FEATURES
■ ARM720T Processor
—ARM7TDMI CPU
— 8 KB of four-way set-associative cache
— MMU with 64-entry TLB
— Thumb code support enabled
■ Ultra low power
— 90 mW at 74 MHz typical
— 30 mW at 18 MHz typical
— 10 mW in the Idle State
— <1 mW in the Standby State
■ Advanced audio decoder/decompression capability
— Supports bit streams with adaptive bit rates
— Allows for support of multiple audio
decompression algorithms (MP3, WMA, AAC,
ADPCM, Audible, etc.)
EP7309 Data Sheet
High-Performance,
Low-Power System on Chip
Enhanced
Digital Audio Interface
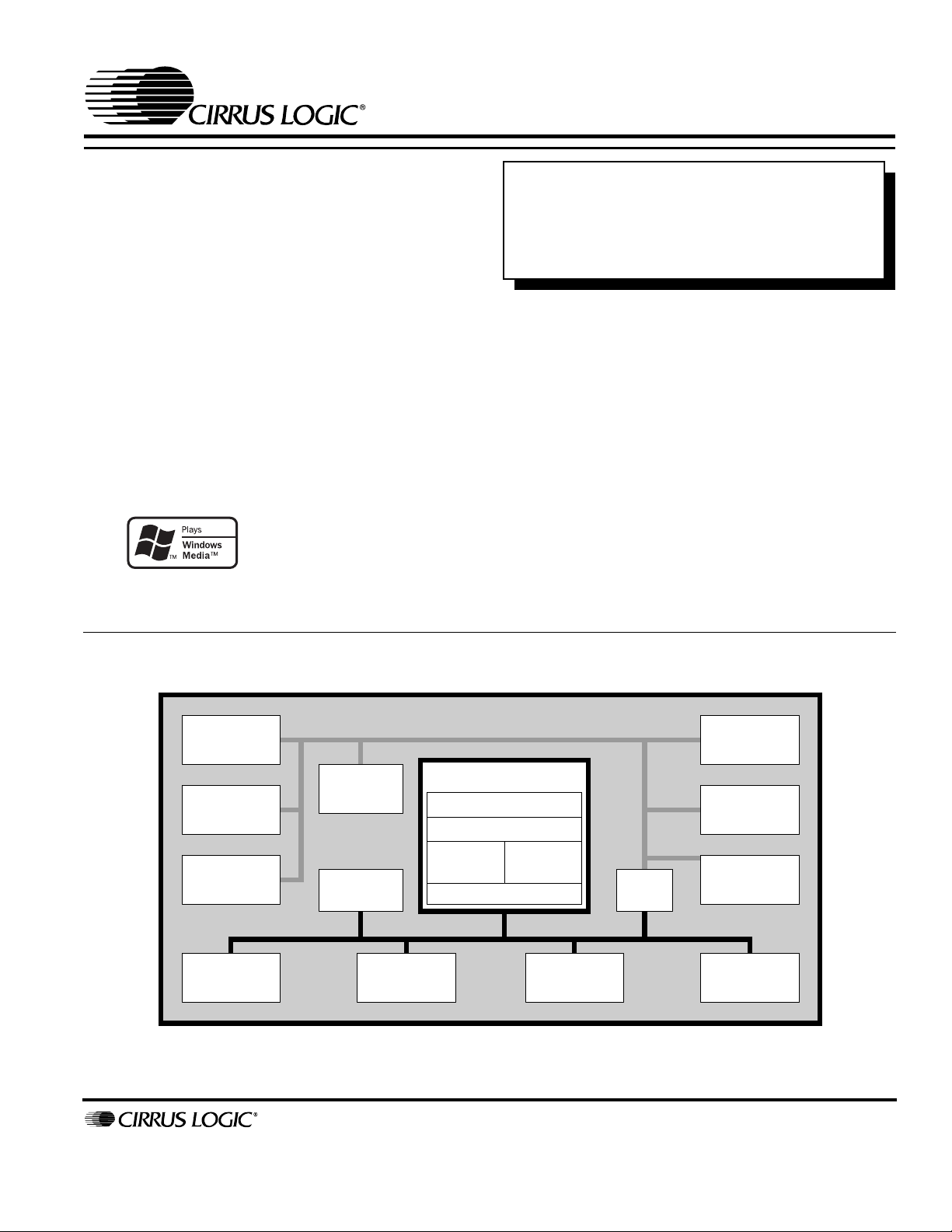
OVERVIEW
The Maverick™ EP7309 is designed for ultra-low-power
applications such as digital music players, internet
appliances, smart cellular phones or any hand-held
device that features the added capability of digital audio
decompression. The core-logic functionality of the device
is built around an ARM720T processor with 8 KB of fourway set-associative unified cache and a write buffer.
Incorporated into the ARM720T is an enhanced memory
management unit (MMU) which allows for support of
sophisticated operating systems like Microsoft
Windows® CE and Linux®.
®
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Digital
Audio
Interface
Serial
Interface
(2) UARTs
w/ IrDA
SERIAL PORTS
Internal Data Bus
MaverickKey
(cont.)
EPB Bus
Power
Management
Boot
ROM
TM
SRAM &
FLASH I/F
ICE-JTAG
ARM720T
ARM7TDMI CPU Core
8 KB
Cache
Write
Buffer
MMU
On-chip SRAM
Bus
Bridge
48 KB
Clocks &
Timers
Interrupts,
PWM & GPIO
Keypad&
Touch
Screen I/F
LCD
Controller
(cont.)
USER INTERFACE
MEMORY AND STORAGE
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7581
http://www.cirrus.com
Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) June ’01
DS507PP1
1

