FEATURES
EP7211
Preliminary Data Sheet
■ Dynamically programmable clock speeds of
18, 36, 49, and 74 MHz at 2.5 V
■ Performance matching 100-MHz Intel
Pentium-based PC
■ Socket and register compatible with CL-PS7111
■ Ultra low power
— Designed for applications that require long battery life
while using standard AA/AAA batteries or rechargeable
cells
— 170 mW at 74 MHz in the Operating State
— 50 mW at 18 MHz in the Operating State
— 15 mW in the Idle State (clock to the CPU stopped,
everything else running)
—10µW in the Standby State (realtime clock ‘on’,
everything else stopped)
■ LCD controller
— Interfaces directly to a single-scan panel monochrome
LCD
— Panel width size is programmable from 32 to 1024 pixels
in 16-pixel increments
— Video frame buffer size programmable up to 128 kbytes
— Bits per pixel programmable from 1, 2, or 4
(cont.) (cont.)
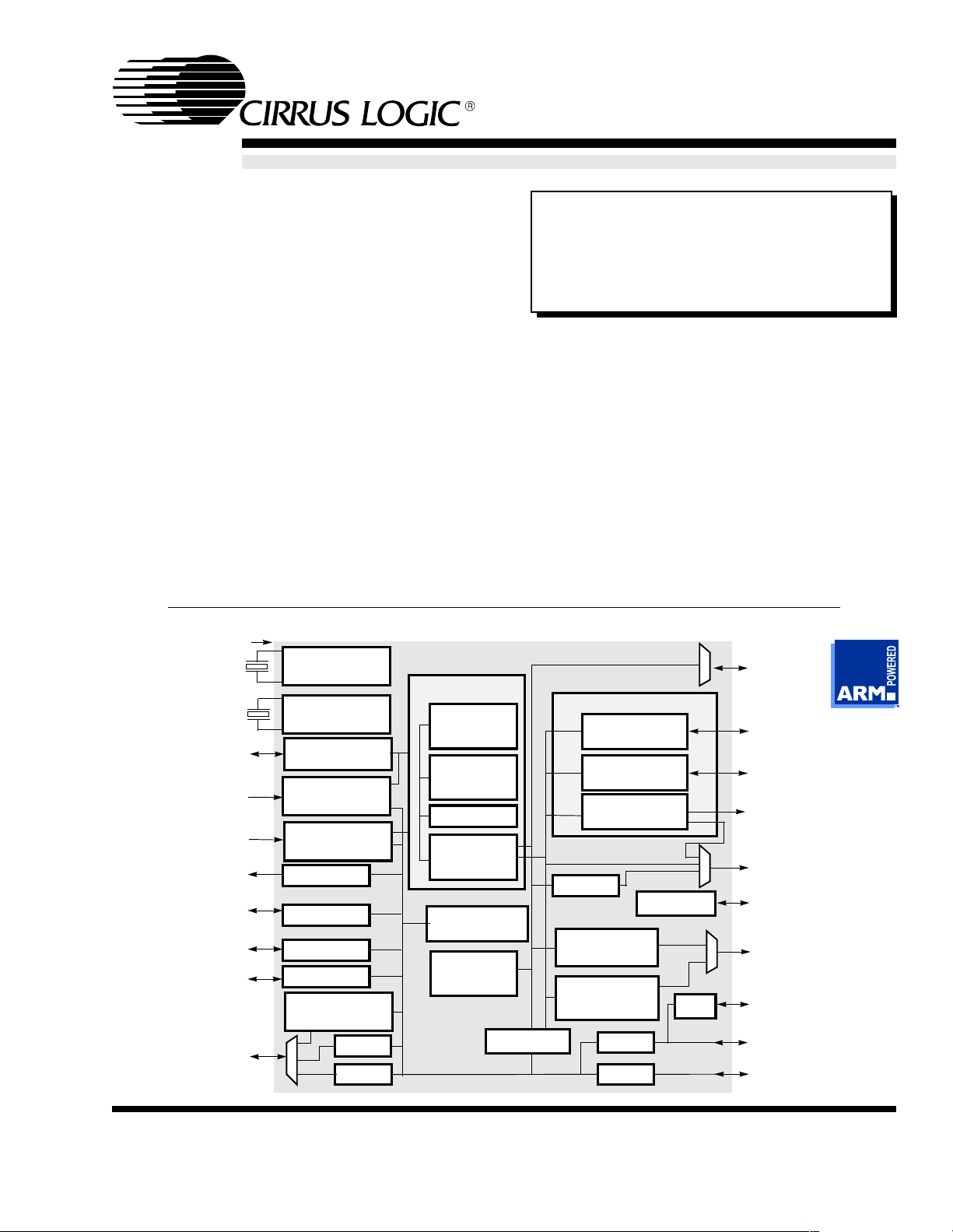
Functional Block Diagram
13-MHZ INPUT
3.6864 MHZ
32.768 KHZ
POR, RUN,
RESET, WAKEUP
BATOK, EXTPWR
PWRFL, BATCHG
EINT[1–3], FIQ,
MEDCHG
FLASHING LED DRIVE
PORTS A, B, D (8-BIT)
PORT E (3-BIT)
KEYBD DRIVERS (0–7)
BUZZER DRIVE
DC-TO-DC
ADCCLK, ADCIN,
ADCOUT, SMPCLK,
ADCCS
SSICLK, SSITXFR,
SSITXDA, SSIRXDA,
SSIRSFR
PLL
32.768-KHZ
OSCILLATOR
STATE CONTROL
POWER
MANAGEMENT
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
RTC
GPIO
PWM
SSI1 (ADC)
MULTIMEDIA
CODEC PORT
SSI2
CODEC
ARM720T
ARM7TDMI
CPU CORE
8-KBYTE
CACHE
WRITE
BUFFER
COUNTERS (2)
ON-CHIP
BOOT ROM
EPB BUS
MMU
TIMER
High-Performance Ultra-Low-
Power System-on-Chip with
LCD Controller
OVERVIEW
The EP7211 is designed for ultra-low-power applications such as organizers/PDAs, two-way pagers,
smart cellular phones, and industrial hand-held information appliances. The core-logic functionality of the
device is built around an ARM720T processor with 8
kbytes of four-way set-associative unified cache and
a write buffer. Incorporated into the ARM720T is an
enhanced memory management unit (MMU), which
allows for Microsoft Windows CE support.
The EP7211 also includes a 32-bit Y2K-compliant
Real Time Clock (RTC) and comparator.
APB BRIDGE
INTERNAL DATA BUS
MEMORY CONTROL BLOCK
CL-PS6700
INTFC.
EXPANSION
CONTROL
DRAM
CONTROLLER
INTERNAL ADDRESS BUS
LCD DMA
ICE-JTAG
LCD
CONTROLLER
ON-CHIP SRAM
37.5 KBYTES
UART1
UART2
IrDA
D0–D31
PB[0–1], CS[4–5]
EXPCLK, WORD,
CS[0–3], EXPRDY,
WRITE
MOE, MWE,
RAS[0–1], CAS[0–3]
A[0–27],
DRA[0–12]
TEST AND
DEVELOPMENT
LCD DRIVE
LED AND
PHOTODIODE
ASYNC
INTERFACE 1
ASYNC
INTERFACE 2
Cirrus Logic, Inc. Copyright © Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2001
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760 (All Rights Reserved)
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7851
http://www.cirrus.com
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
1

High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
FEATURES (cont.)
■ ARM720T processor
— ARM7TDMI CPU
— 8 kbytes of four-way set-associative cache
— MMU with 64-entry TLB (transition look aside buffer)
— Write buffer
— Windows
— Thumb
■ DRAM controller
— Supports both 16- and 32-bit-wide DRAMs
— EDO support (fast page mode support for 13 MHz and
18 MHz operation only)
■ ROM/SRAM/FLASH memory control
— Decodes 4, 5, or 6 separate memory segments of up to
256 Mbytes each
— Each segment can be configured as 8, 16, or 32 bits
wide and supports page-mode access
— Programmable access time for conventional
ROM/SRAM/Flash memory
■ 37.5 kbytes of on-chip SRAM for fast program
execution and/or as a frame buffer
■ On-chip ROM; for manufacturing boot-up support
■ Four synchronous serial interfaces
— ADC (SSI1) Interface: Master mode only; SPI1 and
Microwire1
— SSI2 Interface: Master/Slave mode; SPI/Microwire2
compatible (512 kbps operation)
— Audio Codec Interface (64 kbps operation)
— Multimedia Codec Port (Interfaces to Philips’ UCB1100
CE enabled
®
code support enabled
2
-compatible (128 kbps operation)
EP7211
and UCB1200 codecs) (9.216 Mbps operation)
■ 27 bits of general-purpose I/O
— Three 8-bit and one 3-bit GPIO port
— Supports scanning keyboard matrix
■ Two UARTs (16550 type)
— Supports bit rates up to 115.2 kbps
— Contains two 16-byte FIFOs for TX and RX
— UART1 supports modem control signals
■ SIR (up to 115.2 kbps) infrared encoder
— IrDA (Infrared Data Association) SIR protocol encoder
can be optionally switched into TX and RX signals of
UART1
■ PWM interface
— Provides two 96-kHz clock outputs with programmable
duty ratio (from 1-in-16 to 15-in-16) that can be used to
drive a DC-to-DC converter
■ Two timer counters
■ 208-pin LQFP or 256-ball PBGA packages
■ Evaluation kit available with BOM, schematics,
sample code, and design database
■ Support for up to two ultra-low-power CL-PS6700
PC Card controllers
■ Dedicated LED flasher pin from RTC
■ Full JTAG boundary scan and Embedded ICE
support
1
SPI is a registered trademark of Motorola.
2
Microwire is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor.
OVERVIEW (cont.)
Power Management
The EP7211 is designed for ultra-low-power operation. Its core operates at only 2.5 V, while its I/O has
an operating range of 2.5 V–3.3 V. The device has
three basic power states:
Operating — This state is the full performance
state. All the clocks and peripheral logic are
enabled.
Idle — This state is the same as the Operating
State, except the CPU clock is halted while waiting for an event such as a key press.
Standby — This state is equivalent to the computer
being switched off (no display), and the main
oscillator shut down. An event such as a key
press can wake up the processor.
2
Memory Interfaces
There are two main external memory interfaces.
The first one is the ROM/SRAM/Flash-style interface
that has programmable wait-state timings and
includes burst-mode capability, with six chip selects
each decoding 256-Mbyte sections of addressable
space. For maximum flexibility, each bank can be
specified to be 8, 16, or 32 bits wide. This allows the
use of 8-bit-wide boot ROM options to minimize overall system cost. The on-chip boot ROM can be used
in product manufacturing to serially download system
code into system Flash memory. To further minimize
system memory requirements and cost, the ARM
Thumb
instruction set is supported, providing for the
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
OVERVIEW (cont.)
use of high-speed 32-bit operations in 16-bit opcodes and yielding industry-leading code density.
The second is the programmable 16- or 32-bit-wide
DRAM interface that allows direct connection of up to
two banks of DRAM, each bank containing up to 256
Mbytes. To assure the lowest possible power consumption, the EP7211 supports self-refresh DRAMs,
which are placed in a low-power state by the device
when it enters the low-power Standby State. EDO
and Fast Page DRAM are supported.
A DMA address generator is also provided that
fetches video display frame buffer data for the LCD
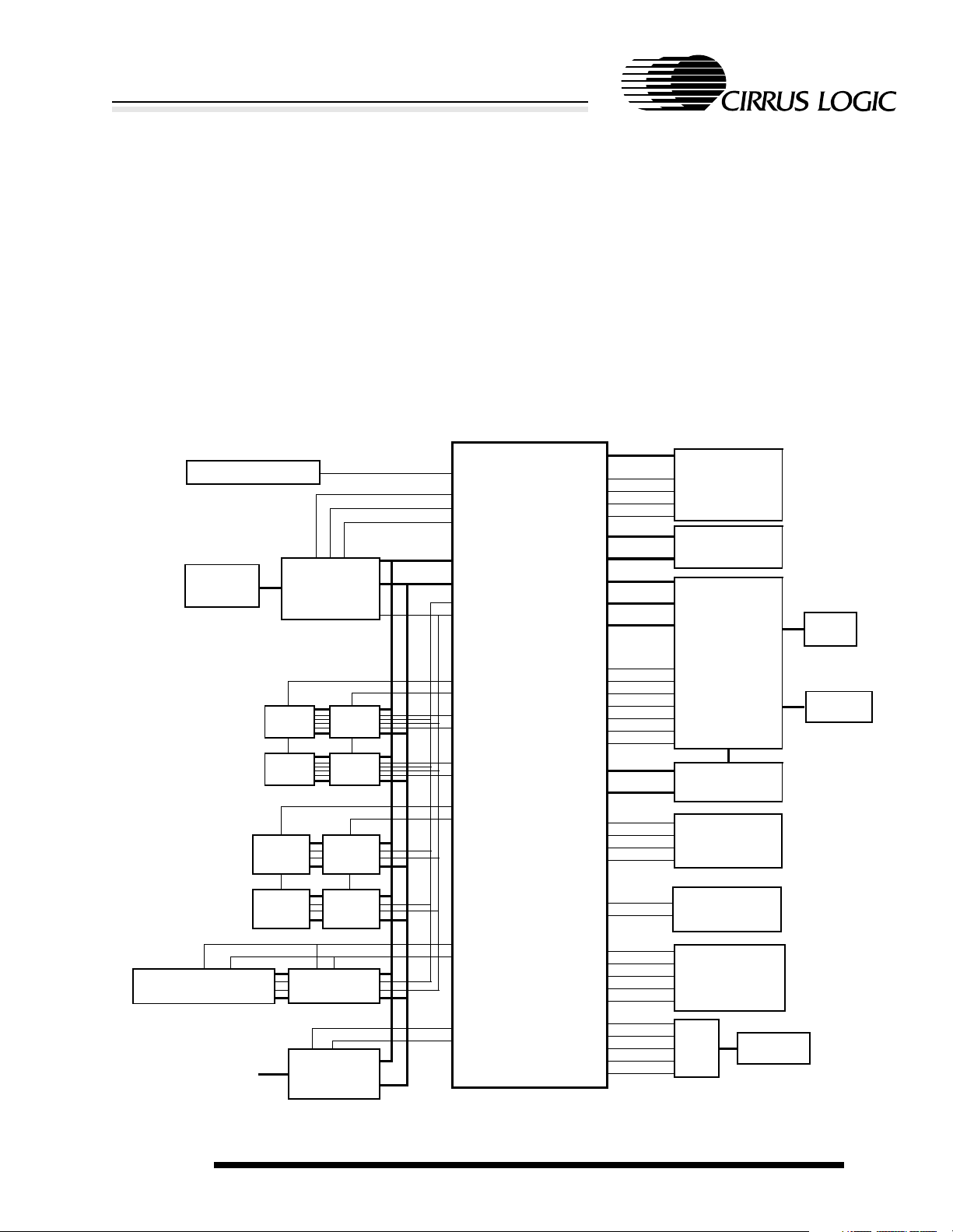
CRYSTAL
PC CARD
SOCKET
CL-PS6700
PC CARD
CONTROLLER
×16
DRAM
×16
DRAM
×16
FLASH
×16
DRAM
×16
DRAM
×16
ROM
MOSCIN
CS[4]
PB0
EXPCLK
D[31:0]
A[27:0]
MOE
WRITE
RAS[1]
RAS[0]
CAS[0]
CAS[1]
CAS[2]
CAS[3]
CS[0]
CS[1]
controller from main memory (typically DRAM). The
display frame buffer start address is programmable.
