Page 1
Evaluation Board for CS42L51
CDB42L51
Features
MUXed Analog Input
– Stereo RCA Inputs
– Two Microphone Input Jacks
MUXed Analog Output
– Stereo RCA Output (w/Optional Load or
LPF)
– Stereo Headphone Jack
– Mono Speaker Driver w/Banana Posts
8 kHz to 96 kHz S/PDIF Interface
– CS8415 Digital Audio Receiver
– CS8406 Digital Audio Transmitter
I/O Stake Headers
– External Control Port Accessibility
– External DSP Serial Audio I/O Accessibility
Independent, Regulated Supplies
1.8 V to 3.3 V Logic Interface
Hardware Control
– 11 Pre-Defined Switch Settings
FlexGUI S/W Control - Windows
– Pre-Defined & User-Configurable Scripts
Layout and Grounding Recommendations
®
Compatible
Description
The CDB42L51 evaluation board is an excellent means
for evaluating the CS42L51 CODEC. Evaluation requires an analog/digital signal source and analyzer, and
power supplies. Optionally, a Windows
computer may be used to evaluate the CS42L51 in Software Mode.
System timing can be provided by the CS8415, by the
CS42L51 with supplied master clock, or by an I/O stake
header with a DSP connected.
RCA phono jacks are provided for the CS42L51 analog
inputs and outputs. 1/8th inch jacks are also available
for microphone input and headphone output. Digital
data I/O is available via RCA phono or optical connectors to the CS8415 and CS8406.
The Windows software provides a GUI to make configuration of the CDB42L51 easy. The software
communicates through the PC’s serial port to configure
the control port registers so that all features of the
CS42L51 can be evaluated. The evaluation board may
also be configured to accept external timing and data
signals for operation in a user application during system
development.
ORDERING INFORMATION
CDB42L51 Evaluation Board
PC-compatible
http://www.cirrus.com
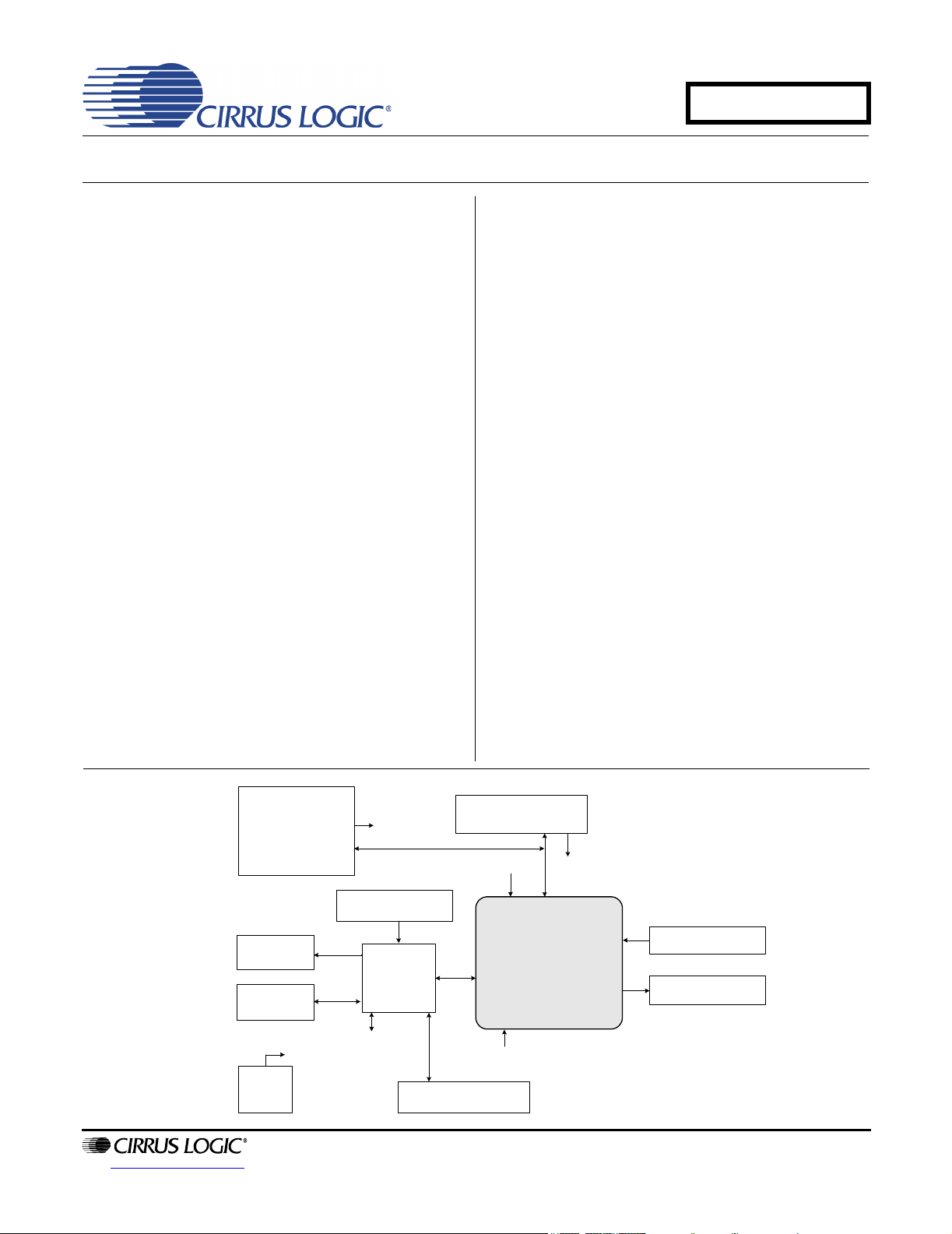
Software Mode
Control Port
S/PDIF Output
(CS8406)
S/PDIF Input
(CS8415)
MCLK
Oscillator
(socket)
I²C/SPI Header
Reset
MCLK
Hardware Mode
Switches
FPGA
Reset
Reset
Clocks/Data Header
Copyright © Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2007
(All Rights Reserved)
Reset
CS42L51
Analog Input
(Line + MIC)
Analog Output
(Line + Headphone)
OCTOBER '07
DS679DB2
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................ 4
1.1 Power ............................................................................................................................................. 4
1.2 Grounding and Power Supply Decoupling ......................................................................................4
1.3 FPGA .............................................................................................................................................. 4
1.4 CS42L51 Audio CODEC ................................................................................................................ 4
1.5 CS8406 Digital Audio Transmitter .................................................................................................. 5
1.6 CS8415 Digital Audio Receiver ...................................................................................................... 5
1.7 Oscillator ......................................................................................................................................... 5
1.8 I/O Stake Headers .......................................................................................................................... 5
1.9 Analog Input ................................................................................................................................... 6
1.10 Analog Outputs ............................................................................................................................. 6
1.11 Stand-Alone Switches .................................................................................................................. 6
1.12 USB and RS-232 Control Port Connectors .................................................................................. 6
2. SOFTWARE MODE CONTROL ............................................................................................................ 7
2.1 General Configuration Tab ............................................................................................................. 8
2.2 CODEC Configuration Tab ............................................................................................................. 9
2.3 ADC Volume Controls Tab ........................................................................................................... 10
2.4 DAC Volume Controls Tab ........................................................................................................... 11
2.5 Register Maps Tab ....................................................................................................................... 12
3. HARDWARE MODE CONTROL ......................................................................................................... 13
3.1 FPGA H/W Control ....................................................................................................................... 13
3.2 CS42L51 H/W Control .................................................................................................................. 17
4. SYSTEM CONNECTIONS AND JUMPERS ....................................................................................... 17
5. CDB42L51 BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................................................................................... 19
6. CDB42L51 SCHEMATICS .................................................................................................................. 20
7. CDB42L51 LAYOUT ........................................................................................................................... 26
8. ERRATA .............................................................................................................................................. 29
9. REVISION HISTORY ........................................................................................................................... 29
CDB42L51
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. General Configuration Tab........................................................................................................... 8
Figure 2. CODEC Configuration Tab .......................................................................................................... 9
Figure 3. ADC Volume Controls Tab......................................................................................................... 10
Figure 4. DAC Volume Controls Tab......................................................................................................... 11
Figure 5. Register Maps Tab - CS42L51 .................................................................................................. 12
Figure 6. Routing 0.................................................................................................................................... 14
Figure 7. Routing 1.................................................................................................................................... 14
Figure 8. Routing 3.................................................................................................................................... 14
Figure 9. Routing 4.................................................................................................................................... 15
Figure 10. Routing 5.................................................................................................................................. 15
Figure 11. Routing 6.................................................................................................................................. 15
Figure 12. Routing 7.................................................................................................................................. 15
Figure 13. Routing 8.................................................................................................................................. 16
Figure 14. Routing 9.................................................................................................................................. 16
Figure 15. Routing 10................................................................................................................................ 16
Figure 16. Routing 11................................................................................................................................ 16
Figure 17. Block Diagram.......................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 18. CS42L51 and Analog I/O (Schematic Sheet 1) ....................................................................... 20
Figure 19. S/PDIF I/O (Schematic Sheet 2) .............................................................................................. 21
Figure 20. FPGA (Schematic Sheet 3)...................................................................................................... 22
Figure 21. Level Shifters & I/O Stake Header (Schematic Sheet 4) ......................................................... 23
Figure 22. Control Port I/O (Schematic Sheet 5) ...................................................................................... 24
2 DS679DB2
Page 3

