Page 1
Single-Package Heat Pump Units
Visit www.carrier.com
Installation, Start-Up and Service Instructions
NOTE: Read the entire instruction manual before starting the
installation.
Index
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS ...............................................1-4
General
RECEIVING AND INSTALLATION..................................4-15
Check Equipment......................................................................4-5
Provide Unit Support...................................................................5
Provide Clearances.......................................................................5
Rig and Place Unit....................................................................5-6
Select and Install Ductwork ....................................................6-8
Provide for Condensate Disposal............................................6-8
Install Electrical Connections.....................................................8
PRE-START-UP.........................................................................15
START-UP.............................................................................15-20
MAINTENANCE..................................................................20-23
SYSTEM INFORMATION.......................................................23
TROUBLESHOOTING .......................................................24-25
START-UP CHECKLIST.........................................................25
NOTE TO INSTALLER — READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS
CAREFULLY AND COMPLETELY before installing this unit.
Also, make sure the Owner’s Manual and Service Instructions are
left with the unit after installation.
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment can be
hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only
trained and qualified personnel should install, repair, or service
air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of
cleaning coils andfilters. All other operations should be performed
by trained service personnel. When working on air-conditioning
equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags and labels
attached to the unit, and other safety precautions that may apply.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and work gloves. Use
quenching cloth for unbrazing operations. Have fire extinguisher
available for all brazing operations.
.................................................................................4
Identify Unit..............................................................................4
Inspect Shipment.......................................................................5
Roof Curb..................................................................................5
Slab Mount................................................................................5
Ground Mount...........................................................................5
Converting Horizontal DischargeUnits to Downflow (Vertical)
Discharge...................................................................................6
High-Voltage Connections........................................................8
Routing Power Leads Into Unit..........................................8-14
Connecting Ground Lead to Ground Lug..............................14
Special Procedures for 208-V Operation...............................15
Check for Refrigerant Leaks..................................................15
Unit Start-Up Adjustment .................................................15-20
Time Delay Relay...................................................................23
Pressure Switches....................................................................23
Defrost Thermostat .................................................................23
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
50JS,JX018-060
C99001
Fig. 1—Model 50JS/JX
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, maintenance, or use can cause explosion, fire, electric shock, or
other occurrences, which could cause serious injury or death
or damage your property. Consult a qualified installer or
service agency for information or assistance. The qualified
installer or agency must use only factory-authorized kits or
accessories when modifying this product.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert symbol .
When you see this symbol on the product or in instructions or
manuals, be alert to the potential for personal injury.
Understand the signal words — DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION, and NOTE. Danger identifies the most serious hazards,
which will result in severe personal injury or death. Warning
indicates a condition that could cause serious personal injury or
death. Caution is used to identify unsafe practices, which would
result in minor personal injury or product and property damage.
NOTE is used to highlight suggestions which will result in
enhanced installation, reliability or operation.
1. The power supply (volts, phase, and hertz) must correspond to
that specified on unit rating plate.
2. The electrical supply provided by the utility must be sufficient
to handle load imposed by this unit.
3. This installation must conform with local building codes and
with NEC (National Electrical Code). Refer to provincial and
local plumbing or wastewater codes andother applicablelocal
codes.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 4
Tab 5a 5a
PC 101 Catalog No. 565-057 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50JS,JX-1SI Pg 1 5-00 Replaces: 50JX-2SI
Page 2
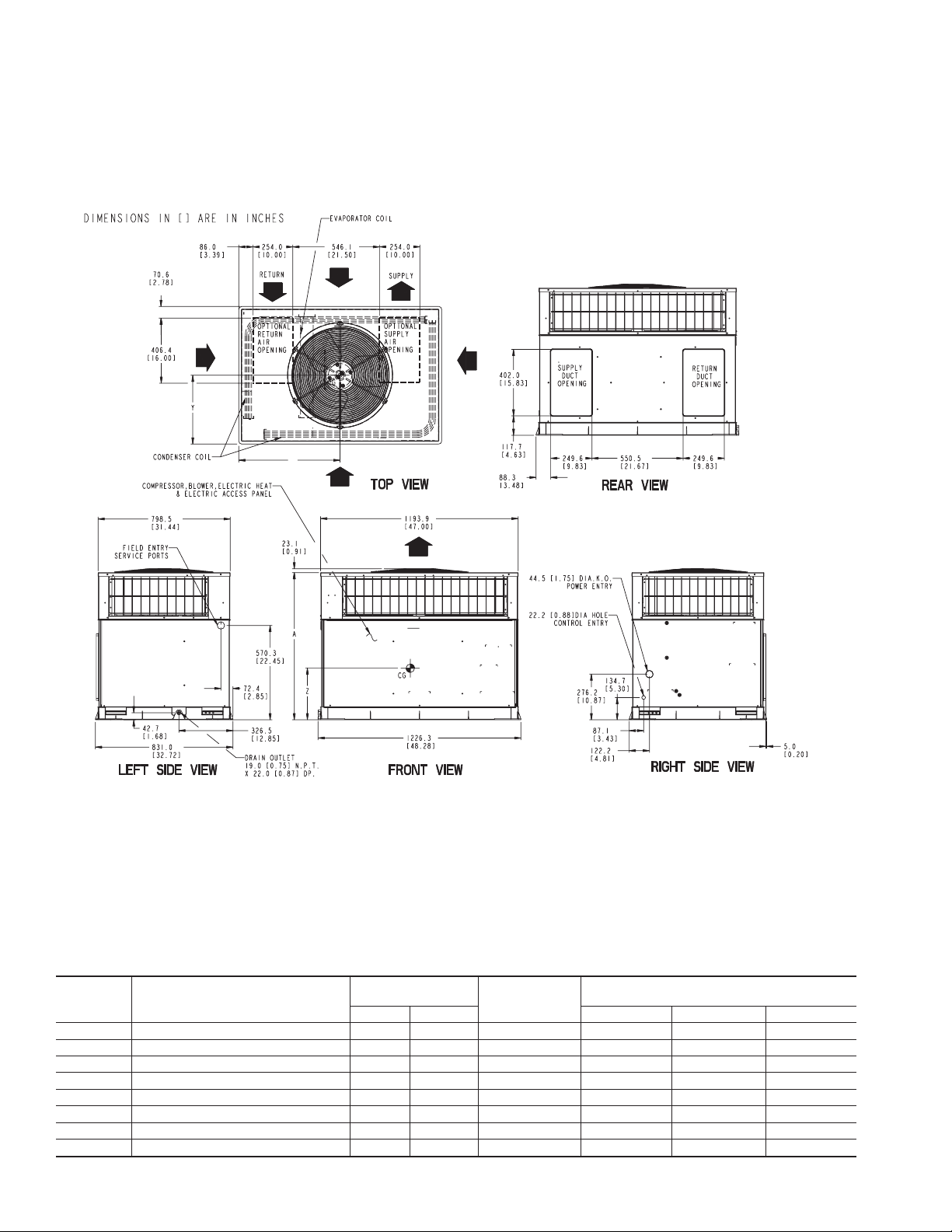
REQUIRED CLEARANCE TO COMBUSTIBLE MATL.
TOP OF UNIT...................................................................................14.00 [355.6]
DUCT SIDE OF UNIT.........................................................................2.00 [50.8]
SIDE OPPOSITE DUCTS ................................................................14.00 [355.6]
BOTTOM OF UNIT.............................................................................0.50 [12.7]
ELECTRIC HEAT PANEL.................................................................36.00 [914.4]
NEC. REQUIRED CLEARANCES.
BETWEEN UNITS, POWER ENTRY SIDE....................................42.00 [1066.8]
UNIT AND UNGROUNDED SURFACES, POWER ENTRY SIDE .36.00 [914.0]
UNIT AND BLOCK OR CONCRETE WALLS AND OTHER
GROUNDED SURFACES, POWER ENTRY SIDE.........................42.00 [1066.8]
UNIT ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
50JS018 208/230-1-60 283 128.4 37.02 [940.3] 19.5 [495.3] 16.8 [425.5] 15.0 [381.0]
50JS024 208/230-1-60 289 131.1 39.02 [991.1] 18.5 [469.9] 16.8 [425.5] 15.0 [381.0]
50JS030 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60 287 130.2 39.02 [991.1] 19.5 [495.3] 17.5 [444.5] 15.0 [381.0]
50JS036 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 291 132.0 37.02 [940.3] 19.5 [495.3] 17.8 [450.9] 13.0 [330.2]
50JS042 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 323 146.5 37.02 [940.3] 19.5 [495.3] 17.8 [450.9] 13.0 [330.2]
50JX024 208/230-1-60 299 135.6 41.02 [1041.9] 19.0 [482.6] 18.3 [463.6] 16.0 [406.4]
50JX030 208/230-1-60,208/230-3-60 320 145.2 37.02 [940.3] 20.0 [ 508] 19.3 [ 489.0] 17.6 [447.0]
50JX036 208/230-1-60,208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 328 148.8 37.02 [940.3] 20.0 [508] 19.0 [482.6] 16.5 [419.1]
INCHES [mm]
INCHES [mm]
UNIT WEIGHT
lb kg X Y Z
REQUIRED CLEARANCE FOR OPERATION AND SERVICING
EVAP. COIL ACCESS SIDE............................................................36.00 [914.0]
POWER ENTRY SIDE....................................................................42.00 [1066.8]
(EXCEPT FOR NEC REQUIREMENTS)
UNIT TOP.......................................................................................48.00 [1219.2]
