Page 1

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
Q72WLANTUBGR
802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
- 1 -
Page 2

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
Contents
1 Introduction........................................................................................................................................ 2
1.1 Product introduction............................................................................................................... 3
1.2 Main Features.......................................................................................................................... 3
1.3 System Requirements..............................................................................................................3
2 Installation Guide............................................................................................................................... 3
2.1 Software Installation............................................................................................................... 4
2.1.1 Overview..................................................................................................................... 4
2.1.2 Software Installation................................................................................................ 4
2.2 Uninstall Software................................................................................................................... 7
2.2.1 Uninstall the utility software.................................................................................. 7
2.2.2 Uninstall the driver software .................................................................................8
2.3 Hardware Installation........................................................................................................... 10
3 Configuration ...................................................................................................................................10
3.1 Profile..................................................................................................................................... 11
3.2 Link Status............................................................................................................................. 14
3.3 Site Survey ............................................................................................................................. 15
3.4 Statistics ................................................................................................................................. 16
3.5 Advanced................................................................................................................................ 17
3.6 About...................................................................................................................................... 18
3.7 An example for application...................................................................................................19
Appendix A: Glossary..................................................................................................................... 20
Appendix B: Specifications........................................................................................................... 22
1 Introduction
- 2 -
Page 3

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
1.1 Product introduction
The 54M Wireless USB Adapter is a USB 2.0 pen-size wireless adapter supporting IEEE
802.11b/g 2.4GHz radio operation. It provides high-speed wireless connection with data
rate up to 54Mbps. Additionally, wireless roaming allows the user to move among
different APs without losing the current connection. The adapter provides excellent
security features includingTKIP, AES, WPA, and up to 128 bit WEP encryption
security making the network almost impenetrable.
Featuring high performance transmission rates, simple installation and adaptability, as
well as strong security, the CNE Wireless USB Adapter is the perfect solution for small
office and home uses
.
LED Status:
The LED on the top of this card indicates Link/Act status. It blinks at green light when
sending and receiving data.
1.2 Main Features
Complies with IEEE802.11g, IEEE802.11b standards
Supports WPA data security, IEEE802.1x authentication, TKIP/AES encryption,
64/128-bitWEP encryption
Supports 54/48/36/24/18/12/9/6Mbps or 11/5.5/2/1Mbps wireless LAN data transfer
rates
Provides USB interface
Supports Ad-Hoc and Infrastructure modes
Supports roaming between access points when configured in Infrastructure mode
Eases configuration and provides monitoring information
Internal Antenna
1.3 System Requirements
• A computer or laptop with an available USB 2.0 port
• Windows 98SE, Windows® 2000 (Service Pack 4), XP (Service Pack 2), ME.
• CD-ROM Drive
• 300MHz processor and at least 64MB of RAM
• A draft 802.11b/g access point (for Infrastructure mode).
2 Installation Guide
- 3 -
Page 4

