Page 1

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 1
Contents
Document Use and Disclaimers ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Section A .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Body Control System Description and Operation ........................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Power Mode Master ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Gateway ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Body Control ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Power Mode Description and Operation ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Serial Data Power Mode Master .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Relay Controlled Power Mode ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 15
Battery Saver Mode (Transport Mode) ................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
BCM Awake/Sleep States ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Retained Accessory Power .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
RAP Description and Operation ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Relay Controlled Retained Accessory Power ........................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Serial Data Controlled Retained Accessory Power .................................................................................................................................................................. 18
Back-up Alarm and Camera ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Back-up Alarm and Camera relay installation schematic ........................................................................................................................................................ 20
Back-up Alarm, Camera and Lamps schematic ........................................................................................................................................................................ 21
Chassis Harness Routing .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Charging System Description of Operation ................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Electrical Power Management Overview ................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
Charging System .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 2

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 2
Charging System Components ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 24
Charge Mode ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Fuel Economy Mode ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 27
Headlamp Mode ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Start Up Mode ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Voltage Reduction Mode ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 28
Instrument Panel Cluster Operation ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 28
Charge Indicator Operation ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 28
Display Message: ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 28
Charging System schematic ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 29
Engine Idle Up .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 30
Elevated Idle ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 30
High Idle ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
PTO (power take-off) ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Vehicle Regular Production Option (RPO) Content ................................................................................................................................................................. 30
ADDING PTO OPTION TO A VEHICLE WITHOUT THE OPTION .................................................................................................................................................. 31
Installation of Electrical Aftermarket Accessories ...................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Installation of a Diode to Suppress Voltage Spikes ................................................................................................................................................................. 32
Remote Vehicle Immobilizer ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 33
Exterior Lighting Systems Description and Operation ................................................................................................................................................................. 34
Low Beam Headlamps ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 34
Run Up Of the Lamp................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 36
When to Change the HID Bulb ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 36
Light Color ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 37
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 3

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 3
High Beam Headlamps ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 37
Adaptive Forward Lighting (AFL) .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 37
Automatic Headlamp Leveling ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 38
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL)................................................................................................................................................................................................. 39
Automatic Lamp Control .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Flash to Pass (FTP) ................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Hazard Lamps ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Park, Tail, and License Lamps .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 40
Stop Lamps ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Turn Signal Lamps .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
Backup Lamps .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
Battery Run Down Protection/Inadvertent Power .................................................................................................................................................................. 41
X110 Left Forward Lamp Harness to Headlamp - Connector End View and Pin-out .................................................................................................................. 42
X120 Right Forward Lamp Harness to Headlamp – Connector End View and Pin-out................................................................................................................ 44
Headlamp Replacement .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 46
Under hood Harness Routing ...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Tail lamp Replacement ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 47
Chassis Harness Routing .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 49
Rear Body Junction Block X63A –Connector X5........................................................................................................................................................................... 50
Rear Body Junction Block X63A –Connector X1........................................................................................................................................................................... 51
X63A Junction Block - Rear Body X1 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................................................. 52
Bulb Replacement ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 54
Rearward Lighting Separate Stop and Turn ................................................................................................................................................................................. 55
Rearward Lighting Separate Stop and Turn (continued) ............................................................................................................................................................. 56
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 4

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 4
Dome/Courtesy Lamps (-E29), DH6 ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 57
Dome/Courtesy Lamps E29 ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 58
Roof Mounted Beacon ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 59
Park Neutral Signal-Shift Lock Control ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 60
Shift Lock Control Schematic ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 61
Trailer Brake Control System ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 62
The Trailer Brake Control System is compatible with two types of Trailer Brake Systems as listed below: ........................................................................... 62
Trailer Brake Output versus Trailer Brake Type ....................................................................................................................................................................... 62
The vehicle is equipped with the following trailer braking components: ............................................................................................................................... 63
Chassis Control Module ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 63
Trailer Brake Power Control Module ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Trailer Brake Control Panel ...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Trailer Gain Adjustment ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Trailer Gain Adjustment Procedure ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Hill Start Assist ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Trailer Sway Control ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 65
Driver Information Center Indicators and Messages (Trailer Brake System) .............................................................................................................................. 66
Trailer Connected .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 66
Check Trailer Wiring ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 66
Service Trailer Brake System .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 67
Trailer Gain and Output Display .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 67
Trailer Brake Control System Schematic...................................................................................................................................................................................... 68
Chassis Control Module Connector ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 69
Trailer Connector 1 of 3 (Terminals A, B, D, E, F & G) ................................................................................................................................................................. 70
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 5

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 5
Trailer Connector 2 of 3 (Terminal C except E29) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 71
Trailer Connector 3 of 3 (Terminal C with E29) ........................................................................................................................................................................... 72
Trailer Connector Location .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 73
Trailer Connector Pin Out ............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 74
Section B .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 75
Understanding the Alpha Numeric Naming Convention ............................................................................................................................................................. 75
Fuse, Relay, and Block Names ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 75
Battery Fuse Block –Top View ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 76
Fuse Block (X50) Under-hood - Label........................................................................................................................................................................................... 77
Fuse Block (X50) Under-hood - Top View .................................................................................................................................................................................... 78
Fuse Block (X50) Under-hood - Bottom View .............................................................................................................................................................................. 79
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X1 ........................................................................................................................................................................... 86
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X2 ........................................................................................................................................................................... 88
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X3 ........................................................................................................................................................................... 90
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X4 ........................................................................................................................................................................... 92
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X5 ........................................................................................................................................................................... 94
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left - Label.......................................................................................................................................................................... 96
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left - Top View ................................................................................................................................................................... 97
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left - Bottom View ............................................................................................................................................................. 98
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left – Connector X1 ........................................................................................................................................................... 99
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left – Connector X1 Pin-out ............................................................................................................................................. 100
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left – Connector X2 ......................................................................................................................................................... 102
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left – Connector X2 Pin-out ............................................................................................................................................. 103
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left – Connector X3 ......................................................................................................................................................... 105
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 6

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 6
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel – Connector X3 Pin-out .................................................................................................................................................... 106
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel Right - Label ..................................................................................................................................................................... 107
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel Right - Top View .............................................................................................................................................................. 108
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel – Bottom View ................................................................................................................................................................. 109
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel - Connector X1 ................................................................................................................................................................. 110
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel - Connector X1 Pin-outs ................................................................................................................................................... 111
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel - Connector X2 ................................................................................................................................................................. 113
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel - Connector X2 Pin-outs ................................................................................................................................................... 114
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel - Connector X3 ................................................................................................................................................................. 116
Fuse Block (X51R) Instrument Panel - Connector X3 Pin-outs ................................................................................................................................................... 117
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Top View ................................................................................................................................................................... 118
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Bottom View ............................................................................................................................................................. 119
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X1 ............................................................................................................................................................ 119
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X1 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 121
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X2 ............................................................................................................................................................ 123
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X3 ............................................................................................................................................................ 126
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X3 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 127
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X4 ............................................................................................................................................................ 129
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X4 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 129
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X5 ............................................................................................................................................................ 132
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X5 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 133
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X6 ............................................................................................................................................................ 135
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X6 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 135
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X7 ............................................................................................................................................................ 136
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 7

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 7
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X7 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 137
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X8 ............................................................................................................................................................ 138
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X8 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 139
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X9 ............................................................................................................................................................ 140
Junction Block (X61) Instrument Panel – Connector X9 Pin-outs .............................................................................................................................................. 140
Section C......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 143
K9 Body Control Module ............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 143
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X1 ................................................................................................................................................................... 143
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X1 Pin-outs ..................................................................................................................................................... 144
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X2 ................................................................................................................................................................... 146
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X2 Pin-outs ..................................................................................................................................................... 147
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X4 ................................................................................................................................................................... 149
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X4 Pin-outs ..................................................................................................................................................... 150
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X5 ................................................................................................................................................................... 152
K9 Body Control Module (BCM) – Connector X5 Pin-outs ..................................................................................................................................................... 153
Component Locations ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 177
Front of Vehicle - Chevrolet ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 177
Front of Vehicle - GMC .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 178
Right Side of Engine Compartment Components .................................................................................................................................................................. 179
Left Side of Engine Compartment Components .................................................................................................................................................................... 179
Underside of Engine Compartment & Cooling Fans .............................................................................................................................................................. 180
Engine Component Views (Top & Left Front) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 181
Engine Component Views (Right Rear, Manual Transmission & Transfer Case) ................................................................................................................... 182
Section D ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 183
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 8

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 8
Electrical System - Vehicle Zoning Strategy ............................................................................................................................................................................... 183
Adjustable Pedals (With A45) .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 185
Adjustable Pedals (Without A45) ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 186
Fixed and Moveable Windows –Front Doors ............................................................................................................................................................................ 187
Fixed and Moveable Windows – Rear Doors & Rear Sliding Window ....................................................................................................................................... 188
Rear Defogger/Horns ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 189
Exterior Lighting - Headlights/Daytime Running Lights (DRL) ................................................................................................................................................... 190
Exterior Lighting – Park Lamps and Controls ............................................................................................................................................................................. 191
Exterior Lighting – Outside Mirror Lamps and Controls ............................................................................................................................................................ 192
Exterior Lighting – Turn Signal Lamps ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 193
Exterior Lighting – Fog Lamps and Roof Lighting ....................................................................................................................................................................... 194
Exterior Lighting –Tail lamps ...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 194
Exterior Lighting – CHMSL and License Plate lamps .................................................................................................................................................................. 196
Interior Lighting – Controls (DD7) .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 197
Interior Lighting – Front Dome Lamps (-E29), DH6 ................................................................................................................................................................... 198
Interior Lighting – Front Dome Lamps (E29) .............................................................................................................................................................................. 199
Interior Lighting – Accent Lamps ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 200
Interior Lighting – Dimming (1 of 3) .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 201
Interior Lighting – Dimming (2 of 3) .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 202
Interior Lighting – Dimming (3 of 3) .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 203
Mirrors – Inside Rearview (DD8) ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 204
Mirrors – Outside Rearview Driver (with A45) .......................................................................................................................................................................... 205
Mirrors – Outside Rearview Passenger (with A45) .................................................................................................................................................................... 206
Mirrors – Outside Rearview Position Controls (without A45) ................................................................................................................................................... 207
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 9

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 9
Mirrors – Outside Rearview Heat (DL8, DL3 or DPN) ................................................................................................................................................................ 208
Vehicle Access - Front Switches and Indicators (1 of 2) ............................................................................................................................................................ 209
Vehicle Access - Front Switches and Indicators (2 of 2) ............................................................................................................................................................ 210
Vehicle Access - Rear Switches and Indicators .......................................................................................................................................................................... 211
Vehicle Access – Actuators ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 212
Wipers and Washers – Controls ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 213
Wipers and Washers – Motor and Washers .............................................................................................................................................................................. 214
Cigar Lighter/Power Outlets – 12V DC ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 215
Cigar Lighter/Power Outlets – 110V AC ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 216
Cigar Lighter/Power Outlets – 220V AC ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 217
Power Moding Schematics - Ignition Off, Ignition I and Retained Accessory ............................................................................................................................ 218
Power Moding Schematics - Ignition II and Ignition III .............................................................................................................................................................. 219
Power Distribution Schematics - X50D Fuse Block - Battery ..................................................................................................................................................... 220
Power Distribution Schematics X50A Fuse Block – Under-hood Bussing .................................................................................................................................. 221
Power Distribution Schematics - F1UA, F2UA, F11UA, F12UA, F18UA, F20UA and F54UA ...................................................................................................... 222
Power Distribution Schematics - 4WD Fuse, F9UA, F35UA, F47UA and F53UA ........................................................................................................................ 223
Power Distribution Schematics - F14UA, F27UA and F57UA ..................................................................................................................................................... 224
Power Distribution Schematics - F13UA, F16U and F28UA ....................................................................................................................................................... 225
Power Distribution Schematics - F15UA, F32UA, F37UA and F48UA ........................................................................................................................................ 226
Power Distribution Schematics - F33UA, F39UA and F49UA ..................................................................................................................................................... 227
Power Distribution Schematics - F42UA, F44UA, F45UA and F50UA ........................................................................................................................................ 228
Power Distribution Schematics - F43UA .................................................................................................................................................................................... 229
Power Distribution Schematics - F3UA, F4UA, F7UA, F24UA and F56UA ................................................................................................................................. 230
Power Distribution Schematics - X51L Fuse Block - Instrument Panel Left Bussing .................................................................................................................. 231
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 10

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 10
Power Distribution Schematics - F6DL, F7DL, F9DL, F17DL, F25DL, F26DL, F34DL and F44DL ................................................................................................. 232
Power Distribution Schematics - F22DL, F23DL, F30DL, F31DL and F32DL ............................................................................................................................... 233
Power Distribution Schematics - F1DL, F2DL, F3DL, F10DL, F11DL, F12DL, F13DL, F40DL and F41DL...................................................................................... 234
Power Distribution Schematics - X51R Fuse Block - Instrument Panel Right Bussing ............................................................................................................... 235
Power Distribution Schematics - F7DR, F22DR, F31DR, F41DR, F44DR and F46DR .................................................................................................................. 236
Power Distribution Schematics - F18DR, F25DR and F38DR ..................................................................................................................................................... 237
Power Distribution Schematics - F6DR, F8DR, F27DR, F34DR, F35DR, F42DR and F43DR ........................................................................................................ 238
Ground Distribution Schematics - G101 and G102 .................................................................................................................................................................... 239
Ground Distribution Schematics - G108, G130, G140 and G327 ............................................................................................................................................... 240
Ground Distribution Schematics - G110 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 241
Ground Distribution Schematics - G121 and G400 .................................................................................................................................................................... 242
Ground Distribution Schematics - G210 (1 of 2) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 243
Ground Distribution Schematics - G210 (2 of 2) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 244
Ground Distribution Schematics - G218 (except E29) ............................................................................................................................................................... 245
Ground Distribution Schematics - G218 (E29) ........................................................................................................................................................................... 246
Ground Distribution Schematics - G311 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 247
Ground Distribution Schematics - G312 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 248
Ground Distribution Schematics - G325 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 249
Ground Location Views – G101 ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 250
Ground Location Views G102 .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 251
Ground Location Views G110 .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 252
Ground Location Views G120 .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 253
Ground Location Views G121 and G400 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 254
Ground Location Views G130 .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 255
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 11

