Page 1
1604
Temperature Controller
Issue date r USER'S MANUAL
May 2000
Chromalox
1604
1604-0-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM1
Page 2

CONTENTS
MOUNTING REQUIREMENTS ........................... 1
OUTLINE AND CUT OUT DIMENSIONS ........... 2
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS ................................ 3
PRELIMINARY HARDWARE SETTINGS ........... 9
CONFIGURATION PROCEDURE .................... 10
OPERATIVE MODE .......................................... 18
Display function .......................................... 18
Indicators ................................................... 18
Pushbutton function during
operating mode .......................................... 19
Enable/disable the control output ............... 20
SP/SP2 selection ....................................... 20
OUT 1 failure detection function ................. 20
Direct access to the set point ..................... 20
Manual function .......................................... 21
Serial link ................................................... 21
Lamp test ................................................... 22
SMART function ......................................... 22
OPERATIVE PARAMETERS ............................ 23
ERROR MESSAGES ........................................ 26
GENERAL INFORMATIONS ............................ 28
MAINTENANCE ................................................ 32
DEFAULT PARAMETERS ...............................A.1
II
1604-0-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM2
Page 3
III
Model identification
Model
1604 1/16 DIN Temperature Controller
Code Output 1 - Heat or Cool
1 Relay, 3 Amps at 250 Vac (Resistive)
6 SSR Drive, 14 Vdc at 20 mA
Code Output 2 - Alarm
1 Relay, 2 Amp at 250 VAC (Resistive load)
Code
0 None
1 Out #3, 2 Amps at 250 V AC (Resistive load)
2 Heater Break Down input, Out #3
3 RS 485 Digital communications, Out #3
4 RS 485 Digital comm., Heater Break Down input, Out #3
Code Instrument Power
3 100 - 240 Vac
5 24 Vac/dc
Code
0 Add to complete model number
1601 6 1 0 3 0 Typical Model Number
1604-0-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM3
Page 4
1
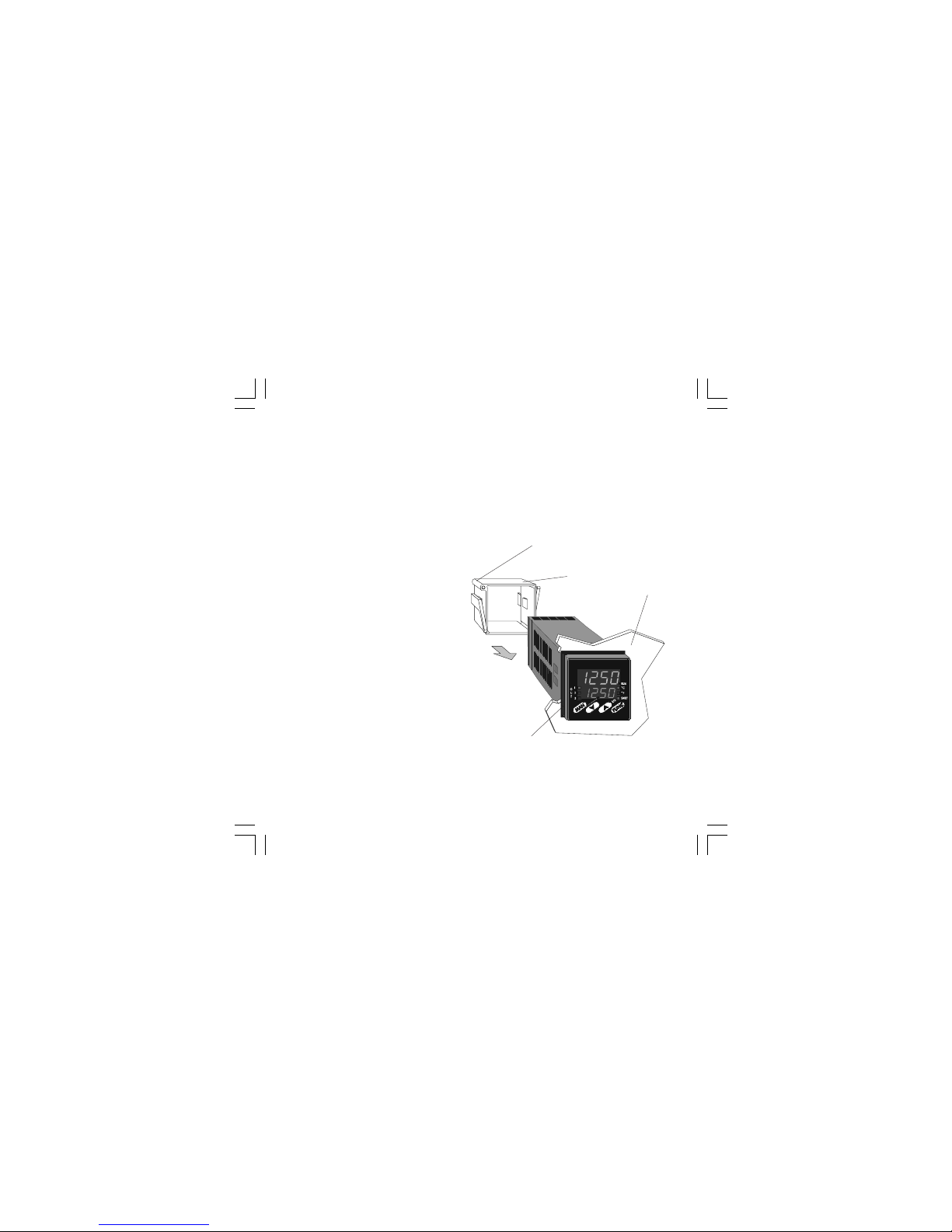
MOUNTING REQUIREMENTS
Select a location, for instrument mounting, where
minimum vibrations are present and the ambient
temperature is within 0 and 50 °C (32 and 122°F).
The instrument can be mounted on a panel up to
15 mm thick with a square cutout of 45 x 45 mm.
For outline and cutout dimensions refer to Fig. 2.
The surface texture of the panel must be better
than 6,3 mm.
The instrument is shipped with rubber panel
gasket (50 to 60 Sh).
To assure the IP65 and NEMA 4 protection, insert
the panel gasket between the instrument and the
panel as show in fig. 1.
While holding the instrument against the panel
proceed as follows:
1) insert the gasket in the instrument case;
2) insert the instrument in the panel cutout;
3) pushing the instrument against the panel,
insert the mounting bracket;
4) with a screwdriver, turn the screws with a
torque between 0.3 and 0.4 Nm.
Panel
bracket
Screw
Gasket
Fig. 1
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM1
Page 5
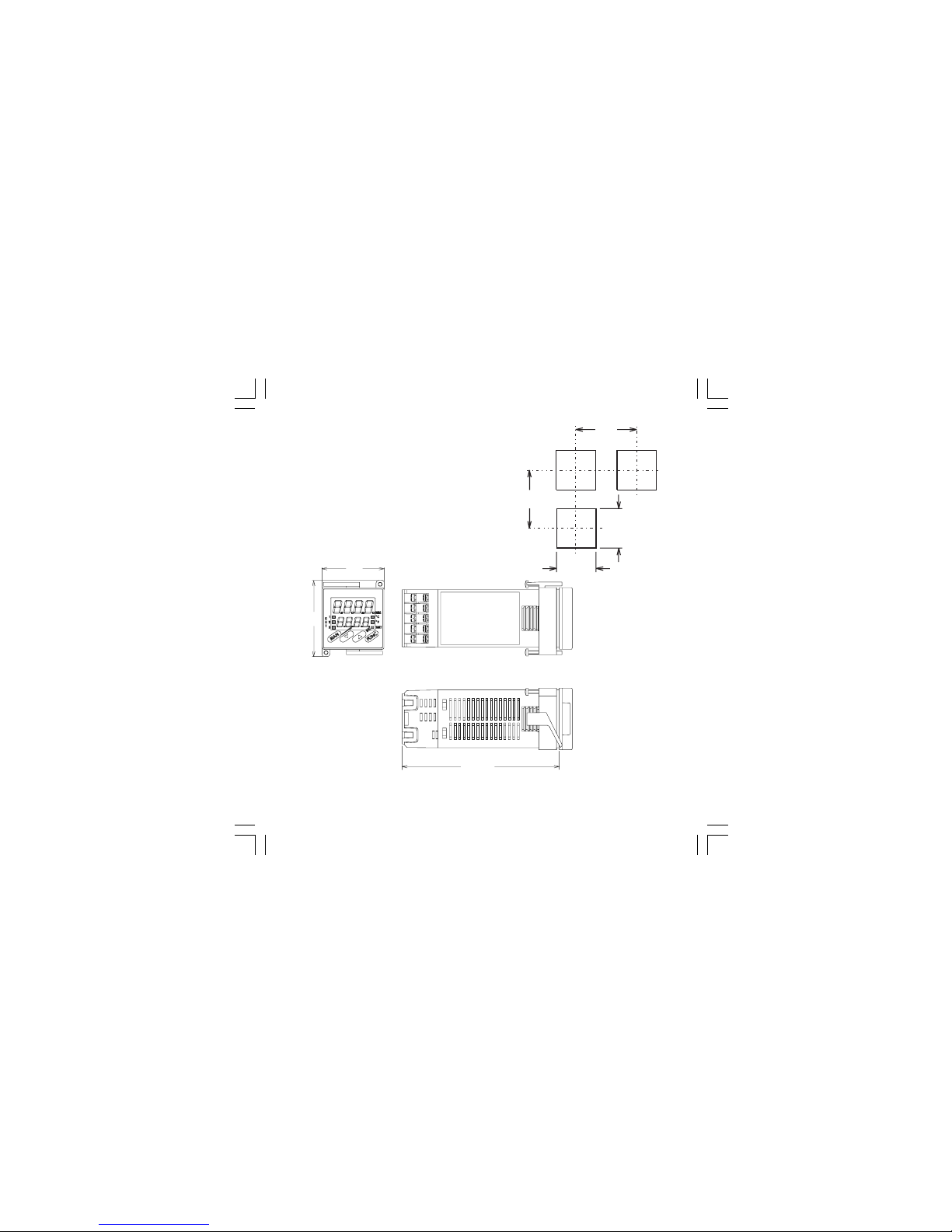
2
OUTLINE AND CUT OUT
DIMENSIONS
Fig. 2 OUTLINE AND CUT-OUT DIMENSIONS
1.9
(48)
2.2
(56)
4.8
(122)
3.0
(75)
2.4
(60)
1.77
(45)
1.77
(45)
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM2
Page 6
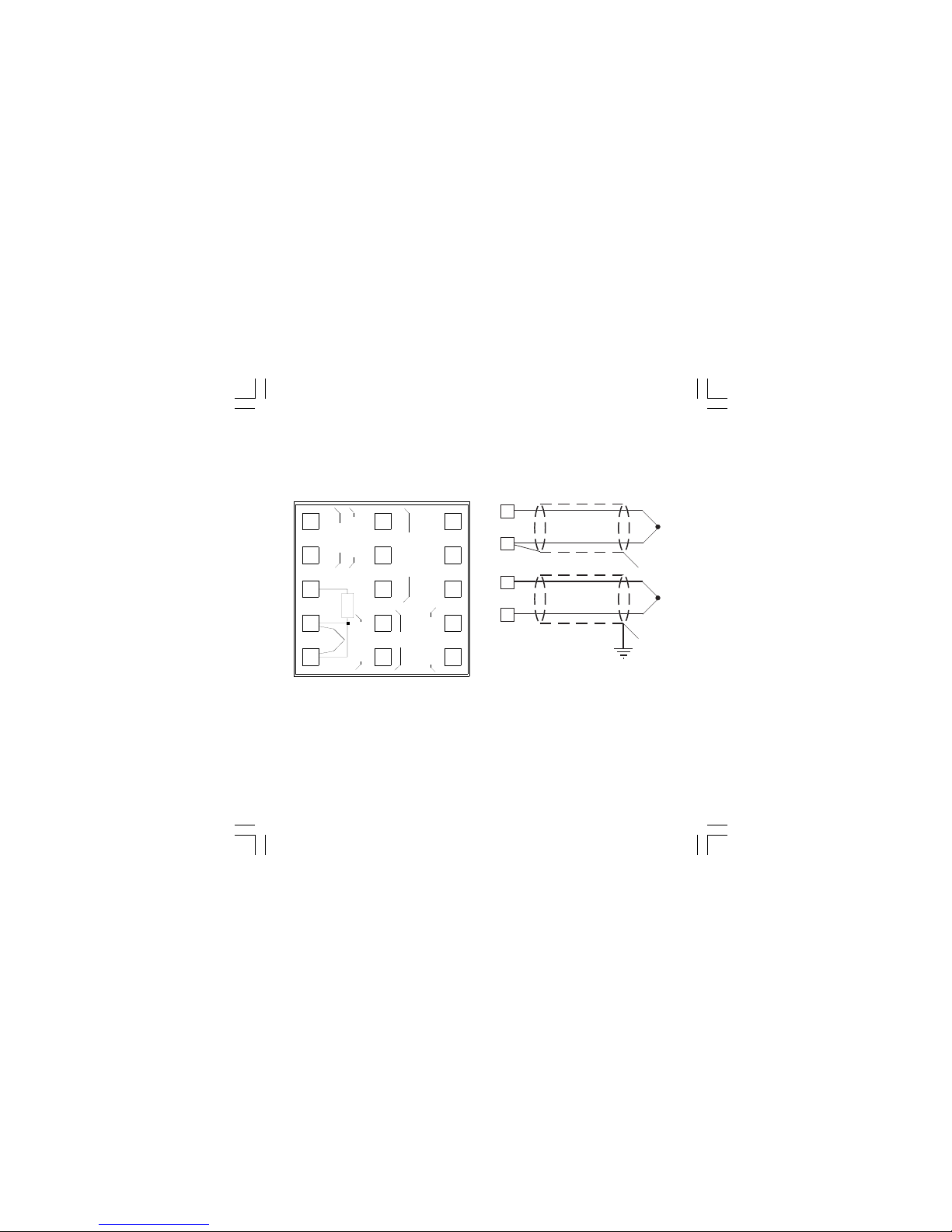
3
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
Connections are to be made with the instrument
housing installed in its proper location.
Fig. 3
REAR TERMINAL BLOCK
NO
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
11
13
14
15
12
RS 485
NO
OUT3
SSR
OUT1
OUT2/3
LINEAR
NO
C
CPWR LINE
100/240VAC
A/A’B/B’
OUT2
IN
CT/SP-SP2
C
+
-
T/C
RTD
+
-
A) MEASURING INPUTS
NOTE: Any external component (like zener
barriers etc.) connected between sensor and
input terminals may cause errors in measurement
due to excessive and/or not balanced line
resistance or possible leakage currents.
TC INPUT
Fig. 4 THERMOCOUPLE INPUT WIRING
NOTE:
1) Don’t run input wires together with power cables.
2) For TC wiring use proper compensating cable
preferable shielded.
3) When a shielded cable is used, it should be
connected at one point only.
9
+
_
Shield
9
+
_
Shield
10
10
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM3
Page 7
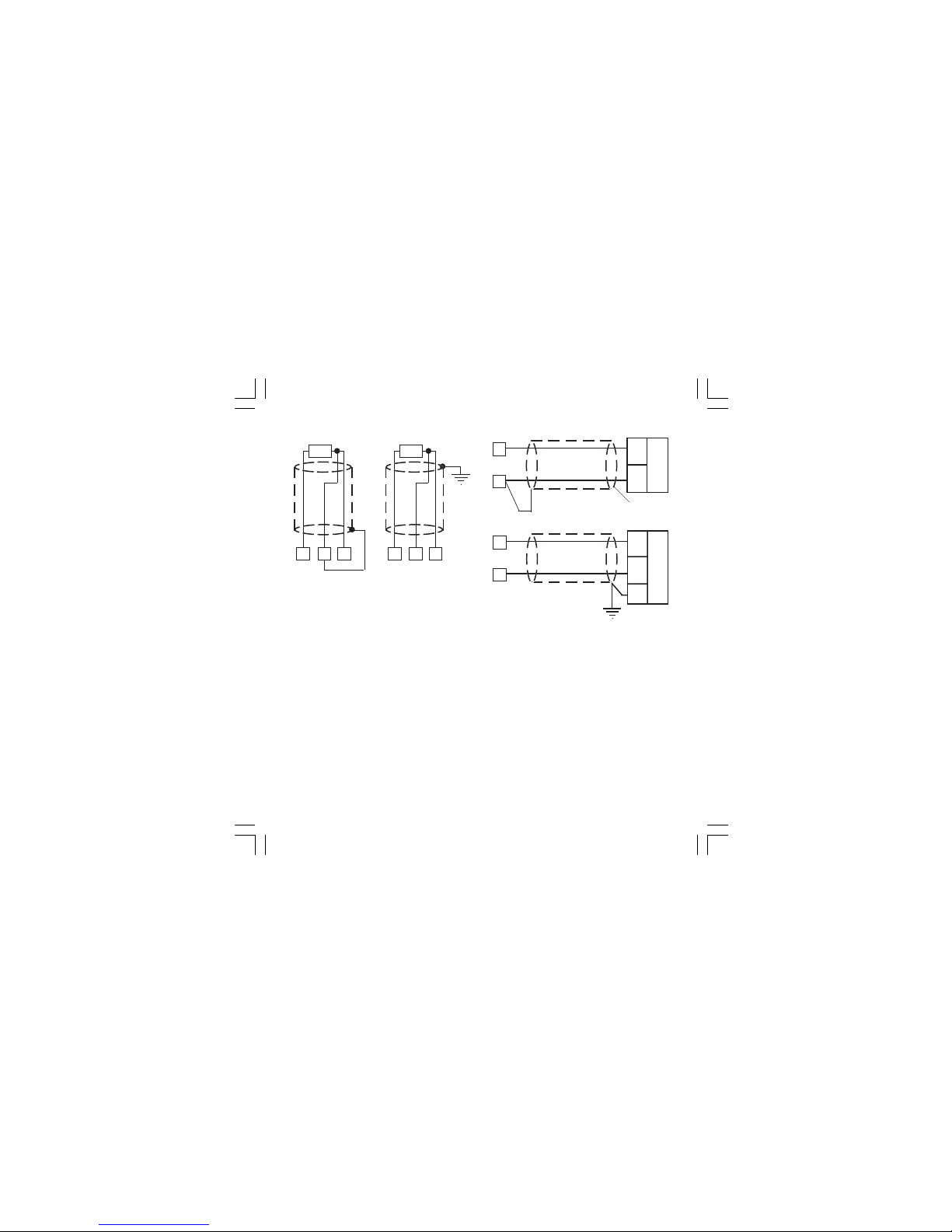
4
LINEAR INPUT
Fig. 6 mA, mV AND V INPUTS WIRING
NOTE:
1) Don’t run input wires together with power
cables.
2) Pay attention to the line resistance; a high line
resistance may cause measurement errors.
3) When shielded cable is used, it should be
grounded at one side only to avoid ground loop
currents.
4) The input impedance is equal to:
< 5 W for 20 mA input
> 1 MW for 60 mV input
> 200 kW for 5 V input
> 400 kW for 10 V input
RTD INPUT
Fig. 5 RTD INPUT WIRING
NOTE:
1) Don’t run input wires together with power
cables.
2) Pay attention to the line resistance; a high line
resistance may cause measurement errors.
3) When shielded cable is used, it should be
grounded at one side only to avoid ground loop
currents.
4) The resistance of the 3 wires must be the
same.
8
RTD
10
9 8
RTD
10
9
Shield
_
+
mA,
mV
or
V
9
+
_
G
mA
mV
or
V
10
9
10
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM4
Page 8
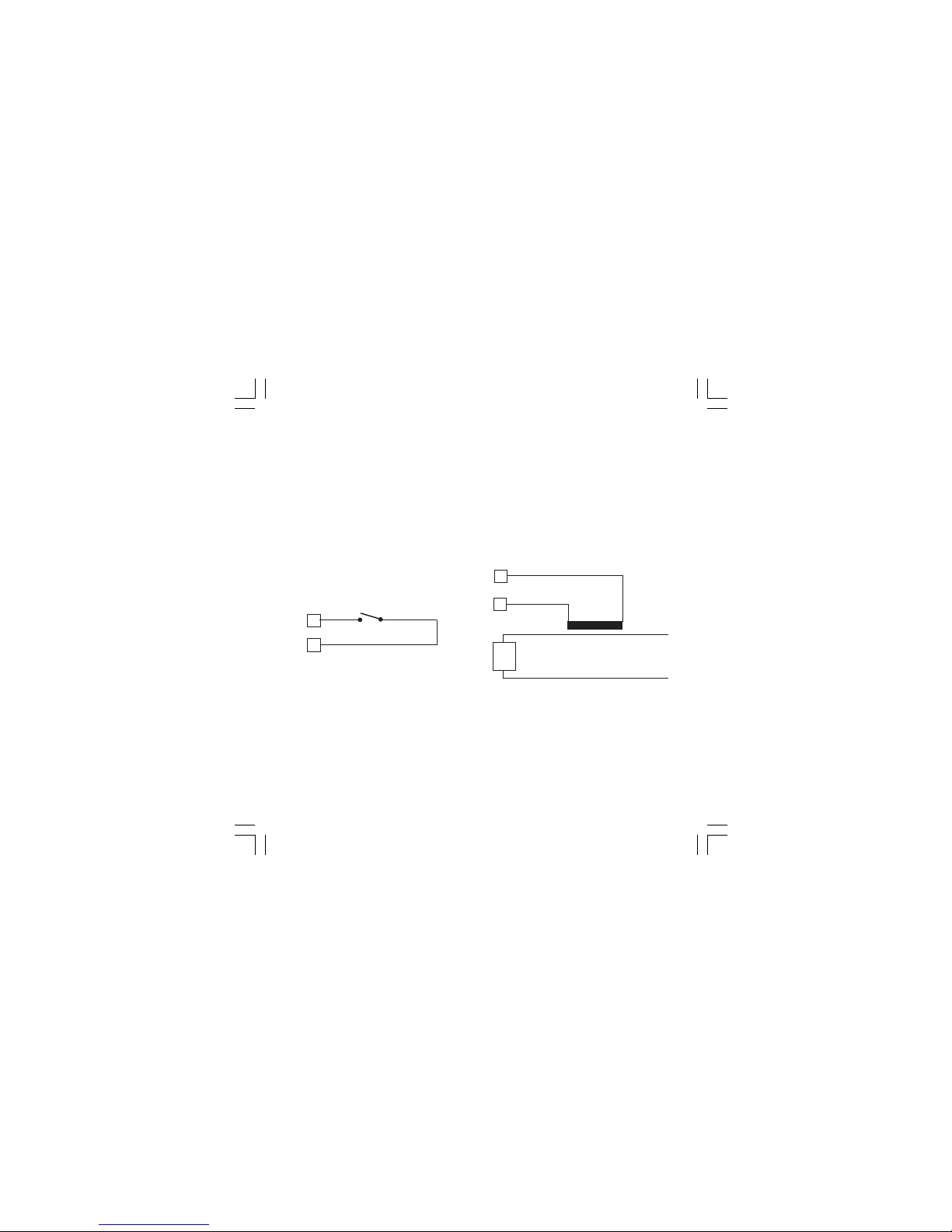
5
B.1) LOGIC INPUT
This instrument can use the input "IN CT/SPSP2" (connections 14 and 15) as current
transformer input or logic input.
Safety note:
1) Do not run logic input wiring together with
power cables.
2) Use an external dry contact capable of
switching 0.5 mA, 5 V DC.
3) The instrument needs 100 ms to recognize a
contact status variation.
4) The logic inputs are NOT isolated by the
measuring input.
5) This feature excludes the current transformer
input.
Fig. 7 - LOGIC INPUT WIRING
When the logic input is selected, it is used to
switch, by an external contact, from main set
point to second set point and viceversa.
logic input op. set point
open SP
close SP2
14
IN CT/SP-SP2
15
B.2) CURRENT TRANSFORMER INPUT
This instrument can use the input "IN CT/SPSP2" (connections 14 and 15) as current
transformer input or logic input.
Safety note:
1) Do not run current transformer input wiring
together with AC power cables.
