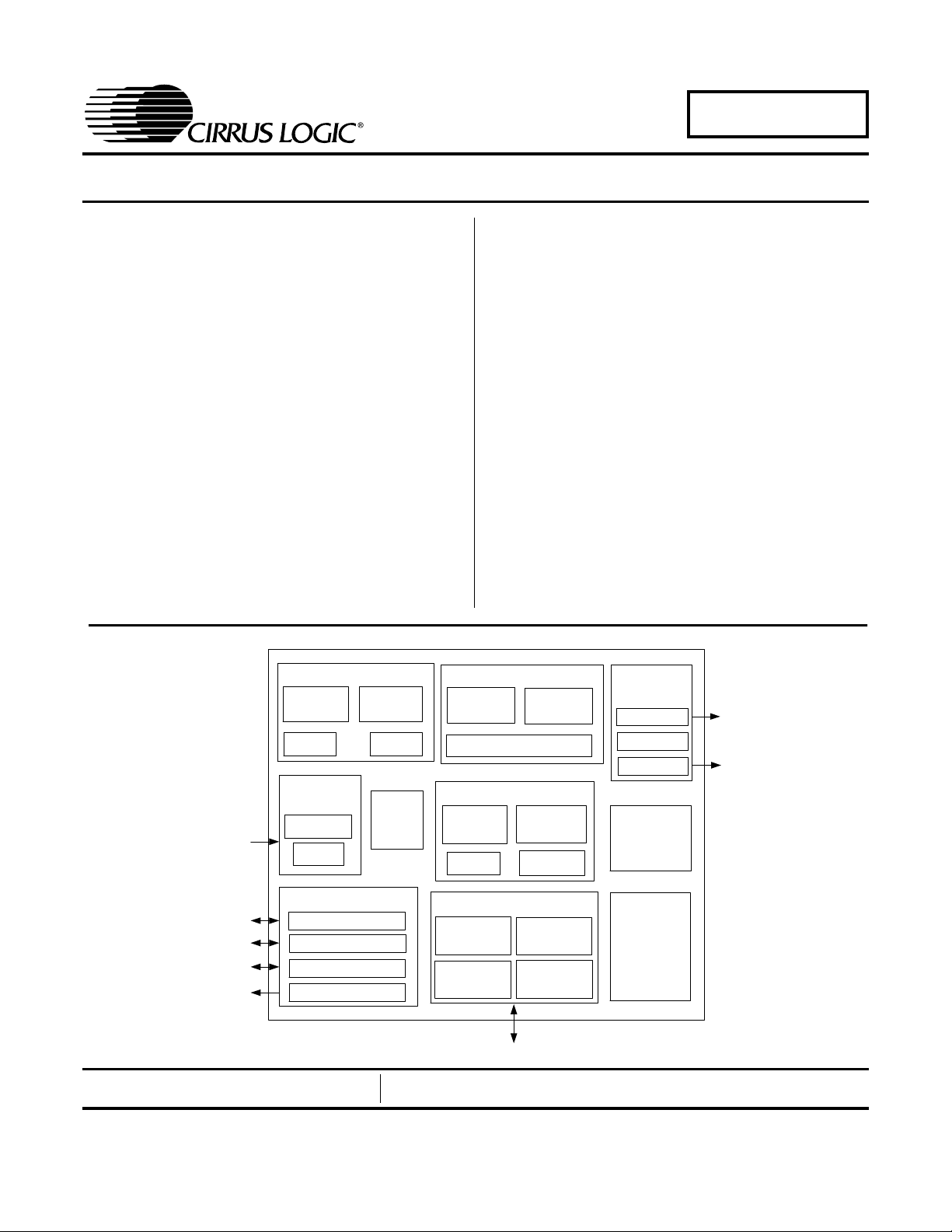
CD/MP3/WMA Audio Controller
CS7410
Features
l Super on-chip Integration for low cost and low count bill of
materials
l 32-Bit RISC Processor performs audio decode and system
management functions
l 16-bit DSP for audio special effects
l 80 Kbytes internal SRAM, and 256 Kbytes internal ROM
l Interfaces to external SDRAM or EDO DRAM (for shock
protection), and to external ROM/FLASH (for custom
program storage)
l CD serial interface with advanced pattern matching and
software error handling
l Integrated DAC functionality
l Simultaneous 4 channels PCM audio output and IEC-958
output.
l Large number of GPIO pins for servo control, key scan, LCD
control, etc.
l Three serial control/status ports
l Sophisticated clock management and low power
consumption
l Supports ISO9660 and multi-session write methods
l Low power 0.18 micron technology
l 100-pin MQFP package
l 100-pin LQFP package
Description
The CS7410 is a true system-on-a-chip for the CDbased digital audio market. With a powerful RISC processor, one DSP, integrated audio ∆Σ modulator, large
internal SRAM and program ROM, and glueless interface to popular CD chip sets, the CS7410 is a complete
single chip low-power programmable audio decoder.
This powerful architecture is easily capable of MP3,
WMA, and other future audio formats. The CS7410’s
flexible architecture and low power consumption make it
an ideal low-cost solution for a wide range of player applications. For portable audio systems, the memory
interface can be used to add DRAM or SRAM for Electronic Shock Protection (ESP). A flexible set of interfaces
are available for end-user I/O such as a keypad and LCD
control for use in mass market CD players, boom boxes,
and shelf-top systems.
ORDERING INFORMATION
CS7410-CM 0° to 70° C 100-pin MQFP
CS7410-CQ 0° to 70° C 100-pin LQFP
RISC-32
Instruction
Cache
CPU
CD
Interface
Control
FIFO
External Interface
2-Wire Debug Interface
3/4 Wire Serial
Programmable I/O
PWM Out
Preliminary Product Information
Cirrus Logic, Inc.
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7581
http://www.cirrus.com
Data
Cache
MAC
DSP-16
Instruction
Cache
CPU / MAC
X,Y Data
memory
Audio
Interface
∆Σ Modulator
PCM Out
IEC-958
System Miscellaneous
PLL
Clock
Control
Timers Get Bits
Register
Bank
80 KB
Internal
SRAM
Memory Controller
ROM/SRAM
Control
Flash
Control
This document contains information for a new product.
Cirrus Logic reserves the right to modify this product without notice.
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2002
Mini
DMA
DRAM
Control
(All Rights Reserved)
256 KB
Internal
ROM
JUL ‘02
DS553PP1
1

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................ 5
1.1 AC and DC Parametric Specifications ...............................................................................5
1.1.1 Absolute Maximum Rating .................................................................................... 5
1.1.2 Recommended Operating Conditions ...................................................................5
1.1.3 Electrical Specifications ........................................................................................5
1.1.4 DC Characteristics ................................................................................................ 7
1.1.4.1 SDRAM Interface .................................................................................. 7
1.1.4.2 Serial Interface .................................................................................... 11
1.1.4.3 EDO DRAM interface ..........................................................................12
1.1.4.4 FLASH / ROM Interface ...................................................................... 15
1.1.4.5 Audio Output Interface ........................................................................ 17
1.1.4.6 CD Interface ........................................................................................18
1.1.4.7 Miscellaneous Timings ........................................................................20
2. CS7410 SUMMARY ................................................................................................................ 21
2.1 CS7410 Typical Application ............................................................................................. 21
2.2 CS7410 Block Summaries ..............................................................................................21
2.2.1 RISC-32 ..............................................................................................................21
2.2.2 DSP-16 ................................................................................................................21
2.2.3 System Controls ..................................................................................................21
2.2.4 Memory System ..................................................................................................22
2.2.5 CD Interface ........................................................................................................ 22
2.2.6 Audio Interface ....................................................................................................22
2.2.7 External Interface ................................................................................................ 22
2.2.8 System Functions ................................................................................................22
3. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ...............................................................................................23
3.1 RISC-32 Processor .......................................................................................................... 23
3.2 DSP-16 Processor ...........................................................................................................23
3.3 Memory Control ...............................................................................................................23
3.4 CD Interface ..................................................................................................................... 23
3.5 System Control Functions ................................................................................................ 23
3.6 Audio Output ....................................................................................................................24
4. PIN DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................................25
CS7410
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/corporate/contacts/sales.cfm
IMPORTANT NOTICE
“Preliminary” product information describes products that are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet available. “Advance” product infor-
mation describes products that are in development and subject to development changes. Cirrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries (“Cirrus”) believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided “AS IS” without warranty
of any kind (express or implied). Customers are advised to obtain the latest version of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that information being
relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus for the use of this information, including use of this
information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infringement of patents or other rights of third parties. This document is the property of Cirrus
and by furnishing this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask work rights, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or
other intellectual property rights. Cirrus owns the copyrights of the information contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only
for use within your organization with respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other parts of Cirrus. This consent does not extend to other copying such as copying
for general distribution, advertising or promotional purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
An export permit needs to be obtained from the competent authorities of the Japanese Government if any of the products or technologies described in this material and controlled under the “Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Law” is to be exported or taken out of Japan. An export license and/or quota needs to be
obtained from the competent authorities of the Chinese Government if any of the products or technologies described in this material is subject to the PRC Foreign
Trade Law and is to be exported or taken out of the PRC.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE
PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL APPLICATIONS”). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS
IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER'S RISK.
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, and the Cirrus Logic logo designs are trademarks of Cirrus Logic, Inc. All other brand and product names in this document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners.
2 DS553PP1

