CS8406
192 kHz Digital Audio Interface Transmitter
Features
Complete EIAJ CP1201, IEC-60958, AES3,
S/PDIF-compatible Transmitter
+3.3 V or 5.0 V Digital Supply (VD)
+3.3 V or 5.0 V Digital Interface (VL)
On-Chip Channel Status and User Bit Buffer
Memories Allow Block-Sized Updates
Flexible 3-Wire Serial Digital Audio Input Port
Up to 192-kHz Frame Rate
Microcontroller Write Access to Channel Status
and User Bit Data
On-Chip Differential Line Driver
Generates CRC Codes and Parity Bits
Stand-Alone Mode Allows Use without a
Microcontroller
General Description
The CS8406 is a monolithic CMOS device which encodes and transmits audio data according to the AES3,
IEC60958, S/PDIF, o r EIAJ CP1201 standards. The
CS8406 accepts aud io and digital data, which is then
multiplexed, encoded, and driven onto a cable.
The audio data is input through a configurable, 3-wire
input port. The channel status and user bit data are input through an SPI™ or I²C
may be assembled in block-sized buffers. For systems
with no microcontroller, a Stand-Alone Mode allows direct access to channel status and user bit data pins.
The CS8406 is available in a 28-pin TSSOP and SOIC
package for both Co mmercial (-10º to +70ºC) and
Automotive grade (-40º to +85ºC). The CDB8416
Demonstration board is also available for device
evaluation and implementation suggestions. Please
refer to “Ordering Information” on page 34 for complete
details.
Target applications include A/V Receivers, CD-R, DVD
receivers, digital mixin g consoles, effects processors,
set-top boxes, and computer and automotive audio
systems.
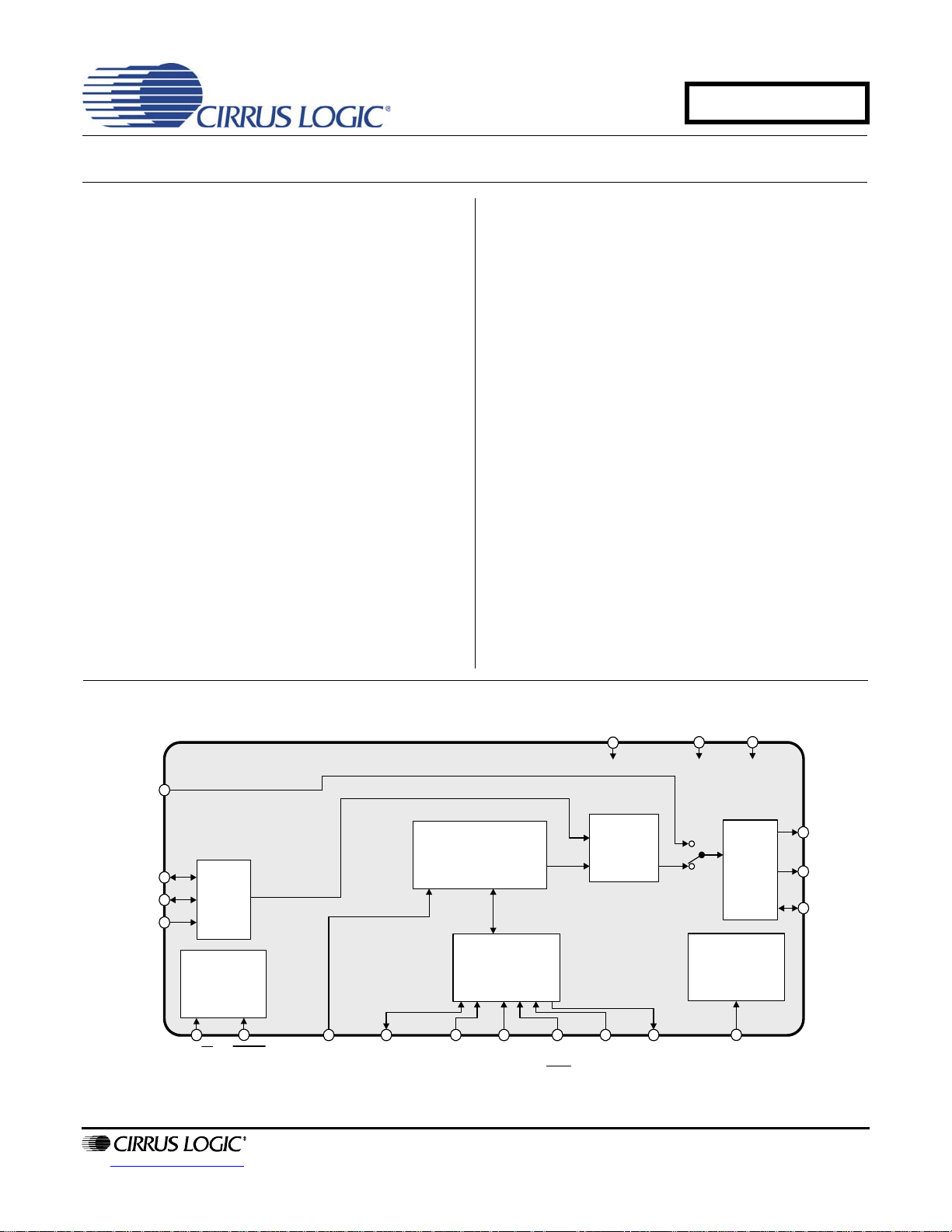
®
microcontroller port, and
RXP
ILRCK
ISCLK
SDIN
http://www.cirrus.com
VD
AES3
C or U Data Buffer
Serial
Audio
Input
Control Port &
Misc.