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 11
Ground Location Views G140 .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 256
Ground Location Views G210 and G218 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 257
Ground Location Views G311 and G325 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 258
Ground Location Views G312 and G327 .................................................................................................................................................................................... 259
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 12

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 12
Document Use and Disclaimers
GM Upfitter Integration Body Builder Manuals and Technical Bulletins are intended for use by professional technicians,
NOT a "do-it-yourselfer". They are written to inform technicians of conditions that may occur on some vehicles and/or
models, or to provide information that could assist in the proper service and/or modification of a vehicle. Properly
trained technicians have the equipment, tools, safety instructions, and know-how to do a job properly and safely. If a
condition is described, DO NOT assume that the bulletin applies to the vehicle and/or model, Also do NOT assume that
every vehicle and/or model will have that condition.
Contact GM Upfitter Integration for information on whether the information is applicable your vehicle.
GM Upfitter Integration does not take responsibility for nor approve alterations to GM Commercial Chassis, Pickup &
Utility Vehicles.
If an Upfitter or Second Stage Manufacturer (SSM) or Individual chooses to modify a GM Chassis/Vehicle and/or its
components, liability and possible recertification responsibility for compliance with all related FMVSS/CMVSS and
regional standards lies with the Upfitter/SSM or Individual.
In addition liability for Non-OEM (aftermarket) installed components used in modifications to a GM Chassis/Vehicle
and/or its components is solely with the responsible aftermarket component manufacturer and the installer. If an
Upfitter/SSM or Individual chooses to modify a GM part/s design or function they risk voiding the GM warranty and
assume liability for the modification
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 13

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 13
Section A
Body Control System Description and Operation
The body control system consists of the body control module (BCM), communications, and various input and outputs. Some inputs, outputs and
messages require other modules to interact with the BCM. The BCM also has discrete input and output terminals to control the vehicle's body
functions. The BCM is wired to the high speed GMLAN serial data bus, low speed GMLAN serial data bus and Multiple LIN buses and acts as a
gateway between them.
Power Mode Master
This vehicle body control module (BCM) functions as the power mode master (PMM). The ignition switch is a low current switch with
multiple discrete ignition switch signals to the PMM for determining the power mode that will be sent over the serial data circuits to the
other modules that need this information; the PMM will activate relays and other direct outputs of the PMM as needed. Refer to Power
Mode Description and Operation for a complete description of power mode functions.
Gateway
The body control module (BCM) in this vehicle functions as a gateway or translator. The purpose of the gateway is to translate serial
data messages between the GMLAN high speed bus and the GMLAN low speed bus for communication between the various modules.
The gateway will interact with each network according to that network's transmission protocol.
All communication between the BCM and a scan tool is on the high speed GMLAN serial data circuits. A lost communication DTC
typically is set in modules other than the module with a communication failure.
Body Control
The various body control module (BCM) input and output circuits are illustrated in the corresponding functional areas on the BCM
electrical schematics. Refer to the Body Control System Schematics for more detailed information.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 14

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 14
Power Mode Parameters
Ignition Switch Position
Power Mode Transmitted
Ign. Off/Run/Crank
(Off/Run Crank Voltage Circuit)
Ignition Accessory/Run
(Accessory Voltage Circuit)
Ignition Run/Crank
(Ignition 1 Voltage Circuit)
Off Key Out
Off
Key Out / ACC
Inactive
Inactive
Off Key IN
Off
Key In / Off
Inactive
Inactive
Accessory
Accessory
Key Out / ACC
Active
Inactive
Run
Run
Run
Active
Active
Start
Crank Request
Crank
Inactive
Active
Power Mode Description and Operation
Serial Data Power Mode Master
Power to many of this vehicles circuits is controlled by the module that is designated the power mode master. This vehicles power mode
master is the body control module (BCM). The BCM has multiple B+ circuits that feed into it. Each of those circuits are partitioned within
the controller to drive certain outputs of the vehicle’s body functions. An open or short in any one of the B+ circuits may induce multiple
codes/or a section of non-functionality within the BCM with the rest of the BCM functioning normally. In this case it is useful to refer to
the power distribution schematics to determine if the non-functional partition of the controller shares a common B+ circuit. The ignition
switch is a low current switch with multiple discrete ignition switch signals to the power mode master for determination of the power
mode that will be sent over the serial data circuits to the other modules that need this information. The power mode master will also
activate relays and other direct outputs of the power mode master as needed. The power mode master determines which power mode
(Off, Accessory, Run, Crank Request) is required, and reports this information to other modules via serial data. Modules which have
switched voltage inputs may operate in a default mode if the power mode serial data message does not match what the individual
module can see from its own connections.
The power mode master receives ignition switch signals to identify the operators desired power mode. The Power Mode Parameter
tables below illustrate the correct state of these input parameters (circuits) in correspondence to the ignition switch position:
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 15

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 15
Relay Controlled Power Mode
The BCM uses the discrete ignition switch inputs Off/Run/Crank Voltage, Accessory Voltage, and Ignition 1 Voltage, to distinguish the
correct power mode. The BCM, after determining the desired power mode, will activate the appropriate relays for that power mode.
The retained accessory power relay 1 and retained accessory power relay 2 remain on for a timed period after the Ignition key is
removed. Refer to Retained Accessory Power Description and Operation for more information on the retained accessory power
function.
Battery Saver Mode (Transport Mode)
Battery saver mode (transport mode) reduces the parasitic load of some modules during overseas shipment or during vehicle storage
conditions. This improves the drain time on the battery (up to 70 days without the battery going dead). When a vehicle is in
transport/storage, some features may have reduced functionality while in the battery saver mode, such as disabling keyless entry, afterblow, and content theft features. Battery saver mode is initiated by turning on the hazard flashers, applying the brake pedal, and then
turning the ignition key to the start position or pushing the ignition mode switch with the foot on the brake for greater than 15 seconds.
The mode is disengaged by repeating the previous process. The driver information center (if equipped) will display Transport Mode is On
when battery saver mode is enabled and Transport Mode is Off when battery saver mode is disabled. For vehicles not equipped with a
driver information center, the battery indicator light will constantly flash on the Instrument Cluster when battery saver mode is enabled.
This feature can be used as many times as necessary if the vehicle is to be stored for an extended period of time.
BCM Awake/Sleep States
The BCM is able to control or perform all of the BCM functions in the awake state. The BCM enters the sleep state when active control
or normal monitoring of system functions has stopped and a time limit has passed. The BCM must detect certain wake-up inputs before
entering the awake state. The BCM monitors for these inputs during the sleep state.
The BCM will enter the awake state if any of the following wake-up inputs are detected:
Activity on the serial data line
Detection of a battery reconnect
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 16

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 16
Any door open signal
Headlamps ON
Key-in-ignition
Ignition ON
Park lamps ON
Keyless entry or remote start message
The BCM will enter a sleep state when all of the following conditions exist:
The ignition switch is OFF, key out.
Ignition OFF, transmitter is out of range
No activity exists on the serial data line.
No outputs are commanded.
No delay timers are actively counting.
No wake-up inputs are present.
If all these conditions are met, the BCM will enter a low power or sleep condition.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 17

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 17
Retained Accessory Power
RAP Description and Operation
The Body Control Module (BCM) monitors the ignition switch position, battery condition, and each door ajar/open switch status to
determine whether the retained accessory power should be initiated or terminated. Retained accessory power is controlled by two
different methods; relay control and serial data. Some modules receive a retained accessory power message from the BCM over the
serial data circuits. Serial data controlled retained accessory power is deactivated as required by their modules retained accessory
power mode operation. Other subsystems are activated directly by the BCM through a relay. Components and systems that are active in
retained accessory power are also activated anytime the ignition is any position other than OFF regardless of the door switch signals.
Relay Controlled Retained Accessory Power
The BCM keeps the retained accessory power relay 1 and retained accessory power relay 2 energized during all power modes, except
Off-Awake and Crank. The retained accessory power relay 1 and retained accessory power relay 2 are also energized for approximately
10 minutes after shutting the ignition OFF and removing the key, providing no door is opened.
Relay controlled retained accessory power will end when one of the following conditions is met:
The BCM receives an input from any door ajar or open switch indicating the opening of any door after the ignition key is out of
the ignition.
Note: If the BCM is receiving any door ajar or open signal from those switches when the ignition key is turned OFF, retained
accessory power will not initiate.
The BCM internal timer for the retained accessory power expires after approximately 10 minutes.
The BCM detects a decrease in battery capacity below a prescribed limit.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 18

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 18
Relay Controlled Retained Accessory Power (continued)
Systems powered by the retained accessory power relay 1 and retained accessory power relay 2 during the retained accessory power
mode are as follows:
Note: The vehicle may not be equipped with all components as listed below.
Accessory Power Receptacle
Cigarette Lighter Receptacle
Sunroof Control Module
Sunroof Switch
Sliding Rear Window Switch
Mobile Device Wireless Charger Module
Serial Data Controlled Retained Accessory Power
Retained accessory power systems controlled by serial data are as follows:
Radio:
Radio retained accessory power activation / termination is the same as relay operation with one exception; the only door switch that
will turn off the radio during retained accessory power is the driver door open switch.
Vehicle Communication Interface Module (VCIM) (Onstar®) (If Equipped)
VCIM RAP activation/termination is the same as radio operation with 1 exception; if there is an active call when the ignition key is
turned off the VCIM will remain in RAP mode, and keep the radio in RAP mode until the call is terminated.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 19

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 19
Back-up Alarm and Camera
For installation of a Back-up Alarm/Camera on vehicles not equipped with 8S3 (factory back-up alarm) connections can be made at the rear
body junction block (X63A).
In addition to when the vehicle is operated in reverse, the back-ups are illuminated during a lighted exit and as a key fob acknowledgement.
When using the back –lamps circuit to activate a back-up alarm, in which the perimeter lighting feature is set to ON for exiting, the back-up
alarm will be activated during the exit lighting event. To prevent this undesired alarm (or camera) activation during the exit lighting mode use
one of the two options listed below…
1. Have the vehicle’ BCM (Body Control Module) reprogramming with a new calibration that includes RPO (regular production Option)
code SFW. This option will suppress the activation of the Back-up lamps during the exit lighting mode operation.
OR
2. Install an ignition controlled relay to which only allows for the Back-up lamp signal to be provided to the alarm/camera if the ignition
is in the “RUN” mode, and the vehicle is being operated in reverse mode. (see sample schematic)
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 20

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 20
BACKUP LAMP WIRE
BACKUP ALARM
Relay
Ground
Back-up Alarm and Camera relay installation schematic
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 21

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 21
Back-up Alarm, Camera and Lamps schematic
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 22

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 22
Chassis Harness Routing
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 23

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 23
Charging System Description of Operation
Electrical Power Management Overview
The electrical power management system is designed to monitor and control the charging system and send diagnostic messages to alert
the driver of possible problems with the battery and generator. This electrical power management system primarily utilizes existing onboard computer capability to maximize the effectiveness of the generator, to manage the load, improve battery state-of-charge and life,
and minimize the system's impact on fuel economy. The electrical power management system performs 3 functions:
It monitors the battery voltage and estimates the battery condition.
It takes corrective actions by boosting idle speeds, and adjusting the regulated voltage.
It performs diagnostics and driver notification.
The battery condition is estimated during ignition-off and during ignition-on. During ignition-off the state-of-charge of the battery is
determined by measuring the open-circuit voltage. The state-of-charge is a function of the acid concentration and the internal resistance of
the battery, and is estimated by reading the battery open circuit voltage when the battery has been at rest for several hours.
The state-of-charge can be used as a diagnostic tool to tell the customer or the dealer the condition of the battery. Throughout ignition-on,
the algorithm continuously estimates state-of-charge based on adjusted net amp hours, battery capacity, initial state-of-charge, and
temperature.
While running, the battery degree of discharge is primarily determined by a battery current sensor, which is integrated to obtain net amp
hours.
In addition, the electrical power management function is designed to perform regulated voltage control to improve battery state-ofcharge, battery life, and fuel economy. This is accomplished by using knowledge of the battery state-of-charge and temperature to set the
charging voltage to an optimum battery voltage level for recharging without detriment to battery life.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 24

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 24
Charging System
The Charging System Description and Operation is divided into 3 sections. The first section describes the charging system components and
their integration into the electrical power management. The second section describes charging system operation. The third section
describes the instrument panel cluster operation of the charge indicator, driver information center messages, and voltmeter operation.
Charging System Components
Generator
The generator is a serviceable component. If there is a diagnosed failure of the generator it must be replaced as an assembly. The engine
drive belt drives the generator. When the rotor is spun it induces an alternating current (AC) into the stator windings. The AC voltage is
then sent through a series of diodes for rectification. The rectified voltage has been converted into a direct current (DC) for use by the
vehicles electrical system to maintain electrical loads and the battery charge. The voltage regulator integral to the generator controls the
output of the generator. It is not serviceable. The voltage regulator controls the amount of current provided to the rotor. If the generator
has field control circuit failure, the generator defaults to an output voltage of 13.8 V.
Body Control Module (BCM)
The body control module (BCM) is a GMLAN device. It communicates with the engine control module (ECM) and the instrument panel
cluster for electrical power management (electrical power management) operation. The BCM determines the output of the generator and
sends the information to the ECM for control of the generator turn on signal circuit. It monitors the generator field duty cycle signal circuit
information sent from the ECM for control of the generator. It monitors a battery current sensor, the battery positive voltage circuit, and
estimated battery temperature to determine battery state of charge. The BCM performs idle boost.
Battery Current Sensor
The battery current sensor is a serviceable component that is connected to either the negative or positive battery cable at the battery. The
battery current sensor is a 3-wire Hall Effect current sensor. The battery current sensor monitors the battery current. It directly inputs to
the BCM. It creates a 5-volt pulse width modulation (PWM) signal of 128 Hz with a duty cycle of 0–100 percent. Normal duty cycle is
between 5–95 percent. Between 0–5 percent and 95–100 percent are for diagnostic purposes.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 25