Figure 23. Power (Schematic Sheet 6) ..................................................................................................... 25
Figure 24. Silk Screen............................................................................................................................... 26
Figure 25. Top-Side Layer ........................................................................................................................ 27
Figure 26. Bottom-Side Layer ................................................................................................................... 28
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. MCLK and Clock/Data Routing Options....................................................................................... 13
Table 2. CS42L51 H/W Mode Control........................................................................................................ 17
Table 3. System Connections .................................................................................................................... 17
Table 4. Jumper Settings ........................................................................................................................... 18
CDB42L51
DS679DB2 3
Page 4

CDB42L51
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The CDB42L51 evaluation board is an excellent means for evaluating the CS42L51 CODEC. Digital audio signal
interfaces are provided, and an FPGA is used for easily configuring the board. Section 2. “Software Mode Control”
on page 7 and Section 3. “Hardware Mode Control” on page 13 provide configuration details.
The CDB42L51 schematic set has been partitioned into six pages and is shown in Figures 18 through 23. “System
Connections and Jumpers” on page 17 provides a description of all stake headers and connectors, including the
default factory settings for all jumpers.
1.1 Power
Power is supplied to the evaluation board through the +5.0 V binding posts. Jumpers connect the CODEC’s
supplies to a regulated voltage of +1.8 V, 2.5 V or +3.3 V for VL and +1.8 V or 2.5 V for VD, VA and VA_HP.
All voltage inputs must be referenced to the black binding post ground connector.
For current measurement purposes only, a series resistor is connected to each supply. The current is easily
calculated by measuring the voltage drop across this resistor. NOTE: The stake headers connected in parallel with these resistors must be shunted with the supplied jumper during normal operation.
WARNING: Please refer to the CS42L51 data sheet for allowable voltage levels.
1.2 Grounding and Power Supply Decoupling
The CS42L51 requires careful attention to power supply and grounding arrangements to optimize performance. The CDB42L51 demonstrates these optimal arrangements. Figure 17 on page 19 provides an overview of the connections to the CS42L51. Figure 24 on page 26 shows the component placement, Figure 25
on page 27 shows the top layout, and Figure 26 on page 28 shows the bottom layout. The decoupling ca-
pacitors are located as close to the CS42L51 as possible. Extensive use of ground plane fill in the evaluation
board yields large reductions in radiated noise.
1.3 FPGA
The FPGA provides digital signal routing between the CS42L51, CS8406, CS8415 and the I/O stake header. It also configures the hardware mode options of the CS8406 and CS8415 and provides routing control
of the system master clock from an on-board oscillator, the CS8415 and the I/O stake header. The Cirrus
FlexGUI software and “FPGA H/W Control” switches provide full control of the FPGA’s routing and configuration options. Section 2. “Software Mode Control” on page 7 and Section 3. “Hardware Mode Control” on
page 13 provide configuration details.
1.4 CS42L51 Audio CODEC
A complete description of the CS42L51 (Figure 18 on page 20) is included in the CS42L51 product data
sheet.
The CS42L51 may be configured using either the Cirrus FlexGUI or the on-board “CS42L51 H/W Control”
switches. The Software Mode control port registers are accessible through the “Register Maps” tab of the
Cirrus FlexGUI software. This tab provides low-level control of each bit. For easier configuration, additional
tabs provide high-level control. The Hardware Mode, stand-alone controls for the CS42L51 are accessible
through the on-board, stand-alone switches, “CS42L51 H/W Control.”
Clock and data source selections are made in the control port of the FPGA, accessible through the “General
Configurations” tab of the Cirrus FlexGUI software or through the on-board “FPGA H/W Control” switches.
Section 2. “Software Mode Control” on page 7 and Section 3. “Hardware Mode Control” on page 13 provide
configuration details. provide configuration details.
4 DS679DB2
Page 5