2) The minimum active period to perform this
measurement is equal to 400 ms.
3) This feature excludes the logic input function.
4) The input impedance is equal to 10 W.
Fig. 8 - CURRENT TRANSFORMER INPUT
WIRING
This input allows to measure and display the
current running in the load driven by the
OUTPUT1 during the ON and OFF period of the
OUT 1 cycle time. By this feature it is also
available the "OUT 1 failure detection" function
(see page 20).
14
15
Load
Current
transformer
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM5
Page 9
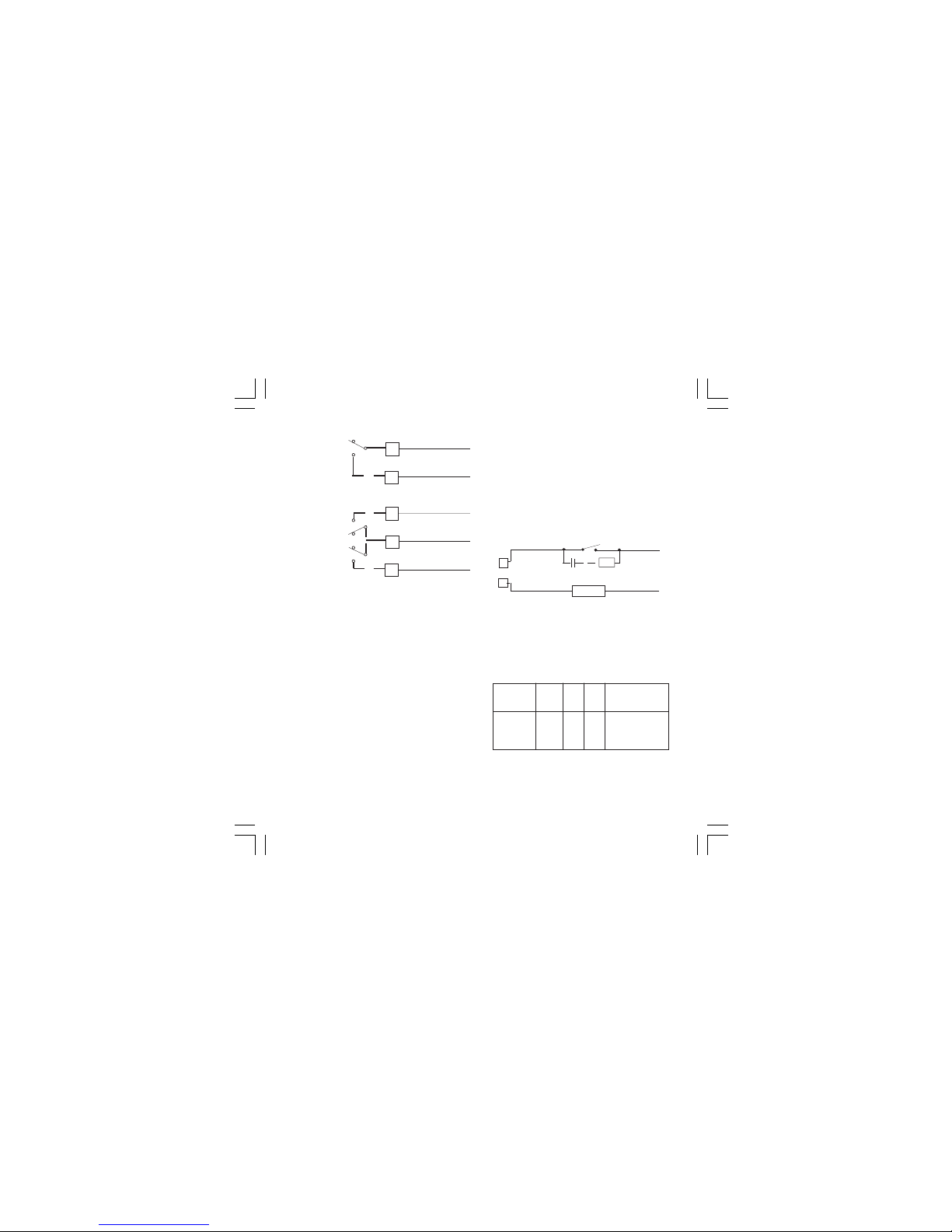
6
INDUCTIVE LOADS
High voltage transients may occur switching
inductive loads.
Through the internal contacts these transients
may introduce disturbances which can affect the
performance of the instrument.
For all the outputs, the internal protection
(varistor) assures a correct protection up to 0.5 A
of inductive component.
The same problem may occur when a switch is
used in series with the internal contacts as shown
in Fig. 10.
Fig. 10 EXTERNAL SWITCH IN SERIES WITH
THE INTERNAL CONTACT
In this case it is recommended to install an
additional RC network across the external contact
as show in Fig. 10
The value of capacitor (C) and resistor (R) are
shown in the following table.
The cable involved in relay output wiring must be
as far away as possible from input or communication cables.
C) RELAY OUTPUTS
Fig. 9 RELAY OUTPUTS WIRING
The contact rating of the OUT 1 is 3A/250V AC
on resistive load.
The contact rating of the OUT 2 and 3 is 2A/250V
on AC resistive load.
The number of operations is 1 x 105 at specified
rating.
NOTES 1) To avoid electrical shock, connect
power line at the end of the wiring
procedure.
2) For power connections use No 16 AWG
or larger wires rated for at last 75 °C.
3) Use copper conductors only.
4) Don’t run input wires together with
power cables.
All relay contacts are protected by varistor against
inductive load with inductive component up to 0.5 A.
The following recommendations avoid serious
problems which may occur, when using relay
output for driving inductive loads.
OUT 1
(heating or
cooling)
OUT 2
(cooling /AL1)
OUT 3
(AL 2)
6
7
C
NO
1
2
3
NO - OUT 2
C - OUT 2/3
NO - OUT 3
LOAD
R
C
POWER
LINE
LOAD
(mA)
<40 mA
<150 mA
<0.5 A
C
(mF)
0.047
0.1
0.33
R
(W)
100
22
47
P.
(W)
1/2
2
2
OPERATING
VOLTAGE
260 V AC
260 V AC
260 V AC
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM6
Page 10
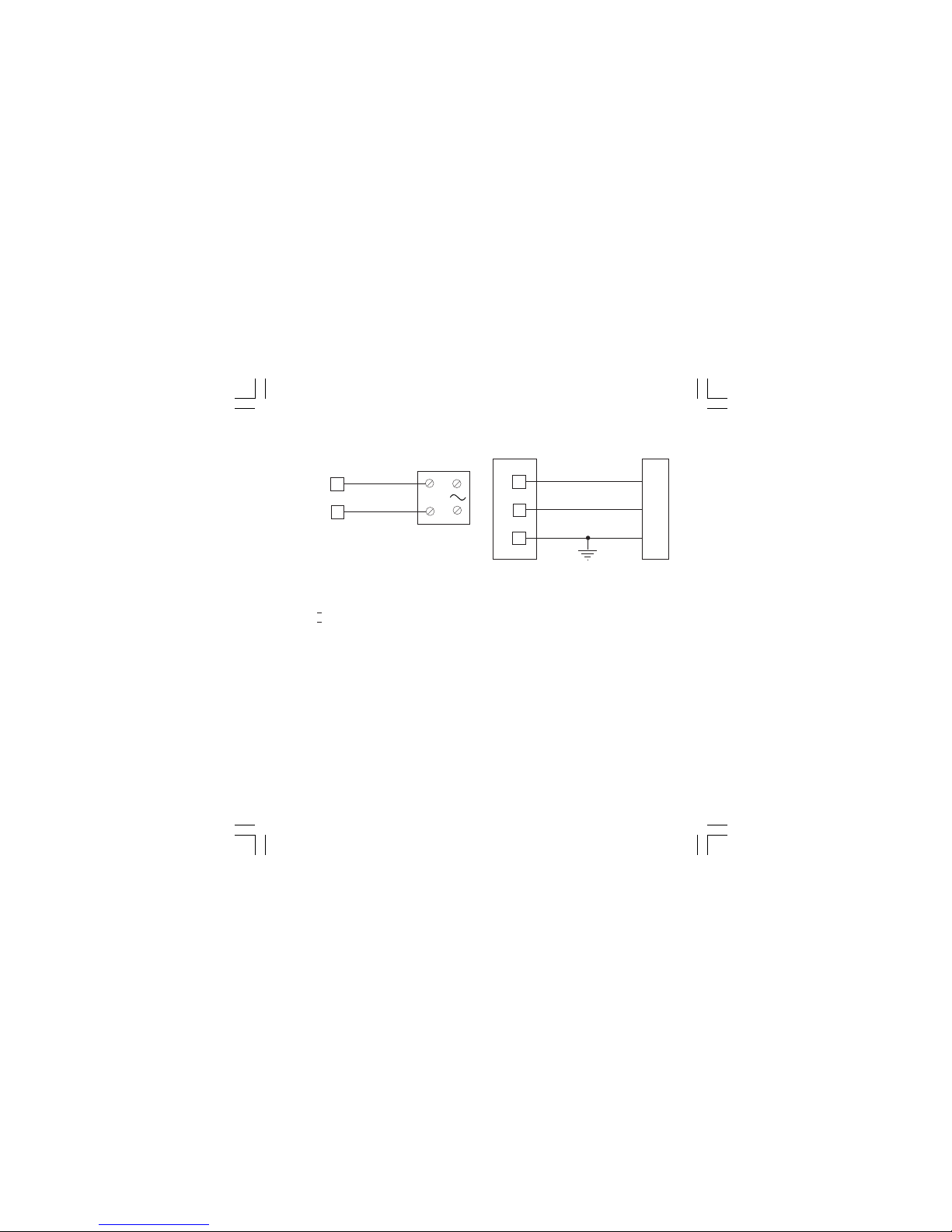
7
VOLTAGE OUTPUTS FOR SSR DRIVE
Fig. 11 SSR DRIVE OUTPUT WIRING
It is a time proportioning output.
Logic level 0: Vout < 0.5 V DC.
Logic level 1:
- 14 V
+ 20 % @ 20 mA
- 24 V
+ 20 % @ 1 mA.
Maximum current = 20 mA.
NOTE: This output is not isolated. A double or
reinforced isolation between instrument output
and power supply must be assured by the
external solid state relay.
SERIAL INTERFACE
RS-485 interface allows to connect up to 30
devices with one remote master unit.
Fig. 12 - RS-485 WIRING
The cable length must not exceed 1.5 km at 9600
BAUD.
NOTE: 1) This is an RS485 isolated interface.
2)The following report describes the
signal sense of the voltage appearing
across the interconnection cable as
defined by EIA for RS-485.
a) The ” A ” terminal of the generator shall
be negative with respect to the ” B ”
terminal for a binary 1 (MARK or OFF)
state.
b) The ” A ” terminal of the generator shall
be positive with respect to the ” B ”
terminal for a binary 0 (SPACE or ON)
12
13
COMMON
11
B'/B
B/B'
A/A'
A'/A
M
A
S
T
E
R
I
N
S
T
R
U
M
E
N
T
+
_
_
+
6
7
OUT 1
SOLID STATE
RELAY
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM7
Page 11
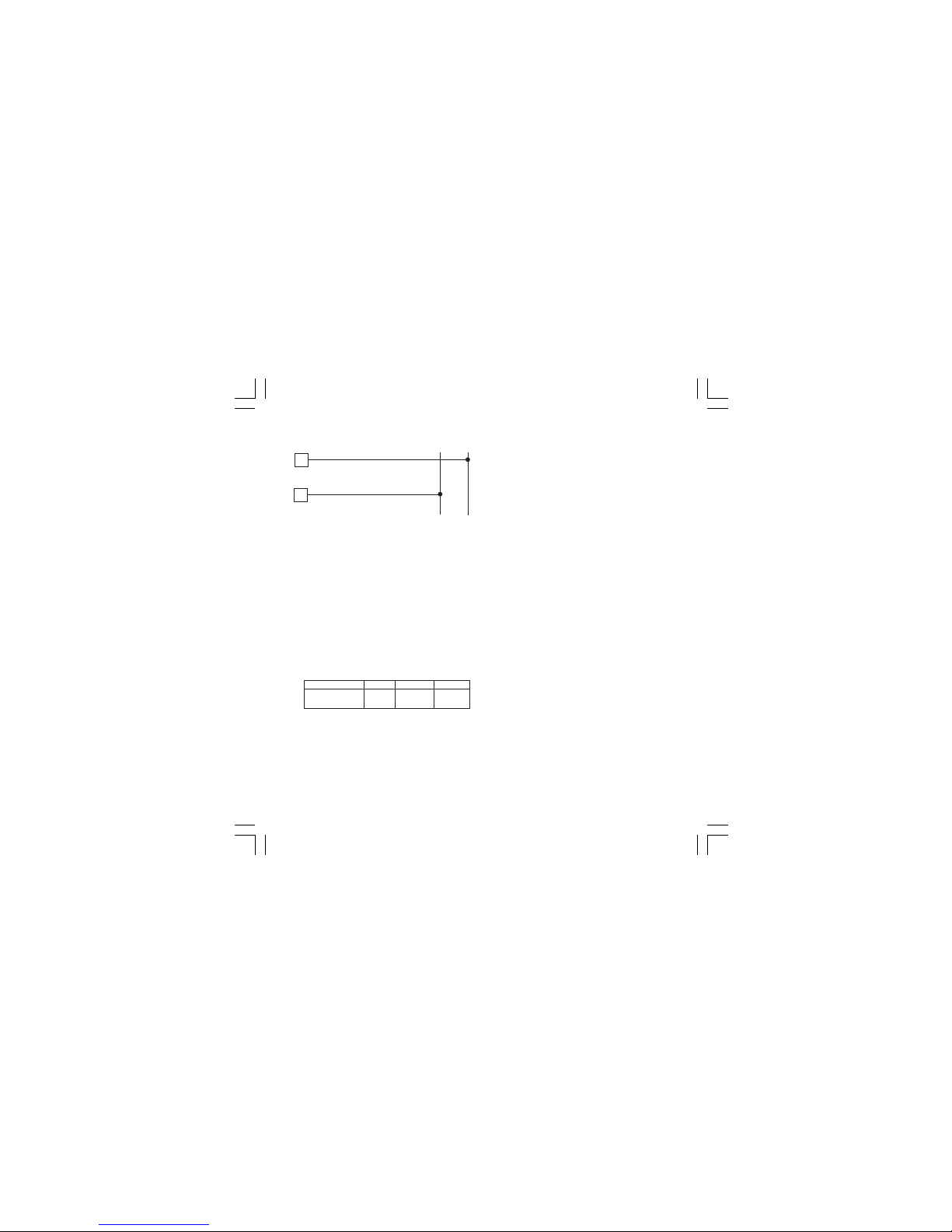
8
and within easy reach of the operator;
- it shall be marked as the disconnecting
device for the equipment.
NOTE: a single switch or circuit-breaker can drive
more than one instrument.
9) When a neutral line is present, connect it to
terminal 4
5
4
POWER LINE 100 V to 240 V A.C
(50/60Hz)
or 24 V AC/DC
D) POWER LINE WIRING
Fig. 13 POWER LINE WIRING
NOTES:
1) Before connecting the instrument to the power
line, make sure that line voltage corresponds to
the descrtiption on the identification label.
2) To avoid electrical shock, connect power line at
the end of the wiring procedure.
3) For supply connections use No 16 AWG or larger
wires rated for at last 75 °C.
4) Use copper conductors only.
5) Don’t run input wires together with power cables.
6) For 24 V DC the polarity is a do not care condition.
7) The power supply input is NOT fuse protected.
Please, provide it externally.
Power supply Type Current Voltage
24 V AC/DC T 500 mA 250 V
100/240 V AC T 125 mA 250 V
When fuse is damaged, it is advisable to verify
the power supply circuit, so that it is necessary to
send back the instrument to your supplier.
8) The safety requirements for Permanently
Connected Equipment say:
- a switch or circuit-breaker shall be included in
the building installation;
- It shall be in close proximity to the equipment
N (L2)
P (L1)
N (L2)
P (L1)
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM8
Page 12
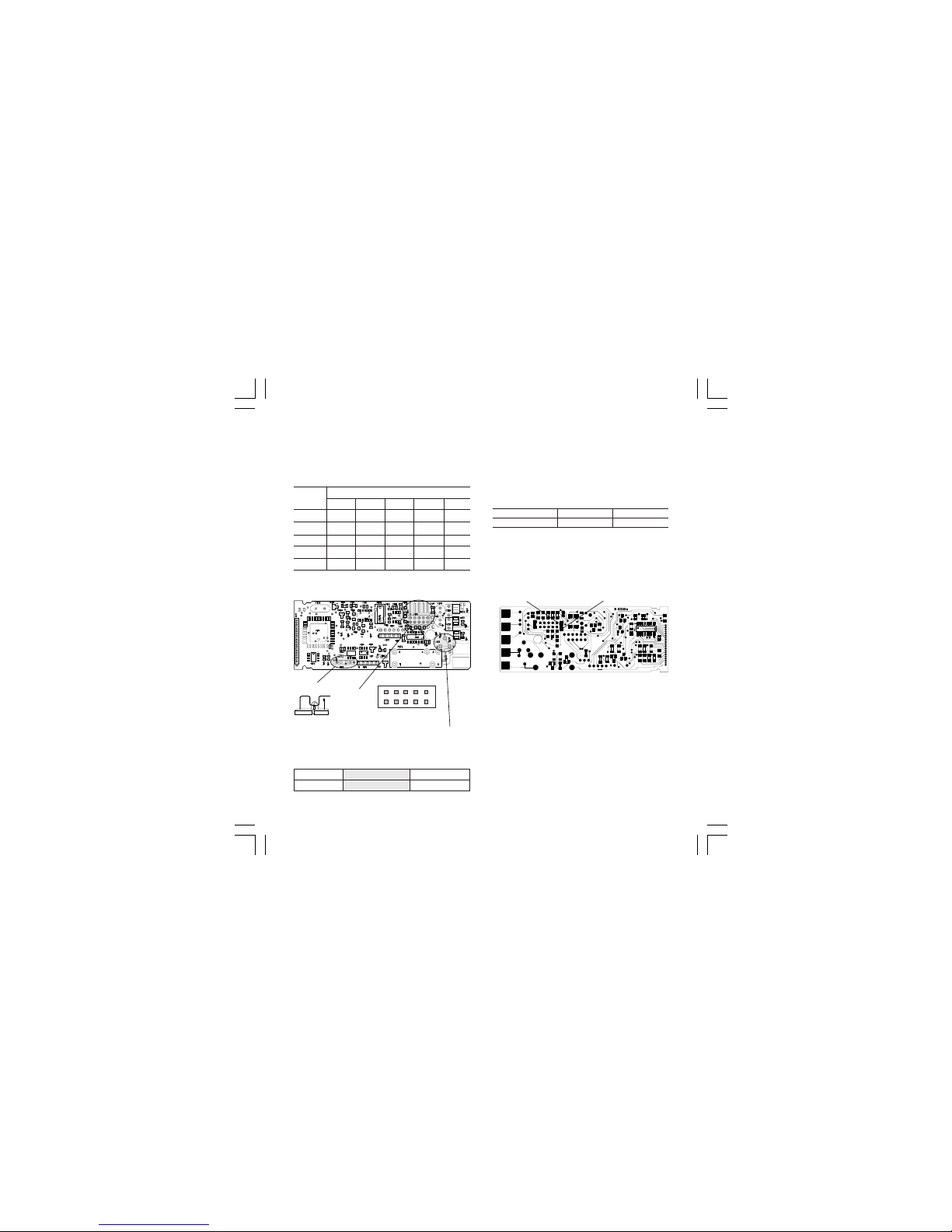
9
OPEN INPUT CIRCUIT
This instrument is able to identify the open circuit
for TC and RTD inputs.
The open input circuit condition for RTD input is
shown by an "overrange" indication.
For TC input, it is possible to select overrange
indication (standard) or underrange indication setting the CH101 and SH101 according to the following table:
Overrange (STD) CH101 = close SH101 = open
Underrange CH101 = open SH101 = close
Both pads are located on the soldering side of the
CPU card
Fig. 15
PRELIMINARY HARDWARE
SETTINGS
1) Remove the instrument from its case.
2) It is necessary to set J106 according to the
desired input type as shown in the following figure.
INPUT J106
TYPE 1-2 3-4 5-6 7-8 9-10
TC-RTD open close open open open
60 mV open close open open open
5 V close open close open open
10 V open open close open open
20 mA open open open close close
NOTE : the not used jumper can be positioned on
pin 7-9
CH101
SH101
1 3 5 7 9
2 4 6 8 10
J106
V101
J102
Fig. 14
3) Select the output 1 contact : NO (standard) or
NC by setting J102 according to the following
table:
Contact NO (standard) NC
J102 1 - 2 2 - 3
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM9
Page 13