SIDE OPPOSITE DUCTS ..............................................................36.00 [914.0]
DUCT PANEL.................................................................................12.00 [304.8] *
*MINIMUM DISTANCES: IF UNIT IS PLACED LESS THAN 304.8 [12.00] FROM
WALL SYSTEM, THEN SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MAYBE COMPROMISE.
UNIT HEIGHT
IN. [MM]
"A"
CENTER OF GRAVITY
IN. [MM]
INCHES [mm]
Fig. 2—50JS018-042/50JX024-036 Unit Dimensions
2
C99007
Page 3
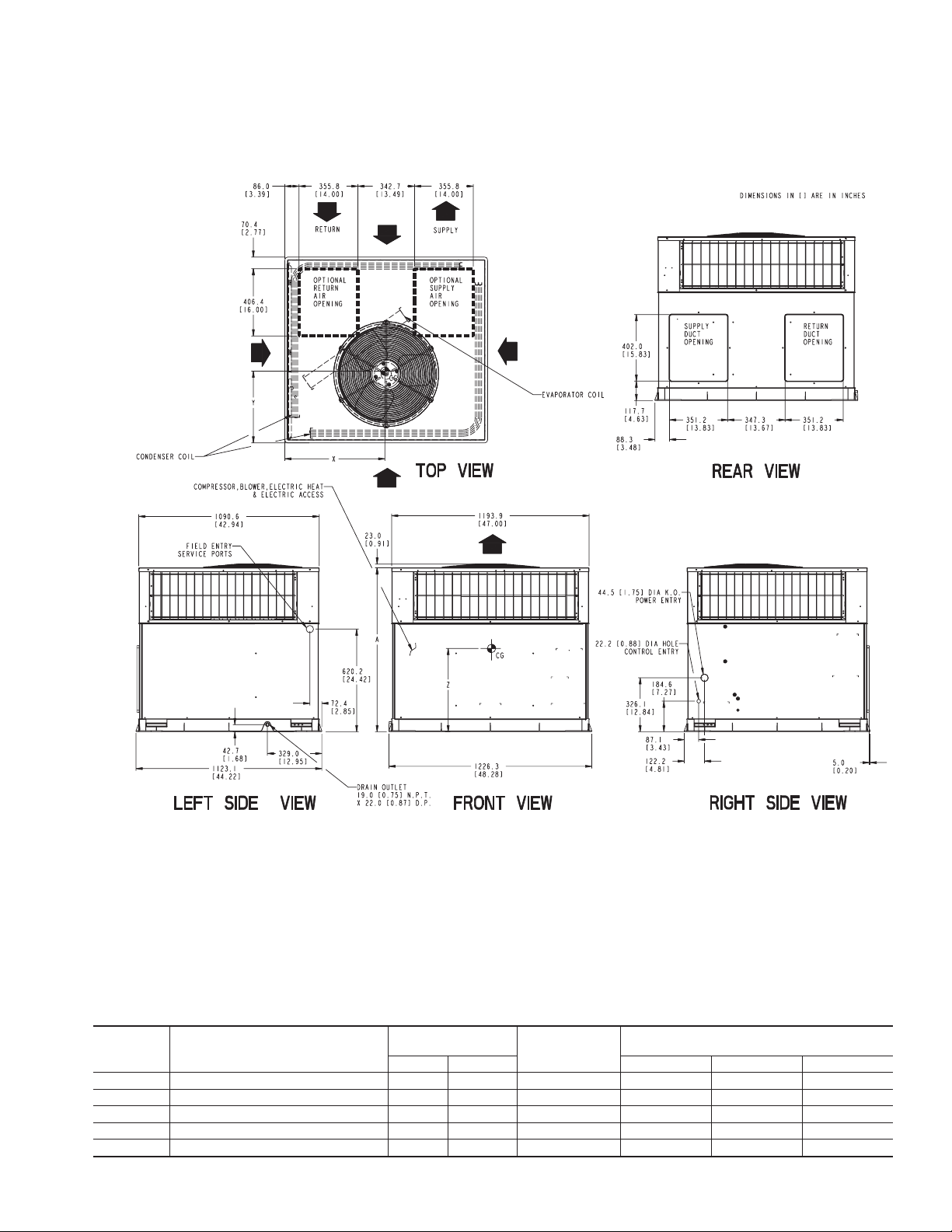
REQUIRED CLEARANCE TO COMBUSTIBLE MATL.
TOP OF UNIT...................................................................................14.00 [355.6]
DUCT SIDE OF UNIT.........................................................................2.00 [50.8]
SIDE OPPOSITE DUCTS ................................................................14.00 [355.6]
BOTTOM OF UNIT.............................................................................0.50 [12.7]
ELECTRIC HEAT PANEL.................................................................36.00 [914.4]
NEC. REQUIRED CLEARANCES.
BETWEEN UNITS, POWER ENTRY SIDE....................................42.00 [1066.8]
UNIT AND UNGROUNDED SURFACES, POWER ENTRY SIDE .36.00 [914.0]
UNIT AND BLOCK OR CONCRETE WALLS AND OTHER
GROUNDED SURFACES, POWER ENTRY SIDE.........................42.00 [1066.8]
UNIT ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
50JS048 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 353 160.1 38.98 [990.2] 20.5 [520.7] 20.6 [523.8] 17.0 [431.8]
50JS060 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 418 189.6 38.98 [990.2] 19.5 [495.3] 19.8 [501.7] 17.0 [431.8]
50JX042 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 350 158.8 40.98 [1040.9] 21.0 [533.4] 20.5 [520.7] 16.6 [421.6]
50JX048 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 355 161.0 40.98 [1040.9] 20.0 [508.0] 21.3 [539.8] 18.0 [457.2]
50JX060 208/230-1-60, 208/230-3-60, 460-3-60 428 194.1 42.98 [1091.7] 21.0 [533.4] 20.0 [508.0] 17.6 [447.0]
INCHES [mm]
INCHES [mm]
UNIT WEIGHT
lb kg X Y Z
REQUIRED CLEARANCE FOR OPERATION AND SERVICING
EVAP. COIL ACCESS SIDE............................................................36.00 [914.0]
POWER ENTRY SIDE....................................................................36.00 [914.0]
(EXCEPT FOR NEC REQUIREMENTS)
UNIT TOP.......................................................................................48.00 [1219.2]
SIDE OPPOSITE DUCTS ..............................................................36.00 [914.0]
DUCT PANEL.................................................................................12.00 [304.8] *
*MINIMUM DISTANCES: IF UNIT IS PLACED LESS THAN 304.8 [12.00] FROM
WALL SYSTEM, THEN SYSTEM PERFORMANCE MAYBE COMPROMISE.
UNIT HEIGHT
IN. [MM]
"A"
CENTER OF GRAVITY
IN. [MM]
INCHES [mm]
Fig. 3—50JS048-060/50JX042-060 Unit Dimensions
3
C99006
Page 4
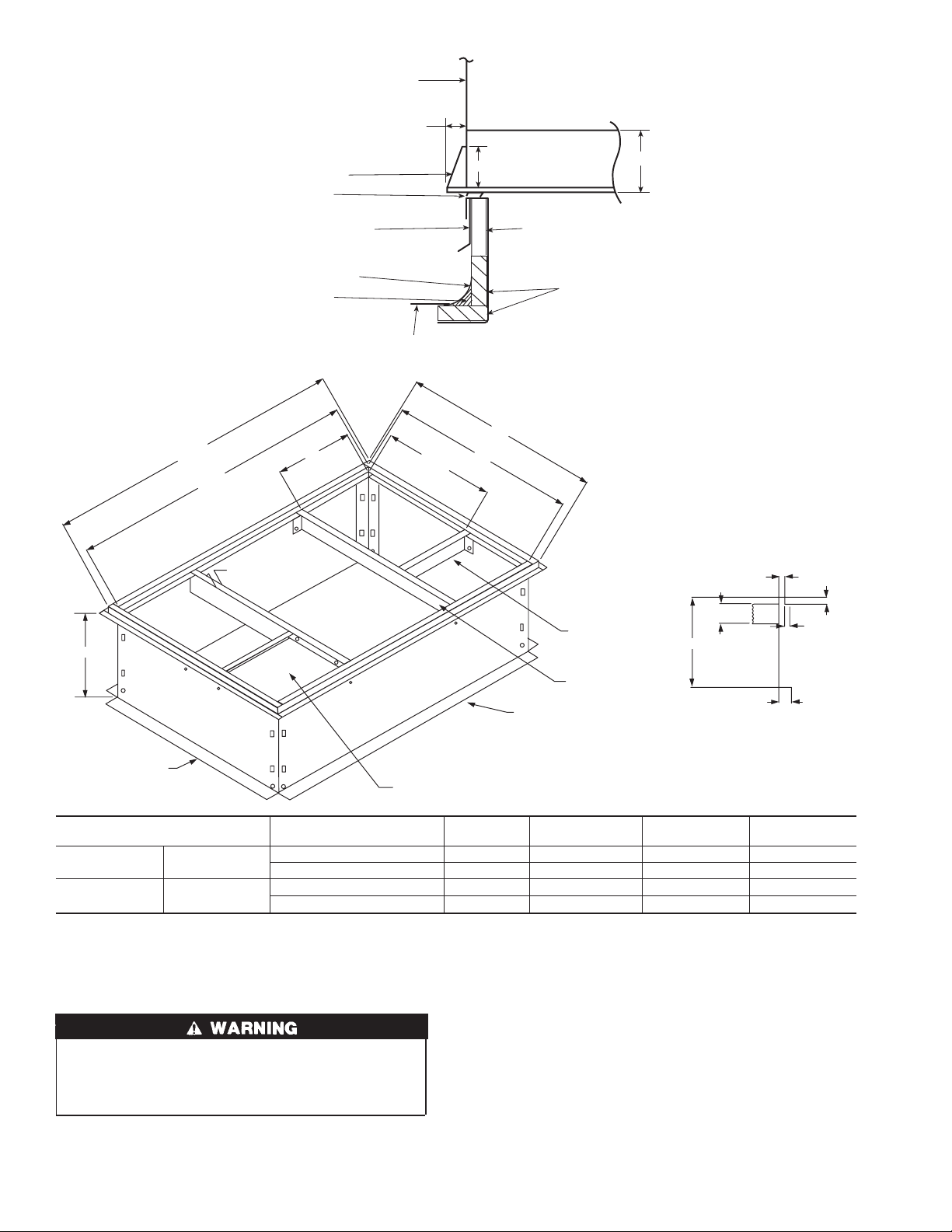
46 3/16
44 5/16
SIDE PANEL
SUPPORT RIB(S)
SEAL STRIP
(FACTORY SUPPLIED)
COUNTER FLASHING
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
ROOFING FELT
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
CANT STRIP
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
B
0.75"
ROOFING MATERIAL
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
17 3/8
TYP.
3.0"
C
D
BASE PAN
BOTTOM SUPPLY
NAILER
INSULATION
(FIELD SUPPLIED)
4.0"
A99340
1 TYP.
B
END
(2)
DECK PAN (INSULATED)
UNIT SIZE ODS CATALOG NUMBER
50JS018-042 50JX024-036
50JS048-060 50JX042-060
CPRFCURB006A00 8 [203] 11-27/32 [301] 30-5/8 [778] 28-3/4 [730]
CPRFCURB007A00 14 [356] 11-27/32 [301] 30-5/8 [778] 28-3/4 [730]
CPRFCURB008A00 8 [203] 15/27/32 [402] 42-18/ [1070] 40-1/4 [1022]
CPRFCURB009A00 14 [356] 15-27/32 [402] 42-1/8 [1070] 40-1/4 [1022]
Fig. 4—Roof Curb Dimensions
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
2. Roof curb is made of 16 gage steel.
3. Table lists only the dimensions per part number that have changed.
4. Insulated panels: 1-in. thick fiberglass 1 lb density.
Before performing service or maintenance operations on
system, turn offmain power to unit. Turnoff accessory heater
power switch if applicable. Electrical shock could cause
severe injury or death.
Step 1—General
The 50JS and 50JX heat pumps are fully self-contained and
designed for outdoor installation (See Fig. 1). Standard units are
3
SIDE
(2)
SUPPORT B
SUPPORT A (2)
A
END VIEW
A
IN. [MM]
B
IN. [MM]
C
IN. [MM]
shipped in a horizontal-discharge configuration for installation on
a ground-level slab. Standard units can be converted to downflow
(vertical) discharge configurations for rooftop applications.
RECEIVING AND INSTALLATION
Step 1—Check Equipment
IDENTIFY UNIT — The unit model number and serial number
are stamped onthe unit identification plate. Check this information
against shipping papers.
4
7/8
2
D
IN. [MM]
13/16
A99320
Page 5
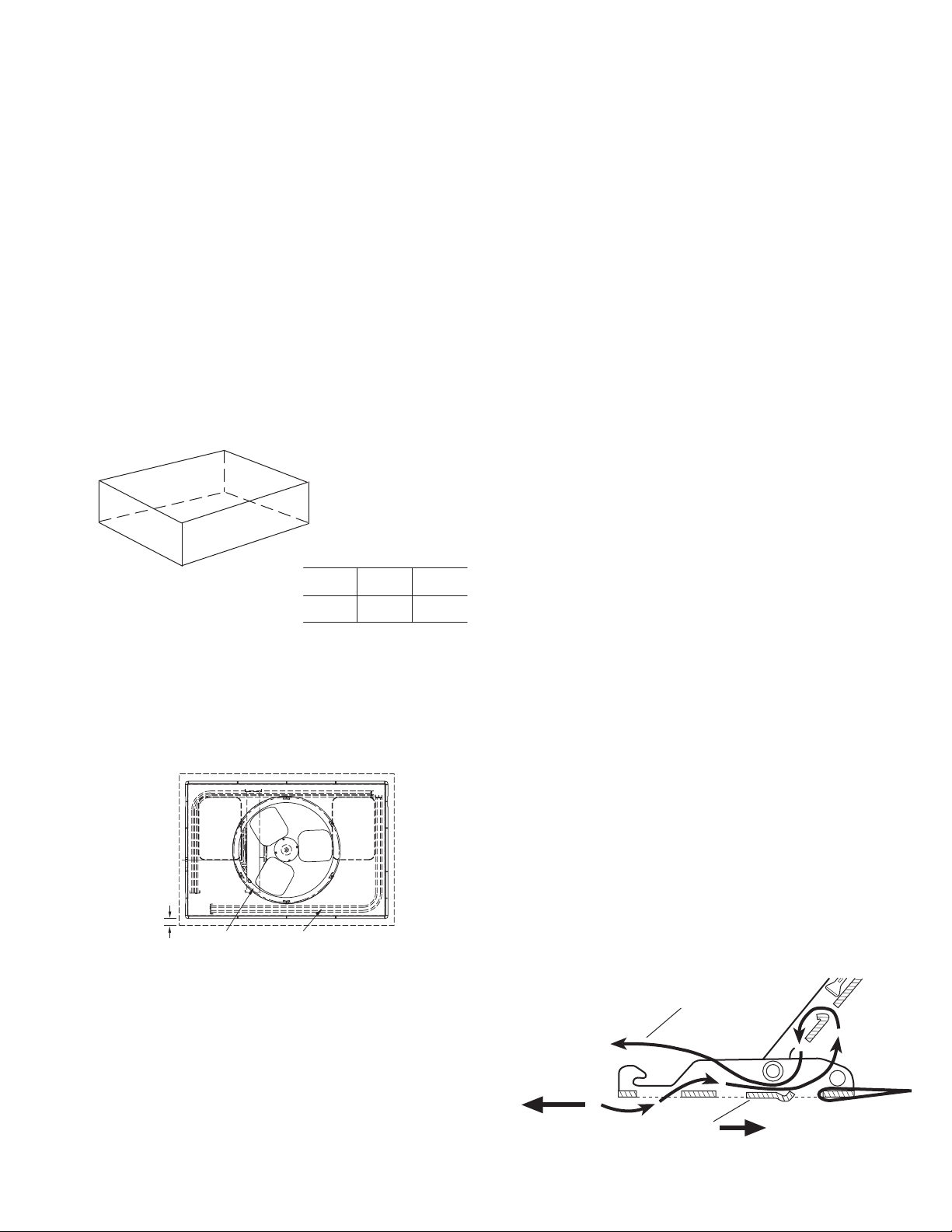
INSPECT SHIPMENT — Inspect for shipping damage while unit
is still on shipping pallet. If unit appears to be damaged or is torn
loose from its anchorage, have it examined by transportation
inspectors before removal. Forward claim papers directly to
transportation company. Manufacturer is not responsible for any
damage incurred in transit. Check all items against shipping list.
Immediately notify the nearest Carrier Air Conditioning office if
any item is missing. To prevent loss or damage, leave all parts in
original packages until installation.
Step 2—Provide Unit Support
ROOF CURB — Install accessory roof curb in accordance with
instructions shipped with curb (See Fig. 4). Install insulation, cant
strips, roofing, and flashing. Ductwork must be attached to curb.
IMPORTANT: Thegasketing ofthe unitto the roof curb is critical
for a watertight seal. Install gasketing material supplied with the
roof curb. Improperly applied gasketing also can result in air leaks
and poor unit performance.
Curb should be level to within 1/4 in. (See Fig. 5). This is
necessary for unit drain to function properly. Refer to accessory
roof curb installation instructions for additional information as
required.
A
B
C
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE
DIFFERENCE (in.)
A-B B-C A-C
1/4 1/4 1/4
C99065
Fig. 5—Unit Leveling Tolerances
SLAB MOUNT — Place the unit on a solid, level concrete pad
that is a minimum of 4 in. thick with 2 in. above grade (See Fig.
6). The slab should extend approximately 2 in. beyond the casing
on all 4 sides of the unit. Do not secure the unit to the slab except
when required by local codes.
OPTIONAL
RETURN
AIR
OPENING
2"
EVAP. COIL COND. COIL
OPTIONAL
SUPPLY
AIR
OPENING
C99096
Fig. 6—Slab Mounting Detail
corner or under an overhead obstruction. The minimum clearance
under a partial overhang (such as a normal house overhang) is 36
in. above the unit top. The maximum horizontal extension of a
partial over-hang must not exceed 36 in. For extended overhangs,
provide a minimum clearance of 36 in.
IMPORTANT: Do not restrict outdoor airflow. An air restriction
at either the outdoor-air inlet or the fan discharge may be
detrimental to compressor life.
Do not place the unit where water, ice, or snow from an overhang
or roof will damage or flood the unit. Do not install the unit on
carpeting, tile, or other combustible materials. Slab-mounted units
should be at least 4 in. above the highest expected water and runoff
levels. Do not use unit if it has been under water.
Step 4—Rig and Place Unit
Rigging and handling ofthis equipmentcan behazardous formany
reasons due to the installation location (roofs, elevated structures,
etc.)
Only trained, qualified crane operators and ground support staff
should handle and install this equipment.
When working with this equipment, observe precautions in the
literature, on tags, stickers and labels attached to the equipment,