In addition, the built-in LCD controller can utilize
external or internal SRAM for memory, thus eliminating the need for DRAMs.
Serial Interfaces
The EP7211 includes two 16550-type UARTs for RS232 serial communications, both of which have two
16-byte FIFOs for receiving and transmitting data.
The UARTs support bit rates up to 115.2 kbps. An
IrDA SIR protocol encoder/decoder can be optionally
switched into the RX/TX signals to/from one of the
DD[3:0]
COL[7:0]
PA[7:0]
PB[7:0]
PD[7:0]
PE[2:0]
PWRFL
BATOK
EXTPWR
BATCHG
EP7211
WAKEUP
DRIVE[1:0]
FB[1:0]
SSICLK
SSITXFR
SSITXDA
SSIRXDA
CL1
CL2
FM
POR
RUN
LCD MODULE
M
KEYBOARD
POWER
SUPPLY UNIT
AND
COMPARATORS
DC-TO-DC
CONVERTERS
CODEC
DC
INPUT
BATTERY
EXTERNAL MEMORY-
MAPPED EXPANSION
ADDITIONAL I/O
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
×16
FLASH
×16
ROM
BUFFERS
BUFFERS
AND
LATCHES
LEDDRV
PHDIN
CS[n]
WORD
CS[2]
CS[3]
RXD1/2
TXD1/2
DSR
CTS
DCD
ADCCLK
ADCCS
ADCOUT
ADCIN
SMPCLK
TRANSCEIVERS
ADC
Figure 1-1. A EP7211–Based System
IR LED AND
PHOTODIODE
2× RS-232
DIGITIZER
3

High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
OVERVIEW (cont.)
UARTs to enable these signals to drive an infrared
communication interface directly.
Four synchronous serial interfaces (codec, SSI1,
SSI2, and MCP) are provided. Three of them (codec,
SSI2, and MCP) are multiplexed onto a single set of
interface pins. The full-duplex codec interface allows
direct connection of a standard audio codec chip to
the EP7211, allowing storage and playback of sound.
SSI2 supports both master and slave mode. SSI1
supports master mode only. Both SSI1 and SSI2 support two industry-standard protocols (SPI
Microwire
) for interfacing standard devices (e.g.,
Max148/9 or AD7811/12 ADC), and for allowing
peripheral expansion (e.g., a digitizer pen). A Multimedia Codec Port (MCP) can be used to communicate with a multi-functional codec device like the
Philips
UCB1100.
Packaging
and
EP7211
System Design
As shown in system block diagram, simply adding
desired memory and peripherals to the highly
integrated EP7211 completes a low-power system
solution. All necessary interface logic is integrated
on-chip.
Development Boards
Cirrus Logic offers an evaluation and development
environment for the EP7211 in the form of the
EDB7211-2 Development Kit.
The EDB7211-2 development kit is a complete development platform with access to the features and
capabilities of the EP7211. The kit provides the tools
required for developing and testing the design of a
highly integrated EP7211 system.
The EP7211 is available in a 208-pin LQFP package
and a 256-ball PBGA package.
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/corporate/contacts/
Preliminary product information describes products which are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet available. Advance product information
describes products which are in development and subject to development changes. Cirrus Logic, Inc. has made best efforts to ensure that the information contained
in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided “AS IS” without warranty of any kind (express
or implied). No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus Logic, Inc. for the use of this information, nor for infringements of patents or other rights of third parties. This document is the property of Cirrus Logic, Inc. and implies no license under patents, copyrights, trademarks, or trade secrets. No part of this publication may be copied,
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or otherwise) without the prior written
consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. Items from any Cirrus Logic website or disk may be printed for use by the user. However, no part of the printout or electronic files may
be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or otherwise) without the prior
written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc.Furthermore, no part of this publication may be used as a basis for manufacture or sale of any items without the prior written consent
of Cirrus Logic, Inc. The names of products of Cirrus Logic, Inc. or other vendors and suppliers appearing in this document may be trademarks or service marks of
their respective owners which may be registered in some jurisdictions. A list of Cirrus Logic, Inc. trademarks and service marks can be found at http://www.cirrus.com.
4
DS352PP3
JUL 2001

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CONVENTIONS........................................................................................................................11
1.1 Acronyms and Abbreviations................................................................................................................... 11
1.2 Units of Measurement ............................................................................................................................. 12
1.3 General Conventions............................................................................................................................... 12
1.4 Pin Description Conventions ...................................................................................................................12
2. PIN INFORMATION..................................................................................................................13
2.1 Pin Diagrams...........................................................................................................................................13
2.2 Pin Descriptions ......................................................................................................................................14
2.2.1 External Signal Functions........................................................................................................... 15
2.3 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing...................................................................................................................... 20
2.3.1 PBGA Ground Connections ....................................................................................................... 25
2.4 208-Pin LQFP Pin Listing ........................................................................................................................26
2.5 JTAG Pin Ordering for 208-Pin LQFP Package ......................................................................................31
3. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION.................................................................................................34
3.1 Main Functional Blocks ........................................................................................................................... 35
3.2 CPU Core ................................................................................................................................................37
3.3 Interrupt Controller .................................................................................................................................. 37
3.3.1 Interrupt Latencies in Different States ........................................................................................39
3.3.1.1 Operating State ..........................................................................................................39
3.3.1.2 Idle State .................................................................................................................... 40
3.3.1.3 Standby State ............................................................................................................. 40
3.4 Memory and I/O Expansion Interface ...................................................................................................... 42
3.5 EP7211 Boot ROM ..................................................................................................................................43
3.6 CL-PS6700 PC Card Controller Interface ...............................................................................................44
3.7 DRAM Controller with EDO Support ....................................................................................................... 47
3.8 Serial Interfaces ...................................................................................................................................... 51
3.8.1 Codec Sound Interface............................................................................................................... 52
3.8.1.1 Codec Interrupt Timing...............................................................................................52
3.8.2 MCP Interface ............................................................................................................................ 53
3.8.2.1 MCP Operation ..........................................................................................................54
3.8.2.2 MCP Frame Format ...................................................................................................54
3.8.2.3 Audio and Telecom Sample Rates and Data Transfer ...............................................56
3.8.2.4 MCP FIFO Operation .................................................................................................58
3.8.2.5 MCP Codec Control Register Data Transfer .............................................................. 59
3.8.3 ADC Interface — Master Mode Only SSI1 (Synchronous Serial Interface) ...............................60
3.8.4 Master/Slave SSI2 (Synchronous Serial Interface 2) .................................................................61
3.8.4.1 Read Back of Residual Data ...................................................................................... 62
3.8.4.2 Support for Asymmetric Traffic ...................................................................................63
3.8.4.3 Continuous Data Transfer .......................................................................................... 63
3.8.4.4 Discontinuous Clock...................................................................................................63
3.8.4.5 Error Conditions .........................................................................................................64
3.8.4.6 Clock Polarity ............................................................................................................. 64
3.9 LCD Controller with Support for On-Chip Frame Buffer ..........................................................................64
3.10 Internal UARTs (Two) and SIR Encoder..................................................................................................67
3.11 Timer Counters........................................................................................................................................ 67
3.11.1 Free Running Mode....................................................................................................................68
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
5

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
3.11.2 Prescale Mode ........................................................................................................................... 68
3.12 Realtime Clock ........................................................................................................................................ 68
3.13 Dedicated LED Flasher ...........................................................................................................................68
3.14 Two PWM Interfaces ...............................................................................................................................69
3.15 State Control............................................................................................................................................ 69
3.16 Resets .....................................................................................................................................................72
3.17 Clocks...................................................................................................................................................... 73
3.17.1 On-Chip PLL............................................................................................................................... 73
3.17.2 External Clock Input (13 MHz) ................................................................................................... 74
3.18 Dynamic Clock Switching When in the PLL Clocking Mode....................................................................75
3.19 Endianness.............................................................................................................................................. 75
3.20 Maximum EP7211-Based System........................................................................................................... 77
3.21 Boundary Scan........................................................................................................................................ 78
3.22 In-Circuit Emulation .................................................................................................................................79
3.22.1 Introduction................................................................................................................................. 79
3.22.2 Functionality ...............................................................................................................................79
4. MEMORY MAP .........................................................................................................................80
5. REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS ...................................................................................................81
5.1 Internal Registers .................................................................................................................................... 81
5.1.1 PADR Port A Data Register........................................................................................................85
5.1.2 PBDR Port B Data Register ....................................................................................................... 85
5.1.3 PDDR Port D Data Register ....................................................................................................... 85
5.1.4 PADDR Port A Data Direction Register ...................................................................................... 85
5.1.5 PBDDR Port B Data Direction Register...................................................................................... 85
5.1.6 PDDDR Port D Data Direction Register ..................................................................................... 85
5.1.7 PEDR Port E Data Register ....................................................................................................... 86
5.1.8 PEDDR Port E Data Direction Register...................................................................................... 86
5.2 SYSTEM Control Registers .....................................................................................................................86
5.2.1 SYSCON1 The System Control Register 1 ................................................................................ 86
5.2.2 SYSCON2 System Control Register 2 ....................................................................................... 89
5.2.3 SYSCON3 System Control Register 3 ....................................................................................... 91
5.2.4 SYSFLG — The System Status Flags Register ......................................................................... 92
5.2.5 SYSFLG2 System Status Register 2..........................................................................................94
5.3 Interrupt Registers ...................................................................................................................................95
5.3.1 INTSR1 Interrupt Status Register 1............................................................................................95
5.3.2 INTMR1 Interrupt Mask Register 1.............................................................................................97
5.3.3 INTSR2 Interrupt Status Register 2............................................................................................97
5.3.4 INTMR2 Interrupt Mask Register 2.............................................................................................98
5.3.5 INTSR3 Interrupt Status Register 3............................................................................................98
5.3.6 INTMR3 Interrupt Mask Register 3.............................................................................................99
5.4 Memory Configuration Registers............................................................................................................. 99
5.4.1 MEMCFG1 Memory Configuration Register 1............................................................................99
5.4.2 MEMCFG2 Memory Configuration Register 2..........................................................................100
5.4.3 DRFPR DRAM Refresh Period Register .................................................................................. 102
5.5 Timer/Counter Registers .......................................................................................................................103
5.5.1 TC1D Timer Counter 1 Data Register ...................................................................................... 103
5.5.2 TC2D Timer Counter 2 Data Register ...................................................................................... 103
5.5.3 RTCDR Realtime Clock Data Register .....................................................................................103
5.5.4 RTCMR Realtime Clock Match Register .................................................................................. 103
6
DS352PP3
JUL 2001

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
5.6 LEDFLSH Register ................................................................................................................................104
5.7 PMPCON Pump Control Register ......................................................................................................... 105
5.8 CODR — The CODEC Interface Data Register .................................................................................... 106
5.9 UART Registers .................................................................................................................................... 106
5.9.1 UARTDR1–2 UART1–2 Data Registers ................................................................................... 106
5.9.2 UBRLCR1–2 UART1–2 Bit Rate and Line Control Registers................................................... 107
5.10 LCD Registers.......................................................................................................................................108
5.10.1 LCDCON — The LCD Control Register ................................................................................... 108
5.10.2 PALLSW Least Significant Word — LCD Palette Register ....................................................... 110
5.10.3 PALMSW Most Significant Word — LCD Palette Register ....................................................... 110
5.10.4 FBADDR LCD Frame Buffer Start Address .............................................................................. 111
5.11 SSI Register .......................................................................................................................................... 111
5.11.1 SYNCIO Synchronous Serial ADC Interface Data Register ..................................................... 111
5.12 STFCLR Clear all ‘Start Up Reason’ flags location ............................................................................... 113
5.13 ‘End Of Interrupt’ Locations................................................................................................................... 113
5.13.1 BLEOI Battery Low End of Interrupt ......................................................................................... 113
5.13.2 MCEOI Media Changed End of Interrupt ................................................................................. 113
5.13.3 TEOI Tick End of Interrupt Location ......................................................................................... 113
5.13.4 TC1EOI TC1 End of Interrupt Location .................................................................................... 113
5.13.5 TC2EOI TC2 End of Interrupt Location .................................................................................... 113
5.13.6 RTCEOI RTC Match End of Interrupt ....................................................................................... 113
5.13.7 UMSEOI UART1 Modem Status Changed End of Interrupt ..................................................... 114
5.13.8 COEOI Codec End of Interrupt Location .................................................................................. 114
5.13.9 KBDEOI Keyboard End of Interrupt Location ........................................................................... 114
5.13.10 SRXEOF End of Interrupt Location .......................................................................................... 114
5.14 State Control Registers ......................................................................................................................... 114
5.14.1 STDBY Enter the Standby State Location ................................................................................ 114
5.14.2 HALT Enter the Idle State Location .......................................................................................... 114
5.15 SS2 Registers ....................................................................................................................................... 115
5.15.1 SS2DR Synchronous Serial Interface 2 Data Register ............................................................ 115