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
This
chapter
will walk you through the installation process. If you have a built-in wireless
adapter, please disable it in device manager before installing your wireless USB adapter.
Also, if you have previously installed another wireless adapter, please make sure any
software is uninstalled.
Before installing your new wireless USB adapter, please verify the following:
• Remove any previous installations of wireless adapters.
• Disable any built-in wireless adapters.
• Verify the settings such as the SSID and security settings of the network(s) you want to
connect to.
If you need instructions as to how to remove the old driver or existing unused
Installations and several of the above, please refer to the next section Uninstall Software.
2.1 Software Installation
2.1.1 Overview
The Adapter’s Setup Wizard will guide you through the installation procedure for
Windows 98SE, ME, 2000 and XP. The Setup Wizard will guide you install the Utility
and drivers.
If you install the hardware before the software, you will be prompted “Found New
Hardware Wizard”, click the Cancel button, and run the Setup Wizard program on the
CD-ROM.
All of following sections are written based on Windows XP. Note that the comments and
conditions for other OS platforms may be different from this chapter.
2.1.2 Software Installation
1. Insert the Resource CD into your CD-ROM drive, double click the driver to installing
button, Figure 2-1 should then appear.
- 4 -
Page 5
Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
Figure 2-1 Preparing Setup
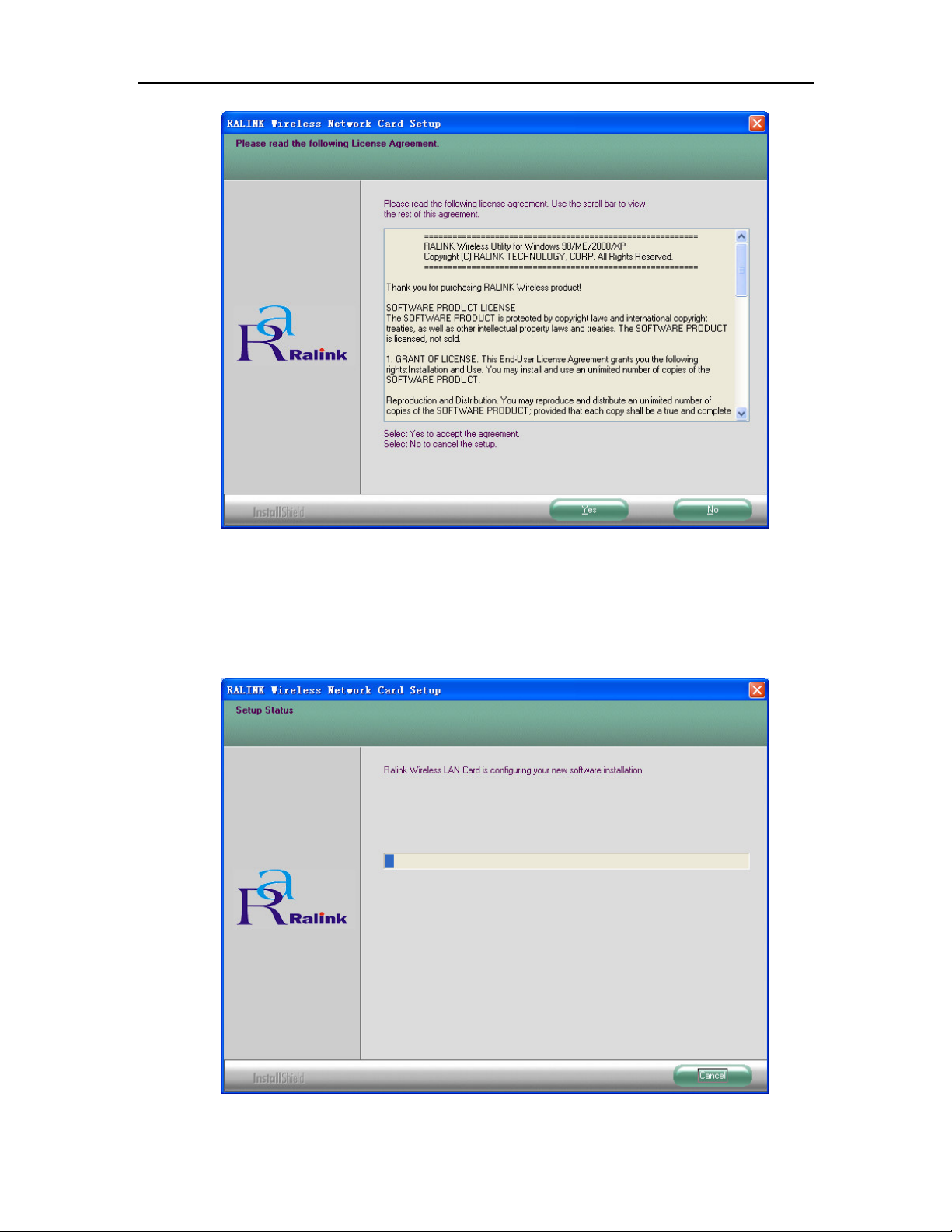
2. You will see a warning box shown in Figure 2-1, click the No button to end the
installation. Otherwise, click the Yes button to install driver, the Setup Wizard will
display a screen similar to that shown in Figure 2-2 after a moment.
Figure 2-2 Start Setup
- 5 -
uide
Page 6
Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
3. To continue, please wait for running automatically for a moment, Figure 2-2. Click
the Cancel button to end the Installation.
4. The soft install automatically in the operating system, and appear a dialog box Figure
2-3. Now, only a thing which you can do is Waiting!
Figure 2-3 waiting state dialog box
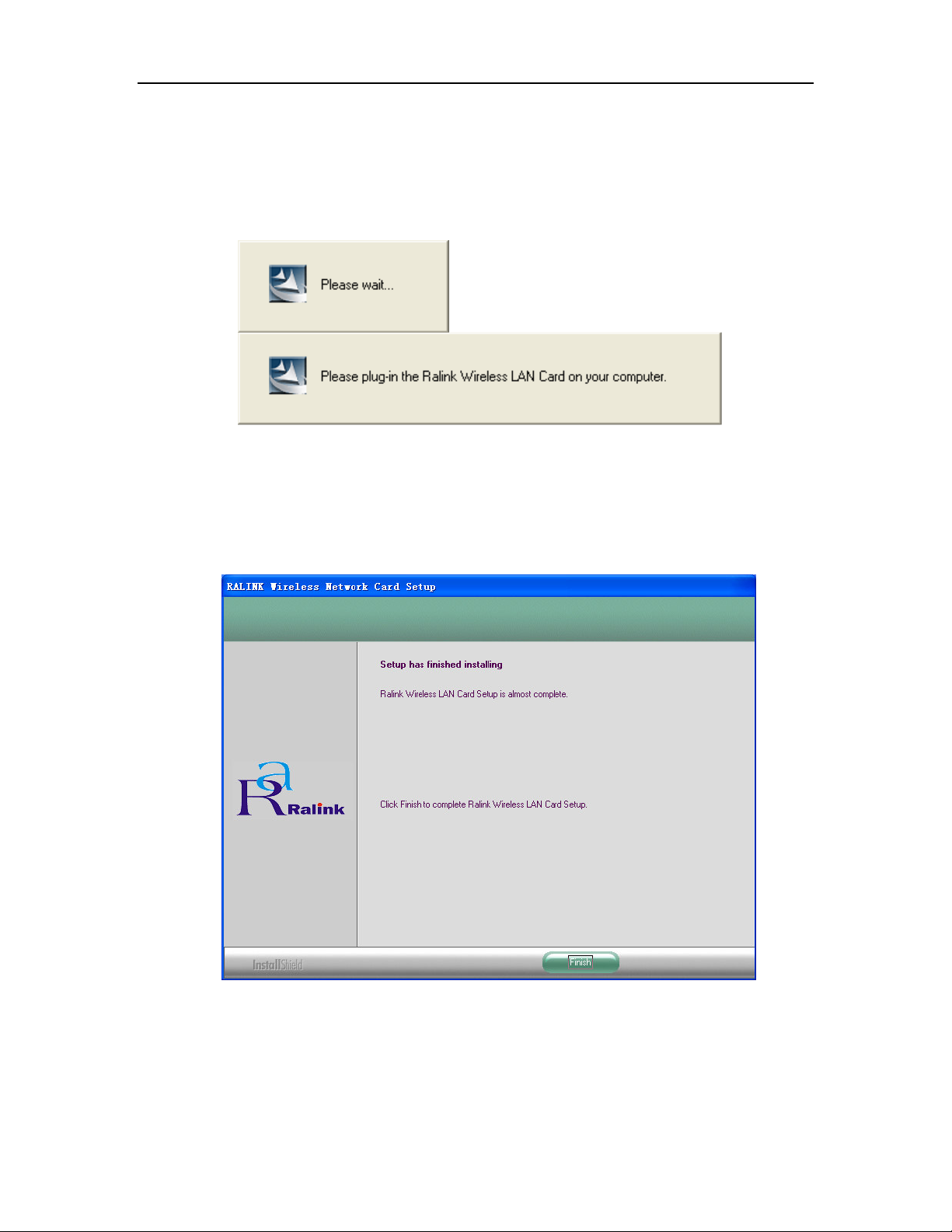
5. After the files have been successfully installed, the screen in Figure 2-4 will appear.
Click the Finish button to finish the wizard.
Figure 2-4 Finish installing
6. After installing the software, Please plug the adapter into your PC. If you need
instructions as to how to do this, please refer to next section - Hardware Installation.
If you have plugged it into you PC already, please unplug it and plug it back in. The
- 6 -
Page 7
Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
OS will automatically detect the adapter and automatically setup the driver for the
adapter. If it does not, please follow the setup steps to finish the driver installation.
After installing the driver successfully, you should see an icon appear in your
system icon box.
2.2 Uninstall Software
2.2.1 Uninstall the utility software
If you’ve installed a different manufacture’s adapter or a different model 802.11b/g