and any other safety precautions that might apply.
Follow all applicable safety codes. Wear safety shoes and work
gloves.
INSPECTION — Prior to initial use, and at monthly intervals, all
rigging brackets and straps should be visually inspected for any
damage, evidence of wear, structural deformation, or cracks.
Particular attention should be paid to excessive wear at hoist
hooking points and load support areas. Brackets or straps showing
any kind of wear in these areas must not be used and should be
discarded.
INSTALLATION
1. Remove unit from shipping carton. Leave top shipping skid on
the unit as a spreader bar to prevent the rigging straps from
damaging the unit. If the wood skid is not available, use a
spreader bar of sufficient length to protect unit from damage.
2. Position the lifting bracket assembly around the base of the
unit. Be sure the strap does not twist.
3. Place each of the 4 metal lifting brackets into the handholds in
the composite pan.
4. Thread lifting bracket strapping around bottom perimeter of
unit as follows:
a. Open lever of tension buckle (ratchet type).
b. Feed strapping through tension buckle as shown in Fig. 7.
c. Pull strapping through tension buckle unit taut.
d. Snap lever down to lock strap in tension buckle. To release
strapping, squeeze safety latch, lift lever, and pull webbing
outward.
GROUND MOUNT — The unit may be installed either on a slab
or placed directly on the ground if local codes permit. Place the
unit on level ground prepared with gravel for condensate discharge.
Step 3—Provide Clearances
The required minimum service clearances are shown in Figs. 2 and
3. Adequate ventilation and outdoor air must be provided. The
outdoor fan draws air through the outdoor coil and discharges it
through the top fan grill. Be sure that the fan discharge does not
recirculate to the outdoor coil. Do not locate the unit in either a
HANDHOLD
HOOK
FEED
C99067
Fig. 7—Threading Belt
5
Page 6
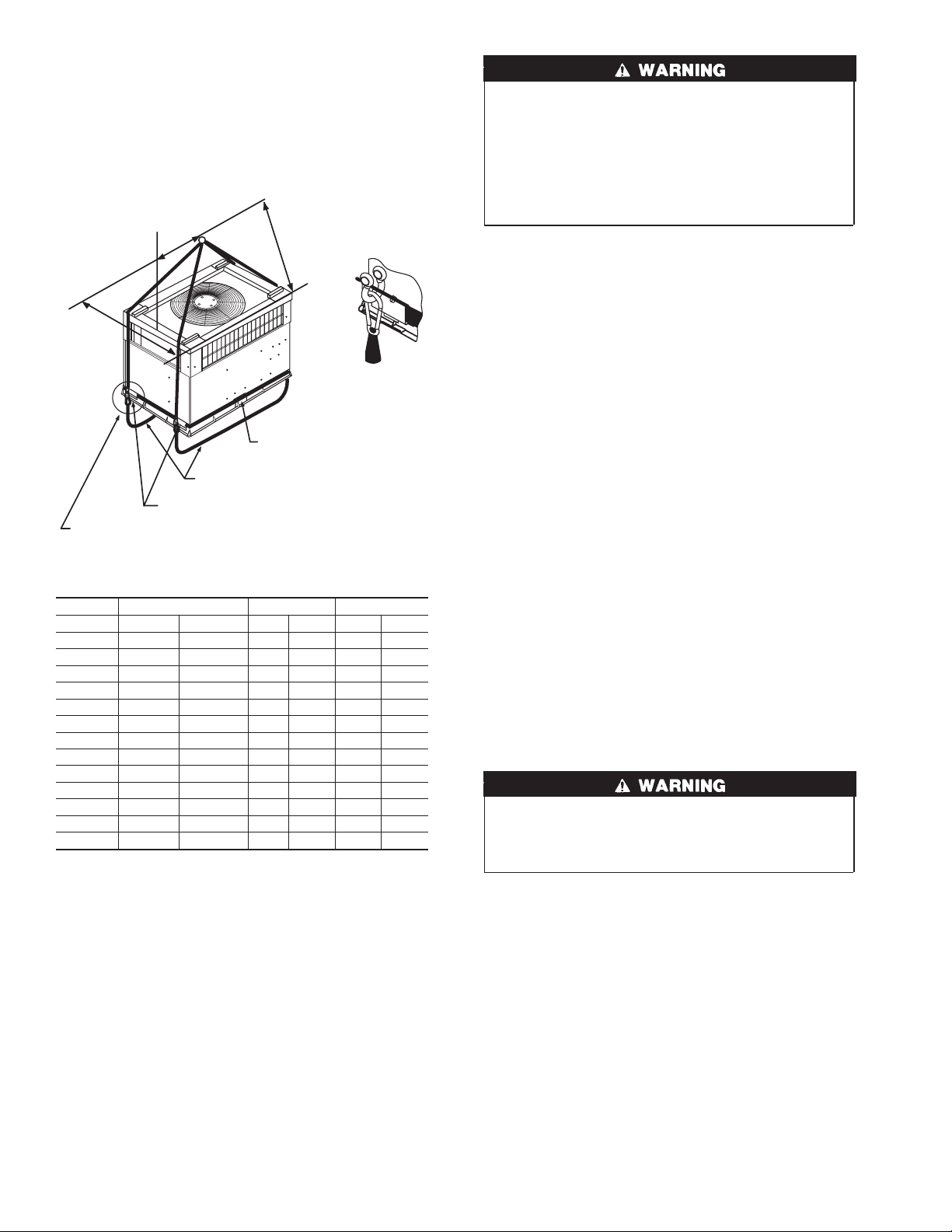
5. Tighten the tension buckle until it is taut. Lifting brackets
must be secure in the handholds.
6. Attach field-supplied clevis or hook of sufficient strength to
hole in the lifting bracket (See Fig. 8).
7. Attach the 2 safety straps directly to the clevis or hook at the
4 rigging brackets. DO NOT attach the safety straps to the
lifting brackets (See Fig. 8).
914-137"
“A”
“B”
INSTALL SAFETY STRAPS TO
RIGGING CLEVIS AT 4 RIGGING BRACKETS
PLACE RIGGING BRACKET ASSEMBLY IN 4
HAND HOLES AND INSTALL TIE DOWN STRAP
AROUND PERIMETER OF UNIT AND THROUGH
SEE DETAIL A
UNIT MAXIMUM WEIGHT A B
Size lb. kg. in. mm. in. mm.
50JS018 305 138.4 19.5 495.3 16.75 425.5
50JS024 311 141.1 18.5 469.9 16.75 425.5
50JS030 309 140.2 19.5 495.3 17.50 444.5
50JS036 313 142.0 19.5 495.3 17.75 450.9
50JS042 345 156.4 19.5 495.3 17.75 450.9
50JS048 375 170.1 20.5 520.7 20.62 523.8
50JS060 440 199.6 19.5 495.3 19.75 501.7
50JX024 321 145.6 19.0 482.6 18.25 463.6
50JX030 342 155.2 20.0 508 19.25 489
50JX036 350 158.8 20.0 508 19.0 482.6
50JX042 372 168.8 21.0 533.4 20.5 520.7
50JX048 377 171.0 20.0 508 21.25 539.8
50JX060 450 204.2 21.0 533.4 20.0 508.0
SPACE IN BRACKET ASSEMBLY
(36"-54")
SCALE 0.250
TIGHTEN STRAPPING SECURELY
WITH TENSION BUCKLE
DETAIL A
C99075
Fig. 8—Suggested Rigging
For vertical supply and return units, tools or parts could drop
into ductwork and cause serious injury or death. Install a 90
degree turn in the return ductwork between the unit and the
conditioned space. If a 90 degree elbow cannot be installed,
then a grille of sufficient strength and density should be
installed to prevent objects from falling into the conditioned
space. Units with electric heaters require 90 degree elbow in
supply duct.
1. All units should have field-supplied filters or accessory filter
rack installed in the return-air side of the unit. Recommended
sizes for filters are shown in Tables 1A and 1B.
2. Avoid abrupt duct size increases and reductions. Abrupt
change in duct size adversely affects air performance.
IMPORTANT: Use flexible connectors between ductwork and
unit to prevent transmission of vibration. Use suitable gaskets to
ensure weather tight and airtight seal. When electric heat is
installed, use fireproof canvas (or similar heat resistant material)
connector between ductwork and unit discharge connection. If
flexible duct is used, insert a sheet metal sleeve inside duct. Heat
resistant duct connector (or sheet metal sleeve) must extend 24-in.
from electric heater element.
3. Size ductwork for cooling air quantity (cfm). The minimum
air quantity for proper electric heater operation is listed in
Tables 2A and 2B. Heater limit switches may trip at air
quantities below those recommended.
4. Seal, insulate and weatherproof all external ductwork. Seal,
insulate and cover with a vapor barrier all ductwork passing
through conditioned spaces. Follow latest Sheet Metal and Air
Conditioning Contractors National Association (SMACNA)
and Air Conditioning Contractors Association (ACCA) minimum installation standards for residential heating and air
conditioning systems.
5. Secure all ducts to building structure. Flash,weatherproof, and
vibration-isolate duct openings in wall or roof according to
good construction practices.
CONVERTING HORIZONTAL DISCHARGE UNITS TO
DOWNFLOW (VERTICAL) DISCHARGE UNITS
Before performing service or maintenance operations on
system, turn offmain power to unit. Turnoff accessory heater
power switch if applicable. Electrical shock could cause
serious injury or death.
8. Position lifting point directly over the unit’s center of gravity.
9. Lift unit. When unit is directly over the roof curb, remove the
2 safety straps. Lower the equipment onto the roof curb.
Step 5—Select and Install Ductwork
The design and installation of the duct system must be in
accordance with the standards of the NFPA for installation of
non-residence type air conditioning andventilating systems,NFPA
90A or residence-type, NFPA 90B and/or local codes and ordinances.
Select and sizeductwork, supply-air registers, and return air grilles
according to ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air Conditioning Engineers) recommendations.
The unit hasduct flanges on the supply- and return-airopenings on
the side of the unit.
When designing and installing ductwork, consider the following:
1. Open all electrical disconnects before starting any service
work.
2. Remove side duct covers to access bottom return and supply
knock outs.
3. Use a screwdriver and hammer to remove the panels in the
bottom of the base pan.
4. Reinstall the side duct covers to block off the horizontal air
openings.
NOTE: These panels are held in place with tabs similar to an
electrical knockout.
NOTE: Avoid abrupt duct size increases and reductions. Abrupt
change in duct size adversely affects air performance.
Step 6—Provide for Condensate Disposal
NOTE: Ensure that condensate-water disposal methods comply
with local codes, restrictions, and practices.
6
Page 7
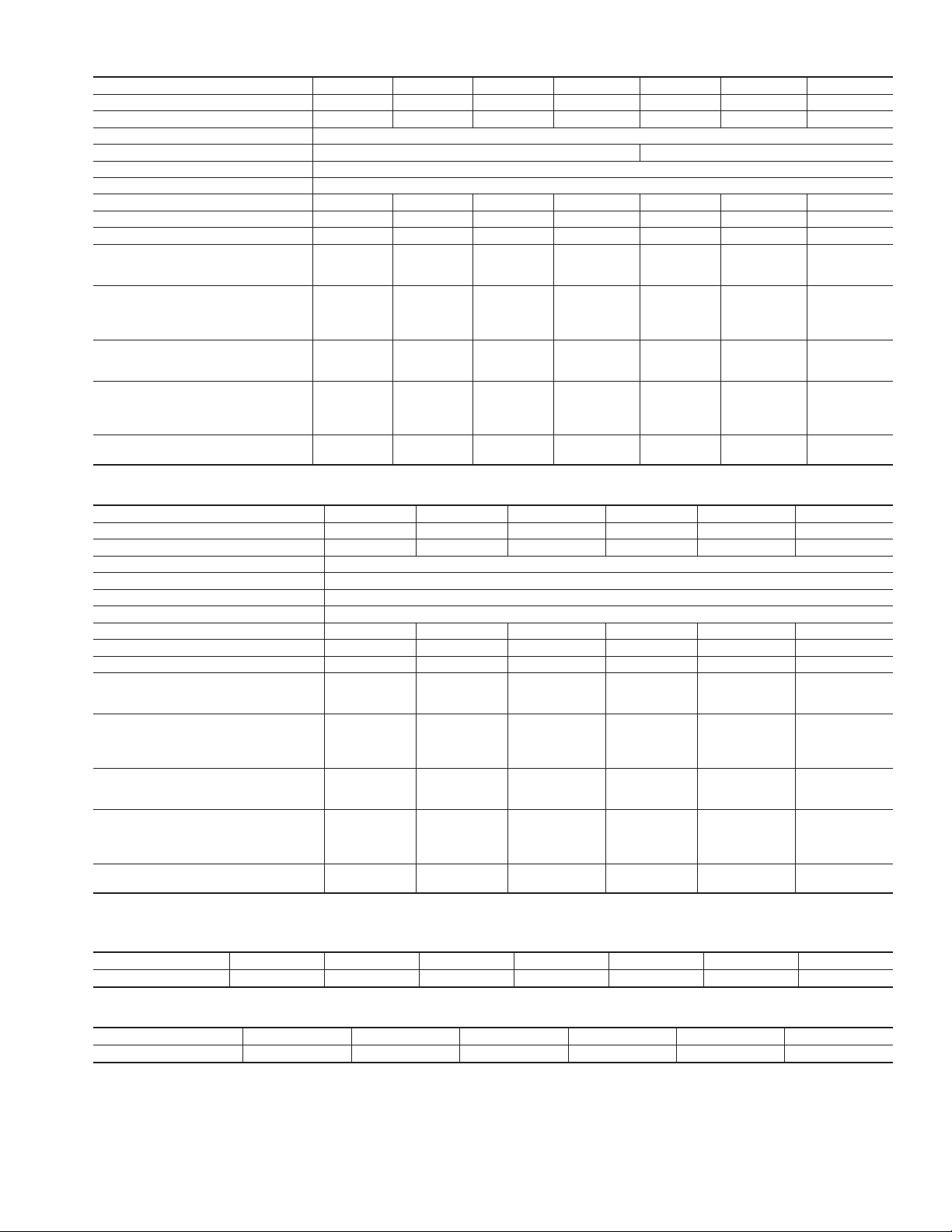
Table 1A—Physical Data
UNIT SIZE 50JS018 50JS024 50JS030 50JS036 50JS042 50JS048 50JS060
NOMINAL CAPACITY (ton) 1-1/2 2 2-1/2 2-1/2 3-1/2 4 5
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb) 283 289 287 291 323 353 418
COMPRESSOR QUANTITY 1
TYPE RECIPROCATING COMPRESSOR SCROLL COMPRESSOR
REFRIGERANT R-22
REFRIGERANT METERING DEVICE Accurater ®
Refrigerant (R-22) Quantity (lb.) 5.6 5.2 5.8 7.1 7.6 7.8 8.6
ORIFICE ID (in.) 0.053 0.061 0.068 0.078 0.078 0.088 0.093
ORIFICE OD (in.) 0.040 0.049 2@0.042 2@0.046 2@0.052 2@0.057 2@0.061
OUTDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Face Area (sq ft)
OUTDOOR FAN
Nominal Airflow (CFM)
Diameter
Motor HP (RPM)
INDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Face Area (Sq Ft)
INDOOR BLOWER
Nominal Airflow (CFM)
Size (in.)
