Page 1

Water-to-Water Water Source Heat Pump
with PURON
®
Refrigerant (R-410A)
Installation, Start-Up, and
Service Instructions
AQUAZONE™
50PSW036-360
50 Hz
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1,2
GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Step 1 — Check Jobsite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Step 2 — Check Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
• STORAGE
•PROTECTION
•INSPECT UNIT
Step 3 — Locate Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Step 4 — Mount Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Step 5 — Connect Piping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
• WATER SUPPLY AND QUALITY
• WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS
• GROUND-WATER APPLICATIONS
• GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS
• UNIT LOAD PIPING
Step 6 — Wire Electrical Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . 7
• POWER CONNECTION
• SUPPLY VOLTAGE
• EXTERNAL LOOP POWER CONNECTION
• 220-V OPERATION
• 380-V OPERATION
Step 7 — Wire Low Voltage Connections . . . . . . . . 12
• THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS
• WATER FREEZE PROTECTION
• ACCESSORY CONNECTIONS
• WATER SOLENOID VALVES
PRE-START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
System Checkout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
FIELD SELECTABLE INPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13,14
Complete C Control Jumper Settings. . . . . . . . . . . 13
Complete C Control DIP Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Deluxe D Control Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Deluxe D Control DIP Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Deluxe D Control Accessory Relay
Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-16
Operating Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Unit Start-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Scroll Compressor Rotation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Flow Regulation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Cleaning and Flushing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Antifreeze . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Cooling Tower/Boiler Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Ground Coupled, Closed Loop and Plateframe
Heat Exchanger Well Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
OPERATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Power Up Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Units with Aquazone Complete C Control . . . . . . . 16
Units with Aquazone Deluxe D Control . . . . . . . . . . 16
SYSTEM TEST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16,17
Page
Test Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Retry Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Aquazone Deluxe D Control LED Indicators . . . . . 17
SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18,19
Water Coil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Refrigerant System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Condenser Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Checking System Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Refrigerant Charging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
TROUBLESHOOTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19-21
50PSW START-UP CHECKLIST . . . . . . . . . . . CL-1,CL-2
IMPORTANT: Read the entire instruction manual before
starting installation.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment can
be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only trained and qualified service personnel should
install, repair, or service air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance function of cleaning coils. All other operations should be performed
by trained service personnel. When working on air-conditioning equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags and
labels attached to the unit, and other safety precautions that
may apply.
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, maintenance, or use can cause explosion, fire, electrical shock or
other conditions which may cause personal injury or property
damage. Consult a qualified installer, service agency, or your
distributor or branch for information or assistance. The
qualified installer or agency must use factory-authorized kits or
accessories when modifying this product. Refer to the individual instructions packaged with the kits or accessories when
installing.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and work
gloves. Use quenching cloth for brazing operations. Have fire
extinguisher available. Read these instructions thoroughly and
follow all warnings or cautions attached to the unit. Consult
local building codes and the National Electrical Code (NEC,
U.S.A.) for special installation requirements.
Understand the signal words — DANGER, WARNING,
and CAUTION. DANGER identifies the most serious hazards
which will result in severe personal injury or death. WARNING signifies hazards that could result in personal injury or
death. CAUTION is used to identify unsafe practices, which
would result in minor personal injury or product and property
damage.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53500073-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50PSW-C1SI Pg 1 10-10 Replaces: New
Page 2
Recognize safety information. This is the safety alert
symbol ( ). When you see this symbol on the unit and in
instructions or manuals, be alert to the potential for personal
injury.
WARNING
Electrical shock can cause personal injury or death. Before
installing or servicing system, always turn off main power
to system. There may be more than one disconnect switch.
Turn off accessory heater power if applicable. Install lockout tag.
GENERAL
The Aquazone™ 50PSW water source heat pump (WSHP)
is a single-package vertically mounted unit with electronic controls designed for year-round cooling and heating.
IMPORTANT: The installation of water source heat pump
units and all associated components, parts, and accessories
which make up the installation shall be in accordance with
the regulations of ALL authorities having jurisdiction and
MUST conform to all applicable codes. It is the responsibility of the installing contractor to determine and comply
with ALL applicable codes and regulations.
INSTALLATION
Step 1 — Check Jobsite —
maintenance instructions are provided with each unit. Before
unit start-up, read all manuals and become familiar with the
unit and its operation. Thoroughly check out the system before
operation. Complete the inspections and instructions listed
below to prepare a unit for installation. See Table 1 for unit
physical data.
Units are designed for indoor installation only. Be sure to allow adequate space around the unit for servicing. See Fig. 1
and 2 for overall unit dimensions.
These units are not approved for outdoor installation and
must be installed indoors in the structure being conditioned. Do
not locate in areas where ambient conditions are not maintained within 4.4 to 37.8 C.
Installation, operation and
CAUTION
To avoid equipment damage, do not use these units as a
source of heating or cooling during the construction process. The mechanical components used in these units can
quickly become clogged with construction dirt and debris
which may cause system damage.
Step 2 — Check Unit — Upon receipt of shipment at
the jobsite, carefully check the shipment against the bill of
lading. Make sure all units have been received. Inspect the carton or crating of each unit, and inspect each unit for damage.
Ensure the shipping company makes proper notation of any
shortages or damage on all copies of the freight bill. Concealed
damage not discovered during unloading must be reported to
the shipping company within 15 days of receipt of shipment.
NOTE: It is the responsibility of the purchaser to file all
necessary claims with the shipping company.
1. Verify unit is correct model for entering water temperature of job.
2. Be sure the location chosen for unit installation provides
ambient temperatures maintained above freezing. Well
water applications are especially susceptible to freezing.
3. Be sure the installation location is isolated from sleeping
areas, private offices and other acoustically sensitive
spaces.
NOTE: A sound control accessory package may be used
to help eliminate sound in sensitive spaces.
4. Provide sufficient access to allow maintenance and
servicing of the compressor and coils.
5. Provide an unobstructed path to the unit within the closet
or mechanical room. Space should be sufficient to allow
removal of unit if necessary.
6. Provide ready access to water valves and fittings, and
screwdriver access to unit side panels.
7. Where access to side panels is limited, pre-removal of the
control box side mounting screws may be necessary for
future servicing.
STORAGE — If the equipment is not needed for immediate
installation upon its arrival at the jobsite, it should be left in its
shipping carton and stored in a clean, dry area of the building
or in a warehouse. Units must be stored in an upright position
at all times. If carton stacking is necessary, stack units a maximum of 3 cartons high. Do not remove any equipment from its
shipping package until it is needed for installation.
Table 1 — 50PSW Unit Physical Data
50PSW UNIT SIZE 036 060 120 180 360
NOMINAL CAPACITY (kW) 10.5 17.6 35.2 49.2 105.5
WEIGHT (kg)
Operating 158 163 329 358 604
Packag ed 169 175 349 363 608
COMPRESSOR (qty) Scroll (1) Scroll (1) Scroll (2) Scroll (1) Scroll (2)
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A
Factory Charge Per Circuit (kg) 2.04 2.83 2.83 6.80 6.80
CONNECTIONS, FPT (in.)
Commercial Load/Source
HWG Water In/Out
WATER VOL UM E ( L) 3.64 5.04 10.02 13.27 25.44
LEGEND NOTES:
HWG — Hot Water Generator
3
/
4
11
1
/
2
1. Maximum working pressure on the base unit is 3445 kPa.
2. Units have a dual isolated compressor mounting.
3. Units have a balanced port expansion valve (TXV).
4. Insulated source and load water coils are standard.
5. Insulated refrigerant circuit is standard.
6. Compressor is on (green) light and fault on (red) light.
1
/
2
2
N/A
2
2
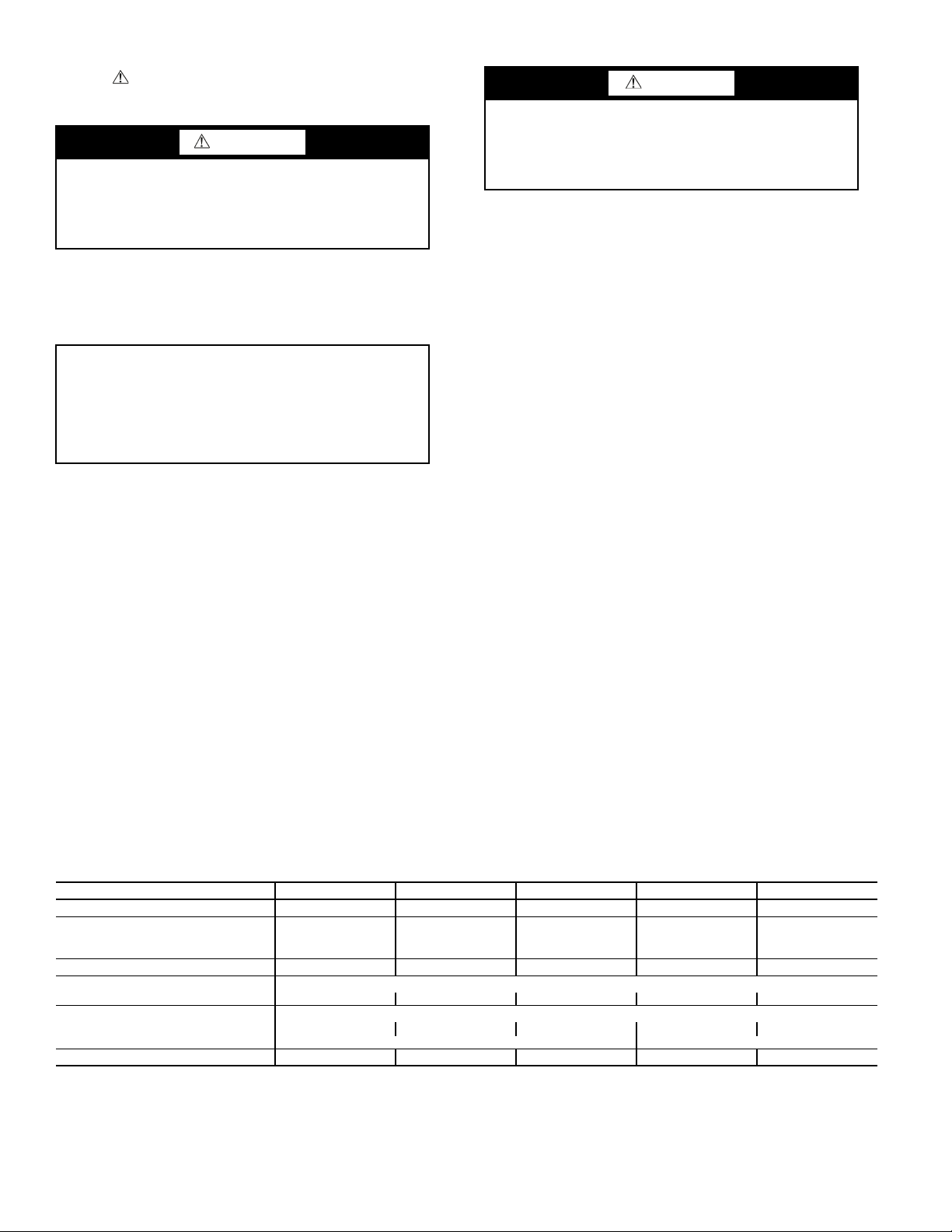
Page 3
B
Fig. 1 — 50PSW036-120 Unit
SIZES 036,060
LEGEND
NOTES:
1. Dimensions shown in centimeters unless noted otherwise.
2. HACR circuit breaker in U.S.A. only.
50PSW
UNIT
SIZE
OVERALL CABINET
(mm)
WATER CONNECTIONS (mm)
ELECTRIC ACCESS PLUGS
(mm)
1234 5 6
Source (Outdoor) Load (Indoor) HWG
A
DepthBWidthCHeightDWater InEWate r OutFWater InGWater OutHReturn InJWater Out
K
Low
Volt ag e
L
External
Pump
M
Power
Supply
036,060 778 645 838 69 239 493 622 709 772 531 582 785
120 778 1344 940 640 640 765 765 886 886 759 810 874
HWG — Hot Water Generator
HACR —
Heating, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration
SIZE 120
A
5
6
4.6 cm
2.5 cm
C
Optional
Service Access
2.5 cm
M
L
K
Req
Service
4
3
2
1
uire
Access
C
J
H
G
F
E
D
d
18.5 cm
B
A
4.3 cm
5
6
4
2
3.3 cm
6.9 cm
3
1
Optional
Service Access
Required
Access
Service
3
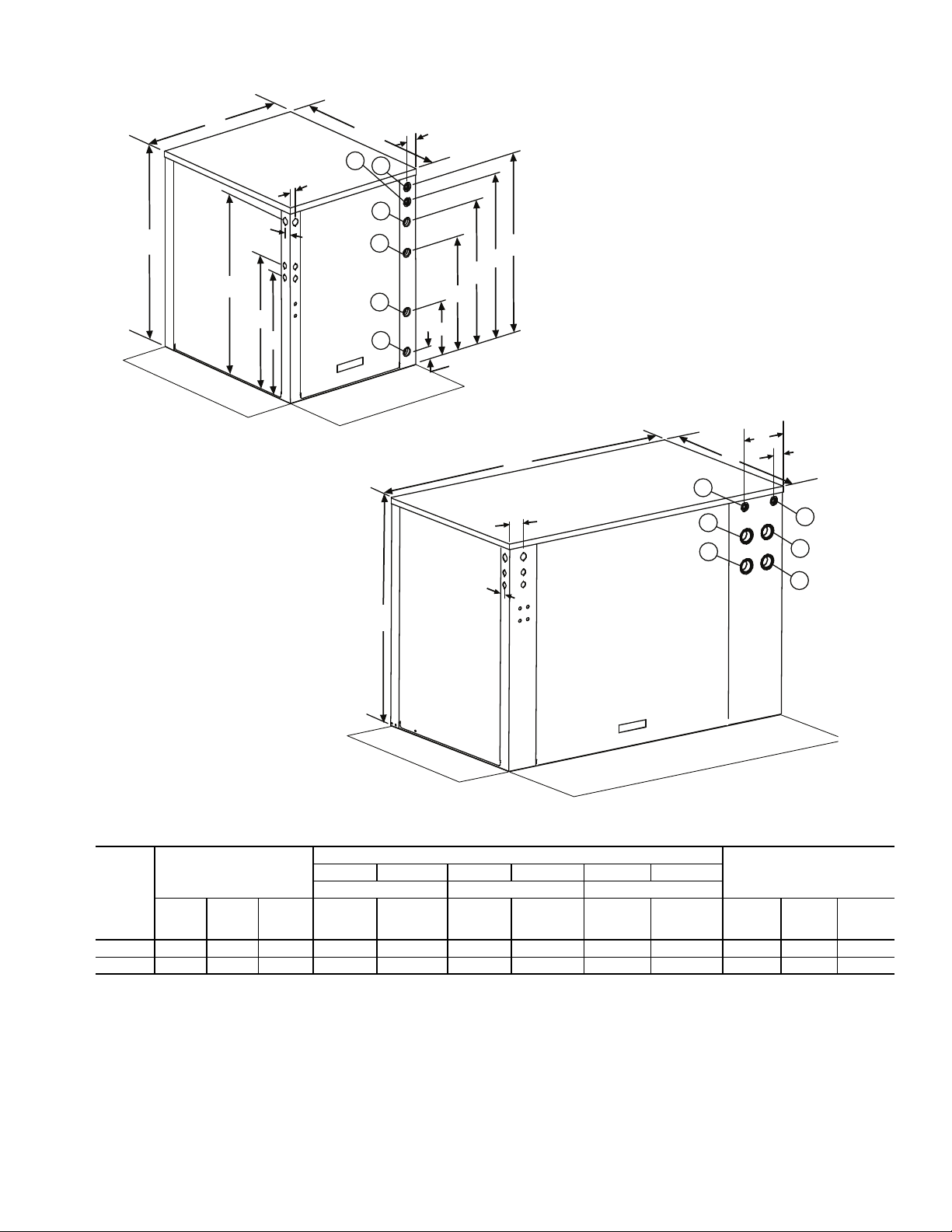
Page 4
31.338.1 11.4
10.8
Power Supply Wiring
34.9 x 50.8 mm Double Knockout
10.8
Control Wiring
28.6 x 34.9 mm Double Knockout
11.4
2”FPT Water Connections
38.1
13.8
53.3
Fault/Run Lights
163.8
Left
Side
View
Front
View
To p
View
Load
Source
Side
Refrig.
Circuit
Access
Panel
Front
Compressor
Access
Panel
Electrical
Access
Panel
Header
Access
Panel
To p
Minimum91cm
Required Service
Access
114.6
66.9
Optional (Single Unit)
91cm Additional
Service Access
Fig. 2 — 50PSW180,360 Unit
LEGEND
FPT — Female Pipe Thread
NOTES:
1. Dimensions shown in centimeters unless noted otherwise.
2. For multiple units placed side by side, allow 1.2 m minimum front access for service and maintenance.
PROTECTION — Once the units are properly positioned on
the jobsite, they must be covered with either a shipping carton,
vinyl film, or an equivalent protective covering. Open ends of
pipes stored on the jobsite must be capped. This precaution is
especially important in areas where painting, plastering, or
spraying of fireproof material, etc., is not yet complete. Foreign
material that is allowed to accumulate within the units can prevent proper start-up and necessitate costly clean-up operations.
Before installing any of the system components, be sure to
examine each pipe, fitting, and valve, and remove any dirt or
foreign material found in or on these components.
CAUTION
DO NOT store or install units in corrosive environments or
in locations subject to temperature or humidity extremes
(e.g., attics, garages, rooftops, etc.). Corrosive conditions
and high temperature or humidity can significantly reduce
performance, reliability, and service life. Always move
units in an upright position. Tilting units on their sides may
cause equipment damage.
INSPECT UNIT — To prepare the unit for installation, complete the procedures listed below:
1. Compare the electrical data on the unit nameplate with
ordering and shipping information to verify that the
correct unit has been shipped.
2. Verify that the unit is the correct model for the entering
water temperature of the job.
3. Wait to remove the packaging until the unit is ready for
installation.
4. Verify that the refrigerant tubing is free of kinks or dents,
and that it does not touch other unit components.
5. Inspect all electrical connections. Be sure connections are
clean and tight at the terminals.
6. Loosen bolts and remove shipping clamps on compressors equipped with external spring vibration isolators.
Compressors are internally spring-mounted.
7. Locate and verify any accessory kit located in compressor
section.
4
Page 5
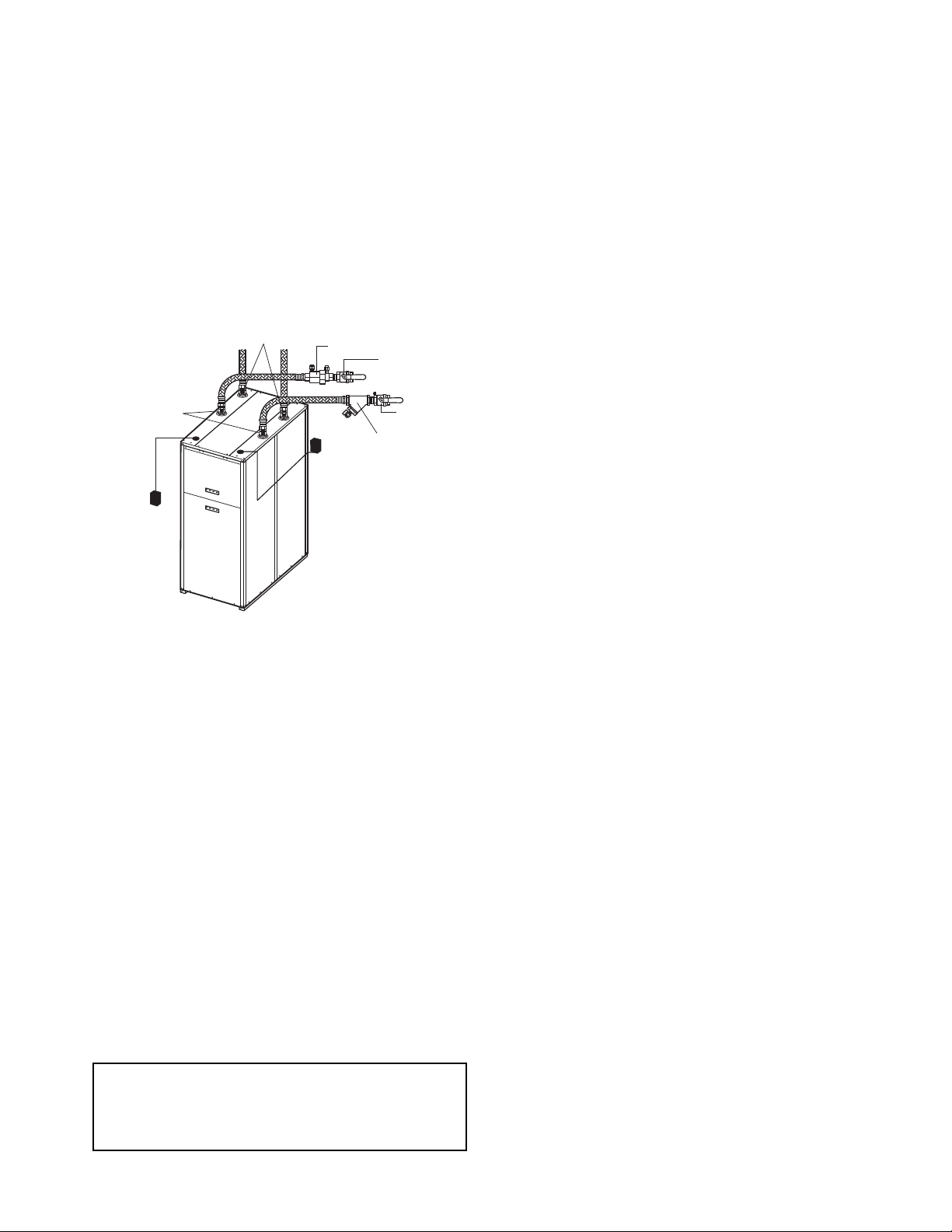
Fig. 3 — Typical Water Loop System —
Boiler, Tower, or Ground (Sizes 180,360 Shown)
Control
Wiring
Power
Disconnect
Source Connections
(Boiler/Tower/Ground)
Load Connections (Hot
Water/Chilled Water)
Automatic Flow
Regulator
Ball Valve
with Pressure
Temperature Port
Ball Valve
with Pressure
Temperature Port
Y Strainer with
Blow Down Valve
a50-8138
8. Remove any access panel screws that may be difficult to
remove once unit is installed.