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
FEATURES (cont)
■ Dynamically programmable clock speeds of 18, 36, 49,
and 74 MHz
■ 48 KB of on-chip SRAM
™
■ MaverickKey
IDs
— 32-bit unique ID can be used for SDMI compliance
— 128-bit random ID
■ LCD controller
— Interfaces directly to a single-scan panel
monochrome STN LCD
— Interfaces to a single-scan panel color STN LCD
with minimal external glue logic
■ Full JTAG boundary scan and Embedded ICE
support
■ Integrated Peripheral Interfaces
— 8/32/16-bit SRAM/FLASH/ROM Interface
— Digital Audio Interface providing glueless
interface to low-power DACs, ADCs and CODECs
— Two Synchronous Serial Interfaces (SSI1, SSI2)
— CODEC Sound Interface
OVERVIEW (cont.)
—8×8Keypad Scanner
— 27 General Purpose Input/Output pins
— Dedicated LED flasher pin from the RTC
■ Internal Peripherals
— Two 16550 compatible UARTs
—IrDA Interface
—Two PWM Interfaces
—Real-time Clock
— Two general purpose 16-bit timers
— Interrupt Controller
—Boot ROM
■ Package
— 208-Pin LQFP
—256-Ball PBGA
—204-Ball TFBGA
■ The fully static EP7309 is optimized for low power
dissipation and is fabricated on a 0.25 micron CMOS
process
The EP7309 is designed for ultra-low-power operation.
Its core operates at only 2.5 V, while its I/O has an
operation range of 2.5 V–3.3 V. The device has three basic
power states: operating, idle and standby.
The EP7309 integrates an interface to enable a direct
connection to many low cost, low power, high quality
audio converters. In particular, the DAI can directly
interface with the Crystal‚ CS43L41/42/43 low-power
audio DACs and the Crystal‚ CS53L32 low-power ADC.
MaverickKey unique hardware programmed IDs are a
solution to the growing concern over secure web content
and commerce. With Internet security playing an
Some of these devices feature digital bass and treble
boost, digital volume control and compressor-limiter
functions.
important role in the delivery of digital media such as
books or music, traditional software methods are quickly
becoming unreliable. The MaverickKey unique IDs
provide OEMs with a method of utilizing specific
hardware IDs such as those assigned for SDMI (Secure
Simply by adding desired memory and peripherals to the
highly integrated EP7309 completes a low-power system
solution. All necessary interface logic is integrated on-
chip.
Digital Music Initiative) or any other authentication
mechanism.
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/corporate/contacts
Preliminary product information describes products which are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet available. Advance product information describes products which are in development and subject to development changes. Cirrus Logic, Inc. has made best efforts to ensure that the information contained in this
document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided “AS IS” without warranty of any kind (express or implied).
No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus Logic, Inc. for the use of this information, nor for infringements of patents or other rights of third parties. This document is the property
of Cirrus Logic, Inc. and implies no license under patents, copyrights, trademarks, or trade secrets. No part of this publication may be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or otherwise) without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. Items from
any Cirrus Logic website or disk may be printed for use by the user. However, no part of the printout or electronic files may be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or otherwise) without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc.Furthermore,
no part of this publication may be used as a basis for manufacture or sale of any items without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. The names of products of Cirrus
Logic, Inc. or other vendors and suppliers appearing in this document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners which may be registered in some
jurisdictions. A list of Cirrus Logic, Inc. trademarks and service marks can be found at http://www.cirrus.com.
2 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Processor Core - ARM720T
The EP7309 incorporates an ARM 32-bit RISC
microcontroller that controls a wide range of on-chip
peripherals. The processor utilizes a three-stage pipeline
consisting of fetch, decode and execute stages. Key
features include:
• ARM (32-bit) and Thumb (16-bit compressed)
instruction sets
• Enhanced MMU for Microsoft Windows CE and other
operating systems
• 8 KB of 4-way set-associative cache.
• Translation Look Aside Buffers with 64 Translated
Entries
Power Management
The EP7309 is designed for ultra-low-power operation.
Its core operates at only 2.5 V, while its I/O has an
operation range of 2.5 V–3.3 V allowing the device to
achieve a performance level equivalent to 60 MIPS. The
device has three basic power states:
• Operating — This state is the full performance
state. All the clocks and peripheral logic are
enabled.
• Idle — This state is the same as the Operating
State, except the CPU clock is halted while
waiting for an event such as a key press.
• Standby — This state is equivalent to the
computer being switched off (no display), and
the main oscillator shut down. An event such as
a key press can wake-up the processor.
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
BATOK I Battery ok input
nEXTPWR I
nPWRFL I Power fail sense input
nBATCHG I Battery changed sense input
Table A. Power Management Pin Assignments
External power supply sense
input
Digital Music Initiative) or any other authentication
mechanism.
Both a specific 32-bit ID as well as a 128-bit random ID is
programmed into the EP7309 through the use of laser
probing technology. These IDs can then be used to match
secure copyrighted content with the ID of the target
device the EP7309 is powering, and then deliver the
copyrighted information over a secure connection. In
addition, secure transactions can benefit by also
matching device IDs to server IDs. MaverickKey IDs
provide a level of hardware security required for today’s
Internet appliances.
Memory Interfaces
The EP7309 is equiped with a ROM/SRAM/FLASHstyle interface that has programmable wait-state timings
and includes burst-mode capability, with six chip selects
decoding six 256 MB sections of addressable space. For
maximum flexibility, each bank can be specified to be 8-,
16-, or 32-bits wide. This allows the use of 8-bit-wide
boot ROM options to minimize overall system cost. The
on-chip boot ROM can be used in product manufacturing
to serially download system code into system FLASH
memory. To further minimize system memory
requirements and cost, the ARM Thumb instruction set is
supported, providing for the use of high-speed 32-bit
operations in 16-bit op-codes and yielding industryleading code density.
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
nCS[5:0] O Chip select out
A[27:0] O Address output
D[31:0] I/O Data I/O
nMOE O ROM expansion OP enable
nMWE O ROM expansion write enable
HALFWORD O
WORD O Word access select output
WRITE O Transfer direction
Table B. Static Memory Interface Pin Assignments
Halfword access select
output
MaverickKey™ Unique ID
MaverickKey unique hardware programmed IDs are a
solution to the growing concern over secure web content
and commerce. With Internet security playing an
important role in the delivery of digital media such as
books or music, traditional software methods are quickly
becoming unreliable. The MaverickKey unique IDs
provide OEMs with a method of utilizing specific
Digital Audio Capability
The EP7309 uses its powerful 32-bit RISC processing
engine to implement audio decompression algorithms in
software. The nature of the on-board RISC processor, and
the availability of efficient C-compilers and other
software development tools, ensures that a wide range of
audio decompression algorithms can easily be ported to
and run on the EP7309
hardware IDs such as those assigned for SDMI (Secure
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 3
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UARTs)
The EP7309 includes two 16550-type UARTs for RS-232
serial communications, both of which have two 16-byte
FIFOs for receiving and transmitting data. The UARTs
support bit rates up to 115.2 kbps. An IrDA SIR protocol
encoder/decoder can be optionally switched into the
RX/TX signals to/from UART 1 to enable these signals
to drive an infrared communication interface directly.
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
TXD[1] O UART 1 transmit
RXD[1] I UART 1 receive
CTS I UART 1 clear to send
DCD I UART 1 data carrier detect
DSR I UART 1 data set ready
TXD[2] O UART 2 transmit
RXD[2] I UART 2 receive
LEDDRV O Infrared LED drive output
PHDIN I Photo diode input
Table C. Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters Pin
Assignments
Digital Audio Interface (DAI)
The EP7309 integrates an interface to enable a direct
connection to many low cost, low power, high quality
audio converters. In particular, the DAI can directly
interface with the Crystal
audio DACs and the Crystal
Some of these devices feature digital bass and treble
boost, digital volume control and compressor-limiter
functions.
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
SCLK O Serial bit clock
SDOUT O Serial data out
SDIN I Serial data in
LRCK O Sample clock
MCLKIN I Master clock input
MCLKOUT O Master clock output
Table D. DAI Interface Pin Assignments
‚
CS43L41/42/43 low-power
‚
CS53L32 low-power ADC.
CODEC Interface
The EP7309 includes an interface to telephony-type
CODECs for easy integration into voice-over-IP and
other voice communications systems. The CODEC
interface is multiplexed to the same pins as the DAI and
SSI2.
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
PCMCLK O Serial bit clock
PCMOUT O Serial data out
PCMIN I Serial data in
PCMSYNC O Frame sync
Table E. CODEC Interface Pin Assignments
Note: See Table Q on page 7 for information on pin
multiplexes.
SSI2 Interface
An additional SPI/Microwire1-compatible interface is
available for both master and slave mode
communications. The SSI2 unit shares the same pins as
the DAI and CODEC interfaces through a multiplexer.
• Synchronous clock speeds of up to 512 kHz
• Separate 16 entry TX and RX half-word wide FIFOs
• Half empty/full interrupts for FIFOs
• Separate RX and TX frame sync signals for
asymmetric traffic
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
SSICLK I/O Serial bit clock
SSITXDA O Serial data out
SSIRXDA I Serial data in
SSITXFR I/O Transmit frame sync
SSIRXFR I/O Receive frame sync
Table F. SSI2 Interface Pin Assignments
Note: See Table Q on page 7 for information on pin
multiplexes.
Note: See Table Q on page 7 for information on pin
multiplexes.
4 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Synchronous Serial Interface
• ADC (SSI) Interface: Master mode only; SPI and
Microwire1-compatible (128 kbps operation)
• Selectable serial clock polarity
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
ADCLK O SSI1 ADC serial clock
ADCIN I SSI1 ADC serial input
ADCOUT O SSI1 ADC serial output
nADCCS O SSI1 ADC chip select
SMPCLK O SSI1 ADC sample clock
Table G. Serial Interface Pin Assignments
LCD Controller
A DMA address generator is provided that fetches video
display data for the LCD controller from memory. The
display frame buffer start address is programmable,
allowing the LCD frame buffer to be in SDRAM, internal
SRAM or external SRAM.
• Interfaces directly to a single-scan panel monochrome
STN LCD
• Interfaces to a single-scan panel color STN LCD with
minimal external glue logic
• Panel width size is programmable from 32 to 1024
pixels in 16-pixel increments
• Video frame buffer size programmable up to
128 KB
• Bits per pixel of 1, 2, or 4 bits
• Column outputs can be individually set high with the
remaining bits left at high-impedance
• Column outputs can be driven all-low, all-high, or allhigh-impedance
• Keyboard interrupt driven by OR'ing together all Port
A bits
• Keyboard interrupt can be used to wake up the
system
×8 keyboard matrix usable with no external logic,
• 8
extra keys can be added with minimal glue logic
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
COL[7:0] O Keyboard scanner column drive
Table I. Keypad Interface Pin Assignments
Interrupt Controller
When unexpected events arise during the execution of a
program (i.e., interrupt or memory fault) an exception is
usually generated. When these exceptions occur at the
same time, a fixed priority system determines the order
in which they are handled. The EP7309 interrupt
controller has two interrupt types: interrupt request
(IRQ) and fast interrupt request (FIQ). The interrupt
controller has the ability to control interrupts from 22
different FIQ and IRQ sources.
• Supports 22 interrupts from a variety of sources (such
as UARTs, SSI1, and key matrix.)
• Routes interrupt sources to the ARM720T’s IRQ or
FIQ (Fast IRQ) inputs
• Five dedicated off-chip interrupt lines operate as level
sensitive interrupts
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
CL1 O LCD line clock
CL2 O LCD pixel clock out
DD[3:0] O LCD serial display data bus
FRM O LCD frame synchronization pulse
M O LCD AC bias drive
Table H. LCD Interface Pin Assignments
64-Keypad Interface
Matrix keyboards and keypads can be easily read by the
EP7309. A dedicated 8-bit column driver output
generates strobes for each keyboard column signal. The
pins of Port A, when configured as inputs, can be
selectively OR'ed together to provide a keyboard
interrupt that is capable of waking the system from a
STANDBY or IDLE state.
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 5
.
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
nEINT[2:1] I External interrupt
EINT[3] I External interrupt
nEXTFIQ I External Fast Interrupt input
nMEDCHG/nBROM (Note) I Media change interrupt input
Table J. Interrupt Controller Pin Assignments
Note: Pins are multiplexed. See Table R on page 7 for more
information.
Real-Time Clock
The EP7309 contains a 32-bit Real Time Clock (RTC) that
can be written to and read from in the same manner as
the timer counters. It also contains a 32-bit output match
register which can be programmed to generate an
interrupt.
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
• Driven byan external 32.768 kHz crystal oscillator
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
Pin Mnemonic Pin Description
RTCIN Real-Time Clock Oscillator Input
RTCOUT Real-Time Clock Oscillator Output
VDDRTC Real-Time Clock Oscillator Power
VSSRTC Real-Time Clock Oscillator Ground
Table K. Real-Time Clock Pin Assignments
PLL and Clocking
• Processor and Peripheral Clocks operate from a single
3.6864 MHz crystal or external 13 MHz clock
• Programmable clock speeds allow the peripheral bus
to run at 18 MHz when the processor is set to 18 MHz
and at 36 MHz when the processor is set to 36, 49 or
74 MHz
Pin Mnemonic Pin Description
MOSCIN Main Oscillator Input
MOSCOUT Main Oscillator Output
VDDOSC Main Oscillator Power
VSSOSC Main Oscillator Ground
Table L. PLL and Clocking Pin Assignments
DC-to-DC converter interface (PWM)
PA[7:0] I GPIO port A
PB[7:0] I GPIO port B
PD[0]/LEDFLSH (Note) I/O GPIO port D
PD[5:1] I/O GPIO port D
PD[7:6]/SDQM[1:0] (Note) I/O GPIO port D
PE[1:0]/BOOTSEL[1:0] (Note) I GPIO port E
PE[2]/CLKSEL (Note) I GPIO port E
Table N. General Purpose Input/Output Pin Assignments
Note: Pins are multiplexed. See Table R on page 7 for more
information.
Hardware debug Interface
• Full JTAG boundary scan and Embedded ICE
support
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
TCLK I JTAG clock
TDI I JTAG data input
TDO O JTAG data output
nTRST I JTAG async reset input
TMS I JTAG mode select
Table O. Hardware Debug Interface Pin Assignments
• Provides two 96 kHz clock outputs with
programmable duty ratio (from 1-in-16 to 15-in-16)
that can be used to drive a positive or negative DC to
DC converter
LED Flasher
A dedicated LED flasher module can be used to generate
a low frequency signal on Port D pin 0 for the purpose of
blinking an LED without CPU intervention. The LED
flasher feature is ideal as a visual annunciator in battery
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
DRIVE[1:0] I/O PWM drive output
FB[1:0] I PWM feedback input
Table M. DC-to-DC Converter Interface Pin Assignments
Timers
powered applications, such as a voice mail indicator on a
portable phone or an appointment reminder on a PDA.
• Software adjustable flash period and duty cycle
• Operates from 32 kHz RTC clock
• Will continue to flash in IDLE and STANDBY states
• 4 mA drive current
• Internal (RTC) timer
• Two internal 16-bit programmable hardware count-
down timers
General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
• Three 8-bit and one 3-bit GPIO ports
• Supports scanning keyboard matrix
6 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
Pin Mnemonic I/O Pin Description
PD[0]/LEDFLSH (Note) O LED flasher driver
Table P. LED Flasher Pin Assignments
Note: Pins are multiplexed. See Table R on page 7 for more
information.
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Internal Boot ROM
The internal 128 byte Boot ROM facilitates download of
saved code to the on-board SRAM/FLASH.
Packaging
The EP7309 is available in a 208-pin LQFP package, 256ball PBGA package or a 204-ball TFBGA package.
Pin Multiplexing
The following table shows the pin multiplexing of the
DAI, SSI2 and the CODEC. The selection between SSI2
and the CODEC is controlled by the state of the SERSEL
bit in SYSCON2. The choice between the SSI2, CODEC,
and the DAI is controlled by the DAISEL bit in SYSCON3
(see the EP7309 User’s Manual for more information).
Pin
Mnemonic
SSICLK I/O SCLK SSICLK PCMCLK
SSITXDA O SDOUT SSITXDA PCMOUT
SSIRXDA I SDIN SSIRXDA PCMIN
Table Q. DAI/SSI2/CODEC Pin Multiplexing
I/O DAI SSI2 CODEC
Pin
Mnemonic
SSITXFR I/O LRCK SSITXFR PCMSYNC
SSIRXFR I MCLKIN SSIRXFR p/u
BUZ O MCLKOUT
Table Q. DAI/SSI2/CODEC Pin Multiplexing
I/O DAI SSI2 CODEC
The following table shows the pins that have been
multiplexed in the EP7309.
Signal Block Signal Block
RUN
nMEDCHG
PD[0] GPIO LEDFLSH LED Flasher
PE[1:0] GPIO BOOTSEL[1:0]
PE[2] GPIO CLKSEL
System
Configuration
Interrupt
Controller
Table R. Pin Multiplexing
CLKEN
nBROM
System
Configuration
Boot ROM
select
System
Configuration
System
Configuration
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 7
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
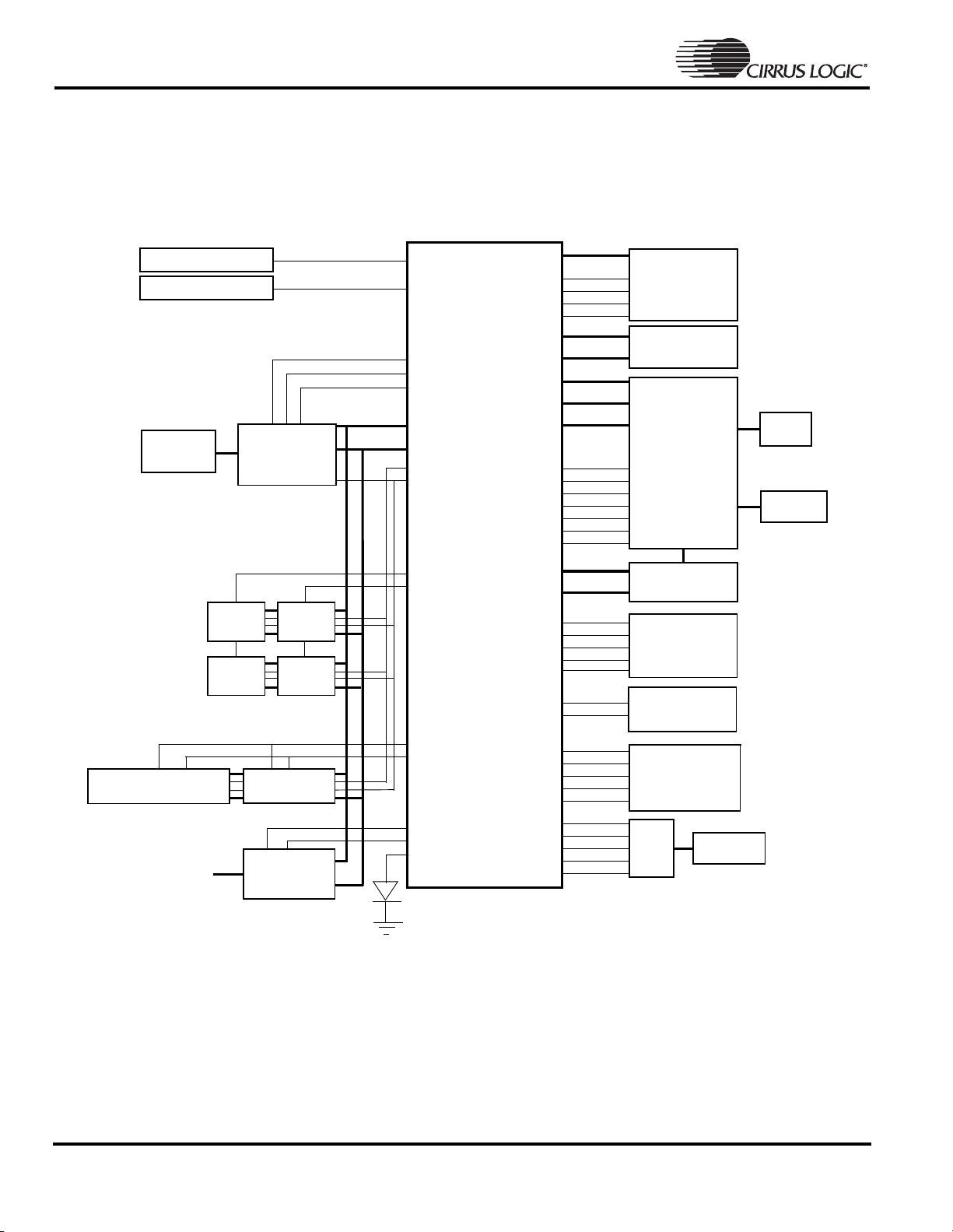
System Design
As shown in system block diagram, simply adding
desired memory and peripherals to the highly integrated
CRYSTAL
CRYSTAL
PC CARD
SOCKET
EXTERNAL MEMORYMAPPED EXPANSION
ADDITIONAL I/O
PC CARD
CONTROLLER
×16
FLASH
×16
FLASH
BUFFERS
BUFFERS
LATCHES
×16
FLASH
×16
FLASH
AND
MOSCIN
RTCIN
nCS[4]
PB0
EXPCLK
D[0-31]
A[0-27]
nMOE
WRITE
nCS[0]
nCS[1]
CS[n]
WORD
nCS[2]
nCS[3]
LEDFLSH
EP7309 completes a low-power system solution. All
necessary interface logic is integrated on-chip.
DD[0-3]
COL[0-7]
PA[0-7]
PB[0-7]
PD[0-7]
PE[0-2]
nPWRFL
BATOK
nEXTPWR
EP7309
nBATCHG
WAKEUP
DRIVE[0-1]
FB[0-1]
SSICLK
SSITXFR
SSITXDA
SSIRXDA
SSIRXFR
LEDDRV
RXD1/2
ADCCLK
nADCCS
ADCOUT
SMPCLK
CL1
CL2
FRM
nPOR
RUN
PHDIN
TXD1/2
DSR
CTS
DCD
ADCIN
M
LCD
KEYBOARD
POWER
SUPPLY UNIT
AND
COMPARATORS
DC-TO-DC
CONVERTERS
CODEC/SSI2/
DAI
IR LED AND
PHOTODIODE
2× RS-232
TRANSCEIVERS
ADC
DIGITIZER
DC
INPUT
BATTERY
Figure 1. A Maximum EP7309 Based System
Note: A system can only use one of the following peripheral
interfaces at any given time: SSI2,CODEC or DAI.
8 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
DC Core, PLL, and RTC Supply Voltage 2.9 V
DC I/O Supply Voltage (Pad Ring) 3.6 V
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
DC Pad Input Current
Storage Temperature, No Power –40
±10 mA/pin; ±100 mA cumulative
°C to +125°C
Recommended Operating Conditions
DC core, PLL, and RTC Supply Voltage 2.5 V
DC I/O Supply Voltage (Pad Ring) 2.3 V - 3.6 V
DC Input / Output Voltage O–I/O supply voltage
Operating Temperature
± 0.2 V
Extended -20
Industrial -40
°C to +70°C; Commercial 0°C to +70°C;
°C to +85°C
DC Characteristics
All characteristics are specified at VDD = 2.5 V and VSS = 0 V over an operating temperature of 0°C to +70°C for all
frequencies of operation. The current consumption figures relate to typical conditions at 2.5 V, 18.432 MHz operation
with the PLL switched “on.”
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Conditions
VIH CMOS input high voltage
0.65
× V
DDIO
V
DDIO
+ 0.3
V
V
DDIO
= 2.5 V
× V
VIL CMOS input low voltage -0.3
VT+
VT-
Vhst Schmitt trigger hysteresis 0.1 0.4 V VIL to VIH
VOH
VOL
IIN
IOZ
CIN Input capacitance 8 10.0 pF
Schmitt trigger positive going
threshold
Schmitt trigger negative going
threshold
a
CMOS output high voltage
Output drive 1
Output drive 2
CMOS output low voltage
Output drive 1
Output drive 2
Input leakage current
Bidirectional 3-state leakage
current
b c
a
a
a
a
a
1.6 (Typ) 2.0 V
0.8 1.2 (Typ) V
VDD – 0.2
2.5
2.5
25 100 µA
0.25
DDIO
0.3
0.5
0.5
1.0 µA
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
= 2.5 V
V
DDIO
IOH = 0.1 mA
IOH = 4 mA
IOH = 12 mA
IOL = –0.1 mA
IOL = –4mA
IOL = –12 mA
VIN = V
VOUT = V
or GND
DD
DD
or GND
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 9
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Conditions
COUT Output capacitance 8 10.0 pF
CI/O Transceiver capacitance 8 10.0 pF
Only 32 kHz oscillator running,
Cache disabled, all other I/O
static, VIH = V
VIL = GND ± 0.1 V
IDD
Standby current consumption
Core, Osc, RTC @2.5 V
standby
I/O @ 3.3 V
TBD
TBD
300 µA
Both oscillators running, CPU
static, Cache disabled, LCD
refresh active, VIH = V
VIL = GND ± 0.1 V
IDD
Idle current consumption
Core, Osc, RTC @2.5 V
idle
I/O @ 2.5 V
TBD
TBD
4.2 mA
At 13 MHz
IDD
Operating current consumption
Core, Osc, RTC @2.5 V
operatin
I/O @ 3.3 V
TBD
TBD
mA
All system active, running typical
program, cache disabled, and
LCD inactive
Minimum standby voltage for
V
DDstandby
Standby supply voltage TBD V
state retention and RTC
operation only
a. See Table S on page 23.
b. Assumes buffer has no pull-up or pull-down resistors.
c. The leakage value given assumes that the pin is configured as an input pin but is not currently being driven.
Note: 1) All power dissipation values can be derived from taking the particular IDD current and multiplying by 2.5 V.
2) The RTC of the EP7309 should be brought up at room temperature. This is required because the RTC OSC will NOT function
properly if it is brought up at –40
°C. Once operational, it will continue to operate down to –20°C extended and 0°C
commercial.
3) A typical design will provide 3.3 V to the I/O supply (i.e., V
IO), and 2.5 V to the remaining logic. This is to allow the I/O to be
DD
compatible with 3.3 V powered external logic.
4) Pull-up current = 50 µA typical at V
= 3.3 V.
DD
± 0.1 V,
DD
± 0.1 V,
DD
10 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Timings
Timing Diagram Conventions
This data sheet contains one or more timing diagrams. The following key explains the components used in these
diagrams. Any variations are clearly labelled when they occur. Therefore, no additional meaning should be attached
unless specifically stated.
Clock
High to Low
High/Low to High
Bus Change
Bus Valid
Undefined/Invalid
Valid Bus to Tristate
Bus/Signal Omission
Timing Conditions
Unless specified otherwise, the following conditions are true for all timing measurements. All characteristics are
specified at V
marked with a # will be significantly different for 13 MHz mode because the EXPCLK is provided as an input rather
than generated internally. These timings are estimated at present. The timing values are referenced to 1/2 V
= 2.3 - 2.7 V and VSS = 0 V over an operating temperature of 0°C to +70°C. Those characteristics
DD
.
DD
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 11
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Static Memory
Figure 2 through Figure 5 define the timings associated with all phases of the Static Memory. The following table
contains the values for the timings of each of the Static Memory modes.
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
EXPCLK rising edge to nCS assert delay time
EXPCLK falling edge to nCS deassert hold time
EXPCLK rising edge to A assert delay time
EXPCLK falling edge to A deassert hold time
EXPCLK rising edge to nMWE assert delay time
EXPCLK rising edge to nMWE deassert hold time
EXPCLK falling edge to nMOE assert delay time
EXPCLK falling edge to nMOE deassert hold time
EXPCLK falling edge to HALFWORD deassert delay time
EXPCLK falling edge to WORD assert delay time
EXPCLK rising edge to data valid delay time
EXPCLK falling edge to data invalid delay time
Data setup to EXPCLK falling edge time
EXPCLK falling edge to data hold time
t
CSd
t
CSh
t
Ad
t
Ah
t
MWd
t
MWh
t
MOEd
t
MOEh
t
HWd
t
WDd
t
Dv
t
Dnv
t
Ds
t
Dh
TBD 8 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 8 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 4 TBD ns
TBD 20 TBD ns
TBD 8 TBD ns
TBD - TBD ns
TBD - TBD ns
EXPCLK rising edge to WRITE assert delay time
EXPREADY setup to EXPCLK falling edge time
EXPCLK falling edge to EXPREADY hold time
t
WRd
t
t
EXs
EXh
TBD 8 TBD ns
TBD - TBD ns
TBD - TBD ns
12 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
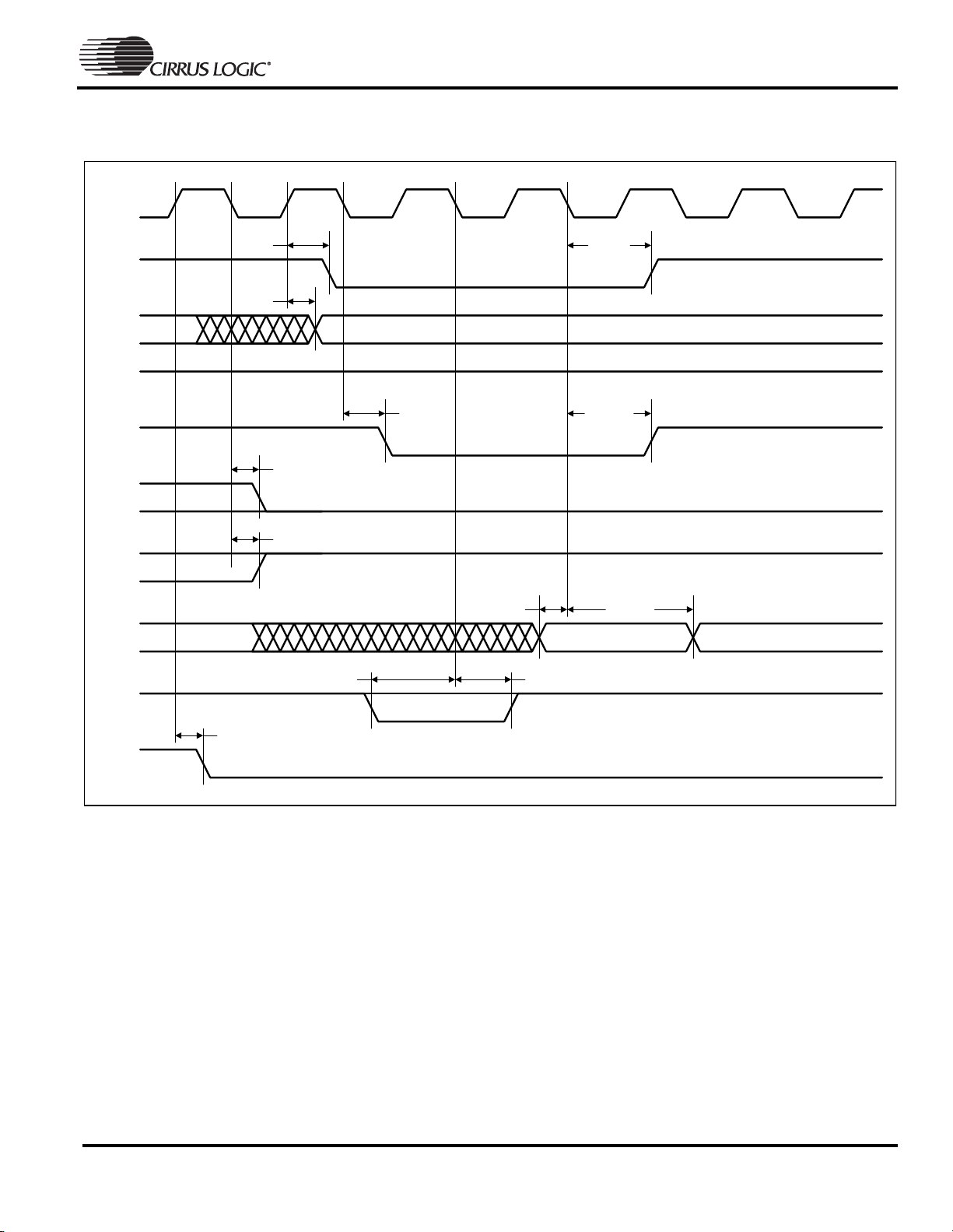
Static Memory Single Read Cycle
EXPCLK
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
nCS
A
nMWE
nMOE
HALF
WORD
WORD
D
EXPRDY
t
CSd
t
t
CSh
Ad
t
MOEh
t
Dh
t
t
HWd
WDd
t
MOEd
t
Ds
t
EXs
t
EXh
t
WRd
WRITE
Figure 2. Static Memory Single Read Cycle Timing Measurement
Note: 1. The cycle time can be extended by integer multiples of the clock period (27 ns at 36 MHz, 54 ns at 18.432 MHz, and
77 ns at 13 MHz), by either driving EXPRDY low and/or by programming a number of wait states. EXPRDY is sampled on
the falling edge of EXPCLK before the data transfer. If low at this point, the transfer is delayed by one clock period where
EXPRDY is sampled again. EXPCLK need not be referenced when driving EXPRDY, but is shown for clarity.
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 13
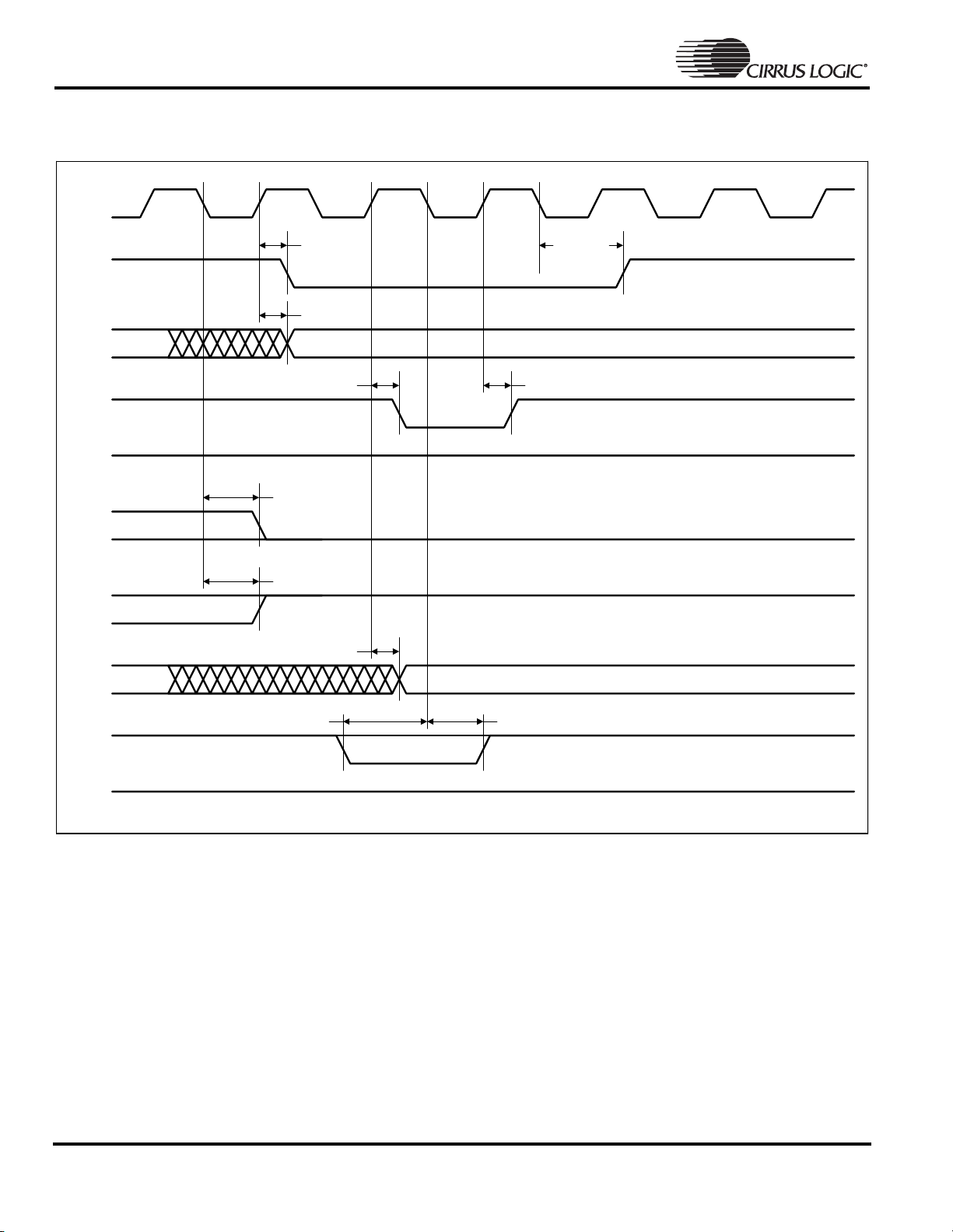
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Static Memory Single Write Cycle
EXPCLK
nCS
nMWE
nMOE
HALF
WORD
WORD
t
CSd
t
Ad
t
CSh
A
t
t
HWd
WDd
t
MWd
t
Dv
t
MWh
D
t
EXs
t
EXh
EXPRDY
WRITE
Figure 3. Static Memory Single Write Cycle Timing Measurement
Note: 1. The cycle time can be extended by integer multiples of the clock period (27 ns at 36 MHz, 54 ns at 18.432 MHz, and
77 ns at 13 MHz), by either driving EXPRDY low and/or by programming a number of wait states. EXPRDY is sampled on
the falling edge of EXPCLK before the data transfer. If low at this point, the transfer is delayed by one clock period where
EXPRDY is sampled again. EXPCLK need not be referenced when driving EXPRDY, but is shown for clarity.
2. Zero wait states for sequential writes is not permitted for memory devices which use nMWE pin, as this cannot be driven with
valid timing under zero wait state conditions.
14 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

