CC and C Technologies WL1401 User Manual
IEEE802.11b
Wireless LAN m ini-PCI Module
Software Installation Manual
Version 1.0
2003/6 /26
1

REGULATION INFORMATION
The Wireless mini-PCI module must be installed and used in strict accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions. This device complies with the following radio frequency
and safety standards.
FCC (Federal Communications Commission)
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment.
This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
The equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B Digital
Device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction, may cause harmful interference to radio
communication. However, there is no grantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment dose cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
--Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
--Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
--Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
--Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Notice: The Part 15 radio device operates on a non-interference basis with other
devices operating at this frequency. Any changes or modification not expressly
approved by the party responsible could void the user’s authority to operate the device.
R&TTE Directive
This device complies with the specifications listed below:
• ETS 301-489 -1&-17 General EMC requirements for Radio equipment.
• ETS 300-328 Technical requirements for Radio equipment.
• EN60950 Safety Requirements for Radio equipment
2
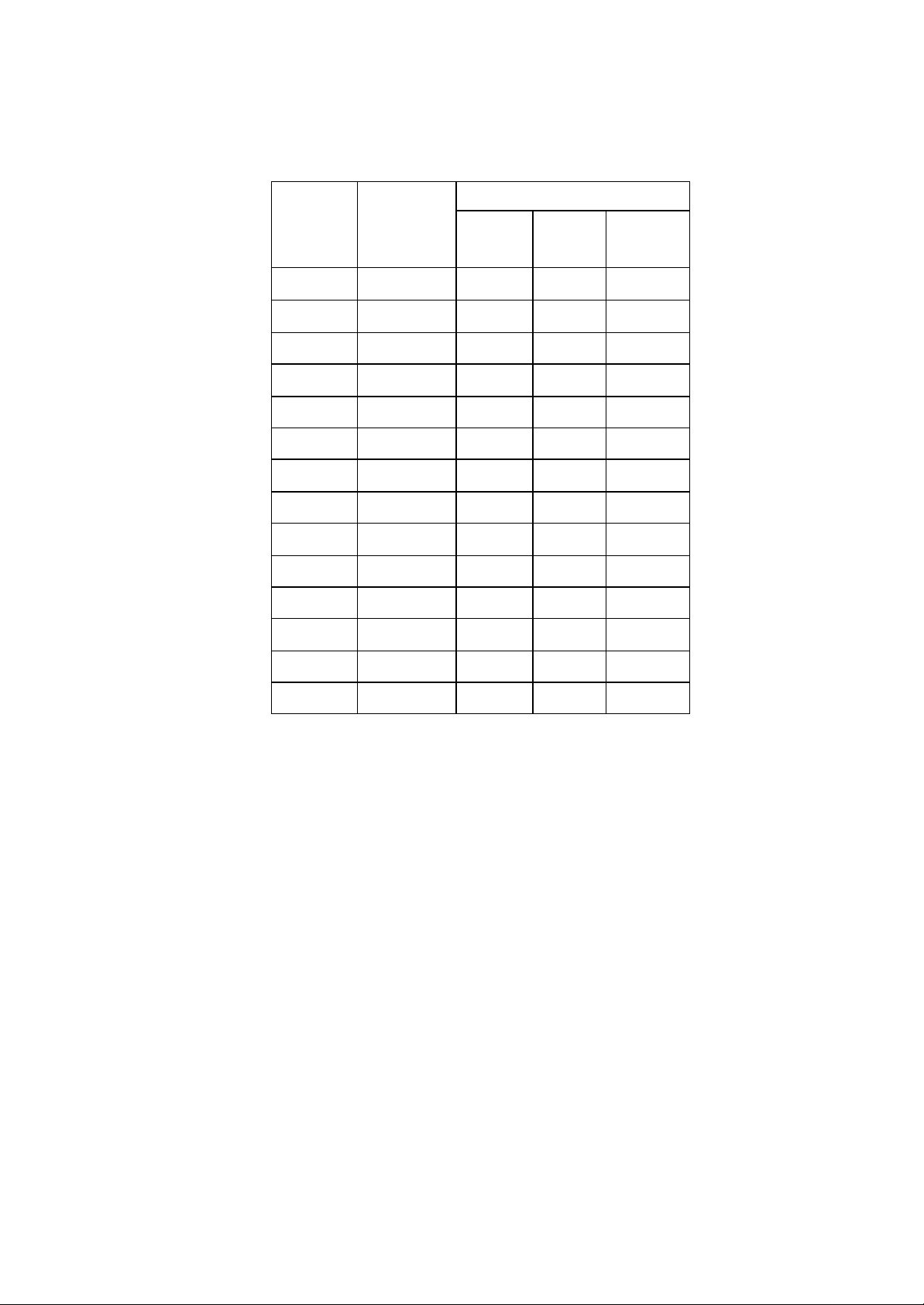
The channel identifiers, channel center frequencies, and regulatory domains of
each 22-MHz-wide channel are shown in following Table.