4.1 Pin Identification .............................................................................................................. 25
4.2 Miscellaneous Pins .......................................................................................................... 30
4.3 Serial Interface Pins ........................................................................................................ 30
4.4 SDRAM / DRAM Interface ............................................................................................... 31
4.5 ROM/NVRAM Interface ................................................................................................... 32
4.6 Digital Audio Output Interface .......................................................................................... 33
4.7 ∆Σ Modulator Interface .................................................................................................... 33
4.8 CD Interface .................................................................................................................... 34
4.9 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) ............................................................................ 35
4.10 Power and Ground ........................................................................................................ 36
5. 100-PIN MQFP PACKAGE SPECIFICATIONS (20X14X2.85MM) ....................................... 38
6. 100-PIN LQFP PACKAGE SPECIFICATIONS (14X14X1.4MM) ........................................... 39
LIST OF FIGURES
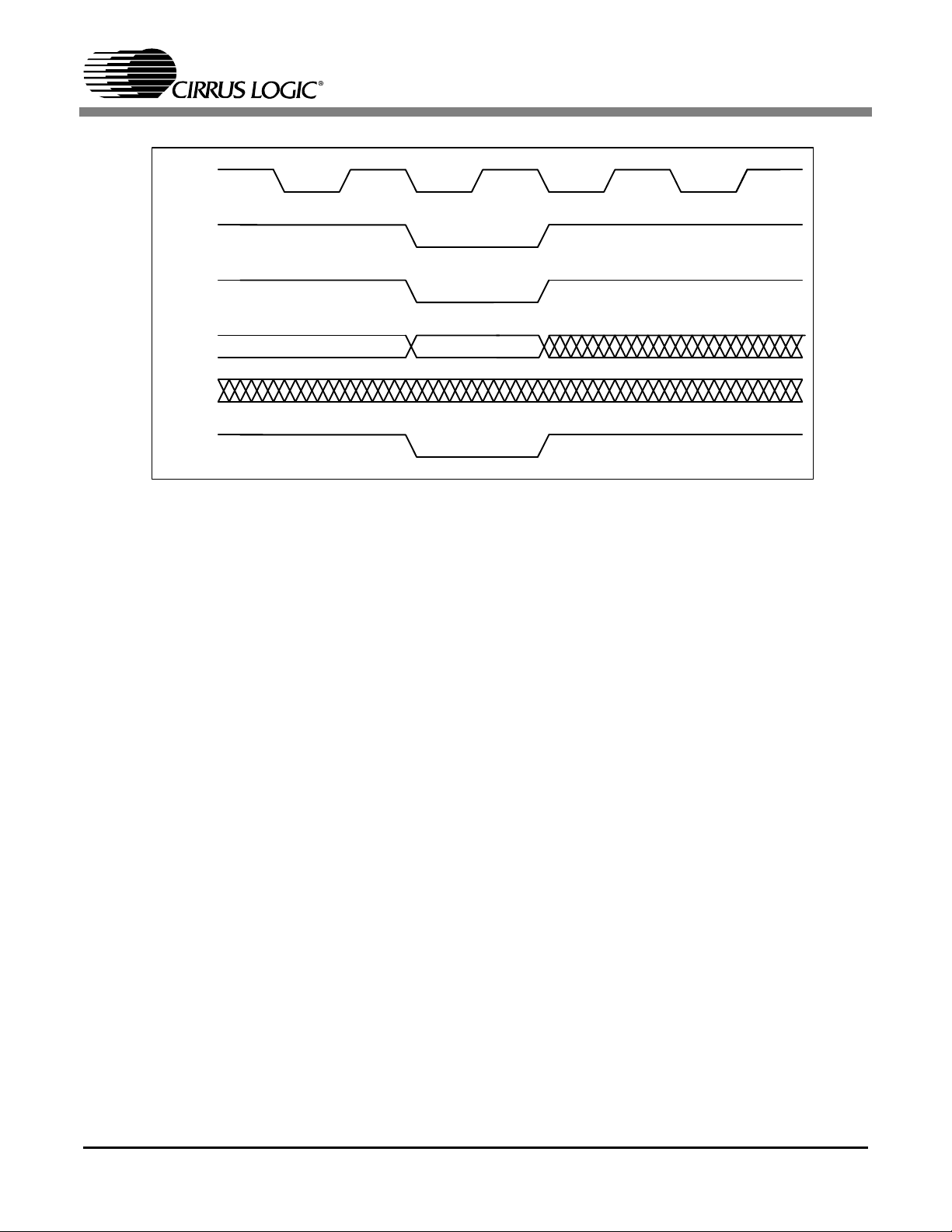
Figure 1. SDRAM Timing................................................................................................................ 7
Figure 2. SDRAM Load Mode......................................................................................................... 8
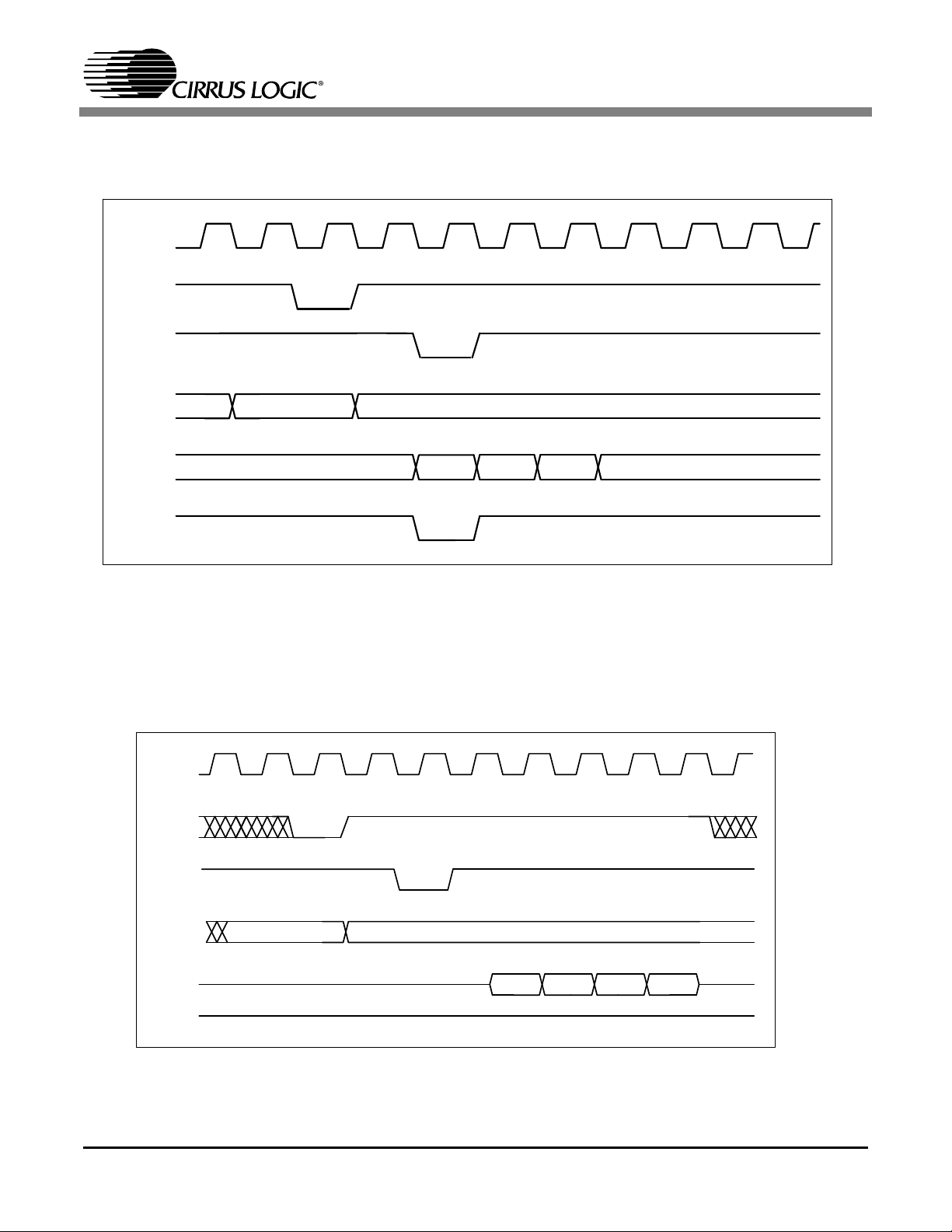
Figure 3. SDRAM Burst Write......................................................................................................... 9
Figure 4. SDRAM Burst Read......................................................................................................... 9
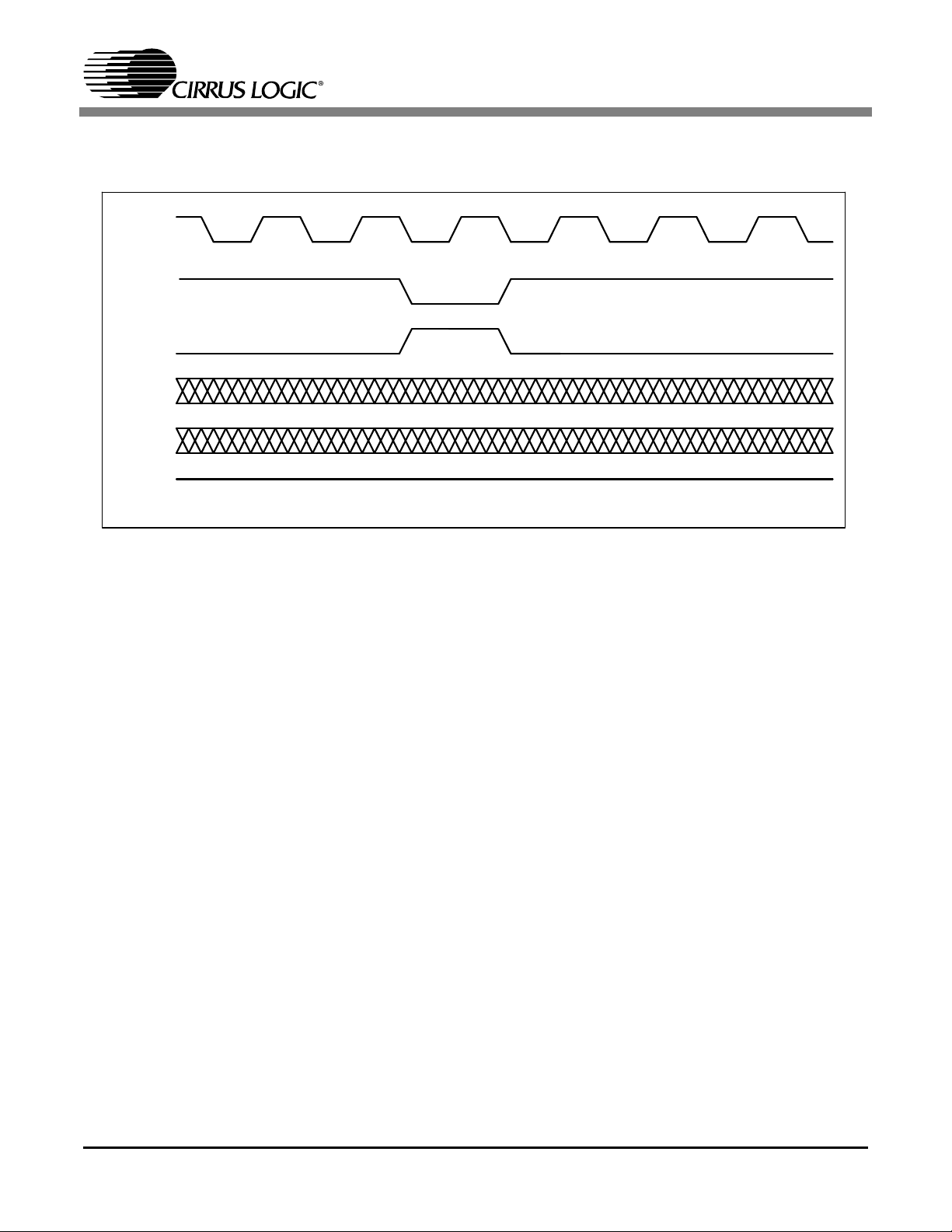
Figure 5. SDRAM Refresh ............................................................................................................ 10
Figure 6. Serial Interface Timing Diagram .................................................................................... 11
Figure 7. EDO Page Write Timing Diagram.................................................................................. 13
Figure 8. EDO Page Read Timing Diagram.................................................................................. 13
Figure 9. EDO Refresh Timing Diagram....................................................................................... 14
Figure 10. FLASH/ROM Read ...................................................................................................... 15
Figure 11. FLASH/ROM Write....................................................................................................... 16
Figure 12. Audio Output Timing.................................................................................................... 17
Figure 13. CD Interface Timing..................................................................................................... 18
Figure 14. CD Interface Timing Diagrams..................................................................................... 19
Figure 15. Miscellaneous Timings................................................................................................. 20
Figure 16. CS7410 Application ..................................................................................................... 21
Figure 17. CS7410 Pin Identification............................................................................................. 25
Figure 18. 100-Pin MQFP Package (20x14x2.85mm).................................................................. 38
Figure 19. 100-Pin LQFP Package (14X14X1.4mm).................................................................... 39
CS7410
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. SDRAM Characterization Data ......................................................................................... 7
Table 2. Serial Interface Characterization Data............................................................................ 11
Table 3. EDO DRAM Characterization Data................................................................................. 12
Table 4. FLASH/ROM Read Characterization Data...................................................................... 15
Table 5. Audio Output Interface Symbols and Characterization Data........................................... 17
Table 6. Pin Type and Direction Legend....................................................................................... 25
Table 7. Pin Assignments ............................................................................................................. 26
Table 8. Miscellaneous Interface Pins .......................................................................................... 30
Table 9. Serial Interface Pins........................................................................................................ 30
Table 10. SDRAM Interface.......................................................................................................... 31
Table 11. EDO DRAM Interface.................................................................................................... 31
Table 12. ROM/NVRAM Interface ................................................................................................. 32
Table 13. Audio Output Interface.................................................................................................. 33
Table 14. ∆Σ Output Interface....................................................................................................... 33
Table 15. CD Interface.................................................................................................................. 34
DS553PP1 3

