Chrontel Inc CH7003B-V, CH7003B-T Datasheet
CHRONTEL
Digital PC to TV Encoder
CH7003B
Features
• Input data path handles 8, 12, or 16-bit words in
multiplexed or non-multiplexed form
• Decodes pixel data in YCrCb (CCIR601 or 656) or
RGB (15, 16 or 24-bit) formats
• Supports 640x480, 640x400, 720x400, 800x600 and
512x384 input resolutions
• Adjustable underscan for most modes† ¥
• High quality 4-line flicker filtering †
• High resolution on-chip PLL
• Fully programmable through I2C port
• Supports NTSC, NTSC-EIA (Japan), and PAL (B, D,
G, H, I, M and N) TV formats
• Provides Composite, S-Video and SCART outputs
• CCIR624-3 compliant (see exceptions)
• Auto-detection of TV presence
• Sub-carrier genlock and dot crawl control
• Programmable power management
• 9-bit video DAC outputs
• Complete Windows and DOS driver software
• Offered in a 44-pin PLCC, 44-pin TQFP
† Patent number 5,781,241
General Description
Chrontel’s CH7003 digital PC to TV encoder is a standalone integrated circuit which provides a PC 99 compliant
solution for TV output. It provides a universal digital input
port to accept a pixel data stream from a compatible VGA
controller (or equivalent) and converts this directly into
NTSC or PAL TV format, with simultaneous composite
and S-Video outputs.
This circuit integrates a digital NTSC/PAL encoder with 9bit DAC interface, and new adaptive flicker filter, and high
accuracy low-jitter phase locked loop to create outstanding
quality video. Through its TrueScaleTM scaling and deflickering engine, the CH7003 supports full vertical and
horizontal underscan capability and operates in 5 different
resolutions including 640x480 and 800x600.
A new universal digital interface along with full
programmability make the CH7003 ideal for system-level
PC solutions. All features are software programmable
through a standard I2C port, to enable a complete PC
solution using a TV as the primary display.
¥ Patent number 5,914,753
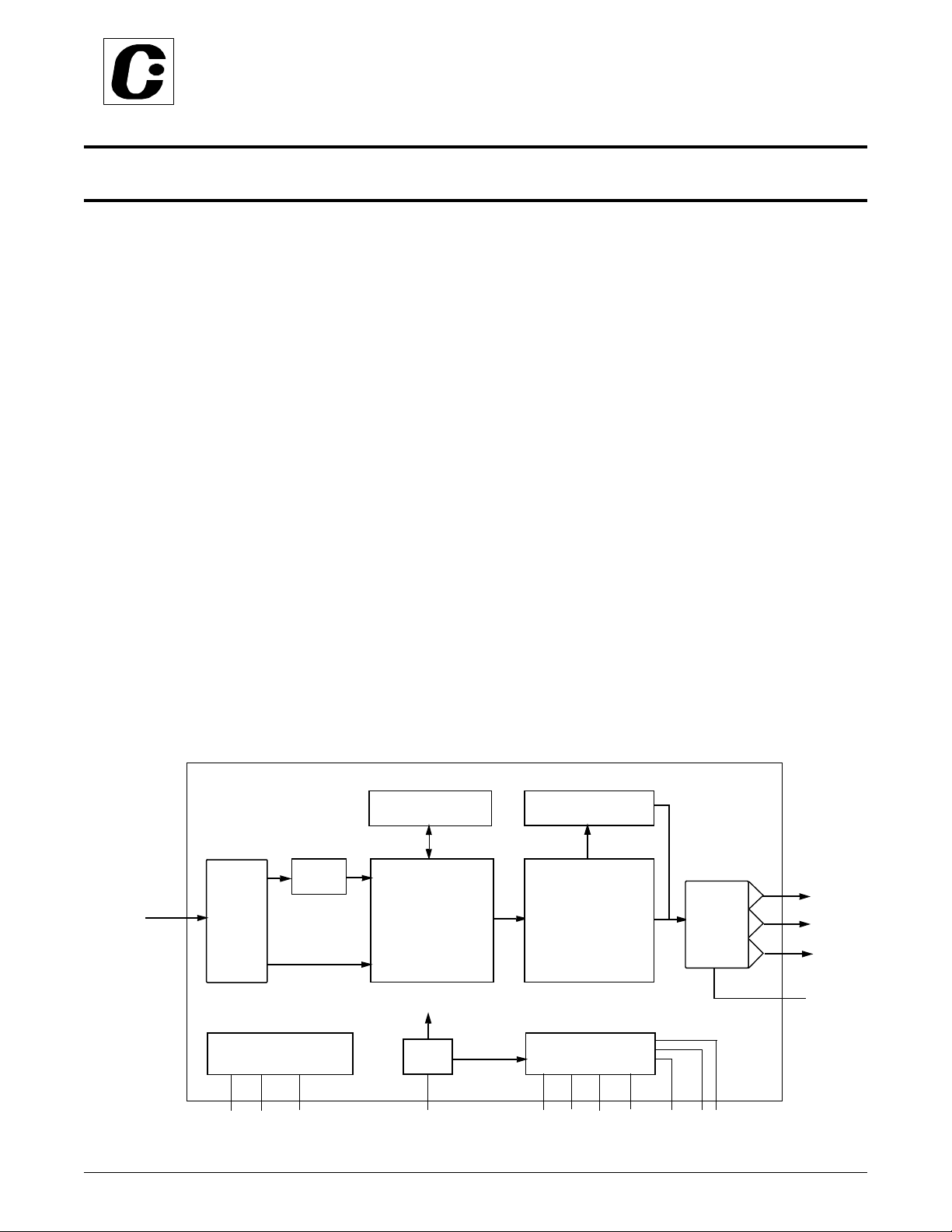
LINE
MEMORY
RGB-YUV
D[15:0
PIXEL DATA
]
CONVERTER
DIGITAL
INPUT
INTERFACE
I2C REGISTER & CONTROL
BLOCK
SC SD ADDR
TRUE SCALE
SCALING & DEFLICKERING
ENGINE
SYSTEM CLOCK