Motor (HP)
RETURN-AIR FILTERS (in.)
Throwaway
1....17
10.2
2400
22
1/8 (825)
2....15
3.7
700
10x10
1/8
20x20x1 20x20x1 20x20x1 20x24x1 24x30x1 24x30x1 24x30x1
1....17
12.0
2400
22
1/8 (825)
2....15
3.7
800
10x10
1/4
1....17
12.0
2400
22
1/8 (825)
3....15
3.7
1000
11x10
1/4
2....17
10.3
2800
22
1/4 (1100)
3....15
3.7
1200
11x10
1/2
2....17
10.3
2400
22
1/8 (825)
4....15
3.7
1250
11x10
3/4
2....17
11.6
3300
22
1/4 (1100)
3....15
4.7
1600
11x10
3/4
Table 1B—Physical Data
UNIT SIZE 50JX024 50JX030 50JX036 50JX042 50JX048 50JX060
NOMINAL CAPACITY (ton) 2 2 1/2 3 3-1/2 4 5
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb) 299 320 328 350 355 420
COMPRESSOR QUANTITY 1
TYPE SCROLL COMPRESSOR
REFRIGERANT R-22
REFRIGERANT METERING DEVICE Accurater ®
Refrigerant (R-22) Quantity (lb.) 5.5 6.4 7.0 10.8 10.4 12.3
ORIFICE ID (in.) 0.065 0.073 0.076 0.080 0.088 0.0.93
ORIFICE OD (in.) 0.055 0.065 0.067 2@0.052 2@0.057 2@0.063
OUTDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Face Area (sq ft)
OUTDOOR FAN
Nominal Airflow (CFM)
Diameter
Motor HP (RPM)
INDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Face Area (Sq Ft)
INDOOR BLOWER
Nominal Airflow (CFM)
Size (in.)
Motor (HP)
RETURN-AIR FILTERS (in.)
Throwaway
NOTE: Air filter pressure drop for non-standard filters must not exceed 0.08 in. wg.
1...17
14.6
2350
22
1/8 (825)
3...15
3.7
800
10x10
1/4
20x20x1 20x20x1 20x24x1 24x30x1 24x30x1 24x30x1
2...17
10.9
2350
22
1/8 (825)
3...15
3.7
1000
11x10
1/4
2...17
10.9
2800
22
1/4 (1100)
4...15
3.7
1200
11x10
1/2
2...17
14.4
2800
22
1/8 (825)
4..15
4.7
1400
11x10
3/4
2...17
14.4
3300
22
1/4 (1100)
4...15
4.7
1600
11x10
3/4
2....17
11.6
3300
22
1/4 (1100)
4....15
4.7
2000
11x10
1
2...17
16.4
3300
22
1/4 (1100)
4...15
5.7
2000
11x10
1
Table 2A—Minimum Airflow for Reliable Electric Heater Operation (Cfm)
SIZE 50JS018 50JS024 50JS030 50JS036 50JS042 50JS048 50JS060
AIRFLOW (CFM) 650 800 1000* 1200 1400 1600 2000
Table 2B—Minimum Airflow for Reliable Electric Heater Operation (Cfm)
SIZE 50JX024 50JX030 50JX036 50JX042 50JX048 50JX060
AIRFLOW (CFM) 800 1000* 1200 1400 1600 2000
* The 030 size models must be run on medium or high speed when used in conjunction with 15 Kw electric heat accessory.
7
Page 8
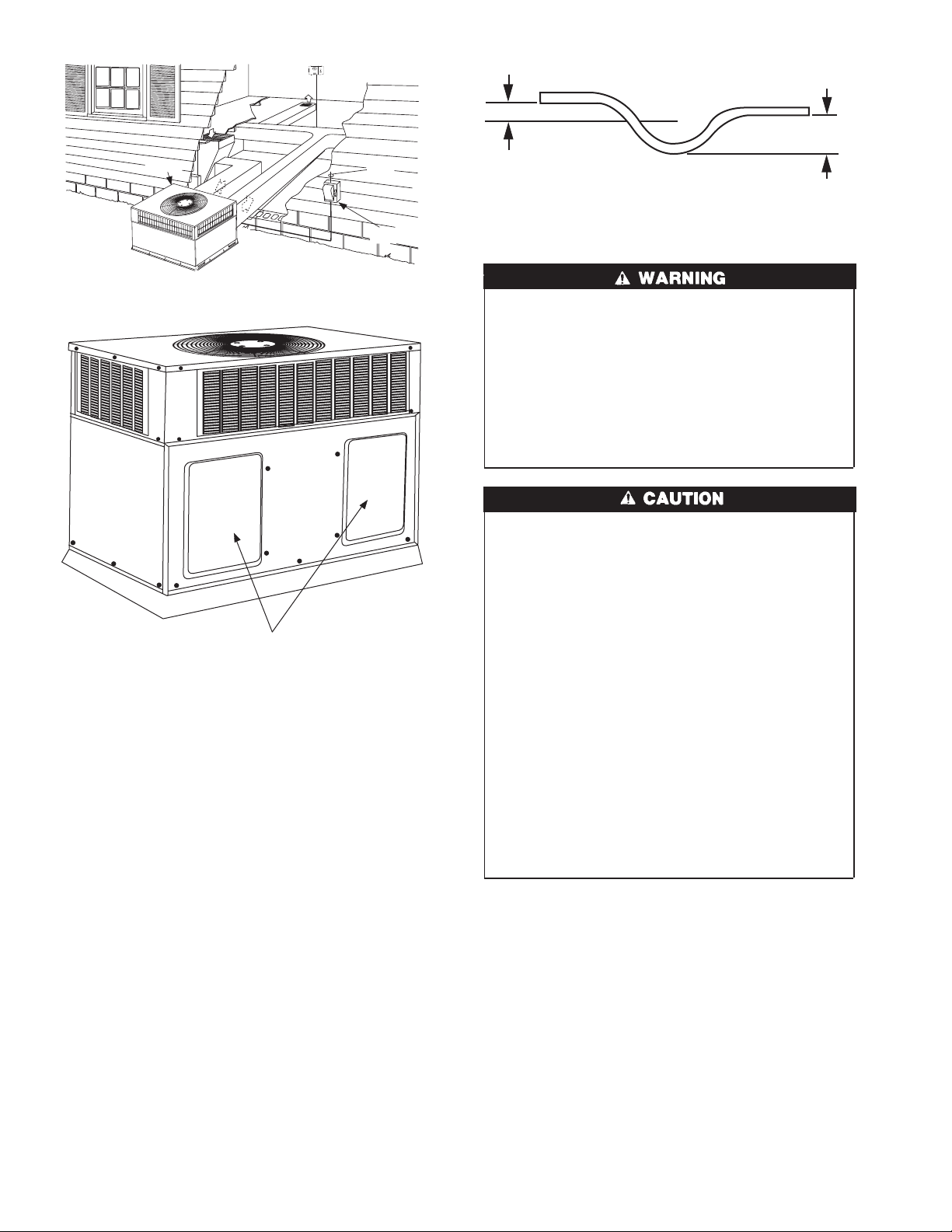
RETURN
AIR
INDOOR
THERMOSTAT
1” MIN.
TRAP
OUTLET
2” MIN.
TOP COVER
FROM
POWER
SOURCE
DISCONNECT
PER NEC
C99061
Fig. 9—Typical Installation
Accessory Duct Covers
C99030
Fig. 10—50JX with Duct Covers On
(Unit shown with optional louvered grille)
The units dispose of condensate through a 3/4 in. NPT female
fitting that exits on the compressor end of the unit. Condensate
water can be drained directly onto the roof in rooftop installations
(where permitted) or onto a gravel apron in ground level installations. Install a field-supplied condensate trap at end of condensate
connection to ensure proper drainage. Make sure that the outlet of
the trap is at least 1 in. lower than the drain-pan condensate
connection to prevent the pan from overflowing. Prime the trap
with water. When using a gravel apron, make sure it slopes away
from the unit.
If the installation requires draining the condensate water away
from the unit, install a field-supplied 2 -in. trap at the condensate
connection to ensure proper drainage. Condensate trap is available
as an accessory oris field-supplied.Make surethat theoutlet ofthe
trap is at least 1 in. lower than the unit drain-pan condensate
connection to prevent the pan from overflowing. Connect a drain
trough using a minimum of field-supplied 3/4 -in. PVC or
field-supplied 3/4 -in. copper pipe at outlet end of the 2 -in. trap
(See Fig. 11). Do not undersize the tube. Pitch the drain trough
downward at a slope of at least 1 in. every 10 ft of horizontal run.
Be sure to check the drain trough for leaks. Prime the trap at the
beginning of the cooling season start-up.
C99013
Fig. 11—Condensate Trap
Step 7—Install Electrical Connections
The unit cabinet must have an uninterrupted, unbroken
electrical ground to minimize the possibility of personal
injury if an electrical fault should occur. This ground may
consist of an electrical wire connected to the unit ground lug
in the control compartment, or conduit approved for electrical
ground when installed in accordance with NEC, ANSI/NFPA
American National Standards Institute/National Fire Protection Association (latest edition) (in Canada, Canadian Electrical Code CSA C22.1) and local electrical codes. Failure to
adhere to this warning could result in serious injury or death.
Failure to follow these precautions could result in damage to
the unit being installed:
1. Make all electrical connections in accordance with NEC
ANSI/NFPA (latest edition) and local electrical codes
governing such wiring. In Canada, all electrical connections must be in accordance with CSA standard C22.1
Canadian Electrical Code Part 1 and applicable local
codes. Refer to unit wiring diagram.
2. Use only copper conductor for connections between
field-supplied electrical disconnect switch and unit. DO
NOT USE ALUMINUM WIRE.
3. Be sure that high-voltage power to unit is within operating
voltage range indicated on unit rating plate. On 3-phase
units, ensure phases are balanced within 2%. Consult local
power company for correction of improper voltage and/or
phase imbalance.
4. Insulate low-voltage wires for highest voltage contained
within conduit when low-voltage control wires are in same
conduit as high-voltage wires.
5. Do not damage internal components when drilling through
any panel to mount electrical hardware, conduit, etc.
HIGH-VOLTAGE CONNECTIONS — The unit must have a
separate electrical service with a field-supplied, waterproof disconnect switch mounted at, or within sight from the unit. Refer to
the unit rating plate, NEC and local codes for maximum
fuse/circuit breaker size and minimum circuit amps (ampacity) for
wire sizing (See Tables 3A and 3B for electrical data).
The field-supplied disconnectmay be mounted on theunit over the
high-voltage inlet hole (See Figs. 2-3).
If the unit has an electric heater, a second disconnect may be
required. Consult the Installation, Start-Up and Service Instructions provided with the accessory for electrical service connections.
Operation of unit on improper line voltage constitutes abuse and
may cause unit damage that could affect warranty.
ROUTING POWER LEADS INTO UNIT — Use only copper
wire between disconnect and unit. The high-voltage leads should
8
Page 9
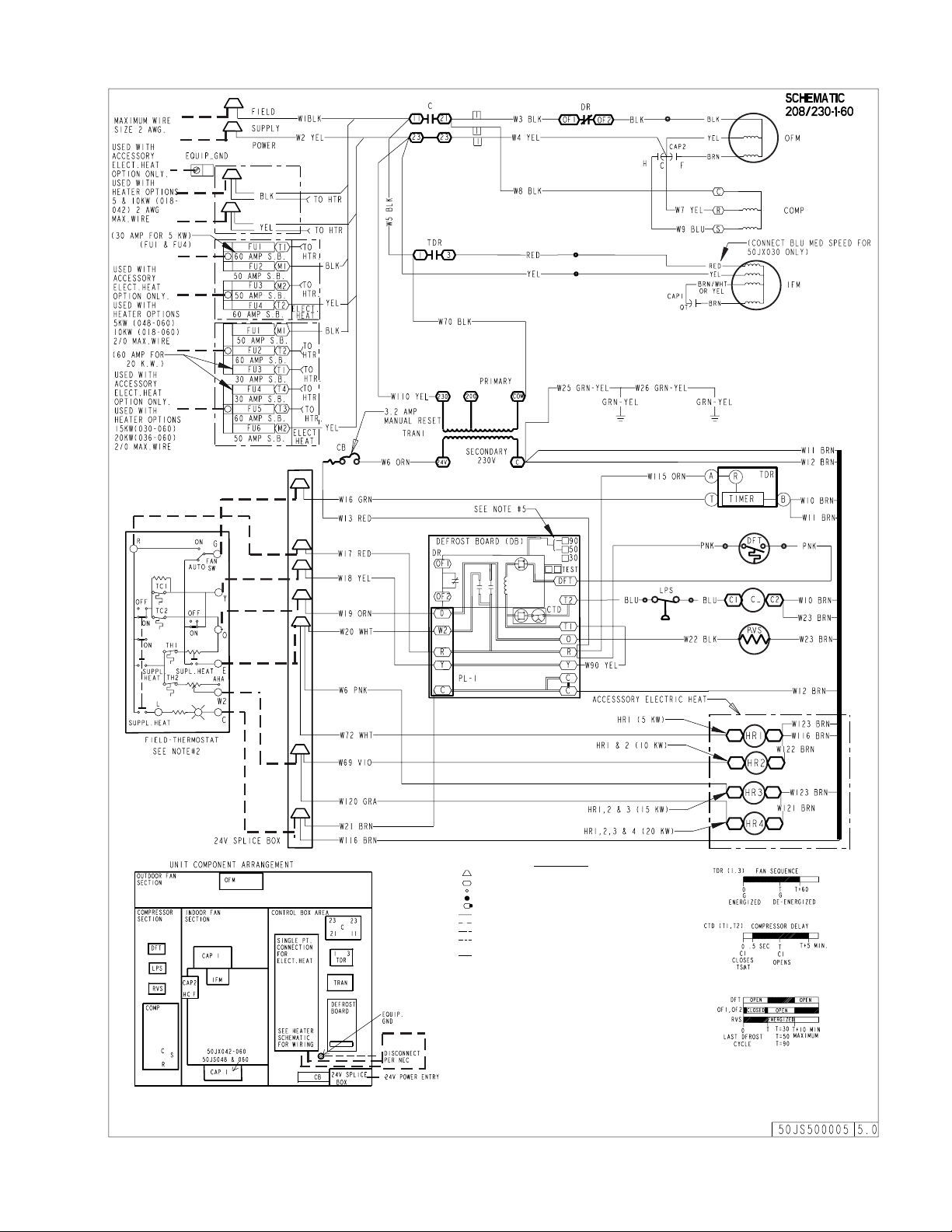
FIELD SPLICE
TERMINAL (MARKED)
TERMINAL (UNMARKED)
SPLICE
SPLICE (MARKED)
FACT OR Y WIRING
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FIELD POWER WIRING
ACCESSORY OR OPTIONAL
WIRING
TO INDICATE COMMON
POTENTIAL ONLY:
NOT TO REPRESENT WIRING
NOTES:
1. IF ANY OF THE ORIGINAL WIRES FURNISHED ARE REPLACED, IT MUST BE
REPLACED WITH TYPE 90 DEGREE C WIRE OR IT’S EQUIVALENT.
2. SEE PRICE PAGES FOR THERMOSTAT AND SUBBASES.
3. USE 75 DEGREE COPPER CONDUCTORS FOR FIELD INSTALLATION.
4. FOR HIGH SPEED IFM, DISCONNECT RED
WIRE FROM TDR 3 AND CONNECT BLK WIRE FROM IFM.
FOR MEDIUM SPEED, DISCONNECT RED WIRE
FROM TDR 3 AND CONNECT BLU WIRE FROM IFM.
5. DEFROST TIMER TO BE SET AT 90 MINUTES EXCEPT FOR 50JS048, 060 MODELS
SET AT 50 MINUTES.
LEGEND
AHA ADJUSTABLE HEAT ANTICIPATOR
C CONTACTOR
CAP CAPACITOR
CB CIRCUIT BREAKER
COMP COMPRESSOR MOTOR
CTD COMPRESSOR TIME DELA Y
DB DEFROST BOARD
DFT DEFROST THERMOST AT
DR DEFROST RELAY
EQUIP EQUIPMENT
FU FUSE
GND GROUND
HR HEATER RELAY
HTR HEATER
IFM INDOOR FAN MOTOR
LPS LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
OFM OUTDOOR FAN MOTOR
QT QUADRUPLE TERMINAL
RVS REVERSING VALVE SOLENOID
S.B. SLOW BLOW FUSE
TC THERMOSTAT - COOLING
TDR TIME DELAY RELAY
TH THERMOSTAT - HEATING
TRAN TRANSFORMER
Fig. 12—Wiring Schematics
9
A00073
Page 10

