Page 1

GROUP TAB LOCATOR
Maintenance Schedules
0
Cooling 2.5L Turbo Diesel
7
Electronic Control Modules
8E
Engine Systems
8F
Ignition Control
8I
Engine
9
Exhaust System and Turbocharger
11
Fuel System
14
Emissions Control 2.5L Turbo Diesel
25
Service Manual Comment Forms (Rear of Manual)
Page 2

RG MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES 0-1
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES FOR ALL
MARKETS EXCEPT U.S., CANADA and
MEXICO
DESCRIPTION — DIESEL ENGINES .........1
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
FOR ALL MARKETS EXCEPT
U.S., CANADA and MEXICO
DESCRIPTION — DIESEL ENGINES
Maintenance Schedule Information not included in
this section, is located in the appropriate Owner’s
Manual.
There are two maintenance schedules that show
the required service for your vehicle.
First is Schedule “B”. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
• Extensive engine idling.
• Driving in dusty conditions.
• More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32° C (90° F).
• Trailer towing.
• Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
NOTE: Most vehicles are operated under the conditions listed for Schedule ⴖBⴖ.
Second is Schedule “A”. It is for vehicles that are
not operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule ⬙B⬙.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
CAUTION: Failure to perform the required maintenance items may result in damage to the vehicle.
At Each Stop for Fuel
• Check the engine oil level about 5 minutes after
a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the oil
level while the vehicle is on level ground will
improve the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
• Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
• Check the tire pressure and look for unusual
wear or damage.
• Inspect the battery and clean and tighten the
terminals as required.
• Check the fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transmission
and add as needed.
• Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
• Change the engine oil filter.
• Inspect the exhaust system.
• Inspect the brake hoses.
• Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents.
• Check the manual transmission fluid level.
• Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
• Inspect engine accessory drive belts. Replace as
necessary.
• Inspect for the presence of water in the fuel filter/water separator unit.
• Rotate the tires at each oil change interval (20
000 km).
SCHEDULE “B”
Follow schedule “B” if you usually operate your
vehicle under one or more of the following conditions.
• Extensive engine idling.
• Driving in dusty conditions.
• More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32° C (90° F).
• Trailer towing.
• Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
Page 3
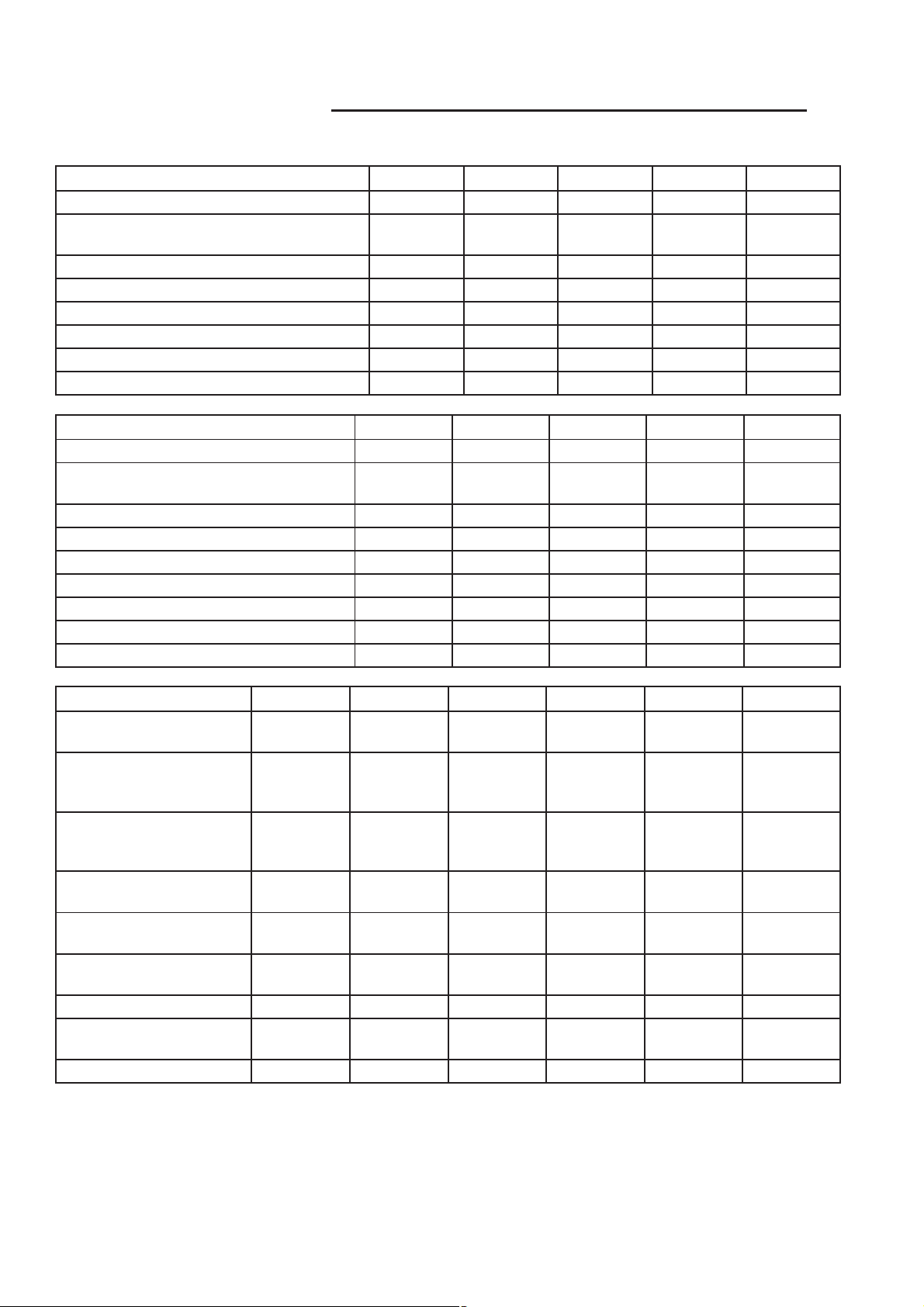
0 - 2 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES RG
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES FOR ALL MARKETS EXCEPT U.S., CANADA and MEXICO (Continued)
Kilometers 10 000 km 20 000 km 30 000 km 40 000 km 50 000 km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. XXXXX
Inspect engine air filter element. Replace as
necessary.
Replace engine air filter element X X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit. X X
Check front end alignment. X X
Change the manual transaxle fluid. X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X
Inspect the brake linings. XXXXX
Kilometers 60 000 km 70 000 km 80 000 km 90 000 km 100 000 km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. XXXXX
Inspect engine air filter element. Replace
as necessary.
Replace engine air filter element X X X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit. X X X
Replace engine timing belt. X
Check front end alignment. X X
Change the manual transaxle fluid. X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X
Inspect the brake linings. XXXXX
XXX
XX
Kilometers 110 000 km 120 000 km 130 000 km 140 000 km 150 000 km 160 000 km
Change engine oil and
engine oil filter.
Inspect engine air filter
element. Replace as
necessary.
Inspect accessory drive
belts and replace if
necessary.
Replace engine air filter
element
Replace fuel filter/water
separator unit.
Flush and replace engine
coolant.
Check front end alignment. X X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and
boot seals.
Inspect the brake linings. XXXXXX
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.
XXXXXX
XXX
X
XXX
XXX
X
XX
Page 4
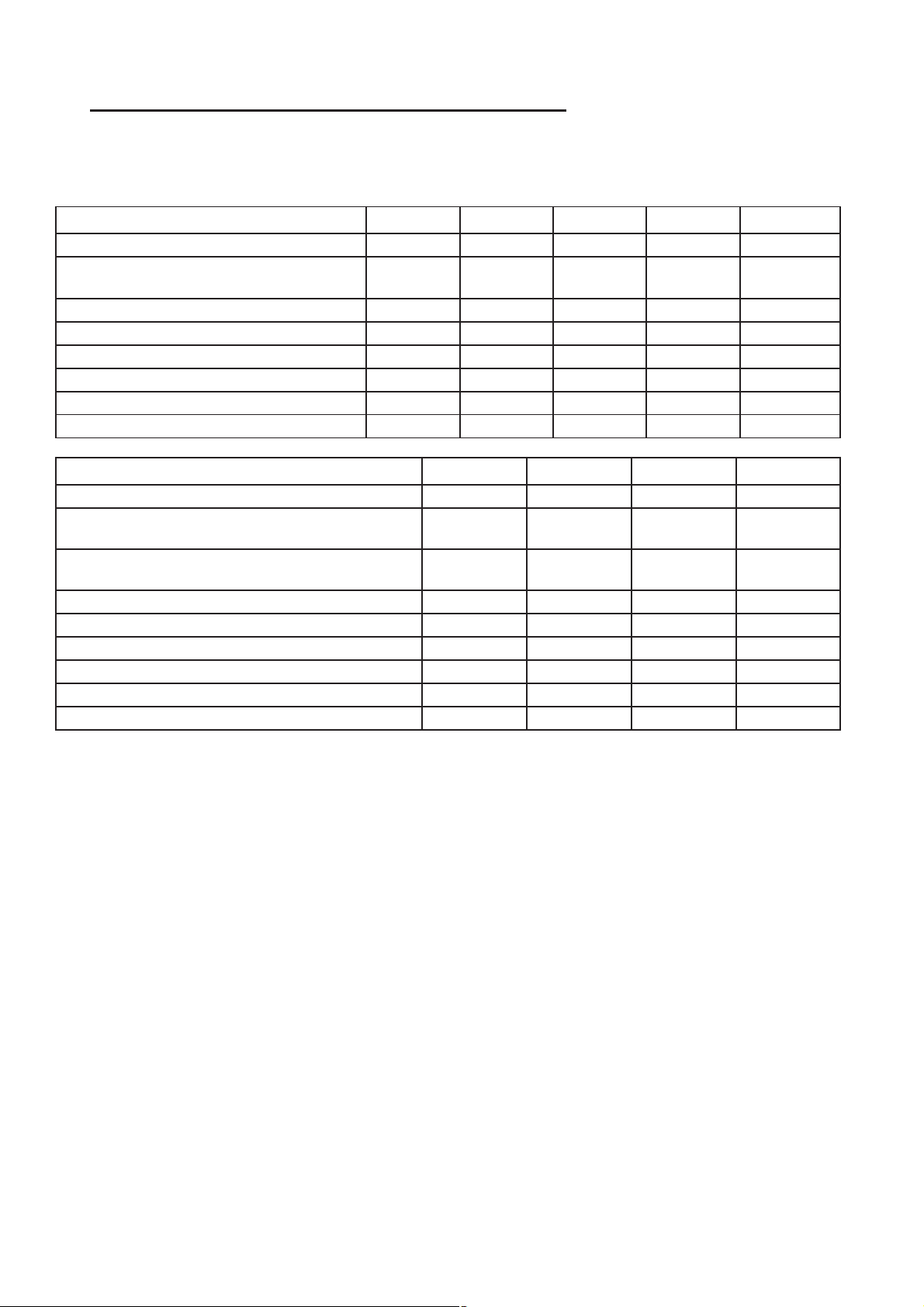
RG MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES 0-3
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES FOR ALL MARKETS EXCEPT U.S., CANADA and MEXICO (Continued)
SCHEDULE “A”
Kilometers 20 000 km 40 000 km 60 000 km 80 000 km 100 000 km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. XXXX X
Inspect engine air filter element. Replace
as necessary.
Replace engine air filter element X X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit. XXXX X
Replace engine timing belt. X
Check front end alignment. X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X X
Inspect the brake linings. XXXX X
Kilometers 120 000 km 140 000 km 160 000 km 180 000 km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X X X X
Inspect engine air filter element. Replace as
necessary.
Inspect accessory drive belts and replace if
necessary.
Replace engine air filter element X X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit. X X X X
Flush and replace engine coolant. X
Check front end alignment. X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X X
Inspect the brake linings. X X X X
XX X
XX
X
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.
WARNING: You can be badly injured working on or
around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work
for which you have the knowledge and the right
equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability
to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a
competent mechanic.
Page 5

Page 6

RG COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL 7-1
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM .........1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM .............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM LEAK TEST....................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM FLOW CHECK .................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM AERATION ....................7
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating temperature. It allows the engine to reach normal operating temperature as quickly as possible, maintains
normal operating temperature and prevents overheating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heating the passenger compartment. The cooling system
is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water pump to
circulate coolant throughout the system. A separate
and remotely mounted, pressurized coolant tank
using a pressure/vent cap is used.
COOLING SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The cooling system consists of:
• Charge Air Cooler
• Electric Cooling Fans
• A aluminum-core radiator with plastic side
tanks
• A separate pressurized coolant tank
• A pressure/vent cap on the coolant tank
• Fan shroud
• Thermostat
• Coolant
• Low coolant warning lamp
• Coolant temperature gauge
• Water pump
• Hoses and hose clamps
CLEANING .............................7
INSPECTION ...........................7
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE .............8
SPECIFICATIONS - COOLING SYSTEM
CAPACITY............................8
ACCESSORY DRIVE .......................9
ENGINE ...............................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
Establish what driving conditions caused the complaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause:
(1) PROLONGED IDLE, VERY HIGH AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE, SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT IDLE,
SLOW TRAFFIC, TRAFFIC JAMS, HIGH SPEED
OR STEEP GRADES.
• Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
(2) TRAILER TOWING:
Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
(3) RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT REPAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been performed on vehicle that may effect cooling system.
This may be:
• Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
• Slipping engine accessory drive belt
• Brakes (possibly dragging)
• Changed parts (incorrect water pump)
• Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refill-
ing (possibly under filled or air trapped in system).
NOTE: If investigation reveals none of the previous
items as a cause for an engine overheating complaint, refer to following Cooling System Diagnosis
charts.
These charts are to be used as a quick-reference
only.
Page 7
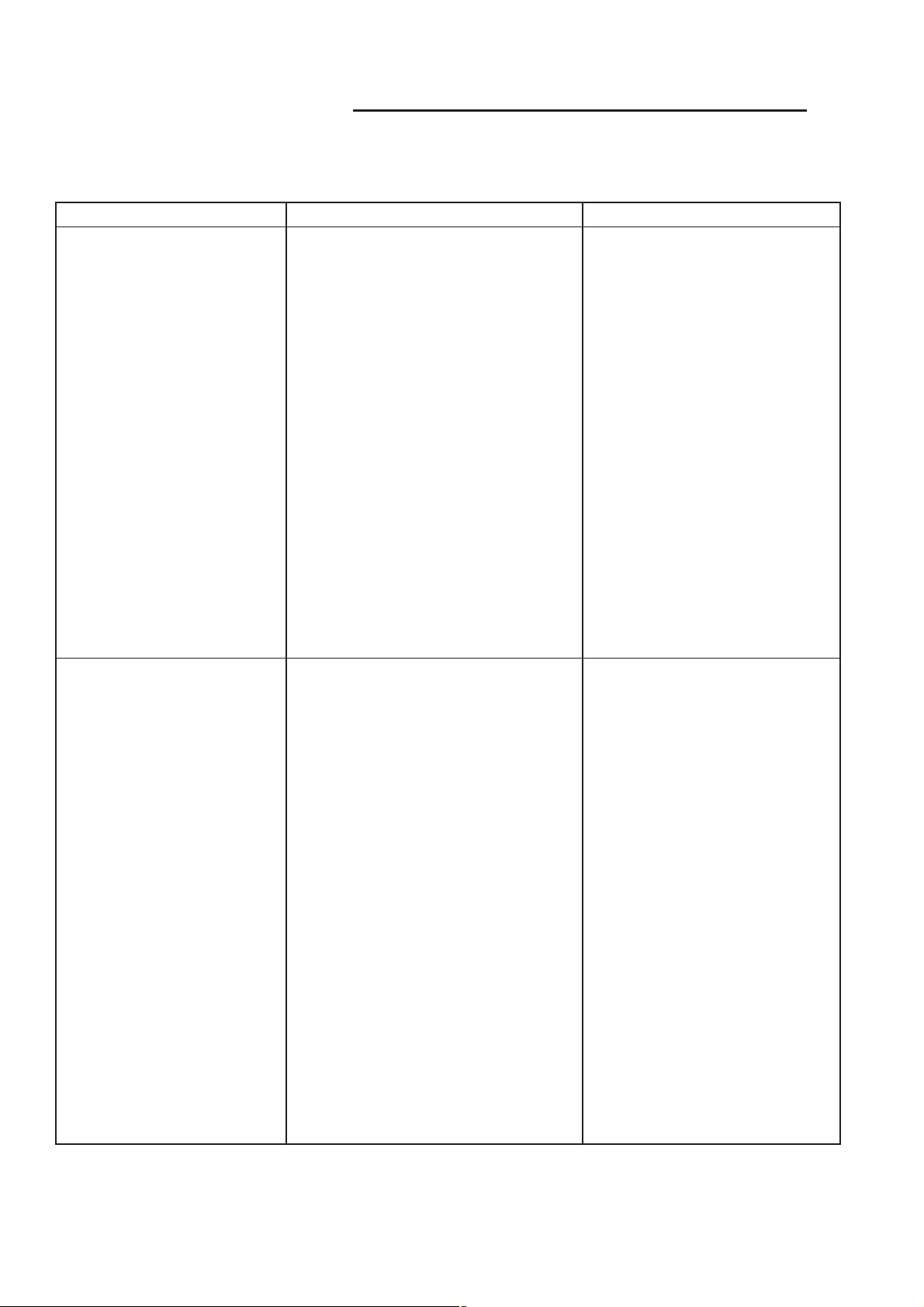
7 - 2 COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL RG
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS-DIESEL ENGINE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READS LOW
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READS HIGH. COOLANT
MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST OR LEAKING FROM
COOLING SYSTEM
1. Diesel engines, due to their
inherent efficiency are slower to
warm up than gasoline powered
engines, and will operate at lower
temperatures when the vehicle is
unloaded.
2. Is the temperature gauge
connected to the temperature gauge
coolant sensor on the engine?
3. Is the temperature gauge
operating OK?
4. Coolant level low in cold ambient
temperatures accompanied with poor
heater performance.
5. Improper operation of internal
heater doors or heater controls.
1. Trailer is being towed, a steep hill
is being climbed, vehicle is operated
in slow moving traffic, or engine is
being idled with very high ambient
(outside) temperature and the air
conditioning is on. Higher altitudes
could aggravate these conditions.
2. Temperature gauge reading
incorrectly.
3. Coolant low in coolant tank and
radiator.
4. Pressure cap not installed tightly.
If cap is loose, boiling point of
coolant will be lowered.
5. Poor seals at pressure/vent cap. 5. (a) Check condition of cap
1. The low gauge reading may
be normal. Refer to thermostats
in the manual text for
information. See Thermostat
Diagnosis-Diesel Engine.
2. Check, the engine
temperature sensor connector
in the engine compartment.
3. Check gauge operation.
Repair as necessary.
4. Check coolant level in the
coolant tank. Inspect system for
leaks. Repair leaks as
necessary. Refer to the Coolant
section for WARNINGS and
precautions before removing
the pressure cap.
5. Inspect heater and repair as
necessary. Refer to Heating
and Air Conditioning for
procedures.
1. This may be a temporary
condition and repair is not
necessary. Turn off the air
conditioning and attempt to
drive the vehicle without any of
the previous conditions.
Observe the temperature
gauge. The gauge should return
to the normal range. If the
gauge does not return to
normal range, determine the
cause for the overheating and
repair.
2. Check gauge. Refer to I/P
group.
3. Check for coolant leaks and
repair as necessary.
4. Tighten cap.
and cap seals. (b) Check
condition of coolant tank filler
neck. Make sure it does not
leak pressure.
Page 8
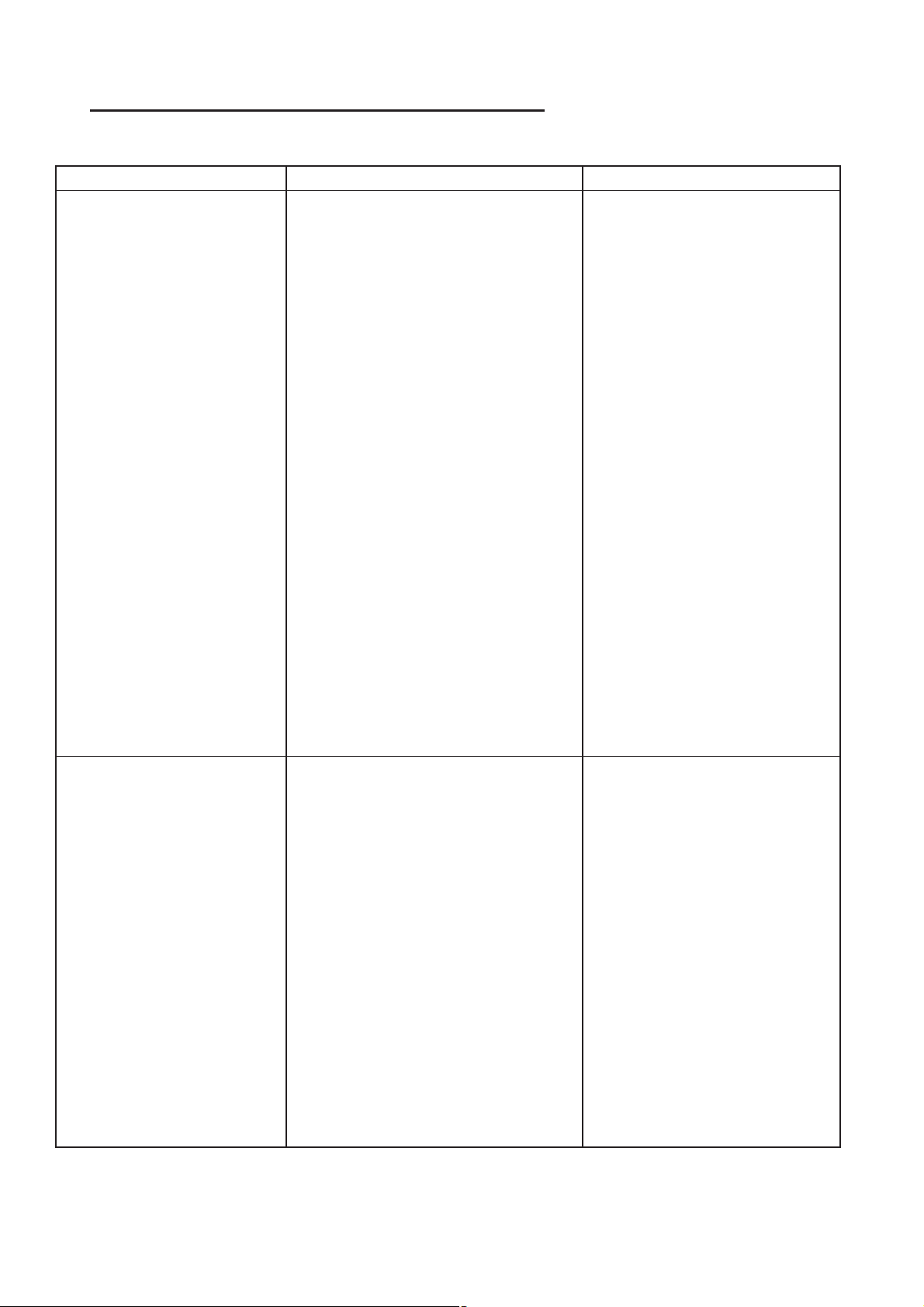
RG COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL 7-3
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
6. Freeze point of antifreeze not
correct. Mixture may be too rich.
7. Coolant not flowing through
system.
8. Radiator or A/C condenser fins
are dirty or clogged.
9. Radiator core is corroded or
plugged.
10. Aftermarket A/C installed without
proper A/C condenser.
11. Dragging Brakes. 11. Check and correct as
12. Non-factory bug screen is being
used reducing air flow.
13. Thermostat partially or
completely shut. This is more
prevalent on high mileage vehicles.
14. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 14. Check cylinder head gasket
15. Heater core leaking. 15. Check heater core for
6. Check antifreeze. Adjust
antifreeze-to-water ratio as
required.
7. Check for coolant flow in
coolant tank with engine warm
and thermostat open. Coolant
should be observed flowing
through the tank. If flow is not
observed, determine reason for
lack of flow and repair as
necessary.
8. Clean debris from radiator or
A/C condenser
9. Have radiator re-cored or
replaced.
10. Install proper A/C
condenser.
necessary.
12. Only a factory screen
should be used.
13. Check thermostat and
replace if necessary.
for leaks.
leaks. Repair as necessary.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING IS
INCONSISTENT
(FLUCTUATES, CYCLES
OR IS ERRATIC)
1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly. Fluctuation is also
influenced by loads, outside
temperature and extended idle time
with diesel engines.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.
3. Gauge reading rises when vehicle
is brought to a stop after heavy use
(engine still running).
4. Gauge reading high after starting
a warm-up (hot) engine.
1. A normal condition. No
correction is necessary.
2. Check operation of gauge
and repair as necessary.
3. A normal condition. No
correction needed. Gauge
should return to normal range
after vehicle is driven.
4. A normal condition. No
correction needed. Gauge
should return to normal after a
few minutes of engine
operation.
Page 9
7 - 4 COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL RG
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
PRESSURE CAP IS
BLOWING OFF STEAM
AND/OR COOLANT.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING MAY BE ABOVE
NORMAL BUT NOT HIGH.
COOLANT LEVEL MAY BE
HIGH IN COOLANT TANK
5. Coolant level low in the coolant
tank (air will build up in the cooling
system causing the thermostat to
open late).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gases to enter the
cooling system causing the
thermostat to open late.
7. Water pump impeller loose on
shaft.
8. Loose accessory drive belt (water
pump slipping).
9. Air leak on the suction side of the
water pump allowing air to build up
in the cooling system causing the
thermostat to open late.
1. Pressure relief valve in pressure/
vent cap is defective.
2. Head gasket leak or cracked
cylinder head.
5. Check and correct coolant
leaks.
6. (a) Check for cylinder head
gasket leaks with a
commercially available leak
tester. (b) Check for coolant in
engine oil. Inspect for white
steam emitting from exhaust
system. Repair as necessary.
7. Check water pump and
replace as necessary.
8. Check and correct as
necessary.
9. Locate leak and repair as
necessary.
1. Check condition of
pressure/vent cap and cap
seals.
2. Repair as necessary.
COOLANT LOSS TO THE
GROUND WITHOUT
PRESSURE CAP
BLOWOFF. GAUGE IS
READING HIGH OR HOT
HOSE OR HOSES
COLLAPSE WHEN
ENGINE IS COOLING
NOISY FAN 1. Cooling fan blades loose. 1. Replace cooling fan
1. Coolant leaks in radiator, cooling
system hoses, water pump, or
engine.
1. Vacuum created in cooling system
on engine cool-down is not being
relieved through pressure/vent cap.
2. Cooling fan blades striking a
surrounding object.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or A/C
condenser.
1. Pressure test cooling system
and repair as necessary.
1. Cap relief valve stuck.
Replace if necessary.
assembly.
2. Locate point of fan blade
contact and repair as
necessary.
3. Remove obstructions or
clean debris from radiator or
A/C condenser.
Page 10
RG COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL 7-5
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
INADEQUATE AIR
CONDITIONER
PERFORMANCE
(COOLING SYSTEM
SUSPECTED)
INADEQUATE HEATER
PERFORMANCE. MAY BE
ACCOMPANIED BY LOW
GAUGE READING
1. Radiator and/or A/C condenser is
restricted, obstructed or dirty
(insects, leaves, etc.)
2. Engine is overheating (heat may
be transferred from radiator to A/C
condenser. High Under hood
temperatures due to engine
overheating may also transfer heat
to A/C condenser).
3. The cooling system is equipped
with air seals at the radiator and/or
A/C condenser. If these seals are
missing or damaged, not enough air
flow will be pulled through the
radiator and A/C condenser.
1. Diesel engines, due to their
inherent efficiency are slower to
warm up than gasoline powered
engines, and will operate at lower
temperatures when the vehicle is
unloaded.
2. Coolant level low. 2. Pressure test cooling system.
3. Obstruction in heater hose fitting
at engine.
4. Heater hose kinked. 4. Locate kinked area. Repair
5. Water pump is not pumping water
to heater core. When the engine is
fully warmed up, both heater hoses
should be hot to the touch. If only
one of the hoses is hot the water
pump may not be operating correctly.
The accessory drive belt may also
be slipping causing poor water pump
operation.
1. Remove restriction or clean
debris from radiator or A/C
condenser.
2. Correct overheating
condition.
3. Check for missing or
damaged air seals. Repair as
necessary.
1. The lower gauge reading
may be normal.
Repair leaks as necessary.
3. Remove heater hoses and
check for obstructions. Repair
as necessary.
as necessary.
5. Refer to water pumps in this
group. Repair as necessary. If a
slipping belt is detected, refer to
Engine Accessory Drive Belts in
this group. Repair as
necessary.
Page 11
7 - 6 COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL RG
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HEAT ODOR 1. Various heat shields are used at
certain drive line components. One
or more of these shields may be
missing.
2. Is temperature gauge reading
above the normal range?
3. Is the Cooling fan operating
correctly?
4. Has undercoating been applied to
any unnecessary components?
STEAM IS COMING FROM
FRONT OF VEHICLE
NEAR GRILL AREA WHEN
WEATHER IS WET,
ENGINE IS WARMED UP
AND RUNNING, AND
VEHICLE IS STATIONARY.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
IS IN NORMAL RANGE
COOLANT ODOR 1. Coolant color is not necessarily an
1. During wet weather, moisture
(snow, ice, or rain condensation) on
the radiator will evaporate when the
thermostat opens. This opening
allows heated water into the radiator.
When the moisture contacts the hot
radiator, steam may be emitted. This
usually occurs in cold weather with
no fan or air flow to blow it away.
indication of adequate corrosion or
temperature protection. Do not rely
on coolant color for determining
condition of coolant.
1. Locate missing shields.
Repair or replace as necessary.
2. Refer to the previous
Temperature Gauge Reads
High in these Diagnostic
Charts. Repair as necessary.
3. Refer to Cooling System Fan
in this group for diagnosis.
Repair as necessary.
4. Clean undercoating as
necessary.
1. Occasional steam emitting
from this area is normal. No
repair is necessary.
1. Refer to Coolant in this group
for antifreeze tests. Adjust
antifreeze-to-water ratio as
necessary.
COOLANT LEVEL
CHANGES IN COOLANT
TANK. TEMPERATURE
GAUGEISINNORMAL
RANGE
1. Level changes are to be expected
as coolant volume fluctuates with
engine temperature. If the level in
the tank was between the HOT and
COLD marks at normal engine
operating temperature, the level
should return to within that range
after operation at elevated
temperatures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
LEAK TEST
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS “DO NOT OPEN
HOT” ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
1. This a normal condition. No
repair necessary.
With engine not running, remove pressure/vent cap
from the coolant recovery pressure container and
wipe the filler neck sealing seat clean. The coolant
recovery pressure container should be full.
Attach the Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to the radiator, as shown in (Fig. 1) and apply
104 kPa (15 psi) pressure. If the pressure drops more
than 13.8 kPa (2 psi) in 2 minutes, inspect all points
for external leaks.
All radiator and heater hoses should be shaken
while at 104 kPa (15 psi), since some leaks occur only
while driving due to engine movement.
Page 12

