Page 1
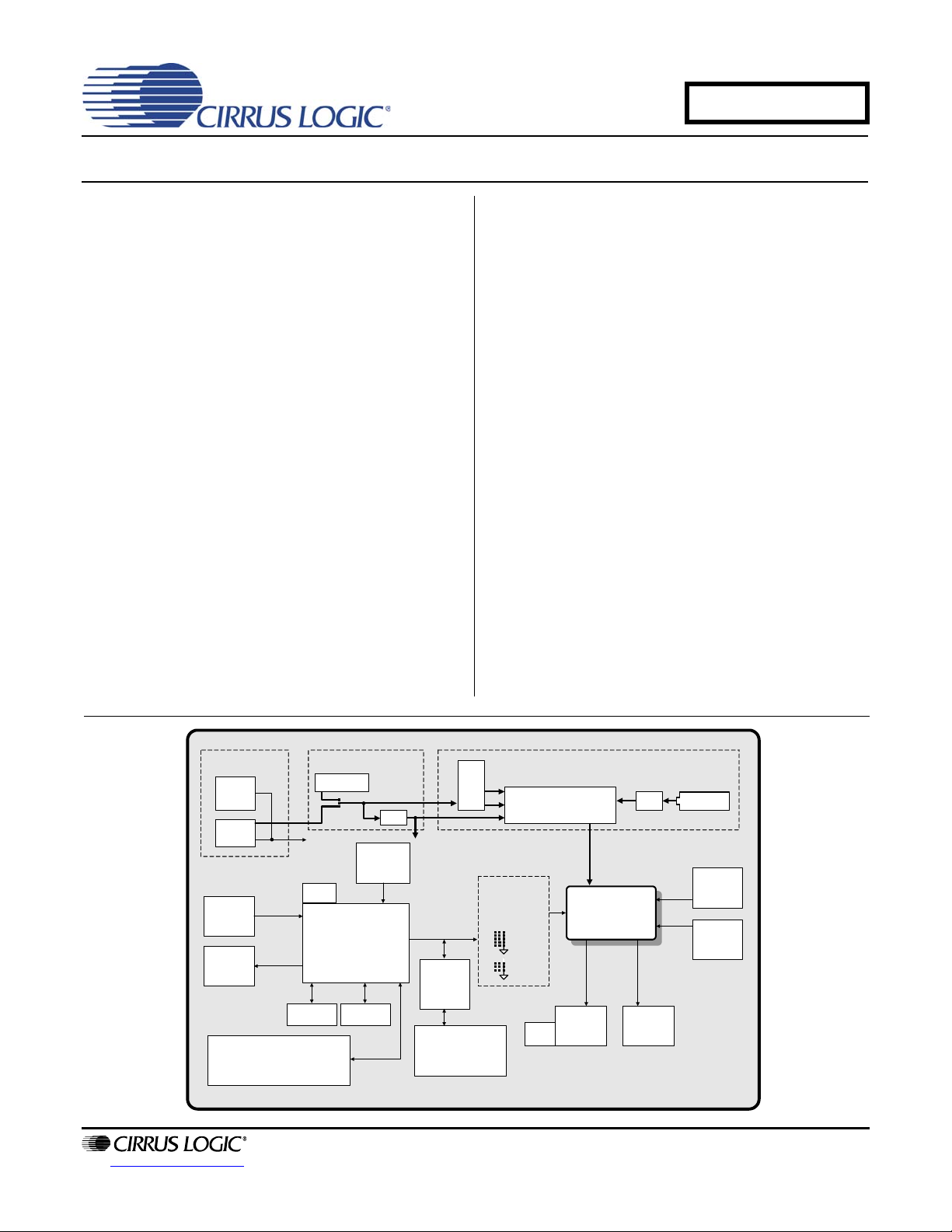
Evaluation Board for CS42L55
CDB42L55
Features
Line-level Analog Inputs
– 4 RCA Input Jacks
Line-Level & HP Analog Output
– Stereo Headphone Out Jack
– RCA Audio Jacks for Headphone and Line
Outputs
S/PDIF Interface
– CS8416 Digital Audio Receiver
– CS8406 Digital Audio Transmitter
I/O Stake Headers and SMA Connectors
™
– External I²C
– External DSP Serial Audio I/O Accessibility
– Direct DSP Serial Audio I/O accessibility
with CS42L55 through SMA connectors
Multiple Power Supply options via USB, Battery
or External Power Supplies
1.65 V to 3.3 V Logic Interface
FlexGUI S/W Control - Windows
– Pre-defined & User-configurable Scripts
Control Port Accessibility
®
Compatible
Description
The CDB42L55 is the ideal evaluation platform solution to test
and evaluate the CS42L55.The CS42L55 is a highly integrated, 24-bit, ultra-low-power stereo CODEC based on multi-bit
Delta-Sigma modulation suitable for low-power portable system applications. Use of the board requires an analog or digital signal source, an analyzer, and power supplies. A
Windows PC-compatible computer is also needed in order to
configure the CS42L55 and the board.
System timing can be provided by the CS8416 S/PDIF Receiver, by the CS42L55 supplied with a master clock, or via an
I/O stake header with a DSP connected.
RCA connectors are provided for CS42L55 analog inputs and
HP/Line outputs. A 1/8 inch audio jack is provided for headphone stereo out. Digital I/O connections are available via
RCA phono or optical connectors to the CS8416 and CS8406
(S/PDIF Rx and Tx).
The CDB42L55 is programmed via the PC’s USB using Cirrus
Logic’s Microsoft
evaluation board may also be configured to accept external
timing and data signals for operation in a user application during system development.
Ordering Information
CDB42L55 Evaluation Board
®
Windows®-based FlexGUI software. The
PC Control Board Power
Serial
USB
S/PDIF Rx
S/PDIF Tx
I/O Stake Headers for Audio
Precision’s Programmable Serial
Interface Adapter (PSIA)
http://www.cirrus.com
External 5.0 V
Supply
I²C for all
applicable
devices
PLL
FPGA
Clock/Data Routing
Clock dividers and PLL used
to derive all applicable Fs
from 24 MHz oscillator
SRC (Tx)
SRC (Rx)
LDO’s
1.8 V
LDO
24 MHz
Oscillator
3.3 V
Tri-state
Buffers
I/O SMA Connectors
for External System
3.3 V (VL only)
Interface
2.5 V
Circuit Break for
External System
Interface
PCM
Clocks/Data
I²C Clocks/
Data
Copyright © Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2008
(All Rights Reserved)
CODEC Power
VL, VCP, VLDO, VA
MUX
Stereo HP
HP
Output
Jack
1.8 V
CS42L55
Buck
Stereo Line
Output
x3
AAA Alkaline
(not included)
Stereo
Input 1
Stereo
Input 2
DEC '08
DS773DB1
Page 2

