Page 1
R
Diesel Engine
V2203-DI (26--00128)
62--11362 Rev --
WORKSHOP MANUAL
for
Tier 4i
Page 2

WORKSHOP MANUAL
DIESEL ENGINE
V2203-DI (26-00118)
Tier 4i
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PARAGRAPH NUMBER Page
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS iv...................................................................
SPECIFIC WARNING AND CAUTION STATEMENTS iv..........................................
General 1--1......................................................................................
1.1 ENGINE IDENTIFICATION 1--1............................................................
Engine Serial Number 1--1.......................................................................
1.2 ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS 1--2............................................................
1.3 CYLINDER NUMBER 1--3.................................................................
1.4 GENERAL PRECAUTIONS 1--3............................................................
1.5 TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS 1--4...........................................................
1.5.1 Torque Specifications For Special Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts 1--4..........................
1.5.2 Torque Specifications For General Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts 1--4..........................
1.6 TROUBLESHOOTING 1--5................................................................
1.7 SERVICING SPECIFICATIONS 1--7........................................................
1.7.1 Engine Body 1--7......................................................................
1.7.2 Lubricating System 1--11................................................................
1.7.3 Cooling System 1--11...................................................................
1.7.4 Fuel System 1--11......................................................................
1.7.5 Electrical System 1--12..................................................................
1.8 CHECK AND MAINTENANCE 1--13..........................................................
1.8.1 Checking Engine Oil Level 1--13..........................................................
1.8.2 Checking Coolant Level 1--13............................................................
1.8.3 Checking Fuel Hose 1--13...............................................................
1.8.4 Bleeding Fuel System 1--14..............................................................
1.8.5 Checking V--Belt 1--14..................................................................
1.8.6 Changing Engine Oil 1--14...............................................................
1.8.7 Valve Clearance 1--15..................................................................
1.8.8 Fuel Injection 1--15.....................................................................
1.9 SPECIAL TOOLS 1--16.....................................................................
1.9.1 Diesel Engine Compression Tester (Glow Plug) 1--16.......................................
1.9.2 Adapter, Injector T o Tester Hose 1--16....................................................
1.9.3 Tester Injector Nozzle 1--16..............................................................
1.9.4 Replacement Bowl, Tester Injector Nozzle 1--16............................................
1.9.5 Adapter, Injector Line 1--16..............................................................
1.9.6 Oil Pressure Tester 1--17................................................................
1.9.7 Auxiliary Socket For Fixing Crankshaft Sleeve 1--17........................................
1.9.8 Gauge, Belt Tension 1--17...............................................................
1.9.9 Tester, Belt Tension 1--17................................................................
1.9.10 Rubber Band 1--17.....................................................................
1.9.11 Main Bearing Install Tool 1--17...........................................................
1.9.12 Main Bearing Extract Tool 1--17..........................................................
1.9.13 Valve Guide Replacing Tool 1--18.........................................................
1.9.14 Bushing Replacing T ools 1--18...........................................................
1.9.15 Flywheel Stopper 1--18..................................................................
1.9.16 Crankshaft Bearing 1 Replacing Tool 1--19.................................................
i
62--11362
Page 4

PARAGRAPH NUMBER
ENGINE BODY 2--1...............................................................................
2.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING 2--1.........................................................
2.1.1 Compression Pressure 2--1.............................................................
2.1.2 Top Clearance 2-- 1....................................................................
2.2 DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY 2--2....................................................
2.2.1 Draining Coolant And Engine Oil 2--2....................................................
2.2.2 External Components 2--2..............................................................
2.2.3 Cylinder Head And V alves 2--3..........................................................
2.2.4 Injection Pump and Gear Case 2--6......................................................
2.2.5 Oil Pan and Oil Strainer 2--12............................................................
2.2.6 Piston and Connecting Rod 2--13.........................................................
2.2.7 Crankshaft 2--15.......................................................................
2.3 SERVICING 2--18.........................................................................
2.3.1 Cylinder Head And V alves 2--18..........................................................
2.3.2 Timing Gears, Camshaft and Fuel Camshaft 2--23..........................................
2.3.3 Piston and Connecting Rod 2--26.........................................................
2.3.4 Crankshaft 2--28.......................................................................
2.3.5 Cylinder 2--33..........................................................................
LUBRICATING SYSTEM 3--1.......................................................................
3.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING 3--1.........................................................
3.1.1 Engine Oil Pressure 3--1...............................................................
3.2 SERVICING 3--2.........................................................................
3.2.1 Rotor Lobe Clearance 3--2.............................................................
3.2.2 Rotor to Cover Clearance 3--2..........................................................
COOLING SYSTEM 4--1...........................................................................
4.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING 4--1.........................................................
4.1.1 Notched V--Belt Service 4--1............................................................
4.1.1a Poly V--Belt Service 4--1...............................................................
4.1.2 Fan Belt Damage and Wear 4--1........................................................
4.1.3 Checking Coolant Level 4--1............................................................
4.1.4 Radiator Cap 4--2.....................................................................
4.1.5 Radiator 4--2.........................................................................
4.1.6 Thermostat Opening Temperature 4--2...................................................
4.2 SERVICING 4--3.........................................................................
4.2.1 Thermostat Assembly 4--3..............................................................
4.2.2 Water Pump Assembly 4--3.............................................................
Page
62-11362
ii
Page 5