RG COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL 7-7
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
FLOW CHECK
To determine whether coolant is flowing through
the cooling system, use the following procedures:
(1) If engine is cold, idle engine until normal operating temperature is reached. Then feel the upper
radiator hose. If it is hot, coolant is circulating.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND
UNDER PRESSURE BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS
FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
(2) Remove pressure/vent cap when engine is cold,
idle engine until thermostat opens, you should
observe coolant flow while looking down in the coolant recovery pressure container. Once flow is
detected install the pressure/vent cap.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
AERATION
Fig. 1 PRESSURE TESTING COOLING SYSTEM
1 - COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
If there are no external leaks, after the gauge dial
shows a drop in pressure, detach the tester. Start
engine and run until the thermostat opens, allowing
the coolant to expand. Reattach the cooling system
tester. If the needle on the dial fluctuates it indicates
a combustion leak, usually a head gasket leak.
WARNING: WITH TOOL IN PLACE, PRESSURE WILL
BUILD UP FAST. EXCESSIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP,
BY CONTINUOUS ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE
RELEASED TO A SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER
PERMIT PRESSURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
If the needle on the dial does not fluctuate, raise
the engine rpm a few times. If an abnormal amount
of coolant or steam emits from the tailpipe, it may
indicate a coolant leak caused by a faulty head gasket, cracked engine block, or cracked cylinder head.
There may be internal leaks that can be determined by removing the oil dipstick. If water globules
appear intermixed with the oil it will indicate an
internal leak in the engine. If there is an internal
leak, the engine must be disassembled for repair.
Low coolant level in a cross flow radiator will
equalize in both tanks with engine off. With engine
at running and at operating temperature, the high
pressure inlet tank runs full and the low pressure
outlet tank drops, resulting in cooling system aeration. Aeration will draw air into the water pump
resulting in the following:
• High reading shown on the temperature gauge.
• Loss of coolant flow through the heater core.
• Corrosion in the cooling system.
• Water pump seal may run dry, increasing the
risk of premature seal failure.
• Combustion gas leaks into the coolant can also
cause aeration.
CLEANING
Drain cooling system and refill with clean water.
Refer to procedures in this section. Run engine with
pressure/vent cap installed until upper radiator hose
is hot. Stop engine and drain water from system. If
water is dirty; fill, run, and drain system again, until
water runs clear.
INSPECTION
After performing a cleaning/flush procedure,
inspect all hoses, clamps and connections for deterioration and leaks. Inspect radiator and heater core for
leaks.
Page 13
7 - 8 COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL RG
COOLING 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
2.5L DIESEL - TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N·m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Water Pump Housing Nuts 24.4 18 215
Thermostat Housing Bolts 27.5 21 —
Accessory Drive Belt
Tensioner Bolt
Accessory Drive Belt Idler
Bolt
47.1 35 —
53 39 —
SPECIFICATIONS - COOLING SYSTEM
CAPACITY
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Cooling System With
Auxiliary Heater
Cooling System With Out
Auxiliary Heater
16.6 Liters (17.5 qts.)
13.8 Liters (14.6 qts.)
Page 14
RG ACCESSORY DRIVE 7-9
ACCESSORY DRIVE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ACCESSORY DRIVE
SPECIFICATIONS - ACCESSORY BELT
TENSION .............................9
BELT TENSIONER
REMOVAL .............................9
INSTALLATION ..........................9
IDLER PULLEY
REMOVAL .............................10
INSTALLATION .........................10
DRIVE BELTS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT . 10
ACCESSORY DRIVE
SPECIFICATIONS - ACCESSORY BELT TENSION
ACCESSORY DRIVE
BELT
2.5L DIESEL ENGINE
A/C Compressor/
Generator
Power Steering Belt 300 N (67 lbs.)
GAUGE
Dynamic Tensioner
DESCRIPTION - POWER STEERING BELT . . 10
OPERATION
OPERATION-ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT ....10
OPERATION-POWER STEERING BELT .....11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ACCESSORY
DRIVEBELT .........................11
REMOVAL
REMOVAL-ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT ......11
REMOVAL ...........................11
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION-ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT . . 13
INSTALLATION-POWER STEERING BELT . . . 13
BELT TENSIONER
REMOVAL
WARNING:: BECAUSE OF HIGH SPRING TENSION,
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO DISASSEMBLE THE AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER. THE TENSIONER IS SERVICED AS AN ASSEMBLY.
(1) Remove the power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(3) Remove the belt tensioner retaining bolt and
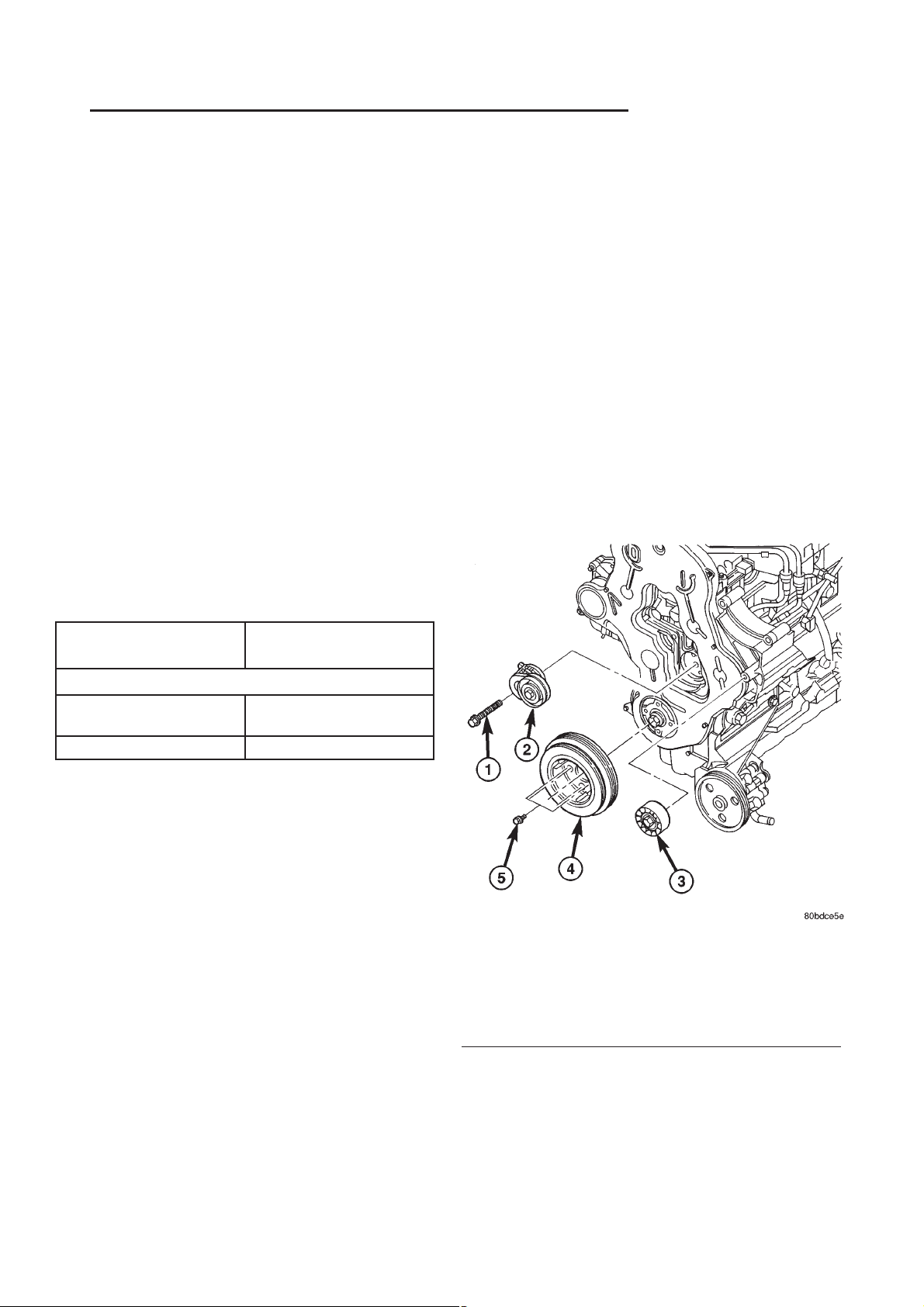
remove tensioner (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 BELT TENSIONER AND IDLER PULLEY
1 - BELT TENSIONER RETAINING BOLT
2 - BELT TENSIONER
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY RETAINING
BOLTS
INSTALLATION
(1) Install belt tensioner and retaining bolt (Fig.
1). Torque bolt to 47 N·m (35ft. lbs.).
(2) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
Page 15
7 - 10 ACCESSORY DRIVE RG
BELT TENSIONER (Continued)
(3) Install the power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
IDLER PULLEY
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
CAUTION: IDLER PULLEY RETAINING BOLT HAS
LEFT HAND THREAD
(2) Remove the idler pulley (Fig. 2).
DRIVE BELTS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
The accessory drive belt is a serpentine type belt
(Fig. 3). Satisfactory performance of these belts
depends on belt condition and proper belt tension.
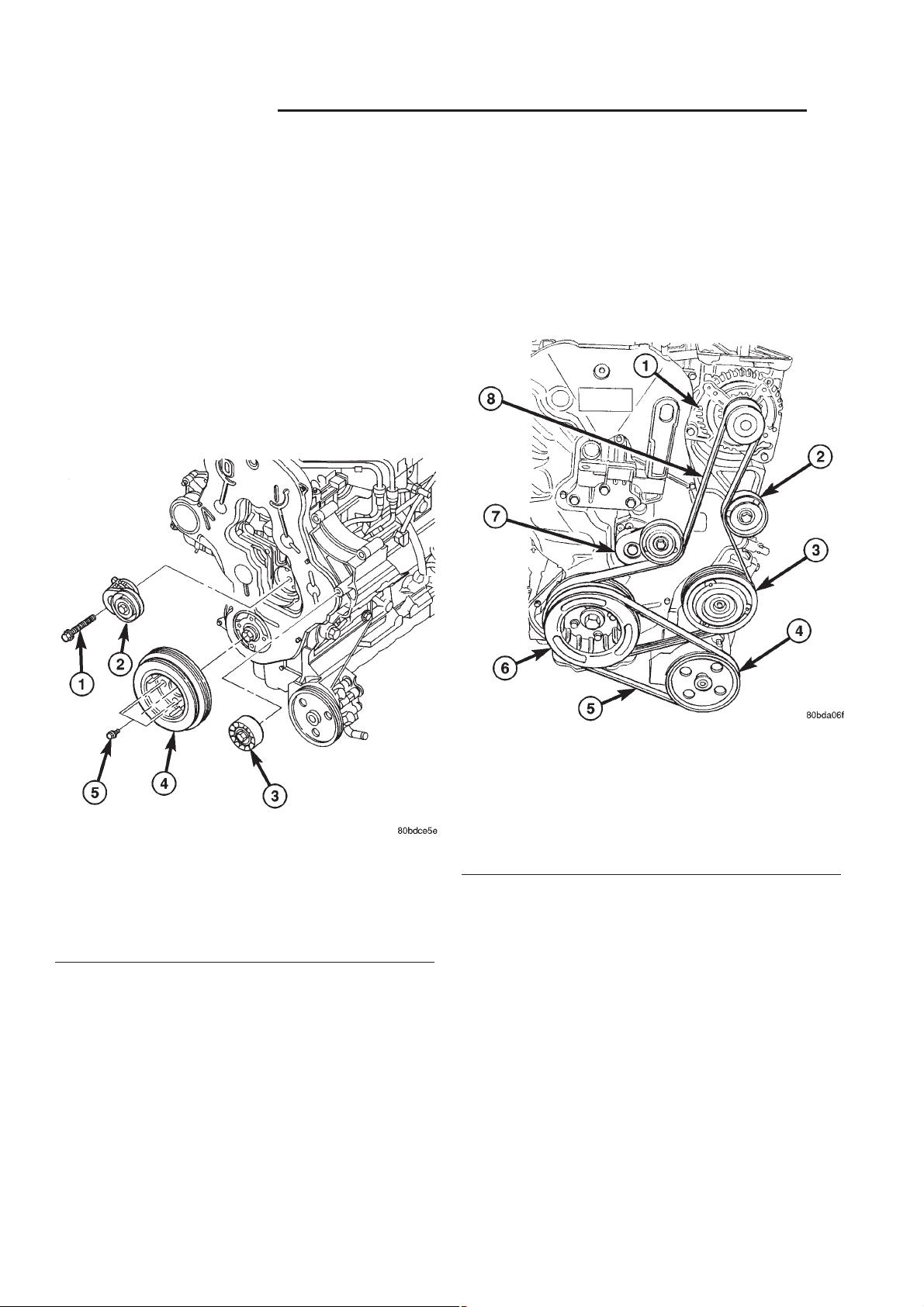
Fig. 2 BELT TENSIONER AND IDLER PULLEY
1 - BELT TENSIONER RETAINING BOLT
2 - BELT TENSIONER
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY RETAINING
BOLTS
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the idler pulley (Fig. 2). Torque retain-
ing bolt to 22 N·m (16 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(3) Install the power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
Fig. 3 ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT ROUTING
1 - GENERATOR
2 - IDLER PULLEY
3 - A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
4 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
5 - POWER STEERING BELT
6 - CRANKSHAFT DAMPER/PULLEY
7 - BELT TENSIONER
8 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
DESCRIPTION - POWER STEERING BELT
The power steering belt is a serpentine type belt
(Fig. 3). Satisfactory performance of this belt depends
on condition of the belt.
OPERATION
OPERATION-ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
The accessory drive belts form the link between
the engine crankshaft and the engine driven accessories.
Page 16
RG ACCESSORY DRIVE 7-11
DRIVE BELTS (Continued)
OPERATION-POWER STEERING BELT
The power steering belt forms a link between the
engine crankshaft and the power steering pump.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
INSUFFICIENT ACCESSORY
OUTPUT DUE TO BELT SLIPPAGE
BELT SQUEAL WHEN
ACCELERATING ENGINE
BELT SQUEAK AT IDLE 1. Belts too loose 1. Replace belt
BELT ROLLED OVER IN GROOVE
OR BELT JUMPS OFF
1. Belt too loose 1. Replace belt (auto-tensioned
belts)
2. Faulty belt tensioner 2. Replace tensioner as necessary
3. Belt excessively glazed or worn 3. Replace belt
1. Belts too loose 1. Check and replace belt tensioner
if necessary
2. Belt glazed 2. Replace belt
2. Dirt or paint imbedded in belt or
pulley
3. Non-uniform belt 3. Replace belt
4. Misaligned pulleys 4. Align accessories
5. Non-uniform groove or eccentric
pulley
1. Broken cord in belt 1. Replace belt
2. Belt too loose, or too tight 2. Replace belt
3. Misaligned pulleys 3. Align accessories
4. Non-uniform groove or eccentric
pulley
2. Replace belt, clean pulley
5. Replace pulley
4. Replace pulley
REMOVAL
REMOVAL-ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
(1) Remove the power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(2) Relieve tension on belt tensioner using a suitable wrench (Fig. 4) and lock tensioner with a drift
punch (Fig. 5).
(3) Remove the accessory drive belt.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove right front fender inner splash shield.
(3) Install power steering belt remover tool on
crankshaft damper (Fig. 6).
(4) Rotate engine clockwise to remove belt (Fig. 7).
Page 17
7 - 12 ACCESSORY DRIVE RG
DRIVE BELTS (Continued)
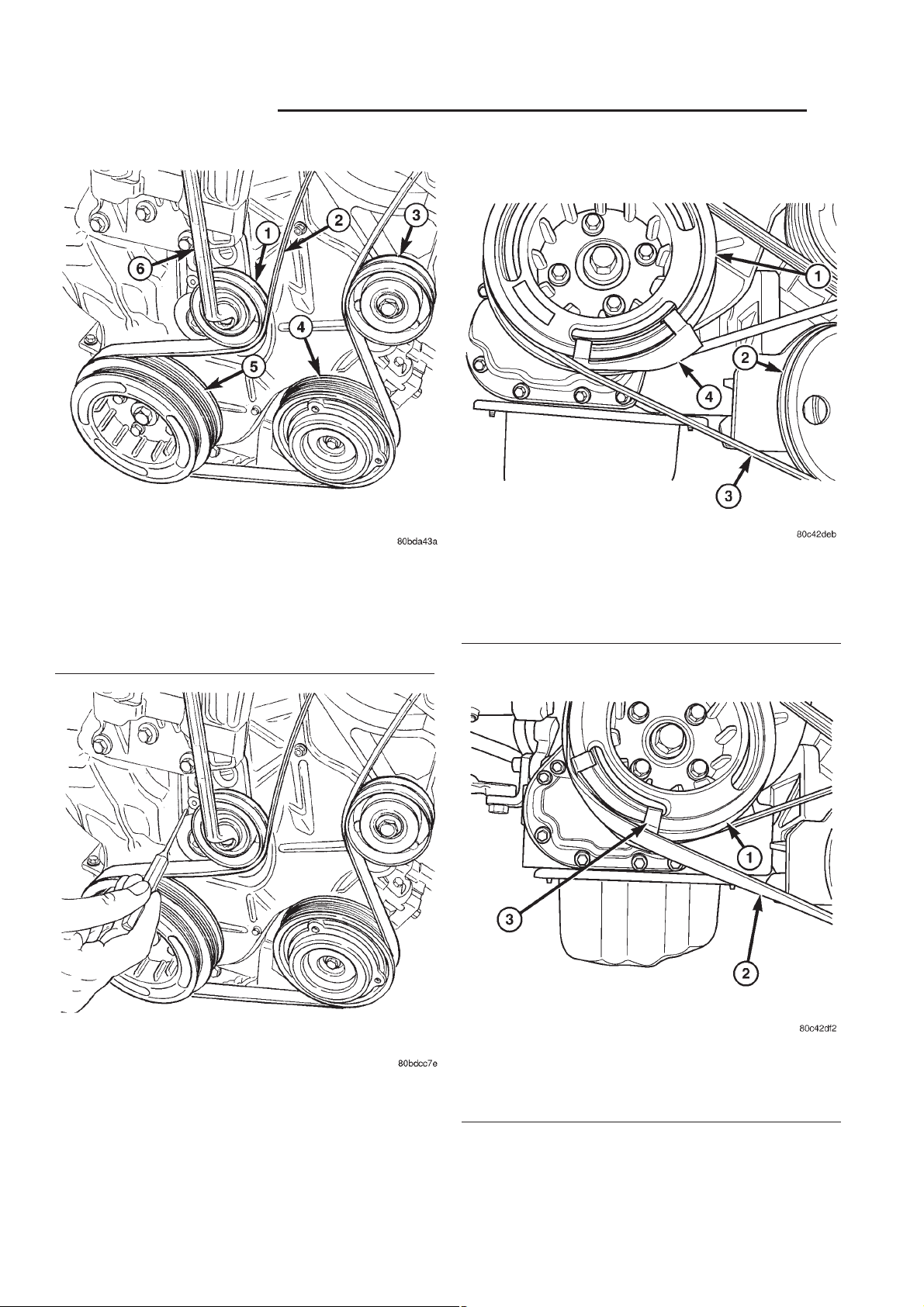
Fig. 4 ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT REMOVAL
1 - BELT TENSIONER
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
5 - CRANKSHAFT DAMPER/PULLEY
6 - WRENCH
Fig. 6 POWER STEERING BELT REMOVAL TOOL
1 - VIBRATION DAMPER
2 - POWER STEERING PULLEY
3 - POWER STEERING BELT
4 - POWER STEERING BELT REMOVER
Fig. 5 LOCKING/LOCKING BELT TENSIONER
Fig. 7 POWER STEERING BELT REMOVAL
1 - VIBRATION DAMPER
2 - POWER STEERING BELT
3 - POPWER STEERING BELT REMOVER
Page 18
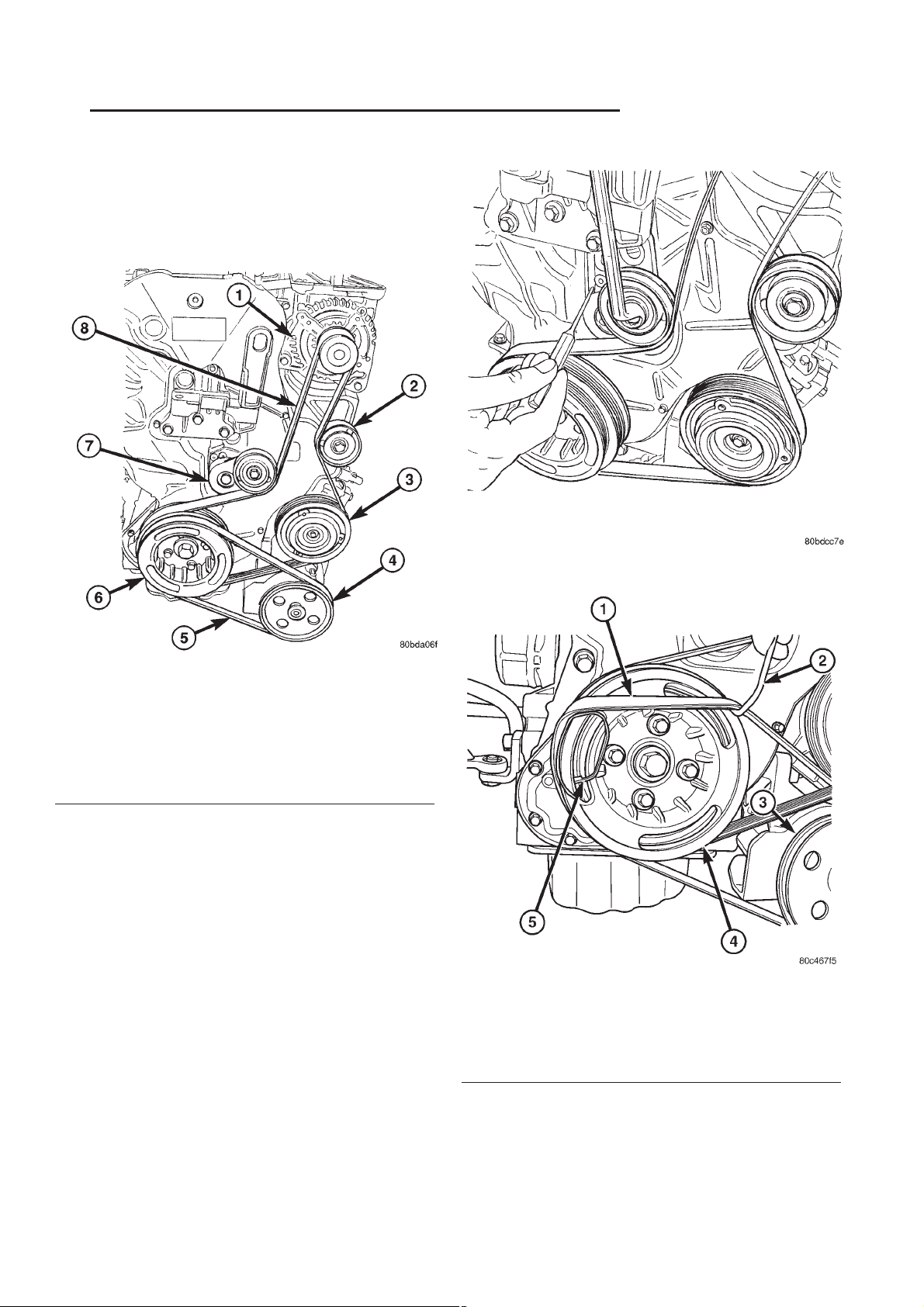
RG ACCESSORY DRIVE 7-13
DRIVE BELTS (Continued)
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION-ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
(1) Install the accessory drive belt in proper popsition (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8 ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT ROUTING
1 - GENERATOR
2 - IDLER PULLEY
3 - A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
4 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
5 - POWER STEERING BELT
6 - CRANKSHAFT DAMPER/PULLEY
7 - BELT TENSIONER
8 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
(2) Unlock belt tensioner by removing punch and
apply tension to accessory drive belt (Fig. 9).
(3) Install the power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
INSTALLATION-POWER STEERING BELT
(1) Install power steering belt installation tool
(Fig. 10).
(2) Install power steering belt on crankshaft and
rotate crankshaft clockwise until belt is fully
installed on crankshaft (Fig. 10).
(3) Remove installation tool from crankshaft.
(4) Install right front fender inner splash shield.
(5) Lower vehicle from hoist.
Fig. 9 LOCKING/UNLOCKING BELT TENSIONER
Fig. 10 POWER STEERING BELT INSTALLATION
1 - POWER STEERING BELT
2 - HOLDING HOOK
3 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
4 - VIBRATION DAMPER
5 - POWER STEERING BELT INSTALLATION TOOL
Page 19