5.15.2 SS2POP Synchronous Serial Interface 2 Pop Residual Byte .................................................. 115
5.16 MCP Register Definitions ...................................................................................................................... 115
5.16.1 MCP Control Register .............................................................................................................. 116
5.16.1.1 Audio Sample Rate Divisor (ASD) ........................................................................... 116
5.16.1.2 Telecom Sample Rate Divisor (TSD) ....................................................................... 117
5.16.1.3 Multimedia Communications Port Enable (MCE) ..................................................... 117
5.16.1.4 A/D Sampling Mode (ADM) ...................................................................................... 118
5.16.1.5 MCP Interrupt Generation ........................................................................................ 118
5.16.1.6 Telecom Transmit FIFO Interrupt Mask (TTM) ......................................................... 118
5.16.1.7 Telecom Receive FIFO Interrupt Mask (TRM) ......................................................... 118
5.16.1.8 Audio Transmit FIFO Interrupt Mask (ATM) ............................................................. 119
5.16.1.9 Audio Receive FIFO Interrupt Mask (ARM) ............................................................. 119
5.16.1.10 Loop Back Mode (LBM) ........................................................................................... 119
5.16.2 MCP Data Registers................................................................................................................. 121
5.16.2.1 MCP Data Register 0 ............................................................................................... 121
5.16.2.2 MCP Data Register 1 ............................................................................................... 123
5.16.2.3 MCP Data Register 2 ............................................................................................... 125
5.16.3 MCP Status Register ................................................................................................................ 127
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
7

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
5.16.3.1 Audio Transmit FIFO Service Request Flag (ATS) (read-only, maskable
interrupt)................................................................................................................... 127
5.16.3.2 Audio Receive FIFO Service Request Flag (ARS) (read-only, maskable interrupt) .127
5.16.3.3 Telecom Transmit FIFO Service Request Flag (TTS) (read-only,
maskable interrupt) ..................................................................................................127
5.16.3.4 Telecom Receive FIFO Service Request Flag (TRS) (read-only, maskable
interrupt)................................................................................................................... 128
5.16.3.5 Audio Transmit FIFO Underrun Status (ATU) (read/write, non-maskable interrupt). 128
5.16.3.6 Audio Receive FIFO Overrun Status (ARO) (read/write, non-maskable interrupt)...128
5.16.3.7 Telecom Transmit FIFO Underrun Status (TTU) (read/write, non-maskable
interrupt)................................................................................................................... 128
5.16.3.8 Telecom Receive FIFO Overrun Status (TRO) (read/write, non-maskable
interrupt)................................................................................................................... 128
5.16.3.9 Audio Transmit FIFO Not Full Flag (ANF) (read-only, non-interruptible) .................. 129
5.16.3.10 Audio Receive FIFO Not Empty Flag (ANE) (read-only, non-interruptible) .............. 129
5.16.3.11 Telecom Transmit FIFO Not Full Flag (TNF) (read-only, non-interruptible) ..............129
5.16.3.12 Telecom Receive FIFO Not Empty Flag (TNE) (read-only, non-interruptible) .......... 129
5.16.3.13 Codec Write Completed Flag (CWC) (read-only, non-interruptible) ......................... 129
5.16.3.14 Codec Read Completed Flag (CRC) (read-only, non-interruptible)..........................129
5.16.3.15 Audio Codec Enabled Flag (ACE) (read-only, non-interruptible).............................. 130
5.16.3.16 Telecom Codec Enabled Flag (TCE) (read-only, non-interruptible).......................... 130
6. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS......................................................................................... 133
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings................................................................................................................... 133
6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions ................................................................................................... 133
6.3 DC Characteristics ................................................................................................................................ 133
6.4 AC Characteristics................................................................................................................................. 135
6.5 I/O Buffer Characteristics ......................................................................................................................150
7. TEST MODES ........................................................................................................................ 151
7.1 Oscillator and PLL Bypass Mode ..........................................................................................................151
7.2 Oscillator and PLL Test Mode ...............................................................................................................151
7.3 Debug/ICE Test Mode ..........................................................................................................................152
7.4 Hi-Z (System) Test Mode...................................................................................................................... 152
7.5 Software Selectable Test Functionality................................................................................................. 152
8. PACKAGE SPECIFICATIONS.............................................................................................. 154
8.1 EP7211 256-Ball PBGA (17 × 17 × 1.53-mm Body) Dimensions .......................................................... 154
8.2 208-Pin LQFP Package Outline Drawing .............................................................................................155
9. ORDERING INFORMATION ................................................................................................. 156
10. APPENDIX A: BOOT CODE................................................................................................. 157
11. INDEX..................................................................................................................................... 162
8
DS352PP3
JUL 2001

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2-1. SSI/Codec/MCP Pin Multiplexing.................................................................................................... 18
Table 2-2. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing ............................................................................................................ 20
Table 2-3. PBGA Balls to Connect to Ground (V
Table 2-4. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing ................................................................................................. 24
Table 2-5. JTAG Pin Ordering for 208-Pin LQFP Package ............................................................................. 28
Table 3-1. Interrupt Allocation in First Interrupt Register ................................................................................. 35
Table 3-2. Interrupt Allocation in Second Interrupt Register ............................................................................ 36
Table 3-3. Interrupt Allocation in Third Interrupt Register ................................................................................ 36
Table 3-4. External Interrupt Source Latencies................................................................................................ 38
Table 3-5. Boot Options ................................................................................................................................... 40
Table 3-6. Chip Select Address Ranges After Boot From On-Chip Boot ROM ............................................... 40
Table 3-7. CL-PS6700 Memory Map ............................................................................................................... 41
Table 3-8. Space Field Decoding..................................................................................................................... 42
Table 3-9. Physical to DRAM Address Mapping .............................................................................................. 45
Table 3-10. DRAM Address Mapping When Connected to an External 32-Bit DRAM Memory System ........... 46
Table 3-11. DRAM Address Mapping for a 16-Bit-Wide DRAM Memory System .............................................. 47
Table 3-12. Serial Interface Options .................................................................................................................. 48
Table 3-13. Serial-Pin Assignments ................................................................................................................... 48
Table 3-14. ADC Interface Operation Frequencies............................................................................................ 57
Table 3-15. Peripheral Status in Different Power Management States.............................................................. 67
Table 3-16. Effect of Endianness on Read Operations...................................................................................... 73
Table 3-17. Effect of Endianness on Write Operations ...................................................................................... 73
Table 3-18. Instructions Supported in JTAG Mode ............................................................................................ 75
Table 4-1. EP7211 Memory Map ..................................................................................................................... 77
Table 5-1. CL-PS7111-Compatible................................................................................................................... 79
Table 5-2. Internal I/O Memory Locations (EP7211 Only) ............................................................................... 81
Table 5-3. Port Byte Addresses in Big Endian Mode ....................................................................................... 81
Table 5-4. Values of the Bus Width Field ......................................................................................................... 97
Table 5-5. Values of the Wait State Field at 13 MHz and 18 MHz ...................................................................98
Table 5-6. Values of the Wait State Field at 36 MHz........................................................................................ 98
Table 5-7. LED Flash Rates........................................................................................................................... 101
Table 5-8. LED Duty Ratio ............................................................................................................................. 101
Table 5-9. Sense of PWM control lines.......................................................................................................... 102
Table 5-10. UART Bit Rates Running from the PLL Clock............................................................................... 104
Table 5-11. UART Bit Rates Running from an External 13.0 MHz Clock ........................................................ 104
Table 5-12. Grey Scale Value to Color Mapping .............................................................................................. 107
Table 5-13. MCP Control Register ................................................................................................................... 117
Table 5-14. MCP Data Register 0 .................................................................................................................... 120
Table 5-15. MCP Data Register 1 .................................................................................................................... 121
Table 5-16. MCP Data Register 2 .................................................................................................................... 123
Table 5-17. MCP Control, Data and Status Register Locations ....................................................................... 128
Table 6-1. DC Characteristics ........................................................................................................................ 130
Table 6-2. AC Timing Characteristics ............................................................................................................ 132
Table 6-3. Timing Characteristics .................................................................................................................. 133
Table 6-4. I/O Buffer Output Characteristics .................................................................................................. 147
Table 7-1. EP7211 Hardware Test Modes ..................................................................................................... 148
Table 7-2. Oscillator and PLL Test Mode Signals .......................................................................................... 149
Table 7-3. Software Selectable Test Functionality ......................................................................................... 150
) ........................................................................................ 23
SS
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
9

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1-1. A EP7211–Based System................................................................................................................... 3
Figure 2-1. 208-Pin LQFP (Low Profile Quad Flat Pack) Pin Diagram ............................................................... 13
Figure 2-2. 256-Ball Plastic Ball Grid Array Diagram .......................................................................................... 14
Figure 3-1. EP7211 Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................... 37
Figure 3-2. Codec Interrupt Timing ..................................................................................................................... 52
Figure 3-3. Data Format of MCP Subframe 0 ..................................................................................................... 55
Figure 3-4. MCP Packet Organization ................................................................................................................ 55
Figure 3-5. Audio Codec Enable Timing .............................................................................................................57
Figure 3-6. Format for the Audio and Telecom FIFOs......................................................................................... 59
Figure 3-7. SSI2 Port Directions in Slave and Master Mode............................................................................... 61
Figure 3-8. Residual Byte Reading ..................................................................................................................... 63
Figure 3-9. Video Buffer Mapping ....................................................................................................................... 66
Figure 3-10. State Diagram ................................................................................................................................... 72
Figure 3-11. CLKEN Timing Entering the Standby State.......................................................................................74
Figure 3-12. CLKEN Timing Leaving the Standby State ...................................................................................... 75
Figure 3-13. A Maximum EP7211 Based System ................................................................................................. 77
Figure 5-1. MCP Data Register 0: MCDR0 ....................................................................................................... 122
Figure 5-2. MCP Data Register 1: MCDR1 ....................................................................................................... 124
Figure 5-3. MCP Data Register 2: MCDR2 ....................................................................................................... 126
Figure 5-4. MCP Status Register: MCSR ......................................................................................................... 131
Figure 6-1. Expansion and ROM Timing ...........................................................................................................137
Figure 6-2. Expansion and ROM Sequential Read Timings..............................................................................138
Figure 6-3. Expansion and ROM Write Timings................................................................................................139
Figure 6-4. DRAM Read Cycles at 13 MHz and 18.432 MHz ........................................................................... 140
Figure 6-5. DRAM Read Cycles at 36 MHz ...................................................................................................... 141
Figure 6-6. DRAM Write Cycles at 13 MHz and 18 MHz .................................................................................. 142
Figure 6-7. DRAM Write Cycles at 36 MHz....................................................................................................... 143
Figure 6-8. Video Quad Word Read from DRAM at 13 MHz and 18 MHz ........................................................ 144
Figure 6-9. Quad Word Read from DRAM at 36 MHz .......................................................................................145
Figure 6-10. DRAM CAS Before RAS Refresh Cycle at 13 MHz and 18 MHz.................................................... 146
Figure 6-11. DRAM CAS Before RAS Refresh Cycle at 36 MHz ........................................................................ 147
Figure 6-12. LCD Controller Timings................................................................................................................... 148
Figure 6-13. SSI Interface for AD7811/2 ............................................................................................................. 148
Figure 6-14. SSI Timing Interface for MAX148/9 ................................................................................................149
Figure 6-15. SSI2 Interface Timings.................................................................................................................... 149
10
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
1. CONVENTIONS
This section presents acronyms, abbreviations, units of measurement, and conventions used in this
data book.
1.1 Acronyms and Abbreviations
The following table lists abbreviations and acronyms used in this data book.
Acronym/
Abbreviation
AC alternating current
A/D analog-to-digital
ADC analong-to-digital converter
codec coder/decoder
CMOS complementary metal oxide
semiconductor
CPU central processing unit
D/A digital-to-analog
DC direct current
DMA direct-memory access
DRAM dynamic random access memory
EPB embedded peripheral bus
FCS frame check sequence
FIFO first in/first out
GPIO general purpose I/O
ICT in circuit test
IR infrared
IrDA Infrared Data Association
JTAG Joint Test Action Group
LCD liquid crystal display
LED light-emitting diode
LSB least significant bit
Definition
Acronym/
Abbreviation
MIPS millions of instructions per second
LQFP low profile quad flat pack
MMU memory management unit
MSB most significant bit
PBGA plastic ball grid array
PCB printed circuit board
PDA personal digital assistant
PIA peripheral interface adapter
PLL phase locked loop
PSU power supply unit
p/u pull-up resistor
RAM random access memory
RISC reduced instruction set computer
ROM read-only memory
RTC realtime clock
SIR slow (9600–115.2 kbps) infrared
SRAM static random access memory
SSI synchronous serial interface
TAP test access port
TLB translation look aside buffer
UART universal asynchronous receiver
transmitter
Definition
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Conventions
11
1.2 Units of Measurement
\
Symbol Unit of Measure
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Symbol Unit of Measure
°C
Hz hertz (cycle per second)
kbits/s kilobits per second
kbyte kilobyte (1,024 bytes)
kHz kilohertz
kΩ kilohm
Mbps megabits (1,048,576 bits) per second
Mbyte megabyte (1,048,576 bytes)
MHz megahertz (1,000 kilohertz)
µA microampere
degree Celsius
µF microfarad
µWmicrowatt
µs microsecond (1,000 nanoseconds)
mA milliampere
mW milliwatt
ms millisecond (1,000 microseconds)
ns nanosecond
Vvolt
Wwatt
1.3 General Conventions
Hexadecimal numbers are presented with all letters in uppercase and a lowercase h appended. For
example, 14h and 03CAh are hexadecimal numbers. Binary numbers are enclosed in single quotation
marks when in text (for example, ‘11’ designates a binary number). Numbers not indicated by an h
or quotation marks are decimal.
Registers are referred to by acronym, as listed in the tables on the previous page, with bits listed in
brackets MSB-to-LSB separated by a colon (:) (for example, CODR[7:0]), or LSB-to-MSB
separated by a hyphen (for example, CODR[0–2]).
The use of ‘tbd’ indicates values that are ‘to be determined’, ‘n/a’ designates ‘not available’, and
‘n/c’ indicates a pin that is a ‘no connect’.