wireless USB adapter, make sure the software is uninstalled before installing the new
software. Some utilities may cause a conflict with the new software. If you plan to use
multiple adapters at different times, make sure the utilities are not set to load when your
computer boots up.
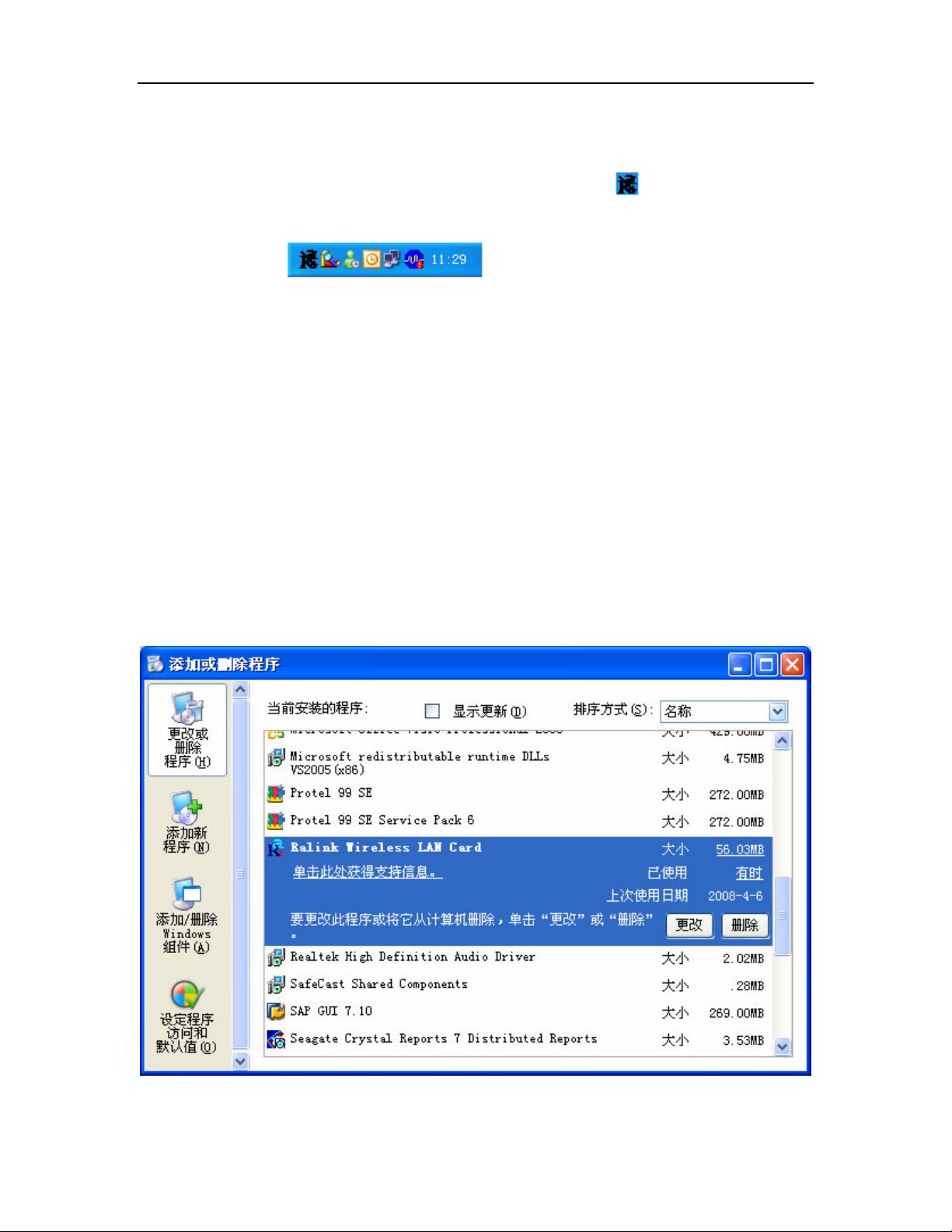
To remove any old software in Windows XP:
1. On the Windows taskbar, click the Start button, point to Settings, and then click
Control Panel.
Figure 2-5 uninstall utility
- 7 -
Page 8
Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
2. Double-click the Add/Remove Programs icon, find the Ralink wireless LAN Card
program from the installed program list, highlight it and click the Remove button, the
screen in Figure 2-5 will appear.
3. Following the Install Shield Wizard will uninstall the utility software from your PC.
2.2.2 Uninstall the driver software
Most newer laptops may include a built-in wireless adapter. To prevent any conflicts with
the 802.11b/g wireless USB adapter, this section describes how to uninstall any old or
unused Ethernet Adapters and the driver for Ralink wireless adapter from your PC.
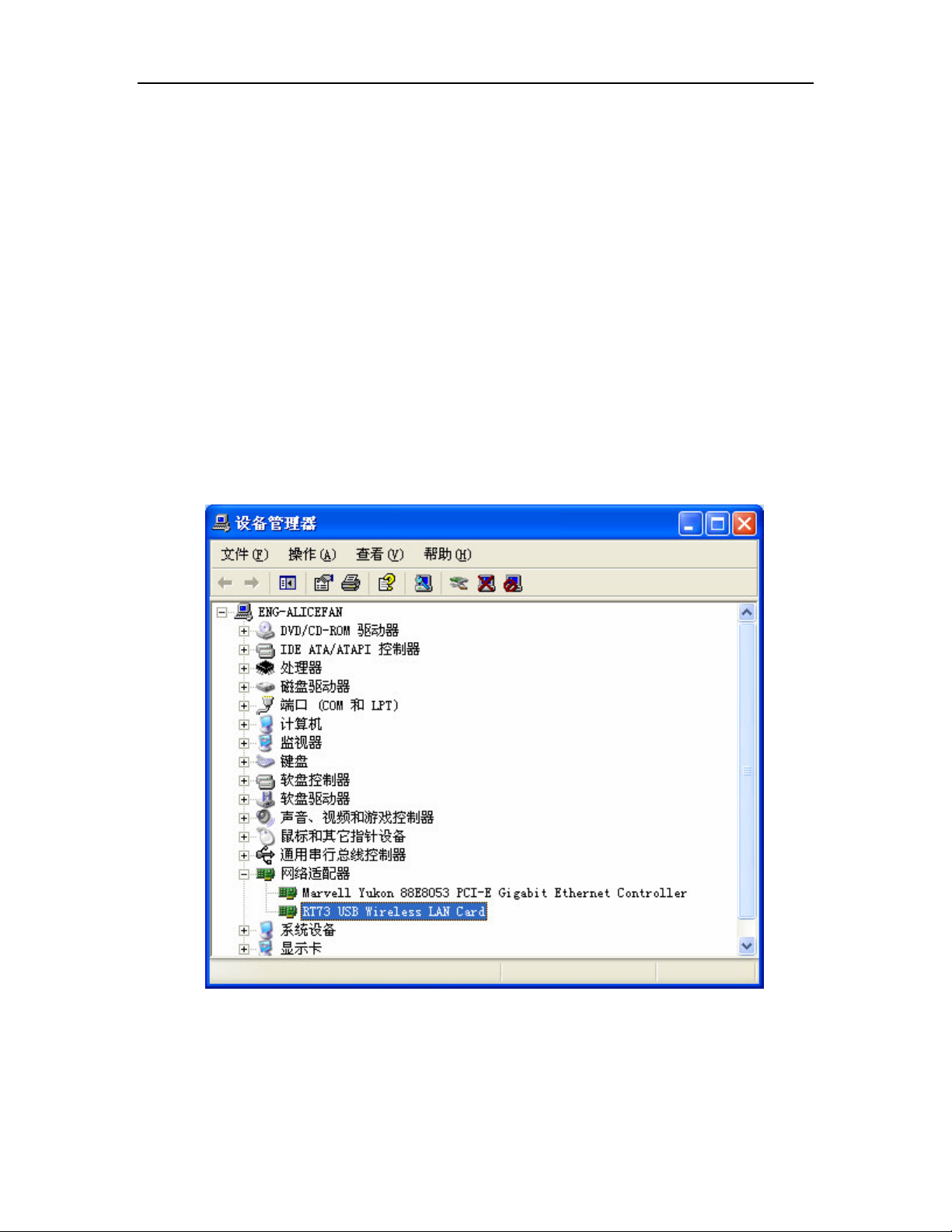
1. From the desktop, right-click on the My Computer icon and select Properties.
2. Click the Hardware tab and then click Device Manager. Scroll down the list and
click the + sign to the left of Network Adapters, show in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6 the adapter hardware
3. Right-click the adapter you would like to uninstall and select Unistall.
- 8 -
Page 9