7 - 14 ENGINE RG
ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION .........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLANT
CONCENTRATION TESTING .............15
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
SERVICE............................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT.................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
LEVEL CHECK........................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM FILLING .....................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM DRAINING....................17
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION .........................17
OPERATION ...........................17
REMOVAL .............................18
INSTALLATION .........................18
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION .........................18
OPERATION ...........................18
REMOVAL .............................19
INSTALLATION .........................19
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION .........................20
OPERATION ...........................20
REMOVAL .............................20
INSTALLATION .........................20
RADIATOR
DESCRIPTION .........................21
OPERATION ...........................21
REMOVAL .............................21
INSTALLATION .........................21
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
REMOVAL .............................22
INSTALLATION .........................22
WATER PUMP
DESCRIPTION .........................22
OPERATION ...........................22
REMOVAL
REMOVAL-WATERPUMP ..............22
REMOVAL-WATERPUMPHOUSING ......22
CLEANING ............................23
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION-WATERPUMP ..........23
INSTALLATION - WATER PUMP HOUSING . . 23
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION .........................23
OPERATION ...........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP...............25
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
RELIEFTEST ........................25
CLEANING ............................26
INSPECTION ..........................26
RADIATOR FAN
DESCRIPTION .........................26
OPERATION ...........................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR FAN
MOTOR .............................27
REMOVAL .............................27
INSTALLATION .........................27
HOSE CLAMPS
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS ...........28
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS .............28
RADIATOR FAN RELAY
DESCRIPTION .........................28
OPERATION ...........................28
COOLANT SYSTEM HOSES
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE .....29
REMOVAL-LOWERRADIATORHOSE .....29
REMOVAL-COOLANTBYPASSHOSE .....29
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE . . 29
INSTALLATION - LOWER RADIATOR HOSE . 29
INSTALLATION - COOLANT BYPASS HOSE . 29
Page 20

RG ENGINE 7-15
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION
Coolant flows through the engine water jackets
and cylinder heads absorbing heat produced by the
engine during operation. The coolant carries heat to
the radiator and heater core. Here it is transferred to
ambient air passing through the radiator and heater
core fins.
The required ethylene-glycol (antifreeze) and water
mixture depends upon the climate and vehicle operating conditions. The recommended mixture of 50/50
ethylene-glycol and water will provide protection
against freezing to -37 deg. C (-35 deg. F). The antifreeze concentration must always be a minimum of
44 percent, year-round in all climates. If percentage
is lower than 44 percent, engine parts may be
eroded by cavitation, and cooling system components may be severely damaged by corrosion.
Maximum protection against freezing is provided
with a 68 percent antifreeze concentration, which
prevents freezing down to -67.7 deg. C (-90 deg. F). A
higher percentage will freeze at a warmer temperature. Also, a higher percentage of antifreeze can
cause the engine to overheat because the specific
heat of antifreeze is lower than that of water.
100 Percent Ethylene-Glycol—Should Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Use of 100 percent ethylene-glycol will cause formation of additive deposits in the system, as the corrosion inhibitive additives in ethylene-glycol require
the presence of water to dissolve. The deposits act as
insulation, causing temperatures to rise to as high as
149 deg. C (300 deg. F). This temperature is hot
enough to melt plastic and soften solder. The
increased temperature can result in engine detonation. In addition, 100 percent ethylene-glycol freezes
at -22 deg. C (-8 deg. F ).
Propylene-glycol Formulations—Should Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol formulations do not meet
Chrysler coolant specifications. It’s overall effec-
tive temperature range is smaller than that of ethylene-glycol. The freeze point of 50/50 propylene-glycol
and water is -32 deg. C (-26 deg. F). 5 deg. C higher
than ethylene-glycol’s freeze point. The boiling point
(protection against summer boil-over) of propyleneglycol is 125 deg. C (257 deg.F)at96.5 kPa (14 psi),
compared to 128 deg. C (263 deg. F) for ethylene-glycol. Use of propylene-glycol can result in boil-over or
freeze-up in Chrysler vehicles, which are designed for
ethylene-glycol. Propylene glycol also has poorer heat
transfer characteristics than ethylene glycol. This
can increase cylinder head temperatures under certain conditions.
Propylene-glycol/Ethylene-glycol Mixtures—Should Not Be
Used in Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol/ethylene-glycol Mixtures can
cause the destabilization of various corrosion inhibitors, causing damage to the various cooling system
components. Also, once ethylene-glycol and propylene-glycol based coolants are mixed in the vehicle,
conventional methods of determining freeze point will
not be accurate. Both the refractive index and specific gravity differ between ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethylene-glycol.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLANT
CONCENTRATION TESTING
Coolant concentration should be checked when any
additional coolant was added to system or after a
coolant drain, flush and refill. The coolant mixture
offers optimum engine cooling and protection against
corrosion when mixed to a freeze point of -37°C
(-34°F) to -59°C (-50°F). The use of a hydrometer or a
refractometer can be used to test coolant concentration.
A hydrometer will test the amount of glycol in a
mixture by measuring the specific gravity of the mixture. The higher the concentration of ethylene glycol,
the larger the number of balls that will float, and
higher the freeze protection (up to a maximum of
60% by volume glycol).
A refractometer will test the amount of glycol in a
coolant mixture by measuring the amount a beam of
light bends as it passes through the fluid.
Some coolant manufactures use other types of glycols into their coolant formulations. Propylene glycol
is the most common new coolant. However, propylene
glycol based coolants do not provide the same freezing protection and corrosion protection and is not recommended.
CAUTION: Do not mix types of coolant—corrosion
protection will be severely reduced.
Page 21
7 - 16 ENGINE RG
COOLANT (Continued)
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT SERVICE
For engine coolant recommended service schedule,
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT
The pressure/vent cap should not be removed
from the coolant recovery pressure container
when the engine is hot. When additional coolant is
needed to maintain this level, it should be added to
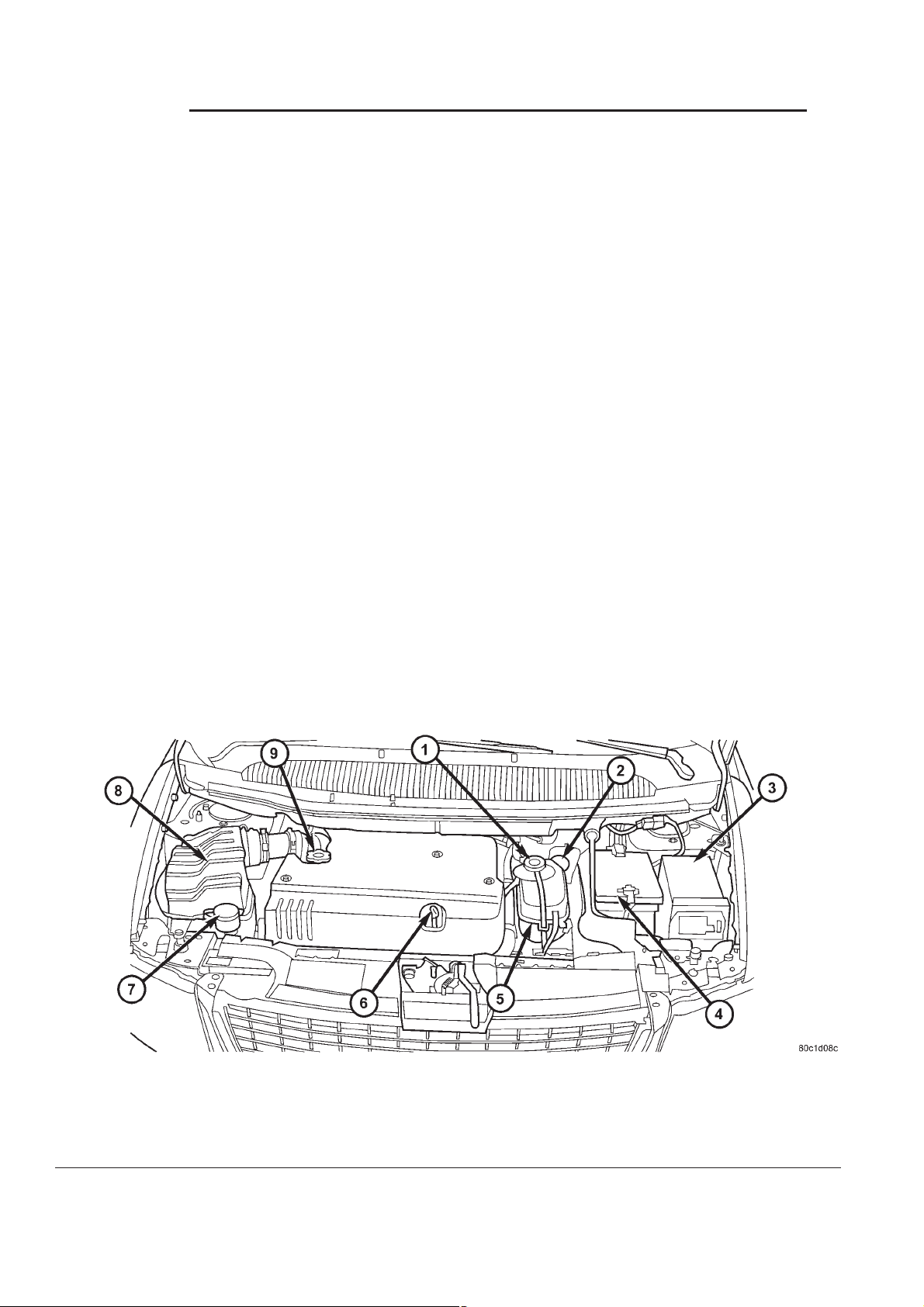
the coolant recovery pressure container (Fig. 1). Use
only 50/50 mix of ethylene glycol type antifreeze and
distilled water. For the recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES - DESCRIPTION).
CAUTION: Do not use well water, or suspect water
supply in cooling system. A 50/50 ethylene glycol
and distilled water mix is recommended. For the
recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT LEVEL
CHECK
NOTE: Do not remove pressure/vent cap for routine
coolant level inspections.
The coolant reserve system provides a quick visual
method for determining the coolant level without
removing the pressure/vent cap. With the engine
cold and not running, simply observe the level of
the coolant in the coolant recovery pressure container
(Fig. 2). The coolant level should be between the MIN
and MAX marks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING SYSTEM
FILLING
(1) Remove pressure vent cap from coolant recovery pressure container.
(2) Loosen air bleed screw on the thermostat housing.
(3) Slowly fill the cooling through the coolant
recovery pressure container until a steady stream of
coolant comes out of the air bleed.
(4) Tighten the air bleed screw.
(5) Continue filling coolant recovery pressure container until level reaches the full line.
Fig. 1 UNDERHOOD FLUID FILL LOCATIONS
1 - COOLANT PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE
4 - BATTERY
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
6 - OIL DIPSTICK
7 - WINDSHIELD SOLVENT RESEVOIR
8-AIRFILTERHOUSING
9 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
Page 22
RG ENGINE 7-17
COOLANT (Continued)
(1) Without removing pressure/vent cap and
with system not under pressure, open the drain-
cock. The draincock is located on the lower right side
of radiator (Fig. 3).
(2) After the coolant recovery pressure container is
empty, then remove coolant pressure/vent cap.
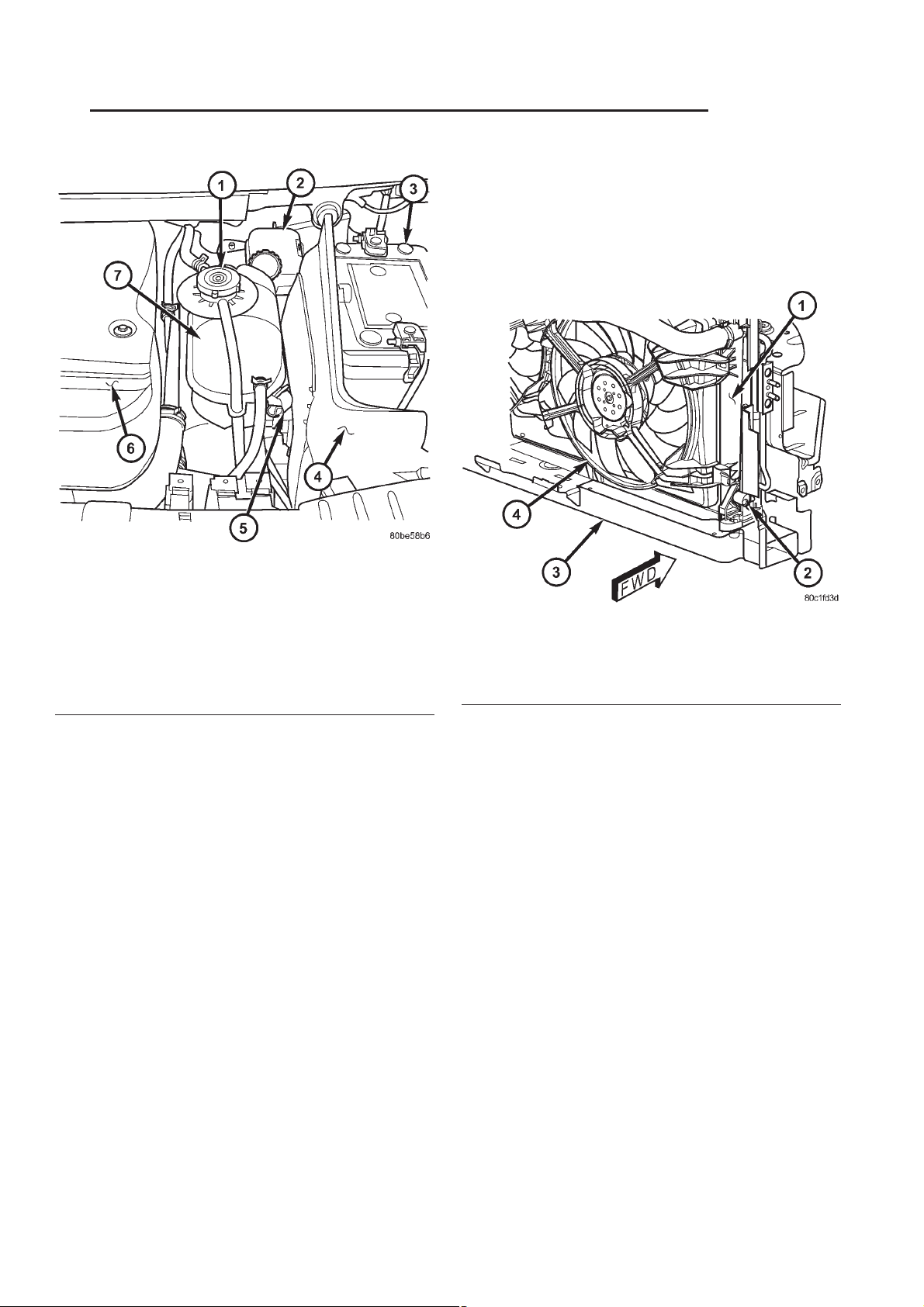
Fig. 2 COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE
CONTAINER LOCATION
1 - PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - BATTERY
4 - BATTERY SHIELD
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER RETAING
CLIP
6 - ENGINE COVER
7 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
(6) Without installing the pressure/vent cap, start
and run engine at idle for a couple minutes.
(7) Recheck coolant level and fill as necessary.
(8) Install pressure/vent cap and drive vehicle for
approx. 10 km to reach normal operating temperatures.
(9) Allow vehicle to cool. Check and fill coolant as
needed.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING SYSTEM
DRAINING
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE OR LOOSEN THE
COOLANT PRESSURE/VENT CAP, CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, OR THE DRAINCOCK WHEN
THE SYSTEM IS HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Fig. 3 DRAINCOCK LOCATION
1 - RADIATOR
2 - DRAINCOCK
3-LOWERRADIATORSUPPORT
4 - ELECTRIC COOLING FAN
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS
CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION
The coolant recovery pressure container is
mounted in the engine compartment next to the battery. The coolant recovery pressure container is made
of plastic (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The coolant recovery pressure container works
with the pressure/vent cap to use thermal expansion
and contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant
free of trapped air. Provides a convenient and safe
method for checking coolant level and adjusting level
at atmospheric pressure without removing the pressure/vent cap. It also provides some reserve coolant
to cover deaeration, evaporation, or boiling losses.
Page 23
7 - 18 ENGINE RG
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER (Continued)
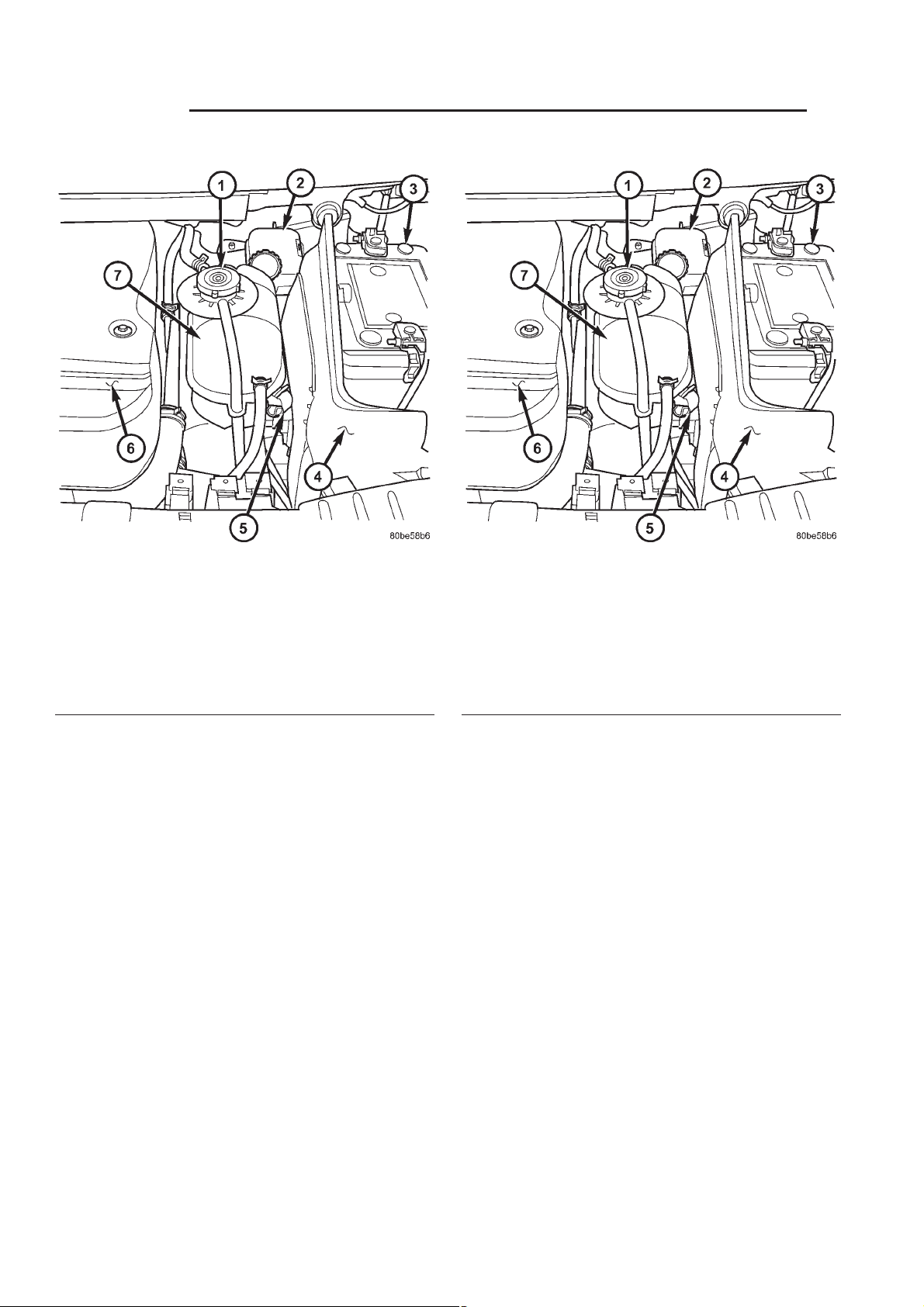
Fig. 4 COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE
CONTAINER LOCATION
1 - PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - BATTERY
4 - BATTERY SHIELD
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER RETAING
CLIP
6 - ENGINE COVER
7 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system below level of coolant
recovery pressure bottle. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect coolant bypass and overflow hoses
from coolant recovery pressure container (Fig. 6).
(3) Unclip the coolant recovery pressure container
retaining clip (Fig. 5).
(4) Raise coolant recovery pressure container from
mounting bracket and disconnect coolant hose from
bottom of container (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove coolant recovery pressure bottle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect coolant hose at bottom of coolant
recovery pressure container (Fig. 6) and install in
mounting bracket.
(2) Connect coolant recovery pressure container
retaining clip (Fig. 5).
(3) Connect coolant bypass and overflow hoses to
coolant recovery pressure container.
Fig. 5 COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE
CONTAINER LOCATION
1 - PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - BATTERY
4 - BATTERY SHIELD
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER RETAING
CLIP
6 - ENGINE COVER
7 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
(4) Refill cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The engine coolant temperature sensor threads
into a coolant passage in the cylinder head (Fig. 7).
New sensors have sealant applied to the threads.
OPERATION
The coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor (resistance varies inversley with temperature). This means
at cold tempertures its resistance is high so the voltage signal will be high. As coolant temperture
increases, resistance decreases and the signal voltage
will be low. This allows the sensor to provide an analog voltage signal to the ECM.
Page 24
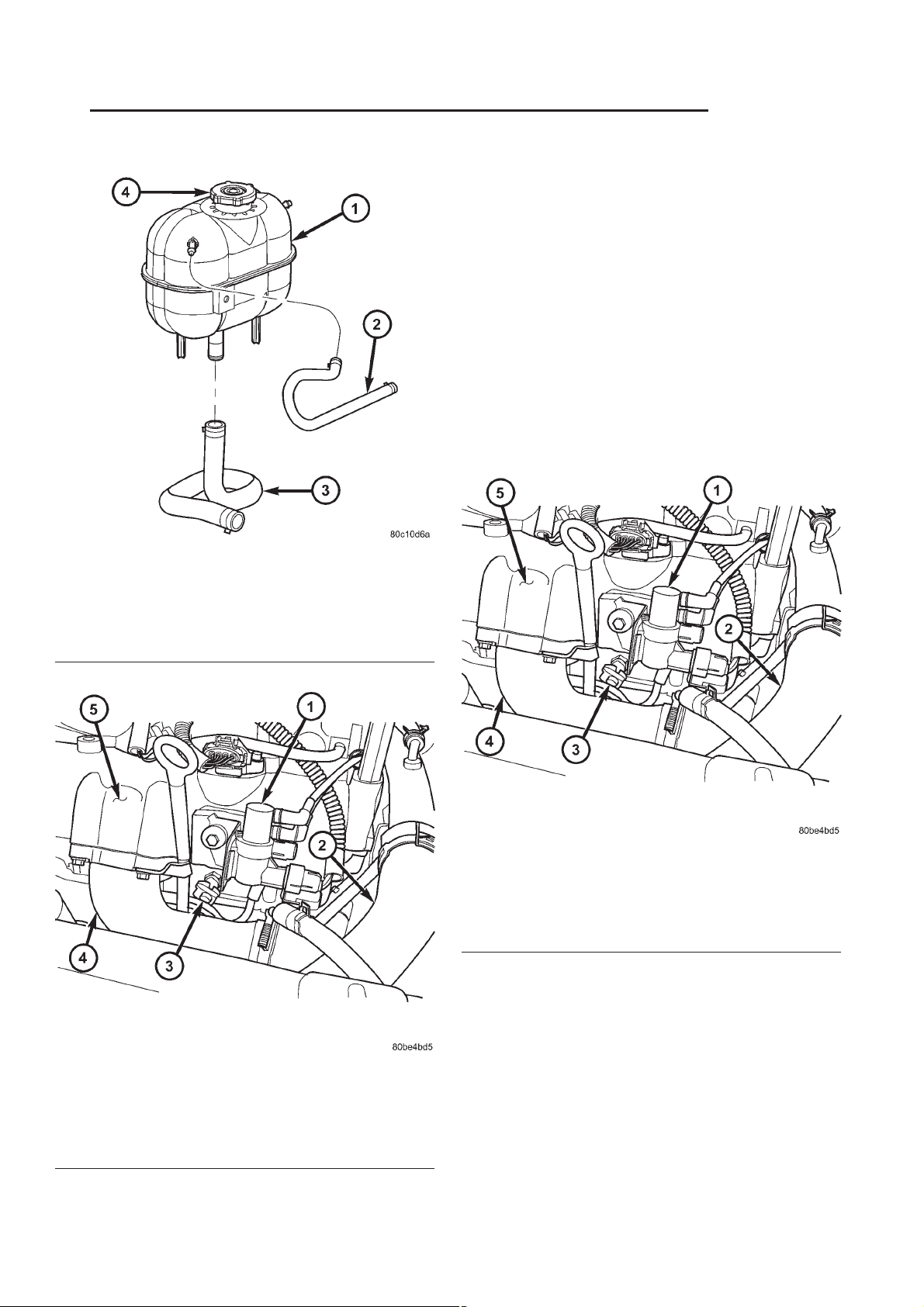
RG ENGINE 7-19
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR (Continued)
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE OR LOOSEN THE
COOLANT PRESSURE/VENT CAP, CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, OR THE DRAINCOCK WHEN
THE SYSTEM IS HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect coolant temperature sensor electrical connector (Fig. 8).
(3) Remove coolant temperature sensor from cylinder head (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE
CONTAINER
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
2 - COOLANT BYPASS HOSE
3 - OUTLET HOSE
4 - PRESSURE/VENT CAP
Fig. 7 COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
LOCATION
1 - EGR SOLENOID
2 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
3 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - INTAKE MANIFOLD INLET
5 - INTAKE MANIFOLD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER
Fig. 8 COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
LOCATION
1 - EGR SOLENOID
2 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
3 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - INTAKE MANIFOLD INLET
5 - INTAKE MANIFOLD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coolant temperature sensor in cylinder
head (Fig. 8).
(2) Connect coolant temperature sensor electrical
connector (Fig. 8).
(3) Refill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 25
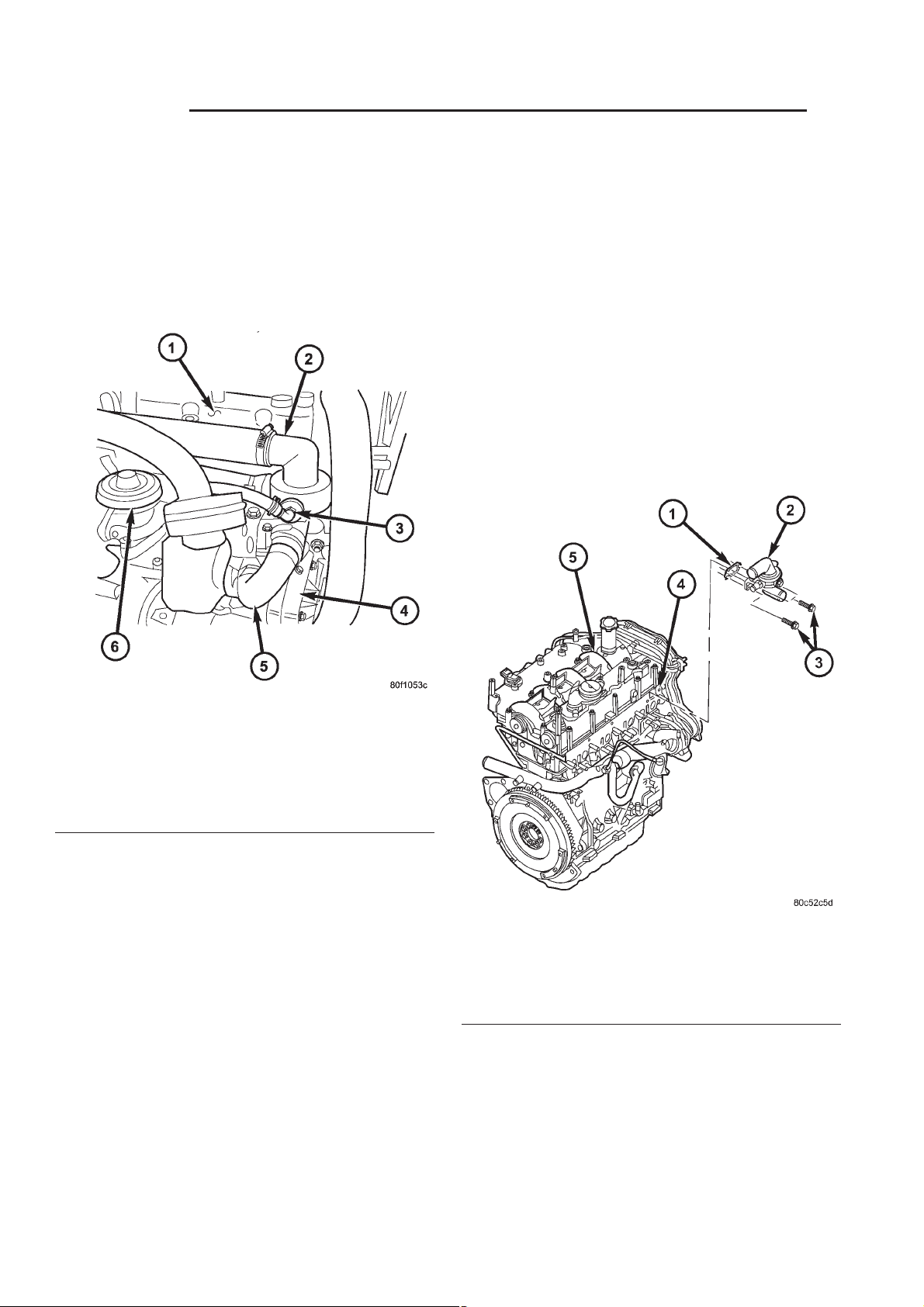
7 - 20 ENGINE RG
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION
A pellet-type thermostat controls the operating
temperature of the engine by controlling the amount
of coolant flow to the radiator (Fig. 9).
REMOVAL
NOTE: The thermostat is not serviced separately.
The thermostat and housing must be replaced as
an assembly.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove front wiper unit to gain access to thermostat housing(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/
WASHERS/WIPER MODULE - REMOVAL).
(4) Disconnect upper radiator hose adapter tube,
water pump hose, and EGR hose at thermostat housing.
(5) Remove both thermostat housing attaching
bolts and housing (Fig. 10).
Fig. 9 THERMOSTAT HOUSING
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
3 - AIR BLEED
4-WATERPUMP
5 - WATER PUMP HOUSING TO THERMOSTAT HOUSING
BYPASS HOSE
6 - EGR VALVE
OPERATION
The thermostat starts to open at 88°C (190°F).
Above this temperature, coolant is allowed to flow to
the radiator. This provides quicker engine warmup
and overall temperature control.
The same thermostat is used for winter and summer seasons. An engine should not be operated without a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other problems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreliable warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This condensation can result in sludge formation.
Fig. 10 THERMOSTAT HOUSING ASSEMBLY
1 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING GASKET
2 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
3 - RETAINING BOLTS
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
INSTALLATION
(1) Install thermostat housing, gasket, and retain-
ing bolts (Fig. 10). Torque bolts to 27.5N·m.
(2) Connect upper radiator hose adapter tube,
water pump hose, and EGR cooler hose to thermostat
housing.
Page 26
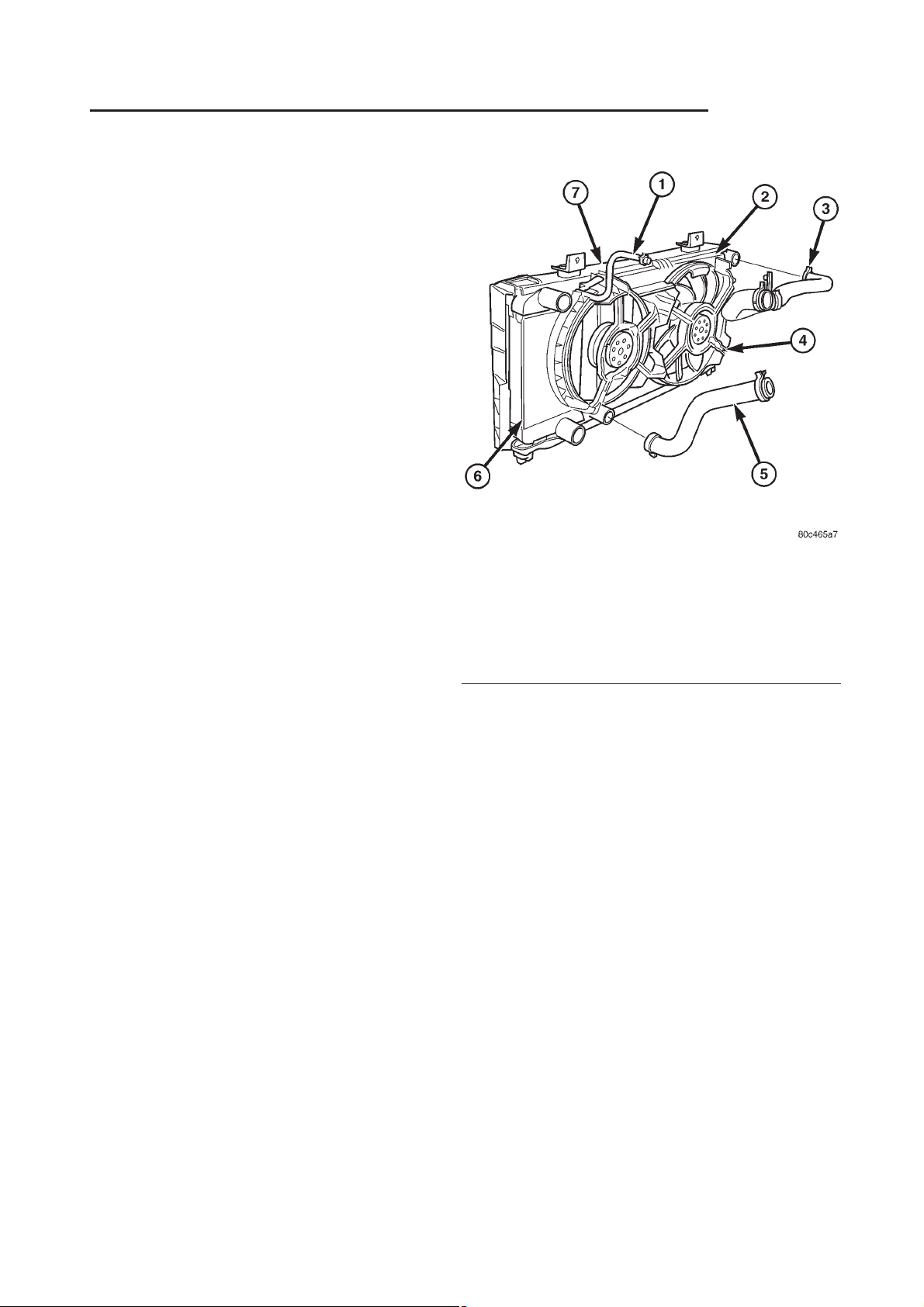
RG ENGINE 7-21
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT (Continued)
(3) Install front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE INSTALLATION).
(4) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Connect negative battery cable.
RADIATOR
DESCRIPTION
The radiator is a cross-flow type (horizontal tubes)
with design features that provide greater strength
along with sufficient heat transfer capabilities to
keep the engine satisfactorily cooled. The radiator
has plastic side tanks and aluminum cooling tubes.
OPERATION
The radiator functions as a heat exchanger, using
air flow across the exterior of the radiator tubes. This
heat is then transferred from the coolant and into
the passing air.
Fig. 11 UPPER AND LOWER RADIATOR HOSES
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove radiator upper crossmember support.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPENING
REINFORCEMENT - REMOVAL)
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK PLUG OR THE RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
(3) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Remove the radiator fans. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL)
(5) Disconnect coolant bypass hose (Fig. 11).
(6) Disconnect upper and lower hoses from the
radiator (Fig. 11).
(7) Remove the A/C condenser side brackets to
radiator attaching screws (Fig. 12). Separate the condenser from the radiator by lifting upward to disengage from lower mounts (Fig. 12). Allow the
condenser to rest in front of radiator.
(8) Radiator can now be lifted free from engine
compartment. Care should be taken not to dam-
age radiator cooling fins or water tubes during
removal.
1 - COOLANT BYPASS HOSE
2 - RADIATOR ASSEMBLY
3 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
4 - COOLING FAN
5-LOWERRADIATORHOSE
6 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
7 - RADIATOR BRACKET
INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure the air seal is in position before
radiator is installed. Slide radiator down into posi-
tion. Seat the radiator with the rubber isolators into
the mounting holes provided, with a 10 lbs. force.
(2) Position air conditioning condenser onto the
radiator lower mounts and install upper screws (Fig.
12). Tighten fasteners to 5 N·m (45 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the radiator upper and lower hoses (Fig.
11).
(4) Connect the coolant bypass hose.
(5) Install the radiator fans. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install the radiator upper crossmember sup-
port. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE
OPENING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION)
(7) Fill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
Page 27
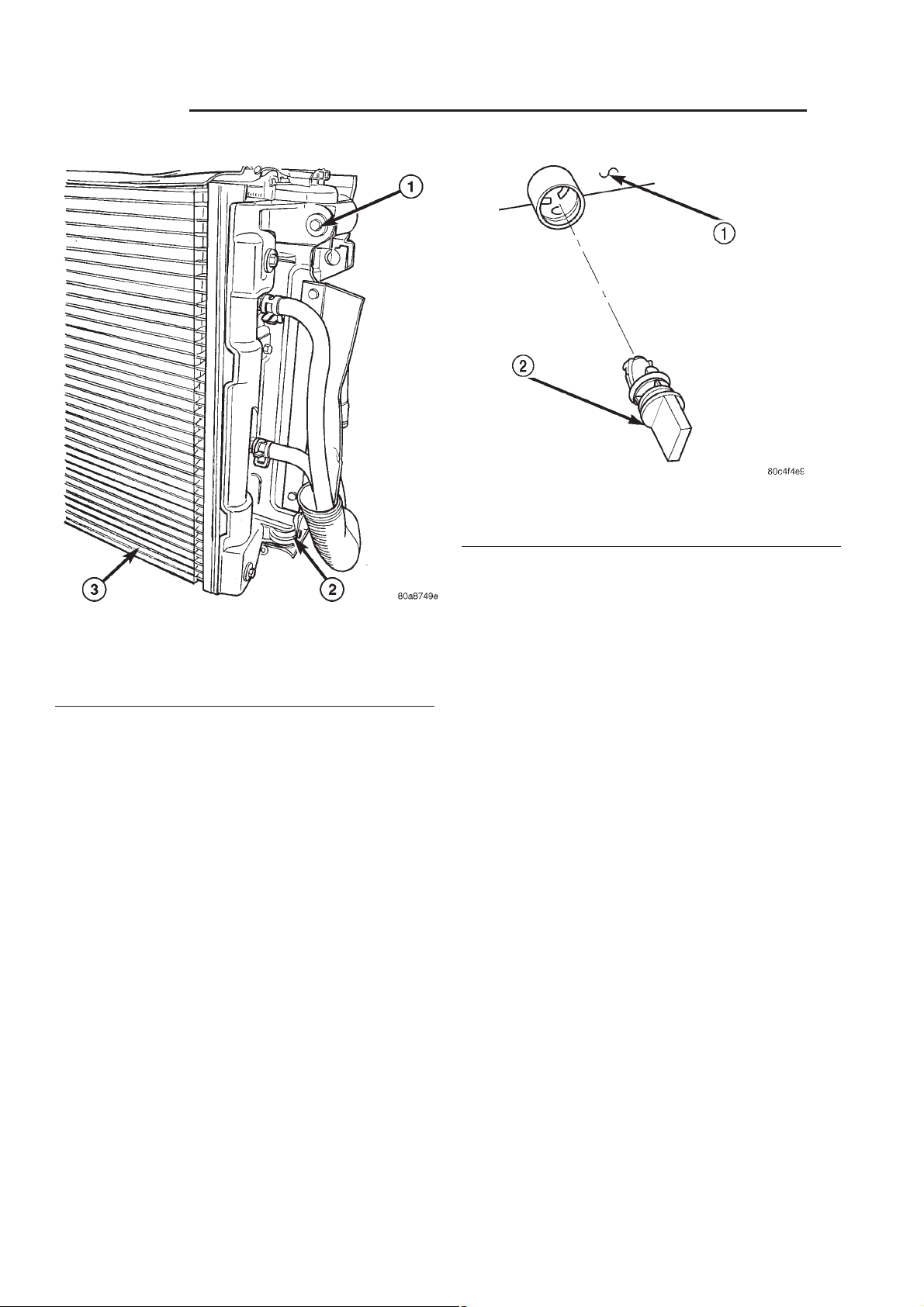
7 - 22 ENGINE RG
RADIATOR (Continued)
Fig. 13 Draincock
1 - RADIATOR TANK
2 - DRAINCOCK
Fig. 12 Radiator to A/C Condenser Mounting (left
mount shown, right similar)
1 - SCREW - A/C CONDENSER SIDE BRACKET TO RADIATOR
2 - LOWER MOUNT
3 - A/C CONDENSER
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Use of pliers on draincock is not recommended. Damage may occur to radiator or draincock.
NOTE: It is not necessary to remove draincock during a routine coolant drain.
(1) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Open the draincock by turning it counterclockwise until it stops.
(3) Turn the draincock back (clockwise) 1/8 turn.
(4) Pull the draincock (Fig. 13) from the radiator
tank.
(4) Fill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WATER PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The water pump on the 2.5L CRD diesel has a die
cast aluminum housing. It bolts to a aluminum housing which attaches to the engine block (Fig. 14).
OPERATION
The water pump is used to circulate coolant
through the cooling system. The coolant is pumped
through the engine block, cylinder head, heater core,
EGR cooler, cabin heater, and radiator.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - WATER PUMP
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove timing belt inner and outer covers
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove water pump retaining bolts and pump
(Fig. 15).
INSTALLATION
(1) Align draincock stem to radiator tank opening.
(2) Push draincock into the radiator tank opening.
(3) Tighten the draincock by turning clockwise
until it stops.
REMOVAL - WATER PUMP HOUSING
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Page 28

