time
WRn / DQMn deassert to DA transition time
WRn / DQMn assert to DA valid time
t
ADs
t
ADd
t
ADh
t
CSh
t
WRd
t
WRpwL
t
WRpwH
t
DQMd
t
DQMpwL
t
DQMpwH
t
DAh
t
DAV
t
− 3-
HCLK
--
t
HCLK
× 2
--ns
-ns
+ 6
t
HCLK
ns
7--ns
--2ns
× (WST1 + 1)
-
-
t
HCLK
× 2(t
t
HCLK
-ns
× 2) + 14
HCLK
ns
--1ns
× (WST1 + 1)
-
t
HCLK
--
t
HCLK
-
-ns
× 2) + 7
(t
HCLK
-ns
ns
--8ns
AD
CSn
WRn
RDn
DQMn
DA
Figure 9. Static Memory Multiple Word Write 8-bit Cycle Timing Measurement
22 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 23

Static Memory 32-bit Read on 16-bit External Bus
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AD setup to CSn assert time
CSn assert to AD transition time
AD transition to CSn deassert time
AD hold from CSn deassert time
RDn assert time
CSn to RDn delay time
CSn assert to DQMn assert delay time
DA setup to AD transition time
DA to RDn deassert time
DA hold from AD transition time
DA hold from RDn deassert time
t
ADs
t
ADd1
t
ADd2
t
ADh
t
RDpwL
t
RDd
t
DQMd
t
DAs1
t
DAs2
t
DAh1
t
DAh2
t
HCLK
-
-
t
HCLK
-
--3ns
--1ns
15 - - ns
t
+ 12
HCLK
0--ns
0--ns
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
-
× (WST1 + 1)
t
HCLK
× (WST1 + 2)
t
HCLK
× ((2 × WST1) + 3)
t
HCLK
--ns
--ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
EP9315
CSn
WRn
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
AD
t
ADs
t
ADd1
t
RDd
t
DQMd
Figure 10. Static Memory Multiple Word Read 16-bit Cycle Timing Measurement
t
RDpwl
t
DAs1
t
DAh1
t
t
DAs2
ADd2
t
DQMh
t
RDh
t
DAh2
t
ADh
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 23
Page 24

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Static Memory 32-bit Write on 16-bit External Bus
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AD setup to WRn assert time
WRn/DQMn deassert to AD transition time
AD hold from WRn deassert time
CSn hold from WRn deassert time
CSn to WRn assert delay time
WRn assert time
WRn deassert time
CSn to DQMn assert delay time
DQMn assert time
DQMn deassert time
WRn / DQMn deassert to DA transition time
WRn / DQMn assert to DA valid time
t
ADs
t
ADd
t
ADh
t
CSh
t
WRd
t
WRpwL
t
WRpwH
t
DQMd
t
DQMpwL
t
DQMpwH
t
DAh1
t
DAV
t
HCLK
t
HCLK
t
– 3 -
× 2 -
7
-t
-
-ns
HCLK
+ 6
ns
-ns
-ns
--2ns
× (WST1 + 1)
-
t
HCLK
--
-ns
× 2) + 14
(t
HCLK
ns
--1ns
× (WST1 + 1)
-
t
HCLK
--
HCLK
-
--
-ns
× 2) + 7
(t
HCLK
ns
-ns
8ns
AD
CSn
WRn
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
ADs
t
WRd
t
DQMd
t
DAV
t
WRpwL
t
DQpwL
t
DAh
t
WRpwH
t
DQpwH
t
ADd
t
DAV
t
WRpwL
t
DQpwL
t
ADh
t
CSh
t
DAh
Figure 11. Static Memory Multiple Word Write 16-bit Cycle Timing Measurement
24 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 25

Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Static Memory Burst Read Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
CSn assert to Address 1 transition time
Address assert time
AD transition to CSn deassert time
AD hold from CSn deassert time
CSn to RDn delay time
CSn to DQMn assert delay time
DA setup to AD transition time
DA setup to CSn deassert time
DA hold from AD transition time
DA hold from RDn deassert time
Note: These characteristics are valid when the Page Mode Enable (Burst Mode) bit is set. See the User 's Guide for details.
t
ADd1
t
ADd2
t
ADd3
t
ADh
t
RDd
t
DQMd
t
DAs1
t
DAs2
t
DAh1
t
DAh2
-
-
-
t
HCLK
--3ns
--1ns
15 - - ns
t
+ 12
HCLK
0--ns
0--ns
× (WST1 + 1)
t
HCLK
× (WST2 + 1)
t
HCLK
× (WST1 + 2)
t
HCLK
--ns
--ns
EP9315
-ns
-ns
-ns
AD
CSn
WRn
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
ADs
t
t
RDd
DQMd
t
ADd1
t
DAs1
t
ADd2
t
DAh1
t
DAs1
t
t
DAh1
ADd2
t
DAs1
t
ADd3
t
DAh1
t
DAs2
t
DAh2
t
ADh
Figure 12. Static Memory Burst Read Cycle Timing Measurement
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 25
Page 26

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Static Memory Burst Write Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
t
AD setup to WRn assert time
AD hold from WRn deassert time
WRN/DQMn deassert to AD transition time
CSn hold from WRn deassert time
CSn to WRn assert delay time
CSn to DQMn assert delay time
DQMn assert time
DQMn deassert time
WRn assert time
WRn deassert time
WRn/DQMn deassert to DA transition time
WRn/DQMn assert to DA valid time
t
ADs
t
ADh
t
ADd
t
CSh
t
WRd
t
DQMd
t
DQpwL
t
DQpwH
t
WRpwL
t
WRpwH
t
DAh
t
DAv
Note: These characteristics are valid when the Page Mode Enable (Burst Mode) bit is set. See the User's Guide for details.
HCLK
t
HCLK
t
7
HCLK
− 3
× 2
t
× (WST1 + 1)
HCLK
t
× (WST1 + 11)
HCLK
t
+ 6
HCLK
2ns
1ns
(t
× 2) + 14
HCLK
(t
× 2) + 7
HCLK
8ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
AD
CSn
WRn
RD
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
t
DQMd
t
ADs
WRd
t
t
DAv
t
WRpwL
DQpwL
t
ADd
t
WRpwH
t
DQpwH
t
DAh
t
ADh
t
CSh
Figure 13. Static Memory Burst Write Cycle Timing Measurement
26 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 27

Static Memory Single Read Wait Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
CSn assert to WAIT time
WAIT assert time
WAIT to CSn deassert delay time
AD
CSn
WRn
t
WAITd
t
WAITpw
t
CSnd
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
--
t
HCLK
t
HCLK
× 2
× 3
-
-
t
HCLK
t
× (WST1-2)
× 510
HCLK
t
× 5
HCLK
EP9315
ns
ns
ns
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
WAITd
Figure 14. Static Memory Single Read Wait Cycle Timing Measurement
t
WAITpw
t
CSnd
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 27
Page 28

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Static Memory Single Write Wait Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
WAIT to WRn deassert delay time
CSn assert to WAIT time
WAIT assert time
WAIT to CSn deassert delay time
AD
CSn
WRn
t
WRd
t
WAITd
t
WAITpw
t
CSnd
t
× 2
HCLK
--
t
× 2
HCLK
t
× 3
HCLK
t
WRd
-
-
-
t
HCLK
t
HCLK
t
× 4
HCLK
× (WST1-2)
× 510
t
× 5
HCLK
ns
ns
ns
ns
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
t
WAITd
Figure 15. Static Memory Single Write Wait Cycle Timing Measurement
t
WAITpw
t
CSnd
28 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 29

Static Memory Turnaround Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
CSnX deassert to CSnY assert time
Notes: 1. X and Y represent any two chip select numbers.
2. IDCY occurs on read-to-write and write-to-read.
3. IDCY is honored when going from a asynchronous device (CSx) to a synchronous device (/SDCSy).
AD
CSnX
CSnY
t
BTcyc
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
× (IDCY+1)
BTcyc
t
HCLK
-
t
-ns
WRn
RDn
DQMn
DA
WAIT
Figure 16. Static Memory Turnaround Cycle Timing Measurement
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 29
Page 30

