Page 1
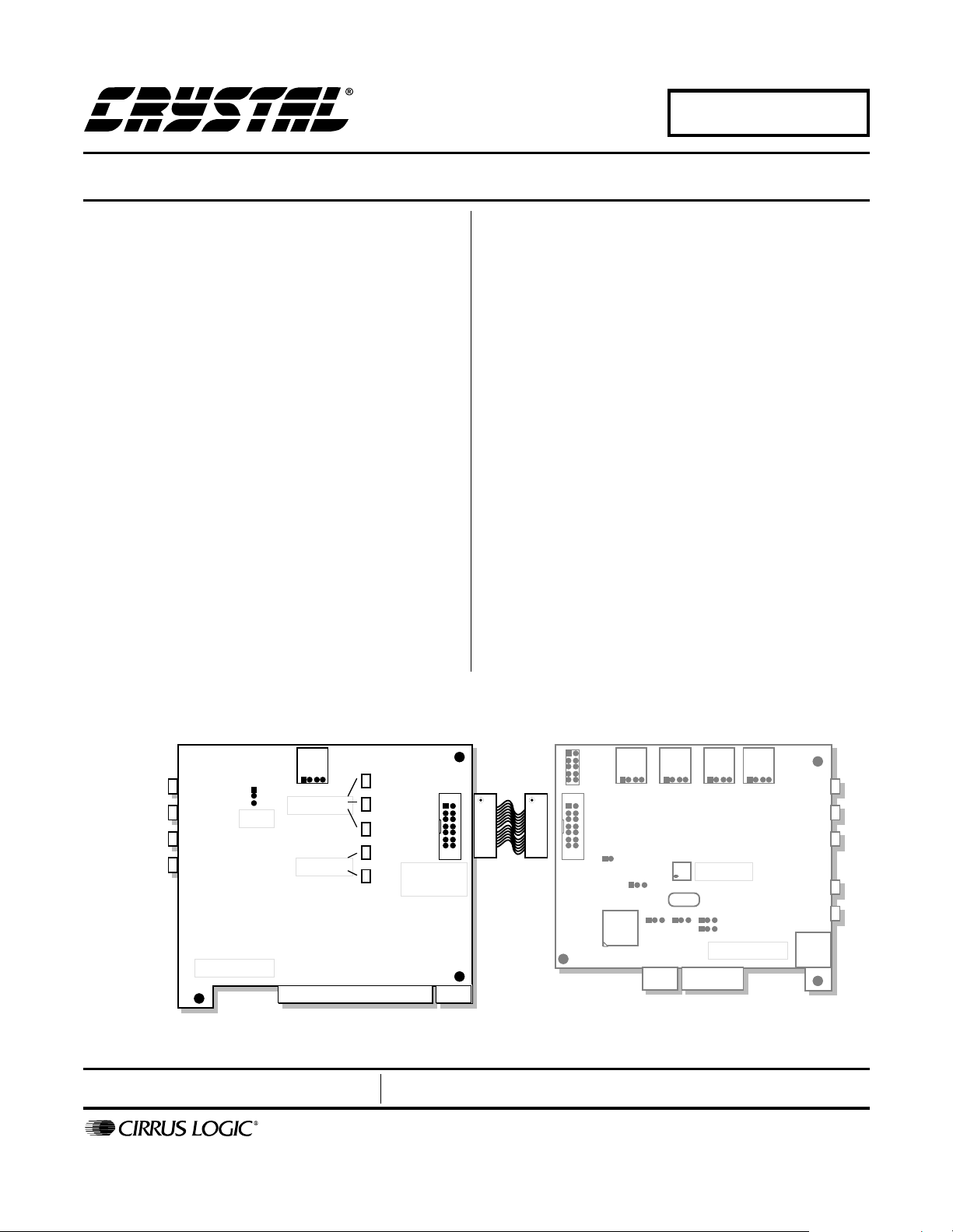
CRD4205-2
CrystalClear® PC Audio Docking Station Companion Board
Features
lCompanion board to CRD4205-1
lEmulates Docking Station Environment
–Simulates audio portion of PC docking station.
–Digital Interface to CRD4205-1
lHigh quality, low cost analog to digital (ADCs)
and digital to analog (DACs) converters
– CS5334 18-bit serial ADCs
– CS4334 24-bit serial DACs
lPCI Slot card (power only)
lTwo stereo inputs
lOne microphone inpu t
lFour channel audio output
Description
The CRD4205-2 reference design is a comp anion card
to the CRD4205-1. The CRD4205-2 emulates the audio
sub-system in a PC digital docking station, and the
CRD4205-1 simulates the audio sub-system in a PC
notebook computer.
This reference design features stereo analog inputs for
Line, CD, and a mono input for Microphone. The card
also has four channel analog audio outputs. The docking
port is completely digital. The analog inputs in the
CRD4205-2 are processed by high quality 18-bit serial
ADCs. The analog outputs are processed by high quality
serial 24-bit DACs.
The CRD4205-2 is available by ordering the CMK42053 manufacturing kit. This kit includes a full set of sc hematics (OrCAD
ASCII), PCB Gerber files, bill of materials and WDM audio drivers that support Windows 98se, Millennium
Windows 2000.
ORDERING INFORMATION
CMK4205-3 Manufacturing Kit for the CRD4205-2
®
7.2 format), PCB job files (PADS
®
and
®
CD IN
MIC IN
LINE IN
LINE OUT1
LINE OUT2
JP1
CRD4205-2
CS5331A
CS4334
Preliminary Product Information
P.O. Box 17847, Austin, Texas 78760
(512) 445 7222 FAX: (512) 445 7581
http://www.cirrus.com
DOCKING
PORT
This document contains information for a new product.
Cirrus Logic reserves the right to modify this product without notice.
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2000
(All Rights Reserved)
CS4205
CRD4205-1
DS489RD2A1
DEC ‘00
1
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. GENERAL INFORMATION ..........................................................................3
2. SCHEMATIC DESCRIPTION ....................................................................... 3
2.1 Block Diagram ....................... ...... ....... ...... ............................................ 3
2.2 Analog Inputs ......................................................................................3
2.3 Analog Output ...................................................................................... 3
2.4 PCI Bus ...............................................................................................4
2.5 Component Selection ........................................................................... 4
2.6 EMC Components ................................................................................ 4
3. GROUNDING AND LAYOUT ....................................................................... 4
4. REFERENCES ............................................................................................. 5
5. ADDENDUM ..................... .......................... ......................... ......................... 5
6. BILL OF MATERIALS ............................................................................15
Printed Circuit Board Assembly.................................................................15
Mechanical Assembly................................................................................16
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. Block Diagram........................................................................................... 6
Figure 2. Analog In................................................................................................... 7
Figure 3. Analog Out ................................................................................................ 8
Figure 4. PCI Bus......................................................... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ............ 9
Figure 5. Assembly Drawing .................................................................................. 10
Figure 6. Silkscreen................................................................................................ 11
Figure 7. Top Layer................................................................................................ 12
Figure 8. Bottom Layer................. ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ............................. 13
Figure 9. Drill Drawing............................................................................................ 14
CRD4205-2
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. Microphone Input Jumper JP1 ................................................................... 3
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus. com/corporat e/contact s/
Microsoft, Windows 95, Windows 98 and Windows Millenium and WHQL is registered trademark of Microsoft.
CrystalClear is a trademark of Cirrus Logic, Inc.
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
OrCAD is a registered trademark of OrCAD, Inc.
PADS is a registered trademark of, PADS Software, Inc.
Preliminary product information describes products which are in production, but for which full characterization data is not yet available. Advance product information
describes products which are in develo pment and subj ect to devel opment changes. Cirr us Logic, Inc. has made best ef forts to en sure t hat the inf ormati on contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject to change without notice and is provided “AS IS” without warranty of any kind
(express or im plied). No responsib ility is assu med by Cir rus Logic, Inc. for the use of this information, nor for infringements of patents or other rights of third parties.
This document is the property of Cirrus Logic, Inc. and implies no license under patents, copyrights, trademarks, or trade secrets. No part of this publication may
be copied, reproduced, stored in a retrieva l system, or transm i tted, i n an y form or by any m eans (e l ectron i c, mechani cal , pho togra phi c, or otherwise) without th e
prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. Items from any Cirrus Logic websi te or disk may be printed for use by the user. H owever , no par t of t he pri ntout o r
electronic files may be copied, reprodu ced, stored in a retrie val system, or transmitted, i n any form or by any means (electro nic, mechanical, photographic, o r
otherwise) without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc.Furthermore, no part of this publication may be used as a basis for manufacture or sale of any it ems
without the prior written consent of Cirrus Logic, Inc. The names of products of Cirrus Logic, Inc. or other vendors and suppliers appearing in this document may
be trademarks or service marks of their respective owners which may be registered in some jurisdictions. A list of Cirrus Logic, Inc. trademarks and service marks
can be found at http://www.cirrus.com.
2 DS489RD2A1
Page 3