RG ENGINE 7-23
WATER PUMP (Continued)
Fig. 14 WATER PUMP
1 - WATER PUMP HOUSING STUDS
2-WATERPUMP
3 - RETAINING NUTS
4 - OIL COOLER RETAINING STUD
5 - OIL COOLER TO ENGINE BLOCK RETAINING BOLT
6 - OIL COOLER COOLANT HOSE
7 - ENGINE BLOCK
(3) Remove both outer and inner timing belt covers
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(4) Disconnect water pump housing to thermostat
housing bypass hose (Fig. 16).
(5) Remove the water pump housing retaining
nuts (Fig. 17).
(6) Remove water pump housing from engine block
(Fig. 17).
CLEANING
Clean gasket mating surfaces as necessary.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - WATER PUMP
(1) Clean gasket mating surfaces as necessary.
(2) Place water pump and gasket in place. Install
water pump retaining bolts (Fig. 15). Torque bolts to
24.4N·m.
(3) Install both inner and outer timing belt covers
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(4) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Connect negative battery cable.
Fig. 15 WATER PUMP LOCATION
1 - CYLINDER HEAD
2 - ENGINE BLOCK
3 - OIL COOLER
4 - OIL FILTER HOUSING
5-WATERPUMP
INSTALLATION - WATER PUMP HOUSING
(1) Clean mating surfaces of water pump housing
and engine block as necessary.
(2) Place new o-ring in groove in water pump
housing (Fig. 18).
(3) Be sure lower radiator hose tube o-ring is in
place.
(4) Install water pump housing on lower radiator
hose tube and push on mounting studs (Fig. 17).
Torque retaining nuts to 24.4N·m.
(5) Connect water pump housing to thermostat
housing bypass hose (Fig. 16).
(6) Install both inner and outer timing belt covers
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
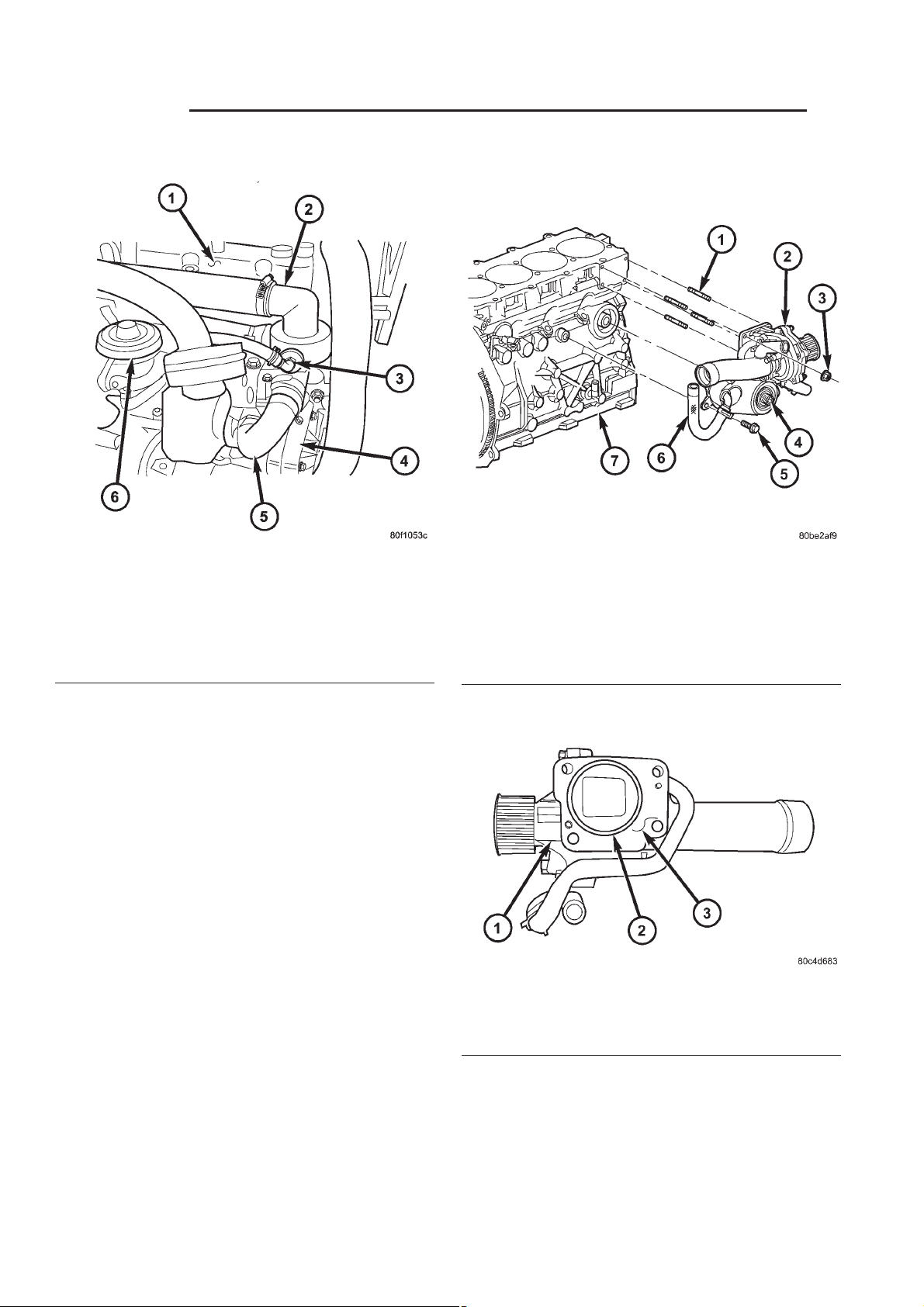
DESCRIPTION
The cooling system pressure cap is located on the
coolant recovery pressure container. The cap construction includes; stainless steel swivel top, rubber
seals, and retainer, main spring, and a spring loaded
valve (Fig. 19).
Page 29
7 - 24 ENGINE RG
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)
Fig. 16 THERMOSTAT HOUSING LOCATION
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
3 - AIR BLEED
4-WATERPUMP
5 - WATER PUMP HOUSING TO THERMOSTAT HOUSING
BYPASS HOSE
6 - EGR VALVE
OPERATION
The cooling system is equipped with a pressure cap
that releases excessive pressure; maintaining a range
of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi).
The cooling system will operate at higher than
atmospheric pressure. The higher pressure raises the
coolant boiling point thus, allowing increased radiator cooling capacity.
There is also a vent valve in the center of the cap.
This valve also opens when coolant is cooling and
contracting, allowing the coolant to return to cooling
system from coolant reserve system tank by vacuum
through a connecting hose. If valve is stuck shut,
or the coolant recovery hose is pinched, the
radiator hoses will be collapsed on cool down.
Clean the vent valve (Fig. 19) and inspect coolant recovery hose routing, to ensure proper
sealing when boiling point is reached.
The gasket in the cap seals the filler neck, so that
vacuum can be maintained, allowing coolant to be
drawn back into the radiator from the reserve tank.
If the gasket is dirty or damaged, a vacuum
may not be achieved, resulting is loss of coolant
and eventual overheating due to low coolant
level in radiator and engine.
Fig. 17 WATER PUMP ASSEMBLY
1 - WATER PUMP HOUSING STUDS
2-WATERPUMP
3 - RETAINING NUTS
4 - OIL COOLER RETAINING STUD
5 - OIL COOLER TO ENGINE BLOCK RETAINING BOLT
6 - OIL COOLER COOLANT HOSE
7 - ENGINE BLOCK
Fig. 18 WATER PUMP HOUSING O-RING
1-WATERPUMP
2 - WATER PUMP HOUSING O-RING
3-WATERPUMPHOUSING
Page 30
RG ENGINE 7-25
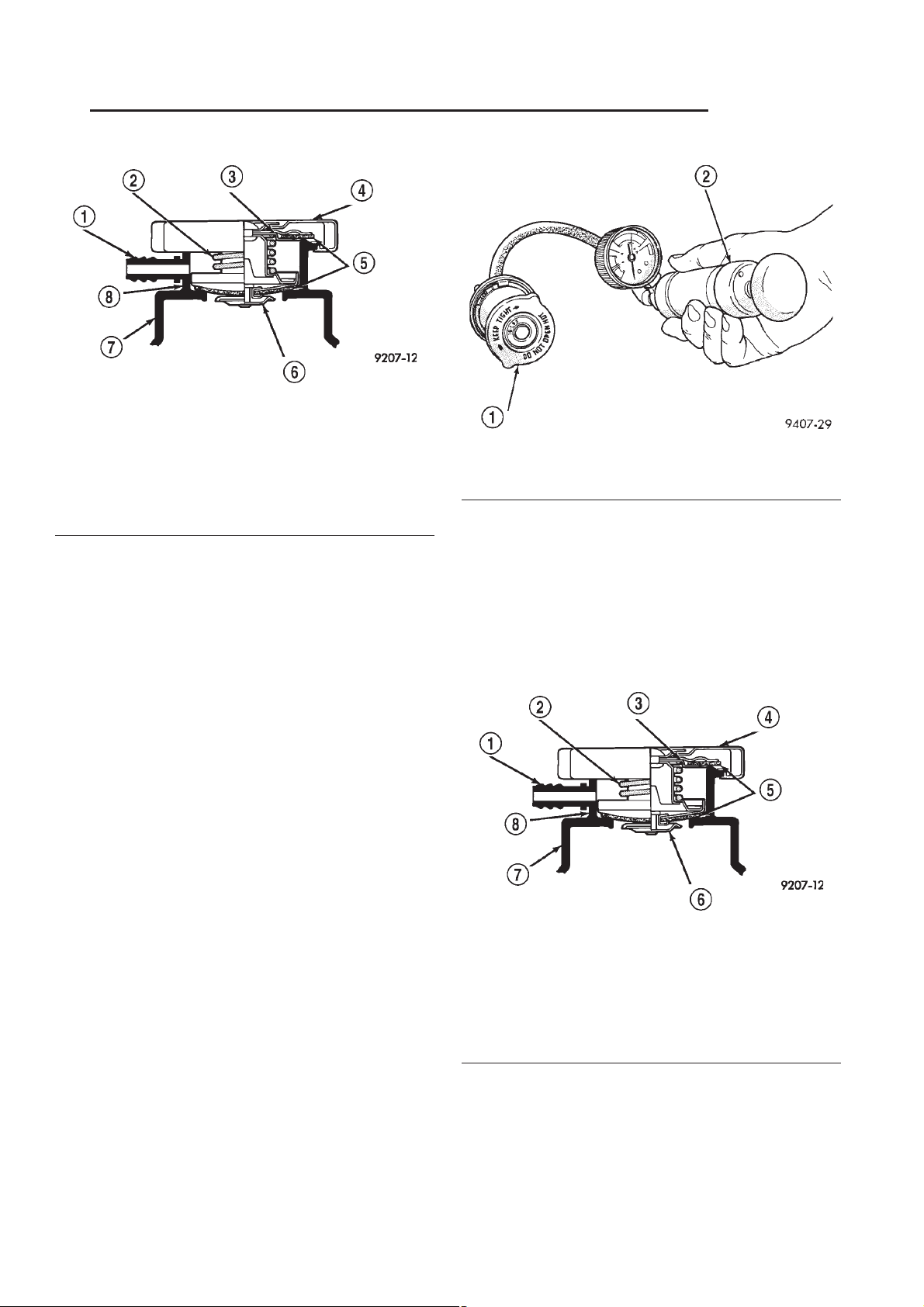
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)
Fig. 19 Cooling System Pressure Cap Filler Neck
1 - OVERFLOW NIPPLE
2 - MAIN SPRING
3 - GASKET RETAINER
4 - STAINLESS-STEEL SWIVEL TOP
5 - RUBBER SEALS
6 - VENT VALVE
7 - PRESSURE BOTTLE
8-FILLERNECK
Fig. 20 Testing Cooling System Pressure Cap
1 - PRESSURE CAP
2 - PRESSURE TESTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
RELIEF TEST
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
PRESSURE CAP
Dip the pressure cap in water. Clean any deposits
off the vent valve or its seat and apply cap to end of
the Pressure Cap Test Adaptor that is included with
the Cooling System Tester 7700. Working the
plunger, bring the pressure to 104 kPa (15 psi) on the
gauge. If the pressure cap fails to hold pressure of at
least 97 kPa (14 psi), replace the pressure cap.
The pressure cap upper gasket (seal) pressure
relief can be checked by removing the overflow hose
at the radiator filler neck nipple (Fig. 21). Attach the
Radiator Pressure Tool to the filler neck nipple and
pump air into the radiator. Pressure cap upper gasket should relieve at 69-124 kPa (10-18 psi) and hold
pressure at 55 kPa (8 psi) minimum.
CAUTION: The Cooling System Tester Tool is very
sensitive to small air leaks that will not cause cooling system problems. A pressure cap that does not
have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to the tool. Turn tool
upside down and recheck pressure cap to confirm
that cap is bad.
If the pressure cap tests properly while positioned
on Cooling System Tester (Fig. 20), but will not hold
pressure or vacuum when positioned on the filler
neck. Inspect the filler neck and cap top gasket for
irregularities that may prevent the cap from sealing
properly.
Fig. 21 Radiator Pressure Cap Filler Neck
1 - OVERFLOW NIPPLE
2 - MAIN SPRING
3 - GASKET RETAINER
4 - STAINLESS-STEEL SWIVEL TOP
5 - RUBBER SEALS
6 - VENT VALVE
7 - PRESSURE BOTTLE
8-FILLERNECK
Page 31

