Page 1

晶訊科技股份有限公司 8F, No. 150, Jian Yi Road, Chung Ho City, Taipei County,
CC&C Technologies, Inc. Taiwan 235, R.O.C. Tel: 886-2-8226-5088 Fax: 886-2-8226-5077
User’s Manual
802.11b WLAN mini USB Adapter WL-1207
Version1.2
2004/03/01
Page 2

Table of Contents
Information to User……………………………….. 3
1 Introduction………………………………………... 5
2
Wireless LAN basics……………………………… 6
Windows Installation……………………………… 7
3
Install Driver/Utility………………………………..
3.1
Configuration Utility………………………………………….
3.2
3.2.1 Configured at “Windows XP configuration”……..
3.2.2 Configured at “Advanced configuration”…….
Technical Specifications of WLAN Mini USB Adapter… 15
4
Troubleshooting…………………………………… 17
Glossary…………………………………………… 18
8
10
10
11
Product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
2
Page 3

INFORMATION TO USER
"CC&C TECHNOLOGIES INC. declare that WL-1207 (802.11b WLAN mini USB Adapter) is limited in
CH1~CH11 by specified firmware controlled in USA."
FCC INFORMATION
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
The equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
Digital Device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction, may cause harmful interference
to radio communication. However, there is no grantee that interference will not occur
in a particular installation. If this equipment dose causes harmful interference to radio
or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on,
the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
--Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
--Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
--Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
--Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Notice: The Part 15 radio device operates on a non-interference basis with other
devices operating at this frequency. Any changes or modification not
expressly approved by the party responsible could void the user’s authority to
operate the device.
3
Page 4

REGULATORY INFORMATION
WLAN Mini USB Adapter must be installed and used in strict accordance with the
instructions. This device complies with the following radio frequency and safety
standards.
USA - Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference that may cause undesired operation.
Europe - R&TTE Directive
This device complies with the specifications listed below
• ETS 300-826 General EMC requirements for Radio equipment.
• ETS 300-328 Technical requirements for Radio equipment.
• EN60950 Safety Requirements for Radio equipment
The channel identifiers, channel center frequencies, and regulatory domains of each
22-MHz-wide channel are shown in following Table.
Channel
Center
Frequency
Identifier
(MHZ)
1 2412
2 2417
3 2422
4 2427
5 2432
6 2437
7 2442
8 2447
9 2452
10 2457
11 2462
12 2467
Regulatory Domains
North
Japan ETSI
America
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ
Israel France Mexico
ˇ ˇ
ˇ ˇ
ˇ
13 2472
14 2484
ˇ ˇ
ˇ
ˇ
4
Page 5