Fig. 13—Wiring Schematics
A00074
Page 11

LEGEND
FIELD SPLICE
TERMINAL (MARKED)
TERMINAL (UNMARKED)
SPLICE
SPLICE (MARKED)
FACT OR Y WIRING
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FIELD POWER WIRING
ACCESSORY OR OPTIONAL
WIRING
TO INDICATE COMMON
POTENTIAL ONLY:
NOT TO REPRESENT WIRING
NOTES:
1. IF ANY OF THE ORIGINAL WIRES FURNISHED ARE REPLACED, IT MUST BE
REPLACED WITH TYPE 90 DEGREE C WIRE OR IT’S EQUIVALENT.
2. SEE PRICE PAGES FOR THERMOSTAT AND SUBBASES.
3. USE 75 DEGREE COPPER CONDUCTORS FOR FIELD INSTALLATION.
4. FOR HIGH SPEED IFM, DISCONNECT RED
WIRE FROM TDR 3 AND CONNECT BLK WIRE FROM IFM.
FOR MEDIUM SPEED, DISCONNECT RED WIRE
FROM TDR 3 AND CONNECT BLU WIRE FROM IFM.
5. DEFROST TIMER TO BE SET AT 90 MINUTES EXCEPT FOR 50JS048, 060 MODELS
SET AT 50 MINUTES.
Fig. 14—Wiring Schematics
11
AHA ADJUSTABLE HEAT ANTICIPATOR
C CONTACTOR
CAP CAPACITOR
CB CIRCUIT BREAKER
COMP COMPRESSOR MOTOR
CTD COMPRESSOR TIME DELA Y
DB DEFROST BOARD
DFT DEFROST THERMOST AT
DR DEFROST RELAY
EQUIP EQUIPMENT
GND GROUND
HR HEATER RELAY
HTR HEATER
IFM INDOOR FAN MOTOR
LPS LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
OFM OUTDOOR FAN MOTOR
OFR OUTDOOR FAN RELAY
QT QUADRUPLE TERMINAL
RVS REVERSING VALVE SOLENOID
TC THERMOSTAT - COOLING
TDR TIME DELAY RELAY
TH THERMOSTAT - HEATING
TRAN TRANSFORMER
A00075
Page 12

Table 3A—Electrical Data—50JS
UNIT 50JS
SIZE
018 208/230-1-60 187 253 9 48 0.9 1.8
024 208/230-1-60 187 253 12.8 61 0.9 2
030
036
042
048
060
* Heater capacity (KW) based on heater voltage of 208v, 240v, and 480v. If power distribution voltage to unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater KW will vary
accordingly.
V-PH-HZ
208/230-1-60 187 253 14.7 82 0.9 2
208/230-3-60 187 253 9.9 78 0.9 2
208/230-1-60 187 253 16.8 82 1.5 4.1
208/230-3-60 187 253 9.9 85 1.5 4.1
460-3-60 414 506 5.5 40 0.8 1.9
208/230-1-60 187 253 20.6 115 0.9 3.8
208/230-3-60 187 253 12.4 90 0.9 3.8
460-3-60 414 506 6.7 45 0.8 1.8
208/230-1-60 187 253 24.4 140 1.5 3.5
208/230-3-60 187 253 14.1 105 1.5 3.5
460-3-60 414 506 7.1 53 0.8 1.8
208/230-1-60 187 253 28.8 165 1.5 6.2
208/230-3-60 187 253 19.4 125 1.5 6.2
460-3-60 414 506 8 63 0.8 3.2
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA FLA FLA Nominal KW* FLA MCA Max Fuse or CRCT Breaker MOCP
COMPRESSOR ODFM IDFM ELECTRIC HEAT POWER SUPPLY
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
-/5
10
15
-/5
10
15
20
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
15/19.94
-/5
10
15
15-20
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
15/20
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
15/19.94
-/5
10
15
20
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
15/20
-/-
3.8/5
7.5/10
11.3/15
15/19.94
-/5
10
15
20
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
-/-
10.4/12
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
-/-
10.4/12
31.3/36.1
36.1/41.7
-/-
6.0
12.0
18.0
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
72.2/83.3
-/-
10.4/12
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
41.6/48
-/-
6.0
12.0
18.0
24.1
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
72.2/83.3
-/-
10.4/12
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
41.6/48.0
-
6.0
12.0
18.0
24.1
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
72.2/83.3
-/-
10.4/12
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
41.6/48.0
-
6.0
12.0
18.0
24.1
14.0/14.0
24.8/28.3
47.4/54.3
18.9/18.9
25.1/28.5
47.6/54.6
21.3/21.3
25.1/28.5
47.6/54.6
72.8/83.3
15.3/15.3
15.5/17.5
28.6/32.6
44.2/50.2
26.6/26.6
27.7/31.2
50.3/57.2
72.8/83.3
18.0/18.0
18.2/20.2
44.2/50.2
47.8/54.7
9.6
9.9
17.4
24.9
30.5/30.5
30.5/30.8
49.9/56.8
72.4/82.9
95.0/108.9
20.2/20.2
20.2/20.2
30.8/34.8
43.8/49.9
56.7/64.7
11.0
11.0
17.3
24.8
32.3
35.5/35.5
35.5/35.5
49.5/56.5
72.1/82.5
94.6/108.5
22.6/22.6
22.6/22.6
30.4/34.4
43.5/49.5
56.3/64.3
11.5
11.5
17.3
24.8
32.3
43.7/43.7
43.7/43.7
52.9/59.8
75.4/85.9
98.0/111.9
32.0/32.0
32.0/32.0
33.8/37.8
46.8/52.9
59.7/67.7
14.0
14.0
19.0
26.6
34.1
20/20
25/25
50/60
25/25
25/30
50/60
25/25
25/30
50/60
-
20/20
20/20
30/35
45/60
35/35
35/35
60/60
-
25/25
25/25
35/40
45/60
15
15
20
25
40/40
40/40
50/60
-
-
25/25
25/25
35/35
45/50
-
15
15
20
25
35
45/45
45/45
50/60
-
-
30/30
30/30
35/35
45/50
-
15
15
20
25
35
60/60
60/60
60/60
-
-
40/40
40/40
35/40
50/60
-
20
20
20
30
35
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
80/90
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
80/90
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
90.0
100/110
-
-
-
-
60/70
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
90.0
100/110
-
-
-
-
60/70
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
90.0
100/125
-
-
-
-
60/70
-
-
-
-
-
12
Page 13