Step 3 — Locate Unit — The following guidelines
should be considered when choosing a location for the WSHP:
• Units are for indoor use only.
• Provide sufficient space for water and electrical
connections.
• Locate unit in an area that allows for easy access and
removal of access panels.
• Allow enough space for service personnel to perform
maintenance.
Step 4 — Mount Unit — Mount unit as shown in Fig. 3.
Rod attachments must be able to support the weight of the unit.
See Table 1 for unit operating weight.
Step 5 — Connect Piping — Depending on the appli-
cation, there are 3 types of WSHP piping systems to choose
from: water loop, ground-water and ground loop. Refer to the
Carrier System Design Manual for additional information.
All WSHP units utilize low temperature soldered female
pipe thread fittings for water connections to prevent annealing
and out-of-round leak problems which are typically associated
with high temperature brazed connections. When making piping connections, consider the following:
• A backup wrench must be used when making screw connections to unit to prevent internal damage to piping.
• Insulation may be required on piping to avoid condensation in the case where fluid in loop piping operates at
temperatures below dew point of adjacent air.
• Piping systems that contain steel pipes or fittings may
be subject to galvanic corrosion. Dielectric fittings may
be used to isolate the steel parts of the system to avoid
galvanic corrosion.
• Units may be manifolded together via top water connects
to get increased temperatures, when piped in series, or
greater capacity, when piped in parallel.
WATER SUPPLY AND QUALITY — Check water supply.
Water supply should be plentiful and of good quality. See
Table 2 for water quality guidelines.
IMPORTANT: Failure to comply with the above required
water quality and quantity limitations and the closedsystem application design requirements may cause damage
to the tube-in-tube heat exchanger that is not the responsibility of the manufacturer.
In all applications, the quality of the water circulated
through the heat exchanger must fall within the ranges listed in
the Water Quality Guidelines table. Consult a local water treatment firm, independent testing facility, or local water authority
for specific recommendations to maintain water quality within
the published limits.
WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS — Water loop applications usually include a number of units plumbed to a common
piping system. Maintenance to any of these units can introduce
air into the piping system. Therefore, air elimination
equipment comprises a major portion of the mechanical room
plumbing.
The flow rate is usually set between 2.9 L/m and 3.9 L/m
per kW of cooling capacity. For proper maintenance and servicing, pressure-temperature (P/T) ports are necessary for temperature and flow verification.
In addition to complying with any applicable codes, consider the following for system piping:
• Piping systems utilizing water temperatures below
10.0 C require 13 mm closed cell insulation on all piping
surfaces to eliminate condensation.
• All plastic to metal threaded fittings should be avoided
due to the potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Teflon* tape thread sealant is recommended to minimize
internal fouling of the heat exchanger.
• Use backup wrench. Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• The piping system should be flushed prior to operation to
remove dirt and foreign materials from the system.
Cooling tower/boiler systems typially use a common loop
maintained between 16 and 32 C. The use of a closed circuit
evaporative cooling tower with a secondary heat exchanger between the tower and the water loop is recommended. If an open
type cooling tower is used continuously, chemical treatment
and filtering will be necessary.
GROUND-WATER APPLICATIONS — In addition to
complying with any applicable codes, consider the following
for system piping:
• Install shut-off valves for servicing.
• Install pressure-temperature plugs to measure flow and
temperature.
• Boiler drains and other valves should be connected using
a “T” connector to allow acid flushing for the heat
exchanger.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Use PVC SCH80 or copper piping material.
NOTE: PVC SCH40 should not be used due to system high
pressure and temperature extremes.
GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS — Temperatures be-
tween –3.9 and 43.3 C and a cooling capacity of 2.9 L/m and
3.9 L/m per kW are recommended. In addition to complying
with any applicable codes, consider the following for system
piping:
• Piping materials should be limited to only polyethylene
fusion in the buried sections of the loop.
• Galvanized or steel fittings should not be used at any
time due to corrosion.
• All plastic to metal threaded fittings should be avoided
du
e to the potential to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Pressure-temperature (P/T) plugs should be used to mea-
sure flow of pressure drop.
*Teflon is a trademark of E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company.
5
Page 6
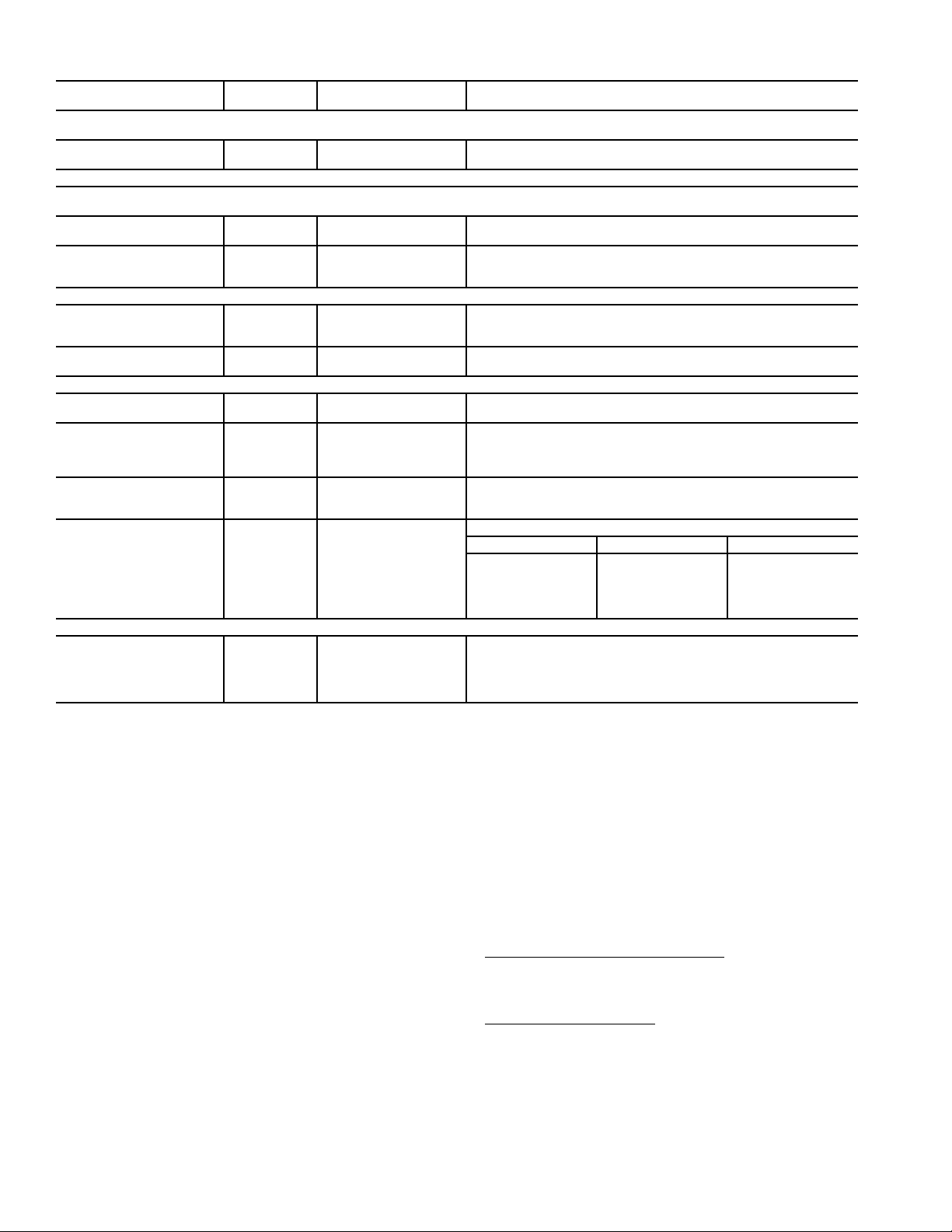
Table 2 — Water Quality Guidelines
CONDITION
Scaling Potential — Primary Measurement
Above the given limits, scaling is likely to occur. Scaling indexes should be calculated using the limits below.
pH/Calcium
Hardness Method
Index Limits for Probable Scaling Situations (Operation outside these limits is not recommended.)
Scaling indexes should be calculated at 150 F for direct use and HWG applications, and at 90 F for indirect HX use. A monitoring plan should be
implemented.
Ryznar Stability Index
Langelier Saturation Index
Iron Fouling
Corrosion Prevention††
Erosion and Clogging
HWG— Hot Water Generator
HX — Heat Exchanger
N/A — Design Limits Not Applicable Consid-
NR — Application Not Recommended
SS — Stainless Steel
*Heat exchanger materials considered are copper, cupronickel,
†Closed recirculating system is identified by a closed pressurized
**Recirculating open wells should observe the open recirculating
2+
Iron Fe
(Bacterial Iron Potential) All N/A
Iron Fouling
pH
Hydrogen Sulfide (H
Ammonia Ion as Hydroxide, Chloride, Nitrate and
Sulfate Compounds
Maximum Chloride Levels Maximum allowable at maximum water temperature.
Particulate Size and
Erosion
304 SS (stainless steel), 316 SS, titanium.
piping system.
design considerations.
(Ferrous)
S)
2
LEGEND
ering Recirculating Potable Water
HX
MATERIAL*
All N/A pH < 7.5 and Ca Hardness, <100 ppm
All N/A
All N/A
All N/A
All
All N/A
All N/A
Copper N/A
Cupronickel N/A <150 ppm NR NR
304 SS N/A <400 ppm <250 ppm <150 ppm
316 SS N/A <1000 ppm <550 ppm <375 ppm
Titanium N/A >1000 ppm >550 ppm >375 ppm
All
CLOSED
RECIRCULATING†
Monitor/treat as needed.
<10 ppm of particles and
6 - 8.5
a maximum velocity of
6 fps.
Filtered for maximum
800 micron size.
OPEN LOOP AND RECIRCULATING WELL**
If >7.5 minimize steel pipe use.
Based upon 150 F HWG and direct well, 85 F indirect well HX.
2+
If Fe
Minimize steel pipe below 7 and no open tanks with pH <8.
At H2S>0.2 ppm, avoid use of copper and cupronickel piping of HXs.
Copper alloy (bronze or brass) cast components are okay to <0.5 ppm.
50 F (10 C) 75 F (24 C) 100 F (38 C)
<20 ppm NR NR
<10 ppm (<1 ppm “sandfree” for reinjection) of particles and a maximum velocity of 6 fps. Filtered for maximum 800 micron size. Any particulate that is not removed can potentially clog components.
††If the concentration of these corrosives exceeds the maximum
allowable level, then the potential for serious corrosion problems
exists.
Sulfides in the water quickly oxidize when exposed to air, requir-
ing that no agitation occur as the sample is taken. Unless tested
immediately at the site, the sample will require stabilization with a
few drops of one Molar zinc acetate solution, allowing accurate
sulfide determination up to 24 hours after sampling. A low pH and
high alkalinity cause system problems, even when both values are
within ranges shown. The term pH refers to the acidity, basicity, or
neutrality of the water supply. Below 7.0, the water is considered
to be acidic. Above 7.0, water is considered to be basic. Neutral
water contains a pH of 7.0.
To convert ppm to grains per gallon, divide by 17. Hardness in
mg/l is equivalent to ppm.
If <–0.5 minimize steel pipe use.
(ferrous) >0.2 ppm with pH 6 - 8, O2<5 ppm check for
Above this level deposition will occur.
Rotten egg smell appears at 0.5 ppm level.
6.0 - 7.5
–0.5 to +0.5
<0.2 ppm (Ferrous)
iron bacteria.
<0.5 ppm of Oxygen
6 - 8.5
<0.5 ppm
<0.5 ppm
UNIT LOAD PIPING — For applications with wide temperature variation such as heating/cooling coils:
• Use piping materials that are rated for the maximum temperature and pressure combination. This excludes PVC
for most heating applications.
• Ensure load water flow in high temperature heating
applications is at least 3.2 L/m per kW to improve performance and reduce nuisance high pressure faults.
• DO NOT employ plastic to metal threaded joints.
• Utilize a pressure tank and air separator vent system to
equalize pressure and remove air.
• Employ an 800-micron particulate strainer in both load
and source plumbing to protect the plate heat exchanger.
Swimming Pool Hot Tub Applications
— Load heat exchanger should be isolated with secondary heat exchanger
constructed of anti-corrosion material in all chlorine/bromine
fluid applications.
Potable Water Applications
• Load coax material should always be vented double
walled for use in potable water systems.
• Ensure load water flow in high temperature heating
applications is at least 3.2 L/m per kW to improve performance and reduce nuisance high pressure faults.
6
Page 7
Step 6 — Wire Electrical Connections
WARNING
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock,
open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in
an open position during installation. Install lockout tag.
CAUTION
Use only copper conductors for field-installed electrical
wiring. Unit terminals are not designed to accept other
types of conductors. Failure to heed this warning could
result in equipment damage.
All field-installed wiring, including the electrical ground,
MUST comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) as
well as applicable local codes. In addition, all field wiring must
conform to the Class II temperature limitations described in the
NEC.
Operating voltage must be the same voltage and phase as
shown in Table 3.
Refer to unit wiring diagrams Fig. 4-8 for a schematic of the
field connections which must be made by the installing (or
electrical) contractor.
Consult the unit wiring diagram located on the inside of the
compressor access panel to ensure proper electrical hookup.
The installing (or electrical) contractor must make the field
connections when using field-supplied disconnect.
Make all final electrical connections with a length of flexible conduit to minimize vibration and sound transmission to
the building.
POWER CONNECTION — Line voltage connection is
made by connecting incoming line voltage wires to L1, L2, and
L3 on the power distribution block.
SUPPLY VOLTAGE — Operating voltage to unit must be
within voltage range indicated on unit nameplate.
Voltages between phases must be balanced within 2%.
Use the following formula to determine the percentage voltage
imbalance:
% Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Example: Supply voltage is 380-3-50.
AB = 372 volts
BC = 376 volts
AC = 384 volts
Average Voltage =
372 + 376 + 384
3
1132
=
3
= 377
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage:
(AB) 372 – 377 = 5 v
(BC) 376 – 377 = 1 v
(AC) 384 – 377 = 7 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
7
377
= 1.86%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is
below the maximum allowable 2%.
Operation on improper line voltage or excessive phase
imbalance constitutes abuse and may cause damage to electrical components.
NOTE: If more than 2% voltage imbalance is present, contact
local electric utility.
Table 3 — 50PSW Electrical Data
50PSW UNIT
SIZE
036
060
120
180
360
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Minimum Overcurrent Protection
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Time-delay fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
VOLTAGE
(V-Ph-Hz)
220/240-1-50 198/264 13.5 67 1 13.5 16.9 30
380/420-3-50 342/462 5.4 38 1 5.4 6.8 15
220/240-1-50 198/264 24.5 153 1 24.5 30.6 50
380/420-3-50 342/462 9.6 74 1 9.6 12.0 20
220/240-1-50 198/264 24.5 153 2 49.0 55.1 80
380/420-3-50 342/462 9.6 74 2 19.2 21.6 30
220/240-1-50 198/264 44.9 273 1 44.9 56.1 100
380/420-3-50 342/462 18.6 118 1 18.6 23.3 40
220/240-1-50 198/264 44.9 273 2 89.8 101.0 125
380/420-3-50 342/462 18.6 118 2 37.2 46.6 60
LEGEND
VOLTAGE RANGE
MIN/MAX
COMPRESSOR
RLA LRA QTY
TOTAL
FLA
MCA MOCP*
7
Page 8
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Indicator Light
G=Green, R=Red
(Comp On) (Alarm Light)
Circuit Breaker
High Pressure Switch
Low Pressure Switch
Fuse
F
a50-8621
Fig. 4 — Typical Aquazone™ 50PSW036-060 Complete C Control Wiring, Single-Phase
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
Factory Line Voltage Wiring
Factory Low Voltage Wiring
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Relay/Contactor Coil
NOTES:
1. Compressor motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 265 v lead (BRN) for 265-1-50 units. For 220/240 v
operation, disconnect BRN lead at L1 and connect ORG lead to L1. Insulate
open ends of BRN and RED leads. Transformer is energy limiting or may have
circuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for source water. When using anti-
freeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Refer to or Thermostat Installation, Application and Operation Manual for con-
trol wiring to the unit. Low voltage wiring must be “Class 1” and voltage rating
equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
CC — Compressor Contactor
FP1 — Sensor, Source Low Temp Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Load Low Temp Protection
HP — High Pressure Switch
JW1 — Jumper Wire for Alarm
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
Complete C
Complete C
8
Page 9

