Page 1
Visit www.carrier.com
Installation, Start-up,
and Operating Instructions
NOTE: Read the entire instruction manual before starting the
installation.
This symbol → indicates a change since last issue.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS.....................................................1
INTRODUCTION..........................................................................2
LOCATION....................................................................................3
General......................................................................................3
Location Relative to Cooling Equipment ................................3
INSTALLATION...........................................................................3
Air for Combustion and Ventilation........................................3
General......................................................................................4
Unconfined Space.....................................................................4
Confined Space.........................................................................4
All Air from Inside the Structure .......................................4
All Air from Outside of Structure......................................5
Duct Work Recommendations............................................5
Venting.................................................................................5
Oil Burner............................................................................6
Oil Connections...................................................................6
Barometric Draft Control....................................................6
Electrical Connections.........................................................6
Horizontal or Downflow Installation..................................7
Filters ...................................................................................7
START-UP, ADJUSTMENT, AND SAFETY CHECKOUT......7
Operational Checkout ...............................................................7
Combustion Check....................................................................7
Fan Adjustment Check ...........................................................10
Limit Control Check...............................................................11
For Year-Round Air Conditioning.........................................11
Heating....................................................................................11
Cooling....................................................................................11
Constant Blower Switch.........................................................11
MAINTENANCE.........................................................................11
General....................................................................................11
Oil Burner ...............................................................................11
Heat Exchanger and Flue Pipe...............................................11
Blower Removal .....................................................................12
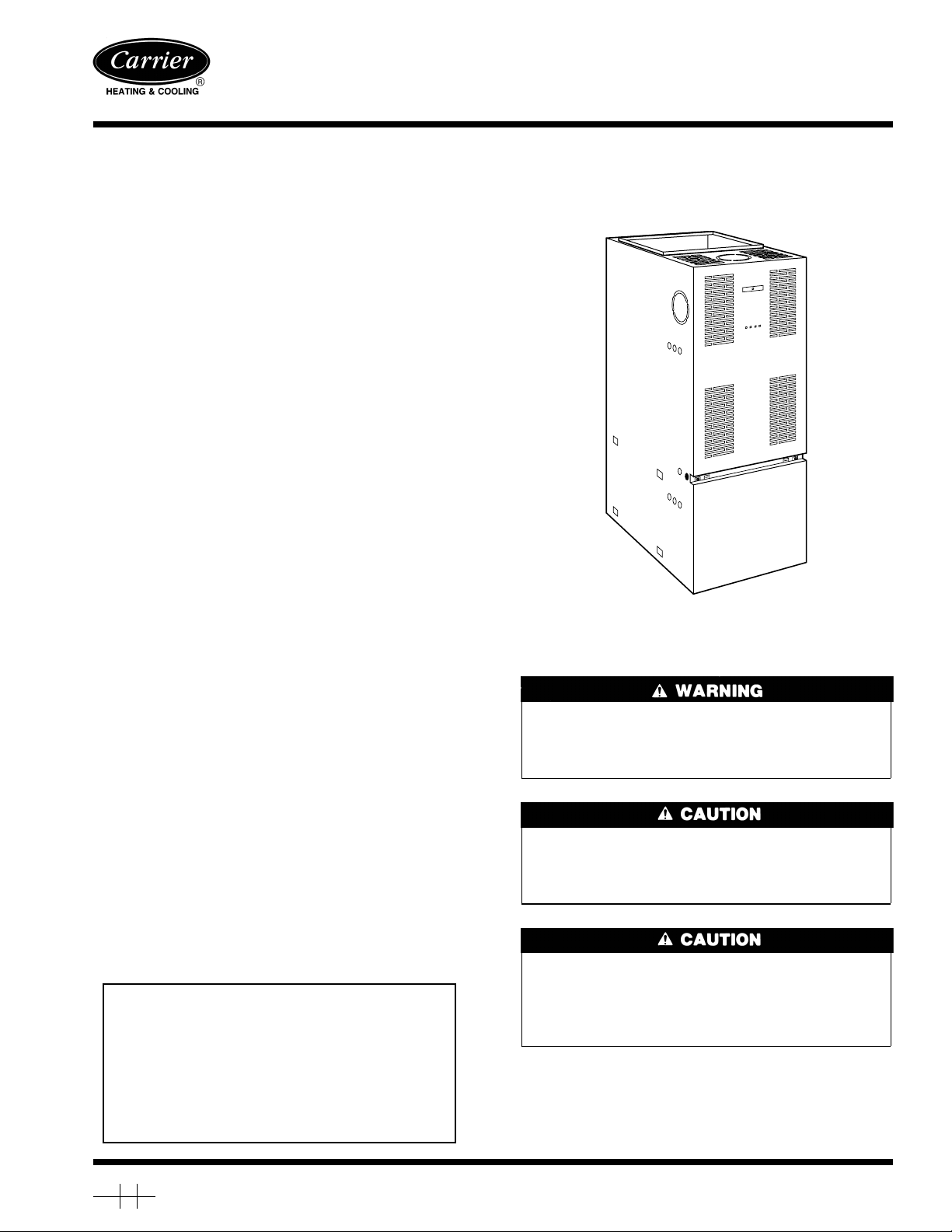
58CMA
Series 130
Multipoise Oil Furnace
A97247
Fig. 1—58CMA Multipoise Oil Furnace
For use with grade 1 or 2 Fuel Oil. Do not use Gasoline,
Crankcase Oil, or any Oil containing Gasoline! Failure to
follow this warning could lead to sooting, fire, explosion,
and/or severe bodily harm.
Never burn garbage or paper in the heating system and never
leave rags, paper, or any flammable items around the unit.
Failure to follow this caution will result in minor unit or
property damage.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
FOR YOUR SAFETY
DO NOT STORE OR USE GASOLINE OR OTHER
FLAMMABLE VAPORS AND LIQUIDS IN THE
VICINITY OF THIS OR ANY OTHER APPLIANCE.
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO START THE BURNER
WHEN EXCESS OIL HAS ACCUMULATED, WHEN
THE FURNACE IS FULL OF VAPOR, OR WHEN
THE COMBUSTION CHAMBER IS VERY HOT.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 4
Tab 6a 8a
PC 101 Catalog No. 535–80076 Printed in U.S.A. Form 58CMA-4SI Pg 1 9-03 Replaces: 58CMA-3SI
These instructions are intended to be used by qualified
personnel who have been trained in installing this type of
furnace. Installation of this furnace by an unqualified person
may lead to equipment damage and/or a hazardous condition
which may lead to bodily harm.