1.4 Pin Description Conventions
Abbreviations used for signal directions in Section 2 are listed in the following table:
Abbreviation Direction
I Input
OOutput
I/O Input or Output
12
Conventions
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
2. PIN INFORMATION
2.1 Pin Diagrams
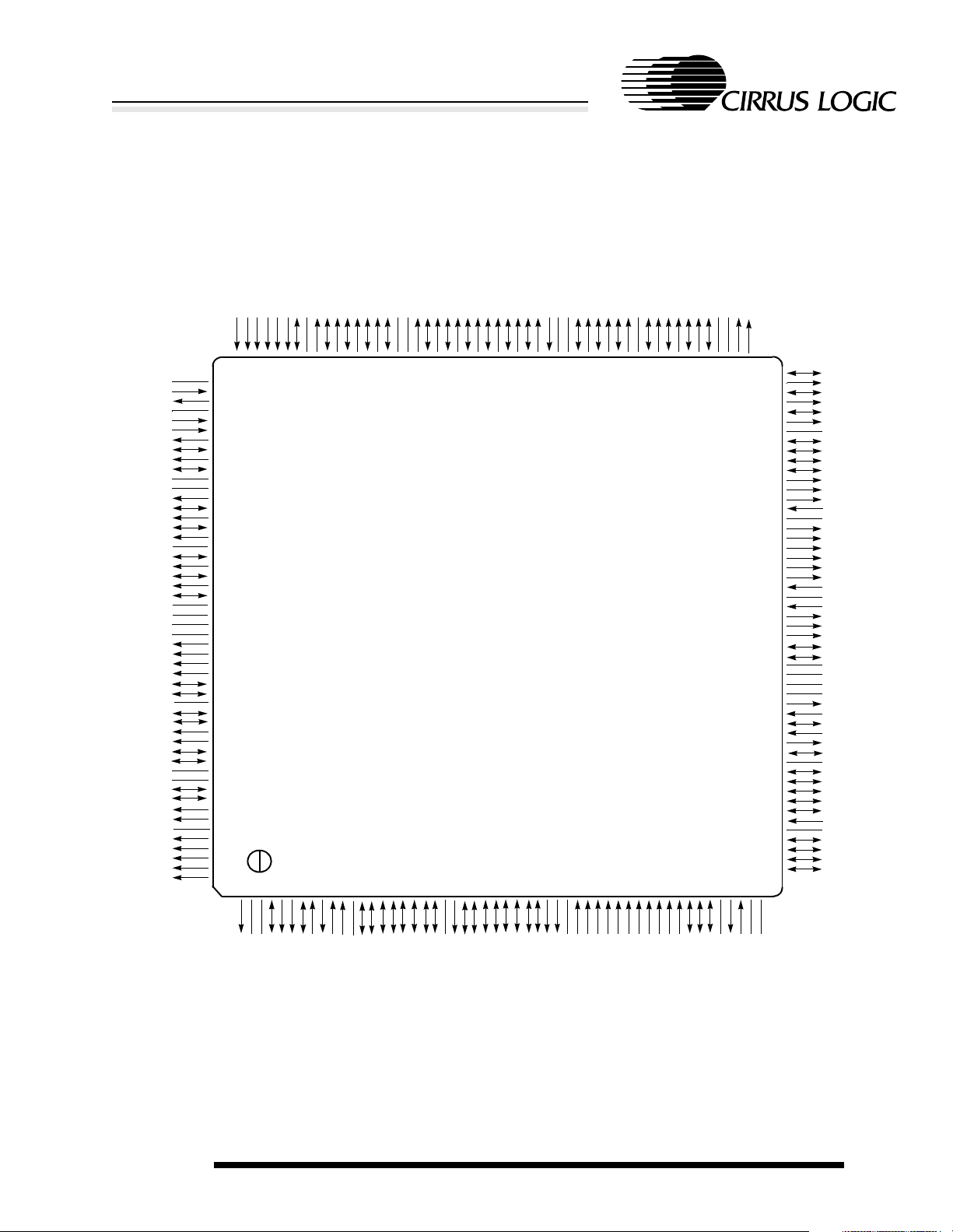
NMEDCHG/NBROM
NEXTPWR
NURESET
NPOR
D[7]
A[7]
D[8]
A[8]
D[9]
D[10]
A[10]
VSSIO
VDDIO
A[11]
D[12]
A[12]
D[13]
A[13]
D[14]
NBATCHG
VSSIO
BATOK
D[11]
A[9]
A[14]
D[17]
D[15]
A[15]/DRA[12]
A[17]/DRA[10]
NTRST
A[16]/DRA[11]
VSSIO
D[16]
VDDIO
D[18]
A[18]/DRA[9]
D[19]
A[19]/DRA[8]
D[20]
VSSIO
A[21]/DRA[6]
D[22]
D[23]
A[23]/DRA[4]
D[24]
VSSIO
VDDIO
A[24]/DRA[3]
A[22]/DRA[5]
D[21]
A[20]/DRA[7]
HALFWORD
VDDOSC
MOSCIN
MOSCOUT
VSSOSC
WAKE UP
NPWRFL
A[6]
D[6]
A[5]
D[5]
VDDIO
VSSIO
A[4]
D[4]
A[3]
D[3]
A[2]
VSSIO
D[2]
A[1]
D[1]
A[0]
D[0]
VSSCORE
VDDCORE
VSSIO
VDDIO
CL[2]
CL[1]
FRM
DD[3]
DD[2]
VSSIO
DD[1]
DD[0]
NRAS[1]
NRAS[0]
NCAS[3]
NCAS[2]
VDDIO
VSSIO
NCAS[1]
NCAS[0]
NMWE
NMOE
VSSIO
NCS[0]
NCS[1]
NCS[2]
NCS[3]
NCS[4]
130
131
132
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
140
139
141
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
M
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
2345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849515052
1
142
134
138
137
136
135
133
EP7211
208-Pin LQFP
(Top View)
123
111
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
106
107
108
109
110
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
124
125
126
127
128
129
D[25]
A[25]/DRA[2]
D[26]
A[26]/DRA[1]
D[27]
A[27]/DRA[0]
VSSIO
D[28]
D[29]
D[30]
D[31]
BUZ
COL[0]
COL[1]
TCLK
VDDIO
COL[2]
COL[3]
COL[4]
COL[5]
COL[6]
COL[7]
FB[0]
VSSIO
FB[1]
SMPCLK
ADCOUT
ADCCLK
DRIVE[0]
DRIVE[1]
VDDIO
VSSIO
VDDCORE
VSSCORE
NADCCS
ADCIN
SSIRXFR
SSIRXDA
SSITXDA
SSITXFR
VSSIO
SSICLK
PD[0]/LEDFLSH
PD[1]
PD[2]
PD[3]
TMS
VDDIO
PD[4]
PD[5]
PD[6]
PD[7]
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
NCS[5]
VSSIO
VDDIO
TDI
PB[7]
PB[6]
PB[5]
PB[4]
TXD[2]
WORD
WRITE
EXPCLK
VSSIO
RXD[2]
EXPRDY
PB[3]
RUN/CLKEN
TDO
PB[2]
PB[1]/PRDY[2]
PA[6]
PA[5]
PA[4]
PA[3]
PA[2]
PA[1]
VDDIO
PA[7]
PA[0]
PB[0]/PRDY[1]
TXD[1]
LEDDRV
CTS
DSR
DCD
VSSIO
PHDIN
RXD[1]
EINT[3]
NEINT[2]
NEINT[1]
NTEST[1]
NEXTFIQ
NTEST[0]
PE[2]/CLKSEL
PE[1]BOOTSEL[1]
PE[0]BOOTSEL[0]
N/C
RTCIN
VDDRTC
VSSRTC
RTCOUT
Figure 2-1. 208-Pin LQFP (Low Profile Quad Flat Pack) Pin Diagram
Pin Information
13
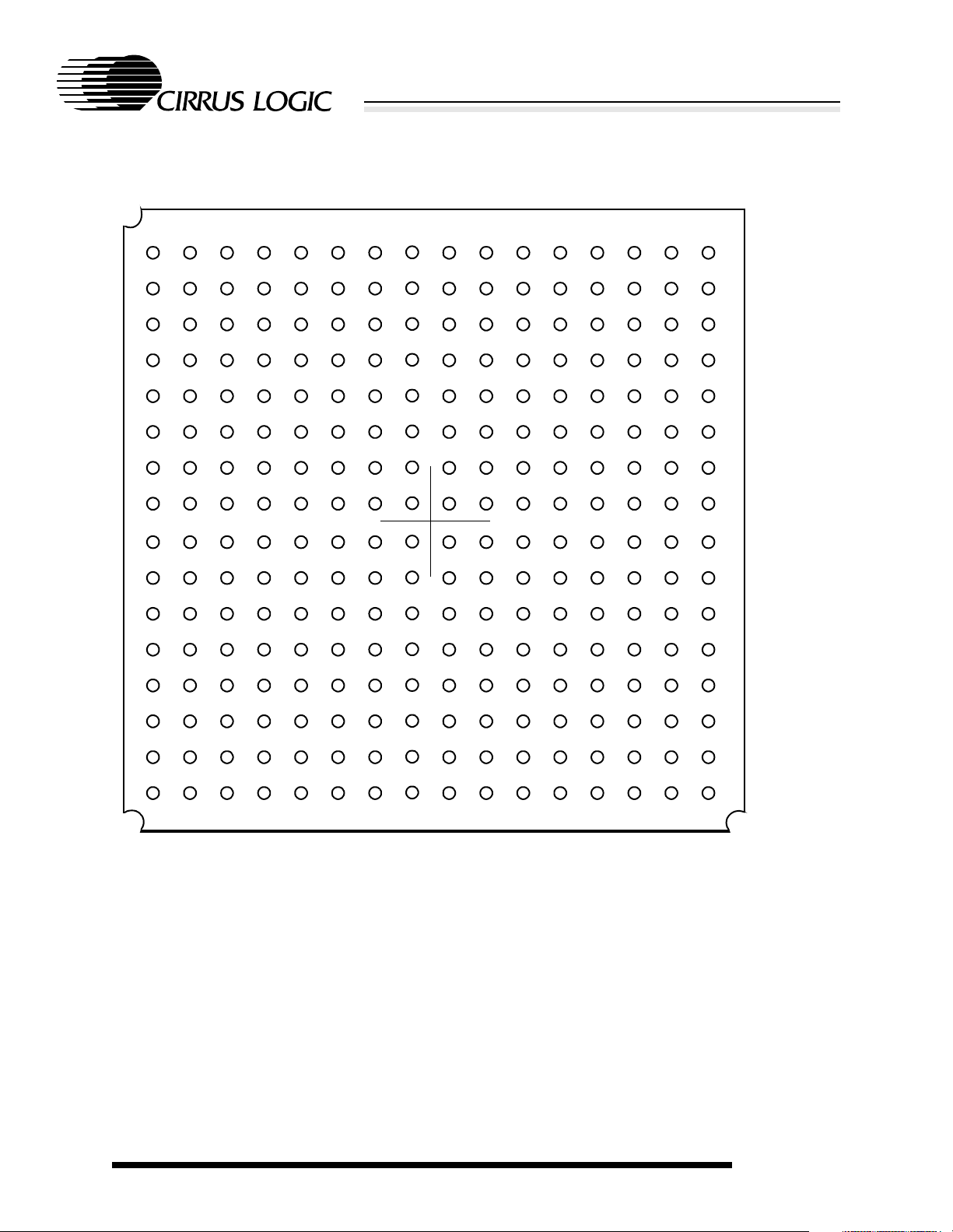
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
EP7211
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
256-Ball PBGA
(Bottom View)
(Call Factory for Availability)
Figure 2-2. 256-Ball Plastic Ball Grid Array Diagram
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
2.2 Pin Descriptions
This table describes the function of all the external signals to the EP7211. Note that all output signals
are tri-stateable to enable the Hi-Z test modes to be supported.
14
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
2.2.1 External Signal Functions
Function
Data bus D[0–31] I/O 32-bit system data bus for DRAM, ROM/SRAM/Flash, and memory mapped
Address bus
Signal
Name
A[0–14] O Least significant 15 bits of system byte address during ROM/SRAM/Flash and
A[15]/
DRA[12]–
A[27]/DRA[0]
NRAS[0–1] O DRAM RAS outputs to DRAM banks 0 to 1
NCAS[0–3] I/O DRAM CAS outputs for bytes 0 to 3 within 32-bit word
NMOE O DRAM, ROM/SRAM/Flash, and expansion output enable
NMWE O DRAM, ROM/SRAM/Flash, and expansion write enable
Signal Description
I/O expansion
expansion cycles
O 13-bit multiplexed DRAM word address during DRAM cycles or address bits
16 to 27 of system byte address during ROM/SRAM/Flash and expansion
cycles
– Whenever the EP7211 is in the Standby State, the external address and
data buses are driven low. The RUN signal is used internally to force these
buses to be driven low. This is done to prevent peripherals that are powerdown from draining current. Also, the internal peripheral’s signals get set to
their Reset State
– For additional power saving, the multiplexed DRAM address lines are output
on the high order ROM address lines where the lightest loading is expected.
.
Memory and
Expansion
Interface
NCS[0–3] O Expansion channel I/O strobes; active low SRAM-like chip selects for expan-
sion
NCS[4–5] O Expansion channel I/O strobes; active low CS for expansion or for
CL-PS6700 select
EXPRDY I/O Expansion channel ready; external expansion devices drive this low to extend
the bus cycle
WRITE O Transfer direction, low during reads, high during writes from the
EP7211
WORD O Word access enable; driven high during word-wide cycles, low during byte-
wide cycles
HALFWORD O Half-Word access flag; driven high to denote upper half-word accesses
EXPCLK I/O Expansion clock rate is the same as the CPU clock for 13 MHz and 18 MHz. It
runs at 36.864 MHz for 36,49 and 74 MHz modes; in 13 MHz mode this pin is
used as the clock input
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
15

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Function
Interrupts
Power
Management
Signal
Name
NMEDCHG/
BROM
NEXTFIQ I External active low fast interrupt request input
EINT3 I External active high interrupt request input
NEINT[1–2] I Two general purpose, active low interrupt inputs
NPWRFL I Power fail input; active low deglitched input to force system into the Standby
BATOK I Main battery OK input; falling edge generates a FIQ, a low level in the Standby
NEXTPWR I External power sense; must be driven low if the system is powered by an
NBATCHG I New battery sense; driven low if battery voltage falls below the "no-battery"
NPOR I Power-on reset input; active low input completely resets the entire system;
Signal Description
I Media changed input; active low, deglitched — it is used as a general purpose
FIQ interrupt during normal operation. It is also used on power up to configure
the processor to either boot from the internal Boot ROM, or from external
memory. When low, the chip will boot from the internal Boot ROM.
State
State inhibits system start up; deglitched input
external source
threshold; it is a deglitched input
must be held active for at least two clock cycles to be detected cleanly
State Control
MCP, Codec or
SSI2
Interface
(See Note)
RUN/CLKEN This pin is programmed to either output the RUN signal or the CLKEN signal.
The CLKENSL bit is used to configure this pin. When RUN is selected, the pin
will be high when the system is active or idle, low while in the Standby State.
When CLKEN is selected, the pin will only be driven low when in the Standby
State.
WAKEUP I Wake up deglitched input signal; rising edge forces system into the Operating
State; active after a power-on reset
NURESET I User reset input; active low deglitched input from user reset button.
This pin is also latched upon the rising edge of NPOR and read along with the
input pins NTEST[0–1] to force the device into special test modes.
SSICLK I/O MCP/Codec/SSI2 clock signal
SSITXFR I/O MCP/Codec/SSI2 serial data output frame/synchronization pulse output
SSITXDA O MCP/Codec/SSI2 serial data output
SSIRXDA I MCP/Codec/SSI2 serial data input
SSIRXFR I/O SSI2 serial data input frame/synchronization pulse
16
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Function
ADC
Interface
(SSI1)
IrDA and
RS232
Interfaces
Signal
Name
ADCCLK O Serial clock output
NADCCS O Chip select for ADC interface
ADCOUT O Serial data output
ADCIN I Serial data input
SMPCLK O Sample clock output
LEDDRV O Infrared LED drive output (UART1)
PHDIN I Photo diode input (UART1)
TXD[1–2] O RS232 UART1 and 2 TX outputs
RXD[1–2] I RS232 UART1 and 2 RX inputs
DSR I RS232 DSR input
DCD I RS232 DCD input
CTS I RS232 CTS input
DD[0–3] I/O LCD serial display data; pins can be used on power up to read the ID of some
Signal Description
LCD modules
LCD
Keyboard &
Buzzer drive
LED Flasher
General
Purpose I/O
CL1 O LCD line clock
CL2 O LCD pixel clock
FRM O LCD frame synchronization pulse output
M O LCD AC bias drive
COL[0–7] O Keyboard column drives
BUZ O Buzzer drive output
PD[0]/
LEDFLSH
PA[0–7] I/O Port A I/O (Bit 6 for boot clock option, Bit 7 for CL-PS6700 PRDY input); also
PB[0]/PRDY1 I/O Port B I/O. All eight Port B bits can be used as GPIOs.