10
SELECTION OF THE "IN CT/SP-SP2" FUNCTION
This instrument can use the input "IN CT/SP-SP2"
(connections 14 and 15) as current transformer
input or a logic input.
The current transformer input allows to measure
and display the current running in the load driven
by the OUTPUT1 during the ON and OFF period
of the OUT 1 cycle time. By this feature it is also
available the "OUT 1 failure detection" function
(see page 20). The logic input is used to switch,
by an external contact, from main set point to
second set point and viceversa.
To select the desired input type, set J504 as
detailed in the figure shown below:
Current transformer input Logic input
Fig. 16
GENERAL NOTES for configuration.
FUNC = This will memorize the new value of
the selected parameter and go to the
next parameter (increasing order).
MAN = This will scroll back the parameters
without memorization of the new value.
s = This will increase the value of the
selected parameter
t = This will decrease the value of the
selected parameter.
CONFIGURATION PROCEDURE
1) Remove the instrument from its case.
2) Set the dip switch V101 to the open condition
(see fig. 14).
3) Re-insert the instrument.
4) Switch on the instrument.
The display will show COnF.
NOTE : If "CAL" indication is displayed, press
immediately the s pushbutton and return to
the configuration procedure.
5) Push the FUNC pushbutton.
SEr1 = Serial interface protocol
OFF = No serial interface
Ero = Polling/selecting ERO
nbUS = Modbus
jbUS = Jbus
SEr2 = Serial link device address
Not available when SEr1 = OFF
From 1 to 95 for ERO protocol.
From 1 to 255 for all the other protocols.
NOTE: the electrical characteristic of the RS 485
serial interface will allow the connection of 31
devices maximum.
1 2 3 1 2 3
J504
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM10
Page 14