PLL
XCLK
Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 1
YUV-RGB CONVERTER
NTSC/PAL
ENCODER
& FILTERS
TIMING & SYNC GENERATOR
V
XI XO/FIN
H
CSYNC
P-OUT
TRIPLE
DAC
BCO
Y/R
C/G
CVBS/G
RSET
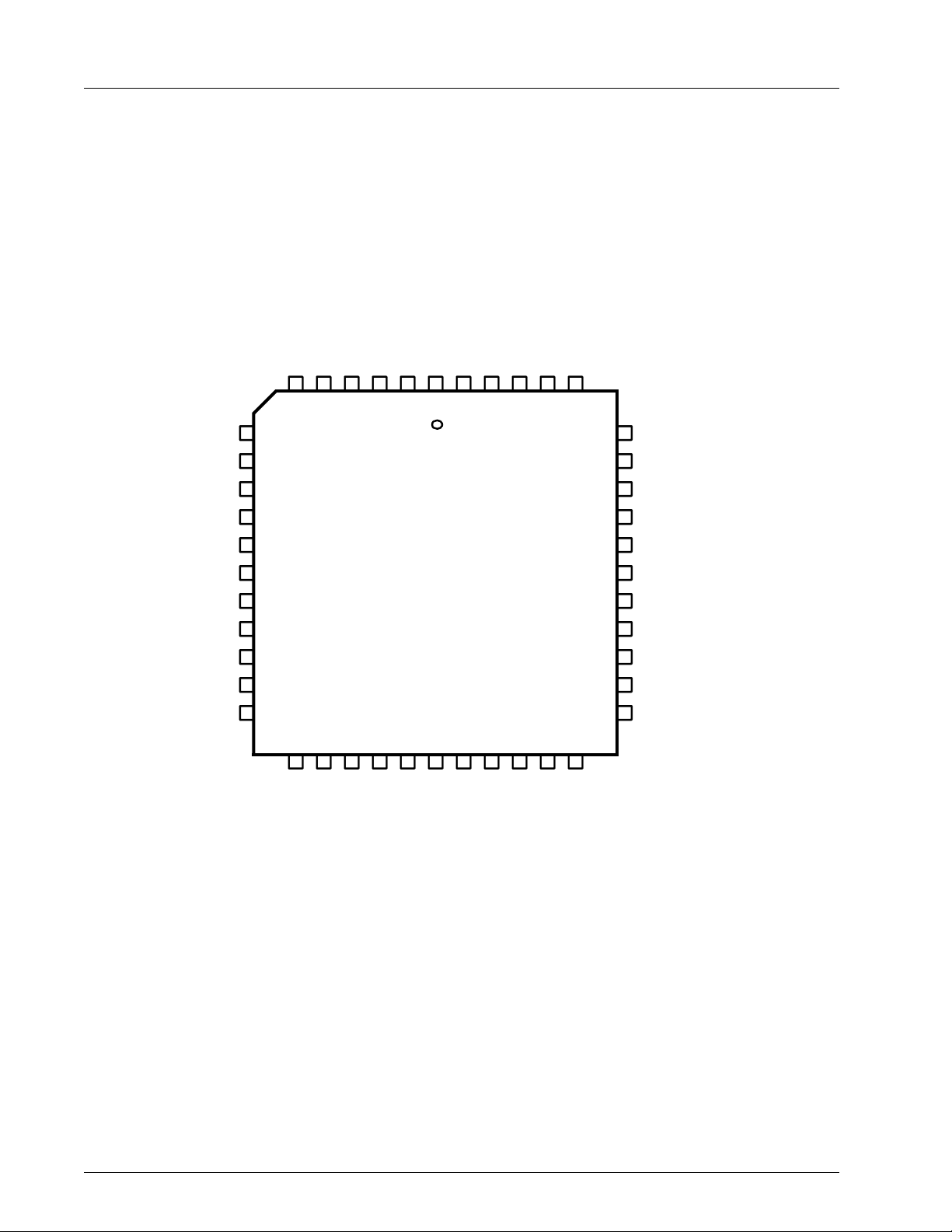
CHRONTEL CH7003B
D[2]
D[3]
D[1]
6
5
7
V
H
XCLK
DVDD
D[0]
4
3
2
1
P-OUT
DGND
BCO
AGND
44
43
42
41
40
39
XO/FIN
D[4]
D[5]
D[6]
DVDD
8
9
10
11
38
37
36
35
XI
AVDD
DVDD
ADDR
CHRONTEL
D[7] DGND
D[8]
D[9]
D[10]
D[11]
12
13
14
15
16
17
34
CH7003
18
19
20
21
22
D[12]
D[13]
D[14]
D[15]
DVDD
24
23
CSYNC
25
26
27
28
Y
C
GND
DGND
CVBS
33
32
31
30
29
SC
SDDGND]
VDD
RSET
GND
Figure 2: 44-pin PLCC
2 201-0000-023 Rev.4.1, 8/2/99
CHRONTEL CH7003B
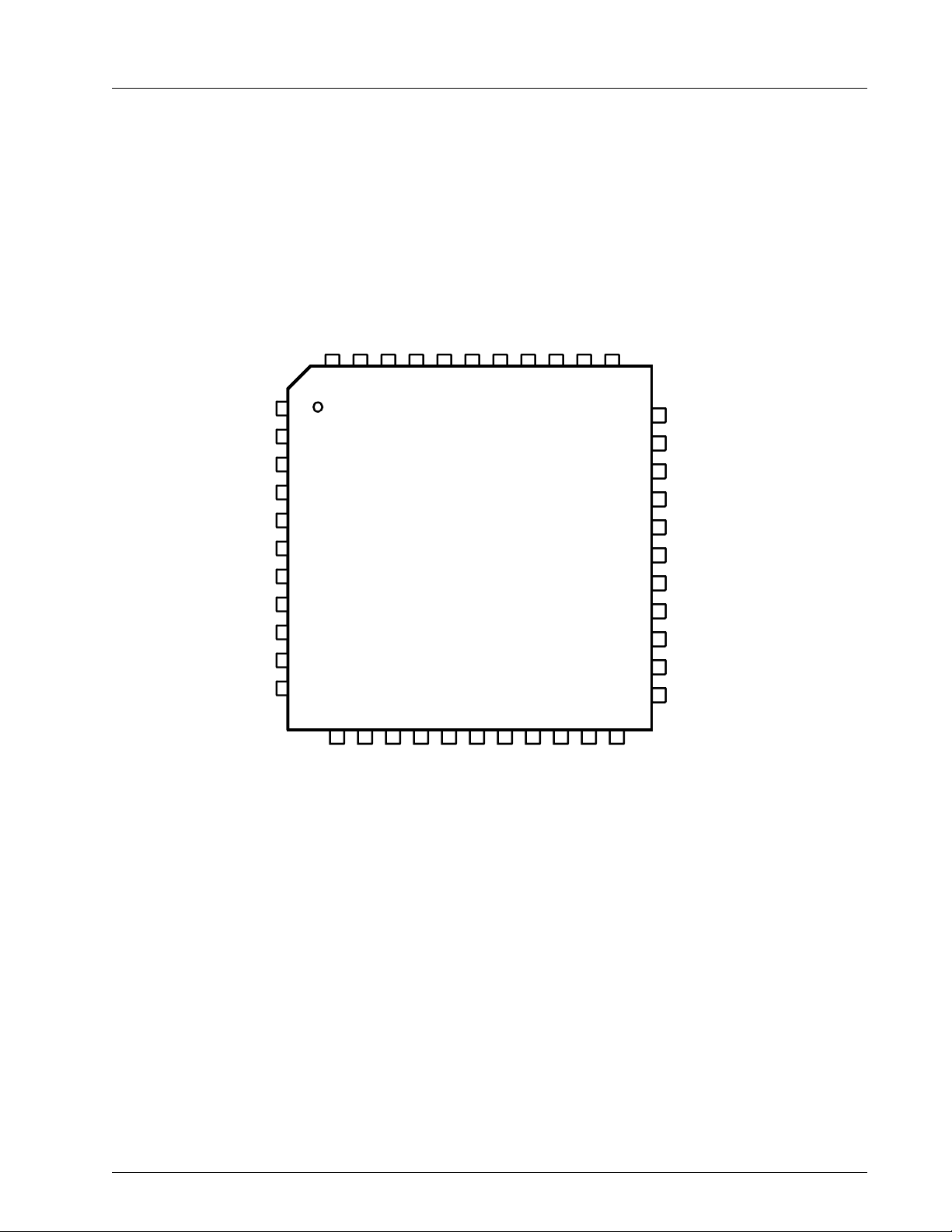
Figure 3: 44-pin TQFP
D[2]
D[3]
D[3]
D[4]
D[4]
D[5]
D[5]
D[6]
D[6]
DVDD
DVDD
D[7]
D[7]
D[8]
D[8]
DGND]
DGND]
D[9]
D[9]
D[10]
D[10]
D[11]
D[11]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
D[1]
44
43
12
13
V
H
XCLK
DVDD
D[0]
42
41
40
39
P-OUT
38
37
CHRONTEL
CH7003
14
15
16
18
17
DGND
BCO
AGND
36
35
34
33
XO/FIN
XO/FIN
32
XI
XI
AVDD
31
AVDD
DVDD
30
DVDD
ADDR
29
ADDR
DGND
28
DGND
SC
27
SC
SD
26
SD
VDD
25
VDD
RSET
24
RSET
GND
23
GND
19
20
21
22
Y
C
D[12]
D[13]
D[14]
D[15]
DVDD
CSYNC
GND
DGND
CVBS
Figure 3: 44-PIN TQFP
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 3
CHRONTEL CH7003B
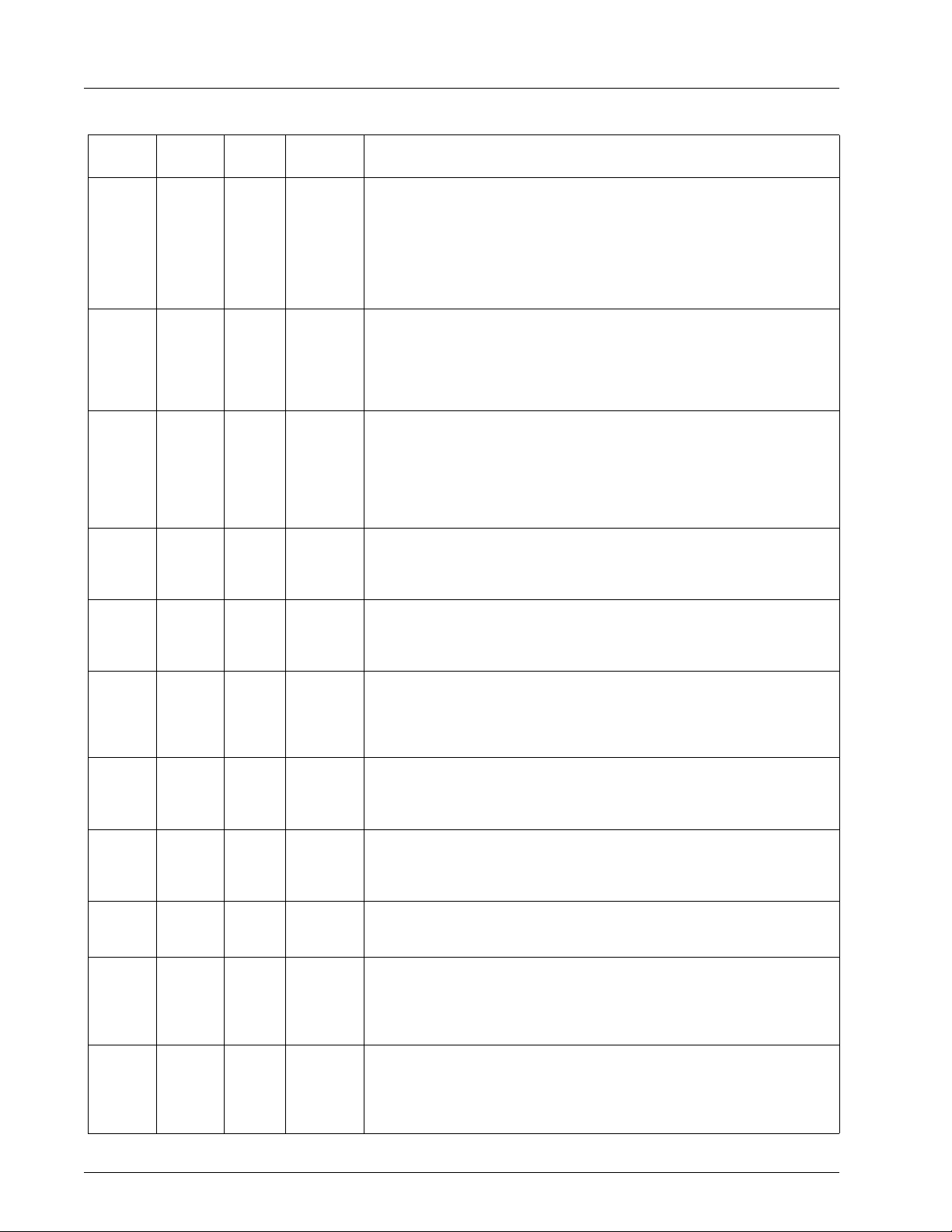
Table 1. Pin Description
44-Pin
PLLC
21-15,
13-12,
10-4
43 37 Out P-OUT
1 39 In XCLK
3 41 In/Out V
2 40 In/Out H
41 35 Out BCO
38 32 In XI
39 33 In XO/FIN
30 24 In RSET
28 22 Out Y/R
27 21 Out C/G
44-Pin
TQFP
15,14,
13,12,
11,10,
9,7,6,4,
3,2,
1,44,43,
42
Type Symbol Description
In D15-D0
Digital Pixel Inputs
These pins accept digital pixel data streams with either 8, 12, or 16-bit
multiplexed or 16-bit non-multiplexed formats, determined by the input
mode setting (see Registers and Programming section). Inputs D0 - D7 are
used when operating in 8-bit multiplexed mode. Inputs D0 - D11 are used
when operating in 12-bit mode. Inputs D0 - D15 are used when operating
in 16-bit mode. The data structure and timing sequence for each mode is
described in the section on Digital Video Interface.