Control
RST OMCK
USDA/
CDOUT
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2012
Registers
SCL/
CCLK
(All Rights Reserved)
AD1/
CDIN
AD0/
CS
S/PDIF
Encoder
AD2H/S
INT
GND
VL
Driver
Output Clock
Generator
TXP
TXN
TCBL
AUG '12
DS580F6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................................................... 4
SPECIFIED OPERATING CONDITIONS .............................................................................................. 4
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ........................................................................................................4
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................................... 4
DIGITAL INPUT CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................................................. 5
DIGITAL INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................ 5
TRANSMITTER CHARACTERISTICS .................................................................................................. 5
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS .......................................................................................................5
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORTS ............................................................. 6
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - SPI MODE................................................... 7
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - I²C MODE.................................................... 8
2. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS .................................................................................................. 9
3. GENERAL DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................................. 11
3.1 AES3 and S/PDIF Standards Documents .................................................................................... 11
4. THREE-WIRE SERIAL INPUT AUDIO PORT ..................................................................................... 12
5. AES3 TRANSMITTER ......................................................................................................................... 13
5.1 TXN and TXP Drivers ................................................................................................................... 13
5.2 Mono Mode Operation .................................................................................................................. 13
5.3 Transmitted Frame and Channel Status Boundary Timing ........................................................... 13
6. CONTROL PORT DESCRIPTION ....................................................................................................... 16
6.1 SPI Mode ...................................................................................................................................... 16
6.2 I²C Mode ....................................................................................................................................... 17
7. CONTROL PORT REGISTER SUMMARY ......................................................................................... 18
8. CONTROL PORT REGISTER BIT DEFINITIONS .............................................................................. 19
8.1 Memory Address Pointer (MAP) ................................................................................................... 19
8.2 Default = ‘000000’Control 1 (01h) ................................................................................................. 19
8.3 Control 2 (02h) .............................................................................................................................. 19
8.4 Data Flow Control (03h) ............................................................................................................... 20
8.5 Clock Source Control (04h) .......................................................................................................... 20
8.6 Serial Audio Input Port Data Format (05h) ................................................................................... 21
8.7 Interrupt 1 Status (07h) (Read Only) ............................................................................................ 22
8.8 Interrupt 2 Status (08h) (Read Only) ............................................................................................ 22
8.9 Interrupt 1 Mask (09h) .................................................................................................................. 22
8.10 Interrupt 1 Mode MSB (0Ah) and Interrupt 1 Mode LSB (0Bh) ................................................... 23
8.11 Interrupt 2 Mask (0Ch) ................................................................................................................ 23
8.12 Interrupt 2 Mode MSB (0Dh) and Interrupt Mode 2 LSB (0Eh) .................................................. 23
8.13 Channel Status Data Buffer Control (12h) ..................................................................................23
8.14 User Data Buffer Control (13h) ................................................................................................... 24
8.15 Channel Status Bit or User Bit Data Buffer (20h - 37h) .............................................................. 24
8.16 CS8406 I.D. and Version Register (7Fh) (Read Only) ................................................................ 24
9. PIN DESCRIPTION - SOFTWARE MODE ....................................................................................... 25
10. HARDWARE MODE .......................................................................................................................... 27
10.1 Channel Status, User and Validity Data ..................................................................................... 27
10.2 Serial Audio Port ......................................................................................................................... 28
11. PIN DESCRIPTION - HARDWARE MODE ....................................................................................... 29
12. APPLICATIONS ................................................................................................................................ 31
12.1 Reset, Power Down and Start-Up ...........................................................................................
ID Code and Revision Code ....................................................................................................... 31
2
12.
12.3 Power Supply, Grounding, and PCB layout ................................................................................ 31
12.4 Synchronization of Multiple CS8406s ......................................................................................... 31
13. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS ................................................................................................................ 32
14. ORDERING INFORMATION ............................................................................................................. 34
CS8406
... 31
2 DS580F6

15. APPENDIX A: EXTERNAL AES3/SPDIF/IEC60958 TRANSMITTER COMPONENTS ................... 35
15.1 AES3 Transmitter External Components .................................................................................... 35
15.2 Isolating Transformer Requirements .......................................................................................... 35
16. APPENDIX B: CHANNEL STATUS AND USER DATA BUFFER MANAGEMENT ........................ 36
16.1 AES3 Channel Status(C) Bit Management ................................................................................. 36
16.1.1 Accessing the E buffer ................................................................................................... 36
16.1.2 Serial Copy Management System (SCMS) .................................................................... 37
16.1.3 Channel Status Data E Buffer Access ........................................................................... 37
16.2 AES3 User (U) Bit Management ................................................................................................. 38
16.2.1 Mode 1: Transmit All Zeros ............................................................................................ 38
16.2.2 Mode 2: Block Mode ......................................................................................................38
17. REVISION HISTORY ......................................................................................................................... 39
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. Audio Port Master Mode Timing ................................................................................................... 6
Figure 2. Audio Port Slave Mode and Data Input Timing............................................................................. 6
Figure 3. SPI Mode Timing .......................................................................................................................... 7
Figure 4. I²C Mode Timing ........................................................................................................................... 8
Figure 5. Recommended Connection Diagram for Software Mode ............................................................. 9
Figure 6. Recommended Connection Diagram for Hardware Mode .......................................................... 10
Figure 7. Serial Audio Input Example Formats .......................................................................................... 12
Figure 8. AES3 Transmitter Timing for C, U, and V Pin Input Data, Stereo Mode..................................... 14
Figure 9. AES3 Transmitter Timing for C, U, and V Pin Input Data, Mono Mode ...................................... 15
Figure 10. Control Port Timing in SPI Mode .............................................................................................. 16
Figure 11. Control Port Timing, I²C Slave Mode Write ............................................................................... 17
Figure 12. Control Port Timing, I²C Slave Mode Read............................................................................... 17
Figure 13. Hardware Mode Data Flow ....................................................................................................... 27
Figure 14. Professional Output Circuit ....................................................................................................... 35
Figure 15. Consumer Output Circuit (VL = 5.0 V) ...................................................................................... 35
Figure 16. TTL/CMOS Output Circuit......................................................................................................... 35
Figure 17. Channel Status Data Buffer Structure....................................................................................... 36
Figure 18. Flowchart for Writing the E Buffer ............................................................................................. 37
CS8406
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. Control Register Map Summary................................................................................................... 18
Table 2. Hardware Mode COPY/C and ORIG Pin Functions ..................................................................... 28
Table 3. Hardware Mode Serial Audio Port Format Selection ................................................................... 28
Table 4. Hardware Mode OMCK Clock Ratio Selection............................................................................. 28
Table 5. Equivalent Register Settings of Serial Audio Input Formats in Hardware Mode .......................... 28
DS580F6 3
CS8406
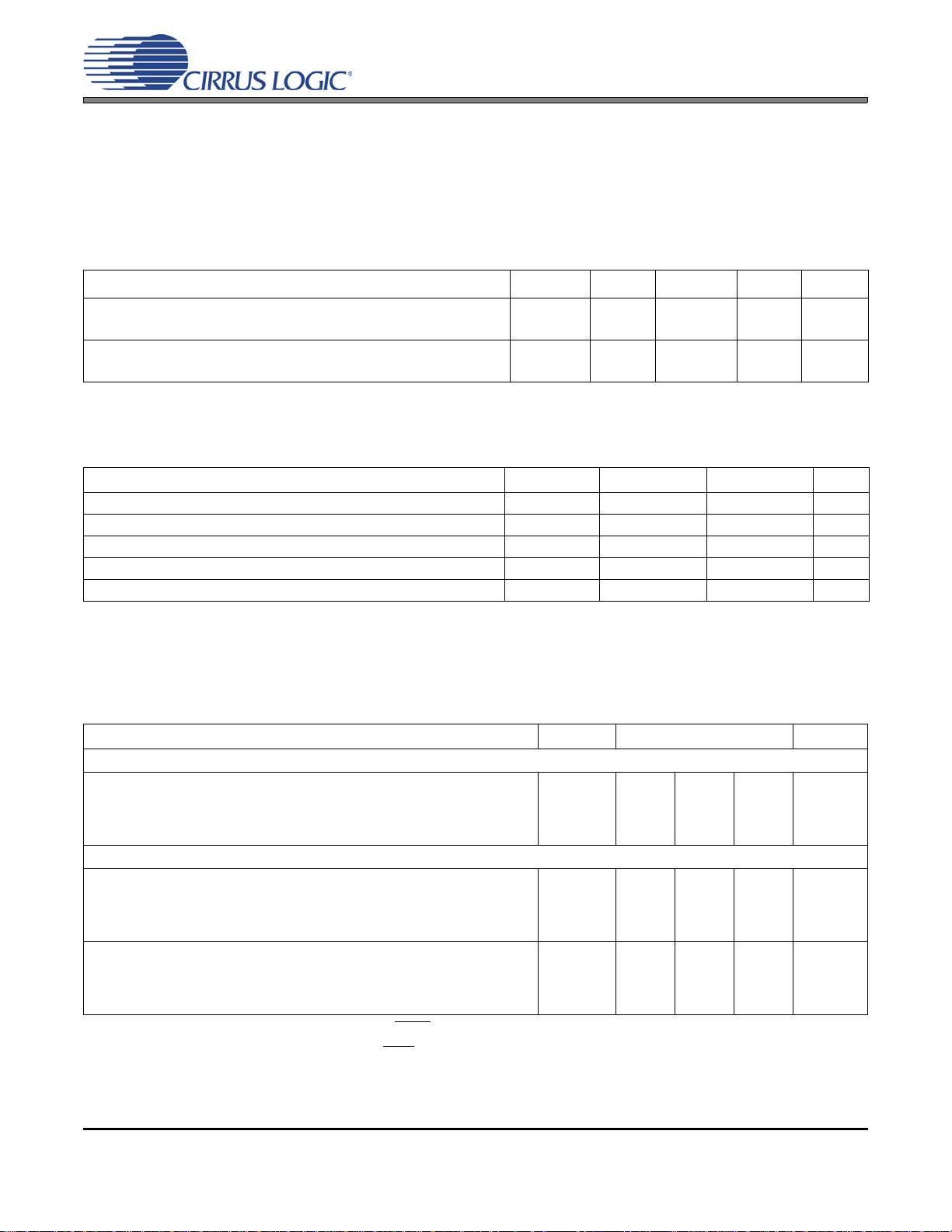
1. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS
(All Min/Max characteristics and specifications are guaranteed over the Specified Operating Conditions. Typical
performance characteristics and specifications are derived from measurements taken at nominal supply voltages
and T
= 25°C.)
A
SPECIFIED OPERATING CONDITIONS
(GND = 0 V, all voltages with respect to 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
Power Supply Voltage VD
VL
Ambient Operating Temperature: Commercial Grade
Automotive Grade
T
T
A
A
3.14
3.14
-10
-40
3.3 or 5.0
3.3 or 5.0
-
-
5.25
5.25
+70
+85
V
V
°C
°C
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(GND = 0 V; all voltages with respect to 0 V. Operation beyond these limits may result in permanent damage to the
device. Normal operation is not guaranteed at these extremes.)
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units
Power Supply Voltage VD, VL - 6.0 V
Input Current, Any Pin Except Supplies (Note 1) I
Input Voltage V
Ambient Operating Temperature (power applied) T
Storage Temperature T
in
in
A
stg
-±10mA
-0.3 VL + 0.3 V
-55 125 °C
-65 150 °C
Notes:
1. Transient currents of up to 100 mA will not cause SCR latch-up.
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(GND = 0 V; all voltages with respect to 0 V.)
Parameters Symbol Min Typ Max Units
Power-Down Mode
Supply Current in power down VD = 3.3 V
Normal Operation (Note 3)
Supply Current at 48 kHz frame rate (Note 4) VD = 3.3 V
Supply Current at 192 kHz frame rate (Note 4) VD = 3.3 V
2. Power Down Mode is defined as RST
3. Normal operation is defined as RST
4. Assumes that no inputs are left floating. It is recommended that all digital inputs be driven high or low
at all times.
(Note 2)
VD = 5.0 V
VL = 3.3 V
VL = 5.0 V
VD = 5.0 V
VL = 3.3 V
VL = 5.0 V
VD = 5.0 V
VL = 3.3 V
VL = 5.0 V
= LO with all clocks and data lines held static.
= HI.