1. Introduction
Thank you for purchasing Wireless Local Area Net (WLAN) Mini USB
Adapter. You are about to install a networking system that is not only fast
and powerful, but also easy to set up and simple to maintain. In a short time
you and those in your network will be able to share a local printer and files,
access the Internet, and roam about the office wire-free.
Using radio frequency (RF) technology, WLANs transmit and receive data
over the air, minimizing the need for wired connections. Thus, WLANs
combine data connectivity with user mobility, and, through simplified
configuration, enable movable LANs.
This wireless networking solution has been designed for both large and
small businesses, and it is scalable so that you can easily add more users
and new network features as your business grows.
This manual will assist you in the installing WLAN Mini USB Adapter.
5
Page 6
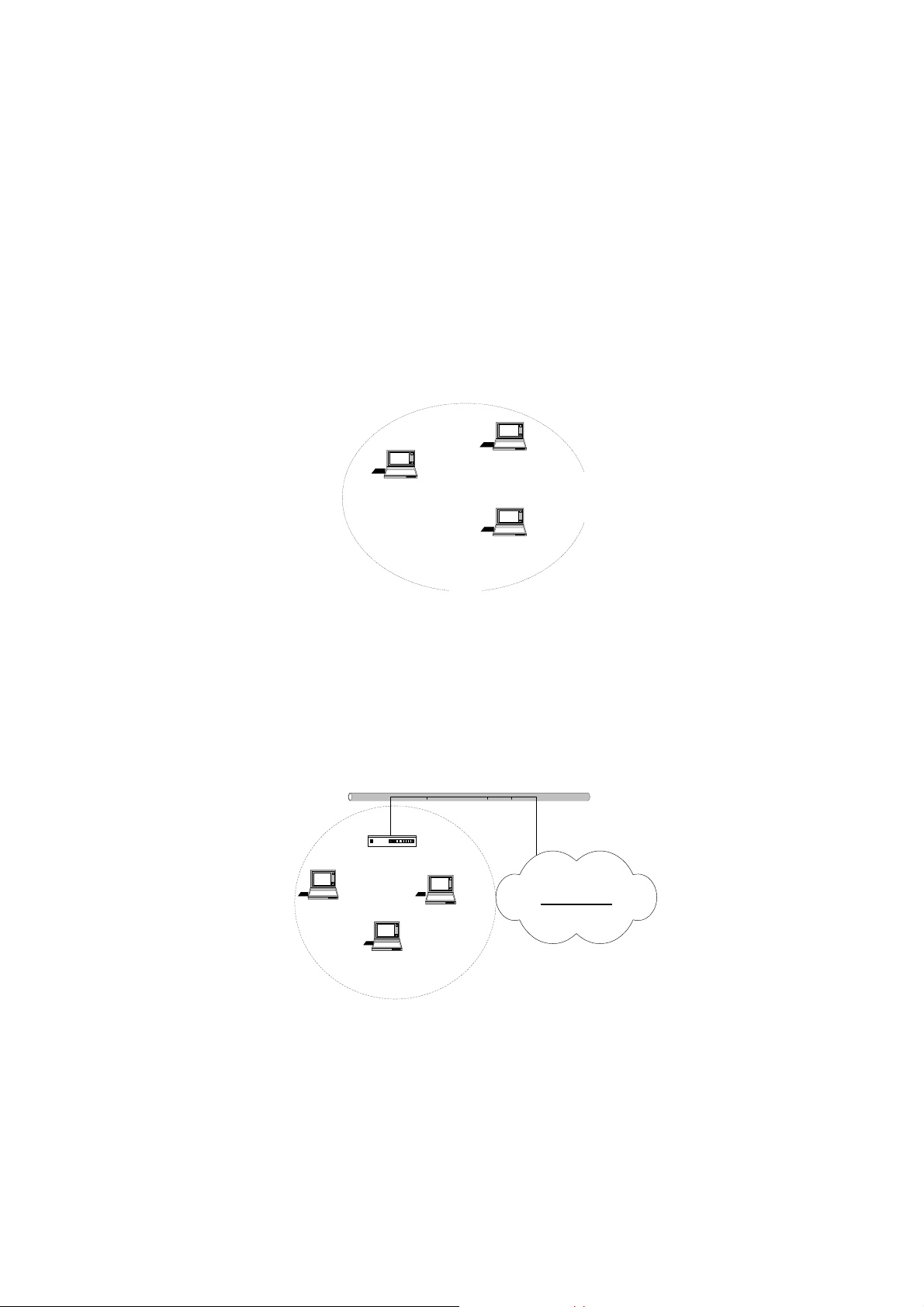
2. Wireless LAN basics
Wireless LAN network defined by IEEE 802.11b standard committee could be
configured as:
• Ad Hoc wireless LAN, or
• Infrastructure wireless LAN.
Ad Hoc network is a group of notebooks with wireless LAN PC card called a
BSS (Basic Service Set). These notebooks use their wireless LAN PC cards to
communicate with each other, and notebooks cannot connect to the Internet.
STA 1
STA 2
STA 3
Figure 2-1 Ad Hoc wireless network
The most obvious differentiation between Infrastructure wireless network and
Ad Hoc wireless network is that the notebooks in Infrastructure wireless
network can make use of the resource in the Internet through Access Point.
Access Point
STA 1
STA 2
STA 3
Figure 2-2 Infrastructure wireless network
Internet
To set up your notebook’s network as the type of “Ad Hoc” or “Infrastructure”
wireless network depends completely on your requirement. Generally, if your
network environment has an Access Point, we recommend that you set it as
“Infrastructure” to connect to the Internet.
6
Page 7