Channel
Frequency
Identifier
1 2412
2 2417
3 2422
4 2427
5 2432
6 2437
7 2442
8 2447
9 2452
10 2457
11 2462
12 2467
Center
(MHZ)
Regulatory Domains
North
Japan ETSI
America
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ
13 2472
14 2484
ˇ ˇ
ˇ
3

Table of Contents
1 Introduction............................................................................ 5
2 Wireless LAN Basics............................................................. 6
3 Drivers and Utility Installation .............................................. 7
4. Wireless Network Configuration ........................................ 13
5.Specifications of Wireless LAN mini-PCI Module ............. 18
6.Glossary ............................................................................... 19
4

1 Introduction
You are about to install a networking system that is not only fast and
powerful, but also easy to set up and simple to maintain. In a short time you and
those in your network will be able to share a local printer and files, access the
Internet, and roam about the office wire-freely.
Using radio frequency (RF) technology, WLAN devices transmit and receive
data over the air, minimizing the need for wired connections. Thus, WLANs
combine data connectivity with user mobility, and, through simplified
configuration, enable movable LANs.
This wireless networking solution has been designed for both large and
small businesses, and it is scalable so that you can easily add more users and
new network features as your business grows.
This software installation guide will assist you in installing Wireless mini-PCI
module application.
5
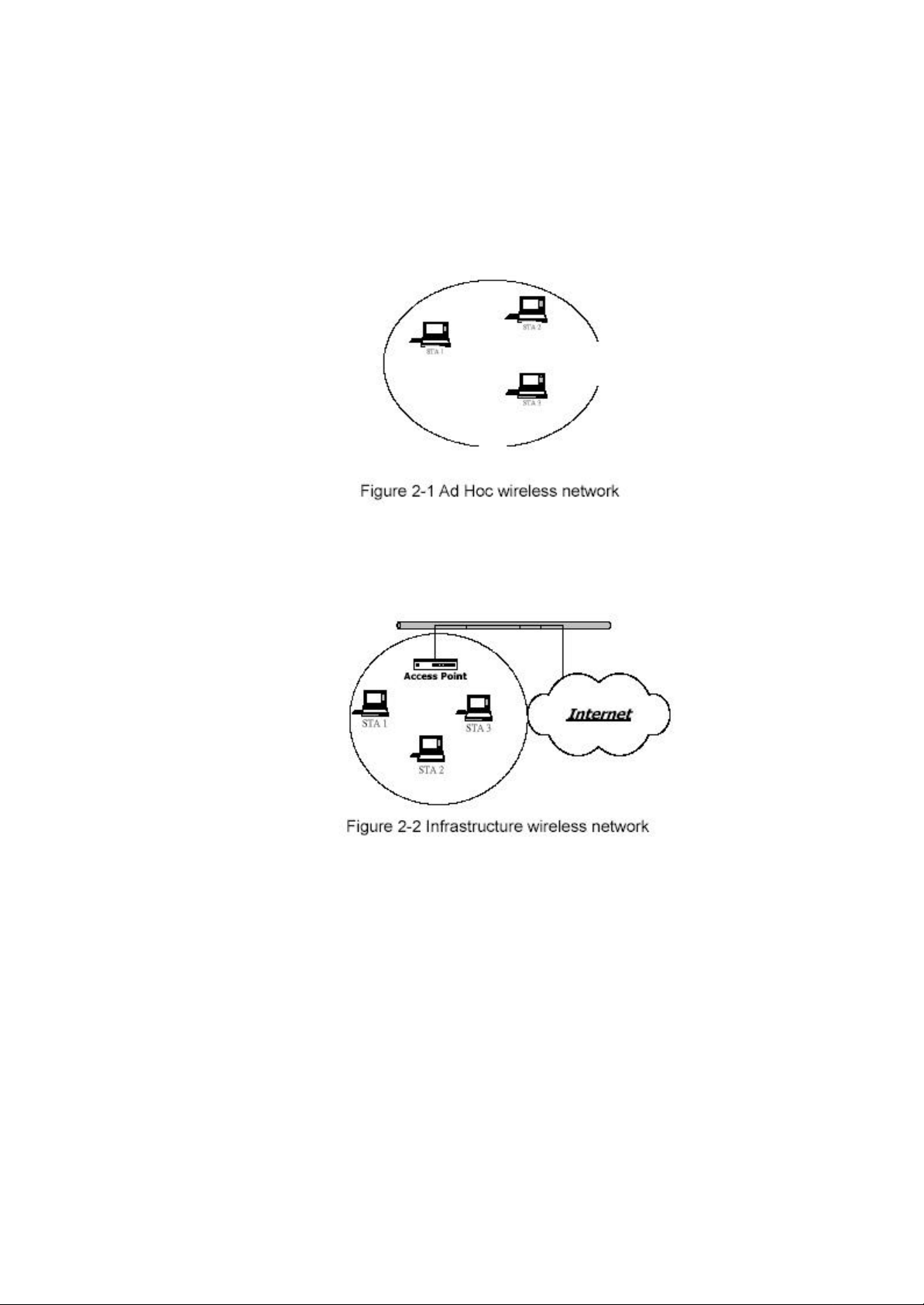
2 Wireless LAN Basics
Wireless LAN network defined by IEEE 802.11b standard committee could be
Configure as: Ad Hoc wireless LAN or Infrastructure wireless LAN.
Ad Hoc network is a group of notebooks with wirel ess LAN adapter, called a BSS
(Basic Service Set). These notebooks use their wireless LAN adapter to communicate
with each other directly.
The most obvious differentiation between Infrastructure wireless network and Ad
Hoc wireless network is that the notebooks in Infrastructure wireless network can
make use of the resource in the Internet through Access Point .