All local and national code requirements governing installation of
oil burning equipment, wiring, and flue connections must be
followed. Some of the codes (issued by the Canadian Standards
Association, the National Fire Protection Agency, and/or the
American National Standards Institute) that may be applicable are:
Page 2
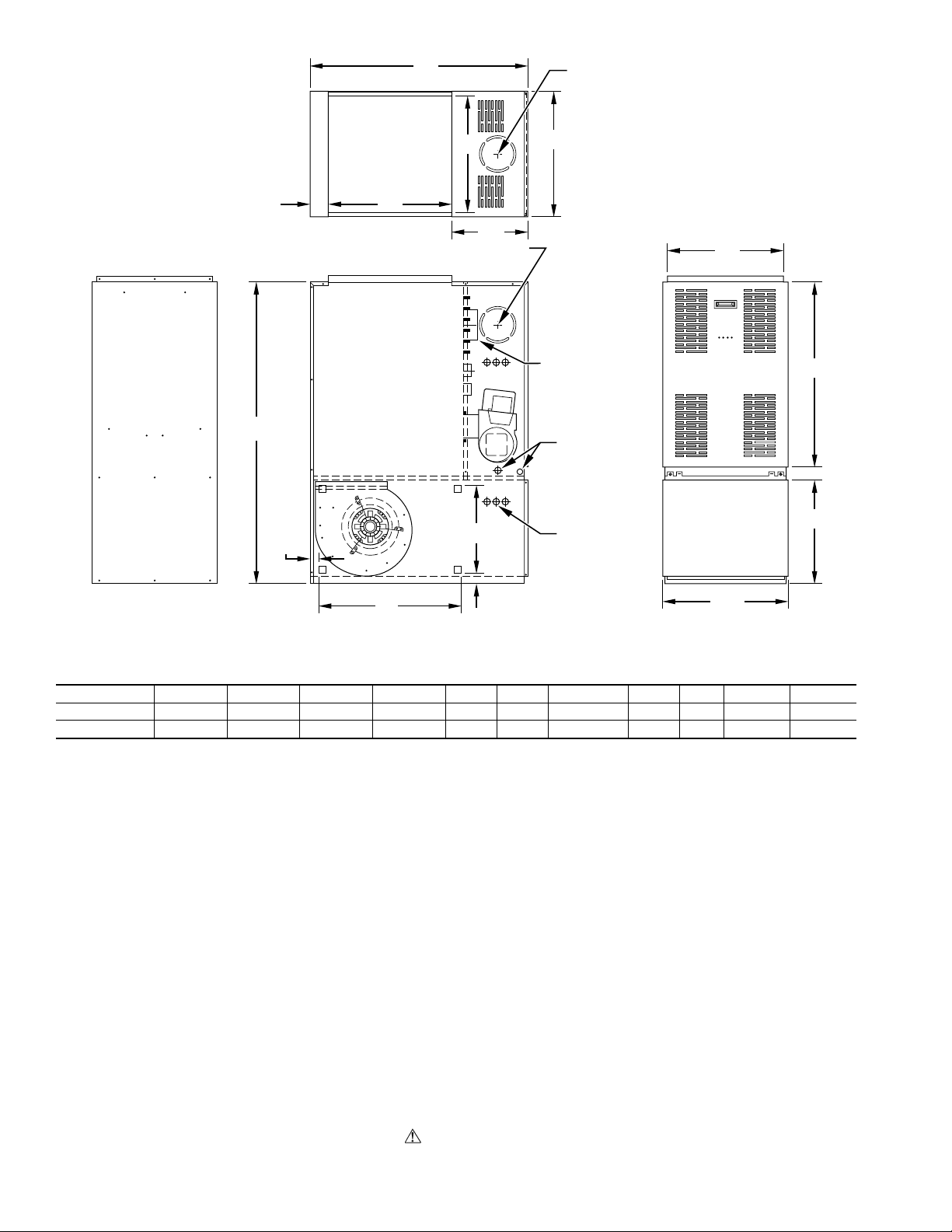
A
TOP KNOCK-OUT
FOR J DIAM VENT
19″
3″
E
20″
G
KNOCK-OUT BOTH SIDES
FOR J DIAM VENT
VENT CONN
B
OIL INLET
(BOTH SIDES)
19″
PULL
C
2″
D
L
H
ELECTRICAL
CONNECTIONS
(BOTH SIDES)
.88 DIAM TYP
F
20″
K
A98037
Dimensions (IN.)
UNIT SIZE ABCDEFGHJKL
105-12 35 48-3/4 30-1/4 16-5/8 20 22 12 14 5 1-1/2 1-3/4
120-20 39-1/2 53 32-1/4 18-3/4 24 28 12-9/32 16 6 1-5/8 1-1/2
Fig. 2—Dimensional Drawing
Understand the signal words DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION
ANSI/NFPA 31:
INSTALLATION OF OIL
BURNING EQUIPMENT
and NOTE. These words are used with the safety-alert symbol.
DANGER identifies the most serious hazards which will result in
severe personal injury or death. WARNING signifies a hazard
ANSI/NFPA 211:
CHIMNEYS, FIREPLACES, VENTS,
AND SOLID FUEL BURNING APPLIANCES
which could result in personal injury or death. CAUTION is used
to identify unsafe practices which would result in minor personal
injury or product and property damage. NOTE is used to highlight
ANSI/NFPA 90B:
ANSI/NFPA 70: NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE
CSA B139:
WARM AIR HEATING AND AIR
CONDITIONING SYSTEMS
INSTALLATION CODE FOR
OIL BURNING EQUIPMENT
suggestions which will result in enhanced installation, reliability,
or operation.
