Page 1
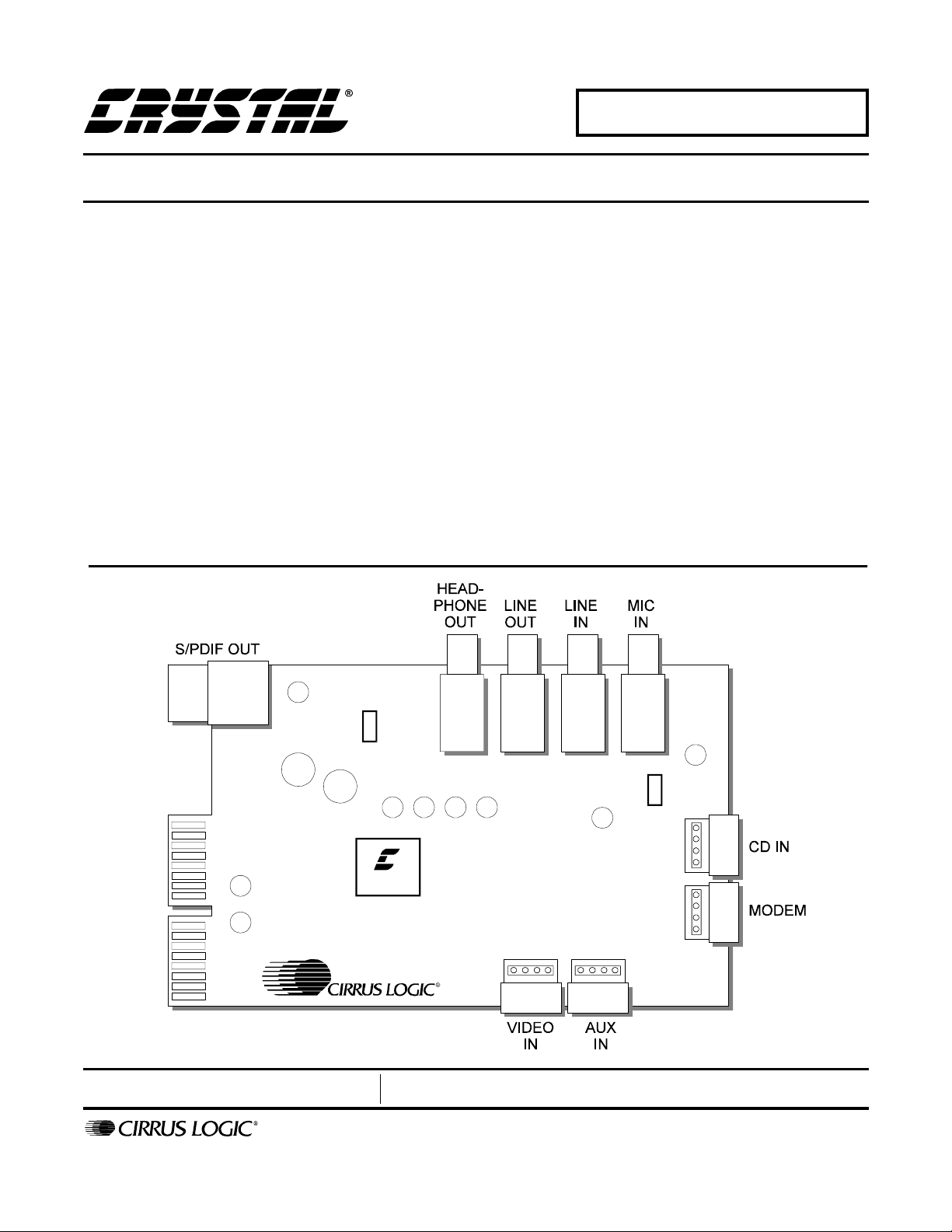
CRD4299-1 AMR
CrystalClear™ AC '97 AMR Reference Design
Features
l AMR Audio Codec add-in card designed to
meet the Intel® Audio/Modem Riser
Specification
l High quality, low cost, 2-layer, single sided
adapter board
l CS4299 Sound Fusion
l Complete suite of Analog and Digital I/O
connections:
- Line In, Line Out, Mic In, Modem Audio
connection, CD Audio In, Video In, Aux In,
Headphone Out and Optical Digital Out
l Meets or exceeds Microsoft’ s PC 97, PC 98,
and PC 99, both required and advanced,
audio performance requirements.
®
Audio Codec ’97
Description
The CRD4299-1 AMR add-in board reference design
showcases Cirrus Logic’s Crystal Audio AC ’97 CS4299
SoundFusion, and is Audio/Modem Riser Specification[2], compliant. The CRD4299-1 AMR card is 2.7"
high by 3.6" long.
The CRD4299-1 AMR reference de sign inc ludes a customer ready manufac turing kit. Include d in the kit are a
full set of schematic desi gn files (OrCAD
PCB job files (PADS
(Gerber) , bracket drawings, and bill of materials. The
design is production ready as is, or can be easily
modified to incorporate specific OEM changes. Documentation source files are available to assist the OEM to
quickly provide an accurate end user manual.
ORDERING INFO CRD4299-1 AMR
®
ASCII), PCB artwork files
®
7.2 format),
Preliminary Product Information
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7581
http://www.cirrus.com
CS4299
This document contains information for a new product.
Cirrus Logic reserves the right to modify this product without notice.
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 1999
(All Rights Reserved)
OCT ‘99
DS319RD1A1
1
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. GENERAL INFORMATION ............................................................................ 4
2. REFERENCE DESIGN FEATURES ............................................................... 4
2.1 Digital Audio Out .................................................................................. 4
2.2 CS4299 Audio Codec ‘97 ....................................................................4
2.2.1 Power Requirements .................................................................. 5
2.3 Analog I/O ............................................................................................ 5
2.4 Audio I/O .............................................................................................. 5
2.4.1 Line Out ......................................................................................5
2.4.2 Headphone Out .......................................................................... 5
2.4.3 Line In ........................................................................................ 5
2.4.4 Mic In ..........................................................................................5
2.4.5 CD Audio In ................................................................................ 6
2.4.6 Aux In ......................................................................................... 6
2.4.7 Video In ...................................................................................... 6
2.4.8 Modem Audio Connection ..........................................................6
3. SCHEMATIC DESCRIPTION ......................................................................... 7
3.1 Figure 11: Block Diagram ....................................................................7
3.2 Figure 12: AMR Bus Interface ............................................................. 7
3.3 Figure 13: Power Supply ..................................................................... 7
3.4 Figure 14: CS4299 AC ‘97 Audio Codec ............................................. 7
3.5 Figure 15: Analog Inputs ...................................................................... 7
3.6 Figure 16: Audio Outputs ..................................................................... 8
3.7 Figure 17: Microphone Pre-amp and Bias ...........................................8
3.8 Component Selection .......................................................................... 8
3.9 EMC Components ...............................................................................8
4. GROUNDING AND LAYOUT ......................................................................... 9
4.1 Partitioned Voltage and Ground Planes .............................................. 9
4.2 CS4299 Layout Notes .......................................................................... 9
5. AUDIO PERFORMANCE EVALUATION .....................................................10
5.1 Plots ................................................................................................... 10
6. REFERENCES ..............................................................................................17
7. ADDENDUM ................................................................................................. 17
8. BILL OF MATERIALS .................................................................................. 25
CRD4299-1 AMR
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/corporate/contacts/
CrystalClear is a trademark of Cirrus Logic, Inc.
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
OrCAD is a registered trademark of OrCAD, Inc.
SoundFusion is a registered trademark of Cirrus Logic, Inc.
Preliminary product inf o rmation describes products whi ch are i n p r od ucti on, b ut for which full characteriza t ion data is not yet available. Advance product information describes products which are in development and subject to development changes. Cirrus Logic, Inc. has made best efforts to ensure that the information
contained in this document i s accurat e and reli able. However , t he infor mation is subje ct to chang e without noti ce and is provi d ed “AS IS” without warrant y of
any kind (express or implied). No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus Logic, Inc. for the use of this information, nor for infringements of patents or other ri g ht s
of third parties. This document is the pro perty of Cirrus Logi c, Inc. and i mplie s no licen se under patents, copyrights, tr ademarks, or trade secre ts. No part of
this publication may be copied, reproduced , stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photographic, or
otherwise) without the pr i or writ ten consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. Ite ms f rom any Ci rrus L ogi c websi t e or disk may be printed for use by the user. However, no
part of the printout or electronic files may be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical,
photographic, or otherwise) without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc.Furthermore, no part of this publication may be used as a basis for manufacture
or sale of any items without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. The names of products of Cirrus Logic, Inc. or other vendors and suppliers appearing
in this document may be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners which may be registered in some jurisdictions. A list of Cirrus Logic, Inc. trademarks and service marks can be found at http://www.cirrus.com.
2 DS319RD1A1
Page 3

LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. Full Duplex (A-D-PC-D-A): Line In/Out Frequency Response ..................................... 10
Figure 2. Full Duplex (A-D-PC-D-A): Line In/Out Dynamic Range .............................................. 10
Figure 3. Full Duplex (A-D-PC-D-A): Line In/Out THD+N vs. Frequency ................................... 11
Figure 4. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out Frequency Response ................................................ 11
Figure 5. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out Dynamic Range ........................................................ 12
Figure 6. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out THD+N vs. Frequency .............................................. 12
Figure 7. Analog Mixer (A-A): Mic In/Line Out Frequency Response ......................................... 13
Figure 8. Analog Mixer (A-A): Mic In/Line Out Dynamic Range .................................................. 13
Figure 9. Analog Mixer (A-A): Mic In/Line Out THD+N vs. Frequency ........................................ 14
Figure 10. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out Crosstalk vs. Frequency ......................................... 14
Figure 11. Block Diagram ............................................................................................................. 16
Figure 12. AMR Bus ..................................................................................................................... 17
Figure 13. Power Supplies ........................................................................................................... 18
Figure 14. CS4299 ....................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 15. Audio In ....................................................................................................................... 20
Figure 16. Audio Out .................................................................................................................... 21
Figure 17. Mic Pre-Amp ............................................................................................................... 22
Figure 18. Assembly Drawing ...................................................................................................... 23
Figure 19. Top Layer .................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 20. Bottom Layer ............................................................................................................... 25
Figure 21. Bracket Drawing .......................................................................................................... 26
CRD4299-1 AMR
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. Reference Designators ..................................................................................................... 9
Table 2. Microphone Support Specifications................................................................................... 9
Table 3. Full Duplex Specifications................................................................................................. 9
Table 4. Analog Mixer, Line In to Line Out Specifications............................................................... 9
Table 5. Analog Mixer, Mic In to Line Out Specifications................................................................ 9
DS319RD1A1 3
Page 4