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
PCMCIA Interface
PCMCIA Read Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AD setup to signal transition time
Attribute access time
Attribute hold time
Attribute space pre-charge delay time
Common access time
Common hold time
Common space pre-charge delay time
I/O access time
I/O hold time
I/O space pre-charge delay time
MCDIR hold time
DA setup to MCRDn / IORDn rising edge
DA hold from MCRDn / IORDn rising edge
t
ADs
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
MCDh
t
t
0--ns
A
H
p
A
H
p
A
H
p
[(AA + 1) × t
[(HA + 1) × t
(PA + 1) × t
[(AC + 1) × t
[(HC + 1) × t
(PC + 1) × t
[(AI + 1) × t
[(HI + 1) × t
(PI + 1) × t
] - 14 (AA + 1) × t
HCLK
] - 3 (HA + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
] - 14 (AC + 1) × t
HCLK
] - 3 (HC + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
] - 14 (AI + 1) × t
HCLK
] - 3 (HI + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
(PA + 1) × t
(PC + 1) × t
(PI + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
0--ns
s
h
10 - - ns
0--ns
AD
MCADENn/
MCDAENn
MCEHn/
MCELn/
MCREGn
MCRDn/
IORDn
MCDIR
DA
(in)
MCWAITn (see Note 1)
t
ADs
t
p
t
A
t
s
t
H
t
MCDh
t
h
Figure 17. PCMCIA Read Cycle Timing Measurement
Note: 1 - MCWAITn asserted will extend the MCRD / IORD strobe time.
30 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 31

PCMCIA Write Cycle
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
AD setup to signal transition time
Attribute access time
Attribute hold time
Attribute space pre-charge delay time
Common access time
Common hold time
Common space pre-charge delay time
I/O access time
I/O hold time
I/O space pre-charge delay time
MCDIR hold time
DATA invalid delay time
t
ADs
t
MCDh
t
DAfo
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
0--ns
t
A
t
H
t
p
t
A
t
H
t
p
t
A
t
H
t
p
[(AA + 1) × t
[(HA + 1) × t
(PA + 1) × t
[(AC + 1) × t
[(HC + 1) × t
(PC + 1) × t
[(AI + 1) × t
[(HI + 1) × t
(PI + 1) × t
] - 14 (AA + 1) × t
HCLK
] - 3 (HA + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
] - 14 (AC + 1) × t
HCLK
] - 3 (HC + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
] - 14 (AI + 1) × t
HCLK
] - 3 (HI + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
(PA + 1) × t
(PC + 1) × t
(PI + 1) × t
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
HCLK
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
-ns
0--ns
0--ns
t
ADs
AD
MCEHn/
MCELn/
MCREGn
t
p
MCWRn/
IOWRn
MCDIR
DA
(out)
MCWAITn (see Note 1)
Figure 18. PCMCIA Write Cycle Timing Measurement
Note: 1 - MCWAITn asserted will extend the MCWR / IOWR strobe time.
t
A
t
H
t
MCDh
t
DAfo
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 31
Page 32

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
IDE Interface
Register Transfers
Parameter Symbol
Cycle time (min) (Notes 1, 4, 5)
Address valid to DIORn / DIOWn setup (min) (Note 4)
DIORn / DIOWn pulse width 8-bit (min) (Note 1, 4)
DIORn / DIOWn recovery time (min) (Note 1, 4)
DIOWn data setup (min) (Note 4)
DIOWn data hold (min)
DIORn data setup (min)
DIORn data hold (min)
DIORn data high impedance state (max) (Note 2, 4)
DIORn / DIOWn to address valid hold (min) (Note 4)
Read Data Valid to IORDY (min)
active (if IORDY initially low after t
IORDY Setup time (Note 3, 4)
IORDY Pulse Width (max) (Note 4)
IORDY assertion to release (max)
DIOWn assert to data valid (max)
) (Note 4)
A
t
t
t
DDV
t
RD
t
t
t
Mode 0
(in ns)
t
0
t
1
t
2
2i
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
6z
t
9
A
B
C
1250 1250 1250 1250 1250
Mode 1
(in ns)
Mode 2
(in ns)
600 383 330 180 120
70 50 30 30 25
290 290 290 80 70
---7025
60 45 30 30 20
00000
20 20 20 20 20
00000
30 30 30 30 30
20 15 10 10 10
00000
35 35 35 35 35
55555
10 10 10 10 10
Note: 1. t0 is the minimum total cycle time, t2 is the minimum DIORn / DIOWn assertion time, and t2i is the minimum DIORn / DIOWn
negation time. A host implementation shall lengthen t
and/or t2i to ensure that t0 is equal to or greater than the value
2
reported in the devices IDENTIFY DEVICE data. A device implementation shall support any legal host implementation.
Mode 3
(in ns)
Mode 4
(in ns)
2. This parameter specifies the time from the negation edge of DIORn to the time that the data bus is released by the device.
3. The delay from the activation of DIORn or DIOWn until the state of IORDY is first sampled. If IORDY is inactive then the host
shall wait until IORDY is active before the register transfer cycle is completed. If the device is not driving IORDY negated at
after the activation of DIORn or DIOWn, then t5 shall be met and tRD is not applicable. If the device is driving IORDY
the t
A
negated at the time t
after the activation of DIORn or DIOWn, then tRD shall be met and t5 is not applicable.
A
4. Timings based upon software control. See User’s Guide.
5. ATA / ATAPI standards prior to ATA / ATAPI-5 inadvertently specified an incorrect value for mode 2 time t
by utilizing the
0
16-bit PIO value.
6. All IDE timing is based upon HCLK = 100 MHz.
32 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 33

ADDR valid
(Note 1)
DIORn/
DIOWn
WRITE
DD (7:0)
(Note 2)
READ
DD (7:0)
(Note 2)
IORDY
(Note 3,3-1)
IORDY
(Note 3,3-2)
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
9
t
1
t
A
t
2
t
0
t
3
t
5
t
C
t
6
t
2i
t
4
t
6z
IORDY
(Note 3,3-3)
Note: 1. Device address consists of signals IDECS0n, IDECS1n and IDEDA (2:0)
2. Data consists of DD (7:0)
3. The negation of IORDY by the device is used to extend the register transfer cycle. The determination of whether the cycle is
to be extended is made by the host after t
are described in the following three cases:
3-1 Device never negates IORDY, devices keeps IORDY released: no wait is generated.
3-2 Device negates IORDY before t
and may be asserted for no more than t
3-3 Device negates IORDY before t
before release: wait generated. The cycle completes after IORDY is reasserted. For cycles where a wait is generated
and DIORn is asserted, the device shall place read data on DD (7:0) for t
Figure 19. Register Transfer to/from Device
from the assertion of DIORn or DIOWn. The assertion and negation or IORDY
A
, but causes IORDY to be asserted before tA. IORDY is released prior to negation
A
A
before release: no wait generated.
C
. IORDY is released prior to negation and may be asserted for no more than t
t
B
RD
t
C
before asserting IORDY.
C
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 33
Page 34

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
PIO Data Transfers
Parameter Symbol
Cycle time (min) (Note 1, 4)
Address valid to DIORn / DIOWn setup (min) (Note 4)
DIORn / DIOWn 16-bit (min) (Note 1, 4)
DIORn / DIOWn recovery time (min) (Note 1, 4)
DIOWn data setup (min) (Note 4)
DIOWn data hold (min)
DIORn data setup (min)
DIORn data hold (min)
DIORn data high impedance state (max) (Note 2, 4)
DIORn / DIOWn to address valid hold (min) (Note 4)
Read Data Valid to IORDY (min)
active (if IORDY initially low after t
IORDY Setup time (Note 3, 4)
IORDY Pulse Width (max) (Note 4)
IORDY assertion to release (max)
DIOWn assert to data valid (max)
) (Note 4)
A
t
t
0
t
1
t
2
t
2i
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
6z
t
9
t
RD
t
A
t
B
t
C
DDV
Mode 0
(in ns)
600 383 240 180 120
165 125 100 80 70
1250 1250 1250 1250 1250
Mode 1
(in ns)
Mode 2
(in ns)
70 50 30 30 25
---7025
60 45 30 30 20
00000
20 20 20 20 20
00000
30 30 30 30 30
20 15 10 10 10
00000
35 35 35 35 35
55555
10 10 10 10 10
Note: 1. t0 is the minimum total cycle time, t2 is the minimum DIORn / DIOWn assertion time, and t2i is the minimum DIORn / DIOWn
negation time. A host implementation shall lengthen t
and/or t2i to ensure that t0 is equal to or greater than the value
2
reported in the devices IDENTIFY DEVICE data. A device implementation shall support any legal host implementation.
2. This parameter specifies the time from the negation edge of DIORn to the time that the data bus is released by the device.
3. The delay from the activation of DIORn or DIOWn until the state of IORDY is first sampled. If IORDY is inactive then the host
shall wait until IORDY is active before the register transfer cycle is completed. If the device is not driving IORDY negated at
the t
after the activation of DIORn or DIOWn, then t5 shall be met and tRD is not applicable. If the device is driving IORDY
A
negated at the time t
after the activation of DIORn or DIOWn, then tRD shall be met and t5 is not applicable.
A
4. Timings based upon software control. See User’s Guide.
5. All IDE timing is based upon HCLK = 100 MHz.
Mode 3
(in ns)
Mode 4
(in ns)
34 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 35