INTRODUCTION
The model 58CMA Furnaces are available in 2 sizes. Each size
→
unit is capable of 3 heat/airflow combinations by a simple nozzle
change. Unit 105-12 covers inputs of 70,000, 91,000, and 105,000
Btuh, and unit 120-20 covers inputs of 119,000, 140,000 and
CAS C22.1: CANADIAN ELECTRICAL CODE
Only the latest issues of these codes should be used, and are
available from either The National Fire Protection Agency, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269 or The Canadian Standards
Association, 178 Rexdale Blvd., Rexdale, Ontario M9W 1R3
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert symbol
When you see this symbol on the furnace and in instructions or
manuals, be alert to the potential for personal injury.
.
154,000 Btuh. This eliminates the need to stock 6 separate units.
This furnace is a multipoise unit. It may be installed in the upflow,
downflow or horizontal configuration.
The furnace is shipped as a packaged unit, complete with burner
and controls. It requires a line voltage (115 vac) connection to
control box, a thermostat hook-up as shown on wiring diagram, oil
line connection(s), adequate duct work, and connection to a
properly sized vent.
2
Page 3
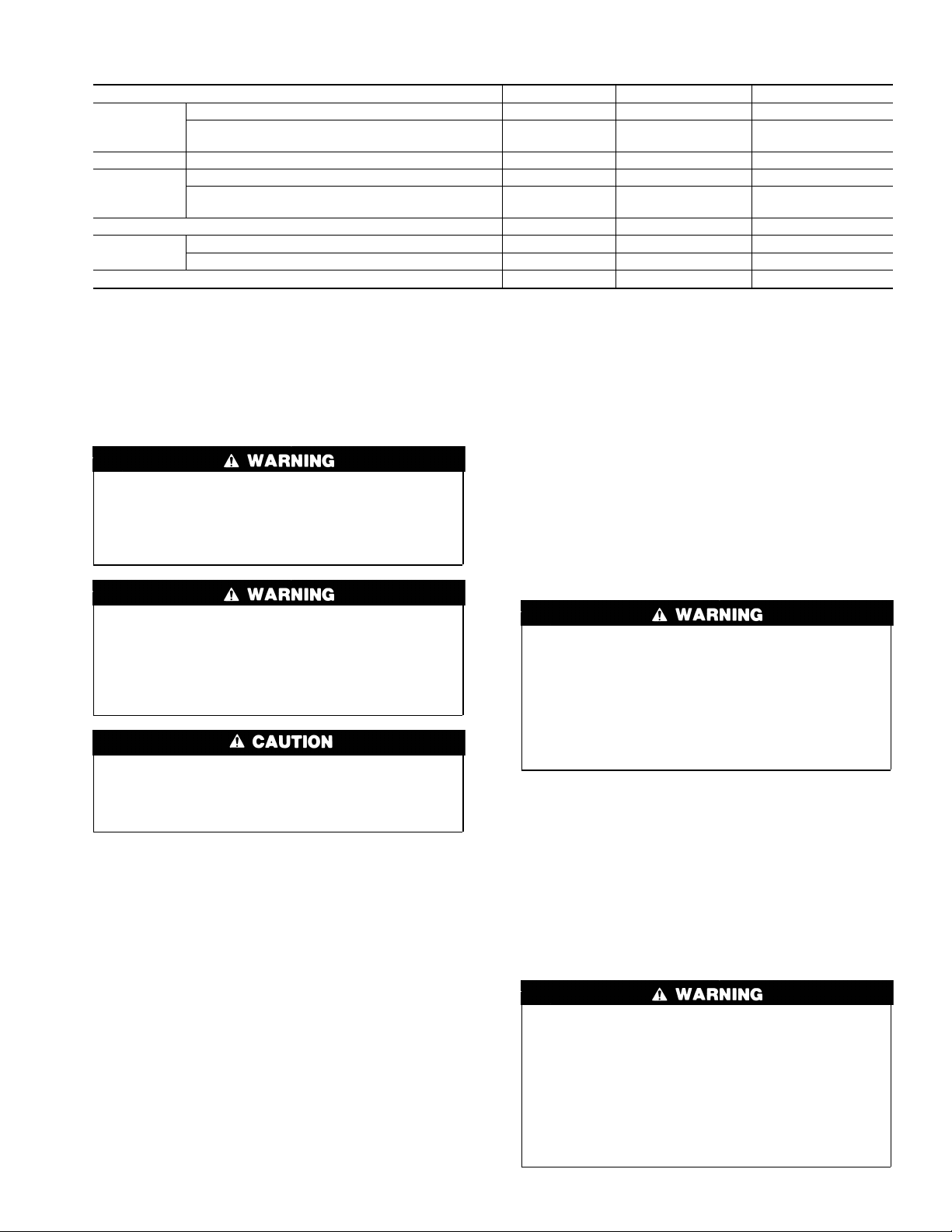
Table 1—Minimum Clearances To Combustible Materials (In.)
UNIT APPLICATION UPFLOW DOWNFLOW HORIZONTAL
Furnace 0 2 2
Sides
Back Service Clearance 0 1 0
Top
Bottom 00* 0*
Flue
Pipe
Front 88 24
* Use approved subbase for combustible floor.
NOTE: Adequate service clearances should be provided over and above these dimensions as required.
Supply Plenum and Warm-Air Duct Within 6 ft
of Furnace
Furnace Casing or Plenum 2 2 2
Horizontal Warm-Air Duct Within 6 ft of
Furnace
Horizontally or Below Pipe 4 4 4
Vertically Above Pipe 9 9 9
12 1
22 3
The air handling capacity of this furnace is designed for cooling
airflow. Refer to Table 12 for expected airflows at various external
duct static pressures.
LOCATION
Step 1—General
This furnace is not water tight and is not designed for outdoor
installation. This furnace shall be installed in such a manner
as to protect electrical components from water. Outdoor
installation would lead to a hazardous electrical condition and
to premature furnace failure.
Do not use this furnace as a construction heater. Use of this
furnace as a construction heater exposes furnace to abnormal
conditions, contaminated combustion air, and lack of air
filters. Failure to follow this warning can lead to premature
furnace failure and/or vent failure which could result in a fire
hazard and/or bodily harm.
For attic installation, it is important to keep insulation 12 in.
or more away from any furnace openings. Some types of
insulating materials may be combustibles and may cause a
fire hazard and property damage.
This furnace is approved for reduced clearances to combustible
construction, therefore, it may be installed in a closet or similar
enclosure. Since this unit may be installed in an upflow, counterflow, or horizontal position, it may be located in a basement or on
the same level as area to be heated. In any case, unit should always
be installed level.
