
CT63 Terminal
User Manual
Revision 1.7

Therefore only touch the CT63 Terminal on the housing or connectors and avoid
touching the components on the board.
When using products which are exposed to electric voltage the valid regulations have to
be observed.
Important information
This technical description contains important information for start up and use of the CT63 Terminal.
Read it carefully before you start working with the CT63 Terminal.
The warranty will be void should damage occur due to non-compliance with these instructions for use.
We cannot accept any responsibility for consequential loss.
We cannot be held responsible for material loss or personal injury that is due to incompetent use or
non-compliance with the safety instructions. The warranty will be void in such circumstances.
The CT63 Terminal contains highly integrated components which can be damaged by electrostatic
discharge if the user would open the housing.
CEP preserves the right to change the included information without notice and doesn’t take
responsibility for errors in the document and/or missing information.
Safety Instructions
Before opening of a device always pull the mains adapter or make sure that the device is disconnected
from the power supply.
You should only use tools on components, modules or devices if they are disconnected from the power
supply and the electric charge, which may still be stored in some components, inside the device has
been discharged.
All cables and wires which are energized and connected to the device, the module or components have
to be checked regularly for any damage of the isolation shield or fractures of the cables. If the supply
cables are visibly damaged the device has to be taken out of operation immediately until the faulty
cable has been exchanged.
When using components or modules it is necessary to strictly observe the specification given in the
corresponding description of these components. If a description for a private end-customer not clearly
states which electric data is valid for a component or a module, how to wire the device, which external
components or additional devices can be connected or which parameters these components are
allowed to have, a specialist must be contacted.
Before putting a device into operation, it has to be clarified, whether this device or module is meant for
the field of application. In case of doubt ask specialists or the manufacturer of the device.
Please note that we are not responsible for any errors in usage or connection. Therefore we cannot
accept any responsibility for consequential loss.
Devices which operate with >35 Volt have to be connected by a specialist. Before putting the device
into operation it should be checked that there is no current leakage on the housing.
2

In case those measurements with the opened housing are necessary, an isolating-transformer has to be
integrated for safety reasons. Alternatively the voltage can be supplied by an appropriate power supply
which complies with the safety regulations. All wiring work has to be done in a voltage free state only
3

Table of Contents
Important information ...................................................................................................................................................... 2
Safety Instructions ............................................................................................................................................................ 2
1 Mechanical Description ............................................................................................................................................ 7
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Physical Dimensions and Weight ...................................................................................................................... 8
2 Electrical Description ................................................................................................................................................ 9
2.1 Power Connector .............................................................................................................................................. 9
2.2 Antenna Connector ......................................................................................................................................... 10
2.3 SIM card reader ............................................................................................................................................... 11
2.4 RS232 Serial Port ............................................................................................................................................. 11
2.5 Serial Data ....................................................................................................................................................... 11
2.6 Serial Data Signals ........................................................................................................................................... 11
2.7 Control Signals – RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, RI ................................................................................................ 12
2.8 Mini USB Connector ........................................................................................................................................ 12
3 Operation ................................................................................................................................................................ 14
3.1 Switch ON the modem .................................................................................................................................... 14
3.2 Switching OFF the modem .............................................................................................................................. 15
3.3 Using low power mode of the modem ........................................................................................................... 15
3.3.1 Enabling the low power mode: ............................................................................................................... 15
3.3.2 Disabling the low power mode by user: ................................................................................................. 15
3.3.3 Disable the low power modes by incoming GSM activity: ...................................................................... 15
3.4 Operating states / LEDs ................................................................................................................................... 16
3.4.1 Power up LED (green LED in the middle) ................................................................................................ 16
4 Power consumption ................................................................................................................................................ 17
4.1 Safety instructions .......................................................................................................................................... 17
4.2 General precautions ........................................................................................................................................ 17
4.3 SIM card precautions ...................................................................................................................................... 18
4.4 Antenna precautions ....................................................................................................................................... 18
5 Installation of the modem ...................................................................................................................................... 19
5.1 Where to install the modem ........................................................................................................................... 19
5.1.1 Environmental conditions ....................................................................................................................... 19
5.1.2 GSM Signal strength ................................................................................................................................ 19
4

5.1.3 Connections of components to CT63 E Terminal .................................................................................... 19
5.1.4 Network and Subscription....................................................................................................................... 20
5.2 How to install the modem .............................................................................................................................. 20
5.2.1 Power supply ........................................................................................................................................... 20
5.2.2 Securing the modem ............................................................................................................................... 20
5.3 Antenna ........................................................................................................................................................... 20
5.3.1 General .................................................................................................................................................... 20
5.3.2 Antenna type ........................................................................................................................................... 21
5.3.3 Antenna placement ................................................................................................................................. 21
5.3.4 The antenna cable ................................................................................................................................... 21
5.3.5 Possible communications disturbances .................................................................................................. 21
6 Optional variants ..................................................................................................................................................... 22
6.1 CT63 with DSUB15 connector with l2C and SPl interface ............................................................................... 22
6.2 CT63 with EGS5 (Java) Module & GPIO’s ........................................................................................................ 23
6.3 CT63 with Mini USB audio interface ............................................................................................................... 25
6.4 CT63 with Mini USB with USB – Power (host powered) ................................................................................. 25
7 Technical Data ......................................................................................................................................................... 27
8 CEP Certified Accessories ........................................................................................................................................ 29
9 Abbreviations .......................................................................................................................................................... 30
10 Mark of Conformity ............................................................................................................................................. 32
11 Service and Support ............................................................................................................................................ 33
12 Documentation Change Log ................................................................................................................................ 34
5