CS7410
Table 16. Dedicated General Purpose I/O Pins............................................................................35
Table 17. Redefined General Purpose Pins..................................................................................35
Table 18. Power and Ground........................................................................................................36
4 DS553PP1
1. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS
1.1 AC AND DC PARAMETRIC SPECIFICATIONS
(AGND, DGND=0V, all voltages with respect to 0V)
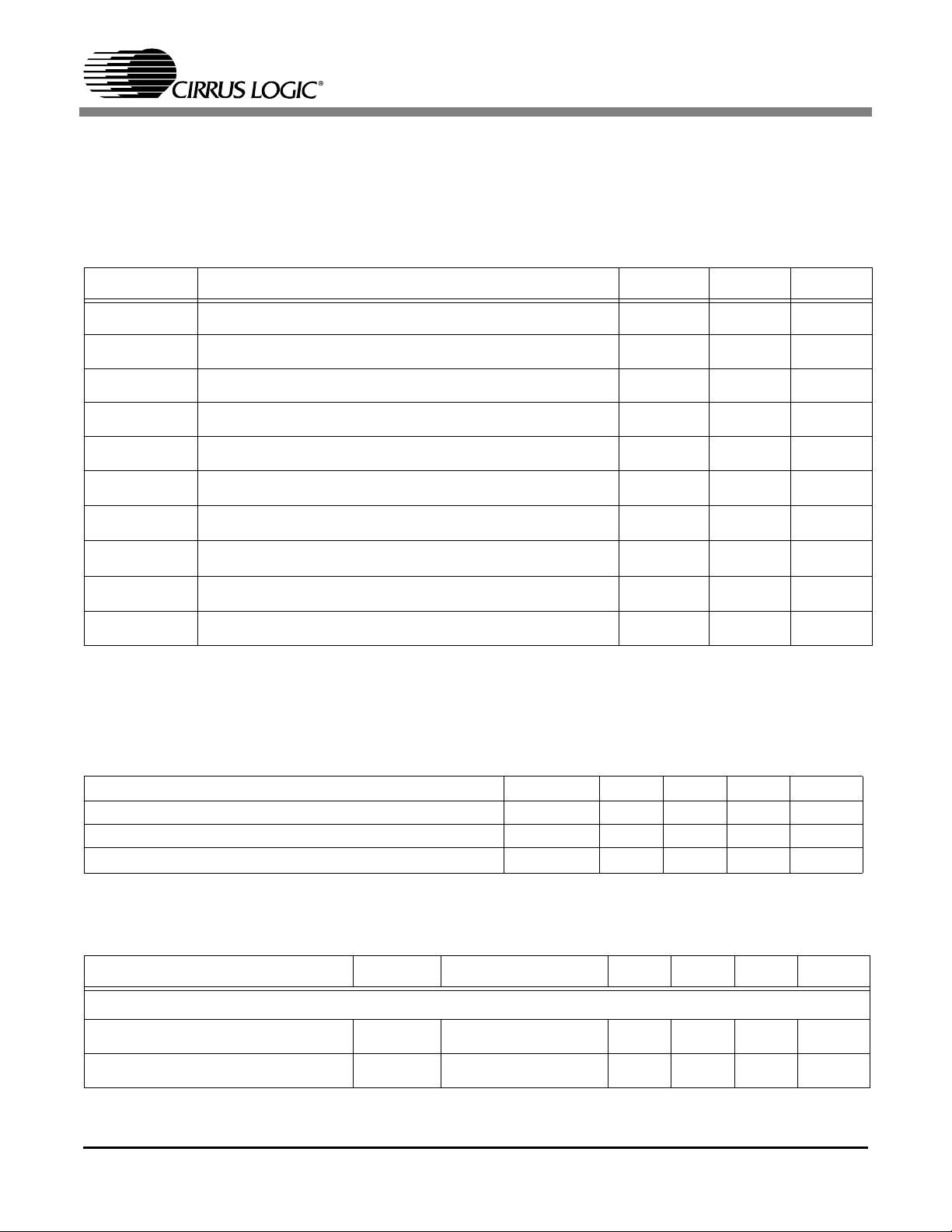
1.1.1 Absolute Maximum Rating
Symbol Description Min. Max. Unit
CS7410
VDD
VDD
V
I
I
I
I
O
T
SOL
T
VSOL
T
STOR
T
AMB
P
TOT
IO
CORE
Power Supply Voltage on I/O ring -0.5 4.6 Volts
Power Supply Voltage on core logic and PLL -0.5 2.5 Volts
Digital Input Applied Voltage (power applied) -0.5 5.5 Volts
Digital Input Forced Current -10 10 mA
Digital Output Forced Current -50 50 mA
Lead Soldering Temperature 260
Vapor Phase Soldering Temperature 235
Storage Temperature (no power applied) -40 125
Ambient Temperature (power applied) 0 70
o
C
o
C
o
C
o
C
Power consumption 1 W
CAUTION: Operating beyond these Minimum and Maximum limits can result in permanent damage to
the device. Cirrus Logic recommends that CS7410 devices operate at the settings described in the next table.
1.1.2 RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
Supply Voltage, IO V
Supply Voltage, core and PLL V
Ambient Temperature (power applied) T
DD
DD
AMB
3.0 3.3 3.6 Volts
1.62 1.8V 1.98 Volts
0 25 70
o
C
1.1.3 Electrical Specifications
(TA = 0 to 70 oC)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Power Supply
Supply Current, IO I
Supply Current, core and PLL I
DD
DD
DS553PP1 5
Normal Operating 13 mA
Normal Operating 70 mA
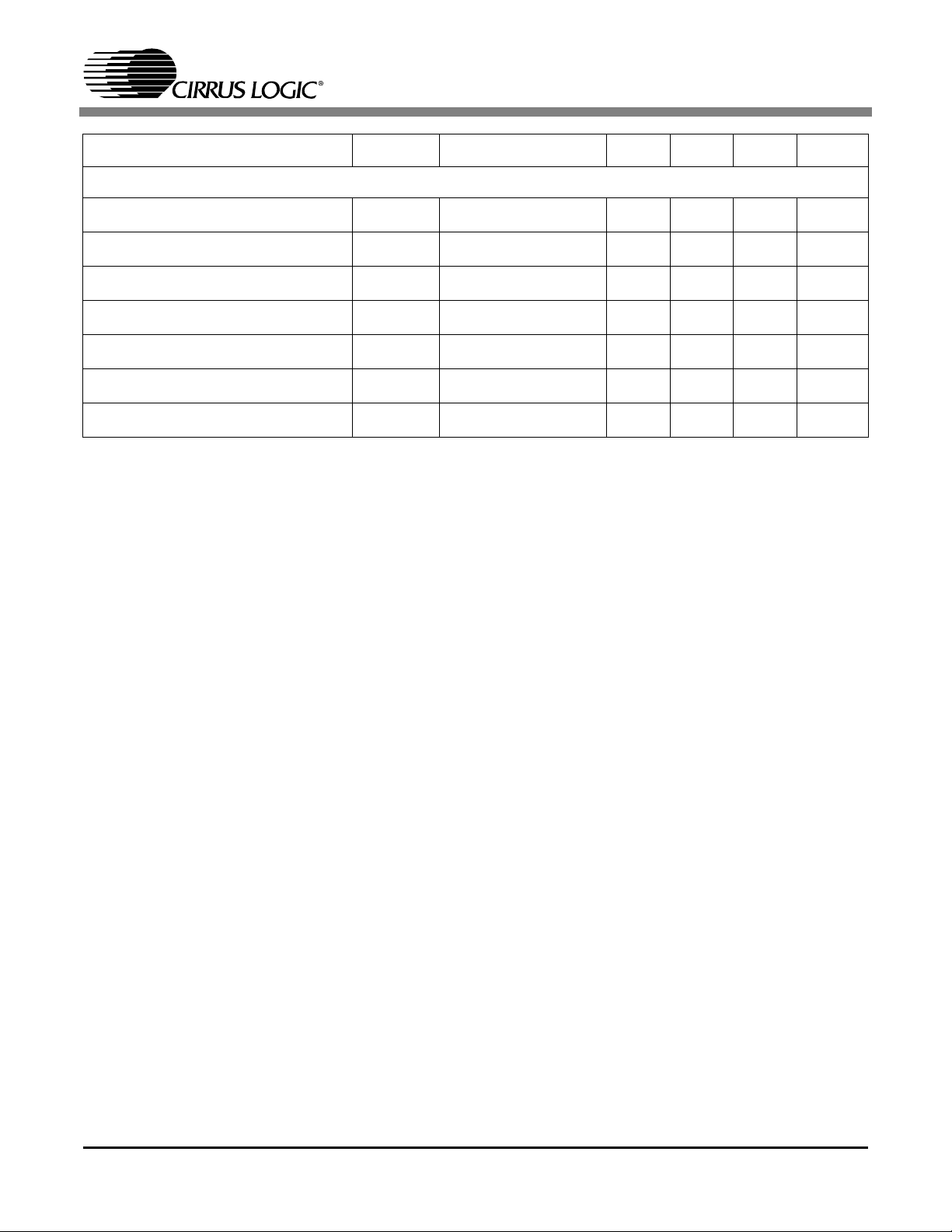
Digital Pins
CS7410
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Input Voltage, High V
Input Voltage, Low V
Input Current I
Input Pull up/down resistor R
Output Voltage, High V
Output Voltage, Low V
High-Z-state Leakage I
IN
OZ
IH
IL
I
OH
OL
2.0 Volts
0.8 Volts
V
= V
IN
DD
or V
SS
-1 +1
75
µA
KΩ
@ buffer rating 2.4 Volts
@ buffer rating 0.4 Volts
V
= VSS or V
OUT
DD
-1 +1
µA
6 DS553PP1
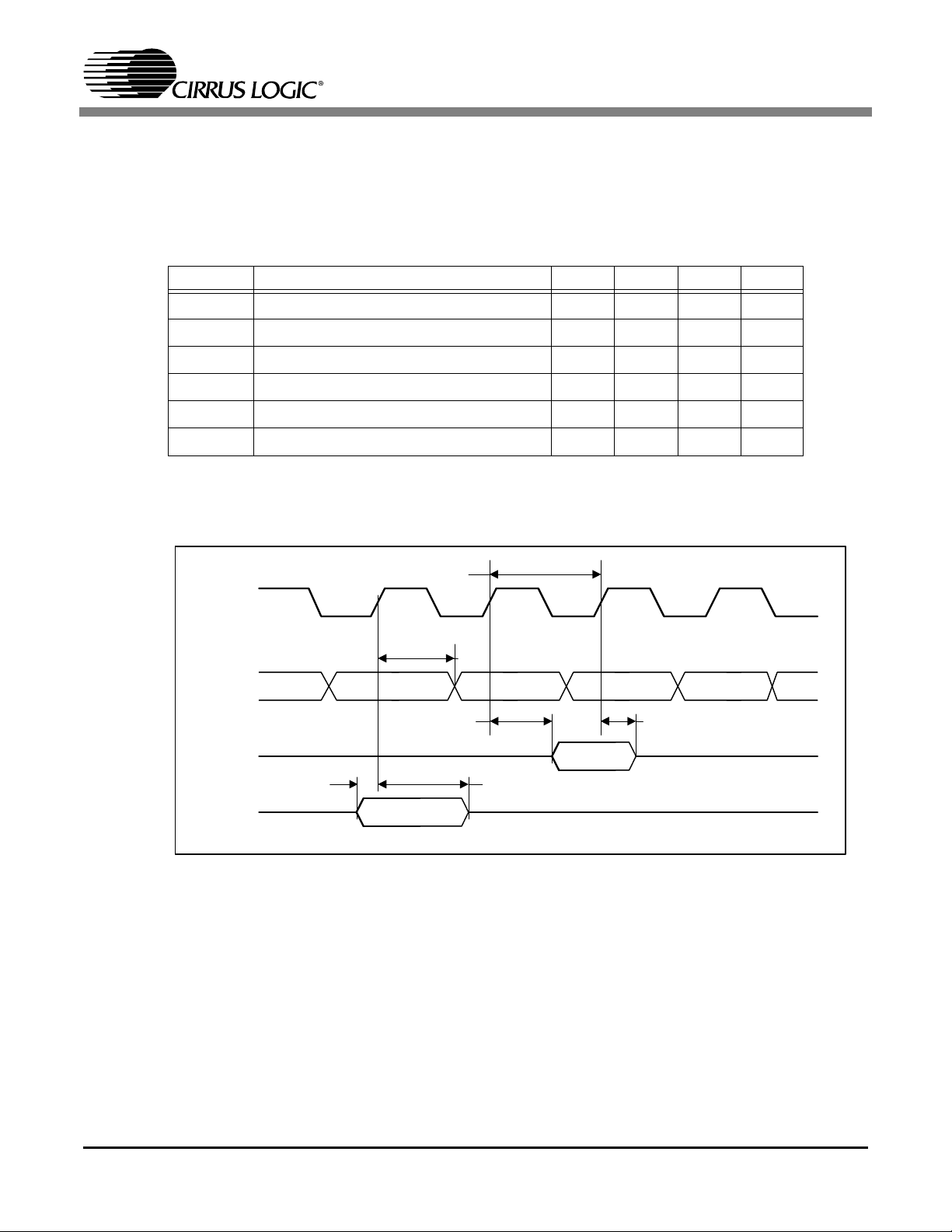
1.1.4 DC CHARACTERISTICS
(TA= 25°C; VDD_PLL=VDD_CORE=1.8V±10%, VDD_IO=3.3V±10%)
1.1.4.1 SDRAM Interface
