Page 1

50RHC,RVC,RHR,RHS,
RVR,RVS,RDS006-060
Water Source Heat Pump Units
Installation, Start-Up, and
Service Instructions
AQUAZONE™
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1,2
GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Step 1 — Check Jobsite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Step 2 — Check Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
• STORAGE
•PROTECTION
•INSPECT UNIT
Step 3 — Unit Location. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
• FIELD CONVERSION OF DISCHARGE AIR
Step 4 — Mounting the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
• HORIZONTAL UNITS
• VERTICAL UNITS
Step 5 — Duct System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
• SO U N D AT T E NUATIO N
• EXISTING DUCT SYSTEM
Step 6 — Condensate Drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
• HORIZONTAL UNITS
• VERTICAL UNITS
• VENTING
Step 7 — Piping Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
• WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS
• GROUND-WATER APPLICATIONS
• GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS
Step 8 — Field Power Supply Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
• POWER CONNECTION
• SUPPLY VOLTAGE
• 208-VOLT OPERATION
Step 9 — Field Control Wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
• THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS
• WATER FREEZE PROTECTION
• AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION
• ACCESSORY CONNECTIONS
• WATER SOLENOID VALVES
PRE-START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26-30
System Checkout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
PSC Blower Speed Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
FIELD SELECTABLE INPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30-32
C Control Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
C Control DIP Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
D Control Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
D Control DIP Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Units with Modulating Hot Water Reheat
(HWR) Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
D Control Accessory Relay Configurations . . . . . 32
Water Valve (Slow Opening) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Outside Air Damper (OAD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32-36
Operating Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Scroll Compressor Rotation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Unit Start-Up Cooling Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Unit Start-Up Heating Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Flow Regulation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Page
Flushing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Antifreeze . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Cooling Tower/Boiler Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Ground Coupled, Closed Loop and Plateframe
Heat Exchanger Well Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
OPERATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36,37
Power Up Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Units with Aquazone Complete C Control . . . . . . . 36
Units with Aquazone Deluxe D Control. . . . . . . . . . 36
Units with HWR Option. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
SYSTEM TEST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37,38
Test Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Retry Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Aquazone Deluxe D Control LED Indicators . . . . . 38
SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38-40
Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Water Coil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Condensate Drain Pans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Refrigerant System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Fan Motors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Condensate Drain Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Air Coil Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Condenser Cleaning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Checking System Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Refrigerant Charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Air Coil Fan Motor Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
TROUBLESHOOTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40-42
Thermistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Control Sensors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
50RHC,RVC,RHR,RHS,RVR,RVS,RDS
START-UP CHECKLIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . CL-1, CL-2
IMPORTANT: Read the entire instruction manual before
starting installation.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment can
be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only trained and qualified service personnel should
install, repair, or service air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of cleaning coils and filters and replacing filters. All other
operations should be performed by trained service personnel.
When working on air-conditioning equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags and labels attached to the unit, and
other safety precautions that may apply.
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, maintenance, or use can cause explosion, fire, electrical shock or other
conditions which may cause personal injury or property damage. Consult a qualified installer, service agency, or your distributor or branch for information or assistance. The qualified installer or agency must use factory-authorized kits or accessories
when modifying this product. Refer to the individual instructions packaged with the kits or accessories when installing.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 4
Ta b 5 a 5 a
Catalog No. 04-53500007-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50R-5SI Pg 1 6-07 Replaces: 50R-4SI
Page 2
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and work
gloves. Use quenching cloth for brazing operations. Have fire
extinguisher available. Read these instructions thoroughly and
follow all warnings or cautions attached to the unit. Consult
local building codes and the National Electrical Code (NEC)
for special installation requirements.
Understand the signal words — DANGER, WARNING,
and CAUTION. DANGER identifies the most serious hazards
which will result in severe personal injury or death. WARNING signifies hazards that could result in personal injury or
death. CAUTION is used to identify unsafe practices, which
would result in minor personal injury or product and property
damage.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert
symbol ( ). When you see this symbol on the unit and in
instructions or manuals, be alert to the potential for personal
injury.
adequate space around the unit for servicing. See Fig. 1-3 for
overall unit dimensions. Refer to Fig. 4 for an illustration of a
typical horizontal installation.
VERTICAL AND DOWNFLOW UNITS (50RVC,RVR,
RVS,RDS) — Vertical units are designed for indoor installations. While vertical units are typically installed in a floor-level
closet or a small mechanical room, the unit access guidelines
for these units are very similar to those described for horizontal
units. See Fig. 5-8 for overall dimensions. Refer to Fig. 9 for an
example of a typical vertical installation. Refer to Fig. 10 for a
sample downflow installation.
To avoid equipment damage, do not use these units as a
source of heating or cooling during the construction
process. The mechanical components and filters used in
these units quickly become clogged with construction
dirt and debris which may cause system damage.
Electrical shock can cause personal injury or death. Before
installing or servicing system, always turn off main power
to system. There may be more than one disconnect switch.
Turn off accessory heater power if applicable.
GENERAL
This Installation and Start-Up Instructions literature is for
Aquazone™ water source heat pump systems.
Water source heat pumps (WSHPs) are single-package horizontally and vertically mounted units with electronic controls
designed for year-round cooling and heating. Aquazone
WSHPs are available in the following unit configurations:
• RHC standard efficiency with horizontal airflow and
right, left or back discharge
• RHR high efficiency with horizontal airflow and right,
left or back discharge
• RHS premium efficiency with horizontal airflow and
right, left or back discharge
• RVC standard efficiency with vertical airflow and top
discharge
• RVR high efficiency with vertical airflow and top
discharge
• RVS premium efficiency with vertical airflow and top
discharge
• RDS premium efficiency with vertical airflow and bot-
tom discharge (downflow)
IMPORTANT: The installation of water source heat pump
units and all associated components, parts, and accessories
which make up the installation shall be in accordance with
the regulations of ALL authorities having jurisdiction and
MUST conform to all applicable codes. It is the responsibility of the installing contractor to determine and comply
with ALL applicable codes and regulations.
INSTALLATION
Step 1 — Check Jobsite —
maintenance instructions are provided with each unit. Before
unit start-up, read all manuals and become familiar with the
unit and its operation. Thoroughly check out the system before
operation. Complete the inspections and instructions listed
below to prepare a unit for installation. See Tables 1-3 for unit
physical data.
HORIZONTAL UNITS (50RHC,RHR,RHS) — Horizontal
units are designed for indoor installation only. Be sure to allow
Installation, operation and
Step 2 — Check Unit — Upon receipt of shipment at
the jobsite, carefully check the shipment against the bill of
lading. Make sure all units have been received. Inspect the carton or crating of each unit, and inspect each unit for damage.
Ensure the shipping company makes proper notation of any
shortages or damage on all copies of the freight bill. Concealed
damage not discovered during unloading must be reported to
the shipping company within 15 days of receipt of shipment.
NOTE: It is the responsibility of the purchaser to file all
necessary claims with the shipping company.
1. Verify unit is correct model for entering water temperature of job.
2. Be sure that the location chosen for unit installation provides ambient temperatures maintained above freezing.
Well water applications are especially susceptible to
freezing.
3. Be sure the installation location is isolated from sleeping
areas, private offices and other acoustically sensitive
spaces.
NOTE: A sound control accessory package may be used
to help eliminate sound in sensitive spaces.
4. Check local codes to be sure a secondary drain pan is not
required under the unit.
5. Be sure unit is mounted at a height sufficient to provide
an adequate slope of the condensate lines. If an appropriate slope cannot be achieved, a field-supplied condensate
pump may be required.
6. Provide sufficient space for duct connection.
7. Provide adequate clearance for filter replacement and
drain pan cleaning. Do not allow piping, conduit, etc. to
block filter access.
8. Provide sufficient access to allow maintenance and
servicing of the fan and fan motor, compressor and coils.
Removal of the entire unit from the closet should not be
necessary.
9. Provide an unobstructed path to the unit within the closet
or mechanical room. Space should be sufficient to allow
removal of unit if necessary.
10. Provide ready access to water valves and fittings, and
screwdriver access to unit side panels, discharge collar,
and all electrical connections.
11. Where access to side panels is limited, pre-removal of the
control box side mounting screws may be necessary for
future servicing.
2
Page 3