Pixel Clock Output
The CH7003, operating in master mode, provides a pixel data clocking
signal to the VGA controller. This pin provides the pixel clock output signal
(adjustable as 1X, 2X or 3X) to the VGA controller (see the section on
Digital Video Interface and Registers and Programming for more details).
The capacitive loading on this pin should be kept to a minimum.
Pixel Clock Input
To operate in a pure master mode, the P-OUT signal should be connected
to the XCLK input pin. To operate in a pseudo-master mode, the P-OUT
clock is used as a reference frequency, and a signal locked to this output (at
1X, 1/2X, or 1/3X the P-OUT frequency) is input to the XCLK pin. To operate
in slave mode, the CH7003 accepts an external pixel clock input at this pin.
The capacitive loading on this pin should be kept to a minimum.
Vertical Sync Input/Output
This pin accepts the vertical sync signal from the VGA controller, or outputs
a vertical sync to the VGA controller. The capacitive loading on this pin
should kept to a minimum.
Horizontal Sync Input/Output
This pin accepts the horizontal sync from the VGA controller, or outputs a
horizontal sync to the VGA controller. The capacitive loading on this pin
should be kept to a minimum.
Buffered Clock Output
This pin provides a buffered output of the 14.31818 MHz crystal input
frequency for other devices and remains active at all times (including
power-down). The output can also be selected to be other frequencies (see
Registers and Programming).
Crystal Input
A parallel resonance 14.31818 MHz (± 50 ppm) crystal should be attached
between XI and XO/FIN. However, if an external CMOS clock is attached to
XO/FIN, XI should be connected to ground.
Crystal Output or External Fref
A 14.31818 MHz (± 50 ppm) crystal may be attached between XO/FIN and
XI. An external CMOS compatible clock can be connected to XO/FIN as an
alternative.
Reference Resistor
A 360 Ω resistor with short and wide traces should be attached between
RSET and ground. No other connections should be made to this pin.
Luminance Output
A 75 Ω termination resistor with short traces should be attached between Y
and ground for optimum performance. In normal operating modes other
than SCART, this pin outputs the luma video signal. In SCART mode, this
pin outputs the red signal.
Chrominance Output
A 75 Ω termination resistor with short traces should be attached between C
and ground for optimum performance. In normal operating modes other
than SCART, this pin outputs the chroma video signal. In SCART mode,
this pin outputs the green signal.
4 201-0000-023 Rev.4.1, 8/2/99

CHRONTEL CH7003B
Table 1. Pin Description (continued)
44-Pin
PLLC
26 20 Out CVBS/B
23 17 Out CSYNC
32 26 In/Out SD
33 27 In SC
35 29 In ADDR
40 34 Power AGND
37 31 Power AVDD
31 25 Power VDD
29, 25 19,23 Power GND
44, 36,
22, 11
42, 34,
24, 14
N/A N/A Out R
N/A N/A Out G
N/A N/A Out B
44-Pin
TQFP
5,16,
30,38
8, 18,
28, 36
Type Symbol Description
Power DVDD
Power DGND
Composite Video Output
A 75 Ω termination resistor with short traces should be attached between
CVBS and ground for optimum performance. In normal operating modes
other than SCART, this pin outputs the composite video signal. In SCART
mode, this pin outputs the blue signal.
Composite Sync Output
A 75 Ω termination resistor with short traces should be attached between
CSYNC and ground for optimum performance. In SCART mode, this pin
outputs the composite sync signal.
Serial Data (External pull-up required)
This pin functins as SD, the serial data pin of the I2C interface port (see the
I 2C Port Operation section for details).
Serial Clock (Internal pull-up)
This pin functions as the serial clock pin of the I2C interface port (see the
I 2C Port Operation section for details).
I2C Address Select (Internal pull-up)
This pin is the I2C Address Select, which corresponds to bits 1 and 0 of the
I2C device address (see the I 2C Port Operation section for details), creating
an address selection as follows:
ADDR I2C Address Selected
1 1110101 = 75H = 117
0 1110110 = 76H = 118
Analog ground
These pins provide the ground reference for the analog section of CH7003,
and MUST be connected to the system ground, to prevent latchup.
Analog Supply Voltage
These pins supply the 5V power to the analog section of the CH7003.
DAC Power Supply
These pins supply the 5V power to CH7003’s internal DACs.
DAC Ground
These pins provide the ground reference for CH7003’s internal DACs.
Digital Supply Voltage
These pins supply the 3.3V power to the digital section of CH7003.
Digital Ground
These pins provide the ground reference for the digital section of CH7003,
and MUST be connected to the system ground to prevent latchup.
R (Red) Component Output
This pin provides the analog Red component of the digital RGB input in the
RGB Pass-Through mode.
G (Green) Component Output
This pin provides the analog Green component of the digital RGB input in
the RGB Pass-Through mode.
B (Blue) Component Output
This pin provides the analog Blue component of the digital RGB input in the
RGB Pass-Though mode.
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 5

CHRONTEL CH7003B
Digital Video Interface
The CH7003 digital video interface provides a flexible digital interface between a computer graphics controller and
the TV encoder IC, forming the ideal quality/cost configuration for performing the TV-output function. This digital
interface consists of up to 16 data signals and 4 control signals, all of which are subject to programmable control
through the CH7003 register set. This interface can be configured as 8, 12 or 16-bit inputs operating in either
multiplexed mode or 16-bit input operation in de-multiplexed mode. It will also accept either YCrCb or RGB (15,
16 or 24-bit) data formats. A summary of the data format modes is as follows:
Table 2. Input Data Formats
Bus Width Transfer Mode Color Space and Depth Format Reference
16-bit Non-multiplexed RGB 16-bit 5-6-5 each word
15-bit Non-multiplexed RGB 15-bit 5-5-5 each word
16-bit Non-multiplexed YCrCb (24-bit) CbY0,CrY1...(CCIR656 style)
8-bit 2X-multiplexed RGB 15-bit 5-5-5 over two bytes
8-bit 2X-multiplexed RGB 16-bit 5-6-5 over two bytes
8-bit 3X-multiplexed RGB 24-bit 8-8-8 over three bytes
8-bit 2X-multiplexed YCrCb (24-bit) Cb,Y0,Cr,Y1,(CCIR656 style)
12-bit 2X-multiplexed RGB 24 8-8-8 over two words - ‘C’ version
12-bit 2X-multiplexed RGB 24 8-8-8 over two words - ‘I’ version
16-bit 2X-multiplexed RGB 24 (32) 8-8,8X over two words
The clock and timing signals used to latch and process the incoming pixel data is dependent upon the clock mode.
The CH7003 can operate in either master (the CH7003 generates a pixel frequency which is either returned as a
phase-aligned pixel clock or used directly to latch data), or slave mode (the graphics chip generates the pixel clock).
The pixel clock frequency will change depending upon the active image size (e.g., 640x480 or 800x600), the desired
ouput format (NTSC or PAL), and the amount of scaling desired. The pixel clock may be requested to be 1X, 2X or
3X the pixel data rate (subject to a 100 MHz frequency limitation). In the case of a 1X pixel clock the CH7003 will
automatically use both clock edges if a multiplexed data format is selected.
Sync Signals: Horizontal and vertical sync signals will normally be supplied by the VGA controller, but may be
selected to be generated by the CH7003. In the case of CCIR656 style input, embedded sync may also be used. In
each case, the horizontal timing signal (horizontal sync) must be derived from the pixel clock, with the period set to
exactly 8 times (9 times for 720x400 modes) the pixel clock period, times an integer value. Each line to be set, is set
up by the leading edge of Horizontal sync. The vertical timing signal must be able to be set to any integer number of
lines between 420 and 836.
Master Clock Mode: The CH7003 generates a clock signal (output at the P-OUT pin) which will be used by the
VGA controller as a frequency reference. The VGA controller will then generate a clock signal which will be input
via the XCLK input. This incoming signal will be used to latch (and de-multiplex, if required) incoming data. The
XCLK input clock rate must match the input data rate, and the P-OUT clock can be requested to be 1X, 2X or 3X
the pixel data rate. As an alternative, the P-OUT clock signal can also be used as the input clock signal (connected
directly to the XCLK input) to latch the incoming data. If this mode is used, the incoming data must meet setup and
hold times with respect to the XCLK input (with the only internal adjustment being XCLK polarity).
Slave Clock Mode: The VGA controller will generate a clock which will be input to the XCLK pin (no clock
signal will be output on the P-OUT pin). This signal must match the input data rate, must occur at 1X, 2X or 3X the
pixel data rate, and will be used to latch (and de-multiplex if required) incoming data. Also, the graphics IC
transmits back to the TV encoder the horizontal and vertical timing signals, and pixel data, each of which must meet
the specified setup and hold times with respect to the pixel clock.
Pixel Data: Active pixel data will be expected after a programmable number pixels times the multiplex rate after
the leading edge of Horizontal Sync. In other words, specifying the horizontal back porch value (as a pixel count),
plus horizontal sync width, will determine when the chip will begin to sample pixels.