PARAGRAPH NUMBER
FUEL SYSTEM 5--1...............................................................................
5.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING 5--1.........................................................
5.1.1 Injection Timing 5--1...................................................................
5.1.2 Shim Identification 5--1.................................................................
5.1.3 Pump Pressure Test 5--2...............................................................
5.1.4 Delivery Valve Fuel Seal 5--2...........................................................
5.2 INJECTION NOZZLE 5--3.................................................................
5.2.1 Nozzle Injection Pressure 5--3..........................................................
5.2.2 Nozzle Spraying Condition 5--3..........................................................
5.2.3 Valve Seat Tightness 5--3..............................................................
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 6--1........................................................................
6.1 STARTER TEST 6--1......................................................................
6.1.1 Motor Test 6--1........................................................................
6.1.2 Magnetic Switch Test 6--1..............................................................
6.2 FUEL SPEED SOLENOID 6-- 2.............................................................
6.2.1 Solenoid Test 6-- 2.....................................................................
6.3 INTAKE AIR HEATER 6--3.................................................................
6.3.1 Intake Air Heater Test 6--3..............................................................
Page
iii
62--11362
Page 6
SAFETY
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Your Carrier Transicoldunit has been designed with the
safety of the operator inmind. During normal operation,
allmovingparts are fully enclosed to help prevent injury.
During all pre-trip inspections, daily inspections, and
problem troubleshooting, you may be exposed to
movingparts.Pleasestayclearofallmovingpartswhen
the unit is in operation and when the unit main power
switch is in the START/RUN position.
Engine Coolant
The engine is equipped with a pressurized cooling
system. Under normal operating conditions, the coolant
in the engine and radiator is under high pressure and is
very hot. Contact with hot coolant can cause severe
burns. Do not remove the cap from a hot radiator. If the
cap must be removed, do so very slowly in order to
release the pressure without spray.
Battery
This unit is equipped with a lead-acid type battery. The
battery normally vents small amounts of flammable
hydrogengas.Donotsmokewhencheckingthebattery.
A battery explosion can cause serious physical harm
and/or blindness.
SPECIFIC WARNING AND CAUTION
STATEMENTS
Tohelpidentifythe labelhazards on the unit andexplain
thelevelof awareness each onecarries, an explanation
is given with the appropriate consequences:
DANGER
DANGER -- warns against an immediate hazard which WILL result in severe personal injury ordeath.
WARNING
WARNING -- warns against hazards or unsafe conditions which COULD res ult in severe personal injury or death.
CAUTION
CAUTION -- warns against potential hazard or unsafe practice which could result in minor personal
injury, or product or property damage.
NOTE
NOTE -- gives helpful information that may help and avoid equipment and property damage.
iv
62-11362
Page 7
The statements listed below are specifically applicable to this unit and appear elsewhere in this manual. These
recommended precautions must be understood and applied during operation and maintenance of the equipment
covered herein.
WARNING
Beware of moving V--belt and belt driven components
WARNING
When removing the radiator cap, wait at least ten minutes after the engine has stopped and cooled
down. Otherwise, hot water may discharge from the radiator, scalding anyone nearby.
WARNING
Checktheinjectionnozzleonly afterconfirming that nobody is near the spray. If the spray fromthe
nozzle contacts the human body, cells may be destroyed and blood poisoning may result.
WARNING
Secure the starter to prevent it from moving when power is applied to it.
CAUTION
Do not removethe radiator cap until the coolant temperatureis below its boiling point. Loosen the
cap slightly to relieve excess pressure before removing the cap completely.
CAUTION
Stop the engine when attempting to check and change the fuel line.
CAUTION
Stop the engine when preparing to change the engine oil.
CAUTION
Never remove the radiator cap until coolant temperature is below its boiling point. Loosen the cap
slightly to the first stop to relieve any excess pressure before removing the cap completely.
v
62-11362
Page 8
SECTION 1
Serial
Numb
General
1.1 ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
S/N
er
V2203--
Y A 4321
Lower 4 digits in numerals
7th Digit Alpabetical Letter (Month of Manufacture)
Alphabetical letter
Month
6th Digit Alpabetical Letter or Numerals (Year of Manufacture).
Alphabetical letter or numerals W XY
Year 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09
When contacting Carrier Transicold, always specify
your engine model number and serial number.
The engine model and its serial number need to be
identified before the engine can be serviced or parts
replaced.
Engine Serial Number
Theengineserialnumber is an identified number forthe
engine. It is marked after the engine model number.
It indicates month and year of manufacture as follows:
A,B C,DE,FG,HJ,KL,M N,P Q,R S,T U,V W,X Y,Z
Jan Feb Mar May Jun Jul Aug Sep OctApr Nov Dec
1234 56789
MODEL NUMBER ENGINE TYPE
V2203L--DI--E3B--CTD--2
V2203L--DI--E3B--CTD--3
V2203L--DI--E3B--CTD--1
V2203L--DI--E3B--CTD--6
V2203L--DI--E3B--CTD--4
CT4--134--DI
(1700 RPM)
CT4--134--DI
(1800 RPM)
CT4--134--DI
(2200 RPM)
CT4--134--DI
(1800 RPM)
CT4--134--DI
(1700 RPM)
Table 1-1. Model Chart
SERVICE ENGINE
PARTNUMBER
26--00128--00
26--00128--01 RG Genset New
26--00128--02
26--00128--04 UG Genset New
26--00128--05 TM Ultra XL New
Ultra XT, Ultra XTC, X2 1800 (2.2),
PRIMARY USE REPLACES
X2 2100, X2 2100A, X2 2100R
UltimaXTC,ExtraXT(2.2),
X2 2500 A, X2 2500 R
New
New
1--1 62--11362
Page 9
1.2 ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1-2. Specification Chart
MODEL NUMBER 26--00128--00 26--00128--01 26--00128--02 26--00128--04 26--00128--05
TYPE Vertical, Water--cooled, 4 cycledieselengine
NUMBER OF CYLINDERS 4
BOREXSTROKE mmXmm(in.Xin.) 83 X 102.4 (3.27 X 4.03)
TOTAL DISPLACEMENT cm3(cu.in.) 2216 (135.2)
BRAKE HORSEPOWER
SAE Intermittent HP kW (HP) / RPM
MAXIMUM SPEED RPM Below 2470
IDLING SPEED RPM 900
COMBUSTION CHAMBER DirectInjection
INJECTION PUMP Bosch “K” Type Mini Pump
GOVERNOR Mechanical Governor + Electronic Governor
INJECTION NOZZLE Bosch “P” Type Hole Nozzle
INJECTION TIMING (UNPRESSURIZED) 2.5° BeforeT.D.C.
FIRING ORDER 1-- 3--4--2
INJECTION PRESSURE
(Valve Opening Pressure)
COMPRESSION RATIO 21.5 : 1
LUBRICATION SYSTEM Forced Lubrication by Pump
OIL PRESSURE INDICATION Electrical Type Switch
LUBRICATION FILTER Full Flow Synthetic Media Filter (Cartridge Type)
COOLING SYSTEM Pressurized Radiator, Forced Circulation With Water Pump
STARTING SYSTEM
STARTING SUPPORT DEVICE Intake Air Heater in Intake Manifold
FUEL Diesel Fuel No.2--D (ASTM D975)
LUBRICATING OIL *Quality Better Than CF Class (API), SAE 10W--30 or 15W--40
LUBRICATING OIL CAPACITY 14.2 L (15.0 U.S. Quarts)
Weight (DRY) kg (lbs.) 199 (439)
23.65 (31.7) /
1700
23.87 (32.0) /
1800
19.35 MPa (197.5 kgf/cm2, 2809 psi.)
Electric Starting With Starting Motor
26.85 (36.0) /
2200
4.0° Before
T.D.C.
12V,2.5 kW
23.87 (32.0) /
1800
2.5° BeforeT.D.C.
23.65 (31.7) /
1700
*See paragraph 1.8.6
62--11632
1--2
Page 10
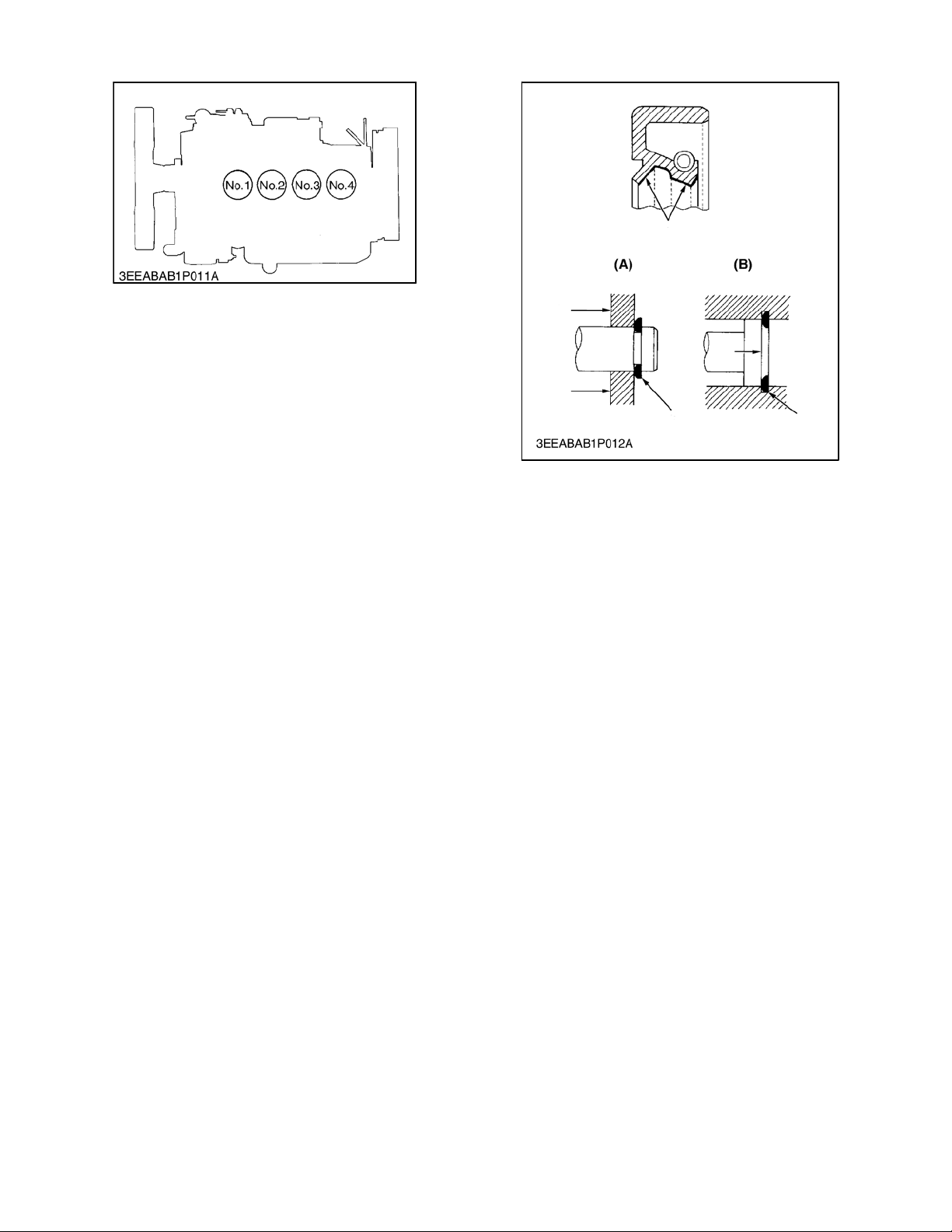
1.3 CYLINDER NUMBER
1.4 GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
1
The cylinder numbers of V2203--DI series engine are
designated as shown above. The sequence of cylinder
numbers is given as No.1, No. 2, No. 3, and No. 4
starting from the gear case end of the engine.
2
2
1. Grease
2. Force
3. Place the Sharp Edge
against the Direction of Force
3
A External Snap Ring
B Internal Snap Ring
3
During disassembly, carefully arrange removed parts in
a clean area to prevent confusion later. Screws, bolts
and nuts should be replaced in their original position to
prevent reassembly errors.
When special tools are required, use KUBOTAgenuine
special tools. Special tools which are not frequently
used should be made according to the drawings
provided.
Before disassembling orservicing live wires, makesure
to always disconnect the grounding cable from the
battery first.
Remove oil and dirt from parts before taking any
measurements.
Use only Carrier Transicold genuine parts for parts
replacements to maintain engine performance and to
ensure safety.
Gaskets and O--rings must be replaced during
reassembly. Apply grease to new O--rings or oil seals
before assembling.
When reassembling external or internal snap rings,
position them so that the sharp edge faces against the
direction from which force is applied.
A newly serviced or reassembled engine should be
run--in with no load for 15 minutes. Serious damage to
the engine may result otherwise.
1--3 62--11362
Page 11
1.5 TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Screws, bolts and nuts must be tightened to the specified torque using a torque wrench. Several screws, bolts and
nuts such as those used on the cylinder head must be tightened in the proper sequence and at the proper torque.
1.5.1 Torque Specifications For Special Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts
In removing andapplyingthe screws, bolts andnuts marked with“*”, a pneumatic wrench or similartool, if employed,
must be used with care. Failure to do so may result in stripped or seized screws, bolts and nuts.
When replacing “*” marked screws, bolt and nuts, apply engine oil to their threads and seats before reassembly.
The letter “M” in size and pitch means that the screw, bolt or nut dimension is metric. The size isthe nominal outside
diameter in mm of the threads. The pitch is the nominal distance in mm between two threads.
Item
Cylinder Head Cover Bolt M6 x 1.0 6.87 to 11.2 0.7to1.15 5.07 to 8.31
*Cylinder Head Bolt M11 x 1.25 93.2 to 98.0 9.5 to 10.0 68.8 to 72.3
*Main Bearing Case Bolt 1 M9 x 1.25 46 to 50 4.7to5.2 34.0to37
*Main Bearing Case Bolt 2 M10 x 1.25 69 to 73 7.0to7.5 51 to 54
*Flywheel Bolt M12 x 1.25 98.1 to 107 10.0 to 11.0 72.4 to 79.5
*Connecting Rod Bolt M8 x 1.0 45 to 49 4.5to5.0 33 to 36
*Rocker Arm Bracket Bolt M8 x 1.25 24 to 27 2.4to2.8 18 to 20
*Idle Gear Shaft Bolt M8 x 1.25 24 to 27 2.4to2.8 18 to 20
Crank Pulley Mounting Nut M30 x 1.5 138 to 156 14.0 to 16.0 102 to 115
*Bearing Case Cover Bolt M8 x 1.25 24 to 27 2.4to2.8 18 to 20
Nozzle Holder Clamp Bolt M10 x 1.25 26 to 29 2.6to3.0 19 to 21
Injection Pipe Retaining Nut M12 x 1.5 15 to 24 1.5to2.5 11 to 18
Overflow Pipe Assembly Retaining Bolt M6 x 1.0 9.81 to 11.2 1.0to1.15 7.24 to 8.31
Camshaft Retaining Bolt M8 x 1.25 24 to 27 2.4to2.8 18 to 20
Hi--idling Body M14 x 1.0 45 to 49 4.5to5.0 33 to 36
Starter’s Terminal B Mounting Nut M8 9.8to11 1.0to1.2 7.3to8.6
1.5.2 Torque Specifications For General Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts
Standard Screw and Bolt
Grade 4
N.m kgf.m ft--lbs N.m kgf.m ft--lbs
M6 7.9to9.3 0.80 to 0.95 5.8to6.8 9.81 to 11.2 1.00 to 1.15 7.24 to 8.31
M8 18 to 20 1.8to2.1 13 to 15 24 to 27 2.4to2.8 18 to 20
M10 40 to 45 4.0to4.6 29 to 33 49 to 55 5.0to5.7 37 to 41
M12 63 to 72 6.4to7.4 47 to 53 78 to 90 7.9to9.2 58 to 66
SizexPitch N.m kgf.m ft--lbs
Special Screw and Bolt
Grade 7
Screw and bolt material grades are shown by numbers punched on the screw and bolt heads. Prior to tightening, be
sure to check out the numbers as shown below
Punched Number
None or 4 Standard Screw And Bolt SS41, S20C
7 Special Screw And Bolt S43C, S48C (Refined)
62--11632
Screw And Bolt Material Grade
1--4
Page 12
1.6 TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom
Engine Does Not
Start
Probable Cause Solution Reference
No fuel
Air in the fuel system
Water in the fuel system
Fuel pipe clogged
Fuel filter clogged
Excessively high viscosity fo fuel or engine oil
at low temperature
Fuel with low cetane number
Incorrect injection timing
Injection nozzle clogged
Injection pump malfunctioning
Seizure of crankshaft, camshaft, piston,
cylinder or bearing
Compression leak from cylinder
Improper valve timing
Piston ring and cylinder worn
Excessive valve clearance
Replenish fuel
Vent Air
Change fuel and
repair or replace fuel
system
Clean
Clean or change
Use specified fuel or
engine oil
Use specified fuel
Adjust
Replace
Replace
Repair or Replace
Replace head
gasket, tighten
cylinder head screw,
glow plug and nozzle
holder
Correct or replace
timing gear
Replace
Adjust
--
1.8.4
1.8.4
1.8.4
--
--
--
5.1.1
1.8.8
--
--
--
--
--
--
2.2.4.f
2.3.3.d
1.8.7
(Starter Does Not
Run)
Battery discharged
Starter malfunctioning
Key switch malfunctioning
Wiring disconnected
Engine Revolution
Is Not Smooth
Fuel filter clogged or dirty
Air cleaner clogged or dirty
Fuel leak due to loose injection pipe retaining
nut
Injection pump malfunctioning
Incorrect nozzle injection pressure
Injection nozzle stuck or clogged
Either White or Blue
Excessive engine oil
Exhaust Gas Is
Observed
Piston ring and liner worn or ring stuck
Incorrect Injection timing
Deficient compression
Either Black or Dark
Exhaust Gas Is
Observed
Overload
Low grade fuel used
Fuel filter clogged
Air cleaner clogged
Deficient nozzle injection
Deficient Output Incorrect injection timing
Engine’s moving parts seem to be seizing
Injection pump malfunctioning
Deficient nozzle injection
Compression leak
Gas leak from exhaust system
Air cleaner dirty or clogged
Charge
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Connect
Clean or change
Clean or change
Tighten retaining nut
Replace
Replace
Replace
Reduce to specified
level
Repair or replace
Adjust
Check the cylinder
compression
pressure and top
clearance
Lesson load
Use specified fuel
Clean or change
Clean or change
Replace nozzle
Adjust
Repair or replace
Replace
Replace nozzle
Check the
compression
pressure and repair
Repair or replace
Clean or replace
6.1
--
--
1.8.4
--
--
5.1
5.2.1
5.2.3
1.8.1
2.3.3.d
5.1.1
2.1.1
--
--
--
--
1.8.8
5.1.1
--
5.1
5.2.2
2.1.1
--
--
1--5 62--11362
Page 13
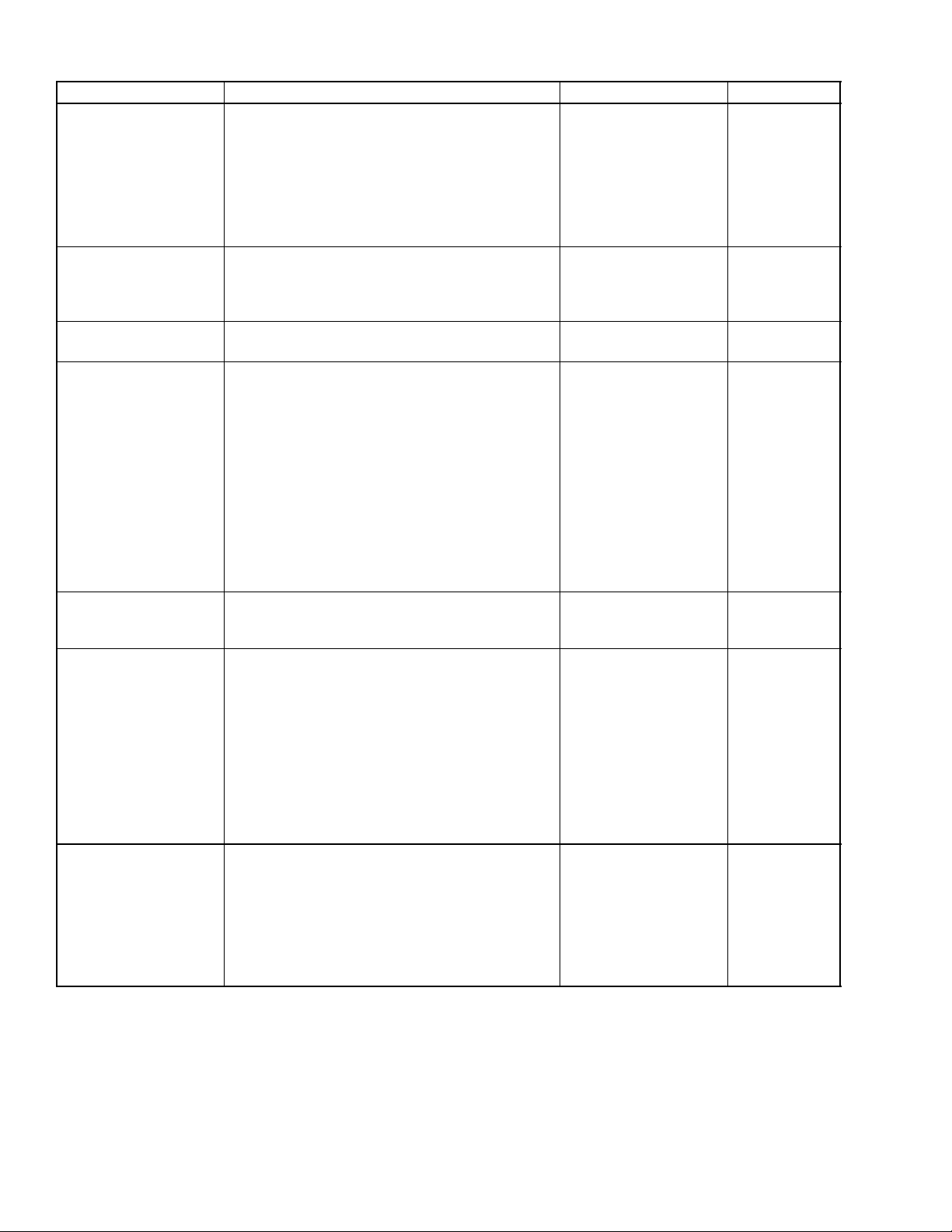
1.6 TROUBLESHOOTING (Continued)
Symptom
Excessive Lubricant
Piston ring’s gap facing the same direction
Probable Cause Solution Reference
Oil Consumption
Oilringwornorstuck
Piston ring groove worn
Valve stem and valve guide worn
Crankshaft bearing, and crank pin bearing
worn
Oil leaking due to defective seals or packing
Fuel Mixed into
Injection pump’s plunger worn
Lubricant Oil
Deficient nozzle injection
Injection pump broken
Water Mixed into
Lubricant Oil
Head gasket defective
Cylinder block or cylinder head flawed
Low Oil Pressure Engine oil level low
Oil strainer clogged
Relief valve stuck with dirt
Relief valve spring weak or broken
Excessive oil clearance of crankshaft bearing
Excessive oil clearance of crankpin bearing
Excessive oil clearance of rocker arm
Oil passage clogged
Incorrect oil type
Oil pump defective
High Oil Pressure Incorrect oil type
Relief valve defective
Engine Overheated Engine oil level low
Fan belt broken or elongated
Coolant insufficient
Radiator net and radiator fin clogged with dust
Inside of radiator corroded
Coolant flow route corroded
Radiator cap defective
Overload running
Head gasket defective
Incorrect injection timing
Unsuitable fuel used
Low Battery Charge Battery electrolyte level low
Fan belt slips
Wiring disconnected
Rectifier defective
Alternator defective
Battery defective
Shift ring gap
direction
Replace
Replace worn piston
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace Injection
pump
Replace nozzle
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replenish
Clean
Clean
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Clean
Use specified type of
oil
Repair or replace
Use specified type of
oil
Replace
Replenish
Replace or adjust
Replenish
Clean
Clean or replace
Clean or replace
Replace
Loosen load
Replace
Adjust
Use specified fuel
Replenish distilled
water and charge
Adjust belt tension or
change belt
Connect
Replace
Replace
Change
2.2.6.a
2.3.3.d
2.3.3.e
2.3.1.d
2.3.4
--
5.1
5.2.3
5.1
2.2.3.e
--
--
--
3.1.1
3.1.1
2.3.4.d
2.3.4.c
2.3.1.k
--
--
3.2
--
3.1.1
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
2.2.3.e
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
62--11632
1--6
Page 14
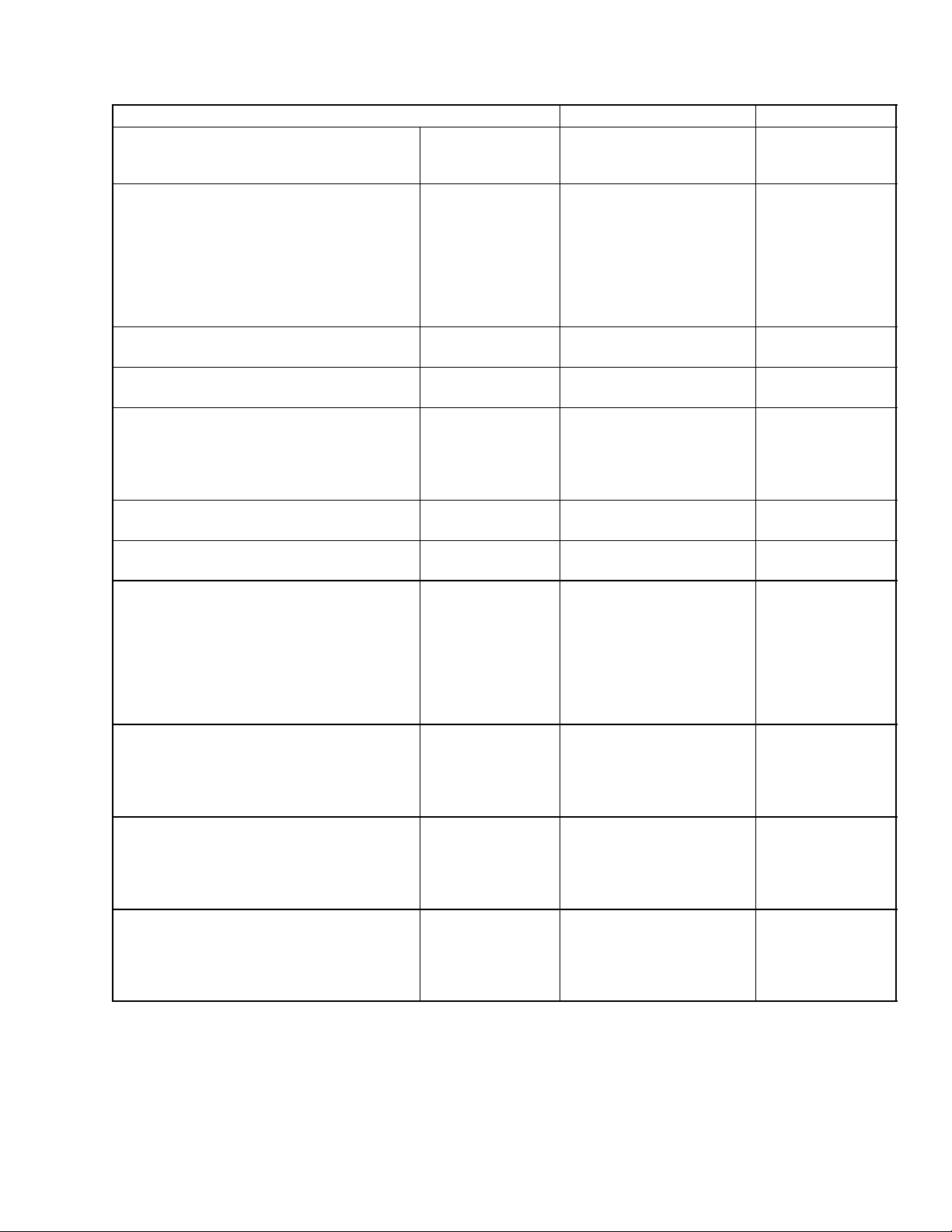
1.7 SERVICING SPECIFICATIONS
1.7.1 Engine Body
Item
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Cylinder Head Surface Flatness -- 0.05 mm/500mm
0.0020 in./
19.69 in.
Compression Pressure
Difference Among Cylinders
Top Clearance 0.60 to 0.70 mm
2.95 to 3.23 MPa/
290 rpm
30 to 33 kgf/cm
290 rpm
427 to 469 psi/
290 rpm
--
2.35 MPa/
2
290 rpm
24kgf/cm
2
290 rpm
341 psi/
290 rpm
10% or less
--
0.0236 to 0.0276 in.
Valve Clearance (When Cold) 0.18 to 0.22 mm
--
0.0071 to 0.0086 in.
Valve Seat Width (Intake)
2.12 mm
--
0.0835 in.
Width (Exhaust)
2.12 mm
--
0.0835 in.
Valve Seat Angle
(Intake / Exhaust)
Valve Face Angle
(Intake / Exhaust)
ValveStemtoValveGuide
Clearance
0.79 rad.
45°
0.79 rad.
45°
0.040 to 0.070 mm
0.0016 to 0.0027 in.
--
--
0.1 mm
0.0039 in.
Valve Stem
Valve Guide
O.D.
I.D.
Valve Recessing Protrusion
Recessing
Valve Timing (Intake Valve) Open
Close
Valve Timing (Exhaust Valve) Open
Close
7.960 to 7.975 mm
0.3134 to 0.3139 in.
8.015 to 8.030 mm
0.3156 to 0.3161 in.
0.65 mm
0.026 in.
to
0.85 mm
0.033 in.
0.1 rad. (8°)
before T.D.C.
0.35 rad. (20°)
before T.D.C
0.87 rad. (50°)
before B.D.C.
0.21 rad. (12°)
before B.D.C
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
1--7 62--11362
Page 15
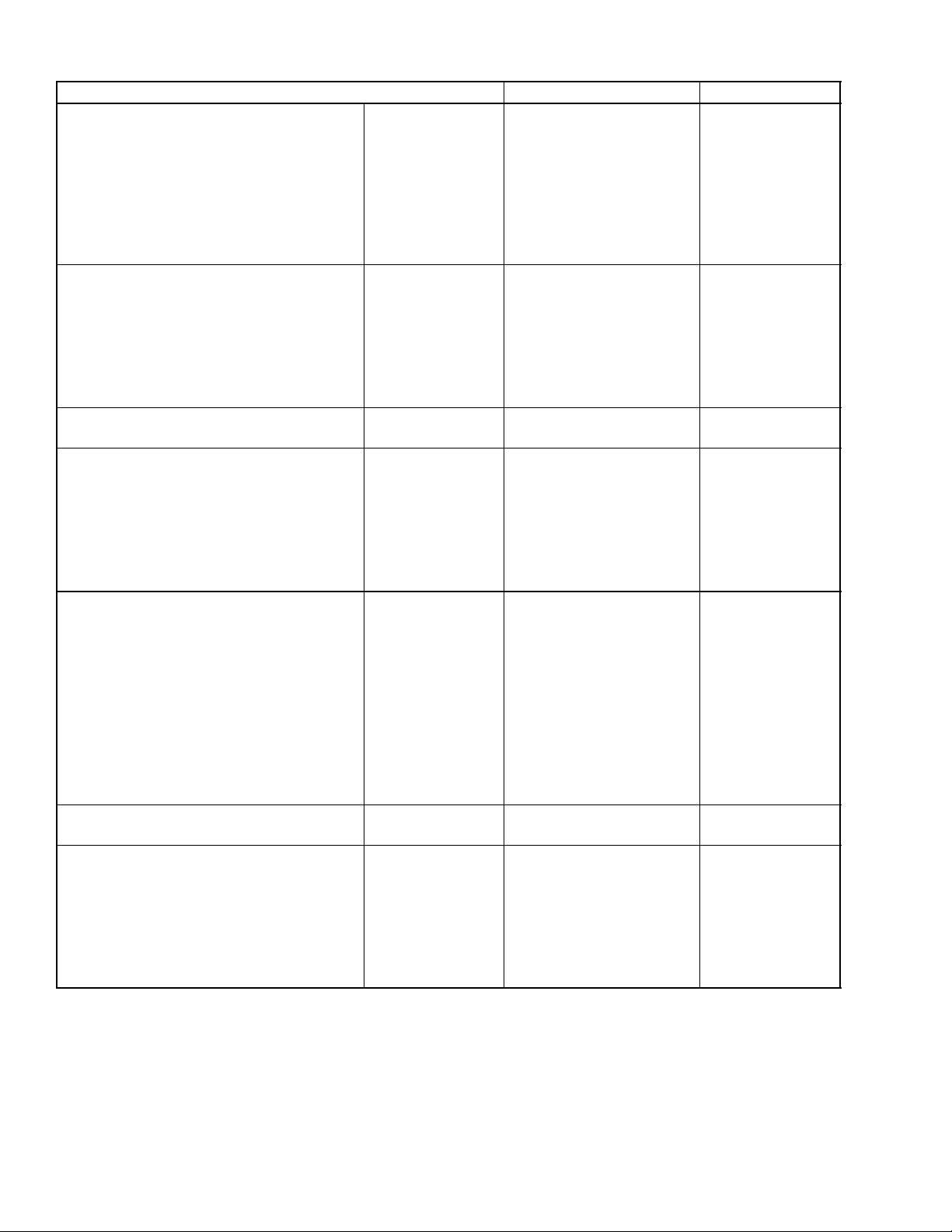
1.7.1 Engine Body (Continued)
Item
Valve Spring Free Length
Setting Load/
Setting Length
Tilt
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
41.7 to 42.2 mm
1.65 to 1.66 in.
118N/35.0mm
12.0 kgf / 35.0 mm
26.5 lbs. / 1.38 in.
--
41.2 mm
1.62 in.
100.0N / 35.0 mm
10.2kgf / 35.0 mm
22.5lbs /1.38 in
1.0 mm
0.039 in.
Rocker Arm Shaft to Rocker Arm
Rocker Shaft
Clearance
O.D.
0.016 to 0.045 mm
0.00063 to 0.0017 in.
13.973 to 13.984 mm
1.0 mm
0.039 in.
--
0.55012 to 0.55055 in.
Rocker Arm
I.D.
14.000 to 14.018 mm
--
0.55119 to 0.55188 in.
Push Rod Alignment -- 0.25mm
0.0098 in.
Tappet to Tappet Guide Clearance
O.D.
0.020 to 0.062 mm
0.00079 to 0.0024 in.
23.959 to 23.980 mm
0.07 mm
0.003 in.
--
0.94327 to 0.94409 in.
I.D.
24.000 to 24.021 mm
0.94489 to 0.94570 in.
Timing Gear
Crank Gear to Idle Gear
Backlash
0.0415 to 0.1122 mm
0.001634 to 0.004417 in.
Idle Gear to Cam Gear
Backlash
0.0415 to 0.1154 mm
0.00163 to 0.004543 in.
Idle Gear to Injection Pump Gear
Backlash
0.0415 to 0.1154 mm
0.001634 to 0.004543 in.
Crank Gear to Oil Pump Gear
Backlash
0.0415 to 0.1090 mm
0.001634 to 0.004291 in.
Idle Gear Side Clearance 0.12 to 0.48 mm
0.0048 to 0.018 in.
Idle Gear Shaft to Idle Gear Bushing
Clearance
0.025 to 0.066 mm
0.00099 to 0.0025 in.
Idle Gear Shaft
O.D.
37.959 to 37.975 mm
1.4945 to 1.4950 in.
Idle Gear Bushing
I.D.
38.000 to 38.025 mm
1.4961 to 1.4970 in.
_
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.9 mm
0.04 in.
0.1 mm
0.0039 in.
--
--
62--11632
1--8
Page 16
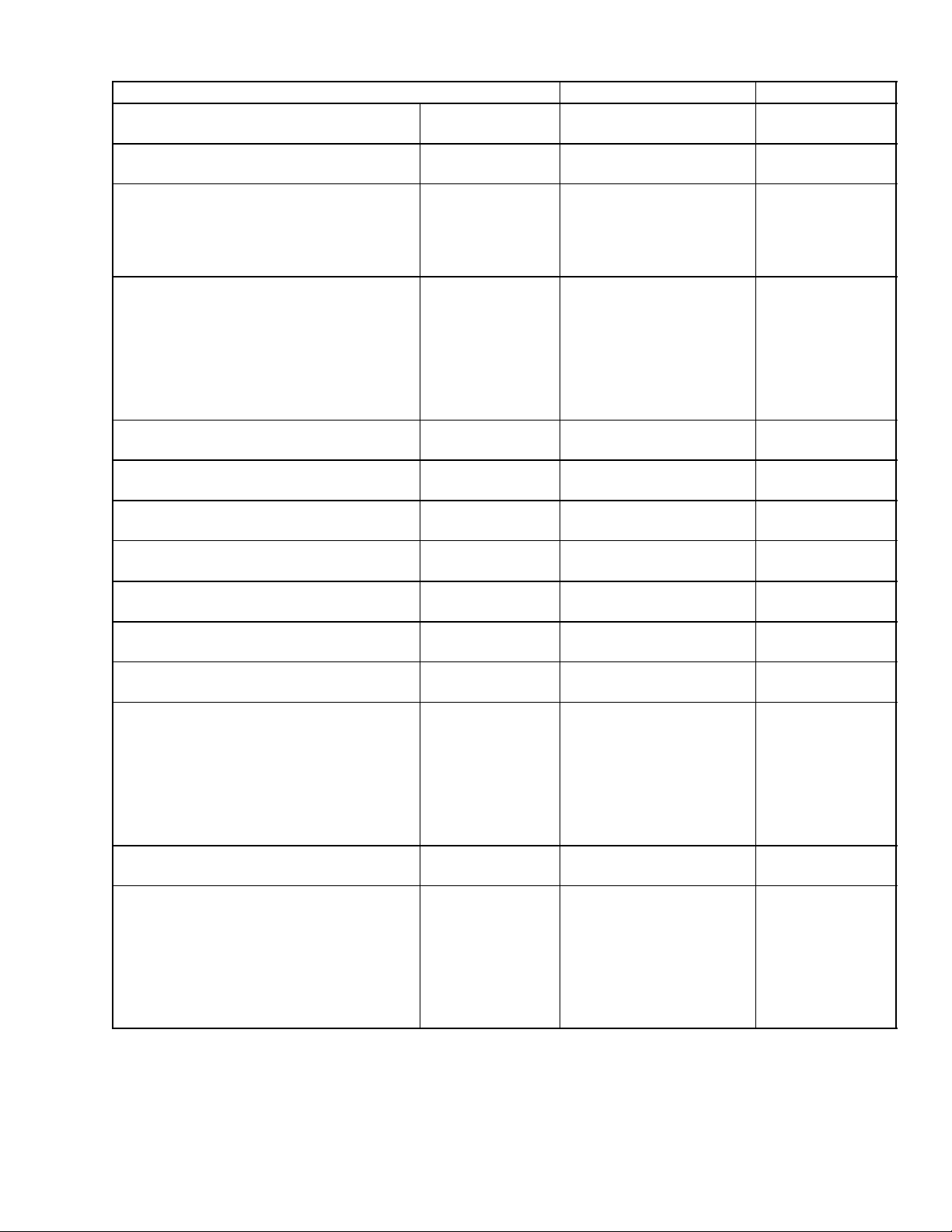
1.7.1 Engine Body (Continued)
Item
Camshaft Side Clearance 0.07 to 0.22 mm
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
0.3 mm
0.0028 to 0.0086 in.
0.012 In.
Camshaft Alignment -- 0.01 mm
0.0004 in.
Cam (Lobe) Height (Intake)
Height (Exhaust)
Camshaft Journal to Cylinder Block Bore
Camshaft Journal
Clearance
O.D.
33.27 mm
1.310 in.
33.47 mm
1.318 in.
0.050 to 0.091 mm
0.0020 to 0.0035 in.
39.934 to 39.950 mm
33.22 mm
1.308 in.
33.42
1.316 in.
0.15 mm
0.00059 in.
--
1.5722 to 1.5728 in.
Cylinder Block Bore
I.D.
40.000 to 40.025 mm
--
1.5748 to 1.5757
Piston Pin Bore I.D. 25.000 to 25.013 mm
0.98425 to 0.98476 in.
Second Ring to Ring Groove Clearance 0.093 to 0.128 mm
0.00367 to 0.00503 in.
Oil Ring to Ring Groove Clearance 0.020 to 0.060 mm
0.00079 to 0.0023 in.
Top Ring Ring Gap 0.20 to 0.35 mm
0.0079 to 0.013 in.
Second Ring Ring Gap 0.40 to 0.55 mm
0.016 to 0.021 in.
Oil Rng Ring Gap 0.25 to 0.45 mm
0.0099 to 0.017 in.
25.05 mm
0.9862 in.
0.2 mm
0.0079 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
1.25 mm
0.0492 in.
1.25 mm
0.0492 in.
1.25 mm
0.0492 in.
Connecting Rod Alignment -- 0.05 mm
0.002 in.
Piston Pin to Small End Bushing
Clearance
0.014 to 0.036 mm
0.00056 to 0.0014 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
Piston Pin
O.D.
25.004 to 25.011 mm
--
0.98441 to 0.98468 in.
Small End Bushing
I.D.
25.025 to 25.040 mm
--
0.98524 to 0.98582 in.
Crankshaft Alignment -- 0.02 mm
0.0008 in.
Crankshaft Journal to Crankshaft Bearing1
Crankshaft Journal
Oil Clearance
O.D.
0.040 to 0.118 mm
0.00158 to 0.00464 in.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
0.2 mm
0.0079 in.
--
2.3591 to 2.3598 in.
Crankshaft Bearing1
I.D.
59.980 to 60.039 mm
--
2.3615 to 2.3637 in.
1--9 62--11362
Page 17
1.7.1 Engine Body (Continued)
Item
Crankshaft Journal to Crankshaft Bearing2
Crankshaft Journal
Crankshaft Bearing2
Crankpin to Crankpin Bearing
Crankpin
Crankpin Bearing
Crankshaft Side Clearance 0.15 to 0.31 mm
Crankshaft Sleeve Wear -- 0.1mm
Cylinder Bore
(Standard)
Oil Clearance
O.D.
I.D.
Oil Clearance
O.D.
I.D.
I.D.
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
0.040 to 0.104 mm
0.00158 to 0.00409 in.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
2.3591 to 2.3598 in.
59.980 to 60.025 mm
2.3615 to 2.3631 in.
0.025 to 0.087 mm
0.00099 to 0.0034 in.
46.959 to 46.975 mm
1.8488 to 1.8494 in.
47.000 to 47.046 mm
1.8504 to 1.8522 in.
0.0059 to 0.012 in.
83.00 to 83.022mm
3.2678 to 3.2685 in.
0.2 mm
0.0079 in.
--
--
0.2 mm
0.0079 in.
--
--
0.5 mm
0.02 in.
0.0059 in.
83.170 mm
3.2744 in.
(Oversize)
I.D.
83.250 to 83.272 mm
3.2776 to 3.2784 in.
83.420 mm
3.2843 in.
62--11632
1--10
Page 18
1.7.2 Lubricating System
Item
Engine Oil Pressure At Idle Speed
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
More Than 98 kPa
1.0 kgf/cm
2
14 psi
At Rated Speed
300 to 440 kPa
3.0 to 4.5kgf/cm
2
43 to 64 psi
Engine Oil Pressure Switch Working
Pressure
50 kPa
0.5kgf/cm
2
7psi
Inner Rotor to Outer Rotor Clearance 0.03 to 0.14 mm
0.0012 to 0.0055 in.
Outer Rotor to Pump Body Clearance 0.11 to 0.19 mm
0.0044 to 0.0074 in.
Inner Rotor to Cover Clearance 0.105 to 0.150 mm
0.00414 to 0.00590 in.
1.7.3 Cooling System
Item
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
V--Belt Tension 7.0to9.0mm(0.28to
0.35 in.) deflection at
98N(10kgf, 22 lbs.)
of force
Thermostat Valve Opening
Temperature
80.5 to 83.5°C
176.9 to 182.3°F
(At Beginning)
50 kPa
0.5 kgf/cm
7psi
250 kPa
2.5 kgf/cm
36 psi
--
0.2 mm
0.008 in.
0.25 mm
0.0098 in.
0.2 mm
0.008 in.
--
--
2
2
Valve Opening
Temperature
95°C
203°F
(Opened
Completely)
1.7.4 Fuel System
Item
Injection Pump Injection Timing 0.0568 to 0.0829 rad.
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
--
(3.25to4.75°) before
T.D.C.
Pump Element Fuel Tightness -- 18.63 Mpa
190.0 kgf/cm
2702 psi
Delivery Valve Fuel Tightness 10 seconds
18.62 to 17.76 Mpa
190.0 to 180.0 kgf/cm
2702 to 2560 psi
Injection Nozzle Injection Pressure
(1st stage)
18.64 to 20.10 Mpa
190.0 to 205.0 kgf/cm
2
2
5 seconds
18.63 to 17.65 Mpa
190.0 to 180.0kgf/cm
2702 psi to 2560 psi
--
2703 to 2915 psi
Injection Nozzle Valve Seat Valve Seat
Tightness
When the pressure is
16.67 Mpa (170.0 kgf/cm
2
--
2418 psi) the valve seat
must not leak.
--
2
2
1--11 62--11362
Page 19
1.7.5 Electrical System
Item
Starter
Commutator
Mica
Brush
Brush Holder and Holder Support
Intake Air Heater Resistance (cold) Approx. 0.3 ohm --
O.D.
Undercut
Length
Resistance
Factory Specification Allowable Limit
32.0 mm
1.26 in.
0.50 mm
0.020 in.
0.18 mm
0.709 in.
Infinity
31.4 mm
1.24 in.
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
11.0 mm
0.433 in.
--
62--11632
1--12
Page 20
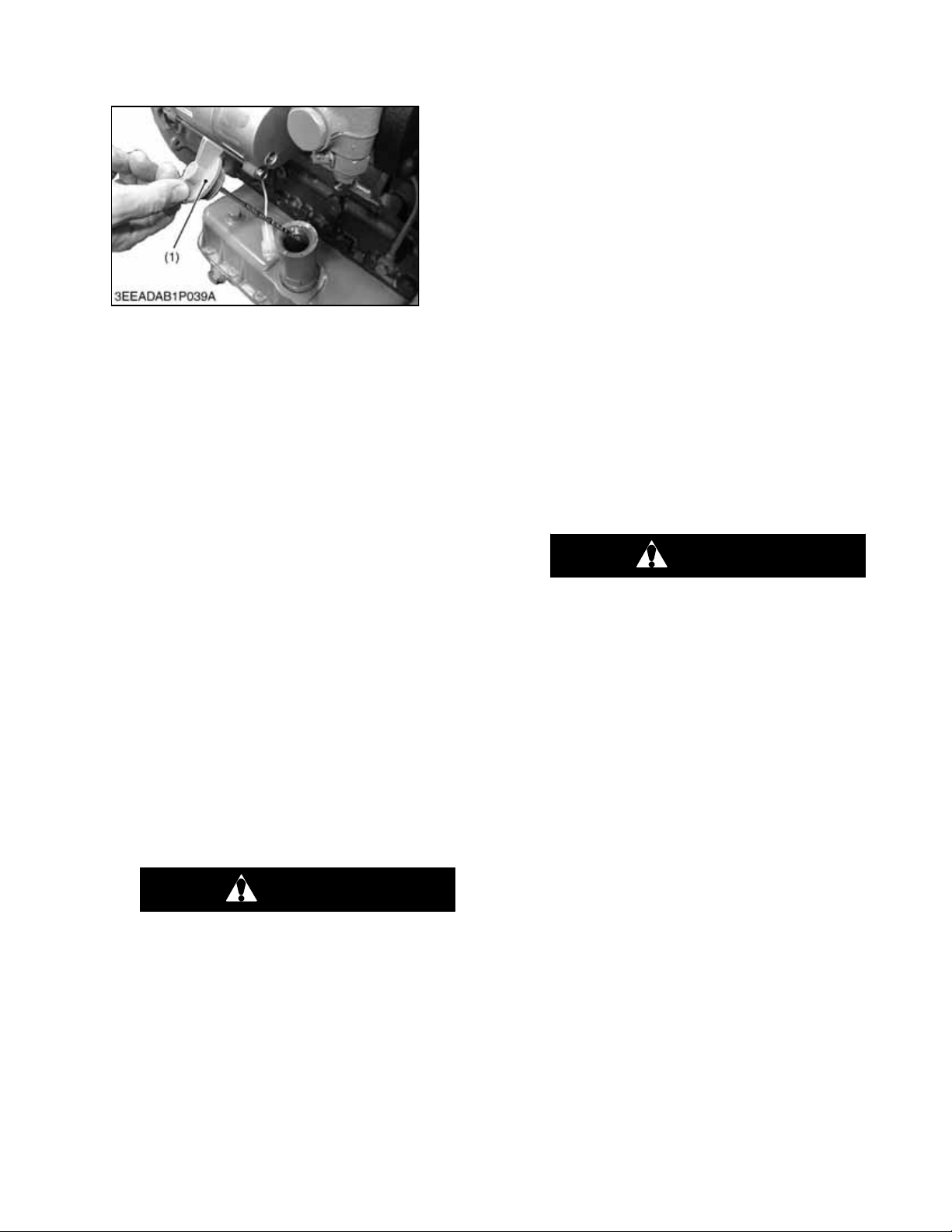
1.8 CHECK AND MAINTENANCE
1.8.1 Checking Engine Oil Level
1. Level the engine.
2. Tochecktheoillevel,draw out the dipstick (1), wipe it
clean, reinsert it, and draw it out again. Check to see
that the oil level lies between the two notches.
3. If the level is too low, add new oil to the specified
level.
NOTE
When adding oil to the crankcase, be sure that
the fresh oil is the same type and viscosity as
the oil that is already in the crankcase. Never
mix two different types of oil. Never over fill a
crankcase.
1.8.2 Checking Coolant Level
1. Remove the radiator cap and check to see that the
coolant level is just below the port.
With the recovery tank: Check to see that thecoolant
level lies between FULL and LOW.
2. Ifthe coolant level istoolow,checkthe reason for the
lost coolant.
a. If coolant loss is due to evaporation, add only clean
soft water.
b. If coolant loss is due to a leak, repair the leak, then
add a coolant mixture of the same type and specificationthatisinthesystem. If thecoolantbrandcannot be identified, drain out all of the remaining coolant and refill with a totally new mix.
NOTE
Whenaddingcoolanttothe system,airmustbe
vented from the engine coolant passages.
Venting air can be accomplished by jigglingthe
upper and lower radiator hoses.
Besureto close the radiator capsecurely.Ifthe
cap is loose or improperly closed, coolant may
leak out and the engine could overheat.
Do not use an antifreeze and scale inhibitor at
thesametime.
Nevermix different types orbrands of coolants.
1.8.3 Checking Fuel Hose
1. If the clamp is loose, apply oil to the threads and
securely retighten it.
2. The fuel hose is made of rubber and agesregardless
of the service period. Change the hose and clamps
together every two years.
3. Change the fuel hose and clamps whenever any deterioration or damage is detected.
4. After the fuel hose and clamps have been changed,
bleed air out of the fuel system.
CAUTION
Stop the engine when attempting to check
and change the fuel line.
CAUTION
Do not remove the radiator cap until the
coolant temperature is below its boiling
point. Loosen the cap slightly to relieve excess pressure before removing the cap
completely.
1--13 62--11362
Page 21