3. Windows Installation
Before You St art
To use the WLAN Mini USB Adapter with a computing device, the WLAN Mini
USB Adapter must be equipped with an USB 1.1 or 2.0 Interface. All drivers
and supporting software for the WLAN Mini USB Adapter must be loaded and
configured.
Ask your system administrator for the following information, which you may
need to provide during driver installation:
• Your Wireless Client Name
• Your Wireless SSID
• Your computer’s unique client name and workgroup name
• For your network account, your user name and password.
• Your IP address, gateway address, and subnet mask if you’re not using a
DHCP server.
Every computer on a network is identified by a unique network address. There
are two methods of assigning network addresses to computer on a TCP/IP
network:
• Static IP addressing
• Dynamic IP addressing (DHCP)
In networks with static IP addressing, the network administrator manually
assigns an IP address to each computer. Once a static IP address is assigned,
a computer uses the same IP address every time it reboots and logs on to the
network. You may manually change the IP address in the Network Properties
dialog box. Networks using static IP addresses are easy to set up and do not
require additional network management software.
In networks with dynamic IP addressing, a DHCP server in the network
dynamically assigns IP addresses to all clients every time they log on to the
network. Network using dynamic IP addresses require setting up and running a
DHCP Server or installing the Wingate software package.
7
Page 8

3.1 Install Driver/Utility
Step 1. Please insert the Device CD Windows XP/2000 was automatically
running autorun. The Welcome dialog as below, please click Next
Step 2. Setup WLAN Driver and Utility, please click Next
8
Page 9

Step 3. Starting Copy.
Step 4. Click Finish to complete installation.
Step 5 After you install Utility, Hold the Mini USB Adapter with the logo facing
up, and insert the Adapter into the USB receptacle, applying just enough
pressure to make sure it is fully seated. Windows XP/2000 automatically
detects the Mini USB Adapter.
After finished install driver and utility on your system. Let’s starting to setup
your wireless card. First of all we will see the connection notice in the right
come.
9
Page 10

3.2 Configuration Utility
There are two different utility to configure you wireless setting on XP, although
we provide another choice, but in functional, both of them are similar. You can
choose any one of them, which you more like or convenience to use.
3.2.1 Configured at “ Windows XP configuration ”
1. After finished install driver and utility on your system. Let’s starting to setup
your wireless card. First of all we will see the connection notice in the right
corner (Fig. 3.1-1)
Fig. 3.1-1
2.Click the View Available Wireless Networks and it will popup a setup dialog
as below (Fig. 3.1-2). If there have some efficient access point, which efficient
range contains your Mini USB Adapter range, then the SSID will show in the
“Available networks” list. Select one and click the Connect button.
Fig. 3.1-2
10
Page 11

3.2.2 Configured at “Advanced configuration ”
We provide another wireless setting utility for Windows (2000/me/98SE) use.
Of course, XP version already prepared. Every function is the same like
Windows 2k version.
The Configuration Tab contains several fields where operating parameters of
the driver can be viewed or changed. Changes to any of the parameters in this
panel can be applied to the driver without a need to restart the PC.
1. Plug-in wireless card and you will see SiS utility appear on your system tray.
2. Double-click the rotate circle icon, following dialog box will appear. (Fig3.2-1)
The NetStatus tab shows the Link Status, Network mode, SSID, Channel, Tx
Rate.You also can change your Ad hoc/Infrastructure network, Data Encryption,
SSID, Channel, Tx Rate in this tab.
Fig 3.2-1
3. Then select the Site Scan tab, following dialog box will appear. (Fig3.2-2)
Please wait system to scan or click Re-fresh, all Access Point and Ad-hoc
devices within detectable range will be found and their related information will
be displayed in the list. You can assign Access Point or Ad-hoc devices which
you want connect to. We also can change presently connection just double
click SSID from the list. If you check the Use Windows XP to configure my
wireless network settings that will change to Windows XP configuration to set
the Wireless link function.
11
Page 12