11
SEr3 = Baud rate for serial link
Not available when SEr1 = OFF
From 600 to 19200 baud.
NOTE: 19200 baud is shown on display as 19.20.
SEr4 = Byte format for serial link
Not available when SEr1 = OFF
7E = 7 bits + even parity (For ERO protocol only)
7O = 7 bits + odd parity (For ERO protocol only)
8E = 8 bits + even parity
8O = 8 bits + odd parity
8 = 8 bits no parity
P1 - Input type and standard range
0 = TC type L range 0 / +400.0°C
1 = TC type L range 0 / +900 °C
2 = TC type J range -100.0 / +400.0 °C
3 = TC type J range -100 / +1000 °C
4 = TC type K range -100.0 / +400.0 °C
5 = TC type K range -100 / +1370 °C
6 = TC type N range -100 / +1400 °C
7 = TC type R range 0 / +1760 °C
8 = TC type S range 0 / +1760 °C
9 = RTD type Pt 100 range -199.9 / +400.0 °C
10 = RTD type Pt 100 range -200 / +800 °C
11 = mV Linear range 0 / 60 mV
12 = mV Linear range 12 / 60 mV
13 = mA Linear range 0 / 20 mA
14 = mA Linear range 4 / 20 mA
15 = V Linear range 0 / 5 V
16 = V Linear range 1 / 5 V
17 = V Linear range 0 / 10 V
18 = V Linear range 2 / 10 V
19 = TC type L range 0 / +1650 °F
20 = TC type J range -150 / +1830 °F
21 = TC type K range -150 / +2500 °F
22 = TC type N range -150 / +2550 °F
23 = TC type R range 0 / +3200 °F
24 = TC type S range 0 / +3200 °F
25 = RTD type Pt 100 range -199.9 / +400.0 °F
26 = RTD type Pt 100 range -330 / +1470 °F
27 = TC type T range -199.9 / +400.0 °C
28 = TC type T range -330 / +750 °F
NOTE: selecting P1 = 0, 2, 4, 9, 25 or 27, the
instrument set automatically P36 = FLtr. For all
the remaining ranges it will set P36 = nOFL.
If a different selection is desired, P36 may be
modified.
P2 = Decimal point position
This parameter is available only when a linear input
is selected (P1 = 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 or 18).
----. = No decimal figure.
---.- = One decimal figure.
--.-- = Two decimal figures.
-.--- = Three decimal figures.
P3 = Initial scale value
For linear inputs it is programmable from -1999 to
4000.
For TC and RTD input it is programmable within
the input range.
When this parameter is modified, rL parameter
will be re-aligned to it.
P4 = Full scale value
For linear inputs it is programmable from -1999 to
4000.
For TC and RTD input it is programmable within
the input range.
When this parameter is modified, rH parameter
will be re-aligned to it.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM11
Page 15

