Page 1
30RB060-390 Air-Cooled Chillers and
30RB080-390 Air-Cooled Chillers with
Greenspeed® Technology
Installation Instructions
AquaSnap
®
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1,2
INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-73
Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Step 1 — Place, Rig and Mount Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
•PLACING UNIT
• MOUNTING UNIT
• RIGGING UNIT
Step 2 — Remove Compressor Rack
Holddown Bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Step 3 — Remove Compressor Shipping
Braces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
• FOR UNITS WITH COMPRESSOR SOUND
BLANKETS
Step 4 — Make Cooler Fluid, Heat Reclaim and
Drain Piping Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
• FREEZE PROTECTION
• UNITS WITH HYDRONIC PUMP PACKAGE
• UNITS WITHOUT HYDRONIC PUMP PACKAGE
• UNITS WITH OPTIONAL HEAT RECLAIM
• HEAD PRESSURE CONTROL
• FOR ALL UNITS
Step 5 — Fill the Chilled Water and Heat Reclaim
Loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
• WATER SYSTEM CLEANING
• WATER TREATMENT
• SYSTEM PRESSURIZATION
• FILLING THE SYSTEM(S)
• SET WATER FLOW RATE
• PUMP MODIFICATION/TRIMMING
•PUMP VFD
• SENSORLESS CONTROL (CLOSED LOOP)
• REMOTE SENSOR (CLOSED LOOP)
• REMOTE CONTROLLER (OPEN LOOP)
• PREPARATION FOR YEAR-ROUND
OPERATION
• FREEZE PROTECTION
• PREPARATION FOR WINTER SHUTDOWN
• CHILLED WATER SYSTEM
• HEAT RECLAIM SYSTEM
Step 6 — Make Electrical Connections . . . . . . . . . . 57
• POWER SUPPLY
•POWER WIRING
• CONTROL POWER
• FIELD CONTROL OPTION WIRING
• DUAL CHILLER CONTROL OPTION
• CARRIER COMFORT NETWORK
COMMUNICATION BUS WIRING
• NON-CCN COMMUNICATION WIRING
Step 7 — Install Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
• NAVIGATOR™ DISPLAY
• REMOTE ENHANCED DISPLAY
• LOW AMBIENT TEMPERATURE OPERATION
• MINIMUM LOAD ACCESSORY
• UNIT SECURITY/PROTECTION ACCESSORIES
• COMMUNICATION ACCESSORIES
• SERVICE OPTIONS
®
Refrigerant Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
• LEAK TESTING
• DEHYDRATION
• REFRIGERANT CHARGE
BACnet Communication Option Wiring . . . . . . . . . 71
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installing, starting up, and servicing air-conditioning
equipment can be hazardous due to system pressures, electrical
components, and equipment location.
Only trained, qualified installers and service mechanics
should install, start up, and service this equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions such as cleaning coils. All other operations should be
performed by trained service personnel.
When working on the equipment, observe precautions in the
literature and on tags, stickers, and labels attached to the
equipment.
• Follow all safety codes.
• Keep quenching cloth and fire extinguisher nearby when
brazing.
• Wear safety glasses and work gloves.
• Use care in handling, rigging, and setting bulky
equipment.
WARNING
Electrical shock can cause personal injury and death. Shut
off all power to this equipment during installation. There
may be more than one disconnect switch. Tag all disconnect locations to alert others not to restore power until work
is completed.
IMPORTANT: This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and
used in accordance with these instructions may cause
radio interference. It has been tested and found to comply
with the limits of a Class A computing device pursuant to
International Standard in North America EN 61000-2/3,
which are designed to provide reasonable protection
against such interference when operated in a commercial
environment.
CAUTION
This system uses Puron® refrigerant (R-410A), which has
higher pressures than R-22 and other refrigerants. No other
refrigerant can be used in this system. Failure to use gage
set, hoses, and recovery systems designed to handle Puron
refrigerant (R-410A) may result in equipment damage or
personal injury. If unsure about equipment, consult the
equipment manufacturer.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53300124-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 30RB-21SI Pg 1 1218 12-13 Replaces: 30RB-20SI
Page 2
WARNING
DO NOT USE TORCH to remove any component. System
contains oil and refrigerant under pressure.