STORAGE — If the equipment is not needed immediately at
the jobsite, it should be left in its shipping carton and stored in a
clean, dry area of the building or in a warehouse. Units must be
stored in an upright position at all times. If carton stacking is
necessary, stack units a maximum of 3 high. Do not remove
any equipment from its shipping package until it is needed for
installation.
PROTECTION — Once the units are properly positioned on
the jobsite, cover them with either a shipping carton, vinyl film,
or an equivalent protective covering. Cap open ends of pipes
stored on the jobsite. This precaution is especially important in
areas where painting, plastering, or spraying of fireproof material, etc. is not yet complete. Foreign material that accumulates
within the units can prevent proper start-up and necessitate
costly clean-up operations.
Before installing any of the system components, be sure to
examine each pipe, fitting, and valve, and remove any dirt or
foreign material found in or on these components.
DO NOT store or install units in corrosive environments or
in locations subject to temperature or humidity extremes
(e.g., attics, garages, rooftops, etc.). Corrosive conditions
and high temperature or humidity can significantly reduce
performance, reliability, and service life. Always move
units in an upright position. Tilting units on their sides may
cause equipment damage.
INSPECT UNIT — To prepare the unit for installation, complete the procedures listed below:
1. Compare the electrical data on the unit nameplate with
ordering and shipping information to verify that the
correct unit has been shipped.
2. Verify that the unit is the correct model for the entering
water temperature of the job.
3. Do not remove the packaging until the unit is ready for
installation.
4. Verify that the refrigerant tubing is free of kinks or dents,
and that it does not touch other unit components.
5. Inspect all electrical connections. Be sure connections are
clean and tight at the terminals.
6. Loosen compressor bolts until the compressor rides freely
on springs. Remove shipping restraints.
7. Remove the four
1
/4 in. shipping bolts from compressor
support plate (two bolts on each side) to maximize vibration and sound alternation.
Failure to remove shipping brackets from spring-mounted
compressors will cause excessive noise and could cause
component failure due to added vibration.
8. Remove any blower support cardboard from inlet of the
blower.
9. Locate and verify any accessory kit located in compressor
section.
10. Remove any access panel screws that may be difficult to
remove once unit is installed.
3
Page 4
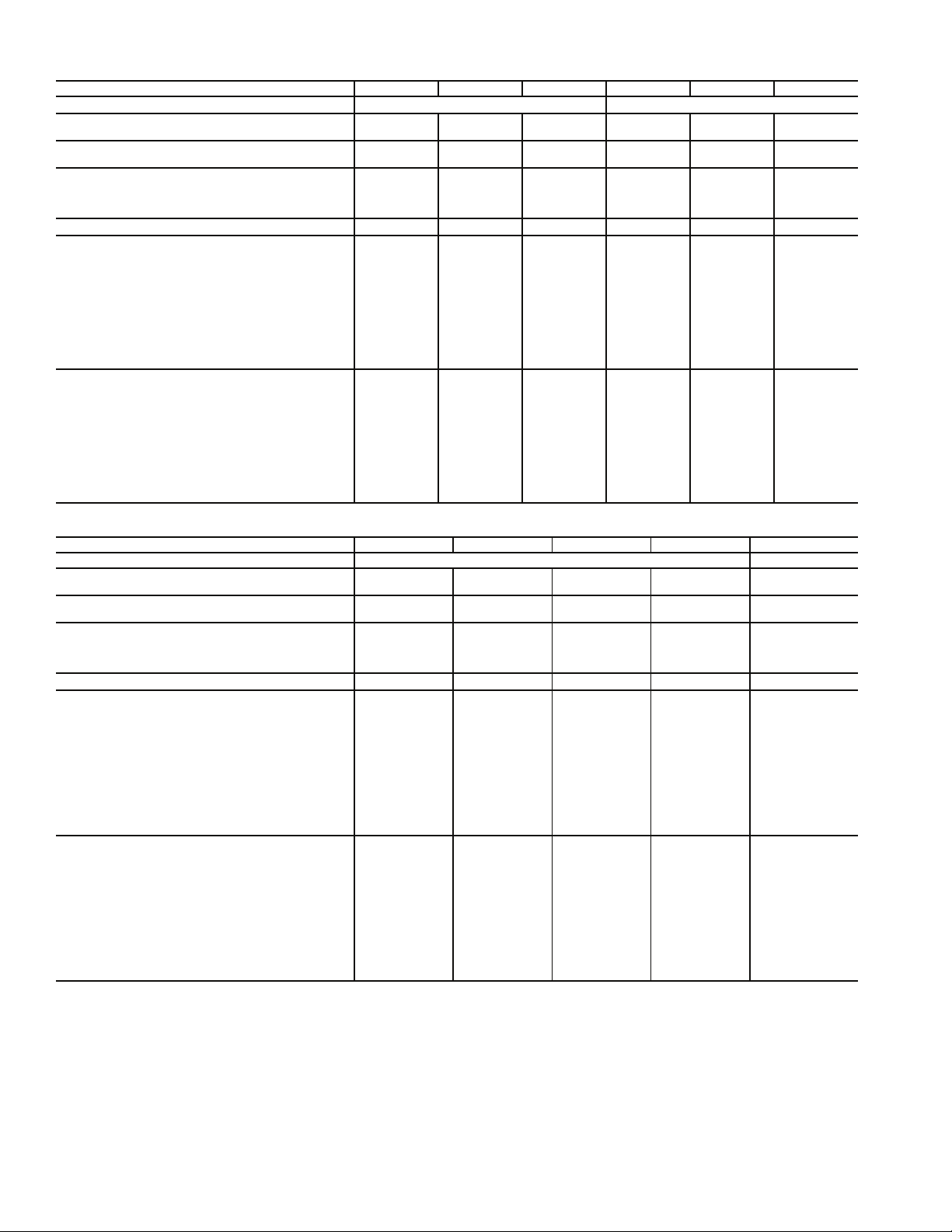
Table 1 — Physical Data — Aquazone™ 50RHC,RVC006-060 Units
UNIT 50RHC,RVC 006* 009 012 018 024 030
COMPRESSOR (1 each) Rotary
FACTORY REFRIGERANT CHARGE R-22
VERTICAL (oz)
FACTORY REFRIGERANT CHARGE R-22
HORIZONTAL (oz)
PSC FAN MOTOR AND BLOWER
Fan Motor Type/Speeds PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3
Fan Motor Std/High Static (Hp)
Blower Wheel Size (D x W) (in.) Std/High Static 5 x 5/— 5 x 5/— 6 x 5/— 8 x 7/8 x 7 9 x 7/9 x 7 9 x 7/10 x 8
WATER CONNECTION SIZE (FPT)
VERTICAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) — 10 x 15 10 x 15 20 x 17.25 20 x 17.25 20 x 17.25
Total Face Area (ft2) — 1.04 1.04 2.4 2.4 2.4
Tube Size (in.) —
Fin Spacing (FPI) —1212121212
Number of Rows —23233
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway — 10 x 18 10 x 18 1 — 20 x 20 1 — 20 x 20 1 — 20 x 20
Weight (lb)
Operating — 105 114 181 189 197
Packaged — 115 124 186 194 202
HORIZONTAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 10 x 15 10 x 15 10 x 15 16 x 22 16 x 22 16 x 22
Total Face Area (ft2) 1.04 1.04 1.04 2.44 2.44 2.44
Tube Size (in.)
Fin Spacing (FPI) 12 12 12 12 12 12
Number of Rows 223233
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway 10 x 18 10 x 18 10 x 18 1 — 16 x 25 1 — 16 x 25 1 — 16 x 25
Weight (lb)
Operating 103 105 114 181 189 197
Packaged 113 115 124 186 194 202
—1414263837
14 14 14 25 38 37
1
/25/—
1
3
/
2
/
8
1
/10/—
1
3
3
1
/10/—
/
2
/
8
/
8
1
/
2
3
/
8
3
/
8
1
/8/1/
1
3
3
/
2
/
8
/
8
6
Reciprocating
1
/4/3/
4
3
/
4
3
/
8
3
/
8
3
/4/3/
3
3
3
4
/
4
/
8
/
8
UNIT 50RHC,RVC 036 041† 042 048 060
COMPRESSOR (1 each) Reciprocating Scroll
FACTORY REFRIGERANT CHARGE R-22
VERTICAL (oz)
FACTORY REFRIGERANT CHARGE R-22
HORIZONTAL (oz)
PSC FAN MOTOR AND BLOWER
Fan Motor Type/Speeds PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3
Fan Motor Std/High Static (Hp)
Blower Wheel Size (D x W) (in.) Std/High Static 9 x 8/10 x 8 9 x 8/— 9 x 8/10 x 8 10 x 10/12 x 10 11 x 10/11 x 10
WATER CONNECTION SIZE (FPT)
VERTICAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 24 x 21.25 1 — 20 x 17.25 24 x 21.25 24 x 28.25 20 x 28.25
Total Face Area (ft2) 3.62 2.4 3.62 4.71 4.71
Tube Size (in.)
Fin Spacing (FPI) 14 11 12 12 12
Number of Rows 2433 3
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway 1 — 24 x 24 1 — 20 x 20 1 — 24 x 24
Weight (lb)
Operating 203 207 218 263 278
Packaged 209 212 224 270 285
HORIZONTAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 20 x 25 — 20 x 25 20 x 35 20 x 35
Total Face Area (ft
Tube Size (in.)
Fin Spacing (FPI) 14 — 12 12 12
Number of Rows 2—3 3 3
2
) 3.47 — 3.47 4.86 4.86
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway
Weight (lb)
Operating 203 — 218 263 278
Packaged 209 — 224 270 285
LEGEND
FPI — Fins per Inch
PSC — Permanent Split Capacitor
*Size 006 available in 50RHC unit only.
†Size 041 available in 50RVC unit only.
42 50 51 66 74
41 50 51 66 74
1
/2/3/
4
3
/
4
3
/
8
3
/
8
1 — 20 x 28
2 — 20 x 14
3
/4/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
—
—
NOTES:
1. All units have grommet compressor mountings, and
electrical knockouts.
2. All sizes available as high-static units.
3
/4/3/
4
3
/
4
3
/
8
3
/
8
1 — 20 x 28
2 — 20 x 14
3
/4/1 1/1
11
3
/
8
1 — 14 x 24
1 — 18 x 24
3
/
8
1 — 20 x 24
1 — 20 x 14
3
/
8
1 — 14 x 24
1 — 18 x 24
3
/
8
1 — 20 x 24
1 — 20 x 14
1
/2 and 3/4-in.
4
Page 5
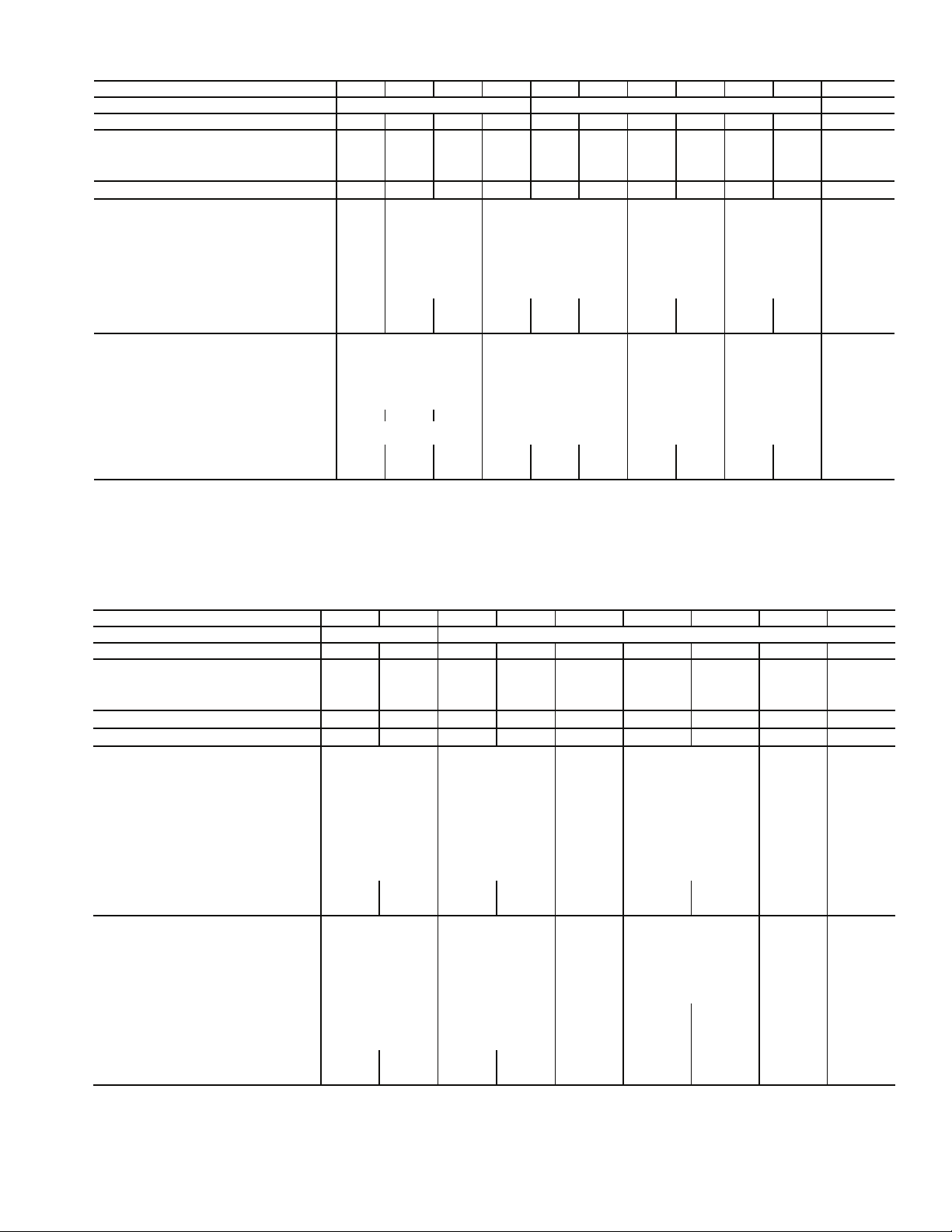
Table 2 — Physical Data — Aquazone™ 50RHR,RVR006-060 Units
UNIT 50RHR,RVR 006* 009 012 015 019 024 030 036 042 048 060
COMPRESSOR (1 each) Rotary Reciprocating Scroll
FACTORY CHARGE R-22 (oz) 12 15 15 30 30 30 41 44 46 54 80
PSC FAN MOTOR AND BLOWER
Fan Motor Type/Speeds PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3
Fan Motor (Hp)
Blower Wheel Size (D x W) (in.) 5 x 5 5 x 5 6 x 5 9 x 7 9 x 7 9 x 7 9 x 7 10 x 10 10 x 10 10 x 10 11 x 10
1
WATER CONNECTION SIZE (FPT)
VERTICAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) — 10 x 16 16 x 16 20 x 20 28 x 20 28 x 25
Total Face Area (ft2) — 1.1 1.8 2.8 3.9 4.9
Tube Size (in.)
Fin Spacing (FPI) —1212121210
Number of Rows —33334
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway — 10 x 20 16 x 20 20 x 24 28 x 24 28 x 30
Weight (lb)
Operating — 112 121 147 169 193 219 229 257 267 323
Packaged — 122 131 157 179 203 231 241 269 279 338
HORIZONTAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 10 x 16 16 x 16 18 x 22 18 x 31 20 x 35
Total Face Area (ft2) 1.1 1.8 2.8 3.9 4.9
Tube Size (in.)
Fin Spacing (FPI) 12 12 12 12 10
Number of Rows 223 3 3 3 4
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway 1 — 10 x 20 1 — 16 x 20 1 — 18 x 24 2 — 18 x 18
Weight (lb)
Operating 110 112 121 147 169 193 219 229 257 267 323
Packaged 120 122 131 157 179 203 231 241 269 279 338
LEGEND
FPI — Fins per Inch
PSC — Permanent Split Capacitor
*Size 006 available in 50RHR unit only.
1
/
25
1
1
/
2
—
3
1
/
/
10
1
/
2
3
/
8
/
8
1
10
3
/
2
1
/
6
3
/
4
3
3
NOTES:
1. All units have spring compressor mountings, TXV (thermostatic
expansion valve) expansion devices, and 1/2 and 3/4-in. electrical
knockouts.
2. Size 048 available as high-static unit.
1
/
5
3
/
4
/
8
/
8
1
/
3
3
/
4
3
/
2
3
/
4
3
/
8
3
/
8
3
/
4
/
4
3
/
/
4
4
11 1
3
/
8
3
/
8
1 — 12 x 20
1 — 25 x 20
1
3
/
8
3
/
8
Table 3 — Physical Data — Aquazone 50RHS,RVS,RDS015-070 Units
UNIT 50RHS,RVS,RDS 015 018 024 030 036 042 048 060 070
COMPRESSOR (1 each) Rotary Scroll
FACTORY CHARGE R-22 (oz) 44 44 48 48 60 74 74 102 104
PSC FAN MOTOR AND BLOWER
Fan Motor Type/Speeds PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3 PSC/3
Fan Motor (Hp)
Blower Wheel Size (D x W) (in.) 9 x 7 9 x 7 9 x 7 9 x 7 9 x 7 10 x 10 10 x 10 11 x 10 11 x 10
WATER CONNECTION SIZE (FPT) (in.)
HWG CONNECTION SIZE (FPT) (in.)
VERTICAL/DOWNFLOW
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 20 x 20 24 x 20 28 x 20 28 x 25 32 x 25 36 x 25
Total Face Area (ft
Tube Size (in.)
Fin Spacing (FPI) 12 12 12 10 10 10
Number of Rows 3 33444
2
) 2.8 3.3 3.9 4.9 5.6 6.3
1
/
6
3
/
4
1
/
2
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway 1 — 20 x 24 1 — 24 x 24
Weight (lb)
Operating 174 184 250 252 266 323 327 416 443
Packaged 184 194 260 262 276 333 337 426 453
HORIZONTAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 18 x 22 18 x 27 18 x 31 20 x 35 20 x 40 20 x 45
Total Face Area (ft
Tube Size (in.)
Fin Spacing (FPI) 12 12 12 10 10 10
Number of Rows 3 33444
2
) 2.8 3.4 3.9 4.9 5.6 6.3
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway 1 — 18 x 24 2 — 18 x 18
Weight (lb)
Operating 179 189 250 252 266 323 327 416 443
Packaged 189 199 260 262 276 333 337 426 453
LEGEND NOTES:
FPI — Fins per Inch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
PSC — Permanent Split Capacitor
1
/
6
3
/
4
1
/
2
3
/
8
3
/
8
1
/
5
3
/
4
1
/
2
1
/
3
3
/
4
1
/
2
3
/
8
3
/
8
1. All units have spring compressor mountings, TXV (thermostatic
2. Size 030 and 036 available as high-static units.
1
/
2
3
/
4
1
/
2
3
/
8
2 — 14 x
24
3
/
8
2 — 18 x 182 — 12 x 201 — 20 x
expansion valve) expansion devices, and 1/2 and 3/4-in. electrical
knockouts.
1
/
2
3
/
4
3
/
4
1111
1
/
2
2 — 14 x 30
1
/
2
3
/
8
3
/
8
25
1
/
2
3
/
8
2 — 10 x
30
1 — 12 x
30
3
/
8
1 — 18 x
20
1 — 24 x
20
1
1
/
2
3
/
8
3 — 12 x
30
3
/
8
2 — 24 x
20
5
Page 6
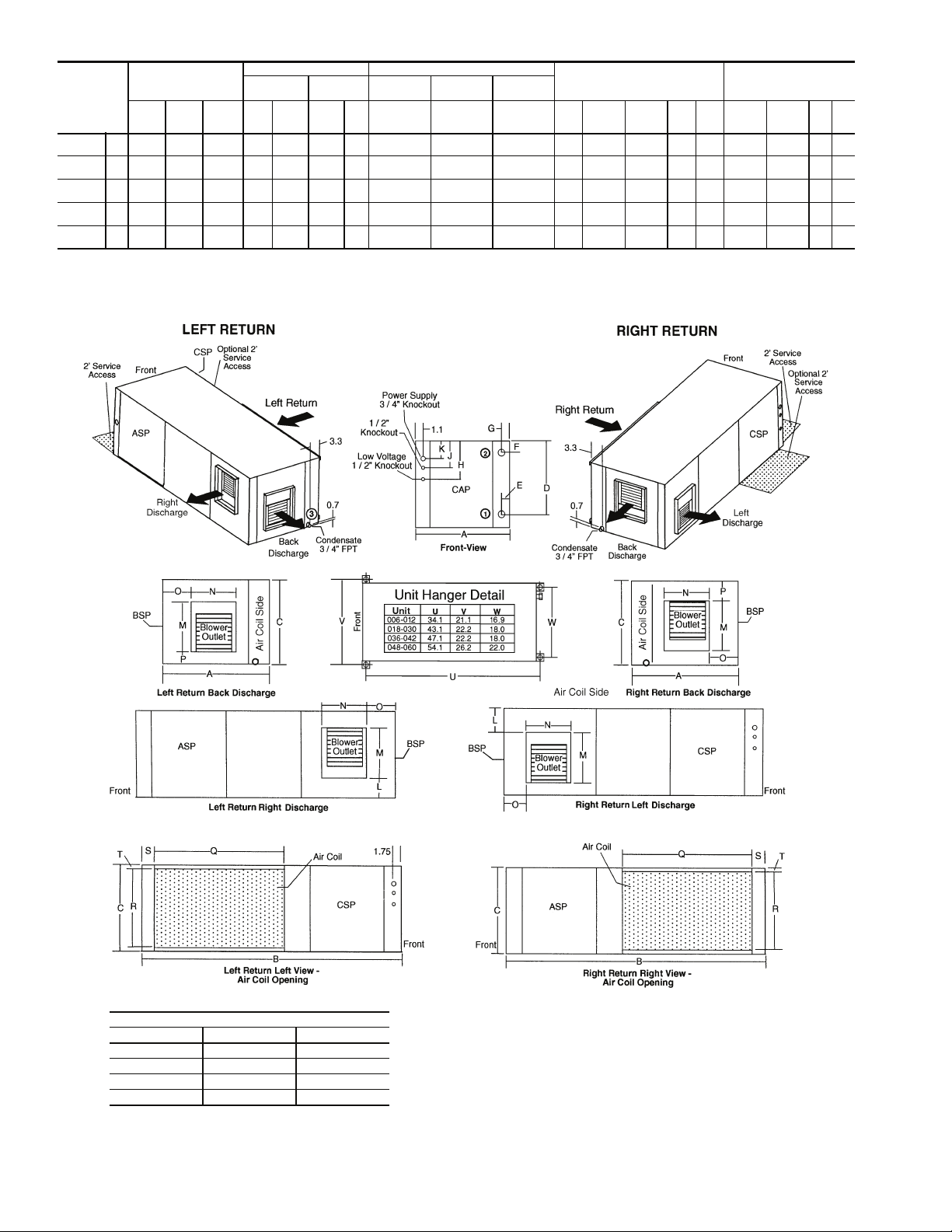
50RHC
UNITS
006-012
018-030
036-042
048
060
NOTES:
1. Condensate is 3/4-in. FPT copper.
2. Horizontal unit shipped with filter bracket only. This bracket should be removed for return duct connection.
3. Hanger kit is factory installed.
OVERALL CABINET
A
WidthBDepthCHeight
in. 19.1 34.1 11.0 9.6 0.8 1.8 0.8 8.1 5.1 2.1 0.8 8.9 6.7 5.2 1.3 16.1 9.8 1.1 0.6
cm 48.5 86.6 27.9 24.4 2.0 4.4 2.0 20.6 13.0 5.4 1.9 22.7 17.0 13.3 3.3 41.0 25.0 2.7 1.5
in. 20.1 43.1 17.1 15.3 2.4 1.9 2.1 12.1 9.1 6.1 2.6 13.3 9.9 4.1 1.3 23.0 15.0 1.1 1.0
cm 51.1 109.5 43.4 38.9 6.1 4.9 5.3 30.8 23.2 15.6 6.6 33.8 25.1 10.5 3.3 58.4 38.1 2.8 2.5
in. 20.1 47.1 21.1 18.8 2.2 4.7 1.2 16.1 13.1 10.1 2.5 16.1 11.0 3.0 2.5 25.9 19.0 1.1 1.0
cm 51.1 119.6 53.6 47.6 5.5 11.9 3.0 41.0 33.3 25.7 6.3 40.9 27.9 7.7 6.4 65.8 48.3 2.8 2.5
in. 24.1 54.1 21.1 19.4 5.9 4.3 2.3 16.1 13.1 10.1 3.7 16.1 13.7 4.1 1.3 35.9 19.0 1.1 1.0
cm 61.2 137.4 53.6 49.2 14.9 11.0 5.8 41.0 33.3 25.7 9.5 41.0 34.8 10.3 3.2 91.2 48.3 2.8 2.5
in. 24.1 54.1 21.1 19.4 5.9 4.3 2.3 16.1 13.1 10.1 1.7 18.1 13.7 4.1 1.3 35.9 19.0 1.1 1.0
cm 61.2 137.4 53.6 49.2 14.9 11.0 5.8 41.0 33.3 25.7 4.4 46.0 34.8 10.3 3.2 91.2 48.3 2.8 2.5
WATER CONNECTIONS ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS (in.)
1 — In 2 — Out
D E F G Therm Ext Pump
H
1
/2 conduit
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
J
1
/2 conduit
LEGEND
K
3
/4 conduit
Power
Supply
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
Duct Flange Installed (±0.10 in.)
LMSupply
Height
N
Supply
Depth
OPQReturn
RETURN CONNECTION
Using Air Coil Opening
R
Return
Depth
Height
ST
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
Code Return Discharge
S Left Right
E Left Back
Z Right Left
B Right Back
Fig. 1 — 50RHC Dimensional Data
a50-8155
6
Page 7
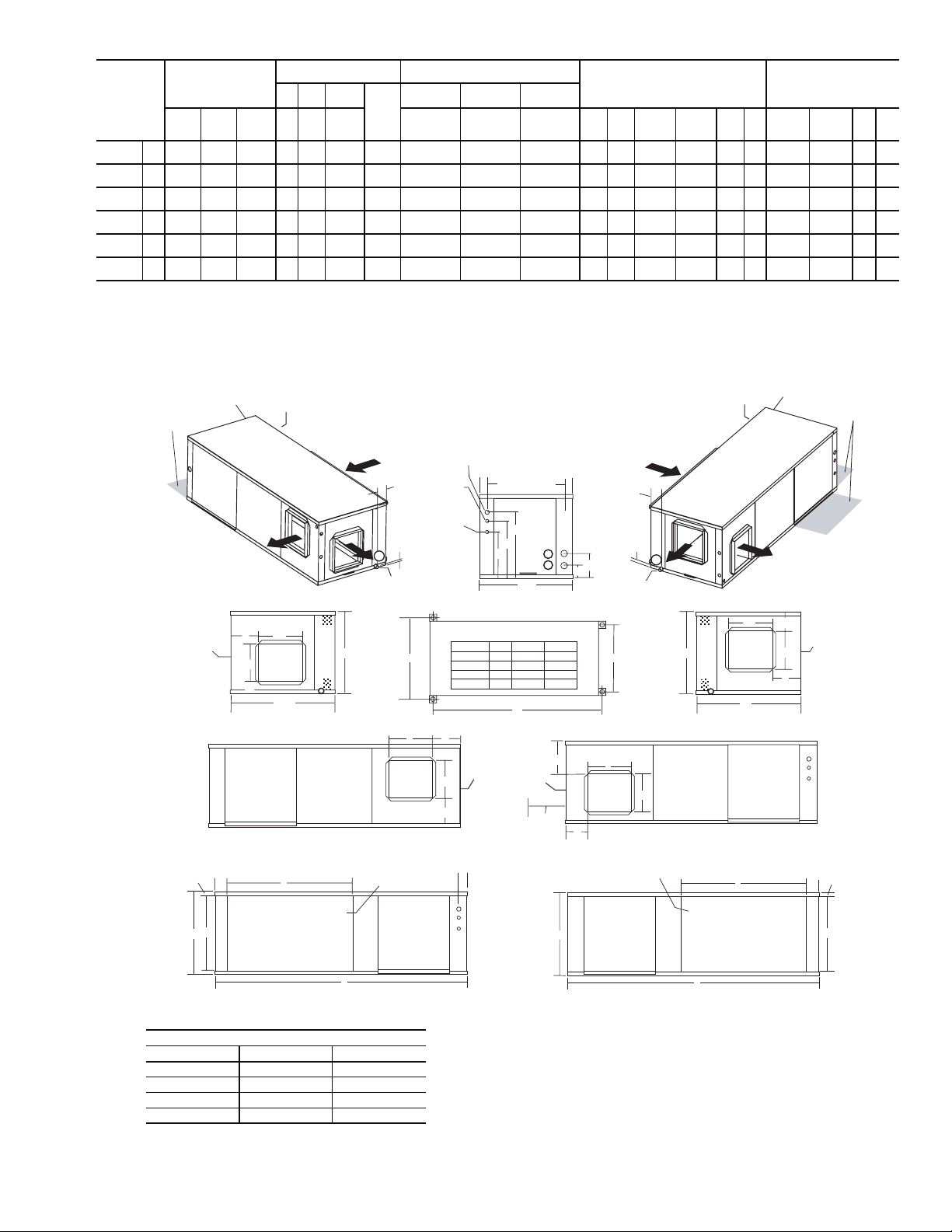
WATER
OVER ALL
50RHR
UNITS
in. 22.4 43.1 11.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
006-012
cm 56.8 109.5 28.7 6.1 13.7 1.5 8.9 14.0 20.8 14.7 10.2 14.7 20.3 14.7 3.8 43.4 23.6 5.6 2.5
in. 22.4 43.1 17.3 2.4 4.9 0.6
015-024
cm 56.8 109.5 43.9 6.1 12.4 1.5 8.9 19.1 25.9 12.7 14.2 26.4 23.6 12.7 3.8 43.4 38.9 5.6 2.5
in. 22.4 53.2 19.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
030
cm 56.8 135.1 49.0 6.1 13.7 1.5 14.5 24.6 31.0 12.7 17.3 26.4 23.6 12.7 5.3 58.7 43.9 5.6 2.5
in. 22.4 53.2 19.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
036
cm 56.8 135.1 49.0 6.1 13.7 1.5 14.5 24.6 31.0 7.4 9.7 34.3 33.3 7.4 4.8 58.7 43.9 5.6 2.5
in. 22.4 62.2 19.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
042-048
cm 56.8 158.0 49.0 6.1 13.7 1.5 14.5 24.6 31.0 7.4 9.7 34.3 33.3 7.4 4.8 81.5 43.9 5.6 2.5
in. 25.4 71.2 21.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
060
cm 64.5 180.8 54.1 6.1 13.7 1.5 20.6 29.7 36.1 14.7 12.7 34.5 33.8 14.7 7.4 91.7 49.0 5.6 2.5
NOTES:
1. Condensate is 3/4-in. FPT copper.
2. Horizontal unit shipped with filter bracket only. This bracket should be removed for return duct connection.
3. Hanger kit is factory installed. Isolation grommets are provided.
4. Right and left orientation is determined by looking at water connection side.
CABINET
A
WidthBDepthCHeightDInEOut
3op?œŸ•‘ “ ’
CONNECTIONS
12 3
²±¢p³µ¶·¸¹º»¼½¾¿ÀÁÂ?‘’“”•…†‡denµ´ÇÆÅÄ´
F
Cond-
ensate
Loop
Wate r
ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS (in.)
G
1
/2 conduit
FPT
Therm
(in.)
1
3
3
3
3.5 5.5 8.2 5.8 4.0 5.8 8.0 5.8 1.5 17.1 9.3 2.2 1.0
/
2
3.5 7.5 10.2 5.0 5.6 10.4 9.3 5.0 1.5 17.1 15.3 2.2 1.0
/
4
5.7 9.7 12.2 5.0 6.8 10.4 9.3 5.0 2.1 23.1 17.3 2.2 1.0
/
4
5.7 9.7 12.2 2.9 3.8 13.5 13.1 2.9 1.9 23.1 17.3 2.2 1.0
/
4
5.7 9.7 12.2 2.9 3.8 13.5 13.1 2.9 1.9 32.1 17.3 2.2 1.0
1
8.1 11.7 14.2 5.8 5.0 13.6 13.3 5.8 2.9 36.1 19.3 2.2 1.0
1
H
1
/2 conduit
Ext
Pump
3
LEGEND
Water
Connection
3‘ Service
Access
ASP
BSP
E Configuration - Left Return Back Discharge
Right
View
Fron t
LEFT RETURN RIGHT RETURN
Fron t
Right
Discharge
CSP
M
N
Blower
L
Outlet
O
ASP
S Configuration - Left Return Right Discharge -
A
Air Coil Opening
Left Return
Back
Discharge
C
Air Coil Side
3
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
Power Supply
“ Knockout
3/4
1/2“
Knockout
3.25
Low Voltage
1/2
“ Knockout
F
Condensate
3/4
“
FPT
Unit Hanger Detail
Model X Y Z
Y
M
Blower
Outlet
006-024 43.1 24.375 20.375
Front
030-036 53.1 24.375 20.375
042-048 62.1 24.375 20.375
060 71.1 27.375 23.375
J
BSP
L
K
1.6 [40.6mm]
I
CAP
H
G
A
Front-View
X
SERVICE
ACCESS
I
/4 conduit
Powe r
Supply
2
1
K
BSP
3‘
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
Duct Flange Installed (±0.10 in.)
JKLSupply
Height
M
Supply
Depth
Right Return
3.25
F
Condensate
3/4
“
FTP
Z
L
3
Back
Discharge
C
Air Coil Side
B Configuration - Right Return Back Discharge
Air Coil Opening
E
D
M
Blower
Outlet
M
Z Configuration - Right Return Left Discharge -
RETURN CONNECTION
Using Return Air Opening
NOPReturn
ASP
M
Blower
Outlet
A
CSP
Depth
Water
Connection
Discharge
O
L
N
Fron t
Left
CSP
BSP
Q
Return
Height
Left
View
Fron t
Service
2
‘
Access
RS
Left
View
S
Q
C
PR
S Configuration - Left Return Right Discharge -
B
Air Coil Opening
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
Code Return Discharge
S Left Right
E Left Back
Z Right Left
B Right Back
Fig. 2 — 50RHR Dimensional Data
Air Coil
CSP
1.1
C
Fron t
Fron t
Air Coil
ASP
Z Configuration - Right Return Left Discharge -
Air Coil Opening
P
B
S
R
Q
Right
View
a50-8156
7
Page 8
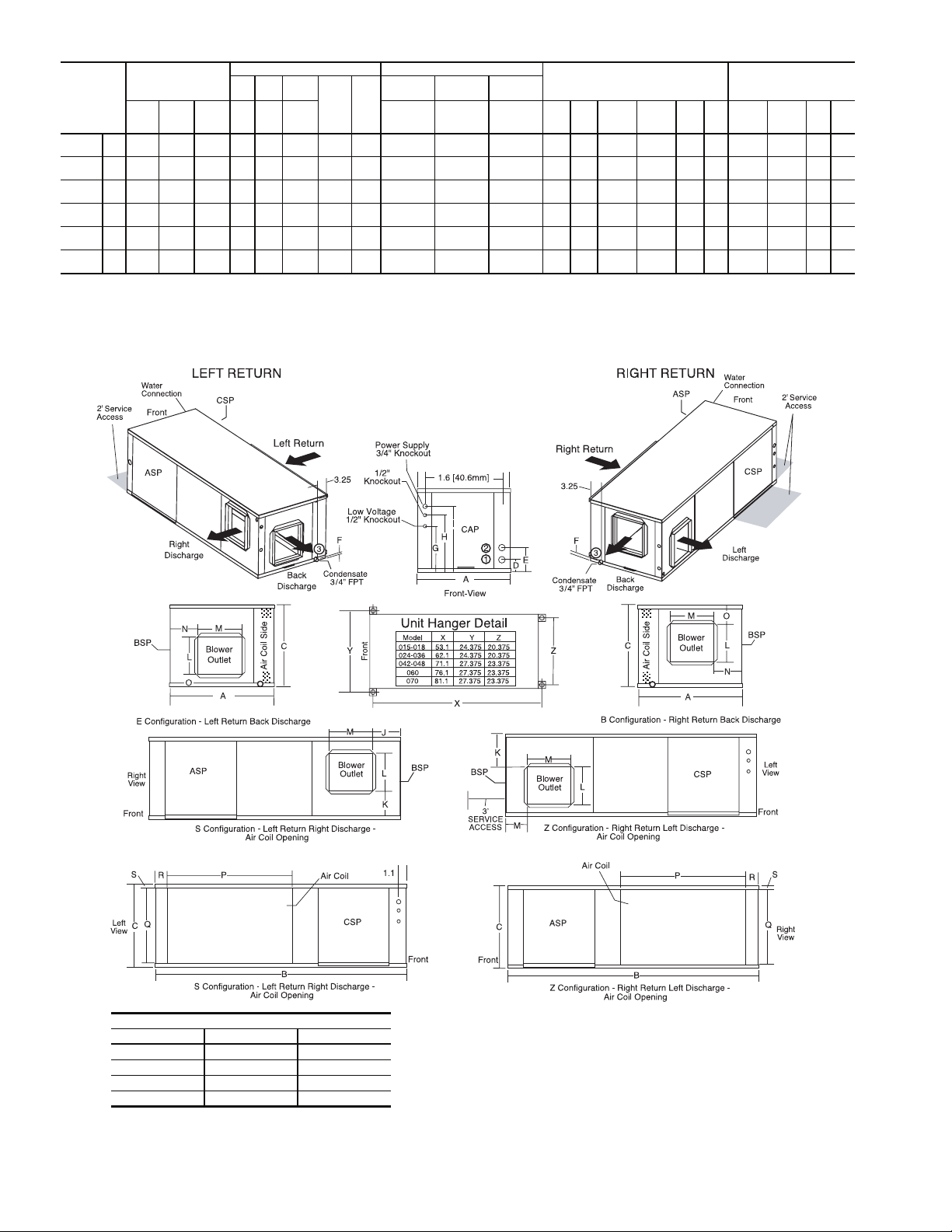
50RHS
UNITS
015-018
024-030
036
042-048
060
070
NOTES:
1. Condensate is 3/4-in. FPT copper.
2. Horizontal unit shipped with filter bracket only. This bracket should be removed for return duct connection.
3. Hanger kit is factory installed. Isolation grommets are provided.
4. Right and left orientation is determined by looking at water connection side.
OVERALL CABINET
A
WidthBDepthCHeightDInEOut
in. 22.4 53.2 19.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
cm 56.8 135.1 49.0 6.1 13.7 1.5 14.5 24.6 31.0 12.7 17.3 26.4 23.6 12.7 5.3 58.7 43.9 5.6 2.5
in. 22.4 62.2 19.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
cm 56.8 158.0 49.0 6.1 13.7 1.5 14.5 24.6 31.0 12.7 17.3 26.4 23.6 12.7 5.3 71.4 43.9 5.6 2.5
in. 22.4 62.2 19.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
cm 56.8 158.0 49.0 6.1 13.7 1.5 14.5 24.6 31.0 12.7 17.3 26.4 23.6 12.7 5.3 81.5 43.9 5.6 2.5
in. 25.4 71.2 21.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
cm 64.5 180.8 54.1 6.1 13.7 1.5 20.6 29.7 36.1 14.7 12.7 34.5 33.8 14.7 7.4 91.7 49.0 5.6 2.5
in. 25.4 76.2 21.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
cm 64.5 193.5 54.1 6.1 13.7 1.5 20.6 29.7 36.1 14.7 12.7 34.5 33.8 14.7 7.4 104.4 49.0 5.6 2.5
in. 25.4 81.2 21.3 2.4 5.4 0.6
cm 64.5 206.2 54.1 6.1 13.7 1.5 20.6 29.7 36.1 14.7 12.7 34.5 33.8 14.7 7.4 117.1 49.0 5.6 2.5
WATER CONNECTIONS ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS (in.)
12 3
F
Cond-
ensate
Loop
Water
FPT
(in.)
3
/
3
/
3
/
1
11/
11/
G
1
/2 conduit
HWG
FPT
(in.)
Therm Ext Pump
5.7 9.7 12.2 5.0 6.8 10.4 9.3 5.0 2.1 23.1 17.3 2.2 1.0
1
/
4
2
5.7 9.7 12.2 5.0 6.8 10.4 9.3 5.0 2.1 28.1 17.3 2.2 1.0
1
/
4
2
5.7 9.7 12.2 5.0 6.8 10.4 9.3 5.0 2.1 32.1 17.3 2.2 1.0
1
/
4
2
8.1 11.7 14.2 5.8 5.0 13.6 13.3 5.8 2.9 36.1 19.3 2.2 1.0
1
/
2
8.1 11.7 14.2 5.8 5.0 13.6 13.3 5.8 2.9 41.1 19.3 2.2 1.0
2
8.1 11.7 14.2 5.8 5.0 13.6 13.3 5.8 2.9 46.1 19.3 2.2 1.0
2
H
1
/2 conduit
LEGEND
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
I
3
/4 conduit
Power
Supply
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
Duct Flange Installed (±0.10 in.)
JKLSupply
Height
M
Supply
Depth
RETURN CONNECTION
Using Air Coil Opening
NOPReturn
Depth
Q
Return
Height
RS
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
Code Return Discharge
S Left Right
E Left Back
Z Right Left
B Right Back
Fig. 3 — 50RHS Dimensional Data
a50-8157
8
Page 9
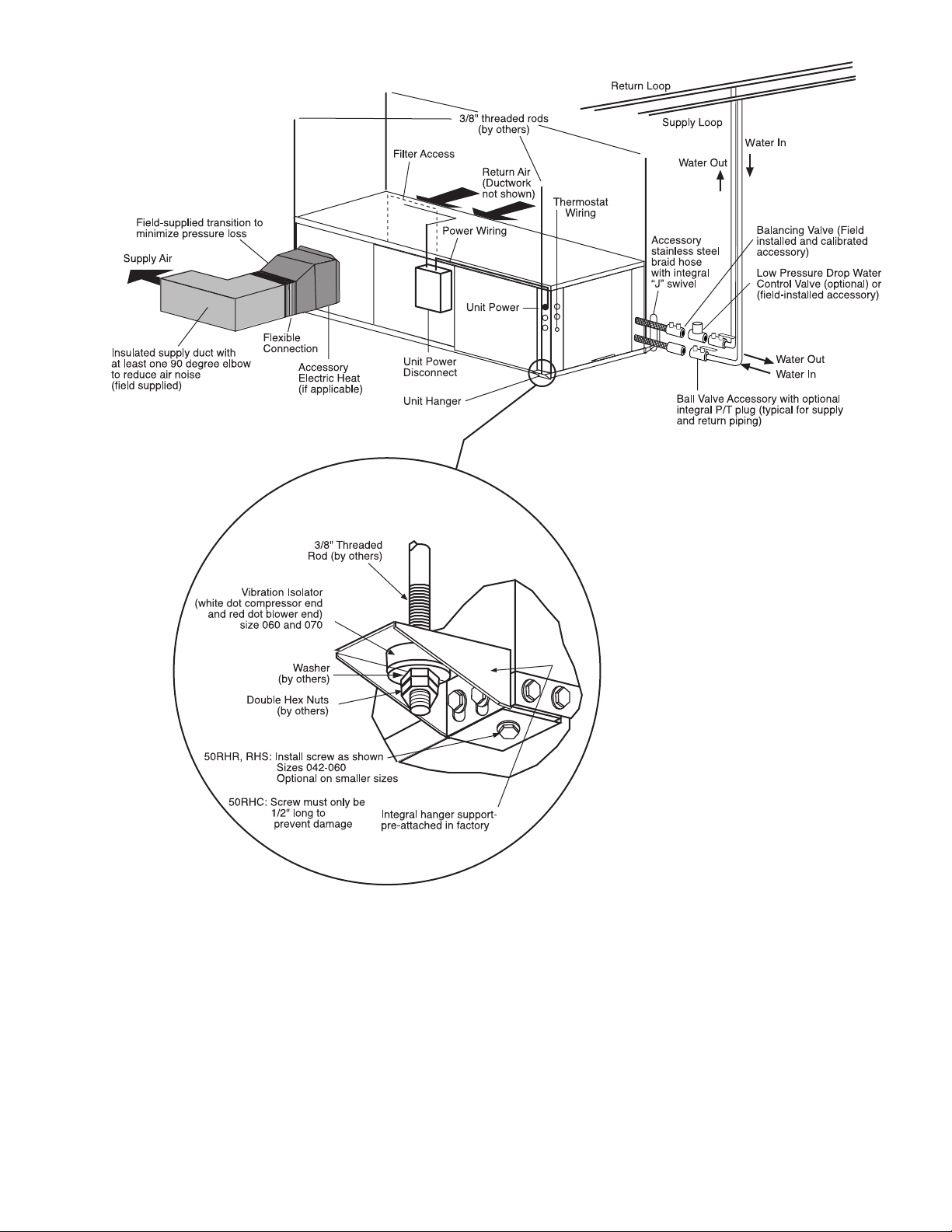
UNIT HANGER ISOLATION DETAIL
Fig. 4 — Typical Installation — 50RHC,RHR,RHS Units
9
Page 10
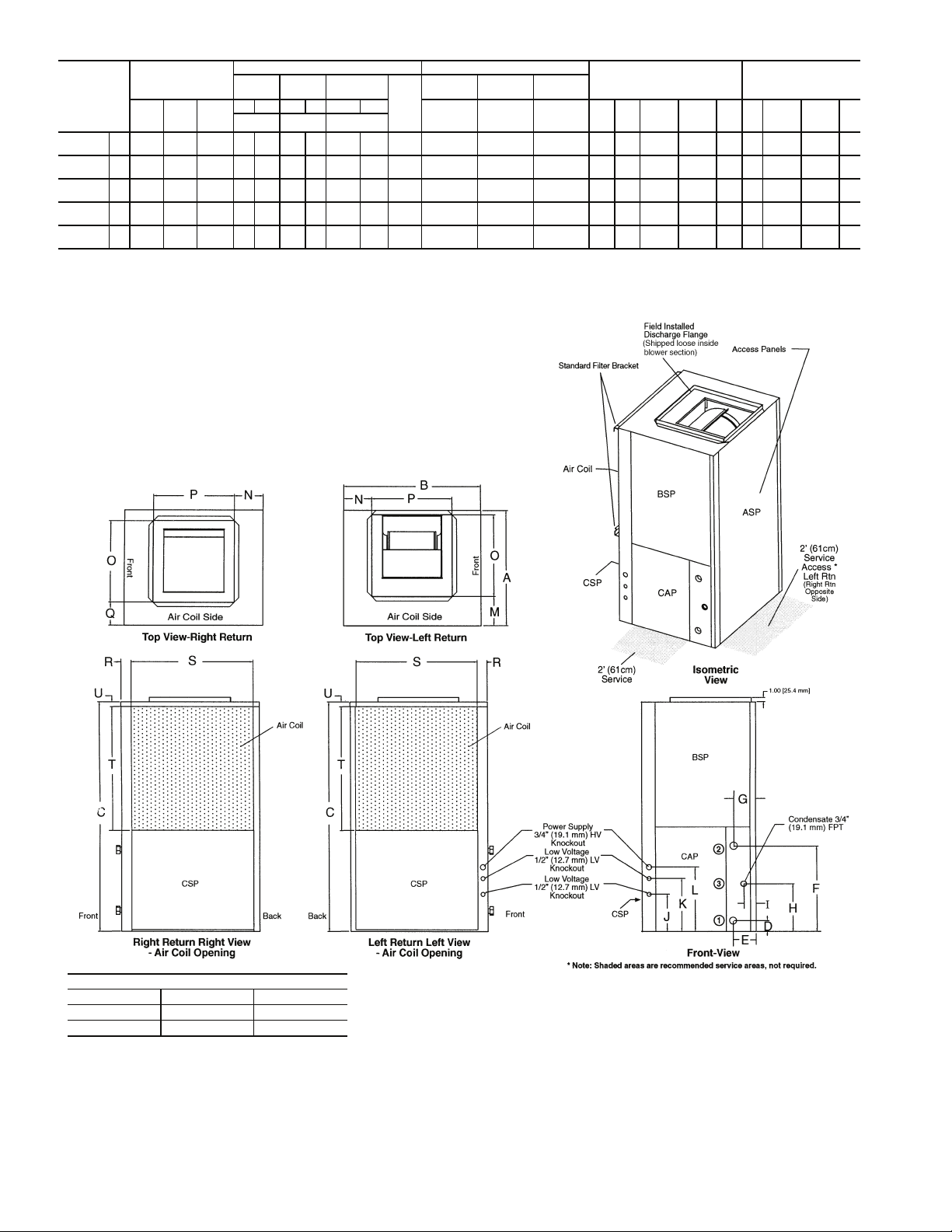
50RVC
UNITS
009-012
018-030
036 & 042
041
048-060
NOTES:
1. Condensate is 3/4-in. (19.1 mm) FPT.
2. Filter bracket extending from unit 2.5-in. (6.4 cm). This bracket should be removed when connecting return duct.
3. Discharge flange field installed.
OVERALL CABINET
A
WidthBDepthCHeight
in. 19.1 19.1 22.0 1.4 2.8 9.4 2.8 6.1 2.3 1/2 2.9 5.9 8.9 8.9 5.1 9.0 9.0 5.5 2.1 16.2 9.9 0.7
cm 48.5 48.5 55.9 3.6 7.1 24.0 7.1 15.6 5.9 1.3 7.3 14.9 22.5 22.7 12.9 22.9 22.9 14.0 5.3 41.1 25.1 1.9
in. 21.5 21.5 39.0 1.8 3.8 15.2 3.6 8.1 2.33/
cm 54.6 54.6 99.1 4.5 9.7 38.6 9.1 20.6 5.8 1.9 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.6 5.8 46.5 51.3 1.9
in. 21.5 26.0 44.0 2.0 3.7 16.2 2.6 10.4 2.33/
cm 54.6 66.0 111.8 5.1 9.4 41.1 6.6 28.4 5.8 1.9 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.1 5.8 57.9 61.4 1.9
in. 21.5 21.5 39.0 1.7 3.6 16.4 2.6 8.1 2.33/
cm 54.6 54.6 99.1 4.4 9.1 41.7 6.6 20.6 5.8 1.9 10.5 18.1 25.7 16.1 9.5 35.6 35.6 13.6 5.8 46.5 51.3 1.9
in. 24.0 32.5 46.0 1.8 5.9 16.7 2.3 10.1 2.3 1 4.1 7.1 10.1 6.9 7.3 16.0 18.0 5.1 2.3 29.3 24.2 0.7
cm 6.10 82.6 116.8 4.5 14.9 42.4 5.8 25.7 5.8 2.5 10.5 18.1 25.7 17.4 18.4 40.6 45.7 13.1 5.8 74.4 61.4 1.9
WATER CONNECTIONS ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS (in.)
12 3
DE FG H I
In Out Condensate
Water
FPT
Size
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
J
4
4
4
LEGEND
1
/2 conduit
1
/2 conduit
Therm
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.3 2.3 18.3 20.2 0.7
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.1 2.3 22.8 24.2 0.7
4.1 7.1 10.1 6.4 3.8 14.0 14.0 5.3 2.3 18.3 20.2 0.7
Pump
K
Ext.
L
3
/4 conduit
Power
Supply
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
Duct Flange Installed (±0.10 in.)
MNOSupply
Width
P
Supply
Depth
RETURN CONNECTION
Using Air Coil Opening
QRSReturn
Depth
T
Return
Height
U
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
Code Return Discharge
L Left Top
R Right Top
a50-8158
Fig. 5 — 50RVC Dimensional Data
10
Page 11
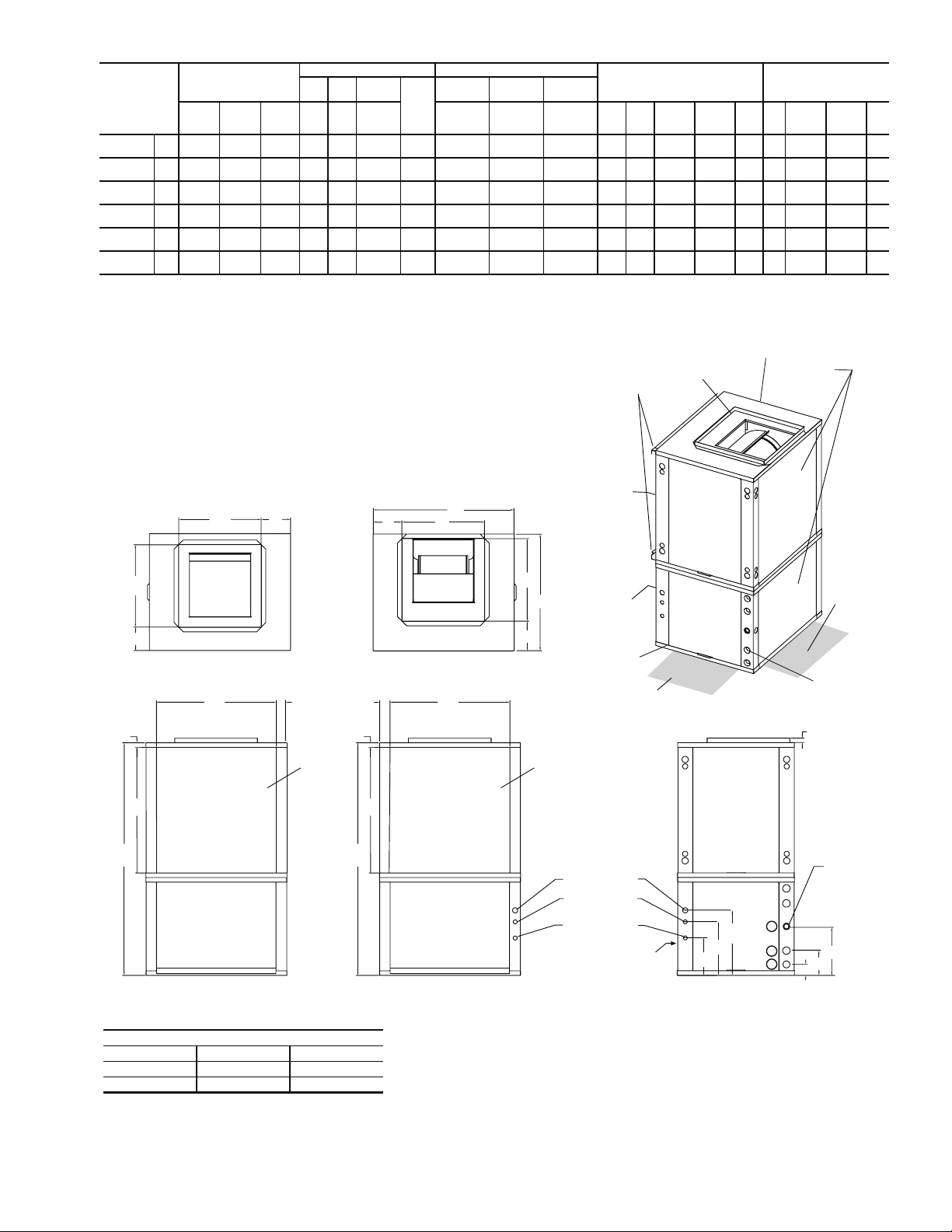
50RVR
UNITS
009-012
015-024
030
036
042-048
060
NOTES:
1. Condensate is 3/4-in. FPT and is switchable from side to front.
2. Vertical unit shipped with filter bracket only extending from unit 2.5 inches. This bracket should be removed when connecting return duct.
3. Discharge flange field installed.
4. Right and left orientation is determined by looking at water connection side.
OVERALL CABINET
A
WidthBDepthCHeightDInEOut
in. 22.4 21.6 22.6 2.6 5.4 7.8
cm 56.8 54.9 57.4 6.6 13.7 19.8 8.9 14.0 20.8 26.9 17.3 14.7 20.3 15.2 5.6 43.4 23.6 2.5
in. 22.4 21.6 34.6 2.4 4.8 8.5
cm 56.8 54.9 87.9 6.1 12.2 21.6 8.9 19.1 25.9 18.3 9.7 35.6 35.6 10.9 5.6 43.4 38.9 2.5
in. 22.4 25.6 40.6 2.4 5.4 9.7
cm 56.8 65.1 103.1 6.1 13.7 24.6 14.5 24.6 31.0 18.3 14.7 35.6 35.6 10.9 5.6 53.6 48.8 2.5
in. 22.4 25.6 40.6 2.4 5.4 9.7
cm 56.8 65.1 103.1 6.1 13.7 24.6 14.5 24.6 31.0 18.3 14.7 35.6 35.6 10.9 5.6 53.6 48.8 2.5
in. 22.4 25.6 48.6 2.4 5.4 9.7
cm 56.8 65.1 123.4 6.1 13.7 24.6 14.5 24.6 31.0 18.3 14.7 35.6 35.6 10.9 5.6 53.6 69.1 2.5
in. 25.4 30.6 50.6 2.4 5.4 10.7
cm 64.5 77.8 128.5 6.1 13.7 27.2 20.6 29.7 36.1 15.7 16.0 45.7 45.7 13.0 5.6 66.3 69.1 2.5
WATER CONNECTIONS ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS (in.)
12 3
Loop
Wate r
F
FPT
Cond-
(in.)
ensate
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
G
1
/2 conduit
Therm Ext Pump
3.5 5.5 8.2 10.6 6.8 5.8 8.0 6.0 2.2 17.1 9.3 1.0
1
/
2
3.5 7.5 10.2 7.2 3.8 14.0 14.0 4.3 2.2 17.1 15.3 1.0
3
/
4
5.7 9.7 12.2 7.2 5.8 14.0 14.0 4.3 2.2 21.1 19.2 1.0
3
/
4
5.7 9.7 12.2 7.2 5.8 14.0 14.0 4.3 2.2 21.1 19.2 1.0
3
/
4
5.7 9.7 12.2 7.2 5.8 14.0 14.0 4.3 2.2 21.1 27.2 1.0
1
8.1 11.7 14.2 6.2 6.3 18.0 18.0 5.1 2.2 26.1 27.2 1.0
1
LEGEND
H
1
/2 conduit
3
/4 conduit
Power
Supply
I
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
Duct Flange Installed (±0.10 in.)
JKLSupply
Standard Filter Bracket
Height
Field Installed
Discharge Flange
(Shipped loose in
blower section)
M
Supply
Depth
RETURN CONNECTION
Using Air Coil Opening
NOPReturn
Depth
Water Connection
Access Panels
Q
Return
Height
R
RIGHT RETURN
M
Fron t
L
N
Air Coil Side
R Configuration - Top View-Right Return
P
K
O
R
Q
C
ASP
Front
R Configuration - Right Return Right View
- Air Coil Opening
Back
LEFT RETURN
K
L Configuration - Top View-Left Return
M
Air Coil Side
O
R
Air Coil
Q
C
Back
L Configuration - Left Return Left View
- Air Coil Opening
P
CSP
Air Coil
B
BSP
L
Front
A
CSP
CAP
ASP
ASP
3’ Service
Access
Left Return
(right
Opposite)
J
Fron t
Water
Connections
1.000
E
D
Condensate
3/4
“
FPT
F
Air Coil
Fron t
Power Supply
3/4“ HV Knockout
Power for
Condensate Pump
1/2“ Knockout
Low Voltage
1/2“ LV Knockout
3’ Service
Access
CSP
CAP
H
G
Front View
Isometric
View
I
3
2
1
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
Code Return Discharge
L Left Top
R Right Top
a50-8159
Fig. 6 — 50RVR Dimensional Data
11
Page 12
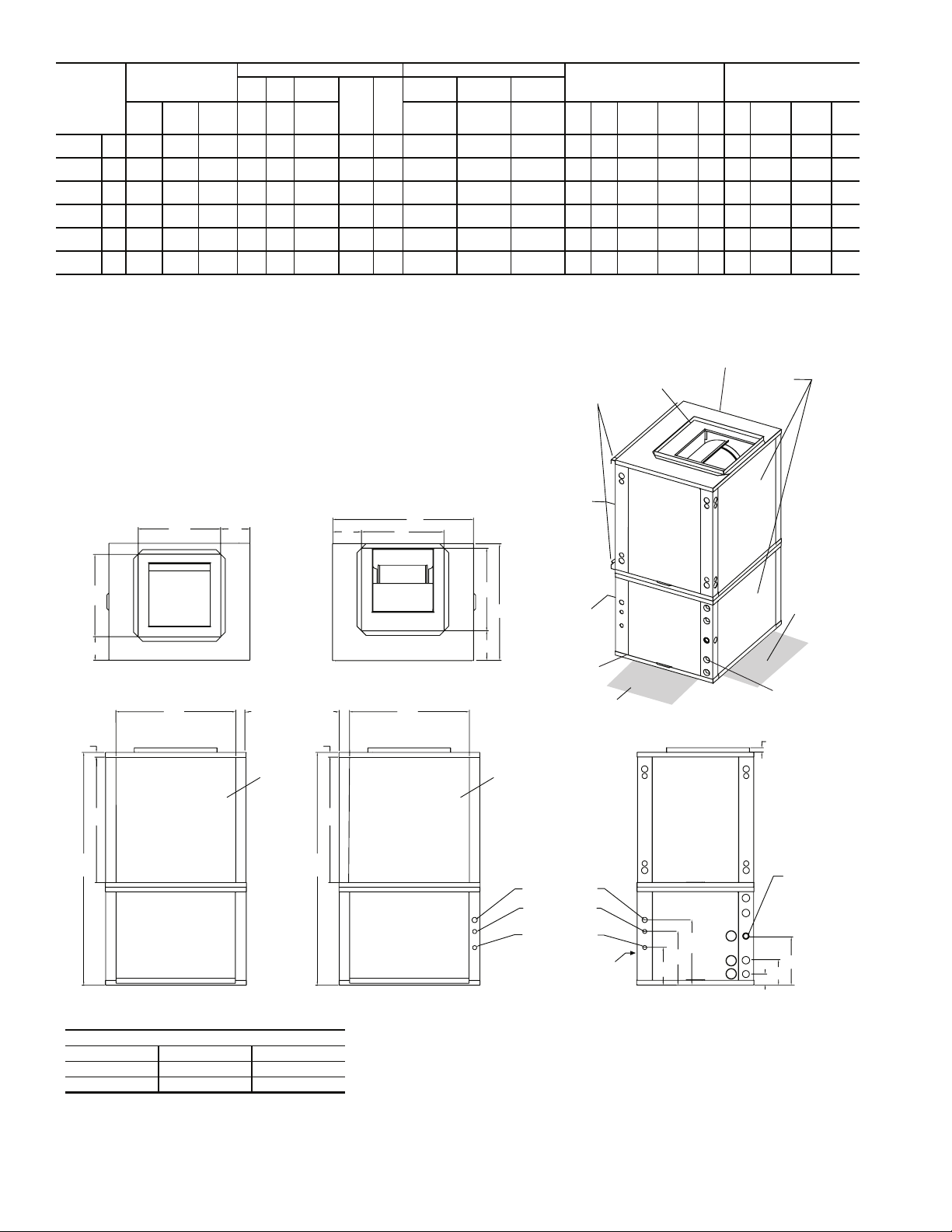
50RVS
UNITS
015-018
024-030
036
042-048
060
070
NOTES:
1. Condensate is 3/4-in. FPT and is switchable from side to front.
2. Vertical unit shipped with filter bracket only extending from unit 2.5 inches. This bracket should be removed when connecting return duct.
3. Discharge flange field installed.
4. Right and left orientation is determined by looking at water connection side.
OVERALL CABINET
A
WidthBDepthCHeightDInEOut
in. 22.4 25.6 40.6 2.4 5.4 9.7
cm 56.8 65.1 103.1 6.1 13.7 24.6 14.5 24.6 31.0 18.3 14.7 35.6 35.6 10.9 5.6 53.6 48.8 2.5
in. 22.4 25.6 44.6 2.4 5.4 9.7
cm 56.8 65.1 113.3 6.1 13.7 24.6 14.5 24.6 31.0 18.3 14.7 35.6 35.6 10.9 5.6 53.6 58.9 2.5
in. 22.4 25.6 48.6 2.4 5.4 9.7
cm 56.8 65.1 123.4 6.1 13.7 24.6 14.5 24.6 31.0 18.3 14.7 35.6 35.6 10.9 5.6 53.6 69.1 2.5
in. 25.4 30.6 50.6 2.4 5.4 10.7
cm 64.5 77.8 128.5 6.1 13.7 27.2 20.6 29.7 36.1 15.7 16.0 45.7 45.7 13.0 5.6 66.3 69.1 2.5
in. 25.4 30.6 54.6 2.4 5.4 10.7
cm 64.5 77.8 138.7 6.1 13.7 27.2 20.6 29.7 36.1 15.7 16.0 45.7 45.7 13.0 5.6 66.3 79.2 2.5
in. 25.4 30.6 58.6 2.4 5.4 10.7
cm 64.5 77.8 148.8 6.1 13.7 27.2 20.6 29.7 36.1 15.7 16.0 45.7 45.7 13.0 5.6 66.3 89.4 2.5
WATER CONNECTIONS ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS (in.)
12 3
F
Cond-
ensate
Loop
Water
FPT
(in.)
3
/
4
3
/
4
3
/
4
11/
11/
11/
HWG
FPT
(in.)
G
1
/2 conduit
Therm Ext Pump
5.7 9.7 12.2 7.2 5.8 14.0 14.0 4.3 2.2 21.1 19.2 1.0
1
/
2
5.7 9.7 12.2 7.2 5.8 14.0 14.0 4.3 2.2 21.1 23.2 1.0
1
/
2
5.7 9.7 12.2 7.2 5.8 14.0 14.0 4.3 2.2 21.1 27.2 1.0
1
/
2
8.1 11.7 14.2 6.2 6.3 18.0 18.0 5.1 2.2 26.1 27.2 1.0
2
8.1 11.7 14.2 6.2 6.3 18.0 18.0 5.1 2.2 26.1 31.2 1.0
2
8.1 11.7 14.2 6.2 6.3 18.0 18.0 5.1 2.2 26.1 35.2 1.0
2
H
1
/2 conduit
I
3
/4 conduit
Power
Supply
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
Duct Flange Installed (±0.10 in.)
JKLSupply
Height
M
Supply
Depth
RETURN CONNECTION
Using Air Coil Opening
NOPReturn
Depth
Q
Return
Height
R
RIGHT RETURN
M
Fron t
L
N
Air Coil Side
R Configuration - Top View-Right Return
P
K
O
R
Air Coil
LEGEND
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
LEFT RETURN
B
K
L Configuration - Top View-Left Return
O
M
Air Coil Side
P
Front
J
R
L
A
Air Coil
Standard Filter Bracket
Air Coil
CSP
Fron t
3’ Service
Access
Field Installed
Discharge Flange
(Shipped loose in
blower section)
BSP
CAP
Isometric
Water Connection
Access Panels
ASP
ASP
View
Water
Connections
1.000
3’ Service
Access
Left Return
(right
Opposite)
Q
C
ASP
Front
R Configuration - Right Return Right View
- Air Coil Opening
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
Code Return Discharge
L Left Top
R Right Top
Back
Q
C
CSP
Back
L Configuration - Left Return Left View
- Air Coil Opening
Fron t
Fig. 7 — 50RVS Dimensional Data
12
Power Supply
3/4“ HV Knockout
Power for
Condensate Pump
1/2“ Knockout
Low Voltage
1/2“ LV Knockout
a50-8169
CSP
H
G
Front View
CAP
I
Condensate
3/4
“
FPT
3
2
1
F
E
D
Page 13
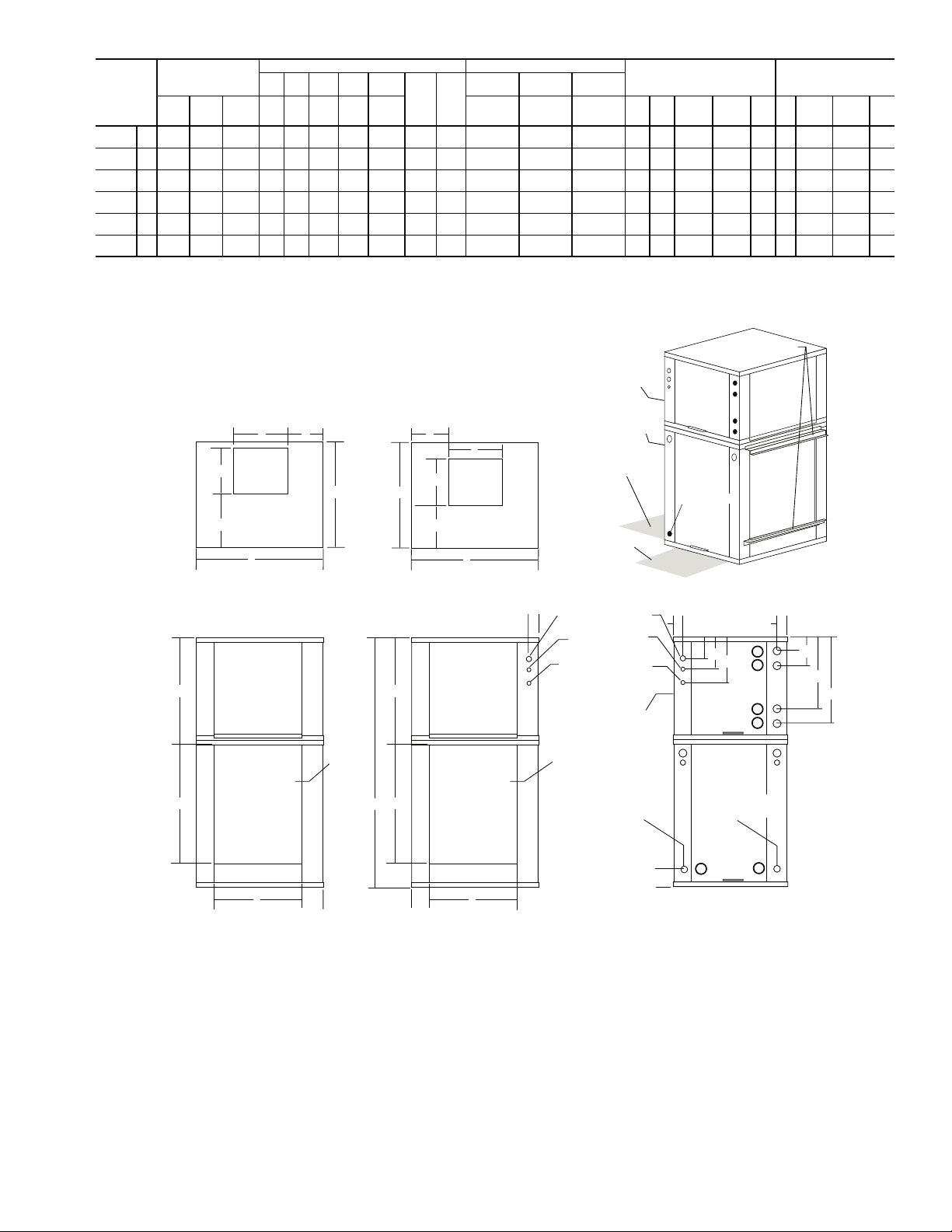
50RDS
UNITS
015-018
024-030
036
042-048
060
070
HWG — Hot Water Generator
NOTES:
1. Condensate is
2. Vertical unit shipped with filter bracket only extending from unit 2.5 inch. This bracket should be removed when connecting return duct.
OVERALL CABINET
A
WidthBDepthCHeightDInEOut
in.
22.4 25.6 44.6 16.9 13.9 5.4 2.4 3.5
cm 56.8 65.1 113.3 42.9 35.3 13.7 6.1 8.9 34.5 24.6 18.3 15.4 20.8 26.4 23.5 27.9 5.6 53.6 51.3 51.8
in.
22.4 25.6 48.6 16.9 13.9 5.4 2.4 3.5
cm 56.8 65.1 123.4 42.9 35.3 13.7 6.1 8.9 34.5 24.6 18.3 15.4 20.8 26.4 23.5 27.9 5.6 53.6 61.5 51.8
in.
22.4 25.6 52.6 16.9 13.9 5.4 2.4 3.5
cm 56.8 65.1 133.6 42.9 35.3 13.7 6.1 8.9 34.5 24.6 18.3 15.4 20.8 26.4 23.5 27.9 5.6 53.6 71.6 51.8
in.
25.4 30.6 54.6 18.9 15.9 5.4 2.4 3.5
cm 64.5 77.8 138.7 48.0 40.4 13.7 6.1 8.9 33.3 24.6 18.3 18.3 22.1 34.4 33.7 26.7 5.6 66.3 71.6 56.9
in.
25.4 30.6 58.6 18.9 15.9 5.4 2.4 3.5
cm 64.5 77.8 148.8 48.0 40.4 13.7 6.1 8.9 33.3 24.6 18.3 18.3 22.1 34.4 33.7 26.7 5.6 66.3 81.8 56.9
in.
25.4 30.6 62.6 18.9 15.9 5.4 2.4 3.5
cm 64.5 77.8 159.0 48.0 40.4 13.7 6.1 8.9 33.3 24.6 18.3 18.3 22.1 34.4 33.7 26.7 5.6 66.3 91.9 56.9
LEGEND
3
/4-in. PVC FPT and is switchable from side to front.
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.) ELECTRICAL KNOCKOUTS (in.)
12 3 4 5
F
G
HWG
HWG
In
Out
H
Cond-
ensate
Loop
HWG
Water
FPT
FPT
(in.)
(in.)
3/4 1/2
3/4 1/2
3/4 1/2
11/2
11/2
11/2
J
1
/2 conduit
Therm
13.6 9.7 7.2 6.1 8.2 10.4 9.3 11.0 2.2 21.1 20.2 20.4
13.6 9.7 7.2 6.1 8.2 10.4 9.3 11.0 2.2 21.1 24.2 20.4
13.6 9.7 7.2 6.1 8.2 10.4 9.3 11.0 2.2 21.1 28.2 20.4
13.1 9.7 7.2 7.2 8.7 13.6 13.3 10.5 2.2 26.1 28.2 22.4
13.1 9.7 7.2 7.2 8.7 13.6 13.3 10.5 2.2 26.1 32.2 22.4
13.1 9.7 7.2 7.2 8.7 13.6 13.3 10.5 2.2 26.1 36.2 22.4
K
1
/2 conduit
Ext
Pump
L
3
/4 conduit
Power
Supply
DISCHARGE CONNECTION
Outlet Opening Only
MNOSupply
Width
Supply
Depth
P
RETURN CONNECTION
Using Return Air Opening
QRSReturn
Depth
T
Return
Height
U
a506743ef.
eps
P
Blower
O
Opening
Front
Q
Air Coil Side
B
Right Return/Bottom Discharge
Floor Foot Print
(Top View)
U
ASP
LEGEND
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
N
N
P
Blower
O
A
A
Opening
Front
CSP
ASP
3’ Service
Access Left Rtn
(right opposite)
Standard Filter Bracket
CAP
BSP
Condensate 3/4”
FPT
ASP
M
Air Coil Side
3’ Service
Access
B
Air Coil
Left Return/Bottom Discharge
Floor Foot Print
(Top View)
1.1
U
CSP
Power Supply
”
HV Knockout
3/4
1/2
”
Low Voltage
1/2
”
LV Knockout
Air Coil
Knockout
CSP
Isometric View
1.6
L
K
J
CAP
BSP
1.6
G
4
3
F
E
D
2
1
T
Front
S
Right ReturnAir Coil Opening
(Right Side View)
Front
Condensate
”
FPT
3/4
Right Return
T
C
Back
R
Back
R
S
Left Return -
Air Coil Opening
(Left Side View)
H
Condensate
3/4
”
FPT
5
Front-View
Left Return
5
Fig. 8 — 50RDS Dimensional Data
13
Page 14
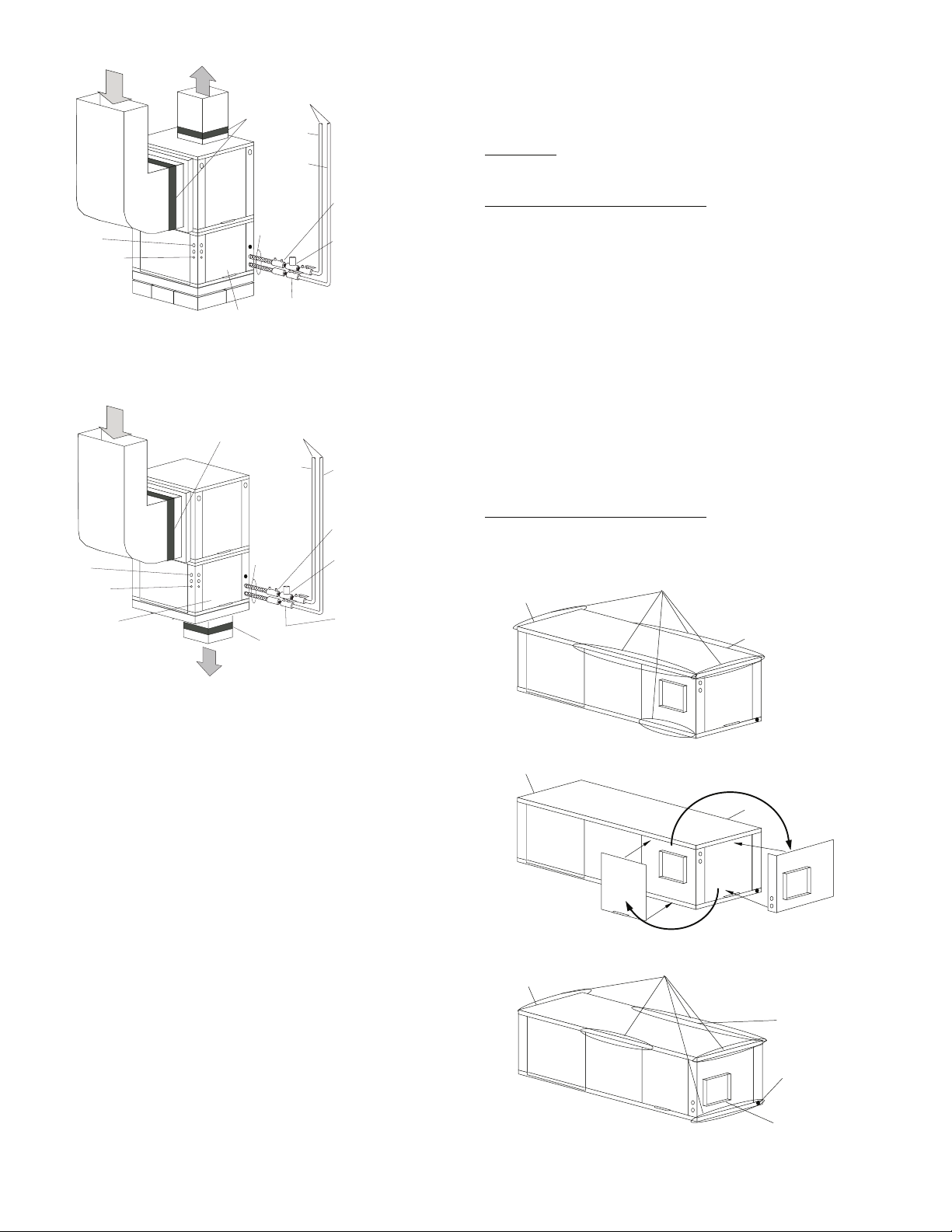
Supply Air
Building
Flexible
Connection
Return
Air
Power
Thermostat
Wiring
Compressor
Access Panel
NOTE: Ball valve with integral pressure temperature plug recommended.
Loop
Water
Out
Water
In
Field-supplied
stainless steel
braid hose
with integral
“ J” swivel
Ball Valve with optional
integral P/T plug
(typical for supply and
return piping)
Balancing Valve
(field installed
and calibrated
accessory)
Low Pressure
Drop Water
Control Valve
(optional)
(field-installed
accessory)
Fig. 9 — Typical Vertical Installation —
50RVC,RVR,RVS Units
Flexible
Connection
Return
Air
Power
Thermostat
Wiring
Compressor
Access Panel
NOTE: Ball valve with integral pressure temperature plug recommended.
Supply Air
Building
Loop
Water
Out
Field-supplied
stainless steel
braid hose
with integral
“ J” swivel
Flexible
Connection
Water
In
Balancing Valve
(field-installed
and calibrated
accessory)
Low Pressure
Drop Water
Control Valve (optional)
(field-installed
accessory)
Ball Valve with optional
integral P/T plug
(typical for supply and
return piping)
conversion process is the same for right and left return configurations. See Fig. 11 and 12.
NOTE: It is not possible to convert return air between left or
right return models in the field due to refrigerant piping
changes.
Preparation
— The unit should be on the ground in a well lit
area for conversion. Hung units should be taken down to
ground level before converting.
Side to Back Discharge Conversion
1. Remove screws to free the top and discharge panels. See
Fig. 11.
2. Remove the access panel and set aside.
3. Lift the discharge panel from side of unit and rotate it to
back using care not to damage blower wiring.
4. Check blower wire routing and connections for undo
tension or contact with sheet metal edges. Re-route if
necessary.
5. Check refrigerant tubing for contact with other components. Adjust if necessary.
6. Reinstall top panel using screws set aside in Step 1.
NOTE: Location for some screws at bottom of discharge panel
may have to be changed.
7. Manually spin fan wheel to check for obstructions.
Adjust for any obstruction found.
8. Replace access panel.
Back to Side Discharge Conversion
— Follow instructions
above for Side to Back Discharge Conversion, noting the
panels would be reversed.
Water
Connection End
Remove Screws
Return Air
Fig. 10 — Typical Downflow Installation —
50RDS Units
Step 3 — Unit Location — The following guidelines
should be considered when choosing a location for a WSHP:
• Units are for indoor use only.
• Locate in areas where ambient temperatures are between
40 F and 100 F and relative humidity is no greater than
75%.
• Provide sufficient space for water, electrical and duct
connections.
• Locate unit in an area that allows easy access and
removal of filter and access panels.
• Allow enough space for service personnel to perform
maintenance.
• Return air must be able to freely enter the space if unit
needs to be installed in a confined area such as a closet.
NOTE: Correct placement of the horizontal unit can play an
important part in minimizing sound problems. Since ductwork is normally applied to these units, the unit can be
placed so that the principal sound emission is outside the occupied space in sound-critical applications. A fire damper
may be required by the local code if a fire wall is penetrated.
FIELD CONVERSION OF DISCHARGE AIR — The discharge air of the 50RHC,RHR,RHS horizontal units can be
converted between side and back discharge in the field. The
Side Discharge
Water
Connection End
Return Air
Move to Side
Water
Connection End
Back Discharge
Replace Screws
Fig. 11 — Conversion Left Return,
Side Discharge to Back Discharge
Rotate
Return Air
Drain
Discharge Air
14
Page 15
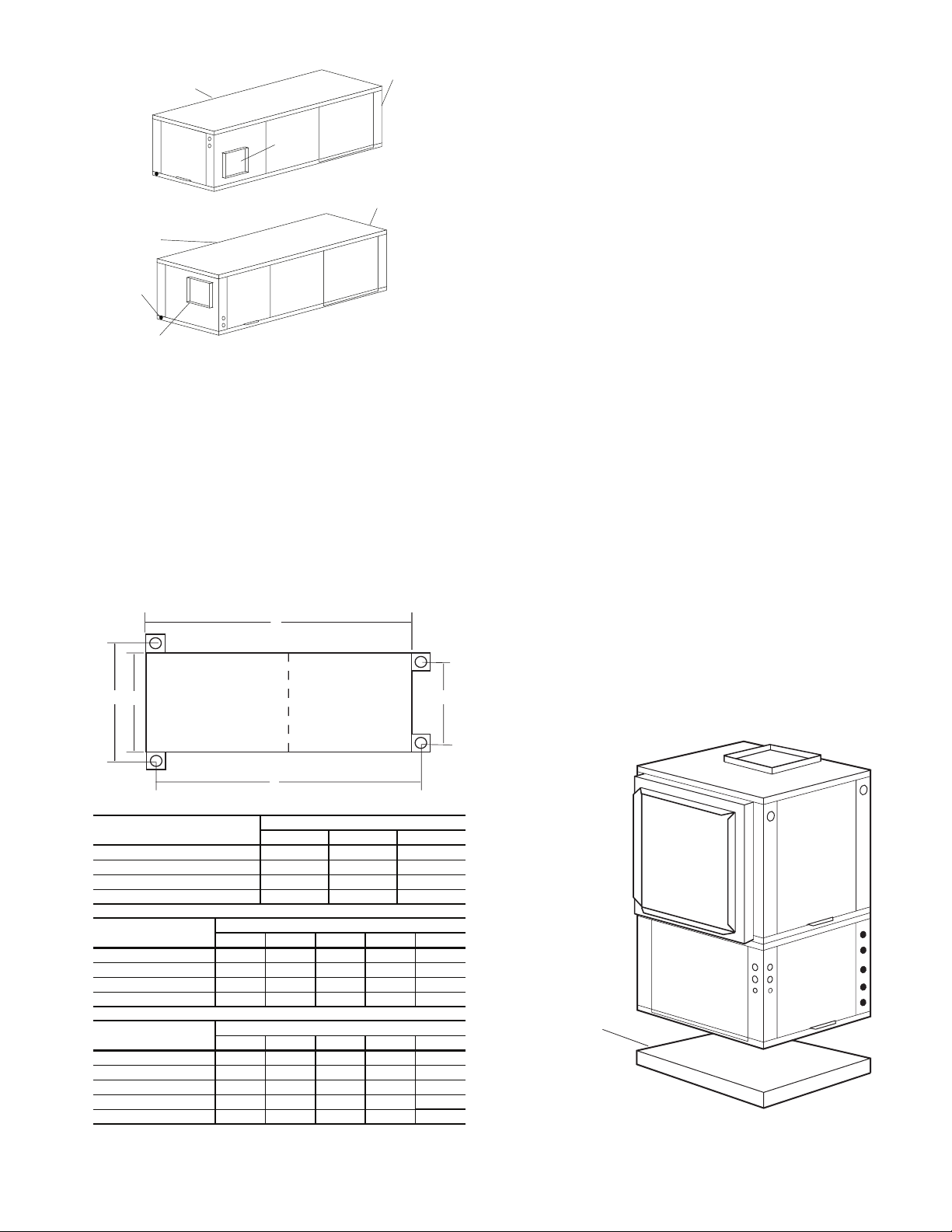
Water
Connection End
Water
Connection End
Return Air
Drain
Discharge Air
Return Air
Supply
Duct
Side Discharge
Back Discharge
Fig. 12 — Conversion Right Return,
Side Discharge to Back Discharge
Step 4 — Mounting the Unit
HORIZONTAL UNITS (50RHC,RHR,RHS) — Horizontal units
should be mounted using the factory-installed hangers. Proper
attachment of hanging rods to building structure is critical for
safety. See Fig. 4 and 13. Rod attachments must be able to support the weight of the unit. See Tables 1-3 for unit operating
weights.
VERTICAL UNITS (50RVC,RVR,RVS,RDS) — Vertical and
downflow units are available in left or right return air configurations. See Fig. 6-8. Mount the unit (except 50RDS) on a
D
D
A
C
Compressor
Section
Air Handler
Section
E
vibration absorption pad slightly larger than the entire base to
minimize vibration transmission. It is not necessary to mount
the unit on the floor. See Fig. 14.
NOTE: Some codes require the use of a secondary drain pan
under vertical units. Check local codes for more information.
Step 5 — Duct System — Size the duct system to han-
dle the design airflow quietly.
NOTE: Depending on the unit, the fan wheel may have a shipping support installed at the factory. This must be removed
before operating unit.
SOUND ATTENUATION — To eliminate the transfer of
vibration to the duct system, a flexible connector is recommended for both discharge and return air duct connections on
metal duct systems. The supply and return plenums should include internal duct liner of fiberglass or be made of duct board
construction to maximize sound attenuation of the blower.
Installing the WSHP unit to uninsulated ductwork in an unconditioned space is not recommended since it will sweat and
adversely affect the unit’s performance.
To reduce air noise, at least one 90-degree elbow could be
included in the supply and return air ducts, provided system
performance is not adversely impacted. The blower speed can
also be changed in the field to reduce air noise or excessive airflow, provided system performance is not adversely impacted.
EXISTING DUCT SYSTEM — If the unit is connected to
existing ductwork, consider the following:
• Verify that the existing ducts have the proper capacity to
handle the unit airflow. If the ductwork is too small,
install larger ductwork.
• Check existing ductwork for leaks and repair as
necessary.
NOTE: Local codes may require ventilation air to enter the
space for proper indoor air quality. Hard-duct ventilation may
be required for the ventilating air supply. If hard ducted ventilation is not required, be sure that a proper air path is provided
for ventilation air to unit to meet ventilation requirement of the
space.
B
50RHC UNITS
006-012 16.9 34.1 21.1
018-030 18 43.1 22.2
036,042 18 47.1 22.2
048,060 22 54.1 26.2
50RHR UNITS
006-024 22.375 43.1 24.375 43.1 20.375
030,036 22.375 52.1 24.375 52.1 20.375
042,048 22.375 61.1 24.375 61.1 20.375
060 25.375 71.1 27.375 71.1 23.375
50RHS UNITS
015,018 22.375 51 24.375 53 20.375
024-036 22.375 61 24.375 63 20.375
042,048 25.375 70 27.375 72 20.375
060 25.375 75 27.375 77 23.375
070 25.375 80 27.375 82 23.375
ABCDE
ABCDE
DIMENSIONS (in.)
ABC
DIMENSIONS (in.)
DIMENSIONS (in.)
Fig. 13 — Horizontal Hanger Bracket
(Factory Installed)
15
Vibration
Absorption
Pad
Fig. 14 — 50RVC,RVR,RVS Units Mounted With
Vibration Absorption Pad
Page 16
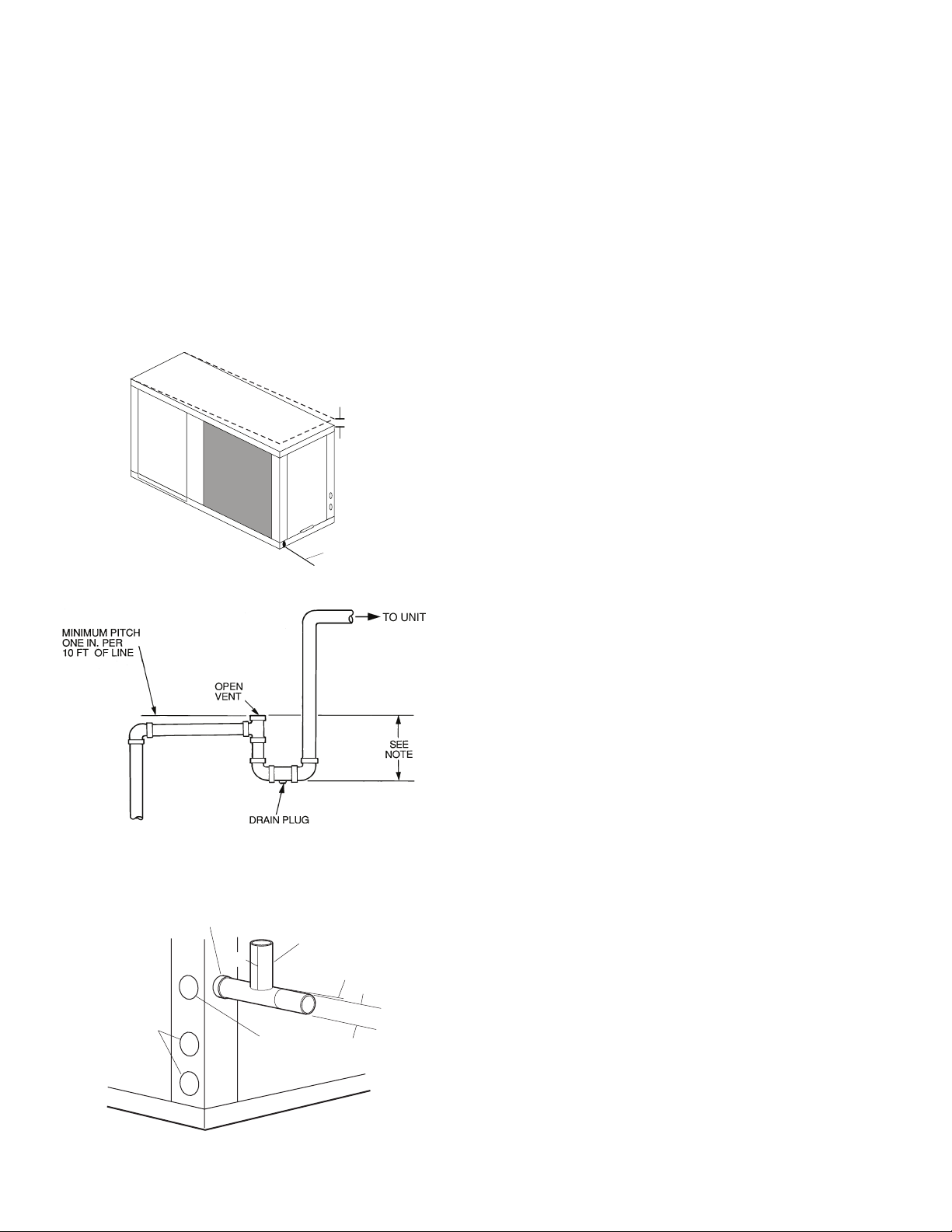
Step 6 — Condensate Drain
HORIZONTAL UNITS (50RHC,RHR,RHS) — Slope the
unit toward the drain at a
If it is not possible to meet the required pitch, install a condensate pump at the unit to pump condensate to building drain.
Horizontal units are not internally trapped, therefore an external trap is necessary. Install each unit with its own individual
trap and means to flush or blowout the condensate drain line.
Do not install units with a common trap or vent. For typical
condensate connections see Fig. 16.
NOTE: Never use a pipe size smaller than the connection.
VERTICAL UNITS (50RVC,RVR,RVS) — Each unit uses a
condensate hose inside all cabinets as a trapping loop, therefore
an external trap is not necessary. See Fig. 17.
Each unit must be installed with its own individual vent and
means to flush or blowout the condensate drain line. Do not install units with a common trap or vent.
Fig. 15 — Horizontal Unit Pitch
NOTE: Trap should be deep enough to offset maximum unit static
difference. A 4-in. trap is recommended.
Fig. 16 — Trap Condensate Drain
3/4” Copper FPT/PVC
Water
Connections
NOTE: Unit does not need to be sloped toward drain.
Fig. 17 — Vertical Condensate Connection
1
/4 in. drop at drain end. See Fig. 15.
1/4” Pitch for
Drainage
Pitch Toward
Drain
Drain Connection
3/4” PVC
Vent
1/2”
Alternate
Condensate
Location
1/4” per foot
slope to drain
1/2”
VENTING — Install a vent in the condensate line of any
application that may allow dirt or air to collect in the line. Consider the following:
• Always install a vent where an application requires a
long horizontal run.
• Always install a vent where large units are working
against higher external static pressure and to allow
proper drainage for multiple units connected to the same
condensate main.
• Be sure to support the line where anticipated sagging from
the condensate or when “double trapping” may occur.
• If condensate pump is present on unit, be sure drain connections have a check valve to prevent back flow of condensate into other units.
Step 7 — Piping Connections — Depending on the
application, there are 3 types of WSHP piping systems to
choose from: water loop, ground-water and ground loop. Refer
to Piping Section of Carrier System Design Manual for additional information.
All WSHP units use low temperature soldered female pipe
thread fittings for water connections to prevent annealing and
out-of-round leak problems which are typically associated with
high temperature brazed connections. Refer to Tables 1-3 for
connection sizes. When making piping connections, consider
the following:
• Use a backup wrench when making screw connections to
unit to prevent internal damage to piping.
• Insulation may be required on piping to avoid condensation in the case where fluid in loop piping operates at
temperatures below dew point of adjacent air.
• Piping systems that contain steel pipes or fittings may
be subject to galvanic corrosion. Dielectric fittings may
be used to isolate the steel parts of the system to avoid
galvanic corrosion.
WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS — Water loop applications
usually include a number of units plumbed to a common piping system. Maintenance to any of these units can introduce air
into the piping system. Therefore, air elimination equipment
comprises a major portion of the mechanical room plumbing.
The flow rate is usually set between 2.25 and 3 gpm per ton
of cooling capacity. For proper maintenance and servicing,
pressure-temperature (P/T) ports are necessary for temperature
and flow verification.
In addition to complying with any applicable codes, consid-
er the following for system piping:
• Piping systems using water temperatures below 50 F
require
to eliminate condensation.
• Avoid all plastic to metal threaded fittings due to the
potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Teflon tape thread sealant is recommended to minimize
internal fouling of the heat exchanger.
• Use backup wrench. Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Flush the piping system prior to operation to remove dirt
and foreign materials from the system.
GROUND-WATER APPLICATIONS (Not Applicable to
50RHC,RVC Units) — Typical ground-water piping is
shown in Fig. 18. In addition to complying with any applicable codes, consider the following for system piping:
• Install shut-off valves for servicing.
• Install pressure-temperature plugs to measure flow and
temperature.
• Connect boiler drains and other valves using a “T” connector to allow acid flushing for the heat exchanger.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Use PVC SCH80 or copper piping material.
NOTE: PVC SCH40 should not be used due to system high
pressure and temperature extremes.
1
/2-in. closed cell insulation on all piping surfaces
16
Page 17
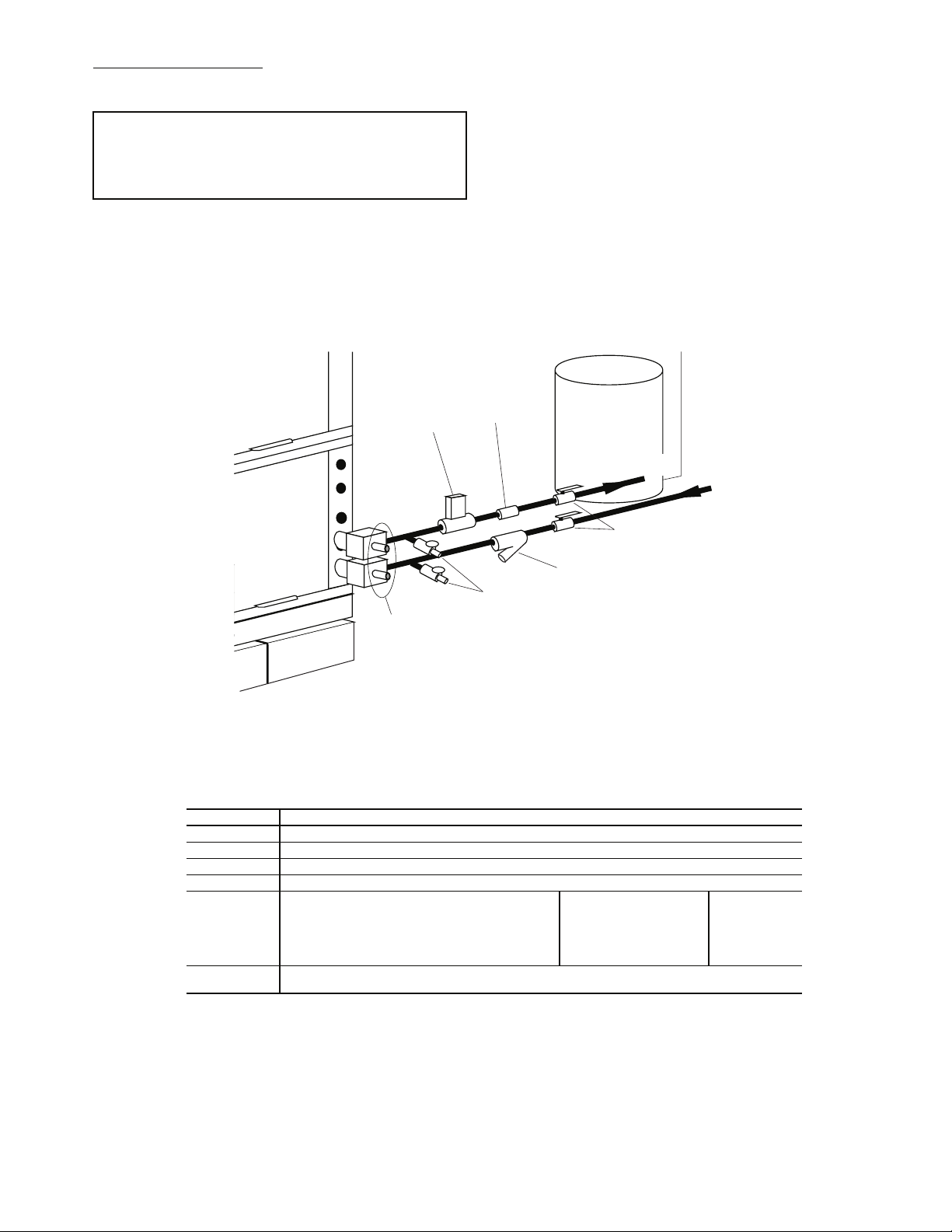
Water Supply and Quantity
— Check water supply. Water
supply should be plentiful and of good quality. See Table 4 for
water quality guidelines.
IMPORTANT: Failure to comply with the above required
water quality and quantity limitations and the closedsystem application design requirements may cause damage
to the tube-in-tube heat exchanger that is not the responsibility of the manufacturer.
In all applications, the quality of the water circulated
through the heat exchanger must fall within the ranges listed in
the Water Quality Guidelines table. Consult a local water treatment firm, independent testing facility, or local water authority
for specific recommendations to maintain water quality within
the published limits.
GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS (Not Applicable to
50RHC,RVC Units) — Temperatures between 25 to 110 F
and a cooling capacity of 2.25 to 3 gpm of flow per ton is recommended. In addition to complying with any applicable
codes, consider the following for system piping:
• Limit piping materials to only polyethylene fusion in the
buried sections of the loop.
• Do not use galvanized or steel fittings at any time due to
corrosion.
• Avoid all plastic to metal threaded fittings due to the
potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Use pressure-temperature (P/T) plugs to measure flow of
pressure drop.
Water
Control
Valve
PressureTemperature
Plugs
Flow
Regulator
Boiler
Drains
Pressure
Tank
Water Out
Water In
From Pump
Shut-Off
Valve
Strainer – Field-Installed Accessory
(16 to 20 mesh recommended for
filter sediment)
Fig. 18 — Typical Ground-Water Piping Installation
Table 4 — Water Quality Guidelines
CONDITION ACCEPTABLE LEVEL
pH 7 to 9 range for copper. Cupronickel may be used in the 5 to 9 range.
Total Hardness Calcium and magnesium carbonate should not exceed 20 grains per gallon (350 ppm).
Iron Oxides Less than 1 ppm.
Iron Bacteria No level allowable.
Corrosion* Max Allowable Level Coaxial Metal
Brackish Use Cupronickel heat exchanger when concentrations of calcium or sodium chloride are greater
*If the concentration of these corrosives exceeds the maximum allowable level, then the potential for serious corrosion
problems exists.
†Sulfides in the water quickly oxidize when exposed to air, requiring that no agitation occur as the sample is taken.
Unless tested immediately at the site, the sample will require stabilization with a few drops of one Molar zinc acetate
solution, allowing accurate sulfide determination up to 24 hours after sampling. A low pH and high alkalinity cause system problems, even when both values are within ranges shown. The term pH refers to the acidity, basicity, or neutrality
of the water supply. Below 7.0, the water is considered to be acidic. Above 7.0, water is considered to be basic. Neutral
water contains a pH of 7.0.
NOTE: To convert ppm to grains per gallon, divide by 17. Hardness in mg/l is equivalent to ppm.
Ammonia, Ammonium Hydroxide 0.5 ppm Cu
Ammonium Chloride, Ammonium Nitrate 0.5 ppm Cu
Ammonium Sulfate 0.5 ppm Cu
Chlorine/Chlorides 0.5 ppm CuNi
Hydrogen Sulfide† None Allowable —
than 125 ppm are present. (Seawater is approximately 25,000 ppm.)
17
Page 18