Table Overview
Table 1: RJ11 Pin and Signals Description ....................................................................................................................... 10
Table 2: Recommended antenna parameters ................................................................................................................ 10
Table 3: Electrical characteristics of the serial port signals ............................................................................................ 11
Table 4: Mini USB Pin Description ................................................................................................................................... 13
Table 5: Operating states of the power up LED .............................................................................................................. 16
Table 6: Power consumption in idle and low power mode ............................................................................................ 17
Table 7: CT63 with DSUB15 connector with l2C and SPl interface ................................................................................. 22
Table 8: Mini USB Pin Signal ............................................................................................................................................ 23
Table 9: RJ11 Connector Description .............................................................................................................................. 24
Table 10: CT63 with EGS5 (Java) Module % GPIO‘s ........................................................................................................ 24
Table 11: Mini USB audio interface Pin Signal ................................................................................................................ 25
Table 12: Mini USB with host powered Pin Signal .......................................................................................................... 26
Table 13: Accessories List ................................................................................................................................................ 29
Table 14: Abbreviation .................................................................................................................................................... 31
Table 15: Documentation Change Log ............................................................................................................................ 34
Figure Overview
Figure 1: Connector on rear side of the Terminal ............................................................................................................. 7
Figure 2: Connectors on front side of the Terminal .......................................................................................................... 7
Figure 3: Schematic of the Terminal’s Housing................................................................................................................. 8
Figure 4: RJ11 Pin Connector ............................................................................................................................................ 9
Figure 5: Mini USB Type A/B connector .......................................................................................................................... 12
6

1 Mechanical Description
1.1 Overview
The pictures below show the mechanical design of the CT63 Terminal along with the positions of the
different connectors and mounting holes. The CT63 Terminal case is made of durable PC/ABS plastic.
Figure 1: Connector on rear side of the Terminal
Figure 2: Connectors on front side of the Terminal
7

Please note the following:
Mounting holes positioned at two of the corners make it possible to securely bolt the modem into your
application.
Keypad, display, microphone, speaker and battery are not part of the modem.
The SIM card is mounted in the modem, accessible by the user under a lid without any tools.
The pins and electrical characteristics or the modem’s various connectors are described in “2. Electrical
Description”
Information about the antenna connector is found in “2.3 Antenna Connector”
1.2 Physical Dimensions and Weight
Overall dimensions: 77 x 67 26 mm
Weight: approx. 100g
Figure 3: Schematic of the Terminal’s Housing
8

This does not apply for the GND on the antenna connector if this coax GND / shield are
connected to your applications ground-plane.
2 Electrical Description
The modem uses the following standard connectors:
RJ11 6-way (power connector)
Mini USB (USB 2.0)
SIM card reader
FME male coaxial jack (antenna connector)
Sub-D female socket, 9 pin (RS232 serial port)
2.1 Power Connector
An RJ11 6-way connector, as shown and described below, serves as a means of supplying and
controlling DC power to the modem. It is necessary to connect an external power supply, since the
available power on the USB port is not sufficient to run the modem.
The supply voltage, VCC, required by the modem is 5V - 32V DC. Application of the supply voltage does
not switch the modem on. To do so an additional active-high control signal, TO_IN, must be applied for
> 1 second.
Please see chapter “3.1 Switching ON the modem” for further important details about TO_IN and
power supply requirements, especially if TO_IN is applied in parallel to VCC.
VCC and GND are reverse-polarity and over-voltage protected.
PIN: -> 6 5 4 3 2 1
Figure 4: RJ11 Pin Connector
9

PIN
Signal
Direction
Limits
Description
1
VCC
Input
5 – 32V
Positive power input, DC
2
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
3
EMERG_OFF
Input
5 – 32V
Active high control line used to
switch off
VIH > 5V, VIL < .5V
Power off: t >1s
4
TO_IN
Input
5 – 32V
Positive edge triggered signal;
used to switch on the modem
VIH > 5V, VIL < 0.5V
Power on: t >1s
5
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
Not connected
6
GND
Input
-
Negative power (ground) input
and return path for TO_IN and
EMERG_OFF
Frequency range
GSM 900/ 1800 MHz
Bandwidth
80 MHz in EGSM 90
Gain
<3dBi
Impedance
50ohm
Input power
>33 dBm (2W) peak power in GSM
VSWR recommended
< 2
Table 1: RJ11 Pin and Signals Description
2.2 Antenna Connector
The antenna connector allows transmission of radio frequency (RF) signals between the modem and an
external customer-supplied antenna. The modem is fitted with a 50Ω, FME male coaxial jack.
Output Power:
2 Watt Peak (Class 4) GSM 900/850 MHz
1 Watt Peak (Class 1) GSM 1800/1900 MHz
The antenna that the customer chooses to use should fulfil the following requirements:
Table 2: Recommended antenna parameters
10