7
Fig. 5 — Typical Aquazone™ 50PSW120 Complete C Control Wiring, 3-Phase
Circuit Breaker
High Pressure Switch
Low Pressure Switch
Fuse
F
NOTES:
1. Compressor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 380 v lead (VIO) for 380-3-50 operation. For 420 v
operation switch VIO and BRN leads at L1 and insulate VIO lead.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for source water. When using anti-
freeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Check installation wiring information for controller hookup. Control wiring must
be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
6. Transformer secondary ground via Complete C board standoff and screws to
control box. (Ground available from top 2 standoffs as shown.)
7. Aquastat is supplied with unit and must be wired in series with the hot leg of
the pump. Aquastat is rated for voltages up to 277 v.
L-WTR — Load Water
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
S-WTR — Source Water
TRANS — Transformer
Factory Line Voltage Wiring
Factory Low Voltage Wiring
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat Device
COMP — Compressor
CC — Compressor Contactor
DTS — Discharge Temperature Switch
FP1 — Sensor, Source Low Temp Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Load Low Temp Protection
HP — High Pressure Switch
HPWS — High Pressure Water Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper Wire for Alarm
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
Relay/Contactor Coil
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Indicator Light
G=Green, R=Red
(Comp On) (Alarm Light)
7
Complete C
Complete C
Complete C Complete C
9
Page 10