Step 8 — Field Power Supply Wiring
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock,
open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in
an open position during installation.
Use only copper conductors for field-installed electrical
wiring. Unit terminals are not designed to accept other
types of conductors. Failure to follow this safety precaution
could lead to equipment damage.
All field installed wiring, including the electrical ground,
MUST comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) as
well as applicable local codes. In addition, all field wiring must
conform to the Class II temperature limitations described in the
NEC.
Refer to unit wiring diagrams Fig. 19-22 for a schematic of
the field connections, which must be made by the installing (or
electrical) contractor. Refer to Tables 5-7 for fuse sizes.
Consult the unit wiring diagram located on the inside of the
compressor access panel to ensure proper electrical hookup.
The installing (or electrical) contractor must make the field
connections when using field-supplied disconnect.
Operating voltage must be the same voltage and phase as
shown in Electrical Data shown in Tables 5-7.
Make all final electrical connections with a length of flexible conduit to minimize vibration and sound transmission to
the building.
POWER CONNECTION — Make line voltage connection
by connecting the incoming line voltage wires to the L side
of the CC terminal as shown in Fig. 23. See Tables 5-7 for
correct wire and maximum overcurrent protection sizing.
SUPPLY VOLTAGE — Operating voltage to unit must be
within voltage range indicated on unit nameplate.
On 3-phase units, voltages under load between phases must
be balanced within 2%. Use the following formula to determine the percentage voltage imbalance:
% Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Example: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
AB = 452 volts
BC = 464 volts
AC = 455 volts
Average Voltage =
452 + 464 + 455
1371
=
3
= 457
3
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage:
(AB) 457 – 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 – 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 – 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is
below the maximum allowable 2%.
Operation on improper line voltage or excessive phase
imbalance constitutes abuse and may cause damage to electrical components.
NOTE: If more than 2% voltage imbalance is present, contact
your local electric utility.
208-VOLT OPERATION — All 208-230 volt units are factory
wired for 208 volts. The transformers may be switched to
230-volt operation by switching the red (208 volt) wire with
the orange (230 volt) wire at the L1 terminal.
7
457
Step 9 — Field Control Wiring
THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS — The thermostat should
be wired directly to the Aquazone™ control board. See
Fig. 19-22, and 24.
WATER FREEZE PROTECTION — The Aquazone control
allows the field selection of source fluid freeze protection
points through jumpers. The factory setting of jumper JW3
(FP1) is set for water at 30 F. In earth loop applications, jumper
JW3 should be clipped to change the setting to 10 F when
using antifreeze in colder earth loop applications. See Fig. 25.
AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION — The air coil freeze
protection jumper JW2 (FP2) is factory set for 30 F and should
not need adjusting.
ACCESSORY CONNECTIONS — Terminal A on the control
is provided to control accessory devices such as water valves,
electronic air cleaners, humidifiers, etc. This signal operates
with the compressor terminal. See Fig. 26. Refer to the specific
unit wiring schematic for details.
NOTE: The A terminal should only be used with 24 volt
signals — not line voltage signals.
WATER SOLENOID VALVES — Water solenoid valves may
be used on primary secondary pump and ground water installations. A typical well water control valve wiring, which can
limit waste water in a lockout condition is shown in Fig. 26. A
slow closing valve may be required to prevent water hammer.
When using a slow closing valve, consider special wiring conditions. The valve takes approximately 60 seconds to open
(very little water will flow before 45 seconds) and it activates
the compressor only after the valve is completely opened by
closing its end switch. When wired as shown, the valve will
have the following operating characteristics:
1. Remain open during a lockout
2. Draw approximately 25 to 35 VA through the “Y” signal
of the thermostat.
IMPORTANT: Connecting a water solenoid valve can
overheat the anticipators of electromechanical thermostats. Only use relay based electronic thermostats.
18
Page 19

AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
COMPR — Compressor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HWTS — High (Leaving) Water Temperature
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
*Optional wiring.
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 265 v (BRN) lead for 265/1/60 units, or
208 v (RED) lead for 208/1/60. For 230/1/60 switch RED and
ORG leads at L1 and insulate RED lead. Transformer is energy
limiting or may have circuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using
antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Typical Aquazone thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat
installation instructions for wiring to the unit. Thermostat wiring
must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit
supply voltage.
Switch
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
PM — Performance Monitor
RV — Reversing Valve Coil
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW1 jumper
and dry contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via control board standoffs and
screws to control box. (Ground available from top two standoffs
as shown.)
8. For high or low speed remove BLU wire from BR ‘NO’
and replace with BLK or RED wire respectively. Tape off unused
terminal.
9. Both DIP switches need to be in the ON position.
a50-8160
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Fig. 19 — Typical Aquazone™ Complete C Control Wiring
19
Page 20
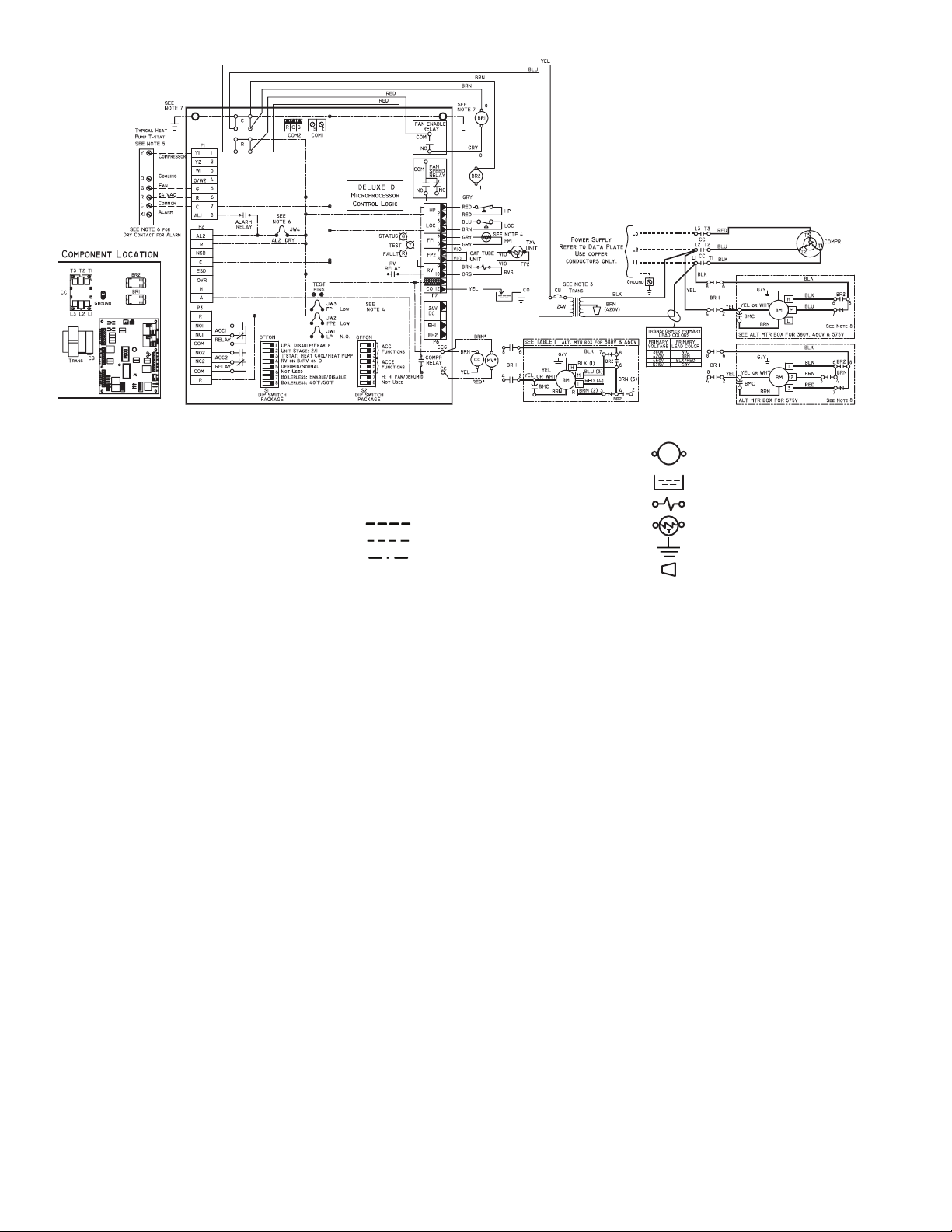
LEGEND
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
COMPR — Compressor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
*Optional wiring.
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 208 v (RED) lead for 208/3/60. For 230/3/60
switch RED and ORG leads at L1 and insulate RED lead.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Typical Aquazone thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wiring to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1
and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
a50-8161
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut AL2 dry
jumper and dry contact will be available between AL1 and
AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via control board standoffs
and screws to control box. (Ground available from top two
standoffs as shown.)
8. Blower motor is factory wired for medium and high speeds.
For any other combination of speeds, attach the lower speed
wire to fan speed relay N.O. wire.
Fig. 20 — Typical Aquazone™ Deluxe D Control Wiring
20
Page 21
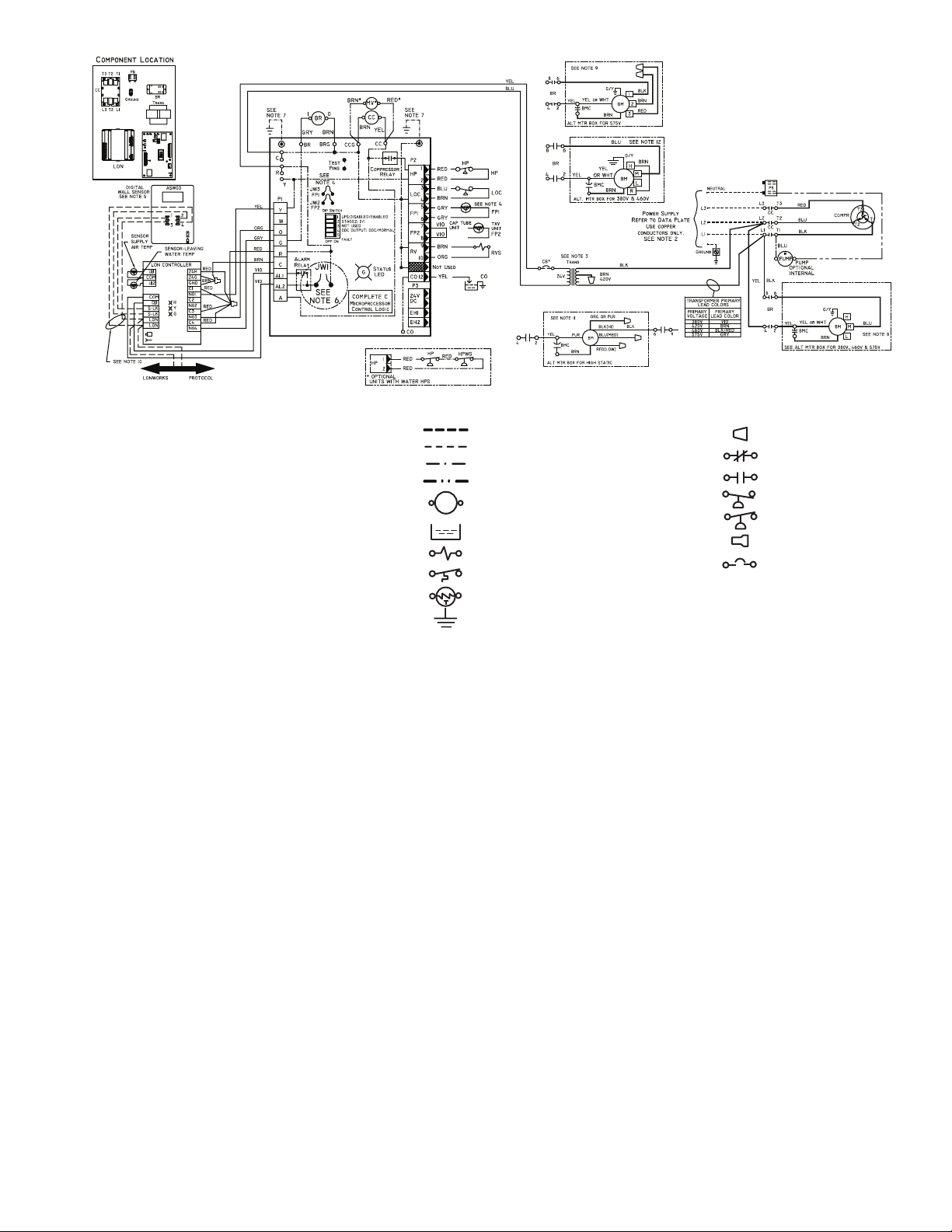
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
COMPR — Compressor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High Pressure Water Switch
JW1 — Clippable Field Selection Jumper
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
LON — Local Operating Network
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
PB — Power Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
*Optional wiring.
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
a50-8153
Wire Nut
Relay Contacts - N.C.
Relay Contacts - N.O.
Low Pressure Switch
High Pressure Switch
Splice Cap
Circuit Breaker
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 460 v (BLK/RED) lead for 460/3/60 units, 575 v (GRY) lead for 575/3/60 units, or 380 v (VIO) lead for 380/3/50 units.
For 420/3/50 operation, switch VIO and BRN leads at L1 and insulate VIO lead. Transformer is energy limiting or may have circuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Typical thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wiring to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
6. Factory cut JW1 jumper. Dry contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Complete C board standoffs and screws to control box. (Ground available from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Fan motors are factory wired for medium speed. For high or low speed, remove BLU wire from fan motor speed tap “M” and connect to “H” for
high speed or “L” for low speed.
9. For low speed, remove BLK wire from BR “6” and replace with RED. Connect BLK and BRN wires together.
10. Optional LON wires. Only connect if LON connection is desired at the wall sensor.
11. For blower motors with leads. For medium or low speed, diconnect BLK wire from BR “6”. Connect BLK and ORG/PUR wire together. Connect
RED for low or BLU for medium to BR “6”.
12. Blower motor is factory wired to medium speed. For low speed, remove BLU wire from medium tap and connect to low speed tap. For high
speed, remove BLU wire from existing speed tap and remove BRN jumperwire from high speed tap. Connect BLU wire to high speed tap. Tape
off unconnected end of BRN jumper.
Fig. 21 — Typical Aquazone™ Complete C and LON Controller Wiring
21
Page 22