ID
ID
IL
IL
ID
ID
IL
IL
ID
ID
IL
IL
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
20
40
0
0
1.9
3.5
6.5
10.6
7.6
12.7
7.2
12
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
A
A
A
A
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
4 DS580F6
CS8406
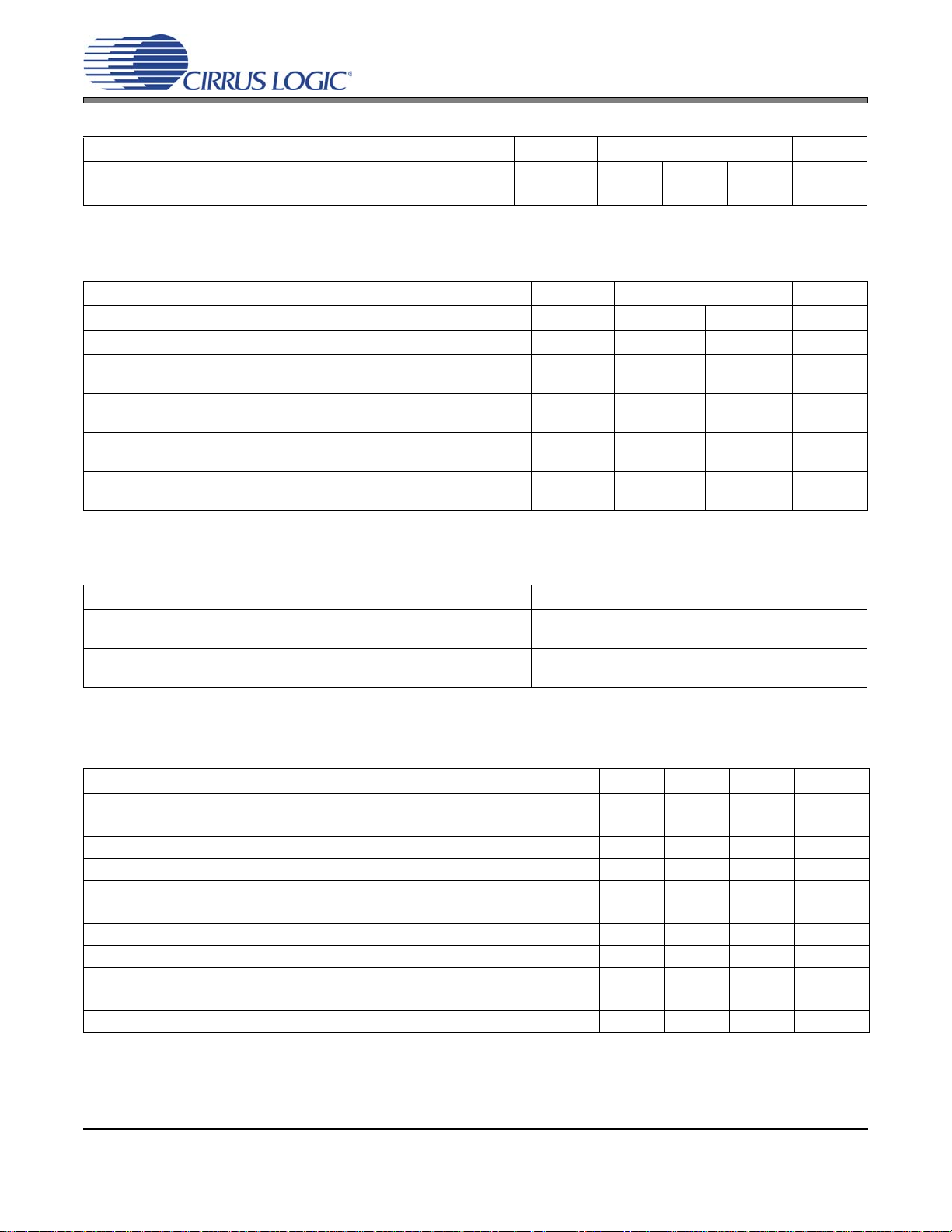
DIGITAL INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Parameters Symbol Min Typ Max Units
Input Leakage Current I
Input Hysteresis (all inputs except OMCK) - 0.25 - V
in
--±0.5A
DIGITAL INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS
(GND = 0 V; all voltages with respect to 0 V.)
Parameters Symbol Min Max Units
High-Level Output Voltage (IOH = -3.2 mA), except TXP/TXN V
Low-Level Output Voltage (IOH = 3.2 mA), except TXP/TXN V
High-Level Output Voltage, TXP, TXN (21 mA at VL = 5.0 V)
(15 mA at VL = 3.3 V)
Low-Level Output Voltage, TXP, TXN (21 mA at VL = 5.0 V)
(16 mA at VL = 3.3 V)
High-Level Input Voltage VD = 5.0 V
VD = 3.3 V
Low-Level Input Voltage VD = 5.0 V
VD = 3.3 V
OH
OL
V
IH
V
IL
VL - 1.0 - V
-0.4V
VL - 0.7
VL - 0.7
-
-
2.75
2.0
-0.3
-0.3
VL
VL
0.7
0.7
VL + 0.3
VL + 0.3
0.8
0.8
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
TRANSMITTER CHARACTERISTICS
Parameters Symbol Typ Units
TXP Output Resistance VL = 5.0 V
VL = 3.3 V
TXN Output Resistance VL = 5.0 V
VL = 3.3 V
R
TXP
R
TXN
26.5
33.5
26.5
33.5
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
(Inputs: Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = VL; CL = 20 pF)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
RST pin Low Pulse Width 200 - - s
OMCK Frequency for OMCK = 512*Fs 4.1 - 98.4 MHz
OMCK Low and High Width for OMCK = 512*Fs 4.1 - - ns
OMCK Frequency for OMCK = 384*Fs 3.1 - 73.8 MHz
OMCK Low and High Width for OMCK = 384*Fs 6.1 - - ns
OMCK Frequency for OMCK = 256*Fs 2.0 - 49.2 MHz
OMCK Low and High Width for OMCK = 256*Fs 8.1 - - ns
OMCK Frequency for OMCK = 128*Fs 1.0 - 24.6 MHz
OMCK Low and High Width for OMCK = 128*Fs 18.3 - - ns
Frame Rate 8-192kHz
AES3 Transmitter Output Jitter - 200 - ps RMS
DS580F6 5
CS8406
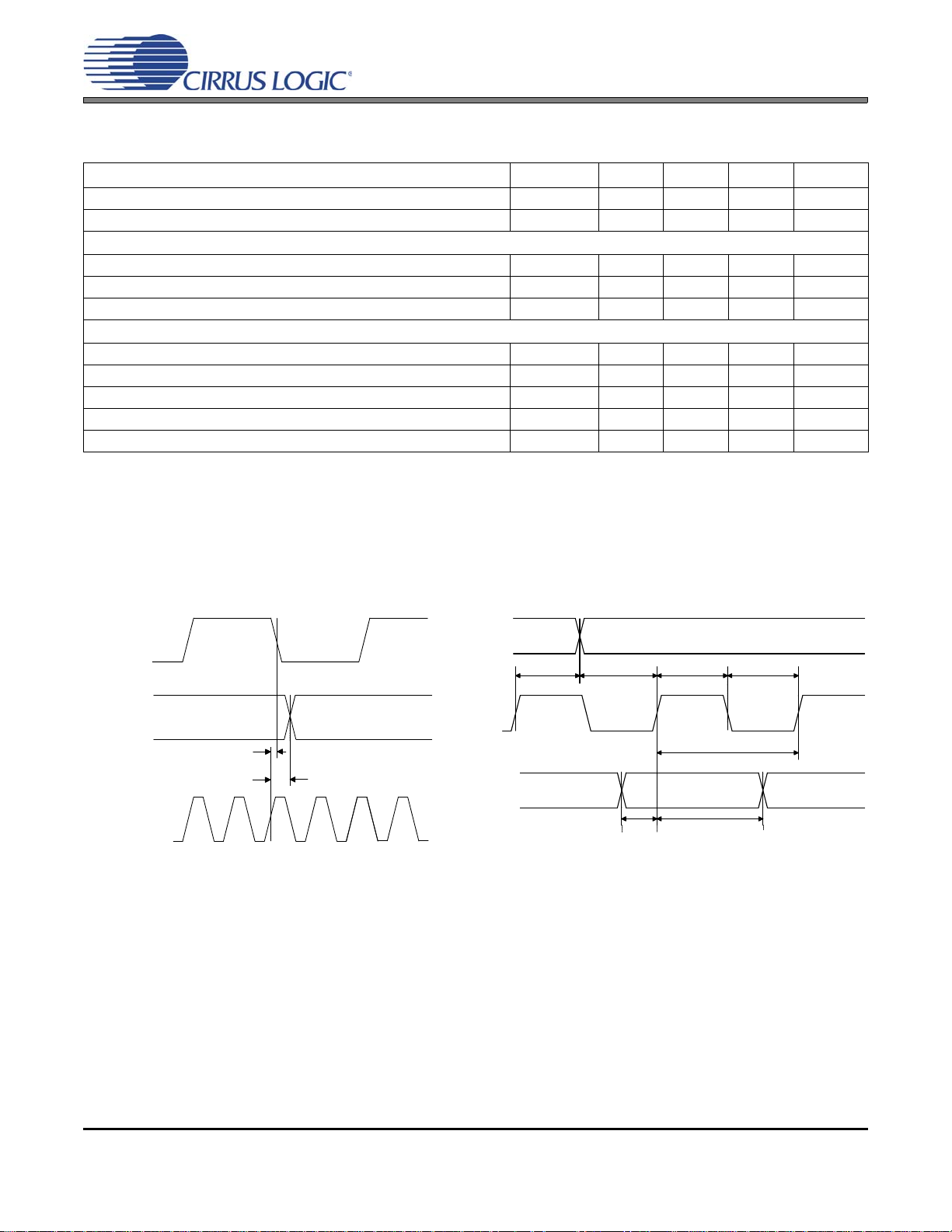
ISCLK
ILRCK
(output)
(output)
OMCK
(input)
t
smd