PIN
Signal
Direction
Limits
Description
1
DCD
Output
> + 4V
<- 4 V
Data carrier detect
2
RD
Output
> + 4V
<- 4 V
Received data
3
TD
Input
> + 2,4V
< 0.8 V
Transmitted data
4
DTR
Input
> + 4V
< 0.8 V
Data terminal ready
5
GND
-
0 V
Ground connection
6
DSR
Output
> + 4V
< - 4 V
Data set ready
7
RTS
Input
> + 2,4V
< 0.8 V
Request to send
8
CTS
Output
> + 4V
< - 4 V
Clear to send
9
RI
Output
> + 4V
< - 4 V
Ring indicator
2.3 SIM card reader
The CT63 Terminal is fitted with a SIM card reader designed for 1.8V and for 3V SIM cards. It is the flipup type which is lockable in the horizontal position and is accessed through a removable panel.
2.4 RS232 Serial Port
The modem supports a standard RS232 serial interface via its 9 pin Sub-D connector, shown below. In
line with serial communication terminology the CT63 Terminal should be considered as the data circuitterminating equipment (DCE) and the external application or computer as the data terminating
equipment (DTE). The maximum baud rate to communicate with the CT63Terminal is 230400 kbit/ s.
2.5 Serial Data
The modem supports the standard data character format of
Programmable baud rate (300bps to 230,400bps).
Auto-configuration mode with auto-baud (1,200bps to 230,400bps).
Multiplex ability according to GSM 07.10 Multiplexer Protocol.
2.6 Serial Data Signals
Serial Data from Modem (RD)
RD is an output signal that the modem uses to send data to the application.
Serial Data To Modem (TD)
TD is an input signal, used by the application to send data to the modem.
Table 3: Electrical characteristics of the serial port signals
11