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 25
Engine Control Module (ECM)
When the engine is running, the generator turn-on signal is sent to the generator from the ECM, turning on the regulator. The generator's
voltage regulator controls current to the rotor, thereby controlling the output voltage. The rotor current is proportional to the electrical
pulse width supplied by the regulator. When the engine is started, the regulator senses generator rotation by detecting AC voltage at the
stator through an internal wire. Once the engine is running, the regulator varies the field current by controlling the pulse width. This
regulates the generator output voltage for proper battery charging and electrical system operation. The generator field duty terminal is
connected internally to the voltage regulator and externally to the ECM. When the voltage regulator detects a charging system problem, it
grounds this circuit to signal the ECM that a problem exists. The ECM monitors the generator field duty cycle signal circuit, and receives
control decisions based on information from the BCM.
Instrument Panel Cluster
The instrument panel cluster provides the customer notification in case a concern with the charging system. There are 2 means of
notification, a charge indicator and a driver information center message of SERVICE BATTERY CHARGING SYSTEM if equipped.
Charging System Operation
The purpose of the charging system is to maintain the battery charge and vehicle loads. There are 6 modes of operation and they include:
Battery Sulfation Mode
Charge Mode
Fuel Economy Mode
Headlamp Mode
Start Up Mode
Voltage Reduction Mode
The engine control module (ECM) controls the generator through the generator turn ON signal circuit. The ECM monitors the generator
performance though the generator field duty cycle signal circuit. The signal is a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal of 128 Hz with a duty
cycle of 0–100 percent. Normal duty cycle is between 5–95 percent. Between 0–5 percent and 95–100 percent are for diagnostic purposes.
The following table shows the commanded duty cycle and output voltage of the generator (see table next page):
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 26

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 26
Commanded Duty Cycle
Generator Output Voltage
10%
11 V
20%
11.56 V
30%
12.12 V
40%
12.68 V
50%
13.25 V
Generator
The generator provides a feedback signal of the generator voltage output through the generator field duty cycle signal circuit to the ECM.
This information is sent to the body control module (BCM). The signal is PWM signal of 128 Hz with a duty cycle of 0–100 percent. Normal
duty cycle is between 5–99 percent. Between 0–5 percent and 100 percent are for diagnostic purposes.
Battery Sulfation Mode
The BCM will enter this mode when the interpreted generator output voltage is less than 13.2 V for 45 minutes. When this condition exists
the BCM will enter Charge Mode for 2–3 minutes. The BCM will then determine which mode to enter depending on voltage requirements.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 27

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 27
Charge Mode
The BCM will enter Charge Mode whenever one of the following conditions are met.
The wipers are ON for more than 3 seconds.
Climate Control Voltage Boost Mode Request via serial data is true, as sensed by the HVAC control head. High speed cooling fan, rear
defogger and HVAC high speed blower operation can cause the BCM to enter the Charge Mode.
The estimated battery temperature is less than 0°C (32°F).
Battery State of Charge is less than 80 percent.
Vehicle speed is greater than 145 km/h (90 mph)
Current sensor fault exists.
System voltage was determined to be below 12.56 V
When any one of these conditions is met, the system will set targeted generator output voltage to a charging voltage between 13.9–15.5 V,
depending on the battery state of charge and estimated battery temperature.
Fuel Economy Mode
The BCM will enter Fuel Economy Mode when the estimated battery temperature is at least 0°C (32°F) but less than or equal to 80°C
(176°F), the calculated battery current is less than 15 amperes and greater than −8 amperes, and the battery state-of-charge is greater
than or equal to 80 percent. Its targeted generator output voltage is the open circuit voltage of the battery and can be between 12.5–
13.1 V. The BCM will exit this mode and enter Charge Mode when any of the conditions described above are present.
Headlamp Mode
The BCM will enter Headlamp Mode whenever the headlamps are ON (high or low beams). Voltage will be regulated between 13.9–14.5 V.
Start Up Mode
When the engine is started the BCM sets a targeted generator output voltage of 14.5 V for 30 seconds.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 28

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 28
Voltage Reduction Mode
The BCM will enter Voltage Reduction Mode when the calculated ambient air temperature is above 0°C (32°F). The calculated battery
current is less than 1 ampere and greater than −7 amperes, and the generator field duty cycle is less than 99 percent. Its targeted
generator output voltage is 12.9 V. The BCM will exit this mode once the criteria are met for Charge Mode.
Instrument Panel Cluster Operation
Charge Indicator Operation
The instrument panel cluster illuminates the charge indicator and displays a warning message in the driver information center if equipped,
when the one or more of the following occurs:
The engine control module (ECM) detects that the generator output is less than 11 V or greater than 16 V. The instrument panel
cluster receives a serial data message from the ECM requesting illumination.
The instrument panel cluster determines that the system voltage is less than 11 V or greater than 16 V for more than 30 seconds.
The instrument panel cluster receives a GMLAN message from the body control module (BCM) indicating there is a system voltage
range concern.
The instrument panel cluster performs the displays test at the start of each ignition cycle. The indicator illuminates for
approximately 3 seconds.
Display Message:
BATTERY NOT CHARGING SERVICE CHARGING SYSTEM or SERVICE BATTERY CHARGING SYSTEM
The BCM and the ECM will send a serial data message to the driver information center for the BATTERY NOT CHARGING SERVICE
CHARGING SYSTEM or SERVICE BATTERY CHARGING SYSTEM message to be displayed. It is commanded ON when a charging system DTC is
a current DTC. The message is turned OFF when the conditions for clearing the DTC have been met.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 29

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 29
Charging System schematic
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 30

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 30
Engine Idle Up
Elevated Idle
Is a standard option on all 6.6L Diesel Engines, which elevates the engine idle speed from base idle to 1050 RPMs when outside
temperatures are below 32°F (0°C) and the engine coolant temperature is below 150°F (65°C). This feature enhances heater performance
by raising the engine coolant temperature faster. It can be turned on or off, please refer to the ″Duramax Diesel Supplement″ Owner’s
Manual for more information.
High Idle
An option (RPO UF3) is available on certain HD models with cruise control. This system can be used to increase your engine idle speed for
whatever reason an owner wishes: more generator output at idle, belt driven add on equipment, etc. The cruise control buttons located on
the left hand side of the steering wheel are used to operate the High Idle option. For more information see the Owner’s Manual or online
at ″www.gmupfitter.com″.
PTO (power take-off)
An option (RPO PTO) is available only on 3500 Chassis Cab models (31xxx series) equipped with the 6.6L Diesel Engine and Allison 6-speed
transmission. The PTO allows the user to create an auxiliary power source for running add-on equipment, such as salt spreaders, pumps,
winches, lift buckets, etc. The dash mounted PTO switch is used to turn on the PTO and controls engine speed to values higher than normal
base idle. For more information see the ″Duramax Diesel Supplement″ Owner’s Manual or online at ″www.gmupfitter.com″.
Vehicle Regular Production Option (RPO) Content
When attempting to determine a vehicle’s option refer to the vehicle’s SPID (Service Parts IDentfication) label.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 31

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 31
Engine Idle Up (continued)
ADDING PTO OPTION TO A VEHICLE WITHOUT THE OPTION
Condition/Concern:
Some owners may request to add the PTO option to their vehicle when it is not equipped with the option. This option is available on 3500
Chassis Cab Models with the 6.6L Diesel engine only. The PTO option is now far more integrated with the vehicle than past models and
utilizes the following components:
• The Body Control Module (BCM)
• The Engine Control Module (ECM)
• The Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC)
• The PTO gear
• The PTO mode select switch
• The Power Take Off Module (PTOM)
• The remote PTO enable switch
• The PTO relay
• The Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Recommendation/Instructions:
Due to the PTO's complex integration with the vehicle it is NOT recommended to add this option to any vehicle not already equipped with
the OEM PTO option.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 32
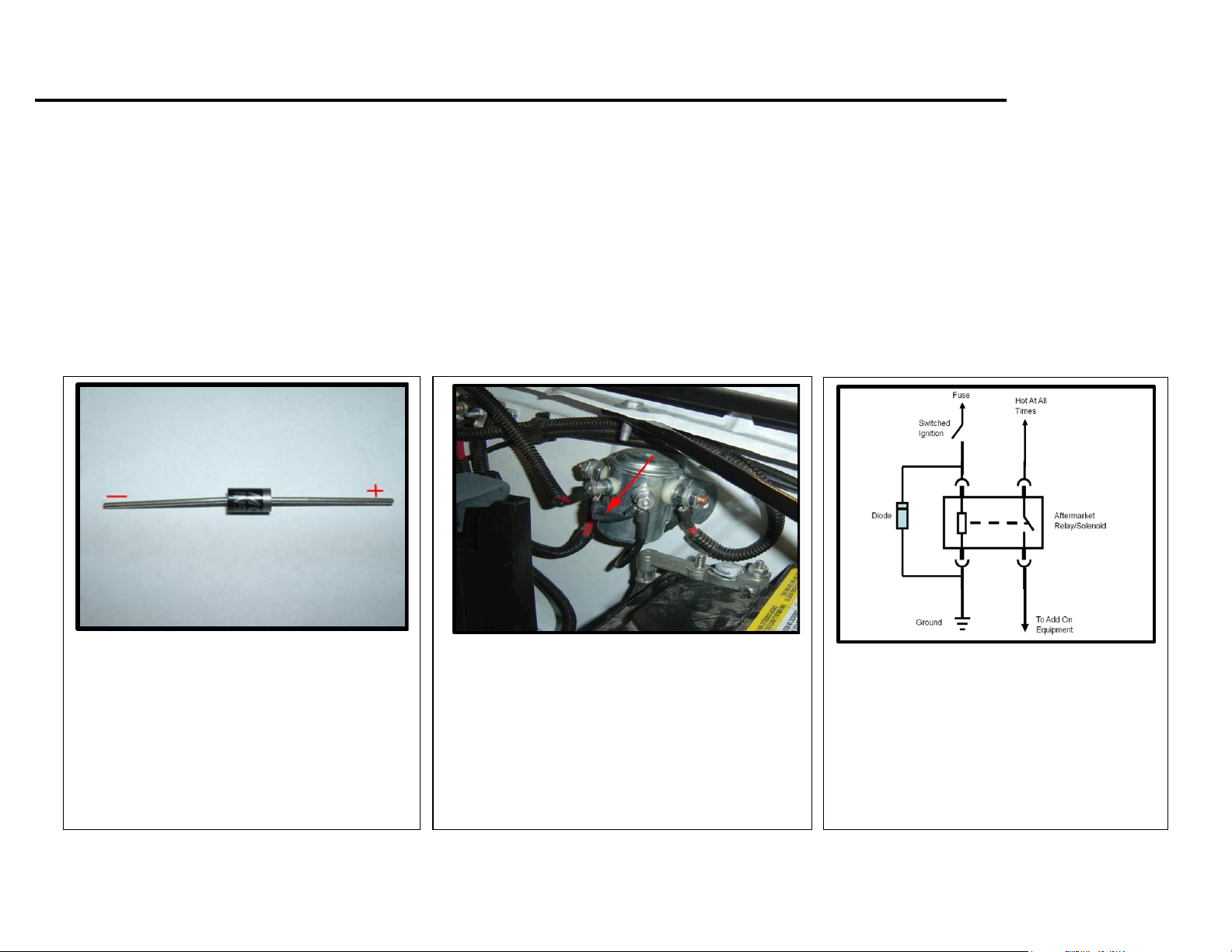
Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 32
Install a diode, P/N 12112422, across the coil of
the solenoid. It is important that the striped
end of the diode be connected to the positive
terminal of the coil and the other end of the
diode be connected to ground.
Important: Be sure to insulate the diode with heat
shrink tubing before installing as shown in the picture
above.
Notice: Some solenoids/relays may only have a
positive post and will get their ground through the
mounting bracket. In this case, the striped end of the
diode is to be connected to the positive terminal and
the other end should be connected to the ground of
the solenoid/relay.
Install a diode, P/N 12112422, across the coil of the
relay. It is important that the striped end of the
diode be connected to the positive terminal of the
coil and the other end of the diode be connected to
ground. Be sure to insulate the diode with heat
shrink tubing before installing.
Installation of Electrical Aftermarket Accessories
Installation of a Diode to Suppress Voltage Spikes
When an electromechanical solenoid or relay is de-energized rapidly by a mechanical switch or semiconductor, the collapsing magnetic field
produces a substantial transient voltage in its effort to disperse the stored energy and oppose the sudden change in current flow. These
voltage spikes can occur at the positive terminal when the solenoid or relay is de-energized (keyed-off). If a solenoid or relay is wired onto
the Run/Crank circuit of the vehicle to control aftermarket equipment, the spikes can be transmitted onto the circuit. The spikes can
permanently damage the internal circuitry of the sensitive electronic components and/or control modules that are on this bussed circuit. To
prevent damage to these components, the solenoid or relay MUST have the control circuit suppressed with a diode.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 33

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 33
BCM
Transmission Shift Interlock Schematic
Remote Vehicle Immobilizer
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 34

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 34
Exterior Lighting Systems Description and Operation
The exterior lighting system consists of the following lamps:
Adaptive forward lighting
Automatic headlamp leveling
Backup lamps
Daytime running lamps (DRL)
Hazard warning lamps
Headlamps
Park, tail, license, and marker lamps
Stop lamps
Turn signal lamps
Low Beam Headlamps
Warning: The high intensity discharge system produces high voltage and current. To reduce the risk of severe shocks and burns:
Never open the high intensity discharge system ballast or the arc tube assembly starter.
Never probe between the high intensity discharge system ballast output connector and the arc tube assembly.
The headlamps consist of 2 high intensity discharge (HID) arc tubes and ballast on each side of the vehicle which provide high and low
beams.
The headlamps may be turned ON in 3 different ways:
When the headlamp switch is placed in the ON position, for normal operation
When the headlamp switch is placed in the AUTO position, for automatic lamp control (ALC)
When the headlamp switch is placed in the AUTO position, with the windshield wipers ON in daylight conditions, after a 6 second
delay
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 35