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
mper
t
mco
t
mdow
t
mhw
t
msur
t
mhr
DR_CKO Period 22 ns
Output Delay from DR_CKO active edge 19 ns
M_D[15:0] delay from DR_CKO 19 ns
M_D[15:0] valid time after DR_CKO 5 ns
M_D[15:0] setup to DR_CKO 13 ns
M_D[15:0] hold time after DR_CKO 0 ns
Table 1. SDRAM Characterization Data
CS7410
DR_CKO
M_WE_L
M_A
DR_RAS_L
DR_CAS_L
M_D
(write)
M_D
(read)
t
msur
t
mper
t
mco
t
mdow
t
mhr
Figure 1. SDRAM Timing
t
mhw
DS553PP1 7
DR_CKO
DR_RAS_L
DR_CAS_L
M_A
M_D
M_WE_L
CS7410
Figure 2. SDRAM Load Mode
8 DS553PP1
DR_CKO
DR_RAS_L
DR_CAS_L
CS7410
M_A
M_D
M_WE_L
DR_CKO
DR_RAS_L
ADRAS
ADCAS
D0
Figure 3. SDRAM Burst Write
Dn...D1
DR_CAS_L
M_A
M_D
M_WE_L
ADRAS ADCAS
D1 Dn...D2
Figure 4. SDRAM Burst Read
DS553PP1 9
DR_CKO
DR_RAS_L
DR_CAS_L
M_A
M_D
M_WE_L
CS7410
Figure 5. SDRAM Refresh
10 DS553PP1
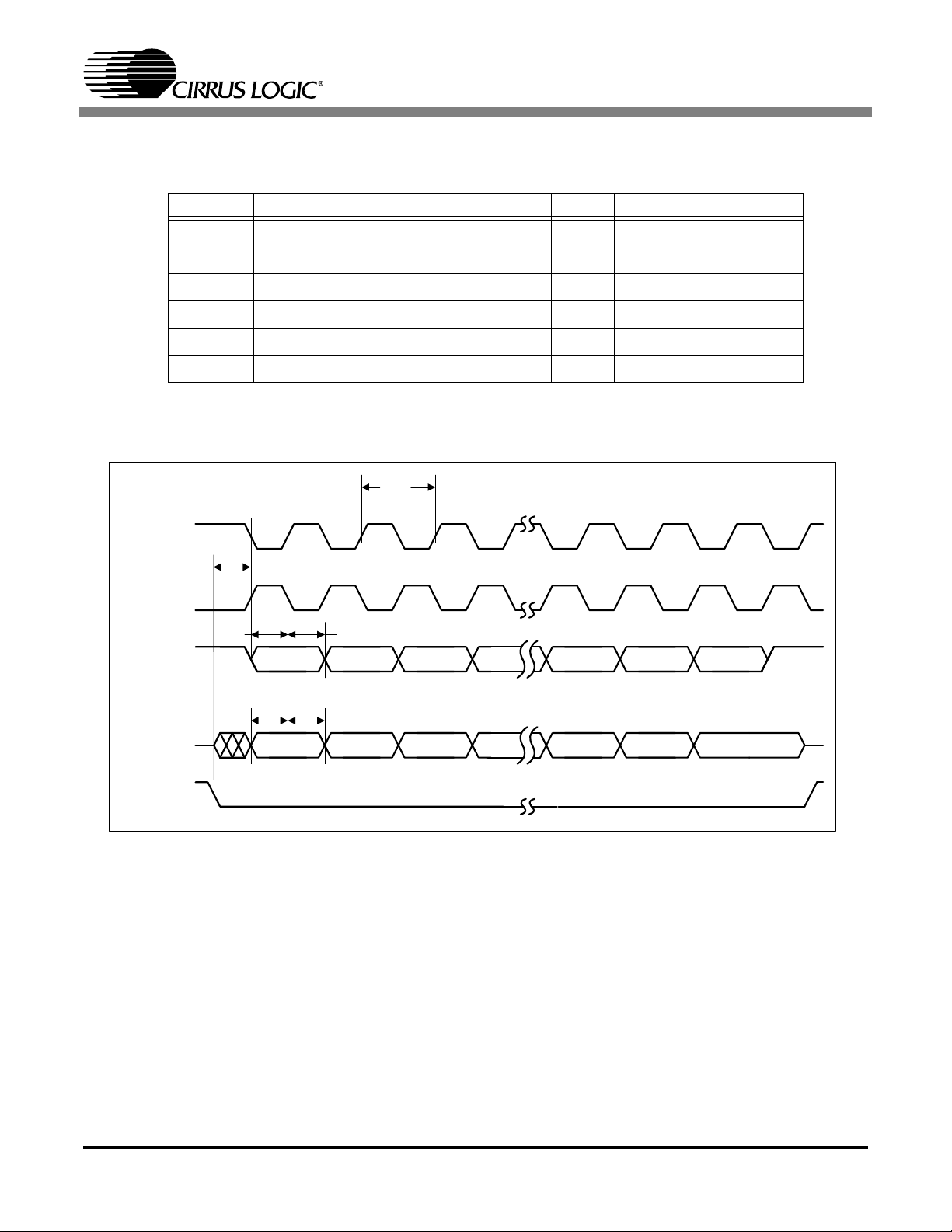
1.1.4.2 Serial Interface
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
clk_per
t
DMs
t
DMh
t
DSs
t
CMs
t
DSh
SER2_CLK
(CPOL=0)
SER2_CLK
(CPOL=1)
Clock period 66 ns
Master-mode data setup 28 ns
Master-mode data hold 28 ns
Slave-mode data setup 15 ns
Master chip select to clock setup 28 ns
Slave mode data hold 0 ns
t
CMs
Table 2. Serial Interface Characterization Data
t
clk_per
CS7410
SER2_DO
(master)
SER2_DI
(slave)
SER2_CS
t
DMs
t
DSs
MSB LSB
t
t
DMh
DSh
Figure 6. Serial Interface Timing Diagram
LSBMSB
DS553PP1 11
1.1.4.3 EDO DRAM interface
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
RAS
t
RP
t
RCL
t
CAS
t
CPN
t
CAH
t
ASR
t
RAH
t
ASC
t
AA
t
CAC
t
CSR
t
CHR
t
CRH
t
WDS
t
WDH
t
WS
t
WH
t
ROE
t
OER
t
DCH
RAS low time 72 ns
RAS high pulse time 40 ns
RAS fall to CAS fall 38 ns
CAS low time 30 ns
CAS high time 15 ns
CAS fall to address row 29 ns
Address row to RAS fall 10 ns
RAS fall to address column 18 ns
second address column (burst) to CAS fall 10 ns
Column address to data setup 35 ns
CAS fall to data setup 17 ns
CAS fall to RAS fall 19 ns
RAS fall to CAS rise 18 ns
CAS rise to RAS rise 6 ns
Write data setup to CAS fall 12 ns
Write data hold to CAS fall 29 ns
Write enable setup to CAS fall 13 ns
Write enable hold to CAS fall 20 ns
RAS fall to OE fall -5 5 ns
RAS rise to OE rise -5 5 ns
Read data hold to CAS rise 0 ns
CS7410
Table 3. EDO DRAM Characterization Data
Note:Values shown are for minimum internal clock period (11ns) and all programmed wait states enabled.
12 DS553PP1