2.7 Control Signals – RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, RI
Request to Send (RTS)
RTS is used to condition the DCE for data transmission. The default level is high by internal pull up. The
exact behaviour of RTS is defined by an AT command. Software or Hardware control can be selected.
Hardware flow is the default control. The application must pull RTS low to communicate with the
modem. The modem will respond by asserting CTS low, indicating it is ready for communication.
Clear To Send (CTS)
CTS indicate that the DCE is ready to transmit data. The default level is high. You can define the exact
behaviour of CTS through an AT command, and can select software or hardware flow control.
Data Terminal Ready (DTR)
DTR indicates that the DTE is ready to transmit and receive data. It also acts as hardware ‘hang-up’,
terminating calls when switched high. The signal is active low. You can define the exact behaviour of
DTR with an AT command. The DTR line can also be used to switch on the modem when activated for
0.2 seconds. The DTR line must be deactivated prior to switching off the modem to ensure it switches
off (powers down) correctly.
Data Set Ready (DSR)
An active DSR signal is sent from the modem to the application (DTE) to confirm that a communications
path has been established. DSR has two modes of operation, settable using the AT command AT&S.
Data Carrier Detect (DCD)
DCD indicates that the DCE is receiving a valid carrier (data signal) when low. You can define the exact
behaviour of DCD with an AT command.
Ring Indicator (RI)
RI indicates that a ringing signal is being received by the DCE when low. You can define the exact
behaviour for RI with an AT command.
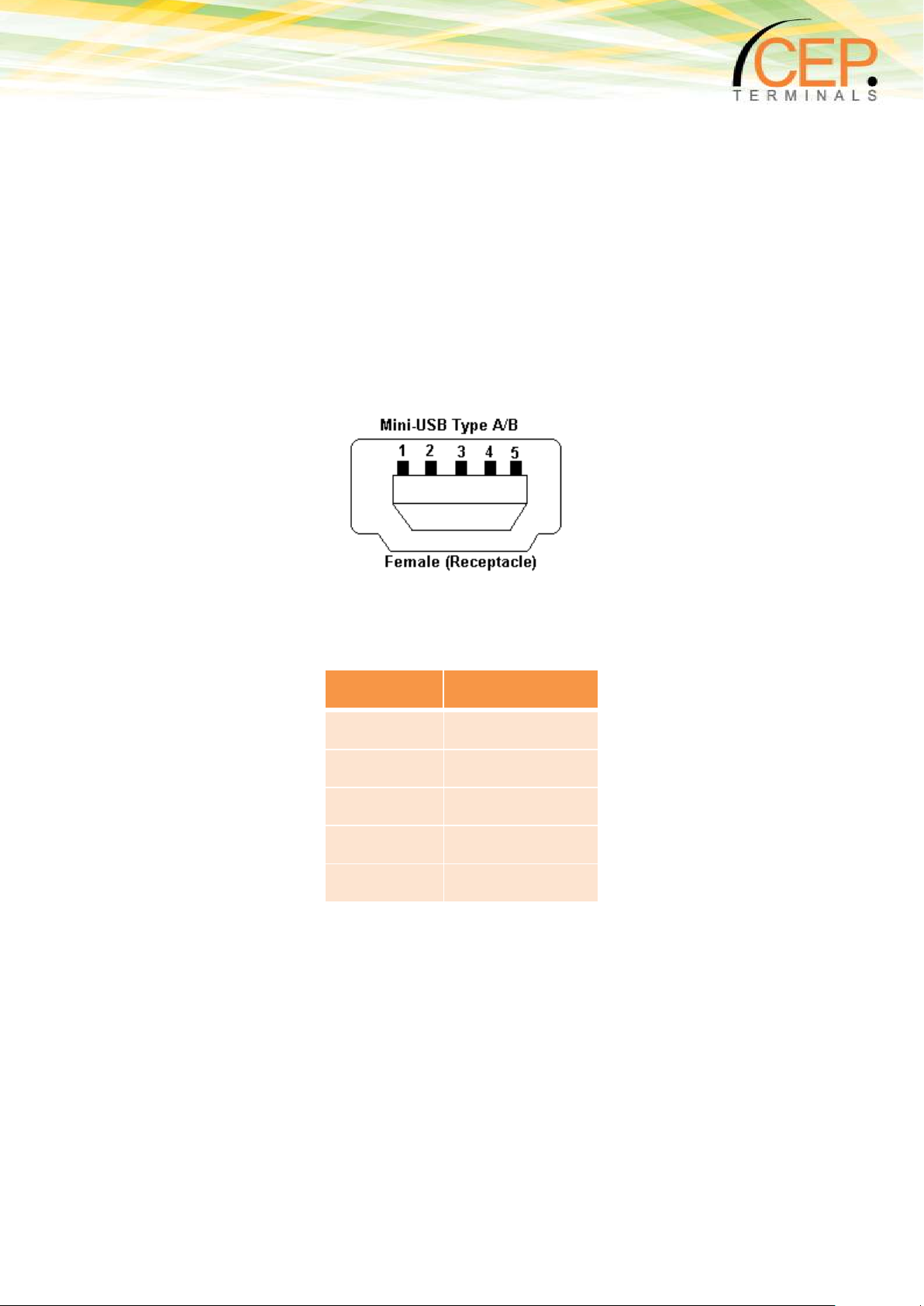
2.8 Mini USB Connector
The modem supports a standard USB 2.0 Full Speed slave interface interface for AT-commands. The
maximum baud rate to communicate with the CT63 Terminal is up to 12Mbit/s.
Drivers for several operating systems (e.g. Windows Vista, Windows XP or Linux) are available. Please
ask us (support@cepag.de).
Figure 5: Mini USB Type A/B connector
12

Pin
Signal
1
VUSB
2
D - 3 D +
4
not connected
5
GND
Table 4: Mini USB Pin Description
13

DTR must be cycled from low to high.
The TO_IN signal requires a positive “edge” (a sharp” signal transition from low to high)
to turn the modem on. This transition should be a rising signal from 0V (GND) to VCC, or
at least a large fraction of that voltage range, and must be applied at the same time as
VCC or after it. Very slow transitions (significantly slower than many milliseconds) or
very small transitions (e.g. only few volts instead of 0V to VCC) will not turn on the
module (since they are not considered to be a “positive edge”).
3 Operation
3.1 Switch ON the modem
There are two ways to switch on the modem, once power is applied:
assert TO_IN to high level for > 1s
activate the RS232 control line DTR
The modem is fully operational after 4 seconds. Logging onto a network may take longer than this and
is outside the control of the modem. The modem can be configured to start up at the time power is
applied by permanently tying power connector signals TO_IN (pin 4) and VCC (pin 1) together. In this
case DTR must be used to switch the modem on again after it has been switched off or reset, while
power is still applied.
Although this will not be an issue in almost all typical applications of the modem, please consider
following points:
Large capacitors in your power supply which will lead to slow leading and falling edges (issue does not
apply with modern stabilized switching regulator power-adaptors) AND TO_IN tied in parallel to VCC
(instead of separate dedicated digital signal)
Slow analogue signals used to assert TO_IN
TO_IN signal not before VCC
All 3 cases above might prevent the modem from recognizing the power-up signal this is no failure of
the modem itself, the same would apply to almost any electronic device that provides a separate
“power-on” or “reset” signal.
If you are in doubt, please
Use the mains power adapter that is provided by your distributor and is know to work properly with your
modem
Make sure that your signal and system design is according to the above
Consult our support team that will be more than happy to assist you.
14