PB[1]/PRDY2
PB[2–7]
PD[0–7] I/O Port D I/O
O LED flasher driver — multiplexed with Port D Bit 0. This pin can provide up to
4 mA of drive current.
used as keyboard row inputs
When the PC CARD1 or 2 control bits in the SYSCON2 register are deasserted, PB[0] and PB[1] are available for GPIO. When asserted, these port
bits are used as the PRDY signals for connected
CL-PS6700 PC Card Host Adapter devices.
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
17
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Function
PWM
Drives
Boundary
Scan
Signal
Name
PE[0]/
BOOTSEL0
PE[1]/
BOOTSEL1
PE[2]/
CLKSEL
DRIVE[0–1] I/O PWM drive outputs. These pins are inputs on power up to determine what
FB[0–1] I PWM feedback inputs
TDI I JTAG data in
TDO O JTAG data out
TMS I JTAG mode select
TCLK I JTAG clock
Signal Description
I/O Port E I/O (3 bits only). Can be used as general purpose I/O during normal
operation.
I/O During power-on reset, PE[0] and PE[1] are inputs and are latched by the ris-
ing edge of NPOR to select the memory width that the
EP7211 will use to read from the boot code storage device (e.g., external 8-bitwide Flash bank).
I/O During power-on reset, PE[2] is latched by the rising edge of NPOR to select
the clock mode of operation (i.e., either the PLL or external
13 MHz clock mode).
polarity the output of the PWM should be when active. Otherwise, these pins
are always an output.
TNRST I JTAG async reset
Test NTEST[0–1] I Test mode select inputs. These pins are used in conjunction with the power-on
latched state of NURESET.
MOSCIN
MOSCOUT
Oscillators
RTCIN
RTCOUT
I
O
I
O
Main 3.6864 MHz oscillator for 18.432MHz–73.728 MHz PLL
Realtime clock 32.768 kHz oscillator
NOTE: See table below for pin assignment and direction following pin multiplexing.
.
Table 2-1. SSI/Codec/MCP Pin Multiplexing
SSI2 Codec MCP Direction Strength
SSICCLK PCMCLK SIBCLK I/O 1
SSITXFR PCMSYNC SIBSYNC I/O 1
SSITXDA PCMOUT SIBDOUT Output 1
SSIRXDA PCMIN SIBDIN Input
SSIRXFR p/u* p/u* I/O 1
18
* p/u = use an ~10 k pull-up
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001

EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
The selection between SSI2 and the codec is controlled by the state of the SERSEL bit in SYSCON2
(Section 5.2.2 SYSCON2 System Control Register 2). The choice between the SSI2, codec, and
the MCP is controlled by the MCPSEL bit in SYSCON3 (Section 5.2.3 SYSCON3 System Control
Register 3).
NOTE: All deglitched inputs are via the 16.384 kHz clock. Therefore, the input signal must be active for at
least ~61 µs to be detected cleanly.
The following output pins are implemented as bi-directional pins to enable the output side of the pad
to be monitored and hence provide more accurate control of timing or duration:
RUN The RUN pin is looped back in to skew the address and data bus from each other.
NCAS[3:0] The NCAS pins are looped back into the EP7211 to be used as the actual clock
source for the data to be latched internally.
Drive 0 and 1 Drive 0 and 1 are looped back in on power up to determine what polarity the output
of the PWM should be when active.
DD[3:0] DD[3:0] are looped back in on power up to enable the reading of the ID of some
LCD modules.
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
19
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
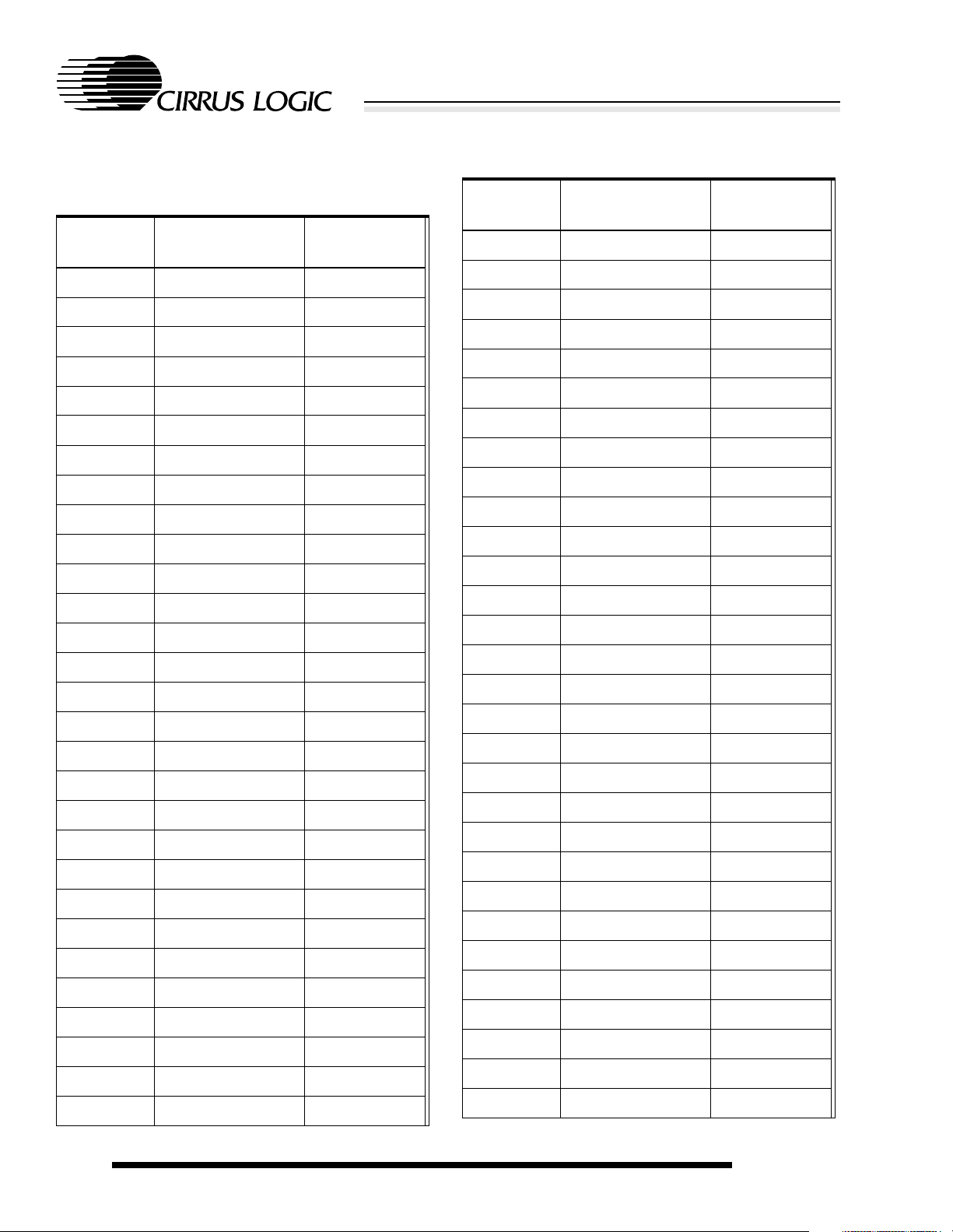
2.3 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
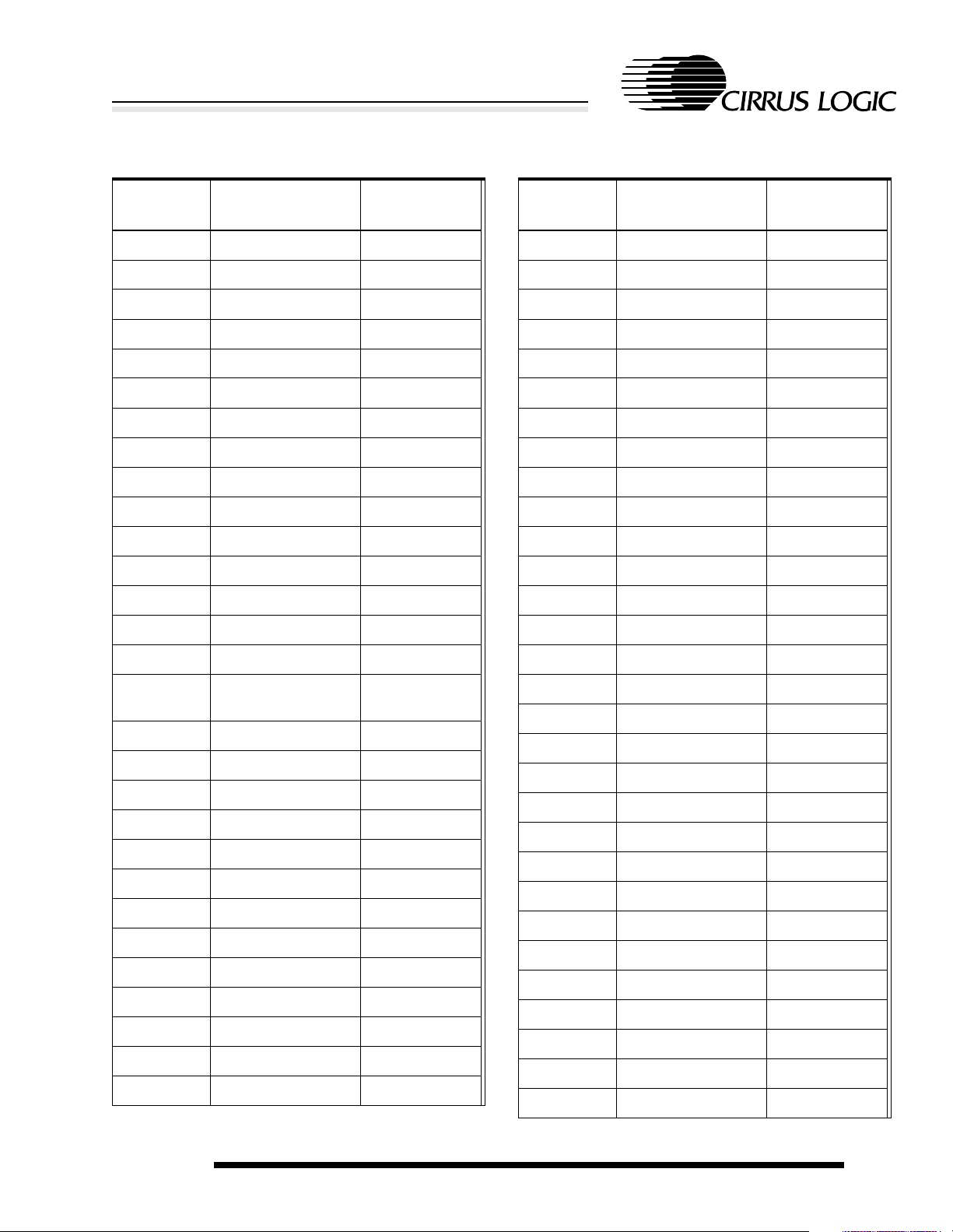
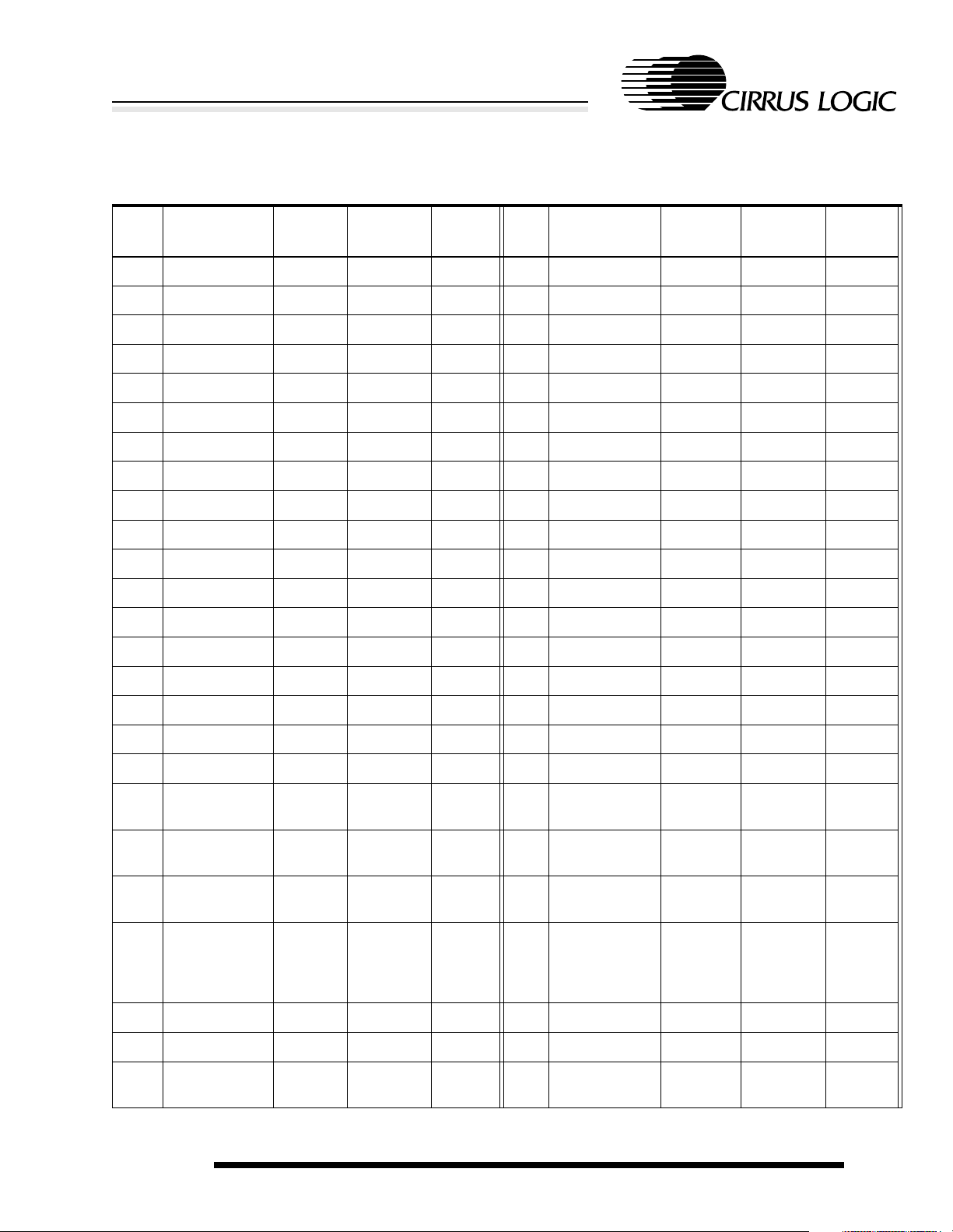
Table 2-2. 256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
A1 VDDIO Pad power
A2 NCS[4] O
A3 NCS[1] O
A4 NCAS[0] O
A5 NCAS[3] O
A6 DD[1] O
A7 M O
A8 VDDIO Pad power
A9 D[0] I/O
A10 D[2] I/O
A11 A[3] O
A12 VDDIO Pad power
A13 A[6] O
A14 MOSCOUT O
A15 VDDOSC Oscillator power
A16 VSSIO Pad ground
B1 NCS[5] O
B2 VDDIO Pad power
B3 NCS[3] O
B4 NMOE O
B5 VDDIO Pad power
B6 NRAS[1] O
B7 DD[2] O
B8 CL[1] O
B9 VDDCORE Core power
B10 D[1] I/O
B11 A[2] O
B12 A[4] O
B13 A[5] O
Name Type
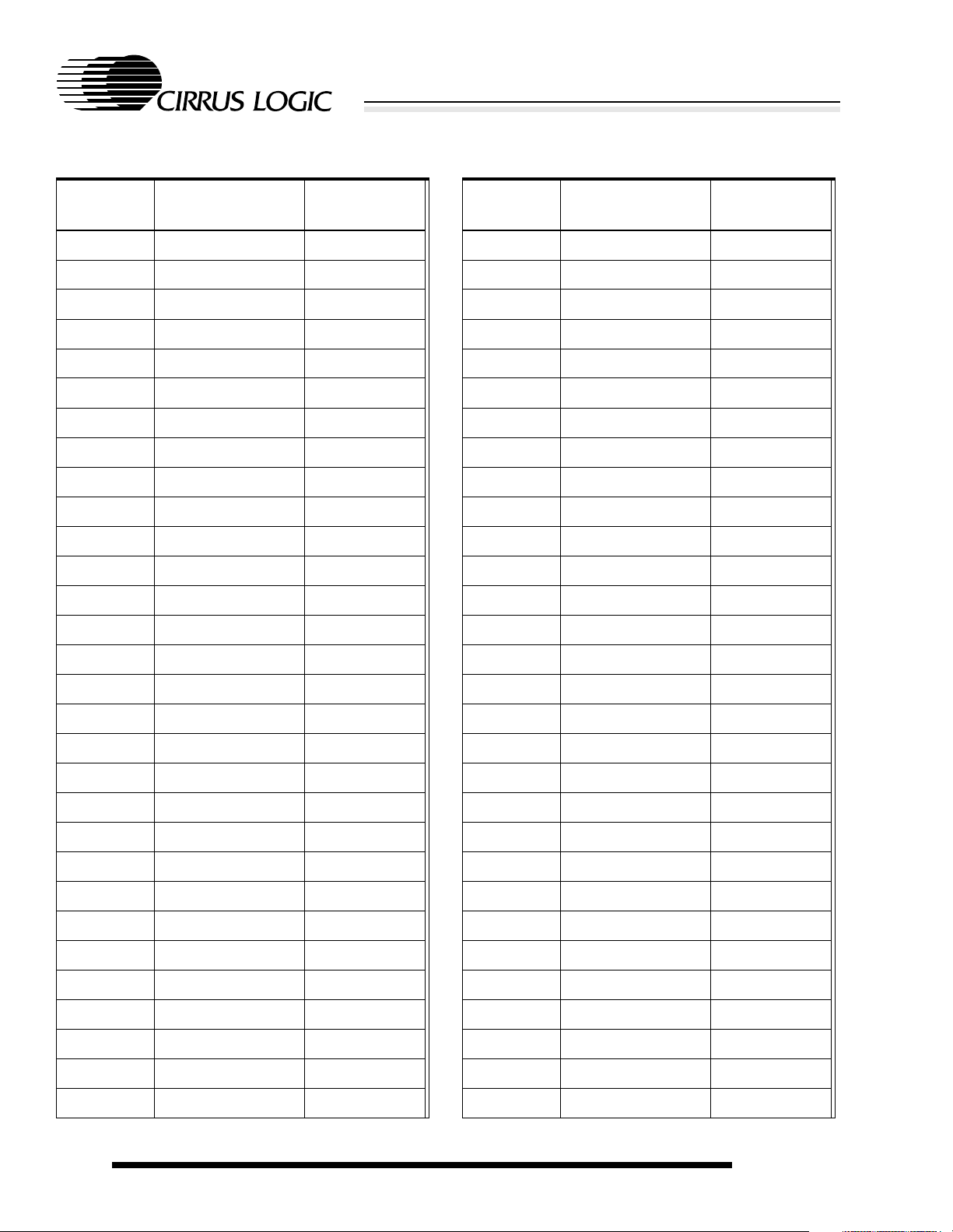
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
B14 WAKEUP I
B15 VSSIO Pad ground
B16 NURESET I
C1 VDDIO Pad power
C2 EXPCLK I
C3 VSSIO Pad ground
C4 VDDIO Pad power
C5 VSSIO Pad ground
C6 VSSIO Pad ground
C7 VSSIO Pad ground
C8 VDDIO Pad power
C9 VSSIO Pad ground
C10 VSSIO Pad ground
C11 VSSIO Pad ground