In a basement, or when installed on floor (as in a crawlspace), it is
recommended that unit be installed on a concrete pad that is 1 in.
to 2 in. thick.
When installed in counterflow position, furnace must not be
installed on combustible flooring, unless approved subbase is used.
Also, since flue pipe is in a counterflow position, Downflow
Conversion/Vent Guard Kit MUST be used. (Also, read page 9.)
When installed in a horizontal position, furnace may be suspended
by using an angle iron frame, as long as total weight of both
furnace and frame are allowed for in support calculations. (Other
methods of suspending are acceptable.) When installed in the
Horizontal Position, this furnace must not be installed on combustible flooring, unless the approved Horizontal Subbase is used.
The required minimum clearances for furnace are specified in
Table 1.
The furnace should be located as close as possible to chimney or
vent in order to keep vent connections short and direct. The
furnace should also be located as near as possible to center of air
distribution system.
Step 2—Location Relative to Cooling Equipment
When installing furnace with cooling equipment for year-round
operation, the following recommendations must be followed for
series or parallel airflow:
1. In series airflow applications, coil is mounted after furnace in
an enclosure in supply-air stream. The furnace blower is used
for both heating and cooling airflow.
The coil MUST be installed on air discharge side of furnace.
Under no circumstances should airflow be such that cooled,
conditioned air can pass over furnace heat exchanger. This
will cause condensation in heat exchanger and possible
failure of heat exchanger which could lead to a fire hazard
and/or a hazardous condition which may lead to bodily harm.
Heat exchanger failure due to improper installation may not
be covered by warranty.
2. In parallel airflow applications, dampers must be provided to
direct air over furnace heat exchanger when heat is desired and
over cooling coil when cooling is desired.
IMPORTANT: The dampers should be adequate to prevent cooled
air from entering furnace. If manually operated, dampers must be
equipped with a means to prevent operation of either cooling unit
or furnace unless damper is in full cool or heat position.
INSTALLATION
Step 1—Air for Combustion and Ventilation
Installation of this furnace in an area where it will receive
contaminated combustion air must be avoided. Such contamination would include the following: ammonia, chlorine,
hydrogen sulfide, halogenated hydrocarbons, carbon tetrachloride, cleaning solvents, hydrochloric acid, water softening chemicals, and similar chemicals. Failure to follow this
warning will lead to premature rusting of heat exchanger and
possible premature furnace failure and/or vent failure which
could result in fire hazard and/or bodily harm.
3
Page 4

Do not block combustion-air openings in the furnace. Any
blockage will result in improper combustion which may result
in a fire hazard and/or cause bodily harm.
Step 2—General
This furnace should be installed in a location in which facilities for
ventilation permit satisfactory combustion of oil, proper venting,
and maintenance of ambient temperature at safe limits under
normal conditions of use. The location should not interfere with
proper circulation of air within the confined space. (See NFPA-31,
Section 1.5.)
In addition to air needed for combustion, process air shall be
provided as required for: cooling of equipment or material,
controlling dew point, heating, drying, oxidation or dilution, safety
exhaust, and odor control.
In addition to air needed for combustion, air shall be supplied for
ventilation, including all air required for comfort and proper
working conditions for personnel.
The barometric draft regulator (included with furnace) shall be
installed in same room or enclosure as furnace in such a manner as
to prevent any difference in pressure between regulator and
combustion-air supply.
Air requirements for operation of exhaust fans, kitchen ventilation
systems, clothes dryers, and fireplaces shall be considered in
determining the adequacy of a space to provide combustion-air
requirements.
The lack of a proper amount of combustion air can lead to serious
furnace operational problems. Some of these problems are:
1. Excessive oil burner after-drip, and oil fumes.
2. Sooting.
3. Melted oil burner ignitor/relay control.
4. Air band or air turbulator settings more open than normal.
5. Lockouts on start-up.
The requirements for combustion and ventilation air depend upon
whether furnace is located in a CONFINED or UNCONFINED
space.
Step 3—Unconfined Space
An unconfined space must have at least 50 cu ft for each 1000
Btuh of total input for all the appliances (such as furnaces, clothes
dryers, water heaters, etc.) in the space.
In unconfined spaces in buildings of conventional frame, brick, or
stone construction, infiltration MAY be adequate to provide air for
combustion, ventilation, and dilution of flue gases. This determination must be made on an individual installation basis and must
take into consideration the overall volume of unconfined space, the
number of windows and ventilation openings, the number of doors
to the outside, internal doors which can close off unconfined space,
and overall tightness of building construction. Consideration must
also be given to the amount of storage items (furniture, boxes, etc.)
within the unconfined space which take away from the air volume.
(See Table 2.)
Many new buildings and homes (and older ones that have been
weatherized) MUST BE considered as being of tight construction,
therefore, infiltration will not be sufficient to supply necessary air
for combustion and ventilation.
Table 2—Minimum Floor Area
For Unconfined Space
58CMA FURNACE
INPUT BTUH
70,000 467
91,000 607
105,000 700
119,000 793
140,000 933
154,000 1026
A building can be considered as being of tight construction when:
• Walls and ceilings exposed to outside atmosphere have a
continuous water vapor retarder with a rating of 1 perm or less
with openings gasketed or sealed, and/or
• Weatherstripping has been added on operable windows and
doors and/or
• Caulking or sealants are applied to areas such as joints around
window and door frames, between sole plates and floors,
between wall-ceiling joints, between wall panels, at penetrations for plumbing, electrical, and fuel lines, and at other
openings.
If combustion and ventilation air must be supplied to an unconfined space from outside, an opening with a FREE AREA of not
less than 1 sq in. per 1000 Btuh of total input of all appliances
within unconfined space (but not less than 100 sq in.) must be
provided. This opening must be located such that it can not be
blocked at any time.
Step 4—Confined Space
A confined space has a volume of less than 50 cu ft per 1000 Btuh
of the total input rating for all appliances installed in that space.
When furnace is installed in a closet or enclosure, 2 ventilation
openings, with OPEN AREA as dimensioned in example below
are required for combustion air. The openings should be located
about 6 in. from top and bottom of enclosure at front of furnace.
(See Table 3.)