DR_RAS_L
DR_CAS_L
M_A
t
ASR
t
RCL
t
CAS
t
t
RAH
CPN
ADRAS ADCAS
t
RAS
t
ASC
t
CRH
ADCAS
t
RP
CS7410
t
CAH
M_D
M_AP_WE
M_AP_OE
DR_RAS_L
DR_CAS_L
M_A
M_D
t
ASR
t
DATA DATA
t
WS
Figure 7. EDO Page Write Timing Diagram
t
ROE
t
RAS
t
RCL
t
CAS
t
t
RAH
ADRAS ADCAS
CPN
t
ASC
DATA DATA
WDS
t
WDH
t
WH
t
OER
t
t
CRH
RP
t
CAH
ADCAS
t
t
AA
CAC
t
DCH
Figure 8. EDO Page Read Timing Diagram
DS553PP1 13

DR_RAS_L
DR_CAS_L
t
CSR
t
RAS
t
CHR
Figure 9. EDO Refresh Timing Diagram
CS7410
14 DS553PP1

1.1.4.4 FLASH / ROM Interface
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
CSpw
t
RDd1
t
RDd2
t
ADs
t
DAs Data setup after address
t
WRSU
t
WRPW
t
WRH
1.
Value shown for 3 programmed wait states.
Note:Values shown are for minimum internal clock period (11ns) and no programmed wait states.
CE low period 135 ns
CE fall to output enable fall 5 ns
CE rise to output enable rise -5 5 ns
Address setup to CE fall -10 10 ns
1
28 ns
All outputs setup before WE 95 ns
WE pulse width 170 ns
All outputs hold after WE 95 ns
Table 4. FLASH/ROM Read Characterization Data
CS7410
NVM_CE_L
M_WE_L
M_AP_OE
M_A
M_D
t
RDd1
t
ADs
t
DAS
Figure 10. FLASH/ROM Read
t
CSpw
t
RDd2
DS553PP1 15

NVM_CE_L
M_A
M_D
M_WE_L
M_AP_OE
t
WRSU
t
WRPW
Figure 11. FLASH/ROM Write
CS7410
t
WRH
16 DS553PP1

CS7410
1.1.4.5 Audio Output Interface
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
t
axch
t
axcl PCM_XCLK Low Time (PCM_XCLK is Input/Output
t
axper PCM_XCLK period (Input/Output)
t
aoper PCM_BCK period (Output)
t
sdmo PCM_BCK delay from PCM_XCLK output transition
t
sdmi PCM_BCK delay from PCM_XCLK input transition
t
lrds PCM_LRCK delay from PCM_BCK transition
t
adsm PCM_D[3:0] delay from PCM_BCK transition
1.
PCM_XCLK High Time (PCM_XCLK is Input/Output) 42 50 %
42 50 %
55 ns
440 ns
1
1
1
1
Table 5. Audio Output Interface Symbols and Characterization Data
Active clock edge is programmable. Timing is referenced from the active edge.
t
axper
PCM_XCK(Input/Output)
t
axch
t
axcl
5
15
5
5
ns
ns
ns
ns
PCM_BCK(Output)
PCM_BCK(Output)
PCM_LRCK(Output)
PCM_DO[1:0] (Output)
sdmi
t
sdmo
t
aoper
t
lrds
t
adsm
Figure 12. Audio Output Timing
DS553PP1 17

CS7410
1.1.4.6 CD Interface
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Units
t
slri
t
sdi
t
hsdi
Note:Active edge of CD_BCLK is programmable
CD_LRCK setup to CD_BCK active edge 7 ns
CD_DATA and CD_C2P0 setup to CD_BCK active edge 7 ns
CD_DATA and CD_C2P0 hold time after CD_BCK active edge 3 ns
CD_BCK(Input)*
t
slri
CD_LRCK(Input)
CD_DO (Input)
CD_C2PO (Input)
t
sdi
Figure 13. CD Interface Timing
t
hsdi
18 DS553PP1

CD_BCK
CD_LRCK
DATA
C2P0
CD_BCK
CD_LRCK
DATA
C2P0
CD_BCK
CD_LRCK
DATA
C2P0
LeftChannel RightChannel
Invalid0
Lower (Left Channel) Upper(LeftChannel) Lower(RightChannel) Upper(RightChannel)
MSB LSB MSB LSB
15
14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
01
Invalid
150114 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
32-bit BCK, MSB First, Right Channel Low, C2P0 LSB First, Data latch timing high
RightChannel LeftChannel
0 15 0114 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Invalid
Upper(RightChannel) Lower(RightChannel) Upper(LeftChannel) Lower(LeftChannel)
MSB LSB MSB LSB
15 01
14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Invalid
32-bit BCK, MSB First, Left Channel Low, C2P0 MSB First, Data latch timing low
LeftChannel RightChannel
Invalid
0
MSB LSB
15
14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Lower(LeftChannel)Upper(Left Channel) Lower (RightChannel)Upper(RightChannel)
Invalid
01
MSB LSB
150114 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Invalid
Upper (LeftChannel)
LeftChannel
MSB
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5
24-bit BCK, MSB First, Right Channel Low, C2P0 MSB First, Data latch timing high
CS7410
CD_BCK
CD_LRCK
DATA
C2P0
CD_BCK
CD_LRCK
DATA
CD_BCK
CD_LRCK
DATA
C2P0
LeftChannel RightChannel
Invalid
0
LSB MSB
0151
24-bit BCK, LSB First, Right Channel Low, C2P0 MSB First, Data latch timing low
LeftChannel RightChannel
0
Invalid
MSB LSB
15
14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
24-bit BCK, MSB First, Right Channel Low, Data latch timing high (Note: no C2P0 for this format)
MSB LSB
0
15
14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
16-bit BCK, MSB First, Left Channel Low, C2P0 LSB First, Data latch timing high
141312111098765432
Lower(LeftChannel)Upper(Left Channel) Lower (RightChannel)Upper(RightChannel)
MSB LSB
01
150114 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Lower (Left Channel) Upper(LeftChannel)Lower(RightChannel) Upper (RightChannel)
Invalid
01
Invalid
LeftChannelRightChannel
LSB MSB
0151
MSB LSB
150114 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
MSB LSB
150114 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Figure 14. CD Interface Timing Diagrams
LeftChannel
141312111098765432
Invalid
Upper (LeftChannel)
Invalid
MSB LSB
150114 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Lower (Left Channel) Upper (LeftChannel)Lower(RightChannel) Upper(RightChannel)
LSB
0 1
LeftChannel
MSB
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5
LeftChannelRightChannel
MSB
15 14 13
1098765432
DS553PP1 19