Fig. 6 — Typical Aquazone™ 50PSW360 Complete C Control Wiring, 3-Phase
Circuit Breaker
High Pressure Switch
Low Pressure Switch
Fuse
Complete C
Complete C 1
Complete C 2
Complete C
6
NOTES:
1. Compressor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and
local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 380 v lead (VIO) for 380-
3-50 operation. For 420 v operation switch VIO
and BRN leads at L1 and insulate VIO lead.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for
source water. When using antifreeze solutions,
cut JW3 jumper.
5. Check installation wiring information for controller
hookup. Control wiring must be Class 1 and volt-
age rating equal to or greater than unit supply
voltage.
6. Transformer secondary ground via Complete C
board standoff and screws to control box.
(Ground available from top 2 standoffs as
shown.)
7. Aquastat is supplied with unit and must be wired
in series with the hot leg of the pump. Aquastat is
rated for voltages up to 277 v.
MS — Motor Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
S-WTR — Source Water
TRANS — Transformer
Factory Line Voltage Wiring
Factory Low Voltage Wiring
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat Device
COMP — Compressor
CC — Compressor Contactor
DTS — Discharge Temperature Switch
FP1 — Sensor, Source Low Temp Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Load Low Temp Protection
HP — High Pressure Switch
HPWS — High Pressure Water Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper Wire for Alarm
LED — Light Emitting Diode
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
L-WTR — Load Water
Relay/Contactor Coil
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Indicator Light
G=Green, R=Red
(Comp On) (Alarm Light)
F
10
Page 11

Fig. 7 — Typical Aquazone™ 50PSW360 Deluxe D Control Wiring, 3-Phase
Circuit Breaker
High Pressure Switch
Low Pressure Switch
Fuse
F
MS — Motor Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
S-WTR — Source Water
TRANS — Transformer
Factory Line Voltage Wiring
Factory Low Voltage Wiring
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat Device
COMP — Compressor
CC — Compressor Contactor
DTS — Discharge Temperature Switch
FP1 — Sensor, Source Low Temp Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Load Low Temp Protection
HP — High Pressure Switch
HPWS — High Pressure Water Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper Wire for Alarm
LED — Light Emitting Diode
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
L-WTR — Load Water
Relay/Contactor Coil
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Indicator Light
G=Green, R=Red
(Comp On) (Alarm Light)
See notes on page 10.
Deluxe D
Deluxe D
Deluxe D
Deluxe D
6
Deluxe D
Deluxe D
Deluxe D
Deluxe D
11
Page 12