MINIMUM SQ FT WITH
7-1/2 FT CEILING
Table 3—Combustion Air
From Confined Space
58CMA FURNACE
INPUT BTUH
70,000-105,000 16 8
119,000 20 10
NOTE: In calculating free area, consideration shall be given to
blocking effect of louvers, grilles, or screens protecting openings.
Screens used shall not be smaller than 1/4-in. mesh and shall be
readily accessible for cleaning. If free area through a louver or
grille is known, it shall be used in calculating size and free area
specified. If design and free area are not known, it may be assumed
that wood louvers have 20 percent free area and metal louvers and
grilles have 60 percent free area. Louvers shall be fixed in open
position or interlocked with furnace so they open automatically at
furnace start-up and remain open during furnace operation.
The size of the openings depends upon whether the air comes from
outside of the structure or an unconfined space inside the structure.
LENGTH
(IN.)
HEIGHT
(IN.)
ALL AIR FROM INSIDE THE STRUCTURE
For a confined space, where air is taken from an interior space, 2
permanent openings of equal area are required. One opening must
be within 12 in. of ceiling and the other within 12 in. of floor. Each
4
Page 5

opening must have a free area of at least 1 sq in. per 1000 Btuh of
total input rating but not less than 100 sq in. (See Table 4.)
DUCT WORK RECOMMENDATIONS
Table 4—Combustion Air
From Unconfined Space
58CMA FURNACE
INPUT BTUH
70,000 100
91,000 100
105,000 105
119,000 119
140,000 140
154,000 154
ALL AIR FROM OUTSIDE OF STRUCTURE
If outside air is supplied to a confined space, then the 2 openings
must be equal and located as above.
1. If combustion air is taken through a permanent opening
directly communicating with the outdoors, the opening shall
have a minimum free area of 1 sq in. per 4000 Btuh of total
input rating for all equipment in the enclosure.
2. If combustion air is taken from outdoors through vertical
ducts, the openings and ducts MUST have at least 1 sq in. of
free area per 4000 Btuh of the total input for all equipment
within the confined space. (See Table 5.)
FREE AREA PER
OPENING
(SQ IN.)
Table 5—Combustion Air From Outdoors
Through Vertical Ducts
58CMA FURNACE
INPUT BTUH
70,000 17.5 5
91,000 22.8 6
105,000 26.3 6
119,000 29.8 6
140,000 35.0 6
154,000 38.5 6
3. If combustion air is taken from outdoors through horizontal
ducts, the openings and ducts MUST have at least 1 sq in. of
free area per 2000 Btuh of the total input for all equipment
within the confined space. (See Table 6.)
FREE AREA PER
OPENING
(SQ IN.)
ROUND PIPE
(IN. DIAM)
Table 6—Combustion Air From Outdoors
Through Horizontal Ducts
58CMA FURNACE
INPUT BTUH
70,000 35.0 7
91,000 45.5 8
105,000 52.5 9
119,000 59.5 9
140,000 70.0 10
154,000 77.0 10
When ducts are used to supply air, they must be of the same cross
sectional area as free area of openings to which they connect.
The minimum dimension of rectangular air ducts must not be less
than 3 in.
FREE AREA PER OPENING
(SQ IN.)
ROUND PIPE
(IN. DIAM)
When supply ducts carry air circulated by furnace to areas
outside spaces containing furnace, return air MUST also be
handled by a duct sealed to furnace casing and terminating
outside space containing furnace. Incorrect duct work termination and sealing will create a hazardous condition which
could lead to bodily harm.
Return-air grilles and warm air registers MUST NOT be
obstructed. Failure to follow this caution will result in
premature failure of the heat exchanger.
The proper sizing of warm air ducts is necessary to ensure
satisfactory furnace operation. Duct work should be in accordance
with the latest editions of NFPA-90A (Installation of Air Conditioning and Ventilating Systems) and NFPA-90B (Warm Air
Heating and Air Conditioning Systems) or Canadian equivalent.
The supply duct work should be attached to flanged front opening
provided at discharge end of furnace. The return-air duct work
should be attached to flanged rear opening of furnace. See Fig. 2
for dimensions of these openings.
NOTE: The back (blower access opening) should not be used for
return air.
The following recommendations should be followed when installing duct work:
1. Install locking-type dampers in all branches of individual
ducts to balance out system. Dampers should be adjusted to
impose proper static at outlet of furnace.
2. A flexible duct connector of noncombustible material should
be installed at unit on both supply- and return-air systems. In
applications where extremely quiet operation is necessary, the
first 10 ft (if possible) of supply and return ducts should be
internally lined with acoustical material.
3. In cases where return-air grille is located close to fan inlet,
there should be at least one 90° air turn between fan inlet and
grille. Further reduction in sound level can be accomplished
by installing acoustical air turning vanes or lining duct as
described in item 2 above.
4. When a single air grille is used, duct between grille and
furnace must be the same size as return opening in furnace.
VENTING
Venting of furnace should be to the outside and in accordance with
local codes or requirements of local utility.
OIL-FIRED APPLIANCES SHALL BE CONNECTED TO
FLUES HAVING SUFFICIENT DRAFT AT ALL TIMES TO
ENSURE SAFE AND PROPER OPERATION OF APPLIANCE.
For additional venting information, refer to ANSI/NFPA 211
Chimney, Fireplaces, Vents, and Solid Fuel Burning Appliances
and/or CSA B139 Installation Code.
This furnace is certified for use with Type ″L″ vent (maximum flue
gas temperature 575°F).
Vent System Inspection
Before furnace is installed, it is highly recommended that any
existing vent system be completely inspected.
For any chimney or vent, this should include the following:
1. Inspection for any deterioration in chimney or vent. If deterioration is discovered, chimney must be repaired or vent must
be replaced.
5
Page 6

Table 7—Electrical Data
UNIT
SIZE
105-12 115—60—1 132 104 12.2 14 26 15
120-20 115—60—1 132 104 15.7 12 26 20
* Permissible limits of voltage range at which unit will operate satisfactorily.
† Length shown is as measured 1 way along wire path between unit and service panel for maximum 2 percent voltage drop.
‡ Time-delay fuse is recommended.