1.8.4 Bleeding Fuel System
1. Open the air vent cock (1) on top of the fuel injection
pump.
2. Loosen the priming pump handle (2), and pump the
handle until bleeding is completed.
3. Depress and twist the priming pump handle clockwisetolockintoplace.
4. Close the air vent cock (1).
NOTE
Always keep the air vent cock on the fuelinjectionpumpclosed except when bleeding the fuel
system, or the engine may not run.
1.8.5 Checking V--Belt
Refer to Section 4.1
1.8.6 Changing Engine Oil
CAUTION
Stop the engine when preparing to change
the engine oil.
1. After warming up the engine, shut it off.
2. Place a pan underneath the engine.
3. Remove the drain plug, drain the engine oil
completely.
4. Inspect the drain plug gasket. Replace if necessary.
5. Reinstall the drain plug.
6. Replace the oil filter with a new oil filter.
7. Fill the crankcase with new oil.
8. Check for thecorrectoillevel.(RefertoSection1.8.1)
NOTE
When changing to a different oil manufacturer
or viscosity, be sure to remove all of the old oil
completely. Never mix different types of oil.
Use only API classification CG--4 or better oils.
Use the proper SAE engine oil according to the
ambient temperatures.
Above 25°C(77°F).............SAE 30 or10W--30
10W--40
0° to25°C(32° to77°F)......SAE20 or 10W--30
10W--40
Below0°C(32°F)............SAE10Wor10W--30
NOTE
With emission controls now in effect, theCG--4
or CH--4 / CI lubricating oils have been developed for use of a low--sulfur fuel on--road vehicles engines. When an off--road vehicle engine runs on a high--sulfur fuel, it is advisableto
employ the CH--4 / CI lubricating oil with a high
total base number. If the CG--4 lubricating oil is
usedwithahighsulfurfuel,changethelubricating oil at shorter intervals.
Lubricating oil recommended when a low--sulfur or
high--sulfur fuel is employed.
ubricating Oil Class Fuel
L
Low--sulfur High--sulfur
CG--4 O O
CH--4 or CI O X
O : Recommended X : Not Recommended
62--11632
1--14
Page 22
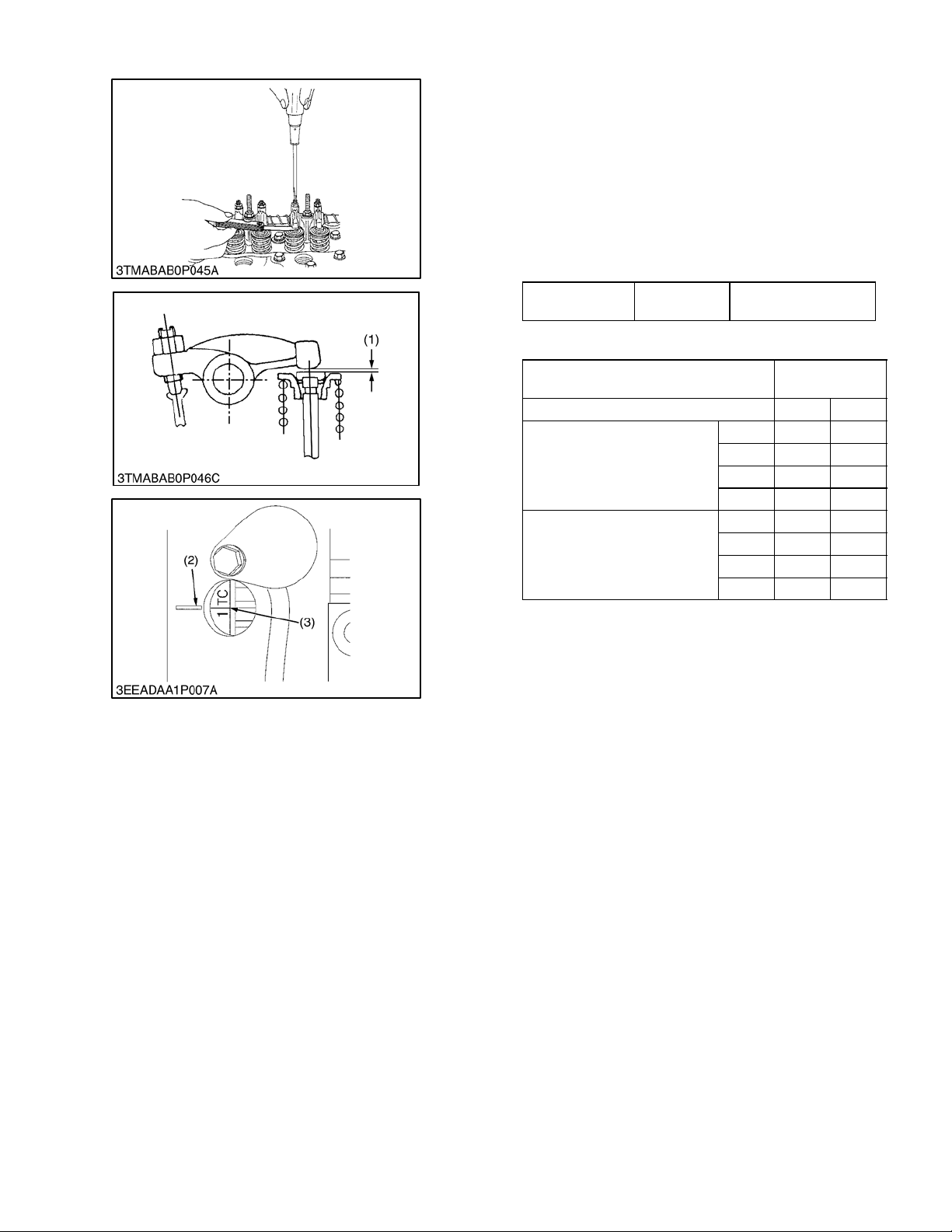
1.8.7 Valve Clearance
NOTE
Valveclearancemust be checked and adjusted
when the engine is cold.
1. Remove the valve cover.
2. Align the“1TC” mark line (3)on the flywheel and projection (2) on the housing so that the Number 1piston
comes to compression or overlap top dead center
(TDC).
3. Check the following valve clearance (1) marked with
“*” using a feeler guage.
Valve Clearance
Factory
Specification
4. If the clearance is not within the factory specifications, adjust with the adjusting screw.
Piston Location in Cylinder IN. EX.
When No. 1 piston is at TDC
When No. 1 piston is at past TDC
0.18 to 0.22 mm
0.0071 to 0.0086 in.
Valve
Arrangement
No. 1 * *
No. 2 *
No. 3 *
No. 4
No. 1
No. 2 *
No. 3 *
No. 4 * *
1.8.8 Fuel Injection
Refer to Section 5.2
1--15 62--11362
Page 23