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
Figure 2-7 uninstall the driver
4. Click Yes to uninstall the adapter.
- 9 -
Page 10

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
2.3 Hardware Installation
1. Connect one end of the USB cable to the Adapter.
2. Connect the other end of the USB cable to the USB port on your computer. Because
the Adapter gets its power from the host, there is no external power supply. The LED
should light up when the Adapter is plugged in and the PC is on.
3 Configuration
CNE 802.11b/g Wireless USB Adapter can be configured by its utility. This chapter
describes how to configure your Wireless USB Adapter for wireless connectivity on your
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) and use the data security encryption features.
After the Adapter's driver and utility has been installed, the adapter’s tray icon or
will appear in your system tray. It means the utility is running on your system. If the
utility does not run, you can run the utility by clicking: Start> Program>RaLink
Wireless> RaLink Wireless Utility. If the icon still does not appear, the driver or utility
may be installed incorrectly or the adapter is unplugged, please try again.
Figure 3-1 start-up the Utility
Icon means the connection has been established. Icon means there is no
connection.
Double-click the icon and the configuration screen of the utility will appear. You can
also run the utility by clicking: Start> Program>RaLink Wireless> RaLink Wireless
Utility. The utility provides a complete and easy to use set of tools to:
Display current status information
Edit and add configured profiles
Display current diagnostics information
- 10 -
Page 11