→Table 3B—Electrical Data—50JX
UNIT 50JX
SIZE
024 208/230-1-60 187 253.00 10.8 56 0.90 2
030
036
042
048
060
* Heater capacity (KW) based on heater voltage of 208v, 240v, and 480v. If power distribution voltage to unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater KW will vary
accordingly.
V-PH-HZ
208/230-1-60 187 253 14 73 0.9 2.1
208/230-3-60 187 253 10.3 63 0.9 2.1
208/230-1-60 187 253 16.7 97 1.6 3.6
208/230-3-60 187 253 11.9 75 1.6 3.6
460-3-60 414 506 5.4 37.5 0.9 1.9
208/230-1-60 187 253 18.4 104 0.9 4.1
208/230-3-60 187 253 12.4 88 0.9 4.1
460-3-60 414 506 5.8 44 0.9 2.0
208/230-1-60 187 253 23.4 104 1.6 4.1
208/230-3-60 187 253 13.5 88 1.6 4.1
460-3-60 414 506 6.8 44 0.9 2
208/230-1-60 187 253 28.8 169 1.4 6.2
208/230-3-60 187 253 17.3 123 1.4 6.2
460-3-60 414 506 9 62 0.9 3.2
VOLTAGE
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA FLA FLA Nominal KW* FLA MCA Max Fuse or CRCT Breaker MOCP
COMPRESSOR ODFM IDFM ELECTRIC HEAT POWER SUPPLY
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
--/5
10
15
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
15.0/20.0
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
15.0/20.0
-/5
10
15
20
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
15.0/20.0
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
15.0/20.0
-/5
10
15
20
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
15.0/20.0
-/-
3.75/5.0
7.5/10
11.3/15
15.0/20.0
-/5
10
15
20
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
-/-
10.4/12.0
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
-/-
10.4/12.0
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
--/6
12
18
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
72.2/83.3
-/-
10.4/12.0
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
41.6/48.0
-/6
12
18
24
-/-
18.1/20
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
72.2/83.8
-/-
10.4/12.0
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
41.6/48
-/6
12
18
24
-/-
18.1/20.8
36.1/41.7
54.2/62.5
72.2/83.3
-/-
10.4/12.0
20.8/24.1
31.3/36.1
41.6/48.0
-/6
12
18
24
16.4/16.4
25.1/28.5
47.6/54.6
20.5/20.5
25.2/28.7
47.8/54.7
72.2/82.6
16.0/16.0
16.0/17.7
28.7/32.7
41.7/47.7
26.1/26.1
27.1/30.5
49.6/56.6
72.2/82.6
19.2/19.2
19.2/19.5
47.8/54.7
43.6/49.6
9.6
9.9
17.4
24.9
28.0/28.0
28.0/31.2
50.3/57.2
72.8/83.3
95.4/109.3
20.5/20.5
20.5/20.5
31.2/35.2
44.2/50.2
57.1/65.1
10.2
10.2
17.5
25.1
32.6
35.0/35.0
35.0/35.0
50.3/57.2
72.8/83.3
95.4/109.3
22.6/22.6
22.6/22.6
31.2/35.2
44.2/50.2
57.1/65.1
11.4
11.4
17.5
25.1
32.6
43.6/43.6
43.6/43.6
52.9/59.8
75.4/85.9
98.0/111.9
29.2/29.2
29.2/29.2
33.8/37.8
46.8/52.9
59.7/67.7
15.4
15.4
19.0
26.6
34.1
20/20
25/30
50/60
25/25
25/30
50/60
-
20/20
20/20
30/35
45/50
35/35
35/35
50/60
-
25/25
25/25
35/35
45/50
15
15
20
25
35/35
35/35
60/60
-
-
25/25
25/25
35/40
45/60
-
15
15
20
30
35
45/45
45/45
60/60
-
-
30/30
30/30
35/40
45/60
-
15
15
20
30
35
60/60
60/60
60/60
-
-
35/35
35/35
35/40
50/60
-
20
20
20
30
35
-
-
-
-
-
-
80/90
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
80/90
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
90.0
100/110
-
-
-
-
60/70
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
90.0
100/110
-
-
-
-
60/70
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
90.0
100/125
-
-
-
-
60/70
-
-
-
-
-
13
Page 14

LEGEND
FLA — Full Load Amps
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum CircuitAmps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
RLA — Rated Load Amps
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements
for multimotor and combination load equipment (refer to NEC
Articles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective device for the
unit shall be Power Supply fuse. The CGA (Canadian Gas
Association) units may be fuse or circuit breaker.
2. Minimum wire size is based on 60 C copper wire. If other than
60 C wire is used, or if length exceeds wire length in table,
determine size from NEC.
3. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than 2%.
the percentage of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage imbalance
max voltage deviation from average voltage
= 100 x
Use the following formula to determine
average voltage
®
Fig. 15—Electrical Data Legend
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457
(BC) 464
(AC) 457
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the
maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is
more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company
immediately.
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
452=5v
457=7v
455=2v
= 1.53%
7
457
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
C99024
be in a conduit until they enter the duct panel; conduit termination
at the duct panel must be watertight. Run the high-voltage leads
through the power entry knockout on the power entry side panel
(See Fig. 2 and 3 for location and size). When the leads are inside
the unit, run leads up the high-voltage raceway to the line wiring
splice box (See Fig. 12 through 14). For single-phase units,
connect leads to the black and yellow wires; for 3-phase units,
connect the leads to the black, yellow, and blue wires (See Fig.
17).
C
O
R
G
Y
E
W2
THERMOSTAT
AND SUBBASE
UNIT CONTROL POWER
BRN
ORN
RED
GRN
YEL
WHT
SPLICE BOX
C99056
Fig. 16—Control Connections
CONNECTING GROUND LEAD TO GROUND LUG — Refer
to Fig. 17. Connect the ground lead to the chassis using the ground
lug in the wiring splice box.
ROUTING CONTROL POWER WIRES — (24 V) — Form a
drip-loop with the thermostat leads before routing them into the
unit. Route the thermostat leads through grommeted, low-voltage
hole provided in unit into unit control power splice box (See Fig.
2 and 3). Connect thermostat leads to unit control power leads as
shown in Fig. 16.
The unit transformer supplies 24-v power for complete system
including accessory electrical heater. An automatic-reset circuit
breaker (See Fig. 18)is provided inthe 24-vcircuit; seethe caution
label on the transformer or Fig. 19. Transformer is factory wired
for 230-v operation. If supply voltage is 208 v, rewire transformer
primary as described in Special Procedures for 208-V Operation
section.
GROUND LUG
(IN SLPICE BOX)
GROUND
LEAD
SINGLE-PHASE
L1
CONNECTIONS
TO DISCONNECT
PER NEC
3-PHASE
CONNECTIONS
LEGEND
L2
L3
NOTE: Use copper wire only.
NEC – National Electrical Code
Field Wiring
Splice Connections
Fig. 17—Line Power Connections
BLK
YEL
BLU
C99057
24 V Circuit Breaker
24 V olt Compartment
C99070
Fig. 18—Control Wiring Plate
14
Page 15

TRANSFORMER CONTAINS A MANUAL
RESET OVERCURRENT PROTECTOR
IT WILL NOT AUTOMATICALLY RESET
DISCONNECT POWER PRIOR TO
SERVICING
THIS COMPARTMENT MUST BE CLOSED
EXCEPT WHEN SERVICING
Fig. 19—Transformer Label
C99058
SPECIAL PROCEDURES FOR 208-V OPERATION
1. Disconnect the yellow primary lead (w110) from the transformer. See unit wiring label (See Fig. 12 through 14).
2. Connect the yellow primary lead (w110) to the transformer
terminal labeled 200v.
Indoor blower-motor speeds may need to be changed for 208-v
operation. Refer to indoor airflow and airflow adjustments section.
PRE-START-UP
Failure to observe the following warnings could result in
serious personal injury or death:
1. Follow recognized safety practices and wear protective
goggles when checking or servicing refrigerant system.
2. Do not operate compressor or provideany electric power to
unit unless compressor terminal cover is in place and
secured.
3. Do not remove compressor terminal cover until all electrical sources are disconnected.
4. Relieve and recover all refrigerant from system before
touching or disturbing anything inside terminal box if
refrigerant leak is suspected around compressor terminals.
5. Never attempt to repair soldered connection while refrigerant system is under pressure.
6. Do not use torch to remove any component. System
contains oil and refrigerant under pressure.
To remove a component, wear protective goggles and
proceed as follows:
a. Shut off electrical power to unit.
b. Relieve and reclaim all refrigerant from system using
both high- and low-pressure ports.
c. Cut component connecting tubing with tubing cutter and
remove component from unit.
d. Carefully unsweat remaining tubing stubs when neces-
sary. Oil can ignite when exposed to torch flame.
Use the Start-Up Checklist supplied at the end of this book and
proceed as follows to inspect and prepare the unit for initial
start-up:
1. Remove access panel.
2. Read and follow instructions on all DANGER, WARNING,
CAUTION, and INFORMATION labels attached to, or
shipped with, unit.
3. Make the following inspections:
a. Inspect for shipping and handling damages such as broken
lines, loose parts, disconnected wires, etc.
b. Inspect for oil at all refrigerant tubing connections and on
unit base. Detecting oil generally indicates a refrigerant
leak. Leak-test all refrigerant tubing connections using
electronic leak detector, or liquid-soap solution. If a refrigerant leak is detected, see following Check for Refrigerant
Leaks section.
c. Inspect all field and factory-wiring connections. Be sure
that connections are completed and tight.
d. Inspect coil fins. If damaged during shipping and handling,
carefully straighten fins with a fin comb.
4. Verify the following conditions:
a. Make sure that outdoor-fan blade is correctly positioned in
fan orifice.
b. Make sure that condensate drain pan and trap are filled
with water to ensure proper drainage.
c. Make sure that all tools and miscellaneous loose parts have
been removed.
5. Compressors are internally spring mounted. Do not loosen or
remove compressor hold-down bolts.
6. Each unit system has 2 Schrader-type ports, one low-side
Schrader fitting located on the suction line, and one high-side
Schrader fitting located on the compressor discharge line. Be
sure that caps on the ports are tight.
MOTOR
1/8" MAX BETWEEN
MOTORAND FAN HUB
MOTOR SHAFT
FAN GRILLE
C99009
Fig. 20—Fan Blade Clearance
START-UP
Using the Start-Up Checklist supplied at the end of this book,
proceed as follows:
Step 1—Check for Refrigerant Leaks
Locate and repair refrigerant leaks and charge the unit as follows:
1. Use both high- and low-pressure ports to relieve system
pressure and reclaim remaining refrigerant
2. Repair leak following accepted practices.
NOTE: Install a bi-flow filter drier whenever the system has
been opened for repair.
3. Check system for leaks using an approved method.
4. Evacuate refrigerant system and reclaim refrigerant if no
additional leaks are found.
5. Charge unit with R-22 refrigerant, using a volumetriccharging cylinder or accurate scale. Refer to unit rating plate
for required charge. Be sure to add extra refrigerant to
compensate for internal volume of filter drier.
Step 2—Start-Up Adjustments
Complete the required procedures given in the Pre-Start-Up
section on this page before starting the unit. Do not jumper any
safety devices when operating the unit. Do not operate the unit in
Cooling mode when the outdoor temperature is below 40°F (unless
accessory low-ambient kit is installed). Do not rapid-cycle the
compressor. Allow 5 min. between ‘‘on’’ cycles to prevent
compressor damage.
CHECKING COOLING AND HEATING CONTROL OPERATION — Start and check the unit for proper control operation as
follows:
1. Place room thermostat SYSTEM switch in OFF position.
Observe that blower motor starts when FAN switch is placed
in ON position and shuts down within 60 sec. when FAN
switch is placed in AUTO position.
15
Page 16

OUTDOOR COIL
ACCUMULATOR
COMPRESSOR
Metering
Position
Bypass
Position
LCS
INDOOR COIL
LEGEND
LCS – Loss of Charge Switch
Accurater® Metering Device
Arrow indicates direction of flow
C99027
1. Hot gas from compressor flows through the 4-way valve and is directed to the indoor coil. It is then condensed and subcooled through the coil circuits and then leaves
the indoor coil by way of the ID Accurater in the bypass position to the liquid line.
2. The refrigerant then feeds the outdoor coil through the OD Accurater device in the metering position and distributes to each circuit.
3. Each circuit evaporates the refrigerant and the circuits are combined in the outdoor coil header.
4. The refrigerant then flows through the 4-way valve, accumulator, and back to the compressor.
Fig. 21—Typical Heat Pump Operation, Heating Mode
INDOOR COIL
ACCUMULATOR
LEGEND
COMPRESSOR
OUTDOOR COIL
Bypass
Position
Metering
Position
LCS
LCS – Loss of Charge Switch
®
Accurater
Metering Device
Arrow indicates direction of flow
C99028
1. Hot gas from compressor flows through the 4-way valve and is directed to the outdoor coil. It is then condensed and subcooled through the coil circuits. Refrigerant leaves
the outdoor coil by way of the OD Accurater in the bypass position to the liquid line.
2. The refrigerant then feeds the indoor coil through the ID Accurater device in the metering position and distributes to each circuit.
3. Each circuit evaporates the refrigerant and the circuits are combined in the indoor coil header.
4. The refrigerant then flows through the 4-way valve, accumulator, and back to the compressor.
Fig. 22—Typical Heat Pump Operation, Cooling Mode
16
Page 17

Table 4A—Wet Coil Air Delivery
Unit 50JS 018-060 (Deduct 10% for 208v)*
UNIT MOTOR SPEED
Low
018
024
30
36
42
48
60
* Air delivery valuesare basedon operating voltage of 230 v or 460 v,wet coil, without filter or electric heater. Deduct filter and electricheater pressure drops to obtain
static pressure available for ducting.
NOTES:
1. Do not operate the unit at a cooling airflow that is less than 350 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling capacity. Evaporator coil frosting may occur at airflows below
this point.
2. Dashes indicate portions of table that are beyond the blower motor capacity or are not recommended.
3. Deduct 10% for 208v.
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Watts - - - 214 191 170 -----
Cfm---821696575-----
Watts -----------
Cfm-----------
Watts ----283274267----
Cfm----848707555----
Watts - - 237 214 191 ------
Cfm--971821696------
Watts ----368366365360---
Cfm----957872785688---
Watts -------425414--
Cfm-------891735--
Watts 295 292 289 --------
Cfm928882802--------
Watts 388 383 377 372 366 361 -----
Cfm 1203 1120 1062 1004 930 838 -----
Watts ----469458449442---
Cfm----1141 1027 924 828 - - -
Watts 592 581 567 552 538 525 512 499 - - -
Cfm 1499 1421 1351 1281 1207 1125 1034 936 - - -
Watts - - - 660 636 617 603 592 581 566 -
Cfm - - - 1475 1371 1274 1186 1105 1024 928 -
Watts -----776761744725706689
Cfm-----1452 1356 1254 1145 1030 910
Watts 606 596 586 575 563 550 537 - - - -
Cfm 1464 1399 1341 1282 1218 1146 1066 - - - -
Watts 680 665 649 635 622 611 600 590 - - -
Cfm 1608 1535 1461 1387 1316 1247 1180 1111 - - -
Watts 768 755 742 730 718 707 696 684 671 - -
Cfm 1656 1576 1508 1447 1390 1331 1268 1198 1119 - -
Watts 741 724 709 690 664 631 594 562 543 552 -
Cfm 1994 1937 1869 1797 1722 1645 1566 1480 1384 1269 -
Watts - - - 773 744 715 687 662 640 625 -
Cfm - - - 1957 1867 1787 1719 1653 1575 1463 -
Watts -----799782773756704-
Cfm-----1914 1842 1774 1686 1538 -
Watts 742 723 698 666 629 591 559 540 - - -
Cfm 2197 2141 2103 2057 1988 1894 1783 1674 - - -
Watts 838 822 803 780 752 721 689 661 639 632 -
Cfm 2485 2406 2269 2127 2012 1937 1894 1855 1770 1571 -
Watts - 934 913 891 866 837 806 776 750 735 -
Cfm - 2483 2391 2283 2170 2061 1960 1868 1780 1687 -
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (IN. WG)
2. Place SYSTEM switch in COOL position and FAN switch in
AUTO position. Setcontrol below room temperature. Observe
that cooling cycleshuts down when control settingis satisfied.
3. Place system switch in HEAT position. Set control above
room temperature. Observe that compressor, outdoor fan, and
indoor blower motors start. Observe that heating cycle shuts
down when control setting is satisfied.
4. When using an automatic changeover room thermostat, place
both SYSTEM and FAN switches in AUTO positions. Observe that unit operates in Cooling mode when temperature
control is setto ‘‘call for Cooling’’ (below room temperature),
and unit operates in Heating mode when temperature control
is set to "call for Heating" (above room temperature).
IMPORTANT: Three-phase, scroll compressors are direction oriented. Unit must be checked to ensure proper compressor 3-phase
power lead orientation. If not corrected within 5 min., the internal
protector will shut off the compressor. The 3-phase power leads to
the unit must be reversed to correct rotation. When turning
backwards, scroll compressors emit elevated noise levels, and the
difference between compressor suction and discharge pressures
may be dramatically lower than normal.
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING REFRIGERANT CHARGE
— The refrigerant system is fully charged with R-22 refrigerant
and is tested and factory sealed.
NOTE: Adjustment of the refrigerant charge is not required
unless the unit is suspected of not having the proper R-22 charge.
17
Page 18