1.9 SPECIAL TOOLS
Additional tools may be found in the Carrier Transicold Performance Parts Service Tool Catalog Number
62--03213.
1.9.1 Diesel Engine Compression Tester (Glow
Part No. 07--00179--01 (Assembly)
Application: Use to measure diesel engine
1.9.2 Adapter, Injector To Tester Hose
Part No. 07--00484--00
Application: Accessory for 07--00179--01
1.9.3 Tester Injector Nozzle
Part No. 07--00140--00
Application: Injector nozzle tester kit used for
checking and adjusting of the fuel injectors in diesel
engines.
Plug)
compression and diagnosis for
major overhaul.
62--11632
1.9.4 Replacement Bowl, Tester Injector Nozzle
Part No. 07--00140--10
Application: Accessory for 07--00140--00
1.9.5 Adapter, Injector Line
Part No. 07--00036--00
Application: Accessory for 07--00140--00
1--16
Page 24

1.9 SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
Adapte
3
8.Adapto
3
1.9.6 Oil Pressure Tester
Code No. 07916--32032
Application: Use to measure lubricating oil
pressure.
1. Guage
2. Adapter 2
3. Cable
4.
r
5. Threaded Joint
6. Adapter 4
7. Adaptor 1
r
1.9.7 Auxiliary Socket For Fixing Crankshaft
Sleeve
Code No. 07916--32091
Application: Use to fix the crankshaft sleeve of the
diesel engine.
1.9.8 Gauge, Belt Tension
Part No. 07--00203--00
Application: Used to adjust belt tension of all
cogged V--belts.
1.9.9 Tester, Belt Tension
Part No. 07--00253--00
Application: Used to test belt tension.
1.9.10 Rubber Band
Part No. 07--00253--01
Application: Replacement part for belt tension
tester (Part No. 07--00253--00)
1.9.11 Main Bearing Install Tool
Part No. 07--00472--00
Application: Used on engines starting with
S/N 3S0001
1.9.12 Main Bearing Extract Tool
Part No. 07--00473--00
Application: Used on engines starting with
S/N 3S0001
1--17 62--11362
Page 25

1.9 SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
The following are drawings for special tools that may need to be fabricated.
1.9.13 Valve Guide Replacing Tool
Application: Use to press out and press fit the valve
A
B 11.7 to 11.9 mm dia. (0.460 to 0.468 in. dia.)
C 6.5to 6.6 mm dia. (0.256 to 0.259 in. dia.)
D 225mm(8.86 in.)
E 70 mm (2.76 in.)
F 45 mm (1.77 in.)
G 25 mm (0.98 in.)
H 5 mm (0.197 in.)
I 6.7 to 7.0 mm dia. (0.263 to 0.275 in. dia.)
J 20 mm dia. (0.787 in. dia.)
K 12.5 to 12.8 mm dia. (0.492 to 0.504 in. dia.)
L 8.9 to 9.1 mm (0.350 to 0.358 in.)
C1 Chamfer 1.0 mm (0.039in.)
C2 Chamfer 2.0 mm (0.079in.)
C0.3 Chamfer 0.3 mm (0.012in.)
1.9.14 Bushing Replacing Tools
Application: Use to press out and press fit the bushing.
1. For small end bushing.
A
B 35 mm (1.38 in.)
C 27 mm (1.06 in.)
D 35 mm dia. (1.38 in. dia.)
E 27.90 to 27.95 mm dia. (1.098 to 1.100 in. dia.)
F 25.00 to 25.01 mm dia. (0984 to 0.985 in. dia.)
2. For idle gear bushing.
A
B 40 mm (1.57 in.)
C 38 mm (1.49 in.)
D 45 mm (1.77 in.)
E 41.90 to 41.95 mm dia. (1.650 to 1.652 in. dia.)
F 37.95 to 37.97 mm dia. (1.494 to 1.495 in. dia.)
1.9.15 Flywheel Stopper
Application: Use to loosen and tighten the flywheel
A
B 20 mm (0.79 in.)
C 30 mm (1.18 in.)
D 8 mm (0.31 in.)
E 10 mm (0.39 in.)
guide.
20 mm dia. (0.79 in. dia.)
162 mm (6.38 in.)
175 mm (6.89 in.)
screw.
200 mm (7.87 in.)
62--11632
1--18
Page 26

