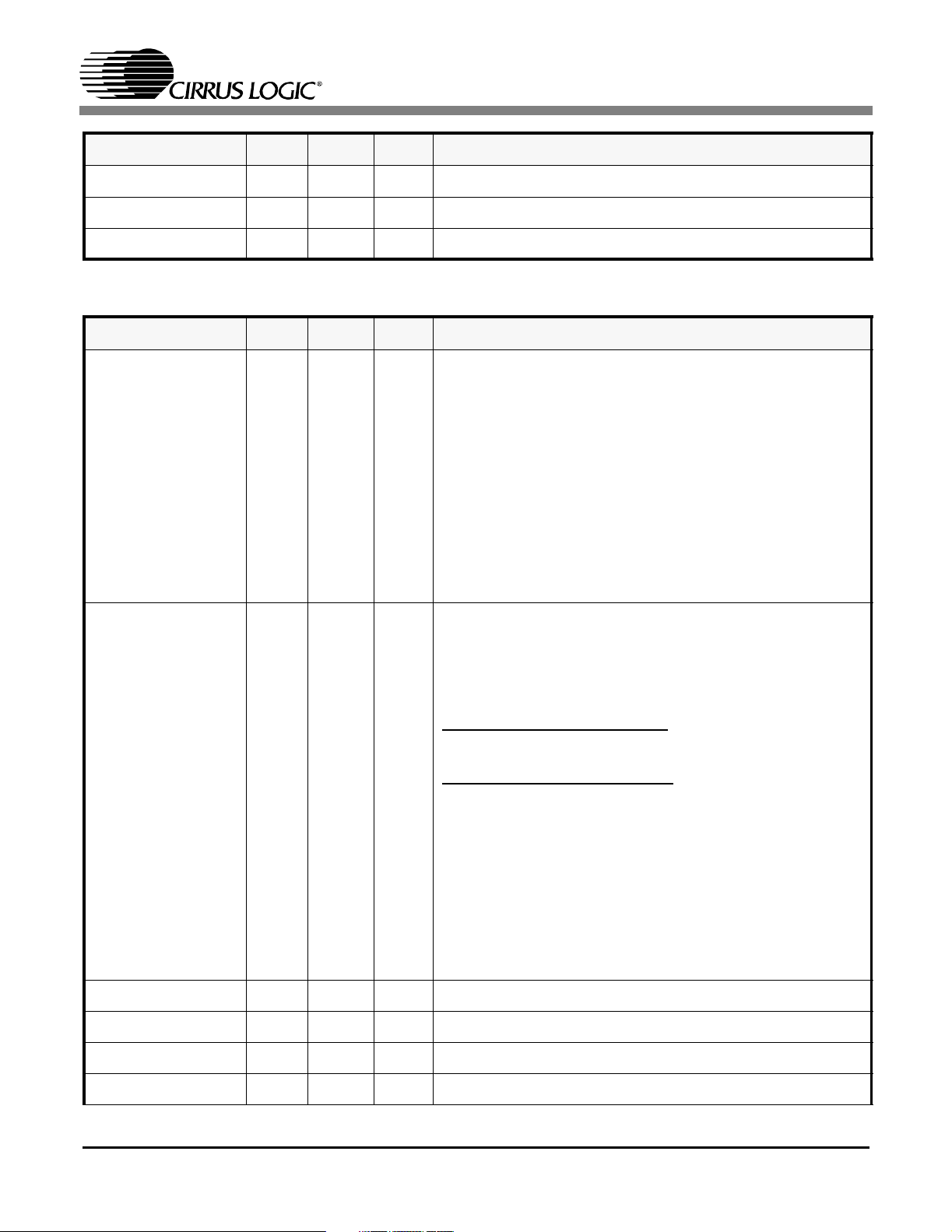
Octal T1/E1/J1 Line Interface Unit
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
CS61884
Features
Industry Standard Footprint
Octal E1/T1/J1 Short-haul Line Interface Unit
Low Power
No External Component Changes for
100 Ω/120 Ω/75 Ω Operation
Pulse Shapes can be customized by the user
Internal AMI, B8ZS, or HDB3 Encoding/Decoding
LOS Detection per T1.231, ITU G.775, ETSI 300-233
G.772 Non-Intrusive Monitoring
G.703 BITS Clock Recovery
Crystal-less Jitter Attenuation
Serial/Parallel Microprocessor Control Interfaces
Transmitter Short Circuit Current Limiter (<50mA)
TX Drivers with Fast High-Z and Power Down
JTAG Boundary Scan compliant to IEEE 1149.1
144-Pin LQFP or 160-Pin BGA Package
ORDERING INFORMATION
CS61884-IQ 144-pin LQFP
CS61884-IB 160-pin FBGA
Description
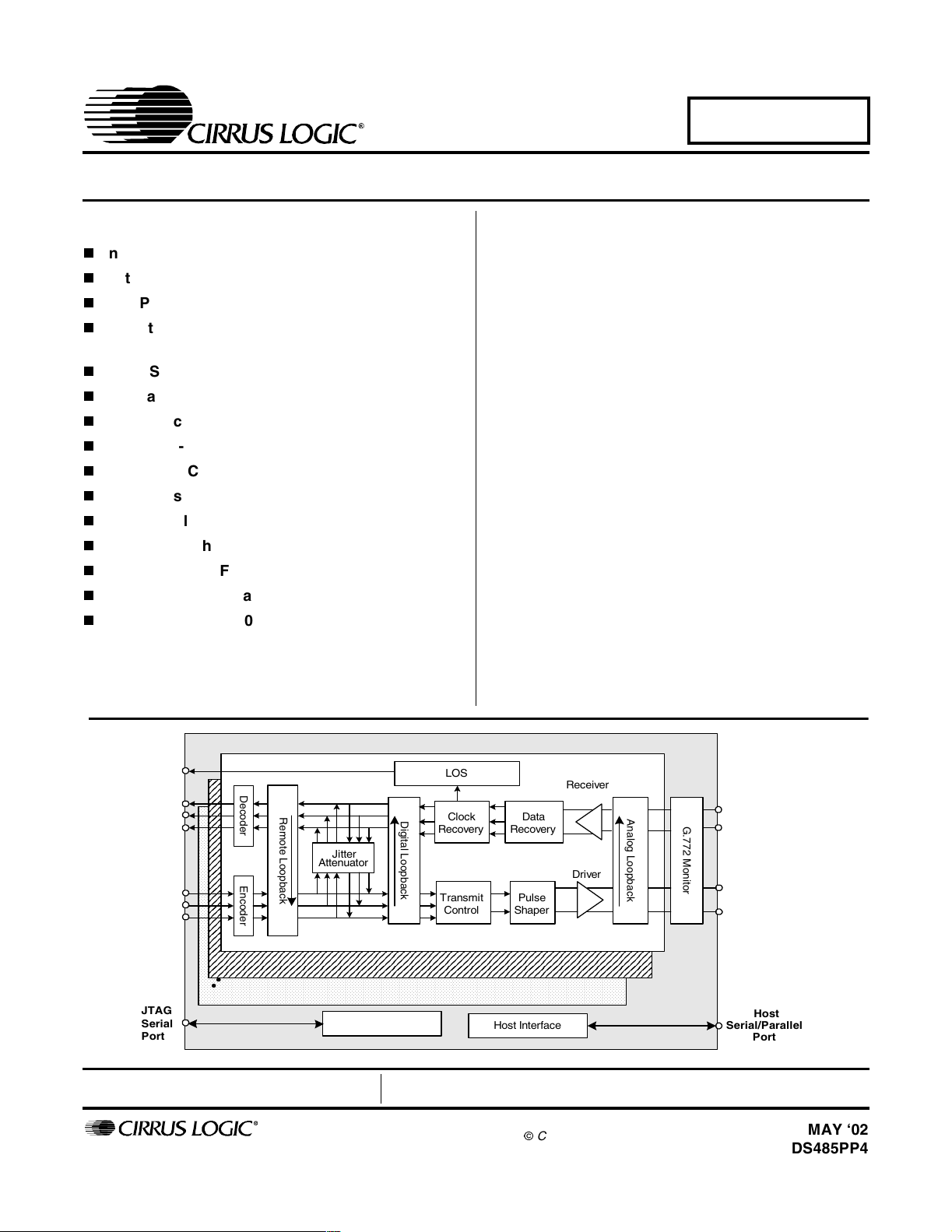
The CS61884 is a full-featured Octal E1/T1/J1 shorthaul LIU that supports both 1.544 Mbps or 2.048 Mbps
data transmission. Each channel provides crystal-less
jitter attenuation that complies with the most stringent
standards. Each channel also provides internal
AMI/B8ZS/HDB3 encoding/decoding. To support enhanced system diagnostics, channel zero can be
configured for G.772 non-intrusive monitoring of any of
the other 7 channels’ receive or transmit paths.
The CS61884 makes use of ultra low power matched impedance transmitters and receivers to reduce power
beyond that achieved by traditional driver designs. By
achieving a more precise line match, this technique also
provides superior return loss characteristics. Additionally, the internal line matching circuitry reduces the
external component count. All transmitters have controls
for independent power down and High-Z.
Each receiver provides reliable data recovery with over
12 dB of cable attenuation. The receiver also incorporates LOS detection compliant to the most recent
specifications.
Note: Click on any text in blue to go to cross-references.
LOS
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Decoder
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
RCLK
RPOS
RNEG
TCLK
TPOS
TNEG
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
1
00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
0
Encoder
Remote Loopback
Jitter
Attenuator
7
JTAG
Serial
Port
JTAG Interface
Preliminary Product Information
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7581
http://www.cirrus.com
LOS
Digital Loopback
Clock
Recovery
Recovery
Data
Receiver
Analog Loopback
G.772 Monitor
RTIP
RRING
Driver
Transmit
Control
Pulse
Shaper
Host Interface
This document contains information for a new product.
Cirrus Logic reserves the right to modify this product without notice.
CopyrightCirrus Logic, Inc. 2002
(All Rights Reserved)
TTIP
TRING
Host
Serial/Parallel
Port
DS485PP4
MAY ‘02
1

CS61884
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PINOUT - LQFP ........................................................................................................................................ 7
2. PINOUT - FBGA ........................................................................................................................................ 8
3. PIN DESCRIPTIONS ................................................................................................................................. 9
3.1 Power Supplies .................................................................................................................................. 9
3.2 Control .............................................................................................................................................. 10
3.3 Address Inputs/Loopbacks ............................................................................................................... 14
3.4 Cable Select ..................................................................................................................................... 15
3.5 Status ............................................................................................................................................... 15
3.6 Digital Rx/Tx Data I/O ....................................................................................................................... 16
3.7 Analog RX/TX Data I/O .................................................................................................................... 19
3.8 JTAG Test Interface ......................................................................................................................... 21
3.9 Miscellaneous ................................................................................................................................... 21
4. OPERATION ........................................................................................................................................... 22
5. POWER-UP ............................................................................................................................................. 22
6. MASTER CLOCK .................................................................................................................................... 22
7. G.772 MONITORING ............................................................................................................................... 22
8. BUILDING INTEGRATED TIMING SYSTEMS (BITS) CLOCK MODE .................................................. 23
9. TRANSMITTER ....................................................................................................................................... 24
9.1 Bipolar Mode .................................................................................................................................... 25
9.2 Unipolar Mode .................................................................................................................................. 25
9.3 RZ Mode ........................................................................................................................................... 25
9.4 Transmitter Powerdown / High-Z ...................................................................................................... 25
9.5 Transmit All Ones (TAOS) ................................................................................................................ 25
9.6 Automatic TAOS ............................................................................................................................... 26
9.7 Driver Failure Monitor ....................................................................................................................... 26
9.8 Driver Short Circuit Protection .......................................................................................................... 26
10. RECEIVER ............................................................................................................................................ 26
10.1 Bipolar Output Mode ...................................................................................................................... 26
10.2 Unipolar Output Mode .................................................................................................................... 26
10.3 RZ Output Mode ............................................................................................................................. 27
10.4 Receiver Powerdown/High-Z .......................................................................................................... 27
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/corporate/contacts/sales.cfm
IMPORTANT NOTICE
"Preliminary" product inf ormation describes products that are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet available. "Advance" product inf ormation describes products that are i n development and subject to development changes. Cirrus Logic, I nc. and its subsidiaries ("Cirrus") believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided "AS IS" without warranty
of any kind (express or implied). Customers are advised to obtain the latest version of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that information being
relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and l imitation of liability. No responsibil ity is assumed by Ci rrus f or the use of this information, including use of this
information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for i nfringement of patents or other rights of third parties. This document is the property of Cir rus
and by furnishi ng this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask work rights, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or
other intellectual property rights. Cirr us owns the copyrights of the i nformation contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only
for use within your or ganization with respect to Cirrus integrated circui ts or ot her parts of Cir rus. This consent does not ext end to other copying such as copying
for general distribution, advertising or pr omotional purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
An export permit needs to be obtained from the competent authorities of the Japanese Government if any of the products or technologies described in thismaterial and controll ed under the "Foreign Exchange and Forei gn Trade Law" i s to be exported or taken out of Japan. An export l icense and/or quota needs to be
obtained from the competent authorities of the Chinese Government if any of the products or technologies describe d in this material is subject to the PRC Foreign
Trade Law and i s to be exported or taken out of the PRC.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE
PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE ("CRITICAL APPLICATIONS"). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS
IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER'S RISK.
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, and the Ci rrus Logi c logo designs are trademarks of Cirrus Logic, Inc. All other brand and product names in thi s document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners.
2 DS485PP4

CS61884
10.5 Loss-of-Signal (LOS) .......................................................................................................................27
10.6 Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) ..........................................................................................................28
11. JITTER ATTENUATOR .........................................................................................................................28
12. OPERATIONAL SUMMARY ..................................................................................................................29
12.1 Loopbacks .......................................................................................................................................29
12.2 Analog Loopback ............................................................................................................................29
12.3 Digital Loopback ..............................................................................................................................30
12.4 Remote Loopback ...........................................................................................................................30
13. HOST MODE ..........................................................................................................................................32
13.1 SOFTWARE RESET ....................................................................................................................... 32
13.2 Serial Port Operation .......................................................................................................................32
13.3 Parallel Port Operation ....................................................................................................................33
13.4 Register Set ....................................................................................................................................34
14. REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS .................................................................................................................35
14.1 Revision/IDcode Register (00h) ......................................................................................................35
14.2 Analog Loopback Register (01h) .....................................................................................................35
14.3 Remote Loopback Register (02h) ...................................................................................................35
14.4 TAOS Enable Register (03h) ..........................................................................................................35
14.5 LOS Status Register (04h) ..............................................................................................................35
14.6 DFM Status Register (05h) .............................................................................................................35
14.7 LOS Interrupt Enable Register (06h) ...............................................................................................36
14.8 DFM Interrupt Enable Register (07h) ..............................................................................................36
14.9 LOS Interrupt Status Register (08h) ................................................................................................36
14.10 DFM Interrupt Status Register (09h) .............................................................................................36
14.11 Software Reset Register (0Ah) .....................................................................................................36
14.12 Performance Monitor Register (0Bh) ............................................................................................36
14.13 Digital Loopback Reset Register (0Ch) .........................................................................................37
14.14 LOS/AIS Mode Enable Register (0Dh) ..........................................................................................37
14.15 Automatic TAOS Register (0Eh) ...................................................................................................37
14.16 Global Control Register (0Fh) .......................................................................................................38
14.17 Line Length Channel ID Register (10h) .........................................................................................38
14.18 Line Length Data Register (11h) ...................................................................................................39
14.19 Output Disable Register (12h) .......................................................................................................39
14.20 AIS Status Register (13h) ............................................................................................................. 39
14.21 AIS Interrupt Enable Register (14h) ..............................................................................................39
14.22 AIS Interrupt Status Register (15h) ...............................................................................................40
14.23 AWG Broadcast Register (16h) .....................................................................................................40
14.24 AWG Phase Address Register (17h) ............................................................................................40
14.25 AWG Phase Data Register (18h) ..................................................................................................40
14.26 AWG Enable Register (19h) ..........................................................................................................40
14.27 AWG Overflow Interrupt Enable Register (1Ah) ............................................................................41
14.28 AWG Overflow Interrupt Status Register (1Bh) .............................................................................41
14.29 JA Error Interrupt Enable Register (1Ch) ......................................................................................41
14.30 JA Error Interrupt Status Register (1Dh) .......................................................................................41
14.31 Bits Clock Enable Register (1Eh) ..................................................................................................41
14.32 Reserved Register (1Fh) ...............................................................................................................41
14.33 Status Registers ............................................................................................................................42
14.33.1 Interrupt Enable Registers ...................................................................................................42
14.33.2 Interrupt Status Registers ....................................................................................................42
15. ARBITRARY WAVEFORM GENERATOR ............................................................................................43
16. JTAG SUPPORT ....................................................................................................................................45
16.1 TAP Controller .................................................................................................................................45
16.1.1 JTAG Reset ...........................................................................................................................45
DS485PP4 3

CS61884
16.1.2 Test-Logic-Reset ................................................................................................................... 45
16.1.3 Run-Test-Idle ........................................................................................................................ 45
16.1.4 Select-DR-Scan .................................................................................................................... 46
16.1.5 Capture-DR ........................................................................................................................... 46
16.1.6 Shift-DR ................................................................................................................................ 46
16.1.7 Exit1-DR ................................................................................................................................ 46
16.1.8 Pause-DR ............................................................................................................................. 46
16.1.9 Exit2-DR ................................................................................................................................ 46
16.1.10 Update-DR .......................................................................................................................... 46
16.1.11 Select-IR-Scan .................................................................................................................... 47
16.1.12 Capture-IR .......................................................................................................................... 47
16.1.13 Shift-IR ................................................................................................................................ 47
16.1.14 Exit1-IR ............................................................................................................................... 47
16.1.15 Pause-IR ............................................................................................................................. 47
16.1.16 Exit2-IR ............................................................................................................................... 47
16.1.17 Update-IR ........................................................................................................................... 47
16.2 Instruction Register (IR) ................................................................................................................. 47
16.2.1 EXTEST ................................................................................................................................ 47
16.2.2 SAMPLE/PRELOAD ............................................................................................................. 47
16.2.3 IDCODE ................................................................................................................................ 47
16.2.4 BYPASS ............................................................................................................................... 47
16.3 Device ID Register (IDR) ................................................................................................................ 48
17. BOUNDARY SCAN REGISTER (BSR) ................................................................................................ 48
18. APPLICATIONS .................................................................................................................................... 51
18.1 Transformer specifications ............................................................................................................. 53
18.2 Crystal Oscillator Specifications ..................................................................................................... 53
18.3 Designing for AT&T 62411 ............................................................................................................. 53
18.4 Line Protection ............................................................................................................................... 53
19. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................................................... 54
19.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................................................................ 54
19.2 Recommended Operating Conditions ............................................................................................ 54
19.3 Digital Characteristics ..................................................................................................................... 55
19.4 Transmitter Analog Characteristics ................................................................................................ 55
19.5 Receiver Analog Characteristics .................................................................................................... 56
19.6 Jitter Attenuator Characteristics ..................................................................................................... 57
19.7 Master Clock Switching Characteristics .........................................................................................59
19.8 Transmit Switching Characteristics ................................................................................................ 59
19.9 Receive Switching Characteristics ................................................................................................. 59
19.10 Switching Characteristics - Serial Port ......................................................................................... 61
19.11 Switching Characteristics - Parallel Port (Multiplexed Mode) ...................................................... 62
19.12 Switching Characteristics- Parallel Port (Non-multiplexed Mode) ............................................... 65
19.13 Switching Characteristics - JTAG ................................................................................................. 68
20. COMPLIANT RECOMMENDATIONS AND SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................... 69
21. FBGA PACKAGE DIMENSIONS .......................................................................................................... 70
22. LQFP PACKAGE DIMENSIONS ..................................................................................................... 71
4 DS485PP4