CRD4205-2
1.GENERAL INFORMATION
The CRD4205-2 is designed to emulate a high
quality PC audio docking station. This is not a
stand-alone card but used in conjunction with the
CRD4205-1. The CRD4205-1 contains a CS4205
audio codec and simulates the audio sub-system in
a PC notebook computer.
The CRD4205-2 has all the circuitry typically
found in a high quality PC digital docking audio
sub-system. In addition, this reference design includes four channel analog audio outputs driven by
24-bit serial DACs. Microphone, stereo Line, and
stereo CD inputs feature high quality serial 18-bit
ADCs.
2.SCHEMATIC DESCRIPTION
This section describes the CRD4205-2 schematics
shown in figures 1 through 4. These schematics are
also available in the CMK4205-3 manufacturing
kit as ORCAD 7.2 files.
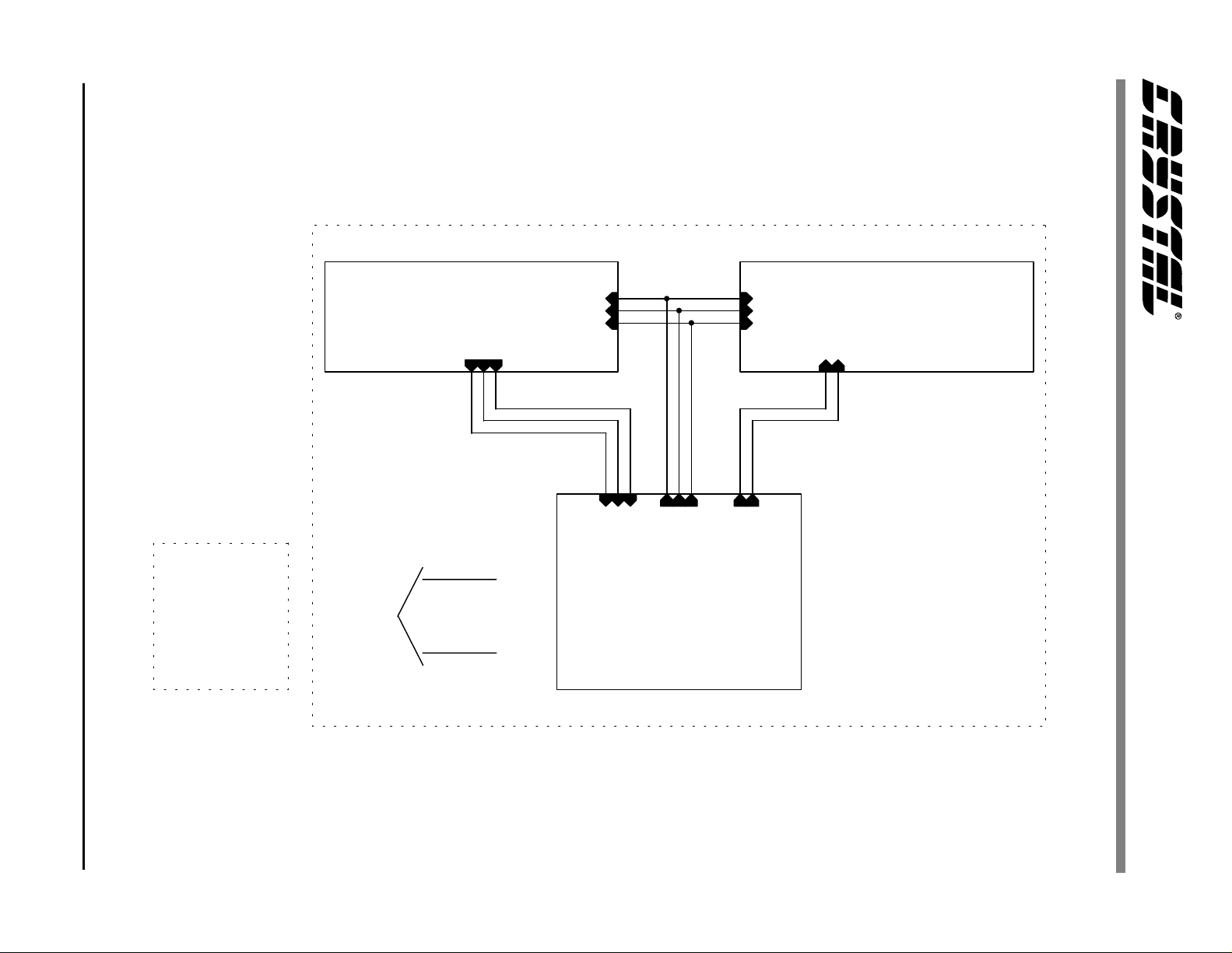
2.1 Block Diagram
The analog audio input signals are converted to
digital data by three CS5331A 18-bit ADCs. The
ADCs share a common clock, but have independent data outputs. The clock and serial data signals
are routed to the docking port header.
The MIC IN circuit complies with PC-99 requirements for microphone phantom power and recommendations for frequency response roll-off. The
3dB roll-off frequencies are 60Hz and 15kHz.
Phantom power for the microphones is derived
from the +5V analog supply and filtered by R11,
C13, and R12.
Jumper JP1 controls how the microphone signal is
routed to the ADC, U3.
JP1 Position Description
Out Microphone signal routed to AINL of
the CS5331A. The AINR is floating.
1-2 Not Used!
2-3 Microphone signal routed to both
AINL and AINR of the CS5331A.
Table 1. Microphone Input Jumper JP1
The block diagram in Figure1, shows the interconnection between schematic pages. The schematic is
divided into three blocks: Analog In, Analog Out,
and PCI Bus.
2.2 Analog Inputs
The Analog Input page in Figure2 illustrates the
Mic, stereo Line and stereo CD inputs and their associated ADCs. The LINE inputs connect to a divider circuit that reduces the voltage by 6dB to
allow for line level sources up to 2Vrms. The
100pF capacitors are provided on Line In and Mic
In for EMI suppression. These may be removed if
EMC testing determines they are not required.
Since the analog inputs of the CS5331 ADCs are
DC biased, all of the analog inputs must be AC coupled. The microphone input is coupled with a
0.1µF capacitor. The Line and CD inputs are AC
coupled with 2.2µF capacitors to minimize the
low frequency roll-off.
2.3 Analog Output
The CS4205 sends audio to the docking port
through I2S serial digital outputs, as shown in
figure3. These signals are converted to analog audio through two CS4334 serial DACs. Both
CS4334s share common clocks but have independent data inputs. All clocks originate from the
CS4205 on the CRD4205-1 card.
The output of the DACs are connected to a Motorola MC34072 dual op-amp which is capable of
driving high impedance (10kΩ or higher) line level signals. This circuit has a gain of 3dB.
It is possible to drive headphones with impedances
as low as 32Ω by replacing the MC34072 with a
TDA1308 and increasing the values of C23, C24,
C29, and C30 to 220µF. These op-amps are pin
compatable.
DS489RD2A1 3
Page 4