7 - 26 ENGINE RG
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS “DO NOT OPEN
HOT” ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
There is no need to remove the radiator cap at any
time except for the following purposes:
(1) Check and adjust coolant freeze point.
(2) Refill system with new coolant.
(3) Conducting service procedures.
(4) Checking for vacuum leaks.
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING CAP. THEN
PLACE A SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITHOUT PUSHING DOWN ROTATE COUNTERCLOCKWISE TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS TO
ESCAPE THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND
WHEN THE SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING COOLANT
AND STEAM INTO THE CRS TANK AND PRESSURE
DROPS PUSH DOWN AND REMOVE THE CAP COMPLETELY. SQUEEZING THE RADIATOR INLET HOSE
WITH A SHOP TOWEL (TO CHECK PRESSURE)
BEFORE AND AFTER TURNING TO THE FIRST
STOP IS RECOMMENDED.
CLEANING
Use only a mild soap to clean the pressure cap.
INSPECTION
Hold the cap in your hand, top side up (Fig. 21).
The vent valve at the bottom of the cap should open.
If the rubber gasket has swollen, preventing the
valve from opening, replace the cap.
Hold the cleaned cap in your hand, upside down.
If any light can be seen between vent valve and the
rubber gasket, replace the cap. Do not use a
replacement cap that has a spring to hold the
vent shut.
A replacement cap must be of the type designed for
coolant reserve systems. This design ensures coolant
return to the radiator.
RADIATOR FAN
DESCRIPTION
The dual radiator fans are mounted to the back
side of the radiator (Fig. 22). The radiator fan consist
of the fan blade, electric motor and a support shroud
which are all serviced as an assembly.
OPERATION
Fan Operation
Speeds:
RADIATOR FAN OPERATION CHART
COOLANT TEMPERATURE A/C PRESSURE
Initial Max Initial Max
Fan On: 104°C (220°F) 110°C (230°F) Fan
Speed Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-up) from
30% to 99%
Fan Off: 101°C (214°F) Fan Speed
Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-down) from
99% to 30%
1,724 Kpa (250 psi) 2,068 Kpa (300 psi)
1,710 Kpa (248 psi) Fan Speed
Fan Speed
Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-up) from
30% to 99%
Duty-Cycles
(Ramps-down) from
99% to 30%
Page 32

RG ENGINE 7-27
RADIATOR FAN (Continued)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR FAN
MOTOR
RADIATOR FAN DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY RADIATOR FAN 1. Fan blade loose. 1. Replace fan assembly. (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FAN - REMOVAL)
2. Fan blade striking a surrounding
object.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or A/C
condenser.
4. Electric fan motor defective. 4. Replace fan assembly. (Refer to
2. Locate point of fan blade contact
and repair as necessary.
3. Remove obstructions and/or
clean debris.
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FAN - REMOVAL)
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR DOES
NOT OPERATE
ELECTRIC RADIATOR FAN
OPERATES ALL THE TIME
1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM), coolant temperature
sensor, or wiring defective.
2. Defective A/C pressure
transducer.
1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM), coolant temperature
sensor or wiring defective.
2. Check for low coolant level. 2. Add coolant as necessary.
3. Defective A/C pressure
transducer.
REMOVAL
There are no repairs to be made to the fan or
shroud assembly. If the fan is warped, cracked, or
otherwise damaged, it must be replaced as an assembly (Fig. 22).
(1) Remove the radiator upper crossmember. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPENING REINFORCEMENT - REMOVAL)
(2) Disconnect the radiator fan electrical connectors.
(3) Remove radiator fan(s) retaining screw (Fig.
22).
(4) Remove the radiator fan(s) by lifting upward to
release from mounts.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the radiator fan(s) into mounts and
attaching clips on the radiator.
(2) Install radiator fan(s) attaching screws (Fig.
22). Tighten to 5 N·m (45 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the radiator fan(s) electrical connectors.
1. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
2. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
1. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
3. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
Fig. 22 Radiator Fans
1 - SCREWS - RADIATOR FAN ATTACHING
2 - RADIATOR FAN - RIGHT
3 - MOUNT - RIGHT RADIATOR FAN
4 - CLIPS - RADIATOR FAN LOWER
5 - MOUNT - LEFT RADIATOR FAN
6 - RADIATOR FAN - LEFT
(4) Install the radiator upper support crossmember. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPENING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION)
Page 33

7 - 28 ENGINE RG
RADIATOR FAN (Continued)
(5) Install the upper radiator mounts to the crossmember bolts, if removed. Tighten to 8 N·m (70 in.
lbs.).
(6) Install the radiator upper hose to the support
clip (2.4L engine).
HOSE CLAMPS
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system uses spring type hose clamps.
If a spring type clamp replacement is necessary,
replace with the original Mopar威 equipment spring
type clamp.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter (Fig. 23).
Fig. 23 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS
The spring type hose clamp applies constant tension on a hose connection. To remove a spring type
hose clamp, use Special Tool 6094 or equivalent, constant tension clamp pliers (Fig. 24) to compress the
hose clamp.
RADIATOR FAN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The low and high speed fan relays are mounted to
the upper radiator support above the charge air
cooler (Fig. 25).
Fig. 24 Hose Clamp Tool
1 - HOSE CLAMP TOOL 6094
2 - HOSE CLAMP
Fig. 25 RELAY LOCATIONS
1 - GLOW PLUG RELAY
2 - UPPER RADIATOR SUPPORT
3 - CHARGE AIR COOLER OUTLET HOSE
4 - RADIATOR FAN RELAYS
5 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
6 - EGR SOLENOID
OPERATION
The cooling system uses two fans. Both fans operate at two different speeds, low and high. Depending
on engine coolant temperature and A/C system high
side pressure, the fans operate at either low or high.
The ignition switch supplies voltage to the coil side of
the relay. When the ECM grounds the coil side of the
relay, the contacts close and the battery supplies
power to the fans.
Page 34

RG ENGINE 7-29
COOLANT SYSTEM HOSES
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS “DO NOT OPEN
HOT” ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
(1) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove upper radiator hose (Fig. 26).
REMOVAL - LOWER RADIATOR HOSE
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS “DO NOT OPEN
HOT” ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
(1) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Remove lower radiator hose (Fig. 26).
REMOVAL - COOLANT BYPASS HOSE
WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS “DO NOT OPEN
HOT” ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
(1) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Remove the coolant bypass hose (Fig. 26).
Fig. 26 UPPER AND LOWER RADIATOR HOSES
1 - COOLANT BYPASS HOSE
2 - RADIATOR ASSEMBLY
3 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
4 - COOLING FAN
5-LOWERRADIATORHOSE
6 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
7 - RADIATOR BRACKET
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
(1) Install upper radiator hose (Fig. 26).
(2) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE INSTALLATION).
INSTALLATION - LOWER RADIATOR HOSE
(1) Install lower radiator hose (Fig. 26).
(2) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - COOLANT BYPASS HOSE
(1) Install cooling system bypass hose (Fig. 26).
(2) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Page 35

Page 36

RG ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E-1
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION ..........................1
OPERATION ............................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PCM/ECM/SKIM
PROGRAMMING - DIESEL ...............2
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The ECM is located in the left front corner of the
engine compartment attached to the radiator support
(Fig. 1).
REMOVAL .............................4
INSTALLATION ..........................4
entered into the ECM memory. The criteria may be a
range of: engine rpm, engine temperature, time or
other input signals to the ECM. If all of the criteria
for monitoring a system or circuit are met, and a
problem is sensed, then a DTC will be stored in the
ECM memory. It is possible that a DTC for a monitored circuit may not be entered into the ECM memory, even though a malfunction has occurred. This
may happen when the monitoring criteria have not
been met. The ECM compares input signal voltages
from each input device with specifications (the established high and low limits of the input range) that
are programmed into it for that device. If the input
voltage is not within the specifications and other
trouble code criteria are met, a DTC will be stored in
the ECM memory.
ECM OPERATING MODES
As input signals to the ECM change, the ECM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For example, the ECM must calculate a different fuel quantity
and fuel timing for engine idle condition than it
would for a wide open throttle condition. There are
several different modes of operation that determine
how the ECM responds to the various input signals.
Fig. 1 ENGINE CONTROL MODULE LOCATION-
TYPICAL
1 - BATTERY
2 - IPM (INTEGRATED POWER MODULE)
3 - ECM (ENGINE CONTROL MODULE)
4 - RETAINING BOLT
5 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
6 - CLUTCH CABLE BRACKET (LHD)
7 - CLUTCH CABLE BRACKET RETAINING BOLT (LHD)
OPERATION
The ECM has been programmed to monitor different circuits of the diesel fuel injection system. This
monitoring is called on-board diagnostics. Certain criteria must be met for a diagnostic trouble code to be
Ignition Switch On (Engine Off)
When the ignition is turned on, the ECM activates
the glow plug relay for a time period that is determined by engine coolant temperature, atmospheric
temperature and battery voltage.
Engine Start-Up Mode
The ECM uses the engine temperature sensor and
the crankshaft position sensor (engine speed) inputs
to determine fuel injection quantity.
Normal Driving Modes
Engine idle, warm-up, acceleration, deceleration
and wide open throttle modes are controlled based on
all of the sensor inputs to the ECM. The ECM uses
these sensor inputs to adjust fuel quantity and fuel
injector timing.
Page 37

8E - 2 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES RG
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Limp-In Mode
If there is a fault detected with the accelerator
pedal position sensor, the ECM will set the engine
speed at 1100 RPM.
Overspeed Detection Mode
If the ECM detects engine RPM that exceeds 5200
RPM, the ECM will set a DTC in memory and illuminate the MIL until the DTC is cleared.
After-Run Mode
The ECM transfers RAM information to ROM and
performs an Input/Output state check.
MONITORED CIRCUITS
The ECM is able to monitor and identify most
driveability related trouble conditions. Some circuits
are directly monitored through ECM feedback circuitry. In addition, the ECM monitors the voltage
state of some circuits and compares those states with
expected values. Other systems are monitored indirectly when the ECM conducts a rationality test to
identify problems. Although most subsytems of the
engine control module are either directly or indirectly
monitored, there may be occasions when diagnostic
trouble codes are not immediately identified. For a
trouble code to set, a specific set of conditions must
occur and unless these conditions occur, a DTC will
not set.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Each diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is diagnosed by
following a specific procedure. The diagnostic test
procedure contains step-by-step instruction for determining the cause of the DTC as well as no trouble
code problems. Refer to the appropriate Diesel Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for more information.
HARD CODE
A DTC that comes back within one cycle of the
ignition key is a hard code. This means that the
problem is current every time the ECM/SKIM checks
that circuit or function. Procedures in this manual
verify if the DTC is a hard code at the beginning of
each test. When the fault is not a hard code, an
intermittent test must be performed. NOTE: If the
DRBIII威 displays faults for multiple components (i.e.
ECT, VSS, IAT sensors) identify and check the
shared circuits for possible problems before continuing (i.e. sensor grounds or 5-volt supply circuits).
Refer to the appropriate schematic to identify shared
circuits. Refer to the appropriate Diesel Powertrain
Diagnostic Manual for more information.
INTERMITTENT CODE
A DTC that is not current every time the ECM/
SKIM checks the circuit or function is an intermittent code. Most intermittent DTCs are caused by
wiring or connector problems. Problems that come
and go like this are the most difficult to diagnose;
they must be looked for under specific conditions that
cause them. NOTE: Electromagnetic (radio)
interference can cause an intermittent system
malfunction. This interference can interrupt com-
munication between the ignition key transponder and
the SKIM. The following checks may assist you in
identifying a possible intermittent problem:
• Visually inspect the related wire harness connectors. Look for broken, bent, pushed out or corroded
terminals.
• Visually inspect the related wire harness. Look
for chafed, pierced or partially broken wire.
• Refer to hotlines or technical service bulletins
that may apply.
Refer to the appropriate Diesel Powertrain Diag-
nostic Manual for more information.
ECM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
IMPORTANT NOTE: Before replacing the ECM for
a failed driver, control circuit or ground circuit, be
sure to check the related component/circuit integrity
for failures not detected due to a double fault in the
circuit. Most ECM driver/control circuit failures are
caused by internal failures to components (i.e. relays
and solenoids) and shorted circuits (i.e. sensor pullups, drivers and ground circuits). These faults are
difficult to detect when a double fault has occurred
and only one DTC has set. If the DRBIII威 displays
faults for multiple components (i.e.VSS, ECT, Batt
Temp, etc.) identify and check the shared circuits for
possible problems before continuing (i.e. sensor
grounds or 5-volt supply circuits). Refer to the appropriate wiring diagrams to identify shared circuits.
Refer to the appropriate Diesel Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for more information.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PCM/ECM/SKIM
PROGRAMMING - DIESEL
NOTE: Before replacing the PCM/ECM for a failed
driver, control circuit or ground circuit, be sure to
check the related component/circuit integrity for
failures not detected due to a double fault in the circuit. Most PCM/ECM driver/control circuit failures
are caused by internal component failures (i.e. relay
and solenoids) and shorted circuits (i.e. pull-ups,
drivers and switched circuits). These failures are
difficult to detect when a double fault has occurred
and only one DTC has set.
Page 38

RG ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E-3
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
PCM/SKIM PROGRAMMING
When a PCM (JTEC) and the SKIM are replaced
at the same time perform the following steps in
order:
(1) Program the new PCM (JTEC)
(2) Program the new SKIM
(3) Replace all ignition keys and program them to
the new SKIM.
ECM/SKIM PROGRAMMING
When an ECM (Bosch) and the SKIM are replaced
at the same time perform the following steps in
order:
(1) Program the new SKIM
(2) Program the new ECM (Bosch)
PROGRAMMING THE ECM (Bosch)
(1) To program the VIN, connect the DRB III威 and
turn the ignition on.
(2) Select Engine from the main menu. The DRB
III威 will require the VIN to be entered before continuing.
(3) Select ENTER to update the VIN. The DRB
III威 will display the updated VIN.
(4) If the engine is equipped with air conditioning,
the ECM A/C function must be enabled. Enable the
ECM A/C function as follows:
• Using the DRB III威 select ENGINE, MISCEL-
LANEOUS, then ENABLE/DISABLE A/C
• Push 1 to enable A/C. DRB III威 screen should
display A/C Activated.
PROGRAMMING THE PCM (JTEC)
The SKIS Secret Key is an ID code that is unique
to each SKIM. This code is programmed and stored
in the SKIM, PCM and transponder chip (ignition
keys). When replacing the PCM it is necessary to
program the secret key into the new PCM using the
DRB III威. Perform the following steps to program the
secret key into the PCM.
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRB III威 and select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PCM REPLACED (GAS ENGINE).
(4) Enter secured access mode by entering the
vehicle four-digit PIN.
(5) Select ENTER to update PCM VIN.
NOTE: If three attempts are made to enter secure
access mode using an incorrect PIN, secured
access mode will be locked out for one hour. To
exit this lockout mode, turn the ignition to the RUN
position for one hour then enter the correct PIN.
(Ensure all accessories are turned off. Also monitor
the battery state and connect a battery charger if
necessary).
(6) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
SKIM will send the secret key to the PCM).
(7) Press Page Back to get to the Select System
menu and select ENGINE, JTEC (diesel only), MISCELLANEOUS, and SRI MEMORY CHECK.
(8) The DRB III威 will ask, Is odometer reading
between XX and XX? Select the YES or NO button on
the DRB III威. If NO is selected, the DRB III威 will
read, Enter odometer Reading<From I.P. odometer>.
Enter the odometer reading from the Instrument
Panel and press ENTER.
PROGRAMMING THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRB III威 and select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PCM REPLACED (GAS ENGINE).
(4) Program the vehicle four-digit PIN into SKIM.
(5) Select COUNTRY CODE and enter the correct
country.
NOTE: Be sure to enter the correct country code. If
the incorrect country code is programmed into
SKIM, the SKIM must be replaced.
(6) Select YES to update VIN (the SKIM will learn
the VIN from the PCM).
(7) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
PCM will send the secret key to the SKIM).
(8) Program ignition keys to SKIM.
NOTE: If the PCM and the SKIM are replaced at the
same time, all vehicle keys will need to be replaced
and programmed to the new SKIM.
PROGRAMMING IGNITION KEYS TO THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRB III威 and select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PROGRAM IGNITION KEY’S.
(4) Enter secured access mode by entering the
vehicle four-digit PIN.
NOTE: A maximum of eight keys can be learned to
each SKIM. Once a key is learned to a SKIM it (the
key) cannot be transferred to another vehicle.
If ignition key programming is unsuccessful, the
DRB III威 will display one of the following messages:
Programming Not Attempted - The DRB III威
attempts to read the programmed key status and
there are no keys programmed into SKIM memory.
Page 39

8E - 4 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES RG
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Programming Key Failed (Possible Used Key From
Wrong Vehicle) - SKIM is unable to program key due
to one of the following:
• faulty ignition key transponder
• ignition key is programmed to another vehicle.
8 Keys Already Learned, Programming Not Done SKIM transponder ID memory is full.
(5) Obtain ignition keys to be programmed from
customer (8 keys maximum).
(6) Using the DRB III威, erase all ignition keys by
selecting MISCELLANEOUS and ERASE ALL CURRENT IGN. KEYS.
(7) Program all ignition keys.
Learned Key In Ignition - Ignition key transponder
ID is currently programmed in SKIM memory.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove left front headlamp module (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/
HEADLAMP UNIT - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove lower headlamp assembly mounting
bolt (Fig. 2).
(4) Remove ECM upper mounting bolts (Fig. 3).
(5) Lift ECM from radiator support.
(6) Disconnect ECM electrical connectors.
(7) Separate ECM from mounting bracket.
Fig. 2 ENGINE CONTROL MODULE-LOWER
MOUNTING BOLT
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - ECM LOWER MOUNTING BOLT
INSTALLATION
(1) Install ECM on mounting bracket.
(2) Connect ECM electrical connectors.
(3) Place ECM and bracket assembly in position on
radiator support.
(4) Install upper and lower mounting bolts.
(5) Install left headlamp module (Refer to 8 ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/
HEADLAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION).
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
(7) Program ECM as necessary (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/ENGINE CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Fig. 3 ENGINE CONTROL MODULE-UPPER
MOUNTING BOLTS
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
4 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
5 - ECM UPPER MOUNTING BOLTS
6 - ECM ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
Page 40

RG ENGINE SYSTEMS 8F-1
ENGINE SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING ............................... 1 STARTING................................ 4
CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERATOR
REMOVAL-2.5L .........................1
GENERATOR
REMOVAL - 2.5L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable (Fig. 1).
INSTALLATION-2.5L .....................3
(2) Remove the engine cover (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 ENGINE COVER
Fig. 1 BATTERY CONNECTION
Page 41

8F - 2 CHARGING RG
GENERATOR (Continued)
(3) Raise vehicle and support.
(4) Turn wheels to the right. Remove the right
front splash shield (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 SPLASH SHIELD
(5) Remove the generator drive belt (Fig. 4).
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Disconnect the generator battery connection
(Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 GENERATOR CONNECTIONS
1 - Battery Connection
2 - Field Connection
Fig. 4 GENERATOR BELT
(8) Disconnect the field connection (Fig. 5).
(9) Relocate the wiring harness on upper generator
bracket (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6 UPPER SUPPORT BRACKET
1 - Wiring Harness
2 - Upper Bracket
Page 42

RG CHARGING 8F-3
GENERATOR (Continued)
(10) Remove the Air Cleaner Box (Fig. 7).
Fig. 8 GENERATOR LOWER BOLTS
Fig. 7 AIR BOX REMOVED
(11) Remove the 2 lower mounting Bolts (Fig. 8).
(12) Remove generator.
INSTALLATION - 2.5L
(1) Install generator.
(2) Install the 2 lower mounting Bolts (Fig. 8).
(3) Install the Air Cleaner Box (Fig. 7).
(4) Install the upper support bracket (Fig. 6).
(5) Install the wiring harness on upper generator
bracket (Fig. 6).
1 - Lower Mounting Bolts
(6) Connect the field connection (Fig. 5).
(7) Connect the generator battery connection (Fig.
5).
(8) Raise vehicle and support.
(9) Install the generator drive belt (Fig. 4).
(10) Install the right front splash shield (Fig. 3).
(11) Lower vehicle.
(12) Install the engine cover (Fig. 2).
(13) Connect the negative battery cable (Fig. 1).
Page 43

8F - 4 STARTING RG
STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTER MOTOR
REMOVAL-2.5L .........................4
STARTER MOTOR
REMOVAL - 2.5L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle and support.
(3) Remove the lower engine splash shield.
(4) Remove the electrical connectors from the
starter (Fig. 1).
INSTALLATION-2.5L .....................4
Fig. 2 STARTER MOUNTING BOLTS
1 - Starter
2 - Mounting Bolts
Fig. 1 STARTER LOCATION
(5) Remove the starter mounting bolts (Fig. 2).
(6) Remove the starter.
INSTALLATION - 2.5L
(1) Raise vehicle and support.
(2) Install the starter.
(3) Install the starter mounting bolts (Fig. 2).
(4) Install the electrical connectors to the starter
(Fig. 1).
(5) Install the lower engine splash shield.
(6) Connect the negative battery cable.
(7) Lower vehicle.
Page 44

RG IGNITION CONTROL 8I-1
IGNITION CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GLOW PLUG
DESCRIPTION ..........................1
OPERATION ............................1
GLOW PLUG RELAY
DESCRIPTION ..........................1
OPERATION ............................1
GLOW PLUG
DESCRIPTION
Glow plugs are used to help start a cold or cool
engine (Fig. 1). The glow plugs will heat up and glow
to heat the combustion chamber of each cylinder. An
individual glow plug is used for each cylinder. Each
glow plug is threaded into the left side of the cylinder
head below the cylinder head cover/intake manifold.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION ..........................2
OPERATION ............................2
REMOVAL .............................2
INSTALLATION ..........................2
GLOW PLUG RELAY
DESCRIPTION
There are two glow plug relays. These relays are
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) in
the engine compartment (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 GLOW PLUG
OPERATION
Each glow plug will momentarily draw approximately 25 amps of electrical current during the initial key “ON” cycle. This is on a cold or cool engine.
After heating the current draw will drop to approximately 9–12 amps per plug.
Total momentary cuurent draw for all four glow
plugs is approximately 100 amps on a cold engine
dropping to a total of approximately 40 amps after
the plugs are heated.
Electrical operation of the glow plugs is controlled
by two glow plug relays. Each glow plug relay controls two glow plugs. Refer to glow plug relays for
more information.
Fig. 2 RELAY LOCATIONS
1 - GLOW PLUG RELAY
2 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
3 - CHARGE AIR COOLER OUTLET HOSE
4 - COOLING FAN RELAY
5 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
6 - EGR SOLENOID
OPERATION
When the ignition (key) switch is place in the ON
position, a signal is sent to the ECM relating current
engine coolant temperature. This signal is sent from
the engine coolant temperature sensor.
After receiving this signal, the ECM will determine
if, when and for how long of a period the glow plug
relays should be activated. This is done before, during and after the engine is started. Whenever the
glow plug relays are activated, it will control the 12
volt 100 amp circuit for the operation of the four
glow plugs. Each relay control two glow plugs.
Page 45

8I - 2 IGNITION CONTROL RG
GLOW PLUG RELAY (Continued)
The Glow Plug lamp is tied to this circuit. Lamp
operation is also controlled by the ECM.
With a cold engine, the glow plug relays and glow
plugs may be activated for a maximum time of 200
seconds. Refer to the following Glow Plug Control
chart for a temperature/time comparison of the glow
plug relay operation.
In this chart, Pre-Heat and Post-Heat times are
mentioned. Pre-Heat is the amount of time the glow
plug relay control circuit is activated when the ignition (key) is switched ON, without the engine running. Post-Heat is the amount of time the glow plug
relay control circuit is activated after the engine is
operated. The Glow Plug lamp will not be activated
during the post-heat cycle.
Engine
Coolant
Temperature
⬙Key ON⬙
-30C 20 SEC. 35 SEC. 200 SEC.
-10C 8 SEC. 23 SEC. 180 SEC.
+10C 6 SEC. 21 SEC. 160 SEC.
+30C 5 SEC. 20 SEC. 140 SEC.
+40C 4 SEC. 19 SEC. 70 SEC.
+70C 1 SEC. 16 SEC. 20 SEC.
Wait-To
Start Lamp
⬙ON⬙
(Seconds)
Pre-Heat
Cycle
(Glow
Plugs On
Seconds)
Post-Heat
Cycle
(Seconds)
OPERATION
The CMP sensor is a hall effect switch. A tooth
made of a ferromagnetic material is attached to the
camshaft. When this tooth passes the CMP sensor an
electronic signal is created. This signal is then sent
to the engine control module (ECM). This signal is
used by the ECM to determine which cylinder has
just entered its compression phase.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect camshaft position sensor electrical
connector (Fig. 4).
CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is mounted in
the top of cylinder head cover/intake manifold at the
rear of the engine. The CMP sensor is a hall effect
device (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 4 CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR LOCATION
1 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ELCTRICAL SENSOR
3 - FUEL INJECTOR
4 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
5 - OIL SEPARATOR
(4) Remove sensor retaining bolt and remove sen-
sor from cylinder head cover.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate O-ring and install sensor in cylinder
head cover. Torque retaining bolt to 5.4 N·m.
(2) Connect camshaft position sensor electrical
connector.
(3) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
COVER - INSTALLATION).
(4) Connect negative battery cable.
Page 46