6 201-0000-023 Rev.4.1, 8/2/99
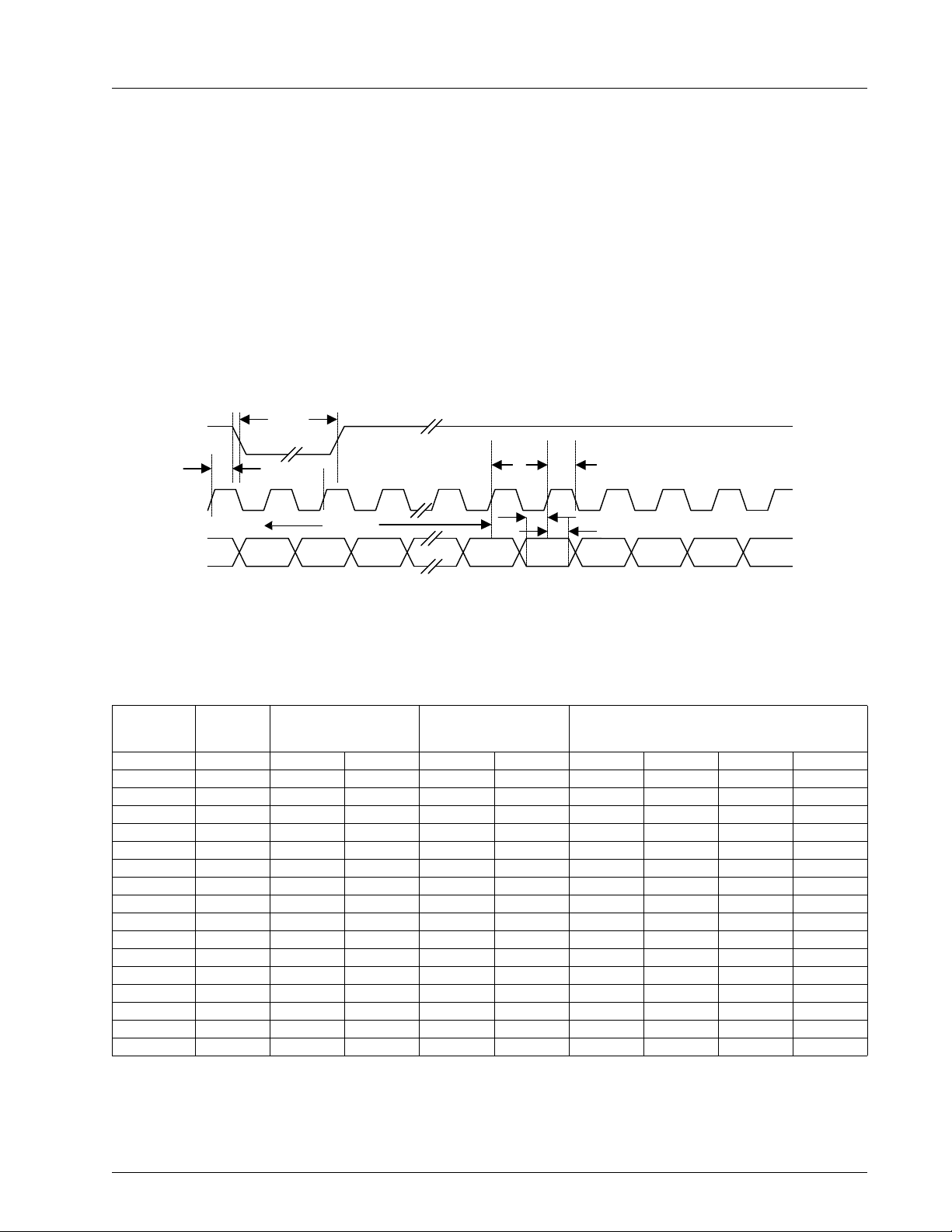
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Digital Video Interface (continued)
Non-multiplexed Mode
In the 15/16-bit mode shown in Figure4, the pixel data bus represents a 15/16-bit non-multiplexed data stream,
which contains either RGB or YCrCb formatted data. When operating in RGB mode, each 15/16-bit Pn value will
contain a complete pixel encoded in either 5-6-5 or 5-5-5 format. When operating in YCrCb mode, each 16-bit Pn
word will contain an 8-bit Y (luminance) value on the upper 8 bits, and an 8-bit C (color difference) value on the
lower 8 bits. The color difference will be transmitted at half the data rate of the luminance data, with the sequence
being set as Cb followed by Cr. The Cb and Cr data will be co-sited with the Y value transmitted with the Cb value,
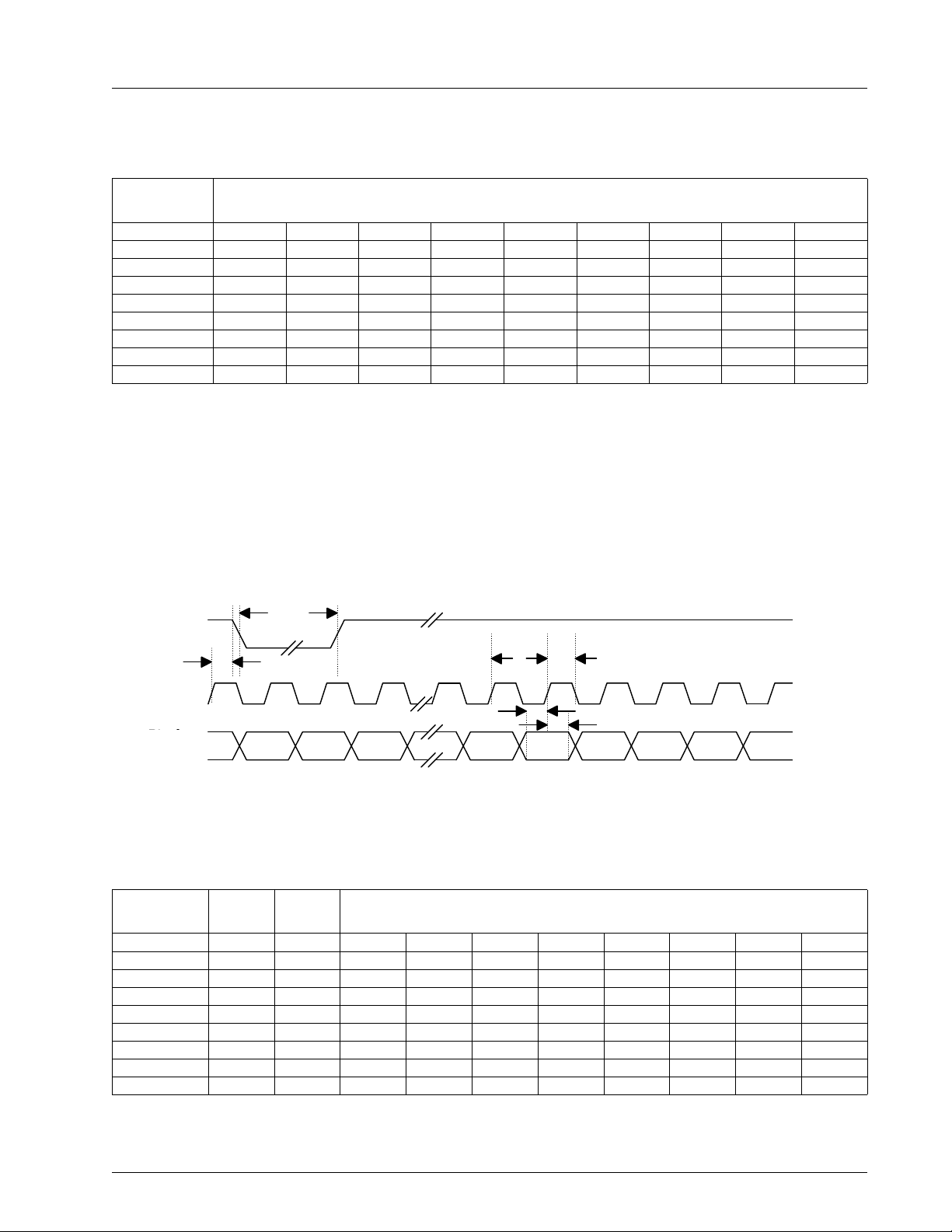
with the data sequence described in Table3. The first active pixel is SAV pixels after the leading edge of horizontal
sync, where SAV is a bus-controlled register.