CRD4205-2
2.4 PCI Bus
The PCI bus is only used to supply power to the
board, so that an external supply is not required.
The PCI bus connections are shown in Figure 4.
The digital power is supplied from the PCI bus. A
Motorola MC78M05C regulates the +12 V supply
from the PCI bus down to a clean +5 V analog supply. For the best audio performance, the analog
voltage regulator is located over the analog ground
plane near the partition between the analog and digital planes. The regulator ground pin is connected
to the analog ground.
Figure 4 also shows the docking port header. This
connector couples the serial data from the
CRD4205-1 and is buffered by a 74HC244 octal
buffer.
2.5 Component Selection
Great attention was given to the particular components used on the CRD4205-2 board with cost, performance, and package selection as the most
important factors. Listed are some of the guidelines
used in the selection of components:
• No components smaller than 0805 package.
• Only single package components; no resistor
packs.
• All ICs are in surface mount packages.
2.6 EMC Components
A number of capacitors and inductors are included
to help the board meet EMI compliance tests, such
as FCC Part 15. The EMC part values are only
meant as starting points. Modify these values to
meet individual EMC requirements.
3. GROUNDING AND LAYOUT
One of the most critical aspects of PC audio design
is good PC board layout. The PC is a hostile environment for audio, and good layout is essential for
achieving high audio quality.
The CRD4205-2 is partitioned into a digital and analog sections to help isolate noisy digital circuitry
from quiet analog audio circuitry. The most important rule for successful PC audio layout is to keep
all digital signal traces and components over the
digital ground plane, and all analog signal traces
and components over an analog ground plane.
These planes are separated by a minimum of 60 to
100 mils (0.060 to 0.100 inches).
When digital and analog signals cross planes, they
introduce noise into the audio section reducing performance. The CS4334 DACs and CS5331A
ADCs are placed over the partition of the analog
and digital ground planes. The ADCs and DACs
both have their analog and digital signals partitioned to opposite sides of the ICs to help simplify
PCB layout. Digital and analog ground are tied together by a wide trace (over 50 mils or
0.050 inches) at a single point underneath the converters in order to provide a common ground reference.
For more information on layout specifically for the
CS4334 and the CS5331A, see their respective
datasheets.
4 DS489RD2A1
Page 5