CDB42L55
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. QUICK START GUIDE ........................................................................................................................... 4
2. SYSTEM OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................. 5
2.1 Control Port and Board Configuration ...................................................................... ... ... .... ... ... ........ 5
2.2 Power ............................................................................................................................................... 5
2.3 Digital Input ....................................................................................................................................... 5
2.3.1 CS8416 S/PDIF Digital Audio Receiver .................................................................................. 5
2.3.2 CS8421 Sample Rate Converter (Tx SRC to CS42L55) ......................................................... 6
2.4 Digital Output .................................................................................................................................... 6
2.4.1 CS8406 S/PDIF Digital Audio Transmitter .............................................................................. 6
2.4.2 CS8421 Sample Rate Converter (Rx SRC from CS42L55) .................................................... 6
2.5 FPGA ................................................................................................................................................ 6
2.6 Oscillator ........................................................................................................................................... 7
2.7 CS42L55 Audio CODEC .................................................................................................................. 7
3. CONFIGURATION OPTIONS ................................................................................................................. 8
3.1 S/PDIF or PSIA In to Analog Out ...................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Analog In to S/PDIF or PSIA Out ...................................................................................................... 9
4. SOFTWARE MODE CONTROL.......................................................................................................... . 10
4.1 Board Configuration Tab ................................................................................................................ 11
4.2 CODEC Configuration Tab ............................................................................................................. 12
4.3 Analog Input Volume Tab ............................................................................................................... 13
4.4 DSP Engine Tab ............................................................................................................................. 14
4.5 Analog Output Volume Tab ............................................................................................................ 15
4.6 Register Maps Tab ......................................................................................................................... 16
5. SYSTEM CONNECTIONS AND JUMPERS ........................................................................................ 17
6. PERFORMANCE PLOTS ..................................................................................................................... 19
7. CDB42L55 BLOCK DIAGRAM ............................................................................................................ 24
8. CDB42L55 SCHEMATICS ................................................................................................................... 25
9. CDB42L55 LAYOUT ............................................................................................................................ 30
10. REVISION HISTORY .......................................................................................................................... 35
2 DS773DB1
Page 3

LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1.Quick Start Board Layout .............................................................................................................. 4
Figure 2.S/PDIF or PSIA In to Analog Out .................................................................................................. 8
Figure 3.Analog In to S/PDIF or PSIA Out .................................................................................................. 9
Figure 4.Board Configuration Tab ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ................ 11
Figure 5.CODEC Configuration Tab ......................................................................................................... 12
Figure 6.ADC Input Channel Volume Tab ................................................................................................. 13
Figure 7.DSP Engine Tab ......................................................................................................................... 14
Figure 8.Analog Output Volume Tab ......................................................................................................... 15
Figure 9.Register Maps Tab - CS42L55 ................................................................................................... 16
Figure 10.THD+N vs Freq. - Analog In to Digital Out ................................................................................ 19
Figure 11.THD+N vs Amplitude - Analog In to Digital Out ........................................................................19
Figure 12.FFT - Analog In to Digital Out @ -1 dBFS ................................................................................ 19
Figure 13.FFT - Analog In to Digital Out @ -60 dBFS .............................................................................. 19
Figure 14.FFT - Analog In to Digital Out - no input ................................................................................... 20
Figure 15.FFT Crosstalk - Analog In to Digital Out @ -1 dBFS ................................................................ 20
Figure 16.Freq. Response - Analog In to Digital Out ................................................................................ 20
Figure 17.Fade-to-Noise Linearity - Analog In to Digital Out .................................................................... 20
Figure 18.THD+N vs Freq. - Digital In to HP Out ...................................................................................... 20
Figure 19.THD+N vs Amplitude - Digital In to HP Out .............................................................................. 20
Figure 20.THD+N vs Volume - Digital In to HP Out ..................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...... 21
Figure 21.FFT - Digital In to HP Out @ 0 dBFS ........................................................................................ 21
Figure 22.FFT - Digital In to HP Out @ -60 dBFS ..................................................................................... 21
Figure 23.FFT - Digital In to HP Out - no input ......................................................................................... 21
Figure 24.Freq. Response - Digital In to HP Out ...................................................................................... 21
Figure 25.Fade-to-Noise Linearity- Digital In to HP Out ............................................................................ 21
Figure 26.FFT Crosstalk - Digital In to HP Out @ 0 dBFS ........................................................................22
Figure 27.THD+N vs Freq. - Digital In to Line Out .................................................................................... 22
Figure 28.THD+N vs Amplitude - Digital In to Line Out ............................................................................ 22
Figure 29.THD+N vs Volume - Digital In to Line Out ................................................................................ 22
Figure 30.FFT - Digital In to Line Out @ 0 dBFS ...................................................................................... 22
Figure 31.FFT - Digital In to Line Out @ -60 dBFS ................................................................................... 22
Figure 32.FFT - Digital In to Line Out - no input ........................................................................................ 23
Figure 33.FFT Crosstalk - Digital In to Line Out @ 0 dBFS ......................................................................23
Figure 34.Freq. Response - Digital In to Line Out ..................................................................................... 23
Figure 35.Fade-to-Noise Linearity- Digital In to Line Out .......................................................................... 23
Figure 36.Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 37.CS42L55 & Analog I/O (Schematic Sheet 1) ............................................................................ 25
Figure 38.S/PDIF & Digital Interface (Schematic Sheet 2) .......................................................................26
Figure 39.PLL, oscillator and external I/O connections (Schematic Sheet 3) ........................................... 27
Figure 40.Microcontroller and FPGA (Schematic Sheet 4) ....................................................................... 28
Figure 41.Power (Schematic Sheet 5) ...................................................................................................... 29
Figure 42.Silk Screen ................................................................................................................................ 30
Figure 43.Top-Side Layer ......................................................................................................................... 31
Figure 44.GND (Layer 2) ........................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 45.Power (Layer 3) .....................................................................................................
Figure 46.Bottom Side Layer .................................................................................................................... 34
CDB42L55
................... 33
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. System Connections ................ ... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ......................................... 17
Table 2. Jumper Settings ................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ................................... 18
DS773DB1 3
Page 4
CDB42L55
s
1 QUICK START GUIDE
The following figure is a simplified quick-start guide made for user convenience. The guide configures the board with
a 1.8 V power supply to VLDO, VA and VCP and a 3.3 V power supply to VL. The user may choose from steps 7
through 10 depending on the desired measurement. Refer to Section 3 on page 8 for details on how the various
components on the board interface with each other in different board configuration modes. Refer to Section 4 on
page 10 for descriptions on control settings in the Cirrus FlexGUI software.
.
Set jumper settings for VL to 3.3V
1
and VCP,VLDO and VA to 1.8V
J48,J53,J52, J74, J7 and
3
J11 should be shunted
Apply analog input
10
6
Connect USB to board. Open Flex
GUI software on PC and load
quick setup script.
2
Set Board Power setting to USB
7
Provide digital inputs to
the board either through
the S/PDIF optical or
RCA connectors or
through the PSIA I/O
header J78.
8
Receive digital outputs from the board
either through the S/PDIF optical or
RCA phono connectors or thro ugh the
PSIA I/O header J40.
Figure 1. Quick Start Board Layout
5
Left pins on J109 and
J104 should be
shunted
9
Monitor analog outputs via HP or Line Channel RCA
connectors or HP stereo jack
4
Set desired jumper
settings for
J12,J4,J2 and J3.
4 DS773DB1
Page 5