EXTERNAL LOOP POWER CONNECTION — If the unit
Contactor -CC1
Transformer
C Control #1
Low Voltage
Connector
Grnd
L2
L3L1
Low Voltage
Connector
Contactor -CC2
C Control #2
Power Distribution
Block
Fig. 8 — Typical Field Wiring
Fig. 9 — Typical Aquazone Control Board
Jumper Locations (Complete C Control Shown)
Typical
Water
Valve
C
A
24 VAC
Terminal Strip
Fig. 10 — Typical Aquazone Accessory Wiring
(Deluxe D Control Shown)
is to be connected to an external loop pump or flow controller,
connect the pump to the loop pump terminal block PB1. The
maximum power handling is 4 amps at 240-v. The pumps will
automatically cycle as required by the unit.
220-V OPERATION — All 220/240-v units are factory
wired for 220-v. The transformers may be switched to 240-v
operation (as illustrated on the wiring diagram) by switching
the red (220-v) wire with the orange (240-v) wire at the L2
terminal.
380-VOLT OPERATION — All 380/415 volt units are factory
wired for 420 volts. The transformers may be switched to
380-volt operation by switching the brown (380 volt) wire
with the violet (420 volt) wire at the L1 terminal.
Step 7 — Wire Low Voltage Connections
THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS
The thermostat should be wired directly to the Aquazone™
control board. See Fig. 4-7.
WATER FREEZE PROTECTION — The Aquazone control
allows the field selection of source fluid freeze protection
points through jumpers. The factory setting of jumper JW3
(FP1) is set for water at –1.1 C. In earth loop applications,
jumper JW3 should be clipped to change the setting to –12.2 C
when using antifreeze in colder earth loop applications. See
Fig. 9.
ACCESSORY CONNECTIONS — The terminal labeled A
on the control is provided to control accessory devices such as
water valves, electronic air cleaners, humidifiers, etc. This signal operates with the compressor terminal. See Fig. 10. Refer
to the specific unit wiring schematic for details.
NOTE: The A terminal should only be used with 24-v signals,
not line voltage signals.
IMPORTANT: Two-compressor units with Complete C or
Deluxe D controls wired to terminal A will be turned off if
the controls are in lockout mode, even if the other board is
in normal operating mode.
WATER SOLENOID VALVES — Water solenoid valves
may be used on variable flow systems and ground water installations. A typical well water control valve wiring which can
limit waste water in a lockout condition is shown in Fig. 10. A
slow closing valve may be required to prevent water hammer.
When using a slow closing valve, special wiring conditions
need to be considered. The valve takes approximately 60 seconds to open (very little water will flow before 45 seconds) and
it activates the compressor only after the valve is completely
opened by closing its end switch. When wired as shown, the
valve will have the following operating characteristics:
1. Remain open during a lockout.
2. Draw approximately 25 to 35-va through the “Y” signal
of the thermostat.
IMPORTANT: This can overheat the anticipators of
electromechanical thermostats. Only use relay based
electronic thermostats.
PRE-START-UP
System Checkout —
follow the system checkout procedure outlined below before
starting up the system. Be sure:
1. Voltage is within the utilization range specifications of the
unit compressor and fan motor, and voltage is balanced
for 3-phase units.
2. Fuses, breakers and wire are correct size.
3. Low voltage wiring is complete.
4. Piping and system flushing is complete.
5. Air is purged from closed loop system.
6. System is balanced as required. Monitor if necessary.
7. Isolation valves are open.
8. Water control valves or loop pumps are wired.
9. Transformer switched to lower voltage tap if necessary.
10. Service/access panels are in place.
11. Control field-selected settings are correct.
When the installation is complete,
12
Page 13

FIELD SELECTABLE INPUTS
Jumpers and DIP (dual in-line package) switches on the
control board are used to customize unit operation and can be
configured in the field.
IMPORTANT: Jumpers and DIP switches should only
be clipped when power to control board has been turned
off.
Complete C Control Jumper Settings (See
Fig. 4-6)
WATER COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP1) LIMIT
SETTING — Select jumper 3, (JW3-FP1 Low Temp) to
choose FP1 limit of –12.2 C or –1.1 C. To select –1.1 C as the
limit, DO NOT clip the jumper. To select –12.2 C as the limit,
clip the jumper.
ALARM RELAY SETTING — Select jumper 1 (JW1-AL2
Dry) for connecting alarm relay terminal (AL2) to 24 vac (R)
or to remain as a dry contact (no connection). To connect AL2
to R, do not clip the jumper. To set as dry contact, clip the
jumper.
Complete C Control DIP Switches — The
Complete C control has one DIP switch block with five
switches. See Fig. 4-6.
PERFORMANCE MONITOR (PM) — DIP switch 1 will
enable or disable this feature. To enable the PM, set the switch
to ON. To disable the PM, set the switch to OFF.
STAGE 2 — DIP switch 2 will enable or disable compressor
delay. Set DIP switch to OFF for Stage 2 in which the compressor will have a 3-second delay before energizing. DIP switch 3
is not used. DIP switch 4 is not used. DIP switch 5 is used to
initiate one or 3 tries for the FP1 fault. If water freeze protection for the water coil is needed, then DIP switch 5 can be set to
lock out on the FP1 fault after one try.
Deluxe D Control Jumper Settings (See
Fig. 7)
WATER COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP1) LIMIT
SETTING — Select jumper 3, (JW3-FP1 Low Temp) to
choose FP1 limit of –12.2 C or –1.1 C. To select –1.1 C as the
limit, DO NOT clip the jumper. To select –12.2 C as the limit,
clip the jumper.
ALARM RELAY SETTING — Select jumper 4 (JW4-AL2
Dry) for connecting alarm relay terminal (AL2) to 24 vac (R)
or to remain as a dry contact (no connection). To connect AL2
to R, do not clip the jumper. To set as dry contact, clip the
jumper.
LOW PRESSURE SETTING — The Deluxe D control can
be configured for Low Pressure Setting (LP). Select jumper 1
(JW1-LP Norm Open) for choosing between low pressure input normally opened or closed. To configure for normally
closed operation, do not clip the jumper. To configure for normally open operation, clip the jumper.
Deluxe D Control DIP Switches — The Deluxe D
control has 2 DIP switch blocks. Each DIP switch block has 8
switches and is labeled either S1 or S2 on the circuit board. See
Fig. 7.
DIP SWITCH BLOCK 1 (S1) — This set of switches offers
the following options for Deluxe D control configuration:
Performance Monitor (PM)
able performance monitor. To enable the PM, set the switch to
ON. To disable the PM, set the switch to OFF.
Compressor Relay Staging Operation
able or disable compressor relay staging operation. The compressor relay can be set to turn on with Stage 1 or Stage 2 call
from the thermostat. This setting is used with dual stage units
— Set switch 1 to enable or dis-
— Switch 2 will en-
(units with 2 compressors and 2 Deluxe D controls) or in master/slave applications. In master/slave applications, each compressor and fan will stage according to its switch 2 setting. If
switch is set to Stage 2, the compressor will have a 3-second
delay before energizing during Stage 2 demand.
NOTE: If DIP switch is set for Stage 2, the alarm relay will not
cycle during Test mode.
Heating/Cooling Thermostat Type
— Switch 3 provides selection of thermostat type. Heat pump or heat/cool thermostats
can be selected. Select OFF for heat/cool thermostats. When in
heat/cool mode, Y1 is used for cooling Stage 1, Y2 is used for
cooling Stage 2, W1 is used for heating Stage 1 and O/W2 is
used for heating Stage 2. Select ON for heat pump applications.
In heat pump mode, Y1 used is for compressor Stage 1, Y2 is
used for compressor Stage 2, W1 is used for heating Stage 3 or
emergency heat, and O/W2 is used for RV (heating or cooling)
depending upon switch 4 setting.
O/B Thermostat Type
— Switch 4 provides selection for heat
pump O/B thermostats. O is cooling output. B is heating output. Select ON for heat pumps with O output. Select OFF for
heat pumps with B output.
Switches 5, 6, 7, 8
— Not used.
DIP SWITCH BLOCK 2 (S2) — Used for accessory relay
configurations.
Deluxe D Control Accessory Relay Configurations (See Tables 4 and 5) —
sory relay settings are applicable for Deluxe D control only:
CYCLE WITH COMPRESSOR — In this configuration, the
relay will be ON any time the compressor relay is on.
DIGITAL NIGHT SETBACK (NSB) — In this configura-
tion, the relay will be ON if the NSB input is connected to
ground C.
NOTE: If there are no relays configured for digital NSB, then
the NSB and OVR inputs are automatically configured for
mechanical operation.
MECHANICAL NIGHT SETBACK — When NSB input is
connected to ground C, all thermostat inputs are ignored. A
thermostat setback heating call will then be connected to the
OVR input. If OVR input becomes active, then the Deluxe D
control will enter night low limit (NLL) staged heating mode.
The NLL staged heating mode will then provide heating during
the NSB period.
WATER VALVE (SLOW OPENING) — If relay is configured for water valve (slow opening), the relay will start 60 seconds prior to starting compressor relay.
The following acces-
CAUTION
To avoid equipment damage, DO NOT leave system filled
in a building without heat during the winter unless antifreeze is added to system water. Condenser coils never
fully drain by themselves and will freeze unless winterized
with antifreeze.
Table 4 — DIP Switch Block S2 —
Accessory 1 Relay Options
ACCE SSORY 1
RELAY OPTIONS
Digital NSB Off On On
Water Valve — Slow Opening On Off On
LEGEND
NSB — Night Setback
NOTE: All other DIP switch combinations are invalid.
DIP SWITCH POSITION
123
13
Page 14

Table 5 — DIP Switch Block S2 —
Accessory 2 Relay Options
ACCESSORY 2
RELAY OPTIONS
Digital NSB Off On On
Water Valve — Slow Opening On Off On
LEGEND
NSB — Night Setback
NOTE: All other DIP switch combinations are invalid.
DIP SWITCH POSITION
456
START-UP
Use the procedure outlined below to initiate proper unit
start-up.
NOTE: This equipment is designed for indoor installation
only.
Operating Limits (See Table 6)
ENVIRONMENT — This equipment is designed for indoor
installation ONLY. Extreme variations in temperature, humidity and corrosive water or air will adversely affect the unit performance, reliability and service life.
POWER SUPPLY — A voltage variation of ± 10% of nameplate utilization voltage is acceptable.
NOTE: These operating conditions are not normal or continuous operating conditions. It is assumed that start-up is for the
purpose of bringing the building space up to occupancy
temperature.
WARNING
When the disconnect switch is closed, high voltage is present in some areas of the electrical panel. Exercise caution
when working with the energized equipment.
Table 6 — 50PSW Unit Operating Limits (C)
BUILDING COMMISSIONING
50PSW
UNIT SIZE
036 10/43 16/27 7/43 –1/27 16/49 4/29
060,120 10/49 16/32 7/43 –1/27 16/49 4/29
180,360 10/32 16/32 7/43 10/21 27/49 4/29
50PSW
UNIT SIZE
036 10/49 10/32 7/43 –7/27 16/54 4/29
060,120 10/49 10/32 7/43 –7/27 16/54 4/29
180,360 10/43 10/32 7/43 –7/21 16/49 4/29
Source
Min/Max
Source
Min/Max
COOLING HEATING
Load
Min/Max
BUILDING OPERATING
COOLING HEATING
Load
Min/Max
Ambient
Min/Max
Ambient
Min/Max
Source
Min/Max
Source
Min/Max
Load
Min/Max
Load
Min/Max
Ambient
Min/Max
Ambient
Min/Max
Unit Start-Up
1. Turn off all power to unit.
2. Adjust all valves to full open position.
3. Restore power to unit.
4. Operate each unit in the cooling cycle. See Table 6 for
unit entering water temperatures.
5. Operate each heat pump in the heating cycle immediately
after checking cooling cycle operation.
NOTE: A time delay will prevent the compressor from
re-starting for approximately 5 minutes. The time delay
function can be overridden on the Complete C control
board.
6. If unit fails to operate, perform the following system
checks:
a. Check the voltage and current. Be sure they com-
ply with electrical data on unit nameplate.
b. Check for loose terminal screws where wire con-
nections have been made on both the line and lowvoltage terminal boards.
c. Check the supply and return piping. Be sure they
are properly connected to the inlet and outlet connections on the unit.
d. If the checks described above fail to reveal the
problem and the unit still will not operate, contact
a trained service technician to ensure proper
diagnosis.
Scroll Compressor Rotation — It is important to be
certain compressor is rotating in the proper direction. To
determine whether or not compressor is rotating in the proper
direction:
1. Connect service gages to suction and discharge pressure
fittings.
2. Energize the compressor.
3. The suction pressure should drop and the discharge
pressure should rise, as is normal on any start-up.
If the suction pressure does not drop and the discharge
pressure does not rise to normal levels:
1. Turn off power to the unit. Install disconnect tag.
2. Reverse any two of the unit power leads.
3. Reapply power to the unit and verify pressures are correct. The suction and discharge pressure levels should
now move to their normal start-up levels.
CAUTION
When the compressor is rotating in the wrong direction, the
unit makes an elevated level of noise and does not provide
cooling. Damage to compressor will occur if allowed to
operate in this manner.
After a few minutes of reverse operation, the scroll compressor internal overload protection will open, thus activating
the unit lockout. This requires a manual reset. To reset, turn the
thermostat on and then off.
NOTE: There is a 5-minute time delay before the compressor
will start.
Flow Regulation — Flow regulation can be accom-
plished by two methods. Most water control valves have a flow
adjustment built into the valve. By measuring the pressure drop
through the unit heat exchanger, the flow rate can be determined. Adjust the water control valve until the flow of 0.09 to
0.13 L/s is achieved. Since the pressure constantly varies, two
pressure gages may be needed in some applications. See
Table 7 for heat exchanger pressure drops.
An alternative method is to install a flow control device.
These devices are typically an orifice of plastic material designed to allow a specified flow rate that are mounted on the
outlet of the water control valve. Occasionally these valves
produce a velocity noise that can be reduced by applying some
back pressure. To accomplish this, slightly close the leaving
isolation valve of the water regulating device.
14
Page 15