1.5 CS8406 Digital Audio Transmitter
A complete description of the CS8406 transmitter (Figure 19 on page 21) and a discussion of the digital au-
dio interface are included in the CS8406 data sheet.
The CS8406 converts the PCM data generated by the CS42L51 to the standard S/PDIF data stream and
routes this signal to the optical and RCA connectors. The CS8406 operates in slave mode only, accepting
either a 128xFs or 256xFs master clock, and can operate in either the Left-Justified or I²S interface format.
Selections are made in the control port of the FPGA, accessible through the “General Configurations” tab
of the Cirrus FlexGUI software or through the on-board switches, “FPGA H/W Control.” Section 2. “Software
Mode Control” on page 7 and Section 3. “Hardware Mode Control” on page 13 provide configuration details.
provide configuration details.
1.6 CS8415 Digital Audio Receiver
A complete description of the CS8415 receiver (Figure 19 on page 21) and a discussion of the digital audio
interface are included in the CS8415 data sheet.
The CS8415 converts the input S/PDIF data stream from the optical or the RCA connector into PCM data
for the CS42L51. The CS8415 operates in master or slave mode, generates a 256xFs master clock, and
can operate in either the Left-Justified or I²S interface format.
Selections are made in the control port of the FPGA, accessible through the “General Configurations” tab
of the Cirrus FlexGUI software or through the on-board “FPGA H/W Control” switches. Section 2. “Software
Mode Control” on page 7 and Section 3. “Hardware Mode Control” on page 13 provide configuration details.
provide configuration details.
CDB42L51
1.7 Oscillator
The on-board oscillator provides one of the system master clocks. Selections are made in the control port
of the FPGA, accessible through the “General Configurations” tab of the Cirrus FlexGUI software or through
the on-board switches, “FPGA H/W Control.” Section 2. “Software Mode Control” on page 7 and Section 3.
“Hardware Mode Control” on page 13 provide configuration details. provide configuration details.
The oscillator is mounted in pin sockets, allowing easy removal or replacement. Additional sockets are also
installed, allowing the optional use of a full- or half-can-sized oscillator.
1.8 I/O Stake Headers
The evaluation board has been designed to allow interfacing with external systems via a serial port header
(reference designation J5) and a control port header, “CS42L51 S/W Control.” The serial port header provides access to the serial audio signals required to interface with a DSP (Figure 21 on page 23). Selections
are made in the control port of the FPGA, accessible through the “General Configurations” tab of the Cirrus
FlexGUI software or through the on-board switches, “FPGA H/W Control.” Section 2. “Software Mode Con-
trol” on page 7 and Section 3. “Hardware Mode Control” on page 13 provide configuration details.
The control port header provides bidirectional access to the SPI™/I²C
moving all the shunt jumpers from the “PC” position. The user may then choose to connect a ribbon cable
to the “CONTROL” position, allowing operation of the CS42L51 in a user-application for system development. A single “GND” row for the ribbon cable’s ground connection is provided to maintain signal integrity.
Two unpopulated pull-up resistors are also available should the user choose to use the CDB for the I²C power rail.
®
control port signals by simply re-
DS679DB2 5
Page 6

1.9 Analog Input
RCA connectors supply the line-level analog inputs through an AC-coupled passive filter. The signal from
these inputs may be driven to individual inputs or to all inputs of the CS42L51. A microphone may be connected to one or both of the 1/8th inch jacks, MIC1 and MIC2.
To accommodate the microphone bias output available on certain input pins of the CS42L51, additional
stake headers are provided to MUX both the input audio signal and the output bias signal to or from the
CS42L51. Figure 18 on page 20 in the schematic set illustrates how signals are routed. Table 4 on page 18
provides more details for how to connect the jumpers. The CS42L51 data sheet details the required singleended signal amplitude that will drive the inputs to full scale.
1.10 Analog Outputs
RCA connectors are connected directly to the output of the CS42L51 to allow evaluation of the ground-centered analog outputs. The Right Channel and Left Channel stake headers optionally connect a passive-filtered output to the RCA connectors. For evaluation of the CS42L51’s drive strength into a load, the 16 Ω
HP Load stake headers connect the analog outputs to 16 Ω. Headphones may also be connected to the
1/8th inch jack. When connecting headphones, the 16 Ω load resistors should be disconnected by removing
the jumpers on each stake header.
One of the analog outputs may be connected to a speaker driver through the “Speaker” stake header. A
mono speaker may then be driven via the red and black banana jack. The red banana jack designates the
positive terminal while black designates the negative.
CDB42L51
1.11 Stand-Alone Switches
The “FPGA H/W Control” and “CS42L51 H/W Control” switches control all Hardware Mode options.
Section 3. “Hardware Mode Control” on page 13 provides a description of each topology.
1.12 USB and RS-232 Control Port Connectors
A graphical user interface is available for the CDB42L51, allowing easy manipulation of each register. This
GUI interfaces with the CDB via the USB and RS-232 connectors and controls all Software Mode options.
Section 2. “Software Mode Control” on page 7 provides a description of the Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Simply connect a cable from the USB or RS-232 connector to the PC and launch the Cirrus Logic FlexGUI
software to enable software control of the CDB42L51.
6 DS679DB2
Page 7