12
The initial and full scale values determine the input
span which is used by the PID algorithm, the
SMART and the alarm functions.
NOTE: the minimum input span (S = P4 - P3), in
absolute value, should be set as follows:
For linear inputs, S
> 100 units.
For TC input with °C readout, S
> 300 °C.
For TC input with °F readout, S
> 550 °F.
For RTD input with °C readout, S
> 100 °C.
For RTD input with °F readout, S
> 200 °F.
P5 = Output 1 type
rEL = Relay [the cycle time (Cy1) will be forced to
15 s]
SSr = SSR [the cycle time (Cy1) will be forced to
4 s]
P6 = Output 1 action.
This parameter is skipped if P7 = 4
rEV = Reverse action (Heating action)
dir = Direct action (Cooling action)
P7 = Output 2 function.
0 = output not used.
1 = it is used as alarm 1 output and the alarm 1
is programmed as process alarm.
2 = it is used as alarm 1 output and the alarm 1 is
programmed as band alarm.
3 = it is used as alarm 1 output and the alarm 1 is
programmed as deviation alarm.
4 = it is used as second control output (Cooling
output).
NOTE: setting P7 = 4, the P6 parameter is forced
to "rEV".
P8 = Cooling media.
Available only when P7 = 4
AIr = Air is used as cooling media.
OIL = Oil is used as cooling media.
H2O = Direct water is used as cooling media.
Changing P8 parameter, the instrument forces the
cycle time and relative cooling gain parameter to the
default value related with the chosen cooling media
When P8 = AIr - Cy2 = 10 s and rC = 1.00
P8 = OIL - Cy2 = 4 s and rC = 0.80
P8 = H2O - Cy2 = 2 and rC = 0.40
P9 = Alarm 1 operating mode
Available only when P7 is equal to 1, 2 or 3.
H.A. = High alarm (outside for band
alarm) with automatic reset.
L.A. = Low alarm (inside for band alarm) with
automatic reset.
H.L. = High alarm (outside band) with manual
reset (latched).
L.L. = low alarm (inside band) with manual reset
(latched).
P10 = Option feature ( see also "Display
function" and "OUT 1 failure detection")
OFF = No option
SP2 = Digital input for SP / SP2 selection.
n.O. = Set P10 to n.O. when the load is
REVERSE ACTION DIRECT ACTION
t
Input
t
Output
t
Input
t
Output
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM12
Page 16

13
energized during the ON status of the
instrument output (relay energized or SSR
output status 1).
n.C. = Set P10 to n.C. when the load is energized
during the OFF status of the instrument
output (relay de-energized or SSR output
status 0).
P11 = Current transformer range
This parameter is present only if P10 is different
from OFF or SP2 and it is programmable from 10
to 100 A.
P12 = Output 3 function
0 = Output not used for alarm 2.
1 = it is used as alarm 2 output and the alarm 2
is programmed as process alarm.
2 = it is used as alarm 2 output and the alarm 2
is programmed as band alarm.
3 = it is used as alarm 2 output and the alarm 2
is programmed as deviation alarm.
NOTE : The output 3 relay operates as a logic OR
between the alarm 2 and the "OUT 1 failure
detection" function.
P13 = Alarm 2 operating mode & OUT 1 failure
detection reset
Available only when P12 is different from 0 or P10
is equal to n.O or n.C.
H.A. = High alarm (outside for band alarm) with
automatic reset.
L.A. = Low alarm (inside for band alarm) with
automatic reset.
H.L. = High alarm (outside band) with manual
reset (latched).
L.L. = Low alarm (inside band) with manual reset
(latched).
NOTE:The "Out 1 failure detection" function
assumes only the selected reset type (manual or
automatic).
P14 = Programmability of the alarm 2
threshold and hysteresis values
Available only when P12 is different from 0.
OPrt = Alarm 2 threshold and hysteresis are
programmable in the operating mode.
COnF = Alarm 3 threshold and hysteresis are
programmable in configuration mode.
P15 = Alarm 2 threshold value
Available only when P12 is different from 0 and
P14 is equal to "COnF".
Range: For process alarm - within the range limits.
For band alarm - from 0 to 500 units.
For deviation alarm - from -500 to 500
units.
P16 = Alarm 2 hysteresis value
Available only when P12 is different from 0 and
P14 is equal to "COnF".
Range: from 0.1% to 10.0 % of the range
selected with P3 and P4 parameters or
1 LSD.
P17 = Threshold of the “Soft Start” function.
Threshold value in eng. units to initiate the "Soft
start" function (output power limiting) at start up.
Range : within the readout span.
NOTE: This threshold value will not be taken into
account when tOL = InF.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM13
Page 17

14
P18 = Safety lock
0 = No parameter protection. The device is
always in unlock condition and all parameters
can be modified.
1 = The device is always in lock condition and no
parameter (exception made for the set points
[SP/SP2] and alarm manual reset) can be
modified (for SMART status see P27).
From 2 to 4999 = This combination number is a
secret value to be used, in run time (see nnn
parameter) to put device in lock/unlock
condition.
For SP, SP2 and manual reset of the alarms,
the lock/unlock condition has no effect (for
SMART status see P27).
From 5000 to 9999 = This combination number is
a secret value to be used, in run time (see
nnn parameter) to put device in lock/unlock
condition.
For SP, SP2, manual reset of the alarm, AL1,
AL2, Hbd and SCA, the lock/unlock
condition has no effect (for SMART status
see P27).
NOTE:when safety lock is selected, the secret
value can not be displayed again and the
display will show 0, 1, SFt.A (when P18 is
encompassed between 2 and 4999) or SFt.b
(when P18 is encompassed between 5000
and 9999)
The configuration procedure is completed and the
instrument shows "
-.-.-.-. " on both displays.
If no other setting is necessary, push the FUNC
pushbutton, the display returns to show "COnF".
Otherwise access to the advanced configuration
parameter proceeding as follows:
1) using s and t pushbutton to set the 234
code on the display.
2) push the FUNC pushbutton.
P19 = Alarm 1 action
Available only when P7 is different from 0 or 4.
dir = direct action (relay energized in alarm
condition)
rEV = reverse action (relay deenergized in alarm
condition)
P20 = alarm 1 stand-by function
Available only when P7 is different from 0 or 4.
OFF = stand-by function disabled
On = stand-by function enabled
NOTE: If the alarm is programmed as band or
deviation alarm, this function masks the alarm
condition after a set point change or at the
instrument start-up until the process variable
reaches the alarm threshold plus or minus
hysteresis. If the alarm is programmed as a
process alarm, this function masks the alarm
condition at instrument start-up until process
variable reaches the alarm threshold plus or
minus hysteresis.
P21 = Action of the alarm 2 and "OUT 1 failure
detection" function
Available only when P12 is different from 0 or P10
is equal to "n.O" or "n.C".
dir = direct action (relay energized in alarm
condition)
rEV = reverse action (relay de-energized in alarm
condition)
P22 = Alarm 2 stand-by function
Available only when P12 is different from 0.
OFF = Stand-by function disabled
On = Stand-by function enabled
NOTE: for more details on stand-by function, see
P20 parameter.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM14
Page 18

15
P23 = OFFSET adjustment added to the
measured value
This parameter allows to set a constant OFFSET
throughout the readout range.
It is skipped for linear inputs
- For readout ranges with decimal figure, P23 is
programmable from -19.9 to 19.9.
- For readout ranges without decimal figure, P23
is programmable from -199 to 199.
P24 = NOT AVAILABLE
P25 = Displayable protected parameters
This parameter is skipped when P18 = 0.
OFF = Protected parameters cannot be
displayed.
On = Protected parameter can be
displayed.
P26 = MANUAL function
OFF = manual function is disabled
On = manual function can be enabled/
disabled by MAN pushbutton.
P27 = SMART function
0 = SMART function disabled.
1 = SMART function in NOT protected by safety
lock.
2 = SMART function is under safety lock protection.
P28 = Relative cooling gain calculated by
SMART function.
This parameter is present only if P7 = 4 and P27
is different from 0.
OFF = SMART algorithm does not calculate the
rC parameter value
On = SMART algorithm calculates the rC
parameter value.
P29 = Maximum value of the proportional
band calculated by the SMART
algorithm.
This parameter is present only if P27 is different
from 0.
This parameter is programmable from P30 or P31
value to 100.0 %.
P30 = Minimum value of the proportional
band calculated by the SMART
algorithm when the instrument has two
control outputs.
This parameter is available only when P7 = 4 and
P27 is different from 0.
It is programmable from 1.5% to P29 value.
P31 = Minimum value of the proportional band
calculated by the SMART algorithm when
the instrument has one control output.
This parameter is available only when P7 is
different from 4 and P27 is different from 0.
It is programmable from 1.0 % to P29 value.
Real curve
Readout
Adjusted
curve
Input
P23
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM15
Page 19