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 35
Low Beam Headlamps (continued)
The body control module (BCM) monitors three signal circuits from the turn signal/multifunction switch. When the turn
signal/multifunction switch is in the AUTO position, all three signal circuits are open. When placed in the AUTO position, the BCM
monitors inputs from the ambient light sensor to determine if headlamps are required or if daytime running lamps will be activated
based on outside lighting conditions. When the turn signal/multifunction switch is placed in the OFF position, the turn
signal/multifunction switch headlamps OFF signal circuit is grounded, indicating to the BCM that the exterior lamps should be turned
OFF. With the turn signal/multifunction switch in the PARK position, the turn signal/multifunction switch park lamps ON signal circuit is
grounded, indicating that the park lamps have been requested. When the turn signal/multifunction switch is placed in the HEADLAMP
position, both the turn signal/multifunction switch park lamps ON signal circuit and the turn signal/multifunction switch headlamps ON
signal circuit are grounded. The BCM responds to the low beam request by applying ground to the low beam relay control circuit which
energizes the low beam relay. With the low beam relay energized, the switch contacts close allowing battery voltage to flow through the
low beam fuses. Battery voltage is then applied from the fuses, through the low beam control circuits to the left and right headlamp
ballast located in each headlamp assembly. When battery voltage is applied to the headlamp ballast through the low beam control
circuits, the ballast charge the starter to start the lamp. High intensity discharge (HID) headlamps do not have filaments like traditional
bulbs, instead the starter uses a high voltage transformer to convert the input voltage into a higher voltage. This increased voltage is
used in order to create an arc between the electrodes in the bulb.
The BCM will also command the low beam headlamps ON during daylight conditions when the following conditions are met:
Headlamp switch in the AUTO position
Windshield wipers ON
Vehicle in any gear but PARK
When the BCM commands the low beam headlamps ON, the operator will notice the interior backlighting for the instrument cluster and
the various other switches dim to the level of brightness selected by the instrument panel dimmer switch.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 36

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 36
Run Up Of the Lamp
Each ballast requires higher amperage in order to ensure normal startup and run up of the lamp. Run up is the term used to describe the
extra power level given to the bulb. The input current during the steady state operation is lower that the start up amperage. After the
lamp receives the strike from the starter and the arc is established, the ballast uses its operating voltage in order to provide the run up
power needed in order to keep the lamp on. The lamp rapidly increases in intensity from a dim glow to a very high-intensity, bright light
called a steady state. Within a few seconds of the arc being established in the bulb, the majority of steady state is complete. 100 percent
of the steady state is completed shortly thereafter. A high watt power level is necessary in order to bring the lamp to a steady state in
such a short period of time. The high watt power level allows the lamp to meet the SAE light vs. time specification.
When to Change the HID Bulb
Bulb failure, end of life occurs when the bulb gets old and becomes unstable. The bulb may begin shutting itself off sporadically and
unpredictably at first, perhaps only once during a 24-hour period. When the bulb begins shutting itself off occasionally, the ballast will
automatically turn the bulb back on again within 0.5 seconds. The ballast will re-strike the bulb so quickly that the bulb may not appear
to have shut off. As the bulb ages, the bulb may begin to shut off more frequently, eventually over 30 times per minute. When the bulb
begins to shut off more frequently, the ballast receives excessive, repetitive current input. Repetitive and excessive restarts or re-strikes,
without time for the ballast to cool down, will permanently damage the ballast. As a safeguard, when repetitive re-strikes are detected,
the ballast will not attempt to re-strike the lamp. The ballast then shuts down and the bulb goes out.
The following symptoms are noticeable signs of bulb failure:
Flickering light, caused in the early stages of bulb failure
Lights go out, caused when the ballast detects excessive, repetitive bulb re-strike
Color change—the lamp may change to a dim pink glow.
Input power to the ballast must be terminated in order to reset the ballast's fault circuitry. In order to terminate the input power to the
ballast, turn the lights off and back on again. Turning the lights off and back on again resets all of the fault circuitry within the ballast
until the next occurrence of excessive, repetitive bulb re-strikes. When excessive, repetitive bulb re-strikes occur, replace the starter/arc
tube assembly. The ballast will begin the start-up process when the starter/arc tube assembly is replaced. Repeatedly resetting the input
power can overheat the internal components and cause permanent damage to the ballast. Allow a few minutes of cool-down time in
between reset attempts.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 37

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 37
Light Color
White light has a different color rating than regular headlamps. The range of white light that is acceptable is broad when compared to
halogens. Therefore, some variation in headlight coloring between the right and left headlamp will be normal. One high intensity
discharge (HID) at the end of the normal range may appear considerably different in color from one at the other end of the range.
Difference in color is normal. Replace the arc tube only if the arc tube is determined to be at the bulb failure stage.
High Beam Headlamps
When the low beam headlamps are ON and the turn signal/multifunction switch is placed in the high beam position, ground is applied
to the BCM through the high beam signal circuit. The BCM responds to the high beam request by applying ground to the high beam
relay control circuit which energizes the high beam relay. With the high beam relay energized, the switch contacts close allowing battery
voltage to flow through the left and right high beam fuses to the high beam control circuits and on to the left and right high beam
solenoid actuators within the headlamp assemblies. Once the high beam solenoid actuators are active, the solenoid shutters open in
each headlamp assembly exposing the remaining portion of the headlamp that was covered by the shutters illuminating the high beams
at full intensity.
Adaptive Forward Lighting (AFL)
The AFL consists of the following components:
Headlamp control module
Headlamp actuator - left
Headlamp actuator - right
Battery positive voltage is applied to the headlamp control module at all times and when the ignition switch is in the RUN and CRANK
positions. The headlamp control module has an operational voltage range of about 10.5-16 volts and is only fully functional when the
ignition switch is in the RUN position. The voltage input from the ignition switch wakes the headlamp control module microprocessor.
The headlamp control module receives serial data messages from the engine control module (ECM), transmission control module (TCM),
electronic brake control module (EBCM), and body control module (BCM) with regards to power mode, speed, steering angle,
transmission gear selection, and headlamp switch status. The headlamp control module calculates the headlamp angle and sends
commands to the left and right headlamp actuators. The headlamp actuators drive the headlamps to the position commanded by the
headlamp control module. The headlamp control module monitors the headlamp actuator motor control circuits for proper circuit
continuity and for shorts to ground or voltage.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 38

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 38
Adaptive Forward Lighting (AFL) (continued)
If a malfunction is detected, a DTC will be stored in memory and the driver will be notified with a message displayed over the driver
information center (DIC) located on the instrument panel cluster (IPC).
The headlamp control module controls the left headlamp movement by 15 degrees to the left and 5 degrees to the right, and the right
headlamp movement by 5 degrees to the left and 15 degrees to the right. The direction the headlamps move is controlled by the
steering wheel angle and is limited by steering angles of approximately +/- 90 degrees. The AFL will not operate with the transmission in
reverse or at vehicle speeds less than 2 mph. Movement of the headlamps is restricted at low vehicle speeds and full movement of the
lamps is not allowed until vehicle speed is greater than approximately 30 mph. The following conditions must be met before the AFL will
operate:
Headlamp switch in the AUTO position and high or low beam headlamps must be active
Steering angle position must be received from the EBCM with the steering signal validity bit set
Vehicle speed must be received from the ECM with the steering signal validity bit set
Transmission gear position must be received from the TCM with the transmission gear position validity bit set
Automatic Headlamp Leveling
The Automatic Headlamp Leveling Systems consist of the following components:
Headlamp control module
Headlamp leveling actuator - left
Headlamp leveling actuator - right
Suspension position sensor - front
Suspension position sensor - rear
The automatic headlamp leveling system automatically maintains the vertical alignment of the headlamps when the vehicle load and
driving conditions change. Each headlamp assembly contains a headlamp leveling motor that is controlled by the headlamp control
module. The front and rear suspension position sensors provide the headlamp control module with suspension position information.
Each sensor receives a 5-volt reference, signal, and low reference circuits from the headlamp control module. The sensors are
connected to the control arms of the front and rear suspension. As the vehicle travels, the suspension compresses and rebounds moving
the suspension position sensor arms. This causes the signal output of the sensor to change. The headlamp control module compares the
information from both suspension position sensors and adjusts the headlamp leveling as needed.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 39

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 39
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL)
The daytime running lamps (DRL) will illuminate continuously when the following conditions are met:
The ignition is in the RUN or CRANK position
The shift lever is out of the PARK position for vehicles equipped with automatic transmissions or the parking brake is released for
vehicles with manual transmissions
The low and high beam headlamps are OFF
The ambient light sensor is used to monitor outside lighting conditions. The ambient light sensor provides a voltage signal that will vary
between 0.2 and 4.9 volts depending on outside lighting conditions. The body control module (BCM) provides a 5-volt reference signal
to the ambient light sensor and the HVAC control module provides a low reference ground. The BCM monitors the ambient light sensor
signal circuit to determine if outside lighting conditions are correct for either daytime running lights (DRL) or automatic lamp control
(ALC) when the headlamp switch is in the AUTO position. In daylight conditions the BCM will command the designated DRLs ON. During
low light conditions the BCM will command the low beam headlamps ON. Any function or condition that turns on the headlamps will
cancel DRL operation.
Automatic Lamp Control
Place the turn signal/multifunction switch in the AUTO position for automatic lamp control. During automatic lamp control the
headlamps will be off during daylight conditions but will turn on when the ambient light sensor detects low outside light level. The
ambient light sensor is a light sensitive transistor that varies the voltage signal to the HVAC control module. The HVAC control module
sends a signal to the body control module (BCM) via serial data commanding the BCM to apply ground to the headlamp low beam relay
control circuit. This energizes the low beam relay, closing the switched side and applies battery voltage to the LEFT and RIGHT LOW
BEAM fuses. Battery voltage is applied from the low beam fuses, through the low beam voltage supply circuits to low headlamp
assemblies.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 40

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 40
Flash to Pass (FTP)
When the turn signal/multifunction switch is momentarily placed in the flash to pass (FTP) position, ground is applied to the turn
signal/multifunction switch. The turn signal/multifunction switch applies ground to the body control module (BCM) through the FTP
switch signal circuit. The BCM responds to the FTP request by applying ground to the high beam relay control circuit. This energizes the
high beam relay, closing the switch side contacts of the high beam relay, applying battery voltage to the left and right high beam fuses.
Battery voltage is applied from the high beam fuses through the high beam control circuit to the high beam headlamp assemblies. This
causes the high beam headlamps to illuminate at full brightness momentarily.
Hazard Lamps
The hazard flashers may be activated in any power mode. The hazard switch signal circuit is momentarily grounded when the hazard
switch is pressed. The body control module (BCM) responds to the hazard switch signal input by supplying battery voltage to all four
turn signal lamps in an ON and OFF duty cycle. When the hazard switch is activated, the BCM sends a serial data message to the
instrument panel cluster (IPC) requesting both turn signal indicators to be cycled ON and OFF.
The I/P dimmer switch controls the brightness of the interior backlighting components. When the I/P dimmer switch is placed in a
desired brightness position, the body control module (BCM) receives a signal from the I/P dimmer switch and responds by applying a
pulse width modulated (PWM) voltage to the hazard switch light emitting diode (LED) backlighting control circuit illuminating the LED to
the desired level of brightness.
Park, Tail, and License Lamps
When the headlamp switch is placed in the HEAD or PARK position, ground is applied to the park lamp switch ON signal circuit to the
body control module (BCM). The BCM responds by applying voltage to the park lamps, tail lamps, and license lamps control circuits
illuminating the park, tail, and license lamps.
Stop Lamps
The brake pedal position (BPP) sensor is used to sense the action of the driver application of the brake pedal. The BPP sensor provides an
analog voltage signal that will increase as the brake pedal is applied. The body control module (BCM) provides a low reference signal and
a 5-volt reference voltage to the BPP sensor. When the variable signal reaches a voltage threshold indicating the brakes have been
applied, the BCM will apply battery voltage to the left and right stop lamp control circuits as well as the center high mounted stop lamp
(CHMSL) control circuit illuminating the left and right stop lamps and the CHMSL.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 41

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 41
Turn Signal Lamps
Ground is applied at all times to the turn signal/multifunction switch. The turn signal lamps may only be activated with the ignition switch
in the ON or START positions. When the turn signal/multifunction switch is placed in either the TURN RIGHT or TURN LEFT position,
ground is applied to the body control module (BCM) through either the right turn or left turn signal switch signal circuit. The BCM
responds to the turn signal switch input by applying a pulsating voltage to the front and rear turn signal lamps through their respective
control circuits. When a turn signal request is received by the BCM, a serial data message is sent to the instrument panel cluster (IPC)
requesting the respective turn signal indicator be pulsed ON and OFF.
Backup Lamps
With the engine ON and the transmission in the REVERSE position, the transmission control module (TCM) sends a serial data message to
the body control module (BCM). The message indicates that the gear selector is in the REVERSE position. The BCM applies battery voltage
to the backup lamps control circuit illuminating the backup lamps. Once the driver moves the gear selector out of the REVERSE position, a
message is sent by the TCM via serial data requesting the BCM to remove battery voltage from the backup lamps control circuit. The
engine must be ON for the backup lamps to operate.
Battery Run Down Protection/Inadvertent Power
To provide battery run down protection, the exterior lamps will be deactivated automatically under certain conditions. The BCM
monitors the state of the headlamp switch. If the park or headlamp switch is ON when the ignition switch is placed in either the CRANK
or RUN position and then placed in the OFF position, the BCM initiates a 10 min timer. At the end of the 10 min, the BCM will turn off the
control power output to the park lamp controls as well as the headlamp relay coils, deactivating the exterior lamps. This feature will be
cancelled if any power mode other than OFF becomes active. The BCM will disable battery run down protection if any of the following
conditions exist. The park or headlamp switch is placed in the ON to OFF position, and back to the ON position during battery run down
protection. The BCM determined that the park or headlamp switch was not active when the ignition was turned OFF.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 42

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 42
Connector Part Information
Harness Type: Forward Lamp
OEM Connector: 15326654
Service Connector: SEE NOTE
Description: 8-Way F 280 GT 5.8 Series, Sealed (BK)
Connector Part Information
Harness Type: Left Headlamp
OEM Connector: Not Available
Service Connector: Service by Harness - See Part Catalog
Description:
X110 Left Forward Lamp Harness to Headlamp - Connector End View and Pin-out
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 43