To set up your notebook’s network as the type of “Ad Hoc” or “Infrastructure”
wireless network depends completely on your requirement. General ly, if your network
environment has an Access Point , it’s recommend that you set it as “Infrastructure”
mode to connect to the Internet.
6

3 Drivers and Utility Installation
This section describes the procedures for installing Wireless mini-PCI module.
Before You Start
Before installation, please check your system in advance and make sure that the
Mini PCI is installed with your Notebook. Consult to your dealer for the existence,
compatibility or installation of Mini PCI module with your Notebook.
Note: To prevent potential problems during installation, please use the auto -run
installation tool on the CD to finish the driver installation before you plug The
WLAN Module into the computer.
All drivers and supporting software for Wireless mini-PCI module must be installed
and configured.
Ask your system administrator for the following information, which you may need
during driver installation:
• Your Wireless LAN SSID.
• Your computer’s unique client name and workgroup name
• For your network account, your user name and password.
• Your IP address, gateway address, and subnet mask. (I f you’re not using a
DHCP server)
• Every computer on a network is identified by a unique network address. There
are two methods to assign network addresses to computers on a TCP/IP
network:
• Static IP addressing
• Dynamic IP addressing (DHCP)
In networks with static IP addressing, the network administrator manually assigns
an IP address to each computer. Once a static IP address is assigned, a computer
uses the same IP address every time it reboots and logs on to the network. You may
manually change the IP address in the Network Properties dialog box. Networks
using static IP addresses are easy to set up and do not require additional network
management software.
In networks with dynamic IP addressing, a DHCP server in the network
dynamically assigns IP addresses to all clients every time they log on to the network.
Network using dynamic IP addresses require setting up and running a DHCP Server .
7
 Loading...
Loading...