16
2 = Safety value applied when overrange
condition is detected.
3 = Safety value applied when underrange
condition is detected.
P38 = Output safety value
This parameter is skipped when P37 = 0
This value can be set
- from 0 to 100 % when P7 is different from 4
- from -100 % to 100 % when P7 is equal to 4
P39 =Extension of the anti-reset wind up
Range: from -30 to +30 % of the proportional
band.
NOTE: a positive value increases the high limit of
the anti-reset-wind up (over set point) while a
negative value decreases the low limit of the antireset-wind up (under set point).
P40 = Control action type
Pid - the instrument operates with a PID algorithm.
Pi - the instrument operates with a PI algorithm.
P41 = Set point indication
Fn.SP = during operative mode, when the
instrument performs a ramp, it will show
the final set point value.
OP.SP =during operative mode, when the
instrument performs a ramp, it will show
the operative set point.
P32 = Minimum value of the integral time
calculated by the SMART algorithm.
This parameter is present only if P27 is different
from 0.
It is programmable from 1 second (00.01) to
2 minutes (02.00).
P33 = Device status at instrument start up.
This parameter is skipped when P26 = OFF.
0 = the instrument starts in AUTO mode.
1 = It starts in the same way it was left prior to
power shut down.
P34 = NOT AVAILABLE
P35 = Timeout selection
This parameter allows to set the time duration of
the timeout for parameter setting used by the
instrument during the operating mode.
tn. 10 = 10 seconds
tn 30 = 30 seconds
P36 = Digital filter on the measured value
It is possible to apply to the displayed value a
digital filter of the first order with a time constant
equal to :
- 4 s for TC and RTD inputs
- 2 s for linear inputs
noFL. = no filter
FLtr = filter enabled
P37 = Conditions for output safety value
0 = No safety value (see"Error Messages" Chapter)
1 = Safety value applied when overrange or
underrange condition is detected.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM16
Page 20

17
P42 = Operative set point alignment at
instrument start up
0 = At start up, the operative set point will be
aligned to SP or SP2 according to the digital
input status.
1 = At start up, the operative set point will be
aligned to the measured value, the selected
set point value will be reached by the
programmed ramp (see Grd1 and Grd2
operative parameters).
NOTE: if the instrument detects an out of range
or an error condition on the measured value it will
ever operate as described for P42 = 0.
The configuration procedure is terminated and the
display returns to show "COnF".
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM17
Page 21

18
OPERATIVE MODE
1) Remove the instrument from its case.
2) Set the internal dip switch V101 in closed
condition
3) Re-insert the instrument.
4) Switch on the instrument.
DISPLAY FUNCTION
The upper display shows the measured value
while the lower display shows the programmed
set point value (we define the above condition as
“normal display mode”).
Note: When the rate of change (Grd1, Grd2) is
utilized, the displayed set point value may
be different from the operating set point.
It is possible to change the information on the
lower display as follows:
- By pushing the FUNC pushbutton within 3s to
10s. The lower display will show " A." followed
by the current consumed by the load (driven by
the OUT 1) when
the load is in ON condition
(see also "OUT 1 failure detection").
- Push FUNC pushbutton again, the lower
display will show " b." followed by the leakage
current running in the load (driven by the OUT
1) when the load is in OFF condition (see also
"OUT 1 failure detection").
- Push FUNC pushbutton again, the lower
display will show "H." followed by OUT 1 power
value (from 0 to 100%).
- Push FUNC pushbutton again, the lower
display will show "C." followed by OUT 2 power
value (from 0 to 100%).
- Push FUNC pushbutton again. The display will
return in "Normal Display Mode".
NOTE : The "A", "b" and "C" informations will be
displayed only if the relative function has been
previously configured.
When no pushbutton are pressed during the time
out (see P35), the display will automatically return
in "Normal Display Mode".
In order to keep the desired information
continuously on the lower display, depress s or
t push-button to remove the timeout.
When return in "Normal Display Mode" is desired,
push FUNC push-button again.
INDICATORS
°C Lit when the process variable is shown in
Celsius degree.
°F Lit when the process variable is shown in
Fahrenheit degree.
SMRT Flashing when the first part of the SMART
algorithm is active.
Lit when the second part of the SMART
algorithm is active.
OUT1 Lit when OUT 1 is ON.
OUT2 Lit when OUT 2 is ON or alarm 1 is in the
alarm state.
OUT3 Lit when the alarm 2 is in the alarm state.
Flashing with slow rate when the OUT 1
failure detection is in the alarm state.
Flashing with high rate when the OUT 1
failure detection and alarm 2 are in the
alarm state.
Other functions are shown by decimal points:
REM = Flashing, when the instrument is
controlled via serial link.
REM
SP2
MAN
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM18
Page 22

19
SP2 = Flashing at slow rate when SP2 is used.
Flashing at fast rate when a set point from
serial link is used.
MAN= Flashing at slow rate, when the instrument
is in MANUAL mode.
Pushbutton functionality during operating mode.
FUNC = o when the instrument is in "normal
display mode"
1)with a brief pressure (<3s) it starts
the parameter modification
procedure.
2)with a pressure within 3s to 10s it
changes the indication on the lower
display (see "display function").
3)with a pressure longer than 10s it
enables the lamp test (see "Lamp
Test" paragraph).
o During parameter modification, it
allows to memorize the new value of
the selected parameter and go to the
next parameter (increasing order).
MAN = o when the instrument is in "normal
display mode", pushing MAN
pushbutton for more than 1 s, it is
possible to enable or disable the
manual function.
o During parameter modification, it
allows to scroll back the parameters
without memorizing the new setting.
s = o During parameter modification, it
allows to increase the value of the
selected parameter
o During MANUAL mode, it allows to
increase the output value.
t = o During parameter modification, it
allows to decrease the value of the
selected parameter
o During MANUAL mode, it allows to
decrease the output value.
s+FUNC = when device is in normal display
mode, they allow to enable/disable
the control output (see "Enable/
disable the control output" paragraph).
s+MAN = During parameter modification they
allow to jump to the maximum
programmable value.
t+MAN = During parameter modification they
allow to jump to the minimum
programmable value.
NOTE: a 10 or 30 seconds time out (see P 35)
can be selected for parameter modification during
run time mode.
If, during parameter modification, no pushbutton
is depressed for more than 10 (30) seconds, the
instrument goes automatically to the “normal
display mode” and the eventual modification of
the last parameter will be lost.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM19
Page 23

20
ENABLE/DISABLE THE CONTROL OUTPUT
When the instrument is in "normal display mode",
by keeping depressed for more than 5s s and
FUNC pushbuttons, it is possible to disable the
control outputs. In this open loop mode the device
will function as an indicator, the lower display will
show the word OFF and all control outputs will
also be in the OFF state.
When the control outputs are disabled the alarms
are also in non alarm condition.
The alarm outputs conditions depend on the
alarm action type (see P19-P21).
Depress for more than 5s s and FUNC
pushbuttons to restore the control status.
The alarm stand-by function, if configured, will be
activated as if it was at power up.
If a power down occurs when the control output is
disabled, at intrument power up the control output
will be automatically disabled.
SP - SP2 SELECTION
It is possible to select the operating set point (SP
or SP2) only by an external contact (terminals 14
and 15).
This function excludes the "OUT 1 failure
detection" function and the current transformer.
By setting P41, it is possible to display the final or
the operative set point during a ramp execution.
OUT 1 FAILURE DETECTION FUNCTION
The device is capable (for the load driven by the
OUT 1) to measure and display:
- the current running in the load when the load is
energized;
- the leakage current, flowing through the load,
when the load is de-energized.
If the P10 parameter has been correctly set, the
instrument generates an alarm when:
- the current running in the load is lower than the
"Hbd" parameter value (It shows a partial or
total break down of the load, the break down of
the actuator or a power down due to a
protection or a fuse intervention);
- the leakage current is higher than the "SCA"
parameter value (It shows a short circuit of the
actuator).
The "Display function" paragraph describes how
to show the two current values.
A fault condition is shown by OUT 3 LED flashing
and by OUT 3 relay status.
If the ON or OFF period is lower than 400 ms the
relative measurement couldn't be performed and
the instrument will show flashing the last
measured value.
DIRECT ACCESS TO THE SET POINT
When the device is in AUTO mode and in “Normal
Display Mode”, it is possible to access directly to
set point modification (SP or SP2).
Pushing s or t for more than 2 s, the set point
will begin changing.
The new set point value becomes operative since
no pushbutton has been depressed at the end of
2 s timeout.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM20
Page 24

21
MANUAL FUNCTION
The MANUAL mode function can be accessed
(only if enabled by P26=On) by depressing the
MAN pushbutton for more than 1 sec.
The command is accepted and executed only if
the display is in "Normal Display Mode".
When in MANUAL mode the LED's MAN
annunciator will light up while the lower display
shows the power output values.
The value of OUT 1 is shown in the two most
significant digit field while the value of OUT 2 (if
present) is shown in the two less significant digit
field.
The decimal point between the two values will be
flashing to indicate instrument in manual mode.
Note: A graphic symbol "
" is used for
OUT1 = 100
A graphic symbol " " is used for
OUT2 = 100
The power output can be modified by using s
and t pushbuttons.
By depressing, for more than 1 second, MAN
pushbutton the device returns in AUTO mode.
The transfer from AUTO to MANUAL and
viceversa is bumpless (this function is not
provided if integral action is excluded).
If transfer from AUTO to MANUAL is performed
during the first part of SMART algorithm (TUNE)
when returning in AUTO the device will be forced
automatically in the second part of the SMART
algorithm (ADAPTIVE).
At power up the device will be in the AUTO mode
or as it was left prior to power shut down
depending on P33 configuration selection.
Note: When start up occurs in Manual mode the
power output (OUT1 - OUT2) is set to 0.
SERIAL LINK
The device can be connected to a host computer
by a serial link.
The host can put the device in LOCAL (functions
and parameters are controlled via keyboard) or in
REMOTE (functions and parameters are
controlled via serial link).
The REMOTE status is signalled by the decimal
point (labelled REM) at the right hand of the LSD
of the upper display.
This instrument allows to modify the operative
and configuration parameters, via serial link.
The necessary conditions to implement this
function are the following:
1) Serial parameters from SEr1 to SEr4 should be
properly configured using the standard front
keyboard procedure
2) Device must be in the OPERATING mode
During the downloading configuration the device
goes in open loop with all output in OFF state.
At the end of configuration procedure, the device
performs an automatic reset and then returns to
close loop control.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM21
Page 25

22
LAMP TEST
When it is desired to verify the display efficiency,
push FUNC pushbutton for more than 10 s. The
instrument will turn ON, with a 50 % duty cycle,
all the LEDs of the display (we define this function
"LAMP TEST").
No time out is applied to the LAMP TEST.
When it is desired to come back to the normal
display mode, push FUNC pushbutton again.
During the LAMP TEST the instrument continues
to control the process but no keyboard functions
are available (exception made for the FUNC
pushbutton).
SMART function
It is used to automatically optimize the control
action.
To enable the SMART function, push the FUNC
pushbutton until "Snrt" parameter is shown.
Pushing s or t set the display "On" and push
the FUNC pushbutton.
The SMRT LED will turn on or flashing according
to the algorithm selected.
When the smart function is enabled, it is possible to
display but not to modify the control parameters.
To disable the SMART function, push the FUNC
pushbutton again until "Snrt" parameter is shown.
Pushing s or t set the display "OFF" and
push the FUNC pushbutton.
The SMRT LED will turn off.
The instrument maintains the actual set of control
parameters and it enables parameter modification.
NOTES : 1) When ON/OFF control is pro-
grammed (Pb=0), the SMART
function is disabled.
2) The SMART enabling/disabling can
be protected by safety key (see
P27).
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM22
Page 26