CS61884
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. CS61884 144-Pin Outs ....................................................................................................... 7
Figure 2. CS61884 160-Ball FBGA Pin Outs .................................................................................... 8
Figure 3. G.703 BITS Clock Mode in NRZ Mode .......................................................................... 23
Figure 4. G.703 BITS Clock Mode in RZ Mode ............................................................................. 23
Figure 5. G.703 BITS Clock Mode in Remote Loopback ............................................................... 23
Figure 6. Pulse Mask at T1/J1 Interface .......................................................................................... 24
Figure 7. Pulse Mask at E1 Interface .............................................................................................. 24
Figure 8. Analog Loopback Block Diagram .................................................................................... 30
Figure 9. Analog Loopback with TAOS Block Diagram ................................................................ 30
Figure 10. Digital Loopback Block Diagram .................................................................................. 31
Figure 11. Digital Loopback with TAOS ........................................................................................ 31
Figure 12. Remote Loopback Block Diagram ................................................................................. 31
Figure 13. Serial Read/Write Format (SPOL = 0) ........................................................................... 33
Figure 14. Arbitrary Waveform UI .................................................................................................. 43
Figure 15. Test Access Port Architecture ........................................................................................ 45
Figure 16. TAP Controller State Diagram ....................................................................................... 46
Figure 17. Internal RX/TX Impedance Matching ............................................................................ 51
Figure 18. Internal TX, External RX Impedance Matching ............................................................ 52
Figure 19. Jitter Transfer Characteristic vs. G.736, TBR 12/13 & AT&T 62411 ........................... 58
Figure 20. Jitter Tolerance Characteristic vs. G.823 & AT&T 62411 ............................................ 58
Figure 21. Recovered Clock and Data Switching Characteristics ................................................... 60
Figure 22. Transmit Clock and Data Switching Characteristics ...................................................... 60
Figure 23. Signal Rise and Fall Characteristics ............................................................................... 60
Figure 24. Serial Port Read Timing Diagram .................................................................................. 61
Figure 25. Serial Port Write Timing Diagram ................................................................................. 61
Figure 26. Parallel Port Timing - Write; Intel Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode ................... 63
Figure 27. Parallel Mode Port Timing - Read; Intel Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode ........ 63
Figure 28. Parallel Port Timing - Write in Motorola Multiplexed Address / Data Bus .................. 64
Figure 29. Parallel Port Timing - Read in Motorola Multiplexed Address / Data Bus ................... 64
Figure 30. Parallel Port Timing - Write in Intel Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode ....... 66
Figure 31. Parallel Port Timing - Read in Intel Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode ........ 66
Figure 32. Parallel Port Timing - Write in Motorola Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode 67
Figure 33. Parallel Port Timing - Read in Motorola Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode . 67
Figure 34. JTAG Switching Characteristics .................................................................................... 68
DS485PP4 5

CS61884
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. Operation Mode Selection ................................................................................................. 10
Table 2. Mux/Bits Clock Selection .................................................................................................. 11
Table 3. Cable Impedance Selection ................................................................................................ 15
Table 4. G.772 Address Selection ....................................................................................................22
Table 5. Hardware Mode Line Length Configuration Selection ...................................................... 25
Table 6. Jitter Attenuator Configurations .........................................................................................28
Table 7. Operational Summary ........................................................................................................ 29
Table 8. Host Control Signal Descriptions ...................................................................................... 32
Table 9. Host Mode Register Set ..................................................................................................... 34
Table 10. JTAG Instructions ............................................................................................................ 47
Table 11. Boundary Scan Register ................................................................................................... 48
Table 12. Transformer Specifications .............................................................................................. 53
6 DS485PP4
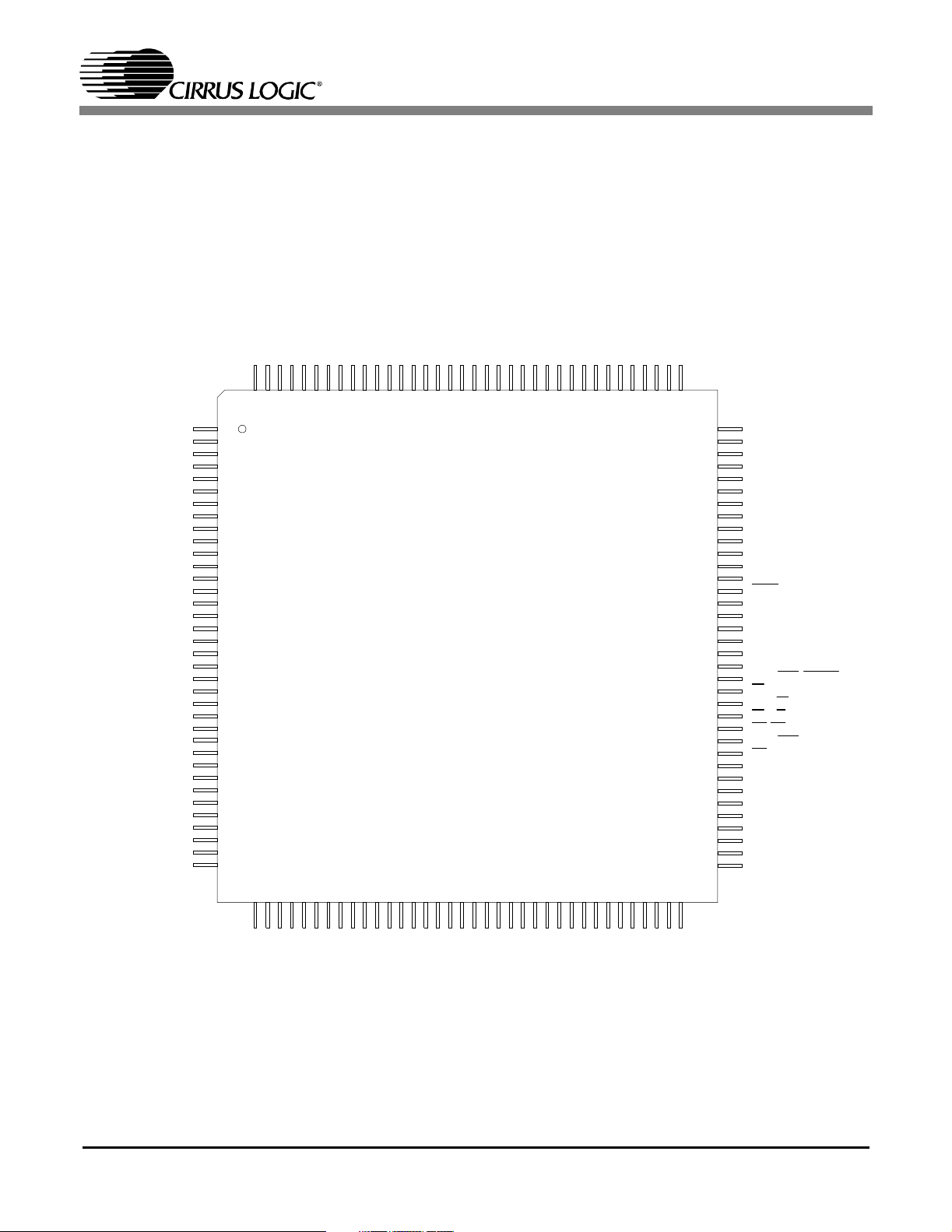
1. PINOUT - LQFP
TPOS7/TDATA7
TCLK7
LOS6
RNEG6/BPV6
RPOS6/RDATA6
RCLK6
TNEG6/UBS6
TPOS6/TDATA6
TCLK6
MCL K
MOD E
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
VCCIO
GNDIO
RV0+
RGND0
LOOP0/D0
LOOP1/D1
LOOP2/D2
LOOP3/D3
LOOP4/D4
LOOP5/D5
LOOP6/D6
LOOP7/D7
TCLK1
TPOS1/TDATA1
TNEG1/UBS1
RCLK1
RPOS1/RDATA1
RNEG1/BPV1
LOS1
TCLK0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
TNEG7/UBS7
144
RCLK7
RPOS7/RDATA7
143
142
CS61884
RNEG7/BPV7
LOS7
RTIP7
RRING7
TV+7
TTIP7
TRING7
TGND7
RRING6
RTIP6
TGND6
TRING6
TTIP6
TV+6
RTIP5
RRING5
TV+5
TTIP5
TRING5
TGND5
RRING4
RTIP4
TGND4
TRING4
TTIP4
TV+4
CLKE
TXOE
LOS4
RNEG4/BPV4
RPOS4/RDATA4
RCLK4
TNEG4/UBS4
118
116
115
140
139
138
137
136
141
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
127
126
125
124
123
122
120
128
121
119
CS6188 4
144-Pin
LQFP
(Top View)
117
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
TPOS4/TDATA4
TCLK4
LOS5
RNEG5/BPV5
RPOS5/RDATA5
RCLK5
TNEG5/UBS5
TPOS5/TDATA5
TCLK5
TDI
TDO
TCK
TMS
TRST
REF
CBLSEL
VCCIO
GNDIO
RV1+
RGND1
INTL/MOT/CODEN
CS/JASEL
ALE/AS/SCLK/LEN2
RD/RW/LEN1
WR/DS/SDI/LEN0
RDY/ACK/SDO
INT
TCLK2
TPOS2/TDATA2
TNEG2/UBS2
RCLK2
RPOS2/RDATA2
RNEG2/BPV2
LOS2
TCLK3
TPOS3/TDATA3
37
3839414243
40
RCLK0
TNEG0/USB0
TPOS0/TDATA0
RPOS0/RDATA0
47
444546
TV+0
LOS0
RNEG0/BPV0
MUX/BITSEN0
484950
TTIP0
RTIP0
TGND0
TRING0
525354
51
TGND1
TRING1
RRING0
TV+1
TTIP1
5556575859
TV+2
RTIP1
RRING1
TTIP2
61
60
RTIP2
TGND2
TRING2
RRING2
626364
TGND3
TRING3
TTIP3
65
TV+3
66
67
RTIP3
RRING3
6869707172
LOS3
RCLK3
RNEG3/RBPV3
RPOS3/RDATA3
TNEG3/UBS3
Figure 1. CS61884 144-Pin Outs
DS485PP4 7
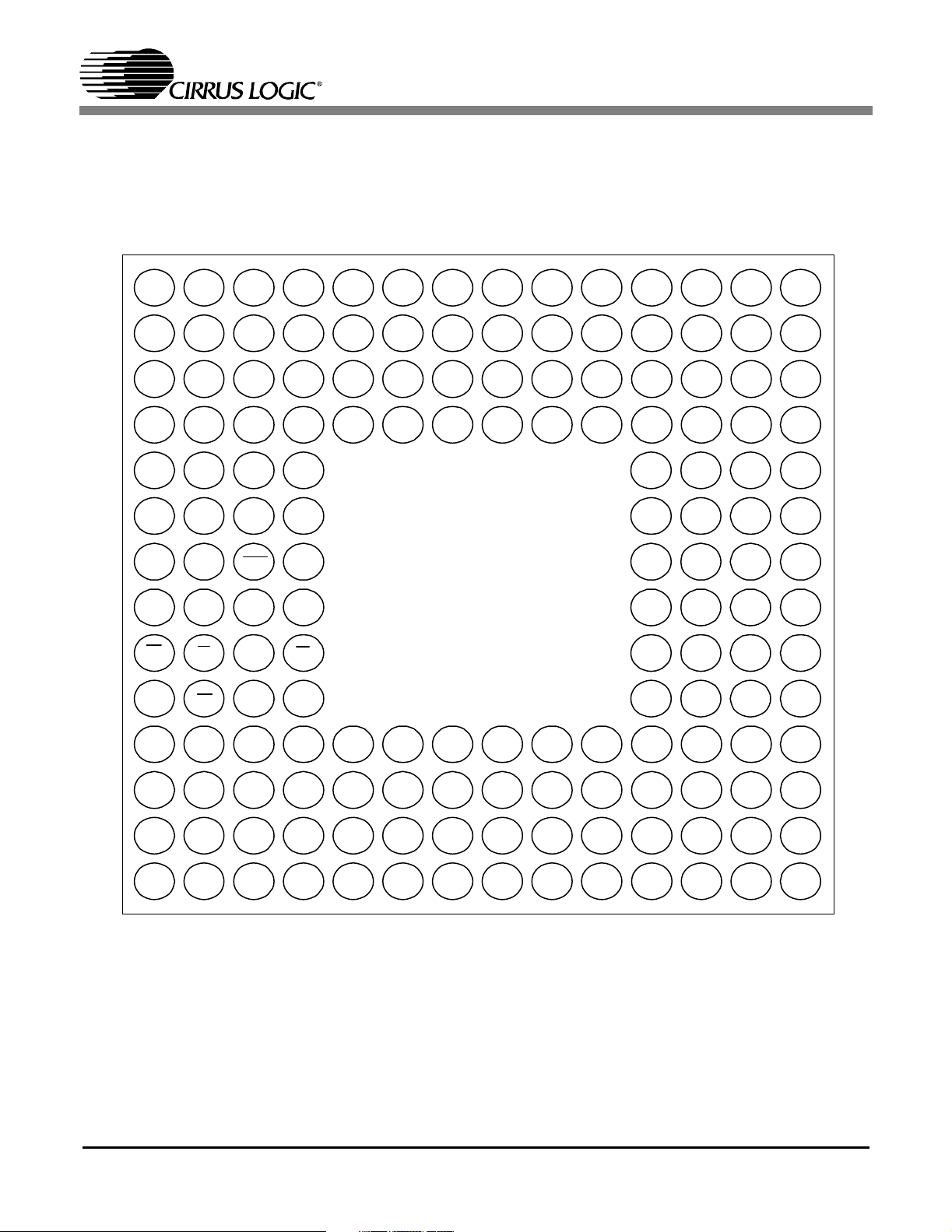
2. PINOUT - FBGA
CS61884
1234567891011121314
G
4
4
5
5
TCK
RPOS
TPOS
RPOS
TPOS
CLKE
CBLSEL
RCLK
A
TCLK
B
RCLK
C
TCLK
D
E
TXOE
F
VCCIO
4
4
5
5
TDO
RNEG
TNEG
RNEG
TNEG
TRST
4
4
5
5
LOS
TDI
TVCC
TVCC
TVCC
TVCC
5
GNDIO
4
4
5
5
LOS
4
TMS
TRING
4
TTIP
4
TRING
5
TTIP
5
TGND
4
TGND
4
TGND
5
TGND
5
RTIP
RRING
RTIP
RRING
RTIP
4
4
5
5
7
RRING
7
RTIP
6
RRING
6
CS61884
TGND
7
TGND
7
TGND
6
TGND
6
TRING
TTIP
TRING
TTIP
TVCC
7
TVCC
7
TVCC
6
TVCC
6
GNDIO
7
6
6
LOS
7
A4
RNEG
7
TNEG
RNEG
TNEG
LOS
A3
A0
RPOS
7
TPOS
7
RPOS
6
TPOS
6
MODE
6
LOOP
RCLK
7
TCLK
7
RCLK
6
TCLK
6
MCLK
A2
A1
VCCIO
0
A
7
B
7
C
6
D
6
E
F
G
160 FBGA
RGND
INTL
ALE
LOS
2
CS
LOS
1
3
(Bottom View)
WR
REF
RD
INT
RV1+
H
J
RDY
K
RGND
0
LOOP
3
LOS
0
LOOP
1
LOOP
4
LOS
1
LOOP
2
LOOP
5
MUX
RV0+
LOOP
6
LOOP
7
H
J
K
TVCC
2
TVCC
2
TVCC
3
TVCC
3
TTIP
2
TRING
2
TTIP
3
TRING
3
TGND
2
TGND
2
TGND
3
TGND
3
RRING
2
2
RRING
3
3
2
RTIP
2
3
RTIP
3
RRING
1
RTIP
1
RRING
0
RTIP
0
TGND
1
TGND
1
TGND
0
TGND
0
TTIP
1
TRING
1
TTIP
0
TRING
0
TVCC
1
TVCC
1
TVCC
0
TVCC
0
TNEG
1
RNEG
1
TNEG
0
RNEG
0
TPOS
1
RPOS
1
TPOS
0
RPOS
0
TCLK
1
RCLK
1
TCLK
0
RCLK
0
L
M
N
P
M
TCLK
L
RCLK
TCLK
N
RCLK
P
TPOS
2
RPOS
2
TPOS
3
RPOS
3
TNEG
2
RNEG
2
TNEG
3
RNEG
3
1234567891011121314
Figure 2. CS61884 160-Ball FBGA Pin Outs
8 DS485PP4
3. PIN DESCRIPTIONS
3.1 Power Supplies
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
CS61884
17
VCCIO
GNDIO 18
RV0+
RV1+
RGND0
RGND1
TV+0 44 N4, P4 Power Supply, Transmit Driver 0
TGND0 47 N6, P6 Ground, Transmit Driver 0
TV+1 53 L4, M4 Power Supply, Transmit Driver 1
TGND1 50 L6, M6 Ground, Transmit Driver 1
TV+2 56 L11
TGND2 59 L9, M9 Ground, Transmit Driver 2
TV+3 65 N11
92
91
19
90
20
89
G1
G14
G4
G11
H1
H14
H4
H11
M11
P11
Power Supply, Digital Interface: Power supply for digital
interface pins; typically 3.3V.
Ground, Digital Interface:
Power supply ground for the digital interface; typically 0 Volts
Power Supply, Core Circuitry: Power supply for all sub-circuits except the transmit driver; typically +3.3 Volts
Ground, Core Circuitry:
Ground for sub-circuits except the TX driver; typically 0 Volts
Power supply for transmit driver 0; typically +3.3 Volts
Power supply ground for transmit driver 0; typically 0 Volts
Power Supply, Transmit Driver 2
Power Supply, Transmit Driver 3
TGND3 62 N9, P9 Ground, Transmit Driver 3
TV +4 116 A11
B11
TGND4 119 A9, B9 Ground, Transmit Driver 4
TV+5 125 C11
D11
TGND5 122 C9,
D9
TV+6 128 C4,
D4
TGND6 131 C6,
D6
TV+7 137 A4, B4 Power Supply, Transmit Driver 7
TGND7 134 A6, B6 Ground, Transmit Driver 7
DS485PP4 9
Power Supply, Transmit Driver 4
Power Supply, Transmit Driver 5
Ground, Transmit Driver 5
Power Supply, Transmit Driver 6
Ground, Transmit Driver 6
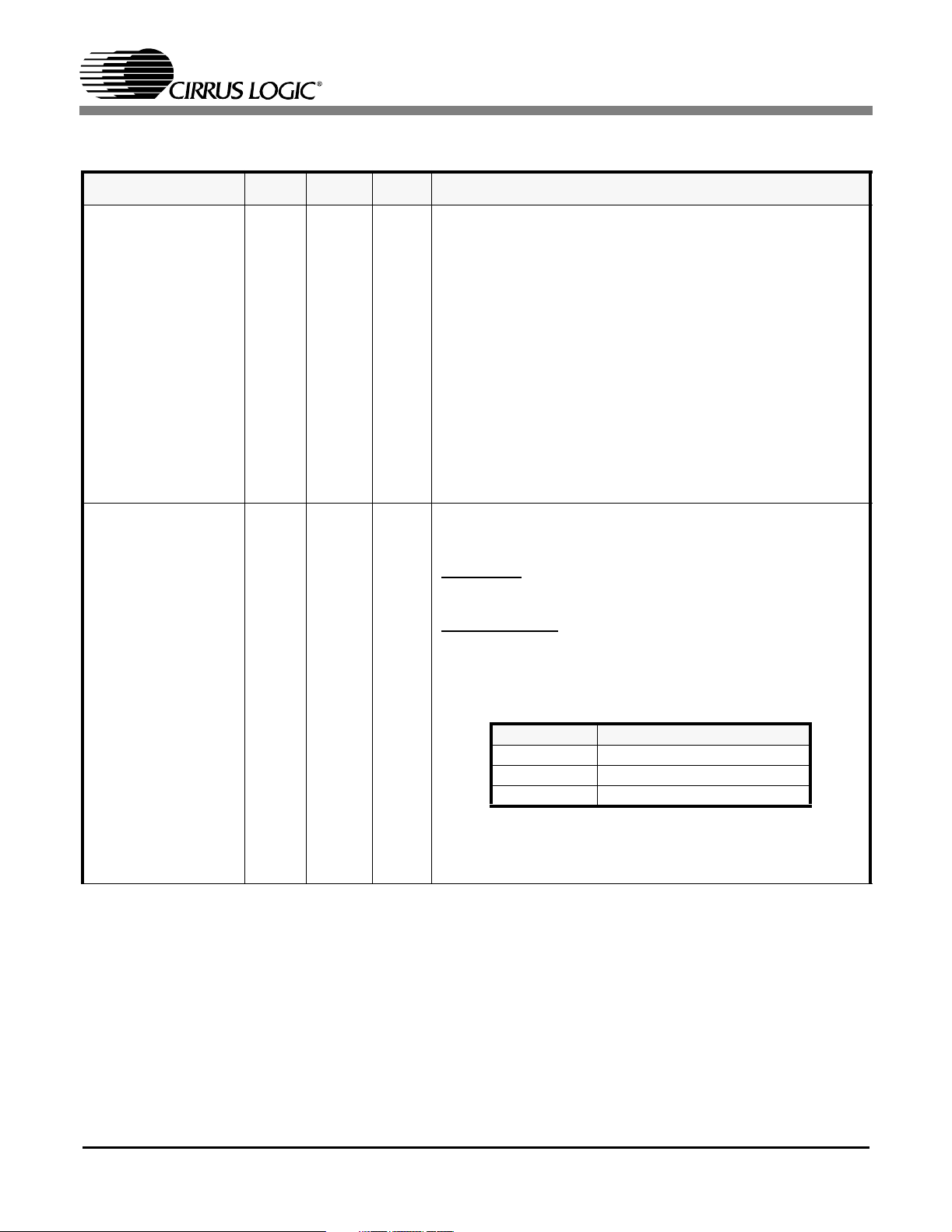
3.2 Control
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
MCLK 10 E1 I
MODE 11 E2 I
CS61884
Master Clock Input
This pin is a free running reference clock that should be
either 1.544 MHz for T1/J1 or 2.048 MHz for E1 operation.
This timing reference is used as follows:
- Timing reference for the clock recovery and jitter attenuation circuitry.
- RCLK reference during Loss of Signal (LOS) conditions
- Transmit clock reference during Transmit all Ones (TAOS)
condition
- Wait state timing for microprocessor interface
- When this pin is held “High”, the PLL clock recovery circuit is disabled. In this mode, the CS61884 receivers
function as simple data slicers.
- When this pin is held “Low”, the receiver paths are powered down and the output pins RCLK, RPOS, and RNEG
are High-Z.
Mode Select
This pin is used to select whether the CS61884 operates in
Serial host, Parallel host or Hardware mode.
Host Mode
serial or a parallel microprocessor interface (Refer to HOST
MODE (See Section 13 on page 32).
Hardware Mode
and the device control/status are provided through the pins
on the device.
- The CS61884 is controlled through either a
- The microprocessor interface is disabled
Table 1. Operation Mode Selection
Pin State OPERATING Mode
LOW Hardware Mode
HIGH Parallel Host Mode
VCCIO/2 Serial Host Mode
NOTE: For serial host mode connect this pin to a resistor
divider consisting of two 10KΩ resistors between
VCCIO and GNDIO.
10 DS485PP4
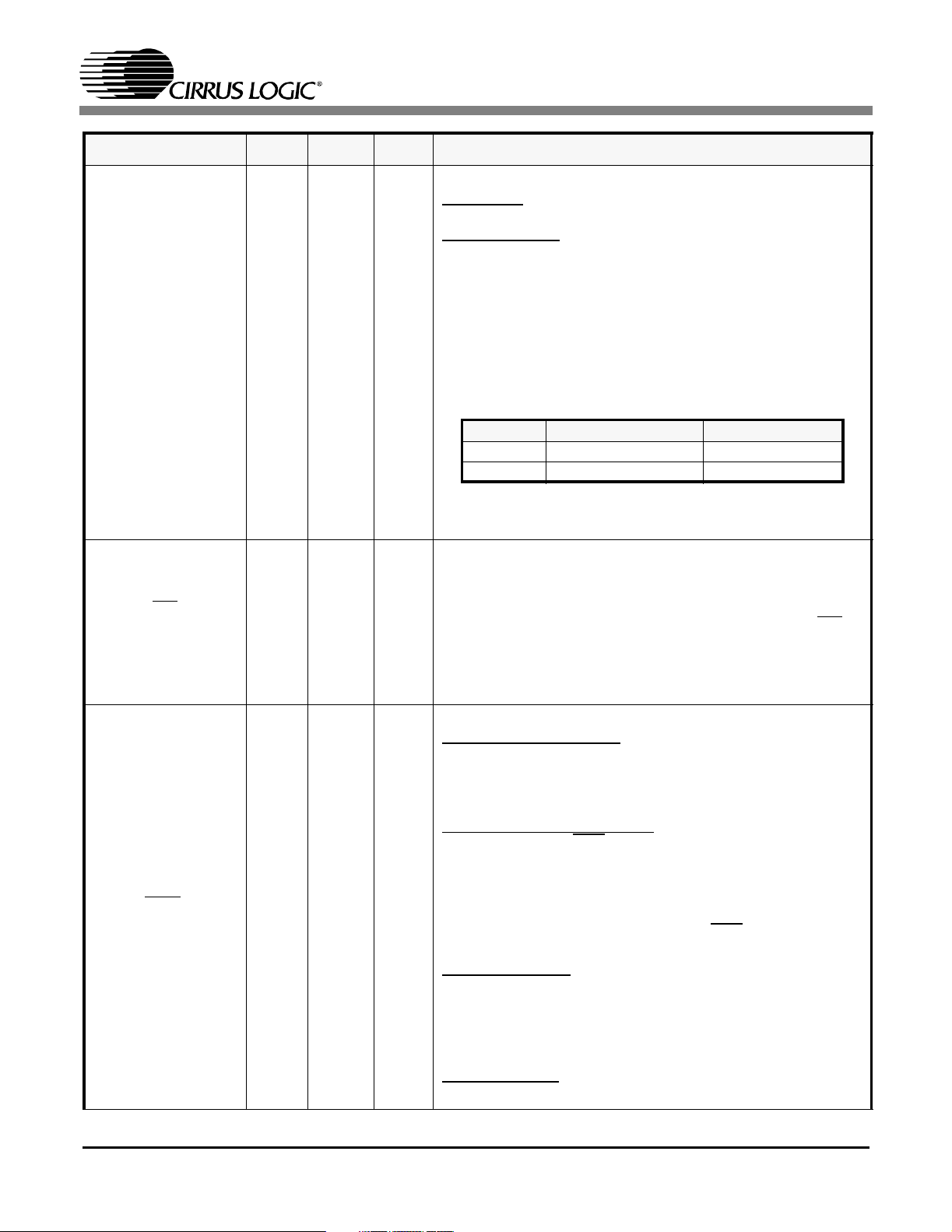
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
Multiplexed Interface/Bits Clock Select
MUX/BITSEN0 43 K2 I
Host Mode
face for multiplexed or non-multiplexed operation.
Hardware mode
a G.703 BITS Clock recovery channel (Refer to BUILDING
INTEGRATED TIMING SYSTEMS (BITS) CLOCK MODE
(See Section 8 on page 23). Channel 1 through 7 are not
affected by this pin during hardware mode. During host
mode the G.703 BITS Clock recovery function is enabled by
the Bits Clock Enable Register (1Eh) (See Section 14.31
on page 41).
-This pin configures the microprocessor inter-
- This pin is used to enable channel 0 as
Table 2. Mux/Bits Clock Selection
Pin State Parallel Host Mode Hardware Mode
HIGH multiplexed BITS Clock ON
LOW non multiplexed BITS Clock OFF
NOTE: The MUX pin only controls the BITS Clock function in
Hardware Mode
CS61884
INT
RDY/ACK
82 K13 O
/SDO 83 K14 O
Interrupt Output
This active low output signals the host processor when one
of the CS61884’s internal status register bits has changed
state. When the status register is read, the interrupt is
cleared. The various status changes that would force INT
active are maskable via internal interrupt enable registers.
NOTE: This pin is an open drain output and requires a 10 kΩ
pull-up resistor.
Data Transfer Acknowledge/Ready/Serial Data Output
IntelParallelHostMode
access, RDY is asserted “Low” to acknowledge that the device has been accessed. An asserted “High” acknowledges
that data has been written or read. Upon completion of the
bus cycle, this pin High-Z.
Motorola Parallel Host Mode
operation this pin “ACK
data on the bus is valid. An asserted “Low” on this pin during a write operation acknowledges that a data transfer to
the addressed register has been accepted. Upon completion of the bus cycle, this pin High-Z.
NOTE: Wait state generation via RDY/ACK
RZ mode (No Clock Recovery).
Serial Host Mode
configured for serial bus operation, “SDO” is used as a serial data output. This pin is forced into a high impedance
state during a serial write access. The CLKE pin controls
whether SDO is valid on the rising or falling edge of SCLK.
Upon completion of the bus cycle, this pin High-Z.
Hardware Mode
open.
- When the microprocessor interface is
- This pin is not used and should be left
- During a read or write register
- During a data bus read
” is asserted “High” to indicate that
is disabled in
DS485PP4 11

SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
Data Strobe/ Write Enable/Serial Data/Line Length Input
WR/DS/SDI/LEN0 84 J14 I
RD
/RW/LEN1 85 J13 I
IntelParallelHostMode
write enable.
Motorola Parallel Host Mode
a data strobe input.
Serial Host Mode
data input.
Hardware Mode
pulse shapes for both E1 and T1/J1 modes. This pin also
selects which mode is used E1 or T1/J1 (Refer to Ta b le 5
on page 25).
Read/Write/ Read Enable/Line Length Input
IntelParallelHostMode
read enable.
Motorola Parallel Host Mode
the read/write input signal.
Hardware Mode
pulse shapes for both E1 and T1/J1 modes. This pin also
selects which mode is used E1 or T1/J1 (Refer to Ta b le 5
on page 25).
- This pin “SDI” functions as the serial
- As LEN0, this pin controls the transmit
- As LEN1, this pin controls the transmit
- This pin “WR” functions as a
- This pin “RD” functions as a
CS61884
- This pin “DS“ functions as
- This pin “R/W” functions as
ALE/AS
CS
/SCLK/LEN2 86 J12 I
/JASEL 87 J11 I
Address Latch Enable/Serial Clock/Address Strobe/Line
Length Input
IntelParallelHostMode
Address Latch Enable when configured for multiplexed address/data operation.
Motorola Parallel Host Mode
the active “low” address strobe when configured for multiplexed address/data operation.
Serial Host Mode
used for data I/O on SDI and SDO.
Hardware Mode
pulse shapes for both E1 and T1/J1 modes. This pin also
selects which mode is used E1 or T1/J1 (Refer to Ta b le 5
on page 25).
Chip Select Input/Jitter Attenuator Select
Host Mode
cesses to the microprocessor interface in either serial or
parallel mode.
Hardware Mode
Attenuator.
- This active low input is used to enable ac-
Pin State Jitter Attenuation Position
LOW Transmit Path
HIGH Receive Path
OPEN Disabled
- This pin “SCLK” is the serial clock
- As LEN2, this pin controls the transmit
- This pin controls the position of the Jitter
- This pin “ALE” functions as the
- This pin “AS” functions as
12 DS485PP4
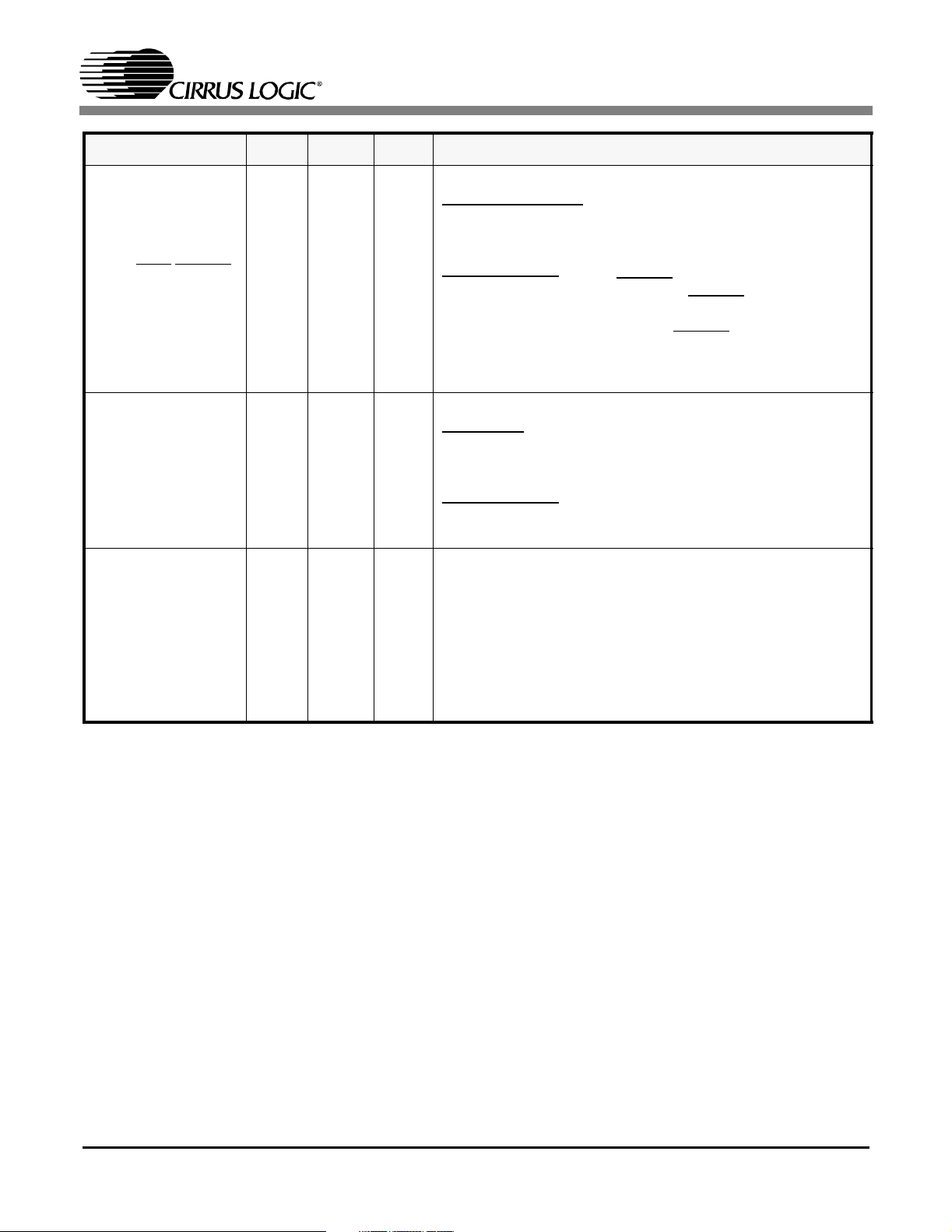
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
Motorola/Intel/Coder Mode Select Input
INTL/MOT/CODEN 88 H12 I
TXOE 114 E14 I
Parallel Host Mode
cessor interface is configured for operation with Motorola
processors. When this pin is “High” the microprocessor interface is configured for operation with Intel processors.
Hardware Mode
polar operation, this pin, CODEN
encoding/decoding function. When CODEN
B8ZS/HDB3 encoders/decoders are enabled for T1/J1 or
E1 operation respectively. When CODEN
coding/decoding is activated. This is done for all eight
channels.
Transmitter Output Enable
Host mode
dividual drivers can be set to a high impedance state via
the Output Disable Register (12h) (See Section 14.19 on
page 39).
Hardware Mode
TX drivers are forced into a high impedance state. All other
internal circuitry remains active.
- Operates the same as in hardware mode. In-
- When this pin is “Low” the micropro-
- When the CS61884 is configured for uni-
- When TXOE pin is asserted Low, all the
CS61884
, configures the line
is low,
is high, AMI en-
CLKE 115 E13 I
Clock Edge Select
In clock/data recovery mode, setting CLKE “high” will cause
RPOS/RNEG to be valid on the falling edge of RCLK and
SDOtobevalidontherisingedgeofSCLK.WhenCLKEis
set “low”, RPOS/RNEG is valid on the rising edge of RCLK,
and SDO is valid on the falling edge of SCLK. When the
part is operated in data recovery mode, the RPOS/RNEG
output polarity is active “high” when CLKE is set “high” and
active “low” when CLKE is set “low”.
DS485PP4 13
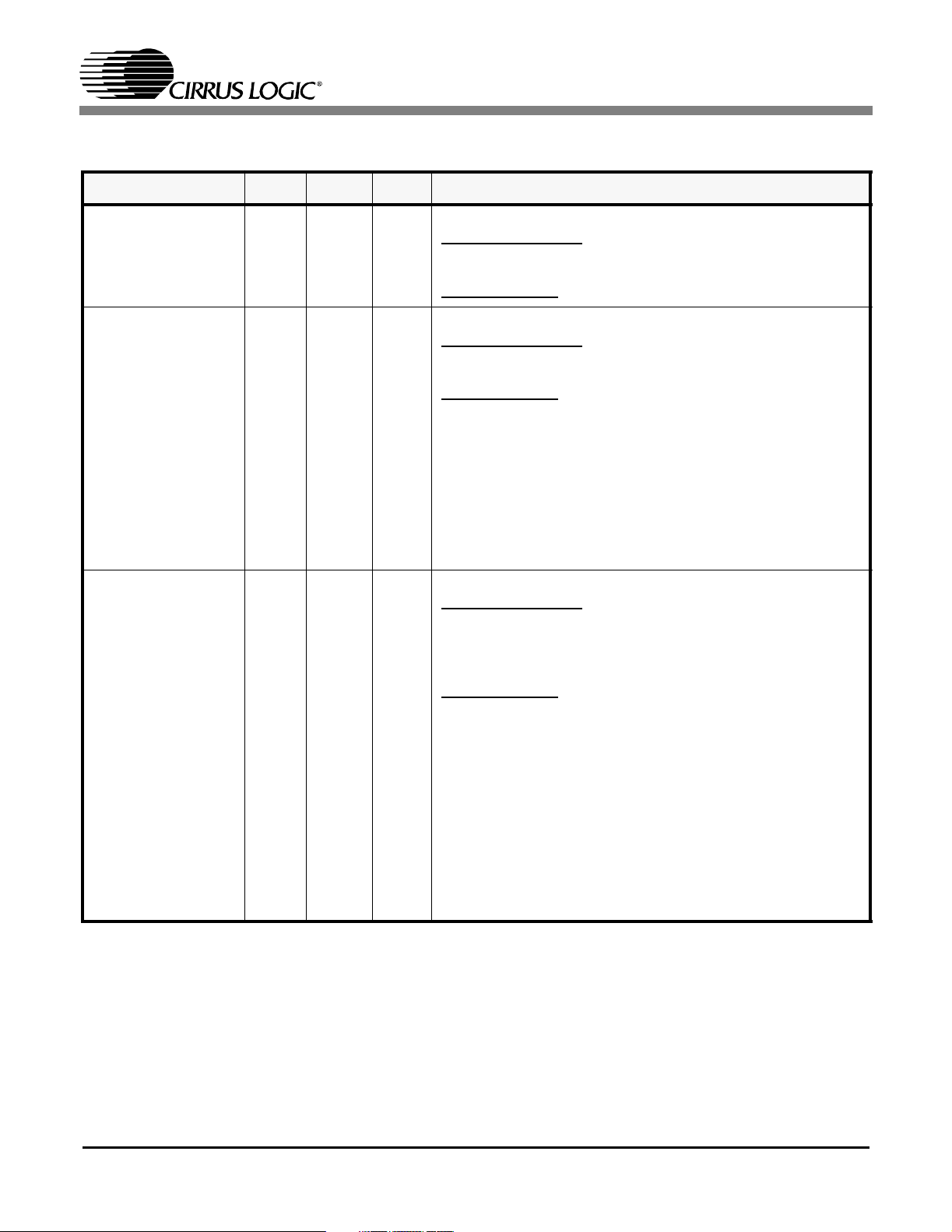
3.3 Address Inputs/Loopbacks
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
A4 12 F4 I
A3
A2
A1
A0
13
14
15
16
F3
F2
F1
G3
Address Selector Input
Parallel Host Mode
mode operation, this pin function as the address 4 input for
the parallel interface.
Hardware Mode
Non-Intrusive Monitoring/Address Selector Inputs
Parallel Host Mode
mode operation, these pins function as address A[3:0] inputs for the parallel interface.
Hardware Mode
tion during non-intrusive monitoring. In non-intrusive
I
monitoring mode, receiver 0’s input is internally connected
to the transmit or receive ports on one of the other 7 chan-
I
nels. The recovered clock and data from the selected port
are output on RPOS0/RNEG0 and RCLK0. Additionally, the
I
data from the selected port can be output on
TTIP0/TRING0 by activating the remote loopback function
I
for channel 0 (Refer to Performance Monitor Register
(0Bh) (See Section 14.12 on page 36).
- During non-multiplexed parallel host
- The A4 pin must be tied low at all times.
- During non-multiplexed parallel host
- The A[3:0] pins are used for port selec-
CS61884
LOOP0/D0
LOOP1/D1
LOOP2/D2
LOOP3/D3
LOOP4/D4
LOOP5/D5
LOOP6/D6
LOOP7/D7
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
G2
H3
H2
J4
J3
J2
J1
K1
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Loopback Mode Selector/Parallel Data Input/Output
Parallel Host Mode
terface mode, these pins function as the bi-directional 8-bit
data port. When operating in multiplexed microprocessor interface mode, these pins function as the address and data
inputs/outputs.
Hardware Mode
- No Loopback - The CS61884 is in a normal operating
state when LOOP is left open (unconnected) or tied to
VCCIO/2.
- Local Loopback - When LOOP is tied High, data transmitted on TTIP and TRING is looped back into the analog
input of the corresponding channel’s receiver and output on
RPOS and RNEG. Input Data present on RTIP and RRING
is ignored.
- Remote Loopback - When LOOP is tied Low the recovered clock and data received on RTIP and RRING is looped
back for transmission on TTIP and TRING. Data on TPOS
and TNEG is ignored.
- In non-multiplexed microprocessor in-
14 DS485PP4
3.4 Cable Select
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
CS61884
Cable Impedance Select
Host Mode
normal operation.
Hardware Mode
LEN control pins (Refer to Ta bl e 5 , “Hardware Mode Line
Length Configuration Selection,” on page 25)tosettheline
impedance for all eight receivers and transmitters. This pin
also selects whether or not all eight receivers use an internal or external line matching network (Refer to the Table
below for proper settings).
- The input voltage to this pin does not effect
- Thispinisusedincombinationwiththe
3.5
CBLSEL 93 G13 I
E1/T1/J1 CBLSEL Transmitters Receivers
NOTE: Refer to Figure 17 on page 51 and Figure 18 on
Table 3. Cable Impedance Selection
T1/J1 No Connect 100 Ω Internal Internal
T1/J1 HIGH 100 Ω Internal Internal
T1/J1 LOW 100 Ω Internal External
E1 No Connect 120 Ω Internal Inter or Ext
E1 HIGH 75 Ω Internal Internal
E1 LOW 75 Ω Internal External
page 52 for appropriate external line matching com-
ponents. All transmitters use internal matching networks.
Status
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
Loss of Signal Output
LOS0
LOS1
LOS2
LOS3
LOS4
LOS5
LOS6
LOS7
42
35
75
68
113
106
3
140
K4
K3
K12
K11
E11
E12
E3
E4
O
O
The LOS output pins can be configured to indicate a loss of
O
signal (LOS) state that is compliant to either T1.231, ITU
O
G.775 or ETSI 300 233. These pins are asserted “High” to
O
indicate LOS. The LOS output returns low when an input
O
signal is present for the time period dictated by the associ-
O
ated specification (Refer to Loss-of-Signal (LOS) (See
O
Section 10.5 on page 27)).
DS485PP4 15
3.6 Digital Rx/Tx Data I/O
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
TCLK0 36 N1 I
CS61884
Transmit Clock Input Port 0
- When TCLK is active, the TPOS and TNEG pins function
as NRZ inputs that are sampled on the falling edge of
TCLK.
- If MCLK is active, TAOS will be generated when TCLK is
held High for 16 MCLK cycles.
NOTE: MCLK is used as the timing reference during TAOS
and must have the appropriate stability.
-IfTCLKisheldHighintheabsenceofMCLK,theTPOS
and TNEG inputs function as RZ inputs. In this mode, the
transmit pulse width is set by the pulse-width of the signal
input on TPOS and TNEG. To enter this mode, TCLK must
be held high for at least 12 µS.
- If TCLK is held Low, the output drivers enter a low-power,
high impedance state.
Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 0
Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 0
The function of the TPOS/TDATA and TNEG/UBS inputs
are determined by whether Unipolar, Bipolar or RZ input
mode has been selected.
Bipolar Mode
TNEG are sampled on the falling edge of TCLK and transmitted onto the line at TTIP and TRING respectively. A
“High” input on TPOS results in transmission of a positive
pulse; a “High” input on TNEG results in a transmission of a
negative pulse. The translation of TPOS/TNEG inputs to
TTIP/TRING outputs is as follows:
- In this mode, NRZ data on TPOS and
TPOS0/TDATA0
TNEG0/UBS
16 DS485PP4
37
38
N2
N3
I
I
TPOS TNEG OUTPUT
0 0 Space
1 0 Positive Mark
0 1 Negative Mark
1 1 Space
Unipolar mode
TNEG/UBS “High” for more than 16 TCLK cycles, when
MCLK is present. The falling edge of TCLK samples a unipolar data steam on TPOS/TDATA.
RZ Mode
absence of MCLK. In this mode, the duty cycle of the
TPOS and TNEG inputs determine the pulse width of the
output signal on TTIP and TRING.
- Unipolar mode is activated by holding
- To activate RZ mode tie TCLK “High” with the
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
Receive Clock Output Port 0
- When MCLK is active, this pin outputs the recovered clock
from the signal input on RTIP and RRING. In the event of
LOS, the RCLK output transitions from the recovered clock
RCLK0 39 P1 O
RPOS0/RDATA0
RNEG0/BPV0
40
41
P2
P3
to MCLK.
- If MCLK is held “High”, the clock recovery circuitry is disabled and the RCLK output is driven by the XOR of RNEG
and RPOS.
- If MCLK is held “Low”, this output is in a high-impedance
state.
Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 0
Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 0
The function of the RPOS/RDATA and RNEG/BPV outputs
are determined by whether Unipolar, Bipolar, or RZ input
mode has been selected. During LOS, the RPOS/RNEG
outputs will remain active.
NOTE: The RPOS/RNEG outputs can be High-Z by holding
MCLK Low.
Bipolar Output Mode
O
tion, NRZ Data is recovered from RTIP/RRING and output
on RPOS/RNEG. A high signal on RPOS or RNEG corre-
O
spond to the receipt of a positive or negative pulse on
RTIP/RRING respectively. The RPOS/RNEG outputs are
valid on the falling or rising edge of RCLK as configured by
CLKE.
Unipolar Output Mode
the recovered data is output on RDATA. The decoder signals bipolar Violations on the RNEG/BPV pin.
RZ Output Mode
output RZ data recovered by slicing the signal present on
RTIP/RRING. A positive pulse on RTIP with respect to
RRING generates a logic 1 on RPOS; a positive pulse on
RRING with respect to RTIP generates a logic 1 on RNEG.
The polarity of the output on RPOS/RNEG is selectable using the CLKE pin. In this mode, external circuitry is used to
recover clock from the received signal.
- When configured for Bipolar opera-
- When unipolar mode is activated,
- In this mode, the RPOS/RNEG pins
CS61884
TCLK1 29 L1 I Transmit Clock Input Port 1
TPOS1/TDATA1 30 L2 I Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 1
TNEG1/UBS1 31 L3 I Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 1
RCLK1 32 M1 O Receive Clock Output Port 1
RPOS1/RDATA1 33 M2 O Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 1
RNEG1/BPV1 34 M3 O Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 1
TCLK2 81 L14 I Transmit Clock Input Port 2
TPOS2/TDATA2 80 L13 I Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 2
TNEG2/UBS2 79 L12 I Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 2
DS485PP4 17
CS61884
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
RCLK2 78 M14 O Receive Clock Output Port 2
RPOS2/RDATA2 77 M13 O Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 2
RNEG2/BPV2 76 M12 O Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 2
TCLK3 74 N14 I Transmit Clock Input Port 3
TPOS3/TDATA3 73 N13 I Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 3
TNEG3/UBS3 72 N12 I Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 3
RCLK3 71 P14 O Receive Clock Output Port 3
RPOS3/RDATA3 70 P13 O Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 3
RNEG3/BPV3 69 P12 O Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 3
TCLK4 107 B14 I Transmit Clock Input Port 4
TPOS4/TDATA4 108 B13 I Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 4
TNEG4/UBS4 109 B12 I Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 4
RCLK4 110 A14 O Receive Clock Output Port 4
RPOS4/RDATA4 111 A13 O Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 4
RNEG4/BPV4 11 2 A12 O Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 4
TCLK5 100 D14 I Transmit Clock Input Port 5
TPOS5/TDATA5 101 D13 I Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 5
TNEG5/UBS5 102 D12 I Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 5
RCLK5 103 C14 O Receive Clock Output Port 5
RPOS5/RDATA5 104 C13 O Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 5
RNEG5/BPV5 105 C12 O Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 5
TCLK6 9 D1 I Transmit Clock Input Port 6
TPOS6/TDATA6 8 D2 I Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 6
TNEG6/UBS6 7 D3 I Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 6
RCLK6 6 C1 O Receive Clock Output Port 6
RPOS6/RDATA6 5 C2 O Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 6
RNEG6/BPV6 4 C3 O Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 6
TCLK7 2 B1 I Transmit Clock Input Port 7
TPOS7/TDATA7 1 B2 I Transmit Positive Pulse/Transmit Data Input Port 7
TNEG7/UBS7 144 B3 I Transmit Negative Pulse/Unipolar-Bipolar Select Port 7
18 DS485PP4
CS61884
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
RCLK7 143 A1 O Receive Clock Output Port 7
RPOS7/RDATA7 142 A2 O Receive Positive Pulse/ Receive Data Output Port 7
RNEG7/BPV7 141 A3 O Receive Negative Pulse/Bipolar Violation Output Port 7
3.7 Analog RX/TX Data I/O
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
Transmit Tip Output Port 0
Transmit Ring Output Port 0
TTIP and TRING pins are the differential outputs of the
transmit driver. The driver internally matches impedances
for E1 75 Ω, E1 120 Ω and T1/J1 100 Ω lines requiring only
TTIP0
TRING0
45
46
N5
P5
a1:2transformer.TheCBLSELpinisusedtoselectthe
O
appropriate line matching impedance only in “Hardware”
mode. In host mode, the appropriate line matching imped-
O
ance is selected by the Line Length Data Register (11h)
(See Section 14.18 on page 39).
NOTE: TTIP and TRING are forced to a high impedance state
when the TCLK pin is “Low” for over 12µSorthe
TXOE pin is forced “Low”.
Receive Tip Input Port 0
Receive Ring Input Port 0
RTIP and RRING are the differential line inputs to the receiver. The receiver uses either Internal Line Impedance or
External Line Impedance modes to match the line imped-
RTIP0
RRING0
TTIP1 52 L5 O Transmit Tip Output Port 1
48
49
P7
N7
ances for E1 75Ω, E1 120Ω or T1/J1 100Ω modes.
I
Internal Line Impedance Mode
same external resistors to match the line impedance (Refer
I
to Figure 17 on page 51).
External Line Impedance Mode
ent external resistors to match the line impedance (Refer to
Figure 18 on page 52).
- In host mode, the appropriate line impedance is selected
by the Line Length Data Register (11h) (See Section
14.18 on page 39).
- In hardware mode, the CBLSEL pin in combination with
the LEN pins select the appropriate line impedance. (Refer
to Table 3 on page 15 for proper line impedance settings).
NOTE: Data and clock recovered from the signal input on
these pins are output via RCLK, RPOS, and RNEG.
- The receiver uses the
- The receiver uses differ-
TRING1 51 M5 O Transmit Ring Output Port 1
RTIP1 55 M7 I Receive Tip Input Port 1
RRING1 54 L7 I Receive Ring Input Port 1
DS485PP4 19
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
TTIP2 57 L10 O Transmit Tip Output Port 2
TRING2 58 M10 O Transmit Ring Output Port 2
RTIP2 60 M8 I Receive Tip Input Port 2
RRING2 61 L8 I Receive Ring Input Port 2
TTIP3 64 N10 O Transmit Tip Output Port 3
TRING3 63 P10 O Transmit Ring Output Port 3
RTIP3 67 P8 I Receive Tip Input Port 3
RRING3 66 N8 I Receive Ring Input Port 3
TTIP4 117 B10 O Transmit Tip Output Port 4
TRING4 118 A10 O Transmit Ring Output Port 4
RTIP4 120 A8 I Receive Tip Input Port 4
RRING4 121 B8 I Receive Ring Input Port 4
CS61884
TTIP5 124 D10 O Transmit Tip Output Port 5
TRING5 123 C10 O Transmit Ring Output Port 5
RTIP5 127 C8 I Receive Tip Input Port 5
RRING5 126 D8 I Receive Ring Input Port 5
TTIP6 129 D5 O Transmit Tip Output Port 6
TRING6 130 C5 O Transmit Ring Output Port 6
RTIP6 132 C7 I Receive Tip Input Port 6
RRING6 133 D7 I Receive Ring Input Port 6
TTIP7 136 B5 O Transmit Tip Output Port 7
TRING7 135 A5 O Transmit Ring Output Port 7
RTIP7 139 A7 I Receive Tip Input Port 7
RRING7 138 B7 I Receive Ring Input Port 7
20 DS485PP4
3.8 JTAG Test Interface
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
TRST
TMS 96 F11 I
TCK 97 F14 I
TDO 98 F13 O
95 G12 I
CS61884
JTAG Reset
This active Low input resets the JTAG controller. This input
is pulled up internally and may be left as a NC when not
used.
JTAG Test Mode Select Input
This input enables the JTAG serial port when active High.
This input is sampled on the rising edge of TCK. This input
is pulled up internally and may be left as a NC when not
used.
JTAG Test Clock
Data on TDI is valid on the rising edge of TCK. Data on
TDO is valid on the falling edge of TCK. When TCK is
stopped high or low, the contents of all JTAG registers remain unchanged. Tie pin low through a 10 KΩ resistor
when not used.
JTAG Test Data Output
JTAG test data is shifted out of the device on this pin. Data
is output on the falling edge of TCK. Leave as NC when not
used.
TDI 99 F12 I
3.9 Miscellaneous
SYMBOL LQFP FBGA TYPE DESCRIPTION
REF 94 H13 I Reference Input
JTAG Test Data Input
JTAG test data is shifted into the device using this pin. The
pin is sampled on the rising edge of TCK. TDI is pulled up
internally and may be left as a NC when not used.
This pin must be tied to ground through 13.3 KΩ 1% resistor. This pin is used to set the internal current level.
DS485PP4 21