1.1.4.7 Miscellaneous Timings
Symbol Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
1
xclper
t
rstl
t
gph
t
gpl
1.
Value represents typical application with 16.934 MHz crystal
XTLCLK period 59.05 ns
RST_N Low Pulse Width 1000 ns
GPIO PW High 50 ns
GPIO PW Low 50 ns
XTLCLOCK
RESET-N
xccper
t
rst
t
CS7410
l
GPIO
tgph
Figure 15. Miscellaneous Timings
gp
t
l
20 DS553PP1
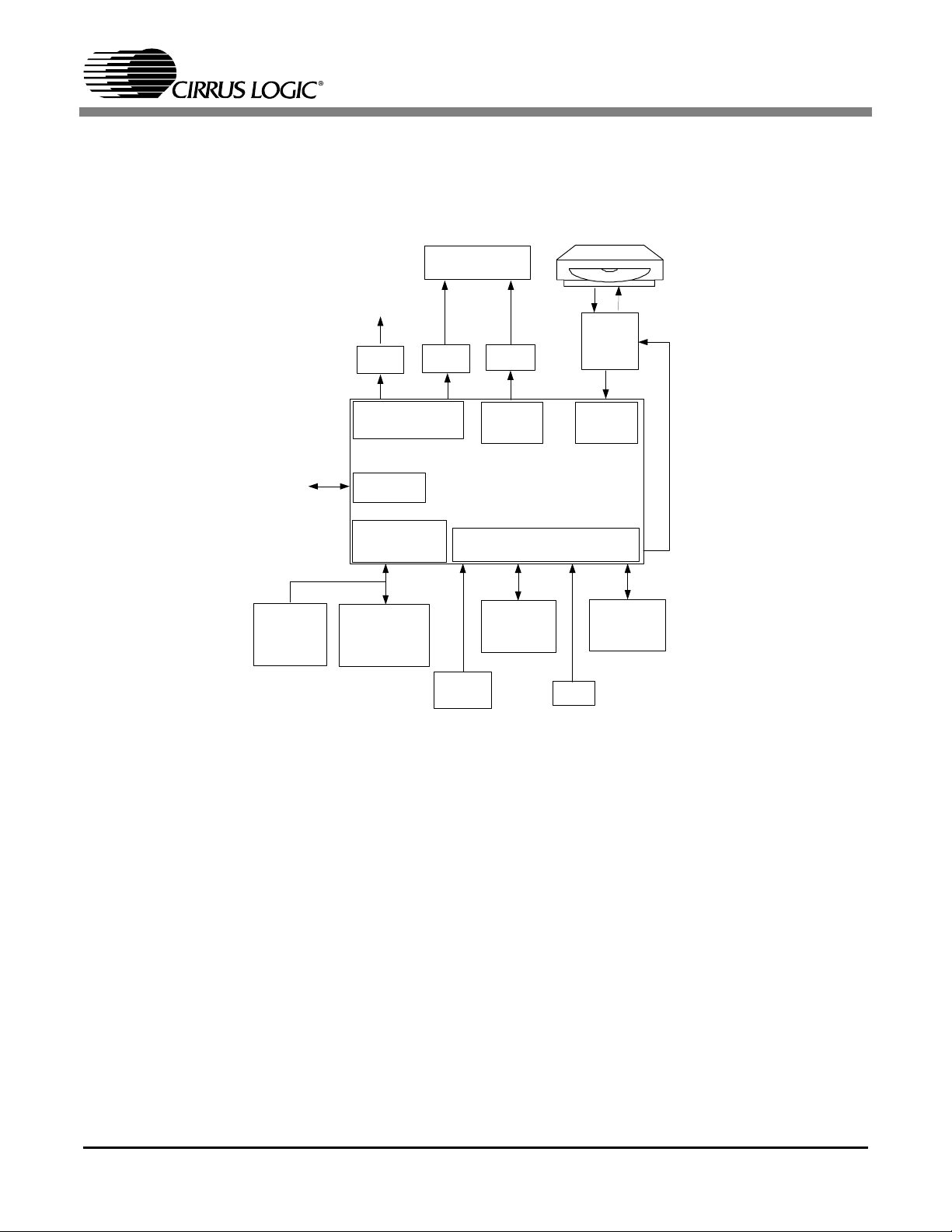
2. CS7410 SUMMARY
2.1 CS7410 Typical Application
Figure16 shows an example of a complete audio player using the CS7410.
Speakers/Headphones
(2 or 4 channel)
CS7410
ROM/FLASH
(optional)
0-2 MB
For new code
Debug
For shock protection
IEC-958
Optical
Driver
Digital Audio Out
Serial
Interface
Memory
Interface
DRAM
EDO/SDRAM
(optional)
0-8 MB
4 Chan.
PCM
DACs
Serial
EEPROM
(optional)
2 Chan.
OP-AMPs
DAC
Out
CS7410
GPIO
Keypad
Matrix
Figure 16. CS7410 Application
IR
receiver
Servo
DSP/Rd
Channel
CD
Interface
LCD
Controller/
Display
2.2 CS7410 Block Summaries
• 16-bit fixed point logic, with 36 bit accumulator.
2.2.1 RISC-32
• Single-cycle throughput, 2-cycle latency multi-
• Powerful 32-bit RISC processor
• Comprehensive development tool support
• Big or little endian data formats supported
• 32x32 (64-bit result) MAC, 2 cycles / multiply
with C support
ply accumulate, 16-bit simple integer logic
• 512 byte instruction cache, 8 Kbyte program
visible local memory
• Single cycle instructions, runs up to 90 MHz
• DSP MAC is pipelined, 1 cycle / multiply
• 4 Kbyte instruction cache, 2 Kbyte data cache
2.2.3 System Controls
• Single cycle instructions, runs up to 90 MHz
• Includes 32 hardware lockable semaphore reg-
2.2.2 DSP-16
• Powerful 16-bit DSP processor
DS553PP1 21
isters
• Two general-purpose registers for inter-proces-

CS7410
sor communication
• Three 32-bit timers for I/O and other uses, with
programmable interval rates
• “Getbits” module accelerates peripheral stream
parsing
• Both hardware and software interrupts on data
or debug
2.2.4 Memory System
• Large internal SRAM (80 Kbyte) and internal
program ROM (256 Kbyte)
• Supports both Synchronous and EDO DRAM
(256 KBytes to 8 MBytes) for ESP
• Supports one bank of FLASH and ROM (up to
2 MBytes) for nonvolatile storage
• 4-, 8-, or16-bit data bus for DRAM, 8-bit data
bus for ROM
2.2.5 CD Interface
• Integrated sigma-delta (∆Σ) stereo audio mod-
ulator
2.2.7 External Interface
• 2-wire serial slave port, used for debug
• 3- or 4-wire synchronous serial master/slave
port for external controller or slave peripheral
• Separate synchronous serial master port optimized for receiving CD sub-codes
• Up to 29 programmable bi-directional I/O
(GPIO) and up to 9 output only (GPO) pins
(some multiplexed with other peripherals)
• All pins defined as GPIOs can be used to receive edge or level detection interrupts.
• Pulse-width modulated (PWM) output pin can
be used to create simple ADC using low-cost
comparator (i.e., for battery voltage monitor)
2.2.8 System Functions
• Glueless interfaces to CD servo chip set, supporting all standard CD formats
• Includes pattern matching hardware to support
fast ESP recovery
2.2.6 Audio Interface
• Supports 4 channels PCM, I2S connectivity at
up to 24 bits
• Flexible audio clocking scheme using internal
PLL and dividers, or external pins
• Simultaneous IEC-958 output with programmable channel status and user data
• Internal oscillator uses external crystal, or receives clock (i.e. 16.9 MHz) from CD servo
• Internal PLL generates any system clock frequency, chip can run up to 90 MHz
• Includes clock divider and clock shutoff circuits for low power/sleep modes
• Advanced 0.18 micron CMOS technology,
runs off 1.8 V and 3.3 V
• All I/O pins are 3.3 V, with 5 V tolerance
• 100-pin MQFP package
• 100-pin LQFP package
22 DS553PP1

CS7410
3. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
3.1 RISC-32 Processor
The CS7410 includes a powerful, proprietary 32bit RISC processor backed by powerful software
development tools. The RISC-32 has a MAC engine which performs multiply/accumulate in 2 cycles with C support, effectively achieving single
cycle throughput.
There are other instructions that are designed to
help with performing audio decoding. The RISC
processor coordinates on-chip multi-threaded
tasks, as well as supervises system activities such
as keypad and front panel display control.
3.2 DSP-16 Processor
The CS7410 contains a proprietary digital signal
processor (DSP) called DSP-16, which is optimized for audio and sound applications. In the
CS7410, the DSP-16 assists with audio decoding
and provides added functions such as surround
sound and equalization. The DSP performs 16-bit
simple integer operations, and has a 16-bit fixed
point logic unit with a 32-bit accumulator.
There are 24 general-purpose registers, and eight
independent address generation registers, featuring: post-increment ALU, linear and circular buffer
operations, bit reverse ALU operations, and dual
operand read from memory. The multiply-accumulator has single-cycle throughput, with two cycle
latency. The DSP is optimized for bit packing and
unpacking operations. The interface to main memory is designed for bursting flexible block sizes and
skip counts.
3.3 Memory Control
The Memory Controller performs the arbitration
functions for all the other modules in the CS7410,
allowing access to internal ROM and SRAM, and
to external ROM and DRAM. The Memory Controller services and arbitrates a number of clients
and stores their code and/or data within the local
memory. This arbitration and scheduling guarantees the allocation of sufficient bandwidth to the
various clients. An optimal application will use
only internal ROM and SRAM for code and data
storage, which results in the best timing and lowest
power consumption.
External DRAM may be used for runtime code
storage or for ESP RAM. In both of these applications, the data throughput requirement is low, and
the Memory Controller acts as a DMA engine to
move data between external and internal memory
with minimal power consumption. The internal
ROM contains most of the code required for audio
decoding and system functions.
Additional code can be stored in external ROM
(managed by the Memory Controller) or a small serial ROM (controlled by GPIOs). The CS7410 also
supports code storage in external FLASH with insystem write capability for customer code updates.
Future firmware releases will provide a complete
solution requiring no external ROM.
3.4 CD Interface
The CD Interface receives compressed or uncompressed (direct audio) data from the CD servo/read
channel chip, performs descrambling and CRC
checking, and writes the data to an internal FIFO.
Additional C3 error decoding is done in software.
The CD interface is compatible with all commonly
used CD formats.
The CS7410 contains a hardware pattern matching
circuit to scan the incoming CD data for a pattern
of up to 64 bytes. This circuit is used to assist the
Electronic Shock Protection function by quickly locating and matching the incoming data with data
stored in the ESP RAM.
3.5 System Control Functions
The system control functions are used to coordinate
the activities of the multiple processors, and to provide the supporting system operations. Two 32-bit
communication registers are available for inter-
DS553PP1 23

CS7410
processor communication, and 32 semaphore registers are used for resource locking. Three timers
are available for general-purpose functions, as well
as more specialized functions, such as watchdog
timers and performance monitoring.
The large number of general purpose I/Os offers
flexibility in system configurations. Three separate
synchronous serial interfaces, conforming to industry-standard protocols, are available for a variety of
system interface functions. Four general purpose
software interrupts and twelve hardware interrupts
help reduce peripheral overhead and improve UI
responsiveness. Power-down control of the internal
clocks is also possible. An internal PLL is used to
generate the internal system and memory clocks as
well as audio clocks for all supported sample rates.
3.6 Audio Output
Decoded audio data is written into an output FIFO
in 16-, 18-, 20- or 24-bit PCM format. A flexible
audio output stage can simultaneously output 4
channels of PCM data to external audio DACs, plus
an independent IEC-958 encoded output. The IEC958 output has fully programmable channel status
(commercial), and provides a flexible solution to
support all IEC-958 modes for user data. The audio
output circuit contains an auto-mute detect circuit,
which can generate internal or external mute controls
PCM FIFO data up to 18 bits can also be output by
the on-board sigma-delta stereo modulator. The
sigma-delta modulator yields a typical 85 dB signal-to-noise ratio with few external components required, resulting in a low-cost, low parts count
analog front end. The modulator has a 32x upsampling filter, followed by a 32x interpolator, and finally a 5th-order Sigma-Delta modulator. The
auto-mute circuit also works on the modulator output, and there are separate programmable attenuators for the modulator output and both PCM
outputs.
24 DS553PP1