1.9 SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
1.9.16 Crankshaft Bearing 1 Replacing Tool
Application: Usetopressoutandpressfitthecrankshaft
bearing No. 1
1. Extracting tool
130 mm (5.31 in.)
A
B 72 mm (2.83 in.)
C R40 mm (R1.57 in.)
D 10 mm (0.39 in.)
E 20 mm (0.79 in.)
F 20 mm dia. (0.79 in. dia.)
G 64.8 to 64.9 mm dia. (2.551 to 2.555 in. dia.)
H 59.8 to 59.9 mm dia. (2.354 to 2.358 in. dia.)
2. Extracting tool
A
130 mm (5.31 in.)
B 72 mm (2.83 in.)
C R40 mm (R1.57 in.)
D 10 mm (0.39 in.)
E 20 mm (0.79 in.)
F 20 mm (0.79 in.)
G 20 mm dia. (0.79 in. dia.)
H 68 mm dia. (2.68 in. dia.)
I 59.8 to 59.9 mm dia. (2.354 to 2.358 in. dia.)
J 64.8 to 64.9 mm dia. (2.551 to 2.555 in. dia.)
1--19 62--11362
Page 27

SECTION 2
ENGINE BODY
2.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
2.1.1 Compression Pressure
1. Run the engine until it is warmed up.
2. Stop the engine and disconnect the 2P connector
from the stop solenoid to prevent fuel delivery to the
engine.
3. Remove the the aircleaner, the muffler and allthe injection nozzles.
4. Install acompression testerwith the adapter in one of
the nozzle hole.
5. While cranking the engine with the starter measure
the compression pressure.
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 for each cylinder.
2.1.2 Top Clearance
7. Ifthe measurement is below the allowable limit, adda
smallamount of oil to the cylinder thruthenozzlehole
and measure the compression again.
a. If the compression pressure is still less than the al-
lowable limit, check the top clearance, valves and
cylinder head.
b. If the compression pressureincreasesafterapplying
oil, check the cylinder wall and piston rings.
NOTE
Check the compression pressure with the specified valve clearance
Always use a fully charged battery for performing this test.
Variances in cylinder compression values
should be under 10%.
2.95 to 3.23 MPa
30 to 33 kgt/cm
427 to 469 psi
2.35 MPa
24 kgt/cm
2
341 psi
2
Compression Pres-
sure
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit
1. Piston 2 Plastic gauge
1. Remove the valve cover. (Refer to Section 2.2.3.a)
2. Remove the cylinder head.
3. Move the piston (1) up and stick a strip of plastic
gauge(2)onthepistonheadatthreepositionsshown
on the illustration.
4. Lower the piston and install the cylinder head. (Use a
new cylinder head gasket and tighten the cylinder
head bolts to the proper torque.
5. Turn the flywheel until the piston (1) passes through
top dead center.
6. Remove the cylinder head and measure the plastic
gauge.
7. Ifthe measurement is not withinthefactory specifications, check the clearances between the crank pin
and bearing and betweenthe pistonpin and bushing.
Top Clearance
Tightening
Torque
Factory
Specification
Cylinder Head
Bolts
0.60 to 0.70 mm
0.024 to 0.027 in.
93.2 to 98.0 N.m
9.5 to 10.0 kgf
68.8 to 72.3 ft--lbs
.
m
2--1
62--11362
Page 28

2.2 DISASSEMBLE AND REASSEMBLY
2.2.1 Draining Coolant And Engine Oil
CAUTION
Never remove the radiator cap until coolant
temperature is below its boiling point.
Loosen the cap slightly to the first stop to
relieve any excess pressure before removing the cap completely.
1. Open the coolant drain cock or remove the coolant
drain plug and drain the coolant into a proper receptacle/bucket.
2. Removetheoildrainpluganddraintheengineoilinto
a proper receptacle/bucket.
2.2.2 External Components
Air Cleaner, Muffler and Others
1. Remove the air cleaner and muffler.
2. Remove the fan, fan belt, alternator and starter.
When Reassembling
NOTE
Check to see that there are no cracks on the belt
surface.
After reinstaling the fan belt, be sure to adjust
the fan belt tension.
When reinstalling the fan, make sure that it is
put on correctly.
62--11362
2--2
Page 29

2.2.3 Cylinder Head And Valves
2.2.3.a Valve Cover
1. Remove the breather hose (2).
2. Remove the valve cover bolts (1).
3. Remove the valve cover (3).
When Reassembling
Check to see that the valve cover gasket (4) is in good
condition and in place.
Tightening
Torque
1. Valve Cover Bolt
2. Breather Hose
3. Valve Cover
Valve Cover
Bolts
6.87 to 11.2 N.m
0.7to1.15kgf
5.07 to 8.31 ft--lbs
4. Valve Cover Gasket
5. Breather Valve
6. Plate
.
m
2.2.3.b Injection Pipes
1. Loosen the bolts on the pipe clamps (1).
2. Detach the injection pipes (2).
When Reassembling
Blow out any debris that may be in the pipes.
Tightening
Torque
Injection Pipe
Retaining
Nut
2--3
15 to 24 N.m
1.5to2.5kgf
11to 18 ft--lbs
62--11362
.
m
Page 30

2.2.3 Cylinder Head And Valves (Continued)
ArmA
y
2.2.3.c Nozzle Holder Assembly
1. Remove the overflow pipe assembly.
2. Remove the nozzle holder assemblies (1).
When Reassembling
Replace the copper gasket with a new one.
26 to 29 N.m
2.6to3.0kgf
19 to 21 ft--lbs
9.81 to 11.2 N.m
1.00 to 1.15 kgf
7.24 to 8.31 ft--lbs
.
m
.
m
Tightening
Torque
Nozzle Holder
Assembly
Overflow Pipe
Assembly
Retaining Bolt
2.2.3.d Rocker Arm and Push Rod
1. Remove the rocker arm bracket mounting bolts (1).
2. Detach the rocker arm assembly (2).
3. Remove the push rods (3).
When Reassembling
When putting the push rods (3) onto the tappets (4),
check to see if the push rod end is properly seated in the
tappet dimples.
3
1. RockerArmBracket
Mounting Bolt
2. Rocker
ssembl
62--11362
4
3. Push Rod
4. Tappet
2--4
NOTE
After instaling the rocker arm, besure to adjust
the valve clearance. (Refer to Section 1.8.7)
Tightening
Torque
Rocker Arm
Bracket Mounting
Bolt
24 to 27 N.m
2.4to2.8kgf
18 to 20 ft--lbs
.
m
Page 31

2.2.3 Cylinder Head And Valves (Continued)
14
18
17
1. Hose Clamp
2. Filter--Drier Inlet
A: Gear Case Side
B: Flywheel Side
10
2
1
3
4513 12
6
11
157
1689
2.2.3.e Cylinder Head
1. Loosen the hose clamp (1),andremove the waterreturn pipe (2).
2. Remove the cylinder headbolts in the order of (18)to
(1).
3. Lift up the cylinder head and remove.
4. Remove the cylinder head gasket (3).
When Reassembling
Replace the cylinder head gasket (3) with a new one.
Apply oil to, then re--install the cylinder head bolts.
Tighten the cylinder head bolts in sequence starting
from the center in the order of (1)to(18).
Tighten the head bolts uniformly or head warpage may
occur.
Tightening
Torque
Cylinder Head
Bolt
93.1 to 98.0 N.m
9.5 to 10.0 kgf
68.7 to 72.3 ft--lbs
.
m
NOTE
Whenreplacingthecylinderheadgasket (3), be
sure you are using a new gasket that matches
the original gasket.
2.2.3.f Tappets
1. Remove the tappets (1) from the crankcase.
When Reassembling
Visually check the contact between the tappets (1) and
individual cam lobes.
Coat the tappets with engine oil before installing them.
NOTE
When re--installing tappets into the engine,
make sure that they arere--installed in their original location.
2.2.3.g Valves
1. Remove the valve caps (3).
2. Remove the valve springcollet (4), pushing thevalve
springretainer(5)bythevalvespringcompressor(1).
3. Removethevalve spring retainer (5),valve spring (6)
and valve stem seal (2).
4. Remove the valve (7).
When Reassembling
Clean the valve stem and the valveguide. Apply engine
oil to the valve stem when reassembling.
After installing the valve spring collets (4), lightly tap the
stem with a plastic hammer to assure the collets have
seated on the valve stem.
NOTE
When re--installing valves into the engine,
make sure that they are re--installed in their
original location.
2--5
62--11362
Page 32

2.2.4 Injection Pump and Gear Case
2.2.4.a Injection Pump
1. Remove the fuel speed solenoid (2) and hi--idling
body (3).
2. Remove the engine stop lever (5) and stop solenoid
guide (6).
3. Remove the fuel injection pump assembly (7).
NOTE
Remove the injection pump assembly (7) after
removing the fuel speed solenoid(2) and hi--idling body (3), engine stop lever (5) and stop
solenoid guide (6).
When Reassembling
Install the fuel speed solenoid (2), the hi--idling body (3)
and the stop solenoid guide (6) after Installing the
injection pump (7).
Replace the hi--idling body gasket (4) with a new one.
Install the fuel speed solenoid guide (6) and then the
stop lever (5) into the gear case. Cycle the stop leverto
insure that it functions.
NOTE
Wheninstalling the fuel speedsolenoid(2), use
care to keep the O--ring (1) in place.
Be sure to insert the push rod of the stop solenoid into
the hole at the center of the solenoid guide (6).
Tightening
Torque
Hi--idling Body
45.0 to 49.0 N.m
4.5to5.0kgf
33 to 36 ft--lbs
.
m
62--11362
1. O--ring
2. Fuel Speed Solenoid
3. Hi--Idling Body
4. Hi--Idling Body Gasket
2--6
5. Stop Lever
6. Stop Solenoid Guide
7. Injection Pump Assembly
Page 33

2.2.4 Injection Pump and Gear Case (Continued)
g
2.2.4.b Governor Springs and Speed Control Plate
NOTE
SpecificTool(1):A1.2mm(.050inch)diameter
wire with a total length of 200mm (8 inch) with
the tip bent into a hook as depicted in the
illustration is required to hang the governor
springs.
1. Remove the injection pump cover.
2. Removethespeedcontrol plate (7)mounting nuts (3)
and bolts (4).
3. Using the Specific Tool (1), undo the the large
governor spring (5) from the fork lever (2).
4. Set thespeed control lever (6)as shown in the figure.
5. Remove the speed control plate (7), usingcarenot to
let the governor spring (5) disengage from the plate
and fall into the gear case.
1. Specific Tool
2. Fork Lever
3. Speed Control Plate
Mounting Nut
4. Speed Control Plate
Mountin
Bolt
5. Large Governor Spring
6. Speed Control Lever
7. Speed Control Plate
2--7
62--11362
Page 34

2.2.4 Injection Pump and Gear Case (Continued)
g
2.2.4.b Governor Springs and Speed Control Plate
(Continued)
When Reassembling
NOTE
A length of string passed thru the governor
spring can be usedto retrievethe spring if it unhooks from both the specific tool and thespeed
control plate.
Begin reassembly by inserting the specific tool (1) thru
the injection pump cover opening thru to the speed
control plate opening.
1. Using the specific tool (1), capture the governor
spring (5) and speed control plate (7) assembly.
2. Pull the governor spring (5) / speed control plate (7)
assembly thru and secure it to the fork lever (2).
3. Seat and assemble the speed control (5) plate with
two bolts and two nuts to the gear case.
4. Check the movement of the speed control lever (4).
NOTE
The speed control lever (6) must be free to
move from low idle position to maximum speed
position and should always return to the high
idle position.
5. Finally, install the injection pump cover to the gear
case.
1. Specific Tool
2. Fork Lever
3. Speed Control Plate
Mounting Nut
4. Speed Control Plate
Mountin
Bolt
5. Large Governor Spring
6. Speed Control Lever
7. Speed Control Plate
62--11362
2--8
Page 35

2.2.4 Injection Pump and Gear Case (Continued)
y
2.2.4.c Fan Drive Pulley
1. Lock the flywheel using the flywheel stopper
2. Remove the fan drive pulley mounting nut (1) using
the 46 mm deep socket wrench (3).
3. Remove the fan drivepulley (2) with a gear puller (4).
4. Remove the feather key.
When Reassembling
Apply grease to the splines of the coupling.
1. Nut
2. Fan Drive Pulle
3. 46 mm Deep Socket wrench
4. Gear Puller
Tightening
Torque
Drive Pulley
Mounting Nut
2.2.4.d Gear Case
1. Remove the gear case (1).
2. Remove the O--rings (3)(4).
138 to 156 N.m
14.0 to 16.0 kgf
102 to 115 ft--lbs
.
m
When Reassembling
Replace the gear case gasket and O--rings (3)(4).
Apply gasket sealant to both sides of the gear case
gasket (2).
Check/insure that thefour O--rings (3)(4) are in place on
1. Gear Case
2. Gear Case Gasket
3. O--ring
4. O--ring
5. Oil seal
the gear case (1).
Applyathinfilm of oil to the crankshaftoilseallip(5)and
take care not to rollthe lipwhen installing the gearcase.
2--9
62--11362
Page 36

2.2.4 Injection Pump and Gear Case (Continued)
g
2.2.4.e Crankshaft Oil Slinger
1. Remove the crankshaft collar (1).
2. Remove the O--ring (2).
3. Remove the crankshaft oil slinger (3).
When Reassembling
Insert the crankshaft collar (1) after installing the gear
case to the crankcase.
1. Crankshaft Collar
2. O--rin
1. Injection Pump Gear
2. Idle Gear
3. Cam Gear
3. Crankshaft Oil Slinger
4. Crank Gear
5. Oil Pump Drive Gear
2.2.4.f Idle Gear
1. Detach the external snap ring.
2. Remove the idle gear collar.
3. Remove the idle gear (2).
When Reassembling
Checkto see eachgearisalignedwithits aligning mark.
Idle gear (2) and crank gear (4)
Idle gear (2) and cam gear (3)
Idle gear (2) and injection pump gear (1)
2.2.4.g Camshaft
1. Remove the camshaft retaining bolt (1) and pull the
camshaft (2) out.
When Reassembling
1. Camshaft Set Screw 2. Camshaft
1. Oil Pipe
2. Fuel Feed Pump
3. O--ring
4. Fuel Feed Pump Holder
62--11362
Refer to installation of Idle Gear (Refer to Section
2.2.4.f).
Tightening
Torque
Camshaft
retaining bolt
24 to 27 N.m
2.4to2.8kgf
18 to 20 ft--lbs
2.2.4.h Fuel Feed Pump Holder
1. Disconnect the oil pipe (1).
2. Remove the fuel feed pump (2).
3. Remove the fuel feed pump holder (4).
When Reassembling
Replace the O--rings (3) with new O--rings.
2--10
.
m
Page 37

2.2.4 Injection Pump and Gear Case (Continued)
2.2.4.i Fuel Camshaft And Fork Lever Assembly
1. Detach the fuel camshaft stopper (1).
2. Remove the three fork lever holder mounting screws
(2).
3. Remove the fuel camshaft assembly(5),(6) andfork
lever assembly (3), (4), and (7) at the same time.
When Reassembling
After installation, check to see that the fork levers 1 (3)
and 2 (4) are fixed to the fork lever shaft, and that they
can turn smoothly in the holder (7).
1. Fuel Camshaft Stopper
2. Fork Lever Holder Mounting
Screws
3. Fork Lever 1
4. Fork Lever 2
1. Oil Pump
2. Oil Pump Drive Gear
5. Injection Pump Gear
6. Fuel Camshaft
7. Fork Lever Holder
2.2.4.j Oil Pump
1. Remove the nut.
2. Draw out theoilpumpdrive gear (2) withagearpuller
(3).
3. Removethefour oilpumpmounting bolts. Detachthe
oil pump (1).
3 Gear Puller
2--11
62--11362
Page 38

2.2.5 Oil Pan and Oil Strainer
1. Oil Pan Mounting Screw
2. Oil Pan
3. Oil Pan Cover Gasket
4. Oil Pan Cover
5. O--ring
6. Oil Strainer
7. Oil Pan Gasket
(7)
2.2.5.a Oil Pan and Oil Strainer
1. Remove the oil pan cover (4).
2. Remove the oil pan mounting bolts (1).
3. Removetheoilpan(2)bylightlytappingtherimofthe
pan with a wooden hammer.
4. Remove the old gaskets (3) and (7).
5. Remove the oil strainer (6) and O--ring (5).
When Reassembling
Check to see that the oil filter strainer (6) is clean.
VisuallychecktheO--ring(5),applyengineoil andinstall
it to the pick--up tube.
Install the strainer (6) and O--ring (5).
Apply gasket sealant to the oil pan side of the oil pan
gasket (7) and fit the gasket to the oil pan (2).
Installtheoilpan(2) to theengine,andtightentheoilpan
mounting bolts (1) diagonally. Avoid uneven tightening
of the oil pan mounting bolts. (Refer to Section 1.5.2
Torque Specifications)
Apply gasket sealant to the oil pan cover side of the oil
pan cover gasket (3) and fit the gasket to the oil pan
cover (4).
Install the oil pan cover (4) to the oil pan (2).
Install and tighten the oil pan cover bolts diagonally .
Avoid uneven tightening of the oil pan cover mounting
bolts. (Refer to Section 1.5.2 Torque Specifications)
62--11362
2--12
Page 39