CS61884
4. OPERATION
The CS61884 is a full featured line interface unit
for up to eight E1/T1/J1 lines. The device provides
an interface to twisted pair or co-axial media. A
matched impedance technique is employed that reduces power and eliminates the need for matching
resistors. As a result, the device can interface directly to the line through a transformer without the
need for matching resistors on the transmit side.
The receive side uses the same resistor values for
all E1/T1/J1 settings.
5. POWER-UP
On power-up, the device is held in a static state until the power supply achieves approximately 70%
of the power supply voltage. Once the power supply threshold is passed, the analog circuitry is calibrated, the control registers are reset to their default
settings, and the various internal state machines are
reset. The reset/calibration process completes in
about 30 ms.
6. MASTER CLOCK
7. G.772 MONITORING
The receive path of channel zero of the CS61884
can be used to monitor the receive or transmit paths
of any of the other channels. The signal to be monitored is multiplexed to channel zero through the
G.772 Multiplexer. The multiplexer and channel
zero then form a G.772 compliant digital Protected
Monitoring Point (PMP). When the PMP is connected to the channel, the attenuation in the signal path is
negligible across the signal band. The signal can be
observed using RPOS, RNEG, and RCLK of channelzeroorbyputtingchannelzeroinremoteloopback, the signal can be observed on TTIP and
TRING of channel zero.
The G.772 monitoring function is available during
both host mode and hardware mode operation. In
host modes, individual channels are selected for
monitoring via the Performance Monitor Regis-
ter (0Bh) (See Section 14.12 on page 36)). In hard-
ware mode, individual channels are selected
through the A3:A0 pins (Refer to Table 4 below for
address settings).
The CS61884 requires a 2.048 MHz or 1.544 MHz
reference clock with a minimum accuracy of ±100
ppm. This clock may be supplied from internal system timing or a CMOS crystal oscillator and input
to the MCLK pin.
The receiver uses MCLK as a reference for clock
recovery, jitter attenuation, and the generation of
RCLK during LOS. The transmitter uses MCLK as
the transmit timing reference during a blue alarm
transmit all ones condition. In addition, MCLK
provides the reference timing for wait state generation.
In systems with a jittered transmit clock, MCLK
should not be tied to the transmit clock, a separate
crystal oscillator should drive the reference clock
input. Any jitter present on the reference clock will
not be filtered by the jitter attenuator and can cause
the CS61884 to operate incorrectly.
Table 4. G.772 Address Selection
Address [A3:A0] Channel Selection
0000 Monitoring Disabled
0001 Receiver Channel # 1
0010 Receiver Channel # 2
0011 Receiver Channel # 3
0100 Receiver Channel # 4
0101 Receiver Channel # 5
0110 Receiver Channel # 6
0111 Receiver Channel # 7
1000 Monitoring Disabled
1001 Transmitter Channel # 1
1010 Transmitter Channel # 2
1011 Transmitter Channel # 3
1100 Transmitter Channel # 4
1101 Transmitter Channel # 5
1110 Transmitter Channel # 6
1111 Tr a n smitte r Chan n el # 7
NOTE: In hardware mode the A4 pin must be tied low
at all times.
22 DS485PP4

8. BUILDING INTEGRATED TIMING SYSTEMS (BITS) CLOCK MODE
CS61884
This mode is used to enable one or more channels
as a stand-alone timing recovery unit used for
G.703 Clock Recovery.
In hardware mode, BITS Clock mode is selected by
pulling the MUX pin “HIGH”. This enables only
channel zero as a stand-alone timing recovery unit,
no other channel can be used as a timing recovery
unit.
RCLK
RTIP
CS61884
RPOS
One Receiver
RNEG
RRING
Figure 3. G.703 BITS Clock Mode in NRZ Mode
In host mode, each channel can be setup as an independent G.703 timing recovery unit, through the
Bits Clock Enable Register (1Eh) (See Section
14.31 on page 41), setting the desired bit to “1” enables BITS Clock mode for that channel. The following diagrams show how the BITS clock
function operates.
0.1µF
R1
RECEIVE
LINE
R2
T1 1:2
RCLK
RPOS
RNEG
TCLK
TPOS
TNEG
RCLK
CS61884
RPOS
One Receiver
RNEG
Figure 4. G.703 BITS Clock Mode in RZ Mode
CS61884
One Channel
REMOTE
LOOPBACK
RTIP
RRING
TTIP
TRING
RTIP
RRING
0.1µF
0.1µF
R1
R2
R1
RECEIVE
LINE
R2
T1 1:2
RECEIVE
LINE
T1 1:2
TRANMIT
LINE
T1 1:2
Figure 5. G.703 BITS Clock Mode in Remote Loopback
DS485PP4 23

CS61884
9. TRANSMITTER
The CS61884 contains eight identical transmitters
that each use a low power matched impedance driver to eliminate the need for external load matching
resistors, while providing superior return loss. As a
result, the TTIP/TRING outputs can be connected
directly to the transformer allowing one hardware
circuit for 100 Ω (T1/J1), 120 Ω (E1), and 75 Ω
(E1) applications.
Digital transmit data is input into the CS61884
through the TPOS/TNEG input pins. These pins accept data in one of three formats: unipolar, bipolar,
or RZ. In either unipolar or bipolar mode, the
CS61884 internally generates a pulse shape compliant to the ANSI T1.102 mask for T1/J1 or the
G.703 mask for E1 (Refer to Figure 6 and
Figure 7). The pulse shaping applied to the transmit
data can be selected in hardware mode or in host
mode.
In hardware mode, the pulse shape is selected for
all channels via the LEN[2:0] pins (Refer to
Table 5 on page 25). This sets the pulse shape for
all eight transmitters to one of the prestored line
lengths. The CBLSEL pin in combination with the
LEN[2:0] pins set the line impedance for all eight
channels. The CBLSEL pin also selects between
E1 120Ω or E1 75Ω modes, when the LEN pins are
configured for E1 operation mode.
In host mode, the pulse shape for each channel can
be set independently, during NRZ operation mode,
for proper clock recovery and jitter attenuation. In
RZ Mode each channel can be set to either T1/J1 or
E1, when there is no Mclk present (Refer to RZ
Mode (See Section 9.3 on page 25).
pedance for both the receiver and the transmitter of
the addressed channel.
NOTE: In host mode the CBLSEL pin is not used.
Normalized
Amplitude
1.0
0.5
0
Output Pulse
Shape
-0.5
0 250 750 1000
Figure 6. Pulse Mask at T1/J1 Interface
Percent of
nominal peak
voltage
120
110
100
90
80
50
500
TIME (nanoseconds)
269 ns
244 ns
194 ns
ANSI T1.102,
AT&T CB 119
Specifications
To select the standard pulse shapes, the channels
are selected individually using the Line Length
Channel ID Register (10h) (See Section 14.17 on
page 38), then the LEN[3:0] bits in the Line
Length Data Register (11h) (See Section 14.18 on
page 39) are set for the desired line length for that
10
0
-10
-20
Figure 7. Pulse Mask at E1 Interface
219 ns
488 ns
Nominal Pulse
channel. The LEN bits select the line type and im-
24 DS485PP4

CS61884
The CS61884 also allows the user to customize the
transmit pulse shapes to compensate for non-standard cables, transformers, or protection circuitry.
For further information on the AWG Refer to Ar-
bitrary Waveform Generator (SeeSection15on
page 43).
For more information on the host mode registers,
refer to Register Descriptions (See Section 14 on
page 35).
9.1 Bipolar Mode
Bipolar mode provides transparent operation for
applications in which the line coding function is
performed by an external framing device. In this
mode, the falling edge of TCLK samples NRZ data
on TPOS/TNEG for transmission on TTIP/TRING.
9.2 Unipolar Mode
In unipolar mode, the CS61884 is configured such
that transmit data is encoded using B8ZS, HDB3,
or AMI line codes. This mode is activated by holding TNEG/UBS “High” for more than 16 TCLK
cycles. Transmit data is input to the part via the
TPOS/TDATA pin on the falling edge of TCLK.
When operating the part in hardware mode, the
CODEN pin is used to select between B8ZS/HDB3
or AMI encoding. During host mode operation, the
line coding is selected via the Global Control Reg-
ister (0Fh) (See Section 14.16 on page 38).
NOTE: The encoders/decoders are selected for all
eight channels in both hardware and host
mode.
9.3 RZ Mode
In RZ mode, the internal pulse shape circuitry is
bypassed and RZ data driven into TPOS/TNEG is
transmitted on TTIP/TRING. In this mode, the
pulse width of the transmitter output is determined
by the width of the RZ signal input to
TPOS/TNEG. This mode is entered when MCLK
does not exist and TCLK is held “High” for at least
12 µsec.
9.4 Transmitter Powerdown / High-Z
The transmitters can be forced into a high impedance, low power state by holding TCLK of the appropriate channel low for at least 12µs or 140
MCLK cycles. In hardware and host mode, the
TXOE pin forces all eight transmitters into a high
impedance state within 1µs.
In host mode, each transmitter is individually controllable using the Output Disable Register (12h)
(See Section 14.19 on page 39). The TXOE pin can
be used in host mode, but does not effect the contents of the Output Enable Register. This feature is
useful in applications that require redundancy.
9.5 Transmit All Ones (TAOS)
When TAOS is activated, continuous ones are
transmitted on TTIP/TRING using MCLK as the
transmit timing reference. In this mode, the TPOS
and TNEG inputs are ignored.
In hardware mode, TAOS is activated by pulling
TCLK “High” for more than 16 MCLK cycles.
Table 5. Hardware Mode Line Length Configuration Selection
LEN[2:0] Transmit Pulse Configuration Line Z Operation
000 E1 3.0V / E1 2.37V 120Ω / 75Ω E1
001 DS1, Option A (undershoot) 100Ω T1/J1
010 DS1, Option A (0 dB) 100Ω T1/J1
011 DSX-1: 0-133 ft. (0.6dB) 100Ω T1/J1
100 DSX-1: 133-266 ft. (1.2dB) 100Ω T1/J1
101 DSX-1: 266-399 ft. (1.8dB) 100Ω T1/J1
110 DSX-1: 399-533 ft. (2.4dB) 100Ω T1/J1
111 DSX-1: 533-655 ft. (3.0dB) 100Ω T1/J1
DS485PP4 25