C12 VDDIO Pad power
C13 VSSIO Pad ground
C14 VSSIO Pad ground
C15 NPOR I
C16 NEXTPWR I
D1 WRITE O
D2 EXPRDY I
D3 VSSIO Pad ground
D4 VDDIO Pad power
D5 NCS[2] O
D6 NMWE O
D7 NRAS[0] O
D8 CL[2] O
D9 VSSCORE Core ground
D10 D[4] I/O
D11 NPWRFL I
Name Type
20
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
D12 MOSCIN I
D13 VDDIO Pad power
D14 VSSIO Pad ground
D15 D[7] I/O
D16 D[8] I/O
E1 RXD[2] I
E2 PB[7] I
E3 TDI I
E4 WORD O
E5 VSSIO Pad ground
E6 NCS[0] O
E7 NCAS[2] O
E8 FRM O
Name Type
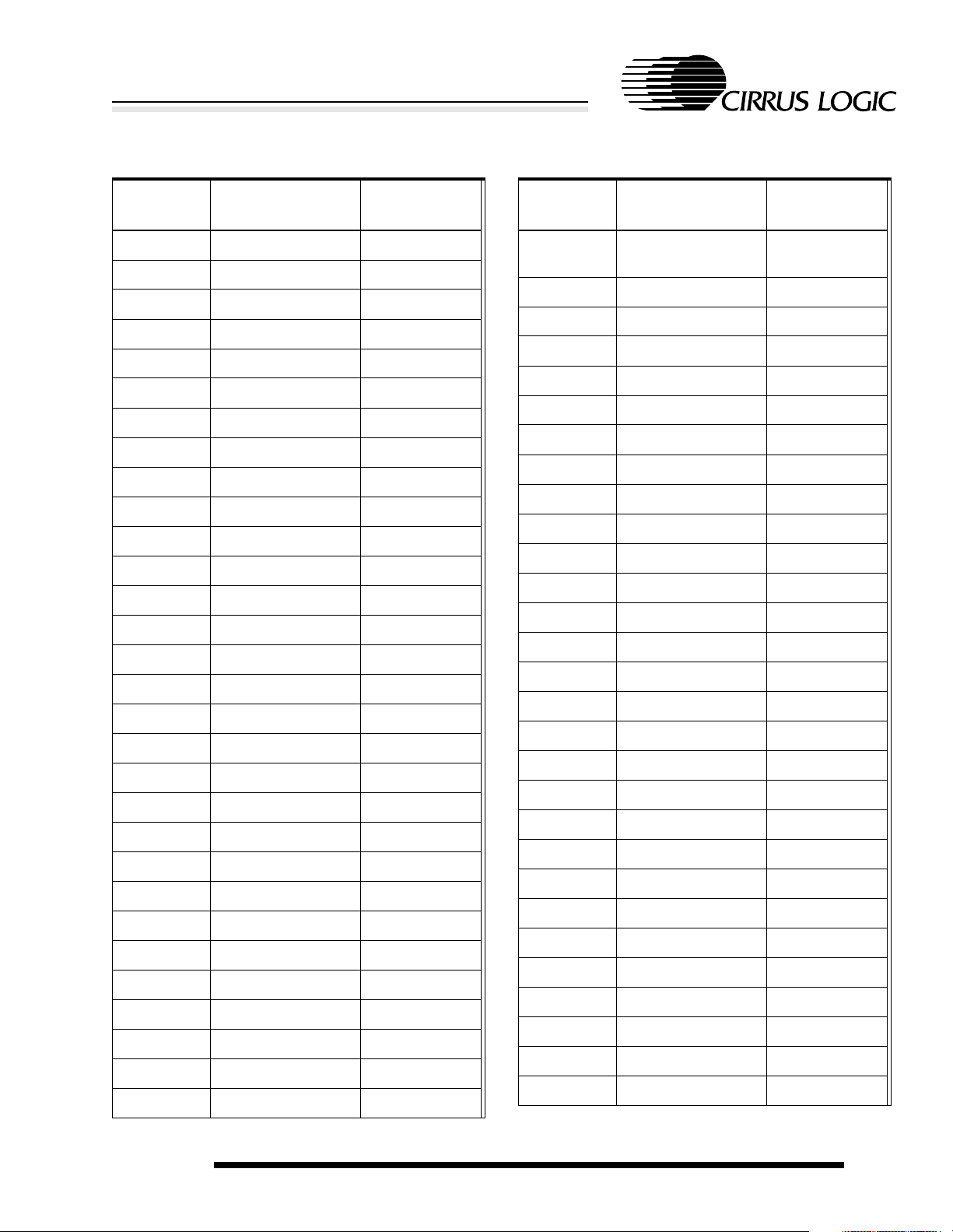
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
F9 A[1] O
F10 D[6] I/O
F11 VSSRTC RTC ground
F12 BATOK I
F13 NBATCHG I
F14 VSSIO Pad ground
F15 D[11] I/O
F16 VDDIO Pad power
G1 PB[1]/PRDY[2] I
G2 VDDIO Pad power
G3 TDO O
G4 PB[4] I
G5 PB[6] I
Name Type
E9 A[0] O
E10 D[5] I/O
E11 VSSOSC Oscillator
ground
E12 VSSIO Pad ground
E13 NMEDCHG/NBROM I
E14 VDDIO Pad power
E15 D[9] I/O
E16 D[10] I/O
F1 PB[5] I
F2 PB[3] I
F3 VSSIO Pad ground
F4 TXD[2] O
F5 RUN/CLKEN O
F6 VSSIO Pad ground
F7 NCAS[1] O
F8 DD[3] O
G6 VSSCORE Core ground
G7 VSSRTC RTC ground
G8 DD[0] O
G9 D[3] I/O
G10 VSSRTC RTC ground
G11 A[7] O
G12 A[8] O
G13 A[9] O
G14 VSSIO Pad ground
G15 D[12] I/O
G16 D[13] I/O
H1 PA[7] I
H2 PA[5] I
H3 VSSIO Pad ground
H4 PA[4] I
H5 PA[6] I
H6 PB[0]/PRDY[1] I
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
21
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
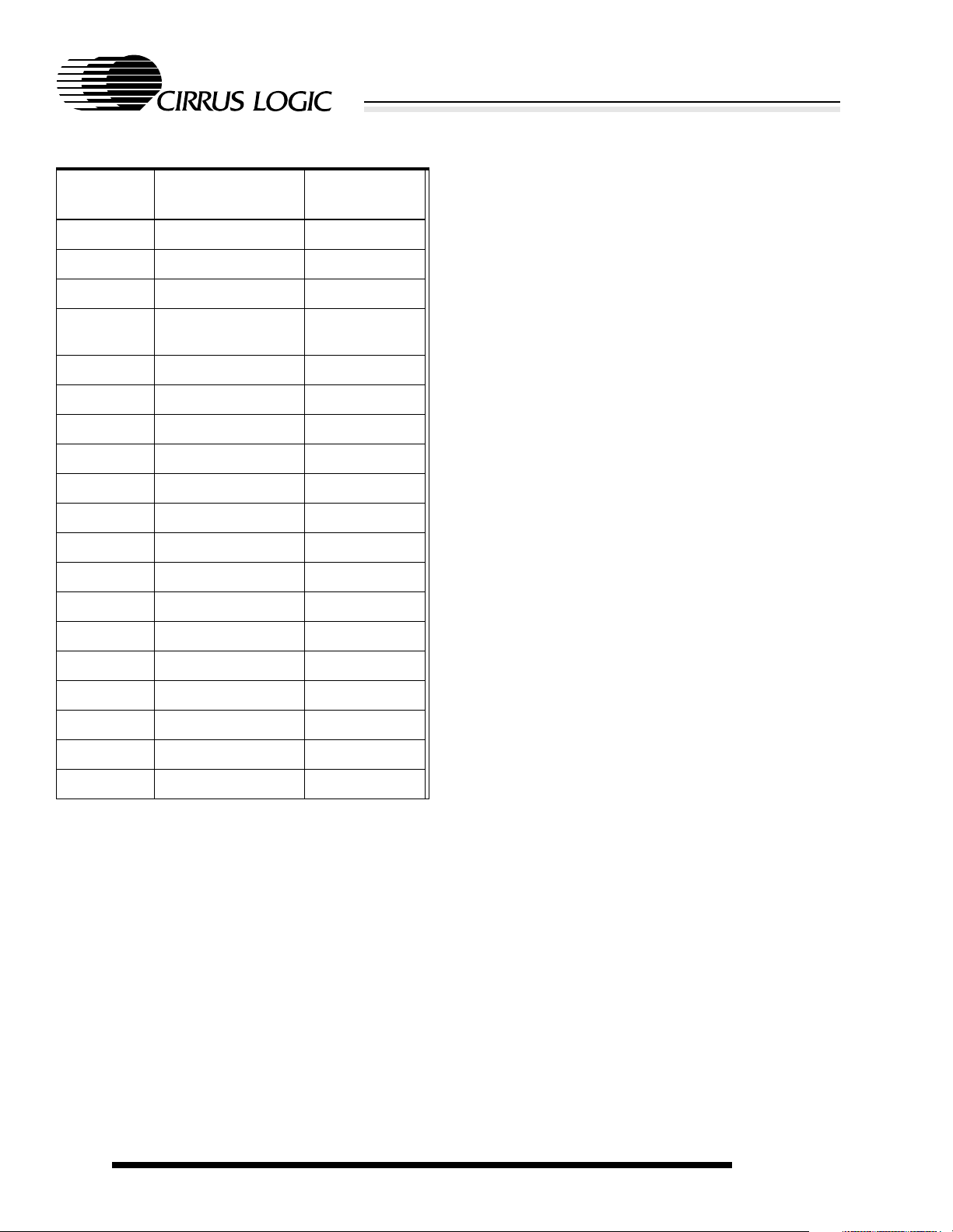
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
H7 PB[2] I
H8 VSSRTC RTC ground
H9 VSSRTC RTC ground
H10 A[10] O
H11 A[11] O
H12 A[12] O
H13 A[13] O
H14 VSSIO Pad ground
H15 D[14] I/O
H16 D[15] I/O
J1 PA[3] I
J2 PA[1] I
J3 VSSIO Pad ground
Name Type
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
K5 NTEST[1] I
K6 EINT[3] I
K7 VSSRTC RTC ground
K8 ADCIN I
K9 COL[4] O
K10 TCLK I
K11 D[20] I/O
K12 D[19] I/O
K13 D[18] I/O
K14 VSSIO Pad ground
K15 VDDIO Pad power
K16 VDDIO Pad power
L1 RXD[1] I
Name Type
J4 PA[2] I
J5 PA[0] I
J6 TXD[1] O
J7 CTS I
J8 VSSRTC RTC ground
J9 VSSRTC RTC ground
J10 A[17]/DRA[10] O
J11 A[16]/DRA[11] O
J12 A[15]/DRA[12] O
J13 A[14] O
J14 TNRST I
J15 D[16] I/O
J16 D[17] I/O
K1 LEDDRV O
K2 PHDIN I
K3 VSSIO Pad ground
L2 DSR I
L3 VDDIO Pad power
L4 NEINT[1] I
L5 PE[2]/CLKSEL I
L6 VSSRTC RTC ground
L7 PD[0]/LEDFLSH I/O
L8 VSSCORE Core ground
L9 COL[6] O
L10 D[31] I/O
L11 VSSRTC RTC ground
L12 A[22]/DRA[5] O
L13 A[21]/DRA[6] O
L14 VSSIO Pad ground
L15 A[18]/DRA[9] O
L16 A[19]/DRA[8] O
M1 NTEST[0] I
K4 DCD I
22
Pin Information
M2 NEINT[2] I
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
M3 VDDIO Pad power
M4 PE[0]/BOOTSEL[0] I
M5 TMS I
M6 VDDIO Pad power
M7 SSITXFR I/O
M8 DRIVE[1] I/O
M9 FB[0] I
M10 COL[0] O
M11 D[27] I/O
M12 VSSIO Pad ground
M13 A[23]/DRA[4] O
M14 VDDIO Pad power
M15 A[20]/DRA[7] O
M16 D[21] I/O
N1 NEXTFIQ I
N2 PE[1]/BOOTSEL[1] I
N3 VSSIO Pad ground
N4 VDDIO Pad power
N5 PD[5] I/O
N6 PD[2] I/O
N7 SSIRXDA I/O
N8 ADCCLK O
N9 SMPCLK O
N10 COL[2] O
N11 D[29] I/O
N12 D[26] I/O
N13 HALFWORD O
N14 VSSIO Pad ground
N15 D[22] I/O
N16 D[23] I/O
Name Type
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
Ball
Location
P1 VSSRTC 32 K oscillator
P2 RTCOUT O
P3 VSSIO Pad ground
P4 VSSIO Pad ground
P5 VDDIO Pad power
P6 VSSIO Pad ground
P7 VSSIO Pad ground
P8 VDDIO Pad power
P9 VSSIO Pad ground
P10 VDDIO Pad power
P11 VSSIO Pad ground
P12 VSSIO Pad ground
P13 VDDIO Pad power
P14 VSSIO Pad ground
P15 D[24] I/O
P16 VDDIO Pad power
R1 RTCIN O
R2 VDDIO Pad power
R3 PD[4] I/O
R4 PD[1] I/O
R5 SSITXDA O
R6 NADCCS O
R7 VDDIO Pad power
R8 ADCOUT O
R9 COL[7]/PTOUT O
R10 COL[3] O
R11 COL[1] O
R12 D[30] I/O
R13 A[27]/DRA[0] O
Name Type
ground
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
23
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Table 2-2. (cont.)256-Ball PBGA Ball Listing
EP7211
Ball
Location
R14 A[25]/DRA[2] O
R15 VDDIO Pad power
R16 A[24]/DRA[3] O
T1 VDDRTC 32 K oscillator
T2 PD[7] I/O
T3 PD[6] I/O
T4 PD[3] I/O
T5 SSICLK I/O
T6 SSIRXFR –
T7 VDDCORE Core power
T8 DRIVE[0] I/O
T9 FB[1] I
T10 COL[5] O
T11 VDDIO Pad power
Name Type
power
T12 BUZ O
T13 D[28] I/O
T14 A[26]/DRA[1] O
T15 D[25] I/O
T16 VSSIO Pad power
24
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
2.4 208-Pin LQFP Pin Listing
Table 2-3. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing
Pin
No.