t
lmd
sckh
sckl
sckw
t
t
t
(input)
(input)
SDIN
dh
t
ds
t
lrcks
t
lrckd
t
ISCLK
ILRCK
Figure 1. Audio Port Master Mode Timing Figure 2. Audio Port Slave Mode and Data Input Timing
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - SERIAL AUDIO PORTS
(Inputs: Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = VL; CL = 20 pF)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
SDIN Setup Time Before ISCLK Active Edge (Note 5) t
SDIN Hold Time After ISCLK Active Edge (Note 5) t
ds
dh
Master Mode
OMCK to ISCLK active edge delay (Note 5) t
OMCK to ILRCK delay (Note 6) t
ISCLK and ILRCK Duty Cycle - 50 - %
smd
lmd
Slave Mode
ISCLK Period t
ISCLK Input Low Width t
ISCLK Input High Width t
ISCLK Active Edge to ILRCK Edge (Note 7) t
ILRCK Edge Setup Before ISCLK Active Edge (Note 8) t
sckw
sckl
sckh
lrckd
lrcks
Notes:
5. The active edge of ISCLK is programmable in Software Mode.
6. The polarity of ILRCK is programmable in Software Mode.
7. Prevents the previous ISCLK edge from being interpreted as the first one after ILRCK has changed.
8. This setup time ensures that this ISCLK edge is interpreted as the first one after ILRCK has changed.
10 - - ns
8--ns
0-17ns
0-16ns
36 - - ns
14.4 - - ns
14.4 - - ns
10 - - ns
10 - - ns
6 DS580F6
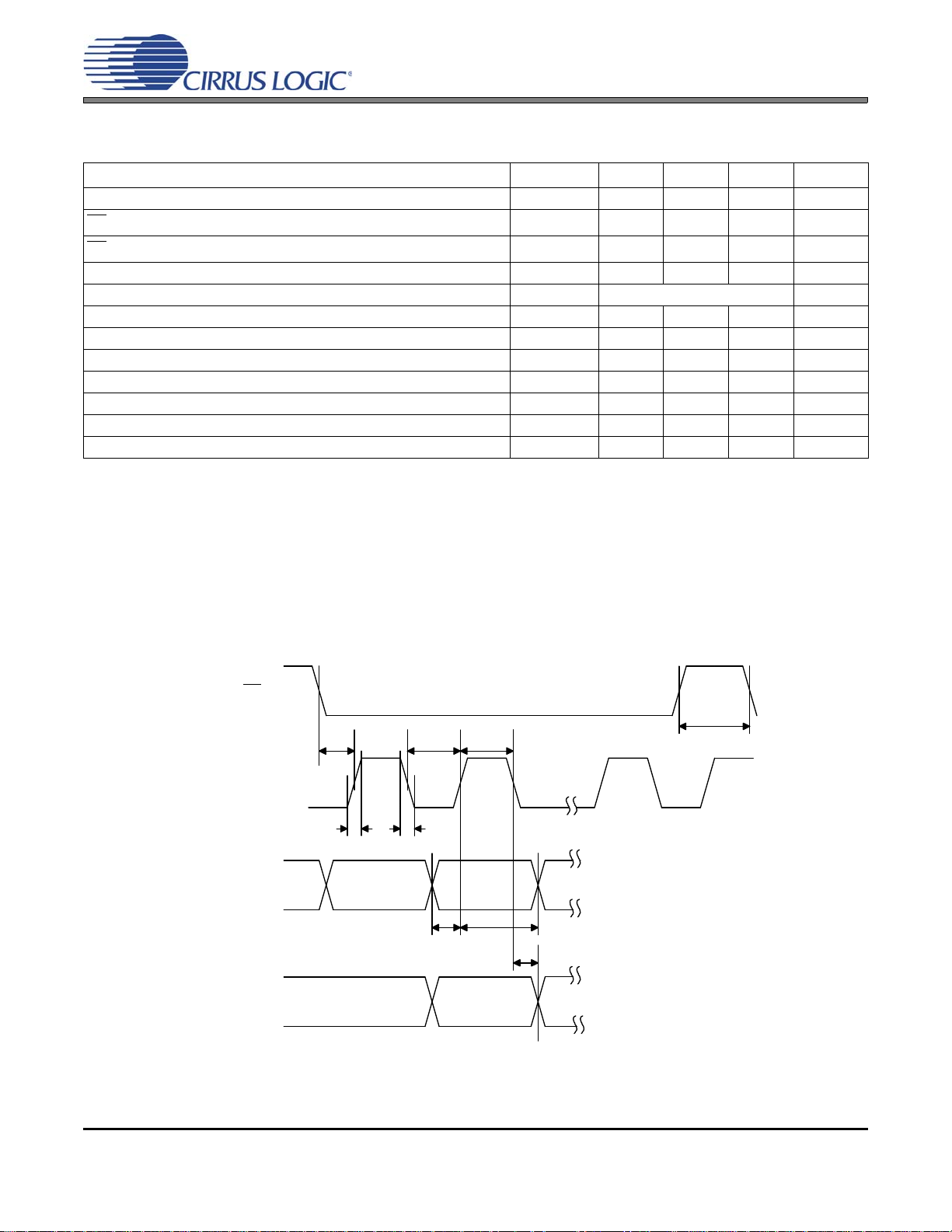
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - SPI MODE
t
r2
t
f2
t
dsu
t
dh
t
sch
t
scl
CS
CCLK
CDIN
t
css
t
pd
CDOUT
t
csh
Figure 3. SPI Mode Timing
(Inputs: Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = VL; CL = 20 pF)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
CCLK Clock Frequency (Note 9) f
High Time Between Transmissions t
CS
Falling to CCLK Edge t
CS
CCLK Low Time t
CCLK High Time (Note 10) t
CDIN to CCLK Rising Setup Time t
CCLK Rising to DATA Hold Time (Note 11) t
CCLK Falling to CDOUT Stable t
Rise Time of CDOUT t
Fall Time of CDOUT t
Rise Time of CCLK and CDIN (Note 12) t
Fall Time of CCLK and CDIN (Note 12) t
Notes:
9. If Fs is lower than 51.850 kHz, the maximum CCLK frequency should be less than 115 Fs. This is dictated by the timing requirements necessary to access the Channel Status and User Bit buffer memory.