CRD4205-2
4. REFERENCES
1) Intel, Audio Codec ‘97 Component Specification, Revision 2.1, May 22, 1998. http://developer.intel.com/ial/scalableplatforms/audio/
2) Communication and Network Riser Specification revision 1.0, Feb 7, 2000 http://developer.intel.com/technology/cnr/
3) Steve Harris, Clif Sanchez, Personal Computer
Audio Quality Measurements, Ver 1.0
http://www.crystal.com/pubs/meas100.pdf
4) Cirrus Logic, CS4205 Data Sheet
5) Cirrus Logic, CS4334/5/6/7/8/9 Data Sheet
http://www.crystal.com/pubs/4334.pdf
6) Cirrus Logic, CS5330A/31A Data Sheet
http://www.crystal.com/pubs/5330a.pdf
5. ADDENDUM
• Schematic drawings
• Layout drawings
DS489RD2A1 5
Page 6
6 DS489RD2A1
Main
Board
Analog_In
>Line In
>CD In
>Mic In
Analog_In
DSSDI1
DSSDI3
DSSDI2
DSMCK
DSLRCK
DSSCK
PCI_Bus
> Clocks
> SDO1
> SDO2
< SDI1
< SDI2
< SDI3
PCI_Bus
DSSDI2
DSSDI1
DSSDI3
DSMCK
DSSCK
DSLRCK
Analog_Out
DSMCK
DSLRCK
DSSCK
Analog_Out
SDATA2
SDATA1
SDATA1
SDATA2
Line1 Out >
Line2 Out >
Figure 1. Block Diagram
CRD4205-2
Page 7