t
HSW
HSYNC
t
t
PH 1
PH
t
t
SP1
SP
t
t
HP
HP1
P2
P3 P4
P5
POut/
XCLK
Pixel
Data
t
t
HD
AVR
SAV
t
P
P 1
P0a P0b P1a P1b P2a P2b
P0
P1
Figure 4: Non-multiplexed Data Transfers
Table 3. 15/16-bit Non-multiplexed Data Formats
IDF#
Format
Pixel# P0 P1 P0 P1 P0 P1 P2 P3
Bus Data D[15] R0[4] R1[4] x x Y0[7] Y1[7] Y2[7] Y3[7]
D[14] R0[3] R1[3] R2[4] R3[4] Y0[6] Y1[6] Y2[6] Y3[6]
D[13] R0[2] R1[2] R2[3] R3[3] Y0[5] Y1[5] Y2[5] Y3[5]
D[12] R0[1] R1[1] R2[2] R3[2] Y0[4] Y1[4] Y2[4] Y3[4]
D[11] R0[0] R1[0] R2[1] R3[1] Y0[3] Y1[3] Y2[3] Y3[3]
D[10] G0[5] G1[5] R2[0] R3[0] Y0[2] Y1[2] Y2[2] Y3[2]
D[9] G0[4] G1[4] G2[4] G3[4] Y0[1] Y1[1] Y2[1] Y3[1]
D[8] G0[3] G1[3] G2[3] G3[3] Y0[0] Y1[0] Y2[0] Y3[0]
D[7] G0[2] G1[2] G2[2] G3[2] Cb0[7] Cr0[7] Cb2[7] Cr2[7]
D[6] G0[1] G1[1] G2[1] G3[1] Cb0[6] Cr0[6] Cb2[6] Cr2[6]
D[5] G0[0] G1[0] G2[0] G3[0] Cb0[5] Cr0[5] Cb2[5] Cr2[5]
D[4] B0[4] B1[4] B2[4] B3[4] Cb0[4] Cr0[4] Cb2[4] Cr2[4]
D[3] B0[3] B1[3] B2[3] B3[3] Cb0[3] Cr0[3] Cb2[3] Cr2[3]
D[2] B0[2] B1[2] B2[2] B3[2] Cb0[2] Cr0[2] Cb2[2] Cr2[2]
D[1] B0[1] B1[1] B2[1] B3[1] Cb0[1] Cr0[1] Cb2[1] Cr2[1]
D[0] B0[0] B1[0] B2[0] B3[0] Cb0[0] Cr0[0] Cb2[0] Cr2[0]
0
RGB 5-6-5
3
RGB 5-5-5
1
YCrCb (16-bit)
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 7
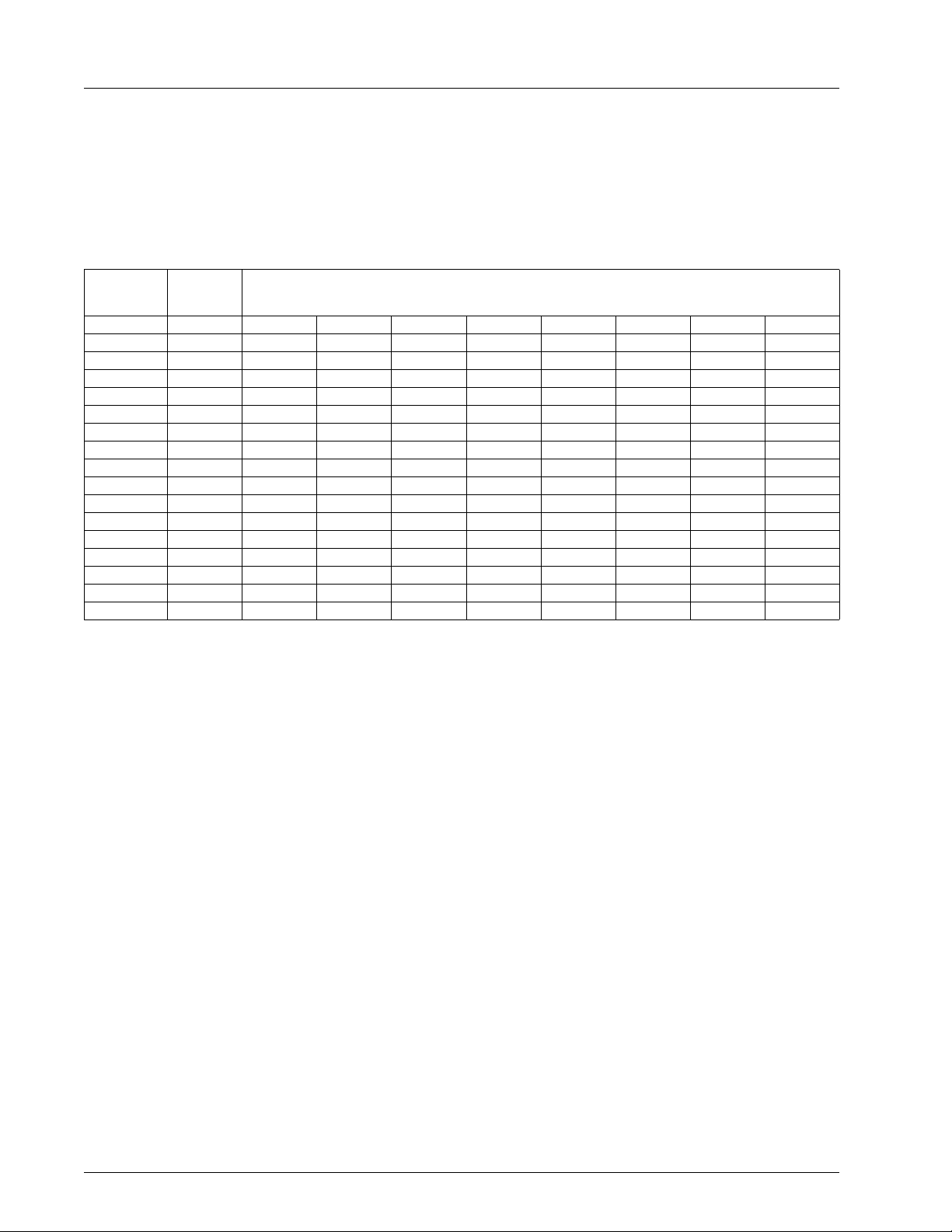
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Digital Video Interface (continued)
When IDF = 1, (YCrCb 16-bit mode), H and V sync signals can be embedded into the data stream. In this mode, the
embedded sync will be similar to the CCIR656 convention (not identical, since that convention is for 8-bit data
streams), and the first byte of the ‘video timing reference code’ will be assumed to occur when a Cb sample would
occur – if the video stream was continuous. This is delineated in Table4 below.
Table 4. YCrCb Non-multiplexed Mode with Embedded Syncs
IDF#
Format
Pixel# P0 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7
Bus Data D[15] 0 S[7] Y0[7] Y1[7] Y2[7] Y3[7] Y4[7] Y5[7]
D[14] 0 S[6] Y0[6] Y1[6] Y2[6] Y3[6] Y4[6] Y5[6]
D[13] 0 S[5] Y0[5] Y1[5] Y2[5] Y3[5] Y4[5] Y5[5]
D[12] 0 S[4] Y0[4] Y1[4] Y2[4] Y3[4] Y4[4] Y5[4]
D[11] 0 S[3] Y0[3] Y1[3] Y2[3] Y3[3] Y4[3] Y5[3]
D[10] 0 S[2] Y0[2] Y1[2] Y2[2] Y3[2] Y4[2] Y5[2]
D[9] 0 S[1] Y0[1] Y1[1] Y2[1] Y3[1] Y4[1] Y5[1]
D[8] 0 S[0] Y0[0] Y1[0] Y2[0] Y3[0] Y4[0] Y5[0]
D[7] 1 0 Cb0[7] Cr0[7] Cb2[7] Cr2[7] Cb4[7] Cr4[7]
D[6] 1 0 Cb0[6] Cr0[6] Cb2[6] Cr2[6] Cb4[6] Cr4[6]
D[5] 1 0 Cb0[5] Cr0[5] Cb2[5] Cr2[5] Cb4[5] Cr4[5]
D[4] 1 0 Cb0[4] Cr0[4] Cb2[4] Cr2[4] Cb4[4] Cr4[4]
D[3] 1 0 Cb0[3] Cr0[3] Cb2[3] Cr2[3] Cb4[3] Cr4[3]
D[2] 1 0 Cb0[2] Cr0[2] Cb2[2] Cr2[2] Cb4[2] Cr4[2]
D[1] 1 0 Cb0[1] Cr0[1] Cb2[1] Cr2[1] Cb4[1] Cr4[1]
D[0] 1 0 Cb0[0] Cr0[0] Cb2[0] Cr2[0] Cb4[0] Cr4[0]
1
YCrCb 16-bit
In this mode, the S[7..0] byte contains the following data:
S[6] = F = 1 during field 2, 0 during field 1
S[5] = V = 1 during field blanking, 0 elsewhere
S[4] = H = 1 during EAV (the synchronization reference at the end of active video)
0 during SAV (the synchronization reference at the start of active video)
Bits S[7] and S[3..0] are ignored.
Multiplexed Mode
Each rising edge (or each rising and falling edge) of the XCLK signal will latch data from the graphics chip. The
multiplexed input data formats are shown in Figure5 and 6. The Pixel Data bus represents an 8-, 12-, or 16-bit
multiplexed data stream, which contains either RGB or YCrCb formatted data. In IDF settings of 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 9,
the input data rate is 2X PCLK, and each pair of Pn values (e.g., P0a and P0b) will contain a complete pixel,
encoded as shown in the tables below. When IDF = 6, the input data rate is 3X PCLK, and each triplet of Pn values
(e.g., P0a, P0b and P0c) will contain a complete pixel, encoded as shown in the tables below. When the input is
YCrCb, the color-difference data will be transmitted at half the data rate of the luminance data, with the sequence
being set as Cb, Y, Cr, Y where Cb0,Y0,Cr0 refers to co-sited luminance and color-difference samples — and the
following Y1 byte refers to the next luminance sample, per CCIR656 standards. However, the clock frequency is
dependent upon the current mode (not 27MHz, as specified in CCIR656.)