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
The section below introduces these above capabilities.
Right-click the icon at the bottom of the screen, and click Exit to exit the utility.
3.1 Profile
Click the Profile tab of the utility and the Profile screen will appear, Figure 3-2. The
Profile screen provides tools to:
Add a Profile
Delete a profile
Edit a profile
Activate a profile
Figure 3-2 Profile Tab
To create a new profile, click the Add button on the Profile tab, the Profile
configuration screen will appear as shown in Figure 3-2.
To edit a profile, highlight the desired profile name on Profile Name list, and click the
Edit button, the Profile configuration screen will appear shown in Figure 3-1.
To delete a profile, highlight the desired profile name on Profile Name list, and click
the Delete button.
- 11 -
Page 12

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
To switch to another profile, highlight the desired profile name on Profile Name list,
and click the Activate button.
*
Note:
Do not forget to click the Apply button when you create a new profile for connection.
T
o add a new configuration profile, click Add button on the Profile Management tab. To
modify a configuration profile, select the configuration from the Profile list and click
Edit. The Profile Management dialog box will display a screen similar to that shown in
Figure 3-3.
1. Edit the Configuration tab
Figure 3-3 Add Profile – configuration
Profile Name - Identifies the configuration profile. This name must be unique. Profile
names are not case-sensitive.
SSID - The IEEE 802.11 wireless network name. This field has a maximum limit of 32
characters.
PSM (Power Save Mode)
CAM (Constantly Awake Mode) – Continuous Access Mode.
- 12 -
Page 13

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
PSM (Power Saving Mode) - Power Saving mode.
Network Type – Displays the wireless mode, either Ad-hoc or Infrastructure mode.
Preamble – Specifies the preamble setting in 802.11b. The default setting is Auto
Switch (access point mode), which allows both short and long headers in the 802.11b
frames. The adapter can only use short radio headers if the access point supports and uses
them.
RTS Threshold – Default is 2312.
Fragment Threshold – Default is 2312.
Ad-hoc mode – Displays the wireless mode, either Only 802.11b or 802.11b/g mode.
Channel – Shows the current channel in use. This field determines which operating
frequency will be used.
2. Edit the Authentication and Security tab
Figure 3-4 Add Profile – configuration
Authentication Type – Three options, Open System, Shared-Key System or LEAP.
- 13 -
Page 14

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
802.1x Setting – It enables when Authentication Type is setting to WPA.
Encryption – Displays which encryption type that the driver is using. When you select
Open System, Shared-Key System as Network Authentication, there are two options:
WEP and None. If you select WPA-PSK as Network Authentication, there are TKIP
and AES options instead of WEP and None.
Wep Key – Key #1, Key #2, Key #3, Key #4, the Key groups. You can enter 10
hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9, a-f, A-F) or 5 ASCII characters for 64-bit
(also called 40bits) encryption. You can enter 26 hexadecimal digits (any combination of
0-9, a-f, A-F) or 13 ASCII characters for 128-bit (also called 104bits) encryption.
3.2 Link Status
The Link Status tab Figure 3-5 displays the adapter's current status.
Figure 3-5 Link Status
The following table describes the items found on the Network Status screen.
Status - Shows whether the station is connected to the wireless network, if not
connected, display RF is closed; if connected, display AP name and BSSID.
Extra Info - Shows link status and the current channel in use.
- 14 -
Page 15