RG ENGINE 9-1
ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 2.5L COMMON RAIL
DIESEL ENGINE .......................3
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COVER ..........3
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE ..........3
REMOVAL-ENGINECOVER .............7
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
ENGINE..............................7
INSTALLATION - ENGINE COVER ..........8
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 2.5L COMMON RAIL
DIESEL ENGINE .......................9
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE .............11
SPECIAL TOOLS .......................13
CYLINDER HEAD
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVE
SERVICE............................19
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
PISTONPROTRUSION .................21
REMOVAL .............................21
CLEANING ............................23
INSPECTION ..........................23
INSTALLATION .........................23
CAMSHAFT(S)
DESCRIPTION .........................25
OPERATION ...........................25
REMOVAL .............................25
INSTALLATION .........................25
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION .........................26
REMOVAL .............................26
INSTALLATION .........................28
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S)
REMOVAL .............................29
INSTALLATION .........................29
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION .........................30
OPERATION ...........................30
REMOVAL .............................30
INSTALLATION .........................30
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DESCRIPTION .........................31
REMOVAL .............................31
INSPECTION ..........................32
INSTALLATION .........................32
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION .........................32
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION .........................33
OPERATION ...........................33
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING
CRANKSHAFTENDPLAY ...............33
REMOVAL .............................34
INSTALLATION .........................34
CYLINDER LINERS
DESCRIPTION .........................36
REMOVAL .............................36
INSPECTION ..........................36
INSTALLATION .........................37
INTERNAL VACUUM PUMP
DESCRIPTION .........................38
REMOVAL .............................38
INSTALLATION .........................38
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION .........................39
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING .............................39
REMOVAL .............................39
INSPECTION ..........................40
INSTALLATION .........................42
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL .............................44
INSTALLATION .........................44
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL .............................45
INSTALLATION .........................45
ENGINE COVER - FRONT
DESCRIPTION .........................45
REMOVAL .............................45
INSTALLATION .........................46
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
REMOVAL .............................47
INSTALLATION .........................48
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL .............................49
INSTALLATION .........................49
OIL PAN
REMOVAL .............................49
INSTALLATION .........................49
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL ...........................50
REMOVAL ...........................50
Page 47

9 - 2 ENGINE RG
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION .......................50
INSTALLATION .......................51
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH
DESCRIPTION .........................51
REMOVAL .............................51
INSTALLATION .........................51
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
DESCRIPTION .........................51
REMOVAL .............................51
INSTALLATION .........................52
OIL COOLER & LINES
REMOVAL .............................52
INSTALLATION .........................53
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION .........................53
REMOVAL .............................53
INSTALLATION .........................53
OIL JET
DESCRIPTION .........................54
REMOVAL .............................54
INSTALLATION .........................54
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION .........................54
REMOVAL .............................54
INSTALLATION .........................54
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - LOCKING ENGINE
90°AFTERTDC .......................55
BALANCE SHAFT
DESCRIPTION .........................56
OPERATION ...........................56
REMOVAL .............................56
INSTALLATION .........................57
TIMING BELT COVER
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TIMING BELT OUTER COVER . . 57
REMOVAL - TIMING BELT INNER COVER . . . 58
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - TIMING BELT OUTER
COVER.............................59
INSTALLATION - TIMING BELT INNER
COVER.............................59
TIMING BELT IDLER PULLEY
REMOVAL .............................59
INSTALLATION .........................60
TIMING BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY
REMOVAL .............................60
INSTALLATION .........................61
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - TIMING BELT TENSIONER . 61
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL .............................61
INSTALLATION .........................63
Page 48

RG ENGINE 9-3
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 2.5L COMMON RAIL DIESEL
ENGINE
This 2.5 Liter (2500cc) four-cylinder “common rail”
direct injection engine is an in-line overhead valve
diesel engine. This engine utilizes a cast iron cylinder block and an aluminum cylinder head. The
engine is turbocharged and intercooled. The engine
also has four valves per cylinder and dual overhead
camshafts (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Displacement 2.5L (2499 cc)
Bore 92.00
Stroke 94.00
Compression Ratio 17.5:1
Vacuum at Idle 685.8 mm/Hg (27.0 In/Hg)
Belt Tension Automatic Belt Tensioner
Thermostat Opening 88°C ± 2°C
Generator Rating Denso 12V-95A
Cooling System Capacity 13.8 Liters W/O Auxiliary
Heater
16.6 Liters With Auxiliary
Heater
Engine Oil Capacity 6.0L With Filter Change
Timing System Belt Driven Camshafts In
Cylinder Head Cover
Air Intake Dry Filter
Fuel Feed Vane Pump Incorporated
In Injection Pump
Fuel System Direct Fuel Injection
Combustion Cycle 4 Stroke
Cooling System Water Cooling
High Pressure Injection
Pump
Lubrication Pressure Lubricated By
Engine Rotation Clockwise Viewed From
Cylinder Compression Maximum Difference
Minimum Oil Pressure,
Warm Engine
Common Rail
Rotary Pump
Front Cover
Between Cylinders Minus
5Bar
0.7 Bar at Idle, 2 Bar at
3800 RPM
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COVER
cover the top of the engine (Fig. 10). It is used to isolate engine noises.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE
ENGINE - REMOVAL)
1 - ENGINE COVER MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - ENGINE COVER
Fig. 1 2.5L COMMON RAIL DIESEL
The engine cover is a black plastic cover used to
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove engine cover (Fig. 2). (Refer to 9 -
Fig. 2 ENGINE COVER
Page 49

9 - 4 ENGINE RG
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
(3) Remove air cleaner housing, MAF sensor, and
air intake tube assembly (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR LOCATION
1 - MAF SENSOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - RETAINING CLAMPS
3 - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR
4 - AIR CLEANER HOUSING
(4) Remove coolant pressure tank pressure cap.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Remove lower splash shield.
(8) Remove splash shield side panels.
(9) Remove power steering reservoir hose from
power steering pump and drain power steering fluid
(Fig. 4).
(10) Disconnect high pressure power steering line
at pump (Fig. 4).
(11) Disconnect power steering pump return hose
clamp (Fig. 4).
(12) Remove power steering return line retaining
clamp (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4 RESERVOIR AND HOSES - 2.5L DIESEL
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
2 - RESERVOIR BRACKET
3 - SUPPLY HOSE BRACKET
4 - RETURN HOSE FROM GEAR
5 - ROUTING CLIP
6 - PRESSURE HOSE TO GEAR
7 - SUPPLY HOSE (PUMP END)
8 - PRESSURE HOSE (PUMP END)
9 - SUPPLY HOSE
10 - RETURN HOSE
(13) Remove power steering line clamps from oil
pan (Fig. 4).
(14) Remove power steering pump reservoir and
bracket (Fig. 4).
(15) Drain coolant system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Page 50

RG ENGINE 9-5
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
(16) Remove coolant pressure tank (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE
CONTAINER LOCATION
1 - PRESSURE/VENT CAP
2 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
3 - BATTERY
4 - BATTERY SHIELD
5 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER RETAING
CLIP
6 - ENGINE COVER
7 - COOLANT RECOVERY PRESSURE CONTAINER
(17) Remove battery shield.
(18) Remove charge air cooler outlet hose.
(19) Remove charge air cooler inlet hose (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6 CHARGE AIR COOLER HOSES
1 - COOLING MODULE
2 - BYPASS HOSE
3 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
4 - CHARGE AIR COOLER OULET HOSE
5 - CHARGE AIR COOLER INLET HOSE
6-LOWERRADIATORHOSE
7 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
Page 51

9 - 6 ENGINE RG
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
(20) Disconnect upper radiator hose at engine (Fig.
7).
(21) Disconnect lower radiator hose at engine (Fig.
7).
Fig. 7 UPPER AND LOWER RADIATOR HOSES
1 - COOLANT BYPASS HOSE
2 - RADIATOR ASSEMBLY
3 - UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
4 - COOLING FAN
5-LOWERRADIATORHOSE
6 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
7 - RADIATOR BRACKET
(22) Disconnect brake booster vacuum supply hose.
(23) Disconnect heater core return hose at engine.
(24) Disconnect EGR solenoid vacuum line at
brake booster check valve.
(25) Disconnect fuel injector, cam sensor, boost
pressure/intake air temperature sensor, fuel rail high
pressure, and EGR solenoid connectors (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8 ENGINE COMPONENT LOCATIONS
1 - FUEL INJECTOR RETURN LINE
2 - FUEL INJECTOR SUPPLY LINE
3 - OIL SEPARATOR
4 - FUEL INJECTOR
5 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
6 - BOOST PRESSURE/INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
7 - EGR SOLENOID
8 - FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
9 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOL
10 - FUEL RAIL
11 - WIRING HARNESS RETAINING CLIPS
(26) Disconnect generator electrical connectors.
(27) Disconnect coolant temperature sensor and
glow plug electrical connectors.
(28) Disconnect high pressure injection pump and
A/C compressor electrical connectors.
(29) Disconnect starter electrical connectors.
(30) Disconnect ground wires at engine block.
(31) Raise vehicle on hoist.
Page 52

RG ENGINE 9-7
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
(32) Disconnect oil pressure switch, engine speed
sensor, and vehicle speed sensor electrical connector
(Fig. 9).
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(44) Disconnect the A/C lines at the A/C compres-
sor.
(45) Raise and support vehicle.
(46) Disconnect the fuel supply and return lines.
(47) Position engine cradle under engine and lower
vehicle over cradle.
(48) Remove right engine mount bolts.
(49) Remove left engine mount through bolt.
(50) Carefully raise vehicle, leaving engine and
transmission on engine cradle.
(51) Lift engine from engine cradle and dissemble
as necessary.
REMOVAL - ENGINE COVER
(1) Remove engine cover retaining bolts.
(2) Remove engine cover from engine (Fig. 10).
Fig. 9 VIEW-REAR ENGINE
1 - SUSPENSION CRADLE
2 - ENGINE BLOCK
3 - OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
4 - VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
5 - TRANSMISSION
(33) Raise and support vehicle.
(34) Remove front wheels.
(35) Remove the suspension cradle assembly (Refer
to 13 - FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/ENGINE
CRADLE CROSSMEMBER - REMOVAL).
(36) Remove both axle shaft assemblies (Refer to 3
- DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT REMOVAL).
(37) Disconnect the clutch slave cylinder quick disconnect line (RHD only)(Refer to 6 - CLUTCH/SLAVE
CYLINDER - REMOVAL).
(38) Disconnect reverse lamp connector.
(39) Disconnect shifter cables at the transmission
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL/GEAR SHIFT CABLE - REMOVAL).
(40) Disconnect exhaust pipe from the turbocharger downpipe and reposition to right side of vehicle.
(41) Disconnect cabin heater coolant line (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CABIN
HEATER/HEATER UNIT - REMOVAL).
(42) Remove front engine mount bracket retaining
bolts from lower radiator support
(43) Lower vehicle. Evacuate the A/C system
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
Fig. 10 ENGINE COVER
1 - ENGINE COVER MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - ENGINE COVER
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.5L TURBO DIESEL ENGINE
(1) Reassembly engine and transmission assembly
and install on engine cradle.
(2) Position engine and cradle assembly under
vehicle.
(3) Slowly lower the vehicle down over the engine
and cradle assembly.
(4) Install right engine mount bolts. Torque to
54N·m (40 ft. lbs.)
Page 53

9 - 8 ENGINE RG
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
(5) Install left engine mount through bolt. Torque
to 75N·m (55 ft. lbs.)
(6) Raise vehicle and engine from engine cradle.
(7) Attach front engine mount bracket to lower
radiator support. Torque to 54N·m (40 ft. lbs.)
(8) Connect cabin heater coolant hose.
(9) Connect exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
downpipe flange. Torque to 28 N·m (250 in. lbs.)
(10) Connect reverse lamp electrical connector at
transmission.
(11) Connect both shifter cables (Refer to 21 TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL/GEAR
SHIFT CABLE - INSTALLATION).
(12) Connect the clutch slave cylinder quick disconnect connector (RHD only)(Refer to 6 - CLUTCH/
SLAVE CYLINDER - INSTALLATION).
(13) Install engine harness into bracket on transmission.
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Connect fuel supply and return lines.
(16) Connect A/C lines to A/C compressor. Torque
to 23N·m (17 ft. lbs.)
(17) Route engine wiring harnes to proper location.
(18) Connect engine harness ground cables to
engine block
(19) Connect starter solenoid electrical connector
and battery positive wire to starter. Torque to 10N·m
(90 in. lbs.)
(20) Connect A/C compressor, injection pump, glow
plugs, and coolant temperature sensor electrical connectors.
(21) Connect generator electrical connector. Torque
to 9N·m (75 in. lbs.)
(22) Connect the fuel injector, fuel pressure sensor,
boost pressure/intake air temp sensor, cam sensor,
and EGR solenoid electrical connectors (Fig. 8).
(23) Connect EGR solenoid vacuum supply line to
brake boost vacuum supply line.
(24) Connect brake booster vacuum supply line.
(25) Connect heater core return hose to coolant
pipe.
(26) Connect lower radiator hose to engine (Fig. 7).
(27) Install charger air cooler inlet hose (Fig. 6).
(28) Install charge air cooler outlet hose (Fig. 6).
(29) Connect upper radiator hose to engine (Fig.
7).
(30) Install battery shield.
(31) Install coolant reserve pressure container
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER - INSTALLATION).
(32) Install power steering reservoir and bracket
(Fig. 4).
(33) Raise vehicle
(34) Connect oil pressure sensor, oil temperature
sensor, engine speed sensor, and vehicle speed sensor
electrical connector (Fig. 9).
(35) Install suspension cradle in vehicle (Refer to
13 - FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/ENGINE CRADLE CROSSMEMBER - INSTALLATION).
(36) Install both axle shaft assemblies (Refer to 3 DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT INSTALLATION).
(37) Connect the power steering supply, pressure,
and return lines to power steering pump (Fig. 4).
(38) Install the power steering line brackets on oil
pan (Fig. 4).
(39) Install lower splash shield and side panels.
(40) Install both front wheel and tire assemblies.
(41) Lower vehicle.
(42) Install air cleaner housing, MAF sensor, and
air intake tube assembly (Fig. 3).
(43) Refill transmission to proper level (Refer to 21
- TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL/FLUID STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(44) Refill engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(45) Fill engine crankcase to proper level, with correct viscosity engine oil.
(46) Connect negative battery cable.
(47) Recharge A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Perform fuel system air purge procedure (Refer to
14 - FUEL SYSTEM - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(48) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE INSTALLATION) (Fig. 2).
INSTALLATION - ENGINE COVER
(1) Install engine cover on engine.
(2) Install the engine cover mounting bolts (Fig.
10).
Page 54

RG ENGINE 9-9
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 2.5L COMMON RAIL
DIESEL ENGINE
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Type R2516C
Number of Cylinders 4
Bore 92 mm
Stroke 94 mm
Displacement 2499.5cc
Injection Order 1-3-4-2
Compression Ratio 17.5:1 (± 0.5)
Maximum Power 105kW (143 PS) @ 4000
RPM
Peak Torque 340Nm @ 2600 RPM
CRANKSHAFT
Front Journal Diameter
Nominal 62.985-63.005 mm
-0.25 62.735-62.755 mm
Front Bearing Diameter
Nominal 63.045-63.074 mm
-0.25 62.795-62.824 mm
Clearance Between
Journal and Bearing
Center Journal Diameter
Nominal 63.005-63.020 mm
-0.25 62.755-62.770 mm
Center Bearing Diameter
Nominal 63.005-63.020 mm
-0.25 62.755-62.770 mm
Clearance Between
Journal and Bearing
Rear Journal Diameter
Nominal 89.980-90.000 mm
-0.25 89.730-99.750 mm
Rear Bearing Diameter
Nominal 90.045-90.065 mm
-0.25 89.795-89.815 mm
Clearance Between
Journal and Bearing
Connecting Rod Journal
Nominal 53.940-53.955 mm
-0.25 53.690-53.705 mm
0.040-0.089 mm
0.008-0.051 mm
0.045-0.080 mm
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Connecting Rod Bearing
Nominal 53.977-54.016 mm
-0.25 53.727-53.766 mm
Clearance Between
Journal and Bearing
Crankshaft End Play
End Play 0.080-0.280 mm
Adjustment Thrust Washers
Thrust Washers Available 2.31-2.36 mm
Carrier with thrust
washers installed
MAIN BEARING CARRIERS
Internal Diameter
Front 67.025-67.050 mm
Center 66.670-66.690 mm
Rear 85.985-86.005 mm
LINERS
Internal Diameter 91.997-92.015 mm
Protrusion 0.00-0.05 mm
Adjustment Shims
Available Shims 0.15 mm
CYLINDER HEAD
Minimum Thickness 94.95-95.05 mm
Gasket Thickness 1.32 mm ± 0.08, 0
CONNECTING RODS
Small End Bearing
Internal Diameter
Large End Internal
Diameter
PISTONS
Skirt Diameter (measured
at approximately 10 mm
above the bottom of the
skirt)
0.022-0.076 mm
2.41-2.46 mm
2.51-2.56 mm
27.670-27.820 mm
0.17 mm
0.20 mm
0.23 mm
0.25 mm
notches
1.42 mm ± 0.08, 1 notch
1.52 mm ± 0.08, 2
notches
32.035-32.050 mm
53.977-54.016 mm
91.912-91.928 mm
Page 55

9 - 10 ENGINE RG
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Piston Clearance 0.065-0.083 mm
Top of Piston to Cylinder
Head
Piston Potrusion 0.49-0.60 Fit Gasket
PISTON PINS
Type Full Floating
Pin Diameter 31.990-31.996 mm
Clearance 0.010-0.020 mm
PISTON RINGS
Clearance in Groove
Top 0.078-0.137 mm
Second 0.065-0.110 mm
Oil Control 0.035-0.080 mm
Fitted Gap
Top 0.30-0.45 mm
Second 0.35-0.50 mm
Oil Control 0.25-0.50 mm
CAMSHAFT
Journal Diameter–Front 29.960-29.980 mm
Bearing Clearance 0.03-0.08 mm
Journal Diameter–Center 39.250-39.270 mm
Bearing Clearance 0.03-0.08 mm
Journal Diameter–Rear 39.250-39.270 mm
Bearing Clearance 0.03-0.08 mm
HYDRAULIC LIFTER
Outside Diameter 11.994 ± 0.006 mm
VALVES
Intake Valve
Opens 15.6° ± 2° A.T.D.C.
Closes 64.4° ± 2° A.B.D.C.
Exhaust Valve
Opens 66° ± 2° B.B.D.C.
Closes 32 ±2° B.T.D.C.
0.69-0.83 mm
Number (1.32), 0 notches
or holes
0.61-0.70 Fit Gasket
Number (1.42), 1 notch
or hole
0.71-0.83 Fit Gasket
Number (1.52), 2 notches
or holes
32.000-32.004
0.004-0.012
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Face Angle
Intake 45° 25’-55° 35’
Exhaust 45° 25’-45° 35’
Head Diameter
Intake 32.30-32.50 mm
Exhaust 30.80-31.00 mm
Head Stand Down
Intake 1.08-1.34 mm
Exhaust 0.99-1.25 mm
Stem Diameter
Intake 5.952-5.970 mm
Exhaust 5.942-5.960 mm
Clearance in Guide
Intake 0.030-0.060 mm
Exhaust 0.040-0.070 mm
VALVE GUIDE
Inside Diameter 6.00-6.012 mm
Fitted Height
Intake 14.5-15.0 mm
Exhaust 16.5-17.0 mm
VALVE SPRINGS
Free Length 45.26 mm
Fitted Length 38.00 mm
Load at Fitted Length 182 ± 5-10% Kg
Load at Top of Lift 395 ± 5% Kg
Number of Coils 8
LUBRICATION
Pressure Relief Valve
Opens
Pressure Relief Valve
Spring-Free Length
OIL PUMP
Outer Rotor End Float 0.060-0.160 mm
Inner Rotor End Float 0.060-0.160 mm
Outer Rotor to Body
Diameter Clearance
Rotor Body to Drive Gear
Clearance (pump not
fitted)
6.50 bar
51.5 mm
0.130-0.240 mm
0.90-1.50 mm
Page 56

RG ENGINE 9-11
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
2.5L DIESEL TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N·m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Oil Pump Bolts 10.8 8 96
Vacuum Pump Bolts 10.8 8 96
Crankshaft Gear Bolts 10.8 8 96
Crankshaft Position
Sensor Bolts
Flywheel Bolts - Refer to
the Service Procedure
Cylinder Head Bolts -
Refer to the Service
Procedure
Reluctor Wheel Bolts 14.6 11 130
Rear Main Bearing
Support Bolts
Oil Cooler to Engine Block
Bolt
Oil Cooler Mounting Stud 50 37 —
Water Pump Housing Nuts 24.4 18 212
Connecting Rod Bolts -
Refer to the Service
Procedure
Balance Shaft Bolts 32.4 24 —
Oil Jet Bolts 10.8 8 96
Oil Pan Bolts 11.8 8 96
Crankshaft Hub Bolt 275 202 —
Front Engine Cover Bolts 11.8 8 96
Transmission to Engine
Bolts
Cylinder Head Cover /
Intake Manifold Bolts
Camshaft Access Plugs 80 59 —
Oil Separator Bolts 10.8 8 96
Camshaft Position Sensor
Bolt
Boost Pressure / Intake
Air Temp. Sensor Bolts
Accessory Drive Bracket
Bolts
Vacuum Line Fitting Bolt 56.9 42 —
Fuel Pump Nuts 27.5 21 —
Fuel Line Fittings at Pump 27.5 21 —
Inner Timing Belt Cover
Bolts
10.8 8 96
27.5 21 240
47.1 35 —
83.4 62 —
27.5 20 —
10.8 8 96
5.4 — 48
47.1 35 —
Page 57

9 - 12 ENGINE RG
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
DESCRIPTION N·m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
8mm 10.8 8 96
10mm 47.1 35 —
Outer Timing Belt Cover
Bolts
3mm 6 — 54
8mm 10.8 8 96
Engine Mount Bracket to
Cylinder Head Bolts
Intake Inlet Tube Bolts 10.1 8 89
Camshaft Sprocket Bolts 108 80 —
Timing Belt Idler Pulley
Bolt
Timing Belt Tensioner Bolt 34.7 26 —
Fuel Pump Nut 88.3 65 —
Engine Lift Hook Bolts 32.4 24 —
Thermostat Housing Bolts 27.5 21 —
Turbocharger Oil Feed
Line Fitting
Exhaust Manifold Nuts
(Must recheck each nut
after tightening sequence
is completed)
Exhaust Manifold
Heatshield Bolts
EGR Valve Nuts 32.4 24 —
EGR Pipe to EGR Bolts 32.4 24 —
Turbocharger Downpipe
Nuts
Turbocharger Bracket
Bolts
Vibration Damper to
Crankshaft Hub Bolts
Crankshaft Support Bolts 44.1 33 —
Turbocharger to Exhaust
Manifold Nuts
47.1 35 —
47.1 35 —
24.5 18 217
36 26.5 —
27.5 21 —
32.4 24 —
47.1 35 —
27.5 21 —
32.4 24 —
Page 58

RG ENGINE 9-13
ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
SPECIAL TOOLS
VM.1013 DIAL INDICATOR
VM.1001 CYLINDER LINER PULLER
VM.1005 TORQUE ANGLE GAUGE
VM.1010 CYLINDER LINER PROTRUSION TOOL
VM.1076 CYLINDER RETAINER
VM.1050 CRANKSHAFT REAR SEAL INSTALLER
Page 59

9 - 14 ENGINE RG
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
VM.1054 RELIEF VALVE REMOVER/CENTRAL
VM.1051 TDC ALIGNMENT PIN
CARRIER PIN REMOVER/INSTALLER
VM.1052 INTAKE CAMSHAFT ALIGNMENT PIN
VM.1053 EXHAUST CAMSHAFT ALIGNMENT PIN
VM.1055 CAMSHAFT/HIGH PRESSURE INJECTION
PUMP GEAR HOLDER
Page 60

RG ENGINE 9-15
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
VM.1056 BALANCE SHAFT LOCKING PIN
VM.1061 FRONT COVER AND FRONT OIL SEAL
INSTALLER
VM.1059 OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE INSTALLER
VM.1060 OIL JET REMOVER /INSTALLER
VM.1062 POWER STEERING PUMP INSTALLER
Page 61

9 - 16 ENGINE RG
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
VM.1065 PISTON RING COMPRESSOR
VM.1063 FUEL INJECTOR REMOVER
VM.1064 POWER STEERING PUMP GEAR
REMOVER
VM.1066 VALVE COVER ALIGNMENT PINS
Page 62

RG ENGINE 9-17
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
VM.1067 HIGH PRESSURE PUMP REMOVER
VM.1068 90 DEGREES AFTER TDC ALIGNMENT PIN
VM.1070 FLYWHEEL LOCKING TOOL
VM.1072 COMPRESSION TESTER ADAPTER
VM.1069 CRANKSHAFT REM/INSTALL SLEEVE
Page 63

9 - 18 ENGINE RG
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
VM.1077 POWER STEERING BELT REMOVER
VM.1073 CRANKSHAFT FRONT BEARING
REMOVER/INSTALLER
VM.1074 TIMING BELT RETAINER
VM.1075 FLYWHEEL ALIGNMENT PINS
VM.1078 POWER STEERING BELT INSTALLER
Page 64

RG ENGINE 9-19
CYLINDER HEAD
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVE SERVICE
This procedure is done with the engine cylinder
head removed from the block.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head from the cylinder block. Refer to cylinder head removal and
installation in this section.
(2) Use Valve Spring Compressor Tool and compress each valve spring.
(3) Remove the valve locks, retainers, and springs.
(4) Inspect and remove any burrs on the top of the
valve stem, especially around the groove for the
locks.
(5) Remove the valves, and place them in a rack in
the same order as removed.
VALVE CLEANING
(1) Clean all carbon deposits from the combustion
chambers, valve ports, valve stems, valve stem
guides and head.
(2) Clean all build-up and gasket material from
the engine cylinder head machined gasket surface.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect for cracks in the combustion chambers
and valve ports.
(2) Inspect for cracks on the exhaust seat.
(3) Inspect for cracks in the gasket surface at each
coolant passage.
(4) Inspect valves for burned, cracked or warped
heads.
(5) Inspect for scuffed or bent valve stems.
(6) Replace valves displaying any damage.
(7) Check valve spring height (Fig. 11).
Fig. 11 VALVE SPRING CHART
LOAD Kg HEIGHT mm STATE
P1 0.00 H1 45.26 FREE LENGTH
P2 182-5 +10% H2 38.00 VALVE CLOSED
P3 395±5% H3 28.20 VALVE OPEN
Page 65