ADDR valid
(Note 1)
DIORn/
DIOWn
WRITE
DD(15:0)
(Note 2)
READ
DD(15:0)
(Note 2)
IORDY
(Note 3,3-1)
IORDY
(Note 3,3-2)
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
9
t
1
t
DDV
t
A
t
2
t
0
t
3
t
5
t
C
t
6
t
RD
t
2i
t
4
t
6z
IORDY
(Note 3,3-3)
Note: 1. Device address consists of signals IDECS0n, IDECS1n and IDEDA (2:0)
2. Data consists of DD (15:0)
3. The negation of IORDY by the device is used to extend the register transfer cycle. The determination of whether the cycle is
to be extended is made by the host after t
are described in the following three cases:
3-1 Device never negates IORDY, devices keeps IORDY released: no wait is generated.
3-2 Device negates IORDY before t
and may be asserted for no more than t
3-3 Device negates IORDY before t
before release: wait generated. The cycle completes after IORDY is reasserted. For cycles where a wait is generated
and DIORn is asserted, the device shall place read data on DD (15:0) for t
Figure 20. PIO Data Transfer to/from Device
from the assertion of DIORn or DIOWn. The assertion and negation or IORDY
A
, but causes IORDY to be asserted before tA. IORDY is released prior to negation
A
A
before release: no wait generated.
C
. IORDY is released prior to negation and may be asserted for no more than t
t
B
t
C
before asserting IORDY.
RD
C
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 35
Page 36

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Ultra DMA Data Transfer
Figure 21 through Figure 30 define the timings associated with all phases of Ultra DMA bursts. The following table
contains the values for the timings for each of the Ultra DMA modes.
Timing reference levels = 1.5 V
Parameter Symbol
Cycle time allowing for asymmetry and clock variations
(from DSTROBE edge to DSTROBE edge)
Two-cycle time allowing for clock variations (from rising edge to next
rising edge or from falling edge to next falling edge of DSTROBE)
Cycle time allowing for asymmetry and clock variations
(from HSTROBE edge to HSTROBE edge)
Two-cycle time allowing for clock variations (from rising edge to next
rising edge or from falling edge to next falling edge of HSTROBE)
Data setup time at recipient (Read)
Data hold time at recipient (Read)
Data valid setup time at sender (Write) (Note 2)
(from data valid until STROBE edge)
Data valid hold time at sender (Write) (Note 2)
(from STROBE edge until data may become invalid)
First STROBE time (for device to first negate DSTROBE from STOP
during a data in burst)
Limited interlock time (Note 3)
Interlock time with minimum (Note 3)
Unlimited interlock time (Note 3)
Maximum time allowed for output drivers to release
(from asserted or negated)
Minimum delay time required for output
Drivers to assert or negate (from released)
Envelope time (from DMACKn to STOP and HDMARDYn during data in
burst initiation and from DMACKn to STOP during data out burst initiation)
Ready-to-final-STROBE time (no STROBE edges shall be sent this long
after negation of DMARDYn)
Ready-to-pause time
(that recipient shall wait to pause after negating DMARDYn)
Maximum time before releasing IORDY
Minimum time before driving STROBE (Note 4)
Setup and hold times for DMACKn (before assertion or negation)
Time from STROBE edge to negation of DMARQ or assertion of STOP
(when sender terminates a burst)
t
CYCRD
t
2CYCRD
t
CYCWR
t
2CYCWR
t
DS
t
DH
t
DVS
t
DVH
t
FS
t
LI
t
MLI
t
UI
t
AZ
t
ZAH
t
ZAD
t
ENV
t
RFS
t
RP
t
IORDYZ
t
ZIORDY
t
ACK
t
SS
Mode 0
(in ns)
Mode 1
(in ns)
Mode 2
(in ns)
Mode 3
(in ns)
min max min max min max min max
112 - 73 - 54 - 39 -
230 - 154 - 115 - 86 -
230 - 170 - 130 - 100 -
460 - 340 - 260 - 200 -
15-10-7-7-
8-8-8-8-
70 - 48 - 30 - 20 -
6-6-6-6-
0 230 0 200 0 170 0 130
0 150 0 150 0 150 0 100
20 - 20 - 20 - 20 -
0-0-0-0-
-10-10-10-10
20 - 20 - 20 - 20 -
0-0-0-0-
20 70 20 70 20 70 20 55
-75-70-60-60
160 - 125 - 100 - 100 -
-20-20-20-20
0-0-0-0-
20 - 20 - 20 - 20 50 - 50 - 50 - 50 -
Note: 1. Timing parameters shall be measured at the connector of the sender or receiver to which the parameter applies.
2. The test load for t
DVS
and t
shall be a lumped capacitor load with no cable or receivers. Timing for t
DVH
DVS
and t
DVH
shall be
met for all capacitive loads from 15 to 40 pf where all signals have the same capacitive load value.
3. t
, t
and tLI indicate sender-to-recipient or recipient-to-sender interlocks, i.e., either sender or recipient is waiting for the
UI
MLI
other to respond with a signal before proceeding. t
time-out that has a defined minimum. t
4. t
may be greater than t
ZIORDY
ENV
is a limited time-out that has a defined maximum.
LI
since the device has a pull up on IORDYn giving it a known state when released.
is an unlimited interlock that has no maximum time value. t
UI
is a limited
MLI
5. All IDE timing is based upon HCLK = 100 MHz.
36 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 37

DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
STOP
(host)
HDMARDYn
(host)
DSTROBE
(device)
DD (15:0)
t
UI
t
ACK
t
ACK
t
ZIORDY
t
ENV
t
ENV
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
FS
t
ZAD
t
ZAD
t
AZ
t
DVS
t
DVH
t
IDEDA[2:0]
ACK
IDECS0n,
IDECS1n
Note: The definitions for the DIOWn:STOP, DIORn:HDMARDYn:HSTROBE and IORDY:DDMARDYn:DSTROBE signal lines are not
in effect until DMARQ and DMACKn are asserted.
Figure 21. Initiating an Ultra DMA data-in Burst
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 37
Page 38

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
CYCRD
DSTROBE
(device)
t
DVH
DD (15:0)
(device)
DSTROBE
(host)
t
DH
t
DS
DD (15:0)
(host)
Note: DD (15:0) and DSTROBE signals are shown at both the host and the device to emphasize that cable settling time as well as
cable propagation delay shall not allow the data signals to be considered stable at the host until some time after they are driven
by the device.
Figure 22. Sustained Ultra DMA data-in Burst
t
DVS
t
2CYCRD
t
CYCRD
t
2CYCRD
t
DVH
t
DH
t
DVS
t
DS
t
DVH
t
DH
DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
STOP
(host)
HDMARDYn
(host)
DSTROBE
(device)
DD(15:0)
(device)
t
RP
t
SR
t
RFS
Figure 23. Host Pausing an Ultra DMA data-in Burst
38 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 39

DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
MLI
t
LI
t
LI
t
ACK
STOP
(host)
t
LI
t
ACK
HDMARDYn
(host)
t
SS
DSTROBE
(device)
t
ZAH
DD (15:0)
t
AZ
t
DVS
CRC
IDEDA[2:0]
t
ACK
IDECS0n,
IDECS1n
Note: The definitions for the DIOWn:STOP, DIORn:HDMARDYn:HSTROBE and IORDY :DDMARDYn:DSTROBE signal lines are no
longer in effect after DMARQ and DMACKn are negated.
Figure 24. Device Terminating an Ultra DMA data-in Burst
t
IORDYZ
t
DVH
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 39
Page 40