Access to the control register file can be carried out at the full 6 MHz rate.
10. T
must be greater than the larger of the two values, either 1/256FS + 8 ns, or 66 ns.
sch
11. Data must be held for sufficient time to bridge the transition time of CCLK.
12. For f
< 1 MHz.
sck
sck
csh
css
scl
sch
dsu
dh
pd
r1
f1
r2
f2
0-6.0MHz
1.0 - - s
20 - - ns
66 - - ns
MAX ((1/256 FS + 8), 66) ns
40 - - ns
15 - - ns
--50ns
--25ns
--25ns
--100ns
--100ns
CS8406
DS580F6 7
CS8406
t
buf
t
hdst
t
hdst
t
low
t
r
t
f
t
hdd
t
high
t
sud
t
sust
t
susp
Stop Start
Start
Stop
Repeated
SDA
SCL
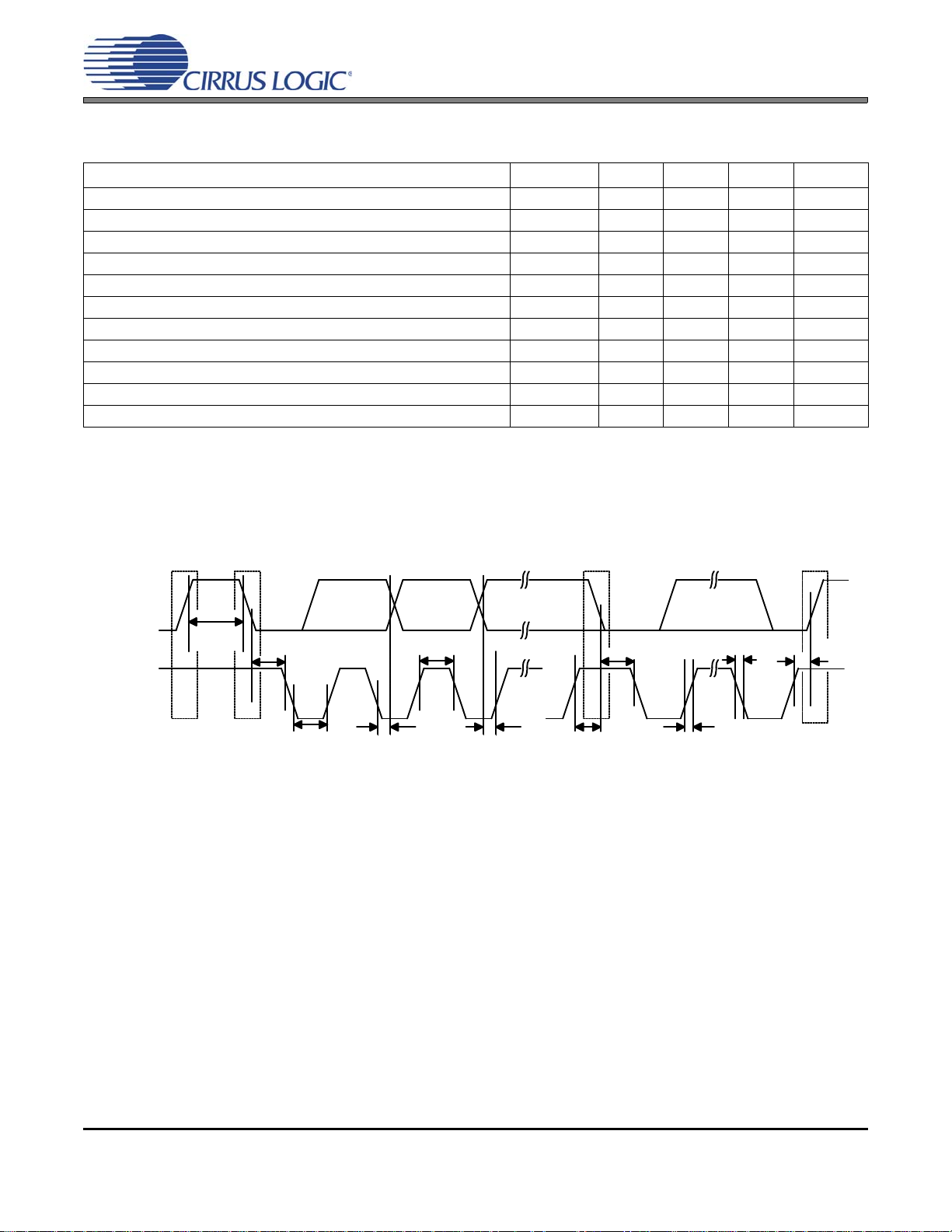
Figure 4. I²C Mode Timing
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS - CONTROL PORT - I²C MODE
(Inputs: Logic 0 = 0 V, Logic 1 = VL; CL = 20 pF)