CRD4299-1 AMR
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
The CRD4299-1 AMR is a production-grade
AMR audio card reference design using the
CS4299 SoundFusion Audio Codec ‘97. The design supports the functionally compatible CS4299,
CS4297A, or CS4297 AC ‘97 SoundFusion Audio
Codecs.
The AMR board advantage lies in the complete
separation of the analog section from the noisy digital environment of a personal computer. A 5-wire
digital link is all that is required to connect the audio codec to the PCI bus-based AC ‘97 controller.
This allows the audio section to reach the required
dynamic range of ~90 dB FS A while making the
layout and placement of the audio section easier to
implement. The CS4299 performs the Digital-toAnalog Conversion (DAC) for the digital audio
output stream and also provides multiple analog
audio inputs and outputs, analog mixing and Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC).
dec. Digital out is provided through a Toshiba
TOTX173 optical TOS-LINK jack on the board
edge. There are many advantages in using a fiber
optic link versus the traditional coaxial link. Fiber
optic is a non-metallic insulator thereby preventing
ground loops and electromagnetic interference.
For signal transmission, it offers low attenuation,
high bandwidth, low propagation delay, low bit error rates, small size, and cost efficiency. The signal
is IEC 958 and CP-1201 compliant.
2.2 CS4299 Audio Codec ‘97
The CS4299 is a mixed-signal serial Codec based
on the AC ‘97 specification revision 2.1 [1]. It is
designed to be paired with a digital controller, located on the PCI bus. The AC ‘97 Controller is responsible for all communications between the
CS4299 and the rest of the system. The CS4299
functions as an analog mixer, a stereo ADC, a stereo DAC, and a control and digital audio stream interface to the AC ‘97 controller.
This card is designed to provide the highest possible functionality, along with industry leading audio
performance at a low manufacturing cost. Care was
taken with component placement and signal routing to minimize sources that can degrade audio performance. Cirrus’ analog design know-how has
resulted in a board that preserves the exceptional
analog performance of the CS4299.
2. REFERENCE DESIGN FEATURES
The CRD4299-1 AMR reference design illustrates
a high quality, low cost two-layer add-in card layout. The card is sectioned i nto three main part s: the
AMR bus section, the CS4299 Audio Codec ‘97
section, and the Analog I/O section.
2.1 Digital Audio Out
The AMR bus provides digital out in a format compatible with the consumer portion of IEC 958. An
older version of this standard is also known as
S/PDIF. Depending upon the codec, the SPDIF signal originates either from the AMR bus or the co-
The CS4299 contains two distinct functional sections: digital and analog. The digital section includes the AC-link registers, power management
support, SYNC detection circuitry, AC-link serial
port interface logic, and the 24.576 MHz crystal
master clock. The analog section includes the analog input multiplexer (mux), stereo input mixer,
stereo output mixer, mono output mixer, stereo
ADC, stereo DAC, and analog volume controls.
For more information refer to the CS4299
Datasheet [3]. The capacitors required for the
CS4299 and their placement are discussed in the
CS4299 Datasheet [3]. Refer to the Grounding and
Layout section of the data sheet for the recommended routing of the audio section.
2.2.1 Power Requirements
The CS4299 requires both a digital +3.3 V and an
analog +5 V supply. The digital power is supplied
from the AMR bus. A voltage regulator is recommended for the analog supply. A Motorola
4 DS319RD1A1
Page 5

CRD4299-1 AMR
MC78L05 regulates the AMR +12 V supply down
to provide a clean +5 V analog supply for the
CS4299. The MC78L05 regulator can provide adequate current, which is enough for the CS4299 and
associated analog circuitry.
2.3 Analog I/O
The CS4299 has many analog inputs and outputs
that may or may not be used depending on the sys-
tem’s application. Unused inputs should be tied to
Vrefout (pin 28) or AC coupled via a 0.1 µF capacitor to the analog ground plane. The analog section
contains the components for a headphone amplifier. The Modem Audio, CD In, Audio In, and Aux
In headers are also part of the Analog I/O secti on.
The header and its associated components may or
may not be necessary depending on the audio inputs implemented.
2.4 Audio I/O
A full feature set of the CS4299’s analog I/O and
digital out is represented on the reference design
card through internal and external connectors:
•Line Out
• Headphone Out
•Line In
•Mic In
• CD Audio In
put voltage of 1 Vrms. The Line Out connection is
made via an external 1/8" jack.
• Maximum output level: 1 Vrms
2.4.2 Headphone Out
An external 1/8" jack is provided for a headphone
connection. This output is driven by an amplifier
for low impedance loads such as 32 Ω headphones.
• Maximum output level: 2.0 Vrms (no load);
1.5 Vrms (32 Ω load)
• Maximum output power: 70 mW/channel
(32 Ω load)
2.4.3 Line In
The Line In 1/8" jack provides an input to the Line
In pins of the CS4299.
• Maximum input level: 2 Vrms
2.4.4 Mic In
The Microphone In 1/8" jack provides an input to a
microphone pre-amplifier circuit that applies 18 dB
of gain to the signal.
• Maximum input level:
- Microphone Boost enabled: 12.5 mVrms
- Microphone Boost disabled: 125 mVrms
• Supports 3-pin electret (power on ring) and 2pin dynamic microphones
• Aux In
•Video In
• Modem Audio connection
• Optical Digital Out
Four external 1/8" jacks, one external TOS-LINK
jack, and four internal header connections are used
for analog and digital inputs and outputs.
2.4.1 Line Out
The output of the CS4299 is capable of driving impedances greater than 10 kΩ with a maximum out-
DS319RD1A1 5
2.4.5 CD Audio In
The CD Audio input provides a 4-pin (0.1 inch center) right-angled connector that is compatible with
the SONY standards and ATAPI.
• Maximum input level: 2 Vrms
• Pseudo differential input using the CD Common pin as the ground
• 0.1 inch connector wired as:
- Pin 1 : Left Channel
- Pin 2 : Common return
Page 6

CRD4299-1 AMR
- Pin 3 : Common return
- Pin 4 : Right Channel
2.4.6 Aux In
• Internal 4-pin (0.1 inch center) right-angled
connector
•Wired as:
- Pin 1 : Left Channel
- Pin 2 : Analog Ground
- Pin 3 : Analog Ground
- Pin 4 : Right Channel
• Maximum input level: 2 Vrms
2.4.7 Video In
• Internal 4-pin (0.1 inch center) right-angled
connector
- Pin 1 : Left Channel
- Pin 2 : Analog Ground
- Pin 3 : Analog Ground
- Pin 4 : Right Channel
• Maximum input level: 2 Vrms
2.4.8 Modem Audio Connection
The modem audio connection can be made through
the internal 4-pin (0.1 inch center) right-angled
connector. This connector carries both a mono input and a mono output.
• Internal 4 pin header (0.1 inch center)
- Pin 1 : Mono Out (to modem)
- Pin 2 : Analog Ground
- Pin 3 : Analog Ground
- Pin 4 : Phone In (from modem)
• Maximum input level: 1 Vrms
• Maximum output level: 1 Vrms
• Minimum load impedance: 10 kΩ
3. SCHEMATIC DESCRIPTION
Figures 11 through 17 show the schematics for the
CRD4299-1 AMR card. This section will describe
particular pages of the schematic that need to be
discussed.
3.1 Figure 11: Block Diagram
The block diagram is an interconnection overview
between schematic pages.
3.2 Figure 12: AMR Bus Interface
The +5 V power pin is decoupled through C1 and
supplies power for the SPDIF_OUT circuit. All
ground pins are tied to digital ground except for B2,
which is tied to analog ground.
The AC-link, which consists of ASDOUT, ARST#,
ASYNC, ASDIN, and ABITCLK, transfers digital
audio data between the audio codec and the host.
PC_BEEP_BUS routes the beep/speaker signal
from the motherboard to the audio subsystem, for
use in hearing POST codes (refer to the Intel Au-
dio/Modem Riser Specification [2]).
The PRIMARY_DN# signal indicates the presence
or the absence of a primary codec on the motherboard. The MSTRCLK is the 24.576 MHz master
clock for the AC ‘97 link. Populate R51 when the
Codec is the primary codec. Populate R50 when the
Codec is the secondary codec.
The CS4297 does not support S/PDIF. Iin this case,
R3 should be populated so the S/PDIF signal originates from the AMR bus. For a CS4297A/99, by
populating R2 instead of R3, the S/PDIF signal
originates from the codec, bypassing the AMR bus.
3.3 Figure 13: Power Supply
The CS4299 requires both a digital +3.3 V and an
analog +5 V supply. The digital power is supplied
from the AMR bus. A separate regulator is recommended for the analog voltage supply to provide
good audio signal quality. A Motorola MC78L05
regulates the +12 V supply from the AMR bus
6 DS319RD1A1
Page 7