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
t
RP
STOP
(host)
HDMARDYn
(host)
t
RFS
DSTROBE
(device)
DD (15:0)
t
LI
t
LI
t
MLI
t
ZAH
t
AZ
t
MLI
t
DVS
t
ACK
t
ACK
t
IORDYZ
t
DVH
CRC
IDEDA[2:0]
t
ACK
IDECS0n,
IDECS1n
Note: The definitions for the DIOWn:STOP, DIORn:HDMARDYn:HSTROBE and IORDY :DDMARDYn:DSTROBE signal lines are no
longer in effect after DMARQ and DMACKn are negated.
Figure 25. Host Terminating an Ultra DMA data-in Burst
40 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 41

DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
UI
t
ACK
t
ENV
STOP
(host)
t
ZIORDY
t
LI
t
UI
DDMARDYn
(device)
HSTROBE
(host)
t
ACK
DD (15:0)
t
DVS
IDEDA[2:0]
t
ACK
IDECS0n,
IDECS1n
Note: The definitions for the DIOWn:STOP, DIORn:HDMARDYn:HSTROBE and IORDY:DDMARDYn:DSTROBE signal lines are not
in effect until DMARQ and DMACKn are asserted.
Figure 26. Initiating an Ultra DMA data-out Burst
t
DVH
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 41
Page 42

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
CYCWR
HSTROBE
(host)
t
DVH
DD (15:0)
(host)
HSTROBE
(device)
t
DH
t
DS
DD (15:0)
(device)
Note: DD (15:0) and HSTROBE signals are shown at both the device and the host to emphasize that cable settling time as well as
cable propagation delay shall not allow the data signals to be considered stable at the device until some time after they are
driven by the host.
Figure 27. Sustained Ultra DMA data-out Burst
t
DVS
t
2CYCWR
t
CYCWR
t
2CYCWR
t
DVH
t
DH
t
DVS
t
DS
t
DVH
t
DH
DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
STOP
(host)
DDMARDYn
(device)
HSTROBE
(host)
DD (15:0)
(host)
Note: 1. The device may negate DMARQ to request termination of the Ultra DMA burst no sooner than t
negated.
2. If the t
t
RP
t
SR
t
RFS
RP
timing is not satisfied, the device may receive zero, one, or two more data words from the host.
SR
Figure 28. Device Pausing an Ultra DMA data-out Burst
after DDMARDYn is
42 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 43

DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
STOP
(host)
DDMARDYn
(device)
HSTROBE
(host)
DD (15:0)
(host)
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
LI
t
t
SS
t
LI
LI
t
t
DVS
MLI
t
ACK
t
IORDYZ
t
ACK
t
DVH
CRC
IDEDA[2:0]
t
ACK
IDECS0n,
IDECS1n
Note: The definitions for the DIOWn:STOP, IORDY:DDMARDYn:DSTROBE and DIORn:HDMARDYn:HSTROBE signal lines are no
longer in effect after DMARQ and DMACKn are negated.
Figure 29. Host Terminating an Ultra DMA data-out Burst
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 43
Page 44

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
DMARQ
(device)
DMACKn
(host)
t
LI
STOP
(host)
DDMARDYn
(device)
HSTROBE
(host)
DD (15:0)
(host)
IDEDA[2:0]
IDECS0n,
IDECS1n
Note: The definitions for the DIOWn:STOP, IORDY:DDMARDYn:DSTROBE and DIORn:HDMARDYn:HSTROBE signal lines are no
t
RP
t
RFS
longer in effect after DMARQ and DMACKn are negated.
Figure 30. Device Terminating an Ultra DMA data-out Burst
t
MLI
t
LI
t
MLI
t
DVS
t
ACK
t
ACK
t
IORDYZ
t
DVH
CRC
t
ACK
44 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 45

Ethernet MAC Interface
Parameter Symbol
TXCLK cycle time
TXCLK high time
TXCLK low time
TXCLK to signal transition delay time
TXCLK rise/fall time
RXCLK cycle time
RXCLK high time
RXCLK low time
RXDVAL / RXERR setup time
RXDVAL / RXERR hold time
RXCLK rise/fall time
MDC cycle time
MDC high time
MDC low time
MDC rise/fall time
MDIO setup time (STA sourced)
MDIO hold time (STA sourced)
MDC to MDIO signal transition delay time
(PHY sourced)
t
TX_per
t
TX_high
t
TX_low
t
TXd
t
TXrf
t
RX_per
t
RX_high
t
RX_low
t
RXs
t
RXh
t
RXrf
t
MDC_per
t
MDC_high
t
MDC_low
t
MDCrf
t
MDIOs
t
MDIOh
t
MDIOd
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Min Typ Max
10 Mbit
mode
100 Mbit
mode
10 Mbit
mode
100 Mbit
mode
10 Mbit
mode
100 Mbit
mode
--40040--ns
140 14 200 20 260 26 ns
140 14 200 20 260 26 ns
0 0 10 10 25 25 ns
----55ns
--40040--ns
140 14 200 20 260 26 ns
140 14 200 20 260 26 ns
1010----ns
1010----ns
----55ns
--400400--ns
160160----ns
160160----ns
----55ns
1010----ns
1010----ns
----300300ns
Unit
STA - Station - Any device that contains an IEEE 802.11 conforming Medium Access Control (MAC) and physical layer
(PHY) interface to the wireless medium.
PHY - Ethernet physical layer interface.
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 45
Page 46

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
TXCLK
TXD[3:0]/
TXEN/
TXERR
RXCLK
RXD[3:0]/
RXDVAL/
RXERR
MDC
t
TXd
t
RXs
t
TX_high
t
TX_per
t
t
RXh
TX_low
t
RX_low
t
RX_per
t
RX_high
MDIO
(Sourced
by STA)
MDC
MDIO
(Sourced
by PHY)
t
MDC_high
t
MDC_per
t
MDC_low
t
MDIOd
Figure 31. Ethernet MAC Timing Measurement
t
MDIOs
t
MDIOh
46 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 47

Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Audio Interface
The following table contains the values for the timings of each of the SPI modes.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
SCLK cycle time
SCLK high time
SCLK low time
SCLK rise/fall time
Data from master valid delay time
Data from master setup time
Data from master hold time
Data from slave setup time
Data from slave hold time
Note: The tspix_clk is programmable by the user.
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
t
clkrf
t
DMd
t
DMs
t
DMh
t
DSs
t
DSh
- tspix_clk - ns
- (tspix_clk) / 2 - ns
- (tspix_clk) / 2 - ns
1-8ns
--3ns
20 - - ns
40 - - ns
20 - - ns
40 - - ns
EP9315
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 47
Page 48

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Texas Instruments’ Synchronous Serial Format
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
SCLK
t
clk_low
SFRM
t
clkrf
SSPTXD/
SSPRXD
Microwire
SCLK
SFRM
SSPTXD
SSPRXD
t
clk_high
MSB
t
clk_per
t
clk_low
MSB LSB
4 to 16 bits
Figure 32. TI Single Transfer Timing Measurement
t
clkrf
LSB
8-bit control
0
MSB LSB
4 to 16 bits output data
Figure 33. Microwire Frame Format, Single Transfer
48 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 49

Motorola SPI
SCLK
(SPO=0)
SCLK
(SPO=1)
t
clk_high
t
clk_per
t
clk_low
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
clkrf
SSPTXD
(master)
SSPRXD
(slave)
SFRM
t
DMs
t
DMd
t
DMh
LSBMSB
t
DSs
t
DSh
MSB LSB
Figure 34. SPI Format with SPH=1 Timing Measurement
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 49
Page 50