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
SCL Clock Frequency fscl - - 100 kHz
Bus Free Time Between Transmissions t
Start Condition Hold Time (prior to first clock pulse) t
Clock Low Time t
Clock High Time t
Setup Time for Repeated Start Condition t
SDA Hold Time from SCL Falling (Note 13) t
SDA Setup Time to SCL Rising t
Rise Time of Both SDA and SCL Lines t
Fall Time of Both SDA and SCL Lines t
Setup Time for Stop Condition t
13. Data must be held for sufficient time to bridge the 300 ns transition time of SCL.
buf
hdst
low
high
sust
hdd
sud
r
f
susp
4.7 - - s
4.0 - - s
4.7 - - s
4.0 - - s
4.7 - - s
0--s
250 - - ns
- - 1000 ns
- - 300 ns
4.7 - - s
8 DS580F6
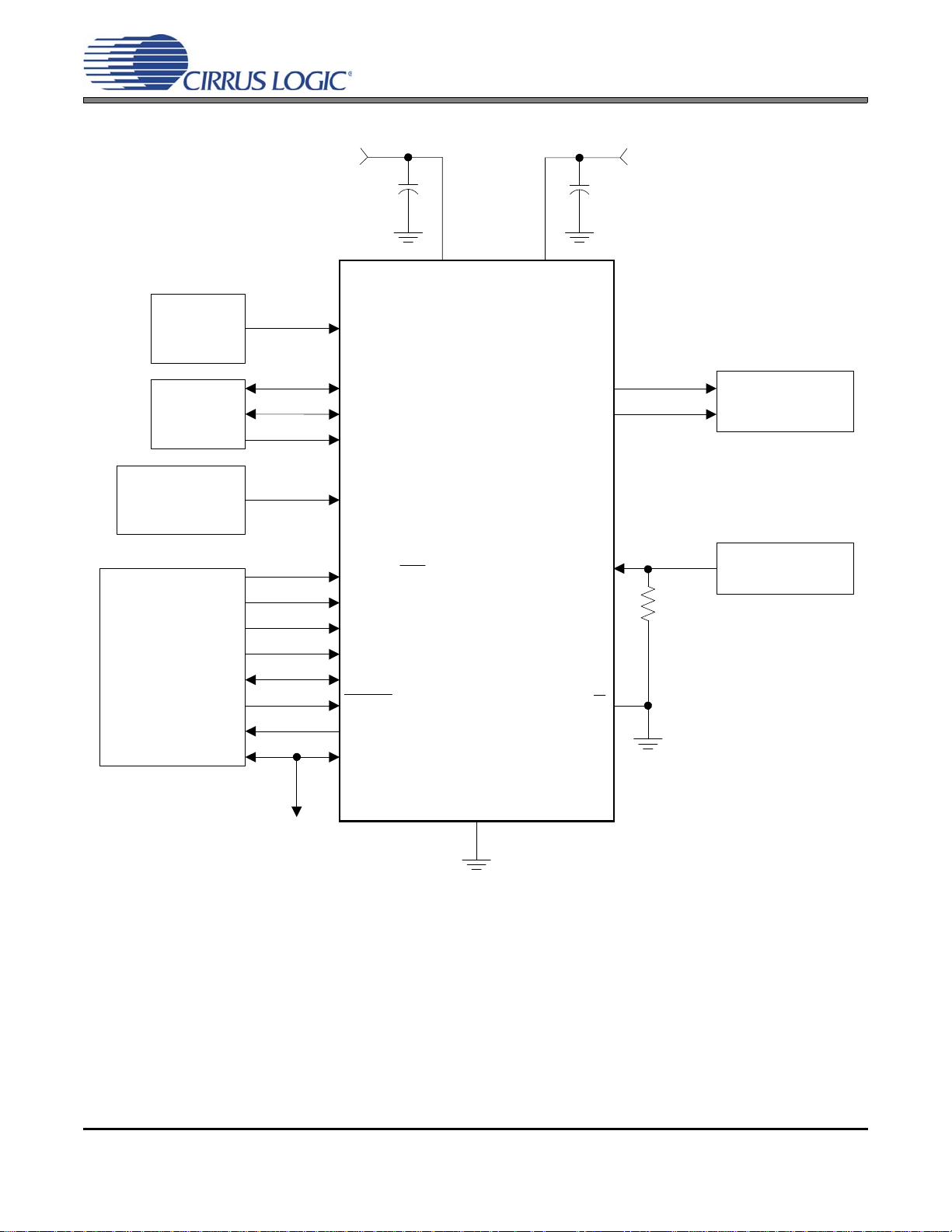
2. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
CS8406
+3.3 V or +5.0 V
GND
RXP
ILRCK
ISCLK
SDIN
AES3 /
S/PDIF
Source
Microcontroller
SCL / CCLK
SDA / CDOUT
RST
AD1 / CDIN
VD VL
TXP
0.1 F
AD0 / CS
Serial
Audio
Source
Clock Source
and Control
OMCK
AD2
TXN
H/S
TCBL
To/from other
CS8406's
INT
47k
U
Transmission
Interface
User Data
Source
+3.3 V or +5.0 V
0.1 F
Figure 5. Recommended Connection Diagram for Software Mode
CS8406
DS580F6 9
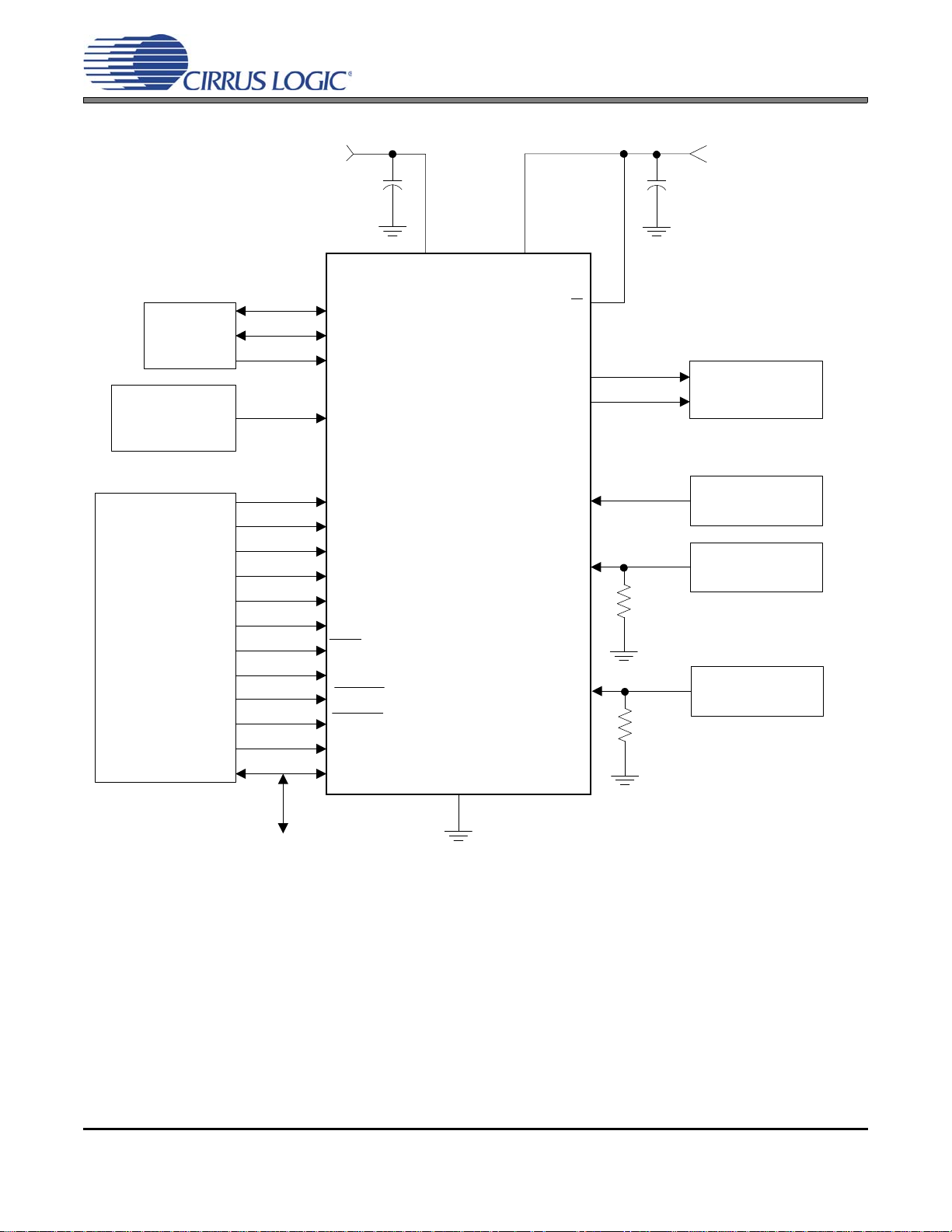
CS8406
CS8406
+3.3 V or +5.0 V
GND
ILRCK
ISCLK
SDIN
Hardware
Control
APMS
TCBLD
RST
SFMT0
VD VL
TXP
0.1 F
Serial
Audio
Source
Clock Source
and Control
OMCK
SFMT1
TXN
H/S
TCBL
To/from other
CS8406's
CEN
47k
U
Transmission
Interface
User Data
Source
EMPH
AUDIO
ORIG
V
Validity
Source
+3.3 V or +5.0 V
0.1 F
47k
C Data
Source
COPY/C
HWCK1
HWCK0
Figure 6. Recommended Connection Diagram for Hardware Mode
10 DS580F6

CS8406
3. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The CS8406 is a monolithic CMOS device which encodes a nd transmits audio data according to the AES3,
IEC60958, S/PDIF, and EIAJ CP1201 interface standards. The CS8406 accepts audio, channel status and user data, which is then multiplexed, encoded, and driven onto a cable.
The audio data is input through a configurable, 3-wire input port. The channel status bits and user bit data are input
through an SPI or I²C Mode microcontroller port and may be assembled in separate block sized buffers.
For systems with no microcontroller, a Stand-Alone Mode allows direct access to channel status and user data input
pins.
Target applications include CD-R, DAT, DVD, MD and VTR equipment, mixing consoles, digital audio transmission
equipment, high quality A/D converters, effects processors, set-top TV boxes, and computer audio systems.
Figure 5 shows the supply and external connections to the CS8406 when configured for operation with a microcon-
troller. Figure 6 shows the supply and external connections to the CS8406 when configured for operation without a
microcontroller.
3.1 AES3 and S/PDIF Standards Documents