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
Link Speed - Shows the current max Transfer rate, unit is Mbit/sec.
Throughput - Displays Tx and Rx rate, unit is Kbits/sec.
Link Quality - Shows the quality of the signal.
Signal Strength - Shows the strength of the signal.
3.3 Site Survey
Click the Site Survey tab of the Utility and the Site Survey screen will appear, Figure
3-6. On the Site Survey screen you can scan the Available Infrastructure and Ad Hoc
Networks.
Figure 3-6 Site Survey tab
Click the Rescan button to refresh the list at any time. Highlight an SSID and click the
Connect button to connect to an available network.
- 15 -
Page 16

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
3.4 Statistics
The Statistics tab as Figure 3-7 shows receiving and transmitting statistical information
for the following receive and transmit diagnostics for frames received by or transmitted
to the wireless network adapter.
Click the Reset Counter button to reset the count of the statistics information.
Figure 3-7 Statistics tab
- 16 -
Page 17

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
3.5 Advanced
On this Screen, you can configure the WEP key or view the configured WEP key.
Figure 3-8 Advanced
Wireless mode - Displays the wireless mode, either 802.11b/g mix or 802.11b only.
B/G Protection - There are three options: either Auto or Enable, or Close.
Tx Rate - Shows the current Transfer rate.
Tx BURST - It can translate more data when it enables.
Fast Roaming - Roaming will disable when Transmit Power is below some dBm.
Turn off RF - The wireless radio of this adapter can be enabled or disabled. You can
turn the wireless radio off by selecting the check-box.
Apply - Click the Apply button to save the current setting.
- 17 -
Page 18

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
3.6 About
This screen displays some information about this adapter, including Driver Date, Driver
Version, Utility Date, RaConfig Version, EEPROM Version, Firmware Version, IP
Address, Phy_ Address, Sub Mask, Default Gateway.
Figure 3-9 About
RaConfig Version - The version of this utility.
Utility Date - The creation date of this utility.
Driver Version - The version of the wireless network adapter driver.
Driver Date - The creation date of the wireless network adapter driver.
EEPROM Version - The version of this EEPROM.
IP Address - The IP address of the wireless network.
Phy_Address - The MAC address of the wireless network adapter.
SubMask - The subnet mask of the wireless network.
Default Gateway - The default gateway of the wireless network.
- 18 -
Page 19

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
3.7 An example for application
Suppose you have an installed and using AP, the SSID is wireless USB adapter and it
adopts 64-bit encryption with the key 0123456789. To establish a connection with this
AP, you should follow these steps below:
1. Launch this Ralink WIRELESS UTILITY Utility.
2. Click the Profile tab of the utility and click the New button on the screen that appears.
3. The Profile configuration screen will appear, please enter Test for the Profile Name,
Ralink for the SSID, select Infrastructure for the Network Mode, select WEP for the Data
Encryption and enter 0123456789 for Network key.
4. Click OK to save this profile.
5. Click Apply on the Profile screen. The utility will establish a connection with this AP
by configured profile.
- 19 -
Page 20