CDB42L51
2. SOFTWARE MODE CONTROL
The CDB42L51 may be used with the Microsoft® Windows-based FlexGUI graphical user interface, allowing software control of the CS42L51 and FPGA registers. The latest control software may be downloaded from
www.cirrus.com/msasoftware. Step-by-step instructions for setting up the FlexGUI are provided as follows:
1. Download and install the FlexGUI software as instructed on the Website.
2. Connect and apply power to the +5.0 V binding post.
3. Connect the CDB to the host PC using either a 9-pin serial or USB cable.
4. Launch the Cirrus FlexGUI. Once the GUI is launched successfully, all registers are set to their default reset
state.
5. Enable the CS42L51 by engaging the “Enable CS42L51” push button.
6. Refresh the GUI by clicking on the “Update” button. The default state of all registers are now visible.
7. Engage and then disengage the “Power Down” push button in the “CODEC Basic Configurations” group.
This performs the necessary write sequence to the CS42L51 for Software Mode operation.
For standard setup:
8. Set up the signal routing in the “General Configurations” tab as desired.
9. Set up the CS42L51 in the “CODEC Configurations”, “ADC Volume Controls” or “DAC Volume Controls” tab
as desired.
10. Begin evaluating the CS42L51.
For quick setup, the CDB42L51 may, alternatively, be configured by loading a predefined sample script file:
11. On the File menu, click "Restore Board Registers..."
12. Browse to Boards\CDB42L51\Scripts\.
13. Choose any one of the provided scripts to begin evaluation.
To create personal scripts files:
14. On the File menu, click "Save Board Registers..."
15. Enter any name that sufficiently describes the created setup.
16. Choose the desired location and save the script.
17. To load this script, follow the instructions from step 11 above.
DS679DB2 7
Page 8
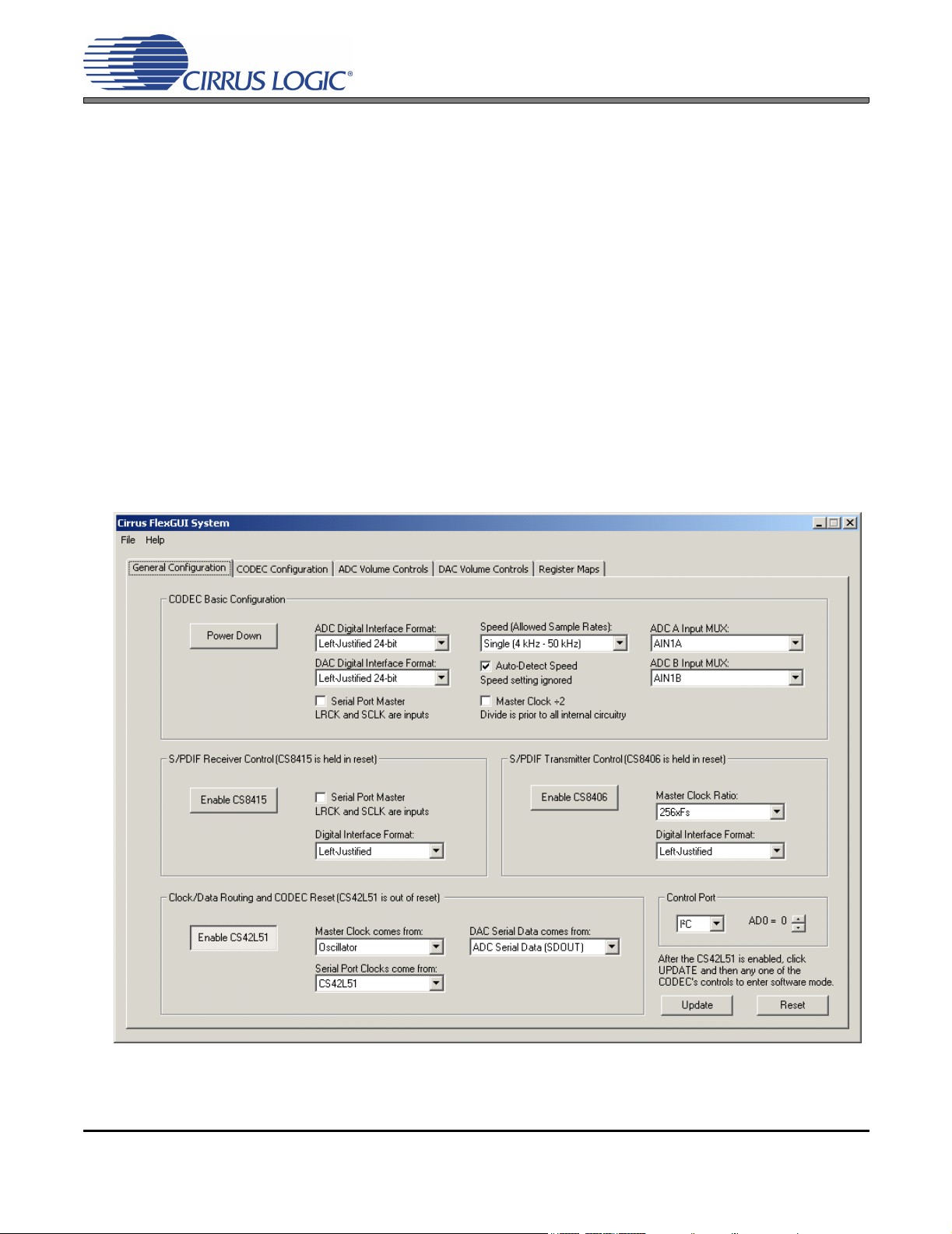
2.1 General Configuration Tab
The “General Configuration” tab provides high-level control of signal routing on the CDB42L51. This tab also
includes basic controls for the CS42L51 for quickly setting up the CDB42L51 in simple configurations. Status text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration is shown in parenthesis or appears directly below the
associated control. This text may change depending on the setting of the associated control. A description
of each control group is outlined below:
CODEC Basic Configuration - Includes basic register controls in the CS42L51 used for setting up the interface format, clocking functions and internal analog input routing. See Section 2.2 through Section 2.4 for
more controls in the CS42L51.
S/PDIF Receiver Control - Includes all available hardware mode controls for setting up the CS8415.
S/PDIF Transmitter Control - Includes all available hardware mode controls for setting up the CS8406.
Clock/Data Routing and CODEC Reset - Includes controls used for routing clocks and data between the
CS42L51, CS8415, oscillator and the I/O stake header. Also includes a reset control for the CS42L51.
Update - Reads all registers in the FPGA and CS42L51 and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets FPGA to default routing configuration.
CDB42L51
Figure 1. General Configuration Tab
8 DS679DB2
Page 9
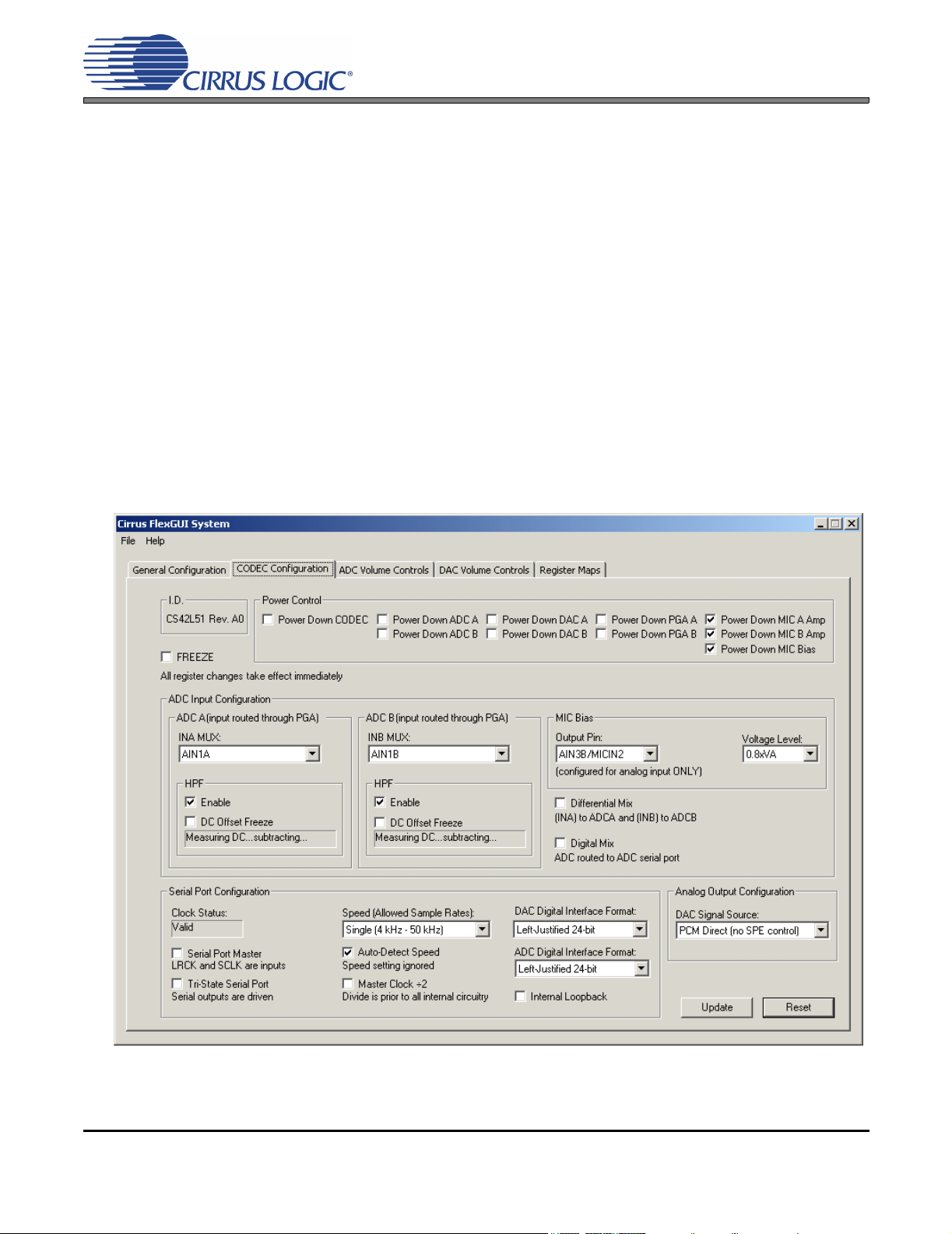
2.2 CODEC Configuration Tab
The “CODEC Configuration” tab provides high-level control of all setup configurations for the CS42L51. Status text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration is shown in parenthesis or appears directly below the
associated control. This text will change depending on the setting of the associated control. A description
of each control group is outlined below (a description of each register is included in the CS42L51 data
sheet):
Power Control - Includes all register controls for powering down each device within the CODEC.
ADC input Configuration - Includes controls for the internal MUX, analog input and microphone bias output.
Serial Port Configuration - Includes controls for all settings related to the transmission and relationship of
data and clocks within the CODEC.
Analog Output Configuration - Includes control for the signal sources of the DAC. NOTE: Most controls in
the “DAC Volume Controls” tab are not accessible unless the SPE (Signal Processing Engine) signal is selected.
Update - Reads all registers in the CS42L51 and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets the CS42L51.
CDB42L51
Figure 2. CODEC Configuration Tab
DS679DB2 9
Page 10