CRD4299-1 AMR
down to a clean +5 V analog supply. Two packaging options are supported, where U5 is an SO8 surface mount package and U4 is a TO-92 pin-in-hole
package. The -12 V power pin is decoupled
through C73/C74, and supplies power to the headphone circuit.
3.4 Figure 14: CS4299 AC ‘97 Audio Codec
For the best audio performance, the analog voltage
regulator, an MC78L05, is located near the
CS4299. A 10 µ F electrolytic capacitor should be
added next to pins 25 and 26 if the capacitor connected to the output of the power regulator is located far away from the CS4299. All filtering
capacitors of audio signals are NPO-type to ensure
minimal added distortion. Two footprints are provided for the crystal: a CA-301 pin-in-hole footprint, Y1, for miniature crystal; and a short height
HC-49S package, Y2. R47 is a termination resistor
in the serial AC-link between the CS4299 and the
AMR bus.
common return path for both the left and right
channels. Therefore, the input impedance of this
block is half of that of the other inputs.
The modem connection is both a mono input and
output. The output is fed from the CS4299’s
MONO_OUT pin through a divider made of
R22/23. The divider ratio is preset to 0 dB for an
output voltage of 1 Vrms. If a lower output voltage
is desired, the resistors can be replaced with appropriate values, as long as the total load on the output
is kept greater than 10 kΩ. The input is not divided
to accommodate line level sources up to 1 Vrms.
3.6 Figure 16: Audio Outputs
The line out is driven directly by the CS4299. The
headphone out amplifier, a Motorola MC1458, is
capable of driving stereo headphones with impedances greater than 32 Ω or powered speakers.
R37/38 are added for short-circuit protection. An
optical S/PDIF (IEC 958 consumer) output is also
supported.
3.5 Figure 15: Analog Inputs
The inputs for AUX, VIDEO, CD, and LINE are
passed through voltage dividers that reduce the levels by 6 dB to allow connection of line level sources up to 2 Vrms. The 220 pF capacitors are
provided on Line_In, Mic_In, CD_In, Aux_In,
Video_In, and Internal Modem connection for
EMC suppression. These may be removed if EMC
testing determines they are not required. 1 µF ACcoupling capacitors are used on the Line_In,
Mic_In, CD_In, Aux_In, Video_In, and Internal
Modem circuit to minimize the low frequency rolloff. The internal CD audio connection utilizes a
pseudo-differential interface with CD_GND as the
3.7 Figure 17: Microphone Pre-amp and Bias
A Motorola MC33078D low noise dual op-amp
provides an +18 dB gain stage f or the microphone
and buffers the phantom power supply for the mic.
The phantom power is derived from the +5 V analog supply and buffered by U1A to provide a maximum of 4.2 V with no load and a minimum of
2.0 V under a 0.8 mA load on the ring. Hardware
rolloffs were implemented at 60 kHz and 15 kHz as
recommended by the PC 99 System Design Guide,
Chapter 17, Audio Components [5].
DS319RD1A1 7
Page 8