CDB42L55
2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The CDB42L55 evaluation platform provides analog and digital interfaces to the CS42L55 and allows for external
DSP and I²C
an external +5 V supply. On-board voltage regulators provide power to the digital and analog cores o f the CS42L55.
The CDB42L55 is configured using Cirrus Logic’s Windows-compatible FlexGUI software to read/write to device
registers.
This section describes the various components on the CDB42L5 5 and how they are used with the CS42L55. Section
1 on page 4 is a simplified quick connect guide provided for us er convenience and may be used to quickly configure
the CS42L55. Section 3 on page 8 describes some of the configura tions available fo r transmi tting and rece iving audio signals. Section 4 on page 10 provides software configuration details. Section 5 on page 17 provides a description of all stake headers and connectors, including the default factory settings of all jumpers. Section 6 on page 19
provides typical performance plots. The CDB42L55 schematic and layout set is shown in Figures 36 through 46.
2.1 Control Port and Board Configuration
interconnects to the board. On-board periph erals are powered eith er from the USB connection or fro m
The CDB42L55 evaluation board must be progr ammed using the Windows compatible software (Cirrus Logic FlexGUI) provided. This software allows the user to program the registers of all the programmable components on the board using an I²C interface.
The GUI interfaces with an on-board micro controller through either the USB or the serial port connector.
For a detailed explanation on software controls, refer to Section 4 on page 10.
Alternatively, the I²C interface to the CS42L55 can be directly accessed through an I/O header (J109) to
accept external timing and data signals in a user application during system development.
2.2 Power
Power is supplied to the evaluation board through e ither the +5.0 V test points or the VBUS supply from the
USB. NOTE: The minimum current required for board operation is approximately 300 mA. It may ther efore
be necessary to connect the CDB42L55 directly to the USB po rt on the PC as opposed to a hub or keybo ard
port where the current might be limited.
Jumpers connect the CS42L55’s supplies to a low dropout regulated vo ltage of +1.8 V, +2.5 V or +3.3 V for
VL and +1.8 V or +2.5 V for VLDO, VA and VCP. A selection for a 1.8 V supply from a buck regulator is also
available, providing a more efficient means of evaluating the CS42L55’s performance when powered from
batteries (3 AAA battery connectors are available on the bottom side of the CDB).
For current measurement purposes only, a 1 Ω ohm series resistor is con nected to each supply. The current
is easily calculated by measuring the voltage drop across this resistor. NOTE: The stake headers connected
in parallel with these resistors must be shunted with the supplied jumper during normal operation.
WARNING: Please refer to the CS42L55 data sheet for allowable voltage levels.
2.3 Digital Input
2.3.1 CS8416 S/PDIF Digital Audio Receiver
The CS8416 S/PDIF receiver converts an incoming S/PDIF data input stream into PCM data for the
CS42L55 (through the “Transmit” (Tx) Sample Rate Converter (SRC)).
A complete description of the CS8416 (Figure 38 on page 26) and a discussion of the digital audio interface can be found in the CS8416 data sheet.
DS773DB1 5
Page 6

Configuration of the CS8416 is made using controls in the “Board Co nfiguratio n” ta b of the Cirrus F lexGUI
software. Section 3 “Configuration Options” on page 8 and Section 4 “Software Mode Control” on page 10
provide configuration examples and software details.
2.3.2 CS8421 Sample Rate Converter (Tx SRC to CS42L55)
The CS8421 Tx SRC receives PCM digital audio data from either the CS8416 S/PDIF receiver o r th e AP
PSIA header and synchronizes this data with the CS42L55, regardless of the CS42L55’s master and a udio clocks.
A complete description of the CS8421 (Figure 38 on page 26) and a discussion of the digital audio interface can be found in the CS8421 data sheet.
Configuration and routing selections for the CS8421 are made using controls in the “Boa rd Configuration”
tab of the Cirrus FlexGUI software. Section 3 “Configuration Options” on page 8 and Section 4 “Software
Mode Control” on page 10 provide configuration examples and software details.
2.4 Digital Output
2.4.1 CS8406 S/PDIF Digital Audio Transmitter
The CS8406 converts the PCM data generated from the CS42L55 (through the “Receive” (Rx) SRC) to
the standard S/PDIF data stream.
CDB42L55
A complete description of the CS8406 (Figure 38 on page 26) and a discussion of the digital audio interface can be found in the CS8406 data sheet.
Configuration of the CS8406 is made using controls in the “Board Configuration” tab of the Cir rus FlexGUI
software. Section 3 “Configuration Options” on page 8 and Section 4 “Software Mode Control” on page 10
provide configuration examples and software details.
2.4.2 CS8421 Sample Rate Converter (Rx SRC from CS42L55)
The CS8421 Rx SRC receives PCM digital audio data from the CS42L55 and synchronizes this data with
either the CS8406 S/PDIF transmitter or the AP PSIA headers, regardless of the CS42L55’s master and
audio clocks.
A complete description of the CS8421 (Figure 38 on page 26) and a discussion of the digital audio interface can be found in the CS8421 data sheet.
Configuration and routing selections for the CS8421 are made using controls in the “Boa rd Configuration”
tab of the Cirrus FlexGUI software.Section 3 “Configuration Options” on page 8 and Section 4 “Software
Mode Control” on page 10 provide configuration examples and software details.
2.5 FPGA
The FPGA controls the digital signal routing between the CS42L55, CS8406, CS8416, CS8421 (Tx SRC
and Rx SRC), PLL and the I/O stake header.
Configuration and routing selections for the FPGA are made using controls in the “Board Configuration” tab
of the Cirrus FlexGUI software. Section 4 on page 10 provides software configuration details.
6 DS773DB1
Page 7