2.2.6 Piston and Connecting Rod
(a)
)
2.2.6.a Pistons
1. Completely remove the carbon ridge (1) at the top of
the cylinder walls.
2. Remove the connecting rod cap (3).
3. Turn the flywheel and bring the piston to top dead
center.
4. Push the piston out by lightly tapping the connecting
rodfrom thebottom of the crankcasewiththegripofa
hammer.
5. Repeat the procedure for the other three cylinders.
When Reassembling
Liberally coat thepiston andpiston rings with engineoil.
When inserting the piston into the cylinder, face the
mark on the connecting rod to the injection pump.
NOTE
If re--installing the original piston assemblies
intothe enginebe sure that theyare returned to
their original cylinder.
Place the piston rings with their gaps at 2.09
rad. (120°) from the piston pin’s direction as
shown.
Carefully insert the pistons into the cylinders
using the piston ring compressor (7).
Wheninsertingthepistonintothecylinderavoid
damagingthemolybdenum disulfide coating on
the piston skirt. This coating is useful in minimizing the clearance between the piston and
cylinder.
When replacing a piston, use a replacement
piston with the same code number. The piston
ID mark (6) is on top of the piston.
6
1. Carbon
2. Connecting Rod Bolt
3. Connecting Rod Cap
4. Connecting Rod
5. Molybdenum Disulfide
CoatingonPistonSkirt
6. Piston ID Mark
Tightening
Torque
2--13
Connecting
7. Piston Ring Compressor
(A) Top Ring Gap
(B) Second Ring Gap
(C)OilRingGap
(D) Piston Pin Hole
2.09 rad.(120°
Rod Bolt
45 to 49 N.m
4.5to5.0kgf
33 to 36 ft--lbs
62--11362
.
m
Page 40

2.2.6 Piston and Connecting Rod (Continued)
7
2.2.6.b Piston Ring and Connecting Rod
1. Remove the piston rings (1), (2), (3).
2. Removethepiston pin(8)and then seperate theconnecting rod (6) from the piston (5).
8
NOTE
Mark both the connecting rod and pistonsothat
if they are to be re--used that the original combinationofpartswillgoback together.Donotinterchange used parts.
When Reassembling
When installing the rings, assemble so that the
manufacturer’s mark (12) near the gap faces the top of
the piston (5).
Wheninstallingtheoilcontrolring(3)ontothepiston(5),
place the expander joint (10) on the opposite side of the
oil ring gap (11).
Apply engine oil to the piston pin (8).
When assembling the connecting rod (6) to the piston
(5),immersethepiston(5)inhot oil(80°C /176°F)for10
to15minutes, then assemblethe piston, piston pin, and
connecting rod.
NOTE
Assemble the piston (5) on to the connecting
rod (6) with the FW mark (9) facing theflywheel
end and the connecting rod mark (7) facing the
injection pump side.
7
1. Top Ring
2. Second Ring
3. Oil Control Ring
4. Piston Pin Snap Ring
5. Piston
6. Connecting Rod
7. Mark
8. Piston Pin
9. FW Mark
10. Expander Joint
11. Oil Ring Gap
12. Manufacturer’s Mark
62--11362
2--14
Page 41

2.2.7 Crankshaft
y
1. Flywheel
2. Fl
wheel Bolt
3. Flywheel Guide Bolts
2.2.7.a Flywheel
1. Prevent the flywheel (1) from rotating.
2. Remove two flywheel bolts (2).
NOTE
Theuseof airtools to remove the flywheelbolts
may damage the threads in the crankshaft.
3. Install two flywheel guide bolts (3).
4. Remove all of the flywheel bolts (2).
5. Remove the flywheel (1) slowly along the flywheel
guide bolts (3).
When Reassembling
Install two flywheel guide bolts (3).
Check to see that the mating surfaces of the crankshaft
and flywheel are clean.
Apply engine oil to the flywheel bolts and install.
Tightening
Torque
Flywheel Bolts
2.2.7.b Bearing Case Cover
1. Removethebearingcasecovermountingbolts.First,
remove the insidebolts (2) andthen the outside bolts
(1).
2. Screw two of the removed bolts into the bolt hole of
the bearing case cover (3) to remove it.
98.0 to 107.8 N.m
10.0 to 11.0 kgf
72.3 to 79.5 ft--lbs
.
m
1. Bearing Case Cover
Mounting Bolt
2. Bearing Case Cover
Mounting bolt
3. Bearing Case Cover
4. Oil Seal
5. Bearing Case Gasket
6. Bearing Case Cover
Gasket
(a). Top
NOTE
The length of the inside (2) and the outside (1)
bolts is different. When reassembling reinstall
the appropriate bolt in the correct location.
When Reassembling
Fit the bearing case gasket (5) and the bearing case
cover gasket (6) to the bearing case cover (3). Orient
them correctly.
Install the bearing case cover (3), again orienting it
correctly, using the “UP” mark (a).
Apply oil to the oil seal (4), and take care not to roll the
seal when installed.
Tighten the bearing case cover bolts diagonally and
evenly.
Tightening
Torque
Bearing Case
Cover Mounting
bolt
24 to 27 N.m
2.4to2.8kgf
18 to 20 ft--lbs
.
m
2--15
62--11362
Page 42

2.2.7 Crankshaft (Continued)
2.2.7.c Crankshaft Assembly Removal
NOTE
Before disassembling, check the side
clearance of the crankshaft. Check it
during reassembly.
1. Remove the three main bearing case bolts (1).
2. Pull out thecrankshaft assembly (2),beingcarefulnot
to damage the crankcase bearings (3).
3. While pulling the crankshaft assembly (2) out, use
care to align eachofthe crank pins (5) (left or right)to
clear the crankcase relief (a).
When Reassembling
When installing the main bearing case assembly, align
the bolt holes of the crankshaft assembly (2) with the
holes of the crankcase.
Applyoiltothethreadsofthemainbearingcasebolts(1)
before re--insertion.
Tightening
Torque
1. Main Bearing Case Screw 2
2. Main Bearing Case 2
3. Crankshaft Bearing 1
4. Crankshaft Assembly
Main Bearing
Case Bolt
69 to 73 N.m
7.0to7.5kgf
51 to 54 ft--lbs
5. Cylinder 4 Crank Pin
(a).Main Bearing Case Relief
.
m
62--11362
2--16
Page 43

2.2.7 Crankshaft (Continued)
2.2.7.d Main Bearing Case Assembly
1. Remove the two main bearing case bolts (7), and remove the main bearing case assembly being careful
with the thrust bearing and crankshaft bearing.
2. Removetheremainingmainbearingcasesasabove.
When Reassembling
Clean the oil passages in the main bearing case.
Apply clean engine oil to the bearings.
Install the main bearing case assembliesintheiroriginal
locations. The diameters of the main bearing cases
vary. Install them in order from the gear case end
according to their markings (A,B,C).
Match the alignment numbers (1) and mark (2) on the
main bearing case.
When installing the main bearing case, face the mark
“FLYWHEEL” to the flywheel.
Install the thrust bearing with its oil groove facing (8)
outward.
Confirm that main bearing case moves smoothly after
torquing the main bearing case bolt to specification.
Tightening
Torque
1. Alignment Number
2. Alignment Mark
3. No Mark
4. C
7
8
Main Bearing
Case bolt
5. B
6. A
7. Main bearing Case Bolt
8. Oil Groove
46 to 50 N.m
4.7to5.2kgf
34 to 37 ft--lbs
.
m
8
2--17
62--11362
Page 44

2.3 SERVICING
g
2.3.1 Cylinder Head And Valves
2.3.1.a Cylinder Head Surface Flatness
1. Clean the cylinder head surface.
2. Place a straightedge on the cylinder head surface, in
six locations as depicted in the drawing.
3. Measure any clearance between the straightedge
and cylinder head with a feeler gauge.
4. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit,
resurface or replace the head.
NOTE
Check the valve recessing after after resurfacing the head.
0.05mm over a span of
Cylinder Head
Surface Flatness
Factory
Specification
500mm
0.002 in. over a span of
20 in.
1. Red Dye
2. Deter
ent
3. White Developer
2.3.1.b Cylinder Head Cracks
1. Cylinder head crack(s) can be found with using a
non--destructive test procedure using a dye/penetrant kit.
2. Clean the cylinder headsurface using a good quality
degreaser and detergent (2).
3. Spray the cylinder headsurface with the red liquid or
dye (1). Let it sit on the surface for ten minutes.
4. Wash the dye offtheheadusingthedetergent(2)and
dry the head.
5. Spray the white developer (3) on to the head.
6. Red marks will bleed through the developer identifying cracks in the head if they are present.
62--11362
2--18
Page 45

2.3.1 Cylinder Head And Valves (Continued)
(B)
1. Cylinder Head
Surface
(A) Recess
Protrusion
2.3.1.c Valve Recessing
1. Clean the cylinder head surface (1), valve face and
valve seat.
2. Insert the valve into the head,making certain that the
valve is fully seated.
3. Measure the valve recessing with a depth gauge.
4. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, replace the valve.
5. If the measurement still exceeds the allowable limit,
replace the cylinder head.
0.065 (protrusion) mm to
Valve
Recessing
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit --
0.085 (recessing) mm
0.026 (protrusion) in. to
0.033 (recessing) in.
2.3.1.d Clearance Between Valve Stem And Valve
Guide
1. Remove carbon from the valve guide section.
2. Measure the valve stem O.D. with a micrometer.
3. Measurethevalve guidewithasmallholegauge,and
calculate the clearance.
4. If the clearance exceeds the the allowable limit, replace the valves. If the clearance still exceeds the allowable limit, replace the valve guide.
Clearance
Between
Valve Stem
and Guide
Valve Stem
O.D.
Valve Guide
I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.040 to 0.070 mm
0.0016 to 0.0027 in.
0.1 mm
0.0039 in.
7.960 to 7.975 mm
0.3134 to 0.3139 in.
8.015 to 8.030 mm
0.3156 to 0.3161 in.
2--19
62--11362
Page 46

2.3.1 Cylinder Head And Valves (Continued)
2.3.1.e Replacing Valve Guide
(A) (When removing)
1. Pressouttheusedvalveguideusingavalveguidereplacing tool.
(B) (When installing)
1. Clean a new valve guide and valve guide bore, then
apply oil to them.
2. Pressinanew valveguideusingavalveguidereplacing tool.
3. Ream the I.D. of the valve guide to the specified dimension (precisely).
(A) When Removing (B) When Installing
Valve Guide I.D.
Intake & Exhaust
Factory
Specification
8.015 to 8.030 mm
0.3156 to 0.3161 in.
2.3.1.f Valve Seating
1. Coat the valve face lightly with prussian blue andput
the valve on its seat to check the contact pattern
2. Ifthe valve does not seat allthe way around the valve
seat,orthecontactislessthan70%, correctthevalve
seating as outlined in paragraph 2.3.1.g.
3. If the valve contact does not comply with the referencevalue, replace the valve or correctthecontactof
valve seating.
1. Correct
2. Incorrect
62--11362
3. Incorrect
2--20
Page 47

2.3.1 Cylinder Head And Valves (Continued)
2.3.1.g Correcting Valve and Valve Seat
NOTE
Before correcting the valve seat, make certain
that the valve and valve guide are withinfactory
specifications.
After correctingthe valveseat, besuretocheck
the valve recessing.
(A) Correcting the Valve
1. Correct the valve with a valve grinder.
ab
(1)
a. 0.26 rad.(15°)or
0.52 rad.(30°)
b. 0.79 rad.(45°)or
1.0 rad.(60°)
c. 0.52 rad.(30°)or
0.26 rad.(15°)
(2)
A. Check Contact
B. Correct Seat Width
C Check Contact
1. Valve Seat Width
2. Identical Dimensions
Valve Face Angle
Factory
Specification
IN. 0.79 rad / 45°
EX. 0.79 rad / 45°
(B) Correcting the Valve Seat
1. Slightly correct the valve seat surface with a 1.0 rad.
(60°) (intake valve) or0.79 rad. (45°) (exhaust valve)
seat cutter.
2. Resurface the seat surface with a 0.52 rad. (30°)
valve seat cutter to the Intake valve seat and with a
0.26 rad. (15°) valve seat cutter to the exhaust valve
seat so that the width is close to the specified valve
seat width (2.12 mm, 0.0835 in.).
3. After resurfacing the seat, apply a thin film of valve
lapping compound between the valve and the seat,
then use a valve lapping tool to seat the valve to the
valve seat.
4. Check the valveseatingwithprussianblue.Thevalve
seating should show goodcontact allthewayaround.
Valve Face Angle
Factory
Specification
IN. 0.79 rad / 45°
EX. 0.79 rad / 45°
2.3.1.h Valve Lapping
1. Apply compound evenly to the valve lapping surface.
2. Insert the valve into the valve guide. Lap the valve
onto its seat with a valve lapper or bolt driver.
3. After lapping the valve, wash the compound away
and apply oil, then repeat valve lapping with oil.
4. Apply prussian blue to the contact surface to check
thecontact pattern, if it is less than 70%, repeatvalve
lapping again.
NOTE
When valve lapping is performed, be sure to
check the valve recessing and adjust the valve
clearance after assembling the valve.
2--21
62--11362
Page 48

2.3.1 Cylinder Head And Valves (Continued)
2.3.1.i Free Length and Tilt of Valve Spring
1. MeasurethefreelengthAofthevalvespringwithvernier calipers. If the measurement is less than the allowable limit, replace the spring.
2. Put the valve spring on a surface plate, place a
square on the side of the valve spring.
3. Check to see if the entire side is in contact with the
square. Rotate the spring andmeasure for maximum
tilt B. Check the entire surface of the valve spring for
defects. If any are found, replace it.
Factory
Specification
Free Length A
Allowable Limit
Tilt B Allowable Limit
41.7 to 42.2 mm
1.65 to 1.66 in.
41.2 mm
1.62 in.
1.0 mm
0.039 in.
2.3.1.j Valve Spring Setting Load
1. Place the valve spring on a tester and compress it to
the same length it is actually compressed in the engine.
2. Read the compression load on the gauge.
3. Ifthemeasurementislessthantheallowablelimit,replace it.
118N/35mm
12.0 kgf / 35 mm.
26.5 lbs. / 1.38 in.
100 N / 35 mm
10.2 kgf / 35 mm.
22.5 lbs. / 1.38 in.
Setting Load /
Setting Length
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
2.3.1.k Oil Clearance Between Rocker Arm and
Rocker Arm Shaft
1. Measure the rocker arm shaft O.D. with an outside
micrometer.
2. MeasuretherockerarmI.D.withainsidemicrometer,
then calculate the oil clearance.
3. If the oil clearance exceeds the allowable limit, re-
place the rocker arm then measure the oil clearance
again. If the clearance is still out of specification, replace the rocker arm shaft.
62--11362
Oil Clearance
Rocker Arm/
Shaft
Rocker Arm
Shaft O.D.
Rocker Arm I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.016 to 0.045 mm
0.0063 to 0.0017 in.
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
13.973 to 13.984 mm
0.55012 to 0.55055 in.
14.000 to 14.018 mm
0.55119 to 0.55188 in.
2.3.1.l Push Rod Alignment
1. Place the push rod on V blocks
2. Measure the push rod alignment.
3. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, re-
place the push rod.
Push Rod
Alignment
Allowable
Limit
0.25 mm
0.0098 in.
2--22
Page 49

2.3.1 Cylinder Head And Valves (Continued)
2.3.1.m Oil Clearance Between T appet and Tappet
Guide Bore
1. Measure the tappet O.D. with a micrometer.
2. MeasuretheI.D. of thetappet guide bore with a cylin-
der gauge and calculate the clearance.
3. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, or
the tappet is damaged, replace the tappet.
Oil Clearance
Tappet/
Tappet Guide
Bore
Tappet O.D.
Tappet Guide I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.020 to 0.062 mm
0.00079 to 0.00244 in.
0.07 mm
0.003 in.
23.959 to 23.980 mm
0.94327 to 0.94409 in.
24.000 to 24.021 mm
0.94489 to 0.94570 in.
2.3.2 Timing Gears, Camshaft and Fuel Camshaft
2.3.2.a Timing Gear Backlash
1. Set a dial indicator (lever type) with its tip on the gear
tooth.
2. Move the gear to measure the backlash, holding its
mating gear.
3. If the backlash exceeds theallowable limit, checkthe
oil clearance of the shafts and the gear.
4. If the oil clearance is proper, replace the gear.
Backlash/
Idle Gear/
Crank Gear
Backlash/
Idle Gear/
Cam Gear
Backlash/
Idle Gear/
Injection Pump
Gear
Backlash/
Crank Gear/
Oil Pump Gear
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
0.0415 to 0.1122 mm
0.00163 to 0.00442 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.0415 to 0.1154 mm
0.00163 to 0.00454 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.0415 to 0.1154 mm
0.00163 to 0.00454 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.0415 to 0.1090 mm
0.00163 to 0.00429 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
2.3.2.b Idle Gear Side Clearance
1. Set a dial indicator with its tip on the idle gear.
2. Movethegear front to rear to measurethe side clear-
ance.
3. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, re-
place the idle gear collar.
Idle Gear
Side
Clearance
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
0.12 to 0.48 mm
0.0047 to 0.018 in.
0.9 mm
0.04 in.
2--23
62--11362
Page 50