Table 7 — Heat Exchanger Pressure Drop
UNIT SIZES 036-120
50PSW
UNIT SIZE
036
060
120
036
060
120
50PSW
UNIT SIZE
180
360
NOTE: Bold values indicate use of antifreeze is required.
L/s
Source/Outdoor Coax
0.28
0.43
0.57
0.47
0.71
0.95
0.95
1.42
1.89
Load/Outdoor Coax
0.28
0.43
0.57
0.47
0.71
0.95
0.95
1.42
1.89
UNIT SIZES 180,360
L/s
Source/Outdoor Coax
1.10
1.67
2.21
2.21
3.34
4.42
PRESSURE DROP (kPa)
–1 C 10 C 21 C 32 C
11.7
28.3
49.0
10.3
27.6
47.6
11.7
30.3
52.4
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
0 C 10 C 20 C 30 C
4.82
17.92
32.40
11.03
26.88
48.95
9.0
23.4
41.4
9.0
23.4
42.8
9.7
26.2
46.9
4.1
9.7
18.0
9.7
24.1
42.8
11.0
26.2
46.9
PRESSURE DROP (kPa)
2.76
11.72
22.75
8.27
24.82
44.82
6.9
19.3
35.2
17.2
47.6
88.3
8.3
22.8
42.1
3.4
9.0
16.5
9.0
22.1
40.0
9.7
24.1
44.1
1.72
11.38
21.37
7.22
23.10
41.36
5.5
16.5
31.0
14.5
42.1
80.0
6.2
18.6
34.5
2.1
7.6
15.2
8.3
20.7
37.9
2.1
22.8
41.1
0.88
9.47
19.30
6.29
21.29
38.47
6. Raise the loop temperature to approximately 29.4 C.
Open the drain at the lowest point in the system. Adjust
the make-up water replacement rate to equal the rate of
bleed.
7. Refill the system and add trisodium phosphate in a proportion of approximately 0.5 kg per 750 L of water (or
other equivalent approved cleaning agent).
CAUTION
To avoid possible damage to a plastic (PVC) piping system, do not allow temperatures to exceed 43.3 C.
Raise the loop temperature to 37.8 C. Circulate the solution for a minimum of 8 to 24 hours. At the end of this
period, shut off the circulating pump and drain the solution. Repeat system cleaning if desired.
8. When the cleaning process is complete, remove the shortcircuited hose. Reconnect the hoses to the proper supply,
and return the connections to each of the units. Refill the
system and bleed off all air.
9. Test the system pH with litmus paper. The system water
should be slightly alkaline (pH of 7.5 to 8.5). Add chemicals, as appropriate, to maintain acidity levels.
10. When the system is successfully cleaned, flushed, refilled
and bled, restore power.
11. Check the main system panels, safety cutouts and alarms.
Set the controls to properly maintain loop temperatures.
CAUTION
DO NOT use “Stop Leak” or any similar chemical agent in
this system. Addition of these chemicals to the loop water
will foul the system and inhibit unit operation.
Cleaning and Flushing — Cleaning and flushing of
the piping system is the single most important step to ensure
proper start-up and continued efficient operation of the system.
WARNING
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock,
open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in
an open position before flushing system. Install lockout
tag.
Follow the instructions below to properly clean and flush
the system:
1. Verify electrical power to the unit is disconnected and
lockout tag installed.
2. Install the system with the supply hose connected directly
to the return riser valve. Use a single length of flexible
hose.
3. Open all air vents. Fill the system with the water. DO
NOT allow system to overflow. Bleed all air from the
system. Pressurize and check the system for leaks and repair appropriately.
4. Verify all strainers are in place. Start the pumps, and systematically check each vent to ensure all air is bled from
the system.
5. Verify make-up water is available. Adjust make-up water
appropriately to replace the air which was bled from the
system. Check and adjust the water/air level in the expansion tank.
Antifreeze — In areas where entering loop temperatures
drop below 4.4 C or where piping will be routed through areas
subject to freezing, antifreeze is needed.
Alcohols and glycols are commonly used as antifreeze
agents. Freeze protection should be maintained to 8.3° C below
the lowest expected entering loop temperature. For example, if
the lowest expected entering loop temperature is –1.1 C, the
leaving loop temperature would be –5.6 to –3.9 C. Therefore,
the freeze protection should be at –9.4 C (–1.1 C – 8.3 C =
–9.4 C).
IMPORTANT: All alcohols should be pre-mixed and
pumped from a reservoir outside of the building or
introduced under water level to prevent alcohols from
fuming.
Calculate the total volume of fluid in the piping system. See
Table 8. Use the percentage by volume in Table 9 to determine
the amount of antifreeze to use. Antifreeze concentration
should be checked from a well mixed sample using a hydrometer to measure specific gravity.
FREEZE PROTECTION SELECTION — The –1.1 C FP1
factory setting (water) should be used to avoid freeze damage
to the unit.
Once antifreeze is selected, the JW3 jumper (FP1) should
be clipped on the control to select the low temperature (antifreeze –12.2 C) set point to avoid nuisance faults.
15
Page 16

Table 8 — Approximate Fluid Volume (L)
C
R
R
C
CC
CCG
BR
BRG
Test
Off On
FP1JW3
TEST
MODE
PINS
Fig. 11 — Test Mode Pins Location
per 30 M of Pipe
PIPE DIAMETER (in.) [mm] VOLUME (gal.) [L]
Copper 1 [25.4] 4.1 [15.5]
Rubber Hose 1 [25.4] 3.9 [14.8]
Polyethylene
LEGEND
IPS — Internal Pipe Size
SCH — Schedule
SDR — Standard Dimensional Ratio
NOTE: Volume of heat exchanger is approximately 1.0 gallon
(3.78 liters).
1.25 [31.8] 6.4 [24.2]
1.5 [38.1] 9.2 [34.8]
3
/4 IPS SDR11 2.8 [10.6]
1 IPS SDR11 4.5 [17.0]
1
/4 IPS SDR11 8.0 [30.8]
1
1
/2 IPS SDR11 10.9 [41.3]
2 IPS SDR11 18.0 [68.1]
11/4 IPS SCH40 8.3 [31.4]
1
/2 IPS SCH40 10.9 [41.3]
1
2 IPS SCH40 17.0 [64.4]
Table 9 — Antifreeze Percentages by Volume
ANTIFREEZE
Methanol (%) 25 21 16 10
100% USP Food Grade
Propylene Glycol (%)
Ethanol (%) 29 25 20 14
MINIMUM TEMPERATURE FOR FREEZE
–12.2 –9.4 –6.7 –3.9
PROTECTION (C)
38 30 22 15
Cooling Tower/Boiler Systems — These systems
typically use a common loop maintained at 15.6 to 32.2 C. The
use of a closed circuit evaporative cooling tower with a secondary heat exchanger between the tower and the water loop is recommended. If an open type cooling tower is used continuously,
chemical treatment and filtering will be necessary.
Ground Coupled, Closed Loop and Plateframe
Heat Exchanger Well Systems — These systems al-
low water temperatures from –1.1 to 43.3 C. The external loop
field is divided up into 51 mm polyethylene supply and return
lines. Each line has valves connected in such a way that upon
system start-up, each line can be isolated for flushing using only
the system pumps. Air separation should be located in the piping system prior to the fluid re-entering the loop field.
OPERATION
NOTE: On all subsequent compressor calls the random start
delay is omitted.
HEATING STAGE 2 — To enter Stage 2 mode, terminal W is
active (Y is already active). Also, the G terminal must be active
or the W terminal is disregarded.
Units with Aquazone Deluxe D Control
STANDBY — The compressor will be off. The reversing
valve (RV) relays will be on if inputs are present.
HEATING STAGE 1 — In Heating Stage 1 mode, the fan enable and compressor relays are turned on immediately. Once
the demand is removed, the relays are turned off and the control reverts to standby mode. If there is a master/slave or dual
compressor application, all compressor relays and related functions will operate per their associated DIP switch 2 setting on
S1.
HEATING STAGE 2 — In Heating Stage 2 mode, the compressor relays remain on. The control reverts to Heating Stage
1 mode once demand is removed. If there is a master/slave or
dual compressor application, all compressor relays and related
functions will operate per their associated DIP switch 2 setting
on S1.
COOLING STAGE 1 — In Cooling Stage 1 mode, the compressor and RV relays are turned on immediately. If configured
as stage 2 (DIP switch set to OFF) then the compressor and fan
will not turn on until there is a stage 2 demand. The compressor
relays are turned off immediately when the Cooling Stage 1 demand is removed. The control reverts to standby mode. The
RV relay remains on until there is a heating demand. If there is
a master/slave or dual compressor application, all compressor
relays and related functions will track with their associated DIP
switch 2 on S1.
COOLING STAGE 2 — In Cooling Stage 2 mode, the compressor and RV relays remain on. The control reverts to Cooling Stage 1 mode once the demand is removed. If there is a
master/slave or dual compressor application, all compressor relays and related functions will track with their associated DIP
switch 2 on S1.
NIGHT LOW LIMIT (NLL) STAGED HEATING — In NLL
staged heating mode, the override (OVR) input becomes
active and is recognized as a call for heating and the control
will immediately go into a Heating Stage 1 mode. With an
additional 30 minutes of NLL demand, the control will go into
Heating Stage 2 mode. With another additional 30 minutes of
NLL demand, the control will go into Heating Stage 3 mode.
Power Up Mode —
The unit will not operate until all the
inputs, terminals and safety controls are checked for normal
operation.
NOTE: The compressor will have a 5-minute anti-short cycle
upon power up.
Units with Aquazone™ Complete C Control
STANDBY — The Y and W terminals are not active in Standby mode, however the O and G terminals may be active, depending on the application. The compressor will be off.
COOLING — The Y and O terminals are active in Cooling
mode. After power up, the first call to the compressor will initiate a 5 to 80 second random start delay and a 5-minute antishort cycle protection time delay. After both delays are complete, the compressor is energized.
NOTE: On all subsequent compressor calls the random start
delay is omitted.
HEATING STAGE 1 — Terminal Y is active in heating
Stage 1. After power up, the first call to the compressor will
initiate a 5 to 80 second random start delay and a 5-minute antishort cycle protection time delay. After both delays are
complete, the compressor is energized.
SYSTEM TEST
System testing provides the ability to check the control
operation. The control enters a 20-minute Test mode by momentarily shorting the test pins. All time delays are increased
15 times. See Fig. 11.
Test Mode — Enter the Test mode on Complete C or
Deluxe D controls by momentarily shorting the test terminals.
The Complete C or Deluxe D control will enter a 20-minute
test mode period in which all time delays are sped up 15 times.
16
Page 17