Static Memory Burst Read Cycle
EXPCLK
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
nCS
A
nMWE
nMOE
HALF
WORD
WORD
D
EXPRDY
WRITE
t
CSd
t
t
CSh
t
Ad
t
MOEd
t
HWd
t
WDd
t
Ah
tDst
t
EXstEXh
t
WRd
Ah
Dh
t
Ds
t
Ah
t
MOEh
t
Dh
t
t
Ds
Dh
t
t
Ds
Dh
Figure 4. Static Memory Burst Read Cycle Timing Measurement
Note: 1. Four cycles are shown in the above diagram (minimum wait states, 1-0-0-0). This is the maximum number of consecutive
cycles that can be driven. The number of consecutive cycles can be programmed from 2 to 4, inclusively.
2. The cycle time can be extended by integer multiples of the clock period (27 ns at 36 MHz, 54 ns at 18.432 MHz, and
77 ns at 13 MHz), by either driving EXPRDY low and/or by programming a number of wait states. EXPRDY is sampled on
the falling edge of EXPCLK before the data transfer. If low at this point, the transfer is delayed by one clock period where
EXPRDY is sampled again. EXPCLK need not be referenced when driving EXPRDY, but is shown for clarity.
3. Consecutive reads with sequential access enabled are identical except that the sequential access wait state field is used to
determine the number of wait states, and no idle cycles are inserted between successive non-sequential ROM/expansion
cycles. This improves performance so the SQAEN bit should always be set where possible.
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 15