2.3 ADC Volume Controls Tab
The “ADC Volume Controls” tab provides high-level control of all volume settings in the ADC of the
CS42L51. Status text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration is shown in parenthesis or inside the
control group of the affected control. This text will change depending on the setting of the associated control.
A description of each control group is outlined below (a description of each register is included in the
CS42L51 data sheet):
Digital Volume Control - Includes digital volume controls and adjustments for the ADC.
ALC Configuration - Includes all configuration settings for the Automatic Level Control (ALC).
Analog Volume Control - Includes all analog volume controls and adjustments for the ADC.
Noise Gate Configuration - Includes all configuration settings for the noise gate.
Update - Reads all registers in the CS42L51 and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets the CS42L51.
CDB42L51
Figure 3. ADC Volume Controls Tab
10 DS679DB2
Page 11

2.4 DAC Volume Controls Tab
The “DAC Volume Controls” tab provides high-level control of all volume settings in the DAC of the
CS42L51. Status text detailing the CODEC’s specific configuration is shown in read-only edit boxes, in parenthesis, or appears directly below the associated control. This text will change, depending on the setting
of the associated control. NOTE: Control groups that include “(SPE)” in its labeling are a part of the Signal
Processing Engine (SPE) and are not accessible unless the SPE signal is selected in the “CODEC Configuration” tab. A description of each control group is outlined below (a description of each register is included
in the CS42L51 data sheet):
Digital Volume Control - Includes all digital volume controls and adjustments for the DAC.
Analog Multipliers - Includes the control for the analog gain of the output amplifier and displays the full scale
output factors.
Limiter Configuration - Includes all configuration settings for the Limiter.
Tone Control - Includes all bass and treble boosting controls and adjustments.
BEEP Generator - Includes all configuration settings for the BEEP generator.
Update - Reads all registers in the CS42L51 and reflects the current values in the GUI.
Reset - Resets the CS42L51.
CDB42L51
Figure 4. DAC Volume Controls Tab
DS679DB2 11
Page 12

2.5 Register Maps Tab
The Advanced Register Debug tab provides low-level control of the CS42L51 individual register settings.
Register values can be modified bit-wise or byte-wise. For bit-wise, click the appropriate push-button for the
desired bit. For byte-wise, the desired hex value can be typed directly into the register address box in the
register map. The “FPGA” and “GPIO” tabs may be ignored.
CDB42L51
Figure 5. Register Maps Tab - CS42L51
12 DS679DB2
Page 13