2.6 Oscillator
The socketed on-board oscillator can be selected as the system master clock source by using the selections
on the “Board Configuration” tab of the Cirrus FlexGUI. ‘Software Mode Control” on pa ge 10 provides configuration details.
The oscillator is mounted in pin sockets, allowing easy removal or replacement. The device footprint on the
board will accommodate full- or half-can-sized oscillators.
2.7 CS42L55 Audio CODEC
A complete description of the CS42L55(U1) can be found in the CS42L55 product data sheet.
The CS42L55 is configured using the Cirrus FlexGUI. The device configurat ion registers are a ccessible via
the “Register Maps” tab of the Cirrus FlexGUI software. This tab provides low-level control of each bit. For
easier configuration, additional tabs provide high-level control.‘Software Mode Control” on page 10 provides
configuration details.
CDB42L55
DS773DB1 7
Page 8
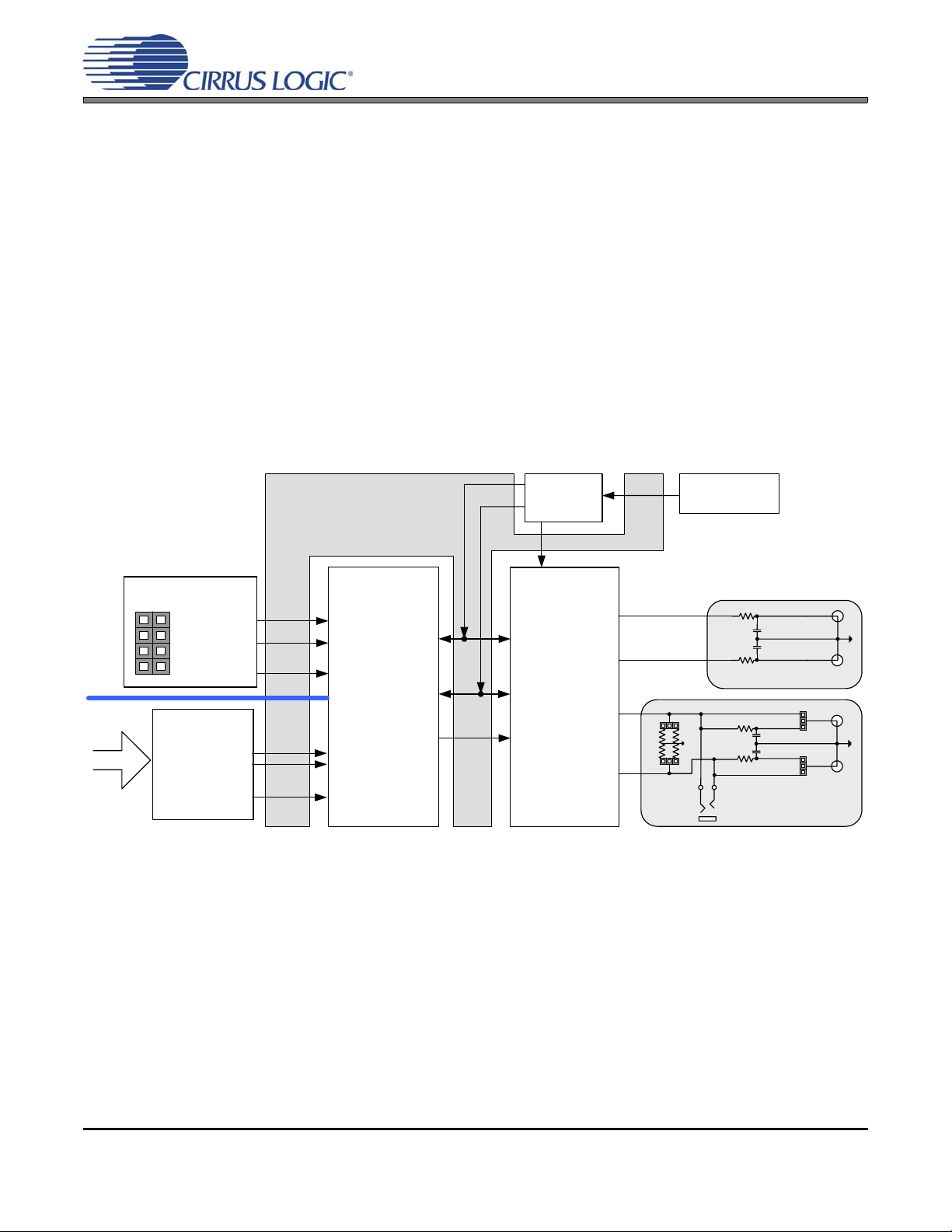
CDB42L55
3 CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
This section highlights two common configurations for the CDB42L55. It p rovides a basic understa nding of ho w the
various components on the board work together.
3.1 S/PDIF or PSIA In to Analog Out
The CS42L55 analog back-end performance can be tested by selecting the “SPDIF In to Analog Out -Analog In to S/PDIF Out” or “PSIA In to Analog Out -- Analog In to PSIA Out” quick setup file provided
with the software package. Note: The Control Port Compensation script for the associated VA supply
must also be selected. The script configures the digital clock and data signal routing on the board as shown
in Figure 2. The quick setup scripts provided in the software assume that a 24.000 MHz on-board oscillator
is populated in Y1.
A S/PDIF input must be provided as the S/PDIF Tx (CS8406) uses the RMCK signal from the S/PDIF Rx
(CS8416) for synchronization in this configuration.
An on-board PLL generates all supported sample and
bit clock rates from an on-board 24 MHz oscillator.
FPGA
PLL
24 MHz
(on-board osc.)
S/PDIF
IN
PSIA Tx (J78)
TX.SCLK
TX.LRCK
TX.SDOUT
S/PDIF Rx
(CS8416)
RX.LRCK
RX.SCLK
RX.SDOUT
(Master)
MCLK
Tx SRC
CS42L55
(CS8421)
Line
Channel
HP
Channel
B
A
B
A
Out
Out
LINEOUTB
SCLK
LINEOUTA
LRCK
HPOUTB
DAC.SDIN
HPOUTA
(Slave) (Slave)
J4
323216
J12
16
J21
HP
Connection
J3
J2
Figure 2. S/PDIF or PSIA In to Analog Out
8 DS773DB1
Page 9
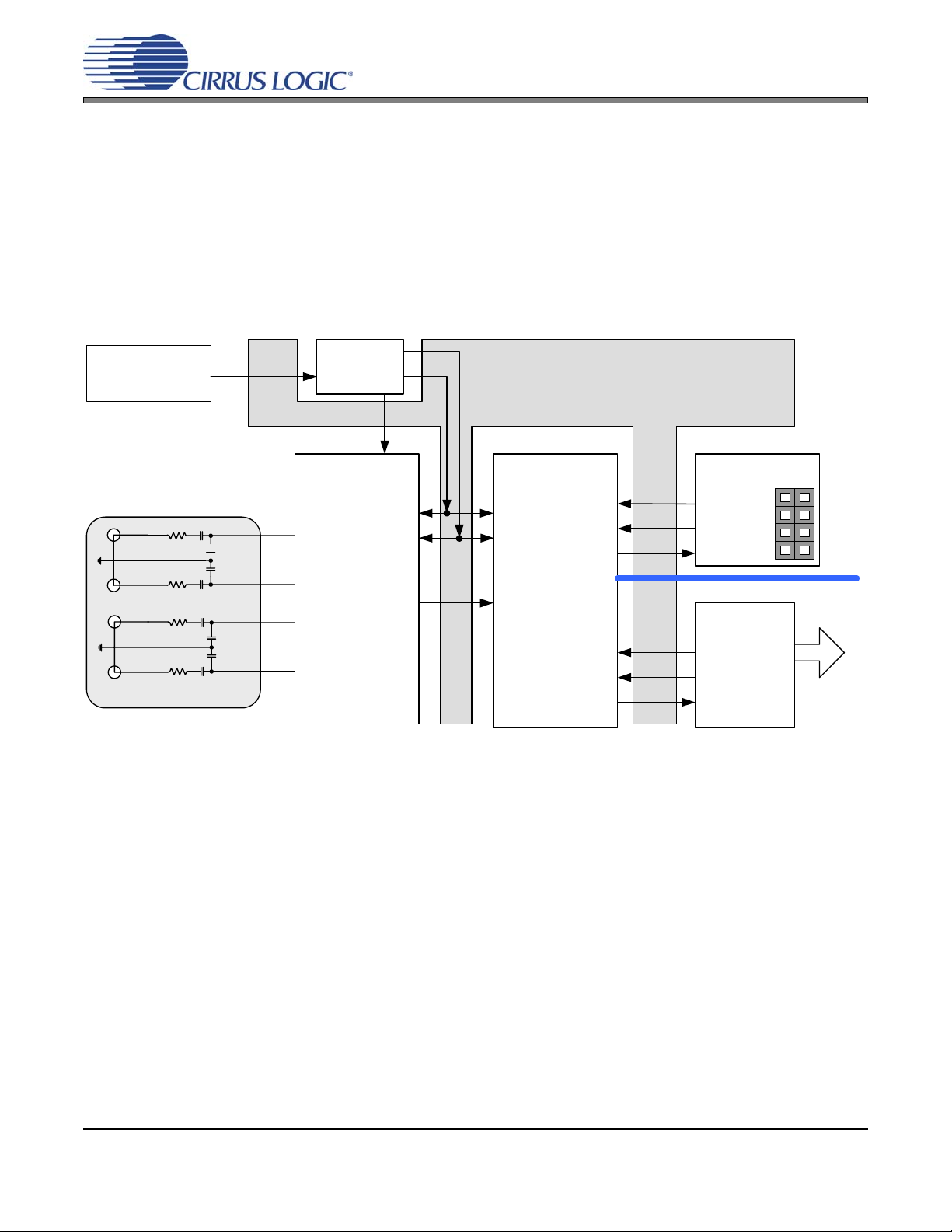
3.2 Analog In to S/PDIF or PSIA Out
The CS42L55 analog front-end performance can be tested by selecting the “SPDIF In to Analog Out -Analog In to S/PDIF Out” or “PSIA In to Analog Out -- Analog In to PSIA Out” quick setup file provided
with the software package. Note: The Control Port Compensation script for the associated VA supply
must also be selected. The script configures the digital clock and data signal routing on the b oard as shown
in Figure 3. The quick setup scripts provided in the software assume that a 24.000 MHz on-board oscillator
is populated in Y1.
A S/PDIF input must be provided as the S/PDIF Tx (CS8406) uses the RMCK signal from the S/PDIF Rx