VOLTS—
HERTZ—
PHASE—
OPERATING
VOLTAGE RANGE
Max.* Min.*
MAX
UNIT
AMPS
MIN
WIRE
GAGE
MAX WIRE
LENGTH (FT)
MAX FUSE OR
CKT BKR AMPS
2. Inspection to ascertain that vent system is clear and free of
obstructions. Any blockage must be cleared before installing
furnace.
3. Cleaning chimney or vent if previously used for venting a
solid fuel burning appliance or fireplace.
4. Confirming that all unused chimney or vent connections are
properly sealed.
5. Verification that chimney is properly lined and sized per the
applicable codes. (Refer to list of codes in Safety Considerations section.)
Masonry Chimneys
This furnace can be vented into an existing masonry chimney. This
furnace must not be vented into a chimney servicing a solid fuel
burning appliance. Before venting furnace into a chimney, the
chimney MUST be checked for deterioration and repaired if
necessary. The chimney must be properly lined and sized per local
or national codes.
If furnace is vented into a common chimney, the chimney must be
of sufficient area to accommodate the total flue products of all
appliances vented into chimney.
The following requirements are provided for a safe venting
system:
1. Be sure that chimney flue is clear of any dirt or debris.
2. Be sure that chimney is not servicing an open fireplace.
3. Never reduce pipe size below the outlet size of furnace. (See
Fig. 2.)
4. All pipe should be supported using proper clamps and/or
straps. These supports should be at least every 4 ft.
5. All horizontal runs of pipe should have at least 1/4-in. per ft of
upward slope.
6. All runs of pipe should be as short as possible with as few
turns as possible.
7. Seams should be tightly joined and checked for leaks.
8. The flue pipe must not extend into chimney but be flush with
inside wall.
9. The chimney must extend 3 ft above highest point where it
passes through the roof of a building and at least 2 ft higher
than any portion of a building within a horizontal distance of
10 ft. It shall also be extended at least 5 ft above highest
connected equipment flue collar.
10. Check local codes for any variance.
Factory-Built Chimneys
Listed factory-built chimneys may be used. Refer to chimney
manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation.
OIL BURNER
This furnace is supplied with a high-pressure atomizing retention
head-type burner (for use with grade 1 or 2 fuel oil). The mounting
flange is fixed to burner air tube and no adjustment is required for
insertion length.
OIL CONNECTIONS
Complete instructions for installing fuel oil piping can be found in
oil burner Installation Instructions included with furnace.
Oil line entry holes are provided in side panels. Two holes are
provided in each location so that a 2-pipe system may be used if
desired.
An oil filter should be used with all oil burners and should be
installed as close to burner as possible.
BAROMETRIC DRAFT CONTROL
The barometric draft control shipped with furnace MUST be used
with furnace to ensure proper operation. Instructions for installing
control are packed with control.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
The unit cabinet must have an uninterrupted or unbroken
electrical ground to minimize personal injury if an electrical
fault should occur. A green ground screw is provided in
control box for this connection.
115-v Wiring
Before proceeding with electrical connections, make certain that
voltage, frequency, and phase correspond to that specified on unit
rating plate. Also, check to be sure that service provided by utility
is sufficient to handle load imposed by this equipment. Refer to
rating plate or Table 7 for equipment electrical specifications.
Make all electrical connections in accordance with National
Electrical Code (NEC) ANSI/NFPA 70-2001 and any local codes
or ordinances that might apply. For Canadian installations, all
electrical connections must be made in accordance with Canadian
Electrical Code CSA C22.1 or subauthorities having jurisdiction.
Do not connect aluminum wire between disconnect switch
and furnace. Use only copper wire. Failure to follow this
caution will lead to intermittent electrical operation and/or
fire hazard.
The control system depends on correct polarity of power supply.
Connect HOT wire (H) and NEUTRAL wire (N) as shown in Fig.
3or4.
A separate line voltage supply MUST be used with a fused
disconnect switch or circuit breaker between main power panel
and unit. (See Fig. 3 or 4.)
Metallic conduit (where required/used) may terminate at side panel
of unit. It is not necessary to extend conduit inside unit from side
panel to control box.
When replacing any original furnace wiring, use only 105°C No.
14 AWG copper wire.
6
Page 7

24-V Wiring
Instructions for wiring thermostat (field supplied) are packed in
thermostat box. Make thermostat connections as shown in Fig. 3 or
4 at 24-v terminal board on fan timer board.
Accessories
When installing optional accessories to this appliance, follow
manufacturer’s Installation Instructions included with accessory.
Other than wiring for thermostat, wire with a minimum of type ″T″
insulation (63°F rise) must be used for accessories.
HORIZONTAL OR DOWNFLOW INSTALLATION
For horizontal installation, determine which ″side″ will become the
″top″, when the unit is laid down. Remove the flue pipe clearance
knock-out from the top of that side panel. Install the flue elbow so
that it exits the cabinet of the furnace through that opening.
For counterflow installation, the flue pipe must exit the cabinet
through 1 of the side panel openings (as above), then extended up
the side of the furnace. Insure that adequate clearances to combustibles are observed. Downflow Conversion/Vent Guard Kit
MUST be used.
Remove burner by loosening mounting nuts and turn oil burner
slightly counterclockwise to unlock the key hole burner flange.
Prevent putting undue strain on burner wiring. (It may be necessary to disconnect burner wiring in some cases.)
To reinstall burner, insert on the four burner studs on key hole
burner flange and turn it clockwise to lock it and tighten nuts.
IMPORTANT: Burner must always be installed in the upright
position with ignition control on top.
FILTERS
Never operate unit without a filter or with filter access door
removed. Failure to adhere to this warning could lead to a
hazardous condition which could lead to equipment damage
and bodily harm.
An external filter rack is provided as standard equipment with
furnace. A sufficient clearance should be provided for air filter
access. See Table 8 for filter rack flange dimensions for return air
duct.
Table 8—Filter and Flange (In.)
UNIT
SIZE
105-12
120-20 20X30X1 19X29
START-UP, ADJUSTMENT, AND SAFETY CHECKOUT
Step 1—Operational Checkout
AIR FILTER
SIZE
16x24x1
or
16X25X1
FLANGE OPENING
SIZE
15X23
4. Blower access door is secured in place.
5. Valve on oil supply line is open.
6. RESET BUTTON on primary control is pushed down.
7. Flame observation door and 2 cleanout access doors located at
front of unit are closed.