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Static Memory Burst Write Cycle
EXPCLK
nCS
A
nMWE
nMOE
HALF
WORD
WORD
D
EXPRDY
t
t
HWd
WDd
t
EXs
t
t
CSd
t
Ad
MWd
t
t
CSh
t
Ah
t
MWd
t
MWh
Dv
t
Dnv
t
EXh
t
Dv
t
Ah
t
MWd
t
MWh
t
Dnv
t
Dv
t
Dnv
t
Ah
t
MWd
t
MWh
t
Dv
t
MWh
WRITE
Figure 5. Static Memory Burst Write Cycle Timing Measurement
Note: 1. Four cycles are shown in the above diagram (minimum wait states, 1-1-1-1). This is the maximum number of consecutive
cycles that can be driven. The number of consecutive cycles can be programmed from 2 to 4, inclusively.
2. The cycle time can be extended by integer multiples of the clock period (27 ns at 36 MHz, 54 ns at 18.432 MHz, and
77 ns at 13 MHz), by either driving EXPRDY low and/or by programming a number of wait states. EXPRDY is sampled on
the falling edge of EXPCLK before the data transfer. If low at this point, the transfer is delayed by one clock period where
EXPRDY is sampled again. EXPCLK need not be referenced when driving EXPRDY, but is shown for clarity.
3. Zero wait states for sequential writes is not permitted for memory devices which use nMWE pin, as this cannot be driven with
valid timing under zero wait state conditions.
16 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
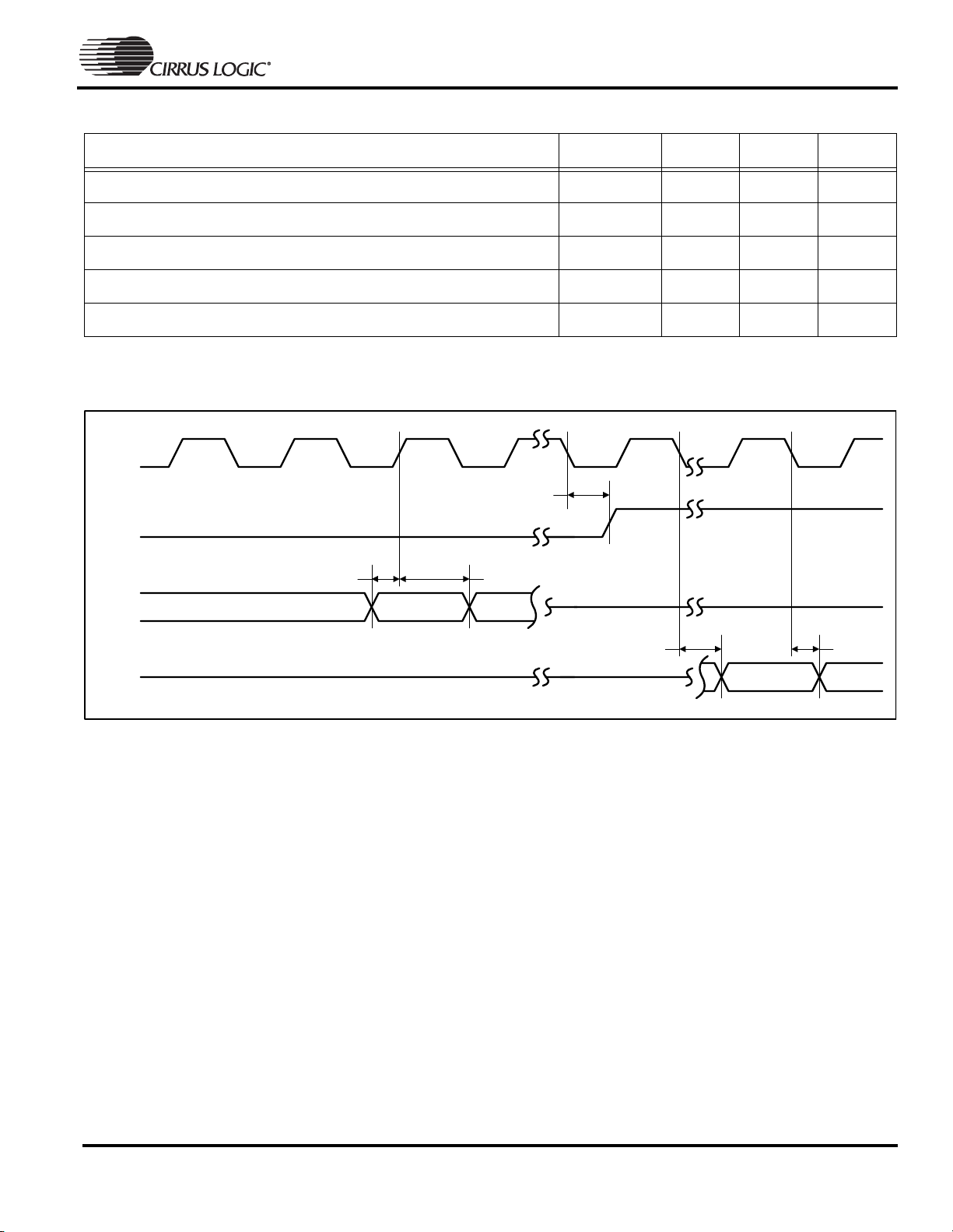
SSI1 Interface
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
ADCCLK falling edge to nADCCSS deassert delay time
ADCIN data setup to ADCCLK rising edge time
ADCIN data hold from ADCCLK rising edge time
ADCCLK falling edge to data valid delay time
ADCCLK falling edge to data invalid delay time
ADC
CLK
nADC
CSS
t
INs
ADCIN
t
Cd
t
INs
t
INh
t
Ovd
t
Od
t
Cd
t
INh
TBD TBD ns
TBD TBD ns
TBD TBD ns
TBD TBD ns
TBD TBD ns
ADC
OUT
Figure 6. SSI1 Interface Timing Measurement
t
Ovd
t
Od
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 17

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
SSI2 Interface
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
SSICLK period (slave mode)
SSICLK high time
SSICLK low time
SSICLK rise/fall time
SSICLK rising edge to RX and/or TX frame sync high time
SSICLK rising edge to RX and/or TX frame sync low time
SSIRXFR and/or SSITXFR period
SSIRXDA setup to SSICLK falling edge time
SSIRXDA hold from SSICLK falling edge time
SSICLK rising edge to SSITXDA data valid delay time
SSITXDA valid time
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
t
clkrf
t
FRd
t
FRa
t
FR_per
t
RXs
t
RXh
t
TXd
t
TXv
0 512 ns
925 1025 ns
925 1025 ns
7ns
528 ns
448 ns
750 ns
30 ns
40 ns
80 ns
ns
SSI
CLK
SSIRXFR/
SSITXFR
SSI
RXDA
SSI
TXDA
t
FRd
t
clk_per
t
clkrf
t
FRa
t
RXh
t
RXs
t
TXd
D7
t
TXv
t
clk_high
t
FR_per
D2
D2 D1
t
clk_low
D1D7
D0
D0
Figure 7. SSI2 Interface Timing Measurement
18 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

LCD Interface
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
CL[1] falling to CL[2] falling time
LCD CL[2] low time
LCD CL[2] high time
CL[2] falling to CL[1] rising delay time
CL[1] falling to CL[2] rising delay time
LCD CL[1] high time
CL[1] falling to FRM transition time
CL[1] falling to M transition time
CL[2] rising to DD (display data) transition time
CL[2]
t
clk
t
clk_low
t
clk_high
t
CL1d
t
CL2d
t
CL2h
t
FRMd
t
Md
t
DDd
t
clk
t
clk_low
200 6,950 ns
80 3,475 ns
80 3,475 ns
025ns
80 3,475 ns
80 3,475 ns
300 10,425 ns
− 10 20 ns
− 10 20 ns
t
clk_high
CL[1]
FRM
DD [3:0]
t
CL1d
t
CL2h
t
CL2d
t
FRMd
t
Md
M
t
DDd
Figure 8. LCD Controller Timing Measurement
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 19

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
JTAG
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units
TCK clock period
TCK clock high time
TCK clock low time
JTAG port setup time
JTAG port hold time
JTAG port clock to output
JTAG port high impedance to valid output
JTAG port valid output to high impedance
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
TCK
TMS
t
clk_per
t
clk_high
t
clk_low
t
JPs
t
JPh
t
JPco
t
JPzx
t
JPxz
t
t
JPs
JPh
100 - ns
50 - ns
50 - ns
20 - ns
45 - ns
-25ns
-25ns
-25ns
TDI
t
JPzx
t
JPco
t
JPxz
TDO
Figure 9. JTAG Timing Measurement
20 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