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Inter-IC Sound - I2S
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
SCLK cycle time
SCLK high time
SCLK low time
SCLK rise/fall time
SCLK to LRCLK assert delay time
Hold between SCLK assert then LRCLK deassert
or
Hold between LRCLK deassert then SCLK assert
SDI to SCLK deassert setup time
SDI from SCLK deassert hold time
SCLK assert to SDO delay time
SDO from SCLK assert hold time
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
t
clkrf
t
LRd
t
LRh
t
SDIs
t
SDIh
t
SDOd
t
SDOh
(t
i2s_clk
(t
i2s_clk
t
i2s_clk
) / 2
) / 2
-ns
-ns
-ns
-
-
-
148ns
--3ns
0--ns
12 - - ns
0--ns
--9ns
1--ns
Note: t
SCLK
LRCLK
SDI
is programmable by the user.
i2s_clk
t
clk_high
t
clk_per
t
LRd
t
clk_low
t
SDIs
t
LRh
t
SDIh
t
clkrf
Figure 35. Inter-IC Sound (I
2
S) Timing Measurement
50 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 51

AC’97
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
ABITCLK input cycle time
ABITCLK input high time
ABITCLK input low time
ABITCLK input rise/fall time
ASDI setup to ABITCLK falling
ASDI hold after ABITCLK falling
ASDI input rise/fall time
ABITCLK rising to ASDO / ASYNC valid, C
ASYNC / ASDO rise/fall time, C
t
= 55 pF t
L
t
clk_hightclk_low
clk_per
= 55 pF t
L
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
t
clkrf
t
s
t
h
t
rfin
co
rfout
- 81.4 - ns
36 - 45 ns
36 - 45 ns
2-6ns
10 - - ns
10 - - ns
2-6ns
2 - 15 ns
2-6ns
EP9315
ABITCLK
ASDI
ASDO
ASYNC
t
clkrf
t
clkrf
t
co
t
rfout
Figure 36. AC ‘97 Configuration Timing Measurement
t
h
t
s
t
rfout
t
rfin
t
co
t
co
t
rfout
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 51
Page 52

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
LCD Interface
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
SPCLK rise/fall time
SPCLK rising edge to control signal transition time
SPCLK rising edge to data transition time
Data valid time
t
clkr
t
CD
t
DD
t
Dv
2-8ns
--3ns
- - 10 ns
t
SPCLK
-
-ns
SPCLK
HSYNC/
V_CSYNC/
BLANK/
BRIGHT
P [17:0]
t
clkrf
t
CD
t
DD
t
Dv
Figure 37. LCD Timing Measurement
t
clkrf
52 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 53

Page 54

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
JTAG
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units
TCK clock period
TCK clock high time
TCK clock low time
TMS / TDI to clock rising setup time
Clock rising to TMS / TDI hold time
JTAG port clock to output
JTAG port high impedance to valid output
JTAG port valid output to high impedance
TMS
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
t
JPs
t
JPh
t
JPco
t
JPzx
t
JPxz
100 - ns
50 - ns
50 - ns
20 - ns
45 - ns
-30ns
-30ns
-30ns
TDI
TCK
TDO
t
clk_high
t
JPzx
t
clk_per
t
clk_low
t
JPs
t
JPco
Figure 39. JTAG Timing Measurement
t
JPh
t
JPxz
54 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 55

352 Pin BGA Package Outline
352-Ball PBGA Diagram
D3
D2
D
E3 E
E2
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
S
Ø
Ø
0.30
0.10
S
BA
C
C
3
Øb
DETAIL B
-B-
-A-
e
B
(Bottom View)
(Top View)
D1
B
A
-C-
2
A1
E1
A'
A2
Figure 40. 352 Pin PBGA Pin Diagram
DETAIL A'
ddd
C
c
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 55
Page 56

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Table R. 352 Pin Diagram Dimensions
Symbol
dimension in mm dimension in inches
MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
A 2.20 2.30 2.50 0.087 0.092 0.098
A1 - 0.60 - - 0.024 A2 1.12 1.17 1.22 0.044 0.046 0.048
b - 0.75 - - 0.030 c 0.51 0.56 0.61 0.020 0.022 0.024
D 26.80 27.00 27.20 1.055 1.063 1.071
D1 - 24.13 - - 0.950 D2 23.80 24.00 24.20 0.937 0.945 0.953
D3 17.95 18.00 18.05 0.707 0.709 0.711
E 26.80 27.00 27.20 1.055 1.063 1.071
E1 - 24.13 - - 0.950 E2 23.80 24.00 24.20 0.937 0.945 0.953
E3 17.95 18.00 18.05 0.707 0.709 0.711
e - 1.27 - - 0.050 -
ddd - - 0.15 - - 0.006
q 30° TYP 30° TYP
Note: 1. Controlling Dimension: Millimeter.
2. Primary Datum C and seating plane are defined by the spherical crowns of the solder balls.
3. Dimension b is measured at the maximum solder ball diameter, parallel to Primary Datum C.
4. There shall be a minimum clearance of 0.25 mm between the edge of the solder ball and the body edge.
5. Reference Document: JEDEC MO-151, BAL-2
352 Pin BGA Pinout (Bottom View)
The following table shows the 352 pin BGA pinout. (For better understanding, compare the coordinates on the x and y
axis on Figure 40, "352 PIN BGA PINOUT", on page 57 with Figure 40, "352 Pin PBGA Pin Diagram", on page 55.
• VDD_core is CVDD.
• VDD_ring is RVDD.
• All core and ring grounds are connected together and are labelled GND.
• Other special power requirements are clearly labelled (i.e. H18=ADC_VDD and H19=ADC_GND).
• NC means that the pin is not connected.
56 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 57

57 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
1 2 34 5678910111213141516171819 20
Y HSYNC DD[1] DD[12] P[2] AD[15] DA[6] DA[4]
W P[12] P[9] DD[0] P[5] P[3] DA[7] DA[5]
V P[16] P[11] P[8] DD[15] DD[13] P[1]
U AD[0] P[15] P[10] P[7] P[6] P[4] P[0]
T DA[8] BLANK P[13] SPCLK
R AD[2] AD[1] P[17] P[14] RVDD
P AD[4] DA[10] DA[9] BRIGHT RVDD
N DA[13] DA[12] DA[11] AD[3] CVDD
M AD[7] DA[14] AD[6] AD[5] CVDD GND GND GND GND GND GND GND COL[4] COL[3] COL[6] CSN[0] M
L DA[18] DA[17] DA[16] DA[15] GND GND GND GND GND GND GND CVDD COL[5] COL[7] RSTON PRSTN L
K AD[22] DA[20] AD[21] DA[19] RVDD GND GND GND GND GND GND CVDD SYM SYP SXM SXP K
J DA[21]
DQMN[
H
SDCSN[0]SDCSN[1]SDWE
G
SDCSN[
F
E AD[23] DA[23] DA[26] CSN[6] GND GND
D AD[24] DA[25] DD[11]
C CSN[1] CSN[3] AD[20] DA[29] DD[10] DD[6] DD[2] MDC
B CSN[2] DA[31] DA[30] DA[27] DD[7] DD[3] WRN MDIO
A CSN[7] DA[28] AD[18] DD[8] DD[4]
DQMN[0]DQMN[
CASN RASN
3]
DA[22] DA[24] AD[25] RVDD GND
3]
1 2 34 5678910111213141516171819 20
DQMN[2
1]
SDCSN[
SDCLK RVDD
N
SDCLK
V_CSYNCDD[1
4]
RVD
D
RVD
D
CVD
D
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND CVDD
]
CVDD GND GND GND GND GND GND RVDD
2]
RVD
D
AD[19] DD[9] DD[5]
EN
AD[1
7]
AD[10
]
AD[11
]
AD[14]AD[12
]
AD[13
]
CVD
GND
D
CVD
GND
D
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND XTALO COL[0] COL[1] COL[2] N
CVD
D
CVDDCVD
D
AD[16]MIIRXD[2]MIITXD[
RXCLKMIIRXD[0]RXDVALMIITXD[
RDN
Figure 40. 352 PIN BGA PINOUT
3]
IDEDA[
TXEN
MIITXD[
MIITXD[
DA[1] AD[8]
IDECS1NIDEDA[
AD[9]
IDECS0NIDEDA[
DA[2]
DA[3] DA[0] DSRN BOOT[1] NC SSPRX1 INT[1]
RVDD GND GND RVDD CVDD GND INT[0]
RVDD GND GND RVDD CVDD CVDD GND ASDI DIOWN
MIIRXD[
MIIRXD[
TXCLK
3]
RXERR
1]
DTRN TDO BOOT[0] EEDAT ASDO SFRM1 RDLED USBP[1] ABITCLK Y
0]
TCK TMS EECLK SCLK1 GRLED INT[3] SLA[1] SLA[0] RXD[2] W
1]
TDI GND ASYNC SSPTX1 INT[2] RTSN USBP[0] CTSN TXD[0] V
2]
PWMO
USBM[1
CVDD GND RVDD RVDD ROW[0] ROW[3]
RVDD RVDD XTALI
RVDD RVDD EGPIO[7]
CVDD GND GND EGPIO[2]
MCWAITNMCDAENNMCADENNEGPIO[
READY MCD2 MCDIR MCELN IORDN MCWRN USBP[2] IORDY DMACKN C
0]
CRS VS1 MCD1
1]
TXERR CLD VS2
2]
14]
MCBVD
MCBVD1MCREGNEGPIO[12]EGPIO[
2
MCEHN
USBM[0] RXD[1] TXD[1] ROW[1] U
UT
RXD[0] TXD[2] ROW[2] ROW[4] T
]
RTCXTA
LI
RTCXTALOADC_VDDADC_G
WP USBM[2] ARSTN DIORN EGPIO[1] D
EGPIO[1
3]
PLL_GN
D
PLL_VD
EGPIO[9]EGPIO[10]EGPIO[11
EGPIO[4]EGPIO[6
EGPIO[0]EGPIO[3
MCRDN WAITN TRSTN B
ROW[6] ROW[7] P
D
XM YP YM J
ND
]
]
IOWRN
15]
ROW[5] R
XP H
]
EGPIO[8] F
EGPIO[5] E
MCRESE
TN
EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
G
A
Page 58