2.3.2 Timing Gears, Camshaft and Fuel Camshaft (Continued)
2.3.2.c Camshaft Side Clearance
1. Set a dial indicator with its tip on the camshaft.
2. Move the camshaft gear front to rear to measure the
side clearance.
3. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, replace the camshaft stopper.
Camshaft
Side
Clearance
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
0.07 to 0.22 mm
0.0028 to 0.0087 in.
0.30 mm
0.0118 in.
2.3.2.d Idle Gear Shaft and Idle Gear Bushing
Clearance
1. Measure the idle gear shaft O.D. with a micrometer.
2. Measure the idle gear bushing I.D. with an inside micrometer, and calculate the the clearance.
3. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, replace the bushing.
Idle Gear Shaft/
Bushing
Clearance
Idle Gear Shaft
O.D.
Idle Gear Shaft
I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.025 to 0.066 mm
0.00099 to 0.00260 in.
0.1 mm
0.0039 in.
23.959 to 23.980 mm
0.94327 to 0.94410 in.
24.000 to 24.021 mm
0.94488 to 0.94571 in.
2.3.2.e Idle Gear Shaft and Idle Gear Bushing
Clearance
(A) When Removing
1. Pressoutthebushingusing an IdleGear BushingReplacing Tool.
(B) When Installing
1. Clean anewidle gear bushing and theidlegearbore,
and apply engine oil to both.
2. Using the idle gear replacing tool, press in the new
bushing to the specified dimension (see B)
62--11362
2--24
Page 51

2.3.2 Timing Gears, Camshaft and Fuel Camshaft (Continued)
2.3.2.f Camshaft Alignment
1. SupportthecamshaftwithVblocksona surfaceplate
at both end journals.
2. Set adialindicatorwithitstipontheintermediatejournal.
3. Rotate the camshaft and measure for run--out.
4. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, replace the camshaft.
Camshaft
Run--out
Allowable
Limit
0.1 mm
0.0004 in.
2.3.2.g Cam Height
1. Measure the cam lobe at its largest O.D. with an outside micrometer.
2. Ifthemeasurementislessthantheallowablelimit,replace the camshaft.
Cam Height
Intake
Cam Height
Exhaust
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
33.27 mm
1.310 in.
33.22 mm
1.308 in.
33.47 mm
1.318 in.
33.42 mm
1.316 in.
2.3.2.h Camshaft Oil Clearance
1. Measure the camshaft journal O.D. with an outside
micrometer.
2. Measure the cylinder block camshaft bore I.D. with a
cylinder gauge, and calculate the oil clearance.
3. If the oil clearance exceeds the allowable limit, replace the camshaft
Camshaft Journal
Clearance
Camshaft Journal
O.D
.
Camshaft Bore
I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.050 to 0.091 mm
0.0020 to 0.0035 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
39.934 to 39.950 mm
1.5722 to 1.5728 in.
40.000 to 40.025 mm
1.5748 to 1.5757 in.
2--25
62--11362
Page 52

2.3.3 Piston and Connecting Rod
2.3.3.a Piston Pin Bore I.D.
1. Measurethepiston pin boreI.D. inboththehorizontal
and vertical directions with a cylinder gauge.
2. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, replace the piston.
Piston Pin Bore
I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
25.000 to 25.013 mm
0.98426 to 0.98476 in.
25.05 mm
0.9862 in.
2.3.3.b Piston Pin and Bushing Clearance
1. MeasurethepistonpinO.D.withanoutsidemicrometer.
2. Measure the connecting rod small end bushing I.D.
with an inside micrometer.
3. If the clearance exceeds the allowable limit, replace
thebushing.Iftheclearanceisstillexcessive, replace
the piston pin.
Piston Pin to
Small End Bush-
ing Clearance
Piston Pin O.D.
Small End
Bushing I.D
.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.014 to 0.038 mm
0.00055 to 0.00150 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
25.002 to 25.011 mm
0.98433 to 0.98468 in.
25.025 to 25.040 mm
0.98523 to 0.98582 in.
2.3.3.c Replacing Connecting Rod Small End Bu-
shing
(A) When Removing
1. Press out the small end bushing using a Small End
Bushing Replacing Tool.
(B) When Installing
1. Clean a new small end bushing and bore, and apply
engine oil to both.
2. Using the small end bushing replacing tool, press in
the new bushing to the specified dimension (see B).
62--11362
NOTE
Be sure to align the bushing so that the oil hole
in the bushing alignswith the oil port in theconnecting rod.
2--26
Page 53

2.3.3 Piston and Connecting Rod (Continued)
2.3.3.d Piston Ring Gap
1. Insert the piston ring into the lower part ofthecylinder
(the least wornsection). Use the piston to square the
ring in the cylinder.
2. Measure the ring gap with a feeler gauge.
3. If the gap exceeds the allowable limit, replace the
ring.
Top Ring
(Keystone Type)
Second Ring
OilControlRing
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit 1.25 mm / 0.0492 in.
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit 1.25 mm / 0.0492 in.
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit 1.25 mm / 0.0492 in.
0.20 to 0.35 mm
0.0079 to 0.013 in.
0.40 to 0.55 mm
0.016 to 0.021 in.
0.25 to 0.45 mm
0.0099 to 0.017 in.
2.3.3.e Piston Ring to Groove Clearance
1. Clean therings and the ring grooves, and install each
ring in its groove.
2. Measure the clearance between the ring and its
groove with a feeler gauge (with the exception of the
top ring, Keystone Type, which cannot be accurately
measured with a feeler gauge).
3. If the clearance exceeds the allowable limit, replace
the ring.
4. If the clearance still exceeds the allowable limit after
replacing the ring, replace the piston.
Second Ring
OilControlRing
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit 0.20 mm / 0.0079 in.
Factory
Specification
Allowable Limit 0.15 mm / 0.0059 in.
0.093 to .128 mm
0.00367 to 0.00503 in.
0.020 to 0.060 mm
0.00079 to 0.0023 in.
2.3.3.f Connecting Rod Alignment
NOTE
Since the I.D. of the connecting rod small end
bushingisthebasisofthisprocedure,checkthe
bushing for wear before proceeding.
1. Install the piston pin into the connecting rod.
2. Install the connecting rod on theconnecting rodalignment tool.
3. Put a gauge over the piston pin and move it against
thefaceplate.
4. If the gauge does not fit squarely against the face
plate, measure the space between the pin of the
gauge and the face plate.
5. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit, replace the connecting rod.
Connecting Rod
Alignment
Allowable Limit 0.05 mm / 0.002 in.
2--27
62--11362
Page 54

2.3.4 Crankshaft
2.3.4.a Crankshaft End Clearance
1. Pushontheendofthecrankshafttoseatittowardthe
flywheel end of the engine block.
2. Attach, thenzeroadialindicatorontheforwardendof
the crankshaft.
3. Measure the end play by pulling the crankshaft forward.
4. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit replace the thrustwashers.
Factory
A
Crankshaft Side
Clearance
B
Specification
Allowable
Limit
0.15 to 0.31 mm
0.0059 to 0.012 in.
0.5 mm
0.02 in.
(Reference)
Oversize dimensions of crankshaft journal.
Oversize 0.2mm / 0.008 in. 0.4mm / 0.02 in.
Dimension A
Dimension B
Dimension C
The crankshaft journal must be fine--finished to higher than
54.5 to 54.7 mm
2.146 to 2.153 in.
26.20 to 26.25 mm
1.032 to 1.033 in.
2.8 to 3.2 mm radius
0.11 to 0.12 in.
radius
0.4--S.
54.6 to 54.8 mm
2.150 to 2.157 in.
26.40 to 26.45 mm
1.040 to 1.041 in.
2.8 to 3.2 mm radius
0.11 to 0.12 in.
radius
2.3.4.b Crankshaft Alignment
1. Support the crankshaft with V blocks on a surface
plate at both endjournals. Set a dial indicator with its
tip on the intermediate journal, perpendicular to the
journal.
2. Rotate the crankshaft on the V blocks and get the
misalignment (half of the measurement).
3. If the misalignment exceeds the allowable limit, replace the crankshaft.
62--11362
2--28
Crankshaft
Alignment
Allowable
Limit
0.02 mm
0.0008 in.
Page 55

2.3.4 Crankshaft (Continued)
2.3.4.c Crankpin to Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance
1. Clean the crankpin and the connecting rod bearing.
2. Put a strip of plastigage on the center of the crankpin
in each direction as shown in the figure.
3. Install the connecting rod cap and tighten the bolts to
the specification. (Refer to 2.2.6.a)
4. Remove the cap again
5. Measuretheamount of the flatteningwiththescaleto
get the clearance.
6. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit re-
place the connecting rod bearing.
7. If the allowable limit is not attainable with a standard
size bearing, install an undersize bearingbyreferring
to the table below.
Crankpin/
Connecting Rod
Clearance
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
0.025 to 0.087 mm
0.00099 to 0.0034 in.
0.2 mm
0.0079 in.
Crankpin O.D.
Connecting Rod
Bearing I.D.
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
46.959 to 46.975 mm
1.8488 to 1.8494 in.
47.000 to 47.046 mm
1.8504 to 1.8522 in.
(Reference)
Undersize dimensions of crankpin journal.
Undersize 0.2mm / 0.008 in. 0.4mm / 0.02 in.
Dimension A
Dimension B
Dimension C
The crankshaft journal must be fine--finished to higher than
0.8--S.
3.3to3.7mm
0.13 to 0.14 in.
1.0 to 1.5 mm radius
0.040 to 0.059 in.
radius
46.759 to 46.775
mm
1.8409 to 1.8415 in.
radius
3.3to3.7mm
0.13 to 0.14 in.
1.0 to 1.5 mm radius
0.040 to 0.059 in.
radius
46.559 to 46.575
mm
1.8331 to 1.8336 in.
radius
*Holestobede---burred and edges rounded with 1.0 to 1.5
mm
(0.040 to 0.059 in. relief.
2--29
62--11362
Page 56

2.3.4 Crankshaft (Continued)
g
2.3.4.d Crankshaft Journal to Crankshaft Bearing
#1 Clearance
1. Measure the O.D. of the crankshaft journal with an
outside micrometer.
2. Measure the I.D. of crankshaft bearing #1 with an in-
side micrometer and calculate clearance.
3. If the clearance exceeds the allowable limit, replace
crankshaft bearing #1.
4. If the allowable limit is not attainable with a standard
size bearing, install an undersize bearingbyreferring
to the table below.
Crankshaft
Journal to #1
Bearing
Clearance
Crankshaft
Journal O.D.
Crankshaft
Bearing Bearing
I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.040 to 0.118 mm
0.00158 to 0.00464 in.
0.2 mm
0.0079 in.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
2.3591 to 2.3598 in.
59.980 to 60.039 mm
2.3615 to 2.3637 in.
(Reference) Undersize dimensions of crankshaft
journal.
Oversize 0.2mm / 0.0008 in. 0.4mm / 0.0016 in.
2.8 to 3.2 mm radius
Dimension A
Dimension B
Dimension C
The crankshaft journal must be fine--finished to higher than
0.4--S.
*Holes to be de--burred and edges rounded with 1.0 to 1.5 mm
(0.040 0.059 in.) relief.
0.11 to 0.12 in.
radius
1.0 to 1.5 mm radius
0.040 to 0.059 in.
radius
59.721 to 59.740
mm
2.3513 to 2.3519 in.
2.8 to 3.2 mm radius
0.11 to 0.12 in.
radius
1.0 to 1.5 mm radius
0.040 to 0.059 in.
radius
59.521 to 59.540
mm
2.3434 to 2.3440 in.
1. Seam
2. Crankshaft Bearin
62--11362
#1
3. Cylinder Block
A Dimension
2.3.4.e Replacing Crankshaft Bearing #1
(A) When Removing
1. Pressoutthecrankshaftbearing#1(2)usingacrank-
shaft bearing (1) replacing tool.
(B) When Installing
1. Clean anewcrankshaftbearing#1(2)andcrankshaft
journal bore, and apply engine oil to both.
2. Using the crankshaft bearing(1)replacing tool, press
in the new bearing #1 (2) so that its seam (1) directs
toward the exhaust manifold side.
NOTE
Be sure to align the bushing so that the oil hole
in the bushing alignswith the oil port in theconnecting rod.
2--30
Dimension A
Factory
Specification
4.2to4.5mm
0.166 to 0.177 in.
Page 57

2.3.4 Crankshaft (Continued)
2.3.4.f Crankshaft Journal to Crankshaft Bearing
#2 Clearance
1. Put a strip of plastigage on the center of the crank-
shaft journal.
2. Install the bearing case and tighten the bolts to spe-
cification.
3. Remove the bearing case again.
4. Measuretheamount of the flatteningwiththescaleto
get the clearance.
5. If the measurement exceeds the allowable limit re-
place crankshaft bearing #2.
6. If the allowable limit is not attainable with a standard
size bearing, install an undersize bearingbyreferring
to the table below.
NOTE
Be sure not to move the crankshaft while the
bearing bolts are tightened.
Crankshaft
Journal to #2
Bearing
Clearance
Crankshaft
Journal O.D
Crankshaft
Bearing Bearing
.
I.D.
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
0.040 to 0.104 mm
0.00158 to 0.00409 in.
0.2 mm
0.0079 in.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
2.3591 to 2.3598 in.
59.980 to 60.025 mm
2.3615 to 2.3631 in.
(Reference)
Undersize dimensions of crankshaft journal.
Oversize 0.2mm / 0.008 in. 0.4mm / 0.016 in.
2.8 to 3.2 mm radius
Dimension A
Dimension B
Dimension C
The crankshaft journal must be fine--finished to higher than
0.4--S.
*Holes to be de--burred and edges rounded with 1.0 to 1.5 mm
(0.040 0.059 in.) relief.
0.11 to 0.12 in.
radius
1.0 to 1.5 mm radius
0.040 to 0.059 in.
radius
59.721 to 59.740
mm
2.3513 to 2.3519 in.
2.8 to 3.2 mm radius
0.11 to 0.12 in.
radius
1.0 to 1.5 mm radius
0.040 to 0.059 in.
radius
59.521 to 59.540
mm
2.3433 to 2.3440 in.
2--31
62--11362
Page 58

2.3.4 Crankshaft (Continued)
2.3.4.g Replacing Crankshaft Sleeve
1. Remove the crankshaft sleeve (3) using a special-use puller set.
2. Set the sleeve guide (2) to the crankshaft (5).
3. Set the stopper (1) to the crankshaft (5) as shown in
the figure.
4. Heat thenewsleevetoatemperaturebetween150to
200°C(302to392°F),andfixthesleeveonthecrankshaft (5) as shown in the figure.
5. Press fit the sleeve using the auxiliary socket for
pushing (4).
NOTE
Install the sleeve with the largest chamfered
surface facing outward.
1. Stopper
2. Sleeve Guide
3. Crankshaft Sleeve
4. Auxiliary Socket For
Pushing
5. Crankshaft
62--11362
2--32
Page 59

2.3.5 Cylinder
2.3.5.a Cylinder Wear
1. Measure the I.D. of the cylinder at the six positions
(seefigure with a cylinder gauge to find the maximum
and minimum I.D.’s.
2. Determine the difference (maximum wear) between
the maximum and minimum I.D.’s.
3. Ifthe wearexceedstheallowablelimit,boreandhone
to the oversize dimension. (refer to Correcting
Cylinder)
4. Visually check the cylinder wall for scratches. If deep
scratches are found, the cylinder walls should be
bored. (refer to Correcting Cylinder)
a. Top
b. Middle
c. Bottom (skirt)
a. Right--angled to
Piston Pin
b. Piston Pin Direction
Cylinder I.D.
Maximum Wear
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
83.000 to 83.022 mm
3.2678 to 3.2685 in.
83.170 mm
3.2744 in.
2.3.5.b Correcting Cylinder (Oversize +0.25 mm)
1. When the cylinder isworn beyond the allowable limit,
bore and hone it to the specified dimension.
Cylinder I.D.
Maximum Wear
Finishing
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Hone to 2.2 to 3.0 mm μRmax.
(0.00087 to 0.00118 in. μRmax.)
83.250 to 83.272 mm
3.2776 to 3.2784 in.
83.420 mm
3.2843 in.
1. Cylinder I.D.
(before correction)
2. Oversize Cylinder I.D.
2. Replace the piston and piston rings with oversize
(+0.25 mm) ones.
2--33
62--11362
Page 60

SECTION 3
LUBRICA TING SYSTEM
3.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING 3.1.1 Engine Oil Pressure
1. Removetheengineoilpressure switch, and installan
oil pressure gauge.
2. Start the engine. After warming up, read the oil pressure at idling and at rated speeds.
3. If the oil pressure is less than the allowable limit,
check the following:
Engine oil sufficient
Oil pump defective
Oil strainer clogged
Oil filter cartridge clogged
Oil gallery clogged
Excessive oil clearance
Relief valve stuck
Factory
Specification
At Idle Speed
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
At Rated Speed
Allowable
Limit
(When Reassembling)
After checking the engine oil pressure, tighten the
engine oil pressure switch to the specified torque.
More than 98 kPa
1.0 kgf/cm
0.5 kgf/cm
300 to 440 kPa
3.0 to 4.5 kgf/cm
43 to 64 psi
250 kPa
2.5 kgf/cm
2
14 psi
50 kPa
2
7psi
2
36 psi
2
3--1
62--11362
Page 61