3.2 Switching OFF the modem
There are two ways to switch off (power down) the modem as described below:
use the “AT^SMSO” command
EMERG_OFF to high level for t < 1s
A delay of up to 10s is experienced as the modem logs off the network
3.3 Using low power mode of the modem
Below are some short descriptions on how to enter and exit the low power state of the modem.
3.3.1 Enabling the low power mode:
wait until the GSM module is logged onto the GSM network
send the AT command "AT+CFUN=9"
set the RTS control line from High level to Low level
after about 1-2 minutes, a stable low-power mode should be achieved
3.3.2 Disabling the low power mode by user:
Set the RTS control line from Low to High
Low-power mode should be exited automatically
The RS-232 transceiver is activated immediately
AT channel is available again after a short period of time (37ms)
If applicable send AT command "AT+CFUN=1" to remain in normal mode
3.3.3 Disable the low power modes by incoming GSM activity:
The RTS control line is still at a low level
GSM module is called or receives an SMS
Low-power mode is exited automatically
RS-232 transceiver is activated immediately
AT channel is available again after 37ms
If activated by a call the text "ring" is transmitted via the serial interface
The RTS control line on the DB-9 should be set from Low level to High level
AT communication with the GSM module is now available
If applicable send AT command "AT+CFUN =1" to remain in normal mode
15

Operating state of CT63 Terminal
Power up LED state
Device off
Permanently off
net search / not registered /
Fast blinking
registered full service
Slow blinking
A call is active
Permanently on
3.4 Operating states / LEDs
3.4.1 Power up LED (green LED in the middle)
The modem has a green power up LED, as depicted below, which is used to indicate various operating
states. These states are described in following table.
Table 5: Operating states of the power up LED
16

[mA] @ 5V
[mA] @ 12V
[mA] @ 24V
[mA] @ 32V
CT63 off (DTR low,
no TO-IN)
0,04
0,11
0,22
0,29
CT63 idle mode
24,0
11,1
6,2
5,5
CT63 low power
mode
3,0
1,1
1,0
0,9
4 Power consumption
The following table shows you the power consumption of the CT63 / in different modes:
Table 6: Power consumption in idle and low power mode
Safety and Product Care
Please read the information in this section and the information in “Installation of the Modem”, before
starting your integration work!
4.1 Safety instructions
PLEASE READ THESE SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND KEEP A COPY OF THEM.
Always ensure that use of the modem is permitted. The modem may present a hazard if used in proximity
to personal medical electronic devices. As a rule, the modem must not be used in hospitals, airports or
planes.
Never use the modem at a gas station, refueling point, blasting area or in any other environment where
explosives may be present.
Operating the modem close to other electronic devices, such as antennas, television sets, and radios may
cause electromagnetic interference.
This product is intended to be used with the antenna or other radiating element at least 20cm away from
any part of the human body. In applications where this rule cannot be applied, the application designer is
responsible for providing the SAR measurement test report and declaration.
You are responsible for observing your country's safety standards, and where applicable, the relevant
wiring rules.
4.2 General precautions
The CT63 Terminal as a stand alone item is designed for indoor use only. To use outside it must be
integrated into a weatherproof enclosure. Do not exceed the environmental and electrical limits as
specified in “Technical Data”.
Avoid exposing the modem to lighted cigarettes, naked flames or to extreme hot or cold temperature.
Never try to dismantle the modem yourself. There are no components inside the modem that can be
serviced by the user. If you attempt to dismantle the modem, you may invalidate the warranty.
The CT63 Terminal must not be installed or located where the surface temperature of the plastic case may
exceed 85°C.
17

CEP AG may refuse warranty claims where evidence of product misuse is found.
All cables connected to the CT63 Terminal must be secured or clamped, immediately adjacent to the
modem's connectors, to provide strain relief and to avoid transmitting excessive vibration to the modem
in the installation.
Ensure the cables, supplying power, audio headset, and input cable to the CT63 Terminal, does not exceed
3 metres.
To protect power supply cables and meet the fire safety requirements when the unit is powered from a
battery or a high current supply, connect a fast 1.25A fuse in line with the positive supply.
Do not connect any incompatible component or product to the CT63 Terminal.
4.3 SIM card precautions
Before handling the SIM card in your application, ensure that you are not charged with static electricity.
Use proper precautions to avoid electrostatic discharges.
When the SIM card hatch is opened, the SIM card connectors lie exposed under the SIM card holder.
Caution! Do not touch these connectors! If you do, you may release an electrical discharge that could
damage the modem or the SIM card.
When designing your application, the SIM card’s accessibility should be taken into account. We always
recommend that you have the SIM card protected by a PIN code. This will ensure that the SIM card
cannot be used by an unauthorized person.
4.4 Antenna precautions
If the antenna is to be mounted outside, consider the risk of lightning. Follow the instructions provided
by the antenna manufacturer.
Never connect more than one modem to a single antenna. The modem can be damaged by radio
frequency energy from the transmitter of another modem.
Like any mobile station, the antenna of the modem emits radio frequency energy. To avoid EMI
(electromagnetic interference), you must determine whether the application itself, or equipment in the
application’s proximity, needs further protection against radio emission and the disturbances it might
cause. Protection is secured either by shielding the surrounding electronics or by moving the antenna
away from the electronics and the external signals cable.
The modem and antenna may be damaged if either come into contact with ground potentials other than
the one in your application. Beware, ground potential are not always what they appear to be.
18