Table 4B—Wet Coil Air Delivery
Unit 50JX 024-060 (Deduct 10% for 208v)*
UNIT MOTOR SPEED
Low
024
30
36
42
48
60
* Air delivery valuesare basedon operating voltage of 230 v or 460 v,wet coil, without filter or electric heater. Deduct filter and electricheater pressure drops to obtain
static pressure available for ducting.
NOTES:
1. Do not operate the unit at a cooling airflow that is less than 350 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling capacity. Evaporator coil frosting may occur at airflows below
this point.
2. Dashes indicate portions of table that are beyond the blower motor capacity or are not recommended.
3. Deduct 10% for 208v.
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Watts 275 273 271 270 -------
Cfm923844754669-------
Watts - - - 359 353 350 347 341 - - -
Cfm - - - 941 876 814 737 622 - - -
Watts ------447439431423-
Cfm------968869765659-
Watts 276 276 272 --------
Cfm963929781--------
Watts 375 377 371 362 354 350 -----
Cfm 1202 1170 1079 976 884 807 -----
Watts ----469449435428---
Cfm----1174 988 828 718 - - -
Watts 462 451 431 411 394 381 -----
Cfm 1374 1290 1205 1116 1020 916 -----
Watts 523 506 490 471 449 426 -----
Cfm 1500 1408 1301 1190 1082 977 -----
Watts - 645 628 610 595 584 575 ----
Cfm - 1474 1369 1267 1169 1069 962 ----
Watts 620 600 586 574 562 548 530 510 487 462 439
Cfm 1662 1621 1581 1540 1496 1447 1392 1331 1263 1186 1103
Watts ----686661634606577547517
Cfm----1722 1662 1594 1515 1427 1330 1227
Watts -------757730704682
Cfm-------1669 1577 1486 1402
Watts 620 600 586 574 562 548 530 - 487 - -
Cfm 1662 1621 1581 1540 1496 1447 1392 1331 1263 - -
Watts 763 747 729 709 686 661 634 606 577 547 517
Cfm 1917 1868 1822 1774 1722 1662 1594 1515 1427 1330 1227
Watts - - - 852 832 809 784 757 730 704 682
Cfm - - - 1982 1914 1839 1757 1669 1577 1486 1402
Watts 597 592 578 526 460 452 445 ----
Cfm 2265 2190 2101 2033 1974 1869 1614 ----
Watts 754 730 707 687 671 658 646 630 603 558 486
Cfm 2383 2282 2202 2134 2070 2005 1935 1858 1771 1667 1576
Watts 901 876 856 836 813 785 755 723 696 681 687
Cfm 2480 2383 2301 2233 2175 2122 2066 1998 1910 1788 1619
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (IN. WG)
The charging label and the tables shown refer to system temperatures and pressures in cooling mode only. A refrigerant charging
label is attached to the outside of the service access door. If charge
level is suspect in Heating mode, reclaim all refrigerant and charge
to nameplate amount. (This information may be obtained from the
physical data table also.)
IMPORTANT: When evaluating the refrigerant charge, an indicated adjustment to the specified factory charge must always be
very minimal. If a substantial adjustment is indicated, an abnormal
condition exists somewhere in the cooling system, such as insufficient airflow across either coil or both coils.
REFRIGERANT CHARGE — The amount of refrigerant charge
is listed on the unit nameplate and /or the physical data table. Refer
to the Refrigeration Service Techniques Manual, Refrigerants
Section.
NO CHARGE — Check for leak. Use standard evacuating techniques. After evacuating system, weigh in the specified amount of
refrigerant (refer to system data plate).
LOW CHARGE COOLING — Use Cooling Charging Charts
(Figs. 23-35). Vary refrigerant until the conditions of the chart are
met. Note that charging charts are different from type normally
used. Charts are based on charging the units to correct superheat
for the various operating conditions. Accurate pressure gage and
temperature sensing devices are required. Connect the pressure
gage to the service port on the suction line. Mount the temperature
sensing device on the suction line and insulate it so that the
outdoor ambient does not effect the reading. Indoor air CFM must
be within the normal operating range of the unit.
TO USE COOLING CHARGING CHARTS — Take the outdoor
ambient temperature and read the suction pressure gage. Refer to
the chart to determine what the suction temperature should be.
NOTE: If the problem causing the inaccurate readings is a
refrigerant leak, refer to Check for Refrigerant Leaks section.
18
Page 19

689
100
620
90
551
80
483
70
414
60
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
345
50
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
276
40
(018) 60HZ CHARGING CHART
OUTDOOR TEMP
° F ° C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
758
110
689
100
620
90
551
80
483
70
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
414
60
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
345
50
(024) 60HZ CHARGING CHART
OUTDOOR TEMP
° F ° C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
207
30
20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°F)
-7 -1 4 10 16 21 27
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°C)
50JS500087
C00026
Fig. 23—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JS 018 Units
OUTDOOR TEMP
° F ° C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JS500089
C00028
689
100
620
90
551
80
483
70
414
60
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
345
50
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
276
40
207
30
20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°F)
-7 -1 4 10 16 21 27
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°C)
(030) 60HZ CHARGING CHART
Fig. 25—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JS030 Units
276
40
20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°F)
-7 -1 4 10 16 21 27
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°C)
50JS500088
C00027
Fig. 24—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JS 024 Units
OUTDOOR TEMP
° F ° C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JS500090
C00029
689
100
620
90
551
80
483
70
414
60
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
345
50
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
276
40
207
30
20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°F)
-7 -1 4 10 16 21 27
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°C)
(036) 60HZ CHARGING CHART
Fig. 26—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JS 036 Units
INDOOR AIRFLOW AND AIRFLOW ADJUSTMENTS
For heating and cooling operation, the recommended airflow
is 350 to 450 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling
capacity. for units withoptional electricheat, theairflow must
not be reduced below the levels stated in Tables 2A and 2B.
Tables 4A and 4B shows both heating and cooling airflows at
various external static pressures. Refer to these tables to determine
the airflow for the system being installed.
NOTE: Be sure that all supply-and return-air grilles are open, free
from obstructions, and adjusted properly.
Airflow can be changed by changing the lead connection of the
blower motor.
Unit 50JS and JX three-speed motors (except sizes JS 018 and JX
030) are factory wired for low speed operation. Unit 50JX 030 is
factory wired for medium speed. Unit 50JS 018 has a two-speed
motor wired for low speed.
For 208/230-v Motors:—The motor leads are color-coded as
follows:
3-SPEED
Black = high speed
Blue = medium speed
Red = low speed
19
Page 20

OUTDOOR TEMP
° F ° C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JS500091
689
100
620
90
551
80
483
70
414
60
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
345
50
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
276
40
207
30
20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°F)
-7 -1 4 10 16 21 27
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°C)
(042) 60HZ CHARGING CHART
C00030
Fig. 27—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JS 042 Units
OUTDOOR TEMP
° F ° C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JS500092
689
100
620
90
551
80
483
70
414
60
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
345
50
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
276
40
207
30
20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°F)
-7 -1 4 10 16 21 27
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°C)
(048) 60HZ CHARGING CHART
C00031
Fig. 28—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JS 048 Units
OUTDOOR TEMP
° F ° C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JS500093
689
100
620
90
551
80
483
70
414
60
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
345
50
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
276
40
207
30
20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 60.0 70.0 80.0
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°F)
-7 -1 4 10 16 21 27
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (°C)
(060) 60HZ CHARGING CHART
C00032
Fig. 29—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JS 060 Units
To change the speed of the blower motor (BM), remove the fan
motor speed leg lead from the blower relay (BR). This wire is
attached to IGC terminal BM for single-phase and 3-phase units.
To change the speed, remove and replace with lead for desired
blower motor speed. Insulate the removed lead to avoid contact
with chassis parts.
For 460-v GE Motors—The motor leads are color coded as
follows:
3-SPEED
Black = high
Violet = jumper
Orange = medium
Red = low
To change the speed of the blower motor (BM), remove fan motor
speed lead from the blower relay (BR) and replace with the lead
for the desired blower motor speed. The motor speed lead is
attached to terminal BM. For low and medium speeds black must
be connected to the jumper wire. Insulate removed lead end to
avoid contact with chassis parts. To select high speed on 460-v GE
motors, separate the black female quick connect (QC) from the
jumper lead male quick connect (QC) and connect the black lead
to the BR. Insulate the jumper to avoid contact with any chassis
parts.
MAINTENANCE
To ensure continuing high performance, and to minimize the
possibility of premature equipment failure, periodic maintenance
must be performed on this equipment. This heat pump unit should
be inspected at least once each year by a qualified service person.
To troubleshoot unit, refer to Table 5.
NOTE TO EQUIPMENT OWNER: Consult your local dealer
about the availability of a maintenance contract.
The ability to properly perform maintenance on this equipment requires certain expertise, mechanical skills, tools and
equipment. If you do not possess these, do not attempt to
perform any maintenance on this equipment, other than those
procedures recommended in the User’s Manual. FAILURE
TO HEED THIS WARNING COULD RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH AND POSSIBLE DAMAGE TO
THIS EQUIPMENT.
20
Page 21

80.070.060.050.040.030.0
OUTDOOR
TEMP
F C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JX500219
689 100.0
620
90.0
551
80.0
483
70.0
414
60.0
345
50.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
276
40.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
207
30.0
20.0
-7 272116104-1
(024) 60 Hz CHARGING CHART
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. F)
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. C)
C99031
Fig. 30—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JX 024 Units
80.070.060.050.040.030.0
OUTDOOR
TEMP
F C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JX500221
C99033
689 100.0
620
90.0
551
80.0
483
70.0
414
60.0
345
50.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
276
40.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
207
30.0
20.0
-7 272116104-1
(036) 60 Hz CHARGING CHART
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. F)
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. C)
Fig. 32—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JX036 Units
80.070.060.050.040.030.0
OUTDOOR
TEMP
F C
125 52
115 46
105 41
95 35
85 29
75 24
65 18
55 13
45 7
50JX500223
C99035
689 100.0
620
90.0
551
80.0
483
70.0
414
60.0
345
50.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
276
40.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
207
30.0
20.0
-7 272116104-1
(048) 60 Hz CHARGING CHART
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. F)
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. C)
Fig. 34—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JX 048 Units
689 100.0
620
90.0
551
80.0
483
70.0
414
60.0
345
50.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
276
40.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
207
30.0
20.0
-7 272116104-1
(030) 60 Hz CHARGING CHART
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. F)
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. C)
115 46
95 35
75 24
55 13
80.070.060.050.040.030.0
OUTDOOR
TEMP
F C
125 52
105 41
85 29
65 18
45 7
50JX500220
C99032
Fig. 31—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JX 030 Units
689 100.0
620
90.0
551
80.0
483
70.0
414
60.0
345
50.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
276
40.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
207
30.0
20.0
-7 272116104-1
(042) 60 Hz CHARGING CHART
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. F)
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. C)
115 46
95 35
75 24
55 13
80.070.060.050.040.030.0
OUTDOOR
TEMP
F C
125 52
105 41
85 29
65 18
45 7
50JX500222
C99034
Fig. 33—Cooling Charging Chart, 50JX 042 Units
115 46
95 35
75 24
55 13
80.070.060.050.040.030.0
OUTDOOR
TEMP
F C
125 52
105 41
85 29
65 18
45 7
50JX500224
C99036
689 100.0
620
90.0
551
80.0
483
70.0
414
60.0
345
50.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (PSIG)
276
40.0
SUCTION LINE PRESSURE (KILOPASCALS)
207
30.0
20.0
-7 272116104-1
(060) 60 Hz CHARGING CHART
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. F)
SUCTION LINE TEMPERATURE (DEG. C)
Fig. 35—Cooling Charging Chart,50JX 060 Units
21
Page 22