23
When it is desired to switch from LOCK
to UNLOCK condition, set a value equal
to P18 parameter.
When it is desired to switch from
UNLOCK to LOCK condition, set a value
different from P18 parameter.
AL1 Alarm 1 threshold
This parameter is available only if P 7 is
equal to 1,2 or 3.
Ranges:
- Span limits for process alarm.
- From 0 to 500 units for band alarm.
- From -500 to 500 units for deviation
alarm.
HSA1 Alarm 1 hysteresis
This parameter is available only if P 7 is
equal to 1,2 or 3.
Range:From 0.1% to 10.0% of the input
span or 1 LSD.
Note: If the hysteresis of a band alarm is
larger than the alarm band, the instrument
will use an hysteresis value equal to the
programmed band minus 1 digit.
AL2 Alarm 2 threshold
This parameter is available only if P 12 is
equal to 1,2 or 3 and P14 is equal to OPrt.
For other details see AL1parameter.
HSA2 Alarm 2 hysteresis
This parameter is available only if P 12 is
equal to 1,2 or 3 and P14 is equal to OPrt.
For other details see HSA1parameter.
Pb Proportional band
Range:
- from 1.0% to 100.0% of the input span
for one control output.
- from 1.5% to 100.0% of the input span
for two control outputs.
When Pb parameter is set to 0.0, the
control action becomes ON-OFF.
OPERATIVE PARAMETERS
Push the FUNC pushbutton, the lower display will
show the code while the upper display will show
the value or the status (ON or OFF) of the
selected parameter.
By s or t pushbutton it is possible to set the
desired value or the desired status.
Pushing the FUNC pushbutton, the instrument
memorizes the new value (or the new status) and
goes to the next parameter.
Some of the following parameter may be skipped
according to the instrument configuration.
Param. DESCRIPTION
SP Set point (in eng. units).
Range: from rL to rH.
SP is operative when the logic input is
open.
Snrt SMART status.
The On or OFF indication shows the
actual status of the SMART function
(enabled or disabled respectively).
Set On to enable the SMART function.
Set OFF to disable the SMART function.
n.rSt Manual reset of the alarms.
This parameter is skipped if none of the
alarms has the manual reset function.
Set On and push FUNC to reset the alarms.
SP2 Set point 2 (in eng. units).
Range: from rL to rH.
SP2 is operative when the logic input is
closed.
nnn Software key for parameter protection.
This parameter is skipped if P18 = 0 or 1
On = the instrument is in LOCK condition
OFF = the instrument is in UNLOCK condition
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM23
Page 27

24
rC Relative Cooling gain.
This parameter is available only when
device is configured with two control
outputs and Pb is different from zero.
Range: from 0.20 to 1.00
Note: When the device is working with
SMART algorithm and P28 is set to On
the RCG value is limited in accordance
with the selected type of cooling media:
- from 0.85 to 1.00 when P8 = AIr
- from 0.80 to 0.90 when P8 = OIL
- from 0.30 to 0.60 when P8 = H2O
OLAP Dead band/Overlap between H/C
outputs.
This parameter is available only when
device is configured with two control
outputs and Pb is different from zero.
Range: from -20 to 50 % of the
proportional band.
A negative OLAP value shows a dead
band while a positive value shows an
overlap.
rL Set point low limit
Range: from initial scale value (P3) to rH.
Note: When P3 has been modified, rL
will be realigned to it
rH Set point high limit
Range:from rL to full scale value (P4)
Note: When P4 has been modified, rH
will be realigned to it
Grd1 Ramp applied to an increasing set
point change
Range: from 1 to 100 digits per minute.
Above this value the display shows “Inf”
meaning that the transfer will be done as
a step change.
Grd2 Ramp applied to a decreasing set
point changes
For other details see Grd1 parameter.
Note:When device is working with SMART
algorithm the Pb value will be limited by
P29, P30 and P31 parameters.
HyS Hysteresis for ON/OFF control action
This parameter is available only when
Pb=0.
Range: from 0.1% to 10.0% of the input
span.
ti Integral time
This parameter is skipped if Pb=0 (ON/
OFF action).
Range: from 00.01 to 20.00 [mm.ss].
Above this value the display blanks and
integral action is excluded
Note: When the device is working with
SMART algorithm, the minimum value of
the integral time will be limited by P32
parameter.
td Derivative time
This parameter is skipped if Pb=0
(ON/OFF action) or P40 = Pi.
Range:From 00.00 to 10.00 mm.ss.
Notes: When device is working with
SMART algorithm the td value will be
equal to a quarter of Ti value.
IP Integral pre-load.
This parameter is skipped if Pb=0
(ON/OFF action).
For one control output, it is programmable from 0 to 100 % of the output span.
For two control outputs it is programmable from -100% (100 % cooling)
to 100 % (100 % heating).
Cy1 Output 1 cycle time
Range:From 1 to 200 s.
Cy2 Output 2 cycle time
This parameter is available only if P 7 is
equal to 4.
Range:From 1 to 200 s.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM24
Page 28

25
OLH Output high limit
Range:
- From 0 to 100 % when device is
configured with one control output.
- From -100 to 100% when device is
configured with two control outputs.
tOL Time duration of the output power
limiter (soft start)
Range: from 1 to 540 min.Above this
value the display shows “InF” meaning
that the limiting action is always on
Note: The tOL can be modified but the
new value will become operative only at
the next instrument start up.
Hbd Threshold value for out 1 break down
alarm
This parameter is available only when
P10 is equal to N.O. or N.C.
Range: From 0 to P11 value (in ampere).
Notes:
The threshold resolution will be equal to
0.1 A for range up to 20 A and 1 A for
range up to 100 A.
The hysteresis of this alarm is fixed to
1% of fsv
SCA Threshold value for OUT 1 short
circuit alarm.
This parameter is available only when
P10 is equal to N.O. or N.C.
Range: From 0 to P11 value (in
ampere).
Notes:
The threshold resolution will be equal to
0.1 A for range up to 20 A and 1 A for
range up to 100 A.
The hysteresis of this alarm is fixed to
1% of fsv
rnP Control output maximum rate of rise
This parameter is available only when
Pb is different from zero
It is programmable from 1% to 25%
of the output per second.
Above the 25%/s, the display will show
"InF" meaning that no ramp is imposed.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM25
Page 29

26
ERROR MESSAGES
OVERRANGE, UNDERRANGE AND
SENSOR LEADS BREAK INDICATIONS
The device is capable to detect a fault on the
process variable (OVERRANGE or
UNDERRANGE or SENSOR LEADS BREAK).
When the process variable exceeds the span
limits set by configuration parameter P 1 an
OVERRANGE condition will be shown on display
as show in the following figure:
An UNDERRANGE condition will be shown on
display as show in the following figure:
When P37 is equal to 0, the following conditions
may occur:
- The instrument is set for one output only and if
an OVERRANGE is detected, the output turns
OFF (if reverse action) or ON (if direct action).
- The instrument is set for heating/cooling action
and an OVERRANGE is detected, "rEV" output
turns OFF and "dir" output turns ON.
- The instrument is set for one output only and if
an UNDERRANGE is detected, the output turns
ON (if reverse action) or OFF (if direct action).
- The instrument is set for heating/cooling action
and an UNDERRANGE is detected, "rEV"
output turns ON and "dir" output turns OFF.
When P37 is different from zero and an out of
range condition is detected, the instrument
operates in accordance with P37 and P38
parameters.
The sensor leads break can be signalled as:
- for TC/mV input : OVERRANGE or
UNDERRANGE selected by
a solder jumper
- for RTD input : OVERRANGE
- for mA/V input : UNDERRANGE
Note: On the mA/V input the leads break can be
detected only when the range selected has a zero
elevation (4/20 mA or 1/5 V or 2/10 V)
On RTD input a special test is provided to signal
OVERRANGE when input resistance is less than
15 ohm (Short circuit sensor detection).
ERROR MESSAGES
The instrument performs self-diagnostic algorithm.
When an error is detected, the instrument shows
on the lower display the “Err” indication while the
upper display shows the code of the detected
error.
ERROR LIST
SEr Serial interface parameter error.
100 Write EEPROM error.
150 CPU error.
200 Tentative to write on protected
memory.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM26
Page 30

27
201 - 2xx Configuration parameter error. The
two less significant digits shown the
number of the wrong parameter (ex.
209 Err shows an Error on P9
parameter)
301 RTD input calibration error
305 TC/mV input calibration error
307 RJ input calibration error
310 CT input calibration error
311 Error on 20 mA input calibration
312 Error on 5 V input calibration
313 Error on 10 V input calibration
400 Control parameters error
500 Auto-zero error
502 RJ error
510 Error during calibration procedure
NOTES
1) When a configuration parameter error is
detected, it is sufficient to repeat the configuration procedure of the specify parameter.
2) If error 400 is detected, push contemporarily
the t and s pushbuttons for loading the
default parameters then repeat control
parameter setting.
3) For all the other errors, contact your supplier.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM27
Page 31

28
GENERAL INFORMATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Case: Polycarbonate dark grey color (RAL 7043);
self-extinguishing degree: V-0 according to UL 94.
Front protection - designed and tested for IP 65 (*)
and NEMA 4X (*) for indoor locations (when panel
gasket is installed).
(*) Test were performed in accordance with
CEI 70-1 and NEMA 250-1991 STD.
Installation: panel mounting.
Rear terminal block: 15 screw terminals ( screw
M3, for cables from f 0.25 to f 2.5 mm
2
or from
AWG 22 to AWG 14 ) with connections diagram
and safety rear cover.
Dimensions: DIN 43700 48 x 48 mm, depth 122
mm.
Weight: 250 g.
Power supply:
- 100V to 240V AC 50/60Hz (-15% to + 10% of
the nominal value).
- 24 V AC/DC (
+ 10 % of the nominal value).
Power consumption: 8 VA max.
Insulation resistance: > 100 MW according to
IEC 1010-1.
Dielectric strength: 1500 V rms according to
IEC 1010-1.
Display updating time: 500 ms.
Sampling time: 250 ms for linear inputs
500 ms for TC and RTD inputs.
Resolution: 30000 counts.
Accuracy:
+ 0,2% f.s.v.. + 1 digit @ 25 °C
ambient temperature.
Common mode rejection: 120 dB @ 50/60 Hz.
Normal mode rejection: 60 dB @ 50/60 Hz.
Electromagnetic compatibility and safety
requirements: This instrument is marked CE.
Therefore, it is conforming to council directives
89/336/EEC (reference harmonized standard
EN 50081-2 and EN 50082-2) and to council
directives 73/23/EEC and 93/68/EEC (reference
harmonized standard EN 61010-1).
Installation category: II
Temperature drift: (CJ excluded)
< 200 ppm/°C of span for mV and TC ranges 1, 3, 5,
6, 19, 20, 21, 22.
< 300 ppm/°C of span for mA/V
< 400 ppm/°C of span for RTD range 10, 26 and
TC range 0, 2, 4, 27, 28.
< 500 ppm/°C of span for RTD range 9 and
TC ranges 7,8, 23, 24.
< 800 ppm/°C of span for RTD range 25.
Operative temperature: from 0 to 50 °C (+32 to
122 °F).
Storage temperature: -20 to +70 °C (-4 to 158
°F)
Humidity: from 20 % to 85% RH, non condensing.
Protections:
1) WATCH DOG circuit for automatic restart.
2) DIP SWITCH for protection against tampering
of configuration and calibration parameters.
INPUTS
A) THERMOCOUPLE
Type : L -J -K -N -R -S -T. °C/°F selectable.
External resistance: 100 W max, maximum error
0,1% of span.
Burn out: It is shown as an overrange condition
(standard). It is possible to obtain an underrange
indication by cut and short.
Cold junction: automatic compensation from 0 to
50 °C.
Cold junction accuracy : 0.1 °C/°C
Input impedance: > 1 MW
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM28
Page 32