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
Appendix A: Glossary
802.11b - The 802.11b standard specifies a wireless networking at 11 Mbps using
direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology and operating in the unlicensed
radio spectrum at 2.4GHz, and WEP encryption for security. 802.11b networks are also
referred to as Wi-Fi networks.
802.11g - specification for wireless networking at 54 Mbps using direct-sequence
spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology, using OFDM modulation and operating in the
unlicensed radio spectrum at 2.4GHz, and backward compatibility with IEEE 802.11b
devices, and WEP encryption for security.
DSSS (Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum) - DSSS generates a redundant bit pattern
for all data transmitted. This bit pattern is called a chip (or chipping code). Even if one or
more bits in the chip are damaged during transmission, statistical techniques embedded in
the receiver can recover the original data without the need for retransmission. To an
unintended receiver, DSSS appears as low power wideband noise and is rejected (ignored)
by most narrowband receivers. However, to an intended receiver (i.e. another wireless
LAN endpoint), the DSSS signal is recognized as the only valid signal, and interference
is inherently rejected (ignored).
FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) - FHSS continuously changes (hops)
the carrier frequency of a conventional carrier several times per second according to a
pseudo-random set of channels. Because a fixed frequency is not used, and only the
transmitter and receiver know the hop patterns, interception of FHSS is extremely
difficult.
Infrastructure Network - An infrastructure network is a group of computers or other
devices, each with a wireless adapter, connected as an 802.11 wireless LAN. In
infrastructure mode, the wireless devices communicate with each other and to a wired
network by first going through an access point. An infrastructure wireless network
connected to a wired network is referred to as a Basic Service Set (BSS). A set of two or
more BSS in a single network is referred to as an Extended Service Set (ESS).
Infrastructure mode is useful at a corporation scale, or when it is necessary to connect the
wired and wireless networks.
Spread Spectrum - Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio frequency
technique developed by the military for use in reliable, secure, mission-critical
communications systems. It is designed to trade off bandwidth efficiency for reliability,
integrity, and security. In other words, more bandwidth is consumed than in the case of
narrowband transmission, but the trade off produces a signal that is, in effect, louder and
thus easier to detect, provided that the receiver knows the parameters of the
spread-spectrum signal being broadcast. If a receiver is not tuned to the right frequency, a
spread-spectrum signal looks like background noise. There are two main alternatives,
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum
(FHSS).
- 20 -
Page 21

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
SSID - A Service Set Identification is a thirty-two character (maximum)
alphanumeric key identifying a wireless local area network. For the wireless devices in a
network to communicate with each other, all devices must be configured with the same
SSID. This is typically the configuration parameter for a wireless PC card. It corresponds
to the ESSID in the wireless Access Point and to the wireless network name.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A data privacy mechanism based on a 64-bit or
128-bit or 152-bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
Wi-Fi - A trade name for the 802.11b wireless networking standard, given by the
Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA, see http://www.wi-fi.net), an industry
standards group promoting interoperability among 802.11b devices.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) - A group of computers and associated
devicescommunicate with each other wirelessly, which network serving users are limited
in a local area.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) - A wireless security protocol use TKIP (Temporal
Key Integrity Protocol) encryption, which can be used in conjunction with a RADIUS
server.
- 21 -
Page 22

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
Appendix B: Specifications
General
Interface A-type USB 2.0 Connector
Standards IEEE 802.1b; IEEE 802.1g
Operating System Windows 98SE, ME, 2000, XP
Transmission Distance
In door up to 100m, out door up to 300m (It is limited to the
environment).
Frequency 2.4 ~ 2.4835 GHz
Sensitivity
54M -70dBm
11M -83dBm
Spread Spectrum Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Wireless
Radio Data Rate
54/48/36/24/18/12/9/6 Mbps 11g OFDM11/5.5/2/1 Mbps 11b
DSSS,(Auto Rate Sensing)
Modulation 11g OFDM , 11b CCK/DSSS
Media Access Protocol CSMA/CA with ACK
Transmit Power Typical 15dBm, 18dBm(Max)
Data Security WPA, 64/128 bit WEP, TKIP/AES, IEEE 802.1X authentication
Physical Environmental
Working Temperature
Storage Temperature
Humidity
0
40 (32
-40
70 (-40
10%90% RH, Non-condensing
104)
158)
Dimensions 77m (L) x 20mm (W) x 4.6mm (H)
THE END
- 22 -
Page 23

Q
7
2
W
L
A
N
T
U
B
G
R
8
0
2
.
1
1
b
/
g
W
L
A
N
U
S
B
U
s
e
r
M
a
n
u
a
l
Regulatory Information
FCC Information to User
This product does not contain any user serviceable components and is to be used with approved
antennas only. Any product changes or modifications will invalidate all applicable regulatory
certifications and approvals.
FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure
War ni ng:
The antenna(s) used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at
least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
FCC Electronic Emission Notices
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to th
This device may not cause harmful interference
1.
This device must accept any interference rece
2.
undesired operation.
e following two conditions:
ived, including interference that may cause
10
Page 24

Q
7
2
W
L
A
N
T
U
B
G
R
8
0
2
.
1
1
b
/
g
W
L
A
N
U
S
B
U
s
e
r
M
a
n
u
a
l
FCC Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area may cause harmful
interferences, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
y Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
y Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
y Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected
y Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
11
Page 25

Q72WLANTUBGR 802.11b/g WLAN USB User Manual
OEM installation Guide
“
Contains TX FCC ID: Q72WLANTUBGR”
12
 Loading...
Loading...