(CS8416) for synchronization in this configuration.
CDB42L55
24 MHz
(on-board osc.)
AIN1B
AIN1A
AIN2A
AIN2B
PLL &
FPGA
Divider
12 MHz MCLK
CS42L55
SCLK
AIN1B
AIN1A
ADC.SDOUT
AIN2A
AIN2B
LRCK
(Slave)
Figure 3. Analog In to S/PDIF or PSIA Out
Rx SRC
(CS8421)
(Slave)
PSIA Rx (J40)
RX.SCLK
RX.LRCK
RX.SDIN
S/PDIF Tx
(CS8406)
TX.LRCK
TX.SCLK
TX.SDIN
(Master)
S/PDIF
OUT
DS773DB1 9
Page 10
CDB42L55
4 SOFTWARE MODE CONTROL
The CDB42L55 may be used with the Microsoft W indows®-based FlexGUI graphical user interface, allowing software control of the CS42L55, FPGA, CS8421, CS8416 and CS8406 registers. The latest control software may be
downloaded from www.cirrus.com/msasoftware. Step-by-step instructions for setting up the FlexGUI are provided
as follows:
1. Download and install the FlexGUI software as instructed on the Website.
2. Connect the CDB to the host PC using a USB cable.
3. Launch the Cirrus FlexGUI. Once the GUI is launch ed successfully, all registers are set to their default reset
state.
4. Refresh the GUI by clicking on the “Update” button. The default state of all registers are now visible.
For standard set-up:
5. Set up the signal routing in the “Board Configuration” tab as desired.
6. Set up the CS42L55 in the “CODEC...” tabs as desired.
7. Begin evaluating the CS42L55.
For quick set-up, the CDB42L55 may, alternatively, be configured by loading a predefined sample script file:
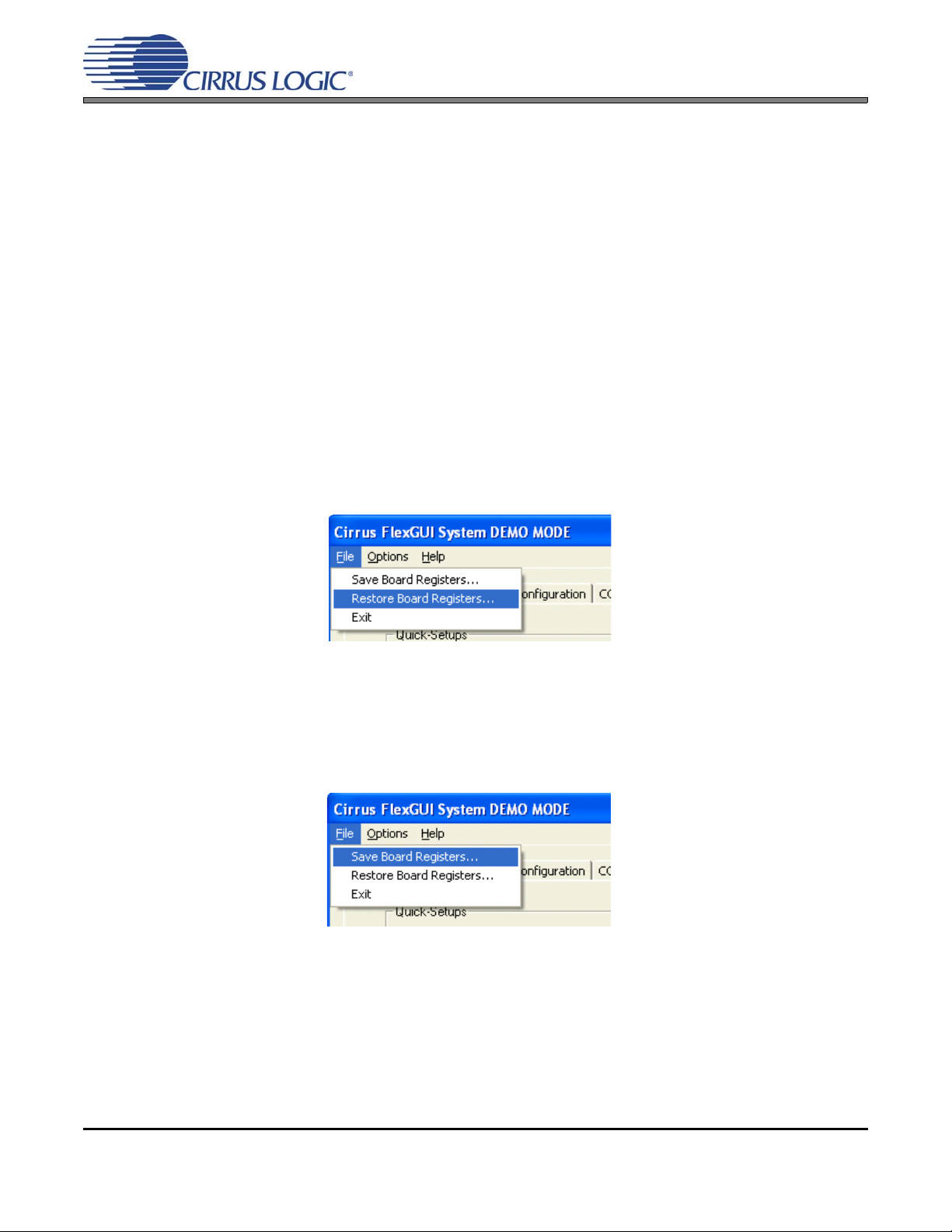
8. On the File menu, click "Restore Board Registers..."
9. Browse to Boards\CDB42L55\Scripts\.
10. Choose any one of the provided scripts to begin evaluation.
To create personal scripts files:
11. On the File menu, click "Save Board Registers..."
12. Enter any name that sufficiently describes the created setup.
13. Choose the desired location and save the scr ipt .
14. To load this script, follow the instructions from step 8 above.
10 DS773DB1
Page 11
4.1 Board Configuration Tab
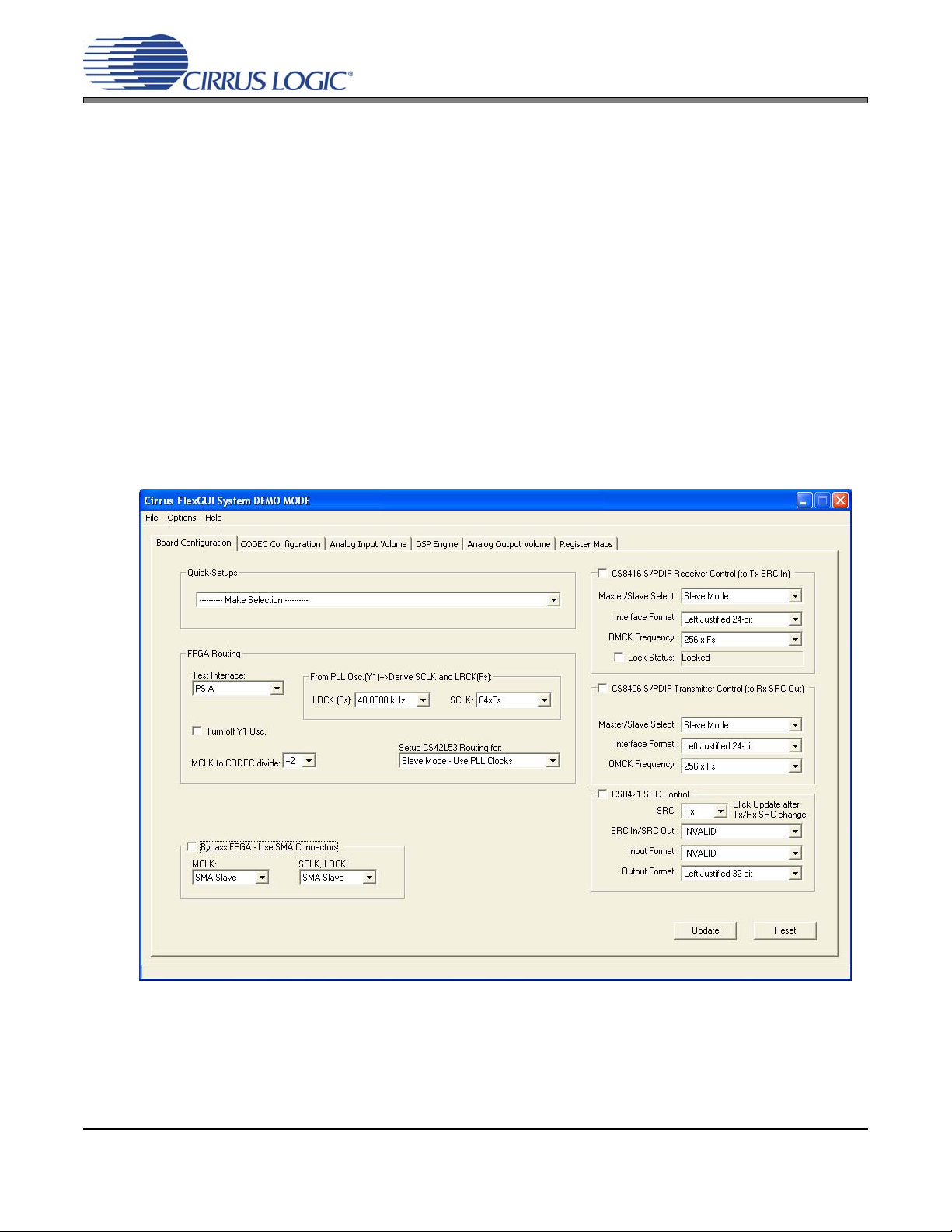
The “Board Configuration” tab provides high-level control of signal routing on the CDB42L55. The controls
in this tab are used to setup the CS8416, CS8406, TxSRC, RxSRC and the FPGA Routing and are divided
into separate sections or control groups for each of th ese individual components. A description of each control group is outlined below. The software loads a predefined configuration when the selection is made from
the Quick-Setups section
FPGA Routing - Includes controls to setup the FPGA for usin g the S/PDIF or the PSIA test interface and for
setting up clock and signal routing for CS42L55 master/slave mode.
CS8416 S/PDIF Receiver Control - Register controls for setting up the CS8416.
CS8406 S/PDIF Transmitter Control - Register controls for setting up the CS8406.
CS8421 SRC Control - Register controls for the receive and transmit SRC’s. To configure, select the desired
SRC from the first drop down box and click update.
Update - Reads all registers in all devices and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets all devices to default configuration.
CDB42L55
Figure 4. Board Configuration Tab
DS773DB1 11
Page 12