3.2 SERVICING
3.2.1 Rotor Lobe Clearance
1. Measuretheclearance between lobes of the inner rotor and the outer rotor with a feeler gauge.
2. Measure the clearance between the outer rotor and
the pump body with a feeler gauge.
3. If the clearance exceeds the factory specifications,
replace the oil pump rotor assembly.
Inner/Outer
Rotor Clearance
Outer Rotor/
Pump Body
Clearance
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
0.03 to 0.14 mm
0.0012 to 0.0055 in.
0.2 mm
0.008 in.
0.11 to 0.19 mm
0.0044 to 0.0074 in.
0.25 mm
0.0098 in.
3.2.2 Rotor to Cover Clearance
1. Put a strip of plastigage onto the rotor face with
grease.
2. Install the cover and tighten the bolts.
3. Remove the cover carefully, and read theplastigage.
4. If the clearance exceeds the factory specifications,
replace the oil pump rotor assembly.
Rotor/Cover
Clearance
Factory
Specification
Allowable
Limit
0.105 to 0.150 mm
0.00414 to 0.00590 in.
0.20 mm
0.008 in.
62--11362
3--2
Page 62

4.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
WARNING
Beware of moving V--belt and belt driven
components
4.1.1 Notched V--Belt Service
NOTE
A frayed, cracked or worn V--belt must be replaced. After installinganewbelt,itisadvisable
to check the adjustment after running the unit
for three orfour hours. This will allow for the initial stretch, which is common on new belts.
Once thisinitial stretchhastakenplace,thebelt
should be checked at regular intervals.
SECTION 4
COOLING SYSTEM
2. Replace the Poly--V--Belt by positioning the belt on
the water pump pulley,and while rotating theengine
(as in step 1),use a flat, bluntobject to guide thebelt
onto the crank pulley. Be careful not to damage
grooves on the pulley or belt.
4.1.2 Fan Belt Damage and Wear
1. Check the fan belt for damage.
2. If the belt is damage in any way, replace it.
(A)
To replace or adjust the notched V--belt, do the
following:
a. Replacing the V--Belt
1. Loosen the idler pivot bolt.
2. Replace the belt and adjust tension in accordance
with the following steps.
b. Adjusting Tension
1. Measure the deflection (A), by depressing the belt
halfway between the fan drive pulley and alternator
pulley at the specified force (Refer to1.7.3).
2. Usehandforceonlyontheidlerpulleytotightenbelt.
Do not use a pry bar or excessive force as it may
cause damage to the engine.
Use of a belt tension gauge (Carrier Part #
07--00203--00) or a belt tension tester (Carrier Part #
07--00253--00) is advised.
3. When belt is at correct tension, tighten pivot bolt.
4.1.1a Poly V--Belt Service
a. Replacing the Poly--V--Belt
1. Apply the proper size socket to the crank pulley nut,
then slowly rotate the crank. At the same time, usea
flat, blunt object to guide the belt offthe crank pulley
towards radiator. Be careful not to damage grooves
on the pulley .
(B)
A. Good B. Bad
3. Check if thebeltiswornandsunk inthepulleygroove.
4. If the fan belt is worn and deeply sunk in the pulley
groove, replace it.
A. Good B. Bad
4.1.3 Checking Coolant Level
WARNING
When removing the radiator cap, wait at
least ten minutes after the engine has
stopped and cooled down. Otherwise, hot
water may discharge from the radiator,
scalding anyone nearby.
1. Remove the radiator cap and check to see that the
coolant level is just below the port.
With the recovery tank: Check to see that thecoolant
level lies between FULL and LOW.
4--1
62--11362
Page 63

FULL
LOW
2. Ifthe coolant level istoolow,checkthe reason for the
lost coolant.
a. If coolant loss is due to evaporation, add only clean
soft water.
b. If coolant loss is due to a leak, repair the leak, then
add a coolant mixture of the same type and specificationthatisinthesystem. If thecoolantbrandcannot be identified, drain out all of the remaining coolant and refill with a totally new mix.
4.1.5 Radiator
1. Fill the radiator with water.
2. Attach the pressuretester to the radiator.
3. Apply pressure and look for leaks.
4. Repair/replaceasnecessarytoassurethat thespecified pressure will hold.
NOTE
Whenaddingcoolanttothe system,airmustbe
ventedfromtheenginecoolantpassagesbyjiggling the upper and lower radiator hoses.
Besureto close the radiator capsecurely.Ifthe
cap is loose or improperly closed, coolant may
leak out and the engine could overheat.
Do not use an antifreeze and scale inhibitor at
thesametime.
Nevermix different types orbrands of coolants.
4.1.4 Radiator Cap
Radiator Leakage
Test
Factory
Specification
157 kPa
1.6 kgf/cm
23 psi
2
4.1.6 Thermostat Opening Temperature
1. Suspend the thermostat in water by a string with one
end of the string inserted between the valve and its
seat.
2. Immerse the thermostat in water and raise the temperature of the water gradually.
3. With a thermometer, read the temperature of the
water when the valve opens and leaves the string.
1. Attach the radiator cap to a pressure tester.
2. Apply pressure andobserve the timefor the pressure
to fall.
3. If the measurement is less than the factory specification, replace the cap.
More than 10 seconds
Pressure Falling
Time
Factory
Specification
for pressure fall from
88 to to 59kPa
0.9 to 0.6 kgf/cm
13to9psi
2
62--11362
4. Continue heating the water, read the temperature of
the water when the valve has opened approximately
6mm (0.236 in).
5. Ifthe measurement is not withinthefactory specifications, replace the thermostat.
Thermostat
Opening
Temperature
Thermostat
Full Open
Temperature
Factory
Specification
Factory
Specification
80.5 to 83.5.5°C
176.9 to 182.3
95°C
203
°F
4--2
°F
Page 64

4.2 SERVICING
4.2.1 Thermostat Assembly
4.2.2 Water Pump Assembly
1. Thermostat Cover Bolt
2. Thermostat Cover
3. Thermostat Cover Gasket
4. Thermostat Assembly
5. Thermostat Housing
1. Removethethermostatcovermountingbolts (1), and
remove the thermostat cover (2).
2. Remove the thermostat assembly (4).
(When Reassembling)
Applyaliquidgasketonlyatthethermostat cover side of
the thermostat cover gasket (3).
1. Water Pump Flange
2. Water Pump Shaft
3 Water Pump Body
4. Water Pump Gasket
5. Mechanical Seal
6. Impeller
1. Remove the fan belt.
2. Remove the water pump pulley.
3. Remove the water pump from the gear case assembly.
4. Remove the water pump flange (1).
5. Press out the water pump shaft (2) with the impeller
(6) on it.
6. Remove the impeller from the water pump shaft.
7. Remove the mechanical seal.
(When Reassembling)
Replace the mechanical seal with a new one.
Apply a liquid gasket to both sides of the gasket (4).
4--3
62--11362
Page 65

5.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
SECTION 5
FUEL SYSTEM
5.1.1 Injection Timing
1. Remove the fuel speed solenoid.
2. Remove the injection pipes and nozzle.
3. Move the speed control lever to the maximum speed
position.
NOTE
Turn the flywheel with a screwdriver.
4. Turn the flywheel counterclockwise (facing the flywheel) until the fuel fills up the hole of the delivery
valve holder for #1 cylinder.
5. Turn the flywheel further and stop turning when the
fuel begins to flow over.
6. Open the view port on the flywheel bell housing and
read the number on the flywheel. The number indicated is the timing value for theengine. (The flywheel
hasamark’1TC’ andmarks every 5° of engine timing
to 25° total).
0.0568 to 0.0829 rad.
3.25
° to 4.75°
B.T.D.C.
Injection Timing
Factory
Specification
NOTE
Injection timing adjustment is accomplished by
adding or removing shims under the injection
pump.
Thetimingadvancesbyremovingone shimand
retards timing by adding the same shim.
Theaddition or removal of 0.05 mm (0.0020in.)
ofshim,changestheinjectiontimingbyapproximately 0.009 rad. (0.5°).
Sealant should be applied to both sides of soft
metal gasket shims except for the .0175mm
shim. A .0175mm shim should have sealant applied to one side only.
When replacing the injection pump be sure to
use the same number and size of new gasket
shims.
5.1.2 Shim Identification
Shims are available in thicknesses of 0.20 mm,
0.25 mm, 0.30 mm, and 0.35mm. Combine
shims for adjustments.
1. Delivery Valve Holder
2. Timing Mark
3. 2--Holes: 0.20 mm shim
4. 1--Hole: 0.25 mm shim
5. 0--Holes: 0.30 mm shim
6. 3--Holes: 0.35 mm shim
7. 2--Holes: 0.175 mm shim
62--113625--1
Page 66

5.1 CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
1. InjectionPump Pressure
Tester
2. InjectionNozzle
3. Protective Cover
5.1.3 Pump Pressure Test
1. Remove the engine fuel speed solenoid.
2. Remove the injection pipes and nozzle.
3. Connect a pressure tester to the fuel injection pump.
4. Connect theinjectionnozzle(2)jetted with theproper
injectionpressuretotheinjectionpumppressuretester (1).
5. Using the starter, rotate the crankshaft until the fuel
pressure is built up.
6. If the pressure does not build up, replace the pump
element with a new one and test again.
Fuel Pump
Pressure Test
Factory
Specification
18.63 MPa
190 kgf/cm
2702 psi
2
5.1.4 Delivery Valve Fuel Seal
1. Remove the engine fuel speed solenoid.
2. Remove the injection pipes and nozzle.
3. Connect a pressure tester to the fuel injection pump.
4. Connect theinjectionnozzle(2)jetted with theproper
injectionpressuretotheinjectionpumppressuretester (1).
5. Using the starter, rotate the crankshaft until the fuel
pressure is built up.
6. Release the pressure in the delivery chamber by rotating the crankshaft to bottom dead center. (turn the
crankshaft 1.57 rad. (90°) clockwise from fuel timing
set point)
7. If the pressure drop for 5 seconds exceeds the allowable limit, replace the delivery valve or pump assembly.
10 seconds
Factory
Specification
Delivery Valve
Fuel Seal
Allowable
Limit
18.63 to 17.65 MPa
190 to 180 kgf/cm
2702 to 2560 psi
5 seconds
18.63 to 17.65 MPa
190 to 180 kgf/cm
2702 to 2560 psi
2
2
62--11362 5--2
Page 67

5.2 INJECTION NOZZLE
WARNING
Checktheinjectionnozzleonly afterconfirming that nobody is near the spray. If the spray fromthe
nozzle contacts the human body, cells may be destroyed and blood poisoning may result.
5.2.1 Nozzle Injection Pressure
1. Set the injection nozzle in a nozzle tester.
2. Slowly move the tester handle to measure the pressure at which fuel begins jetting out from the nozzle.
3. If the measurement is not within factory specifications, replace the nozzle assembly.
(a) GOOD (b)BAD
Fuel Injection
Pressure
1st Stage
Factory
Specification
18.64 to 20.1 MPa
190 to 205 kgt/cm
2703 to 2915 psi
2
5.2.2 Nozzle Spraying Condition
1. Set the injection nozzle in a nozzle tester and check
the nozzle spraying condition.
2. If the spraying condition is defective, replace the
injection nozzle assembly.
5.2.3 Valve Seat Tightness
1. Set the injection nozzle in a nozzle tester.
2. Raise the fuel pressure, and maintain 16.67 MPa
(170 kgf/cm
2
, 2418 psi) for 10 seconds.
3. If any fuel leak is found, replace the injection nozzle
assembly.
No fuel leak at
16.67MPa
170 kgf/cm
2418 psi
2
Valve Seat Tight-
ness
Factory
Specification
62--113625--3
Page 68

6.1 STARTER TEST
1. C Terminal
2. Positive Terminal
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
3. Negative Terminal
SECTION 6
6.1.1 Motor Test
1. Disconnect the cable from the negative terminal on
the battery.
2. Disconnectthecablefromthepositiveterminal onthe
battery.
3. Disconnect the leads from the starter B terminal.
4. Remove the starter from the engine.
5. Connect a jumperleadfromthestartersolenoidCterminal (1) to the positive battery terminal.
6. Connect a jumper lead momentarily between the
starter motor housing and the negative post on the
battery.
7. Ifthestarterdoesnotrun,repairorreplacethestarter.
Tightening Torque
WARNING
Secure the starterto prevent it from moving
when power is applied to it.
B
Terminal Nut
8.8to11.8N.m
0.9to1.2kgf
6.5to8.7ft--lbs.
.
m
1. S Terminal
2. Positive Terminal
3. Negative Terminal
6.1.2 Magnetic Switch Test
NOTE
This test should only be carried out for a 3 to 5
second time period and not longer.
1. Disconnect the cable from the negative terminal on
the battery.
2. Disconnectthecablefromthepositiveterminal onthe
battery.
3. Disconnect the the positive cable and leads from the
starter B terminal.
4. Remove the starter from the engine.
5. Connect a jumper lead from the starter S terminal(1)
to the positive battery post (2).
6. Momentarily, connect a jumper lead between the
starter housing and negative battery terminal (3).
7. If the pinion gear nose does not pop out, replace the
starter.
NOTE
TheBterminal is the terminal that connectsthe
cable from the battery to the starter.
TheSterminal is theterminal that connects the
cable from the starter switch to the magnetic
switch.
6--1
62--11362
Page 69

6.2 FUEL SPEED SOLENOID
6.2.1 Solenoid Test
WARNING
The solenoid can become very warm to the
touch when energized for any length in
time.
1. Disconnect the plug from the solenoid connector (2).
2. Remove the solenoid (1) from the engine.
3. Supply power (12VDC) to the solenoid thruterminals
(3) and (4).
4. Ifthe rod inthesolenoid(1) moves smoothly (approximately 0.6”), the solenoid is normal, if the rod does
not move, or moves only a fraction of that distance,
replace it.
1. Fuel Speed Solenoid
2. Solenoid Connector
3. Terminal 2 (--)
4. Terminal 1 (+)
A. Actuator Rod (Power Off)
B. Actuator Rod (12VDC
applied)
62--11362
6--2
Page 70

6.3 INTAKE AIR HEATER
6.3.1 Intake Air Heater Test
1. Disconnect the lead from the heater terminal (1).
2. Measure the resistance between the heater positive
terminal (1) and the heater body (2).
3. If the resistance is infinity or significantly different
than the specification, replace the heater.
Intake Air Heater
Resistance
1. Positive Terminal 2. Heater Body
Factory
Specification
0.3 ohms
6--3
62--11362
Page 71

INDEX
B
Battery, iv
bearing case, 2--15, 2--17
C
camshaft, 2--10, 2--24, 2--25
compression pressure, 2--1
connecting rod, 2--14, 2--27
coolant, iv, 2--2
coolant level, 1--13, 4--1
cooling system, 4--1
crankshaft, 2--28
crankshaft oil slinger, 2--10
cylinder, 2--33
cylinder head, 2--3, 2--5, 2--18
D
I
Identification, 1--1
idle gear, 2--10
injection nozzle, 5--3
injection timing, 5--1
intake air heater, 6--3
L
lubricating system, 3--1
N
Notched V--Belt, 4--1
O
dye/penetrant, 2--18
E
electrical system, 6--1
engine oil, 1--14, 2--2
F
fan drive pulley, 2--9
flywheel, 2--15
fuel injection, 1--15, 2--3, 2--6
fuel speed solenoid, 6--2
fuel system, 5--1
fuel system -- bleeding , 1--14
G
gear case, 2--9
governor , 2--7, 2--8
oil level, 1--13
oil pan, 2--12
oil pressure, 3--1
oil pump, 2--11, 3--2
P
piston, 2--13, 2--26, 2--27
piston ring, 2--14
Poly V--belt, 4--1
push rod, 2--22
R
radiator, 4--2
radiator cap, 4--2
rocker arm, 2--22
Index--1
62--11362
Page 72

INDEX
S
Safety Precautions, iv
specifications, 1--2
speed control plate, 2--7, 2--8
starter motor, 6--1
T
tappets, 2--5, 2--23
thermostat, 4--2
timing gear, 2--23
Torque Specification, 1--4
V
V--belt, 1--14
valve clearance, 1--15
valve guide, 2--20
valve seat, 2--20
valve spring, 2--22
valves, 2--5, 2--19, 2--21
W
water pump, 4--3
62--11362
Index--2
Page 73

North America
Carrier Transicold
700 Olympic Drive
Athens, GA 30601 USA
Tel: 1--706--357--7223
Fax: 1--706--355--5435
Mexico and
Central America
Ejercito Nacional No. 418
Piso 9, T orreYumal
Col. Chapultepec Morales
11570 Mexico, D.F.
Tel: (5255) 9126.0300
Fax: (5255) 9126.0373
A member of the United Technologies Corporation family. Stock symbol UTX
©2008 Carrier Corporation D Printed in U. S. A. 0508
Carrier Transicold Division,
Carrier Corporation
Truck/Trailer Products Group
P.O. Box 4805
Syracuse, N.Y. 13221 U.S.A.
www.carrier.transicold.com
 Loading...
Loading...