8. Thermostat is set for heating mode and set above room
temperature.
If all of the above items have been performed, set main electrical
switch to ON position and burner should start. When burner starts,
proceed to Combustion Check section.
Step 2—Combustion Check
In order to obtain optimum performance from oil burner, the
following setup procedures must be followed:
1. A test kit to measure smoke, stack draft, over-fire draft, oil
pump pressure, CO
, and stack temperatures MUST be used in
2
order to obtain proper air band setting. Although all of the
above measurements are required for optimum setup and
efficiency data, the most important readings that must be taken
are smoke number, over-fire draft, stack draft, and pump
pressure.
2. The proper smoke number has been established by engineering tests to be between 0 and 1. This degree of smoke emission
is commonly referred to as a ″trace″ of smoke. It is recommended to use a Bacharach true spot smoke test set or
equivalent.
3. In order to ensure proper draft through furnace, a barometric
draft regulator (supplied with furnace) must be installed.
In order for this device to function properly, barometric damper
must be mounted with hinge pins horizontal and face of damper
vertical. (See instructions included with damper.) The draft regulator should be adjusted after furnace has been firing for at least 5
minutes, and set between -0.025 and -0.035 in. wc. (See Table 9.)
4. The over-fire draft, which is taken through observation door
(located in center line above burner in front panel of furnace),
is a measurement necessary to determine if there is a blockage
between oil burner and flue outlet.
There should be a total pressure drop of between 0.020 and 0.05 in.
wc through furnace as shown in Table 9. The over-fire draft must
be set within the range shown in Table 9.
Table 9—Furnace Draft Conditions (In. WC)
FURNACE
INPUT
(BTUH)
70,000 -0.025 0.010 0.020 to 0.035
91,000 -0.025 0.020 0.030 to 0.045
105,000 -0.025 0.025 0.035 to 0.050
119,000 -0.025 0.025 0.035 to 0.050
140,000 -0.025 0.025 0.035 to 0.050
154,000 -0.025 0.025 0.035 to 0.050
FLUE
DRAFT
MINIMUM
OVER-FIRE
DRAFT
MAXIMUM
TOTAL RESTRICTION
THROUGH
HEAT EXCHANGER
DO NOT TAMPER WITH UNIT OR CONTROLS—CALL
YOUR SERVICE TECHNICIAN. Failure to follow this
warning could result in personal and/or property damage.
Installation of furnace is now complete. Run through the following
checkout and ensure each item has been performed.
1. Correct nozzle size has been selected for desired input rate.
2. Blower wheel support is removed.
3. Electrical wiring is completed according to Fig. 3 or 4.
A reading outside the range shown in Table 9 (for example +0.1 in.
wc) would indicate that furnace is in an extremely high-pressure
condition in primary section. This condition may be caused by any
of the following problems:
a. Excessive combustion air due to air shutter being too wide
open.
b. A lack of flue draft (chimney effect) or some other
blockage, such as soot, in secondary section of heat
exchanger.
7
Page 8

X04031 Rev. A
A03164
Fig. 3—Wiring Diagram (105-12)
8
Page 9

X04032 Rev. A
A03165
Fig. 4—Wiring Diagram (120-20)
9
Page 10

c. Use of an oversized nozzle input.
d. Pump pressure over values listed in Table 10.
5. The CO
and stack temperature instruments enable you to
2
obtain data required to determine thermal efficiency of furnace.
6. An oil filter should be installed as close to burner as possible
with ALL oil burners and is essential on lower firing rate
burners. We recommend the use of a low pressure drop oil
filter such as the General Filter, Inc. model #1A-25A or
equivalent.
7. The oil pressure regulator is factory set to give oil pressure of
→
100 psi for the model having 105,000 BTUH input and 100 psi
for the model having 119,000 BTUH input. The firing rate
noted on nameplate may be obtained using the nozzles and
pump pressures indicated in Table 10.
Table 10—Burner Input and Nozzle Size at 100 psi
→
Pump Pressure
FURNACE
INPUT
(BTUH)
70,000 0.50 0.50-70W 100 100
91,000 0.65 0.55-70B 140 140
105,000 0.75 0.65-70B 133 130
120,000 0.85 0.75-70B 128 130
140,000 1.00 0.85-70B 138 140
155,000 1.10 0.85-70B 167 170
8. On a new installation, air entrapped in oil line leading from
tank to nozzle must be thoroughly purged in order to prevent
excessive after drip. The oil pump is provided with a special
fitting which allows purging of any air between tank and oil
pump. The proper procedure for performing this operation is
as follows:
a. Place a piece of clear plastic 1/4 in. diameter tubing over
b. Start oil burner, then open purge fitting and allow burner to
c. Tighten purge fitting. Allow oil to run to nozzle and fire
d. If purging takes longer than 15 sec and no flame has been
e. For detailed information on operation of primary control,
After all the setup procedures mentioned above have been completed, the burner should be allowed to operate and an inspection
mirror should be used to observe the flame pattern at tip of nozzle.
Any irregularities such as burning to 1 side or pulsating flame
patterns should be corrected by changing nozzle.
Step 3—Fan Adjustment Check
This furnace is equipped with a 4-speed direct-drive motor to
deliver a temperature rise within range specified on rating plate,
between return and supply plenums, at external duct static pressure
noted on rating plate.
INPUT
USGPH
NOZZLE
REAL PUMP
PRESSURE
SPECIFICATION
PUMP PRESSURE
purge fitting on oil pump.
run until purge tube is completely free of air bubbles.
burner.
established, burner stops. Push reset button on front of
primary control to restart burner.
refer to instructions included with furnace.
When operating furnace in heating mode, static pressure and
temperature rise (supply-air temperature minus return-air
temperature) must be within those limits specified on rating
label. Failure to follow this warning could lead to severe
furnace damage.
Adjust fan speed ACCORDING TO OIL INPUT SELECTED so
that temperature rise is within rise range specified on rating plate.
(See Table 11.) Consult wiring diagram for speed changes on
direct-drive motor.
Table 11—Speed Selection
UNIT
SIZE
105-12/
120-20
FURNACE
INPUT
(BTUH)
70,000/119,000 Med-Low
91,000/140,000 Med-High
105,000/154,000 High
.