CRD4299-1 AMR
3.8 Component Selection
Great attention was given to the particular components on the CRD4299-1 AMR board with cost,
performance, and package selection as the most important factors. Listed are some of the guidelines
used in the selection of components:
• No components smaller than 0805 package
• Use single package components, no resistor
packs
• Right-angled headers for all internal connections to provide sufficient headroom for the
jacks
• Dual footprint for XTAL. HC-49S, and small
circular CA-301 pin-in-hole package
• Dual footprint for +5 V regulator. Surface
mount and pin-in-hole package are supported.
3.9 EMC Components
A number of capacitors and inductors are included
to help the board meet EMC compliance tests, such
as FCC Part 15. Modifying this selection of components without EMC testing could cause EMC compliance failure.
4. GROUNDING AND LAYOUT
onto these pins. All data converters are highly susceptible to noise on the crystal pins.
A separate chassis ground provides a reference
plane for all of the EMC components. The chassis
ground plane is connected to the analog ground
plane at the external jacks.
4.2 CS4299 Layout Notes
Please refer to the CS4299 Datasheet [3] on how
the area under the chip should be partitioned and
how the bypass capacitors should be placed. Pay
close attention to the suggestions for the bypass capacitors on REFFLT, AFLT1, AFLT2, and the
power supply capacitors. The pinout of the CS4299
is designed to keep digital and analog signals from
crossing when laying out the board.
5. AUDIO PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
In the below reference designators, the letters in parenthesis designate the full-scale value for that particular I/O.These reference designators are used in
the following tables to help clarify which full-scale
value applies to the particular measurement. Values referenced to digital numbers on the PC are listed with the (d) suffix.
4.1 Partitioned Voltage and Ground Planes
The pinout of the CS4299 allows the ground split to
completely separate digital signals on one side and
analog signals on the other. This split is located
very close to the CS4299 so analog and digital
ground return currents originating from the
CS4299 may flow through their respective ground
planes. A bridge is made across the split to maintain the proper reference potential for each ground
plane.
The area around the crystal oscillator and the two
XTAL signals is filled with copper on the top and
bottom sides and attached to digital ground. This
ground plane serves to keep noise from coupling
8 DS319RD1A1
5.1 Plots
In the following plots, stereo measurements have
two sets of data per plot and two vertical axes.
Above each vertical axis is a label indicating a
channel that relates to that axis. The data set extends beyond the vertical axis to indicate its association with that axis. Using Figure 1 as an example,
the top set of data extends beyond the right vertical
axis, which is labeled at the top “RIGHT’, indicating that the top set of data is the right channel and
associated with the right vertical axis. Likewise,
the bottom set of data extends beyond the left vertical axis which is labeled at the top “LEFT”, indicating that the bottom set of data is the left channel
and associated with the left vertical axis.
Page 9
CRD4299-1 AMR
Signal Name Connector Maximum Voltage Reference
Line In (A-D-PC-D-A) Jack 2.376 V
Line In (A-A) Jack 2.142 V
Mic In Jack 0.128 V
Line Out Jack 1.021 V
RMS
RMS
RMS
RMS
Designator
0 dB FS (li)
0 dB FS (li)
0 dB FS (mi)
0 dB FS (lo) N/A
Imp.
(k
Table 1. Reference Designators
Microphones Supported Support Comments
3-Pin Phantom Power (power on ring) Yes
2-Pin Dynamic Yes
2-Pin Phantom Power (power on tip)
Table 2. Microphone Support Specifications
Full Duplex (A-D-PC-D-A):
Line In to Line Out Reference Left Right Units Figures
Dynamic Range -91.4 -91.4 dB FS A (lo) 99 - 1NXL
THD+N -3 dB FS (li) -85.2 -85.2 dB FS (lo) 99 - 1DXL
Frequency Response Ac = -0.4 dB 20-20k 20-20k Hz 99 - 1MXL
NOTE: TM004: combined test used in lieu of TM002 and TM003
Ω)
Table 3. Full Duplex Specifications
Analog Mixer (A-A):
Line In to Line Out Reference Left Right Units Figures
Dynamic Range -95.8 -95.7 dB FS A (lo) 99 - 1NAL
THD+N -3 dB FS (li) -92.9 -92.9 dB FS (lo) 99 - 1DAL
Frequency Response Ac = +-0.2 dB 20-20k 20-20k Hz 99 - 1MAL
Crosstalk f = 10 kHz -66.8 -66.5 dB FS (lo) 99 - 1CAL
Table 4. Analog Mixer, Line In to Line Out Specifications
Analog Mixer (A-A):
Mic In to Line Out Reference Left Right Units Figures
Dynamic Range Gain = 0 dB -94.1 N/A dB FS A (lo) 99 - 1NAM
THD+N -3 dB FS (mi) -91.3 N/A dB FS (lo) 99 - 1DAM
Frequency Response Ac = -3 dB 50-15k N/A Hz 99 - 1MAM
NOTE: Mic In is Mono
Table 5. Analog Mixer, Mic In to Line Out Specifications
DS319RD1A1 9
Page 10

CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
CRD4299-1 AMR
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
Amplitude (dB)
-4
-5
-6
-7
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1MXL.ADXLEFT RIGHT
Frequency (Hz)
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
Figure 1. Full Duplex (A-D-PC-D-A): Line In/Out Frequency Response
Amplitude (dB)
CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
Dynamic Range (dB FS A)
-100
-105
-110
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1NXL.ADXLEFT RIGHT
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 2. Full Duplex (A-D-PC-D-A): Line In/Out Dynamic Range
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
-100
Dynamic Range (dB FS A)
10 DS319RD1A1
Page 11

CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
CRD4299-1 AMR
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
THD+N (dB FS)
-95
-100
-105
-110
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1DXL.ADXLEFT RIGHT
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 3. Full Duplex (A-D-PC-D-A): Line In/Out THD+N vs. Frequency
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
-100
THD+N (dB FS)
CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
Amplitude (dB)
-4
-5
-6
-7
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1MAL.ADXLEFT RIGHT
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 4. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out Frequency Response
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Amplitude (dB)
-1
-2
-3
-4
DS319RD1A1 11
Page 12

CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
CRD4299-1 AMR
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
Dynamic Range (dB FS A)
-100
-105
-110
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1NAL.ADXLEFT RIGHT
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 5. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out Dynamic Range
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
Dynamic Range (dB FS A)
-90
-95
-100
CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
THD+N (dB FS)
-95
-100
-105
-110
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1DAL.ADXLEFT RIGHT
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 6. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out THD+N vs. Frequency
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
-100
THD+N (dB FS)
12 DS319RD1A1
Page 13

CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
CRD4299-1 AMR
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
Amplitude (dB)
-4
-5
-6
-7
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1MAM.ADX
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 7. Analog Mixer (A- A): Mic In/Line Out Frequency Response
CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
Dynamic Range (dB FS A)
-100
-105
-110
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1NAM.ADX
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 8. Analog Mixer (A-A): Mic In/Line Out Dynamic Range
DS319RD1A1 13
Page 14

CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
CRD4299-1 AMR
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
THD+N (dB FS)
-95
-100
-105
-110
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1DAM.ADX
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 9. Analog Mixer (A-A): Mic In/Line Out THD+N vs. Frequency
CwGRAPH 0.65 CrystalWare(tm)
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
-100
Crosstalk (dB)
-105
-110
-115
-120
20 100 1 k 10 k 20 k
CRD429~1\99-1CAL.ADXLEFT RIGHT
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 10. Analog Mixer (A-A): Line In/Out Crosstalk vs. Frequency
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
-100
-105
-110
Crosstalk (dB)
14 DS319RD1A1
Page 15

CRD4299-1 AMR
6. REFERENCES
1) Intel, Audio Codec ‘97 Component Specification, Revision 2.1, http://developer.intel.com/pc-
supp/platform/ac97/
2) Intel, Audio/Modem Riser Specification, Revision 1.01, Sep 10, 1998.
http://developer.intel.com/pc-supp/platform/ac97/INDEX.HTM
3) Cirrus Logic, CS4299 SoundFusion Audio Codec ‘97 Data Sheet, July 1998.
http://www.cirrus.com/products/overviews/
cs4299.html
4) Steve Harris, Clif Sanchez, Personal Computer Audio Quality Measurements, Ver 1.0
http://www.cirrus.com/products/papers/
meas/meas.html
5) Intel and Microsoft, PC 99 System Design Guide
http://www.microsoft.com/hwdev/desguid/
6) M. Montrose. Printed Circuit Board Design Techniques for EMC Compliance, IEEE Press, New York:
1996.
DS319RD1A1 15
Page 16