29
Calibration : according to IEC 584-1 and DIN
43710 - 1977.
STANDARD RANGES TABLE
B) RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector)
Input: for RTD Pt 100 W, 3-wire connection.
Input circuit: current injection.
°C/°F selection: via front pushbuttons or serial link.
Line resistance: automatic compensation up to
20 W/wire with no measurable error.
Calibration: according to DIN 43760
Burnout: up scale. NOTE: a special test is
provided to signal OVERRANGE when input
resistance is less than 15 W.
STANDARD RANGES TABLE
C) LINEAR INPUTS
Read-out: keyboard programmable between
-1999 and +4000.
Decimal point: programmable in any position
Burn out: the instrument shows the burn out condi-
tion as an underrange condition for 4-20 mA, 1-5 V
and 2-10 V input types.
It shows the burn out condition as an underrange or
an overrange condition (selectable by soldering
jumper) for 0-60 mV and 12-60 mV input types. No
indication are available for 0-20 mA, 0-5 V and 0-10
V input types.
D) LOGIC INPUT
The instrument is equipped with one input from
contact (voltage free) for setpoint selection.
Contact open = Main setpoint.
Contact closed = Auxiliary setpoint.
NOTES:
1) Use an external dry contact capable of
switching 0.5 mA, 5 V DC.
2) The instrument needs 100 ms to recognize a
contact status variation.
3) The logic input is NOT isolated by the
measuring input.
4) This optional function is in alternative to
amperometer sensing transformer input.
Input type
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
0 - 60 mV
12 - 60 mV
0 - 20 mA
4 - 20 mA
0 - 5 V
1 - 5 V
0 - 10 V
2 - 10 V
impedance
> 1 MW
< 5 W
> 200 kW
> 400 kW
Accuracy
0.2 % + 1 digit
@ 25°C
T/C
type
L
L
J
J
K
K
N
R
S
T
Ranges
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
27
0 /+ 400.0°C
0 /+ 900 °C
-100.0/+ 400.0°C
-100 /+ 1000 °C
-100.0/+ 400.0°C
-100 /+ 1370 °C
-100 /+ 1400 °C
0 /+ 1760 °C
0 /+ 1760 °C
-199.9/+ 400.0°C
19
20
21
22
23
24
28
---
0 / + 1650 °F
---
-150 / + 1830 °F
---
-150 / + 2500 °F
-150 / + 2550 °F
0 / + 3200 °F
0 / + 3200 °F
-330 / + 750 °F
- 199,9 / + 400,0 °C
- 200 / + 800 °C
-199,9 / +400,0 °F
-330 / + 1470 °F
Input
type
RTD Pt 100 W
DIN 43760
Ranges
9
10
25
26
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM29
Page 33

30
CONTROL ACTIONS
Control action: PID + SMART
Type: One (heating or cooling) or two (heating
and cooling) control outputs.
Proportional Band (Pb):
Range: - from 1.0 to 100.0 % of the input span
for process with one control output.
- from 1.5 to 100.0 % of the input span
for process with two control output.
When Pb=0, the control action becomes ON/OFF.
Hysteresis (for ON/OFF control action):
from 0.1% to 10.0% of the input span.
Integral time (Ti): from 1s to 20 min. or
excluded.
Derivative time (Td): from 0 s to 10 min.
If zero value is selected, the derivative action is
excluded.
Integral pre-load:
- from 0.0 to 100.0 % for one control output
- from -100.0 (cooling) to +100.0 % (heating) for
two control output.
SMART: keyboard enabling/disabling
Auto/Manual: selectable by front pushbutton.
Auto/Manual transfer: bumpless method type
Indicator "MAN" : OFF in auto mode and lit in
manual mode.
OUTPUTS
Control output updating time :
- 250 ms when a linear input is selected
- 500 ms when a TC or RTD input is selected.
Action: direct/reverse programmable by front
keyboard.
Output level indication:
The instrument displays separately the output 1
level (heating) and the output 2 level (cooling).
E) CURRENT TRANSFORMER INPUT FOR
OUT1 FAILURE DETECTION
The instruments equipped with this feature are
capable, by means of a CT, to detect and signal a
possible failure of the line driven by out 1 (see
"OUT 1 failure detection").
Input range: 50 mA AC.
Scaling: programmable from 10 A to 100 A (with
1 A step).
Resolution:
- for full scale up to 20 A: 0.1 A.
- for full scale from 21 A to 100 A: 1 A
Minimum duration of the period (ON or OFF)
to perform the measurement: 400 ms.
NOTE : this function excludes the logic input
(external set point selection).
SET POINTS
This instrument allows to use 2 set points: SP and
SP2.
The set point selection is possible only by logic
input.
Set point transfer:
The transfer between one set point to another (or
between two different set point values) may be
realized by a step transfer or by a ramp with two
different programmable rate of change (ramp up
and ramp down).
Slope value: 1 - 100 eng. unit/min or step.
Set points limiter: RLO and RHI parameters, pro-
grammable.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM30
Page 34

31
Output status indication: Two indicators (OUT 1
and OUT 2) are lits when the respective output is
in ON condition.
Output level limiter:
- For one control medium :
from 0 to 100 % .
- For two control mediums :
from -100 to +100 % .
This function may be operative at instrument start
up for a programmable time (To avoid thermal
shock and/or preheating the plant) otherwise it
can be enabled by an external contact.
Cycle times:
- For out 1 it is programmable from 1 to 200 s.
- For out 2 it is programmable from 1 to 200 s.
Relative cooling gain: programmable from
0.20 to 1.00.
Overlap/dead band: programmable from - 20 %
to + 50 % of the proportional band
OUTPUT 1
Type: relay SPDT contact (NO or NC selectable
by jumper).
Contact rated: 3 A at 250 V AC on resistive load.
Output cycle time:programmable from 1 s to
200 s.
Function: programmable as heating or cooling
output
OUTPUT 2
Type: relay SPST contact .
Contact rated: 2 A at 250 V AC on resistive load.
Function: programmable as:
- control output ( cooling)
- Alarm 1 output
Output cycle time (when used as control output):
programmable from 1 s to 200 s.
OUTPUT 3
Type: relay with SPST contact
Contact rated: 2 A at 250 V AC on resistive load.
Function: Alarm 2 output.
ALARMS
Actions: Direct or reverse acting.
Alarm functions: each alarm can be configured
as process alarm, band alarm or deviation alarm.
Alarm reset: automatic or manual reset
programmable on each alarm.
Stand by (mask) alarm: each alarm can be
configured with or without stand by (mask)
function.
This function allows to delete false indication at
instrument start up and/or after a set point
change.
Process alarm:
Operative mode : High or low programmable.
Threshold : programmable in engineering unit within
the input span.
Hysteresis: programmable from 0.1 % to 10.0 % of
the input span (P4 - P3).
Band alarm
Operative mode: Inside or outside programma-
ble.
Threshold : programmable from 0 to 500 units.
Hysteresis : programmable from 0.1 % to 10.0 % of
the input span.
Deviation alarm:
Operative mode : High or low programmable.
Threshold : programmable from - 500 to +500 units.
Hysteresis : programmable from 0.1 % to 10.0 % of
the input span.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM31
Page 35

32
MAINTENANCE
1) REMOVE POWER FROM THE POWER
SUPPLY TERMINALS AND FROM RELAY
OUTPUT TERMINALS
2) Remove the instrument from case.
3) Using a vacuum cleaner or a compressed air
jet (max. 3 kg/cm
2
) remove all deposit of dust
and dirt which may be present on the louvers
and on the internal circuits trying to be careful
for not damage the electronic components.
4) To clean external plastic or rubber parts use
only a cloth moistened with:
- Ethyl Alcohol (pure or denatured) [C
2H5
OH] or
- Isopropil Alcohol (pure or denatured)
[(CH
3)2
CHOH] or
- Water (H
2
O)
5) Verify that there are no loose terminals.
6) Before re-inserting the instrument in its case,
be sure that it is perfectly dry.
7) re-insert the instrument and turn it ON.
SERIAL COMMUNICATION INTERFACE
Type: RS-485 insulated.
Protocol type: MODBUS, JBUS, ERO polling/
selecting.
Baud rate: programmable from 600 to 19200
BAUD.
Byte format: 7 or 8 bit programmable.
Parity: even, odd or none programmable.
Stop bit : one.
Address :
- from 1 to 95 for ERO protocol
- from 1 to 255 for all the other protocols
Output voltage levels: according to EIA standard.
1604-1-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM32
Page 36

A. 1
DEFAULT PARAMETERS
DEFAULT OPERATIVE PARAMETERS
The control parameters can be loaded with
predetermined default values. These data are the
typical values loaded in the instrument prior to
shipment from factory. To load the default values
proceed as follows:
a) The internal switch (V101, see fig. 14) should
be closed.
b) The SMART function should be disabled.
c) The instrument should be in Stand-by mode.
d) Held down t pushbutton and press s
pushbutton; the display will show:
e) Press s or t pushbutton; the display will
show:
g) Press FUNC pushbutton; the display will show:
It means that the loading procedure has been
initiated.
After about 3 seconds the loading procedure is
finished and the instrument reverts to NORMAL
DISPLAY mode.
The following is a list of the default operative
parameters loaded during the above procedure:
PARAMETER DEFAULT VALUE
SP = Minimum range-value
SnRT = Disable
n.RSt = OFF
SP2 = Minimum range value
nnn = OFF
AL1, AL2 = Minimum range-value for
process alarms
0 for deviation or band alarms
HSA1, HSA2 = 0.1 %
Pb = 4.0 %
hyS = 0.5 %
ti = 4.00 (4 minutes)
td = 1.00 (1 minute)
IP = 30 %
Cy1 = 15 seconds for relay output
4 seconds for SSR output
Cy2 = 10 seconds for P8 = AIr
4 seconds for P8 = OIL
2 seconds for P8 = H2O
rC = 1.00 for P8 = AIr
0.80 for P8 = OIL
0.40 for P8 = H2O
OLAP =0
rL = Initial scale value
rH = Full scale value
Grd 1 = Infinite (step transfer)
Grd 2 = Infinite (step transfer)
OLH = 100 %
tOL = Infinite
Hbd = 50 % of the full scale value.
SCA = 100 % of the full scale value.
rnP = 25 % of the output per second.
O F F
d F L t
O n
d F L t
LOAd
1604-A-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM1
Page 37

A. 2
DEFAULT CONFIGURATION
PARAMETERS
The configuration parameters can be loaded with
predetermined default values. These data are the
typical values loaded in the instrument prior to
shipment from factory. To load the default values
proceed as follows:
a) The internal switch should be open.
b) The upper display will show:
c) Push the t pushbutton; the display will show
the firmware version.
d) Maintaining the pressure on the t
pushbutton, push the s pushbutton also.
The instrument will show:
e) Press s pushbutton to select between table 1
(European) or table 2 (American) default set
parameters; the display will show:
f) Press FUNC pushbutton; the display will show:
It means that the loading procedure has been
initiated.
After about 3 seconds the loading procedure is
terminated and the instrument reverts to
visualization as in point b.
PARA. TABLE 1 TABLE 2
SEr 1 ErO ErO
SEr 2 1 1
SEr 3 19.20 19.20
SEr 4 7E 7E
P1 3 20
P2 ----. ----.
P3 0 0
P4 400 1000
P5 rEL rEL
P6 rEV rEV
P7 1 1
P8 AIr AIr
P9 H.A. H.A.
P10 OFF OFF
P11 10 10
P12 0 0
P13 H.A H.A.
P14 OPrt. OPrt
P15 0 0
P16 0.1 0.1
COnF
C0nF
A. 0 0
O F F
d F L t
t b 1
d F L t
LOAd
1604-A-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM2
Page 38

A. 3
P17 0 0
P18 0 0
P19 rEV rEV
P20 OFF OFF
P21 rEV rEV
P22 OFF OFF
P23 0 0
P24 Not available Not available
P25 On On
P26 On On
P27 2 2
P28 OFF OFF
P29 30 30
P30 1.5 1.5
P31 1.0 1.0
P32 00.50 00.50
P33 0 0
P34 Not available Not available
P35 tn 10 tn 30
P36 nO.FL nO.FL
P37 0 0
P38 0 0
P39 10 10
P40 PId PId
P41 Fn.Sp Fn.Sp
P42 0 0
1604-A-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM3
Page 39

1604-A-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM4
Page 40

170.IU0.160.400
Chromalox
®
INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS
1382 HEIL QUAKER BOULEVARD
LAVERGNE, TN 37086-3536
PHONE (615) 793-3900
FAX (615) 793-3563
WIEGAND INDUSTRIAL DIVISIONWIEGAND INDUSTRIAL DIVISION
WIEGAND INDUSTRIAL DIVISIONWIEGAND INDUSTRIAL DIVISION
WIEGAND INDUSTRIAL DIVISION
EMERSON ELECTRIC CO.
1604-A-BC.p65 5/16/00, 10:25 AM5
 Loading...
Loading...