CS61884
In host mode, TAOS is generated for a particular
channel by asserting the associated bit in the TAOS
Enable Register (03h) (See Section 14.4 on
page 35).
Since MCLK is the reference clock, it should be of
adequate stability.
9.6 Automatic TAOS
While a given channel is in the LOS condition, if
the corresponding bit in the Automatic TAOS
Register (0Eh) (See Section 14.15 on page 37) is
set, the device will drive that channel’s TTIP and
TRING with the all ones pattern. This function is
only available in host mode. Refer to Loss-of-Sig-
nal (LOS) (See Section 10.5 on page 27).
9.7 Driver Failure Monitor
In host mode, the Driver Failure Monitor (DFM)
function monitors the output of each channel and
sets a bit in the DFM Status Register (05h) (See
Section 14.6 on page 35) if a secondary short circuit is detected between TTIP and TRING. This
generates an interrupt if the respective bit in the
DFM Interrupt Enable Register (07h) (See Sec-
tion 14.8 on page 36) is also set. Any change in the
DFM Status Register (05h) (See Section 14.6 on
page 35) will result in the corresponding bit in the
DFM Interrupt Status Register (09h) (See Sec-
tion 14.10 on page 36) being set. The interrupt is
cleared by reading the DFM Interrupt Status
Register (09h) (See Section 14.10 on page 36).
This feature works in all modes of operation E1 75
Ω, E1 120 Ω and T1/J1 100 Ω.
9.8 Driver Short Circuit Protection
The CS61884 provides driver short circuit protection when current on the secondary exceeds 50 mA
RMS during E1/T1/J1 operation modes.
nal components for 100Ω (T1/J1), 120 Ω (E1), and
75Ω (Ε1) operation (Refer to Figure 17 on
page 51). This feature enables the use of a one
stuffing option for all E1/T1/J1 line impedances.
The appropriate E1/T1/J1 line matching is selected
via the LEN[2:0] and the CBLSEL pins in hardware mode, or via the Line Length Channel ID
Register (10h) (See Section 14.17 on page 38) and
bits[3:0] of the Line Length Data Register (11h)
(See Section 14.18 on page 39) in host mode. The
receivers can also be configured to use different external resistors to match the line impedance for E1
75Ω, E1 120Ω or T1/J1 100Ω modes (Refer to
Figure18onpage52).
The CS61884 receiver provides all of the circuitry
to recover both data and clock from the data signal
input on RTIP and RRING. The matched impedance receiver is capable of recovering signals with
12 dB of attenuation (referenced to 2.37 V or 3.0V
nominal) while providing superior return loss. In
addition, the timing recovery circuit along with the
jitter attenuator provide jitter tolerance that far exceeds jitter specifications (Refer to Figure 20 on
page 58).
The recovered data and clock is output from the
CS61884 on RPOS/RNEG and RCLK. These pins
output the data in one of three formats: bipolar, unipolar, or RZ. The CLKE pin is used to configure
RPOS/RNEG, so that data is valid on either the rising or falling edge of RCLK.
10.1 Bipolar Output Mode
Bipolar mode provides a transparent clock/data recovery for applications in which the line decoding
is performed by an external framing device. The recovered clock and data are output on RCLK,
RNEG/BPV, and RPOS/RDATA.
10. RECEIVER
The CS61884 contains eight identical receivers that
utilize an internal matched impedance technique
that provides for the use of a common set of exter-
26 DS485PP4
10.2 Unipolar Output Mode
In unipolar mode, the CS61884 decodes the recovered data with either B8ZS, HDB3 or AMI line decoding. The decoded data is output on the

CS61884
RPOS/RDATA pin. When bipolar violations are
detected by the decoder, the RNEG/BPV pin is asserted “High”. This pin is driven “high” one RCLK
period for every bipolar violation that is not part of
the zero substitution rules. Unipolar mode is entered by holding the TNEG pin “High” for more
than 16 MCLK cycles.
In hardware mode, the B8ZS/HDB3/AMI encoding/Decoding is activated via the CODEN pin. In
host mode, the Global Control Register (0Fh)
(See Section 14.16 on page 38) is used to select the
encoding/decoding for all channels.
10.3 RZ Output Mode
In this mode the RTIP and RRING inputs are sliced
to data values that are output on RPOS and RNEG.
This mode is used in applications that have clock
recovery circuitry external to the LIU. To support
external clock recovery, the RPOS and RNEG outputs are XORed and output on an edge of RCLK.
This mode is entered when MCLK is tied high.
NOTE: The valid RCLK edge of the RPOS/RNEG data
is controlled by the CLKE pin.
10.4 Receiver Powerdown/High-Z
All eight receivers are powered down when MCLK
is held low. In addition, this will force the RCLK,
RPOS, and RNEG outputs into a high impedance
state.
10.5 Loss-of-Signal (LOS)
The CS61884 makes use of both analog and digital
LOS detection circuitry that is compliant to the latest specifications. During T1/J1 operation ANSI
T1.231 is supported and in E1 operation mode, either ITU G.775 or ETSI 300 233 is supported. The
LOS condition in E1 mode is changed from ITU
G.775 to ETSI 300 233 in the LOS/AIS Mode En-
able Register (0Dh) (See Section 14.14 on
page 37).
The LOS detector increments a counter each time a
zero is received, and resets the counter each time a
one “mark” is received. Depending on LOS detection mode, the LOS signal is set when a certain
number of consecutive zeros are received. In
Clock/Data recovery mode, this forces the recovered clock to be replaced by MCLK at the RCLK
output. In addition the RPOS/RNEG outputs are
forced “high” for the length of the LOS period except when local and analog loopback are enabled.
Upon exiting LOS, the recovered clock replaces
MCLK on the RCLK output. In Data recovery
mode, RCLK is not replaced by MCLK when LOS
is active. The LOS detection modes are summarized below.
NOTE: T1.231, G.775 and ETSI 300 233 are all avail-
able in host mode, but in hardware mode only
ETSI 300 233 and T1.231 are available.
ANSI T1.231 (T1/J1 Mode Only) - LOS is detected if the receive signal is less than 200 mV for a period of 176 continuous pulse periods. The channel
exits the LOS condition when the pulse density exceeds 12.5% over 176 pulse periods since the receipt of the last pulse. An incoming signal with a
pulse amplitude exceeding 250 mV will cause a
pulse transition on the RPOS/RDATA or RNEG
outputs.
ITU G.775 (E1 Mode Only) - LOS is declared
when the received signal level is less than 200 mV
for 32 consecutive pulse periods (typical). The device exits LOS when the received signal achieves
12.5% ones density with no more than 15 consecutive zeros in a 32 bit sliding window and the signal
level exceeds 250 mV.
ETSI 300 233 (E1 Host Mode Only) - The LOS
indicator becomes active when the receive signal
level drops below 200 mV for more than 2048
pulse periods (1 msec). The channel exits the LOS
state when the input signal exceeds 250 mV and
has transitions for more than 32 pulse periods
(16 µsec). This LOS detection method can only be
selected while in host mode.
DS485PP4 27

CS61884
During host mode operation, LOS is reported in the
LOS Status Monitor Register. Both the LOS pins
and the register bits reflect LOS status in host mode
operation. The LOS pins and status bits are set high
(indicating loss of signal) during reset, power-up,
or channel powered-down.
10.6 Alarm Indication Signal (AIS)
The CS61884 detects all ones alarm condition per
the relevant ANSI, ITU, and ETSI specifications.
In general, AIS is indicated when the one’s density
of the receive signal exceeds that dictated by the
relevant specification. This feature is only available in host mode (Refer to LOS/AIS Mode En-
able Register (0Dh) (See Section 14.14 on
page 37)).
ANSI T1.231 AIS (T1/J1 Mode) - The AIS condition is declared when less than 9 zeros are received
within a sliding window of 8192 bits. This corresponds to a ones density of 99.9% over a period of
5.3 ms. The AIS condition is cleared when nine or
more zeros are detected in a sliding window of
8192 bits.
ITU G.775 AIS (E1 Mode) - The AIS condition is
declared when less than 3 zeros are received within
two consecutive 512 bit windows. The AIS condition is cleared when 3 or more zeros are received in
two consecutive 512 bit windows.
ETSI 300 233 (E1 Mode) - The AIS condition is
declared when less than 3 zeros are received in a
512 bit window. The AIS condition is cleared when
a 512 bit window is received containing 3 or more
zeros.
11. JITTER ATTENUATOR
The CS61884 internal jitter attenuators can be
switched into either the receive or transmit paths.
Alternatively, it can be removed from both paths to
reduce the propagation delay.
During Hardware mode operation, the location of
the jitter attenuator for all eight channels are con-
trolled by the JASEL pin (Refer to Table 6 for pin
configurations). The jitter attenuator’s FIFO length
and corner frequency, can not be changed in hardware mode. The FIFO length and corner frequency
are set to 32 bits and 1.25Hz for the E1 operational
modes and to 32 bits and 3.78Hz in the T1/J1 operational modes.
Table 6. Jitter Attenuator Configurations
PIN STATE JITTER ATTENUATOR POSITON
LOW Transmit Path
HIGH Receive Path
OPEN Disabled
During host mode operation, the location of the jitter attenuator for all eight channels are set by bits 0
and 1 in the Global Control Register (0Fh) (See
Section 14.16 on page 38). The GLOBAL CONTROL REGISTER (0Fh) also configures the jitter
attenuator’s FIFO length (bit 3) and corner frequency (bit 2).
The attenuator consists of a 64-bit FIFO, a narrowband monolithic PLL, and control logic. The jitter
attenuator requires no external crystal. Signal jitter
is absorbed in the FIFO which is designed to neither overflow nor underflow.
If overflow or underflow is imminent, the jitter
transfer function is altered to ensure that no bit-errors occur. A configuration option is provided to
reduce the jitter attenuator FIFO length from 64
bits to 32 bits in order to reduce propagation delay.
The jitter attenuator -3 dB knee frequency depends
on the settings of the Jitter Attenuator FIFO length
and the Jitter Attenuator Corner Frequency bits 2
and3,intheGlobal Control Register (0Fh) (See
Section 14.16 on page 38)). Setting the lowest corner frequency guarantees jitter attenuation compliance to European specifications TBR 12/13 and
ETSI ETS 300 011 in E1 mode. The jitter attenuator is also compliant with ITU-T G.735, G.742,
G.783 and AT&T Pub. 62411 (Refer to Figure 19
on page 58 and Figure 20 on page 58).
28 DS485PP4

CS61884
12. OPERATIONAL SUMMARY
A brief summary of the CS61884 operations in hardware and host mode is provided in Table 7.
Table 7. Operational Summary
MCLK TCLK LOOP Receive Mode Transmit Mode Loopback
Active Active Open RCLK/Data Recovery Unipolar/Bipolar Disabled
Active Active L RCLK/Data Recovery Unipolar/Bipolar Remote Loopback
Active Active H RCLK/Data Recovery Unipolar/Bipolar Analog Loopback
Active L X RCLK/Data Recovery Power Down Disabled
Active H Open RCLK/Data Recovery TAOS Disabled
Active H L RCLK/Data Recovery Unipolar/Bipolar Remote Loopback
Active H H RCLK/Data Recovery TAOS Analog Loopback
L Active X Power Down Unipolar/Bipolar Disabled
L H X Power Down RZ Data Disabled
L L X Power Down Power Down Disabled
H Active Open Data Recovery Unipolar/Bipolar Disabled
H Active L Data Recovery RZ Data Remote Loopback
H Active H Data Recovery Unipolar/Bipolar Analog Loopback
H L Open Data Recovery Power Down Disabled
H L L Data Recovery RZ Data Remote Loopback
H L H Data Recovery Power Down Disabled
H H Open Data Recovery RZ Data Disabled
H H L Data Recovery RZ Data Remote Loopback
H H H Data Recovery RZ Data Analog Loopback
12.1 Loopbacks
The CS61884 provides three loopback modes for
each port. Analog Loopback connects the transmit
signal on TTIP and TRING to RTIP and RRING.
Digital Loopback Connects the output of the Encoder to the input of the Decoder (through the Jitter
Attenuator if enabled). Remote Loopback connects
the output of the Clock and Data Recovery block to
the input of the Pulse Shaper block. (Refer to detailed descriptions below.) In hardware mode, the
LOOP[7:0] pins are used to activate Analog or Remote loopback for each channel. In host mode, the
Analog, Digital and Remote Loopback registers are
used to enable these functions (Refer to the Analog
Loopback Register (01h) (See Section 14.2 on
page 35), Remote Loopback Register (02h) (See
Section 14.3 on page 35), and Digital Loopback
Reset Register (0Ch) (See Section 14.13 on
page 37).
12.2 Analog Loopback
In Analog Loopback, the output of the
TTIP/TRING driver is internally connected to the
input of the RTIP/RRING receiver so that the data
on TPOS/TNEG and TCLK appears on the
RPOS/RNEG and RCLK outputs. In this mode the
RTIP and RRING inputs are ignored. Refer to
Figure 8 on page 30. In hardware mode, Analog
Loopback is selected by driving LOOP[7:0] high.
In host mode, Analog Loopback is selected for a
given channel using the appropriate bit in the Ana-
log Loopback Register (01h) (See Section 14.2 on
page 35).
NOTE: The simultaneous selection of Analog and
Remote loopback modes is not valid. A TAOS
request overrides the data on TPOS and TNEG
during Analog Loopback. Refer to Figure 9 on
page 30.
DS485PP4 29

CS61884
TPOS
TNEG
TCLK
RPOS
RNEG
RCLK
MCLK
TAOS
TPOS
TNEG
TCLK
RPOS
RNEG
RCLK
EncoderDecoder
EncoderDecoder
Transmit
Jitter
Attenuator
Jitter
Attenuator
Control &
Pulse Shaper
Clock Recovery &
Data Recovery
Figure 8. Analog Loopback Block Diagram
Transmit
Jitter
Attenuator
Jitter
Attenuator
Control &
Pulse Shaper
Clock Recovery &
Data Recovery
TTIP
TRING
RTIP
RRING
TTIP
TRING
(All One's)
RTIP
RRING
Figure 9. Analog Loopback with TAOS Block Diagram
12.3 Digital Loopback
Digital Loopback causes the TCLK, TPOS, and
TNEG (or TDATA) inputs to be looped back
through the jitter attenuator (if enabled) to the
RCLK, RPOS, and RNEG (or RDATA) outputs.
The receive line interface is ignored, but data at
TPOS and TNEG (or TDATA) continues to be
transmitted to the line interface at TTIP and
TRING (Refer to Figure10onpage31).
Digital Loopback is only available during host
mode. It is selected using the appropriate bit in the
Digital Loopback Reset Register (0Ch) (See Sec-
tion 14.13 on page 37).
12.4 Remote Loopback
In remote loopback, the RPOS/RNEG and RCLK
outputs are internally input to the transmit circuits
for output on TTIP/TRING. In this mode the
TCLK, TPOS and TNEG inputs are ignored. (Refer
to Figure 12 on page 31). In hardware mode, Remote Loopback is selected by driving the LOOP
pin for a certain channel low. In host mode, Remote
Loopback is selected for a given channel by writing
a one to the appropriate bit in the Remote Loop-
back Register (02h) (See Section 14.3 on
page 35).
NOTE: In hardware mode, Remote Loopback over-
rides TAOS for the selected channel. In host
NOTE: TAOS can also be used during the Digital Loop-
mode, TAOS overrides Remote Loopback.
back operation for the selected channel (Refer
to Figure 11 on page 31).
30 DS485PP4

CS61884
TPOS
TNEG
TCLK
RPOS
RNEG
RCLK
MCLK
TAOS
TPOS
TNEG
TCLK
EncoderDecoder
EncoderDecoder
Transmit
Jitter
Attenuator
Jitter
Attenuator
Control &
Pulse Shaper
Clock Recovery &
Data Recovery
Figure 10. Digital Loopback Block Diagram
Transmit
Jitter
Attenuator
Control &
Pulse Shaper
TTIP
TRING
RTIP
RRING
TTIP
TRING
(All One's)
RPOS
RNEG
RCLK
TPOS
TNEG
TCLK
RPOS
RNEG
RCLK
EncoderDecoder
Clock Recovery &
Jitter
Attenuator
Data Recovery
Figure 11. Digital Loopback with TAOS
Transmit
Jitter
Attenuator
Control &
Pulse Shaper
Clock Recovery &
Jitter
Data Recovery
Attenuator
Figure 12. Remote Loopback Block Diagram
RTIP
RRING
TTIP
TRING
RTIP
RRING
DS485PP4 31

CS61884
13. HOST MODE
Host mode allows the CS61884 to be configured
and monitored using an internal register set. (Refer
to Table 1, “Operation Mode Selection,” on
page 10). The term, “Host mode” applies to both
Parallel Host and Serial Host modes.
All of the internal registers are available in both Serial and Parallel Host mode; the only difference is
in the functions of the interface pins, which are described in Table 8.
Serial port operation is compatible with the serial
ports of most microcontrollers. Parallel port operation can be configured to be compatible with 8-bit
microcontrollers from Motorola or Intel, with both
multiplexed or non-multiplexed address/data busses. (Refer to Table 9 on page 34 for host mode
registers).
13.1 SOFTWARE RESET
A software reset can be forced by writing the Soft-
ware Reset Register (0Ah) (See Section 14.11 on
page 36). A software reset initializes all registers to
their default settings and initializes all internal state
machines.
13.2 Serial Port Operation
Serial port host mode operation is selected when
the MODE pin is left open or set to VCC/2. In this
mode, the CS61884 register set is accessed by setting the chip select (CS
ing over the SDI, SDO, and SCLK pins. Timing
over the serial port is independent of the transmit
and receive system timing. Figure 13 illustrates the
format of serial port data transfers.
A read or write is initiated by writing an address/command byte (ACB) to SDI. Only the
ADR0-ADR4 bits are valid; bits ADR5-ADR6 are
do not cares. During a read cycle, the register data
addressed by the ACB is output on SDO on the next
eight SCLK clock cycles. During a write cycle, the
data byte immediately follows the ACB.
Data is written to and read from the serial port in
LSB first format. When writing to the port, SDI
data is sampled by the device on the rising edge of
SCLK. The valid clock edge of the data on SDO is
controlled by the CLKE pin. When CLKE is low,
data on SDO is valid on the falling edge of SCLK.
When CLKE is high, data on SDO is valid on the
raising edge of SCLK. The SDO pin is Hi-Z when
not transmitting. If the host processor has a bidirectional I/O port, SDI and SDO may be tied together.
) pin low and communicat-
Table 8. Host Control Signal Descriptions
HOST CONTROL SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
PIN NAME PIN # HARDWARE SERIAL PARALLEL
MODE 11 LOW VDD/2 HIGH
MUX 43 BITSEN0 - MUX
CODEN
LOOP[7:0], DATA[7:0] 28-21 LOOP[7:0] - DATA[7:0]
LEN0/SDI/DS
LEN2/SCLK/AS/ALE 86 LEN2 SCLK AS/ALE
32 DS485PP4
/MOT/INTL88CODEN -MOT/INTL
ADDR [4] 12 GND - ADDR[4]
ADDR[3:0] 13-16 ADDR[3:0] - ADDR [3:0]
INT
SDO/ACK/RDY 83 NC SDO ACK/RDY
/WR 84 LEN0 SDI DS/WR
LEN1/R/W/RD 85 LEN1 - R/W/RD
JASEL/CS
82 Pulled Up INT INT
87 JASEL CS CS