DS489RD2A1 7
ELEC
+
+5VA
+5VA
AGND
JP1
1
2
3
3x1HDR
U3
8
AINL
7
VA+
6
AGND
=Gnd
RightIn
=Left
U1
8
AINL
7
VA+
6
AGND
SDATA
CS5331A
SDATA
SCLK
LRCK
MCLKAINR
CS5331A
+5VA
C12
0.1uF
Z5U
Vee Vcc
AGND
SCLK
LRCK
MCLKAINR
1
2
3
45
Dock LineIn
Dock CDIn
Dock MicIn
1
2
3
45
DSSCK
DSLRCK
DSMCK
DSSDI1
DSSDI2
DSSDI3
LINE IN
4
3
5
2
1
PHONO-1/8
MIC IN
J3
PHONO-1/8
Connect CGND
to AGND at
the jack
4
5
2
1
AGND
AGND
CGND
R2 6.8K
R4 6.8KJ1
>Rt
>Lt
C2
100pF
NPO
R12 2.2K
R5 100 C8
C14
100pF
NPO
CGND
C1
100pF
NPO
C9
100pF
NPO
-3 dB corners at
60 Hz and 16 kHz
(Ri = 28 k, Rs=350ohm)
R1 6.8K
R3 6.8K
R11 1.5K
+
C13
10uF
ELEC
AGND
C4 2.2uF
+5VA
C7
0.022uF
X7R
ELEC
+
C3 2.2uF
0.1uF
X7R
CD IN
J2
4X1HDR-AU
+5VA
U2
8
AINL
7
L1
RtCD
4
3
2
1
LtCD
31@100MHz
L2
31@100MHz
L3
31@100MHz
C6 2.2uF
C11 4.7uF
ELEC
+
C5 2.2uF
ELEC
+
ELEC
+
AGND
6
VA+
AGND
CS5331A
SDATA
SCLK
LRCK
MCLKAINR
1
2
3
45
CRD4205-2
Figure 2. Analog In
Page 8