4. PIN DESCRIPTION
4.1 Pin Identification
Figure17 shows the CS7410 pins grouped by function, also showing the number of pins in each group.
CS7410
Figure 17. CS7410 Pin Identification
Table6 lists the conventions used to identify the pin type and direction.pin assignments.
I: Input
S: Schmitt trigger on input
U: Pull up resistor
O: Output
O4: Output – 4mA drive
T4: High Z output – 4mA drive
B: Bi-direction
B4: Bi-direction – 4mA drive
D4: Bi-direction with 4mA open drain output
Table 6. Pin Type and Direction Legend
DS553PP1 25

CS7410
Pwr: +2.5V or +3.3V power supply voltage
Gnd: Power supply ground
Name_N: Low active
Name_L: Low active
Table 6. Pin Type and Direction Legend (Continued)
Table7 lists the pin number, pin name, and pin type for the 100-pin CS7410 package. For signal pins, the
pin direction after reset is shown. The primary function and pin direction is shown for all signal pins. For
some signal pins, a secondary function and direction are also shown.
Pin Name Type Reset Function #1 Dir Function #2 Dir Note
1 PLL_GND Gnd PLL Ground
2 PLL_1V8 Pwr PLL Power
3 M_D_15 B4 I DRAM Data[15] B NVMem
Address[19]
4 M_D_14 B4 I DRAM Data[14] B NVMem
Address[18]
5 M_D_13 B4 I DRAM Data[13] B NVMem
Address[17]
6 M_D_12 B4 I DRAM Data[12] B NVMem
Address[16]
7 M_D_11 B4 I DRAM Data[11] B NVMem
Address[15]
8 M_D_10 B4 I DRAM Data[10] B NVMem
Address[14]
9 M_D_9 B4 I DRAM Data[9] B NVMem
Address[13]
10 M_D_8 B4 I DRAM Data[8] B NVMem
Address[12]
11 M_D_7 B4 I DRAM Data[7] B NVMem Data[7] B
12 CORE_1V8 Pwr Core Power
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
13 M_D_6 B4 I DRAM Data[6] B NVMem Data[6] B
14 CORE_GND Gnd Core Ground
15 M_D_5 B4 I DRAM Data[5] B NVMem Data[5] B
16 IO_3V3 Pwr I/O Power
17 XTLCLK_O O O Oscillator Out O
Table 7. Pin Assignments
26 DS553PP1

CS7410
Pin Name Type Reset Function #1 Dir Function #2 Dir Note
18 XTLCLK_I I I Oscillator In I
19 IO_GND Gnd I/O Ground
20 M_D_4 B4 I DRAM Data[4] B NVMem Data[4] B
21 M_D_3 B4 I DRAM Data[3] B NVMem Data[3] B
22 M_D_2 B4 I DRAM Data[2] B NVMem Data[2] B
23 M_D_1 B4 I DRAM Data[1] B NVMem Data[1] B
24 M_D_0 B4 I DRAM Data[0] B NVMem Data[0] B
25 M_A_11 B4 I DRAM Address[11] O NVMem
Address[11]
26 M_A_10 B4 I DRAM Address[10] O NVMem
Address[10]
27 M_A_9 B4 I DRAM Address[19] O NVMem
Address[9]
28 M_A_8 B4 I DRAM Address[8] O NVMem
Address[8]
29 M_A_7 B4 I DRAM Address[7] O NVMem
Address[7]
30 M_A_6 B4 I DRAM Address[6] O NVMem
Address[6]
31 M_A_5 B4 I DRAM Address[5] O NVMem
Address[5]
32 M_A_4 B4 I DRAM Address[4] O NVMem
Address[4]
33 M_A_3 B4 I DRAM Address[3] O NVMem
Address[3]
34 M_A_2 T4 I DRAM Address[2] O NVMem
Address[2]
O 1
O 1
O 1
O 1
O 1, 3
O 1, 3
O 1, 3
O 1, 3
O 1, 3
O 3
35 M_A_1 T4 I DRAM Address[1] O NVMem
Address[1]
36 M_A_0 T4 I DRAM Address[0] O NVMem
Address[0]
37 DR_RAS_L T4 I DRAM RAS_L O
38 CORE_1V8 Pwr Core Power
39 DR_CAS_L T4 I DRAM CAS_L O
Table 7. Pin Assignments (Continued)
DS553PP1 27
O 3
O 3

CS7410
Pin Name Type Reset Function #1 Dir Function #2 Dir Note
40 CORE_GND Gnd Core Ground
41 M_WE_L T4 I DRAM WE_L O NVM_WE_L
42 IO_GND Gnd I/O Ground
43 DR_CKO T4 I SDRAM CKO O
44 IO_3V3 Pwr I/O Power
45 DR_CKE T4 I SDRAM CKE O
46 DR_BS_L B4 I SDRAM BS_L O NVMem
Address[20]
47 M_AP_OE B4 I SDRAM AP, EDO DRAM
OE_L
48 NVM_CE_L T4 I NVM_CE_L O
49 KP_IN_0 B4U I GPIO[19] B
50 KP_IN_1 B4U I GPIO[20] B
51 KP_IN_2 B4U I GPIO[21] B
52 KP_IN_3 B4U I GPIO[22] B
53 KP_IN_4 B4U I GPIO[23] B
54 KP_OUT_0 B4 I GPIO[24] B
55 KP_OUT_1 B4 I GPIO[25] B
56 KP_OUT_2 B4 I GPIO[26] B
57 KP_OUT_3 B4 I GPIO[27] B
58 KP_OUT_4 B4 I GPIO[28] B
59 IR_IN B4S I GPIO[4] B
O NVM_ OE_L 1
1
60 SER1_CLK D4S I Debug Port Clock B
61 SER1_DAT D4S I Debug Port Data B
62 SER4_CLK B4S I GPIO[5] B
63 SER4_DAT B4S I GPIO[6] B
64 IO_GND Gnd I/O Ground
65 SER2_CLK B4 I Serial2 Clock B GPIO[7] B
66 SER2_DI B4 I Serial2 Data In B GPIO[8] B
67 SER2_DO B4 I Serial2 Data Out B GPIO[9] B
Table 7. Pin Assignments (Continued)
28 DS553PP1

CS7410
Pin Name Type Reset Function #1 Dir Function #2 Dir Note
68 SER2_CS B4 I Serial2 Chip Select B GPIO[10] B
69 SER3_CLK B4 I Serial3 Clock O GPIO[11] B
70 SER3_DO B4 I Serial3 Data Out O GPIO[12] B
71 CORE_1V8 Pwr Core Power
72 SER3_DI B4 I Serial3 Data In I GPIO[13] B
73 CORE_GND Gnd Core Ground
74 SER3_SS0 B4 I Serial3 Chip Select0 O GPIO[14] B
75 IO_3V3 Pwr I/O Power
76 SER3_SS1 B4 I Serial3 Chip Select1 O GPIO[15] B
77 SERVOCK B4 I Servo Clock In I GPIO[17] B
78 PCM_XCK B4 I PCM_XCK B
79 PCM_MUTE B4 I PCM_MUTE O GPO[4] O 1
80 CD_C2P0 B4 I CD_C2P0 I GPIO[16] B
81 CD_BCLK IS I CD_BCLK I
82 CD_LRCK I I CD_LRCK I
83 CD_DATA I I CD_DATA I
84 DAC_LP O4 O ∆Σ DAC Left Positive Out O GPO[5] O
85 DAC_LN O4 O ∆Σ DAC Left Negative Out O GPO[6] O
86 IO_GND Gnd I/O Ground
87 DAC_RP O4 O ∆Σ DAC Right Positive Out O GPO[7] O
88 DAC_3V3 Pwr ∆Σ DAC I/O Power
89 DAC_RP O4 O ∆Σ DAC Right Negative Out O GPO[8] O
90 RST_N IS I Reset_L I
91 TEST I I Manufacturing Test I
92 PCM_BCK B4 O PCM_BCK O GPO[0] O 1
93 PCM_LRCK B4 O PCM_LRCK O GPO[1] O 1
94 PCM_DO_0 B4 O PCM_Dout[0] O GPO[2] O 2
95 PCM_DO_1 B4 O PCM_Dout[1] O GPO[3] O 1
96 IEC958_O B4 I IEC-958 Out O GPIO[18] B
97 GPIO_0 B4 I GPIO[0] B
Table 7. Pin Assignments (Continued)
DS553PP1 29

CS7410
Pin Name Type Reset Function #1 Dir Function #2 Dir Note
98 GPIO_1 B4 I GPIO[1] B PWM_Out O
99 GPIO_2 B4 I GPIO[2] B
100 GPIO_3 B4 I GPIO[3] B
Table 7. Pin Assignments (Continued)
1. Optional pull up or pull down resistor may be connected to configure internal ROM program
2. Required external resistor required to select processor boot from internal ROM (pull down) or external
ROM (pull up).
3. Drives for a short time after reset, then reverts to high impedance
4.2 Miscellaneous Pins
These pins described in Table8 are used for used for basic functions such as clocking, reset and infrared
receiver interface. The main system clock can be derived from an external crystal connected between the
XTLCLK_I and XTLCLK_O pins, or can be received from the CD servo chip via the XTLCLK_I pin. The
CS7410 can accommodate a variety of input frequencies, such as 44.1 KHz x 256, x 384, or x 512.
Pin Signal Name Type Description
17 XTLCLK_O O Crystal output
18 XTLCLK_I I Crystal input, or oscillator input
90 RST_N I Asynchronous reset input, active low
91 TEST I Manufacturing test, tie to ground
4.3 Serial Interface Pins
The CS7410 Serial Interface pins are described in Table9. CS7410 has three dedicated serial ports, each
with different protocols. The 2-wire serial port (SER1) supports industry standard protocols. This port is typically used for debug, with the CS7410 as the slave. The slave chip select address is programmable, and
defaults to a 7-bit value of 0x1B. A second serial controller (SER2) supports industry standard 3-wire and
4-wire protocols. In master mode, this interface can control a front panel or a small non-volatile memory. In
slave mode, it can operate under control of an external processor, for example, in a combination unit. The
third serial port (SER3) is a 5-wire master device optimized for reading CD subcodes from the servo chip,
and can also be used a general-purpose serial port.
Pin Signal Name Type Description
60 SER1_CLK B Debug port serial clock
61 SER1_DAT B Debug port serial data
65 SER2_CLK B Clock for 4-wire serial port (output for master mode, input
Table 8. Miscellaneous Interface Pins
for slave mode)
66 SER2_DI I Input data for 4-wire serial port
67 SER2_DO B Output data for 4-wire serial port – may function as bidi-
rectional data in 3-wire mode.
Table 9. Serial Interface Pins
30 DS553PP1