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 43
Terminal Part Information
Terminal Type ID
Terminated Lead
Diagnostic Test Probe
Terminal Removal Tool
Service Terminal
Tray
Core Crimp
Insulation Crimp
I
13578906
J-35616-4A (PU)
J-38125-553
15304720
19 4 5
II
13578915
J-35616-4A (PU)
J-38125-553
15304719
19 2 5
III
13578915
J-35616-4A (PU)
J-38125-553
15304719
19 E 5
IV
Pending
Pending
Pending
Not Available
Not Available
Not Available
Not Available
X110 Forward Lamp Harness to Headlamp - Left Harness
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Terminal Type ID
Option
Function
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Terminal Type ID
Option
A
1.5
BK
150 I -
Ground
A
1.5
BK
150
IV
-
B
0.75
YE
712
II
-
Left Headlamp Low Beam Supply Voltage
B
0.75
0.75
YE
YE
712
712
IV
Z88
X88
C
0.5
WH
711
III
-
Left Headlamp High Beam Supply Voltage
C
0.5
0.5
WH
WH
711
711
IV
Z88
X88
D - - - -
-
Not Occupied
D - - - -
-
E
0.5
VT/GY
709
III
-
Left Park Lamp Supply Voltage
E
0.5
0.5
VT/GY
VT/GY
709
709
IV
X88
Z88
F
0.75
D-BU/WH
1314
II
-
Left Front Turn Signal Lamp Supply Voltage
F
0.75
0.75
BU/WH
BU/WH
1314
1314
IV
X88
Z88
G
0.75
GY/D-BU
7538
II
-
Left Front DRL Supply Voltage
G
0.75
GY/BU
7538
IV
Z88/Y91/GAT/SL
T
H
0.5
VT/GY
709
III
-
Left Park Lamp Supply Voltage
H
0.5
VT/GY
709
IV
Z88/Y91/GAT/SL
T
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 44

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 44
Connector Part Information
Harness Type: Right Headlamp
OEM Connector: Not Available
Service Connector: Service by Harness -
See Part Catalog
Description:
Connector Part Information
Harness Type: Forward Lamp
OEM Connector: 15326654
Service Connector: SEE NOTE
Description: 8-Way F 280 GT 5.8 Series, Sealed (BK)
X120 Right Forward Lamp Harness to Headlamp – Connector End View and Pin-out
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 45

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 45
Terminal Part Information
Terminal Type ID
Terminated Lead
Diagnostic Test Probe
Terminal Removal Tool
Service Terminal
Tray
Core Crimp
Insulation Crimp
I
Pending
Pending
Pending
Not Available
Not Available
Not Available
Not Available
II
13578906
J-35616-4A (PU)
J-38125-553
15304720
19 4 5
III
13578915
J-35616-4A (PU)
J-38125-553
15304719
19 2 5
IV
13578915
J-35616-4A (PU)
J-38125-553
15304719
19 E 5
X120 Forward Lamp Harness to Headlamp - Right Harness
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Terminal Type ID
Option
Function
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Terminal Type ID
Option
A
1.5
BK
250 I -
Ground
A
1.5
BK
250
II
-
B
0.75
0.75
YE
YE
312
312
I
X88
Z88
Right Headlamp Low Beam Supply Voltage
Right Headlamp Low Beam Supply Voltage
B
0.75
YE
312
III
-
C
0.5
0.5
WH
WH
311
311
I
X88
Z88
Right Headlamp High Beam Supply Voltage
Right Headlamp High Beam Supply Voltage
C
0.5
WH
311
IV
-
D - - - -
-
Not Occupied
D - - - -
-
E
0.5
0.5
GY/BN
GY/BN
309
309
I
Z88
X88
Right Park Lamp Supply Voltage
Right Park Lamp Supply Voltage
E
0.5
GY/BN
309
IV
-
F
0.75
0.75
GN/VT
GN/VT
1315
1315
I
X88
Z88
Right Front Turn Signal Lamp Supply Voltage
Right Front Turn Signal Lamp Supply Voltage
F
0.75
L-GN/VT
1315
III
-
G
0.75
BU/BN
7539
I
Z88/Y91/GAT/SLT
Right Front DRL Supply Voltage
G
0.75
D-BU/BN
7539
III
- H 0.5
GY/BN
309
I
Z88/Y91/GAT/SLT
Right Park Lamp Supply Voltage
H
0.5
GY/BN
309
IV
-
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 46

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 46
Chevrolet
GMC
Headlamp Replacement
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 47

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 47
1) X50A Fuse Block – Underhood
(2) X105
(3) J130
(4) J115
(1) X150
(2) J125
(3) X100
Left Side
Right Side
Under hood Harness Routing
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 48

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 48
Chevrolet
GMC
Tail lamp Replacement
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 49

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 49
Chassis Harness Routing
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 50

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 50
Connector X5
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
1
0.5
BK/GY
2379
Object Sensor Low Reference
2
0.5
VT/GY
709
Left Park Lamp Supply Voltage
4 - -
-
Not Occupied
5
0.5
BK
1750
Ground
6
0.5
BK
1750
Ground
7
0.5
BK
1750
Ground
8
0.5
BK
1750
Ground
9
0.5
L-
GN/YE
6846
Rear License Lamp Supply
Voltage
10
0.5
L-
GN/YE
6846
Rear License Lamp Supply
Voltage
11
0.5
GY/BN
309
Right Park Lamp Supply
Voltage
12
0.5
YE/VT
2378
Right Rear Corner Object
Sensor Signal
13
0.5
YE/WH
2377
Right Rear Middle Object
Sensor Signal
14
0.5
YE/D-
BU
2376
Left Rear Middle Object
Sensor Signal
15
0.5
YE
2375
Left Rear Corner Object
Sensor Signal
16
0.5
BN/WH
2374
Object Sensor Supply Voltage
Rear Body Junction Block X63A –Connector X5
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 51

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 51
Connector X1
Rear Body Junction Block X63A –Connector X1
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 52

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 52
X63A Junction Block - Rear Body X1
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
1.
0.5
YE/VT
2378
Right Rear Corner Object Sensor Signal
2.
0.5
YE/WH
2377
Right Rear Middle Object Sensor Signal
3.
0.5
YE/D-BU
2376
Left Rear Middle Object Sensor Signal
4.
0.5
YE
2375
Left Rear Corner Object Sensor Signal
5.
0.5
BN/WH
2374
Object Sensor Supply Voltage
6.
1.5
BK
1750
Ground
7.
1.5
BK
2150
Ground
8.
- - -
Not Occupied
9.
0.8
L-GN/WH
24
Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
10.
0.8
WH/VT
1430
Exterior Courtesy Lamp Supply Voltage
11.
- - -
Not Occupied
12.
- - -
Not Occupied
13.
0.5
VT/GY
1054
Stop Lamp Supply Voltage
14.
- - -
Not Occupied
X63A Junction Block - Rear Body X1 Pin-outs
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 53
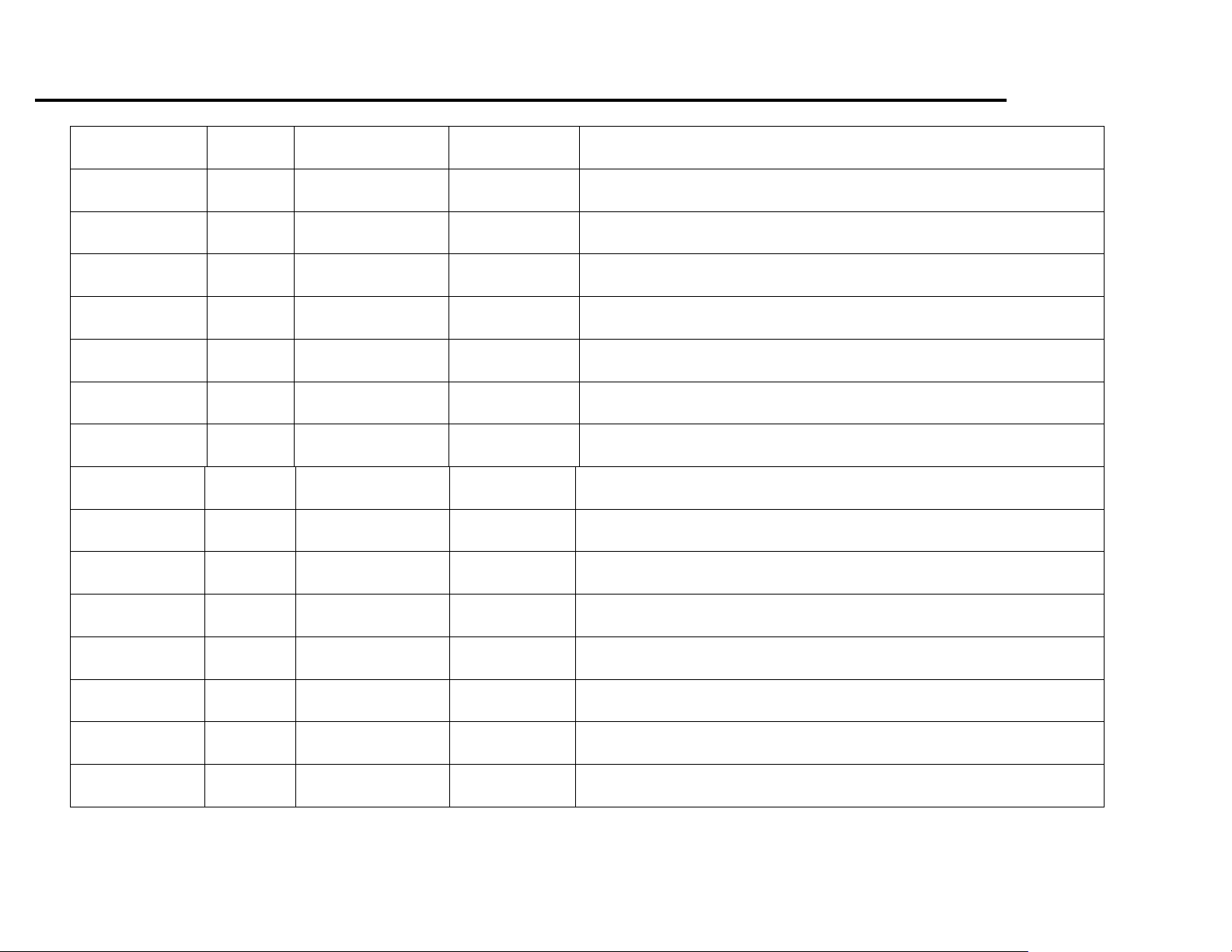
Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 53
15.
- - -
Not Occupied
16.
0.5
L-GN/YE
6846
Rear License Lamp Supply Voltage
17.
0.5
BK/GY
2379
Object Sensor Low Reference
18.
0.8
YE/D-BU
18
Left Rear Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
19.
0.8
BN/L-GN
19
Right Rear Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
20.
- - -
Not Occupied
21.
0.8
GY/BN
309
Right Park Lamp Supply Voltage
22.
0.8
VT/GY
709
Left Park Lamp Supply Voltage
23.
- - -
Not Occupied
24.
1
BK
1750
Ground
25.
0.5
L-GN/WH
24
Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
26.
0.5
VT/L-GN
1739
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
27.
0.5
GY/YE
6972
Camera Signal #2 +
28.
0.5
WH/D-BU
6973
Camera Signal #2
29.
0.5
BK
2550
Ground
30.
0.5
BK
6974
Camera Drain Wire
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 54

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 54
Exterior Lamp
Bulb Number
Chevrolet
GMC
Back-up Lamp
921 (W16W)
921 (W16W)
Back-up Lamp*
1156
1156
Cargo Lamp
921 (W16W)
921 (W16W)
Center High-Mounted Stop lamp
(CHMSL)
921LL
921LL
Fog Lamp
PS24W
PS24W
Front Turn Signal Lamp and Parking Lamp
7443 LL
7443 LL
High-Beam Headlamp (single combined bulb on GMC)
9005 LL
HIR–2 (9012 LL)
Low-Beam Headlamp
H11 LL
---
Marker Lamps
194
194
License Plate Lamp
W5W LL
W5W LL
Stop lamp/Tail lamp/Turn Signal Lamp
7444 LL
7444LL
Stop lamp/Turn Signal Lamp/Tail lamp (*Chassis Cab use only)
1157
1157
Bulb Replacement
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 55

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 55
1. Prior to starting you must disconnect the rear chassis lighting connector (X63A), turn on ignition, and select either right or left
hand turn signal to determine if the vehicle has been properly calibrated. If you experience a “fast flash” the vehicle is not
calibrated with the ZW9 (box delete) option. The ZW9 calibration eliminates the bulb outage detection on the rear lamps and
therefore also eliminates the “fast flash” when using after-market (non-OEM) taillight assemblies, including the LED style lamps.
2. Locate the Violet/Gray wire (Circuit #1054) the under-hood fuse block connector X3 /terminal M6. This is the CHSML feed and
you will need to splice into this wire for your Stop lamp signal.
3. For Left Rear Turn Only locate and cut circuit 18 (Yellow/Blue wire) at the Under-hood fuse block connector X5 Terminal A2.
Locate and splice to the yellow/blue wire to the blue/white wire circuit 1314 X1 terminal F3 at the under-hood fuse block.
4. For Right Rear Turn Only locate and cut circuit 19 (Green/Brown) at the Under-hood fuse block connector X5 Terminal A3.
Locate and splice to the Green/Brown wire to the Green/Violet wire circuit 1315 X1 terminal D3 at the under-hood fuse block.
5. Current Limitation is 6 amps…If you current draw is more than 6 amps you must use the front turn signal circuits to energized
relays provide Battery positive feed to the rear dedicated turn lamps.
See Schematic(s) on next page
Rearward Lighting Separate Stop and Turn
In order to have separated rear stop and turn you must re-wire the rear lamps at the under hood fuse block such that the Stop[ lamps are
served by that of the CHMSL signal and the rear turn lamps are serve by splicing those lamp feeds to that of the front turn signal lamp feeds.
Follow the steps outlined below using the schematic on the following page as a reference.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 56

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 56
19
GN/BN
18
YE/BU
NEW RH
Dedicated
Stop Lamp
NEW LH
Dedicated
Stop Lamp
Rearward Lighting Separate Stop and Turn (continued)
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 57

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 57
Dome/Courtesy Lamps (-E29), DH6
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 58

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 58
Dome/Courtesy Lamps E29
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 59

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 59
A. Black Wire
B. Orange Wire
C. To Roof Mounted Lamp
D. Harness Assembly
E. Grommet (Roof)
F. Foam Insulator (Adhesive-Backed)
G. Harness Connector, Secondary Lock and Terminal
H Brown Black Wire
I. Vehicle Outer Roof Panel
Roof Mounted Beacon
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 60