9 - 20 ENGINE RG
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
VALVE REFACING
(1) Use a valve refacing machine to reface the
intake and exhaust valves to the specified angle.
(2) After refacing, a margin of at least 4.52-4.49
mm (.178-.177 inch) must remain (Fig. 12). If the
margin is less than 4.49 mm (.177 inch), the valve
must be replaced.
VALVE SEAT REFACING
(1) Install a pilot of the correct size in the valve
guide bore. Reface the valve seat to the specified
angle with a good dressing stone. Remove only
enough metal to provide a smooth finish.
(2) Use tapered stones to obtain the specified seat
width when required.
VALVE STAND DOWN
Valve stand down is to maintain the adequate compression ratio.
(1) Invert cylinder head.
(2) Fit each valve to its respective valve guide.
(3) Using a straight edge and feeler gauge, check
valve head stand down: Inlet valve head stand down
1.08 to 1.34 mm (.042 to .052 ins.) and exhaust valve
stand down .99 to 1.25 mm (.035 to .049 ins.).
(4) If valve head stand down is not in accordance
with above, discard original valves, check stand down
with new valves and recut valve seat inserts to
obtain correct stand down.
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Valve Guides height requirement.
(2) Measurement A (Fig. 13): 16.50 - 17.00 mm.
Measurment B : 14.50 - 15.00 mm.
VALVE STEM-TO-GUIDE CLEARANCE
MEASUREMENT
(1) Measure and record internal diameter of valve
guides. Valve guide internal diameter is 8.0 to 8.015
mm (.3149 to .3155 ins.).
(2) Measure valve stems and record diameters.
Intake valve stem diameter 7.94 to 7.96 mm (.3125 to
.3133 in). Exhaust valve stem diameter 7.92 to 7.94
mm (.3118 to .31215 in).
(3) Subtract diameter of valve stem from internal
diameter of its respective valve guide to obtain valve
stem clearance in valve guide. Clearance of inlet
valve stem in valve guide is .040 to .075 mm (.0015
to .0029 in). Clearance of exhaust valve stem in valve
guide is .060 to .093 mm (.0023 to .0036 in).
(4) If valve stem clearance in valve guide exceeds
tolerances, new valve guides must be installed.
Fig. 12 VALVE SPECS.
MEASUREMENT INTAKE EXHAUST
A 7.940-7.960 7.922-7.940
B 8.00-8.015 8.000-8.015
C 1.08-1.34 0.990-1.250
+0.07
D 2.2 ± 0.08 2.09
⫺0.09
E 1.80-2.20 1.65-2.05
F 2.73-3.44 2.45-3.02
G 41.962-41.985 35.964-35.987
H 42.070-42.086 36.050-36.066
I 7.14-7.19 7.00-7.05
L 3.11-3.26 3.10-3.25
Page 66

RG ENGINE 9-21
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
(2) Bring the piston of cylinder no. 1 exactly to top
dead center.
(3) Zero the dial indicator on the cylinder block
mating surface.
(4) Setup the dial indicator on the piston crown
(above the center of the piston pin) 5mm (1/8 in.)
from the edge of the piston and note the measurement.
(5) Repeat the procedure with the rest of the cylinders.
(6) Establish the thickness of the steel gasket by
averaging the four piston potrusion readings.
Fig. 13 VALVE GUIDE HEIGHT
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
PISTON PROTRUSION
(1) Use special tool VM.1010 with dial indicator
special tool VM.1013 (Fig. 14).
Fig. 14 PISTON PROTRUSION
Measure Dimension
(mm)
Cylinder Head Gasket
Thickness (mm)
Piston Clearance (mm) 0.72-0.83
Measure Dimension
(mm)
Cylinder Head Gasket
Thickness (mm)
Piston Clearance (mm) 0.72-0.81
Measure Dimension
(mm)
Cylinder Head Gasket
Thickness (mm)
Piston Clearance (mm) 0.69-0.81
0.49-0.60
1.32
No Holes or Notches
0.61-0.70
1.42
1 Hole or Notch
0.71-0.83
1.52
2 Holes or Notches
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE REMOVAL).
(3) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE REMOVAL).
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(6) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(7) Remove generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(8) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
Page 67

9 - 22 ENGINE RG
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
CAUTION: Before removing the cylinder head cover/
intake manifold or timing belt the engine must put
at 90° after TDC. Failure to do so could result in
valve and/or piston damage during reassembly.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(9) Remove timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(12) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Fig. 15)(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove rocker arm and lifter assemblies from
cylinder head.
(14) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
gasket from cylinder head.
(15) Disconnect glow plug and engine coolant tem-
perture electrical connectors.
(16) Remove coolant recovery pressure container
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER - REMOVAL).
(17) Remove thermostat housing to upper radiator
hose pipe (Fig. 16).
(18) Remove turbocharger outlet to charge air
cooler pipe (Fig. 16).
Fig. 15 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD ASSEMBLY
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD BOLTS(LONG)
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - CYLINDER HEAD
4 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET
5 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD BOLTS(SHORT)
Fig. 16 TURBOCHARGER AND COOLANT PIPES
1 - TURBOCHARGER OUTLET PIPE RETAINING BOLT
2 - TURBOCHARGER OUTLET PIPE
3 - ADAPTOR HOSE
4 - HOSE CLAMPS
5 - TURBOCHARGER INLET PIPE RETAINING BOLT
6 - TURBOCHARGER INLET PIPE
7 - ADAPTOR HOSE
8 - HOSE CLAMPS
9 - EGR VALVE TO INTAKE AIR INLET PIPE
10 - CLAMP
11 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING TO UPPER RADIATOR HOSE PIPE
Page 68

RG ENGINE 9-23
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
(19) Remove exhaust manifold heat shield (Fig.
17).
Fig. 17 EXHAUST MANIFOLD AND
TURBOCHARGER
1 - TURBOCHARGER OIL SUPPLY BANJO BOLT
2 - COPPER WASHER
3 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD GASKET
4 - COPPER WASHER
5 - TURBOCHARGER
6 - HEAT SHIELD RETAINING BOLT
7 - ENGINE LIFT HOOK
8 - LIFT HOOK RETAINING BOLT
9 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD RETAINING NUT
10 - TURBOCHARGER RETURN HOSE
11 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD STUD
(20) Remove exhaust manifold retaining nuts (Fig.
17).
(21) Slide exhaust manifold and turbocharger off of
exhaust manifold studs (Fig. 17).
(22) Remove cylinder head bolts.
(23) Remove cylinder head assembly from engine
block (Fig. 18).
CLEANING
Thoroughly clean the engine cylinder head and cyl-
inder block mating surfaces. Clean the intake and
exhaust manifold and engine cylinder head mating
surfaces. Remove all gasket material and carbon.
Check to ensure that no coolant or foreign material
has fallen into the tappet bore area.
Remove the carbon deposits from the combustion
chambers and top of the pistons.
Fig. 18 CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY
1 - VALVE SPRING
2 - CYLINDER HEAD BOLT
3 - GLOW PLUG
4 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
5 - CYLINDER HEAD ALIGNMENT DOWEL
6 - CYLINDER BLOCK
7 - CYLINDER LINER
8 - ENGINE BLOCK DECK
9 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
10 - CYLINDER HEAD
11 - ROCKER ARM AND LIFTER ASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
Use a straightedge and feeler gauge to check the
flatness of the engine cylinder head and block mating
surfaces.
The minimum cylinder head thickness is 89.95mm
(3.541 in.).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Piston protrusion must be measured to
determine cylinder head gasket thickness if one or
more cylinder liners have been replaced (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
NOTE: If cylinder liner(s) have not been removed,
the same thickness head gasket that was removed
can be used.
(1) Clean and inspect gasket mating surfaces.
Page 69

9 - 24 ENGINE RG
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
(2) Position correct head gasket on engine block.
(3) Place cylinder head on engine block (Fig. 18).
CAUTION: New cylinder head bolts must be used.
(4) Tighten cylinder head bolts following procedure
below.
Cylinder Head Bolt Torquing Procedure
(1) Lubricate cylinder head bolts with engine oil.
(2) Torque bolts to 30N·m in numerical starting
with bolt #1 (Fig. 19).
(3) Tighten all bolts an additional 75°, starting
with bolt #4 then 5-6-7-8-9-10-1-2-3 (Fig. 19).
(4) Tighten all bolts an additional 50° in numerical
order starting with bolt #11 then 12-13-14-15-1617-18 (Fig. 19).
(5) Without loosening any bolts tighten all bolts an
additional 75° in the following seguence: 4-5-6-7-8-910-1-2-3-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18.
Fig. 19 CYLINDER HEAD TORQUE SEQUENCE
(5) Slide exhaust manifold and turbocharger on
exhaust manifold studs (Fig. 17).
(6) Install exhaust manifold retaining nuts. Torque
nuts to 32.4N·m.
(7) Install exhaust manifold heat shield (Fig. 17).
Torque bolts to 27.5N·m.
(8) Install turbocharger outlet to charge air cooler
pipe (Fig. 17).
(9) Install thermostat housing to upper radiator
hose pipe (Fig. 16). Install retaining bolt and torque
to 47.1N·m.
(10) Install coolant recovery pressure container
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS CONTAINER - INSTALLATION).
(11) Connect glow plug and coolant temperature
sensor electrical connectors.
(12) Install new cylinder head cover/intake manifold gasket.
(13) Install rocker arm and lifter assemblies.Be
sure to put rocker arm and lifter assemblies in
same location as removed.
(14) Install cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Fig. 15)(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(16) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(17) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(18) Remove crankshaft and both camshaft
locking pins at this time (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING - STANDARD PROCEDURE) .
(19) Install generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(20) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(21) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(22) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
(23) Install air cleaner housing assembly.
(24) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(25) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE INSTALLATION).
(26) Install front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE INSTALLATION).
(27) Connect negative battery cable.
Page 70

RG ENGINE 9-25
CAMSHAFT(S)
DESCRIPTION
The camshafts are made of gray cast iron with
eight machined lobes and four bearing journals (Fig.
20).
Fig. 20 CAMSHAFTS
1 - INTAKE CAMSHAFT
2 - EXHAUST CAMSHAFT
OPERATION
When the camshaft rotates the lobes actuate the
hydraulic lifters and rocker arms, forcing downward
on the rocker arms which opens the valves.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(10) Remove timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(12) Remove timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) With cylinder head cover/intake manifold on
work bench, remove plugs at rear of cylinder head
cover/intake manifold.
(15) Remove camshaft oil seals (Fig. 21).
(16) Remove snapring and thrust washer from
camshaft (Fig. 21).
(17) Slide camshaft through access hole at rear of
cylinder head cover/intake manifold.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE REMOVAL).
(3) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE REMOVAL).
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove air cleaner housing.
(6) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(7) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(8) Remove generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(9) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: Before removing the cylinder head cover/
intake manifold or timing belt the engine must put
at 90° after TDC. Failure to do so could result in
valve and/or piston damage during reassembly.
Fig. 21 CAMSHAFT ASSEMBLY
1 - INTAKE CAMSHAFT
2 - SNAPRING
3 - CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL
4 - THRUST WASHER
5 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
6 - EXHAUST CAMSHAFT
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the camshafts with Mopar威 Engine
Oil Supplement, or equivalent.
(2) Carefully install camshafts into access holes in
rear of cylinder head cover/intake manifold.
Page 71

9 - 26 ENGINE RG
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
(3) Install thrust washer, snapring, and camshaft
oil seal (Fig. 21).
CHECKING CAMSHAFT ENDPLAY
(1) After camshafts are properly installed in cylinder head cover check end play of camshafts with a
dial indicator. The end play should be between .10
mm – .30 mm.
NOTE: If the camshaft endplay is not within specification, measure thickness of the camshaft spacer.
Camshaft spacer thickness should be 2.8 ± .02mm.
(4) Install access hole plugs and gaskets at rear of
cylinder head cover/intake manifold. Torque plugs to
80N·m.
(5) Install cylinder head cover/intake manifold on
engine block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
(10) Install generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(12) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(13) Install air cleaner housing.
(14) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(15) Install front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE INSTALLATION).
(16) Connect negative battery cable.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head cover is made of cast aluminum
and is also the intake manifold on this engine (Fig.
22).
Fig. 22 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Before removing the cylinder head cover/
intake manifold the engine must put at 90° after
TDC. Failure to do so could result in valve and/or
piston damage during reassembly. (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE REMOVAL).
(3) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE REMOVAL).
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Rotate engine until 90° after TDC is reached.
Install both camshaft locking pins and the crankshaft
locking pin. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(6) Remove air cleaner housing assembly.
(7) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(8) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(9) Remove generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(10) Support engine and remove right engine
mount (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/
RIGHT MOUNT - REMOVAL).
Page 72

RG ENGINE 9-27
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) (Continued)
(11) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(12) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove inner timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Disconnect camshaft position sensor, boost
pressure/intake air temperature sensor, EGR solenoid, and fuel pressure sensor electrical connectors
(Fig. 23).
(18) Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove power steering pump reservoir from
bracket.
(20) Remove oil dipstick tube retaining bolt at
intake manifold inlet.
(21) Disconnect oil separator outlet hose at separa-
tor.
(22) Remove turbo inlet tube retaining bolt at
intake manifold.
(23) Disconnect EGR tube at intake manifold inlet
tube.
(24) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
retaining bolts (Fig. 24).
(25) Lift cylinder head cover/intake manifold from
cylinder head (Fig. 24).
Fig. 23 ENGINE COMPONENT LOCATIONS
1 - FUEL INJECTOR RETURN LINE
2 - FUEL INJECTOR SUPPLY LINE
3 - OIL SEPARATOR
4 - FUEL INJECTOR
5 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
6 - BOOST PRESSURE/INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
7 - EGR SOLENOID
8 - FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
9 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOL
10 - FUEL RAIL
11 - WIRING HARNESS RETAINING CLIPS
(15) Disconnect vacuum lines at EGR solenoid.
(16) Position electrical harness out of way.
(17) Remove fuel injectors (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR REMOVAL).
Fig. 24 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD ASSEMBLY
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD BOLTS(LONG)
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - CYLINDER HEAD
4 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET
5 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD BOLTS(SHORT)
NOTE: When removing rocker arm and lifter assemblies, be sure to keep them in order as they were
removed from the cylinder head. Always keep lifters
in an upright position when removed from cylinder
head.
Page 73

9 - 28 ENGINE RG
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) (Continued)
(26) Remove rocker arm and lifter assemblies from
cylinder head (Fig. 25).
Fig. 25 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD GASKET LOCATION
1 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
2 - ROCKER ARM AND LIFTER ASSEMBLY
3 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
(27) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
gasket from cylinder head.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and inspect sealing surfaces.
(2) Install new gasket on cylinder head.
NOTE: Apply a small amount of grease on each
valve stem. This will help hold the rocker arm in
position during the cylinder head cover installation.
(3) Install rocker arm and lifter assemblies in cylinder head (Fig. 25).Be sure to put rocker arm
and lifter assemblies in same location as
removed.
(4) Install cylinder head cover/intake manifold
alignment studs in cylinder head (Fig. 26).
(5) Install cylinder head cover/intake manifold
over alignment stud.
NOTE: Be sure to lubricate cylinder head cover/intake manifold retaining bolts with engine oil before
assembly. If new bolts are being installed, DO NOT
lubricate before assembly.
Fig. 26 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD ALIGNMENT STUDS VM.1066
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD ALIGNMENT
STUDS VM.1066
2 - CYLINDER HEAD
(6) Install two cylinder head cover/intake manifold
retaining bolts and tighten finger tight.
(7) Remove alignment studs and install remaining
retaining bolts (Fig. 24). Tighten retaining bolts finger tight.
(8) Torque cylinder head cover/intake manifold
retaining bolts following procedure below.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
TIGHTENING PROCEDURE
(1) Coat all bolts being reused with clean engine
oil.
(2) Install the M8x35 bolts into holes 1,2,3,4,5, and
12. Install the M8x85 bolts into holes
6,7,8,9,10,11,13,14,15, and 16. Tighten all bolt hand
tight.
(3) Alternate between bolts #11 and #16 to seat
cylinder head cover/intake manifold on cylinder head
(Fig. 27). Torque bolts to 7 N·m.
(4) Torque all cylinder head cover/intake manifold
retaining bolts to 25 N·m in numerical order starting
with #1 and ending with #16 (Fig. 27).
(9) Connect EGR tube at intake manifold inlet
tube. Torque clamp to 10.8 N·m.
(10) Install turbo inlet tube retaining bolt at
intake manifold. Torque bolt to 27.5 N·m.
(11) Connect oil separator outlet hose at separator.
(12) Install oil dipstick tube retaining bolt at
intake manifold inlet. Torque bolt to 10 N·m.
Page 74

RG ENGINE 9-29
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) (Continued)
(25) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(26) Install air cleaner housing assembly.
(27) Remove crankshaft and both camshaft locking
pins (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(28) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(29) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE INSTALLATION).
(30) Install front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE INSTALLATION).
(31) Connect negative battery cable.
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner housing assembly.
Fig. 27 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
(13) Install power steering pump reservoir in
bracket.
(14) Install fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install fuel injectors and fuel injector supply
lines (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION).
(16) Connect vacuum lines at EGR solenoid.
(17) Clip wiring harness retainers on studs on fuel
rail (Fig. 23).
(18) Connect camshaft position sensor, boost pressure/intake air temperature sensor, EGR solenoid,
and fuel pressure sensor electrical connectors (Fig.
23).
(19) Install inner timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(20) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(21) Install outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(22) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
(23) Install generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(24) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(3) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
WARNING: Before removing the timing belt the
engine must put at 90° after TDC. Failure to do so
could result in valve and/or piston damage during
reassembly. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(5) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(6) Using VM.1055, remove both camshaft gears
(Fig. 28).
(7) Remove both camshaft oil seals.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new camshaft oil seal using VM.1057.
(2) Install camshaft sprockets and tighten retaining bolts finger tight.
(3) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(4) Torque camshaft sprockets to 108 N·m using
VM.1055 (Fig. 28).
(5) Install outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
Page 75

9 - 30 ENGINE RG
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S) (Continued)
Fig. 28 CAMSHAFT GEAR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
1 - TIMING BELT INNER COVER
2 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
3 - IDLER PULLEYS
4 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
5 - VM.1055
(7) Install air cleaner housing assembly.
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION
The rocker arms are made of stamped steel (Fig.
29).
OPERATION
The rocker arms are used as a link between the
camshaft and valves. As the camshaft rotates the
lobes of the camshafts apply downward pressure on
the rocker arms. This pressure is then transmitted to
the valves which causes the valves to open.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE REMOVAL).
(3) Remove air cleaner housing assembly.
(4) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
Fig. 29 CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY
1 - VALVE SPRING
2 - CYLINDER HEAD BOLT
3 - GLOW PLUG
4 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
5 - CYLINDER HEAD ALIGNMENT DOWEL
6 - CYLINDER BLOCK
7 - CYLINDER LINER
8 - ENGINE BLOCK DECK
9 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
10 - CYLINDER HEAD
11 - ROCKER ARM AND LIFTER ASSEMBLY
(5) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove inner timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove rocker arm abd lifter (Fig. 30).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and inspect gasket sealing surfaces.
(2) Install new gasket on cylinder head.
(3) Lubricate lifter ball end of lifter(s), valve(s),
and rocker arm roller(s) with Mopar威 Engine Oil
Supplement or equivlalent.
Page 76

RG ENGINE 9-31
ROCKER ARMS (Continued)
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DESCRIPTION
Valve lash is controlled by hydraulic tappets
located inside the cylinder head, in tappet bores
below the camshafts (Fig. 31).
Fig. 30 ROCKER ARM ASSEMBLY
1 - ROCKER ARM ASSEMBLY
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - HYDRAULIC LIFTER
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5-VALVE
(4) Connect rocker arm(s) to lifter and reposition
on valve(s) (Fig. 30).
(5) Install cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install inner timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
(10) Install air cleaner housing assembly.
(11) Install front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE INSTALLATION).
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
Fig. 31 CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY
1 - VALVE SPRING
2 - CYLINDER HEAD BOLT
3 - GLOW PLUG
4 - COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
5 - CYLINDER HEAD ALIGNMENT DOWEL
6 - CYLINDER BLOCK
7 - CYLINDER LINER
8 - ENGINE BLOCK DECK
9 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
10 - CYLINDER HEAD
11 - ROCKER ARM AND LIFTER ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE REMOVAL).
(3) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE REMOVAL).
(4) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Page 77

9 - 32 ENGINE RG
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (Continued)
CAUTION: Before removing the cylinder head cover/
intake manifold or the timing belt the engine must
put at 90° after TDC. Failure to do so could result in
valve and/or piston damage during reassembly.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(6) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove inner timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Fig. 32)(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install rocker arm and lifter assemblies in
lifter bores.
(2) Install cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Fig. 32) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(3) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
(7) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE INSTALLATION).
(8) Install front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE INSTALLATION).
(9) Connect negative battery cable.
Fig. 32 CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE
MANIFOLD
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD BOLTS(LONG)
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - CYLINDER HEAD
4 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET
5 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD BOLTS(SHORT)
(9) Remove rocker arm and lifter assemblies from
lifter bores.
INSPECTION
Clean each lifter assembly in cleaning solvent to
remove all varnish and sludge deposits. Inspect for
indications of scuffing on the side and base of each
lifter body.
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The 2.5L CRD Diesel engine uses a cast iron
engine block with wet cast iron cylinder liners (Fig.
33).
Fig. 33 ENGINE BLOCK
Page 78

RG ENGINE 9-33
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is a forged steel type design with
five main bearing journals. The crankshaft is located
at the bottom of the engine block and is held in place
with three main bearing supports (Fig. 34).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Mount a dial indicator to a stationary point at
rear of engine. Locate the probe perpendicular
against the flywheel (Fig. 35).
(2) Move the crankshaft all the way to the front of
its travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move the crankshaft all the way to the rear
and read dial indicator. For crankshaft end play
clearances (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) .
Fig. 34 CRANKSHAFT ASSEMBLY TYPICAL
1 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT HALVE
2 - MAIN BEARING HALVE
3 - CRANKSHAFT
4 - MAIN BEARING HALVE
5 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT HALVE
6 - MAIN BEARING SUPPORT BOLTS
7 - WASHERS
OPERATION
The crankshaft transfers force generated by combustion within the cylinder bores to the flywheel or
flexplate.
Fig. 35 CHECKING CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ADAPTER PLATE
3 - REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT
4 - SEALING RING
5 - SEALING RING
6 - ALIGNMENT PIN
7 - CRANKSHAFT
8 - RELUCTOR WHEEL
9 - RELUCTOR WHEEL RETAINING BOLT
10 - REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT RETAINING BOLTS
11 - FLYWHEEL
12 - FLYWHEEL BOLTS
Page 79

9 - 34 ENGINE RG
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove engine from vehicle (Refer to 9 ENGINE - REMOVAL).
(2) Mount engine on an engine stand.
(3) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(4) Remove timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove flywheel.
(10) Remove rear main bearing support/adapter
plate retaining bolts and remove adapter plate (Fig.
36).
Fig. 36 REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT
1 - ADAPTER PLATE
2 - REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT
3 - CRANKSHAFT
4 - REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT RETAINING BOLTS
(11) Remove rear main bearing support by threading two retaining bolts in holes provided. Tighten
bolts equally to push main bearing support out of
block (Fig. 37).
Fig. 37 REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT REMOVAL
1 - BOLTS
2 - REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT
3 - CRANKSHAFT
(12) Remove front engine cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER REMOVAL).
(13) Remove crankshaft sprocket.
(14) Remove oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(15) Remove oil pump pickup tube (Refer to 9 ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL).
(16) Remove balance shaft assembly (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/BALANCE SHAFT REMOVAL).
(17) Remove oil jets (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL JET - REMOVAL).
(18) Remove piston and connecting rod assemblies
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON &
CONNECTING ROD - REMOVAL).
(19) Slide special tool VM.1069 on crankshaft (Fig.
38).
(20) Using special tool VM.1054, remove crankshaft support retainers (Fig. 39).
(21) Slide crankshaft out rear of engine block.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Before installing crankshaft in engine block,
be sure the notches in the crankshaft supports are
facing towards the front of the engine.
Page 80

RG ENGINE 9-35
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
(1) Install crankshaft in engine block. Be sure to
align oil holes in crankshaft supports and
engine block.
NOTE: Before installing the crankshaft support
retainers/balance shaft oil feed be sure that special
tool VM 1079, alignment pins are installed (Fig. 40).
(2) Install crankshaft support retainers using spe-
Fig. 38 CRANKSHAFT SLEEVE VM.1069
1 - CRANKSHAFT SLEEVE VM.1069
2 - ENGINE BLOCK
Fig. 39 CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT RETAINERS/
BALANCE SHAFT OIL FEED
1 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT RETAINERS/BALANCE SHAFT OIL
FEED
2 - O-RINGS (3)
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
4 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT RETAINER/BALANCE SHAFT OIL
FEED REMOVER - INSTALLER VM.1054
Fig. 40 CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT RETAINERS/
BALANCE SHAFT OIL FEED ALIGNMENT PINS
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - ALIGNMENT PINS VM 1079
cial tool VM 1054. (Fig. 39).
(3) Install crankshaft support retainers O-rings.
(4) Remove special tool VM.1069 from crankshaft
(Fig. 38).
(5) Install crankshaft sprocket.
(6) Install front engine cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER INSTALLATION).
(7) Install rear main bearing support in engine
block. Be sure to align oil hole in rear main
bearing support with hole in block.
(8) Install adapter plate and retaining bolts (Fig.
36). Torque bolts to 27.5N·m.
(9) Install flywheel.
(10) Install piston and connecting rod assemblies
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON &
CONNECTING ROD - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install oil jets (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL JET - INSTALLATION).
Page 81

9 - 36 ENGINE RG
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
(12) Install balance shaft assembly (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/BALANCE SHAFT INSTALLATION).
(13) Install oil pump pickup tube (Refer to 9 ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
(16) Install cylinder head cover/intake manifold
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(17) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(18) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(19) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(20) Install engine in vehicle.
(21) Fill engine oil with proper oil to correct level.
CYLINDER LINERS
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder wall liner used on this engine is of
the wet design. O-rings are used to seal the liner to
the engine block.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove engine from vehicle.
(2) With engine completely disassembled, use special tool VM.1001 to remove liner assembly (Fig. 41).
(3) Tighten bolt on VM.1001 to remove liner from
block (Fig. 42).
(4) Remove shims from cylinder liner or cylinder
block recess. Keep shims with each cylinder liner.
INSPECTION
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-ofround and taper with a dial bore gauge. The cylinder
bore out-of-round is 0.100 mm (.0039 in.) maximum
and cylinder bore taper is 0.100 mm (.0039 in.) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly scuffed or
scored, new liners should be installed and honed, and
new pistons and rings fitted.
Fig. 41 CYLINDER LINER REMOVER
Fig. 42 CYLINDER LINER REMOVAL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL VM.1001
2 - CYLINDER LINER
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
Page 82