Packages
208-Pin LQFP Package Characteristics
208-Pin LQFP Package Specifications
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
29.60 (1.165)
30.40 (1.197)
27.80 (1.094)
28.20 (1.110)
0.17 (0.007)
0.27 (0.011)
27.80 (1.094)
28.20 (1.110)
29.60 (1.165)
30.40 (1.197)
0.50
(0.0197)
BSC
0.09 (0.004)
0.20 (0.008)
Pin 208
Pin 1
1.40 (0.055)
1.60 (0.063)
Pin 1 Indicator
0.45 (0.018)
0.75 (0.030)
EP7309
208-Pin LQFP
1.35 (0.053)
1.45 (0.057)
1.00 (0.039) BSC
0.05 (0.002)
0.15 (0.006)
0° MIN
7° MAX
Figure 10. 208-Pin LQFP Package Outline Drawing
Note: 1) Dimensions are in millimeters (inches), and controlling dimension is millimeter.
2) Drawing above does not reflect exact package pin count.
3) Before beginning any new design with this device, please contact Cirrus Logic for the latest package information.
4) For pin locations, please see Figure 11. For pin descriptions see the EP7309 User’s Manual.
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 21
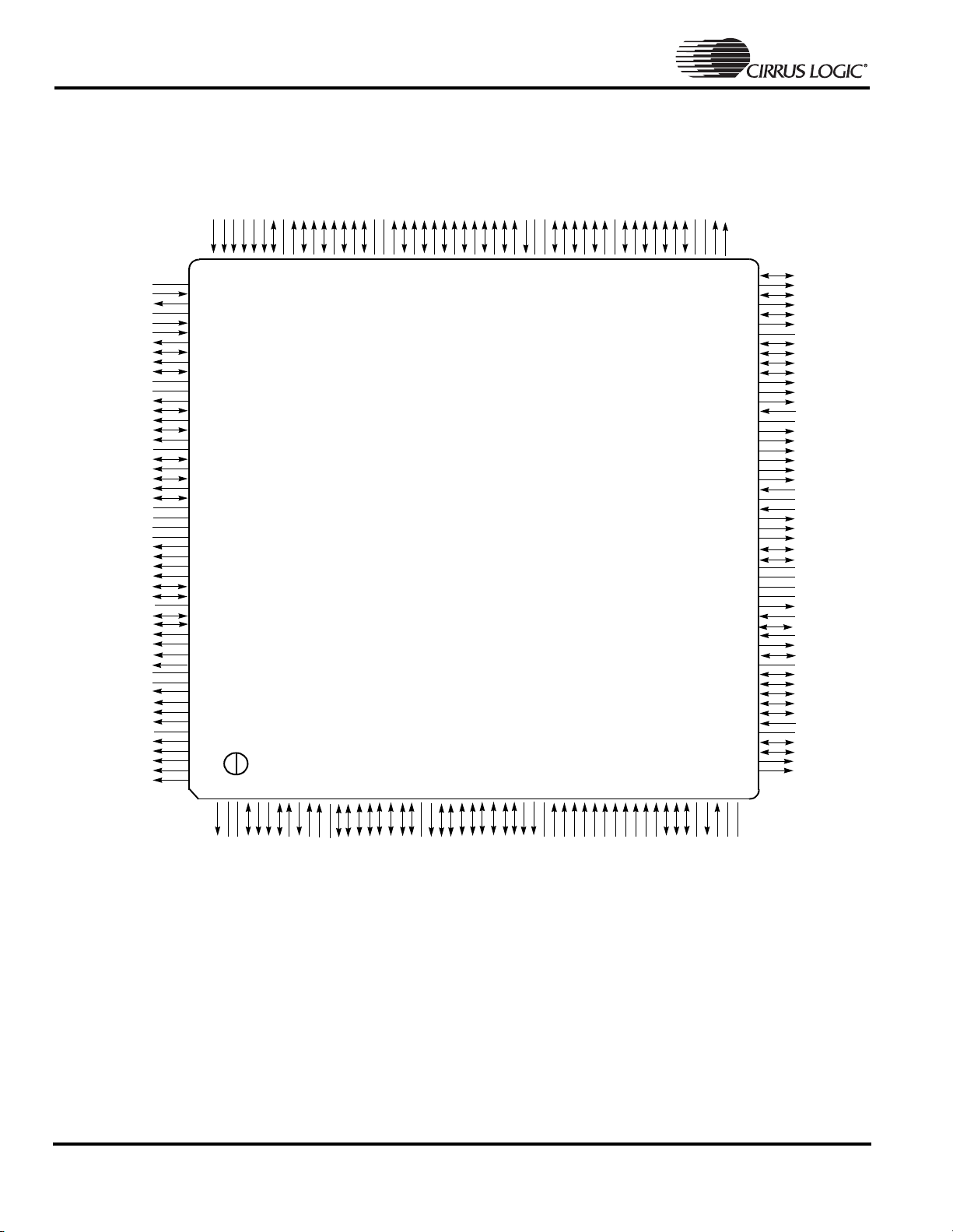
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
208-Pin LQFP Pin Diagram
BATOK
D[7]
A[7]
D[8]
A[8]
D[9]
D[10]
A[10]
A[9]
146
145
144
143
142
VDDOSC
MOSCIN
MOSCOUT
VSSOSC
WAKEUP
nPWRFL
A[6]
D[6]
A[5]
D[5]
VDDIO
VSSIO
A[4]
D[4]
A[3]
D[3]
A[2]
VSSIO
D[2]
A[1]
D[1]
A[0]
D[0]
VSSCORE
VDDCORE
VSSIO
VDDIO
CL[2]
CL[1]
FRM
DD[3]
DD[2]
VSSIO
DD[1]
DD[0]
N/C
N/C
N/C
VDDIO
VSSIO
N/C
N/C
nMWE
nMOE
VSSIO
nCS[0]
nCS[1]
nCS[2]
nCS[3]
nCS[4]
N/C
nBATCHG
VSSIO
nEXTPWR
nURESET
nMEDCHG/nBROM
nPOR
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
M
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
2345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849515052
1
147
VSSIO
VDDIO
A[11]
D[12]
A[12]
D[11]
140
141
D[13]
139
138
137
136
135
EP7309
208-Pin LQFP
(Top View)
A[13]
134
D[14]
A[14]
132
133
D[17]
D[15]
131
A[15]
130
A[17]
nTRST
VSSIO
VDDIO
D[18]
A[18
D[19]
A[19]
D[20]
VSSIO
A[21]
D[22]
D[23]
A[23]
D[24]
VSSIO
VDDIO
A[24]
D[16]
A[16]
122
124
125
126
127
128
129
123
A[20]
117
118
119
120
121
A[22]
D[21]
111
110
112
113
114
115
116
HALFWORD
106
107
108
109
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
D[25]
A[25]
D[26]
A[26]
D[27]
A[27]
VSSIO
D[28]
D[29]
D[30]
D[31]
BUZ
COL[0]
COL[1]
TCLK
VDDIO
COL[2]
COL[3]
COL[4]
COL[5]
COL[6]
COL[7]
FB[0]
VSSIO
FB[1]
SMPCLK
ADCOUT
ADCCLK
DRIVE[0]
DRIVE[1]
VDDIO
VSSIO
VDDCORE
VSSCORE
nADCCS
ADCIN
SSIRXFR
SSIRXDA
SSITXDA
SSITXFR
VSSIO
SSICLK
PD[0]/LEDFLSH
PD[1]
PD[2]
PD[3]
TMS
VDDIO
PD[4]
PD[5]
PD[6]
PD[7]
nCS[5]
VSSIO
VDDIO
TDI
PB[7]
PB[6]
PB[5]
PB[4]
WRITE
TXD[2]
WORD
EXPCLK
EXPRDY
RXD[2]
VSSIO
PB[3]
RUN/CLKEN
TDO
PB[2]
PB[1]
PB[0]
VDDIO
PA[6]
PA[5]
PA[4]
PA[3]
PA[2]
PA[1]
PA[7]
PA[0]
TXD[1]
LEDDRV
CTS
DSR
DCD
VSSIO
PHDIN
RXD[1]
EINT[3]
nEINT[2]
nEINT[1]
nTEST[1]
nEXTFIQ
nTEST[0]
PE[2]/CLKSEL
PE[1]BOOTSEL[1]
PE[0]BOOTSEL[0]
N/C
RTCIN
VDDRTC
VSSRTC
RTCOUT
Figure 11. 208-Pin LQFP (Low Profile Quad Flat Pack) Pin Diagram
Note: 1. N/C should not be grounded but left as no connects.
2. Pin differences between the EP7212 and the EP7309 are bolded.
22 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table S. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing
Pin
No.
1 nCS[5] O 1 High
2 VDDIO Pad Pwr
3 VSSIO Pad Gnd
4 EXPCLK I/O 1
5WORD Out 1 Low
6WRITE Out 1 Low
7 RUN/CLKEN O 1 Low
8EXPRDY I 1
9 TXD[2] O 1 High
10 RXD[2] I
11 TDI I with p/u*
12 VSSIO Pad Gnd
13 PB[7] I/O 1 Input
14 PB[6] I/O 1 Input
15 PB[5] I/O 1 Input
16 PB[4] I/O 1 Input
17 PB[3] I/O 1 Input
18 PB[2] I/O 1 Input
19 PB[1]/PRDY2 I/O 1 Input
20 PB[0]/PRDY1 I/O 1 Input
21 VDDIO Pad Pwr
22 TDO O 1 Three state
23 PA[7] I/O 1 Input
24 PA[6] I/O 1 Input
25 PA[5] I/O 1 Input
26 PA[4] I/O 1 Input
27 PA[3] I/O 1 Input
28 PA[2] I/O 1 Input
29 PA[1] I/O 1 Input
30 PA[0] I/O 1 Input
31 LEDDRV O 1 Low
32 TXD[1] O 1 High
33 VSSIO Pad Gnd 1 High
34 PHDIN I
35 CTS I
36 RXD[1] I
37 DCD I
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
Table S. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (Continued)
Pin
No.
38 DSR I
39 nTEST[1] I With p/u*
40 nTEST[0] I With p/u*
41 EINT[3] I
42 nEINT[2] I
43 nEINT[1] I
44 nEXTFIQ I
45 PE[2]/CLKSEL I/O 1 Input
46
47
48 VSSRTC RTC Gnd
49 RTCOUT O
50 RTCIN I
51 VDDRTC RTC power
52 N/C
53 PD[7] I/O 1 Low
54 PD[6] I/O 1 Low
55 PD[5] I/O 1 Low
56 PD[4] I/O 1 Low
57 VDDIO Pad Pwr
58 TMS I with p/u*
59 PD[3] I/O 1 Low
60 PD[2] I/O 1 Low
61 PD[1] I/O 1 Low
62 PD[0]/LEDFLSH I/O 1 Low
63 SSICLK I/O 1 Input
64 VSSIO Pad Gnd
65 SSITXFR I/O 1 Low
66 SSITXDA O 1 Low
67 SSIRXDA I
68 SSIRXFR I/O Input
69 ADCIN I
70 nADCCS O 1 High
71 VSSCORE Core Gnd
72 VDDCORE Core Pwr
73 VSSIO Pad Gnd
Signal Type Strength
PE[1]/
BOOTSEL[1]
PE[0]/
BOOTSEL[0]
I/O 1 Input
I/O 1 Input
Reset
State
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 23

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table S. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (Continued)
Pin
No.
74 VDDIO Pad Pwr
75 DRIVE[1] I/O 2
76 DRIVE[0] I/O 2
77 ADCCLK O 1 Low
78 ADCOUT O 1 Low
79 SMPCLK O 1 Low
80 FB[1] I
81 VSSIO Pad Gnd
82 FB[0] I
83 COL[7] O 1 High
84 COL[6] O 1 High
85 COL[5] O 1 High
86 COL[4] O 1 High
87 COL[3] O 1 High
88 COL[2] O 1 High
89 VDDIO Pad Pwr
90 TCLK I
91 COL[1] O 1 High
92 COL[0] O 1 High
93 BUZ O 1 Low
94 D[31] I/O 1 Low
95 D[30] I/O 1 Low
96 D[29] I/O 1 Low
97 D[28] I/O 1 Low
98 VSSIO Pad Gnd
99 A[27] O 2 Low
100 D[27] I/O 1 Low
101 A[26] O 2 Low
102 D[26] I/O 1 Low
103 A[25] O 2 Low
104 D[25] I/O 1 Low
105 HALFWORD O 1 Low
106 A[24] O 1 Low
107 VDDIO Pad Pwr —
108 VSSIO Pad Gnd —
109 D[24] I/O 1 Low
110 A[23] O 1 Low
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
High /
Low
High /
Low
Table S. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (Continued)
Pin
No.
111 D[23] I/O 1 Low
112 A[22] O 1 Low
113 D[22] I/O 1 Low
114 A[21] O 1 Low
115 D[21] I/O 1 Low
116 VSSIO Pad Gnd
117 A[20] O 1 Low
118 D[20] I/O 1 Low
119 A[19] O 1 Low
120 D[19] I/O 1 Low
121 A[18] O 1 Low
122 D[18] I/O 1 Low
123 VDDIO Pad Pwr
124 VSSIO Pad Gnd
125 nTRST I
126 A[17] O 1 Low
127 D[17] I/O 1 Low
128 A[16] O 1 Low
129 D[16] I/O 1 Low
130 A[15] O 1 Low
131 D[15] I/O 1 Low
132 A[14] O 1 Low
133 D[14] I/O 1 Low
134 A[13] O 1 Low
135 D[13] I/O 1 Low
136 A[12] O 1 Low
137 D[12] I/O 1 Low
138 A[11] O 1 Low
139 VDDIO Pad Pwr
140 VSSIO Pad Gnd
141 D[11] I/O 1 Low
142 A[10] O 1 Low
143 D[10] I/O 1 Low
144 A[9] O 1 Low
145 D[9] I/O 1 Low
146 A[8] O 1 Low
147 D[8] I/O 1 Low
148 A[7] O 1 Low
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
24 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table S. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (Continued)
Pin
No.
149 VSSIO Pad Gnd
150 D[7] I/O 1 Low
151 nBATCHG I
152 nEXTPWR I
153 BATOK I
154 nPOR I Schmitt
155
156 nURESET I Schmitt
157 VDDOSC Osc Pwr
158 MOSCIN Osc
159 MOSCOUT Osc
160 VSSOSC Osc Gnd
161 WAKEUP I Schmitt
162 nPWRFL I
163 A[6] O 1 Low
164 D[6] I/O 1 Low
165 A[5] Out 1 Low
166 D[5] I/O 1 Low
167 VDDIO Pad Pwr
168 VSSIO Pad Gnd
169 A[4] O 1 Low
170 D[4] I/O 1 Low
171 A[3] O 2 Low
172 D[3] I/O 1 Low
173 A[2] O 2 Low
174 VSSIO Pad Gnd
175 D[2] I/O 1 Low
176 A[1] O 2 Low
177 D[1] I/O 1 Low
178 A[0] O 2 Low
179 D[0] I/O 1 Low
180 VSS CORE Core Gnd
181 VDD CORE Core Pwr
182 VSSIO Pad Gnd
183 VDDIO Pad Pwr
184 CL[2] O 1 Low
185 CL[1] O 1 Low
186 FRM O 1 Low
Signal Type Strength
nMEDCHG/
nBROM
I
Reset
State
Table S. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (Continued)
Pin
No.
187 M O 1 Low
188 DD[3] I/O 1 Low
189 DD[2] I/O 1 Low
190 VSSIO Pad Gnd
191 DD[1] I/O 1 Low
192 DD[0] I/O 1 Low
193 N/C O 1 High
194 N/C O 1 High
195 N/C I/O 2 Low
196 N/C I/O 2 Low
197 VDDIO Pad Pwr
198 VSSIO Pad Gnd
199 N/C I/O 2 Low
200 N/C I/O 2 Low
201 nMWE O 1 High
202 nMOE O 1 High
203 VSSIO Pad Gnd
204 nCS[0] O 1 High
205 nCS[1] O 1 High
206 nCS[2] O 1 High
207 nCS[3] O 1 High
208 nCS[4] O 1 High
*With p/u’ means with internal pull-up on the pin.
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 25