CS61884
As illustrated in Figure 13, the ACB consists of a
bit, address field, and two reserved bits. The
R/W
R/W
bit specifies if the current register access is a
read (R/W
= 1) or a write (R/W = 0) operation. The
address field specifies the register address from
0x00 to 0x1f.
13.3 Parallel Port Operation
Parallel port host mode operation is selected when
the MODE pin is high. In this mode, the CS61884
register set is accessed using an 8-bit, multiplexed
bidirectional address/data bus D[7:0]. Timing over
the parallel port is independent of the transmit and
receive system timing.
The device is compatible with both Intel and Motorola bus formats. The Intel bus format is selected
when the MOT/INTL pin is high and the Motorola
bus format is selected when the MOT
low. In either mode, the interface can have the address and data multiplexed over the same 8-bit bus
or on separate busses. This operation is controlled
with the MUX pin; MUX = 1 means that the parallel port has its address and data multiplexed over
the same bus; MUX = 0 defines a non-multiplexed
bus. The timing for the different modes are shown
in Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28, Figure 29,
Figure 30, Figure 31, Figure 32 and Figure 33.
/INTL pin is
Non-multiplexed Intel and Motorola modes are
shown in Figure 30, Figure 31, Figure 32 and
Figure 33.TheCSpin initiates the cycle, followed
by the DS
out of the part using the rising edge of the DS
,RDor WR pin. Data is latched into or
,WR
or RD pin. Raising CS ends the cycle.
Multiplexed Intel and Motorola modes are shown
in Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28 and Figure 29.A
read or write is initiated by writing an address byte
to D[7:0]. The device latches the address on the
falling edge of ALE(AS
). During a read cycle, the
register data is output during the later portion of the
RD
or DS pulses. The read cycle is terminated and
the bus returns to a high impedance state as RD
transitions high in Intel timing or DS transitions
high in Motorola timing. During a write cycle, valid write data must be present and held stable during
the WR
or DS pulses.
In Intel mode, the RDY output pin is normally in a
high impedance state; it pulses low once to acknowledge that the chip has been selected, and high
again to acknowledge that data has been written or
read. In Motorola mode, the ACK
pin performs a
similar function; it drives high to indicate that the
address has been received by the part, and goes low
again to indicate that data has been written or read.
CS
SCLK
SDI
SDO
CLKE=0
DS485PP4 33
R/W
0
000 001D0D1D2D5D3 D6D4 D7
Address/Command Byte Data Input/Output
D0 D1 D2 D5D3 D6D4 D7
Figure 13. Serial Read/Write Format (SPOL = 0)

CS61884
13.4 Register Set
The register set available during host mode operations are presented in Table 9. While the upper
three bits of the parallel address are don’t cares on
the CS61884, they should be set to zero for proper
operation.
Table9. HostModeRegisterSet
REGISTERS BITS
ADDR NAME TYPE 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
00h
01h
02h
03h
04h
05h
06h
07h
08h
09h
0Ah
0Bh
0Ch
0Dh
0Eh
0Fh
10h
11h
12h
13h
14h
15h
16h
17h
18h
19h
1Ah
1Bh
1Ch
1Dh
1Eh
1Fh
Revision/IDCODE R IDCODE Refer to Device ID Register (IDR) on page 48
Analog Loopback R/W ALBK 7 ALBK 6 ALBK 5 ALBK 4 ALBK 3 ALBK 2 ALBK 1 ALBK 0
Remote Loopback R/W RLBK 7 RLBK 6 RLBK 5 RLBK 4 RLBK 3 RLBK 2 RLBK 1 RLBK 0
TAOS Enable R/W TAOE 7 TAOE 6 TAOE 5 TAOE 4 TAOE 3 TAOE 2 TAOE 1 TAOE 0
LOS Status R LOSS 7 LOSS 6 LOSS 5 LOSS 4 LOSS 3 LOSS 2 LOSS 1 LOSS 0
DFM Status R DFMS 7 DFMS 6 DFMS 5 DFMS 4 DFMS 3 DFMS 2 DFMS 1 DFMS 0
LOS Interrupt Enable R/W LOSE 7 LOSE 6 LOSE 5 LOSE 4 LOSE 3 LOSE 2 LOSE 1 LOSE 0
DFM Interrupt Enable R/W DFME 7 DFME 6 DFME 5 DFME 4 DFME 3 DFME 2 DFME 1 DFME 0
LOS Interrupt Status R LOSI 7 LOSI 6 LOSI 5 LOSI 4 LOSI 3 LOSI 2 LOSI 1 LOSI 0
DFM Interrupt Status R DFMI 7 DFMI 6 DFMI 5 DFMI 4 DFMI 3 DFMI 2 DFMI 1 DFMI 0
Software Reset R/W SRES 7 SRES 6 SRES 5 SRES 4 SRES 3 SRES 2 SRES 1 SRES 0
Performance Monitor R/W RSVD RSVD RSVD RSVD A3 A2 A1 A0
Digital Loopback R/W DLBK 7 DLBK 6 DLBK 5 DLBK 4 DLBK 3 DLBK 2 DLBK 1 DLBK 0
LOS/AIS Mode Enable R/W LAME 7 LAME 6 LAME 5 LAME 4 LAME 3 LAME 2 LAME 1 LAME 0
Automatic TAOS R/W ATAO 7 ATAO 6 ATAO 5 ATAO 4 ATAO 3 ATAO 2 ATAO 1 ATAO 0
Global Control R/W AI Raisen RSVD Coden FIFO JACF JASEL [1:0]
Line Length Channel ID R/W RSVD RSVD RSVD RSVD RSVD Channel ID
Line Length Data R/W RSVD RSVD RSVD IN_EX LEN[3:0]
Output Disable R/W OENB 7 OENB 6 OENB 5 OENB 4 OENB 3 OENB 2 OENB 1 OENB 0
AIS Status R AISS 7 AISS 6 AISS 5 AISS 4 AISS 3 AISS 2 AISS 1 AISS 0
AIS Interrupt Enable R/W AISE 7 AISE 6 AISE 5 AISE 4 AISE 3 AISE 2 AISE 1 AISE 0
AIS Interrupt Status R AISI 7 AISI 6 AISI 5 AISI 4 AISI 3 AISI 2 AISI 1 AISI 0
AWG Broadcast R/W AWGB 7 AWGB 6 AWGB 5 AWGB 4 AWGB 3 AWGB 2 AWGB 1 AWGB 0
AWG Phase Address R/W Channel Address [2:0] Phase Address [4:0]
AWG Phase Data R/W RSVD Sample Data[6:0]
AWG Enable R/W AWGN 7 AWGN 6 AWGN 5 AWGN 4 AWGN 3 AWGN 2 AWGN 1 AWGN 0
AWG Overflow Interrupt Enable R/W AWGE 7 AWGE 6 AWGE 5 AWGE 4 AWGE 3 AWGE 2 AWGE 1 AWGE 0
AWG Overflow Interrupt Status R AWGI 7 AWGI 6 AWGI 5 AWGI 4 AWGI 3 AWGI 2 AWGI 1 AWGI 0
RESERVED R/W RSVD 6 RSVD 5 RSVD 4 RSVD 3 RSVD 2 RSVD 1 RSVD 0 RSVD 6
RESERVED R RSVD 6 RSVD 5 RSVD 4 RSVD 3 RSVD 2 RSVD 1 RSVD 0 RSVD 6
BITS Clock Enable R/W BITS 7 BITS 6 BITS 5 BITS 4 BITS 3 BITS 2 BITS 1 BITS 0
RESERVED R/W RSVD 7 RSVD 6 RSVD 5 RSVD 4 RSVD 3 RSVD 2 RSVD 1 RSVD 0
34 DS485PP4

CS61884
14. REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
14.1 Revision/IDcode Register (00h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:4] REVI 7-4 Bits [7:4] are taken from the least-significant nibble of the Device IDCode, which are 0100.
(Refer to Device ID Register (IDR) (See Section 16.3 on page 48).
Bits [3:0] are the revision bits from the JTAG IDCODE register, CS61884 Revision A = 0000.
[3:0] REVI 3-0
Analog Loopback Register (01h)
14.2
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] ALBK 7-0
14.3 Remote Loopback Register (02h)
These bits are subject to change with the revision of the device (Refer to Device ID Register
(IDR) (See Section 16.3 on page 48).
Enables analog loopbacks. A “1” in bit n enables the loopback for channel n. Refer to Analog
Loopback (See Section 12.2 on page 29) for a complete explanation. Register bits default
to 00h after power-up or reset.
BIT NAME Description
Enables remote loopbacks. A “1” in bit n enables the loopback for channel n. Refer to
[7:0] RLBK 7-0
14.4
TAOS Enable Register (03h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] TAOE 7-0 A “1” in bit n of this register turns on the TAOS generator in channel n. Register bits default
Remote Loopback (See Section 12.4 on page 30) for a complete explanation. Register bits
default to 00h after power-up or reset.
to 00h after power-up or reset.
14.5 LOS Status Register (04h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] LOSS 7-0 Register bit n is read as “1” when LOS is detected on channel n. Register bits default to
00h after power-up or reset.
14.6 DFM Status Register (05h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] DFMS 7-0 Driver Failure Monitor. The DFM will set bit n to “1” when it detects a short circuit in channel
n. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
DS485PP4 35

14.7 LOS Interrupt Enable Register (06h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] LOSE 7-0 Any change in a LOS Status Register bits will cause the INT
in this register is set to “1”. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
14.8 DFM Interrupt Enable Register (07h)
BIT NAME Description
Enables interrupts for failures detected by the DFM. Any change in a DFM Status Register bit
[7:0] DFME 7-0
14.9
LOS Interrupt Status Register (08h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] LOSI 7-0
will cause an interrupt if the corresponding bit is set to “1” in this register. Register bits
default to 00h after power-up or reset.
Bit n of this register is set to “1” to indicate a status change in bit n of the LOS Status Register. The bits in this register indicate a change in status since the last cleared LOS interrupt.
Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
CS61884
pin to go low if corresponding bit
14.10 DFM Interrupt Status Register (09h)
BIT NAME Description
Bit n of this register is set to “1” to indicate a status change in bit n of the DFM Status Regis-
[7:0] DFMI 7-0
ter. The bits in this register indicate a change in status since the last cleared DFM interrupt.
Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
14.11 Software Reset Register (0Ah)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] SRES 7-0 Writing to this register initializes all registers to their default settings. Register bits default to
00h after power-up or reset.
14.12 Performance Monitor Register (0Bh)
BIT NAME Description
[7:4] RSVD 7-4 RESERVED (These bits must be set to 0.)
36 DS485PP4

(Continued)
BIT NAME Description
The G.772 Monitor is directed to a given channel based on the state of the four least significant bits of this register. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset. The follow-
[3:0] A[3:0]
ing table shows the settings needed to select a specific channel’s receiver or transmitter to
perform G.772 monitoring.
A[3:0] Channel Selection
0000 Monitoring Disabled
0001 RX Channel #1
0010 RX Channel #2
0011 RX Channel #3
0100 RX Channel #4
0101 RX Channel #5
0110 RX Channel #6
0111 RX Channel #7
1000 Monitoring Disabled
1001 TX Channel #1
1010 TX Channel #2
1011 TX Channel #3
1100 TX Channel #4
1101 TX Channel #5
1110 TX Channel #6
1111 TX C hannel #7
CS61884
14.13 Digital Loopback Reset Register (0Ch)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] DLBK 7-0 Setting register bit n to “1” enables the digital loopback for channel n. Refer to Digital Loop-
back (See Section 12.3 on page 30) for a complete explanation. Register bits default to
00h after power-up or reset.
14.14 LOS/AIS Mode Enable Register (0Dh)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] LAME 7-0 T1/J1 MODE
E1 Mode - Setting bit n to “1” enables ETSI 300 233 compliant LOS/AIS for channel n; set-
ting bit n to “0” enables ITU G.775 compliant LOS/AIS for channel n. Register bits default to
00h after power-up or reset.
- These bits are “Do Not Care”, T1.231 Compliant LOS/AIS already used.
14.15 Automatic TAOS Register (0Eh)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] ATAO 7-0 Setting bit n to “1” enables automatic TAOS generation on channel n when LOS is detected.
Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
DS485PP4 37

14.16 Global Control Register (0Fh)
BIT NAME Description
This register is the global control for the AWG Auto-Increment, Automatic AIS insertion,
encoding/decoding and the jitter attenuators location, FIFO length and corner frequency for
all eight channels. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
The AWG Auto-Increment bit indicates whether to auto-increment the AWG Phase Address
[7] AWG Auto-
Increment
[6] RAISEN
[5] RSVD RESERVED (This bit must be set to 0.)
[4] CODEN
[3] FIFO
LENGTH
[2] JACF
Register (17h) (See Section 14.24 on page 40) after each access. Thus, when this bit is set,
the phase samples address portion of the address register increments after each read or
write access. This bit must be set before any bit in the AWG Enable register is set, if this
function is required.
On LOS, this bit controls the automatic AIS insertion into all eight receiver paths.
0=Disabled
1 = Enabled
Line encoding/decoding Selection
0 = B8ZS/HDB3 (T1/J1/E1 respectively)
1=AMI
Jitter Attenuator FIFO length Selection
0 = 32 bits
1 = 64 bits
Jitter Attenuator Corner Frequency Selection
E1 T1/J1
0 = 1.25Hz 3.78Hz
1 = 2.50Hz 7.56Hz
These bits select the position of the Jitter Attenuator.
CS61884
JASEL 1 JASEL 0 POSITION
[1:0] JASEL [1:0]
00Disabled
0 1 Transmit Path
10Disabled
11ReceivePath
14.17 Line Length Channel ID Register (10h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:3] RSVD 7-3 RESERVED (These bits must be set to 0.)
The value written to these bits specify the LIU channel for which the Pulse Shape Configuration Data (register 11h) applies. For example, writing a value of a binary 000 to the 3-LSBs
[2:0] LLID 2-0
will select channel 0. The pulse shape configuration data for the channel specified in this register are written or read through the Line Length Data Register (11h). Register bits default
to 00h after power-up or reset.
38 DS485PP4

14.18 Line Length Data Register (11h)
BIT NAME Description
The value written to the 4-LSBs of this register specifies whether the device is operating in
either T1/J1 or E1 modes and the associated pulse shape as shown below is being transmitted. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
[7:5] RSVD RESERVED (These bits must be set to 0.)
This bit specifies the use of internal (Int_ExtB = 1) or external (Int_ExtB = 0) receiver line
[4] INT_EXTB
[3:0] LEN[3:0]
matching. The line impedance for both the receiver and transmitter are chosen through the
LEN [3:0] bits in this register.
These bits setup the line impedance for both the receiver and the transmitter path and the
desired pulse shape for a specific channel. The channel is selected with the Line Length
Channel ID register (0x10). The following table shows the available transmitter pulse
shapes.
LEN [3:0] Operation
Mode
0000 E1 120Ω 3.0V 12
0001 T1/J1 100Ω DS1, Option A (undershoot) 14
0010 T1/J1 100Ω DS1, Option A (0dB) 14
0011 T1/J1 100Ω 0 - 133Ft (0.6dB) 13
0100 T1/J1 100Ω 133 - 266Ft (1.2dB) 13
0101 T1/J1 100Ω 266 - 399Ft (1.2dB) 13
0110 T1/J1 100Ω 399 - 533Ft (2.4dB) 13
0111 T1/J1 100Ω 533 - 655Ft (3.0dB) 13
1000 E1 75Ω 2.37V 12
Line Length Selection Phase Samples
CS61884
per UI
14.19 Output Disable Register (12h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] OENB 7-0 Setting bit n of this register to “1” High-Z the TX output driver on channel n of the device.
Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
14.20 AIS Status Register (13h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] AISS 7-0 A “1” in bit position n indicates that the receiver has detected an AIS condition on channel n,
which generates an interrupt on the INT
reset.
pin. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or
14.21 AIS Interrupt Enable Register (14h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] AISE 7-0 This register enables changes in the AIS Status register to be reflected in the AIS Interrupt
Status register, thus causing an interrupt on the INT
power-up or reset.
pin. Register bits default to 00h after
DS485PP4 39

CS61884
14.22 AIS Interrupt Status Register (15h)
BIT NAME Description
Bitnissetto“1” to indicate a change of status of bit n in the AIS Status Register. The bits in
[7:0] AISI 7-0
14.23 AWG Broadcast Register (16h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] AWGB 7-0
14.24 AWG Phase Address Register (17h)
BIT NAME Description
[7:5] AWGA These bits specify the target channel 0-7. (Refer to Arbitrary Waveform Generator (See
[4:0] PA[4:0] These bits specify 1 of 24 (E1) or 26/28 (T1/J1) phase sample address locations of the AWG,
this register indicate which channel changed in status since the last cleared AIS interrupt.
Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
Setting bit n to “1” causes the phase data in the AWG Phase Data Register to be written to
the corresponding channel or channels simultaneously. (Refer to Arbitrary Waveform Gen-
erator (See Section 15 on page 43). Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
Section 15 on page 43). Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
that the phase data in the AWG Phase Data Register is written to or read from. The other
locations in each channel’s phase sample addresses are not used, and should not be
accessed. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
14.25 AWG Phase Data Register (18h)
BIT NAME Description
[7] RSVD RESERVED (This bit must be set to 0.)
These bits are used for the pulse shape data that will be written to the AWG phase location
specified by the AWG Phase Address Register. The value written to or read from this register
will be written to or read from the AWG phase sample location specified by the AWG Phase
[6:0] AWGD [6:0]
Address register. A software reset through the Software Reset Register does not effect the
contents of this register. The data in each phase is a 7-bit 2’s complement number (the maximum positive value is 3Fh and the maximum negative value is 40h). (Refer to Arbitrary
Waveform Generator (SeeSection15onpage43).Register bits default to 00h after
power-up.
14.26 AWG Enable Register (19h)
BIT NAME Description
The AWG enable register is used for selecting the source of the customized transmission
pulse-shape. Setting bit n to “1” in this register selects the AWG as the source of the output
[7:0] AWGN 7-0
pulse shape for channel n. When bit n is set to “0” the pre-programmed pulse shape in the
ROM is selected for transmission on channel n. (Refer to Arbitrary Waveform Generator
(See Section 15 on page 43). Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
40 DS485PP4

14.27 AWG Overflow Interrupt Enable Register (1Ah)
BIT NAME Description
This register enables changes in the overflow status to be reflected in the AWG Interrupt Sta-
[7:0] AWGE 7-0
tus register, thus causing as interrupt on the INT
nel basis. Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
pin. Interrupts are maskable on a per-chan-
14.28 AWG Overflow Interrupt Status Register (1Bh)
BIT NAME Description
The bits in this register indicate a change in status since the last AWG overflow interrupt. An
[7:0] AWGI 7-0
AWG overflow occurs when invalid phase data are entered, such that a sample-by-sample
addition of UI0 and UI1 results in values that exceed the arithmetic range of the 7-bit representation. Reading this register clears the interrupt, which deactivates the INT
bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
14.29 Reserved Register (1Ch)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] RSVD 7-0 RESERVED (These bits must be set to zero.)
CS61884
pin. Register
14.30 Reserved Register (1Dh)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] RSVD 7-0 RESERVED (These bits must be set to zero.)
14.31 Bits Clock Enable Register (1Eh)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] BITS 7-0 Setting a “1” to bit n in this register changes channel n to a stand-alone timing recovery unit
used for G.703 clock recovery. (Refer to BUILDING INTEGRATED TIMING SYSTEMS
(BITS) CLOCK MODE (See Section 8 on page 23) for a better description of the G.703 clock
recovery function). Register bits default to 00h after power-up or reset.
14.32 Reserved Register (1Fh)
BIT NAME Description
[7:0] RSVD 7-0 RESERVED (These bits must be set to zero.)
DS485PP4 41

CS61884
14.33 Status Registers
The following Status registers are read-only: LOS
Status Register (04h) (See Section 14.5 on
page 35), DFM Status Register (05h) (See Section 14.6 on page 35) and AIS Status Register
(13h) (See Section 14.20 on page 39). The
CS61884 generates an interrupt on the INT
time an unmasked status register bit changes.
pin any
14.33.1 Interrupt Enable Registers
The Interrupt Enable registers: LOS Interrupt En-
able Register (06h) (See Section 14.7 on page 36),
DFM Interrupt Enable Register (07h) (See Sec-
tion 14.8 on page 36), AIS Interrupt Enable Reg-
ister (14h) (See Section 14.21 on page 39) and
AWG Overflow Interrupt Enable Register
(1Ah) (See Section 14.27 on page 41), enable
changes in status register state to cause an interrupt
on the INT
channel basis. When an Interrupt Enable register
bit is 0, the corresponding Status register bit is disabled from causing an interrupt on the INT
NOTE: Disabling an interrupt has no effect on the sta-
pin. Interrupts are maskable on a per
pin.
tus reflected in the associated status register.
14.33.2 Interrupt Status Registers
The following interrupt status registers: LOS In-
terrupt Status Register (08h) (See Section 14.9
on page 36), DFM Interrupt Status Register
(09h) (See Section 14.10 on page 36), AIS Interrupt Status Register (15h) (See Section 14.22 on
page 40) and AWG Overflow Interrupt Status
Register (1Bh) (See Section 14.28 on page 41), in-
dicate a change in status of the corresponding status
registers in host mode. Reading these registers
clears the interrupt, which deactivates the INT
pin.
42 DS485PP4