RG ENGINE 9-37
CYLINDER LINERS (Continued)
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in directions A and B (Fig. 43). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 in.) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 in.) up from the bottom bore.
Fig. 43 LINER INSPECTION
INSTALLATION
(1) Carefully clean liner and engine block, and
degrease the engine block where it comes into contact
with the liners. Install the liners in the engine block
as shown, rotating them back and forth by 45° in
order to guarantee correct positioning (Fig. 44).
(2) Measure the liner recess relative to block deck
with a dial indicator mounted on a special tool
VM-1010 A. All the measurements must be taken
on high pressure pump side of engine block. .
Zero dial gauge on block deck.
(3) Move dial gauge to cylinder liner record reading on dial gauge.
(4) Remove liner and special tool.
(5) Then select the correct shim thickness to give
proper protrusion (0.01 - 0.06 mm).
(6) Fit the shim and the O-rings onto the liner.
(7) Lubricate the lower liner location in the block.
(8) Fit the liners in the crankcase making sure
that the shim is positioned correctly in the seat. Lock
the liners in position using special tool (VM.1076)
and bolts (Fig. 45).
Fig. 44 LINER INSTALLATION
1 - CYLINDER LINER
2 - SHIMS
3 - O-RINGS
4 - BLOCK LEDGE
5 - ENGINE BLOCK
Fig. 45 LINER CLAMP LOCATION
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - LINER RETAINER VM.1076
3 - CYLINDER LINER
(9) Recheck the liner protrusion. It should be 0.00
- 0.05 mm.
(10) Reassemble engine.
(11) Install engine in vehicle.
Page 83

9 - 38 ENGINE RG
INTERNAL VACUUM PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The diesel engine uses a internal vacuum pump.
This vacuum pump is mounted in the front of the
engine block under the engine front cover (Fig. 46).
The vacuum pump is driven by a sprocket on the
crankshaft.
Fig. 46 VACUUM PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner housing.
(3) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(4) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(5) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove vibration damper/crankshaft pulley
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Crankshaft hub has LHD thread.
(10) Remove crankshaft hub.
(11) Remove front engine cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER REMOVAL).
(12) Remove crankshaft sprocket (Fig. 47).
(13) Remove vacuum pump (Fig. 47).
Fig. 47 OIL PUMPAND VACUUM PUMP
1 - VACUUM PUMP
2 - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
3 - OIL PUMP
4 - ENGINE BLOCK
5 - CRANKSHAFT
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Verify the 3 blades on the vacuum pump are
in place and correctly assembled. The tapered edge
should be on the outer side. Make sure the pump
rotates before installation.
(1) Lubricate vacuum pump blades and install in
vacuum pump body as shown (Fig. 48).
(2) Install vacuum pump in engine block (Fig. 47).
Torque bolts to 10.8N·m.
(3) Install crankshaft sprocket (Fig. 47). Torque
bolts to 10.8N·m.
(4) Install front engine cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER INSTALLATION).
(5) Install front crankshaft hub. Torque bolt to
304N·m.
(6) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
Page 84

RG ENGINE 9-39
INTERNAL VACUUM PUMP (Continued)
Fig. 48 VACUUM PUMP COMPONENTS
1 - VACUUM PUMP BODY
2 - VACUUM PUMP BLADE TAPERED EDGE
3 - VACUUM PUMP BLADE
(8) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install vibration damper/crankshaft pulley.
(10) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
(11) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(12) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(13) Install air cleaner housing.
(14) Connect negative battery cable.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are of a free floating design. Oil jets in
the engine block lubricate and cool the piston and pin
assembly. The connecting rods have a pressed in
place wrist pin bushing which is lubricated by the oil
jets (Fig. 49).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert ring and push
down with piston to ensure it is square in bore. The
ring gap measurement must be made with the ring
positioning at least 12 mm (0.50 in.) from bottom of
cylinder bore (Fig. 50). Check gap with feeler gauge.
Fig. 49 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
1 - PISTON PIN
2 - PISTON
3 - SNAP RING
4 - PAINTED CONNECTING ROD ALIGNMENT NUMBERS
5 - CONNECTING ROD BOLT
6 - CONNECTING ROD BEARING
7 - CONNECTING ROD
8 - SNAP RING
Top compression ring gap .30 to .45mm (.0118 to
.0177 in.). Second compression ring gap .30 to .45mm
(.0118 to .0177 in.). Oil control ring gap .25 to .50mm
(.0098 to .0196 in.).
(2) If ring gaps exceed dimension given, new rings
or cylinder liners must be fitted. Keep piston rings in
piston sets.
(3) Check piston ring to groove clearance (Fig. 51).
Top compression ring gap .080 to .130mm (.0031 to
.0051 in.). Second compression ring gap .070 to
.110mm (.0027 to .0043 in.). Oil control ring gap .040
to .080mm (.0015 to .0031 in.).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
Page 85

9 - 40 ENGINE RG
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
(8) Piston and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. Rotate crankshaft so that
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick or scratch crankshaft
journals, connecting rod cap can be separated by
tapping with a plastic hammer on a clean surface.
(9) After removal, install bearing cap on the mating rod and mark piston and connecting rod with
painted matching cylinder number when removed
from engine block.
PISTON PIN - REMOVAL
(1) Secure connecting rods in a soft jawed vice.
(2) Remove 2 snap rings securing piston pin (Fig.
Fig. 50 RING END GAP MEASUREMENT
1 - FEELER GAUGE
52).
(3) Push piston pin out of piston and connecting
rod (Fig. 52).
PISTON RING - REMOVAL
(1) ID mark on face of top and second piston rings
must point toward piston crown.
(2) Using a suitable ring expander, remove top and
second piston rings (Fig. 53).
(3) Remove upper oil ring side rail, lower oil ring
side rail and then the oil expander from piston.
(4) Carefully clean carbon from piston crowns,
skirts and ring grooves ensuring the 4 oil holes in
the oil control ring groove are clear.
Fig. 51 PISTON RING TO GROOVE CLEARANCE
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Remove oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove oil pump pickup tube.(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL)
(6) Remove balance shaft assembly (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/BALANCE SHAFT REMOVAL).
(7) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a ridge
reamer before removing pistons from cylinder block.
Be sure to keep top of pistons covered during
this operation.
INSPECTION
PISTONS
(1) Piston Diameter: Size: 91.912-91.928mm
(3.6185-3.6192 in.) Maximum wear limit .05mm
(.0019 in.).
(2) Check piston pin bores in piston for roundness.
Make 3 checks at 120° intervals. Maximum out of
roundness .05mm (.0019in.).
(3) The piston diameter should be measured
approximately 15 mm (.590 in.) up from the base.
(4) Skirt wear should not exceed 0.1 mm (.00039
in.).
(5) The clearance between the cylinder liner and
piston should not exceed 0.065-0.083 mm
(.0025-.0032 in.).
CONNECTING RODS
CAUTION: When assembling the connecting rod, be
sure that the pawl on each of the connecting rod
caps is facing the rear (fly wheel) side of the engine
(Fig. 54).
(1) Assemble bearing shells and bearing caps to
their respective connecting rods ensuring that the
Page 86

RG ENGINE 9-41
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
serrations on the cap and reference marks are
aligned (Fig. 54).
(2) Tighten connecting cap bolts to 29 N·m (21 ft.
lbs.) plus 60°.
(3) Without loosening connecting rod bolts, tighten
all bolts to 88N·m.
(4) Check and record internal diameter of crank
end of connecting rod.
CAUTION: When changing connecting rods, DO
NOT use a stamp to mark the cylinder location.
Identify the connecting rods and caps location
using a paint marker. All four must have the same
weight and the same number. Replacement connecting rods will only be supplied in sets of four
(Fig. 54).
Connecting rods are supplied in sets of four since
they all must be of the same weight category. Max
allowable weight difference is 5 gr.
NOTE: Lightly heat the piston in oven. Insert piston
pin in position and secure it with provided snap
rings.
Fig. 52 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
1 - PISTON PIN
2 - PISTON
3 - SNAP RING
4 - PAINTED CONNECTING ROD ALIGNMENT NUMBERS
5 - CONNECTING ROD BOLT
6 - CONNECTING ROD BEARING
7 - CONNECTING ROD
8 - SNAP RING
Fig. 53 PISTON RINGS - REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
Fig. 54 CONNECTING ROD IDENTIFICATION
1 - CONNECTING ROD PAWL
2 - CONNECTING ROD
3 - PAINTED CYLINDER IDENTIFIER
4 - CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
5 - CONNECTING ROD
After having coated threads with Molyguard,
tighten con rod bolts to 29 N·m (21 ft. lbs.) plus 60°.
Page 87

9 - 42 ENGINE RG
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
PISTON PINS
(1) Measure the diameter of piston pin in the cen-
ter and both ends.
(2) Piston pin diameter is 31.992 to 31.996mm
(1.259524 in to 1.259681 in.).
INSTALLATION
PISTON PIN INSTALLATION
(1) Secure connecting rod in soft jawed vice.
(2) Lubricate piston pin and piston with clean
engine oil.
(3) Position piston on connecting rod (Fig. 55).
CAUTION: Ensure arrow on piston crown and the
bearing cap numbers on the connecting rod are on
the opposite side.
(4) Install piston pin (Fig. 55).
(5) Install clips in piston to retain piston pin (Fig.
55).
(6) Remove connecting rod from vice.
PISTON RINGS - INSTALLATION
(1) Install rings on the pistons using a suitable
ring expander (Fig. 56).
(2) Top compression ring is tapered and chromium
plated. The second ring is of the scraper type and
must be installed with scraping edge facing bottom of
the piston. The third is an oil control ring. Ring gaps
must be positioned, before inserting piston into the
liners, as follows.
(3) Top ring gap must be positioned at the #3 posi-
tion (looking at the piston crown from above) (Fig.
57).
(4) Second piston ring gap should be positioned at
the #1 position (Fig. 57).
(5) Oil control ring gap should be positioned at the
#2 position (Fig. 57).
(6) When assembling pistons check that compo-
nents are installed in the same position as before disassembly, determined by the numbers stamped on
the crown of individual pistons. Engine cylinders are
numbered starting from gear train end of the engine.
Face arrow on top of piston toward front of
engine. Therefore, the numbers stamped on connect-
ing rod big end should face toward the injection
pump side of engine. To insert piston into cylinder
use a ring compressor (VM.1065) as shown in (Fig.
58).
Fig. 55 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
1 - PISTON PIN
2 - PISTON
3 - SNAP RING
4 - PAINTED CONNECTING ROD ALIGNMENT NUMBERS
5 - CONNECTING ROD BOLT
6 - CONNECTING ROD BEARING
7 - CONNECTING ROD
8 - SNAP RING
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons, and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, be sure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap (Fig. 57).
Fig. 56 PISTON RINGS-INSTALLATION
Page 88

RG ENGINE 9-43
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Fig. 57 PISTON RING GAP LOCATION
1 - SECOND COMPRESSION RING GAP POSITION
2 - OIL CONTROL RING GAP POSITION
3 - TOP COMPRESSION RING GAP POSITION
(2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted together.
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil, slide the ring compressor, over the piston
and tighten (Fig. 58). Ensure position of rings
does not change during this operation.
NOTE: Be sure arrow on top of piston faces
towards front of engine and the connecting rod
pawl faces the rear (flywheel) side of the engine.
Fig. 58 PISTON INSTALLATION USING VM.1065
PISTON
PISTON RING COMPRESSOR VM.1065
ENGINE BLOCK
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(4) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Insert
rod and piston into cylinder bore and guide rod over
the crankshaft journal.
(5) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on connecting rod journal.
NOTE: Connecting rod bolts must be replaced when
disassembled. DO NOT lubracate new connecting
rod bolts as they are already coated.
(6) Install connecting rod caps (Fig. 59). Install rod
bolts and tighten each bolt to 10N·m (89 lbs. in..).
Tighten each bolt again to 30N·m (22 lbs. ft.) plus
40°. Then torque to 88N·m (65 ft.lb).
(7) Install cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install balance shaft assembly (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/BALANCE SHAFT INSTALLATION).
(9) Install oil pump pickup tube (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
Fig. 59 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
INSTALLATION
1 - PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
2 - PAINTED CYLINDER IDENTIFIER
3 - CONNECTING ROD BOLT
4 - PAINTED CYLINDER IDENTIFIER
(11) Connect negative battery cable.
Page 89

9 - 44 ENGINE RG
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL FRONT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner housing.
(3) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(5) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(6) Remove vibration damper/crankshaft pulley
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove outer timing belt cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Crankshaft hub retaining bolt has LHD
thread.
1 - CRANKSHAFT HUB RETAINING BOLT
2 - FRONT ENGINE COVER RETAINING BOLTS
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
4 - FRONT ENGINE COVER ALIGNMENT DOWELS
5 - FRONT ENGINE COVER
6 - CRANKSHAFT HUB
Fig. 60 ENGINE COVER - FRONT
(10) Remove crankshaft hub.
(11) Remove front engine cover (Fig. 60) (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER REMOVAL) .
(12) With cover on work bench, pry out old seal.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do Not use a hammer to install the
crankshaft oil seal.
NOTE: To prevent potential oil leaks, DO NOT touch
the front crankshaft inner seal. Always handle the
seal from the outer diameter.
(1) Clean engine block and front engine cover seal-
ing surfaces.
(2) Install crankshaft oil seal on VM.1061 (Fig.
61).
(3) Place sleeve for VM.1061 on press bench as
shown (Fig. 61).
(4) Press the new seal into front engine cover.
Fig. 61 VM.1061 PLACEMENT
1 - VM.1061
2 - FRONT ENGINE COVER
3 - PRESS BENCH
4 - SLEEVE FROM VM.1061
Page 90

RG ENGINE 9-45
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT (Continued)
(5) Install front engine cover, care must be taken
not to damage the seal(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER - INSTALLATION) .
(6) Install crankshaft hub and retaining bolt.
Torque bolt to 304N·m (224 lbs. ft.).
(7) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install vibration damper/crankshaft pulley
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(12) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(13) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
(14) Install air cleaner housing.
(15) Connect negative battery cable.
1 - BELT TENSIONER RETAINING BOLT
2 - BELT TENSIONER
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY RETAINING
BOLTS
Fig. 62 VIBRATION DAMPER
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(2) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(3) Remove vibration damper retaining bolts and
damper (Fig. 62).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install vibration damper and retaining bolts
(Fig. 62). Torque bolts to 27.5N·m.
(2) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(3) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
ENGINE COVER - FRONT
DESCRIPTION
The front engine cover on this engine is a stamped
steel cover which covers the oil pump and vacuum
pump.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner housing.
(3) Support engine and remove right engine mount
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT
MOUNT - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(5) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(6) Remove vibration damper (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER REMOVAL).
(7) Remove timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Page 91

9 - 46 ENGINE RG
ENGINE COVER - FRONT (Continued)
CAUTION: Before removing the cylinder head cover/
intake manifold or timing belt the engine must put
at 90° after TDC. Failure to do so could result in
valve and/or piston damage during reassembly.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(8) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Crankshaft hub has LHD thread.
(10) Remove crankshaft hub.
(11) Remove front engine cover (Fig. 63).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean engine block and front engine cover sealing surfaces.
(2) Apply a continous 3mm bead of Silicone Sealer
to cover, install within 10 minutes (Fig. 63). Torque
bolts to 11.8N·m.
(3) Install crankshaft hub (Fig. 63). Torque bolt to
304N·m.
(4) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install vibration damper (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT INSTALLATION).
1 - CRANKSHAFT HUB RETAINING BOLT
2 - FRONT ENGINE COVER RETAINING BOLTS
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
4 - FRONT ENGINE COVER ALIGNMENT DOWELS
5 - FRONT ENGINE COVER
6 - CRANKSHAFT HUB
(9) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(11) Install air cleaner housing.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
Fig. 63 ENGINE COVER - FRONT
Page 92

RG ENGINE 9-47
CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS
REMOVAL
The engine must be removed from vehicle and completely disassembled to replace the front main bearing.
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
(1) With crankshaft assembly removed from
engine.
(2) Remove crankshaft supports from crankshaft
and remove bearing halves from supports (Fig. 64).
CRANKSHAFT FRONT MAIN BEARING
(1) Using special tool VM.1073 push front main
bearing out of front of engine block (Fig. 65).
Fig. 64 CRANKSHAFT ASSEMBLY
1 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT HALVE
2 - MAIN BEARING HALVE
3 - CRANKSHAFT
4 - MAIN BEARING HALVE
5 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT HALVE
6 - MAIN BEARING SUPPORT BOLTS
7 - WASHERS
Fig. 65 FRONT MAIN BEARING REMOVAL
1 - VM.1073
2 - FRONT CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
Page 93

9 - 48 ENGINE RG
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
INSTALLATION
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
(1) Install bearing halves in crankshaft supports.
(2) Lubricate crankshaft and main bearings with
clean engine oil.
(3) Install crankshaft supports on crankshaft (Fig.
66). Torque bolts to 44.1N·m.
Fig. 66 CRANKSHAFT ASSEMBLY
1 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT HALVE
2 - MAIN BEARING HALVE
3 - CRANKSHAFT
4 - MAIN BEARING HALVE
5 - CRANKSHAFT SUPPORT HALVE
6 - MAIN BEARING SUPPORT BOLTS
7 - WASHERS
FRONT CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING
(1) Using special tool VM.1073, push front crankshaft main bearing in engine block (Fig. 67).
(2) Be sure oil hole in bearing lines up with oil gallery in engine block (Fig. 68).
(3) Reassemble engine and install in vehicle.
Fig. 67 FRONT MAIN BEARING INSTALLATION
1 - FRONT CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING
2 - ENGINE BLOCK
3 - SPECIAL TOOL VM.1073
Fig. 68 FRONT MAIN BEARING ALIGNMENT
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - OIL HOLE IN BEARING
3 - FRONT CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING
Page 94

RG ENGINE 9-49
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL REAR
REMOVAL
This must be done with either the engine or transmission removed from vehicle.
(1) Remove flywheel assembly.
(2) Pry out old crankshaft oil seal.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: To prevent potential oil leaks, DO NOT touch
the rear crankshaft inner seal. Always handle the
seal from the outer diameter.
(1) Using special tool VM.1050, install rear crankshaft oil seal in rear main bearing support (Fig. 69).
(4) Remove all oil pan retaining bolts and oil pan
(Fig. 70).
Fig. 69 REAR CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL
INSTALLATION USING VM.1050
1 - SPECIAL TOOL VM.1050
2 - REAR MAIN BEARING SUPPORT
3 - OIL PAN
4 - ENGINE TO TRANSMISSION ADAPTER PLATE
(2) Install engine or tranmission in vehicle.
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Drain engine oil from engine.
Fig. 70 OIL PAN AND PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
1 - OIL PAN RETAINING BOLTS
2 - POWER STEERING LINE BRACKETS
3 - OIL PAN GASKET
4 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
5 - ENGINE BLOCK
6 - OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
7 - OIL PAN RETAINING BOLTS
8 - OIL PAN
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean oil pan and sealing surfaces. Inspect oil
pan and engine block.
(2) Install oil pan, gasket, and retaining bolts (Fig.
70).
(3) Be sure power steering line brackets are in
proper location (Fig. 70).
(4) Torque oil pan bolts to 11.8N·m.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Refill engine oil to proper level.
(7) Connect negative battery cable.
Page 95

9 - 50 ENGINE RG
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(3) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS REMOVAL).
(4) Remove timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove front engine cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER REMOVAL).
(8) Remove crankshaft sprocket (Fig. 71).
(9) Remove oil pump retaining bolts and remove
pump from engine block (Fig. 71).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove oil pump pickup tube retaining bolt
and pull pickup tube from engine block (Fig. 72).
Fig. 71 OIL PUMPAND VACUUM PUMP
1 - VACUUM PUMP
2 - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
3 - OIL PUMP
4 - ENGINE BLOCK
5 - CRANKSHAFT
Fig. 72 OIL PUMP PICKUP TUBE ASSEMBLY
1 - BALANCE SHAFT
2 - OIL JET RETAINING BOLT
3 - OIL JET
4 - ENGINE BLOCK
5 - CRANKSHAFT
6 - O- RING(S)
7 - BALANCE SHAFT RETAINING BOLTS
8 - OIL DIPSTICK TUBE RETAINER
9 - RUBBER BUSHING
10 - RETAINING BOLT
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate oil pump rotor with engine oil.
(2) Install oil pump in bore in engine block (Fig.
71).
(3) Install oil pump retaining bolts (Fig. 71).
Torque bolts to 10.8N·m.
(4) Install crankshaft sprocket (Fig. 71). Torque
bolts to 10.8N·m.
(5) Install front engine cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/ENGINE COVER INSTALLATION).
(6) Install timing belt inner cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
Page 96

RG ENGINE 9-51
OIL PUMP (Continued)
(7) Install timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install timing belt outer cover (Refer to 9 ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install power steering belt (Refer to 7 COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS INSTALLATION).
(11) Connect negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate o-ring on oil pump pickup tube with
engine oil.
(2) Install pickup tube in engine block and install
retaining bolt (Fig. 72). Torque bolt to 32.4N·m.
(3) Install oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(4) Refill engine oil to proper level.
(5) Connect negative battery cable.
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/
SWITCH
1 - SUSPENSION CRADLE
2 - ENGINE BLOCK
3 - OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
4 - VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
5 - TRANSMISSION
Fig. 73 VIEW-REAR ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
The oil pressure switch is located on the right side
of the engine block. The switch screws into the
engines main oil gallery (Fig. 73).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect oil pressure switch electrical connector (Fig. 73).
(4) Remove oil pressure switch from engine block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply Mopar威 Thread Sealant to the switch
threads.
(2) Install oil pressure switch in engine block.
(3) Connect oil pressure switch electrical connector
(Fig. 73).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Start engine and check for leaks.
(6) Check and adjust oil level as necessary.
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The oil pressure relief valve mounts in the front of
the engine block and is used to control oil flow
through the engines lubrication system (Fig. 74).
Fig. 74 OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
1 - O-RING
2 - OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE CAP
3 - OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE SPRING
4 - OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE PLUNGER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove engine oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
Page 97

9 - 52 ENGINE RG
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE (Continued)
(2) Using special tool VM.1054, remove oil pres-
sure relief valve from engine block (Fig. 75).
Fig. 76 OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
INSTALLATION
1 - VM.1059
2 - OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
4 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 75 OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE REMOVAL
1 - VM.1054
2 - OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
4 - OIL PUMP
INSTALLATION
(1) Thoroughly clean all components and relief
valve pocket in cylinder block.
(2) Lubricate all oil pressure relief valve compo-
nents with engine oil.
(3) Install oil pressure relief valve plunger, spring,
and cap.
Using special tool VM.1059, push oil pressure
(4)
relief valve cap in untill flush with engine block (Fig. 76).
(5) Install oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
OIL COOLER & LINES
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(Fig. 77).
Fig. 77 OIL FILTER
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - OIL COOLER
Page 98

RG ENGINE 9-53
OIL COOLER & LINES (Continued)
(4) Disconnect coolant hoses at cooler (Fig. 78).
(5) Remove oil cooler retaining bolt at engine block
(Fig. 78).
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The oil filter is a high quality, full flow, disposable
style. (Fig. 79).
REMOVAL
NOTE: Capture any residual oil spill while removing
filter and wipe any oil that comes in contact with
other components
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Twist oil filter counterclockwise with a suitable
oil filter wrench to remove.
Fig. 78 WATER PUMP AND OIL COOLER
ASSEMBLIES
1 - WATER PUMP HOUSING STUDS
2-WATERPUMP
3 - RETAINING NUTS
4 - OIL COOLER RETAINING STUD
5 - OIL COOLER TO ENGINE BLOCK RETAINING BOLT
6 - OIL COOLER COOLANT HOSE
7 - ENGINE BLOCK
(6) Remove oil cooler retaining stud and remove oil
cooler from engine block (Fig. 78).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean oil cooler and engine block sealing sur-
faces.
(2) Install oil cooler, retaining bolt, and stud (Fig.
78). Torque retaining bolt to 47.1N·m and stud to
50N·m.
(3) Connect coolant hoses at cooler (Fig. 78).
(4) Install oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Start engine and check for leaks.
(8) Check and adjust oil level as necessary.
Fig. 79 OIL FILTER
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - OIL COOLER
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubracate oil filter seal with clean engine oil.
(2) Turning clockwise, seat the oil filter then
tighten the oil filter 1/2 turn more (Fig. 79).
(3) Lower vehicle from hoist.
(4) Start engine and check for leaks.
(5) Check and adjust oil level as necessary.
Page 99

9 - 54 ENGINE RG
OIL JET
DESCRIPTION
There are four oil jets installed in the engine block.
These oil jets are used to cool and lubricate the piston assemblies (Fig. 80).
Fig. 80 OIL JET ASSEMBLY
1 - RETAINING BOLT
2 - OIL JET
3 - O-RING
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Use caution when removing and installing oil jets. Damage to oil jet nozzle could cause
severe engine damage.
NOTE: Remove oil jets Before removing pistons,
crankshaft or liners
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(4) Using special tool VM.1060 to hold oil jet.
Remove oil jet retaining bolt and remove oil jet from
engine block (Fig. 81).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Use caution when removing and installaing oil jets. Damage to oil jet nozzle could cause
severe engine damage.
NOTE: Carefully install the oil jets After assembling
the engine liners, crankshaft and pistons.
(1) Lubricate o-ring on oil jet.
(2) Using special tool VM.1060, install oil jet in
engine block (Fig. 81).
(3) Install oil jet retaining bolt. Torque bolt to
10.8N·m.
Fig. 81 OIL JET REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
1 - SPECIAL TOOL VM.1060
2 - OIL JET
3 - CONNECTING ROD
4 - CRANKSHAFT
(4) Install oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(5) Refill engine oil to proper level.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER(S) - DESCRIPTION)
REMOVAL
(1) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYL-
INDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
INSTALLATION
(1) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYL-
INDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
Page 100

RG ENGINE 9-55
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - LOCKING ENGINE
90° AFTER TDC
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove starter motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Crankshaft hub retaining bolt is left hand
thread.
(3) Rotate engine untill notch in hub is in the following position (Fig. 82).
Fig. 82 CRANKSHAFT HUB ALIGNMENT
1 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
2 - CRANKSHAFT HUB NOTCH
3 - VIBRATION DAMPER/CRANKSHAFT PULLEY TO
CRANKSHAFT HUB BOLTS
4 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
(4) Special tool VM.1068 can be install in engine
block as shown at this time (Fig. 83). This will lock
the engine at 90° after TDC.
(5) Remove front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE REMOVAL).
(6) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE REMOVAL).
(7) Remove plug in cylinder head cover/intake
manifold and insert VM.1053 to lock exhaust camshaft in position (Fig. 84).
(8) Remove generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
Fig. 83 90 DEGREES AFTER TDC ALIGNMENT PIN
LOCATION
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - VM.1051 TDC PIN OR VM.1068 90 DEGREES ATDC PIN
3 - FLYWHEEL
Fig. 84 EXHAUST CAMSHAFT LOCKING PIN
VM.1053
1 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD HEAT SHIELD
2 - EXHAUST CAMSHAFT LOCKING PIN VM.1053
3 - COOLANT TUBE FROM THERMOSTAT HOUSING TO UPPER
RADIATOR HOSE
4 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER/INTAKE MANIFOLD
 Loading...
Loading...