CDB42L51
3. HARDWARE MODE CONTROL
The CDB may be configured without the use of a software control port through the use of two switches, “FPGA H/W
Control” and “CS42L51 H/W Control.” These switches are enabled in hardware mode only and ignored in software
mode. The CDB42L51 automatically enters hardware mode upon initial power up, or when exiting software mode,
by terminating the Cirrus FlexGUI software or by disconnecting the RS-232 serial cable.
3.1 FPGA H/W Control
The “FPGA H/W Control” switch sets up the CDB in 11 pre-defined routing topologies in hardware mode.
The tables and figures below describe each switch setting. The At-A-Glance Controls table provides a quick
reference for all presets.
At-A-Glance Controls
S[3:2] S[1] S[0]
00 - CS8415 MCLK / CS8415 clocks/data route through FPGA
01 - I/O Header MCLK / I/O Header clocks/data route through FPGA
10 - Oscillator MCLK / I/O Header clocks/data route through FPGA
11 - Reserved
0 - CS42L51 Slave Routing
1 - CS42L51 Master Routing
0 - No Loopback Routing
1 - Loopback Routing
Signal
S[3:0] General Description Detailed Description
Routing
0
0000 CS8415 Clocks/Data 1) CS8415 masters MCLK. 2) CS8415 masters PCM clocks.
Figure 6
1
0001 CS8415 Clocks, ADC Loopback 1) CS8415 masters MCLK. 2) CS8415 masters PCM clocks.
Figure 7
2 Reserved
3
0011 CS42L51 Clocks, ADC Loopback 1) CS8415 masters MCLK. 2) CS42L51 masters PCM clocks.
Figure 8
4
0100 I/O Clocks/Data 1) I/O masters MCLK. 2) I/O masters PCM clocks.
Figure 9
5
0101 I/O Clocks, ADC Loopback 1) I/O masters MCLK. 2) I/O masters PCM clocks.
Figure 10
6
0110 CS42L51 Clocks, I/O Data 1) I/O masters MCLK. 2) CS42L51 masters PCM clocks.
Figure 11
7
0111 CS42L51 Clocks, ADC Loopback 1) I/O masters MCLK. 2) CS42L51 masters PCM clocks.
Figure 12
8
1000 I/O Clocks/Data 1) Oscillator masters MCLK. 2) I/O masters PCM clocks.
Figure 13
9
1001 I/O Clocks, ADC Loopback 1) Oscillator masters MCLK. 2) I/O masters PCM clocks.
Figure 14
10
1010 CS42L51 Clocks, I/O Data 1) Oscillator masters MCLK. 2) CS42L51 masters PCM clocks.
Figure 15
11
1011 CS42L51 Clocks, ADC Loopback 1) Oscillator masters MCLK. 2) CS42L51 masters PCM clocks.
Figure 16
12-15 Reserved
CS8415 MCLK
3) CS8415 data into SDIN.
3) SDOUT into SDIN.
3) SDOUT into SDIN.
I/O MCLK
3) I/O data into SDIN.
3) SDOUT into SDIN.
3) I/O data into SDIN.
3) SDOUT into SDIN.
Oscillator MCLK
3) I/O data into SDIN.
3) SDOUT into SDIN.
3) I/O data into SDIN.
3) SDOUT into SDIN.
Table 1. MCLK and Clock/Data Routing Options
DS679DB2 13
Page 14

CDB42L51
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
(LJ)
SDIN
SDIN
Oscillator
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
(LJ)
Oscillator
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
SDIN
(LJ)
(LJ)
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
Figure 6. Routing 0 Figure 7. Routing 1
Routing 2 - Reserved
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
Oscillator
(LJ)
SDIN
(LJ)
SDIN
Figure 8. Routing 3
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
14 DS679DB2
Page 15
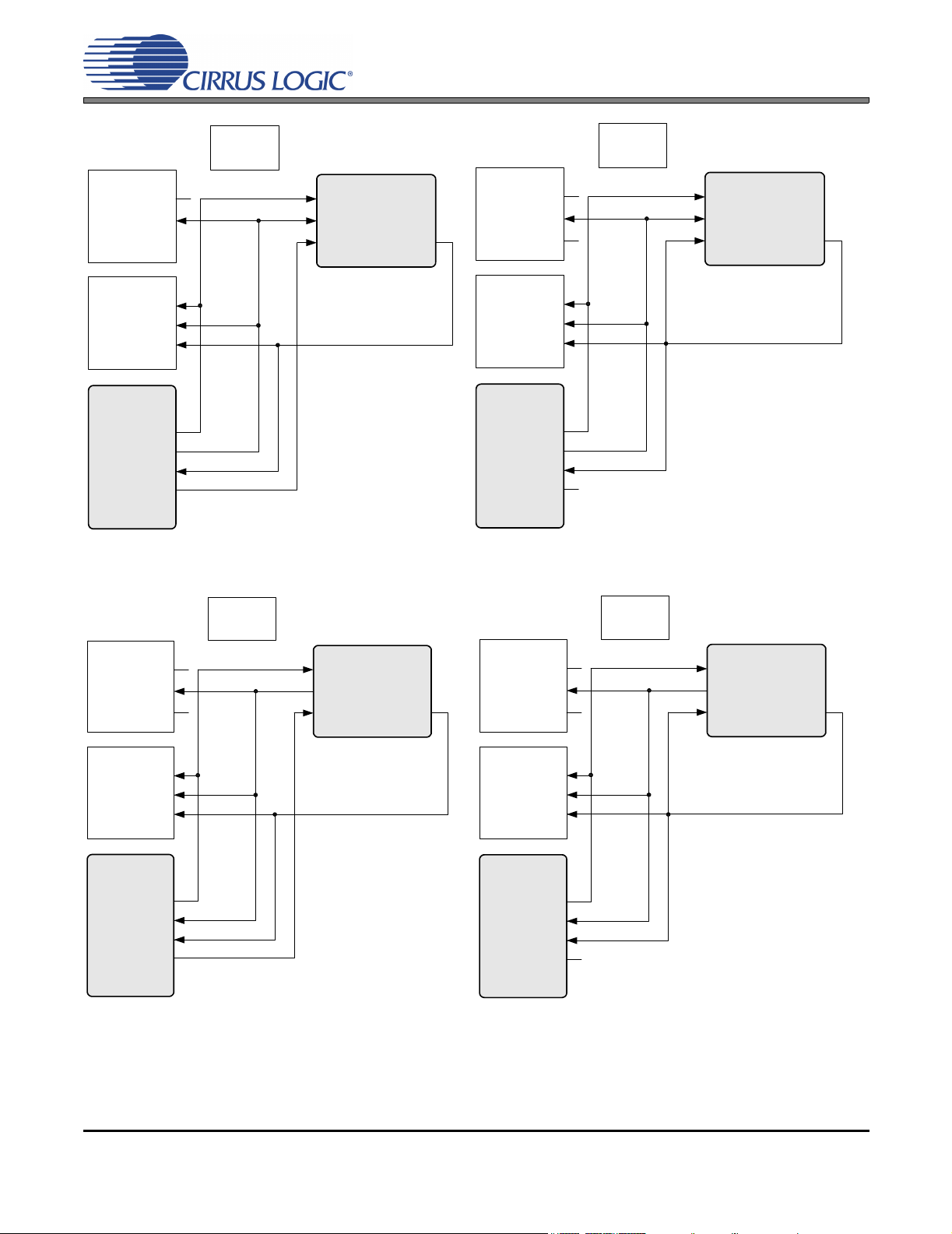
CDB42L51
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
SDIN
Oscillator
CS42L51
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
(LJ)
SDIN
SDOUT
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
(LJ)
Oscillator
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
SDIN
(LJ)
(LJ)
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
Figure 9. Routing 4 Figure 10. Routing 5
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
(LJ)
SDIN
SDIN
Oscillator
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
(LJ)
Oscillator
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
SDIN
(LJ)
(LJ)
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
Figure 11. Routing 6 Figure 12. Routing 7
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
DS679DB2 15
Page 16