1 NCS[5] Out 1 Low 27 PA[3] I/O 1 Input
2 VDDIO Pad Pwr 28 PA[2] I/O 1 Input
3 VSSIO Pad Gnd 29 PA[1] I/O 1 Input
4 EXPCLK I/O 1 30 PA[0] I/O 1 Input
5 WORD Out 1 Low 31 LEDDRV Out 1 Low
6 WRITE Out 1 Low 32 TXD[1] Out 1 High
7 RUN/CLKEN I/O 1 Low 33 VSSIO Pad Gnd 1 High
8 EXPRDY I/O 1 34 PHDIN In
9 TXD[2] Out 1 High 35 CTS In
10 RXD[2] In 36 RXD[1] In
11 TDI In with p/u* 37 DCD In
12 VSSIO Pad Gnd 38 DSR In
13 PB[7] I/O 1 Input 39 NTEST[1] In With p/u* High
14 PB[6] I/O 1 Input 40 NTEST[0] In With p/u* High
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
Pin
No.
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
15 PB[5] I/O 1 Input 41 EINT[3] In
16 PB[4] I/O 1 Input 42 NEINT[2] In
17 PB[3] I/O 1 Input 43 NEINT[1] In
18 PB[2] I/O 1 Input 44 NEXTFIQ In
19 PB[1]/
PRDY[2]
20 PB[0]/
PRDY[1]
21 VDDIO Pad Pwr 47 PE[0]/
22 TDO Out 1 Tristate 48 VSSRTC VDDRTC
23 PA[7] I/O 1 Input 49 RTCOUT 32 K Osc X
24 PA[6] I/O 1 Input 50 RTCIN 32 K Osc X
25 PA[5] I/O 1 Input 51 VDDRTC 32 K Osc
I/O 1 Input 45 PE[2]/
CLKSEL
I/O 1 Input 46 PE[1]/
BOOTSEL[1]
BOOTSEL[0]
I/O 1 Input
I/O 1 Input
I/O 1 Input
VSSRTC
32 K Osc
Gnd
power
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
25
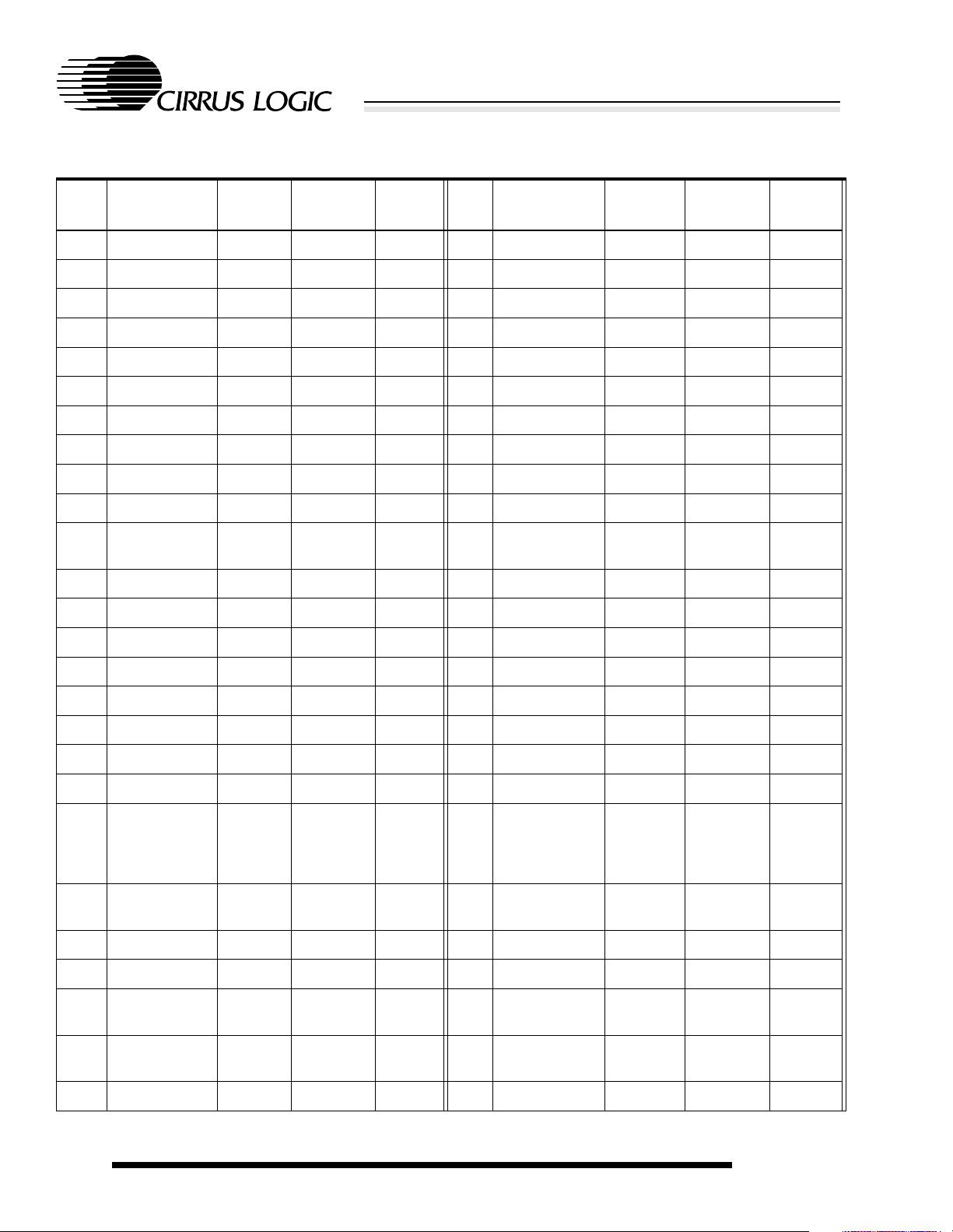
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Table 2-3. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (cont.)
EP7211
Pin
No.
26 PA[4] I/O 1 Input 52 nc —
53 PD[7] I/O 1 Low 80 FB[1] In
54 PD[6] I/O 1 Low 81 VSSIO Pad Gnd 1
55 PD[5] I/O 1 Low 82 FB[0] In 1
56 PD[4] I/O 1 Low 83 COL[7] Out 1 High
57 VDDIO Pad Pwr — 84 COL[6] Out 1 High
58 TMS In with p/u* — 85 COL[5] Out 1 High
59 PD[3] I/O 1 Low 86 COL[4] Out 1 High
60 PD[2] I/O 1 Low 87 COL[3] Out 1 High
61 PD[1] I/O 1 Low 88 COL[2] Out 1 High
62 PD[0]/
63 SSICLK I/O 1 Input 90 TCLK In
64 VSSIO Pad Gnd — 91 COL[1] Out 1 High
65 SSITXFR I/O 1 Low 92 COL[0] Out 1 High
Signal Type Strength
I/O 1 Low 89 VDDIO Pad Pwr
LEDFLSH
Reset
State
Pin
No.
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
66 SSITXDA Out 1 Low 93 BUZ Out 1 Low
67 SSIRXDA In 94 D[31] I/O 1 Low
68 SSIRXFR I/O Input 95 D[30] I/O 1 Low
69 ADCIN In 96 D[29] I/O 1 Low
70 NADCCS Out 1 High 97 D[28] I/O 1 Low
71 VSSCORE VSSCO
REVDD
COREC
ore Gnd
72 VDDCORE Core
Pwr
73 VSSIO Pad Gnd 100 D[27] I/O 1 Low
74 VDDIO Pad Pwr 101 A[26]/DRA[1] Out 2 Low
75 DRIVE[1] I/O 1 High/
Low
76 DRIVE[0] I/O 1 High/
Low
77 ADCCLK Out 1 Low 104 D[25] I/O 1 Low
98 VSSIO Pad Gnd
99 A[27]/DRA[0] Out 2 Low
102 D[26] I/O 1 Low
103 A[25]/DRA[2] Out 2 Low
26
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
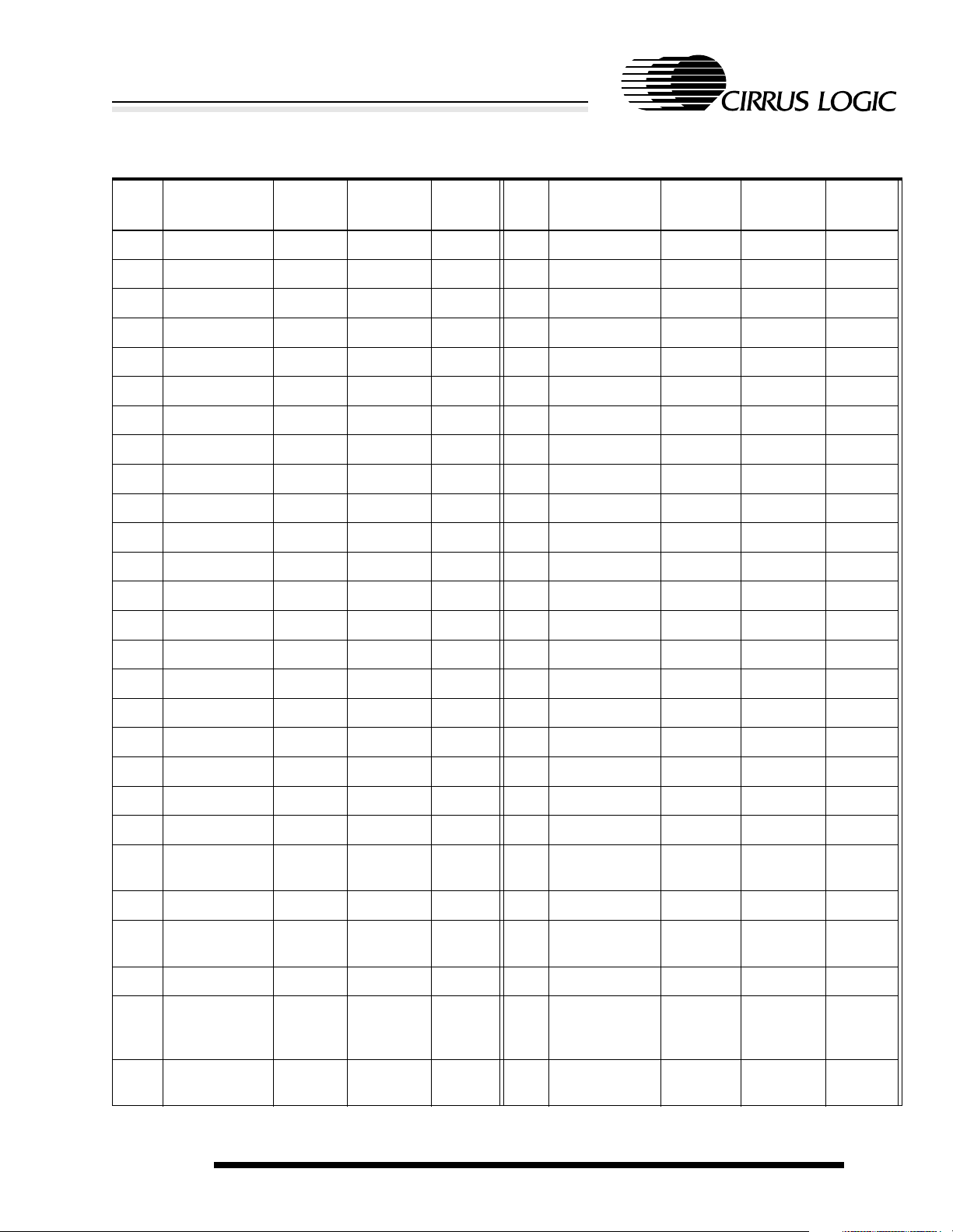
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Table 2-3. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (cont.)