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
204-Ball TFBGA Package Characteristics
204-Ball TFBGA Package Specifications
0.36 0.53±0.05
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
0.20 C
C
TOP VIEW BOTTOM VIEW
A1 CORNER
SEATING PLANE
C
0
.
Ø
0
8
M
Ø0.15 M C A B
Ø0.25~0.35(204X)
17 19 20181614 1512 139101178456231
13±0.05
A
0
0.10 C
.
1
12.35
5
(
20
19181716151413121110987654321
0.65
12.35
B
C
)
4
X
13±0.05
Ball Pitch :
A1 CORNER
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
V
W
Y
0.65
Substrate Thickness :
0.65 0.36
Ball Diameter :
Mold Thickness :
0.530.3
0.20~0.30
1.20 MAX.
Figure 12. 204-Ball TFBGA Package
26 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
204-Ball TFBGA Pinout (Top View)
1 2 3456 7 8 910111213141516 17 18 19 20
A VDDR EXPCLK nCS3 nCS1 nMWE N/C N/C DD2 FRM CL1 GNDD D1 A2 D4 A5 nPWRFL MOSCOUT GNDR GNDR GNDR A
B WORD VDDR nCS5 nCS2 nMOE N/C N/C DD1 M CL2 D0 A1 D3 A4 D6 WAKEUP MOSCIN GNDR GNDR nURESET B
RUN/
C
D PB7 RXD2 VDDR GNDR nBATCHG A7 D
EXPRDY VDDR nCS4 nCS0 N/C N/C DD0 DD3 VDDD A0 D2 A3 D5 A6 GNDO VDDO GNDR BATOK nPOR C
CLKEN
EPB4 TXD2WRITE
FPB3 PB6 TDI D7 A8 D10 F
G PB1 PB2 PB5 D8 A9 D11 G
H PA7 TDO P B0 A10 D12 A12 H
J PA4 PA5 PA6 A11 D13 A13 J
K PA1 PA2 VDDR D14 A14 D15 K
L TXD1 LEDDRV PA3 VDDR D16 A16 L
MRXD1 CTS PA0 A15 A17 nTRST M
N DSR nTEST1 PHDIN D17 D19 A18 N
P EINT3 nEINT2 DCD D18 A20 D20 P
PE1/
BOOT
SEL1
PE2/
nTEST0 A19 D22 A21 R
CLKSEL
PE0/
BOOT
nEINT1 D21 D23 A22 T
SEL0
RnEXTFIQ
T
nMEDCHG
/nBROM
nEXTPWR D9 E
U GNDC RTCOUT RTCIN
V VDDC GNDR GNDR PD7 PD4 PD2 SSICLK SSIRXDA nADCCS VDDR ADCCLK COL7 COL4 TCLK BUZ D29 A26 VDDR VDDR A24 V
W GNDR GNDR GNDR PD6 TMS PD1 SSITXFR SSIRXFR GNDD1 DRIVE1 ADCOUT FB0 COL5 COL2 COL0 D30 A27 D26 VDDR D25 W
Y GNDR GNDR GNDR PD5 PD3
PD0/
LED
SSITXDA ADCIN VDD1 DRIVE0 SMPLCK FB1 COL6 COL3 COL1 D31 D28 D27 A25 VDDR Y
FLSH
HALF
WORD
D24 A23 U
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 27

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
TFBGA Ball List
Table T. 204-Ball TFBGA Ball List
Die Pad Bond Pad Package Ball Signal
U2.1 1 B3 nCS5
U2.2 2 Y20 VDDR
U2.3 3 B18 GNDR
U2.4 4 A2 EXPCLK
U2.5 5 B1 WORD
U2.6 6 E3 WRITE
U2.7 7 C1 RUN/CLKEN
U2.8 8 C2 EXPRDY
U2.9 9 E2 TXD2
U2.10 10 D2 RXD2
U2.11 11 F3 TDI
U2.12 12 B18 GNDR
U2.13 13 D1 PB7
U2.14 14 F2 PB6
U2.15 15 G3 PB5
U2.16 16 E1 PB4
U2.17 17 F1 PB3
U2.18 18 G2 PB2
U2.19 19 G1 PB1
U2.20 20 H3 PB0
U2.21 21 Y20 VDDR
U2.22 22 H2 TDO
U2.23 23 H1 PA7
U2.24 24 J3 PA6
U2.25 25 J2 PA5
U2.26 26 J1 PA4
U2.27 27 L3 PA3
U2.28 28 K2 PA2
U2.29 29 K1 PA1
U2.30 30 M3 PA0
U2.31 31 L2 LEDDRV
U2.32 32 L1 TXD1
U2.33 33 B18 GNDR
U2.34 34 N3 PHDIN
U2.35 35 M2 CTS
U2.36 36 M1 RXD1
U2.37 37 P3 DCD
Table T. 204-Ball TFBGA Ball List (Continued)
Die Pad Bond Pad Package Ball Signal
U2.38 38 N1 DSR
U2.39 39 N2 nTEST1
U2.40 40 R3 nTEST0
U2.41 41 P1 EINT3
U2.42 42 P2 nEINT2
U2.43 43 T3 nEINT1
U2.44 44 R1 nEXTFIQ
U2.45 45 R2 PE2/CLKSEL
U2.46 46 T1 PE1/BOOTSEL1
U2.47 47 T2 PE0/BOOTSEL0
U2.48 48 U1 GNDC
U2.49 49 U2 RTCOUT
U2.50 50 U3 RTCIN
U2.51 51 V1 VDDC
U2.53 52 V4 PD7
U2.54 53 W4 PD6
U2.55 54 Y4 PD5
U2.56 55 V5 PD4
U2.57 56 L18 VDDR
U2.58 57 W5 TMS
U2.59 58 Y5 PD3
U2.60 59 V6 PD2
U2.61 60 W6 PD1
U2.62 61 Y6 PD0/LEDFLSH
U2.63 62 V7 SSICLK
U2.64 63 D18 GNDR
U2.65 64 W7 SSITXFR
U2.66 65 Y7 SSITXDA
U2.67 66 V8 SSIRXDA
U2.68 67 W8 SSIRXFR
U2.69 68 Y8 ADCIN
U2.70 69 V9 nADCCS
U2.71 70 W9 GNDD1
U2.72 71 Y9 VDD1
U2.73 72 W3 GNDR
U2.74 73 V10 VDDR
U2.75 74 L18 VDDR
U2.76 75 W10 DRIVE1
28 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table T. 204-Ball TFBGA Ball List (Continued)
Die Pad Bond Pad Package Ball Signal
U2.77 76 Y10 DRIVE0
U2.78 77 V11 ADCCLK
U2.79 78 W11 ADCOUT
U2.80 79 Y11 SMPLCK
U2.81 80 Y12 FB1
U2.82 81 Y3 GNDR
U2.83 82 W12 FB0
U2.84 83 V12 COL7
U2.85 84 Y13 COL6
U2.86 85 W13 COL5
U2.87 86 V13 COL4
U2.88 87 Y14 COL3
U2.89 88 W14 COL2
U2.90 89 A1 VDDR
U2.91 90 V14 TCLK
U2.92 91 Y15 COL1
U2.93 92 W15 COL0
U2.94 93 V15 BUZ
U2.95 94 Y16 D31
U2.96 95 W16 D30
U2.97 96 V16 D29
U2.98 97 Y17 D28
U2.99 98 Y3 GNDR
U2.100 99 W17 A27
U2.101 100 Y18 D27
U2.102 101 V17 A26
U2.103 102 W18 D26
U2.104 103 Y19 A25
U2.105 104 W20 D25
U2.106 105 U18 HALFWORD
U2.107 106 V20 A24
U2.108 107 A1 VDDR
U2.109 108 Y3 GNDR
U2.110 109 U19 D24
U2.111 110 U20 A23
U2.112 111 T19 D23
U2.113 112 T20 A22
U2.114 113 R19 D22
U2.115 114 R20 A21
Table T. 204-Ball TFBGA Ball List (Continued)
Die Pad Bond Pad Package Ball Signal
U2.116 115 T18 D21
U2.117 116 Y3 GNDR
U2.118 117 P19 A20
U2.119 118 P20 D20
U2.120 119 R18 A19
U2.121 120 N19 D19
U2.122 121 N20 A18
U2.123 122 P18 D18
U2.124 123 A1 VDDR
U2.125 124 Y3 GNDR
U2.126 125 M20 nTRST
U2.127 126 M19 A17
U2.128 127 N18 D17
U2.129 128 L20 A16
U2.130 129 L19 D16
U2.131 130 M18 A15
U2.132 131 K20 D15
U2.133 132 K19 A14
U2.134 133 K18 D14
U2.135 134 J20 A13
U2.136 135 J19 D13
U2.137 136 H20 A12
U2.138 137 H19 D12
U2.139 138 J18 A11
U2.140 139 K3 VDDR
U2.141 140 Y3 GNDR
U2.142 141 G20 D11
U2.143 142 H18 A10
U2.144 143 F20 D10
U2.145 144 G19 A9
U2.146 145 E20 D9
U2.147 146 F19 A8
U2.148 147 G18 D8
U2.149 148 D20 A7
U2.150 149 Y3 GNDR
U2.151 150 F18 D7
U2.152 151 D19 nBATCHG
U2.153 152 E19 nEXTPWR
U2.154 153 C19 BATOK
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 29

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table T. 204-Ball TFBGA Ball List (Continued)
Die Pad Bond Pad Package Ball Signal
U2.155 154 C20 nPOR
U2.156 155 E18 nMEDCHG/nBROM
U2.157 156 B20 nURESET
U2.158 157 C17 VDDO
U2.159 158 B17 MOSCIN
U2.160 159 A17 MOSCOUT
U2.161 160 C16 GNDO
U2.162 161 B16 WAKEUP
U2.163 162 A16 nPWRFL
U2.164 163 C15 A6
U2.165 164 B15 D6
U2.166 165 A15 A5
U2.167 166 C14 D5
U2.168 167 A1 VDDR
U2.169 168 Y3 GNDR
U2.170 169 B14 A4
U2.171 170 A14 D4
U2.172 171 C13 A3
U2.173 172 B13 D3
U2.174 173 A13 A2
U2.175 174 Y3 GNDR
U2.176 175 C12 D2
U2.177 176 B12 A1
U2.178 177 A12 D1
U2.179 178 C11 A0
U2.180 179 B11 D0
U2.181 180 A11 GNDD
U2.182 181 C10 VDDD
U2.183 182 Y3 GNDR
U2.184 183 Y20 VDDR
U2.185 184 B10 CL2
U2.186 185 A10 CL1
U2.187 186 A9 FRM
U2.188 187 B9 M
U2.189 188 C9 DD3
U2.190 189 A8 DD2
U2.191 190 Y3 GNDR
U2.192 191 B8 DD1
U2.193 192 C8 DD0
Table T. 204-Ball TFBGA Ball List (Continued)
Die Pad Bond Pad Package Ball Signal
U2.194 193 A7 N/C
U2.195 194 B7 N/C
U2.196 195 C7 N/C
U2.197 196 A6 N/C
U2.198 197 V18 VDDR
U2.199 198 B18 GNDR
U2.200 199 B6 N/C
U2.201 200 C6 N/C
U2.202 201 A5 nMWE
U2.203 202 B5 nMOE
U2.204 203 B18 GNDR
U2.205 204 C5 nCS0
U2.206 205 A4 nCS1
U2.207 206 B4 nCS2
U2.208 207 A3 nCS3
U2.209 208 C4 nCS4
A1 VDDR
B2 VDDR
C3 VDDR
D3 VDDR
K3 VDDR
L18 VDDR
V18 VDDR
V19 VDDR
W19 VDDR
Y20 VDDR
A18 GNDR
A19 GNDR
A20 GNDR
B18 GNDR
B19 GNDR
C18 GNDR
D18 GNDR
V2 GNDR
V3 GNDR
W1 GNDR
W2 GNDR
W3 GNDR
30 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1
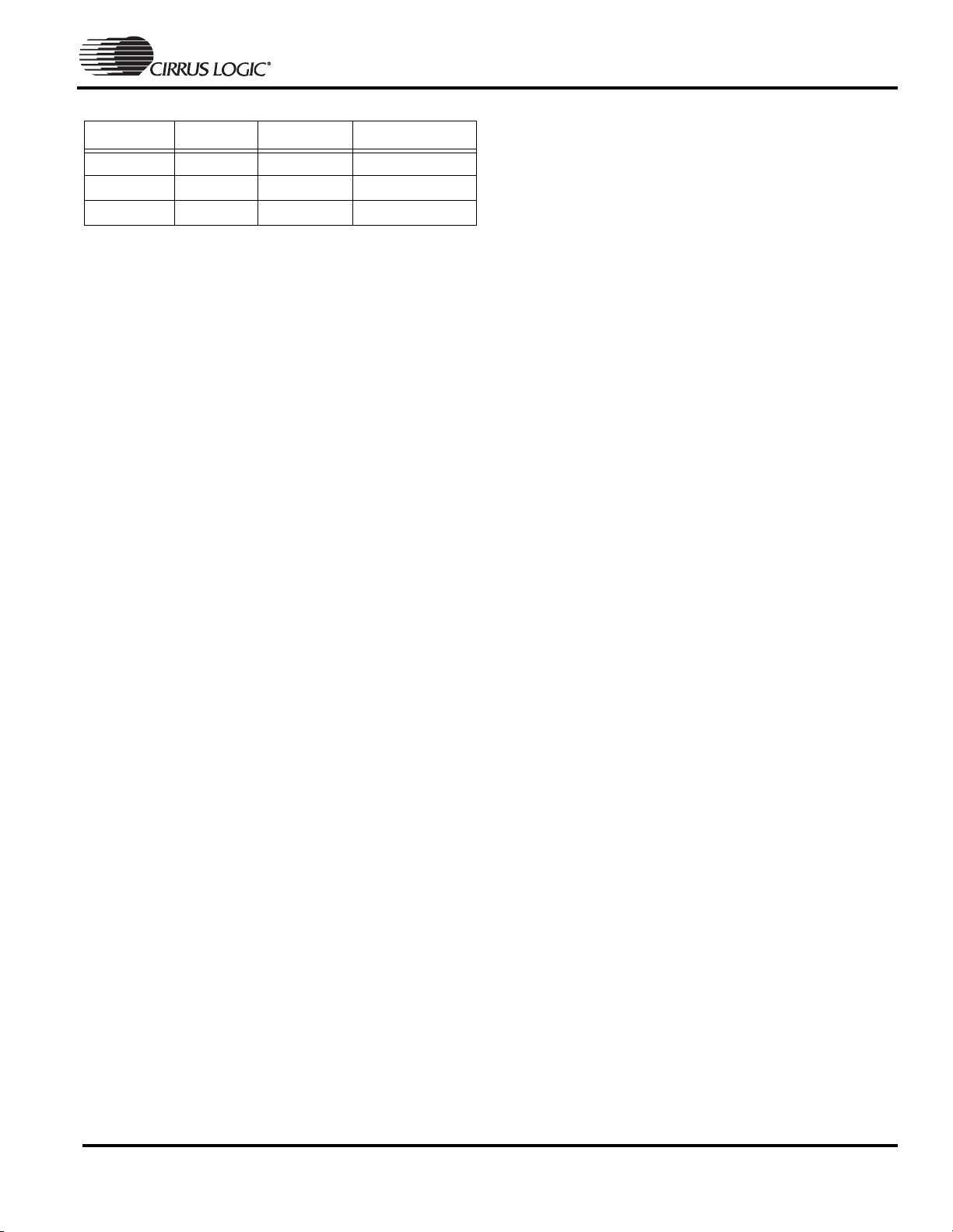
Table T. 204-Ball TFBGA Ball List (Continued)
Die Pad Bond Pad Package Ball Signal
Y1 GNDR
Y2 GNDR
Y3 GNDR
256-Ball PBGA Package Characteristics
256-Ball PBGA Package Specifications
Figure 13. 256-Ball PBGA Package
Note: 1) For pin locations see Tab l e U .
2) Dimensions are in millimeters (inches), and controlling dimension is millimeter
3) Before beginning any new EP7309 design, contact Cirrus Logic for the latest package information.
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 31