4.2 CODEC Configuration Tab
The “CODEC Configuration” tab provides high-level co ntrol of the CS42L55 register settings. Sta tus text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration appears directly below the associated control. This text will
change depending on the setting of the associated control. A description of each control group is outlined
below. See the CS42L55 data sheet for complete register descriptions.
Power Control - Register controls for powering down each device within the CODEC.
ADC Configuration - Controls for the input MUXs, PGA MUX’s, and high-pass filter settings.
Serial Port Configuration - Controls for all settings related to the serial I/O data and clocks on the board.
Update - Reads all registers in the CS42L55 and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets the CS42L55.
CDB42L55
Figure 5. CODEC Configuration Tab
12 DS773DB1
Page 13

4.3 Analog Input Volume Tab
The “Analog Input Volume” tab provides high-level control of all volume settings in the ADC of th e CS42L55.
Status text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration is shown inside the control group of the affected
control. This text will change depending on the setting of the associated con trol. A de scription of each control group is outlined below (a description of each register is included in the CS42L55 data sheet):
Digital Volume Control - Digital volume controls and adjustments (ADC output).
ALC Configuration - Configuration settings for the Automatic Level Control (ALC).
Analog Volume Control - Analog volume controls and adjustments (PGA and MIC amps).
Noise Gate Configuration - All configuration settings for the noise gate.
Update - Reads all registers in the CS42L55 and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets the CS42L55.
CDB42L55
Figure 6. ADC Input Channel Volume Tab
DS773DB1 13
Page 14

4.4 DSP Engine Tab
The “DSP Engine” tab provides high-level control functions to modify the SDIN (PCM) data volume level,
the ADC output/SDIN mix volume level, Tone Control and Beep Generator. Status text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration is shown inside the control group of the affected control. This text will change
depending on the setting of the associated control. A description of each control group is outlined below (a
description of each register is included in the CS42L55 data sheet):
Digital Volume Control - Configures the volume/gain of the ADC mix or the PCM data from the serial data
input (SDIN) in the DSP.
Tone Control - Sets the corner frequencies and the volume/gain of the treble and bass shelving filter s in the
DSP engine.
Beep Generator - Controls for setting the various beep parameters.
Update - Reads all registers in the CS42L55 and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets the CS42L55.
CDB42L55
Figure 7. DSP Engine Tab
14 DS773DB1
Page 15

4.5 Analog Output Volume Tab
The “Analog Output Volume” tab provides high-level control of the CS42L55 Class H output amplifier,
HP/Line output volume levels, charge pump frequency and overall master volume level. This tab also provides control functions for the DAC channel limiter. Status text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration
is shown in read-only edit boxes. This text will change depending on the setting of the associated control.
A description of each control group is outlined below (register descriptions are in the CS42L55 data she et).
Class H Controls - Controls for defining the digital and analog advisory volume, cha rge pump frequency and
adaptive power supply mode for the Class H amplifier.
Headphone/Line Amplifiers - Controls for configuring mutes and for setting the volume of the signal out of
the headphone/line amplifier. Also allows one to configure the HP/Line mux to choose if the input signal to
the HP/Line amplifiers comes from the DAC or the PGA.
Limiter - Configuration settings for the peak detect and limiter in the codec
Master Volume Control - Sets the volume of the signal out of the DSP.
CDB42L55
Figure 8. Analog Output Volume Tab
DS773DB1 15
Page 16