Upon entering Test mode, the status LED (light-emitting diode) will flash a code representing the last fault. For diagnostic
ease at the thermostat, the alarm will also cycle during Test
mode. The alarm relay will cycle on and off similar to the status LED to indicate a code representing the last fault, at the
thermostat. Test mode can be exited by shorting the test terminals for 3 seconds. See Tables 10-12.
NOTE: Deluxe D control has a flashing code and alarm relay
cycling code that will both have the same numerical label.
For example, flashing code 1 will have an alarm relay cycling
code 1. Code 1 indicates the control has not faulted since the
last power off to power on sequence.
Retry Mode — In Retry mode, the status LED will start to
flash slowly to signal that the control is trying to recover from
an input fault. The control will stage off the outputs and try to
again satisfy the thermostat used at terminal Y. Once the thermostat input calls are satisfied, the control will continue normal
operation.
NOTE: If 3 consecutive faults occur without satisfying the
thermostat input call to terminal Y, the control will go into
lockout mode. The last fault causing the lockout is stored in
memory and can be viewed by entering Test mode.
Table 10 — Complete C Control Current LED
Status and Alarm Relay Operations
LED STATUS
On
Off Control is non-functional Open
Slow Flash
Fast Flash Lockout Closed
Flashing Code 1 Test Mode — No fault in memory Cycling Code 1
Flashing Code 2 Test Mode — HP Fault in memory Cycling Code 2
Flashing Code 3 Test Mode — LP Fault in memory Cycling Code 3
Flashing Code 4 Test Mode — FP1 Fault in memory Cycling Code 4
Flashing Code 5 Test Mode — FP2 Fault in memory Cycling Code 5
Flashing Code 7
Flashing Code 8 Test Mode — PM in memory Cycling Code 8
Flashing Code 9
FP — Freeze Protection
HP — High Pressure
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
LP — Low Pressure
PM — Performance Monitor
NOTES:
LEGEND
1. Slow flash is 1 flash every 2 seconds.
2. Fast flash is 2 flashes every 1 second.
3. EXAMPLE: “Flashing Code 2” is represented by 2 fast flashes followed
by a 10-second pause. This sequence will repeat continually until the
fault is cleared.
DESCRIPTION OF
OPERATION
Normal Mode Open
Normal Mode with PM Warning
Fault Retry Open
Over/Under Voltage Shutdown
Test Mode — Over/Under shut-
down in memory
Test Mode — FP1/FP2 swapped
fault in memory
ALARM RELAY
Cycle
(Closed 5 sec.,
Open 25 sec.)
Open
(Closed after
15 minutes)
Cycling Code 7
Cycling Code 9
Aquazone™ Deluxe D Control LED Indicators —
STATUS LED — Status LED indicates the current status or
mode of the Deluxe D control. The Status LED light is green.
TEST LED — Test LED will be activated any time the Deluxe D control is in Test mode. The Test LED light is yellow.
FAULT LED — Fault LED light is red. The fault LED will
always flash a code representing the last fault in memory. If
there is no fault in memory, the fault LED will flash code 1 on
the display and appear as 1 fast flash alternating with a
10-second pause. See Table 12.
(Autoreset)
FP — Freeze Protection
HP — High Pressure
LP — Low Pressure
There are 3 LED indicators on the Deluxe D control:
Table 11 — Complete C Control LED Code and
Fault Descriptions
LED
CODE
1 No fault in memory There has been no fault since
2 High-Pressure Switch HP Open Instantly
3 Low-Pressure Switch LP open for 30 continuous
4 Freeze Protection
5 Freeze Protection (Load)
7
8 PM Warning Performance Monitor
9 FPI and FP2
LEGEND
FAULT DESCRIPTION
the last power-down to power-up
sequence
seconds before or during a
call (bypassed for first
60 seconds)
(Source) Coax — FP1
Coil — FP2
Over/Under Voltage
Shutdown
Thermistors are
swapped
FP1 below Temp limit for
30 continuous seconds
(bypassed for first 60 seconds of
operation)
FP2 below Temp limit for
30 continuous seconds
(bypassed for first 60 seconds of
operation)
"R" power supply is <19 vac
or >30 vac
Warning has occurred.
FP1 temperature is higher than
FP2 in heating/test mode, or FP2
temperature is higher than FP1
in cooling/test mode.
17
Page 18

Table 12 — Aquazone™ Deluxe D Control Current LED Status and Alarm Relay Operations
DESCRIPTION
Normal Mode On Off Flash Last Fault Code in Memory Open
Normal Mode with PM On Off Flashing Code 8
Control is Non-Functional Off Off Off Open
Test Mo de — On Flash Last Fault Code in Memory Cycling Appropriate Code
Night Setback Flashing Code 2 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
ESD Flashing Code 3 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
Invalid T-stat Inputs Flashing Code 4 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
No Fault in Memory On Off Flashing Code 1 Open
HP Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 2 Open
LP Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 3 Open
FP1 Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 4 Open
FP2 Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 5 Open
CO Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 6 Open
Over/Under Voltage Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 7 Open (closed after 15 minutes)
HP Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 2 Closed
LP Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 3 Closed
FP1 Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 4 Closed
FP2 Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 5 Closed
CO Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 6 Closed
LEGEND NOTES:
CO — Condensate Overflow
ESD — Emergency Shutdown
FP — Freeze Protection
HP — High Pressure
LP — Low Pressure
PM — Performance Monitor
STATUS LED
(Green)
TEST LED
(Yellow)
FAULT LED (Red) ALARM RELAY
Cycle (closed 5 sec,
open 25 sec, …)
1. If there is no fault in memory, the Fault LED will flash code 1.
2. Codes will be displayed with a 10-second Fault LED pause.
3. Slow flash is 1 flash every 2 seconds.
4. Fast flash is 2 flashes every 1 second.
5. EXAMPLE: “Flashing Code 2” is represented by 2 fast flashes followed
by a 10-second pause. This sequence will repeat continually until the
fault is cleared.
SERVICE
Perform the procedures outlined below periodically, as
indicated.
IMPORTANT: When a compressor is removed from this
unit, system refrigerant circuit oil will remain in the compressor. To avoid leakage of compressor oil, the refrigerant
lines of the compressor must be sealed after it is removed.
IMPORTANT: To avoid the release of refrigerant into the
atmosphere, the refrigerant circuit of this unit must only be
serviced by technicians which meet local, state and federal
proficiency requirements.
IMPORTANT: All refrigerant discharged from this unit
must be recovered without exception. Technicians must follow industry accepted guidelines and all local, state and federal statutes for the recovery and disposal of refrigerants.
WARNING
To prevent injury or death due to electrical shock or contact
with moving parts, open unit disconnect switch before servicing unit.
Water Coil — Keep all air out of the water coil. Check
open loop systems to be sure the well head is not allowing air
to infiltrate the water line. Always keep lines airtight.
Inspect heat exchangers regularly, and clean more frequently if the unit is located in a “dirty” environment. The heat
exchanger should be kept full of water at all times. Open loop
systems should have an inverted P trap placed in the discharge
line to keep water in the heat exchanger during off cycles.
Closed loop systems must have a minimum of 103 kPa during
the summer and 276 kPa during the winter.
Check P trap frequently for proper operation.
CAUTION
To avoid fouled machinery and extensive unit clean-up,
DO NOT operate units without filters in place. DO NOT
use equipment as a temporary heat source during
construction.
Refrigerant System — Verify air and water flow rates
are at proper levels before servicing. To maintain sealed circuitry integrity, do not install service gages unless unit operation
appears abnormal.
Condenser Cleaning — Water-cooled condensers may
require cleaning of scale (water deposits) due to improperly
maintained closed-loop water systems. Sludge build-up may
need to be cleaned in an open water tower system due to
induced contaminants.
Local water conditions may cause excessive fouling or
pitting of tubes. Condenser tubes should therefore be cleaned at
least once a year, or more often if the water is contaminated.
Proper water treatment can minimize tube fouling and
pitting. If such conditions are anticipated, water treatment
analysis is recommended. Refer to the Carrier System Design
Manual, Part 5, for general water conditioning information.
CAUTION
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and rubber
gloves when using inhibited hydrochloric acid solution.
Observe and follow acid manufacturer’s instructions.
Clean condensers with an inhibited hydrochloric acid solution. The acid can stain hands and clothing, damage concrete,
and, without inhibitor, damage steel. Cover surroundings to
guard against splashing. Vapors from vent pipe are not harmful,
18
Page 19

but take care to prevent liquid from being carried over by the
Fig. 12 — Gravity Flow Method
Fig. 13 — Forced Circulation Method
Fig. 14 — Thermistor Nominal Resistance
gases.
Warm solution acts faster, but cold solution is just as effec-
tive if applied for a longer period.
GRAVITY FLOW METHOD — Do not add solution faster
than vent can exhaust the generated gases.
When condenser is full, allow solution to remain overnight,
then drain condenser and flush with clean water. Follow acid
manufacturer’s instructions. See Fig. 12.
FILL CONDENSER WITH
CLEANING SOLUTION. DO
NOT ADD SOLUTION
MORE RAPIDLY THAN
VENT CAN EXHAUST
GASES CAUSED BY
CHEMICAL ACTION.
VENT
PIPE
1.0 TO 1.2 m
PAI L
1-IN.
(25 mm)
PIPE
1.5 m APPROX
FUNNEL
PAI L
CONDENSER
FORCED CIRCULATION METHOD — Fully open vent
pipe when filling condenser. The vent may be closed when
condenser is full and pump is operating. See Fig. 13.
PUMP
SUCTION
PUMP
SUPPORT
TANK
FINE MESH
SCREEN
PRIMING
CONN.
GAS VENT
GLOBE
VALV ES
SUPPLY
1-IN.
(25 mm)
PIPE
RETURN
CONDENSER
REMOVE WATER
REGULATING VALVE
3. After unit conditions have stabilized, read head pressure
on discharge line gage.
NOTE: Operate unit a minimum of 15 minutes before
checking charge. From standard field-supplied PressureTemperature chart for R-410A, find equivalent saturated
condensing temperature.
4. Read liquid line temperature on thermometer; then
subtract from saturated condensing temperature. The difference equals subcooling temperature.
Refrigerant Charging
WARNING
To prevent personal injury, wear safety glasses and gloves
when handling refrigerant. Do not overcharge system —
this can cause compressor flooding.
NOTE: Do not vent or depressurize unit refrigerant to atmosphere. Remove and recover refrigerant following accepted
practices.
TROUBLESHOOTING
When troubleshooting problems with a WSHP, refer to
Table 13.
Thermistor — A thermistor may be required for single-
phase units where starting the unit is a problem due to low
voltage. See Fig. 14 for thermistor nominal resistance.
Control Sensors — The control system employs 2 nom-
inal 10,000 ohm thermistors (FP1 and FP2) that are used for
freeze protection. Be sure FP1 is located in the discharge fluid
and FP2 is located in the air discharge. See Fig. 15.
90.0
80.0
70.0
60.0
50.0
40.0
30.0
Resistance (kOhm)
20.0
10.0
0.0
-17.7 -6.6 4.4 15.6 26.7 37.8 48.9 60.0
Temperature (C)
Regulate flow to condenser with a supply line valve. If
pump is a nonoverloading type, the valve may be fully closed
while pump is running.
For average scale deposit, allow solution to remain in condenser overnight. For heavy scale deposit, allow 24 hours.
Drain condenser and flush with clean water. Follow acid manufacturer’s instructions.
Checking System Charge — Units are shipped with
full operating charge. If recharging is necessary:
1. Insert thermometer bulb in insulating rubber sleeve on
liquid line near filter drier. Use a digital thermometer for
all temperature measurements. DO NOT use a mercury
or dial-type thermometer.
2. Connect pressure gage to discharge line near compressor.
19
Page 20