8 201-0000-023 Rev.4.1, 8/2/99
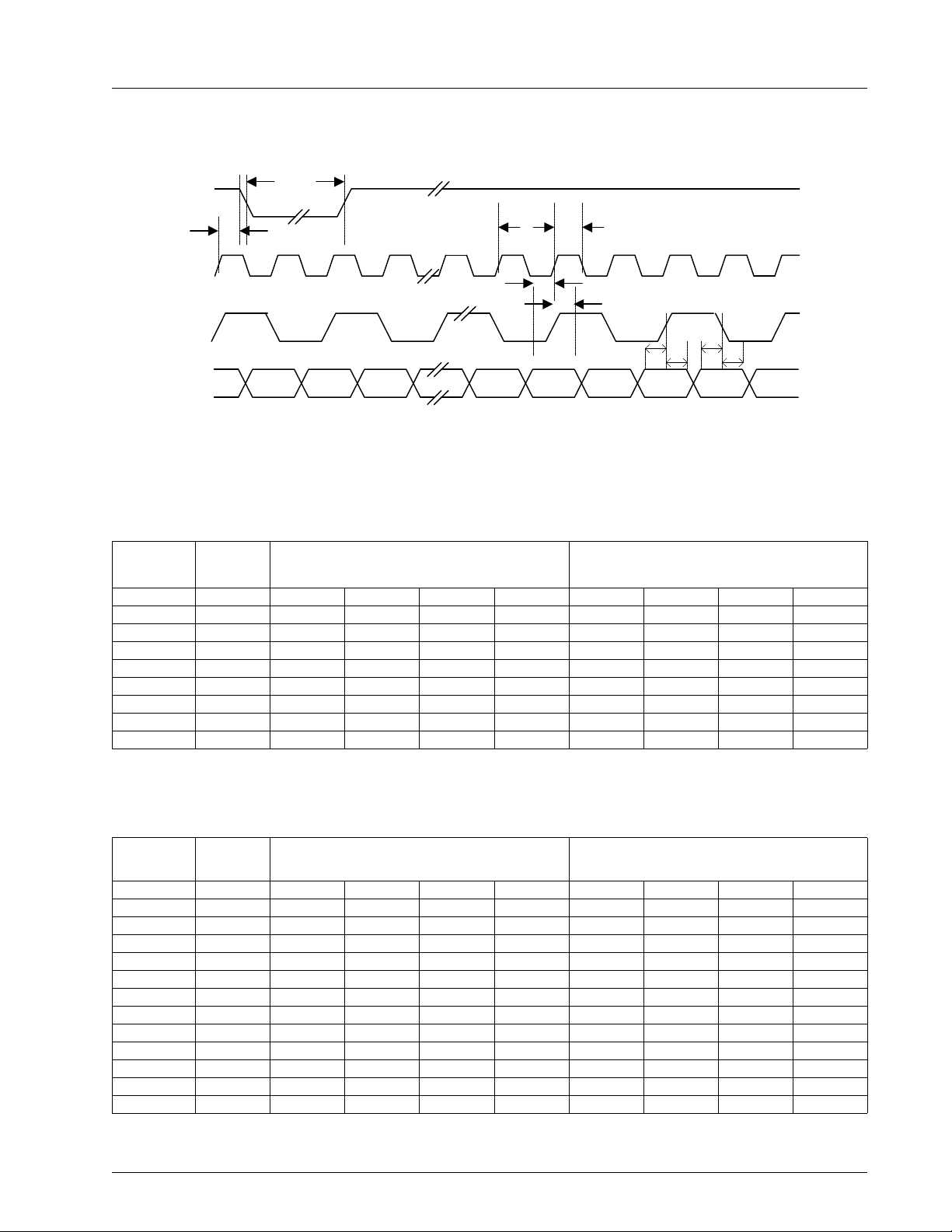
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Digital Video Interface (continued)
t
HSW
HS
t
t
HD
P2
XCLK
DEC = 0
t
SP2
XCLK
DEC = 1
D[15:0] P0a P0b P1a P1b P2a P2b
Figure 5: Multiplexed Pixel Data Transfer Mode
t
PH2
t
HP2
t
t
SP2
HP2
t
t
SP2
HP2
Table 5. RGB 8-bit Multiplexed Mode
IDF#
Format
Pixel# P0a P0b P1a P1b P0a P0b P1a P1b
Bus Data D[7] G0[2] R0[4] G1[2] R1[4] G0[2] x G1[2] x
D[6] G0[1] R0[3] G1[1] R1[3] G0[1] R0[4] G1[1] R1[4]
D[5] G0[0] R0[2] G1[0] R1[2] G0[0] R0[3] G1[0] R1[3]
D[4] B0[4] R0[1] B1[4] R1[1] B0[4] R0[2] B1[4] R1[2]
D[3] B0[3] R0[0] B1[3] R1[0] B0[3] R0[1] B1[3] R1[1]
D[2] B0[2] G0[5] B1[2] G1[5] B0[2] R0[0] B1[2] R1[0]
D[1] B0[1] G0[4] B1[1] G1[4] B0[1] G0[4] B1[1] G1[4]
D[0] B0[0] G0[3] B1[0] G1[3] B0[0] G0[3] B1[0] G1[3]
7
RGB 5-6-5
8
RGB 5-5-5
Table 6. RGB 12-bit Multiplexed Mode
IDF#
Format
12-bit RGB (12-12)
Pixel# P0a P0b P1a P1b P0a P0b P1a P1b
Bus Data D[11] G0[3] R0[7] G1[3] R1[7] G0[4] R0[7] G1[4] R1[7]
D[10] G0[2] R0[6] G1[2] R1[6] G0[3] R0[6] G1[3] R1[6]
D[9] G0[1] R0[5] G1[1] R1[5] G0[2] R0[5] G1[2] R1[5]
D[8] G0[0] R0[4] G1[0] R1[4] B0[7] R0[4] B1[7] R1[4]
D[7] B0[7] R0[3] B1[7] R1[3] B0[6] R0[3] B1[6] R1[3]
D[6] B0[6] R0[2] B1[6] R1[2] B0[5] G0[7] B1[7] G1[7]
D[5] B0[5] R0[1] B1[5] R1[1] B0[4] G0[6] B1[4] G1[6]
D[4] B0[4] R0[0] B1[4] R1[0] B0[3] G0[5] B1[3] G1[5]
D[3] B0[3] G0[7] B1[3] G1[7] G0[0] R0[2] G1[0] R1[2]
D[2] B0[2] G0[6] B1[2] G1[6] B0[2] R0[1] B1[2] R1[1]
D[1] B0[1] G0[5] B1[1] G1[5] B0[1] R0[0] B1[1] R1[0]
D[0] B0[0] G0[4] B1[0] G1[4] B0[0] G0[1] B1[0] G1[1]
4
5
12-bit RGB (12-12)
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 9
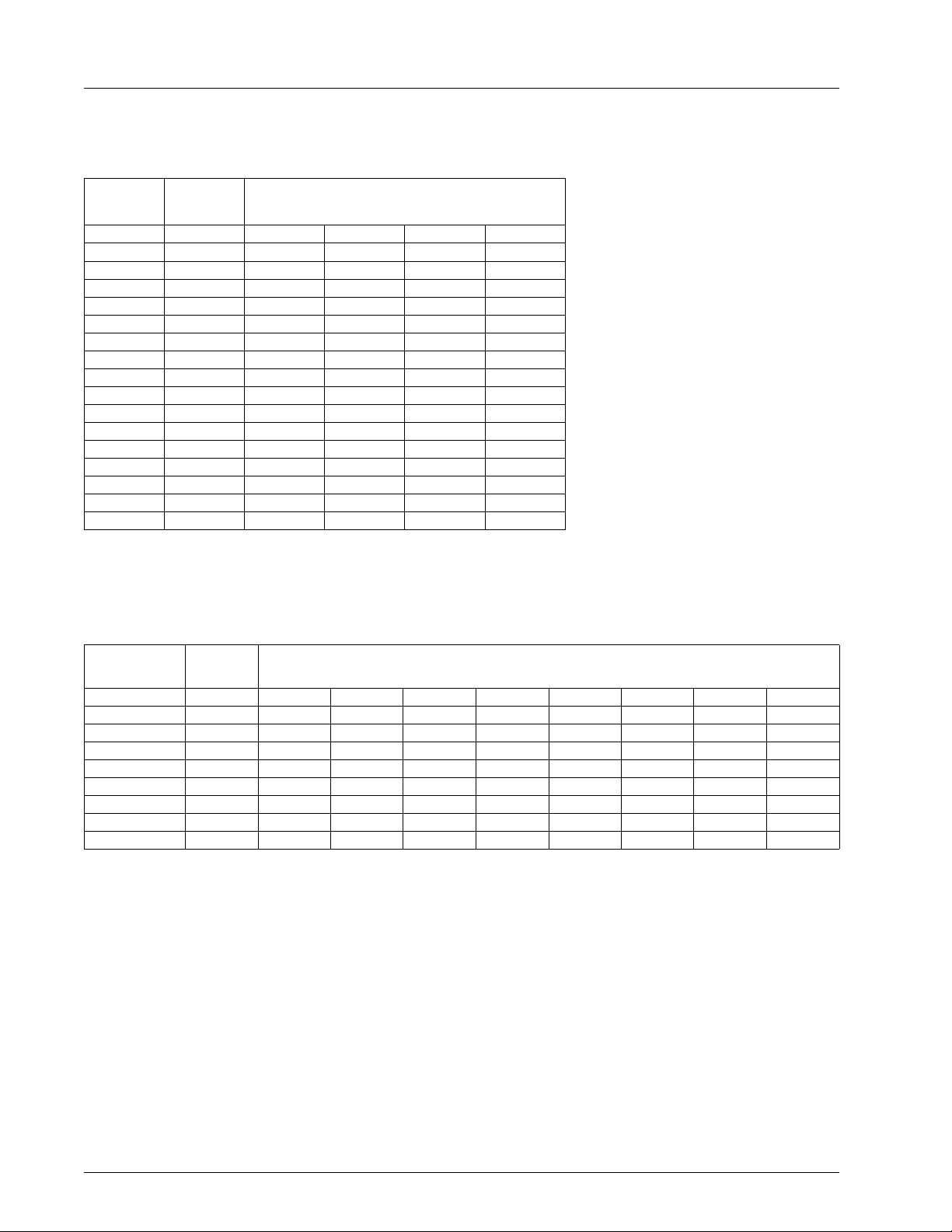
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Digital Video Interface (continued)
Table 7. RGB 16-bit Muliplexed Mode
IDF#
Format
Pixel# P0a P0b P1a P1b
Bus Data D[15] G0[7] A0[7] G1[7] A1[7]
D[14] G0[6] A0[6] G1[6] A1[6]
D[13] G0[5] A0[5] G1[5] A1[5]
D[12] G0[4] A0[4] G1[4] A1[4]
D[11] G0[3] A0[3] G1[3] A1[3]
D[10] G0[2] A0[2] G1[2] A1[2]
D[9] G0[1] A0[1] G1[1] A1[1]
D[8] G0[0] A0[0] G1[0] A1[0]
D[7] B0[7] R0[7] B1[7] R1[7]
D[6] B0[6] R0[6] B1[6] R1[6]
D[5] B0[5] R0[5] B1[5] R1[5]
D[4] B0[4] R0[4] B1[4] R1[4]
D[3] B0[3] R0[3] B1[3] R1[3]
D[2] B0[2] R0[2] B1[2] R1[2]
D[1] B0[1] R0[1] B0[1] R1[1]
D[0] B0[0] R0[0] B0[0] R1[0]
Note: The AX[7:0] data is ignored.