4.6 Register Maps Tab
The Register Maps tabs provide low-level control of the CS42L55, CS8416, CS8406, CS8421, FPGA and
GPIO register settings. Register values can be modified bit-wise or byte-wise. “Left-clicking” on a particular
register accesses that register and shows its contents at the bottom. The use r can change the register contents by using the push-buttons, by selecting a particular bit and typing in the new bit value or by selecting
the register in the map and typing in a new hex value.
CDB42L55
Figure 9. Register Maps Tab - CS42L55
16 DS773DB1
Page 17

CDB42L55
5 SYSTEM CONNECTIONS AND JUMPERS
CONNECTOR REF INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL PRESENT
EXT. +5V TP9 Input +5V power supply
GND TP10 Input GND reference
Ext. Input TP6 Input +4.5V external power supply for U4 buck regulator
GND TP7 Input GND reference
AAA BT1
BT2
BT3
RS232 J95 Input/Output RS232 serial port connection to PC
USB I/O J94 Input/Output USB connection to PC for I²C control port signals
SPDIF Optical IN OPT3 Input CS8416 digital audio input via optical cable
SPDIF Optical OUT OPT2 Output CS8406 digital audio output via optical cable
SPDIF COAX IN J61 Input CS8416 digital audio input via coaxial cable
SPDIF COAX OUT J68 Output CS8406 digital audio input via coaxial cable
MICRO RESET S4 Input Reset for microcontroller (U84)
CS42L55 RESET S1 Input Reset for CS42L55 (U1)
FPGA Program S2 Input Reload Xilinx program into the FPGA from Flash (U14)
FPGA JTAG J75 Input/Output I/O for programming the FPGA (U5)
MICRO JTAG J110 Input/Output I/O for programming the microcontroller (U84)
AP PSIA Transmitter J78 Input Digital Outputs to CS42L55 (typically derived from an Audio Precision Pro-
AP PSIA Receiver J40 Output Digital I/O from CS42L55 (typically derived from an Audio Precision Pro-
MCLK
SCLK
LRCK
ADC.SDOUT
DAC.SDIN
AIN1B
AIN1A
AIN2B
AIN2A
HP Channel A
HP Channel B
Line Channel A
Line Channel B
HP Stereo Connection J1 Output Stereo jack for headphone stereo output from CS42L55
Oscillator Y1 Input Oscillator for providing master clock for system timing
I/O Header J104 Input/Output Unbuffered Digital I/O Interface to CS42L55
S/W CONTROL J109 Intput/Output I/O bus for external I²C control port signals
J77
J42
J45
J46
J47
J8
J6
J14
J10
J38
J37
J15
J17
Input
Input
Input
Input/Output
Input/Output
Input/Output
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Output
Output
Output
Output
RCA connector for headphone analog output from CS42L55
RCA connector for line analog output from CS42L55
Table 1. System Connections
Socket for +1.5 V AAA batteries
grammable Serial Interface Adapter)
grammable Serial Interface Adapter)
Buffered Digital I/O Interface to CS42L55
RCA connectors for analog inputs to CS42L55
DS773DB1 17
Page 18

CDB42L55
JMP LABEL PURPOSE POSITION FUNCTION SELECTED
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
J31 VL
J36 VCP
J25 VA
J28 VLDO
J52
J74
J53
J48
J11 Shunt to RCA Provides RCA reference to GND *SHUNTED
J7 Shunt to RCA Provides RCA reference to GND *SHUNTED
J22 HP Detect
J5 1.8V Buck Input
J12 HPOUTA Selects test load from HPOUTA
J4 HPOUTB Selects test load from HPOUTB
J2
J3
J34 Board Power Selects source of Board Power
VLDO
VA
VL
VCP
HPOUTA
HPOUTA(LPF)
HPOUTB
HPOUTB(LPF)
Selects source of voltage for the
VL supply
Selects source of voltage for the
VCP supply
Selects source of voltage for the
VA supply
Selects source of voltage for the
VLDO supply
Current Measurement
Selects how the HP_Detect pin on
CS42L55is driven
Selects power supply source for
+1.8VB
Connects or removes LPF for
HPOUTA
Connects or removes LPF for
HPOUTB
Table 2. Jumper Settings
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5V regulator.
+3.3V Voltage source is +3.3V regulator.
+1.8VB Voltage source is +1.8V from battery.
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5V regulator. .
+1.8VB Voltage source is +1.8V from battery.
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5V regulator. .
+1.8VB Voltage source is +1.8V from battery.
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5V regulator. .
+1.8VB Voltage source is +1.8V from battery.
*SHUNTED 1 Ω series resistor is shorted.
OPEN 1 Ω series resistor in power supply path.
AIN2B and AIN2A RCAs are given a ground reference.
AIN1B and AIN1A RCAs are given a ground reference.
1 - 2 HPDETECT is driven by FPGA/GUI.
*2 - 3
1 - 2 1.8VB is derived from external input.
*2 - 3 1.8VB is derived from AAA batteries.
1 - 2 32 Ω load selected for HPOUTA.
2 - 3 16 Ω load selected for HPOUTA.
1 - 2 32 Ω load selected for HPOUTB.
2 - 3 16 Ω load selected for HPOUTB.
1 - 2 No filtered output selected for HPOUTA.
*2 - 3 RC filtered output selected for HPOUTA.
1 - 2 No filtered output selected for HPOUTB.
*2 - 3 RC filtered output selected for HPOUTB.
1 - 2
*2 - 3 Board powered from USB.
HPDETECT is driven by HP Jack line when a
stereo connection is inserted in J1.
Board powered from external +5V source connected to TP9/TP10.
*Default factory settings
18 DS773DB1
Page 19

CDB42L55
F
i10
6 PERFORMANCE PLOTS
Test conditions (unless otherwise specified): TA= 25°C; VA=VCP=VLDO=VL=1.8 V; input test signal is a full-scale
997 Hz si ne wave; dB valu es re lativ e to fu ll-scale output; measurement bandwidth 20 Hz to 20 kHz (un-weighted);
sample frequency = 48 kHz; +2 dB analog gain for Line Output path; -4 dB analog gain for Headphone Output path;
headphone test load: R
= 16 Ω; no LPF option for Headphone Output path.
L
-60
-65
-70
-75
d
B
-80
F
S
-85
-90
-95
-100
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
-60
-65
-70
-75
d
B
-80
F
S
-85
-90
-95
-100
-60 -10-50 -40 -30 -20
dBr
Figure 10. THD+N vs Freq. - Analog In to Digital Out Figure 11. THD+N vs Amplitude - Analog In to Digital Out
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
F
-80
S
-100
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
F
-80
S
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 12. FFT - Analog In to Digital Out @ -1 dBFS
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 13. FFT - Analog In to Digital Out @ -60 dBFS
Note: The total harmonic distortion + noise (THD+N) perf ormance of the ADC in the CS42L55 is determined
by the value of the capacitor on the FILT+ pin. Larger capacitor values yield significant improvement
in THD+N at low frequencies. Fig. 10 shows the THD+N vs. frequency performance measured with a
2.2 µF capacitor.
DS773DB1 19
Page 20

CDB42L55
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
F
-80
S
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
F
-80
S
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 14. FFT - Analog In to Digital Out - no input Figure 15. FFT Crosstalk - Analog In to Digital Out
@ -1 dBFS
+0
-0.5
-1
d
B
-1.5
F
S
-2
-2.5
+40
+30
+20
+10
d
B
+0
F
S
-10
-20
-30
-3
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
-40
-125 +0-100 -75 -50 -25
dBr
Figure 16. Freq. Response - Analog In to Digital Out Figure 17. Fade-to-Noise Linearity - Analog In to Digital
Out
-60
-65
-70
d
-75
B
-80
r
-85
A
-90
-95
-100
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 18. THD+N vs. Freq. - Digital In to HP Out
-60
-65
-70
d
-75
B
-80
r
-85
A
-90
-95
-100
-100 +0-80 -60 -40 -20
dBFS
Figure 19. THD+N vs. Amplitude - Digital In to HP Out
20 DS773DB1
Page 21