CDB42L51
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
SDIN
Oscillator
CS42L51
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
(LJ)
SDIN
SDOUT
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
(LJ)
Oscillator
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
SDIN
(LJ)
(LJ)
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
Figure 13. Routing 8 Figure 14. Routing 9
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
Oscillator
CS42L51
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
(LJ)
SDIN
SDOUT
CS8415
RMCK
(256Fs)
OLRCK/
OSCLK
SDOUT
(LJ)
Oscillator
CS8406
OMCK
(256Fs)
ILRCK/
ISCLK
SDIN
(LJ)
SDIN
(LJ)
I/O Header
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDOUT
SDIN
SDIN
Figure 15. Routing 10 Figure 16. Routing 11
MCLK
LRCK/SCLK
SDIN
CS42L51
SDOUT
16 DS679DB2
Page 17

3.2 CS42L51 H/W Control
The stand-alone “CS42L51 H/W Control” switch controls the Hardware Mode options of the CS42L51. A
description of each switch is outlined in the following table:
Switch Position Function
M/S
MCLKDIV2
I2S/LJ
DE-EMPHASIS
LO LRCK and SCLK are inputs to CS42L51
HI LRCK and SCLK are outputs to CS42L51
LO Internal MCLK to CS42L51 not divided
HI Internal MCLK to CS42L51 divided by 2
LO CS42L51 Interface Format: Left-Justified
HI CS42L51 Interface Format: I²S
LO No internal De-emphasis applied to CS42L51
HI 44.1 kHz internal De-emphasis applied to CS42L51
Table 2. CS42L51 H/W Mode Control
4. SYSTEM CONNECTIONS AND JUMPERS
CONNECTOR REF INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL PRESENT
+5V J26 Input +5.0 V Power Supply.
GND J27 Input Ground Reference .
RS232 J95 Input/Output Serial connection to PC for SPI / I²C control port signals.
USB J94 Input/Output USB connection to PC for SPI / I²C control port signals. Not Available.
SPDIF OPTICAL OUT OPT2 Output CS8406 digital audio output via optical cable.
SPDIF COAX OUT J68 Output CS8406 digital audio output via coaxial cable.
SPDIF OPTICAL IN OPT1 Input CS8415 digital audio input via optical cable.
SPDIF COAX IN J61 Input CS8415 digital audio input via coaxial cable.
I/O Header J5 Input/Output I/O for Clocks & Data.
S/W CONTROL J109 Input/Output I/O for external SPI / I²C control port signals.
MICRO JTAG J110 Input/Output I/O for programming the micro controller (U84).
FPGA JTAG J78 Input/Output I/O for programming the FPGA (U14).
MICRO RESET S4 Input Reset for the micro controller (U84).
FPGA PROGRAM S2 Input Reload Xilinx Flash program into the FPGA (U14).
H/W BOARD RESET S1 Input Reset for the CS42L51 (U1).
LINEB
LINEA
MIC1
MIC2
LEFT
RIGHT
SPEAKER +
SPEAKER -
Headphone Jack J11 Output Headphone jack for analog outputs.
J62
J7
J35
J51
J19
J20
J72
J73
Input RCA phono jacks for analog input signal to CS42L51.
Input Microphone jacks for analog input signal to CS42L51.
Output RCA phono jacks for analog outputs.
Output Binding Post connected to LM4889 speaker driver for analog outputs.
Table 3. System Connections
CDB42L51
DS679DB2 17
Page 18