16-bit RGB (16-8)
2
Table 8. YCrCb Multiplexed Mode
IDF#
Format
Pixel# P0a P0b P1a P1b P2a P2b P3a P3b
Bus Data D[7] Cb0[7] Y0[7] Cr0[7] Y1[7] Cb2[7] Y2[7] Cr2[7] Y3[7]
D[6] Cb0[6] Y0[6] Cr0[6] Y1[6] Cb2[6] Y2[6] Cr2[6] Y3[6]
D[5] Cb0[5] Y0[5] Cr0[5] Y1[5] Cb2[5] Y2[5] Cr2[5] Y3[5]
D[4] Cb0[4] Y0[4] Cr0[4] Y1[4] Cb2[4] Y2[4] Cr2[4] Y3[4]
D[3] Cb0[3] Y0[3] Cr0[3] Y1[3] Cb2[3] Y2[3] Cr2[3] Y3[3]
D[2] Cb0[2] Y0[2] Cr0[2] Y1[2] Cb2[2] Y2[2] Cr2[2] Y3[2]
D[1] Cb0[1] Y0[1] Cr0[1] Y1[1] Cb2[1] Y2[1] Cr2[1] Y3[1]
D[0] Cb0[0] Y0[0] Cr0[0] Y1[0] Cb2[0] Y2[0] Cr2[0] Y3[0]
9
YCrCb 8-bit
When IDF = 9 (YCrCb 8-bit mode), H and V sync signals can be embedded into the data stream. In this mode, the
embedded sync will follow the CCIR656 convention, and the first byte of the “video timing reference code” will be
assumed to occur when a Cb sample would occur if the video stream was continuous. This is delineated in Table9.
10 201-0000-023 Rev.4.1, 8/2/99
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Digital Video Interface (continued)
Table 9. YCrCb Multiplexed Mode with Embedded Syncs
IDF#
Format
Pixel# P0a P0b P1a P1b P2a P2b P3a P3b
Bus Data D[7] 1 0 0 S[7] Cb2[7] Y2[7] Cr2[7] Y3[7]
D[6] 1 0 0 S[6] Cb2[6] Y2[6] Cr2[6] Y3[6]
D[5] 1 0 0 S[5] Cb2[5] Y2[5] Cr2[5] Y3[5]
D[4] 1 0 0 S[4] Cb2[4] Y2[4] Cr2[4] Y3[4]
D[3] 1 0 0 S[3] Cb2[3] Y2[3] Cr2[3] Y3[3]
D[2] 1 0 0 S[2] Cb2[2] Y2[2] Cr2[2] Y3[2]
D[1] 1 0 0 S[1] Cb2[1] Y2[1] Cr2[1] Y3[1]
D[0] 1 0 0 S[0] Cb2[0] Y2[0] Cr2[0] Y3[0]
9
YCrCb 8-bit
In this mode, the S[7..0] byte contains the following data:
S[6] = F = 1 during field 2, 0 during field 1
S[5] = V = 1 during field blanking, 0 elsewhere
S[4] = H = 1 during EAV (the synchronization reference at the end of active video)
0 during SAV (the synchronization reference at the start of active video)
Bits S[7] and S[3..0] are ignored.
t
HSW
HSYNC
t
HD
t
P3
t
PH3
POut/
XCLK
t
Pixel
D[7:0]
Data
SP3
P0a P0b P0c P1a P1b P1c
t
HP3
Figure 6: Multiplexed Pixel Data Transfer Mode (IDF = 6)
Table 10. RGB 8-bit Multiplexed Mode (24-bit Color)
IDF#
Format
Pixel# P0a P0b P0c P1a P1b P1c P2a P2b P2C
Bus Data D[7] B0[7] G0[7] R0[7] B1[7] G1[7] R1[7] B2[7] G2[7] R2[7]
D[6] B0[6] G0[6] R0[6] B1[6] G1[6] R1[6] B2[6] G2[6] R2[6]
D[5] B0[5] G0[5] R0[5] B1[5] G1[5] R1[5] B2[5] G2[5] R2[5]
D[4] B0[4] G0[4] R0[4] B1[4] G1[4] R1[4] B2[4] G2[4] R2[4]
D[3] B0[3] G0[3] R0[3] B1[3] G1[3] R1[3] B2[3] G2[3] R2[3]
D[2] B0[2] G0[2] R0[2] B1[2] G1[2] R1[2] B2[2] G2[2] R2[2]
D[1] B0[1] G0[1] R0[1] B1[1] G1[1] R1[1] B2[1] G2[1] R2[1]
D[0] B0[0] G0[0] R0[0] B1[0] G1[0] R1[0] B2[0] G2[0] R2[0]
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 11
6
RGB 8-bit

CHRONTEL CH7003B
Functional Description
The CH7003 is a TV-output companion chip to graphics controllers providing digital output in either YUV or RGB
format. This solution involves both hardware and software elements which work together to produce an optimum
TV screen image based on the original computer generated pixel data. All essential circuitry for this conversion are
integrated on-chip. On-chip circuitry includes memory, memory control, scaling, PLL, DAC, filters, and
NTSC/PAL encoder. All internal signal processing, including NTSC/PAL encoding, is performed using digital
techniques to ensure that the high-quality video signals are not affected by drift issues associated with analog
components. No additional adjustment is required during manufacturing.
CH7003 is ideal for PC motherboards, web browsers, or VGA add-in boards where a minimum of discrete support
components (passive components, parallel resonance 14.31818 MHz crystal) are required for full operation.
Architectural Overview
The CH7003 is a complete TV output subsystem which uses both hardware and software elements to produce an
image on TV which is virtually identical to the image that would be displayed on a monitor. Simply creating a
compatible TV output from a VGA input involves a relatively straightforward process. This process includes a
standard conversion from RGB to YUV color space, converting from a non-interlaced to an interlaced frame
sequence, and encoding the pixel stream into NTSC or PAL compliant format. However, creating an optimum
computer-generated image on a TV screen involves a highly sophisticated process of scaling, deflickering, and
filtering. This results in a compatible TV output that displays a sharp and subtle image, of the right size, with
minimal artifacts from the conversion process.
As a key part of the overall system solution, the CH7003 software establishes the correct framework for the VGA
input signal to enable this process. Once the display is set to a supported resolution (either 640x480 or 800x600),
the CH7003 software may be invoked to establish the appropriate TV output display. The software then programs
the various timing parameters of the VGA controller to create an output signal that will be compatible with the
chosen resolution, operating mode, and TV format. Adjustments performed in software include pixel clock rates,
total pixels per line, and total lines per frame. By performing these adjustments in software, the CH7003 can render
a superior TV image without the added cost of a full frame buffer memory – normally used to implement features
such as scaling and full synchronization.
The CH7003 hardware accepts digital RGB or YCrCb inputs, which are latched in synchronization with the pixel
clock. These inputs are then color-space converted into YUV in 4-2-2 format and stored in a line buffer memory.
The stored pixels are fed into a block where scan-rate conversion, underscan scaling and 2-line, 3-line, 4-line and 5line vertical flicker filtering are performed. The scan-rate converter transforms the VGA horizontal scan-rate to
either NTSC or PAL scan rates; the vertical flicker filter eliminates flicker at the output while the underscan scaling
reduces the size of the displayed image to fit onto a TV screen. The resulting YUV signals are filtered through
digital filters to minimize aliasing problems. The digital encoder receives the filtered signals and transforms them to
composite and S-Video outputs, which are converted by the three 9-bit DACs into analog outputs.
Color Burst Generation*
The CH7003 allows the sub-carrier frequency to be accurately generated from a 14.31818 MHz crystal oscillator,
leaving the sub-carrier frequency independent of the sampling rate. As a result, the CH7003 may be used with any
VGA chip (with an approprate digital interface) since the CH7003 sub-carrier frequency can be generated without
being dependent on the precise pixel rates of VGA controllers. This feature is a significant benefit, since even a
± 0.01% sub-carrier frequency variation may be enough to cause some television monitors to lose color lock.
In addition, the CH7003 has the capability to genlock the color burst signal to the VGA horizontal sync frequency,
which enables a fully synchronous system between the graphics controller and the television. When genlocked, the
CH7003 can also stop "dot crawl" motion (for composite mode operation, in NTSC modes) to eliminate the
annoyance of moving borders. Both of these features are under programmable control through the register set.