a50-8154
LEGEND
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
COMPR — Compressor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High Pressure Water Switch
JW1 — Clippable Field Selection Jumper
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
*Optional wiring.
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 460 v (BLK/RED) lead for 460/3/60 units, 575 v (GRY) lead for 575/3/60 units, or 380 v (VIO) lead for 380/3/50 units.
For 420/3/50 operation, switch VIO and BRN leads at L1 and insulate VIO lead. Transformer is energy limiting or may have circuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Typical thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wiring to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
6. Factory cut JW1 jumper. Dry contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Deluxe D board standoffs and screws to control box. (Ground available from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Blower motor is factory wired for medium and high speeds. For any other combination of speeds, at the motor attach the BLK wire to the higher
of the two desired speed taps and the BLU wire to the lower of the two desired speed taps.
9. Blower motor is factory wired for high and low speeds. No other combination is available.
10. Optional LON wires. Only connect if LON connection is desired at the wall sensor.
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Relay Contacts - N.C.
Relay Contacts - N.O.
Low Pressure Switch
High Pressure Switch
Splice Cap
Circuit Breaker
Fig. 22 — Typical Aquazone™ Deluxe D and LON Controller Wiring
22
Page 23

a50-8162
Fig. 23 — 50RHC,RVC,RHR,RVR,RHS,RVS,RDS Typical Single-Phase
Line Voltage Power Connection
a50-6267tf.tif
NOTE: Low voltage connector may be removed for easy installation.
Fig. 24 — Low Voltage Field Wiring
a50-6268tf.tif
AQUAZONE CONTROL (C Control Shown)
Fig. 25 — Typical Aquazone Control Board
Jumper Locations
TERMINAL STRIP P2
C
TYPICAL
24 VAC
A
WATER
VALVE
Fig. 26 — Typical D Control Accessory Wiring
23
Page 24

Table 5 — 50RHC,RVC Electrical Data
50RHC,RVC
UNITS
006*
009
012
018
024
030
036
041†
042
048
060
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
RLA — Rated Load Amps
VOLTS-PHASE
60 Hz
208/230-1 197/254 2.9 17.7 0.40 3.3 4.1 15
265-1 239/292 2.5 15.0 0.35 2.8 3.5 15
208/230-1 197/254 3.9 22.2 0.80 4.7 5.7 15
265-1 239/292 3.3 18.8 0.70 4.0 4.8 15
208/230-1 197/254 5.3 27.9 0.80 6.1 7.5 15
265-1 239/292 4.2 22.2 0.70 4.9 6.0 15
208/230-1 197/254 8.6 49.0 1.00 9.6 11.7 20
265-1 239/292 8.1 44.0 0.86 8.9 11.0 15
208/230-1 197/254 9.8 56.0 1.50 11.3 13.8 20
265-1 239/292 9.1 55.0 1.30 10.4 12.7 20
208/230-3 197/254 6.7 51.0 1.50 8.2 9.9 15
460-3 414/506 3.5 25.0 0.76 4.2 5.1 15
208/230-1 197/254 11.2 61.0 3.00 14.2 16.9 25
265-1 239/292 10.0 58.0 2.70 12.7 15.2 25
208/230-3 197/254 6.9 55.0 3.00 9.9 11.7 15
460-3 414/506 3.6 28.0 1.70 5.3 6.2 15
208/230-1 197/254 15.4 82.0 1.80 17.2 21.1 35
265-1 239/292 14.4 83.0 2.00 16.4 20.0 30
208/230-3 197/254 9.6 70.0 1.80 11.4 13.8 20
460-3 414/506 4.9 33.0 1.24 6.1 7.4 15
208/230-1 197/254 16.2 96.0 3.00 19.2 23.2 35
208/230-3 197/254 10.3 75.0 3.00 13.3 15.8 25
460-3 414/506 4.3 40.0 1.70 6.0 7.1 15
575-3 518/633 4.3 34.0 1.40 5.7 6.8 15
208/230-1 197/254 17.1 105.0 3.00 20.1 24.3 40
208/230-3 197/254 10.7 85.0 3.00 13.7 16.4 25
460-3 414/506 5.3 42.0 1.70 7.0 8.3 15
575-3 518/633 3.7 31.0 1.50 5.2 6.1 15
208/230-1 197/254 18.3 102.0 3.40 21.7 26.3 40
208/230-3 197/254 12.6 91.0 3.40 16.0 19.2 30
460-3 414/506 5.7 42.0 1.80 7.5 8.9 15
575-3 518/633 4.7 39.0 1.40 6.1 7.2 15
208/230-1 197/254 25.6 170.0 4.30 29.9 36.4 60
208/230-3 197/254 14.7 124.0 4.30 19.0 22.7 35
460-3 414/506 7.4 59.6 2.50 9.9 11.8 15
575-3 518/633 5.9 49.4 1.90 7.8 9.3 15
LEGEND *Size 006 available in 50RHC unit only.
VOLTAGE
MIN/MAX
COMPRESSOR FAN
RLA LRA
MOTOR
FLA
†Size 041 available in 50RVC unit only.
NOTES:
1. HACR circuit breaker in U.S.A. only.
2. All fuses Class RK-5.
TOTAL
UNIT
FLA
MIN
CIRCUIT
AMP
MAX
FUSE/HACR
24
Page 25

Table 6 — 50RHR,RVR Electrical Data
50RHR,RVR
UNITS
006*
009
012
015
019
024
030
036
042
048
060
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Size 006 is available in 50RHR units only.
VOLTS-PHASE
LEGEND
60 Hz
208/230-1 197/254 2.9 17.7 0.40 3.3 4.0 15
265-1 239/292 2.5 15.0 0.35 2.8 3.5 15
208/230-1 197/254 3.9 22.2 0.80 4.7 5.7 15
265-1 239/292 3.3 18.8 0.90 4.2 5.0 15
208/230-1 197/254 5.3 27.9 0.80 6.1 7.5 15
265-1 239/292 4.2 22.2 0.90 5.1 6.2 15
208/230-1 197/254 5.9 29.0 1.00 6.9 8.4 15
265-1 239/292 5.4 27.0 0.86 6.3 7.7 15
208/230-1 197/254 7.9 48.3 1.10 9.0 11.0 15
265-1 239/292 7.1 41.0 0.90 8.0 9.7 15
208/230-1 197/254 8.7 48.3 1.30 10.0 12.1 20
265-1 239/292 8.3 47.0 1.58 9.9 12.0 20
208/230-3 197/254 6.0 50.0 1.30 7.3 8.8 15
460-3 414/506 3.2 25.0 0.85 4.1 4.9 15
208/230-1 197/254 11.2 60.0 1.90 13.1 15.9 25
265-1 239/292 10.3 58.0 1.66 11.9 14.5 20
208/230-3 197/254 6.4 50.0 1.90 8.3 9.9 15
460-3 414/506 3.2 25.0 1.00 4.2 5.0 15
208/230-1 197/254 14.1 84.0 3.00 17.1 20.6 30
265-1 239/292 13.5 83.0 2.70 16.2 19.5 30
208/230-3 197/254 8.2 63.4 3.00 11.2 13.3 20
460-3 414/506 4.1 36.0 1.70 5.8 6.8 15
208/230-1 197/254 16.2 96.0 3.00 19.2 23.2 35
208/230-3 197/254 10.3 75.0 3.00 13.3 15.8 25
460-3 414/506 4.3 40.0 1.70 6.0 7.1 15
575-3 518/633 3.7 31.0 1.50 5.2 6.1 15
208/230-1 197/254 18.3 102.0 3.40 21.7 26.2 40
208/230-3 197/254 12.6 91.0 3.40 16.0 19.2 30
460-3 414/506 5.7 42.0 1.80 7.5 8.9 15
575-3 518/633 4.7 39.0 1.60 6.3 7.5 15
208/230-1 197/254 25.6 170.0 4.30 29.9 36.4 60
208/230-3 197/254 14.7 124.0 4.30 19.0 22.7 35
460-3 414/506 7.4 59.6 2.50 9.9 11.8 15
575-3 518/633 5.9 49.4 2.20 8.1 9.8 15
VOLTAGE
MIN/MAX
COMPRESSOR FAN
RLA LRA
MOTOR
FLA
TOTAL
UNIT
FLA
MIN
CIRCUIT
AMP
MAX
FUSE/HACR
25
Page 26

Table 7 — 50RDS, RHS, RVS Electrical Data
50RDS,
RHS,
RVS
UNIT
015
018
024
030
030
HIGH
STATIC
036
036
HIGH
STATIC
042
048
060
070
FLA — Full Load Amps LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration RLA — Rated Load Amps
HWR — Hot Water Reheat
VOLTSPHASE
60 Hz
208/230-1 197/254 4.9 26.0 1.00 5.9 7.2 15 0.8 6.7 7.9 15
265-1 239/292 4.4 28.0 0.86 5.2 6.3 15 0.7 8.0 7.1 15
208/230-1 197/254 7.1 38.0 1.00 8.1 9.8 15 0.8 8.9 10.7 15
265-1 239/292 5.5 32.0 0.86 6.4 7.8 15 0.7 7.1 8.5 15
208/230-1 197/254 10.3 56.0 1.10 11.4 13.9 20 0.8 12.8 15.5 25
265-1 239/292 8.7 47.0 0.90 9.6 11.7 20 0.7 10.6 12.9 20
208/230-3 197/254 7.1 45.0 1.10 8.2 9.9 15 0.8 9.0 10.8 20
460-3 414/506 3.5 22.4 0.57 4.1 5.0 15 0.7 4.8 5.7 15
208/230-1 197/254 12.2 67.0 1.30 13.5 16.5 25 0.8 14.3 17.4 25
265-1 239/292 10.9 56.0 1.58 12.5 15.2 25 0.7 13.2 15.9 25
208/230-3 197/254 7.7 55.0 1.30 9.0 10.9 15 0.8 9.8 11.7 15
460-3 414/506 3.8 27.0 0.85 4.7 5.7 15 0.7 5.4 6.4 15
208/230-1 197/254 12.2 67.0 1.30 13.5 16.5 25 0.8 14.8 17.9 30
265-1 239/292 10.9 56.0 1.58 12.5 15.2 25 0.7 13.6 16.3 25
208/230-3 197/254 7.7 55.0 1.30 9.0 10.9 15 0.8 10.3 12.2 15
460-3 414/506 3.8 27.0 0.85 4.7 5.7 15 0.7 5.8 6.8 15
208/230-1 197/254 13.5 73.0 1.80 15.3 18.6 30 0.8 16.1 19.5 30
265-1 239/292 12.8 71.0 2.00 14.8 18.0 30 0.7 15.5 18.7 30
208/230-3 197/254 9.6 63.0 1.80 11.4 13.8 20 0.8 12.2 14.6 20
460-3 414/506 4.5 31.0 1.24 5.7 6.8 15 0.7 6.5 7.6 15
208/230-1 197/254 13.5 73.0 1.80 15.3 18.6 30 0.8 17.3 20.7 30
265-1 239/292 12.8 71.0 2.00 14.8 18.0 30 0.7 16.2 19.4 30
208/230-3 197/254 9.6 63.0 1.80 11.4 13.8 20 0.8 13.4 15.8 25
460-3 414/506 4.5 31.0 1.24 5.7 6.8 15 0.7 6.9 8.0 15
208/230-1 197/254 16.5 95.0 1.90 18.4 22.6 35 0.8 19.2 23.3 35
208/230-3 197/254 10.3 77.0 1.90 12.2 14.7 25 0.8 13.0 15.6 25
460-3 414/506 5.1 39.0 1.00 6.1 7.4 15 0.7 6.8 8.1 15
575-3 518/633 4.2 31.0 0.80 5.0 6.1 15 N/A N/A N/A N/A
208/230-1 197/254 18.3 109.0 3.00 21.3 25.9 40 1.07 22.4 26.9 45
208/230-3 197/254 12.4 88.0 3.00 15.4 18.5 30 1.07 16.5 19.6 30
460-3 414/506 6.4 44.0 1.70 8.1 9.7 15 1.07 9.2 10.8 15
575-3 518/633 4.8 34.0 1.50 6.3 7.5 15 N/A N/A N/A N/A
208/230-1 197/254 25.0 169.0 3.40 28.4 34.6 50 1.07 29.5 35.7 60
208/230-3 197/254 17.3 123.0 3.40 20.7 25.0 40 1.07 21.8 26.1 40
460-3 414/506 6.7 49.5 1.80 8.5 10.2 15 1.07 9.6 11.2 15
575-3 518/633 5.8 40.0 1.60 7.4 8.8 15 N/A N/A N/A N/A
208/230-1 197/254 28.8 169.0 4.30 33.1 40.4 60 1.07 34.8 42.0 70
208/230-3 197/254 17.3 137.0 4.30 21.6 25.9 40 1.07 23.3 27.6 40
460-3 414/506 9.0 62.0 2.50 11.5 13.7 20 1.07 12.6 14.8 20
575-3 518/633 6.6 49.0 2.20 8.8 10.5 15 N/A N/A N/A N/A
VOLTAGE
MIN/MAX
COMPRESSOR
RLA LRA
LEGEND
FAN
MOTOR
FLA
TOTAL
UNIT
FLA
MIN
CIRCUIT
AMP
MAX
FUSE/HACR
REHEAT
PUMP
FLA
UNITS WITH HWR
TOTAL
UNIT
FLA
MIN
CIRCUIT
AMP
MAX
FUSE /
HACR
PRE-START-UP
System Checkout —
follow the system checkout procedure outlined below before
starting up the system. Be sure:
1. Voltage is within the utilization range specifications of the
unit compressor and fan motor and voltage is balanced
for 3 phase units.
2. Fuses, breakers and wire are correct size.
3. Low voltage wiring is complete.
4. Piping and system flushing is complete.
5. Air is purged from closed loop system.
6. System is balanced as required. Monitor if necessary.
When the installation is complete,
7. Isolation valves are open.
8. Water control valves or loop pumps are wired.
9. Condensate line is open and correctly pitched.
10. Transformer switched to lower voltage tap if necessary.
11. Blower rotates freely — shipping support is removed.
12. Blower speed is on correct setting.
13. Air filter is clean and in position.
14. Service/access panels are in place.
15. Return-air temperature is between 40 to 80 F heating and
50 to 110 F cooling.
16. Air coil is clean.
17. Control field selected settings are correct.
26
Page 27
AIR COIL — To obtain maximum performance, clean the air
coil before starting the unit. A ten percent solution of dishwasher detergent and water is recommended for both sides of
the coil. Rinse thoroughly with water.
PSC (Permanent Split Capacitor) Blower
Speed Selection —
factory set to deliver rated airflow at nominal static (0.15 in.
wg) on medium speed. Where higher static is needed, high
speed can be utilized (0.4 to 0.5 in. wg). Low speed will
deliver approximately 85% of rated airflow (0.10 in. wg). The
PSC blower fan speed can be changed on all units by swapping
wires connected to the relay contacts that control the fan. See
Fig. 27.
FOR 50RHR,RVR,RHS,RVS AND RDS UNITS — On the
control, the black wire is connected to High, blue wire is
connected to Medium and red wire is connected to Low. See
Fig. 19-22.
NOTE: Available airflows for all units are shown in Tables 8-13.
FOR 50RHC,RVC UNITS — The PSC blower fan speed
can be changed by moving the blue wire on the fan motor terminal block to the desired speed as shown in Fig. 27. The
50RHC,RVC units are designed to deliver rated airflow at
nominal static (0.15 in. wg) on medium speed (factory setting)
and rated airflow at a higher static (0.4 to 0.5 in. wg) on high
All water source heat pumps are
Table 8 — 50RHR,RVR Blower Performance
CONNECT THE BLUE WIRE TO:
H FOR HIGH SPEED FAN
M FOR MEDIUM SPEED FAN
L FOR LOW SPEED FAN
BLU
MEDIUM FACTORY SETTING
L
M
H
FAN MOTOR
Fig. 27 — 50RHC,RVC Blower Speed Selection
speed for applications where higher static is required. Low
speed will deliver approximately 85% of rated airflow at
0.10 in. wg. An optional ‘High Static’ blower is available by
using the special option code in the model nomenclature.
50RHR,RVR
UNITS
006* 200 150
009 300 225
012 375 300
015 500 375
019 600 450
024 800 600
030 1000 750
036 1200 900
042 1400 1050
048 1600 1200
High Static
048
060 2000 1500
CFM — Cubic Feet Per Minute
*Size 006 available in 50RHR units only.
RATED
CFM
1600 1200
Shaded areas are below minimum CFM. This data is
provided for troubleshooting information only.
MIN
CFM
FAN
SPEED
HI 300 290 280 270 260 250 240 230 210 190 160 110
MED 240 230 220 210 200 190 180 160 140 130 110
LO 220 210 200 200 190 180 160 150 130 130
HI 450 440 430 420 400 390 370 350 320 310 300 230
MED 410 400 390 380 360 350 340 330 310 290 270
LO 370 360 350 340 320 320 310 300 280 260 240
HI 470 460 450 440 430 420 400 390 380 370 350 330 290
MED 410 400 380 370 360 360 350 340 330 320 310 290
LO 340 330 320 320 310 310 300 300 290 290
HI 750 730 710 700 680 660 630 600 570 540 500 400
MED 660 640 620 610 590 570 550 530 500 470 440 370
LO 580 570 550 540 520 500 480 460 430 400 370
HI 850 820 790 770 740 710 670 640 600 560 520 450
MED 700 680 660 640 620 590 560 530 500 470 440
LO 600 580 560 540 510 490 460 460
HI 980 950 920 890 860 830 790 760 720 680 640 540
MED 850 830 800 770 740 720 690 660 620 580 540 460
LO 700 680 660 650 630 610 590 560 530 500 470
HI 1330 1300 1260 1230 1190 1150 1100 1050 1000 960 920 830
MED 1210 1190 1160 1130 1100 1050 1000 970 930 880 830 720
LO 1050 1030 1010 980 950 920 890 850 810 770 730
HI 1580 1540 1500 1470 1440 1410 1370 1330 1280 1240 1200 1090 940
MED 1400 1370 1340 1310 1280 1250 1220 1190 1150 1100 1050 920
LO 1100 1080 1060 1040 1010 980 950 920 890 890
HI 1790 1760 1730 1700 1660 1630 1590 1550 1510 1480 1440 1370 1270 1120
MED 1500 1490 1470 1450 1420 1400 1380 1350 1320 1300 1270 1180 1070
LO 1110 1100 1090 1080 1060 1050 1040
HI 1910 1880 1840 1800 1750 1730 1700 1650 1600 1540 1480 1380 1300
MED 1830 1790 1740 1700 1660 1620 1570 1540 1500 1450 1400 1320 1210 1120
LO 1700 1670 1640 1600 1560 1530 1490 1460 1430 1390 1340 1250 1170
HI 2180 2140 2090 2060 2030 1990 1940 1870 1800 1750 1690 1580 1440 1270
MED 2080 2050 2020 1970 1920 1870 1820 1740 1650 1640 1620 1530 1320 1220
LO 1990 1950 1910 1880 1840 1810 1770 1710 1650 1620 1580 1460 1340
HI 2230 2220 2200 2160 2120 2090 2060 2040 2010 1990 1960 1880 1790 1660
MED 2040 2020 1990 1970 1940 1920 1890 1860 1830 1810 1780 1710 1620
LO 1840 1830 1810 1800 1780 1760 1730 1700 1670 1640 1600 1510
LEGEND
AIRFLOW (Cfm)
External Static Pressure (in. wg)
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90
1180
990
910
1180
NOTES:
1. Units factory shipped on medium speed. Other speeds require
field selection.
2. All airflow is rated on 208 v operating with wet coil and clean air
filter.
3. All units ARI/ISO/ASHRAE 13256-1 rated on high fan speed.
4. Only two-speed fan (H & M) available on 575-v units.
27
Page 28