16 DS319RD1A1
7. SCHEMATIC, LAYOUT, AND BRACKET DRAWINGS
AMR_BUS
PC_BEEP_BUS SPDIF_OUT
AUDIO_IN
PC_BEEP
PC-BEEP-BUS
CD_INL
CD_COM
CD_INR
LINE_IN_L
AUX_INL
AUX_INR
VIDEO_L
VIDEO_R
PHONE_IN
MONO_OUT
PC_BEEP
CD_INL
CD_COM
CD_INR
LINE_IN_L
LINE_IN_R
AUX_INL
AUX_INR
VIDEO_L
VIDEO_R
PHONE_IN
MONO_OUT
PC_BEEP_BUS
CS4299
PC_BEEP
CD_INL
CD_COM
CD_INR
LINE_IN_L
LINE_IN_R
AUX_INL
AUX_INR
VIDEO_L
VIDEO_R
PHONE_IN
MONO_OUT
ARST#
ASYNC
PRIMARY_DN#
MSTRCLK
MSTRCL
ARST#
ARST#
ASYNC
MSTRCLK
PRIMARY_DN#
MIC1
ABITCLK
ASDIN
ASDOUT
ABITCLK
ASDIN
ABITCLK
S/PDIF_OUT
ASDOUT
S/PDIF_CODEC
SPDIF_CODEC
ASDOUT
S/PDIF_CODEC
LINE_OUT_R
LINE_OUT_L
ALT_LINE_OUT_L
ALT_LINE_OUT_R
LINE_OUT_R
LINE_OUT_L
ALT_LINE_OUT_L
ALT_LINE_OUT_R
AUDIO_OUT
LINE_OUT_R
LINE_OUT_L
ALT_LINE_OUT_L
ALT_LINE_OUT_R
CRD4299-1 AMR
POWER
MIC1
AUDIO_MICIN
Figure 11. Block Diagram
Page 17

DS319RD1A1 17
y
y
AGND
+3.3VD
PC_BEEP_BUS
PRIMARY_DN#
+5VD
+12VD
ASDOUT
ARST#
MSTRCLK
-12VD
AMR BUS
P1
B1
AUDIO_MUTE#
B2
GND
B3
MONO_OUT/PC_BEEP
B4
RSVD
B5
RSVD
B6
PRIMARY_DN#
B7
-12V
B8
GND
B9
+12V
B10
GND
B11
+5VD
KEY
KEY KEY
B12
GND
B13
RSVD
B14
RSVD
B15
+3.3VD
B16
GND
B17
AC97_SDATA_OUT
B18
AC97_RESET#
B19
AC97_SDATA_IN3
B20
GND
B21
AC97_SDATA_IN2
B22
GND
B23
AC97_MSTRCLK
AUDIO_PWRDN
MONO_PHONE
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
GND
+5Vdual/+5VSB
USB_OC#
GND
USB+
USB-
KEY
GND
S/PDIF_IN
GND
+3.3Vdual/+3.3VSB
GND
AC97_SYNC
GND
AC97_SDATA_IN1
GND
AC97_SDATA_IN0
GND
AC97_BITCLK
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
A21
A22
A23
R3 0
populate R3 for
CS4297 board
ASYNC
R50 47
R51 47
ABITCLK
+3.3VD
R2 0
populate R2 for
CS4299 board
ASDIN
+
HOLE
M1
1
CGND
DGND
C2
0.1uF
Z5U
populate R51 if
primar
codec.
populate R50 if
secondar
codec.
+5VD
C3
10uF
ELEC
DGND
HOLE
TOOLHOLE
M2
1
S/PDIF_CODEC
S/PDIF_OUT
+
C1
10uF
ELEC
M3
CRD4299-1 AMR
AMR CONNECTOR
DGND DGND
Figure 12. AMR Bus
Page 18

18 DS319RD1A1
POWER SUPPLIES
Do not populate U5
+12VA
+12VD
L2
31@100MHz
Connect AGND to DGND with a 50 mil trace near the 4297
Co n nect CGND to DGND with a 50 mil trace near the finger
edge of the board.
+
C70
100uF
ELEC
U5
5 4
NC2 NC1
7
GND4
3
IN
C71
0.1uF
Z5U
GND2GND3
GND1
VOUTVIN
GND
2
AGND
MC78L05ACD
36
2
18
1
OUT
U4
MC78L05
SURFACE MOUNT
POPULATION
-12VD
-12VA
OPTION
AGNDAGND
+5VA
PIN IN HOLE
L1
31@100MHz
+
C73
100uF
ELEC
C74
0.1uF
Z5U
POPULATION
OPTION
+
C72
10uF
ELEC
AGND
CRD4299-1 AMR
Figure 13. Power Supplies
Page 19

DS319RD1A1 19
Do not popu
late
C62 and C63 for
CS42
97.
Do not popul
ate
R45
layout Y1 on
top of Y2 --
populate only o
ne XTAL
Do not popul
ate
R48
MONO_OUT
ALT_LINE_OUT_L
LINE_OUT_R
LINE_OUT_L
UT_R
AGN
D
+5VA
AGND
+5VA
DGND
AGNDAGNDAGND
+3.3VDDGNDAGND+3.3VDDGNDDGN
D
C681000pF
NP
O
R480C54
0.1uF
Z5U
R4747
C691000pF
NP
O
C670.1uF
Z5U
C63
0.01uFX7
R
C520.1uF
Z5UC51
0.1uF
Z5U
C62
1000pF
NPO
C530.1uF
Z5U
C65
0.1uF
Z5U
U3
CS
4299
36
37
383944414243403433323112
34567810911121314151617
181920
21
22
2324252627
28
29
30
4847464535
LINE_OUT_R
MONO_OUT
AVdd2
ALT_LINE_OUT_L
nc7
ALT_LINE_OUT_R
AVss2
nc6
nc5
FLTO
FLTI
FLT3D
BCFG
DVdd1
XTL_IN
XTL_OUT
DVss1
SDATA_OUT
BIT_CLK
DVss2
SDATA_IN
SYNC
DVdd2
RESET#
PC_BEEP
PHONE
AUX_L
AUX_R
VIDEO_L
VIDEO_R
CD_L
CD_GND
CD_R
MIC1
MIC2
LINE_IN_L
LINE_IN_R
AVdd1
AVss1
REFFLT
Vrefout
AFLT1
AFLT2
S/PDIF_OUT
EAPD
ID1#
ID0#
LINE_OUT_L
C551000pF
NP
O
C561000pF
NP
O
C571000pF
NP
O
C581000pF
NP
O
C591000pF
NPOC641u
F
X7R
C66
1uF
X7
RY224.
576 MHz
C6022pFNPOY124.
576 MHz
R450C6122pF
NPO
ABI
TCLK
LINE_IN_L
VIDEO_R
PC_BEEP
LINE_
OUT_L
ALT_LINE_OUT_L
AUX
_INL
PHONE_IN
AS
DOUT
VIDEO
_L
MONO_OU
T
MIC1
CD_INL
LINE_OUT
_R
ASYNC
S/PDIF_CODEC
LINE_IN_R
PRIMARY_DN#
ASDIN
CD_COM
ARST#CD_INR
AUX_IN
R
ALT_
LINE_OUT_R
MSTRCLK
CRD4299-1 AMR
Figure 14. CS4299
Page 20