Fig 3.2-2
4. Select the Statistics tab (Fig3.2-3), you will see the Link Status, Signal
strength, and transmit/receive statistics. If check the Turn Radio OFF, the radio
interface will be turn off.
Fig 3.2-3
5. If there are several wireless network coexist, we must consider with data
encryption. It depend on your Access Point security setting, one of them not
match, them the connection will be failed.
Select the Encryption tab (Fig3.2-4). If you want to enable the function, please
set the Data Encryption to WEP. WEP encrypts each frame transmitted from
12
Page 13

the radio using one of the Keys entered from this panel. To be written to the
driver and registry, each key must consist of hex digits, which means that only
digit 0-9 and letters A-F are valid entries. If entered incorrectly program will not
write keys to a driver.
Fig 3.2-4
6. The Info tab (Fig3.2-5) shows the Driver version including the detail of
Configuration Utility, and NIC firmware version. Users must use this version
number when reporting their problems for technical support.
Fig 3.2-5
7. The Profile tab (Fig3.2-6) allows you to save the information associated with
a specific, so you can quickly and easily connect to your network when you are
in that location. The Profiles page allows you to new, delete and edit your
profiles.
13
Page 14

Fig 3.2-6
14
Page 15

4. Technical Specifications of WLAN Mini USB Adapter
Standard IEEE802.11b
Frequency Band 2.400GHz ~ 2.4835GHz unlicensed ISM band
Spread Spectrum DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum)
Modulation method DQPSK/DBPSK/CCK
Data Rate 1Mbps, 2Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 11Mbps
Operation mode
Transmitter Output
Power
Receive Sensitivity Operating at 11Mbps: >8% PER @ –86dBm
Operating Range 100 - 400m, depending on surrounding environment
Antenna On board chip antenna
Power consumption
Security 64-bit or 128-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
I/O Interface
LED Blue LED indicator
Operating system
supported
Management
Regulation
Ad hoc
Infrastructure (Access Points is needed)
<13.5 dBm
Transmit: < 350mA;
Receive: < 260mA
USB 1.1
Windows 98Se, Me, 2000 and XP
Windows-based utility for configuration and status
monitoring
FCC part 15B/C for North America;
CE
Dimension 58(L) x 24(W) x 9.9(H) mm
Weight 9.6 g
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Humidity 5 ~ 90% (non-condensing)
0 ~ 55℃
-20 ~ 70℃
15
Page 16

Troubleshooting
Symptom:
The LED is off.
Possible Remedy:
Make sure the PC Card is inserted properly. Otherwise contact your vendor.
Symptom:
The LED is blinking but the PC Card icon does not appear in your icon tray.
Possible Remedy:
Make sure that you have installed the Utility from attached CD.
Symptom:
The PC Card is linking, but can’t share files with others.
Possible Remedy:
Make sure the file and printer sharing function is enabled. You could enable the
function by checking the icon of My Computer → Control Panel → Network → file
and printer sharing → I want to be able to give others to access to my files.
Symptom:
Slow or erratic performance
Possible Remedy:
Try change the channel of the communicating group or move your device closer to the
communicating device.
Symptom:
Can’t find the utility icon in the taskbar when plugged in the WLAN card
Possible Remedy: You could enable the function by click the ic on of start → All Programs → Wirele ss
LAN Utility → SiSCFG
16
Page 17