JMP LABEL PURPOSE POSITION FUNCTION SELECTED
J31 VL
J36 VA_HP
J25 VA
J28 VD
J52
J48
J47
J53
J2 LINEB MUX
J1 LINEA MUX
J3
J8
J14
J12 MIC2 Bias Selects bias for MIC2
J6
J4
J10
J13
VL
+VA_HP
VA
VD
(AIN2B
Select)
(AIN3B
Select)
(AIN3A
Select)
Left
Channel
Right
Channel
16 ohm
HP LOAD
16 ohm
HP LOAD
Selects source of voltage for the
VL supply
Selects source of voltage for the
VA_HP supply
Selects source of voltage for the
VA supply
Selects source of voltage for the
VD supply
Current Measurement
Selects signal source for the ADC
I/O
Selects signal source for the ADC
I/O
Selects signal source for MIC1 and
MIC2 bias or signal source for the
ADC input
Selects signal source for MIC2
bias or signal source for the ADC
input
Selects signal source for the ADC
input
Selects between filtered and non-
filtered output
Selects between filtered and non-
filtered output
Load Simulation
Load Simulation
Table 4. Jumper Settings
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5 V regulator.
+3.3V Voltage source is +3.3 V regulator.
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5 V regulator. .
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5 V regulator. .
*+1.8V Voltage source is +1.8 V regulator.
+2.5V Voltage source is +2.5 V regulator. .
*SHUNTED 1 Ω series resistor is shorted.
OPEN 1 Ω series resistor in power supply path.
(AIN3B Select) LINEB signal routed to jumper J8.
(AIN2B Select) LINEB signal routed to jumper J3.
*AIN1B LINEB signal routed to AIN1B of ADC.
(AIN3A Select) LINEA signal routed to jumper J14.
AIN2A LINEA signal routed to AIN2A of ADC.
*AIN1A LINEA signal routed to AIN1A of ADC.
BIAS1 to MIC2 Bias on AIN2B of ADC routed to jumper J12.
BIAS1 to MIC1 Bias on AIN2B of ADC routed to MIC1.
*LINEB LINEB MUX routed to AIN2B of ADC.
BIAS2 to MIC2 Bias on AIN3B of ADC routed to jumper J12.
MIC2 MIC2 signal routed to AIN3B of ADC.
*LINEB LINEB MUX routed to AIN3B of ADC.
MIC2 MIC2 signal routed to AIN3A of ADC.
MIC1 MIC1 signal routed to AIN3A of ADC.
*LINEA LINEA MUX routed to AIN3A of ADC.
BIAS1 J3 (for Bias on AIN2B of ADC) routed to MIC2.
BIAS2 J8 (for Bias on AIN3B of ADC) routed to MIC2.
*Not connected Jumper placed on pin 2.
*AOUTA Connects AOUTA of part directly to LEFT RCA jack.
AOUTA (LPF) Connects low-pass filtered AOUTA to LEFT RCA jack. .
*AOUTB Connects AOUTB of part directly to RIGHT RCA jack.
AOUTB (LPF) Connects lowpass filtered AOUTA to RIGHT RCA jack. .
SHUNTED 16 Ω resistor shunted from AOUTA to GND.
*Not connected Jumper placed on pin 1.
SHUNTED 16 Ω resistor shunted from AOUTB to GND.
*Not connected Jumper placed on pin 1.
*Default factory settings
CDB42L51
18 DS679DB2
Page 19

DS679DB2 19
5. CDB42L51 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Software Mode
Control Port
S/PDIF Output
(CS8406)
S/PDIF Input
(CS8415)
Reset
Hardware Mode
Switches
FPGA
I²C/SPI Header
Reset
MCLK
Analog Input
(Line + MIC)
CS42L51
Analog Output
(Line + Headphone)
Oscillator
(socket)
MCLK
Reset
Reset
Clocks/Data Header
CDB42L51
Figure 17. Block Diagram
Page 20

DS679DB2 20
6. CDB42L51 SCHEMATICS
Figure 18. CS42L51 and Analog I/O (Schematic Sheet 1)
CDB42L51
Page 21

DS679DB2 21
Figure 19. S/PDIF I/O (Schematic Sheet 2)
CDB42L51
Page 22

DS679DB2 22
Figure 20. FPGA (Schematic Sheet 3)
CDB42L51
Page 23

DS679DB2 23
Figure 21. Level Shifters & I/O Stake Header (Schematic Sheet 4)
CDB42L51
Page 24

DS679DB2 24
Figure 22. Control Port I/O (Schematic Sheet 5)
CDB42L51
Page 25

DS679DB2 25
Figure 23. Power (Schematic Sheet 6)
CDB42L51
Page 26

DS679DB2 26
7. CDB42L51 LAYOUT
Figure 24. Silk Screen
CDB42L51
Page 27

DS679DB2 27
Figure 25. Top-Side Layer
CDB42L51
Page 28

DS679DB2 28
Figure 26. Bottom-Side Layer
CDB42L51
Page 29
CDB42L51
8. ERRATA
Although the CS42L51 does support VL power supply levels of both +1.8 V and +2.5 V, these levels are not supported by the CDB42L51. Accordingly, header J31 (VL) must be set to +3.3 V to ensure correct board operation. It
should be noted that this restriction is due only to the hardware design of the CDB42L51. The CS42L51’s allowed
voltage levels are specified in the CS42L51 data sheet.
9. REVISION HISTORY
Revision Date Changes
DB1 June 2005 Initial Release
Added Section 8. "Errata".
DB2 October 2007
Updated Section 6. "CDB42L51 Schematics" to show latest board revision.
Updated Section 7. "CDB42L51 Layout" to show latest board revision.
Contacting Cirrus Logic Support
For all product questions and inquiries, contact a Cirrus Logic Sales Representative.
To find the one nearest you, go to www.cirrus.com.
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Cirrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Cirrus") believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and reliable. However, the information is subject
to change without notice and is provided "AS IS" without warranty of any kind (express or implied). Customers are advised to obtain the latest version of relevant
information to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to the terms and conditions of sale
supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, indemnification, and limitation of liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus
for the use of this information, including use of this information as the basis for manufacture or sale of any items, or for infringement of patents or other rights of third
parties. This document is the property of Cirrus and by furnishing this information, Cirrus grants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask work rights,
copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or other intellectual property rights. Cirrus owns the copyrights associated with the information contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only for use within your organization with respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other products of Cirrus. This consent
does not extend to other copying such as copying for general distribution, advertising or promotional purposes, or for creating any work for resale.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE (“CRITICAL APPLICATIONS”). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE
IN AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS, MILITARY APPLICATIONS, PRODUCTS SURGICALLY IMPLANTED INTO THE BODY, AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY OR SECURITY DEVICES, LIFE SUPPORT PRODUCTS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER’S RISK AND CIRRUS DISCLAIMS AND MAKES NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS, STATUTORY OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH REGARD TO ANY CIRRUS PRODUCT
THAT IS USED IN SUCH A MANNER. IF THE CUSTOMER OR CUSTOMER’S CUSTOMER USES OR PERMITS THE USE OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS, CUSTOMER AGREES, BY SUCH USE, TO FULLY INDEMNIFY CIRRUS, ITS OFFICERS, DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES, DISTRIBUTORS AND
OTHER AGENTS FROM ANY AND ALL LIABILITY, INCLUDING ATTORNEYS’ FEES AND COSTS, THAT MAY RESULT FROM OR ARISE IN CONNECTION
WITH THESE USES.
Cirrus Logic, Cirrus, and the Cirrus Logic logo designs are trademarks of Cirrus Logic, Inc. All other brand and product names in this document may be trademarks
or service marks of their respective owners.
I²C is a registered trademark of Philips Semiconductor.
SPI is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
Microsoft and Windows
DS679DB2 29
are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
 Loading...
Loading...