5 Installation of the modem
This chapter gives you advice and helpful hints on how to integrate the CT63 Terminal into your
application from a hardware perspective. Please read the information given in “Safety and Product
Care”, page 10 and then read the information in this section before starting your integration work.
5.1 Where to install the modem
There are several conditions which need to be taken into consideration when designing your
application as they might affect the modem and its function. They are:
5.1.1 Environmental conditions
The modem must be installed so that the environmental conditions stated in the Technical Data
chapter, such as temperature, humidity and vibration are satisfied. Additionally, the electrical
specifications in the Technical Data section must not be exceeded.
5.1.2 GSM Signal strength
The modem has to be placed in a way that ensures sufficient GSM signal strength. To improve signal
strength, the antenna can be moved to another position. Signal strength may depend on how close the
modem is to a radio base station. You must ensure that the location, at which you intend to use the
modem, is within the network coverage area. Degradation in signal strength can be the result of a
disturbance from another source, for example an electronic device in the immediate vicinity. More
information about possible communication disturbances can be found in section 5.3.5.
When an application is completed, you can verify signal strength by issuing the AT command AT+CSQ.
See “AT + CSQ Signal Strength”.
Tip! Before installing the modem, use an ordinary mobile telephone to check a possible location for it.
In determining the location for the modem and antenna, you should consider signal strength as well as
cable length
5.1.3 Connections of components to CT63 E Terminal
The integrator is responsible for the final integrated system. Incorrectly designed or installed, external
components may cause radiation limits to be exceeded. For instance, improperly made connections or
improperly installed antennas can disturb the network and lead to malfunctions in the modem or
equipment.
19

5.1.4 Network and Subscription
Before your application is used, you must ensure that your chosen network provides the necessary
telecommunication services. Contact your service provider to obtain the necessary information.
If you intend to use SMS in the application, ensure this is included in your (voice) subscription.
Consider the choice of the supplementary services
5.2 How to install the modem
5.2.1 Power supply
Use a high-quality power supply cable with low resistance. This ensures that the voltages at the connector
pins are within the allowed range, even during the maximum peak current.
When the unit is powered from a battery or a high current supply, connect a fast 1.25A fuse in line with
the positive supply. This protects the power cabling and modem.
5.2.2 Securing the modem
Before securing the modem take into account the amount of additional space required for the mating
connectors and cables that will be used in the application.
Where access is restricted, it may be easier to connect all the cables to the modem prior to securing it in
the application.
Securely attach the CT63 Terminal modem to the host application using two 3mm diameter pan-head
screws
5.3 Antenna
5.3.1 General
The antenna is the component in your system that maintains the radio link between the network and
the modem. Since the antenna transmits and receives electromagnetic energy, its efficient function will
depend on:
the type of antenna (for example, circular or directional);
the placement of the antenna;
Communication disturbances in the vicinity in which the antenna operates.
In the sections below, issues concerning antenna type, antenna placement, antenna cable, and possible
communication disturbances are addressed. In any event, you should contact your local antenna
manufacturer for additional information concerning antenna type, cables, connectors, antenna
placement, and the surrounding area. You should also determine whether the antenna needs to be
grounded or not. Your local antenna manufacturer might be able to design a special antenna suitable
for the application.
20