CS61884
15. ARBITRARY WAVEFORM GENERATOR
Using the Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG)
allows the user to customize the transmit pulse
shapes to compensate for nonstandard cables,
transformers, protection circuitry, or to reduce
power consumption by reducing the output pulse
amplitude. A channel is configured for a custom
pulse shape by storing data representing the pulse
shape into the 24/26/28 phase sample locations and
then enabling the AWG for that channel. Each
channel has a separate AWG, so all eight channels
can have a different customized pulse shape. The
microprocessor interface, is used to read from or
write to the AWG, while the device is in host mode.
In the AWG RAM, the pulse shape is divided into
two unit intervals (UI). For E1 mode, there are 12
sample phases in each UI, while in T1/J1 mode, the
number of sample phases per UI are either 13 or 14.
The first UI is for the main part of the pulse and the
second UI is for the “tail” of the pulse (Refer to
Figure 14). A complete pulse-shape is represented
by 24 phase samples in E1 mode or 26/28 phase
samples in T1/J1 mode. In E1 mode, data written in
the first UI represents a valid pulse shape, while
data in the second UI is ignored and should be set
to zero.
The data in each phase sample is a 7-bit two’s complement number with a maximum positive value of
0x3f, and a maximum negative value of 0x40. The
terms “positive” and “negative” are defined for a
positive going pulse only. The pulse generation circuitry automatically inverts the pulse for negative
going pulses. The data stored in the lowest phase
address corresponds to the first phase sample that
will be transmitted in time. When the mode of operation calls for only 24/26 phase samples if the
phase samples that are not used (25 through 28) are
written to, they are ignored and don’t effect the
shape of the customized pulse shape.
The following procedure describes how to enable
and write data into the AWG to produce customized pulse shapes to be transmitted for a specific
U1 U2
E1 AWG Example
U1 U2
The mode of operation is selected using the Line
Length Channel ID Register (10h) (See Section
14.17 on page 38) and the Line Length Data Reg-
ister (11h) (See Section 14.18 on page 39). A
phase sample, or cell, is accessed by first loading
DSX-1 (54% duty cycle) AWG Example
U1 U2
the channel address and the phase sample address
into the AWG Phase Address Register (17h) (See
Section 14.24 on page 40), and then reading or
writing the AWG Phase Data Register (18h) (See
Section 14.25 on page 40). The upper locations in
each channel’s address space are not used; reading
and writing to these registers produces undefined
DSX-1 (50% duty cycle) AWG Example
results.
Figure 14. Arbitrary Waveform UI
DS485PP4 43

CS61884
channel or channels. To enable the AWG function
for a specific channel or channels the corresponding bit(s) in the AWG Enable Register (19h) (See
Section 14.26 on page 40) must be set to “1”. When
the corresponding bit(s) in the AWG Enable Register are set to “0” pre-programmed pulse shapes are
selected for transmission.
In order to access and write data for a customized
pulse shape to a specific channel or channels, the
following steps are required. First the desired channel and phase sample addresses must be written to
the AWG Phase Data Register (18h) (See Section
14.25 on page 40). Once the channel and phase
sample address have been selected, the actual phase
sample data may be entered into the AWG Phase
Data Register at the selected phase sample address
selected by the lower five bits of the AWG Phase
Address Register (17h) (See Section 14.24 on
page 40)).
To change the phase sample address of the selected
channel the user may use either of the following
steps. First, the user can re-write the phase sample
address to the AWG Phase Address Register or set
the Auto-Increment bit (Bit 7) in the Global Con-
trol Register (0Fh) (See Section 14.16 on
page 38)) to “1”. When this bit is set to “1” only the
first phase sample address (00000 binary) needs to
be written to the AWG Phase Address Register
(17h) (See Section 14.24 on page 40), and each
subsequent access (read or write) to the AWG
Phase Data Register (18h) (See Section 14.25 on
page 40) will automatically increment the phase
sample address. The channel address, however, remains unaffected by the Auto-Increment mode.
Since the number of phase samples forming the
customized pulse shape varies with the mode of operation (E1/T1/J1), the AWG Phase Address Reg-
ister (17h) (See Section 14.24 on page 40) needs to
be re-written in order to re-start the phase sample
address sequence from zero.
The AWG Broadcast function allows the same data
to be written to different channels simultaneously.
This is done with the use of the AWG Broadcast
Register (16h) (See Section 14.23 on page 40)),
each bit in the AWG Broadcast Register corresponds to a different channel (bit 0 is channel 0, and
bit3ischannel3&etc.).
To write the same pulse shaping data to multiple
channels, simple set the corresponding bit to “1” in
the AWG Broadcast Register (16h) (See Section
14.23 on page 40). This function only requires that
one of the eight channel addresses be written to the
AWG Phase Address Register (17h) (See Section
14.24 on page 40). During an AWG read sequence,
the bits in the AWG Broadcast Register are ignored. During an AWG write sequence, the selected channel or channels are specified by both the
channel address specified by the upper bits of the
AWG Phase Address Register (17h) (See Section
14.24 on page 40) and the selected channel or channels in the AWG Broadcast Register (16h) (See
Section 14.23 on page 40).
During a multiple channel write the first channel
that is written to, is the channel that was address by
the AWG Phase Address Register. This channel’s
bit in the AWG Broadcast Register can be set to either “1” or “0”. For a more descriptive explanation
of how to use the AWG refer to the “How To Use
The CS61880/CS61884 Arbitrary Waveform Generator” application note AN204.
44 DS485PP4

CS61884
16. JTAG SUPPORT
The CS61884 supports the IEEE Boundary Scan
Specification as described in the IEEE 1149.1 standards. A Test Access Port (TAP) is provided that
consists of the TAP controller, the instruction register (IR), by-pass register (BPR), device ID register (IDR), the boundary scan register (BSR), and
the 5 standard pins (TRST
TDO). A block diagram of the test access port is
shown in Figure 15. The test clock input (TCK) is
used to sample input data on TDI, and shift output
data through TDO. The TMS input is used to step
the TAP controller through its various states.
The instruction register is used to select test execution or register access. The by-pass register provides a direct connection between the TDI input
and the TDO output. The device identification register contains an 32-bit device identifier.
The Boundary Scan Register is used to support testing of IC inter-connectivity. Using the Boundary
Scan Register, the digital input pins can be sampled
,TCK,TMS,TDI,and
and shifted out on TDO. In addition, this register
can also be used to drive digital output pins to a
user defined state.
16.1 TAP Controller
The TAP Controller is a 16 state synchronous state
machine clocked by the rising edge of TCK. The
TMS input governs state transitions as shown in
Figure 16. The value shown next to each state tran-
sition in the diagram is the value that must be on
TMS when it is sampled by the rising edge of TCK.
16.1.1 JTAG Reset
TRST resets all JTAG circuitry.
16.1.2 Test-Logic-Reset
The test-logic-reset state is used to disable the test
logic when the part is in normal mode of operation.
This state is entered by asynchronously asserting
TRST
or forcing TMS High for 5 TCK periods.
16.1.3 Run-Test-Idle
The run-test-idle state is used to run tests.
TDI
TCK
TMS
Digital output pins
Digital input pins
parallel latched
output
Boundary Scan Data Register
Device ID Data Register
Bypass Data Register
Instruction (shift) Register
parallel latched output
TAP
Controller
Figure 15. Test Access Port Architecture
JTAG BLOCK
MUX TDO
DS485PP4 45

Test-Logic-Reset
1
0
0
Run-Test/Idle
11
Select-DR-Scan
0
1
Capture-DR
0
Shift-D R
1
Exit1-DR
0
Pause-DR
1
0
Exit2-DR
11
Update-DR
11
00
0
1
0
Select- IR-Scan
1
Ca pture- IR
Shift- IR
Exit1- IR
Pause-IR
0
Exit2- IR
Update-IR
CS61884
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
Figure 16. TAP Controller State Diagram
16.1.4 Select-DR-Scan
This is a temporary controller state.
16.1.5 Capture-DR
In this state, the Boundary Scan Register captures
input pin data if the current instruction is EXTEST
or SAMPLE/PRELOAD.
16.1.6 Shift-DR
In this controller state, the active test data register
connected between TDI and TDO, as determined
by the current instruction, shifts data out on TDO
on each rising edge of TCK.
16.1.7 Exit1-DR
This is a temporary state. The test data register selected by the current instruction retains its previous
value.
16.1.8 Pause-DR
The pause state allows the test controller to temporarily halt the shifting of data through the current
test data register.
16.1.9 Exit2-DR
This is a temporary state. The test data register selected by the current instruction retains its previous
value.
16.1.10 Update-DR
The Boundary Scan Register is provided with a
latched parallel output to prevent changes while
data is shifted in response to the EXTEST and
SAMPLE/PRELOAD instructions. When the TAP
controller is in this state and the Boundary Scan
Register is selected, data is latched into the parallel
output of this register from the shift-register path
on the falling edge of TCK. The data held at the
latched parallel output changes only in this state.
46 DS485PP4

CS61884
16.1.11 Select-IR-Scan
This is a temporary controller state. The test data
register selected by the current instruction retains
its previous state.
16.1.12 Capture-IR
In this controller state, the instruction register is
loaded with a fixed value of “01” on the rising edge
of TCK. This supports fault-isolation of the boardlevel serial test data path.
16.1.13 Shift-IR
In this state, the shift register contained in the instruction register is connected between TDI and
TDO and shifts data one stage towards its serial
output on each rising edge of TCK.
16.1.14 Exit1-IR
This is a temporary state. The test data register selected by the current instruction retains its previous
value.
by the current instruction retain their previous value.
16.2 Instruction Register (IR)
The 3-bit Instruction register selects the test to be
performed and/or the data register to be accessed.
The valid instructions are shifted in LSB first and
are listed in Table 10:
Table 10. JTAG Instructions
IR CODE INSTRUCTION
000 EXTEST
100 SAMPLE/PRELOAD
110 ID CODE
111 BYPASS
16.2.1 EXTEST
The EXTEST instruction allows testing of off-chip
circuitry and board-level interconnect. EXTEST
connects the BSR to the TDI and TDO pins.
16.2.2 SAMPLE/PRELOAD
16.1.15 Pause-IR
The pause state allows the test controller to temporarily halt the shifting of data through the instruction register.
16.1.16 Exit2-IR
This is a temporary state. The test data register selected by the current instruction retains its previous
value.
16.1.17 Update-IR
The instruction shifted into the instruction register
is latched into the parallel output from the shift-register path on the falling edge of TCK. When the
new instruction has been latched, it becomes the
current instruction. The test data registers selected
The SAMPLE/PRELOAD instruction samples all
device inputs and outputs. This instruction places
the BSR between the TDI and TDO pins. The BSR
is loaded with samples of the I/O pins by the Capture-DR state.
16.2.3 IDCODE
The IDCODE instruction connects the device identification register to the TDO pin. The device identification code can then be shifted out TDO using
the Shift-DR state.
16.2.4 BYPASS
The BYPASS instruction connects a one TCK delay register between TDI and TDO. The instruction
is used to bypass the device.
DS485PP4 47

CS61884
16.3 Device ID Register (IDR)
Revision section: 0h = Rev A, 1h = Rev B and so on. The device Identification Code [27 - 12] is derived
from the last three digits of the part number (884). The LSB is a constant 1, as defined by IEEE 1149.1.
CS61884 IDCODE REGISTER(IDR)
REVISION DEVICE IDCODE REGISTER MANUFACTURER CODE
3130 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 109876543210
0h 0h 8h 8h 4h 0h Oh 9h
00000000100010000100000011001001
17. BOUNDARY SCAN REGISTER (BSR)
The BSR is a shift register that provides access to the digital I/O pins. The BSR is used to read and write
the device pins to verify interchip connectivity. Each pin has a corresponding scan cell in the register. The
pin to scan cell mapping is given in the BSR description shown in Table 11.
NOTE: Data is shifted LSB first into the BSR register.
Table 11. Boundary Scan Register
BSR
Bit
0 LOS7 O LOS7
1 RNEG7 O RNEG7
2 RPOS7 O RPOS7
3 RCLK7 O RCLK7
4 - Note 2 HIZ7_B
5 TNEG7 I TNEG7
6 TPOS7 I TPOS7
7 TCLK7 I TCLK7
8 LOS6 O LOS6_B
9 RNEG6 O RNEG6
10 RPOS6 O RPOS6
11 RCLK6 O RCLK6
12 - Note 2 HIZ6_B
13 TNEG6 I TNEG6
14 TPOS6 I TPOS6
15 TCLK6 I TCLK6
16 MCLK I MCLK
17 MODE I MODE_TRI
18 MODE I MODE_IN
19 ADDR4 I ADDR4
20 ADDR3 I ADDR3
21 ADDR2 I ADDR2
22 ADDR1 I ADDR1
23 ADDR0 I ADDR0
24 LOOP0/D0 I LPT0
25 LOOP0/D0 I LPI0
26 LOOP0/D0 O LPO0
27 LOOP1/D1 I LPT1
Pin
Name
Cell
Type
Bit
Symbol
48 DS485PP4

Table 11. Boundary Scan Register (Continued)
CS61884
BSR
Bit
28 LOOP1/D1 I LPI1
29 LOOP1/D1 O LPO1
30 LOOP2/D2 I LPT2
31 LOOP2/D2 I LPI2
32 LOOP2/D2 O LPO2
33 LOOP3/D3 I LPT3
34 LOOP3/D3 I LPI3
35 LOOP3/D3 O LPO3
36 LOOP4/D4 I LPT4
37 LOOP4/D4 I LPI4
38 LOOP4/D4 O LPO4
39 LOOP5/D5 I LPT5
40 LOOP5/D5 I LPI5
41 LOOP5/D5 O LPO5
42 LOOP6/D6 I LPT6
43 LOOP6/D6 I LPI6
44 LOOP6/D6 O LPO6
45 LOOP7/D7 I LPT7
46 LOOP7/D7 I LPI7
47 LOOP7/D7 O LPO7
48 - Note 1 LPOEN
49 TCLK1 I TCLK1
50 TPOS1 I TPOS1
51 TNEG1 I TNEG1
52 RCLK1 O RCLK1
53 RPOS1 O RPOS1
54 RNEG1 O RNEG1
55 - Note 2 HIZ1_B
56 LOS1 O LOS1
57 TCLK0 I TCLK0
58 TPOS0 I TPOS0
59 TNEG0 I TNEG0
60 RCLK0 O RCLK0
61 RPOS0 O RPOS0
62 RNEG0 O RNEG0
63 - Note 2 HIZ0_B
64 LOS0 O LOS0
65 MUX I MUX
66 LOS3 O LOS3
67 RNEG3 O RNEG3
68 RPOS3 O RPOS3
69 RCLK3 O RCLK3
70 - Note 2 HIZ3_B
71 TNEG3 I TNEG3
72 TPOS3 I TPOS3
Pin
Name
Cell
Type
Bit
Symbol
DS485PP4 49

Table 11. Boundary Scan Register (Continued)
CS61884
BSR
Bit
73 TCLK3 I TCLK3
74 LOS2 O LOS2
75 RNEG2 O RNEG2
76 RPOS2 O RPOS2
77 RCLK2 O RCLK2
78 - Note 2 HIZ2_B
79 TNEG2 I TNEG2
80 TPOS2 I TPOS2
81 TCLK2 I TCLK2
82 INT_B O INT_B
83 RDY O RDYOUT
84 - Note 3 RDYOEN
85 WR_B I WR_B
86 RD_B I RD_B
87 ALE I ALE
88 CS_B I CS_B
89 CS_B I CS_B_TRI
90 INTL I INTL
91 CBLSEL I CBLSEL_TRI
92 CBLSEL I CBLSEL_IN
93 TCLK5 I TCLK5
94 TPOS5 I TPOS5
95 TNEG5 I TNEG5
96 RCLK5 O RCLK5
97 RPOS5 O RPOS5
98 RNEG5 O RNEG5
99 - Note 2 HIZ5_B
100 LOS5 O LOS5
101 TCLK4 I TCLK4
102 TPOS4 I TPOS4
103 TNEG4 I TNEG4
104 RCLK4 O RCLK4
105 RPOS4 O RPOS4
106 RNEG4 O RNEG4
107 - Note 2 HIZ4_B
108 LOS4 O LOS4
109 TXOE I TXOE
110 CLKE I CLKE
Notes:
1) LPOEN controls the LOOP[7:0] pins. Setting LPOEN to “1” configures LOOP[7:0] as outputs. The output value driven
on the pins are determined by the values written to LPO[7:0]. Setting LPOEN to “0” High-Z all the pins. In this mode,
the input values driven to these LOOP[7:0] can be read via LPI[7:0].
2) HIZ_B controls the RPOSx, RNEGx, and RCLKx pins. When HIZ_B is High, the outputs are enabled; when HIZ_B is
Low, the outputs are placed in a high impedance state (High-Z).
3) RDYOEN controls the ACK_B pin. Setting RDYOEN to “1” enables output on ACK_B. Setting ACKEN to “0” High Z the ACK_B pin.
Pin
Name
Cell
Type
Bit
Symbol
50 DS485PP4

18. APPLICATIONS
0.1
Note 1
+3.3V
µ
F
0.1
Note 1
CS61884
+
+
µ
F
68µF
Note 2
0.1
GNDIO
100
75
Cable
NC
120
Cable
Ω
Ω
Ω
RGND
+3.3V
µ
F
+3.3V
TGND
RV+
VCCIO
+
TV+
RTIP
RRING
0.1
µ
F
R1
RECEIVE
LINE
R2
T1 1:2
CS61884
One Channel
TRING
TRANSMIT
LINE
TTIP
T2 1:2
CBLSEL
13.3k
REF
Ω
GND
T1/J1 100Ω
Twisted P air
Component
R1 (Ω) 15 15 15
R2 (Ω) 15 15 15
Notes:1) Required Capacitor between each TV+, RV+, VCCIO and TGND, RGND, GNDIO respec-
tively.
2) Common decoupling capacitor for all TVCC and TGND pins.
Figure 17. Internal RX/TX Impedance Matching
DS485PP4 51
Cable
E1 75Ω
Coaxial
Cable
E1 120Ω
Twist e d P a ir
Cable

GNDIO
Ω
120
Cable
NC
100
Cable
0.1
75
µ
Ω
Ω
RGND
+3.3V
F
CS61884
+3.3V
+
0.1µF
Note 1
RV+
VCCIO
0.1µF
Note 1
TV+
RTIP
+
+
RRING
CS61884
TRING
One Channel
TTIP
CBLSEL
REF
TGND
1k
0.1
1k
13.3k
68µF
Note 2
Ω
µ
F
Ω
R1
RECEIVE
LINE
R2
T1 1:2
TRANSMIT
LINE
T2 1:2
Ω
GND
T1/J1 100Ω
Twisted P air
Component
R1 (Ω) 12.5 9.31 15
R2 (Ω) 12.5 9.31 15
Notes: 1)Required Capacitor between each TV+, RV+, VCCIO and TGND, RGND, GNDIO
Cable
E1 75Ω
Coaxial
Cable
E1 120Ω
Twist e d P a ir
GND
Cable
respectively.
2)Common decoupling capacitor for all TVCC and TGND pins.
Figure 18. Internal TX, External RX Impedance Matching
52 DS485PP4

CS61884
18.1 Transformer specifications
Recommended transformer specifications are
shown in Table 12. Any transformer used with the
CS61884 should meet or exceed these specifications.
Table 12. Transformer Specifications
Descriptions Specifications
Turns Ratio Receive/Transmit
Primary Inductance 1.5mH min. @ 772 kHz
Primary Leakage Inductance
Secondary leakage Inductance
Inter winding Capacitance 18pF max, primary to
ET-Constant 16V - µsmin.
0.3 µH max @ 772 kHz
0.4 µH max @ 772 kHz
1:2
secondary
18.2 Crystal Oscillator Specifications
When a reference clock signal is not available, a
CMOS crystal oscillator may be used as the reference clock signal. The oscillator must have a mini-
mum symmetry of 40-60% and minimum stability
100ppm for both E1 and T1/J1 applications.
of +
18.3 Designing for AT&T 62411
For information on requirements of the AT&T
62411 and the design of the appropriate system
synchronizer, refer to Application Note AN012
“AT&T 62411 Design Considerations - Jitter and
Synchronization” and Application Note AN011
“Jitter Testing Procedures for Compliance with
AT&T 62411”.
18.4 Line Protection
Secondary protection components can be added to
the line interface circuitry to provide lightning
surge and AC power-cross immunity. For additional information on the different electrical safety
standards and specific applications circuit recommendations, refer to Application Note AN034
“Secondary Line Protection for T1 and E1 Cards”.
DS485PP4 53