CDB42L55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
d
-85
B
-90
r
-95
A
-100
-105
-110
-115
-120
-50 +0-40 -30 -20 -10
Master Volume
(Digital)
Headphone Volume
(Analog)
dBr A
Figure 20. THD+N vs. Volume - Digital In to HP Out
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 21. FFT - Digital In to HP Out @ 0 dBFS
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 22. FFT - Digital In to HP Out @ -60 dBFS Figure 23. FFT - Digital In to HP Out - no input
+3
+2
+1
d
B
+0
r
A
-1
-2
-3
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
+40
+30
+20
d
+10
B
+0
r
-10
A
-20
-30
-40
-125 +0-100 -75 -50 -25
dBFS
Figure 24. Freq. Response - Digital In to HP Out Figure 25. Fade-to-Noise Linearity- Digital In to HP Out
DS773DB1 21
Page 22

CDB42L55
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
-60
-65
-70
d
-75
B
-80
r
-85
A
-90
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
-95
-100
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 26. FFT Crosstalk - Digital In to HP Out @ 0 dBFS Figure 27. THD+N vs. Freq. - Digital In to Line Out
-60
-65
-70
d
-75
B
-80
r
-85
A
-90
-50
-60
-70
d
-80
B
r
-90
A
-100
Master Volume
(Digital)
-95
-100
-100 +0-80 -60 -40 -20
dBFS
-110
-120
-60 +0-50 -40 -30 -20 -10
Line Volume
(Analog)
dBr A
Figure 28. THD+N vs. Amplitude - Digital In to Line Out Figure 29. THD+N vs. Volume - Digital In to Line Out
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 30. FFT - Digital In to Line Out @ 0 dBFS Figure 31. FFT - Digital In to Line Out @ -60 dBFS
22 DS773DB1
Page 23

CDB42L55
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
+0
-20
-40
d
-60
B
r
-80
A
-100
-120
-140
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
Figure 32. FFT - Digital In to Line Out - no input Figure 33. FFT Crosstalk - Digital In to Line Out @
0dBFS
+3
+2
+1
d
B
+0
r
A
-1
-2
+40
+30
+20
d
+10
B
+0
r
-10
A
-20
-30
-3
20 20k50 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k 10k
Hz
-40
-125 +0-100 -75 -50 -25
dBFS
Figure 34. Freq. Response - Digital In to Line Out Figure 35. Fade-to-Noise Linearity- Digital In to Line Out
DS773DB1 23
Page 24

24 DS773DB1
7 CDB42L55 BLOCK DIAGRAM
PC Control Board Power
External 5.0 V
Serial
USB
Supply
I²C for all
applicable
devices
24 MHz
Oscillator
PLL
S/PDIF Rx
S/PDIF Tx
Clock/Data Routing
Clock dividers and PLL used
to derive all applicable Fs
from 24 MHz oscillator
SRC (Tx)
FPGA
SRC (Rx)
I/O Stake Headers for Audio
Precision’s Programmable Serial
Interface Adapter (PSIA)
LDO
LDO’s
3.3 V
3.3 V (VL only)
Tri-state
Buffers
I/O SMA Connectors
for External System
Interface
1.8 V
2.5 V
VL, VCP, VLDO, VA
Circuit Break for
External System
Interface
PCM
Clocks/Data
I²C Clocks/
Data
HP
Jack
CODEC Power
MUX
CS42L55
Stereo HP
Output
1.8 V
Buck
Stereo Line
Output
x3
AAA Alkaline
(not included)
Stereo
Input 1
Stereo
Input 2
Figure 36. Block Diagram
CDB42L55
Page 25

DS773DB1 25
8 CDB42L55 SCHEMATICS
Figure 37. CS42L55 & Analog I/O (Schematic Sheet 1)
CDB42L55
Page 26

26 DS773DB1
Figure 38. S/PDIF & Digital Interface (Schematic Sheet 2)
CDB42L55
Page 27

DS773DB1 27
Figure 39. PLL, oscillator and external I/O connections (Schematic Sheet 3)
CDB42L55
Page 28

28 DS773DB1
Figure 40. Microcontroller and FPGA (Schematic Sheet 4)
CDB42L55
Page 29

DS773DB1 29
Figure 41. Power (Schematic Sheet 5)
CDB42L55
Page 30

30 DS773DB1
9 CDB42L55 LAYOUT
Figure 42. Silk Screen
CDB42L55
Page 31

DS773DB1 31
Figure 43. Top-Side Layer
CDB42L55
Page 32

32 DS773DB1
Figure 44. GND (Layer 2)
CDB42L55
Page 33

DS773DB1 33
Figure 45. Power (Layer 3)
CDB42L55
Page 34

34 DS773DB1
Figure 46. Bottom Side Layer
CDB42L55
Page 35

10REVISION HISTORY
Revision Changes
DB1 Initial Release
CDB42L55
DS773DB1 35
Page 36

CDB42L55
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For all product questions and inquiries, contact a Cirrus Logic Sales Representative.
To find the one nearest you, go to www.cirrus.com.
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Cirrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Cirrus") believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. Howev er, the information is subject
to change without noti ce and is pr ovided " AS IS" wit hout warr anty of any kind (express or impli ed). Cust omers are adv ised to ob tain the latest version of relevant
information to verify, before placin g or ders, th at infor ma tion be ing re lied o n is cu rren t and com ple te. All pr oducts a re so ld s ubject to the terms and conditions of sale
supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, indemnification, and limitation of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus
for the use of this information, including use of this information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infringement of patents or other rights of third
parties. This document is the property of Cirrus and by furnishing this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask work rights,
copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or othe r intellectual prop erty rights. Cirrus owns th e copyrights associated with the information contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only for use with in your organization with respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other products of Cirrus. This consent
does not extend to other copying such as copying for general distribution, advertising or promo tion al purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL APPLICATIONS”). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE
IN PRODUCTS SURGICALLY IMPLANTED INTO THE BODY, AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY OR SECURITY DEVICES, LIFE SUPPORT PRODUCTS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK AND CIRRUS DISCLAIMS AND MAKES NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS, STATUTORY OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH REGARD TO ANY CIRRUS PRODUCT THAT IS USED IN SUCH A MANNER. IF THE CUSTOMER OR CUST OMER’S CUSTOMER USES OR PERMITS THE USE OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN CRITICAL APPLICATIONS, CUSTOMER AGREES, BY SUCH USE, TO FULLY
INDEMNIFY CIRRUS, ITS OFFICERS, DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES, DISTRIBUTORS AND OTHER AGENTS FROM ANY AND ALL LIABILITY, INCLUDING ATTORNEYS’ FEES AND COSTS, THAT MAY RESULT FROM OR ARISE IN CONNECTION WITH THESE USES.
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, and the Cirrus Logic logo designs are trademarks of Cirrus Logic, Inc. All other brand and product names in this document may be trademarks
or service marks of their respective owners.
I2C is a registered tradem ar k of Philips Semiconducto r.
Microsoft and Windows are registed trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
36 DS773DB1
 Loading...
Loading...