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Pin List
The following Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) ball assignment table is sorted in order of ball.
Ball Signal Ball Signal Ball Signal Ball Signal
A1 CSN[7] E9 RVDD L3 DA[16] T13 CVDD
A2 DA[28]
A3 AD[18]
A4 DD[8]
A5 DD[4]
A6 AD[17]
A7 RDN
A8 RXCLK
A9 MIIRXD[0]
A10 RXDVAL
A11 MIITXD[2]
A12 TXERR
A13 CLD
A14 VS2
A15 MCBVD1
A16 MCREGN
A17 EGPIO[12]
A18 EGPIO[15]
A19 IOWRN
A20 MCRESETN
B1 CSN[2]
B2 DA[31]
B3 DA[30]
B4 DA[27]
B5 DD[7]
B6 DD[3]
B7 WRN
B8 MDIO
B9 MIIRXD[1] G3 SDWEN M19 COL[6] V1 P[16]
B10 RXERR
B11 MIITXD[1]
B12 CRS G6 RVDD N2 DA[12] V4 DD[15]
B13 VS1
B14 MCD1
B15 MCBVD2
B16 MCEHN
B17 EGPIO[13]
B18 MCRDN
B19 WAITN
B20 TRSTN
C1 CSN[1]
C2 CSN[3]
E10 GND L4 DA[15] T14 GND
E11 GND L5 GND T15 INT[0]
E12 RVDD L8 GND T16 USBM[1]
E13 CVDD L9 GND T17 RXD[0]
E14 CVDD L10 GND T18 TXD[2]
E15 GND L11 GND T19 ROW[2]
E16 ASDI L12 GND T20 ROW[4]
E17 DIOWN L13 GND U1 AD[0]
E18 EGPIO[0] L16 CVDD U2 P[15]
E19 EGPIO[3] L17 COL[5] U3 P[10]
E20 EGPIO[5] L18 COL[7] U4 P[7]
F1 SDCSN[3] L19 RSTON U5 P[6]
F2 DA[22] L20 PRSTN U6 P[4]
F3 DA[24] M1 AD[7] U7 P[0]
F4 AD[25] M2 DA[14] U8 AD[13]
F5 RVDD M3 AD[6] U9 DA[3]
F6 GND M4 AD[5] U10 DA[0]
F7 CVDD M5 CVDD U11 DSRN
F14 CVDD M8 GND U12 BOOT[1]
F15 GND M9 GND U13 NC
F16 GND M10 GND U14 SSPRX1
F17 EGPIO[2] M11 GND U15 INT[1]
F18 EGPIO[4] M12 GND U16 PWMOUT
F19 EGPIO[6] M13 GND U17 USBM[0]
F20 EGPIO[8] M16 GND U18 RXD[1]
G1 SDCSN[0] M17 COL[4] U19 TXD[1]
G2 SDCSN[1] M18 COL[3] U20 ROW[1]
G4 SDCLK M20 CSN[0] V2 P[11]
G5 RVDD N1 DA[13] V3 P[8]
G15 RVDD N3 DA[11] V5 DD[13]
G16 RVDD N4 AD[3] V6 P[1]
G17 EGPIO[7] N5 CVDD V7 AD[14]
G18 EGPIO[9] N6 CVDD V8 AD[12]
G19 EGPIO[10] N8 GND V9 DA[2]
G20 EGPIO[11] N9 GND V10 IDECS0N
H1 DQMN[3] N10 GND V11 IDEDA[2]
H2 CASN N11 GND V12 TDI
H3 RASN N12 GND V13 GND
H4 SDCSN[2] N13 GND V14 ASYNC
58 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 59

Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
C3 AD[20] H5 CVDD N15 GND V15 SSPTX1
C4 DA[29]
C5 DD[10]
C6 DD[6]
C7 DD[2]
C8 MDC
C9 MIIRXD[3]
C10 TXCLK
C11 MIITXD[0]
C12 READY
C13 MCD2
C14 MCDIR
C15 MCELN
C16 IORDN
C17 MCWRN
C18 USBP[2]
C19 IORDY
H8 GND N16 GND V16 INT[2]
H9 GND N17 XTALO V17 RTSN
H10 GND N18 COL[0] V18 USBP[0]
H11 GND N19 COL[1] V19 CTSN
H12 GND N20 COL[2] V20 TXD[0]
H13 GND P1 AD[4] W1 P[12]
H16 RVDD P2 DA[10] W2 P[9]
H17 RTCXTALO P3 DA[9] W3 DD[0]
H18 ADC_VDD P4 BRIGHT W4 P[5]
H19 ADC_GND P5 RVDD W5 P[3]
H20 XP P6 RVDD W6 DA[7]
J1 DA[21] P15 RVDD W7 DA[5]
J2 DQMN[0] P16 RVDD W8 AD[11]
J3 DQMN[1] P17 XTALI W9 AD[9]
J4 DQMN[2] P18 PLL_VDD W10 IDECS1N
J545(0692B(R542.21997 12.06 13.98 ref0 0 02E99 32701056M Tm[(P14f0_.000S60 314)70127 12.12 13.98 ref0 0 0 scnBT/TT1 1 Tf0.00281 Tcn176.6()])]S[(7.98 331.07999 490.85999 Tm[(P18)-4330(P)-2(LL_V08.00197 0.70197 scnA[50 0 8S74]TJE1)-4705(DQMN[ 574.85999W070C14)701254C0 314)70127 12.12 13..004f0.00C2f0 0 0 scnBT9 ref0B14.20001 1224S76.94 514.200Y1279 Tm[(W9)-13.98 ref5191 Td[(C14)-5143(M)-2(CDIR)]TJET.70197 scn119 Tm.22-1.759m[(YB91 1 Tf0.0513 0 0 scn0 0 7.98 331.07999 532.85999 Tm[(P15)-5148(R)7 0.70197 s.0199997AMW])]T2T[20.(R)26(.5798 r2)EY4A57 12.06 13.98 ref0 0 02E99 32701056M Tm[(PIR)]TJET0.70170160707 12.06 107999 504.89692 -6(45(0692B(R542.21997 12.06 13.98 ref0 0 02E99 119 Tm.22-134f0_.000S60 314)70127 12.12 13.98 ref0 0 0 scnBT/TT1 1 Tf0 0 800Y 460.97998 490.85999 Tm[(W10)-47510176.94 486.17999 12.06 14.03999 ref0 0 0 scn5])0 0 8S74]TJE1)-4705(DQM0X21JE019-00S6C0 314)70127 12.12 13..004f0.00C2f0 0 0 sN07.98 0 0 7.98 401 -1.75191 Td64UX8-5R964UX0 0 7.98 -22 12.06 13.98 ref0 0 05030A463.20001 504.89Y)]TJET0.70197 0. 7.98 460.97998 490.85999 TmC16DECS1N
EP9315
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 59
Page 60