Table 9 — 50RHC,RVC Blower Performance
50RHC,RVC
UNITS
006* 220 150
009 325 225
012 400 300
018 600 450
018
High Static
024 800 600
024
High Static
030 1000 750
030
High Static
036 1200 900
036
High Static
041† 1325 950
042 1350 1050
042
High Static
048 1600 1200
048
High Static
060 2000 1500
060
High Static
*Size 006 is available in 50RHC unit only.
†Size 041 is available in 50RVC unit only.
NOTES:
1. Gray areas denote ESP (external static pressure) where operation is not
recommended.
2. Units factory shipped on medium speed. Other speeds require field
selection.
3. All airflow is rated at lowest voltage if unit is dual voltage rated, i.e., 208 v
for 208-230 v units.
4. All units ARI/ISO/ASHRAE 13256-1 rated on high fan speed.
RATED
CFM
600 450
800 600
1000 750
1200 900
1350 1050
1600 1200
2000 1500
MIN
FAN
CFM
SPEED
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 1.0 1.10 1.20 1.30
HI
MED
LO 210 200 190 180 160 150
HI
MED 390 370 360 340 320 310 290 280 260
LO
HI
MED
LO
HI 760 740 720 710 700 680 650 600 550 460
MED 700 690 680 670 660 650 630 620 600 560 520 430
LO 620 610 600 590 580 570 560 540 520 490 460
HI
MED 750 740 720 710 700 690 670 670 660 650 630 600 490 390
LO 670 660 640 630 620 610 600 590 580 580 570 530 420
HI
MED 1010 1000 990 980 960 940 920 900 880 860 830 770 700 600
LO 820 810 800 790 780 770 760 750 730 720 700 650 600
HI
MED
LO 1030 1010 980 960 930 900 870 790 710
HI
MED 1250 1230 1200 1180 1150 1120 1090 1070 1040 1010 970 890 750
LO 1120 1100 1070 1050 1030 1010 980 960 930 900 870 790 710
HI
MED
LO 1050 1040 1030 1010 990 980 960 940 910 880 840 750
HI 1520 1500 1480 1460 1430 1400 1370 1350 1320 1270 1210 1110 960 840
MED 1150 1150 1140 1140 1130 1130 1120 1110 1100 1070 1040 940
LO 1010 1010 1000 1000 990 990 980 980 970 950 930
HI 1530 1500 1470 1400 1290 1170 960
MED 1360 1350 1340 1330 1320 1310 1300 1280 1260 1250 1230 1150 1070 910
LO 1030 1020 1010 1010 1000 1000 990 980 960 950 930
HI 1380 1370 1350 1330 1300 1260 1220 1170 1120 1080 1040 890
MED 1230 1220 1200 1190 1180 1150 1120 1080 1030 990 950
LO 1040 1030 1010 1000 990 970 950
HI 1640 1610 1580 1550 1520 1490 1450 1410 1370 1330 1290 1190 1100
MED 1490 1470 1440 1420 1390 1370 1340 1310 1270 1230 1190 1120 1010
LO 1140 1140 1130 1130 1120 1110 1100 1080 1060 1010
HI
MED 1390 1380 1370 1360 1350 1340 1320 1310 1300 1280 1250 1180 1080
LO
HI
MED 1940 1920 1900 1880 1860 1820 1770 1740 1710 1660 1600 1410 1000
LO 1770 1750 1730 1710 1690 1670 1650 1610 1570 1510 1450 1330
HI
MED 2050 2050 2040 2020 1990 1970 1940 1920 1890 1860 1830 1780 1710 1620 1490 1320
LO 1850 1850 1840 1830 1810 1800 1780 1760 1730 1700 1670 1600 1510 1380 1220
HI 2240 2240 2230 2220 2200 2160 2120 2090 2060 2040 2010 1960 1880 1790 1660 1510
MED 2050 2050 2040 2020 1990 1970 1940 1920 1890 1860 1830 1780 1710 1620 1490
LO 1850 1850 1840 1830 1810 1800 1780 1760 1730 1700 1670 1600 1510
HI 2400 2400 2390 2380 2370 2360 2340 2320 2300 2270 2240 2200 2130 2060 1980 1890 1790 1660 1500
MED 2160 2160 2150 2150 2140 2110 2080 2060 2040 2030 2020 1980 1930 1880 1490 1750 1660 1530
LO 1930 1930 1920 1920 1910 1900 1890 1890 1880 1870 1850 1830 1800 1750 1700 1620 1530
310 300 290 280 270 250 230 210 180
260 250 240 230 210 200 190 150
410 400 380 360 350 330 320 300 280
340 330 322 310 300 280 260 250 220
470 460 450 440 430 420 400 390 380 320
420 410 400 390 380 370 360 350 340
360 360 350 340 320 320 310 300 290
790 780 770 760 750 730 710 690 650 530 430
1550 1540 1520 1500 1470 1460 1450 1380 1240 1080
1980 1950 1910 1860 1800 1740 1680 1490 1280 1280
AIRFLOW (Cfm)
External Static Pressure (in. wg)
1000 970 930 870 770 690
1040 1010 970 890 750 620
1160 1130 1100 1070 1030 950 840
1130 1080 1030 930 820 750
2060 2040 2010 1960 1880 1790 1660 1510
5. Only two-speed fan (H & M) available on 575-v units.
6. For wet coil performance first calculate the face velocity of the air
coil (Face Velocity [fpm] = Airflow [cfm]/Face Area [sq ft]). Then for velocities of 200 fpm reduce the static capability by 0.03 in. wg, 300 fpm by
0.08 in. wg, 400 fpm by 0.12 in. wg, and 500 fpm by 0.16 in. wg.
7. Airflow in cfm with net dry coil and clean air filter.
1030 950 840 700
1160 1040 920 800 750
Table 10 — 50RVC Blower Performance with Hot Water Reheat (HWR) Option
REHEAT EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (ESP) LOSS
COIL FACE VELOCITY
(fpm)
018, 024, 030
(in. wg)
036, 042
(in. wg)
048, 060
(in. wg)
200 0.060 0.049 0.038
250 0.070 0.055 0.040
300 0.090 0.068 0.045
350 0.124 0.091 0.059
400 0.164 0.129 0.094
450 0.252 0.221 0.189
500 0.380 0.350 0.320
NOTE: For 50RVC units with HWR, calculate coil face velocity of the entering air. Find the
external static pressure loss for the reheat application. This loss includes the wet coil loss.
28
Page 29

Table 11 — 50RVC Blower Performance with Wet Coil
COIL FACE VELOCITY
(fpm)
200 0.030
250 0.055
300 0.080
350 0.100
400 0.120
450 0.140
500 0.160
WET COIL REDUCTION
(in. wg)
Table 12 — 50RHS,RVS,RDS Blower Performance
50RHS,RVS,RDS
UNITS
015 500
018 600
024 800
030 1000
Hi Static
030
036 1150
Hi Static
036
042 1400
048 1600
060 2000
070 2300
LEGEND
— — Not Recommended
NOTES:
1. Includes allowance for wet coil and clean factory-installed filter.
2. Units factory shipped on medium speed (015 on Low). Other speeds require field selection.
3. All airflow is rated on 208 v operating with wet coil and clean air filter.
4. All units ARI/ISO/ASHRAE 13256-1 rated on high (015 rated on medium).
RATED
AIRFLOW
1000
1150
FAN
SPEED
HS Hi 1380 1360 1320 1280 1250 1220 1200 1150 1110 1070 1020 940 850 690 — —
HS Med 1260 1240 1220 1190 1170 1130 1100 1070 1040 990 950 — ————
HS Low 1170 1150 1130 1100 1080 1050 1020 990 960 930 900 — ————
HS Hi 1790 1760 1730 1700 1660 1630 1590 1550 1510 1470 1440 1370 1270 1120 — —
HS Med 1510 1490 1470 1450 1420 1400 1380 1350 1320 1300 1270 1180 1070 — — —
HS Low 1110 1100 1090 1080 1060 1050 1040 —————————
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 1.00
Hi 880860840830820800780750730690660610————
Med 770760750740720710690670640620600—————
Low 670660660650640630620600580550520—————
Hi 870860840830820800780750730690660610————
Med 770760750740720710690670640620600—————
Low 670660660650640630620600580550520—————
Hi 1130 1110 1090 1060 1040 1010 980 950 920 880 840 720 ————
Med 950940930920910880860820790760730—————
Low 880870860840830810800770730700660—————
Hi 1240 1230 1200 1180 1160 1120 1090 1050 1000 970 930 850 650 — — —
Med 1180 1150 1120 1090 1070 1030 1000 970 950 910 870 — ————
Low 1040 1020 1000 980 960 930 910 870 840 820 790 — ————
Hi 1390 1360 1320 1280 1250 1220 1200 1150 1110 1070 1020 940 850 690 — —
Med 1260 1240 1220 1190 1170 1130 1100 1070 1040 990 950 — ————
Low 1170 1150 1130 1100 1080 1050 1020 990 960 930 900 — ————
Hi — — — 1670 1630 1600 1570 1540 1510 1440 1380 1290 1130 — — —
Med 1610 1580 1550 1510 1480 1450 1420 1390 1360 1320 1270 — ————
Low 1270 1260 1250 1240 1220 1210 1190 1160 1120 1080 1030 — ————
Hi — — — 2010 2000 1940 1880 1830 1780 1690 1610 1540 1310 1190 — —
Med 1940 1910 1870 1820 1780 1740 1700 1670 1630 1570 1520 1410 1310 1170 — —
Low 1470 1460 1450 1440 1430 1410 1380 1360 1330 1280 1220 1110 1040 — — —
Hi — — — — — 2270 2230 2200 2170 2140 2110 2040 1970 1870 1720 1640
Med 2260 2240 2220 2190 2170 2140 2110 2100 2080 2050 2020 1960 1870 1760 1660 1550
Low 2050 2030 2010 1990 1970 1950 1930 1910 1880 1850 1830 1780 1700 1650 1570 1430
Hi — — — — — 2460 2430 2390 2340 2310 2280 2230 2180 1990 1860 1740
Med 2530 2500 2470 2450 2420 2400 2370 2340 2310 2280 2260 2200 2100 1890 1740 1640
Low 2270 2260 2250 2240 2230 2210 2180 2160 2140 2120 2100 2040 1900 1790 1690 1570
External Static Pressure (in. wg)
AIRFLOW (Cfm)
29
Page 30

Table 13 — 50RHS, RVS Blower Performance with HWR
COIL FACE
VELOCITY (FPM)
200 0.040 0.037 0.033 0.031 0.028 0.026
250 0.059 0.052 0.046 0.042 0.038 0.034
300 0.088 0.077 0.066 0.059 0.051 0.044
350 0.131 0.113 0.096 0.085 0.073 0.061
400 0.203 0.181 0.160 0.145 0.131 0.117
450 0.258 0.242 0.226 0.215 0.205 0.194
500 0.375 0.360 0.345 0.335 0.326 0.316
LEGEND
ESP — External Static Pressure
HWR — Hot Water Reheat
50RHS, RVS
015, 018 (in. wg)
50RHS, RVS
024, 030 (in. wg)
FIELD SELECTABLE INPUTS
Jumpers and DIP (dual in-line package) switches on the
control board are used to customize unit operation and can be
configured in the field.
50RHS, RVS WITH REHEAT ESP LOSS
50RHS, RVS
036 (in. wg)
50RHS, RVS
042, 048 (in. wg)
to R, do not clip the jumper. To set as dry contact, clip the
jumper.
LOW PRESSURE SETTING — The D Control can be configured for Low Pressure Setting (LP). Select jumper 1 (JW1-
50RHS, RVS
060 (in. wg)
LP Norm Open) for choosing between low pressure input norIMPORTANT: Jumpers and DIP switches should only
be clipped when power to control board has been turned
off.
C Control Jumper Settings (See Fig. 19)
WATER COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP1) LIMIT
SETTING — Select jumper 3, (JW3-FP1 Low Temp) to
choose FP1 limit of 10 F or 30 F. To select 30 F as the limit,
DO NOT clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip the
jumper.
AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP2) LIMIT SETTING — Select jumper 2 (JW2-FP2 Low Temp) to choose
FP2 limit of 10 F or 30 F. To select 30 F as the limit, DO NOT
clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip the jumper.
ALARM RELAY SETTING — Select jumper 1 (JW1-AL2
Dry) for connecting alarm relay terminal (AL2) to 24 vac (R)
or to remain as a dry contact (no connection). To connect AL2
to R, do not clip the jumper. To set as dry contact, clip the
jumper.
C Control DIP Switches — The C Control has 1 DIP
switch block with two switches. See Fig. 19.
PERFORMANCE MONITOR (PM) — DIP switch 1 will
enable or disable this feature. To enable the PM, set the switch
to ON. To disable the PM, set the switch to OFF.
STAGE 2 — DIP switch 2 will enable or disable compressor
delay. Set DIP switch to OFF for stage 2 in which the compressor will have a 3-second delay before energizing.
NOTE: The alarm relay will not cycle during Test mode if
switch is set to OFF, stage 2.
D Control Jumper Settings (See Fig. 20)
WATER COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP1) LIMIT
SETTING — Select jumper 3, (JW3-FP1 Low Temp) to
choose FP1 limit of 10 F or 30 F. To select 30 F as the limit,
DO NOT clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip the
jumper.
AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP2) LIMIT SETTING — Select jumper 2 (JW2-FP2 Low Temp) to choose
FP2 limit of 10 F or 30 F. To select 30 F as the limit, DO NOT
clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip the jumper.
ALARM RELAY SETTING — Select jumper 4 (JW4-AL2
Dry) for connecting alarm relay terminal (AL2) to 24 vac (R)
or to remain as a dry contact (no connection). To connect AL2
mally open or closed. To configure for normally closed opera-
tion, do not clip the jumper. To configure for normally open op-
eration, clip the jumper.
D Control DIP Switches — The D Control has 2 DIP
switch blocks. Each DIP switch block has 8 switches and is
labeled either S1 or S2 on the circuit board. See Fig. 20.
DIP SWITCH BLOCK 1 (S1) — This set of switches offers
the following options for D Control configuration:
Performance Monitor (PM)
able performance monitor. To enable the PM, set the switch to
ON. To disable the PM, set the switch to OFF.
Compressor Relay Staging Operation
able or disable compressor relay staging operation. The com-
pressor relay can be set to turn on with stage 1 or stage 2 call
from the thermostat. This setting is used with dual stage units
(units with 2 compressors and 2 D controls) or in master/slave
applications. In master/slave applications, each compressor and
fan will stage according to its switch 2 setting. If switch is set to
stage 2, the compressor will have a 3-second delay before ener-
gizing during stage 2 demand.
NOTE: If DIP switch is set for stage 2, the alarm relay will not
cycle during Test mode.
Heating/Cooling Thermostat Type
tion of thermostat type. Heat pump or heat/cool thermostats
can be selected. Select OFF for heat/cool thermostats. When in
heat/cool mode, Y1 is used for cooling stage 1, Y2 is used for
cooling stage 2, W1 is used for heating stage 1 and O/W2 is
used for heating stage 2. Select ON for heat pump applications.
In heat pump mode, Y1 used is for compressor stage 1, Y2 is
used for compressor stage 2, W1 is used for heating stage 3 or
emergency heat, and O/W2 is used for RV (heating or cooling)
depending upon switch 4 setting.
O/B Thermostat Type
pump O/B thermostats. O is cooling output. B is heating out-
put. Select ON for heat pumps with O output. Select OFF for
heat pumps with B output.
Dehumidification Fan Mode
of normal or dehumidification fan mode. Select OFF for dehu-
midification mode. The fan speed relay will remain OFF dur-
ing cooling stage 2. Select ON for normal mode. The fan speed
relay will turn on during cooling stage 2 in normal mode.
Switch 6
— Not used.
Boilerless Operation
— Set switch 1 to enable or dis-
— Switch 3 provides selec-
— Switch 4 provides selection for heat
— Switch 5 provides selection
— Switch 7 provides selection of boiler-
less operation and works in conjunction with switch 8. In
50RHS, RVS
070 (in. wg)
— Switch 2 will en-
30
Page 31

boilerless operation mode, only the compressor is used for
heating when FP1 is above the boilerless changeover temperature set by switch 8 below. Select ON for normal operation or
select OFF for boilerless operation.
Boilerless Changeover Temperature
— Switch 8 on S1 provides selection of boilerless changeover temperature set point.
Select OFF for set point of 50 F or select ON for set point
of 40 F.
If switch 8 is set for 50 F, then the compressor will be used
for heating as long as the FP1 is above 50 F. The compressor
will not be used for heating when the FP1 is below 50 F and the
compressor will operates in emergency heat mode, staging on
EH1 and EH2 to provide heat. If a thermal switch is being used
instead of the FP1 thermistor, only the compressor will be used
for heating mode when the FP1 terminals are closed. If the FP1
terminals are open, the compressor is not used and the control
goes into emergency heat mode.
DIP SWITCH BLOCK 2 (S2) — This set of DIP switches is
used to configure accessory relay options. See Fig. 20.
Switches 1 to 3
— These DIP switches provide selection
of Accessory 1 relay options. See Table 14 for DIP switch
combinations.
Switches 4 to 6
— These DIP switches provide selection
of Accessory 2 relay options. See Table 15 for DIP switch
combinations.
Table 14 — DIP Switch Block S2 —
Accessory 1 Relay Options
ACCESSORY 1
RELAY OPTIONS
Cycle with Fan On On On
Digital NSB Off On On
Water Valve — Slow Opening On Off On
OAD On On Off
LEGEND
NSB — Night Setback
OAD — Outside Air Damper
NOTE: All other DIP switch combinations are invalid.
DIP SWITCH POSITION
123
Table 15 — DIP Switch Block S2 —
Accessory 2 Relay Options
ACCESSORY 2
RELAY OPTIONS
Cycle with Fan On On On
Digital NSB Off On On
Water Valve — Slow Opening On Off On
OAD On On Off
LEGEND
NSB — Night Setback
OAD — Outside Air Damper
NOTE: All other switch combinations are invalid.
DIP SWITCH POSITION
456
Auto Dehumidification Mode or High Fan Mode — Switch 7
provides selection of auto dehumidification fan mode or high
fan mode. In auto dehumidification fan mode the fan speed
relay will remain off during cooling stage 2 if terminal H is
active. In high fan mode, the fan enable and fan speed relays
will turn on when terminal H is active. Set the switch to ON for
auto dehumidification fan mode or to OFF for high fan mode.
Switch 8
— Not used.
Units with Modulating Hot Water Reheat
(HWR) Option —
Reheat (HWR) can operate in three modes: cooling, cooling
with reheat, and heating. The cooling and heating modes are
like other Aquazone™ water source heat pumps. The reversing
A heat pump equipped with Hot Water
valve ("O" signal) is energized in cooling, along with the compressor contactor(s) and blower relay. In the heating mode, the
reversing valve is deenergized. Almost any thermostat will
activate the heat pump in heating or cooling modes. The
Deluxe D microprocessor board, which is standard with the
HWR option, will accept either heat pump (Y,O) thermostats
or non-heat pump (Y,W) thermostats.
The reheat mode requires either a separate humidistat/
dehumidistat or a thermostat that has an integrated dehumidification function for activation. The Deluxe D board is configured to work with either a humidistat or dehumidistat input to
terminal “H” (DIP switch settings for the Deluxe D board are
shown in Table 16). Upon receiving an “H” input, the Deluxe
D board will activate the cooling mode and engage reheat.
Table 16 — Humidistat/Dehumidistat Logic and
Deluxe D DIP Switch Settings
Sensor 2.1
Humidistat
Dehumidistat Off On Off Standard 24 VAC 0 VAC
2.2 2.3 Logic
Off Off Off Reverse 0 VAC 24 VAC
Reheat
(ON) - H
Reheat
(OFF) - H
Table 17 shows the relationship between thermostat input
signals and unit operation. There are four operational inputs for
single stage units and six operational inputs for dual stage
units:
•Fan Only
• Cooling Stage 1
• Cooling Stage 2
• Heating Stage 1
• Heating Stage 2
• Reheat Mode
MODULATING HWR APPLICATION CONSIDER-
ATIONS — Unlike most hot gas reheat options, the modulating HWR option (RVC,RHS,RVS,RDS only) will operate over a wide range of entering-water temperatures
(EWTs). Special flow regulation (water regulating valve) is
not required for low EWT conditions. However, below 55 F,
supply-air temperatures cannot be maintained at 72 F
because the cooling capacity exceeds the reheat coil capacity at low water temperatures. Below 55 F, essentially all
water is diverted to the reheat coil (no heat of rejection to
the building loop). Although the HWR option will work fine
with low EWTs, overcooling of the space may result with
well water systems or, on rare occasions, with ground loop
(geothermal) systems (NOTE: Extended range units are
required for well water and ground loop systems). Since
dehumidification is generally only required in cooling, most
ground loop systems will not experience overcooling of the
supply-air temperature. If overcooling of the space is a concern (e.g., computer room well water application), auxiliary
heating may be required to maintain space temperature
when the unit is operating in the dehumidification mode.
Water source heat pumps with HWR should not be used as
makeup air units. These applications should use equipment
specifically designed for makeup air.
HWR COMPONENT FUNCTIONS — The proportional
controller operates on 24 VAC power supply and automatically
adjusts the water valve based on the supply-air sensor. The
supply-air sensor senses supply-air temperature at the blower
inlet, providing the input signal necessary for the proportional
control to drive the motorized valve during the reheat mode of
operation. The motorized valve is a proportional actuator/threeway valve combination used to divert the condenser water
from the coax to the hydronic reheat coil during the reheat
mode of operation. The proportional controller sends a signal
to the motorized valve based on the supply-air temperature
reading from the supply air sensor.
The loop pump circulates condenser water through the hydronic reheat coil during the reheat mode of operation (refer to
Fig. 28). In this application, the loop pump is only energized
31
Page 32
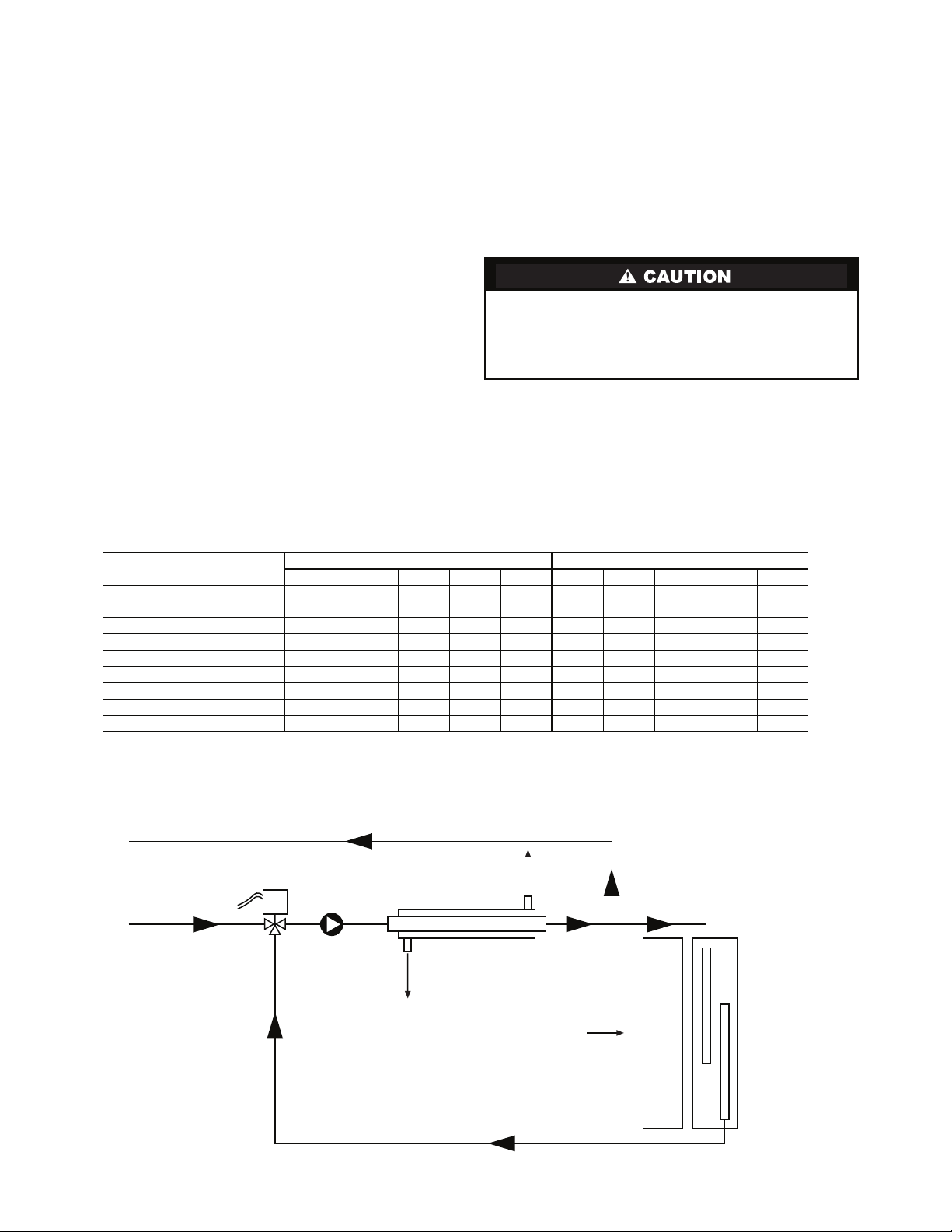
during the reheat mode of operation. The hydronic coil is utilized during the reheat mode of operation to reheat the air to the
set point of the proportional controller. Condenser water is diverted by the motorized valve and pumped through the hydronic coil by the loop pump in proportion to the control set point.
The amount of reheating is dependent on the set point and how
far from the set point the supply air temperature is. The factory
set point is 70 to 75 F, generally considered "neutral" air.
D Control Accessory Relay Configurations —
The following accessory relay settings are applicable for both
D controls only:
CYCLE WITH FAN — In this configuration, the relay will be
ON any time the Fan Enable relay is on.
CYCLE WITH COMPRESSOR — In this configuration, the
relay will be ON any time the Compressor relay is on.
DIGITAL NIGHT SET BACK (NSB) — In this configuration, the relay will be ON if the NSB input is connected to
ground C.
NOTE: If there are no relays configured for digital NSB, then
the NSB and override (OVR) inputs are automatically configured for mechanical operation.
MECHANICAL NIGHT SET BACK — When NSB input is
connected to ground C, all thermostat inputs are ignored. A
thermostat set back heating call will then be connected to the
OVR input. If OVR input becomes active, then the D control
will enter Night Low Limit (NLL) staged heating mode. The
NLL staged heating mode will then provide heating during the
NSB period.
Water Valve (Slow Opening) — If relay is config-
ured for Water Valve (slow opening), the relay will start 60 seconds prior to starting compressor relay.
Outside Air Damper (OAD) — If relay is configured
for OAD, the relay will normally be ON any time the Fan
Enable relay is energized. The relay will not start for
30 minutes following a return to normal mode from NSB,
when NSB is no longer connected to ground C. After 30 minutes, the relay will start if the Fan Enable is set to ON.
To avoid equipment damage, DO NOT leave system filled
in a building without heat during the winter unless antifreeze is added to system water. Condenser coils never
fully drain by themselves and will freeze unless winterized
with antifreeze.
START-UP
Use the procedure outlined below to initiate proper unit
start-up.
NOTE: This equipment is designed for indoor installation only.
Table 17 — HWR Operating Modes
MODE
No Demand On/Off
Fan Only On/Off On Off Off Off On/Off On Off Off Off
Cooling Stage 1
Cooling Stage 2
Cooling and Dehumidistat
Dehumidistat Only
Heating Stage 1
Heating Stage 2
Heating and Dehumidistat**
*Not applicable for single stage units; Full load operation for dual capacity units.
†Cooling input takes priority over dehumidify input.
**Deluxe D is programmed to ignore the H demand when the unit is in heating mode.
NOTE: On/Off is either on or off.
Water Out
(To Water Loop)
Water In
(From Water Loop)
†
Mixing Valve
O
On On On Off Off On On On Off Off
On On On On Off On On On On Off
On On On On/Off On On On On On/Off Off
On/Off Off Off Off
Off
Off
Off
Internal Pump
INPUT
G Y1 Y2* H O G Y1 Y2* Reheat
Off
On On Off Off Off On On Off Off
On On On Off Off On On On Off
On On On/Off On Off On On On/Off Off
Off Off Off On/Off Off Off Off Off
On On On On On On
Refrigerant In
(Cooling)
COAX
OUTPUT
a50-8145.eps
NOTE: All components shown are
internal to the heat pump unit.
Refrigerant Out
(Cooling)
Entering Air
Fig. 28 — HWR Schematic
32
Evaporator Coil
Leaving
Air
Reheat
Coil
Page 33