CS61884
19. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS
19.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
CAUTION: Operations at or beyond these limits may result in permanent damage to the device. Normal operation
is not guaranteed at these extremes.
Parameter Symbol Min. Max Units
DC Supply
(referenced to RGND = TGND = 0V)
DC Supply VCCIO -0.5 4.6 V
Input Voltage, Any Digital Pin except CBLSEL, MODE and
LOOP(n) pins (referenced to GNDIO = 0V)
Input Voltage CBLSEL, MODE & LOOP(n) Pins
(referenced to GNDIO = 0V)
Input voltage, RTIP and RRING Pins TGND -0.5 TV+ +0.5 V
ESD voltage, Any pin Note 1 2k - V
Input current, Any Pin Note 2 I
Maximum Power Dissipation, In package P
Ambient Operating Temperature T
Storage Temperature T
RV+
TV+
V
IH
V
IH
IH
p
A
stg
-
-
4.0
4.0
V
V
GNDIO -0.5 5.3 V
GNDIO -0.5 VCCIO +0.5 V
-10 +10 mA
-1.73W
-40 85 C
-65 150 C
19.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ Max Units
DC Supply RV+, TV+ 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
DC Supply VCCIO 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Ambient operating Temperature T
Power Consumption, T1/J1 Mode, 100 Ω line load Notes 3, 4, 5
Power Consumption, E1 Mode, 75 Ω line load Notes 3, 4, 5
Power Consumption, E1 Mode, 120 Ω line load Notes 3, 4, 5
Notes: 1. Human Body Model
2. Transient current of up to 100 mA will not cause SCR latch-up. Also TTIP, TRING, TV+ and TGND can
withstand a continuous current of 100 mA.
3. Power consumption while driving line load over the full operating temperature and power supply voltage
range. Includes all IC channels and loads. Digital inputs are within 10% of the supply rails and digital
outputs are driving a 50pF capacitive load.
4. Typical consumption corresponds to 50% ones density for E1/T1/J1 modes and medium line length
setting for T1/J1 mode at 3.3Volts.
5. Maximum consumption corresponds to 100% ones density for E1/T1/J1 modes and maximum line
length settings for T1/J1 mode at 3.465Volts.
6. This specification guarantees TTL compatibility (V
=2.4V@I
OH
7. Output drivers are TTL compatible.
8. Pulse amplitude measured at the output of the transformer across a 75 Ω load.
9. Pulse amplitude measured at the output of the transformer across a 120 Ω load.
10. Pulse amplitude measured at the output of the transformer across a 100 Ω load for all line length
settings.
A
-
-
-
-40 25 85 C
- 970 1900 mW
- 810 1400 mW
- 750 1300 mW
= -400 µA).
OUT
54 DS485PP4

19.3 Digital Characteristics
(TA = -40°Cto85°C; TV+, RV+ = 3.3 V ±5%; GND = 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ Max Units
CS61884
High-Level Input Voltage Note 6 V
Low-Level Input Voltage Note 6 V
LOOP[7:0] Low-Level Input Voltage V
LOOP[7:0] Mid-Level Input Voltage V
LOOP[7:0] High-Level Input Voltage V
High-Level Output Voltage Notes 6, 7
I
=-400µA
OUT
Low-Level Output Voltage Notes 6, 7
I
=1.6mA
OUT
V
V
IH
IL
IHL
IHM
IHH
OH
OL
2.0 - - V
--0.8V
- - 1/3 VCCIO-0.2 V
1/3 VCCIO +0.2 1/2 VCCIO 2/3 VCCIO-0.2 V
2/3 VCCIO +0.2 - - V
2.4 - - V
--0.4V
Input Leakage Current -10 - +10 µA
Input leakage for LOOP pins -150 - +150 µA
19.4 Transmitter Analog Characteristics
(TA = -40°Cto85°C; TV+, RV+ = 3.3 V ±5%; GND = 0 V)
Parameter Min. Ty p Max Units
Output Pulse Amplitudes E1 75Ω
Notes 8, 9, 10 E1 120Ω
T1/J1 100Ω
Ratio of Positive to Negative pulses T1/J1 100 Ω
Notes 8, 9, 10 E1, amplitude at center of pulse interval
E1, width at 50% of nominal amplitude
Pulse Amplitude of a space T1/J1 100 Ω
E1 120 Ω
E1 75 Ω
Power in 2 kHz band about 772 kHz
Notes 11, 12 (T1/J1 100 Ω only) 12.6 - - dBm
Power in 2 kHz band about 1.544 MHz Notes 11, 12
(referenced to power in 2 kHz band at 772 kHz, T1/J1 100 Ω only) -29 - - dBm
Transmit Return Loss - E1 51 kHz to 102 kHz
102 kH to 2048 kHz
Notes 11, 12, 13 2048 kHz to 3072 kHz
Transmit Return Loss - T1/J1 51 kHz to 102 kHz
102 kHz to 2048 kHz
Notes 11, 12, 13 2048 kHz to 3072 kHz
Jitter Added by the Transmitter 10 Hz - 8 kHz
8kHz-40kHz
Notes 11, 14 10 Hz - 40 kHz
Broad Band
Transmitter Short Circuit Current per channel - - 50 mA RMS
2.14
2.7
2.4
0.95
0.95
0.95
-0.15
-0.3
-0.237
-14
-14
-14
-14
-14
-14
-
-
-
-
2.37
3.0
3.0
-
-
-
-
-
-
-20
-19
-18
-19
-19
-18
0.010
0.009
0.007
0.015
2.6
3.3
3.6
1.05
1.05
1.05
0.15
0.3
0.237
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.020
0.025
0.025
0.050
V
V
V
V
V
V
dB
dB
UI
DS485PP4 55

CS61884
19.5 Receiver Analog Characteristics
(TA = -40°Cto85°C; TV+, RV+ = 3.3 V ±5%; GND = 0 V))
Parameter Min. Ty p Max Units
Allowable Cable Attenuation @ 1024kHz and 772kHz - - - 12 dB
RTIP/RRING Input Impedance T1/J1 100 Ω Load
(Internal Line matching mode) E1 120Ω Load
Note 11 E1 75Ω Load
RTIP/RRING Input Impedance T1/J1 100 Ω Load
(External Line matching mode) E1 120Ω Load
Note 11 E1 75Ω Load
Receiver Dynamic Range 0.5 - - Vp
Signal to Noise margin (Per G.703, O151 @ 6dB cable Atten). Note 11 --18- dB
Receiver Squelch Level - 150 - mV
LOS Threshold - 200 - mV
LOS Hysteresis - 50 - mV
Data Decision Threshold E1 Modes
Note 11
Data Decision Threshold T1/J1 Modes
Note 11
Input Jitter Tolerance - E1 1 Hz - 1.8 Hz
Notes 11, 15, 17 20 Hz - 2.4 kHz
18 kHz - 100 kHz
Input Jitter Tolerance - T1/J1 0.1 Hz - 1 Hz
Notes 11, 15, 17 4.9 Hz - 300 kHz
10kHz - 100 kHz
Input Return Loss - E1/T1/J1 51 kHz - 102 kHz
102 kHz - 2048 kHz
Notes 11, 12, 13 2048 kHz - 3072 kHz
-
-
-
-
-
-
41 50 59 % of
56 65 74 % of
18
1.5
0.2
138
28
0.4
-18
-18
-18
140
14k
50
14K
14k
14K
-
-
-
-
-
-
-28
-30
-27
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Ω
Ω
peak
peak
UI
UI
dB
Notes: 11. Parameters guaranteed by design and characterization.
12. Using components on the CDB61884 evaluation board in Internal Match Impedance Mode.
13. Return loss = 20log10 ABS((Z1 + Z0) / (Z1 - Z0)) where Z1 - impedance of the transmitter or receiver,
and Z0 = cable impedance.
14. Assuming that jitter free clock is input to TCLK.
15. Jitter tolerance for 0 dB for T1/J1 input signal levels and 6 dB for E1 input signal levels. Jitter tolerance
increases at lower frequencies. HDB3/B8ZS coders enabled.
16. In Data Recovery Mode.
17. Jitter Attenuator in the receive path.
56 DS485PP4

19.6 Jitter Attenuator Characteristics
(TA = -40°Cto85°C; TV+, RV+ = 3.3 V ±5%; GND = 0 V)
Parameter Min. Ty p Max Units
CS61884
Jitter Attenuator Corner Frequency T1/J1 Modes
Note 11, 19 T1/J1 Modes
E1 Modes
(Depends on JACF Bit in host mode) E1 Modes
E1 Jitter Attenuation 3 Hz to 40 Hz
Note 11, 18 400 Hz to 100 kHz
T1/J1 Jitter Attenuation 1 Hz to 20 Hz
1kHz
Note 11, 18 1.4KHz to 100KHz
Attenuator Input Jitter Tolerance before FIFO 32-bit FIFO
over flow and under flow Note 11 64-bit FIFO
Delay through Jitter Attenuator Only 32-bit FIFO
Note 11 64-bit FIFO
Intrinsic Jitter in Remote Loopback Notes 11, 17 --0.11UI
Notes: 18. Attenuation measured with sinusoidal input filter equal to 3/4 of measured jitter tolerance. Circuit
attenuates jitter at 20 dB/decade above the corner frequency. Output jitter can increase significantly
when more than 28 UI’s are input to the attenuator.
19. Measurement is not effected by the position of the Jitter Attenuator.
-
-
-
-
+0.5
- 19.5
0
- 33.3
-40
-
-
-
-
3.78
7.56
1.25
2.50
-
-
-
-
-
24
56
16
32
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Hz
dB
dB
UI
UI
UI
UI
DS485PP4 57

+10
+0.5
-6
-10
- 19.5
-20
CS61884
0
TYP. T1 @ 7.56Hz CF
ITU G.736
Attenuation in dB
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
110
AT&T 62411
Maximum Attenuation
2
Figure 19. Jitter Transfer Characteristic vs. G.736, TBR 12/13 & AT&T 62411
1000
300
138
100
28
18
10
TYP. E1 @ 2.5 Hz CF
100
57
Frequency in Hz
AT&T 62411
TYP. E1 @ 1.25 Hz CF
1K 10K
TYP. E1 Performance
AT&T 62411
Minimum Attenuation
TYP. T1 @ 3.78Hz CF
1.4K20 40040
TYP. T1 Performance
100K
1.5
1
PEAK TO PEAK JITTER (UI)
.4
.2
.1
110 1k100 100k1.8 4.9 20 300 10k2.4k 18k
ITU G.823
FREQUENCY IN Hz
Figure 20. Jitter Tolerance Characteristic vs. G.823 & AT&T 62411
58 DS485PP4

CS61884
19.7 Master Clock Switching Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ Max Units
MASTER CLOCK (MCLK)
Master Clock Frequency E1 Modes MCLK 2.048 MHz
Master Clock Frequency T1/J1 Modes MCLK 1.544 MHz
Master Clock Tolerance - -100 +100 ppm
Master Clock Duty Cycle - 40 50 60 %
19.8 Transmit Switching Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ Max Units
E1 TCLK Frequency 1/t
pw2
E1 TPOS/TNEG Pulse Width (RZ Mode) 236 244 252 nS
T1/J1 TCLK Frequency 1/t
pw2
TCLK Tolerance (NRZ Mode) -50 - 50 PPM
TCLK Duty Cycle t
pwh2/tpw2
TCLK Pulse Width 20 - - nS
TCLK Burst Rate Note 22 --20MHz
TPOS/TNEG to TCLK Falling Setup Time (NRZ Mode) t
TCLK Falling to TPOS/TNEG Hold time (NRZ Mode) t
su2
h2
TXOE Asserted Low to TX Driver HIGH-Z - - 1 µS
TCLK Held Low to Driver HIGH-Z Note 21 81220µS
- 2.048 - MHz
- 1.544 - MHz
--90%
25 - - nS
25 - - nS
19.9 Receive Switching Characteristics
* All parameters guaranteed by production, characterization or design.
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ Max Units
RCLK Duty Cycle 40 50 60 %
E1 RCLK Pulse Width 196 244 328 nS
E1 RPOS/RNEG Pulse Width (RZ Mode 200 244 300 nS
E1 RPOS/RNEG to RCLK rising setup time t
E1 RPOS/RNEG to RCLK hold time t
su
h
T1/J1 RCLK Pulse Width 259 324 388 nS
T1/J1 RPOS/RNEG Pulse Width (RZ Mode) 250 324 400 nS
T1/J1 POS/RNEG to RCLK rising setup time t
T1/J1 RPOS/RNEG to RCLK hold time t
su
h
RPOS/RNEG Output to RCLK Output (RZ Mode) - - 10 nS
Rise/Fall Time, RPOS, RNEG, RCLK, LOS outputs t
r,tf
Notes: 20. Output load capacitance = 50pF.
21. MCLK is not active.
22. Parameters guaranteed by design and characterization.
150 244 - nS
200 244 - nS
150 324 - nS
200 324 - nS
- - 85 nS
DS485PP4 59

RCLK
CS61884
RPOS/RNEG
CLKE = 1
RPOS/RNEG
CLKE = 0
Figure 21. Recovered Clock and Data Switching Characteristics
TCLK
t
t
pwh2
su
t
t
t
su
pw2
h
t
h
TPOS/TNEG
Figure 22. Transmit Clock and Data Switching Characteristics
Any Digital Output
t
su2
t
r
90%
t
90%
10%
Figure 23. Signal Rise and Fall Characteristics
h2
t
10%
f
60 DS485PP4

CS61884
19.10 Switching Characteristics - Serial Port
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ . Max Unit
SDI to SCLK Setup Time t
SCLK to SDI Hold Time t
SCLK Low Time t
SCLK High Time t
SCLK Rise and Fall Time t
to SCLK Setup Time t
CS
SCLK to CS
Inactive Time t
CS
Hold Time Note 23 t
SDO Valid to SCLK Note 23 t
to SDO High Z t
CS
dc
cdh
cl
ch
r,tf
cc
cch
cwh
cdv
cdz
Notes: 23. If SPOL = 0, then CS should return high no sooner than 20 ns after the 16thrising edge of SCLK during
a serial port read.
CS
-20-ns
-20-ns
-50-ns
-50-ns
-15-ns
-20-ns
-20-ns
-70-ns
-60-ns
-50-ns
SCLK
SDI
SDO
CLKE=0
SDO
CLKE=1
CS
SCLK
LAST ADDR BIT
t
t
cdv
cdv
D0
D0 D1
D1 D6 D7
D6
D7
t
cdz
HIGH Z
Figure 24. Serial Port Read Timing Diagram
t
cwh
t
t
cc
ch
t
dc
t
cl
t
cdh
t
cdh
t
cch
SDI
LSB LSB MSB
Figure 25. Serial Port Write Timing Diagram
DS485PP4 61

CS61884
19.11 Switching Characteristics - Parallel Port (Multiplexed Mode)
* All paramters guaranteed by production, characterization or design.
Parameter Ref. # Min. Typ. Max Unit
Pulse Width AS
Muxed Address Setup Time to AS
Muxed Address Hold Time 3 5 - - ns
Delay Time AS
&R/WSetupTimeBeforeWR,RDor DS Low 5 0 - - ns
CS
&R/WHold Time 6 0 - - ns
CS
Pulse Width, WR
Write Data Setup Time 8 30 - - ns
Write Data Hold Time 9 30 - - ns
Output Data Delay Time from RD
Read Data Hold Time 11 5 - - ns
Delay Time WR
or RD Low to RDY Low 13 - - 55 ns
WR
or RD Low to RDY High 14 - - 100 ns
WR
or RD High to RDY HIGH-Z 15 - - 40 ns
WR
Low to ACK High 16 - - 65 ns
DS
Low to ACK Low 17 - - 100 ns
DS
High to ACK HIGH-Z 18 - - 40 ns
DS
or ALE High 1 25 - - ns
or ALE Low 2 10 - - ns
or ALE to WR,RDor DS 45--ns
,RD,orDS 770- -ns
or DS Low 10 - - 100 ns
,RD,orDSto ALE or AS Rise 12 30 - - ns
62 DS485PP4

ALE
CS61884
1
WR
CS
D[7:0]
RDY
12 4
2
ADDRESS Write Data
HIGH-Z
5
3
7
6
8
14
13
9
15
Figure 26. Parallel Port Timing - Write; Intel Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode
1
HIGH-Z
ALE
RD
CS
D[7:0]
RDY
12 4
2
ADDRESS Read Data
HIGH-Z
5
3
7
6
10
14
13
11
15
HIGH-Z
Figure 27. Parallel Mode Port Timing - Read; Intel Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode
DS485PP4 63

AS
DS
R/W
CS
CS61884
1
12
4
5
7
6
D[7:0]
ACK
AS
DS
R/W
2
ADDRESS
HIGH-Z HIGH-Z
3
17
16
8
Write Data
9
18
Figure 28. Parallel Port Timing - Write in Motorola Multiplexed Address / Data Bus
1
12
4
5
7
6
CS
D[7:0]
ACK
2
ADDRESS
HIGH-Z HIGH-Z
3
10
Read Data
17
16
11
18
Figure 29. Parallel Port Timing - Read in Motorola Multiplexed Address / Data Bus
64 DS485PP4

CS61884
19.12 Switching Characteristics- Parallel Port (Non-multiplexed Mode)
* All paramters guaranteed by production, characterization or design.
Parameter Ref. # Min. Typ. Max Unit
Address Setup Time to WR
Address Hold Time 2 5 - - ns
&R/WSetupTimeBeforeWR,RDor DS Low 3 0 - - ns
CS
&R/WHold Time 4 0 - - ns
CS
Pulse Width, WR
Write Data Setup Time 6 30 - - ns
Write Data Hold Time 7 30 - - ns
Output Data Delay Time from RD
Read Data Hold Time 9 5 - - ns
or RD Low to RDY Low 10 - - 55 ns
WR
,RDor DS Low to RDY High 11 - - 100 ns
WR
,RDor DS High to RDY HIGH-Z 12 - - 40 ns
WR
Low to ACK High 13 - - 65 ns
DS
Low to ACK Low 14 - - 100 ns
DS
High to ACK HIGH-Z 15 - - 40 ns
DS
,RD,orDS 570- -ns
,RDor DS Low 1 10 - - ns
or DS 8 - - 100 ns
DS485PP4 65

CS61884
2
4
A[4:0]
ALE
WR
CS
D[7:0]
RDY
(pulled high)
HIGH-Z
1
ADDRESS
5
3
6
Write Data
11 12
10
7
Figure 30. Parallel Port Timing - Write in Intel Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode
HIGH-Z
2
4
12
A[4:0]
ALE
D[7:0]
RDY
RD
CS
(pulled high)
HIGH-Z
1
ADDRESS
5
3
8
Read Data
11
10
9
Figure 31. Parallel Port Timing - Read in Intel Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode
HIGH-Z
66 DS485PP4

CS61884
A[4:0]
DS
R/W
CS
D[7:0]
ACK
AS
1
(pulled high)
HIGH-Z
ADDRESS
5
3 4
6
Write Data
14
13
2
7
15
Figure 32. Parallel Port Timing - Write in Motorola Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode
HIGH-Z
A[4:0]
R/W
CS
D[7:0]
ACK
AS
DS
1
(pulled high)
HIGH-Z
ADDRESS
5
3 4
8
Read Data
14
13
2
9
15
Figure 33. Parallel Port Timing - Read in Motorola Non-Multiplexed Address / Data Bus Mode
HIGH-Z
DS485PP4 67

19.13 Switching Characteristics - JTAG
Parameter Symbol Min. Max Units
Cycle Time t
TMS/TDI to TCK Rising Setup Time t
TCK Rising to TMS/TDI Hold Time t
TCK Falling to TDO Valid t
t
cyc
TCK
cyc
su
h
dv
CS61884
200 - nS
50 - nS
50 - nS
-70nS
TMS
TDI
TDO
t
su
Figure 34. JTAG Switching Characteristics
t
h
t
dv
68 DS485PP4

20. COMPLIANT RECOMMENDATIONS AND SPECIFICATIONS
CS61884
AT&T Pub 62411
FCC Part 68
ANSI T1.102
ANSI T1.105
ANSI T1.231
ANSI T1.403
ANSI T1.408
Bell Core TR-TSY-000009
Bell Core GR-253-Core Sonet
Bell Core GR-499-Core
ETSI ETS 300-011
ETSI ETS 300-166
ETSI ETS 300-233
IEEE 1149.1
ETSI TBR 12/13
ITU-T I.431
ITU-T G.703
ITU-T G.704
ITU-T G.706
ITU-T G.732
ITU-T G.735
ITU-T G.736
ITU-T G.742
ITU-T G.772
ITU-T G.775
ITU-T G.783
ITU-T G.823
ITU-T O.151
OFTEL OTR-001
DS485PP4 69

21. FBGA PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
CS61884
70 DS485PP4

22. LQFP PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
144L LQFP PACKAGE DRAWING
D1
D
CS61884
E
E1
1
e
∝
L
DIM MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
A --- 0.55 0.063 --- 1.40 1.60
A1 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.05 0.10 0.15
B 0.007 0.008 0.011 0.17 0.20 0.27
D 0.854 0.866 BSC 0.878 21.70 22.0 BSC 22.30
D1 0.783 0.787 BSC 0.791 19.90 20.0 BSC 20.10
E 0.854 0.866 BSC 0.878 21.70 22.0 BSC 22.30
E1 0.783 0.787 BSC 0.791 19.90 20.0 BSC 20.10
e* 0.016 0.020 0.024 0.40 0.50 BSC 0.60
∝
L 0.018 0.024 0.030 0.45 0.60 0.75
* Nominal pin pitch is 0.50 mm
0.000° 4° 7.000° 0.00° 4° 7.00°
B
INCHES MILLIMETERS
A
A1
Controlling dimension is mm.
JEDEC Designation: MS022
DS485PP4 71

 Loading...
Loading...