5.3.2 Antenna type
Make sure that you choose the right type of antenna for the modem. Consider the following
requirements:
The antenna must be designed for the one of the frequency bands in use; please ask your network
provider for more information:
o GSM 850/900 MHz
o GSM 1800/1900 MHz;
The impedance of the antenna and antenna cable must be 50Ω;
The antenna output-power handling must be a minimum of 2W;
The VSWR value should be less than 3:1 to avoid any damage to the modem.
5.3.3 Antenna placement
The antenna should be placed away from electronic devices or other antennas. The recommended
minimum distance between adjacent antennas, operating in a similar radio frequency band, is at least
50cm. Therefore we recommend to use a cable antenna and place it away from the terminal. If signal
strength is weak, it is useful to face a directional antenna at the closest radio base station. This can
increase the strength of the signal received by the modem. The modem’s peak output power can reach
2W. RF field strength varies with antenna type and distance. At 10cm from the antenna the field
strength may be up to 70V/m and at 1m it will have reduced to 7V/m. In general, CE-marked products
for residential and commercial areas, and light industry can withstand a minimum of 3V/m.
5.3.4 The antenna cable
Use 50Ω impedance low-loss cable and high-quality 50Ω impedance connectors (frequency range up to
2GHz) to avoid RF losses. Ensure that the antenna cable is as short as possible. The Voltage StandingWave Ratio (VSWR) may depend on the effectiveness of the antenna, cable and connectors. In addition,
if you use an adapter between the antenna cable and the antenna connector, it is crucial that the
antenna cable is a high-quality, low-loss cable. Minimize the use of extension cables, connectors and
adapters. Each additional cable, connector or adapter causes a loss of signal power.
5.3.5 Possible communications disturbances
Possible communication disturbances include the following:
Noise can be caused by electronic devices and radio transmitters.
Path-loss occurs as the strength of the received signal steadily decreases in proportion to the distance
from the transmitter.
Shadowing is a form of environmental attenuation of radio signals caused by hills, buildings, trees or even
vehicles. This can be a particular problem inside buildings, especially if the walls are thick and reinforced.
Multi-path fading is a sudden decrease or increase in the signal strength. This is the result of interference
caused when direct and reflected signals reach the antenna simultaneously. Surfaces such as buildings,
streets, vehicles, etc., can reflect signals.
Hand-over occurs as you move from one cell to another in the GSM network. Your mobile application call
is transferred from one cell to the next. Hand-over can briefly interfere with communication and may
cause a delay, or at worst, a disruption.
21

PIN
Signal
Direction
Voltage levels
Description
1
DCD
Output
> + 4V
<- 4 V
Data carrier detect
2
RD
Output
> + 4V
<- 4 V
Received data
3
TD
Input
> + 2,4V
< 0.8 V
Transmitted data
4
I2CCLK_SPICLK
5 I2CDAT_SPIDO
6 DSR
Output
> + 4V
< - 4 V
Data set ready
7
RTS
Input
> + 2,4V
< 0.8 V
Request to send
8
CTS
Output
> + 4V
< - 4 V
Clear to send
9
SPICS
10
RI
Output
> + 4V
< - 4 V
Ring indicator
11
SPIDI
12
GPIO_05
13
DTR
Input
> + 4V
< 0.8 V
Data terminal ready
14
GND - 0 V
Ground connection
15
VEXT
Output
2,93 V DC
6 Optional variants
Optional variants are available, please find below the technical information for:
I2C/SPI on 15-pin connector
JAVA variant
Audio variant
USB host powered version
EDGE variant
Please contact your distributor or CEP AG directly for further information if necessary.
6.1 CT63 with DSUB15 connector with l2C and SPl interface
Table 7: CT63 with DSUB15 connector with l2C and SPl interface
22
Pin
Signal EGS5
1
GPIO 7
2
GPIO 8
3
GPIO 9
4
GPIO 10
5
GND
6.2 CT63 with EGS5 (Java) Module & GPIO’s
Mini USB Connector will be used as/for::
Full 2.0 USB interface or
USB Power or
Audio interface or
4 digital Inputs
Please Note:
Pinning for USB interface, USB power and audio interface, please see corresponding tables above.
Figure 6: Mini USB with 4 digital inputs
Table 8: Mini USB Pin Signal
23

Pin
Description
1
VCC
2
ADC_IN
3
EMERG_OFF
4
TO_IN
5
DIG_OUT
6
GND
PIN
Signal
Direction
Limits
Description
1
VCC
Input
5 – 32V
Positive power input, DC
2
ADC_IN
Input
0 – 32V
analogue Input
3
EMERG_OFF
Input
5 – 32V
Active high control line used to
switch off
VIH > 5V, VIL < .5V
Power off: t >1s
4
TO_IN
Input
5 – 32V
Positive edge triggered signal;
used to switch on the modem
VIH > 5V, VIL < 0.5V
Power on: t >1s
5
DIG_OUT
Output
5 - VCC
Digital Output; high-side switch
6
GND
Input
-
Negative power (ground) input
and return
path for TO_IN and
EMERG_OFF
RJ11 connector:
PIN: 1 2 3 4 5 6
Figure 7: RJ11 Connector
Table 9: RJ11 Connector Description
Table 10: CT63 with EGS5 (Java) Module % GPIO‘s
24

Pin
Signal
1
MIC -
2
EAR -
3
MIC +
4
EAR +
5
not
connected
6.3 CT63 with Mini USB audio interface
Figure 8: CT63 Mini USB audio interface Pin Connector
Table 11: Mini USB audio interface Pin Signal
6.4 CT63 with Mini USB with USB – Power (host powered)
Figure 9: CT63 Mini USB with USB Power (host powered) Pin Connector
25

Pin
Signal
1
VUSB
(5V DC )
2
D- 3 D+
4
not
connected
5
GND
Table 12: Mini USB with host powered Pin Signal
26