Operating Limits
ENVIRONMENT — This equipment is designed for indoor
installation ONLY. Extreme variations in temperature, humidity and corrosive water or air will adversely affect the
unit performance, reliability and service life.
POWER SUPPLY — A voltage variation of ± 10% of
nameplate utilization voltage is acceptable.
UNIT STARTING CONDITIONS — Depending on the
model, units start and operate in an ambient temperature of
45 F with entering-air temperature at 40 F or 50 F, enteringwater temperature at 20 F or 50 F and with both air and water at
the flow rates used.
NOTE: These operating limits are not normal or continuous
operating conditions. Assume that such a start-up is for the
purpose of bringing the building space up to occupancy
temperature. See Tables 18 and 19 for operating limits.
When the disconnect switch is closed, high voltage is
present in some areas of the electrical panel. Exercise
caution when working with the energized equipment.
Failure to heed this warning could lead to personal
injury.
1. Restore power to system.
2. Turn thermostat fan position to ON. Blower should
start.
3. Balance airflow at registers.
4. Adjust all valves to the full open position and turn on
the line power to all heat pump units.
5. Operate unit in the cooling cycle. Refer to Tables 18
and 19 for unit operating limits.
NOTE: Three factors determine the operating limits of a
unit: (1) entering-air temperature, (2) water temperature and
(3) ambient temperature. Whenever any of these factors are
at a minimum or maximum level, the other two factors must
be at a normal level to ensure proper unit operation. See
Tables 18 and 19.
Scroll Compressor Rotation — It is important to
be certain compressor is rotating in the proper direction. To
determine whether or not compressor is rotating in the proper direction:
1. Connect service gages to suction and discharge pressure
fittings.
2. Energize the compressor.
3. The suction pressure should drop and the discharge
pressure should rise, as is normal on any start-up.
If the suction pressure does not drop and the discharge
pressure does not rise to normal levels:
1. Turn off power to the unit. Install disconnect tag.
2. Reverse any two of the unit power leads.
3. Reapply power to the unit and verify pressures are correct.
The suction and discharge pressure levels should now move
to their normal start-up levels.
When the compressor is rotating in the wrong direction, the
unit makes more noise and does not provide cooling.
After a few minutes of reverse operation, the scroll compressor internal overload protection will open, thus activating
the unit lockout. This requires a manual reset. To reset, turn the
thermostat on and then off.
NOTE: There is a 5-minute time delay before the compressor
will start.
Unit Start-Up Cooling Mode
1. Adjust the unit thermostat to the warmest position.
Slowly reduce the thermostat position until the compressor activates.
2. Check for cool air delivery at unit grille a few minutes
after the unit has begun to operate.
3. Verify that the compressor is on and that the water flow
rate is correct by measuring pressure drop through the
heat exchanger using P/T plugs. See Table 20. Check the
elevation and cleanliness of the condensate lines; any
dripping could be a sign of a blocked line. Be sure the
condensate trap includes a water seal.
4. Check the temperature of both supply and discharge water. Compare to Table 21. If temperature is within range,
proceed. If temperature is outside the range, check the
cooling refrigerant pressures in Table 21.
5. Check air temperature drop across the coil when compressor is operating. Air temperature drop should be
between 15 and 25 F.
Table 18 — Operating Limits — 50RHC,RVC Units
AIR LIMITS
Min. Ambient Air – db 45 F 45 F
Rated Ambient Air – db 80.6 F 68 F
Max. Ambient Air – db 110 F 85 F
Min. Entering Air – db/wb 70/61 F 50 F
Rated Entering Air – db/wb 80.6/66.2 F 68 F
Max. Entering Air – db/wb 95/76 F 80 F
WATER LIMITS
Min. Entering Water 50 F 50 F
Normal Entering Water 60-90 F 60-70 F
Max. Entering Water 110 F 90 F
Normal Water Flow 2.5-3.0 gpm per ton
LEGEND
db — Dry Bulb
wb — Wet Bulb
Table 19 — Operating Limits —
50RHR,RHS,RVR,RVS,RDS Units
AIR LIMITS COOLING (F) HEATING (F)
Min. Ambient Air 45 45
Rated Ambient Air 80 70
Max. Ambient Air 100 85
Min. Entering Air 50 40
Rated Entering Air db/wb 80/67 70
Max. Entering Air db/wb 110/83 80
WATER LIMITS
Min. Entering Water 30 20
Normal Entering Water 50-90 30-60
LEGEND
db — Dry Bulb
wb — Wet Bulb
NOTE: Value in heating column is dry bulb only. Any wet bulb reading is acceptable.
Table 20 — Water Temperature Change
Through Heat Exchanger
WATER FLOW RATE (GPM)
For Closed Loop: Ground Source or
Cooling/Boiler Systems at 3 gpm/ton
For Open Loop: Ground Water Systems at
1.5 gpm/ton
50RHC,RVC
Cooling Heating
COOLING
RISE (F)
Min Max Min Max
91248
20 26 10 17
HEATING
DROP (F)
33
Page 34

Unit Start-Up Heating Mode
NOTE: Operate the unit in heating cycle after checking the
cooling cycle. Allow 5 minutes between tests for the pressure
or reversing valve to equalize.
1. Turn thermostat to lowest setting and set thermostat
switch to HEAT position.
2. Slowly turn the thermostat to a higher temperature until
the compressor activates.
3. Check for warm air delivery at the unit grille within a few
minutes after the unit has begun to operate.
4. Check the temperature of both supply and discharge water. Compare to Table 21. If temperature is within range,
proceed. If temperature is outside the range, check the
heating refrigerant pressures in Table 21.
5. Once the unit has begun to run, check for warm air delivery at the unit grille.
6. Check air temperature rise across the coil when compressor is operating. Air temperature rise should be between
20 and 30 F after 15 minutes at load.
7. Check for vibration, noise and water leaks.
Flow Regulation — Flow regulation can be accom-
plished by two methods. Most water control valves have a flow
adjustment built into the valve. By measuring the pressure drop
through the unit heat exchanger, the flow rate can be determined. See Tables 22-24. Adjust the water control valve until
the flow of 1.5 to 2 gpm is achieved. Since the pressure constantly varies, two pressure gages may be needed in some
applications.
An alternative method is to install a flow control device.
These devices are typically an orifice of plastic material designed to allow a specified flow rate that are mounted on the
outlet of the water control valve. Occasionally these valves
produce a velocity noise that can be reduced by applying some
back pressure. To accomplish this, slightly close the leaving
isolation valve of the well water setup.
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock,
open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in
an open position before flushing system.
Flushing — Once the piping is complete, units require final
purging and loop charging. A flush cart pump of at least 1.5 hp
is needed to achieve adequate flow velocity in the loop to purge
air and dirt particles from the loop. Flush the loop in both
Table 21 — Typical Unit Operating Pressures and Temperatures
ENTERING
WATER
TEMP (F)
(EWT)
30
50
70
90
110
DB — Dry Bulb
EAT — Entering Air Temperature
GPM/
Suction
TON
Pressure
(psig)
1.5 75-85 90-105 25-40 12-20 21-24 21-26 34- 39 167-186 12-16 1-4 7.6- 8.4 14-20
2.3 74-84 80- 95 25-40 11-18 13-16 21-26 37- 43 172-191 12-16 1-4 4.8- 5.6 16-22
3.0 73-83 70- 85 25-40 10-16 6-11 21-26 40- 46 177-196 12-16 1-4 3.4- 4.2 16-22
1.5 75-85 125-155 12-20 10-18 20-23 20-25 50- 60 180-210 10-17 1-5 10.8-11.9 23-29
2.3 74-84 120-142 12-20 9-16 12-15 20-25 53- 62 185-215 10-17 1-5 6.7- 8.1 24-30
3.0 73-83 115-138 12-20 8-14 8-12 20-25 55- 65 190-220 10-17 1-5 5.1- 5.9 25-31
1.5 75-85 179-198 9-16 8-15 19-22 19-24 71- 82 205-230 14-19 1-5 14.0-15.2 28-34
2.3 74-84 168-186 9-16 8-14 12-17 19-24 73- 85 210-238 14-19 1-5 9.0-10.2 30-37
3.0 73-83 158-175 9-16 8-12 7-12 19-24 76- 88 215-242 14-19 1-5 6.7- 7.9 31-38
1.5 75-85 229-251 9-17 8-15 18-21 17-23 85- 95 220-260 18-28 2-5 14.4-16.6 32-39
2.3 74-84 218-241 9-17 8-14 10-14 17-23 90-100 225-265 18-28 2-5 10.8-12.4 33-41
3.0 73-83 208-230 9-17 8-12 6-11 17-23 95-105 230-270 18-28 2-5 7.2- 8.3 35-42
1.5 77-87 280-320 8-15 10-25 17-20 15-20
2.3 76-86 270-310 8-15 10-24 9-13 15-20
3.0 75-85 260-300 8-15 10-22 5-10 15-20
LEGEND
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
COOLING HEATING
Super-
heat
(F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Water
Temp
Rise
(F)
directions with a high volume of water at a high velocity. Follow the steps below to properly flush the loop:
1. Verify power is off.
2. Fill loop with water from hose through flush cart before
using flush cart pump to ensure an even fill. Do not allow
the water level in the flush cart tank to drop below the
pump inlet line to prevent air from filling the line.
3. Maintain a fluid level in the tank above the return tee to
avoid air entering back into the fluid.
4. Shutting off the return valve that connects into the flush
cart reservoir will allow 50 psi surges to help purge air
pockets. This maintains the pump at 50 psi.
5. To purge, keep the pump at 50 psi until maximum pumping pressure is reached.
6. Open the return valve to send a pressure surge through
the loop to purge any air pockets in the piping system.
7. A noticeable drop in fluid level will be seen in the flush
cart tank. This is the only indication of air in the loop.
NOTE: If air is purged from the system while using a 10 in.
PVC flush tank, the level drop will only be 1 to 2 in. since
liquids are incompressible. If the level drops more than this,
flushing should continue since air is still being compressed in
the loop. If level is less than 1 to 2 in., reverse the flow.
8. Repeat this procedure until all air is purged.
9. Restore power.
Antifreeze may be added before, during or after the flushing
process. However, depending on when it is added in the
process, it can be wasted. Refer to the Antifreeze section for
more detail.
Loop static pressure will fluctuate with the seasons. Pressures will be higher in the winter months than during the
warmer months. This fluctuation is normal and should be considered when charging the system initially. Run the unit in
either heating or cooling for several minutes to condition the
loop to a homogenous temperature.
When complete, perform a final flush and pressurize the
loop to a static pressure of 40 to 50 psi for winter months or 15
to 20 psi for summer months.
After pressurization, be sure to remove the plug from the
end of the loop pump motor(s) to allow trapped air to be
discharged and to ensure the motor housing has been flooded.
Be sure the loop flow center provides adequate flow through
the unit by checking pressure drop across the heat exchanger.
Compare the results to the data in Tables 22-24.
Air
Temp
Drop (F)
DB
NOTES:
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
1. Based on nominal 400 cfm per ton airflow, 70 F EAT heating and 80/67 F
EAT cooling.
2. Cooling air and water numbers can vary greatly with changes in humidity.
3. Subcooling is based upon the head pressure at compressor service port.
4. Unit should not be operated in heating mode with an EWT of 110.
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat (F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Water
Temp
Drop (F)
DB
Air
Temp
Rise (F)
34
Page 35

Table 22 — 50RHR,RVR Coaxial
Water Pressure Drop
UNIT
50RHR,RVR
006*
009
012
015
019
024
030
036
042
048
060
*Size 006 available in 50RHR unit only.
GPM
0.8 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.7
1.1 1.2 1.1 1.0 1.0
1.5 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7
1.1 1.2 1.1 1.0 0.9
1.7 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4
2.2 3.5 3.2 3.0 2.8
1.5 2.8 2.6 2.4 2.3
2.3 6.0 5.6 5.2 4.9
3.0 9.6 9.0 8.3 7.9
1.8 2.5 2.3 2.1 2.0
2.6 4.8 4.5 4.1 3.9
3.5 8.1 7.6 7.0 6.6
2.3 1.9 1.7 1.6 1.5
3.4 3.4 3.1 2.9 2.7
4.5 6.6 6.2 5.7 5.4
3.0 2.0 1.9 1.7 1.6
4.5 4.2 3.9 3.6 3.4
6.0 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.7
3.8 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.2
5.5 2.4 2.3 2.1 2.0
7.5 3.9 3.7 3.4 3.2
4.5 1.1 1.1 1.0 0.9
6.8 2.1 2.0 1.9 1.8
9.0 3.5 3.3 3.0 2.9
5.3 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.2
7.9 2.9 2.7 2.5 2.3
10.5 4.6 4.2 3.9 3.7
6.0 2.1 1.9 1.8 1.7
9.0 3.9 3.7 3.4 3.2
12.0 6.4 5.9 5.5 5.2
7.5 2.9 2.7 2.5 2.4
11.3 5.7 5.3 4.9 4.7
15.0 9.4 8.7 8.1 7.7
30 F 50 F 70 F 90 F
Table 23 — 50RHS,RVS,RDS Coaxial
Water Pressure Drop
UNIT
50RHS,RVS,RDS
015
018
024
030
036
042
048
060
070
GPM
1.8 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.5
2.8 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.8
3.8 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2
2.2 0.7 0.7 0.6 0.6
3.5 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.1
4.5 1.8 1.8 1.6 1.5
3.0 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.5
4.5 1.1 1.1 1.0 0.9
6.0 1.8 1.7 1.5 1.5
3.7 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.7
5.5 1.6 1.4 1.3 1.3
7.5 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.1
4.5 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.1
7.0 2.1 1.9 1.8 1.7
9.0 3.9 3.7 3.4 3.2
5.2 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3
8.0 3.2 3.0 2.8 2.6
10.5 5.1 4.7 4.4 4.1
6.0 2.1 1.9 1.8 1.7
9.0 3.9 3.7 3.4 3.2
12.0 6.4 5.9 5.5 5.2
7.5 1.1 1.0 1.0 0.9
11.3 2.2 2.1 1.9 1.8
15.0 3.6 3.4 3.1 3.0
9.0 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2
13.5 3.0 2.8 2.6 2.5
18.0 5.0 4.7 4.3 4.1
WATER TEMPERATURE (F)
Pressure Drop (psi)
WATER TEMPERATURE (F)
30 F 50 F 70 F 90 F
Pressure Drop (psi)
Table 24 — 50RHC,RVC Coaxial
Water Pressure Drop
UNIT
50RHC,RVC
006*
009
012
018
024
030
036
041†
042
048
060
*Size 006 available in 50RHC unit only.
†Size 041 available in 50RVC unit only.
GPM
0.9 0.7 0.7 0.7 0.6
1.1 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.1
1.7 1.9 1.9 1.8 1.8
2.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6
1.1 2.4 2.3 2.3 2.2
1.7 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8
2.3 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7
3.0 5.4 5.3 5.1 4.9
1.5 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.1
2.3 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.0
3.0 6.4 6.2 6.0 5.8
4.013.312.912.612.2
2.3 2.0 2.0 1.9 1.8
3.5 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8
4.5 4.2 4.1 3.9 3.8
6.0 5.9 5.7 5.6 5.4
3.0 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.8
4.5 3.9 3.7 3.6 3.5
6.0 6.4 6.2 6.0 5.8
8.0 10.6 10.3 10.0 9.7
3.8 1.5 1.5 1.4 1.4
5.5 2.7 2.6 2.5 2.4
7.5 4.3 4.2 4.1 3.9
10.0 6.9 6.7 6.5 6.3
4.5 1.7 1.7 1.6 1.6
6.8 3.2 3.1 3.0 2.9
9.0 5.0 4.9 4.8 4.6
12.0 8.2 7.9 7.7 7.5
5.3 0.9 0.9 0.9 0.9
7.9 2.2 2.1 2.1 2.0
10.5 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.6
13.0 6.2 6.0 5.8 5.7
5.3 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.9
8.0 2.6 2.6 2.5 2.4
11.0 5.3 5.1 4.9 4.8
14.0 8.7 8.5 8.2 8.0
6.0 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.1
9.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6
12.0 5.3 5.1 4.9 4.8
16.0 9.5 9.2 8.9 8.6
7.5 4.4 4.2 4.1 4.0
11.3 7.6 7.3 7.1 6.9
15.0 11.4 11.1 10.8 10.4
20.0 17.6 17.1 16.6 16.1
WATER TEMPERATURE (F)
60 F70 F80 F90 F
Pressure Drop (psi)
Antifreeze — In areas where entering loop temperatures
drop below 40 F or where piping will be routed through areas
subject to freezing, antifreeze is needed.
Alcohols and glycols are commonly used as antifreeze
agents. Freeze protection should be maintained to 15 F below
the lowest expected entering loop temperature. For example, if
the lowest expected entering loop temperature is 30 F, the leaving loop temperature would be 22 to 25 F. Therefore, the freeze
protection should be at 15 F (30 F – 15 F = 15 F).
IMPORTANT: All alcohols should be pre-mixed and
pumped from a reservoir outside of the building or
introduced under water level to prevent fuming.
Calculate the total volume of fluid in the piping system. See
Table 25. Use the percentage by volume in Table 26 to determine the amount of antifreeze to use. Antifreeze concentration
should be checked from a well mixed sample using a hydrometer to measure specific gravity.
FREEZE PROTECTION SELECTION — The 30 F FP1
factory setting (water) should be used to avoid freeze damage
to the unit.
Once antifreeze is selected, the JW3 jumper (FP1) should
be clipped on the control to select the low temperature (antifreeze 13 F) set point to avoid nuisance faults.
35
Page 36

Table 25 — Approximate Fluid Volume (gal.)
per 100 Ft of Pipe
PIPE DIAMETER (in.) VOLUME (gal.)
Copper 14.1
Rubber Hose 13.9
Polyethylene
IPS — Internal Pipe Size
SCH — Schedule
SDR — Standard Dimensional Ratio
NOTE: Volume of heat exchanger is approximately 1.0 gallon.
LEGEND
1.25 6.4
1.5 9.2
3
/4 IPS SDR11 2.8
1 IPS SDR11 4.5
1
1
/4 IPS SDR11 8.0
1
/2 IPS SDR11 10.9
2 IPS SDR11 18.0
1
1
/4 IPS SCH40 8.3
1
1
/2 IPS SCH40 10.9
2 IPS SCH40 17.0
Table 26 — Antifreeze Percentages by Volume
MINIMUM TEMPERATURE FOR
ANTIFREEZE
Methanol (%) 25 21 16 10
100% USP Food Grade
Propylene Glycol (%)
Ethanol (%) 29 25 20 14
FREEZE PROTECTION (F)
10 15 20 25
38 30 22 15
Cooling Tower/Boiler Systems — These systems typ-
ically use a common loop temperature maintained at 60 to 90 F.
Carrier recommends using a closed circuit evaporative cooling
tower with a secondary heat exchanger between the tower and
the water loop. If an open type cooling tower is used continuously, chemical treatment and filtering will be necessary.
Ground Coupled, Closed Loop and Plateframe
Heat Exchanger Well Systems (50RHR,RVR,
RHS,RVS,RDS Only) —
temperatures from 30 to 110 F. The external loop field is divided up into 2 in. polyethylene supply and return lines. Each line
has valves connected in such a way that upon system start-up,
each line can be isolated for flushing using only the system
pumps. Locate air separation in the piping system prior to the
fluid re-entering the loop field.
These systems allow water
OPERATION
Power Up Mode —
inputs, terminals and safety controls are checked for normal
operation.
NOTE: The compressor will have a 5-minute anti-short cycle
upon power up.
The unit will not operate until all the
Units with Aquazone™ Complete C Control
STANDBY — Y and W terminals are not active in standby
mode, however the O and G terminals may be active, depending on the application. The compressor will be off.
COOLING — Y and O terminals are active in Cooling mode.
After power up, the first call to the compressor will initiate a
5 to 80 second random start delay and a 5-minute anti-short
cycle protection time delay. After both delays are complete, the
compressor is energized.
NOTE: On all subsequent compressor calls the random start
delay is omitted.
HEATING STAGE 1 — Terminal Y is active in heating
stage 1. After power up, the first call to the compressor will
initiate a 5 to 80 second random start delay and a 5-minute
anti-short cycle protection time delay. After both delays are
complete, the compressor is energized.
NOTE: On all subsequent compressor calls the random start
delay is omitted.
HEATING STAGE 2 — To enter Stage 2 mode, terminal W is
active (Y is already active). Also, the G terminal must be active or the W terminal is disregarded. The compressor relay
will remain on and EH1 is immediately turned on. EH2 will
turn on after 10 minutes of continual stage 2 demand.
NOTE: EH2 will not turn on (or if on, will turn off) if FP1 temperature is greater than 45 F and FP2 is greater than 110 F.
EMERGENCY HEAT — In emergency heat mode, terminal
W is active while terminal Y is not. Terminal G must be active
or the W terminal is disregarded. EH1 is immediately turned
on. EH2 will turn on after 5 minutes of continual emergency
heat demand.
Units with Aquazone Deluxe D Control
STANDBY/FAN ONLY — The compressor will be off. The
Fan Enable, Fan Speed, and reversing valve (RV) relays will be
on if inputs are present. If there is a Fan 1 demand, the Fan
Enable will immediately turn on. If there is a Fan 2 demand,
the Fan Enable and Fan Speed will immediately turn on.
NOTE: DIP switch 5 on S1 does not have an effect upon Fan 1
and Fan 2 outputs.
HEATING STAGE 1 — In Heating Stage 1 mode, the Fan
Enable and Compressor relays are turned on immediately.
Once the demand is removed, the relays are turned off and the
control reverts to Standby mode. If there is a master/slave or
dual compressor application, all compressor relays and related
functions will operate per their associated DIP switch 2 setting
on S1.
HEATING STAGE 2 — In Heating Stage 2 mode, the Fan
Enable and Compressor relays are remain on. The Fan Speed
relay is turned on immediately and turned off immediately
once the demand is removed. The control reverts to Heating
Stage 1 mode. If there is a master/slave or dual compressor
application, all compressor relays and related functions will operate per their associated DIP switch 2 setting on S1.
HEATING STAGE 3 — In Heating Stage 3 mode, the Fan
Enable, Fan Speed and Compressor relays remain on. The EH1
output is turned on immediately. With continuing Heat Stage 3
demand, EH2 will turn on after 10 minutes. EH1 and EH2 are
turned off immediately when the Heating Stage 3 demand is removed. The control reverts to Heating Stage 2 mode.
Output EH2 will be off if FP1 is greater than 45 F AND
FP2 (when shorted) is greater than 110 F during Heating
Stage 3 mode. This condition will have a 30-second recognition time. Also, during Heating Stage 3 mode, EH1, EH2, Fan
Enable, and Fan Speed will be ON if G input is not active.
EMERGENCY HEAT — In Emergency Heat mode, the Fan
Enable and Fan Speed relays are turned on. The EH1 output is
turned on immediately. With continuing Emergency Heat demand, EH2 will turn on after 5 minutes. Fan Enable and Fan
Speed relays are turned off after a 60-second delay. The control
reverts to Standby mode.
Output EH1, EH2, Fan Enable, and Fan Speed will be ON if
the G input is not active during Emergency Heat mode.
COOLING STAGE 1 — In Cooling Stage 1 mode, the Fan
Enable, compressor and RV relays are turned on immediately.
If configured as stage 2 (DIP switch set to OFF) then the compressor and fan will not turn on until there is a stage 2 demand.
The fan Enable and compressor relays are turned off immediately when the Cooling Stage 1 demand is removed. The control reverts to Standby mode. The RV relay remains on until
there is a heating demand. If there is a master/slave or dual
compressor application, all compressor relays and related functions will track with their associated DIP switch 2 on S1.
COOLING STAGE 2 — In Cooling Stage 2 mode, the Fan
Enable, compressor and RV relays remain on. The Fan Speed
relay is turned on immediately and turned off immediately
once the Cooling Stage 2 demand is removed. The control reverts to Cooling Stage 1 mode. If there is a master/slave or dual
36
Page 37

compressor application, all compressor relays and related functions will track with their associated DIP switch 2 on S1.
NIGHT LOW LIMIT (NLL) STAGED HEATING — In
NLL staged Heating mode, the override (OVR) input becomes
active and is recognized as a call for heating and the control
will immediately go into a Heating Stage 1 mode. With an additional 30 minutes of NLL demand, the control will go into
Heating Stage 2 mode. With another additional 30 minutes of
NLL demand, the control will go into Heating Stage 3 mode.
Units with HWR Option
FAN ONLY — A (G) call from the thermostat to the (G)
terminal of the Deluxe D control board will bring the unit
on in fan only mode.
COOLING STAGE 1 — A simultaneous call from (G),
(Y1), and (O) to the (G), (Y1), (O/W2) terminals of the Deluxe
D control board will bring the unit on in 1st Stage Cooling.
COOLING STAGE 2 — A simultaneous call from (G),
(Y1), (Y2), and (O) to the (G), (Y1), (Y2), and (O/W2) terminals of the Deluxe D control board will bring the unit on
in Cooling Stage 2. When the call is satisfied at the thermostat the unit will continue to run in Cooling Stage 1 until the
Cooling Stage 1 call is removed or satisfied, shutting down
the unit.
NOTE: Not all units have two-stage cooling functionality.
HEATING STAGE 1 — A simultaneous call from (G) and
(Y1) to the (G) and (Y1) terminals of the Deluxe D control
board will bring the unit on in Heating Stage 1.
HEATING STAGE 2 — A simultaneous call from (G),
(Y1), and (Y2) to the (G), (Y1), and (Y2) terminals of the
Deluxe D control board will bring the unit on in Heating
Stage 2. When the call is satisfied at the thermostat the unit
will continue to run in Heating Stage 1 until the call is
removed or satisfied, shutting down the unit.
NOTE: Not all units have two-stage heating functionality.
REHEAT MODE — A call from the humidistat/dehumid-
istat to the (H) terminal of the Deluxe D control board will
bring the unit on in Reheat Mode if there is no call for cooling at the thermostat. When the humidistat/dehumidistat call
is removed or satisfied the unit will shut down.
NOTE: Cooling always overrides Reheat Mode. In the Cooling mode, the unit cools and dehumidifies. If the cooling
thermostat is satisfied but there is still a call for dehumidification, the unit will continue to operate in Reheat Mode.
SYSTEM TEST
System testing provides the ability to check the control
operation. The control enters a 20-minute Test mode by momentarily shorting the test pins. All time delays are increased
15 times. See Fig. 19-22.
Test Mode — To enter Test mode on Complete C or Deluxe
D controls, cycle the power 3 times within 60 seconds. The LED
(light-emitting diode) will flash a code representing the last fault
when entering the Test mode. The alarm relay will also power on
and off during Test mode. See Tables 27 and 28. To exit Test
mode, short the terminals for 3 seconds or cycle the power 3
times within 60 seconds.
NOTE: Deluxe D Control has a flashing code and alarm relay
cycling code that will both have the same numerical label.
For example, flashing code 1 will have an alarm relay cycling
code 1. Code 1 indicates the control has not faulted since the
last power off to power on sequence.
Retry Mode — In Retry mode, the status LED will start to
flash slowly to signal that the control is trying to recover from
an input fault. The control will stage off the outputs and try to
again satisfy the thermostat used to terminal Y. Once the thermostat input calls are satisfied, the control will continue normal
operation.
NOTE: If 3 consecutive faults occur without satisfying the
thermostat input call to terminal Y, the control will go into
lockout mode. The last fault causing the lockout is stored in
memory and can be viewed by entering Test mode.
Table 27 — Complete C Control Current LED
Status and Alarm Relay Operations
LED STATUS DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION ALARM RELAY
On
Off
Slow Flash Fault Retry Open
Fast Flash Lockout Closed
Slow Flash Over/Under Voltage Shutdown
Flashing Code 1
Flashing Code 2
Flashing Code 3
Flashing Code 4
Flashing Code 5
Flashing Code 6
Flashing Code 7
Flashing Code 8 Test Mode — PM in memory Cycling Code 8
Flashing Code 9
CO — Condensate Overflow LED — Light-Emitting Diode
FP — Freeze Protection LP — Low Pressure
HP — High Pressure PM — Performance Monitor
NOTES:
1. Slow flash is 1 flash every 2 seconds.
2. Fast flash is 2 flashes every 1 second.
3. EXAMPLE: “Flashing Code 2” is represented by 2 fast flashes followed by
a 10-second pause. This sequence will repeat continually until the fault is
cleared.
Normal Mode Open
Normal Mode with
PM Warning
Complete C Control is
non-functional
Test Mode — No fault in
memory
Test Mode — HP Fault in
memory
Test Mode — LP Fault in
memory
Test Mode — FP1 Fault in
memory
Test Mode — FP2 Fault in
memory
Test Mode — CO Fault in
memory
Test Mode — Over/Under
shutdown in memory
Test Mode — FP1/FP2
Swapped Fault in memory
LEGEND
Cycle
(closed 5 sec.,
Open 25 sec.)
Open
Open
(Closed after
15 minutes)
Cycling Code 1
Cycling Code 2
Cycling Code 3
Cycling Code 4
Cycling Code 5
Cycling Code 6
Cycling Code 7
Cycling Code 9
Table 28 — Complete C Control LED Code and
Fault Descriptions
LED
CODE
1 No fault in memory There has been no fault since
2 High-Pressure Switch HP Open Instantly
3 Low-Pressure Switch LP open for 30 continuous
4 Freeze Protection
5 Freeze Protection Air Coil
6 Condensate overflow Sense overflow (grounded)
7 (Autoreset) Over/Under Voltage
8 PM Warning Performance Monitor Warning
9 FP1 and FP2
CO — Condensate Overflow LED — Light-Emitting Diode
FP — Freeze Protection LP — Low Pressure
HP — High Pressure PM — Performance Monitor
Coax — FP1
— FP2
Shutdown
Thermistors are swapped
FAULT DESCRIPTION
the last power-down to powerup sequence
seconds before or during a
call (bypassed for first 60 seconds)
FP1 below Temp limit for 30
continuous seconds
(bypassed for first 60 seconds
of operation)
FP2 below Temp limit for 30
continuous seconds
(bypassed for first 60 seconds
of operation)
for 30
continuous seconds
"R" power supply is <19VAC
or >30VAC
has occurred.
FP1 temperature is higher
than FP2 in heating/test
mode, or FP2 temperature is
higher than FP1 in cooling/
test mode.
LEGEND
37
Page 38