This data sheet assumes that the user is familiar with the AES3 and S/PDIF data formats. It is advisable to
have current copies of the AES3 and IEC60958 specifications on hand for easy reference.
The latest AES3 standard is available from the Audio Engi neering Society or ANSI at www.aes.org or
www.ansi.org. Obtain the la test IEC60958 standard from ANSI or from the International Electrotechnical
Commission at www.iec.ch. The latest EIAJ CP-1201 standard is available from the Japanese Electronics
Bureau.
Application Note 22: Overview of Digital Audio Interface Data Structures contains a useful tutorial on digital
audio specifications, but it should not be considered a substitute for the standards.
The paper An Understanding and Implementation of the SCMS Serial Copy Management System for Digital
Audio Transmission, by Clifton Sanchez, is an excellent tutorial on SCMS. It is available from the AES as
reprint 3518.
DS580F6 11

CS8406
ILRCK
ISCLK
SDIN
2
Left
Justified
(In)
MSB
LSB
Left Right
MSB
I S
(In)
Right
Justified
(In)
MSB LSB MSB LSB MSB
Left
Right
MSB
LSB
MSB LSB
Left
Right
LSB
MSB LSB
ILRCK
ISCLK
SDIN
ILRCK
ISCLK
SDIN
Figure 7. Serial Audio Input Example Formats
X = don’t care to match format, but does need to be set to the desired setting
+ I²S can accept an arbitrary number of bits, determined by the number of ISCLK cycles
* See Serial Input Port Data Format Register Bit Descriptions for an explanation of the meaning of each bit
SIMS* SISF* SIRES[1:0]* SIJUST* SIDEL* SISPOL* SILRPOL*
Left Justified X X 00+ 0 0 0 0
I²S XX00+0101
Right Justified X X XX 1 0 0 0
4. THREE-WIRE SERIAL INPUT AUDIO PORT
A 3-wire serial audio input port is provided. The interface format can be adjusted to suit the attached device through
the control registers. The following parameters are adjustable:
• Master or slave
• Serial clock frequency
• Audio data resolution
• Left or right justification of the data relative to left/right clock
• Optional one-bit cell delay of the first data bit
• Polarity of the bit clock
• Polarity of the left/right clock (by setting the appropriate control bits, many formats are possible.)
Figure 7 shows a selection of common input formats with the corresponding control bit settings.
In Master Mode, the left/right clock and the serial bit clock are outputs, derived from the OMCK input pin master
clock.
In Slave Mode, the left/right clock and the serial bit clock are inputs. The left/right clock must be synchronous to the
OMCK master clock, but the serial bit clock can be asynchronous and discontinuous if required. The left/right clock
should be continuous, but the duty cycle can be less than the specified typical value of 50% if enough serial clocks
are present in each phase to clock all the data bits.
12 DS580F6
 Loading...
Loading...