To adjust fan off time, set DIP switches on control board to obtain
desired timing. (See Fig. 5.)
12
60 Sec
DELAY OFF DIP SWITCH SETTINGS
12
12 1212
90 Sec
RECOMMENDED
120 Sec
BLOWER
SPEED
12
150 Sec
A95115
Fig. 5—Fan Off Time DIP Switch Settings
(Black Box Represents Switch Position)
Step 4—Limit Control Check
After furnace has been in operation for at least 15 minutes, restrict
return-air supply by blocking filters or closing return registers and
allow furnace to shut down on high limit. The burner should shut
off, and main blower should continue to run.
Remove restriction, and burner should come back on in a few
minutes.
Step 5—For Year-Round Air Conditioning
This furnace is designed for use in conjunction with cooling
equipment to provide year-round air conditioning. The blower has
been sized for both heating and cooling, however, fan motor speed
may need to be changed to obtain necessary cooling airflow.
Step 6—Heating
The blower speed is factory set to deliver required airflow at
normal duct static pressure.
Step 7—Cooling
The blower speed may be field adjusted to deliver required airflow
for cooling application. (See Table 12.)
Step 8—Constant Blower Switch
This furnace is equipped with a constant low-speed blower option.
Whenever room thermostat is not calling for heating or cooling,
blower runs on low speed in order to provide air circulation. If
constant blower option is not desired, the rocker switch on top of
cabinet may be used to turn off constant speed.
10
Page 11

Table 12—Airflow Data (CFM)
UNIT
SIZE
105-12
120-20
NOTES:
1. Airflow values in cubic ft per minute (CFM) rounded to nearest 5 CFM.
2. Data taken with filters in place.
BLOWER
SPEED
High 1425 1350 1305 1250 1170 1030 925 805
Med-High 1130 1045 1000 950 885 820 745 670
Med-Low 840 810 770 740 685 635 580 500
Low 725 730 740 745 730 715 690 665
High 2080 2041 1965 1864 1702 1576 1474 1336
Med-High 1892 1859 1770 1675 1550 1449 1330 1217
Med-Low 1556 1475 1394 1318 1211 1134 1051 938
Low 1221 1164 1081 998 926 855 782 653
0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE IN. WC
MAINTENANCE
The ability to properly perform maintenance on this equipment requires certain expertise, mechanical skills, tools, and
equipment. If you do not possess these, do not attempt to
perform any maintenance on this equipment other than those
procedures recommended in the User’s Manual. FAILURE
TO FOLLOW THIS WARNING COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE DAMAGE TO THIS EQUIPMENT, SERIOUS
PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH.
Before performing any service functions, unless operations
specifically require power to be on, make sure all utilities are
turned off upstream of appliance. Failure to comply with this
warning will cause a fire hazard and/or bodily harm.
To avoid personal injury, make sure electrical supply power
is off before servicing. Failure to follow this warning could
lead to electrical shock, fire, or death.
Step 1—General
In order to keep this furnace in good operating condition and to
maintain its warranty, the furnace MUST be serviced on an annual
basis. This servicing includes a nozzle change, a burner inspection,
a visual check of tube passages through flue outlet and cleanout
ports, and a visual inspection of combustion chamber when burner
is removed.
Depending on above inspection, service could also include a
cleaning and vacuuming of heat exchanger tubes and possibly the
heat exchanger drum section.
Removal of any heat exchanger components which are sealed by
gaskets requires replacement of gasket.
Failure to replace any heat exchanger gaskets with new
gaskets when any heat exchanger plates or covers are removed could lead to heat exchanger leakage, sooting, and/or
a hazardous condition capable of causing bodily harm.
This furnace should never be operated without an air filter.
Disposable filters should be replaced at least once a year. If
equipped to provide cooling, filters should be replaced a minimum
of twice a year. Permanent filters should be cleaned at least twice
a year.
ALWAYS KEEP MAIN OIL VALVE TURNED OFF IF
BURNER IS SHUT DOWN FOR AN EXTENDED PERIOD OF
TIME.
Step 2—Oil Burner
For optimum performance, oil burner nozzle should be replaced
once a year. Contact your service technician if you are unsure of
this procedure.
The procedure for nozzle installation and/or replacement is outlined in oil burner instruction manual which came with furnace.
After replacement of nozzle, burner should be adjusted in accordance with Combustion Check section of this instruction.
Step 3—Heat Exchanger and Flue Pipe
Ordinarily, it is not necessary to clean heat exchanger or flue pipe
every year, but it is necessary to have your service technician
check unit before each heating season to determine whether
cleaning or replacement of parts is required.
If cleaning is necessary, the following steps should be performed:
1. Turn off all oil and electrical supplies upstream of furnace.
If furnace has been in operation, some surfaces may be hot.
Allow time for unit to cool down personal injury will result.
2. Disconnect flue pipe.
3. Remove flue collar panel located in front part of furnace.
4. Remove baffle from secondary heat exchanger.
5. Disconnect oil line and remove oil burner from furnace.
6. Open 2 cleanout doors located in upper part of front panel of
furnace.
7. Clean secondary tubes, and primary cylinder with stiff brush
and vacuum cleaner.
8. Before re-assembly, the heat exchanger and combustion
chamber should be inspected to determine if replacement is
required.
9. After cleaning, replace baffle, flue collar plate, oil burner, and
close the 2 cleanout access doors. Reconnect flue pipe and oil
line.
10. Re-adjust burner for proper operation.
Step 4—Blower Removal
To remove blower from furnace:
1. Turn off all oil and electrical supplies upstream of furnace.
2. Remove burner access and blower door.
3. Remove blower retaining screw (on blower shelf).
11
Page 12

4. Remove cover from control box and disconnect thermostat
and power wires from the board.
5. Slide blower forward on rails toward front of unit.
6. Reverse items 1 through 5 to re-install blower. Refer to wiring
diagram (Fig. 3 or 4) of these instructions or diagram located
on inside of blower door to properly rewire unit.
Copyright 2003 CARRIER Corp. • 7310 W. Morris St. • Indianapolis, IN 46231 58cma4si
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 4
Tab 6a 8a
PC 101 Catalog No. 535–80076 Printed in U.S.A. Form 58CMA-4SI Pg 12 9-03 Replaces: 58CMA-3SI
 Loading...
Loading...