Aquazone™ Deluxe D Control LED Indicators —
STATUS LED — Status LED indicates the current status or
mode of the Deluxe D control. The Status LED light is green.
TEST LED — Test LED will be activated any time the Deluxe D control is in test mode. The Test LED light is yellow.
FAULT LED — Fault LED light is red. The fault LED will always flash a code representing the last fault in memory. If there
is no fault in memory, the fault LED will flash code 1 on the
and appear as 1 fast flash alternating with a 10-second pause.
See Table 29.
There are 3 LED indicators on the Deluxe D Control:
SERVICE
Perform the procedures outlined below periodically, as
indicated.
IMPORTANT: When a compressor is removed from this
unit, system refrigerant circuit oil will remain in the compressor. To avoid leakage of compressor oil, the refrigerant
lines of the compressor must be sealed after it is removed.
IMPORTANT: All refrigerant discharged from this unit
must be recovered without exception. Technicians must follow industry accepted guidelines and all local, state and federal statutes for the recovery and disposal of refrigerants.
IMPORTANT: To avoid the release of refrigerant into the
atmosphere, the refrigerant circuit of this unit must only be
serviced by technicians which meet local, state and federal
proficiency requirements.
IMPORTANT: To prevent injury or death due to electrical
shock or contact with moving parts, open unit disconnect
switch before servicing unit.
Filters — Filters must be clean for maximum performance.
Inspect filters every month under normal operating conditions.
replace when necessary.
IMPORTANT: Units should never be operated without a filter.
Water Coil — Keep all air out of the water coil. Check
open loop systems to be sure the well head is not allowing air
to infiltrate the water line. Always keep lines airtight.
Inspect heat exchangers regularly, and clean more frequently if the unit is located in a “dirty” environment. Keep the heat
exchanger full of water at all times. Open-loop systems should
have an inverted P trap placed in the discharge line to keep
water in the heat exchanger during off cycles. Closed-loop
systems must have a minimum of 15 psi during the summer
and 40 psi during the winter. Generally, the higher the water
flow through the bail, the lower the chance for sealing.
Check P trap frequently for proper operation.
IMPORTANT: To avoid fouled machinery and extensive
unit clean-up, DO NOT operate units without filters in
place. DO NOT use equipment as a temporary heat source
during construction.
Condensate Drain Pans — Check condensate drain
pans for algae growth twice a year. If algae growth is apparent,
consult a water treatment specialist for proper chemical treatment. Applying an algaecide every three months will typically
eliminate algae problems in most locations.
Refrigerant System — Verify air and water flow rates
are at proper levels before servicing. To maintain sealed circuitry integrity, do not install service gauges unless unit operation
appears abnormal.
Check to see that unit is within the superheat and subcooling temperature ranges shown in Table 21. If the unit is not
within these ranges, recover and reweigh in refrigerant charge.
Table 29 — Aquazone Deluxe D Control Current LED Status and Alarm Relay Operations
DESCRIPTION
Normal Mode On Off Flash Last Fault Code in Memory Open
Normal Mode with PM On Off Flashing Code 8
Deluxe D Control is
non-functional
Test Mode — On Flash Last Fault Code in Memory Cycling Appropriate Code
Night Setback Flashing Code 2 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
ESD Flashing Code 3 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
Invalid T-stat Inputs Flashing Code 4 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
No Fault in Memory On Off Flashing Code 1 Open
HP Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 2 Open
LP Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 3 Open
FP1 Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 4 Open
FP2 Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 5 Open
CO Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 6 Open
Over/Under Voltage Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 7 Open (closed after 15 minutes)
HP Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 2 Closed
LP Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 3 Closed
FP1 Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 4 Closed
FP2 Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 5 Closed
CO Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 6 Closed
LEGEND NOTES:
CO — Condensate Overflow HP — High Pressure
ESD — Emergency Shutdown LP — Low Pressure
FP — Freeze Protection PM — Performance Monitor
STATUS LED
(Green)
Off Off Off Open
TEST LED
(Yellow)
FAULT LED (Red) ALARM RELAY
Cycle (closed 5 sec,
open 25 sec, …)
1. If there is no fault in memory, the Fault LED will flash code 1.
2. Codes will be displayed with a 10-second Fault LED pause.
3. Slow flash is 1 flash every 2 seconds.
4. Fast flash is 2 flashes every 1 second.
5. EXAMPLE: “Flashing Code 2” is represented by 2 fast flashes followed by a 10-second pause. This sequence will repeat continually
until the fault is cleared.
38
Page 39
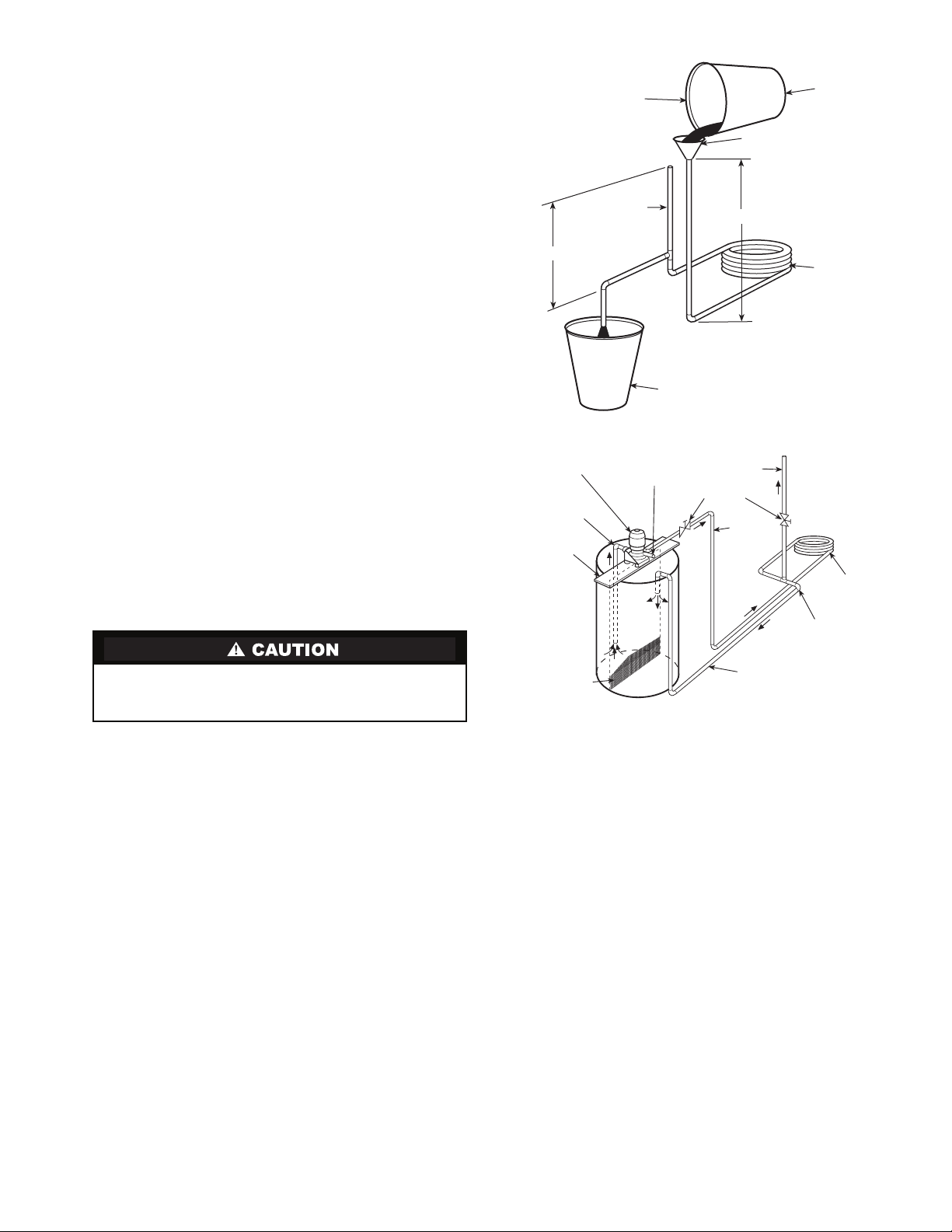
Compressor — Conduct annual amperage checks to in-
sure that amp draw is no more than 10% greater than indicated
on the serial plate data.
Fan Motors — All units have lubricated fan motors. Fan
motors should never be lubricated unless obvious, dry operation is suspected. Periodic maintenance oiling is NOT recommended as it will result in dirt accumulating in the excess oil
and cause eventual motor failure. Conduct annual dry operation check and amperage check to ensure amp draw is no more
than 10% greater than indicated on serial plate data.
Condensate Drain Cleaning — Clean the drain line
and unit drain pan at the start of each cooling season. Check
flow by pouring water into drain. Be sure trap is filled to maintain an air seal.
Air Coil Cleaning — Remove dirt and debris from evap-
orator coil as required by condition of the coil. A 10% solution
of dishwasher detergent and water is recommended for
cleaning both sides of the coil, followed by a thorough water
rinse. Clean coil with a stiff brush, vacuum cleaner, or compressed air. Use a fin comb of the correct tooth spacing when
straightening mashed or bent coil fins.
Condenser Cleaning — Water-cooled condensers may
require cleaning of scale (water deposits) due to improperly
maintained closed-loop water systems. Sludge build-up may
need to be cleaned in an open water tower system due to
induced contaminants.
Local water conditions may cause excessive fouling or
pitting of tubes. Condenser tubes should therefore be cleaned at
least once a year, or more often if the water is contaminated.
Proper water treatment can minimize tube fouling and
pitting. If such conditions are anticipated, water treatment
analysis is recommended. Refer to the Carrier System Design
Manual, Part 5, for general water conditioning information.
FILL CONDENSER WITH
CLEANING SOLUTION. DO
NOT ADD SOLUTION
MORE RAPIDLY THAN
VENT CAN EXHAUST
GASES CAUSED BY
CHEMICAL ACTION.
VENT
PIPE
3’ TO 4’
Fig. 29 — Gravity Flow Method
PUMP
SUCTION
PUMP
SUPPORT
TANK
PRIMING
CONN.
PAIL
1”
PIPE
5’ APPROX
GAS VENT
GLOBE
VALV ES
SUPPLY
1” PIPE
FUNNEL
REMOVE WATER
REGULATING VALVE
PAIL
CONDENSER
CONDENSER
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and rubber
gloves when using inhibited hydrochloric acid solution.
Observe and follow acid manufacturer’s instructions.
Clean condensers with an inhibited hydrochloric acid
solution. The acid can stain hands and clothing, damage
concrete, and, without inhibitor, damage steel. Cover surroundings to guard against splashing. Vapors from vent pipe
are not harmful, but take care to prevent liquid from being
carried over by the gases.
Warm solution acts faster, but cold solution is just as effective if applied for a longer period.
GRAVITY FLOW METHOD — Do not add solution faster
than vent can exhaust the generated gases.
When condenser is full, allow solution to remain overnight,
then drain condenser and flush with clean water. Follow acid
manufacturer’s instructions. See Fig. 29.
FORCED CIRCULATION METHOD — Fully open vent
pipe when filling condenser. The vent may be closed when
condenser is full and pump is operating. See Fig. 30.
Regulate flow to condenser with a supply line valve. If
pump is a nonoverloading type, the valve may be fully closed
while pump is running.
For average scale deposit, allow solution to remain in condenser overnight. For heavy scale deposit, allow 24 hours.
Drain condenser and flush with clean water. Follow acid manufacturer’s instructions.
FINE MESH
SCREEN
RETURN
Fig. 30 — Forced Circulation Method
Checking System Charge — Units are shipped with
full operating charge. If recharging is necessary:
1. Insert thermometer bulb in insulating rubber sleeve on
liquid line near filter drier. Use a digital thermometer for
all temperature measurements. DO NOT use a mercury
or dial-type thermometer.
2. Connect pressure gage to discharge line near compressor.
3. After unit conditions have stabilized, read head pressure
on discharge line gage.
NOTE: Operate unit a minimum of 15 minutes before
checking charge.
4. From standard field-supplied Pressure-Temperature
chart for R-22, find equivalent saturated condensing
temperature.
5. Read liquid line temperature on thermometer; then
subtract from saturated condensing temperature. The difference equals subcooling temperature.
6. Compare the subcooling temperature with the normal
temperature listed in Table 21. If the measured liquid line
temperature does not agree with the required liquid line
temperature, ADD refrigerant to raise the temperature or
REMOVE refrigerant (using standard practices) to lower
the temperature (allow a tolerance of ± 3° F).
39
Page 40

Refrigerant Charging
To prevent personal injury, wear safety glasses and gloves
when handling refrigerant. Do not overcharge system —
this can cause compressor flooding.
NOTE: Do not vent or depressurize unit refrigerant to
atmosphere. Remove and reclaim refrigerant following
accepted practices.
Air Coil Fan Motor Removal
Before attempting to remove fan motors or motor mounts,
place a piece of plywood over evaporator coils to prevent
coil damage.
Disconnect motor power wires from motor terminals before
motor is removed from unit.
1. Shut off unit main power supply.
2. Loosen bolts on mounting bracket so that fan belt can be
removed.
3. Loosen and remove the 2 motor mounting bracket bolts
on left side of bracket.
4. Slide motor/bracket assembly to extreme right and lift out
through space between fan scroll and side frame. Rest
motor on a high platform such as a step ladder. Do not
allow motor to hang by its power wires.
TROUBLESHOOTING
(Fig. 31 and 32, and Table 30)
When troubleshooting problems with a WSHP, consider the
following.
Thermistor — A thermistor may be required for single-
phase units where starting the unit is a problem due to low
voltage. See Fig. 31 for thermistor nominal resistance.
90.0
80.0
70.0
60.0
50.0
40.0
30.0
Resistance (kOhm)
20.0
10.0
0.0
0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 100.0 120.0 140.0
Temperature (degF)
Fig. 31 — Thermistor Nominal Resistance
Control Sensors — The control system employs 2 nom-
inal 10,000 ohm thermistors (FP1 and FP2) that are used for
freeze protection. Be sure FP1 is located in the discharge fluid
and FP2 is located in the air discharge. See Fig. 32.
AIRFLOW
(°F)
a50-8163
THERMISTOR
CONDENSATE
OVERFLOW
LEGEND
COAX — Coaxial Heat Exchanger
Airflow
Refrigerant Liquid Line Flow
AIR
COIL
(CO)
AIR COIL
FREEZE
PROTECTION
AIRFLOW
(°F)
FP2
EXPANSION
VALV E
LIQUID
LINE
WATER
COIL
PROTECTION
FP1
WATER IN
COAX
WATER OUT
Fig. 32 — FP1 and FP2 Thermistor Location
SUCTION
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
40
Page 41
Table 30 — Troubleshooting
FAULT HEATING COOLING POSSIBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
Main Power Problems X X Green Status LED Off Check line voltage circuit breaker and disconnect.
Check for line voltage between L1 and L2 on the contactor.
Check for 24 vac between R and C on controller.
Check primary/secondary voltage on transformer.
HP Fault — Code 2
High Pressure
X Reduced or no airflow in
X Air temperature out of range
X X Overcharged with refrigerant Check superheat/subcooling vs typical operating condition Table 21.
X X Bad HP switch Check switch continuity and operation. Replace.
LP/LOC Fault — Code 3
Low Pressure/Loss of
Charge
FP1 Fault — Code 4
Water Freeze Protection
FP2 Fault — Code 5
Air Coil Freeze
Protection
Condensate Fault —
Code 6
Over/Under Voltage —
Code 7
(Auto Resetting)
Performance Monitor —
Code 8
FP1 and FP2
Thermistors —
Code 9
No Fault Code Shown X X No compressor operation See scroll compressor rotation section.
Unit Short Cycles X X Dirty air filter Check and clean air filter.
Only Fan Runs X X Thermostat position Ensure thermostat set for heating or cooling operation.
LEGEND
RV — Reversing Valve
X X Insufficient charge Check for refrigerant leaks.
X Compressor pump down at
X Reduced or no water flow in
X Inadequate antifreeze level Check antifreeze density with hydrometer.
X Improper freeze protect set-
X Water temperature out of
X X Bad thermistor Check temperature and impedance correlation.
X X Bad thermistor Check temperature and impedance correlation.
X X Blocked drain Check for blockage and clean drain.
X X Improper trap Check trap dimensions and location ahead of vent.
X X Under voltage Check power supply and 24 vac voltage before and during operation.
X X Over voltage Check power supply voltage and 24 vac before and during operation.
X Heating mode FP2>125 F Check for poor airflow or overcharged unit.
X FP1 temperature is higher
X X Compressor overload Check and replace if necessary.
X X Control board Reset power and check operation.
X X Unit in 'Test Mode' Reset power or wait 20 minutes for auto exit.
X X Unit selection Unit may be oversized for space. Check sizing for actual load of space.
X X Compressor overload Check and replace if necessary.
X X Unit locked out Check for lockout codes. Reset power.
X X Compressor overload Check compressor overload. Replace if necessary.
X X Thermostat wiring Check Y and W wiring at heat pump. Jumper Y and R for compressor
X Reduced or no water flow in
cooling
X Water temperature out of
range in cooling
heating
in heating
start-up
heating
ting (30 F vs 10 F)
range
X Reduced or no airflow in
cooling
X Air temperature out of range Too much cold vent air. Bring entering air temperature within design
X Improper freeze protect set-
ting (30 F vs 10 F)
X Poor drainage Check for piping slope away from unit.
X Moisture on sensor Check for moisture shorting to air coil.
X Cooling mode FP1>125 F
OR FP2< 40 F
than FP2 temperature.
X FP2 temperature is higher
than FP1 temperature.
Check pump operation or valve operation/setting.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Bring water temperature within design parameters.
Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
Dirty air coil — construction dust etc.
External static too high. Check Tables 8-13.
Bring return air temperature within design parameters.
Check charge and start-up water flow.
Check pump operation or water valve operation/setting.
Plugged strainer or filter. Clean or replace.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Clip JW2 jumper for antifreeze (10 F) use.
Bring water temperature within design parameters.
Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check Tables 8-13.
parameters.
Normal airside applications will require 30 F only.
Check slope of unit toward outlet.
Poor venting. Check vent location.
Check power supply wire size.
Check compressor starting.
Check 24 vac and unit transformer tap for correct power supply voltage.
Check 24 vac and unit transformer tap for correct power supply voltage.
Check for poor water flow or airflow.
Swap FP1 and FP2 thermistors.
Swap FP1 and FP2 thermistors.
operation in Test mode.
41
Page 42

Table 30 — Troubleshooting (cont)
FAULT HEATING COOLING POSSIBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
Only Compressor Runs X X Thermostat wiring Check G wiring at heat pump. Jumper G and R for fan operation.
X X Fan motor relay Jumper G and R for fan operation. Check for line voltage across BR
X X Fan motor Check for line voltage at motor. Check capacitor.
X X Thermostat wiring Check Y and W wiring at heat pump. Jumper Y and R for compressor
Unit Does Not Operate in
Cooling
X Reversing valve Set for cooling demand and check 24 VAC on RV coil and at control.
X Thermostat setup Check for 'O' RV setup not 'B'.
X Thermostat wiring Check O wiring at heat pump. Check RV to ensure the valve is chang-
Insufficient Capacity/
Not Cooling or Heating
Properly
X X Dirty filter Replace or clean.
X Reduced or no airflow in
heating
X Reduced or no airflow in
cooling
X X Leaky ductwork Check supply and return air temperatures at the unit and at distant duct
X X Low refrigerant charge Check superheat and subcooling Table 21.
X X Restricted metering device Check superheat and subcooling Table 21. Replace.
X Defective reversing valve Manually check the four-way valve to ensure all valves are operational.
X X Thermostat improperly
located
X X Unit undersized Recheck loads and sizing check sensible cooling load and heat pump
X X Scaling in water heat
exchanger
X X Inlet water too hot or cold Check load, loop sizing, loop backfill, ground moisture.
High Head Pressure X Reduced or no airflow in
heating
X Reduced or no water flow in
cooling
X Inlet water too hot Check load, loop sizing, loop backfill, ground moisture.
X Air temperature out of range
in heating
X Scaling in water heat
exchanger
X X Unit overcharged Check superheat and subcooling. Reweigh in charge.
X X Non-condensables in
system
X X Restricted metering device Check superheat and subcooling per Table 21. Replace.
Low Suction Pressure X Reduced water flow in
X Water temperature out of
heating
range
X Reduced airflow in cooling Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
X Air temperature out of range Too much cold vent air. Bring entering air temperature within design
X X Insufficient charge Check for refrigerant leaks.
Low Discharge Air
Temperature in Heating
X Too high airflow Check blower Tables 8-13.
X Poor performance See 'Insufficient Capacity'.
High Humidity X Too high airflow Check blower Tables 8-13.
X Unit oversized Recheck loads and sizing check sensible cooling load and heat pump
LEGEND
RV — Reversing Valve
contacts.
Check fan power enable relay operation (if present).
operation in test mode.
If RV is stuck, run high pressure up by reducing water flow and while
operating engage and disengage RV coil voltage to push valve.
ing over from heating and cooling modes. A 'click' should be heard
when the RV changes modes.
Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower Tables 8-13.
Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower Tables 8-13.
registers if significantly different, duct leaks are present.
Check location and for air drafts behind thermostat.
capacity.
Check for scale (water deposits) and clean if necessary.
Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower Tables 8-13.
Check pump operation or valve operation/setting.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate. See Table 20.
Bring return air temperature within design parameters.
Check for scale (water deposits) and clean if necessary.
Evacuate the refrigerant, recharge the system, and then weigh the new
refrigerant charge.
Check pump operation or water valve operation/setting.
Plugged strainer or filter. Clean or replace.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Bring water temperature within design parameters.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower Tables 8-13.
parameters.
capacity.
Copyright 2007 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 4
Ta b 5 a 5 a
Catalog No. 04-53500007-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50R-5SI Pg 42 6-07 Replaces: 50R-4SI
Page 43

50RHC,RVC,RHR,RHS,RVR,RVS,RDS
START-UP CHECKLIST
CUSTOMER:___________________________ JOB NAME: _______________________________________
MODEL NO.:___________________________ SERIAL NO.:____________________ DATE:_________
I. PRE-START-UP
DOES THE UNIT VOLTAGE CORRESPOND WITH THE SUPPLY VOLTAGE AVAILABLE? (Y/N)
HAVE THE POWER AND CONTROL WIRING CONNECTIONS BEEN MADE AND TERMINALS
TIGHT? (Y/N)
HAVE WATER CONNECTIONS BEEN MADE AND IS FLUID AVAILABLE AT HEAT EXCHANGER?
(Y/N)
HAS PUMP BEEN TURNED ON AND ARE ISOLATION VALVES OPEN? (Y/N)
HAS CONDENSATE CONNECTION BEEN MADE AND IS A TRAP INSTALLED? (Y/N)
IS AN AIR FILTER INSTALLED? (Y/N)
II. START-UP
IS FAN OPERATING WHEN COMPRESSOR OPERATES? (Y/N)
IF 3-PHASE SCROLL COMPRESSOR IS PRESENT, VERIFY PROPER ROTATION PER INSTRUCTIONS.
(Y/N)
UNIT VOLTAGE — COOLING OPERATION
PHASE AB VOLTS PHASE BC VOLTS PHASE CA VOLTS
(if 3 phase) (if 3 phase)
PHASE AB AMPS
PHASE BC AMPS PHASE CA AMPS
(if 3 phase) (if 3 phase)
CONTROL VOLTAGE
IS CONTROL VOLTAGE ABOVE 21.6 VOLTS? (Y/N) .
IF NOT, CHECK FOR PROPER TRANSFORMER CONNECTION.
TEMPERATURES
FILL IN THE ANALYSIS CHART ATTACHED.
COAXIAL HEAT
EXCHANGER
COOLING CYCLE:
FLUID IN
FFLUID OUT F PSI FLOW
HEATING CYCLE:
FLUID IN
FFLUID OUT F PSI FLOW
AIR COIL COOLING CYCLE:
AIR IN
HEATING CYCLE:
AIR IN
FAIR OUT F
FAIR OUT F
CL-1
Page 44

HEATING CYCLE ANALYSIS
AIR
COIL
F
F
LIQUID LINE
a50-8197.eps
COOLING CYCLE ANALYSIS
EXPANSION
VALV E
F
WATER IN
COAX
F
PSI
F
WATER OUT
PSI
F
PSI
LOOK UP PRESSURE DROP IN TABLES 22-24
TO DETERMINE FLOW RATE
PSI
°F
SAT
SUCTION
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
SAT
°F
a50-8165
AIR
COIL
°F
EXPANSION
VALV E
LIQUID LINE
COAX
°F
WATER IN
°F
PSI
WATER OUT
°F
PSI
LOOK UP PRESSURE DROP IN TABLES 22-24
TO DETERMINE FLOW RATE
SUCTION
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
HEAT OF EXTRACTION (ABSORPTION) OR HEAT OF REJECTION =
FLOW RATE (GPM) x TEMP. DIFF. (DEG. F) x FLUID FACTOR* =
SUPERHEAT = SUCTION TEMPERATURE – SUCTION SATURATION TEMPERATURE
=
(DEG F)
SUBCOOLING = DISCHARGE SATURATION TEMPERATURE – LIQUID LINE TEMPERATURE
=
*Use 500 for water, 485 for antifreeze.
(DEG F)
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
(Btu/hr)
Copyright 2007 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 4
Ta b 5 a 5 a
Catalog No. 04-53500007-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50R-5SI Pg CL-2 6-07 Replaces: 50R-4SI
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
 Loading...
Loading...