Failure to follow these warnings could result in serious injury
or death:
1. Turn off electrical power to the unit before performing any
maintenance or service on this unit.
2. Use extreme caution when removing panels and parts. As
with any mechanical equipment, personal injury can result
from sharp edges.
3. Never place anything combustible either on, or in contact
with, the unit.
Errors made when reconnecting wires may cause improper
and dangerous operation. Label all wires prior to disconnection when servicing.
The minimum maintenance requirements for this equipment are as
follows:
1. Inspect air filter(s) each month. Clean or replace when
necessary.
2. Inspect indoor coil, drain pan, and condensate drain each
cooling season for cleanliness. Clean when necessary.
3. Inspect blower motor and wheel for cleanliness each cooling
season. Clean when necessary.
4. Check electrical connections for tightness and controls for
proper operation each cooling season. Service when necessary.
AIR FILTER
IMPORTANT: Never operate the unit without a suitable air filter
in the return-air duct system. Always replace the filter with the
same dimensional size and type as originally installed (See Tables
1A and 1B for recommended filter sizes).
Inspect air filter(s) at least once each month and replace
(throwaway-type) or clean (cleanable-type) at least twice during
each cooling season or whenever the filters become clogged with
dust and lint.
INDOOR BLOWER AND MOTOR
NOTE: All motors are prelubricated. Do not attempt to lubricate
these motors.
For longer life, operating economy, and continuing efficiency,
clean accumulated dirt and grease from the blower wheel and
motor annually.
Disconnect and tag electrical power to the unit before
cleaning and lubricating the blower motor and wheel. Failure
to adhere to thiswarning could cause personal injury or death.
results, spray condenser coil fins from inside to outside the unit.
On units with an outer and inner condenser coil, be sure to clean
between the coils. Be sure to flush all dirt and debris from the unit
base.
Inspect the drain pan and condensate drain line when inspecting
the coils. Clean thedrain pan and condensate drain by removing all
foreign matter from the pan. Flush the pan and drain trough with
clear water. Do not splash water on the insulation, motor, wiring,
or air filter(s). If the drain trough is restricted, clear it with a
‘‘plumbers snake’’ or similar probe device. Ensure that the
auxiliary drain port above the drain trough is also clear.
OUTDOOR FAN
Keep the condenser fan free from all obstructions to ensure
proper cooling operation. Never place articles on top of the
unit. Damage to unit may result.
1. Inspect the fan blades for cracks or bends.
2. If fan needs to be removed, remove screws holding outdoor air
intake grille and remove grille.
3. Loosen the setscrew and slide the fan off the motor shaft.
4. When replacing fan blade,position blade so that the hub is1/8
in. away from the motor end (1/8 in. of motor shaft will be
visible) (See Fig. 20).
5. Ensure that setscrew engages the flat area on the motor shaft
when tightening.
6. Replace grille.
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS AND WIRING — Inspect and check
the electrical controls and wiring annually. Be sure to turn off the
electrical power to the unit.
Remove access panel to locate all the electrical controls and
wiring. Check all electrical connections for tightness. Tighten all
screw connections. If any smoky or burned connections are
noticed, disassemble the connection, clean all the parts, restrip the
wire end and reassemble the connection properly and securely.
After inspecting the electrical controls and wiring, replace all the
panels. Start the unit, and observe at least one complete cooling
cycle to ensure proper operation. If discrepancies are observed in
operating cycle, or if a suspected malfunction has occurred, check
each electrical component with the proper electrical instrumentation. Refer to the unit wiring label when making these checkouts.
NOTE: Refer to the Sequence of Operation section as an aid in
determining proper control operation.
REFRIGERANT CIRCUIT — Inspect all refrigerant tubing connections and the unit base for oil accumulation annually. Detecting
oil generally indicates a refrigerant leak.
OUTDOOR COIL, INDOOR COIL, AND CONDENSATE
DRAIN PAN — Inspect the condenser coil, evaporator coil, and
condensate drain pan at least once each year.
The coils are easily cleaned when dry; therefore, inspect and clean
the coils either before or after each cooling season. Remove all
obstructions, including weeds and shrubs, that interfere with the
airflow through the condenser coil.
Straighten bent fins with a fin comb. If coated with dirt or lint,
clean the coils with a vacuum cleaner, using the soft brush
attachment. Be careful not to bend the fins. If coated with oil or
grease, clean the coils with a mild detergent-and-water solution.
Rinse coils with clear water, using a garden hose. Be careful not to
splash water on motors, insulation, wiring, or air filter(s). For best
System under pressure. Relieve pressure and recover all
refrigerant before system repair or final unit disposal to avoid
personal injury or death. Use all service ports and open all
flow-control devices, including solenoid valves.
If oil is detected or if low performance is suspected, leak-test all
refrigerant tubing using an electronic leak detector, or liquid-soap
solution. If a refrigerant leak is detected, refer to Check for
Refrigerant Leaks section.
If no refrigerant leaks are found and low performance is suspected,
refer to Checking and Adjusting Refrigerant Charge section.
INDOOR AIRFLOW — The indoor airflow does not require
checking unless improper performance is suspected. If a problem
22
Page 23

C99097
Fig. 36—Refrigerant Circuit
exists, be sure that all supply- and return-air grilles are open and
free from obstructions, and that the air filter is clean. When
necessary, refer to Indoor Airflow and Airflow Adjustments
section to check the system airflow.
METERING DEVICES — Refrigerant metering devices are fixed
orifices and are located in the inlet header to the indoor and
outdoor coils.
LIQUID LINE STRAINERS — The liquid line strainers (to protect metering devices) aremade ofwire meshand arelocated in the
liquid lines on the inlet side of the metering devices.
SYSTEM INFORMATION
TIME-DELAY RELAY — The Time-Delay Relay (TDR) is a
solid-state control, recycle delay timer which keeps indoor blower
operating for 60 sec. after thermostat is satisfied. This delay
enables blower to remove residual cooling in coil after compression shutdown, thereby improving efficiency of system. The
sequence of operation is that on closure of wall thermostat and at
end of a fixed on delay of 1 sec., fan relay is energized. When
thermostat is satisfied, an off delay is initiated. When fixed delay
of 60 ± 5 sec. is completed, fan relay is de-energized and fan motor
stops. If wall thermostat closes during this delay, TDR is reset and
fan relay remains energized. TDR is a 24-v device that operates
within a range of 15v to 30v and draws about 0.5 amps. If the
blower runs continuously instead of cycling off when the fan
switch is seton AUTO, the TDR isprobably defective and must be
replaced.
LOSS OF CHARGE SWITCH — The loss of charge switch is a
protective device wired into control circuit (low voltage). It shuts
off the compressor if abnormally low pressures are present in the
refrigeration circuit.
NOTE: Because these switches are attached to refrigeration
system under pressure, it is not advisable to remove this device for
troubleshooting unless you are reasonably certain that a problem
exists. If switch must be removed, remove and recover all system
charge so that pressure gages read 0 psi. Never open system
without breaking vacuum with dry nitrogen.
CHECK DEFROST THERMOSTAT — There is a liquid header
with a brass distributor and feeder tube going into outdoor coil. At
the end of 1 of the feeder tubes, there is a 3/8-in. OD stub tube
approximately 3 in. long. (See Fig. 37.) The defrost thermostat
should be located on stub tube. Note that there is only 1 stub tube
used with liquid header, and on most units it is the bottom circuit.
DEFROST THERMOSTATS — Defrost thermostat signals heat
FEEDER TUBE
STUB TUBE
DEFROST
THERMOST AT
C99029
Fig. 37—Defrost Thermostat
pump that conditions are right for defrost or that conditions have
changed to terminate defrost. It is a thermally actuated switch
clamped to outdoor coil to sense its temperature. Normal temperature range is closed at 30˚ +/- 3˚F and open at 80˚ +/- 5˚F.
NOTE: The defrost thermostat must be located on the liquid side
of the outdoor coil on the bottom circuit and as close to the coil as
possible.
23
Page 24

Table 5—Cooling and Heating Troubleshooting Chart
SYMPTOM CAUSE REMEDY
Compressor and outdoor fan will not start
Compressor will not start but condenser fan
runs
Three-phase scroll compressor (size 030060units) makes excessive noise, and there
may be a low pressure differential
Compressor cycles (other than normally satisfying thermostat)
Compressor operates continuously
Excessive head pressure
Head pressure too low
Excessive suction pressure
Power failure Call power company
Fuse blown or circuit breaker tripped Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker
Defective thermostat, contactor, transformer, con-
trol relay or defrost board
Insufficient line voltage Determine cause and correct
Incorrect or faulty wiring Check wiring diagram and rewire correctly
Thermostat setting too high
Units have a 5-min. time delay
Faulty wiring or loose connections in compressor
circuit
Compressor motor burned out, seized, or internal
overload open
Defective run capacitor, overload, or PTC (positive temperature coefficient) thermistor
One leg of 3-phase power dead
Low input voltage (20% low) Determine cause and correct
Scroll compressor is rotating in the wrong direc-
tion
Refrigerant overcharge or undercharge
Defective compressor Replace and determine cause
Insufficient line voltage Determine cause and correct
Blocked outdoor coil Determine cause and correct
Defective run/start capacitor, overload or start
relay
Defective thermostat Replace thermostat
Faulty outdoor-fan motor or capacitor Replace
Damaged reversing valve Determine cause and correct
Restriction in refrigerant system Locate restriction and remove
Dirty air filter Replace filter
Unit undersized for load Decrease load or increase unit size
Thermostat set too low Reset thermostat
Low refrigerant charge Locate leak, repair, and recharge
Leaking valves in compressor Replace compressor
Frosted coil with incorrect defrost operation
Air in system
Outdoor coil dirty or restricted Clean coil or remove restriction
Dirty air filter Replace filter
Dirty indoor or outdoor coil Clean coil
Refrigerant overcharged Recover excess refrigerant
Air in system
(Heat) Indoor air restricted or recirculating Determine cause and correct
Indoor or outdoor air restricted or air short-cycling Determine cause and correct
Low refrigerant charge Check for leaks, repair and recharge
Compressor valves leaking Replace compressor
Restriction in liquid tube Remove restriction
(Heat) Outdoor coil frosted
(Cool) High Heat load Check for source and eliminate
Compressor valves leaking Replace compressor
Reversing valve hung up or leaking internally Replace valve
Refrigerant overcharged Recover excess refrigerant
Replace component
Lower thermostat setting below room temperature
DO NOT bypass this compressor time
delay—wait for 5 min. until time-delay relay is
deenergized
Check wiring and repair or replace
Determine cause
Replace compressor
Determine cause and replace
Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker
Determine cause
Correct the direction of rotation by reversing the
3-phase power leads to the unit
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge to capacities shown on nameplate
Determine cause and replace
Check defrost time settings
Reset as necessary
Check defrost temperature switch
Replace as necessary
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge
Move timer on control board to 30 min. between
defrost cycles
24
Page 25

Cooling and Heating Troubleshooting Chart (cont’d)
SYMPTOM CAUSE REMEDY
Suction pressure too low (Cool) Dirty air filter Replace filter
(Heat) Outdoor coil frosted
Low refrigerant charge Check for leaks, repair and recharge
Metering device or low side restricted Remove source of restriction
(Cool) Insufficient coil airflow
(Cool) Temperature too low in conditioned area Reset thermostat
(Cool) Outdoor ambient below 40°F Install low-ambient kit
Field-installed filter-drier restricted Replace
Compressor runs but outdoor fan does not
IFM does not run Blower wheel not secured to shaft Properly tighten blower wheel to shaft
IFM runs when it should be off
IFM operation is intermittent
IFM—Indoor Fan Motor
NC (normally closed) contacts on defrost board
open
Insufficient voltage at motor Determine cause and correct
Power connectors not properly sealed Connectors should snap easily; do not force
Motor programmed with a delay profile Allow a few min. for motor to shut off
With thermostat in off state, the voltage on G,
Y1,Y, Y2, W with respect to common, should be
1/2 of actual low voltage supply
Water dripping into motor Verify proper drip loops in connector wires
Connectors not firmly sealed
START-UP CHECKLIST
(REMOVE AND STORE IN JOB FILE)
I. PRELIMINARY INFORMATION
Model No...............................................................................................................................................................................................................
Serial No................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Date........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Technician..............................................................................................................................................................................................................
II. PRE-START-UP
___ Verify that all packing materials have been removed from unit
___ Remove all shipping holddown bolts and brackets per installation instructions
___ Verify that condensate connection is installed per installation instructions
___ Check all electrical connections and terminals for tightness
___ Check that indoor (evaporator) air filter is clean and in place
___ Verify that unit installation is level
___ Check fan wheel and propeller for location in housing and setscrew tightness
III. START-UP
Supply Voltage: L1-L2 __________ L2-L3 _________ L3-L1 __________
Compressor Amps: L1 __________ L2 _________ L3 __________
Indoor Fan Amps: __________
TEMPERATURE
Outdoor-Air Temperature: __________ DB
Return-Air Temperature: __________ DB __________ WB
Heat Pump Supply Air: __________
Electric Heater Supply Air: __________
PRESSURES
Refrigerant Suction __________ psig
Refrigerant Discharge __________ psig
Move timer on control board to 30 min. between
defrost cycles
Increase air quantity
Check filter—replace if necessary
Check condition of relay on board
Replace if necessary
If measured voltage is more than 1/2, the thermostat is incompatible with motor
If voltage is less than 1/2, the motor has failed
Gently pull wires individually to be sure they are
crimped into the housing
___ Verify refrigerant charge using charging tables
___ Verify 3-phase scroll compressor is rotating in correct direction
252627
Page 26

Page 27

Page 28

Copyright 2000 CARRIER Corp. • 7310 W. Morris St. • Indianapolis, IN 46231 50js1si
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 4
Tab 5a 5a PC 101 Catalog No. 565-057 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50JS,JX-1SI Pg 28 5-00 Replaces: 50JX-2SI
 Loading...
Loading...