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Pin 1 Corner
D1
17.00 (0.669)
±0.20 (.008)
(0.590)
15.00
±0.20 (.008)
30° TYP
0.85 (0.034)
±0.05 (.002)
0.40 (0.016)
±0.05 (.002)
17.00 (0.669)
±0.20 (.008)
1.00 (0.040)
1.00 (0.040)
REF
1.00 (0.040)
E1
(0.590)
15.00
±0.20 (.008)
REF
Pin 1 Indicator
TOP VIEW
D
17.00 (0.669)
1.00 (0.040)
E
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
Pin 1 Corner
17.00 (0.669)
SIDE VIEW
2 Layer
0.36 (0.014)
±0.09 (0.004)
0.50
R
3 Places
BOTTOM VIEW
JEDEC #: MO-151
Ball Diameter: 0.50 mm ± 0.10 mm
17 ¥ 17 ¥ 1.61 mm body
32 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
256-Ball PBGA Pinout (Top View))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 910111213141516
A VDDIO nCS[4] nCS[1] N/C N/C DD[1] M VDDIO D[0] D[2] A[3] VDDIO A[6] MOSCOUT VDDOSC VSSIO A
B nCS[5] VDDIO nCS[3] nMOE VDDIO N/C DD[2] CL[1] VDDCORE D[1] A[2] A[4] A[5] WAKEUP VDDIO nURESET B
C VDDIO EXP CLK VSSIO VDDIO VSSIO VSSIO VSSIO VDDIO VSS IO VSSIO VSSIO VDDIO VSSIO VSSIO nPOR nEXTPWR C
D WRITE EXPRDY VSSIO VDDIO nCS[2] nMWE N/C CL[2] VSSRTC D[4] nPWRFL MOSCIN VDDIO VSSIO D[7] D[8] D
E RXD[2] PB[7] TDI WORD VSSIO nCS[0] N/C FRM A[0] D[5] VSSOSC VSSIO
F PB[5] PB[3] VSSIO TXD[2]
G PB[1] VDDIO TDO PB[4] PB[6] VSSRTC VSSRTC DD[0] D[3] VSSRTC A[7] A[8] A[9] VSSIO D[12] D[13] G
H PA[7] PA[5] VSSIO PA[4] PA[6] PB[0] PB[2] VSSRTC VSSRTC A[10] A[11] A[12] A[13] VSSIO D[14] D[15] H
J PA[3] PA[1] VSSIO PA[2] PA[0] TXD[1] CTS VSSRTC VSSRTC A[17] A[16] A[15] A[14] nTRST D[16] D[17] J
K LEDDRV PHDIN VSSIO DCD nTEST[1] EINT[3] VSSRTC ADCIN COL[4] TCLK D[20] D[19] D[18] VSSIO VDDIO VDDIO K
L RXD[1] D SR VDDIO nEINT[1]
M nTEST[0] nEINT[2] VDDIO
N nEXTFIQ
P VSSRTC RTCOUT VSSIO VSSIO VDDIO VS SIO VSSIO VDDIO VSSIO VDDIO VSSIO VSSIO VDDIO VSSIO D[24] VDDIO P
R RTCIN VDDIO PD[4] PD[1] SSITXDA nADCCS VDDIO ADCOUT COL[7] COL[3] COL[1] D[30] A[27] A [25] VDDIO A[24] R
T VDDRTC PD[7] PD[6] PD[3] SSICLK SSIRXFR VDDCORE DRIVE[0] FB[1] COL[5] VDDIO BUZ D[28] A[26] D[25] VSSIO T
PE[1]/
BOOTSEL[1]
VSSIO VDDIO PD[5] PD[2] SSIRXDA ADCCLK SMPCLK COL[2] D[29] D[26] HALFWORD VSSIO D[22] D[23] N
PE[0]/
BOOTSEL[0]
RUN/
CLKEN
PE[2]/
CLKSEL
VSSIO N/C DD[3] A[1] D[6] V SSRTC BATOK nBATCHG VSSIO D[11] VDDIO F
VSSRTC
TMS VDDIO SSITXFR DRIVE[1] FB[0] COL[0] D[27] VSSIO A[23] VDDIO A[20] D[21] M
PD[0]/
LEDFLSH
VSSRTC COL[6] D[31] VSSRTC A[22] A[21] VSSIO A[18] A[19] L
nMEDCHG/
nBROM
VDDIO D[9] D[10] E
256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
The list is ordered by ball location.
Table U. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball Location Name Type Description
A1 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
A2 nCS[4] O Chip select out
A3 nCS[1] O Chip select out
A4 N/C O
A5 N/C O
A6 DD[1] O LCD serial display data
A7 M O LCD AC bias drive
A8 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
A9 D[0] I/O Data I/O
A10 D[2] I/O Data I/O
A11 A[3] O System byte address
Ball Locatio n Name Type Descripti on
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 33
Table U. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing (Continued)
A12 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
A13 A[6] O System byte address
A14 MOSCOUT O Main oscillator out
A15 VDDOSC
A16 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
B1 nCS[5] O Chip select out
B2 VDDIO Pad power I/O ground
B3 nCS[3] O Chip select out
B4 nMOE O ROM, expansion OP enable
B5 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
B6 N/C O
Oscillator
power
Oscillator power in, 2.5V

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table U. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing (Continued)
Ball Location Name Type Description
B7 DD[2] O LCD serial display data
B8 CL[1] O LCD line clock
B9 VDDCORE Core power Digital core power, 2.5V
B10 D[1] I/O Data I/O
B11 A[2] O System byte address
B12 A[4] O System byte address
B13 A[5] O System byte address
B14 WAKEUP I System wake up input
B15 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
B16 nURESET I User reset input
C1 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
C2 EXPCLK I Expansion clock input
C3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C4 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
C5 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C6 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C7 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C8 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
C9 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C10 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C11 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C12 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
C13 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
C15 nPOR I Power-on reset input
C16 nEXTPWR I External power supply sense input
D1 WRITE O Transfer direction
D2 EXPRDY I Expansion port ready input
D3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
D4 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
D5 nCS[2] O Chip select out
D6 nMWE O ROM, expansion write enable
D7 N/C O
D8 CL[2] O LCD pixel clock out
D9 VSSRTC Core ground Real time clock ground
D10 D[4] I/O Data I/O
D11 nPWRFL I Power fail sense input
D12 MOSCIN I Main oscillator input
D13 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
D14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
D15 D[7] I/O Data I/O
D16 D[8] I/O Data I/O
E1 RXD[2] I UART 2 receive data input
E2 PB[7] I GPIO port B
E3 TDI I JTAG data input
E4 WORD O Word access select output
E5 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
E6 nCS[0] O Chip select out
Table U. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing (Continued)
Ball Locatio n Name Type Descripti on
E7 N/C O
E8 FRM O LCD frame synchronization pulse
E9 A[0] O System byte address
E10 D[5] I/O Data I/O
E11 VSSOSC
E12 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
E13 nMEDCHG/nBROM I
E14 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
E15 D[9] I/O Data I/O
E16 D[10] I/O Data I/O
F1 PB[5] I GPIO po rt B
F2 PB[3] I GPIO po rt B
F3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
F4 TXD[2] O UART 2 transmit data output
F5 RUN/CLKEN O Run output / clock enable output
F6 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
F7 N/C O
F8 DD[3] O LCD serial display data
F9 A[1] O System byte address
F10 D[6] I/O Data I/O
F11 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
F12 BATOK I Battery ok input
F13 nBATCHG I Battery changed sense input
F14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
F15 D[11] I/O Data I/O
F16 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
G1 PB[1]/PRDY[2] I
G2 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
G3 TDO O JTAG data out
G4 PB[4] I GPIO port B
G5 PB[6] I GPIO port B
G6 VSSRTC Core ground Real time clock ground
G7 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
G8 DD[0] O LCD serial display data
G9 D[3] I/O Data I/O
G10 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
G11 A[7] O System byte address
G12 A[8] O System byte address
G13 A[9] O System byte address
G14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
G15 D[12] I/O D ata I/O
G16 D[13] I/O D ata I/O
H1 PA[7] I GP IO por t A
H2 PA[5] I GP IO por t A
H3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
H4 PA[4] I GP IO por t A
H5 PA[6] I GP IO por t A
Oscillator
ground
PLL ground
Media change interrupt input / internal
rom boot enable
GPIO port B / CL-PS6700 interface
signal
34 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table U. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing (Continued)
Ball Location Name Type Description
H6 PB[0]/PRDY[1] I
H7 PB[2] I GPIO port B
H8 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
H9 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
H10 A[10] O System byte address
H11 A[11] O System byte address
H12 A[12] O System byte address
H13 A[13] O System byte address
H14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
H15 D[14] I/O Data I/O
H16 D[15] I/O Data I/O
J1 PA[3] I GPIO port A
J2 PA[1] I GPIO port A
J3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
J4 PA[2] I GPIO port A
J5 PA[0] I GPIO port A
J6 TXD[1] O UART 1 transmit data out
J7 CTS I UART 1 clear to send input
J8 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
J9 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
J10 A[17] O System byte address
J11 A[16] O System byte address
J12 A[15] O System byte address
J13 A[14] O System byte address
J14 nTRST I JTAG async reset input
J15 D[16] I/O Data I/O
J16 D[17] I/O Data I/O
K1 LEDDRV O IR LED drivet
K2 PHDIN I Photodiode input
K3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
K4 DCD I UART 1 data carrier detect
K5 nTEST[1] I Test mode select input
K6 EINT[3] I External interrupt
K7 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
K8 ADCIN I SSI1 ADC serial input
K9 COL[4] O Keyboard scanner column drive
K10 TCLK I JTAG clock
K11 D[20] I/O Data I/O
K12 D[19] I/O Data I/O
K13 D[18] I/O Data I/O
K14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
K15 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
K16 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
L1 RXD[1] I UART 1 receive data input
L2 DSR I UART 1 data set ready input
L3 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
L4 nEINT[1] I External interrupt input
L5 PE[2]/CLKSEL I GPIO port E / clock input mode select
GPIO port B / CL-PS6700 interface
signal
Table U. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing (Continued)
Ball Locatio n Name Type Descripti on
L6 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
L7 PD[0]/LEDFLSH I/O GPIO port D / LED blinker output
L8 VSSRTC Core ground Real time clock ground
L9 COL[6] O Keyboard scanner column drive
L10 D[31] I/O Data I/O
L11 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
L12 A[22] O System byte address
L13 A[21] O System byte address
L14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
L15 A[18] O System byte address
L16 A[19] O System byte address
M1 nTEST[0] I Test mode select input
M2 nEINT[2] I External interrupt input
M3 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
M4 PE[0]/BOOTSEL[0] I GPIO port E / Boot mode select
M5 TMS I JTAG mode select
M6 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
M7 SSITXFR I/O DAI/CODEC/SSI2 frame sync
M8 DRIVE[1] I/O PWM drive output
M9 FB[0] I PWM feedback input
M10 COL[0] O Keyboard scanner column drive
M11 D[27] I/O Data I/O
M12 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
M13 A[23] O System byte address
M14 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
M15 A[20] O System byte address
M16 D[21] I/O Data I/O
N1 nEXTFIQ I External fast interrupt input
N2 PE[1]/BOOTSEL[1] I GPIO port E / boot mode select
N3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
N4 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
N5 PD[5] I/O GPIO port D
N6 PD[2] I/O GPIO port D
N7 SSIRXDA I/O DAI/CODEC/SSI2 serial data input
N8 ADCCLK O SSI1 ADC serial clock
N9 SMPCLK O SSI1 ADC sample clock
N10 COL[2] O Keyboard scanner column drive
N11 D[29] I/O Data I/O
N12 D[26] I/O Data I/O
N13 HALFWORD O Halfword access select output
N14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
N15 D[22] I/O Data I/O
N16 D[23] I/O Data I/O
P1 VSSRTC RTC ground Real time clock ground
P2 RTCOUT O Real time clock oscillator output
P3 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P4 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P5 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 35