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 60
Park Neutral Signal-Shift Lock Control
The Automatic Transmission Shift Lock Control System is a safety device that prevents an inadvertent shift out of PARK when the engine is
running. The driver must press the brake pedal before moving the shift lever out of the PARK position. The system consists of the following
components:
The Automatic Transmission Shift Lock Solenoid (serviced as the Automatic Transmission Shift Lock Actuator)
The Body Control Module (BCM)
The Engine Control Module (ECM)
The BCM controls the voltage to the shift lock control solenoid though the shift lock control solenoid controlled voltage circuit. The following
conditions must be met before the BCM will supply voltage to the shift lock control solenoid:
The ignition is in the ON position.
The ECM sends an input via GMLAN serial data to the BCM when the Transmission Control Module (TCM) indicates the transmission is in
the PARK position.
The BCM receives a brake applied input from the stop lamp switch.
Since the shift lock control solenoid is permanently grounded, the BCM supplies voltage to the automatic transmission shift lock control
solenoid, releasing the mechanical lock on the shift lever as the solenoid energizes. The energized solenoid allows the driver to move the shift
lever out of the PARK position. When the brake pedal is not applied, the BCM turns the control voltage output of the shift lock control solenoid
OFF, de-energizing the shift lock control solenoid. When the transmission is in the PARK position, the de-energized shift lock control solenoid
will prevent shifting as the lever is mechanically locked in the PARK position.
During remote start operation, the BCM will energize the shift lock control circuit, locking the shift lever in the PARK position.
Note:
Shift Lock Control can be used as simulated Park signal, but note that the signal is deactivated if and when the brake is applied. Refer to
wiring schematic on the next page for connection recommendations.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 61

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 61
Shift Lock Control Schematic
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 62

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 62
Trailer Brake Control System
A trailer brake control system is used to control the amount of trailer braking power that is made available to trailers with brakes that require a
controlled electrical output signal for actuation.
The power output to the trailer brakes is based on both the amount of braking being applied by the vehicle’s brake system and on the type of
trailer brakes detected.
The Trailer Brake Control System is compatible with two types of Trailer Brake Systems as listed below:
1. Electric Brakes A controlled electrical output signal energizes an electric-magnet/lever arm assembly that directly actuates the brake
mechanism. The GDS name for this system is “Electromagnetic Brakes”.
2. Electric Over Hydraulic Brakes A controlled electrical output signal energizes a remote, trailer mounted hydraulic pump to build brake
pressure in a closed hydraulic system on the trailer. The hydraulic fluid pressure actuates the brake mechanism. The GDS name for this
system is “Electrohydraulic Brakes”.
Trailer Brake Output versus Trailer Brake Type
The trailer brake system characterizes the trailer brakes as either Electric Brake or Electric Over Hydraulic Brake automatically. This
characterization may be affected by the number, type, and age of the trailer brake magnets, as well as any other devices installed on the
trailer brakes (i.e. adapters for Electric Over Hydraulic brake functionality).
The trailer brake system is fully operational with either characterization.
Some features of the trailer brake system may be different based on the trailer brake type characterization. An example of this is at zero
speed, where pressing the service brake pedal will produce output when the trailer brakes are characterized as Electric Brakes, but not
when characterized as Electric Over Hydraulic Brakes.
Sliding the manual trailer brake apply lever will produce output at zero speed for either characterization.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 63

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 63
The user gain allows the driver to adjust the amount of trailer brake output to match the trailer load and road surface. The controller
determines the desired trailer brake output and provides a control signal to the K133 Trailer Brake Power Control Module. The K133 Trailer
Brake Power Control Module amplifies the signal and provides the output required to activate the Electric or Electric-Over Hydraulic trailer
brakes.
The trailer brake control can support up to a maximum of four axles with electric trailer brakes (8 brake magnets).
Connecting a trailer that is not compatible with the trailer brake system may result in reduced or complete loss of trailer braking. There may be
an increase in stopping distance or trailer instability which could result in personal injury or damage to the vehicle, trailer or other property. An
aftermarket controller may be available for use with trailers with surge or air trailer brake systems.
To determine the type of brakes on your trailer and the availability of controllers, check with your trailer manufacturer or dealer. Do not power
up an aftermarket controller with the factory brake controller at the same time.
The vehicle is equipped with the following trailer braking components:
K38 Chassis Control Module
K133 Trailer Brake Power Control Module
S76 Trailer Brake Control Panel
Manual Trailer Brake Apply
Trailer Gain Adjustment
Trailer Brake Driver Information Center Display
Chassis Control Module
The K38 Chassis Control Module (CCM) is a serviceable GMLAN module. The chassis control module sends the low power commanded duty
cycle signal to the trailer brake power control module. The trailer brake power control module amplifies the signal and provides an output that
is required to drive the trailer brakes.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 64

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 64
Trailer Brake Power Control Module
The K133 Trailer Brake Power Control Module (TBPM) is a solid state power switching module that supplies power to the trailer brakes at the
input command duty cycle. Diagnostic messages are sent from the TBPM to the CCM on a dedicated LIN bus.
Trailer Brake Control Panel
The S76 Trailer Brake Control Panel contains the trailer gain and manual apply switches. It is located on the instrument panel to the left of the
steering column. Refer to the instrument panel overview for more information on the location. The control panel and switches allows you to
adjust the amount of output, referred to as trailer gain, available to the Electric or Electric Over Hydraulic brakes. It also allows you to manually
apply the trailer brakes. The trailer brake control panel and switches are used along with the trailer brake display page on the driver
information center to adjust and display power output to the trailer brakes.
Manual Trailer Brake Apply
The manual trailer brake apply lever is located on the S76 Trailer Brake Control Panel and is used to apply the trailer’s Electric or Electric Over
Hydraulic brakes independent of the vehicle’s brakes. This lever is used in the trailer gain adjustment procedure to properly adjust the power
output to the trailer brakes.
Sliding the lever to the left will apply only the trailer brakes. The power output to the trailer is indicated in the trailer brake display page in the
Driver Information Center (DIC). If the vehicle’s service brakes are applied while using the manual trailer brake apply lever, the trailer output
power will be the greater of the two.
The trailer and the vehicle’s brake lamps will come on when either the vehicle’s braking or manual trailer brakes are applied.
Trailer Gain Adjustment
Trailer gain should be set for a specific trailering condition and must be adjusted any time vehicle loading, trailer loading or road surface
conditions change. It is important to re-adjust trailer gain any time the tow vehicle, trailer loading or road surface conditions change or it you
notice trailer wheel lock-up at any time while you are towing.
Setting the trailer gain properly is needed for the best trailer stopping performance. A trailer that is over-gained may result in locked trailer
brakes. A trailer that is under-gained may result in not enough trailer braking. Both of these conditions may result in poor stopping and stability
of the vehicle and trailer.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 65

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 65
Trailer Gain Adjustment Procedure
Adjust trailer gain in 0.5 step increments up to 10 gain setting by using the gain adjustment +/− buttons on the trailer brake control
panel switch. Pressing and holding a gain button will cause the trailer gain to continuously increment or decrement. To turn the output
to the trailer off, set the gain to zero.
Drive the tow vehicle and trailer combination on a level surface representative of the towing condition and free of traffic at
approximately 32–40 km/h (20–25 mph) and fully apply the manual trailer brake apply lever mechanism located on the trailer brake
control panel switch. Adjusting the trailer gain at slower speeds may result in an incorrect gain setting.
Adjust the trailer gain to just below the threshold of trailer wheel lock-up . Trailer wheel lock-up may not occur if towing a heavily
loaded trailer. In this case, adjust the trailer gain to the highest allowable setting for the towing condition.
Hill Start Assist
The hill start assist allows the driver to launch the vehicle without a roll back when the driver is moving their foot from the brake pedal to the
accelerator pedal. Refer to the hill start assist system in the anti-lock brake system description and operation document for more information.
Trailer Sway Control
The trailer sway control can detect the vehicle yaw instability, caused by an attached trailer. Refer to the trailer sway control system in the antilock brake system description and operation document for more information.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 66

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 66
Driver Information Center Indicators and Messages (Trailer Brake System)
The following indicators are used to inform the driver of several different conditions:
Trailer Connected
This message will be briefly displayed when a trailer with Electric or Electric Over Hydraulic brakes is first connected to the vehicle. This
message will automatically turn off in about ten seconds. The driver can also acknowledge this message before it automatically turns off.
Check Trailer Wiring
This message will be displayed if:
The system detects that a trailer with Electric or Electric Over Hydraulic brakes is connected to the vehicle and then the trailer harness
becomes disconnected from the vehicle.
The trailer connection is recognized initially and then a disconnect occurs while the vehicle is stationary. This message will automatically
turn off in about thirty seconds. This message will also turn off if the driver acknowledges this message off or if the trailer harness is
reconnected.
A disconnect of the trailer wiring harness occurs while the vehicle is moving. The Check Trailer Wiring message will continue until the
ignition is turned off. The message will also turn off if the driver acknowledges this message off or it the trailer harness is re-connected
or repairs are completed.
There is an electrical fault in the wiring to the electric trailer brakes. The Check Trailer Wiring message will continue as long as there is
an electrical fault in the trailer wiring. This message will also turn off if the driver acknowledges this message off.
A poor connection at the 7–way connector may cause the Check Trailer Wiring message. Some aftermarket 7–way trailer side connector
adapters or plugs may cause deformation or excessive wear to the vehicle’s trailer terminals. It is recommended that you use an OEM or
Pollak heavy duty 7–way trailer side connector adapter.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 67

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 67
Service Trailer Brake System
This message will be displayed when there is a problem with the trailer brake control system. The trailer brake system may not be fully
functional, or may not be functioning at all. The trailer brake system is designed to provide trailer braking, if possible, even when faults prevent
it from being fully functional. This reduced functionality includes:
1. Providing trailer braking when the master cylinder pressure or brake pedal switch are faulted.
2. Providing trailer braking when hill start assist and trailer sway control communication is faulted.
3. Providing trailer braking when certain manual trailer brake apply lever faults are present.
These conditions should be repaired to allow the trailer brake system to be fully functional.
Trailer Gain and Output Display
This display menu can be accessed by scrolling through the DIC menu, or any time the trailer gain +/− button is depressed, or the manual trailer
brake apply lever is actuated. The trailer output is displayed from 0 to full output and indicates the output power provided to the trailer brakes,
relative to the gain setting.
After the electrical connection is made to a trailer equipped with electric brakes or electric over hydraulic brakes, the TRAILER CONNECTED
message will be displayed momentarily on the DIC. The Trailer Brake Display Page can be selected on the DIC showing TRAILER GAIN and
OUTPUT, after all vehicle related service messages are acknowledged by the driver. Depending on which instrument panel cluster is in the
vehicle, the DIC may display dashed lines, a greyed out display, or it may be blank signifying a disconnected trailer or a trailer brake fault
condition.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 68

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 68
Trailer Brake Control System Schematic
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 69

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 69
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
1
2.5
RD/VT
1940
Battery Positive Voltage
2 - -
-
Not Occupied
3
0.5
BN
3891
Aero Shutter Control
4
0.5
GY
3890
Aero Shutter Control 2
5
0.5
D-BU
2500
High Speed GMLAN Serial Data (+) (1)
6
0.5
D-BU
2500
High Speed GMLAN Serial Data (+) (1)
7 - -
-
Not Occupied
8
0.5
VT/YE
5985
Accessory Wakeup Serial Data
9-10 - -
-
Not Occupied
11
0.5
GY
3890
Aero Shutter Control 2
12
0.5
BN
3891
Aero Shutter Control
13-16 - -
-
Not Occupied
17
0.5
WH
2501
High Speed GMLAN Serial Data (-) (1)
18
0.5
WH
2501
High Speed GMLAN Serial Data (-) (1)
19-20 - -
-
Not Occupied
21
0.75
PU/L-GN
439
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
22-24 - -
-
Not Occupied
25
2.5
BK
2150
Ground
26-38 - -
-
Not Occupied
Chassis Control Module Connector
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 70

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 70
Trailer Connector 1 of 3 (Terminals A, B, D, E, F & G)
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 71

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 71
Trailer Connector 2 of 3 (Terminal C except E29)
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 72

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 72
Trailer Connector 3 of 3 (Terminal C with E29)
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 73

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 73
Trailer Connector Location
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 74

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 74
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
A
0.75
WH/LGN
1624
Trailer Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
B 5 WH
22
Trailer Ground
C
2.5
D-BU
47
Trailer Auxiliary Supply Voltage
D
0.75
LGN/VT
1619
Right Rear Trailer Stop/Turn Lamp
Supply Voltage
E
4
RD/LGN
742
Battery Positive Voltage
F
1.5
GY/BN
2109
Trailer Park Lamp Supply Voltage
G
0.75
YE/GY
1618
Left Rear Trailer Stop/Turn Lamp
Supply Voltage
Trailer Connector Pin Out
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 75

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 75
Section B
Understanding the Alpha Numeric Naming Convention
Fuse, Relay, and Block Names
If a block has text-based names on a label of some sort, those will only appear in the Electrical Center Identification Views Usage Table. Refer to the Electrical Center
Identification Views topic for additional information.
Fuse Names
Fuse names depend on whether they are an inline fuse, or if they are located within a block. Inline fuses are assigned a component code/name, while fuses located
within a block use the following strategy:
Fuse names within blocks will be identified by four characters described below:
1st Character
F = Fuse, Circuit Breaker
R = Diodes, Resistors
2nd Character
Position number within the block
3rd Character
Alpha character defining the block position within the vehicle
U = Engine Compartment (Underhood)
D = I/P (within instrument panel)
P = Passenger Compartment (not in I/P, can be in center console)
R = Body Rear (Rear of the Passenger Compartment or Rear Compartment)
B = Battery or Auxiliary Battery
H = Fuse Holder
4th Character
Alpha character (start with A, B, C,…) at the end identifying whether there is more than one block residing in the same area on the vehicle within the same vehicle
publication.
Example:
Fuse 11 of a vehicle with a single block within the engine compartment would be F11UA
Fuse 13 of a vehicle with two blocks within the engine compartment would be F13UA and F13UB
Only the assigned names, described above will appear on the schematic graphic. Both the assigned name and the name on the label, (if equipped) will appear in the
block usage table in the Electrical Center Identification Views.
If block has fuse numbers on the label that repeat (typically based on fuse type), make the 4th character unique for each type. For example, use A for 1 type, B for
second type, and so on. Additionally, if there are multiple blocks within the same zone, the 4th character can be assigned based on position. For example, if the
instrument panel had two fuse blocks, one at each end, the 4th position can be L for the block on the left and R for the block on the right.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 76