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
The following section focuses on the EP9315 pin signals
from two viewpoints - the pin usage and pad
characteristics, and the pin m ultiplexing usage. The first
table (Table S) is a summary of all the EP9315 pin
signals. The second table (Table T) illustrates the pin
signal multiplexing and configuration options.
Ta b l e S is a summary of the EP9315 pin signals, which
illustrates the pad type and pad pull type (if any). The
symbols used in the table are defined as follo ws. (Note: A
blank box means Not Applicable (NA) or, for Pull Type,
No Pull (NP).)
.
Pin Name Block
TCK JTAG I PD JTAG clock in
TDI JTAG I PD JTAG data in
TDO JTAG 4ma JTAG data out
TMS JTAG I PD JTAG test mode select
TRSTn JTAG I PD JTAG reset
BOOT[1:0] System I PD Boot mode select in
XTALI PLL A Main oscillator input
XTALO PLL A Main oscillator output
VDD_PLL PLL P Main oscillator power, 1.8V
GND_PLL PLL G Main oscillator ground
RTCXTALI RTC A RTC oscillator input
RTCXTALO RTC A RTC oscillator output
WRn E BUS 4ma SRAM Write strobe out
RDn EBUS 4ma SRAM Read / OE strobe out
WAITn EBUS I PU SRAM Wait in
AD[25:0] EBUS 8ma Shared Address bus out
DA[31:0] EBUS 8ma PU Shared Data bus in/out
CSn[3:0] EBUS 4ma PU Chip select out
CSn[7:6] EBUS 4ma PU Chip select out
DQMn[3:0] EBUS 8ma Shared data mask out
SDCLK SDRAM 8ma SDRAM clock out
SDCLKEN SDRAM 8ma SDRAM clock enable out
SDCSn[3:0] SDRAM 4ma SDRAM chip selects out
RASn SDRAM 8ma SDRAM RAS out
CASn SDRAM 8ma SDRAM CAS out
SDWEn SDRAM 8ma SDRAM write enable out
P[17:0] Raster 4ma PU Pixel data bus out
Table S. Pin Descriptions
Pad
Pull
Type
Type
Description
Under the Pad Type column:
• A - Analog pad
•P - Power pad
• G - Ground pad
• I - Pin is an input only
• I/O - Pin is input/output
• 4mA - Pin is a 4 mA output driver
• 8mA - Pin is an 8 mA output driver
• 12mA - Pin is an 12 mA output driver
See the text description for additional information about
bi-directional pins.
Under the Pull Type Column:
• PU - Resistor is a pull up to the RVDD supply
• PD - Resistor is a pull down to the RGND supply
Table S. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pad
Pin Name Block
SPCLK Raster 12ma PU Pixel clock in/out
HSYNC Raster 8ma PU Horizontal synchronization / line pulse out
V_CSYNC Raster 8ma PU
BLANK Raster 8ma PU Composite blanking signal out
BRIGHT Raster 4ma PWM brightness control out
PWMOUT PWM 8ma Pulse width modulator output
Xp, Xm ADC A Touchscreen ADC X axis
Yp, Ym ADC A Touchscreen ADC Y axis
sXp, sXm ADC A Touchscreen ADC X axis feedback
sYp, sYm ADC A Touchscreen ADC Y axis feedback
VDD_ADC ADC P Touchscreen ADC power, 3.3V
GND_ADC ADC G Touchscreen ADC ground
COL[7:0] Key 8ma PU Key matrix column inputs
ROW[7:0] Key 8ma PU Key matrix row outputs
USBp[2:0] USB A USB positive signals
USBm[2:0] USB A USB negative signals
TXD0 UART1 4ma Transmit out
RXD0 UART1 I PU Receive in
CTSn UART1 I PU Clear to send / transmit enable
DSRn UART1 I PU Data set ready / Data Carrier Detect
DTRn UART1 4ma Data Terminal Ready output
RTSn UART1 4ma Ready to send
TXD1 UART2 4ma Transmit / IrDA output
RXD1 UART2 I PU Receive / IrDA input
TXD2 UART3 4ma Transmit
RXD2 UART3 I PU Receive
MDC EMAC 4ma Management data clock
Type
Pull
Type
Vertical or composite synchronization / frame
pulse out
Description
60 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 61

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Table S. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pad
Pin Name Block
MDIO EMAC 4ma PU Management data input/output
RXCLK EMAC I PD Receive clock in
MIIRXD[3:0] EMAC I PD Receive data in
RXDVAL EMAC I PD Receive data valid
RXERR EMAC I PD Receive data error
TXCLK EMAC I PU Transmit clock in
MIITXD[3:0] EMAC I PD Transmit data out
TXEN EMAC 4ma PD Transmit enable
TXERR EMAC 4ma PD Transmit error
CRS EMAC I PD Carrier sense
CLD EMAC I PU Collision detect
GRLED LED 12ma Green LED
RDLED LED 12ma Red LED
EECLK EEPROM 4ma PU EEPROM / Two-wire Interface clock
EEDAT EEPROM 4ma PU EEPROM / Two-wire Interface data
ABITCLK AC97 8ma PD AC97 bit clock
ASYNC AC97 8ma PD AC97 frame sync
ASDI AC97 I PD AC97 Primary input
ASDO AC 97 8ma PU AC97 output
ARSTn AC97 8ma AC97 reset
SCLK1 SPI1 8ma PD SPI bit clock
SFRM1 SPI1 8ma PD SPI Frame Clock
SSPRX1 SPI1 I PD SPI input
SSPTX1 SPI1 8ma SPI output
INT[3:0] INT I PD External interrupts
PRSTn Syscon I PU Power on reset
RSTOn Syscon 4ma User Reset in out - open drain
SLA[1:0] EEPROM 4ma Flash programming voltage control
VS1 PCMCIA I PU Volta ge sense
VS2 PCMCIA I PU Volta ge sense
MCD1 PCMCIA I PU Card detect
MCD2 PCMCIA I PU Card detect
MCBVD1 PCMCIA I PU Voltage detection / status change
MCBVD2 PCMCIA I PU Voltage detection
MCDIR PCMCIA 4ma Data transceiver direction control
MCDAENn PCMCIA 4ma Data bus transceiver enable
MCADENn PCMCIA 4ma Address bus transceiver enable
MCREGn PCMCIA 4ma PU Memory card register
MCEHn PCMCIA 4ma PU Memory card high byte select
MCELn PCMCIA 4ma PU Memory card low byte select
IORDn PCMCIA 4ma PU I/O card read
IOWRn PCMCIA 4ma PU I/O card write
MCRDn PCMCIA 4ma PU Memory card read
MCWRn PCMCIA 4ma PU Memory card write
READY PCMCIA I PU Ready / interrupt
WP PCMCIA I PU Write protect
MCWAITn PCMCIA I PU Wait Input
MCRESETn PCMCIA 4ma Card reset
Type
Pull
Type
Description
Table S. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pad
Pin Name Block
EGPIO[15:0] GPIO I/O, 4 ma PU Enhanced GPIO
DD[15:8] IDE 8ma PU IDE data bus
DD7 IDE 8ma PD IDE data bus
DD[6:0] IDE 8ma PU IDE data bus
IDEDA[2:0] IDE 8ma IDE Device address output
IDECS0n IDE 8ma IDE Chip Select 0 output
IDECS1n IDE 8ma IDE Chip Select 1 output
DIORn IDE 8ma IDE Read strobe output
DIOWn IDE 8ma IDE Write strobe output
DMACKn IDE 8ma IDE DMA acknowledge output
IORDY IDE I PU IDE ready input
CVDD Power P Digital power, 1.8V
RVDD Power P Digital power, 3.3V
CGND Ground G Digital ground
RGND Ground G Digital ground
Type
Pull
Type
Description
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 61
Page 62