68 SER2_CS B Chip select for 4-wire serial port (output if master, input if
69 SER3_CLK O Clock output
70 SER3_DO O Data output – up to 32 bits per transfer.
72 SER3_DI I Data input – up to 96 bits per transfer.
74 SER3_SS0 O Slave select for first peripheral (programmable polarity)
76 SER3_SS1 O Slave select for second peripheral (programmable polar-
Table 9. Serial Interface Pins (Continued)
4.4 SDRAM / DRAM Interface
These pins are used to interface the CS7410 with external synchronous or EDO DRAMs. Data widths of 4
to 16 bits are supported. The CS7410 supports word or block transfers (partial word transfers are not required). Table10 gives instructions on how to interface to any particular configuration of SDRAM. Table11
gives pin definitions for interfacing to EDO DRAM.
Pin Signal Name Type Description
CS7410
slave mode). Can also be used as bidirectional ready line.
ity)
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10, 11, 13, 15, 20,
21, 22, 23, 24
25, 26, 27, 28,
29, 30, 31, 32,
33, 34, 35, 36
37 DR_RAS_L O Memory Row Address Strobe
39 DR_CAS_L O Memory Column Address Strobe
41 M_WE_L O Memory Write Enable
43 DR_CKO O SDRAM Clock
45 DR_CKE O SDRAM Clock Enable
46 DR_BS_L O Bank Selection. Always connect to RAM BS or BS0 pin.
47 M_AP_OE O Memory Auto Pre-charge. Always connect to RAM AP pin.
Pin Signal Name Type Description
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 13,
15, 20, 21, 22,
23, 24
DRAM
Data[15..0]
DRAM
Address[11..0]
DRAM
Data[15..0]
B Memory Data Bus.
O Memory Address Bus. Connect in order starting with
DR_Addr[0] to all RAM address pins not already connected
to DR_BS_L or DR_AP.
Table 10. SDRAM Interface
B Memory Data Bus.
Table 11. EDO DRAM Interface
DS553PP1 31

Pin Signal Name Type Description
CS7410
25, 26, 27, 28,
29, 30, 31, 32,
33, 34, 35, 36
37 DR_RAS_L O Memory Row Address Strobe
39 DR_CAS_L O Memory Column Address Strobe
41 M_WE_L O Memory Write Enable
47 M_AP_OE O Memory Output Enable
DRAM
Address[11..0]
Table 11. EDO DRAM Interface (Continued)
O Memory Address Bus.
4.5 ROM/NVRAM Interface
The ROM/NVRAM Interface pins are described in Table12. This interface connects to the non-volatile
memory that contains the firmware. The memory could be ROM, NVRAM (FLASH), EEPROM, or any combination of these memory types. This interface can also connect to SRAM that would emulate a ROM on a
development system. The bus width is always 8 bits. Most of these pins are shared with the DRAM interface,
which operates simultaneously with the ROM/NVRAM interface. A number of pins are defined to accept configuration input at power-up (see Table7), allowing different branches to be taken in the firmware. A config-
uration resistor is required on pin PCM_DO_0 to select whether the processor will boot from internal or
external ROM.
Pin Signal Name Type Description
11, 13, 15, 20,
21, 22, 23, 24
25, 26, 27, 28,
29, 30, 31, 32,
33, 34, 35, 36
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10NVM_Addr[19..12] O Memory Address Bus[19..12] (shared with bits [15..8] of
46 NVM_Addr[20] O Memory Address Bus[20] (DRAM BS_L pin).
41 NVM_WE_L O NVRAM Write Enable (shared with DRAM WE_L pin)
47 NVM_OE_L O NVRAM Write Enable (shared with DRAM WE_L pin)
48 NVM_CE_L O ROM/NVRAM Chip Enable.
NVMem Data[7..0] B Memory Data Bus (shared with bits [7:0] of DRAM data
bus).
NVM_Addr[11..0] O Memory Address Bus[11..0] (shared with DRAM address
bus)
DRAM data bus).
Table 12. ROM/NVRAM Interface
32 DS553PP1

CS7410
4.6 Digital Audio Output Interface
The Digital Audio Output Interface pins are described in Table13. This is the audio PCM interface that connects to an audio PCM DAC. The sample rate and the size of the samples are programmable to accommodate any commercially available DAC. The CS7410 has two data output pins, for up to 4 channels of PCM
output, and a separate output pin to simultaneously output IEC-958 encoded data (either compressed or
uncompressed).
Pin Signal Name Type Description
78 PCM_XCK B Audio 256x/384x/512x Clock input or output to Serial DAC.
When output, it’s generated from CS7410 internal PLL.
77 SERVOCK I Optional source of Audio 256x/384x/512x Audio Clock. May
be used for CD direct audio to match input and output
clocks.
79 PCM_MUTE O Audio Mute control to external DAC. Polarity is programma-
ble and is three-stated at power up.
92 PCM_BCK O Audio Bit Clock output to serial DAC. Polarity is programma-
ble.
93 PCM_LRCK O Audio Out Left/Right Clock to serial DAC.
94 PCM_DO_0 O Audio Serial PCM Data Out[0].
95 PCM_DO_1 O Audio Serial PCM Data Out[1].
96 IEC958_O O IEC-958 Output
Table 13. Audio Output Interface
4.7 ∆Σ Modulator Interface
The ∆Σ Interface pins are described in Table14. The CS7410 contains a stereo Delta-Sigma (∆Σ) modulator, which outputs two differential digital signals on four pins. These outputs are design to drive an external
op-amp based integrator circuit (contact Cirrus Logic Applications Engineering for details).
Pin Signal Name Type Description
84 DAC_LP O ∆Σ left channel, positive output
85 DAC_LN O ∆Σ left channel, negative output
87 DAC_RP O ∆Σ right channel, positive output
89 DAC_RN O ∆Σ right channel, positive output
Table 14. ∆Σ Output Interface
DS553PP1 33

4.8 CD Interface
The CD Interface pins are described in Table15. This interface is used to read serial CD data from a CD
servo/read channel chip. The interface supports all standard formats, including 16 MHz, 24 MHz and 32
MHz clocks per container. Control of the CD servo chip is done by the RISC processor using GPIOs, and
CD subcode data is read using the dedicated serial interface (SER3).
Pin Signal Name Type Description
81 CD_BCLK I CD clock input – polarity is programmable
82 CD_LRCK I CD left-right clock input
83 CD_DATA I CD serial data input
80 CD_C2P0 I CD error signaling input
CS7410
Table 15. CD Interface
34 DS553PP1

4.9 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
The CS7410 provides a number of General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) pins, each with individual output
three-state controls, and a number of General Purpose Output (GPO) pins. Table16 shows the 17 dedicated GPIO pins. A naming scheme for these pins was chosen to encourage system designers to adhere to
standardized pin usage. Table17 shows the GPIO and GPO pins that can be redefined from other functions.
For redefined pins, mode control register bits select the normal function or GPIO/GPO function for the pins.
Table17 also indicates which mode bit controls each pin.
Pin Signal Name Type Description
100, 99, 98, 97 GPIO[3:0] B 4 General purpose I/O on dedicated pins
53, 52, 51, 50, 49 KP_IN[4:0] B 5 General purpose I/O on dedicated pins
58, 57, 56, 55, 54 KP_OUT[4:0] B 5 General purpose I/O on dedicated pins
59 IR_IN B General purpose I/O on dedicated pin
62 SER4_CLK B General purpose I/O on dedicated pin
63 SER4_DAT B General purpose I/O on dedicated pin
Table 16. Dedicated General Purpose I/O Pins
CS7410
Pin Signal Name Type Description
65 SER2_CLK B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 2
67 SER2_DO B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 2
68 SER2_CS B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 2
66 SER2_DI B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 3
69 SER3_CLK B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 4
70 SER3_DO B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 4
72 SER3_DI B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 4
74 SER3_SS0 B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 4
76 SER3_SS1 B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 5
80 CD_C2P0 B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 6
77 SERVOCK B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 7
92 PCM_BCK O GPO controlled by Mode bit 8
93 PCM_LRCK O GPO controlled by Mode bit 9
94 PCM_DO_0 O GPO controlled by Mode bit 10
95 PCM_DO_1 O GPO controlled by Mode bit 11
79 PCM_MUTE O GPO controlled by Mode bit 12
84 DAC_LP O GPO controlled by Mode bit 13
Table 17. Redefined General Purpose Pins
DS553PP1 35

Pin Signal Name Type Description
85 DAC_LN O GPO controlled by Mode bit 13
87 DAC_RP O GPO controlled by Mode bit 13
89 DAC_RN O GPO controlled by Mode bit 13
96 IEC958_O B GPIO controlled by Mode bit 14
Table 17. Redefined General Purpose Pins (Continued)
4.10 Power and Ground
Table18 describes the power and ground pins. The CS7410 requires 3 different types of power supplies for
the PLLs, internal logic, and IO pins. The PLLs and internal logic use 1.8 V supply voltage. The IO pins use
3.3 V supply voltage. An optional separate supply can be used to provide clean 3.3 V to the Sigma-Delta
DACs digital output pads. It is recommended that you use good layout techniques to provide isolation between the supply types on the board. Contact Cirrus Logic applications engineering for layout guidelines.
Pin Signal Name Type Description
1 PLL_GND Ground for internal PLLs
CS7410
2 PLL_1V8 1.8V for internal PLLs
14, 40, 73 CORE_GND Ground for internal core logic
12, 38, 71 CORE_1V8 1.8V for internal core logic
19, 42, 64, 86 IO_GND Ground for Digital I/Os
16, 44, 75 IO_3V3 3.3V for Digital I/Os
88 DAC_3V3 3.3V for Sigma Delta DAC Digital I/Os
Table 18. Power and Ground
36 DS553PP1

CS7410
DS553PP1 37

5. 100-PIN MQFP PACKAGE SPECIFICATIONS (20X14X2.85mm)
0.310
±
0.050
A
±
DETAIL A
0~8
°
20.000
±
0.100
23.200
±
0.250
315081
305180
14.000±0.100
CS7410
17.200±0.250
100
1
Note: Measurement Units = mm
1.35±0.05
0.150±0.008
2.85
0.200
(MIN)
1.600±0.150
3.300
±0.127
(MAX)
0.800±0.150
Figure 18. 100-Pin MQFP Package (20x14x2.85mm)
38 DS553PP1

6. 100-PIN LQFP PACKAGE SPECIFICATIONS (14X14X1.4mm)
CS7410
Figure 19. 100-Pin LQFP Package (14X14X1.4mm)
DS553PP1 39
 Loading...
Loading...