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table U. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing (Continued)
Ball Location Name Type Description
P6 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P7 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P8 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
P9 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P10 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
P11 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P12 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P13 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power
P14 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
P15 D[24] I/O Data I/O
P16 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
R1 RTCIN I/O Real time clock oscillator input
R2 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
R3 PD[4] I/O GPIO port D
R4 PD[1] I/O GPIO port D
R5 SSITXDA O DAI/CODEC/SSI2 serial data output
R6 nADCCS O SSI1 ADC chip select
R7 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
R8 ADCOUT O SSI1 ADC serial data output
R9 COL[7] O Keyboard scanner column drive
R10 COL[3] O Keyboard scanner column drive
R11 COL[1] O Keyboard scanner column drive
R12 D[30] I/O Data I/O
R13 A[27] O System byte address
R14 A[25] O System byte address
R15 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
R16 A[24] O System byte address
T1 VDDRTC RTC power Real time clock power, 2.5V
T2 PD[7] I/O GPIO port D
T3 PD[6] I/O GPIO port D
T4 PD[3] I/O GPIO port D
T5 SSICLK I/O DAI/CODEC/SSI2 serial clock
T6 SSIRXFR – DAI/CODEC/SSI2 frame sync
T7 VDDCORE Core power Core power, 2.5V
T8 DRIVE[0] I/O PWM drive output
T9 FB[1] I PWM feedback input
T10 COL[5] O Keyboard scanner column drive
T11 VDDIO Pad power Digital I/O power, 3.3V
T12 BUZ O Buzzer drive output
T13 D[28] I/O Data I/O
T14 A[26] O System byte address
T15 D[25] I/O Data I/O
T16 VSSIO Pad ground I/O ground
36 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

JTAG Boundary Scan Signal Ordering
Table V. JTAG Boundary Scan Signal Ordering
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
LQFP
Pin No.
10 D2 E1 RXD2 I 16
13 F3 E2 PB[7] I/O 17
14 D1 G5 PB[6] I/O 20
15 F2 F1 PB[5] I/O 23
16 G3 G4 PB[4] I/O 26
17 E1 F2 PB[3] I/O 29
18 F1 H7 PB[2] I/O 32
19 G2 G1 PB[1]/PRDY2 I/O 35
20 G1 H6 PB[0]/PRDY1 I/O 38
23 H3 H1 PA[7] I/O 41
24 H1 H5 PA[6] I/O 44
25 J3 H2 PA[5] I/O 47
26 J2 H4 PA[4] I/O 50
27 J1 J1 PA[3] I/O 53
28 L3 J4 PA[2] I/O 56
29 K2 J2 PA[1] I/O 59
30 K1 J5 PA[0] I/O 62
31 M3 K1 LEDDRV O 65
32 L2 J6 TXD1 O 67
34 L1 K2 PHDIN I 69
35 N3 J7 CTS I 70
36 M2 L1 RXD1 I 71
37 M1 K4 DCD I 72
38 P3 L2 DSR I 73
39 N1 K5 nTEST1 I 74
40 N2 M1 nTEST0 I 75
41 R3 K6 EINT3 I 76
42 P1 M2 nEINT2 I 77
43 P2 L4 nEINT1 I 78
TFBGA
Ball
1B3B1 nCS[5] O 1
4 A2 C2 EXPCLK I/O 3
5B1E4 WORD O 6
6E3D1 WRITE O 8
7 C1 F5 RUN/CLKEN O 10
8 C2 D2 EXPRDY I 13
9E2F4 TXD2 O 14
PBGA
Ball
Signal Type Position
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 37

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table V. JTAG Boundary Scan Signal Ordering (Continued)
LQFP
Pin No.
44 T3 N1 nEXTFIQ I 79
45 R1 L5 PE[2]/CLKSEL I/O 80
46 R2 N2 PE[1]/BOOTSEL1 I/O 83
47 T1 M4 PE[0]/BOOTSEL0 I/O 86
53 T2 T2 PD[7] I/O 89
54 V4 T3 PD[6] I/O 92
55 W4 N5 PD[5] I/O 95
56 Y4 R3 PD[4] I/O 98
59 V5 T4 PD[3] I/O 101
60 W5 N6 PD[2] I/O 104
61 Y5 R4 PD[1] I/O 107
62 V6 L7 PD[0]/LEDFLSH O 110
68 W6 T6 SSIRXFR I/O 122
69 Y6 K8 ADCIN I 125
70 W8 R6 nADCCS O 126
75 Y8 M8 DRIVE1 I/O 128
76 V9 T8 DRIVE0 I/O 131
77 W10 N8 ADCCLK O 134
78 Y10 R8 ADCOUT O 136
79 V11 N9 SMPCLK O 138
80 W11 T9 FB1 I 140
82 Y11 M9 FB0 I 141
83 Y12 R9 COL7 O 142
84 W12 L9 COL6 O 144
85 V12 T10 COL5 O 146
86 Y13 K9 COL4 O 148
87 W13 R10 COL3 O 150
88 V13 N10 COL2 O 152
91 Y14 R11 COL1 O 154
92 W14 M10 COL0 O 156
93 A1 T12 BUZ O 158
94 V14 L10 D[31] I/O 160
95 Y15 R12 D[30] I/O 163
96 W15 N11 D[29] I/O 166
97 V15 T13 D[28] I/O 169
99 Y16 R13 A[27] Out 172
100 W16 M11 D[27] I/O 174
101 V16 T14 A[26] O 177
TFBGA
Ball
PBGA
Ball
Signal Type Position
38 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table V. JTAG Boundary Scan Signal Ordering (Continued)
EP7309
LQFP
Pin No.
102 Y17 N12 D[26] I/O 179
103 W17 R14 A[25] O 182
104 Y18 T15 D[25] I/O 184
105 V17 N13 HALFWORD O 187
106 W18 R16 A[24] O 189
109 Y19 P15 D[24] I/O 191
110 W20 M13 A[23] O 194
111 U18 N16 D[23] I/O 196
112 V20 L12 A[22] O 199
113 U19 N15 D[22] I/O 201
114 U20 L13 A[21] O 204
115 T19 M16 D[21] I/O 206
117 T20 M15 A[20] O 209
118 R19 K11 D[20] I/O 211
119 R20 L16 A[19] O 214
120 T18 K12 D[19] I/O 216
121 P19 L15 A[18] O 219
122 P20 K13 D[18] I/O 221
126 R18 J10 A[17] O 224
127 N19 J16 D[17] I/O 226
128 N20 J11 A[16] O 229
129 P18 J15 D[16] I/O 231
130 M19 J12 A[15] O 234
131 N18 H16 D[15] I/O 236
132 L20 J13 A[14] O 239
133 L19 H15 D[14] I/O 241
134 M18 H13 A[13] O 244
135 K20 G16 D[13] I/O 246
136 K19 H12 A[12] O 249
137 K18 G15 D[12] I/O 251
138 J20 H11 A[11] O 254
141 J19 F15 D[11] I/O 256
142 H20 H10 A[10] O 259
143 H19 E16 D[10] I/O 261
144 J18 G13 A[9] O 264
145 K3 E15 D[9] I/O 266
146 Y3 G12 A[8] O 269
147 G20 D16 D[8] I/O 271
TFBGA
Ball
PBGA
Ball
Signal Type Position
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 39

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table V. JTAG Boundary Scan Signal Ordering (Continued)
LQFP
Pin No.
148 H18 G11 A[7] O 274
150 F20 D15 D[7] I/O 276
151 G19 F13 nBATCHG I 279
152 E20 C16 nEXTPWR I 280
153 F19 F12 BATOK I 281
154 G18 C15 nPOR I 282
155 D20 E13 nMEDCHG/nBROM I 283
156 F18 B16 nURESET I 284
161 D19 B14 WAKEUP I 285
162 E19 D11 nPWRFL I 286
163 C19 A13 A[6] O 287
164 C20 F10 D[6] I/O 289
165 E18 B13 A[5] O 292
166 B20 E10 D[5] I/O 294
169 B16 B12 A[4] O 297
170 A16 D10 D[4] I/O 299
171 C15 A11 A[3] O 302
172 B15 G9 D[3] I/O 304
173 A15 B11 A[2] O 307
175 C14 A10 D[2] I/O 309
176 B14 F9 A[1] O 312
177 A14 B10 D[1] I/O 314
178 C13 E9 A[0] O 317
179 B13 A9 D[0] I/O 319
184 A13 D8 CL2 O 322
185 C12 B8 CL1 O 324
186 B12 E8 FRM O 326
187 A12 A7 M O 328
188 C11 F8 DD[3] I/O 330
189 B11 B7 DD[2] I/O 333
191 B10 A6 DD[1] I/O 336
192 A10 G8 DD[0] I/O 339
193 A9 B6 N/C O 342
194 B9 D7 N/C O 344
195 C9 A5 N/C I/O 346
196 A8 E7 N/C I/O 349
199 B8 F7 N/C I/O 352
200 C8 A4 N/C I/O 355
TFBGA
Ball
PBGA
Ball
Signal Type Position
40 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Table V. JTAG Boundary Scan Signal Ordering (Continued)
EP7309
LQFP
Pin No.
201 A7 D6 nMWE O 358
202 B7 B4 nMOE O 360
204 C7 E6 nCS[0] O 362
205 A6 A3 nCS[1] O 364
206 B6 D5 nCS[2] O 366
207 C6 B3 nCS[3] O 368
208 A5 A2 nCS[4] O 370
1) See EP7309 Users’ Manual for pin naming / functionality.
2) For each pad, the JTAG connection ordering is input,
output, then enable as applicable.
TFBGA
Ball
PBGA
Ball
Signal Type Position
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 41

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
CONVENTIONS
This section presents acronyms, abbreviations, units of
measurement, and conventions used in this data sheet.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Table W lists abbreviations and acronyms used in this
data sheet.
Table W. Acronyms and Abbreviations
Acronym/
Abbreviation
A/D analog-to-digital
ADC analog-to-digital converter
CODEC coder / decoder
D/A digital-to-analog
DMA direct-memory access
EPB embedded peripheral bus
FCS frame check sequence
FIFO first in / first out
FIQ fast interrupt request
GPIO general purpose I/O
ICT in circuit test
IR infrared
IRQ standard interrupt request
IrDA Infrared Data Association
JTAG Joint Test Action Group
LCD liquid crystal display
LED light-emitting diode
LQFP low profile quad flat pack
LSB least significant bit
MIPS millions of instructions per second
MMU memory management unit
MSB most significant bit
PBGA plastic ball grid array
PCB printed circuit board
PDA personal digital assistant
PLL phase locked loop
p/u pull-up resistor
RISC reduced instruction set computer
RTC Real-Time Clock
SIR slow (9600–115.2 kbps) infrared
SRAM static random access memory
SSI synchronous serial interface
Definition
Table W. Acronyms and Abbreviations (Continued)
Acronym/
Abbreviation
TAP test access port
TLB translation lookaside buffer
UART universal asynchronous receiver
Definition
Units of Measurement
Table X. Unit of Measurement
Symbol Unit of Measure
°C
fs sample frequency
Hz hertz (cycle per second)
kbps kilobits per second
KB kilobyte (1,024 bytes)
kHz kilohertz
Ω kilohm
k
Mbps megabits (1,048,576 bits) per second
MB megabyte (1,048,576 bytes)
MBps megabytes per second
MHz megahertz (1,000 kilohertz)
µA microampere
µFmicrofarad
µWmicrowatt
µs microsecond (1,000 nanoseconds)
mA milliampere
mW milliwatt
ms millisecond (1,000 microseconds)
ns nanosecond
Vvolt
Wwatt
degree Celsius
42 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
General Conventions
Hexadecimal numbers are presented with all letters in
uppercase and a lowercase “h” appended or with a 0x at
the beginning. For example, 0x14 and 03CAh are
hexadecimal numbers. Binary numbers are enclosed in
single quotation marks when in text (for example, ‘11’
designates a binary number). Numbers not indicated by
an “h”, 0x or quotation marks are decimal.
Registers are referred to by acronym, with bits listed in
brackets separated by a colon (:) (for example,
CODR[7:0]), and are described in the EP7309 User’s
Manual. The use of “TBD” indicates values that are “to
be determined,” “n/a” designates “not available,” and
“n/c” indicates a pin that is a “no connect.”
Pin Description Conventions
Abbreviations used for signal directions are listed in
Ta bl e Y .
Table Y. Pin Description Conventions
Abbreviation Direction
I Input
OOutput
I/O Input or Output
DS507PP1 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) 43

EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
ORDERING INFORMATION
The order number for the device is:
EP7309 — CV — C
Product Line:
Embedded Processor
Part Number
Revision †
Package Type:
V = Low Profile Quad Flat Pack
B = Plastic Ball Grid Array (17 mm x 17 mm)
R = Reduced Ball Grid Array (13 mm x 13 mm)
Temperature Range:
C = Commercial
E = Extended Operating Version
I = Industrial Operating Version
Note: Contact Cirrus Logic for up-to-date information on revisions. Go to the Cirrus Logic Internet site at
http://cirrus.com/corporate/contacts to find contact information for your local sales representative.
44 Copyright 2001 Cirrus Logic (All Rights Reserved) DS507PP1

• Notes •

 Loading...
Loading...