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 76
No.
Device
Assigned
Name
Rating
Description
X1
F4UD
175A
K34 Power Steering Control
Module (K4B), M64 Starter
Motor
X2
F3UD
125A
Not Used
X3
F2UD
175A
G13 Generator (KW5), X50A
Fuse Block-Underhood, X55J
Fuse Holder-Generator
(KW5)
X4
F1UD
100A
Not Used
X5
F7UD
60A
X51R Fuse Block-Instrument
Panel Right
X6
F6DA
60A
X51R Fuse Block-Instrument
Panel Right
Battery Fuse Block –Top View
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 77

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 77
Fuse Block (X50) Under-hood - Label
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 78

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 78
Fuse Block (X50) Under-hood - Top View
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 79

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 79
Graphic Not Available
Fuse Block (X50) Under-hood - Bottom View
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 80

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 80
X50A Fuse Block – Under-hood Label Usage
No.
Device Label
Name
Device Assigned
Name
Rating
Description
Micro J-Case Fuses
01
TRLR BRK
F1UA
30 A
Blunt Cut (E29), X61A Junction Clock-Instrument Panel (-E29)
02
TRLR BATT
F2UA
30 A
C1B Battery Auxiliary (K4B), X88 Trailer Connector
J-Case Fuses
03
ABS PUMP
F3UA
60 A
K17 Electronic Brake Control Module
04
I/P BEC 1
F4UA
50 A
F6DL, F7DL, F8DL, F9DL,F17DL, F25DL, F26DL, F34DL, F44DL, F45DL
05
MSB PASS
F5UA
40 A
Not Used
06
ELEC PRK BRK
F6UA
40 A
Not Used
07
IP BEC 2
F7UA
50 A
F3DL, F11DL, F13DL, F29DL, F38DL, F40DL, F41DL, KR74 Ignition Run Relay,
KR76A Retained Accessory Power Relay 1
08
MSB DRVR
F8UA
40 A
Not Used
09
REAR DEFOG
F9UA
30 A
E18 Rear Defogger Grid
10
STRTR
F10UA
40 A
KR27 Starter Relay
11
COOL FAN 1
F11UA
40 A
G10L Cooling Fan Motor-Left
12
COOL FAN 2
F12UA
40 A
G10R Cooling Fan Motor-Right
Mini Fuses 2 Pin
13
TRLR STOP
TRN LT
F13UA
10 A
X88 Trailer Connector
14
TRLR PRK
LAMP
F14UA
20 A
X88 Trailer Connector
15
REV LAMP
F15UA
10 A
A10 Inside Rearview Mirror, B87 Rearview Camera, E5E Tail Lamp-Left, E5F
Tail Lamp-Right
16
TRLR STOP
TRN RT
F16UA
10 A
X88 Trailer Connector
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 81

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 81
X50A Fuse Block – Under-hood Label Usage
No.
Device Label
Name
Device Assigned
Name
Rating
Description
Micro Fuses 2 Pin
17
FUEL PUMP
F17UA
20 A
KR23A Fuel Pump Relay
18
ICCM
F18UA
10 A
K38 Chassis Control Module
19
ESC ELC EXH
F19UA
30 A
Not Used
20
FPPM
F20UA
30 A
K111 Fuel Pump Driver Control Module
21
UPFTR SW1
F21UA
5 A
Not Used
22
UPFTR 2
F22UA
30 A
Not Used
23
FRT/WPR
F23UA
25 A
KR12B Windshield Wiper Relay, KR12C Windshield Wiper Speed Control
Relay
24
ABS VLV
F24UA
25 A
K17 electronic Brake Control Module
25
UPFTR SW2
—
—
Not Used
26
UPFTR SW3
F26UA
5 A
Not Used
27
PRK LMP RT
F27UA
15 A
E5F Tail Lamp Right, E3RF Rear Fender Clearence Lamp-Right Front (-SRW).
E2A Marker Lamp-Endgate (-SRW), E3RR Rear Fender Clearance Lamp-Right
Rear, E4D Daytime Running Lamp-Right, E4K Park Lamp-Right Front (X88),
E2RF Side Marker Lamp-Right Front (Z88)
28
PRK LMP LT
F28UA
15 A
E5E Tail Lamp Left, E3LF Rear Fender Clearance Lamp-Left Front (-SRW).E3A
Roof Clearance Lamp-Left front Outer (U01), E3C Roof Clearance LampFront Middle (U01), E3E Clearance Lamp-Right Front Outer (U01), E3LR
Rear Fender Clearance Lamp-Left Rear, E4C Daytime Running Lamp-Left,
E4J Park Lamp-Left Front (X88), E2LF Side Marker Lamp-Left Front (Z88)
29
UPFTR 3
F29UA
30 A
Not Used
30
UPFTR SW4
—
—
Not Used
31
UPFTR 4
F31UA
30 A
Not Used
32
BCK UP LAMP
F32UA
10 A
X88 Trailer Connector
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 82
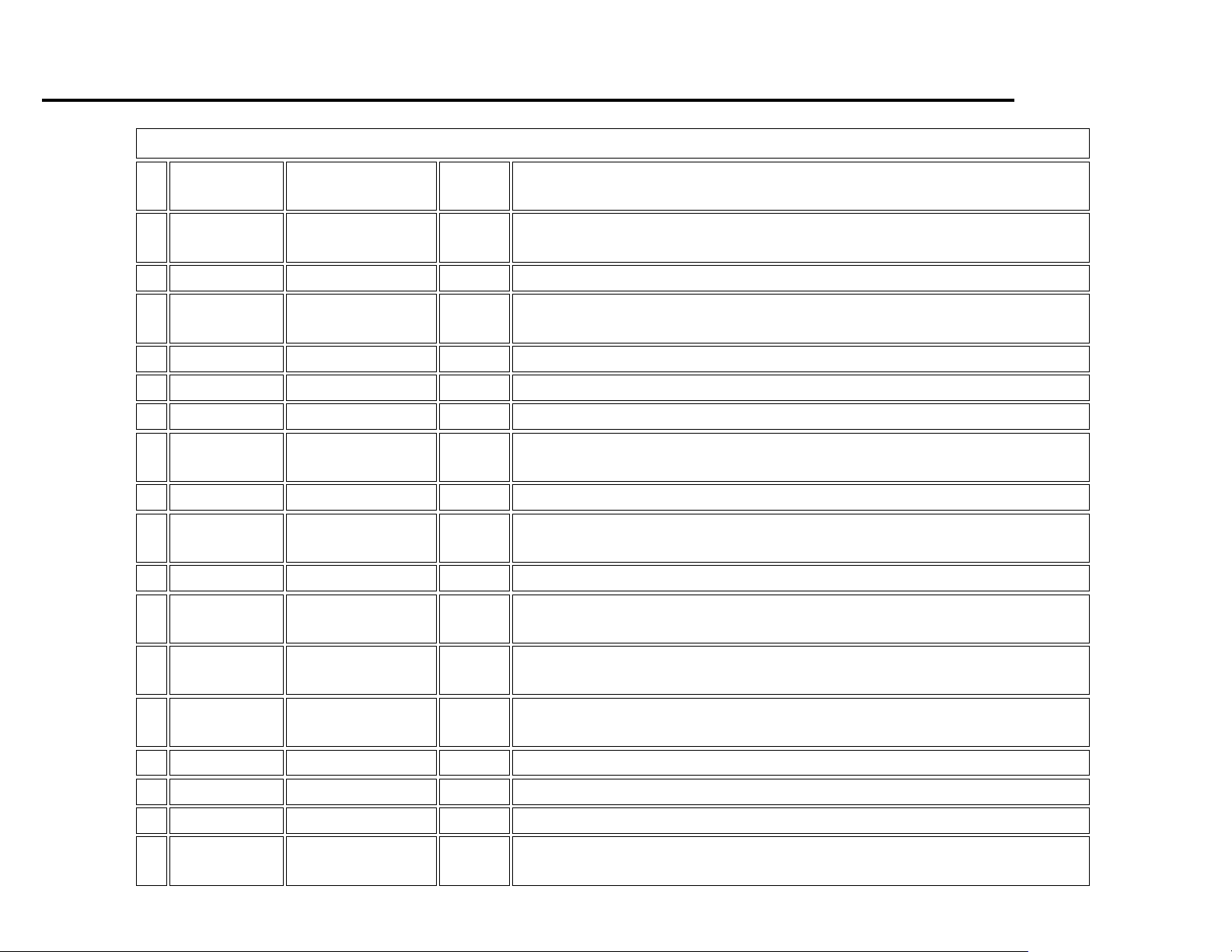
Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 82
X50A Fuse Block – Under-hood Label Usage
No.
Device Label
Name
Device Assigned
Name
Rating
Description
33
ECM IGN
F33UA
15 A
K20 Engine Control Module, K38 Chassis Control Module, K111 Fuel Pump
Driver Control Module,
34
A/C CLTCH
F34UA
10 A
KR29 A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
35
HTD MIR
F35UA
15 A
E17D Outside Rearview Mirror Glass-Driver, E17P Outside Rearview Mirror
Glass-Passenger
36
UPFTR 1
F36UA
30 A
Not Used
37
CHMSL
F37UA
10 A
E6 Center High Mounted Stop Lamp
38
MISC IGN
F38UA
10 A
Not Used
39
TRANS IGN
F39UA
15 A
T12 Automatic Transmission Assembly, M26 Front Axle Engagement
Actuator, K69 Transfer Case Control Module
40
FUEL PUMP 2
—
—
Not Used
41
COOL FAN
CLTCH
—
—
Not Used
42
ENG
F42UA
15 A
B75C Multi Function Intake Air Sensor
43
INJ A ODD
F43UA
20 A
K20 Engine Control Module, T8A Ignition Coil 1, T8C Ignition Coil 3, T8E
Ignition Coil 5, T8G Ignition Coil 7
44
INJ B EVEN
F44UA
20 A
K20 Engine Control Module, T8B Ignition Coil 2, T8D Ignition Coil 4, T8F
Ignition Coil 6, T8H Ignition Coil 8
45
O2 SNSR B
F45UA
15 A
B52D Heated Oxygen Sensor Bank 1 Sensor 2, B52F Heated Oxygen SensorBank 2 Sensor 2
46
THROT CONT
F46UA
15 A
Not Used
47
HORN
F47UA
15 A
P12 Horn
48
FOG LAMP
F48UA
15 A
E29LF Fog Lamp-Left Front, E29RF Fog Lamp-Right Front
49
O2 SNSR A
F49UA
15 A
B52C Heated Oxygen Sensor Bank 1 Sensor 1, B52E Heated Oxygen SensorBank 2 Sensor 1, Q12 Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid Valve, Q43
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 83

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 83
X50A Fuse Block – Under-hood Label Usage
No.
Device Label
Name
Device Assigned
Name
Rating
Description
Valve Lifter Oil Manifold Assembly, Q44 Engine Oil Pressure Control
Solenoid Valve
50
ECM
F50UA
30 A
K20 Engine Control Module
51
INT HTR
F51UA
10 A
Not Used
52
ACCY PWR
MDL/TPIM
PUMP
F52UA
10 A
Not Used
53
FRT WASH
F53UA
15 A
G24 Windshield Washer Pump
Micro Fuses 3 Pin
54
A/C CMPRSR
MDL/BATT
RVC
F54UA
5A/5A
K20 Body Control Module
55
A/C CMPRSR
MDL/BATT
PCK
F55UA
10A/10A
Not Used
56
TCM / ECM
F56UA
15A/15A
K20 Engine Control Module Q13 Evaporative Emission Vent Solenoid Valve,
T12 Automatic Transmission Assembly
57
HDLP RT / LT
F57UA
10A/10A
E4E Headlamp-Left High Beam (X88), E4F Headlamp-Right High Beam (X88),
M28L High Beam Solenoid Actuator-Left (Z88), M28R High Beam Solenoid
Actuator-Right (Z88)
Micro Relays
58
FUEL PUMP
KR23A Fuel Pump
Relay
—
G12 Fuel Pump
59
UPFTR 2
—
—
Not Used
60
UPFTR 3
—
—
Not Used
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 84

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 84
X50A Fuse Block – Under-hood Label Usage
No.
Device Label
Name
Device Assigned
Name
Rating
Description
61
UPFTR 4
—
—
Not Used
62
TRLR PRK
LAMPS
KR125 Trailer Park
Lamps Relay
—
F14UA, F27UA, F28UA, K20 Body Control Module
63
RUN/CRNK
KR73 Ignition Main
relay
—
F33UA, F38UA, F39UA, F55UA, K9 Body Control Module
64
UPFTR 1
—
—
Not Used
65
FUEL PUMP 2
—
—
Not Used
66
A/C CNTRL
KR29 A/C
Compressor Clutch
Relay
—
Q2 A/C Compressor Clutch, K20 Engine Control Module
67
STRTR
KR27 Starter Relay
—
M64 Starter Motor
Mini Relays
68
REAR DEFOG
KR5 Rear Defogger
Relay
—
F9UA, F35UA
69
ECM
KR75 Engine
Controls Ignition
Relay
—
F41UA, F42UA, F43UA, F44UA, F45UA, F46UA, F49UA, F50UA, KR29
Solid State Relays
70
COOL FAN
CLTCH
— — Not Used
Test Points
71
CKT 95
71
—
—
72
CKT 92
72
—
—
Note: Relays listed below are non-serviceable Printed Circuit Board (PCB) relays and are internal to the block.
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 85