7 Technical Data
Product features:
Quad-band EGSM 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
GSM 850/900 Power class 4 (2W)
GSM 1800/1900 Power class 1 (1W)
Control via AT commands according to Hayes 3GPP TS 27.007, 27.005 and proprietary Cinterion
Serial Port Multiplexer GSM 7.10
SIM Access Profile
Supply voltage range: 5 – 32 V/DC
TCP/IP stack access via AT commands
Sensitivity:
o –107 dBm (typ) @ 850/ 900 MHz
o -106 dBm (typ) @ 1800/ 1900 MHz
Overall dimensions (excluding connectors): 77 x 67 x 26mm
Weight: ca. 100g
RoHS compliant
Temperature range
o -40°C to +80°C (Operational)
o -40°C to +85°C (Storage temperature)
Interfaces:
Sub-D female 9 pin connector for RS232 communication
RJ11: Power: 5 – 32 Volt / DC
Antenna: 50 Ohm (FME male)
SIM card reader: 3V interface
Mini USB Interface
Approvals:
Full type approved conforming with R&TTE directive
CE approval
e1
SMS:
Point-to Point mobile originated and mobile terminated SMS
Concatenated SMS supported
SMS cell broadcast
Text and PDU mode
Circuit switched data transmission:
Asynchronous transparent circuit switched Data (CSD) up to 14,4 kbps
Asynchronous non-transparent circuit switched Data (CSD) up to 9,6 kbps
V.110
GPRS Data:
GPRS Class 10
Mobile station class B
GPRS Coding Scheme 1 – 4
Fax:
Fax Group 3, class 1
27

GSM supplementary:
Call forwarding
Call barring
Call waiting and hold
Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP)
Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR)
Unstructured supplementary Services Mobile Originated Data (USSD)
Closed user group
Internet Protocol:
Embedded TCP/IP stack, including TCP/IP, UDP, SMTP and FTP protocol
Additional Features:
SIM phonebook
Fixed dialing number (FDN)
Real time clock
Network LED support
IRA character set
Jamming detection & report
Other features:
Same mounting holes as Siemens / Cinterion TC35, MC35 Terminal
28

Product
Description
12002
Power supply 230V AC / 12 V DC
6pin RJ11 connector
12003
Power cable
6pin RJ11 connector with open ends
12021
Magnetic Antenna / Pentaband
(Quad&UMTS)
FME female
12016
Rectangular Antenna / Pentaband
(Quad&UMTS)
FME female
12020
Patch Antenna/ Pentaband
(Quad&UMTS)
12006
Roof-mount antenna*
FME female waterproof, 900/1800
MHz
RS232 cable
1.5m for PC connection
Mini USB cable for Audio / GPIOs
Mini USB connector with open ends
Mini USB cable for Audio Mini
Klinke
Mini USB cable for Audio RJ11
8 CEP Certified Accessories
Table 13: Accessories List
Please contact your distributor or CEP AG for availability or check CEP’s webpage www.cepag.de.
29

Abbreviation
Explanations
CBM
Cell Broadcast Message
CBS
Cell Broadcast Service
CSD
Circuit Switched Data
DCE
Data Circuit Terminating Equipment
DTE
Data Terminal Equipment
DTMF
Dual Tone Multi Frequency
EFR
Enhanced Full Rate
EMC
Electro-Magnetic Compatibility
ETSI
European Telecommunication Standards
Institute
FR
Full Rate
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service
GSM
Global System for Mobile Communication
HR
Half Rate
HSCSD
High Speed Circuit Switched Data
ITU-T
International Telecommunication Union Telecommunications Standardisation Sector
ME
Mobile Equipment
MO
Mobile Originated
MS
Mobile Station
MT
Mobile Terminated
PDU
Protocol Data Unit
RLP
Radio Link Protocol
RF
Radio Frequency
RTC
Real Time Clock
SIM
Subscriber Identity Module
SMS
Short Message Service
TA
Terminal Adapter
9 Abbreviations
30

Abbreviation
Explanations
TE
Terminal Equipment
TS
Telecom Services
VSWR
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
Table 14: Abbreviation
31

10 Mark of Conformity
The CT63 Terminal will carry the following certificates:
32

CEP AG may, at any time and without notice, make changes or improvements to the
products and services offered and / or cease producing or commercializing them.
11 Service and Support
To contact customer support please use the contact details below:
Customer Support
CEP AG
Raiffeisenallee 12b
82041 Oberhaching
Germany
E-mail: support@cepag.de
or
Tel. +49-89-450 292 – 11
Information about CEP AG, products and accessories is available on the following web site:
http://www.cepag.de.
Please contact us via e-mail if you miss anything on the web and we will provide it to you personally via
e-mail.
33

Revision
Date
Changes
Rev 1.5
21.03.2014
Update Document Layout
Rev 1.6
26.03.2014
Update Section 7
Rev 1.7
04.03.2015
Update Section 6.4
12 Documentation Change Log
Table 15: Documentation Change Log
34
 Loading...
Loading...