8 DS489RD2A1
R24 33K
DSSCK
DSLRCK
DSMCK
SDATA1
SDATA2
U6 CS4334
1
SDATA
2
DEM#/SCLK
3
LRCK
4 5
MCLK AOUTR
C35
10uF
ELEC
AOUTL
AGND
+
VA+
R36
10K
R35
10K
+5VA
8
7
6
AGND
R37 2.2K
R22 27K
C36
100pF
NPO
R21 27K
3
2
R23 33K
5
6
C22 22pF
+
-
+
-
NPO
U4A
1
MC34072D
C21 22pF
NPO
U4B
7
MC34072D
R42 100
R41 100
+5VA
C37
0.1uF
Z5U
Vee VccVee Vcc
AGND
C24 10uF
ELEC
+
C23 10uF
ELEC
+
R25
220K
AGND
C25
100pF
NPO
R26
220K
CGND
Rt >
Lt >
C26
100pF
NPO
J21
4
2
1
PHONO-1/8
LINE
OUT1
U7 CS4334
1
SDATA
2
DEM#/SCLK
3
LRCK
4 5
MCLK AOUTR
AOUTL
VA+
AGND
+5VA
8
7
6
R28 27K
AGND
R27 27K
R30 33K
C28 22pF
NPO
+
-
+
-
U5A
1
MC34072D
C27 22pF
U5B
7
MC34072D
3
2
R29 33K
5
6
8-pin Heaphone Amp
(e.g. TDA1308)can be
substituted for MC34072
NPO
R44 100
R43 100
+5VA
C38
0.1uF
Z5U
AGND
C30 10uF
ELEC
+
C29 10uF
ELEC
+
R31
220K
AGND
C31
100pF
NPO
R32
220K
CGND
Rt >
Lt >
C32
100pF
NPO
J22
4
2
1
PHONO-1/8
LINE
OUT2
CRD4205-2
Figure 3. Analog Out
Page 9