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 85
X50A Fuse Block – Under-hood Label Usage
No.
Device Label
Name
Device Assigned
Name
Rating
Description
— — KR3 Horn Relay
—
F47UA, P12 Horn
—
—
KR11 Windshield
Washer Pump
Relay
—
F53UA, G24 Windshield Washer Pump
—
—
KR12B Windshield
Wiper Relay
—
KR12C Windshield Wiper Speed Control Relay
—
—
KR12C Windshield
Wiper Speed
Control Relay
—
M75 Windshield Wiper Motor
—
—
KR46 Front Fog
Lamp Relay
—
E29LF Fog Lamp-Left Front, E29RF Fog Lamp- Right Front, F48UA
—
—
KR48 Headlamp
High Beam Relay
—
F57UA, E4E Headlamp- Left High Beam (X88), E4F Headlamp-Right High
Beam (X88), M28L High Beam Solenoid Actuator-Left (Z88) M28R High
Beam Solenoid Actuator-Right (Z88)
—
—
KR59 Stop Lamp
Relay
—
F37UA, E6 Center High Mounted Stop Lamp
—
—
KR61 Trailer
Backup Lamp Relay
—
A10 Inside Rearview Mirror, B87 Rearview Camera, E5E Tail lamp-Left, E5F
Tail lamp-Right, F15UA, F32UA, X88 Trailer Connector
—
—
KR63L Trailer
Stop/Turn Signal
Lamp Relay-Left
—
F13UA, X88 Trailer Connector
—
—
KR63R Trailer
Stop/Turn Signal
Lamp Relay-Right
—
F16UA, X88 Trailer Connector
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 86

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 86
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X1
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 87
Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 87
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
A - -
-
Not Occupied
B2 4 RD/GY
642
Battery Positive Voltage
C - -
-
Not Occupied
D1
0.75
YE
712
Left Headlamp Low Beam Supply Voltage
D3
0.75
L-GN/VT
1315
Right Front Turn Signal Lamp Supply Voltage
E2 4 RD/WH
342
Battery Positive Voltage
F1
0.5
GY/BN
309
Right Park Lamp Supply Voltage
F2
0.75
GY/VT
228
Windshield Washer Pump Control
F3
0.75
D-BU/WH
1314
Left Front Turn Signal Lamp Supply Voltage
G1
0.5
VT/GY
709
Left Park Lamp Supply Voltage
G4
0.5
BK
150
Ground
H2
0.75
GY/D-BU
7538
Left Front DRL Supply Voltage
H4
0.5
WH
311
Right Headlamp High Beam Supply Voltage
H6
0.75
D-BU/BN
7539
Right Front DRL Supply Voltage
J2
0.75
BN/GY
29
Horn Control
J3
0.5
BN/VT
2234
Front Fog Lamp Supply Voltage
J4
0.5
WH
711
Left Headlamp High Beam Supply Voltage
J5
0.75
YE
312
Right Headlamp Low Beam Supply Voltage
K- - -
-
Not Occupied
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X1 (continued)
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 88
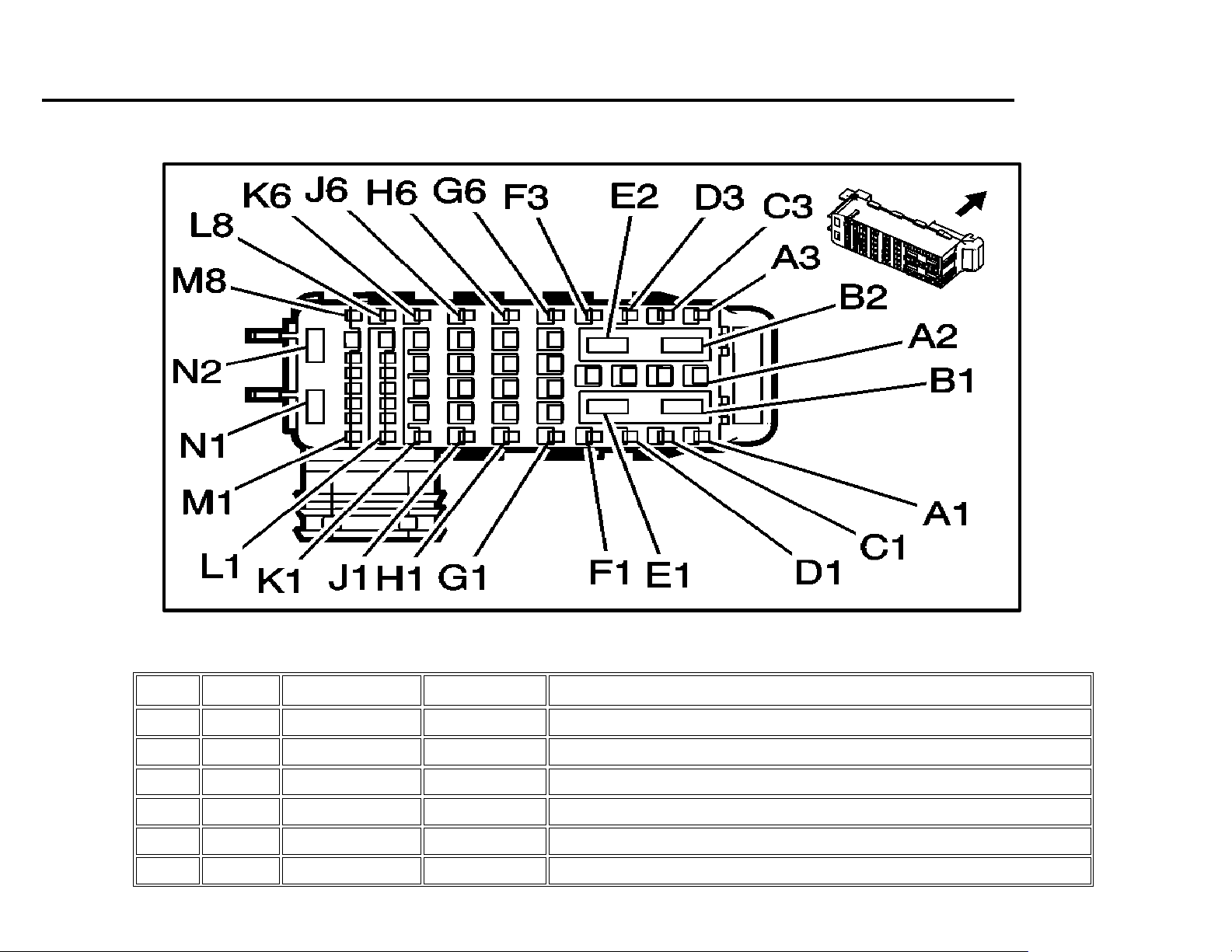
Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 88
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
A1
0.5
WH/GY
459
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay Control
B - -
-
Not Occupied
C1
0.75
BN/L-GN
59
A/C Compressor Clutch Supply Voltage
D3
0.5
YE/BK
625
Starter Enable Relay Control
E2 4 YE
6
Starter Solenoid Crank Voltage
F2
2.5
BK
550
Ground
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X2
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 89

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 89
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
G3
0.5
VT/D-BU
5293
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (4)
G4
2.5
VT/D-BU
5290
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (1)
G5
0.75
RD/L-GN
1840
Battery Positive Voltage
H2
0.75
VT/D-BU
5291
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (2)
H3
0.75
VT/D-BU
5293
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (4)
H5
0.5
RD/BN
440
Battery Positive Voltage
H6
0.5
YE
5991
Powertrain Relay Coil Control
J2
0.5
VT/D-BU
5294
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (5)
J3
0.75
VT/D-BU
5291
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (2)
J4
0.75
VT/D-BU
5292
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (3)
J5
0.5
VT/D-BU
5294
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (5)
K3
0.5
VT/D-BU
5291
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (2)
K4
0.75
VT/D-BU
5292
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (3)
K5
0.5
VT/D-BU
5292
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (3)
L7
0.5
VT/BK
2139
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
M5
0.5
GY
5660
Fuel Pump Controller Data Out Signal
M6
0.75
BK/WH
451
Signal Ground
M7
0.5
VT/L-GN
439
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
N- - -
-
Not Occupied
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 90

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 90
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
A1
0.5
YE/D-BU
18
Left Rear Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
B1 4 RD/GY
1342
Battery Positive Voltage
C1
0.5
BN/L-GN
19
Right Rear Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
D1
0.75
L-GN/VT
1315
Right Front Turn Signal Lamp Supply Voltage
E
- - -
Not Occupied
F1
0.75
D-BU/WH
1314
Left Front Turn Signal Lamp Supply Voltage
F3
0.5
D-BU/L-GN
962
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X3
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 91

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 91
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
G1
0.75
D-BU/BN
7539
Right Front DRL Supply Voltage
H2 1 BK
550
Ground
J1
0.35
WH/VT
860
Front Windshield Wiper Switch High Signal
K1
0.5
VT/WH
5065
Stop Lamp Relay Coil Supply Voltage
K3 1 YE/BN
95
Windshield Wiper Motor Low Speed Control
K4 1 WH
92
Windshield Wiper Motor High Speed Control
K6
0.35
BN/GY
2268
Windshield Washer Relay Control
L2
0.35
BN/VT
1969
Headlamp High Beam Relay Control
L4
0.35
GY
91
Windshield Wiper Motor Relay Coil Supply Voltage
L5
0.5
BN/WH
1317
Fog Lamp Relay Control
L6
0.35
BN/WH
28
Horn Relay Control
L7
0.5
BN/YE
2267
Mirror Heating Element Supply Voltage
M1
0.75
YE
312
Right Headlamp Low Beam Supply Voltage
M5
0.5
D-BU/L-GN
961
M6
0.5
VT/GY
1054
Stop Lamp Supply Voltage
M7
2.5
RD/L-GN
965
N- - -
-
Not Occupied
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 92

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 92
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
A3
0.5
L-GN/WH
24
Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
B2 5 RD/VT
842
Battery Positive Voltage
C
- - -
Not Occupied
D3
0.5
VT/L-GN
1739
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
E2 5 RD/D-BU
42
Battery Positive Voltage
F3
0.35
L-GN/WH
24
Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
G2
2.5
RD/L-GN
966
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X4
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 93

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 93
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
H5
2.5
RD/L-GN
242
Battery Positive Voltage
J6
0.75
BK/WH
451
Signal Ground
J1
0.75
GY/D-BU
7538
Left Front DRL Supply Voltage
K1
0.75
YE
712
Left Headlamp Low Beam Supply Voltage
K2
2.5
RD/L-GN
968
K5
2.5
RD/L-GN
967
K6
0.5
VT/GY
709
Left Park Lamp Supply Voltage
L1
0.5
D-BU/L-GN
964
L2
0.35
YE/GY
5187
Right Trailer Turn Signal Lamp
L3
0.35
D-BU/BN
38
Backup Lamp Relay Control
L4
0.35
D-BU/WH
5186
Left Trailer Turn Signal Lamp
L5
0.35
D-BU
45
Park Lamp Relay Control
L6
0.5
D-BU/L-GN
963
M1
0.75
RD/YE
2340
Battery Positive Voltage
M2
0.35
BN/VT
193
Rear Defog Relay Control
M5
0.35
L-GN/VT
5199
Run/Crank Relay Coil Control
N1
2.5
BN/VT
293
Rear Defog Element Supply Voltage
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 94

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 94
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
A2
0.75
YE/D-BU
18
Left Rear Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
A3
0.75
BN/L-GN
19
Right Rear Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
B1 5 RD/YE
442
Battery Positive Voltage
C1
0.75
L-GN/WH
24
Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
D1
0.5
VT/L-GN
1739
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
E - -
-
Not Occupied
Fuse Block (X50A) Under-hood - Connector X5
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 95

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 95
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
F1
0.5
L-GN/WH
24
Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
F3
0.5
GY
3890
Aero Shutter Control 2
G2
2.5
RD/VT
1940
Battery Positive Voltage
G4
0.75
RD/WH
2040
Battery Positive Voltage
H3
0.5
RD/L-GN
1840
Battery Positive Voltage
H6
0.5
BN
3891
Aero Shutter Control
J2
2.5
RD/L-GN
242
Battery Positive Voltage
J3
1.5
GY/BN
2109
Trailer Park Lamp Supply Voltage
J4
2.5
RD/VT
1640
Battery Positive Voltage
J5
0.5
0.75
VT/L-GN
PU/L-GN
439
439
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
K2
0.75
VT/GY
709
Left Park Lamp Supply Voltage
K4
0.75
GY/BN
309
Right Park Lamp Supply Voltage
K5
0.75
YE/GY
1618
Left Rear Trailer Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
K6
0.75
L-GN/VT
1619
Right Rear Trailer Stop/Turn Lamp Supply Voltage
L - -
-
Not Occupied
M1
0.5
VT/GY
1054
Stop Lamp Supply Voltage
M5
0.5
GY
5660
Fuel Pump Controller Data Out Signal
M7
0.5
VT/D-BU
5294
Powertrain Main Relay Fused Supply (5)
M8
0.75
WH/L-GN
1624
Trailer Backup Lamp Supply Voltage
N2 4 RD/L-GN
742
Battery Positive Voltage
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 96

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 96
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left - Label
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 97

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 97
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left - Top View
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 98

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 98
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left - Bottom View
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 99

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 99
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left – Connector X1
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
Page 100

Electrical Manual-NEW 2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Pg. 100
X51L Fuse Block - Instrument Panel Left X1
Pin
Size
Color
Circuit
Function
1-3 - -
-
Not Occupied
4
0.75
RD/L-GN
5140
Battery Positive Voltage
5
0.5
0.35
RD/L-GN
RD/L-GN
4440
4440
Battery Positive Voltage
Battery Positive Voltage
6-14 - -
-
Not Occupied
15
0.35
L-GN/GY
5286
Adjustable Pedal Switch Forward Signal
16
0.35
RD/VT
1940
Battery Positive Voltage
17
2.5
RD/YE
3740
Battery Positive Voltage
18
0.75
RD/L-GN
5140
Battery Positive Voltage
19 - -
-
Not Occupied
20
0.75
L-GN/VT
5130
Adjustable Pedal Actuator Forward Control
21 5 RD/VT
842
Battery Positive Voltage
22 - -
-
Not Occupied
23 5 RD/D-BU
42
Battery Positive Voltage
24-26 - -
-
Not Occupied
27
2.5
RD/YE
5040
Battery Positive Voltage
28
0.75
YE
5129
Adjustable Pedal Actuator Rearward Control
29 - -
-
Not Occupied
30
0.5
VT/WH
1939
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
31 - -
-
Not Occupied
32
0.5
VT/L-GN
1739
Run/Crank Ignition 1 Voltage
33
0.35
WH/GY
5285
Adjustable Pedal Switch Rearward Signal
Fuse Block (X51L) Instrument Panel Left – Connector X1 Pin-out
Electrical Manual-2014 Light Duty Full Size C/K Trucks Revision Date 06/19/2013 (WIP)
 Loading...
Loading...