Display Modes
The CH7003 display mode is controlled by three independent factors: input resolution, TV format, and scale factor,
which are programmed via the display mode register. It is designed to accept input resolutions of 640x480,
800x600, 640x400 (including 320x200 scan-doubled output), 720x400, and 512x384. It is designed to support
12 *Patent number 5,874,846 201-0000-023 Rev.4.1, 8/2/99
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Display Modes (continued)
output to either NTSC or PAL television formats. The CH7003 provides interpolated scaling with selectable factors
of 5:4, 1:1, 7:8, 5:6, 3:4 and 7:10 in order to support adjustable overscan or underscan operation when displayed on
a TV. This combination of factors results in a matrix of useful operating modes which are listed in detail in
Table11.
Table 11. CH7003 Display Modes
TV Format
Standard
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
NTSC
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
PAL
Input
(active)
Scale
Factor
Active
TV Lines
Percent (1)
Overscan
Pixel
Clock
Horizontal
Total
Vertical
Resolution
640x480 1:1
640x480 7:8
640x480 5:6
800x600 5:6
800x600 3:4
800x600
640x400 5:4 500 16% 21.147 840 420
640x400 1:1 400 (8%) 26.434 840 525
640x400 7:8 350 (19%) 30.210 840 600
720x400 5:4 500 16% 23.790 945 420
720x400 1:1 400 (8%) 29.455 936 525
512x384 5:4 480 10% 20.140 800 420
512x384 1:1 384 (11%) 24.671 784 525
640x480 5:4 600 14% 21.000 840 500
640x480 1:1 480 (8%) 26.250 840 625
640x480 5:6 400 (29%) 31.500 840 750
800x600 1:1 600 14% 29.500 944 625
800x600 5:6 500 (4%) 36.000 960 750
800x600 3:4 450 (15%) 39.000 936 836
640x400 5:4 500 (4%) 25.000 1000 500
640x400 1:1 400 (29%) 31.500 1008 625
720x400 5:4 500 (4%) 28.125 1125 500
720x400 1:1 400 (29%) 34.875 1116 625
512x384 5:4 480 (8%) 21.000 840 500
512x384 1:1 384 (35%) 26.250 840 625
7:10
480
420
400
500
450
420 (3%) 47.832 1064 750
10%
(3%)
(8%)
16%
4%
24.671 784 525
28.196 784 600
30.210 800 630
39.273 1040 630
43.636 1040 700
Total
(1) Note: Percent underscan is a calculated value based on average viewable lines on each TV format, assuming an average TV ovescan
of 10%. (Negative values) indicate modes which are operating in underscan.
For NTSC: 480 active lines - 10% (overscan) = 432 viewable lines (average)
For PAL: 576 active lines - 10% (overscan) = 518 viewable lines (average)
The inclusion of multiple levels of scaling for each resolution have been created to enable optimal use of the
CH7003 for different application needs. In general, underscan (modes where percent overscan is negative) provides
an image that is viewable in its entirety on screen; it should be used as the default for most applications (e.g.,
viewing text screens, operating games, running productivity applications, working within Windows). Overscanning
provides an image that extends past the edges of the TV screen, exactly like normal television programs and movies
appear on TV, and is only recommended for viewing movies or video clips coming from the computer.
Anti-flicker Filter
The CH7003 integrates an advanced 4-line (3-line for 1:1 modes) vertical deflickering filter circuit to help eliminate
the flicker associated with interlaced displays. When operating in scaled display modes, this flicker circuit provides
an adaptive filter algorithm for implementing flicker reduction with selections of high or low flicker content. When
operating in scale factors other than (1:1) display modes, it provides a selection of high or low flicker content. When
operating in non-scaled (1:1) display modes, it provides a selection of four anti-flicker filter modes (non-filtering
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 13
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Anti-flicker Filter (continued)
and three levels of flicker filtering). These modes are fully programmable via I2C, and are listed under the flicker
filter register.
Internal Voltage Reference
An on-chip bandgap circuit is used in the DAC to generate a reference voltage which, in conjunction with a
reference resistor at pin RSET, and register controlled divider, sets the output ranges of the DACs. The CH7003
bandgap reference voltage is 1.235 volts nominal for NTSC or PAL-M, or 1.317 volts nominal (for PAL or NTSCJ), which is determined by IDF register bit 6 (DACG bit). The recommended value for the reference resistor RSET
is 360 ohms (though this may be adjusted in order to achieve a different output level). The gain setting for DAC
output is 1/48th. Therefore, for each DAC, the current output per LSB step is determined by the following equation:
I
= V(RSET)/RSET reference resistor* 1/GAIN
LSB
For DACG=0, this is: I
For DACG=1, this is: I
Power Management
The CH7003 supports five operating states including Normal [On], Power Down, Full Power Down, S-Video Off,
and Composite Off to provide optimal power consumption for the application involved. Using the programmable
power down modes accessed over the I2C port, the CH7003 may be placed in either Normal state, or any of the four
power managed states, as listed below (see “Power Management Register” under the Register Descriptions section
for programming information). To support power management, a TV sensing function (see “Connection Detect
Register” under the Register Descriptions section) is provided, which identifies whether a TV is connected to either
S-Video or composite (or neither). This sensing function can then be used to enter into the appropriate operating
state (e.g., if TV is sensed only on composite, the S-Video Off mode could be set by software).
= 1.235/360 * 1/48 = 71.4 µA (nominal)
LSB
= 1.317/360 * 1/48 = 76.2 µA (nominal)
LSB
Table 12. Power Management
Operating State Functional Description
Normal (On): In the normal operating state, all functions and pins are active
Power Down: In the power-down state, most pins and circuitry are disabled.The BCO
S-Video Off: Power is shut off to the unused DAC’s associated with S-Video
Composite Off: In Composite-off state, power is shut off to the unused DAC associated
Full Power Down: In this power-down state, all but the I2C circuits are disabled. This
pin will continue to provide either the VCO divided by K3, or 14.318
MHz out.
outputs.
with CVBS output.
places the CH7003 in its lowest power consumption mode.
Luminance and Chrominance Filter Options
The CH7003 contains a set of luminance filters to provide a controllable bandwidth output on both CVBS and
S-Video outputs. All values are completely programmable via the Video Bandwidth Register. For all graphs shown,
the horizontal axis is frequency in MHz, and the vertical axis is gain in dBs. The composite luminance and
chrominance video bandwidth output is shown in Table13.
14 201-0000-023 Rev.4.1, 8/2/99
CHRONTEL CH7003B
Luminance and Chrominance Filter Options (continued)
Table 13. Video Bandwidth
Mode Chrominance Bandwidth(MHz) Luminance Bandwidth with Sin(X) /X (MHz)
CBW[1:0] YCV YSV[1:0], YPEAK = 0 YSV[1:0], YPEAK = 1
00 01 10 11
0 0.62 0.68 0.80 0.95 2.26 3.37 2.26 3.37 5.23 2.57 4.44 5.23
1 0.78 0.85 1.00 1.18 2.82 4.21 2.82 4.21 6.53 3.21 5.56 6.53
2 0.53 0.58 0.68 0.81 1.93 2.87 1.93 2.87 4.46 2.19 3.79 4.46
3 0.65 0.71 0.83 0.99 2.36 3.52 2.36 3.52 5.46 2.68 4.64 5.46
4 0.83 0.91 1.07 1.27 3.03 4.51 3.03 4.51 7.00 3.44 5.95 7.00
5 1.03 1.13 1.32 1.57 3.75 5.59 3.75 5.59 8.68 4.27 7.38 8.68
6 0.70 0.77 0.90 1.07 2.56 3.81 2.56 3.81 5.92 2.91 5.04 5.92
7 0.87 0.95 1.12 1.33 3.17 4.72 3.17 4.72 7.33 3.60 6.23 7.33
8 0.74 0.81 0.95 1.13 2.69 4.01 2.69 4.01 6.22 3.06 5.29 6.22
9 0.93 1.02 1.20 1.42 3.39 5.05 3.39 5.05 7.84 3.85 6.67 7.84
10 0.63 0.68 0.80 0.95 2.28 3.39 2.28 3.39 5.26 2.59 4.48 5.26
11 0.78 0.86 1.00 1.19 2.84 4.24 2.84 4.24 6.58 3.23 5.59 6.58
12 0.89 0.98 1.15 1.36 3.25 4.84 3.25 4.84 7.52 3.70 6.39 7.52
13 0.62 0.68 0.80 0.95 2.26 3.37 2.26 3.37 5.23 2.57 4.44 5.23
14 0.78 0.85 1.00 1.18 2.82 4.21 2.82 4.21 6.53 3.21 5.56 6.53
15 0.93 1.02 1.20 1.42 3.39 5.05 3.39 5.05 7.84 3.85 6.67 7.84
16 0.64 0.71 0.83 0.98 2.35 3.50 2.35 3.50 5.43 2.67 4.62 5.43
17 0.74 0.81 0.95 1.13 2.70 4.02 2.70 4.02 6.24 3.07 5.30 6.24
18 0.79 0.87 1.02 1.21 2.89 4.31 2.89 4.31 6.68 3.29 5.68 6.68
19 0.77 0.85 1.00 1.18 2.82 4.20 2.82 4.20 6.53 3.21 5.55 6.53
20 0.95 1.03 1.22 1.44 3.44 5.13 3.44 5.13 7.97 3.92 6.77 7.97
21
22
23 0.86 0.94 1.11 1.31 3.13 4.66 3.13 4.66 7.24 3.56 6.16 7.24
24 0.94 1.03 1.21 1.44 3.43 5.11 3.43 5.11 7.94 3.90 6.75 7.94
1.02 1.12 1.32 1.56 3.73 5.56 3.73 5.56 8.63 4.24 7.34 8.63
0.77 0.85 0.99 1.18 2.82 4.20 2.82 4.20 6.52 3.20 5.54 6.52
CVBS S-Video S-Video
0 1
00 01 1X 00 01 1X
The composite luminance and chrominance frequency response is depicted in Figure7 through 9.
201-0000-023 Rev 4.1, 8/2/99 15
 Loading...
Loading...