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Table T illustrates the pin signal multiplexing and configuration options.
Table T. Pin Multiplex Usage Information
Physical
Pin Name
COL[7:0] GPIO GPIO Port D[7:0]
ROW[7:0] GPIO GPIO Port C[7:0]
EGPIO[0] Ring Indicator Input RI
EGPIO[1] 1Hz clock monitor CLK1HZ
EGPIO[2] IDE DMA request DMARQ
EGPIO[3] Transmit Enable output / HDLC clocks TENn / HDLCCLK1 / HDLCCLK3
EGPIO[4] I2S Transmit Data 1 SDO1
EGPIO[5] I2S Receive Data 1 SDI1
EGPIO[6] I2S Transmit Data 2 SDO2
EGPIO[7] DMA Request 0 DREQ0
EGPIO[8] DMA Acknowledge 0 DACK0
EGPIO[9] DMA EOT 0 DEOT0
EGPIO[10] DMA Request 1 DREQ1
EGPIO[11] DMA Acknowledge 1 DACK1
EGPIO[12] DMA EOT 1 DEOT1
EGPIO[13] I2S Receive Data 2 SDI2
EGPIO[14] PWM 1 output PWMOUT1
EGPIO[15] IDE Device active / present DASP
ABITCLK I2S Serial clock SCLK
ASYNC I2S Frame Clock LRCK
ASDO I2S Transmit Data 0 SDO0
ASDI I2S Receive Data 0 SDI0
ARSTn I2S Master clock MCLK
SCLK1 I2S Serial clock SCLK
SFRM1 I2S Frame Clock LRCK
SSPTX1 I2S Transmit Data 0 SDO0
SSPRX1 I2S Receive Data 0 SDI0
IDEDA[2:0] GPIO GPIO Port E[7:5]
IDECS0n GPIO GPIO Port E[4]
IDECS1n GPIO GPIO Port E[3]
DIORn GPIO GPIO Port E[2]
GRLED LED GPIO Port E[1]
RDLED LED GPIO Port E[0]
DD[7:0] GPIO GPIO Port H[7:0]
DD[15:12] GPIO GPIO Port G[7:4]
SLA[1:0] GPIO GPIO Port G[3:2]
EEDAT GPIO GPIO Port G[1]
EECLK GPIO GPIO Port G[0]
FGPIO[7] GPIO VS2
FGPIO[6] GPIO READY
FGPIO[5] GPIO VS1
FGPIO[4] GPIO MCBVD2
FGPIO[3] GPIO MCBVD1
FGPIO[2] GPIO MCD2
FGPIO[1] GPIO MCD1
FGPIO[0] GPIO WP
Description Multiplex signal name
62 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
Page 63

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Acronyms and Abbreviations
The following tables list abbreviations and acronyms
used in this data sheet.
Term Definition
ADC Analog-to-Digital Converter
ALT Alternative
AMBA Advanced Micro-controller Bus Architecture
ATAPI ATA Packet Interface
CODEC COder / DECoder
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
DAC Digital-to-Analog Converter
DMA Direct-Memory Access
EBUS External Memory Bus
EEPROM Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
EMAC Ethernet Media Access Controller
Term Definition
OHCI Open Host Controller Interface
PHY Ethernet PHYsical layer interface
PIO Programmed I/O
RISC Reduced Instruction Set Computer
SDMI Secure Digital Music Initiative
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic RAM
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
SRAM Static Random Access Memory
Station - Any device that contains an IEEE 802.11
STA
TFT Thin Film Transistor
TLB Translation Lookaside Buffer
USB Universal Serial Bus
conforming Medium Access Control (MAC) and physical
layer (PHY) interface to the wireless medium
FIFO First In / First Out
FIQ Fast Interrupt Request
FLASH Fl ash memory
GPIO General Purpose I/O
HDLC High-level Data Link Control
I/F Interface
2
S
I
IC Integrated Circuit
ICE In-Circuit Emulator
IDE Integrated Drive Electronics
IEEE Institute of Electronics and Electrical Engineers
IrDA Infrared Data Association
IRQ Standard Interrupt Request
ISO International Standards Organization
JTAG Joint Test Action Group
LFSR Linear Feedback Shift Register
MII Media Independent Interface
MMU Memory Management Unit
Inter-IC Sound
Units of Measurement
Symbol Unit of Measure
°C
Hz Hertz = cycle per second
Kbps Kilobits per second
kbyte Kilobyte
kHz KiloHertz = 1000 Hz
Mbps Megabits per second
MHz MegaHertz = 1,000 kHz
µA
µs
mA
ms
mW
ns
pF
VVolt
WWatt
degree Celsius
-3
Watts
-12
-6
Ampere
-3
Ampere
-9
seconds
Farads
microAmpere = 10
microsecond = 1,000 nanoseconds = 10
milliAmpere = 10
millisecond = 1,000 microseconds = 10
milliWatt = 10
nanosecond = 10
picoFarad = 10
-6
seconds
-3
seconds
DS638PP4 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) 63
Page 64

EP9315
Enhanced Universal Platform SOC Processor
Ordering Information
The order numbers for the device are:
EP9315-CB 0
EP9315-CBZ 0
EP9315-IB -40
EP9315-IBZ -40
°C to +70°C 352-pin PBGA
°C to +70°C 352-pin PBGA Lead Free
°C to +85°C 352-pin PBGA
°C to +85°C 352-pin PBGA Lead Free
EP9315 — CBZ
Lead Material:
Z = Lead Free
Part Number
Product Line:
Embedded Processor
Note: Go to the Cirrus Logic Internet site at http://www.cirrus.com to find contact information for your local sales representative.
Package Ty pe:
B = 352-Ball, Plastic Ball Grid Array (27 mm x 27 mm)
Temperature Range:
C = Commercial Version
E = Extended Operating Version
I = Industrial Operating Version
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For all product questions and inquiries contact a Cirrus Logic Sales Representative.
To find one nearest you go to www.cirrus.com
IMPORTANT NOTICE
"Preliminary" product information describes products that are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet available. Cirrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries
("Cirrus") believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided "AS
IS" without warranty of any kind (express or implied). Customers are advised to obtain the latest versio n o f re levant information to verify, before placing orde rs, th at information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including
those pertaining to warranty, indemn ification, and limitation of liability. No resp onsibility is assumed by Cirrus for the use of this information, including use of this information
as the basis for manufac ture or s ale of an y it ems, o r for inf ri ngement of pa te nts o r oth er r ight s of thi rd p arti es. This docume nt i s t he pr oper ty o f Cir rus a nd by fur nis hin g
this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask work rights, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or other intellectual property rights.
Cirrus owns the copyrights associated with the infor mation contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only for use within your organization
with respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other products of Cirrus. This consent does not extend to other copying such as copying for general distribution, advertising or
promotional purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERT Y
OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE ("CRITICAL APP LICATIONS"). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS, MILITARY APPLICATIONS, PRODUCTS SURGICALLY IMPLANTED INTO THE BODY, AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY OR SECURITY DEVICES, LIFE
SUPPORT PRODUCTS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO BE FULLY
AT THE CUSTOMER'S RISK AND CIRRUS DISCLAIMS AND MAKES NO WAR RANTY, EXPRESS, STATUTORY OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH REGARD TO ANY CIRRUS PRODUCT THAT IS USED IN SUCH A MANNER. IF
THE CUSTOMER OR CUSTOMER'S CUSTOMER USES OR PERMITS THE USE OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN CRITICAL APPLICATIONS, CUSTOMER AGREES, BY
SUCH USE, TO FULLY INDEMNIFY CIRRUS, ITS OFFICERS, DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES, DISTRIBUTORS AND OTHER AGENTS FROM ANY AND ALL LIABILITY,
INCLUDING ATTORNEYS' FEES AND COST S, THA T MA Y RE SULT FROM OR ARISE IN CONNECTION WITH THESE US ES .
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, MaverickCrunch, MaverickKey, and th e Cirru s Logic logo d esigns a re tradem ar ks of Cirrus Log ic, Inc. All other brand and product names in this document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Microwire is a trademark of National Semiconductor Corp. National Semiconductor is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corp.
Texas Instruments is a registered tradema rk of Texas Instruments, Inc.
Motorola and SPI are registered tradema rk s of Moto ro la , Inc .
LINUX is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
64 ©Copyright 2005 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Re se r v ed) DS638PP4
 Loading...
Loading...