20 DS319RD1A1
VID
C24
220pF
C11
220pF
LINE IN
J4
PHONO-1/8
AUX IN
J3
R
GND
GND
L
4X1HDR-AU
J2
R
GND
GND
L
4X1HDR-AU
4
3
5
2
1
4
3
2
1
AGND
EO IN
4
3
2
1
AGND
AGND
C23
220pF
C10
220pF
C21
220pF
AGND
AGND
CGND
C22
220pF
AGND
AGND
AGND
R16 6.8K
R17 6.8K
R20 6.8K
R21 6.8K
R14 6.8K
R15 6.8K
R18 6.8K
R19 6.8K
R5 6.8K
R6 6.8K
R10 6.8K
R11 6.8K
C15 1uF
X7R
C25 1uF
X7R
C14 1uF
X7R
C20 1uF
X7R
C5 1uF
X7R
C9 1uF
X7R
LINE_IN_R
LINE_IN_L
AUX_INR
AUX_INL
VIDEO_R
VIDEO_L
CD IN
J1
4
R
L
4X1HDR-AU
3
2
1
C16
C17
220pF
220pF
AGND
GND
GND
PC SPEAKER IN
PC-BEEP-BUS
L3
31@100MHz
C18
220pF
R53 47K
R4 6.8K
R7 6.8K
AGND
R8 6.8K
R9 6.8K
AGND
R12 3.4K
R13 3.4K
AGND
+5VA
R52
Do not
populate R52
4.7K
R31
4.7K
AGND AGND
Z5U
C26 0.1uF
C75
2700pF
X7R
C4 1uF
X7R
C8 1uF
X7R
C13 1uF
X7R
CD_INR
CD_INL
CD_COM
PC_BEEP
INTERNAL MODEM CONNECTION
J5
GND
GND
4X1HDR-AU
4
R23
47K
R22 0
R24
47K
3
2
1
C12
220pF
C19
220pF
AGND AGNDAGND AGND
PHONE IN
MONO OUT
X7R
C28 1uF
C29 1uF
X7R
PHONE_IN
MONO_OUT
Connect CGND to AGND at the jack
Figure 15. Audio In
CRD4299-1 AMR
Page 21

DS319RD1A1 21
+5VA
place close to
pins 8 and 4
J6
PHONO-1/8
4
3
5
2
1
Connect CGND
to the jack
AGND
+5VA
C30
0.1uF
Z5U
AGND
R32 2.7K
C35
220pF
CGND
C36
220pF
AGND
+
C37
10uF
ELEC
R26
68K
R28
100K
AGND
R33 6.8K
1
+5VA
+
-
AGND
C33
X7R
0.068 uF
U1A
MC33078D
3
2
R29
47K
+
C31
10uF
ELEC
AGND
+5VA
5
+
6
-
AGND
C38 220pF
R34 47K
R25
47K
R27
47K
AGND
U1B
MC33078D
7
C34 1uF
X7R
MIC1
CRD4299-1 AMR
Figure 16. Audio Out
Page 22

22 DS319RD1A1
NPO
C41 22pF
R36 56K
-12VA
ALT_LINE_OUT_R
ALT_LINE_OUT_L
LINE_OUT_R
LINE_OUT_L
C40 10uF
+
ELEC
C42 10uF
+
ELEC
C46 10uF
+
ELEC
C47 10uF
+
ELEC
R35 27K
R39 27K
AGND
AGND
R43
100K
AGND
-
2
+
3
+12VA
8 4
NPO
C43 22pF
R40 56K
-12VA
-
6
+
5
+12VA
8 4
R44
100K
1
MC 1458
7
MC 1458
U2A
U2B
C48
220pF
CGND
R37 10
1/4W
R38 10
1/4W
C49
220pF
C44
220pF
AGND
CGND
4
3
5
2
1
4
3
5
2
C45
J9
PHONO-1/8
Connect CGND to
AGND at the
jack
1
220pF
AGND
J7
PHONO-1/8
HEADPHONE JACK
Connect CGND to
AGND at the
jack
LINE OUT
JACK
SPDIF_OUT
+5VD
C50
0.1uF
Z5U
DGND
Digital Output
8.2K
R49
J10
4
3
2
1
TOTX -173
5
DGND
6
DGND
CRD4299-1 AMR
Figure 17. Mic Pre-Amp
Page 23