DS489RD2A1 9
+12VD
P2
PCI BUS 5V A
TRST#
+12V
TMS
TDI
+5V(1)
INTA#
INTC#
+5V(2)
RSVD(1)
+5V(3)
RSVD(2)
GND(1)
GND(2)
RSVD(3)
RST#
+5V(4)
GNT#
GND(3)
PME#
AD[30]
+3.3V(1)
AD[28]
AD[26]
GND(4)
AD[24]
IDSEL
+3.3V(2)
AD[22]
AD[20]
GND(5)
AD[18]
AD[16]
+3.3V(3)
FRAME#
GND(6)
TRDY#
GND(7)
STOP#
+3.3V(4)
SDONE
SBO#
GND(8)
PAR
AD[15]
+3.3V(5)
AD[13]
AD[11]
GND(9)
AD[9]
KEY1
KEY2
C/BE[0]#
+3.3V(6)
AD[6]
AD[4]
GND(10)
AD[2]
AD[0]
+5V(5)
REQ64#
+5V(6)
+5V(7)
Side A
+5VD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
DGND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
-12V
TCK
GND11
TDO
+5V(8)
+5V(9)
INTB#
INTD#
PRSNT1#
RSVD(4)
PRSNT2#
GND(12)
GND(13)
RSVD(5)
GND(14)
CLK
GND(15)
REQ#
+5V(10)
AD[31]
AD[29]
GND(16)
AD[27]
AD[25]
+3.3V(7)
C/BE[3]#
AD[23]
GND(17)
AD[21]
AD[19]
+3.3V(8)
AD[17]
C/BE[2]#
GND(18)
IRDY#
+3.3V(9)
DEVSEL#
GND(19)
LOCK#
PERR#
+3.3V(10)
SERR#
+3.3V(11)
C/BE[1]#
AD[14]
GND(20)
AD[12]
AD[10]
GND(21)
KEY3
KEY4
AD[8]
AD[7]
+3.3V(12)
AD[5]
AD[3]
GND(22)
AD[1]
+5V(11)
ACK64#
+5V(12)
+5V(13)
Side B
P1
C41
0.1uF
Z5U
PCI BUS 5V B
+12VD
+
C42
10uF
ELEC
J14
/OBE
1314
DSMCK
1112
DS MicIn
DS CDIn
DS
LineIn
DGND
U9
DSSDI3
DSSDI2
DSSDI1
+5VA
U8
1
IN
GND
2
AGND
3
OUT
MC78M05C
+
C43
10uF
ELEC
+5VD
2
4
6
8
11
13
15
17
1
19
20
1A1
1A2
1A3
1A4
2A1
2A2
2A3
2A4
1OE
2OE
VCC
74HC244
910
78
56
34
12
7x2CON
To Main
Board
GND
DSLRCK
DSSCK
SDATA1
SDATA2
n.c.
(reserved)
1Y1
1Y2
1Y3
1Y4
2Y1
2Y2
2Y3
2Y4
18
16
14
12
9
7
5
3
10
DGND
SDATA1
SDATA2
DSMCK
DSLRCK
DSSCK
CRD4205-2
Figure 4. PCI Bus
Page 10