Pin
No.
78 ADCOUT Out 1 105 HALFWORD Out 1 Low
79 SMPCLK Out 1 106 A[24]/DRA[3] Out 1 Low
107 VDDIO Pad Pwr — 134 A[13] Out 1 Low
108 VSSIO Pad Gnd — 135 D[13] I/O 1 Low
109 D[24] I/O 1 Low 136 A[12] Out 1 Low
110 A[23]/DRA[4] Out 1 Low 137 D[12] I/O 1 Low
111 D[23] I/O 1 Low 138 A[11] Out 1 Low
112 A[22]/DRA[5] Out 1 Low 139 VDDIO Pad Pwr
113 D[22] I/O 1 Low 140 VSSIO Pad Gnd
114 A[21]/DRA[6] Out 1 Low 141 D[11] I/O 1 Low
115 D[21] I/O 1 Low 142 A[10] Out 1 Low
116 VSSIO Pad Gnd — 143 D[10] I/O 1 Low
117 A[20]/DRA[7] Out 1 Low 144 A[9] Out 1 Low
118 D[20] I/O 1 Low 145 D[9] I/O 1 Low
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
Pin
No.
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
119 A[19]/DRA[8] Out 1 Low 146 A[8] Out 1 Low
120 D[19] I/O 1 Low 147 D[8] I/O 1 Low
121 A[18]/DRA[9] Out 1 Low 148 A[7] Out 1 Low
122 D[18] I/O 1 Low 149 VSSIO Pad Gnd
123 VDDIO Pad Pwr — 150 D[7] I/O 1 Low
124 VSSIO Pad Gnd — 151 NBATCHG In
125 TNRST In — 152 NEXTPWR In
126 A[17]/
DRA[10]
127 D[17] I/O 1 Low 154 NPOR In Schmitt
128 A[16]/
DRA[11]
129 D[16] I/O 1 Low 156 NURESET In Schmitt
130 A[15]/
DRA[12]
131 D[15] I/O 1 Low 158 MOSCIN 3M6864
Out 1 Low 153 BATOK In
Out 1 Low 155 NMEDCHG/
NBROM
Out 1 Low 157 VDDOSC VDDOSC
In
VSSOSC
Osc Pwr
Osc
—
X
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
27
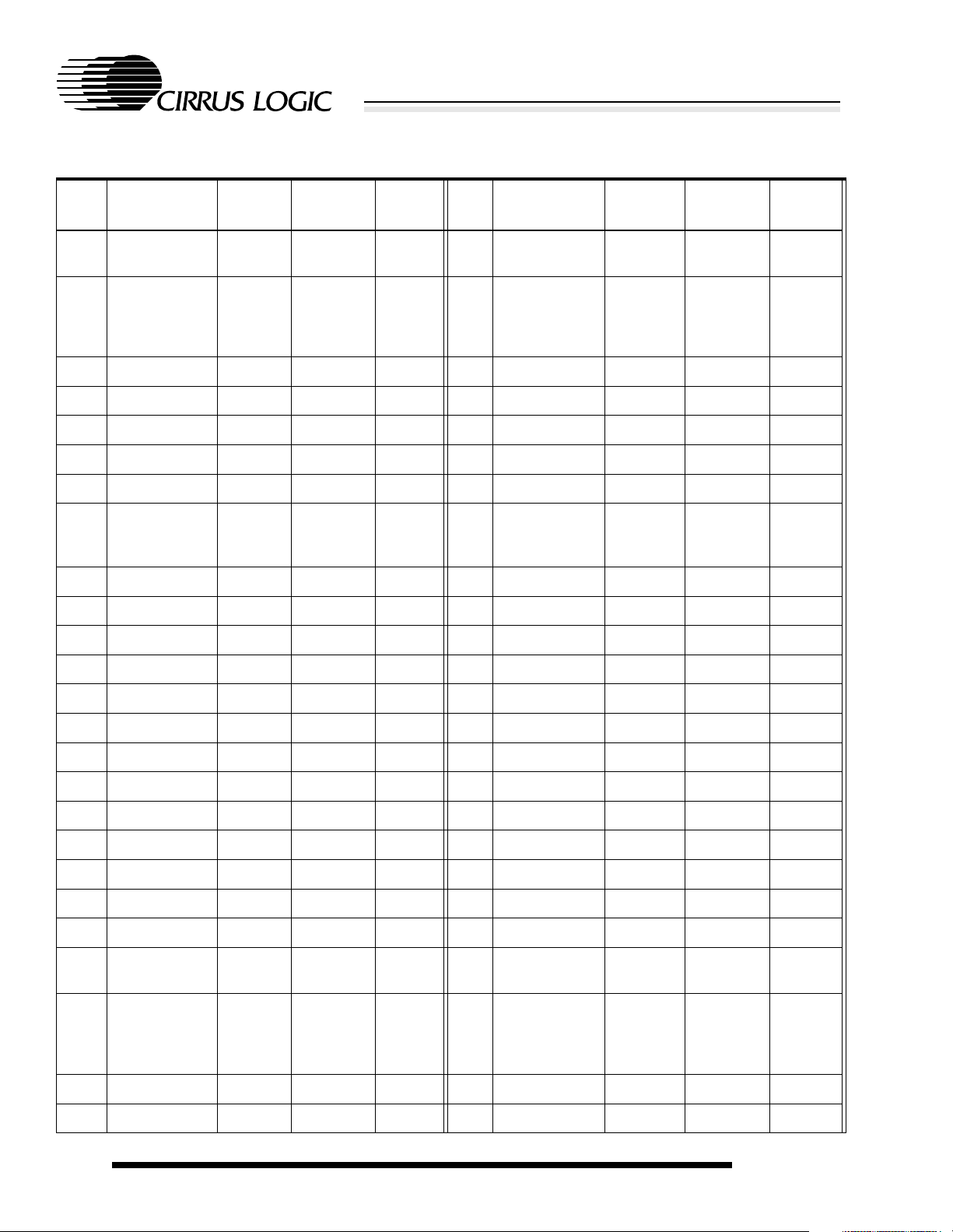
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Table 2-3. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (cont.)
EP7211
Pin
No.
132 A[14] Out 1 Low 159 MOSCOUT 3M6864
133 D[14] I/O 1 Low 160 VSSOSC VSSOSC
161 WAKEUP In Schmitt Input 185 CL[1] Out 1 Low
162 NPWRFL In Input 186 FRM Out 1 Low
163 A[6] Out 1 Low 187 M Out 1 Low
164 D[6] I/O 1 Low 188 DD[3] I/O 1 Low
165 A[5] Out 1 Low 189 DD[2] I/O 1 Low
166 D[5] I/O 1 Low 190 VSSIO VSSIOV
167 VDDIO Pad Pwr 191 DD[1] I/O 1 Low
168 VSSIO Pad Gnd 192 DD[0] I/O 1 Low
169 A[4] Out 1 Low 193 NRAS[1] Out 1 High
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
Pin
No.
Signal Type Strength
Osc
VSSCOR
EOsc
Gnd
DDIOPad
Gnd
Reset
State
X
170 D[4] I/O 1 Low 194 NRAS[0] Out 1 High
171 A[3] Out 2 Low 195 NCAS[3] I/O 2 High
172 D[3] I/O 1 Low 196 NCAS[2] I/O 2 High
173 A[2] Out 2 Low 197 VDDIO Pad Pwr
174 VSSIO Pad Gnd 198 VSSIO Pad Gnd
175 D[2] I/O 1 Low 199 NCAS[1] I/O 2 High
176 A[1] Out 1 Low 200 NCAS[0] I/O 2 High
177 D[1] I/O 1 Low 201 NMWE Out 1 High
178 A[0] Out 1 Low 202 NMOE Out 1 High
179 D[0] I/O 1 Low 203 VSSIO Pad Gnd —
180 VSSCORE Core
Gnd
181 VDDCORE VDDCO
REVDD
RTCCor
e Pwr
182 VSSIO Pad Gnd 206 NCS[2] Out 1 High
183 VDDIO Pad Pwr 207 NCS[3] Out 1 High
204 NCS[0] Out 1 High
205 NCS[1] Out 1 High
28
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
EP7211
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
Table 2-3. 208-Pin LQFP Numeric Pin Listing (cont.)
Pin
No.
184 C[2] Out 1 Low 208 NCS[4] Out 1 High
Signal Type Strength
NOTE: ‘With p/u’ means with internal pull-up on the pin.
Reset
State
Pin
No.
Signal Type Strength
Reset
State
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
Pin Information
29
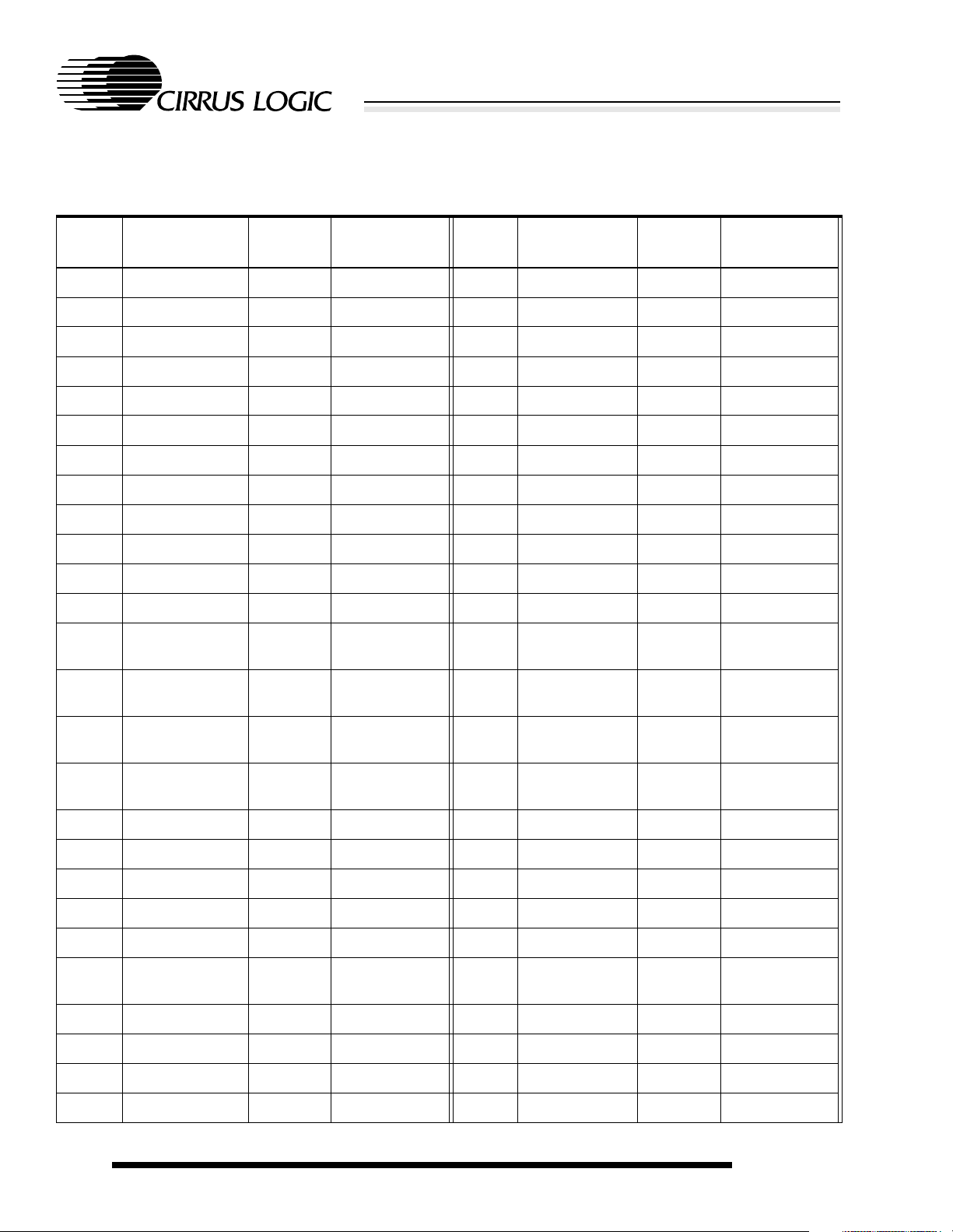
High-Performance Ultra-Low-Power System-on-Chip with LCD Controller
2.5 JTAG Pin Ordering for 208-Pin LQFP Package
Table 2-4. JTAG Pin Ordering for 208-Pin LQFP Package
EP7211
Pin
No.
1 NCS[5] Out 1 34 PHDIN In 69
4 EXPCLK I/O 3 35 CTS In 70
5WORDOut 6 36RXD1 In 71
6 WRITE Out 8 37 DCD In 72
7 RUN/CLKEN I/O 10 38 DSR In 73
8 EXPRDY I/O 13 39 NTEST1 In 74
9 TXD2 Out 14 40 NTEST0 In 75
10 RXD2 In 16 41 EINT3 In 76
13 PB[7] I/O 17 42 NEINT2 In 77
14 PB[6] I/O 20 43 NEINT1 In 78
15 PB[5] I/O 23 44 NEXTFIQ In 79
16 PB[4] I/O 26 45 PE[2]/CLKSEL I/O 80
17 PB[3] I/O 29 46 PE[1]/
18 PB[2] I/O 32 47 PE[0]/
Signal Type Position
Pin
No.
Signal Type Position
I/O 83
BOOTSEL1
I/O 86
BOOTSEL0
19 PB[1]/
PRDY2
20 PB[0]/
PRDY1
23 PA[7] I/O 41 55 PD[5] I/O 95
24 PA[6] I/O 44 56 PD[4] I/O 98
25 PA[5] I/O 47 59 PD[3] I/O 101
26 PA[4] I/O 50 60 PD[2] I/O 104
27 PA[3] I/O 53 61 PD[1] I/O 107
28 PA[2] I/O 56 62 PD[0]/
29 PA[1] I/O 59 63 SSICCLK I/O 113
30 PA[0] I/O 62 65 SSITXFR I/O 116
31 LEDDRV Out 65 66 SSITXDA Out 119
32 TXD1 Out 67 67 SSIRXDA In 121
I/O 35 53 PD[7] I/O 89
I/O 38 54 PD[6] I/O 92
I/O 110
LEDFLSH
30
Pin Information
DS352PP3
JUL 2001
 Loading...
Loading...