DS319RD1A1 23
Figure 18. Assembly Drawing
CRD4299-1 AMR
Page 24

24 DS319RD1A1
Figure 19. Top Layer
CRD4299-1 AMR
Page 25
DS319RD1A1 25
Figure 20. Bottom Layer
CRD4299-1 AMR
Page 26

26 DS319RD1A1
Figure 21. Bracket Drawing
CRD4299-1 AMR
Page 27

DS319RD1A1 27
8. BILL OF MATERIALS
CRD4299-AMR
Item Qty Reference Value Type PCB Footpri nt Mnfr Part Number Description
1 9 C1,C3,C31,C37,C40,C42,
C46,C47,C72
2 12 C2,C26,C30,C50,C51,C52,
C53,C54,C65,C67,C71,
C74
3 14 C4,C5,C8,C9,C13,C14,
C15,C20,C25,C28,C29,
C34,C64,C66
4 18 C10,C11,C12,C16,C17,
C18,C19,C21,C22,C23,
C24,C35,C36,C38,C44,
C45,C48,C49
5 1 C33 0.068 uF X7R CSN_0805 KEMET C0805C683K5RAC CAP, 0805, X7R, 68000pF, 10%, 50V
6 4 C41,C43,C60,C61 22pF NPO CSN_0805 KEMET C0805C220J5GAC CAP, 0805, C0G, 22pF, 5%, 50V
7 8 C55,C56,C57,C58,C59,
C62,C68,C69
8 1 C63 0.01uF X7R CSN_0805 KEMET C0805C103K5RAC CERM CAP, .01uF, 10%, 50V, X7R
9 2 C70,C73 100uF ELEC CSP_ELEC_E PANASONIC ECE-V1CA101P CAP, SMT E, ELEC, 100uF, 20%, 16V
10 1 C75 2700pF X7R CSN_0805 KEMET C0805C272K5RAC CAP, 0805, X7R, 2700pF, 10%, 50V
11 4 J1,J2,J3,J5 4X1HDR-AU CON_MLX_70553 MOLEX 70553-0003 HDR, 4X1, 0.025" PIN, 0.1" CTR, 15u" AU
12 4 J4,J6,J7,J9 PHONO-1/8 CON_STEREO_LZR LZR ELEC-
13 1 J10 TOTX-173 TOTX173 TOSHIBA TOTX173 OPTICAL TOSLINK TRANSMITTER
14 3 L1,L2,L3 31@100MHz FERRITE IND_FB1206 TDK HF50ACB321611-T IND, FBEAD, 1206, 31@100MHz, 25%
15 2 M1,M2 HOLE
16 1 M3 TOOLHOLE TOOLHOLE
17 1 P1 AMR CON-
18 2 R2,R22 0 RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A0R00J RES, SO, 0805, 0, 5%, 1/10W, METAL FILM
19 17 R4,R5,R6,R7,R8,R9,R10,
R11,R14,R15,R16,R17,
R18,R19,R20,R21,R33
20 2 R12,R13 3.4K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A3401F RES, SO, 0805, 3.4K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL
21 7 R23,R24,R25,R27,R29,
R34,R53
22 1 R26 68K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A6802J RES, SO, 0805, 68K, 5%, 1/10W, MET AL FILM
10uF ELEC CSP_ELEC_B PANASONIC ECA-1CM100 ALUM ELEC, 10uF, 20%, 16V,POL
0.1uF Z5U CSN_0805 KEMET C0805C104M5UAC CAP, 0805, Z5U, .1uF, 20%, 50V
1uF X7R CSN_1206 VENKEL C1206X7R500-
105KNE
220pF COG SMT_0805 KEMET C0805C221J5GAC CERM CAP,220pF,5%,50V,COG
1000pF NPO SMT_0805 KEMET C0805C102J5GAC CERM CAP, 1000pF, 5%, 50V,COG
SJ372 CONN, 1/8" DOUBLE SW. STEREO PHONE
TRONICS
AMR5V-46
NECTOR
6.8K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A6801F RES, SO, 0805, 6.8K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL
47K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A4702J RES, SO, 0805, 47K, 5%, 1/10W, MET AL FILM
CAP, 1206, X7R, 1uF, 10%, 25V
JACK
FILM
FILM
CRD4299-1 AMR
Page 28

28 DS319RD1A1
Item Qty Reference Value Type PCB Footpri nt Mnfr Part Number Description
23 3 R28,R43,R44 100K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A1003J RES, SO, 0805, 100K, 5%, 1/10W, METAL
24 1 R31 4.7K RES RES _0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A4701J RES, SO, 0805, 4.7K, 5%, 1/10W, METAL
25 1 R32 2.7K RES RES _0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A2701J RES, SO, 0805, 2.7K, 5%, 1/10W, METAL
26 2 R35,R39 27K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A2702J RES,27K,SO,0805,5%,1/10W,METAL FILM
27 2 R36,R40 56K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A5602J RES,56K,SO,0805,5%,1/10W,METAL FILM
28 2 R37,R38 10 RES RES_1206 PHILIPS 9C12063A10R0J RES, SO, 1206, 10, 5%, 1/4W, METAL FILM
29 2 R47,R51 47 RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A47R0J RES, SO, 0805, 47, 5%, 1/10W, METAL FILM
30 1 R49 8.2K RES RES _1206 Philips 9C12063A 820J RES,8.2k,SM1206,5%,1/4W
31 1 U1 MC33078D DUAL OP AMP SO8 MOTOROLA MC33078D IC, SO, SOIC8, 33078, DUAL OP AMP
32 1 U2 MC1458 DUAL HP OP
AMP
33 1 U3 CS4299 IC QFP48_7X7 CRYSTAL
34 1 U4 MC78L05 V REG TO-92 MOTOROLA MC78L05AC 5V POS.VOLT.REG., 100ma
35 1 Y1 24.576 MHz PAR RES, FUND XTL_HC49S FOX FS24.576 XTAL, 24.576MHz, HC49S, Fund Mode, Par
Do Not Populate
1 1 R50 47 RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A47R0J RES, SO, 0805, 47, 5%, 1/10W, METAL FILM
2 1 R52 4.7K RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A4701J RES, SO, 0805, 4.7K, 5%, 1/10W, METAL
3 2 R45,R48,R3 0 RES RES_0805 PHILIPS 9C08052A0R00J RES, SO, 0805, 0, 5%, 1/10W, METAL FILM
5 1 Y2 24.576 MHz PAR RES, FUND XTL_CA301 EPSON CA-301_24.576M-C XTAL, 24.576MHz, CA-301, Fund Mode, Par
6 1 U5 MC78L05ACD V REG SO8 MOTOROLA MC78L05ACD 5V POS. VOLT. REG., 100ma
SO8 MOTOROLA MC1458 DUAL HEADPHONE AMP
CS4299-KQ IC, TQFP, AC ’97 2.1 SERIAL CODEC W/ SRC
SEMICOND.
FILM
FILM
FILM
Res
FILM
Res
CRD4299-1 AMR
Page 29

• Notes •
Page 30

 Loading...
Loading...