Glossary
IEEE 802.11 Standard
The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN standards subcommittee, which is formulating a
standard for the industry.
Access Point
An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks
together.
Ad Hoc
An Ad Hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter,
connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad Hoc wireless LAN is applicable at a
departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operation.
BSSID
A specific Ad Hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS must
be configured with the same BSSID.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - a method in which IP addresses are assigned
by server dynamically to clients on the network. DHCP is used for Dynamic IP
Addressing and requires a dedicated DHCP server on the network.
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
This is the method the wireless cards use to transmit data over the frequency
spectrum. The other method is frequency hopping. Direct sequence spreads the data
over one frequency range (channel) while frequency hopping jumps from one narrow
frequency band to another many times per second.
ESSID
An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for mobile
workers. More than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Service Set (ESS).
Users within an ESS could roam freely between BSSs while served as a continuous
connection to the network wireless stations and Access Points within an ESS must be
configured with the same ESSID and the same radio channel.
17
Page 18

Ethernet
Ethernet is a 10/100Mbps network that runs over dedicated home/office wiring. Users
must be wired to the network at all times to gain access.
Gateway
A gateway is a hardware and software device that connects two dissimilar systems,
such as a LAN and a mainframe. In Internet terminology, a gateway is another name
for a router. Generally a gateway is used as a funnel for all traffic to the Internet.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Infrastructure
An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration.
Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless access to central database,
or wireless application for mobile workers.
ISM Band
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth for
unlicensed use in the so-called ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band.
Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being made available worldwide.
This presents a truly revolutionary opportunity to place convenient high-speed
wireless capabilities in the hands of users around the globe.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a group of computers, each equipped with the appropriate network adapter
card connected by cable/air, that share applications, data, and peripherals. All
connections are made via cable or wireless media, but a LAN does not use telephone
services. It typically spans a single building or campus.
Network
A network is a system of computers that is connected. Data, files, and messages can
be transmitted over this network. Networks may be local or wide area networks.
Protocol
A protocol is a standardized set of rules that specify how a conversation is to take
place, including the format, timing, sequencing and/ or error checking.
Roaming
In an infrastructure network, this is when a wireless PC moves out of range of the
18
Page 19

previously connected access point and connects to a newly connected access point.
Throughout the network environment where access point is deployed, PCs can
always be connected regardless of where they are located or roam.
SSID
A Network ID unique to a network. Only clients and Access Points that share the same
SSID are able to communicate with each other. This string is case-sensitive.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Simple Network Management Protocol is the network management protocol of TCP/IP. In SNMP, agents-which can be hardware as well as software-monitor the activity in the various devices on the network and report to the network console workstation. Control information about each device is maintained in a structure known as a management information block.
Static IP Addressing
A method of assigning IP addresses to clients on the network. In networks with Static
IP address, the network administrator manually assigns an IP address to each
computer. Once a Static IP address is assigned, a computer uses the same IP
address every time it reboots and logs on to the network, unless it is manually
changed.
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) TCP/IP is the protocol suite developed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). It is widely used in corporate Internet works, because of its superior design for WANs. TCP governs how packet is sequenced for transmission the network. The term “TCP/IP” is often used generically to refer to the entire suite of related protocols.
Transmit / Receive
The wireless throughput in Bytes per second averaged over two seconds.
Wide Area Network (WAN) A WAN consists of multiple LANs that are tied together via telephone services and / or fiber optic cabling. WANs may span a city, a state, a country, or even the world.
Wireless LAN (WLAN) A wireless LAN does not use cable to transmit signals, but rather uses radio or infrared to transmit packets through the air. Radio Frequency (RF) and infrared are the commonly used types of wireless transmission. Most wireless LANs use spread spectrum technology. It offers limited bandwidth, usually under 11Mbps, and users
19
Page 20

share the bandwidth with other devices in the spectrum; however , users can operate a
spread spectrum device without licensing from the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC)
20
 Loading...
Loading...