SUCTIO N
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
COAX
EXP ANSION
VA LV E
FP 2
FP 1
LIQUI D
LIN E
WA TER IN
WA TER OUT
CONDENSA TE
OVERFLO W
(CO)
AIR COI L
FREEZ E
PROTECTIO N
WA TE R
COI L
PROTECTIO N
THERMIST OR
( °C)
( °C)
AI R
COI L
AIRFLOW
AIRFLO W
a50-8163
LEGEND
Fig. 15 — FP1 and FP2 Thermistor Location
COAX — Coaxial Heat Exchanger
Airflow
Refrigerant Liquid Line Flow
a50-8592
20
Page 21

Table 13 — Troubleshooting
FAULT HEATING COOLING POSSIBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
Main Power Problems X X Green Status LED Off Check line voltage circuit breaker and disconnect.
Check for line voltage between L1 and L2 on the contactor.
Check for 24-vac between R and C on controller.
Check primary/secondary voltage on transformer.
HP Fault — Code 2
High Pressure
X X Overcharged with refrigerant Check superheat/subcooling vs. typical operating condition.
X X Bad HP switch Check switch continuity and operation. Replace.
LP/LOC Fault — Code 3
Low Pressure/Loss of
Charge
FP1 Fault — Code 4
Source Water Freeze
Protection
FP2 Fault — Code 5
Load Coil Freeze
Protection
Over/Under Voltage —
Code 7
(Auto Resetting)
Performance Monitor —
Code 8
No Fault Code Shown X X No compressor operation See scroll compressor rotation section.
Unit Short Cycles X X Unit in Test mode Reset power or wait 20 minutes for auto exit.
Unit Does Not Operate in
Cooling
Insufficient Capacity/
Not Cooling or Heating
Properly
High Head Pressure X Scaling in water heat exchanger Perform scaling check and clean if necessary.
Low Suction Pressure X Reduced water flow in heating Check pump operation or water valve operation/setting.
LEGEND
FP — Freeze Protection
HP — High Pressure
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
LOC — Loss of Charge
LP — Low Pressure
RV — Reversing Valve
X X Insufficient charge Check for refrigerant leaks.
X Compressor pump down at
X Reduced or no water flow in
X Inadequate antifreeze level Check antifreeze density with hydrometer.
X Improper freeze protect setting
X Water temperature out of range Bring water temperature within design parameters.
X X Bad thermistor Check temperature and impedance correlation.
X X Bad thermistor Check temperature and impedance correlation.
X X Under voltage Check power supply and 24-vac voltage before and during operation.
X X Over voltage Check power supply voltage and 24-vac before and during operation.
X Heating mode FP2>51.7 C Check for overcharged unit.
X X Compressor overload Check and replace if necessary.
X X Control board Reset power and check operation.
X X Unit selection Unit may be oversized for space. Check sizing for actual load of space.
X X Compressor overload Check and replace if necessary.
X X Low refrigerant charge Check superheat and subcooling.
X X Restricted metering device Check superheat and subcooling. Replace.
X X Thermostat improperly located Check location and for air drafts behind thermostat.
X X Unit undersized Recheck loads and sizing. Check sensible cooling load and heat pump
X X Scaling in water heat exchanger Perform scaling check and clean if necessary.
X X Inlet water too hot or cold Check load, loop sizing, loop backfill, ground moisture.
X X Unit overcharged Check superheat and subcooling. Reweigh in charge.
X X Non-condensables in system Vacuum system and reweigh in charge.
X X Restricted metering device Check superheat and subcooling. Replace.
X Water temperature out of range Bring water temperature within design parameters.
X Reduced or no water flow in
cooling
X Water temperature out of range
in cooling
start-up
heating
(–1.1 C vs –12.2 C)
X Reduced or no water flow in
heating
X Improper freeze protect setting
(–1.1 C vs –12.2 C)
X Water temperature out of range Bring water temperature within design parameters.
X Cooling mode FP1>51.7 C OR
FP2< 4.4 C
X Reversing valve Set for cooling demand and check 24-vac on RV coil and at control.
X Thermostat setup Check for ‘O’ RV setup not ‘B’.
X Thermostat wiring Check O wiring at heat pump. Jumper O and R for RV coil.
X Defective reversing valve Perform RV touch test.
Check pump operation or valve operation/setting.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Bring water temperature within design parameters.
Check charge and start-up water flow.
Check pump operation or water valve operation/setting.
Plugged strainer or filter. Clean or replace.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Clip JW3 jumper for antifreeze (–12.2 C) use.
Check pump operation or water valve operation/setting.
Plugged strainer or filter. Clean or replace.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Clip JW3 jumper for antifreeze (–12.2 C) use.
Check power supply wire size.
Check compressor starting.
Check 24-vac and unit transformer tap for correct power supply voltage.
Check 24-vac and unit transformer tap for correct power supply voltage.
Check for poor water flow or airflow.
If RV is stuck, run high pressure up by reducing water flow and while operating engage and disengage RV coil voltage to push valve.
capacity.
Plugged strainer or filter. Clean or replace.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
21
Page 22

Copyright 2010 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53500073-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50PSW-C1SI Pg 22 10-10 Replaces: New
Page 23

50PSW
START-UP CHECKLIST
CUSTOMER:___________________________ JOB NAME: _______________________________________
MODEL NO.:___________________________ SERIAL NO.:____________________ DATE:_________
LOOP TYPE: ___________________________ ANTIFREEZE TYPE AND %:_________________________
I. PRE-START-UP
DOES THE UNIT VOLTAGE CORRESPOND WITH THE SUPPLY VOLTAGE AVAILABLE? (Y/N)
HAVE THE POWER AND CONTROL WIRING CONNECTIONS BEEN MADE AND TERMINALS
TIGHT? (Y/N)
HAVE WATER CONNECTIONS BEEN MADE AND IS FLUID AVAILABLE AT HEAT EXCHANGER?
(Y/N)
HAS PUMP BEEN TURNED ON AND ARE ISOLATION VALVES OPEN? (Y/N)
HAS CONDENSATE CONNECTION BEEN MADE AND IS A TRAP INSTALLED? (Y/N)
IS AN AIR FILTER INSTALLED? (Y/N)
II. START-UP
IS FAN OPERATING WHEN COMPRESSOR OPERATES? (Y/N)
IF 3-PHASE SCROLL COMPRESSOR IS PRESENT, VERIFY PROPER ROTATION PER INSTRUCTIONS.
(Y/N)
UNIT VOLTAGE — COOLING OPERATION
PHASE AB VOLTS PHASE BC VOLTS PHASE CA VOLTS
(if 3 phase) (if 3 phase)
PHASE AB AMPS
PHASE BC AMPS PHASE CA AMPS
(if 3 phase) (if 3 phase)
CONTROL VOLTAGE
IS CONTROL VOLTAGE ABOVE 21.6 VOLTS? (Y/N) .
IF NOT, CHECK FOR PROPER TRANSFORMER CONNECTION.
TEMPERATURES
FILL IN THE ANALYSIS CHART ATTACHED.
COAXIAL HEAT
EXCHANGER
COOLING CYCLE:
FLUID IN
C FLUID OUT C KPA FLOW
HEATING CYCLE:
FLUID IN
AIR COIL COOLING CYCLE:
AIR IN
HEATING CYCLE:
AIR IN
C FLUID OUT C KPA FLOW
C AIR OUT C
C AIR OUT C
CL-1
Page 24

HEATING AND COOLING CYCLE ANALYSIS
COMPRESS OR
DISCHARGE
SUCTION
HWG*
EXPANSION
VALVE
FILTER
DRIER
REVERSING
VALVE
HEATING POSITION COOLING POSITION
1
COAX
COAX
5
1210
1311
9
7
8
6
4
3
2
FP2:
HEATING
LIQUID
LINE
5
FP1:
COOLING
LIQUID
LINE
CONDENS ER (HTG )
EVAPORATOR (CLG)
CONDENSER ( COOLING)
EVAPORATOR (HEATING)
WA TER-TO- WATER UNITS
REFRIG FLOW - HEATING REFRIG FLOW - COOLING
Source
Load
LEGEND
*Turn off HWG (hot water generator)
before troubleshooting.
CLG — Cooling
HTG — Heating
a50-8465
DESCRIPTION HEATING COOLING NOTES
Voltage
Compressor Amp
1 Suction Temperature
2 Suction Pressure
2a Saturation Temperature
2b Superheat
3 Discharge Temperature
4 Discharge Pressure
4a Saturation Temperature
4b Subcooling
5 Liquid Line Temperature
6 Source Water In Temperature
7 Source Water Out Temperature Temperature Difference —
8 Source Water In Pressure
9 Source Water Out Pressure
9a Pressure Drop
9b Flow Rate (L/s)
10 Load Water In Temperature
11 Load Water Out Temperature Temperature Difference —
12 Load Water In Pressure
13 Load Water Out Pressure
13a Pressure Drop
13b Flow Rate (gpm)
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
HEAT OF EXTRACTION (ABSORPTION) OR HEAT OF REJECTION =
FLOW RATE (L/s) x TEMP. DIFF. (DEG. C) x FLUID FACTOR* =
SUPERHEAT = SUCTION TEMPERATURE – SUCTION SATURATION TEMPERATURE
SUBCOOLING = DISCHARGE SATURATION TEMPERATURE – LIQUID LINE TEMPERATURE
*Use 500 for water, 485 for antifreeze.
Copyright 2010 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53500073-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50PSW-C1SI Pg CL-2 10-10 Replaces: New
= (DEG C)
=
(DEG C)
(kW)
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
 Loading...
Loading...