10 DS489RD2A1
Figure 5. Assembly Drawing
CRD4205-2
Page 11

DS489RD2A1 11
Figure 6. Silkscreen
CRD4205-2
Page 12

12 DS489RD2A1
Figure 7. Top Layer
CRD4205-2
Page 13

DS489RD2A1 13
Figure 8. Bottom Layer
CRD4205-2
Page 14

CRD4205-2
Figure 9. Drill Drawing
14 DS489RD2A1
Page 15

DS489RD2A1 15
6. BILL OF MATERIALS
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD ASSEMBLY
Item Quantity Reference Description Manufacturer Manufacturer PN
1 9 C1,C2,C9,C14,C25,C26,C31. CAP, 0805, COG, 100pF, 5%, 50V. KEMET. C0805C101J5GAC.
C32,C36. . . .
2 4 C3,C4,C5,C6. CAP, SMT A, ELEC, 2.2uF, 20%, 35V. PANASONIC. ECE-V1VS2R2SR.
3 1 C7. CAP, 0805, X7R, .022uF, 10%, 50V. KEMET. C0805C223K5RAC.
4 5 C8,C12,C37,C38,C41. CAP, 0805, X7R, .1uF, 10%, 50V. KEMET. C0805C104K5RAC.
5 1 C11. CAP, SMT A, ELEC, 4.7uF, 20%, 25V. PANASONIC. ECE-V1ES4R7SR.
6 8 C13,C2 3,C24 ,C29,C30, C35. CAP, SMT B, ELEC, 10uF, 20%, 16V. PANASONIC. ECE-V1CA100R.
C42,C43. . . .
7 4 C21,C22,C27,C28. CAP, 0805, C0G, 22pF, 10%, 50V. KEMET. C0805C220K5GAC.
8 1 JP1. HDR, 3x1, 0.025" PIN, 0.1" CTR. SAMTEC. TSW-103-07-T-S.
9 1 J1. CONN, 1/8" DOUBLE SW. STEREO PHONE JACK.
10 1 J2. HDR, 4X1, 0.025" PIN, 0.1" CTR, 15u" AU. MOLEX. 70553-0003.
11 1 J3. CONN, 1/8" SINGLE SW. STEREO PHONE JACK.
12 1 J14. CONN, 7x2 RIBBON, MALE, STRAIGHT, SHROUDED. AMP. 103309-2.
13 2 J21,J22. CONN, 1/8" NON-SW. STEREO PHONE JACK.
14 3 L1,L2,L3. IND, FBEAD, 1206, 31@100MHz, 25%. TDK. HF50ACB321611-T.
15 1 P1. PCI BUS 5V SIDE B. . .
16 1 P2. PCI BUS 5V SIDE A. . .
17 4 R1,R2,R3,R4. RES, SO, 0805, 6.8K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A6801F.
18 1 R11. RES, SO, 0805, 1.5K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A1501F.
19 2 R37,R12. RES, SO, 0805, 2.2K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A2201F.
20 4 R21,R22,R27,R28. RES, SO, 0805, 27K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A2702F.
21 4 R23,R24,R29,R30. RES, SO, 0805, 33K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A3302F.
22 4 R25,R26,R31,R32. RES, SO, 0805, 220K, 5%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A2203J.
23 2 R36,R35. RES, SO, 0805, 10K, 1%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A1002F.
24 5 R41,R42,R43,R44,R5. RES, SO, 0805,100, 1%, 1/10W, METAL FILM. PHILIPS. 9C08052A1000F.
25 3 U1,U2,U3. IC, CS5331A, 18-BIT ADC. CIRRUS LOGIC. CS5331A-KS.
26 2 U5,U4. IC, SO, SOIC8, 34072, SINGLE SUPPLY DUAL OP AMP. MOTOROLA. MC34072D.
27 2 U6,U7. IC, SO, SOIC8, CS4334, DAC, STEREO. CIRRUS LOGIC. CS4334-KS.
28 1 U8.
29 1 U9. IC, 74HC244. MOTOROLA. MC74HC244ADW.
IC, SO, +5V REGULATOR, MC78M05C, DPAK, 4%,
500mA.
LZR ELECTRONICS.
LZR ELECTRONICS.
LZR ELECTRONICS.
MOTOROLA. MC78M05CDT.
SJ372.
SJ374.
SJ373.
CRD4205-2
Page 16

DS489RD2A1 16
MECHANICAL ASSEMBLY
Item Quantity Name Manufacturer PN Comments
1 1 Printed Circuit Board (PCB). . CRD4205-2 Rev A.
2 1 PCI Bracket. Globe. . .
3 1 Label. Internal Crystal. NA.
PN located in upper left
corner of PCB.
Label content "CRD42052".
CRD4205-2
Page 17

• Notes •
Page 18

 Loading...
Loading...