To remove a component, wear protective gloves and goggles and proceed as follows:
a. Shut off electrical power to unit.
b. Recover refrigerant to relieve all pressure from sys-
tem using both high-pressure and low pressure ports.
c. Traces of vapor should be displaced with nitrogen
and the work area should be well ventilated. Refrigerant in contact with an open flame produces toxic
gases.
d. Cut component connection tubing with tubing cutter
and remove component from unit. Use a pan to catch
any oil that may come out of the lines and as a gage
for how much oil to add to the system.
e. Carefully unsweat remaining tubing stubs when nec-
essary. Oil can ignite when exposed to torch flame.
Failure to follow these procedures may result in personal
injury or death.
CAUTION
DO NOT re-use compressor oil or any oil that has been
exposed to the atmosphere. Dispose of oil per local codes
and regulations. DO NOT leave refrigerant system open to
air any longer than the actual time required to service the
equipment. Seal circuits being serviced and charge with
dry nitrogen to prevent oil contamination when timely
repairs cannot be completed. Failure to follow these procedures may result in damage to equipment.
INTRODUCTION
These instructions cover installation of 30RB060-390 aircooled liquid chillers with electronic controls and units with
factory-installed options (FIOPs). See Fig. 1.
NOTE: The 30RB080-390 air-cooled chillers with Green-
®
speed
technology include high-efficiency variable condenser
fans. See Fig. 1.
NOTE: Unit sizes 315-390 are modular units that are shipped
in separate sections as modules A or B as noted in position 8 of
the unit model nomenclature. Installation directions specific to
these units are noted in these instructions. For modules 315A,
315B, 330A, 330B, 345A, 345B, and 360B, follow all general
instructions as noted for unit sizes 30RB160-170. For modules,
360A, 390A, and 390B follow instructions for 30RB190. See
Table 1 for a listing of unit sizes and modular combinations.
NOTE: The nameplate for modular units contains only the first
two digits in the model number. For example, 315A and 315B
nameplates read 31A and 31B.
Table 1 — Modular Combinations
MODULE UNITS MODULE A MODULE B
30RBF315 30RBF160 30RBF160
30RBF330 30RBF170 30RBF160
30RBF345 30RBF170 30RBF170
30RBF360 30RBF190 30RBF170
30RBF390 30RBF190 30RBF190
NOTE: An “F” in the model number indicates the design series.
INSTALLATION
Storage —
before installation or start-up, be sure to protect the machine
from construction dirt and moisture. Keep protective shipping
covers in place until machine is ready for installation.
If the unit is to be stored for a period of time
Step 1 — Place, Rig and Mount the Unit
NOTE: Inspect the unit upon arrival for damage. If damage is
found, file a claim right away with the shipping company.
PLACING UNIT — When considering location for the unit,
be sure to consult National Electrical Code (NEC, U.S.A.) and
local code requirements. Allow sufficient space for airflow,
wiring, piping, and service. See Fig. 2-20. Be sure surface beneath the unit is level, and is capable of supporting the operating weight of the unit. See Fig. 21 and Tables 2-4B for unit lifting points, mounting and operating weights.
Locate the unit so that the condenser airflow is unrestricted
both above and on the sides of the unit. Airflow and service
clearances are 6 ft (1.8 m) around the unit. Acceptable clearance on the cooler connection side or end opposite the control
box unit can be reduced to 3 ft (1 m) without sacrificing performance as long as the remaining three sides are unrestricted. Acceptable clearance on the side with a control box can be reduced to 4 ft (1.3 m) due to NEC regulations, without sacrificing performance as long as the remaining three sides are
unrestricted. Provide ample room for servicing and removing
cooler. See Fig. 2-20 for required clearances. Local codes for
clearances take precedence over the manufacturer’s recommendations when local codes call for greater clearances.
Modular units (30RB315-390) must be installed with a minimum separation end to end of 4 ft (1.3 m) for airflow and service clearance along with NEC regulations.
If multiple units are installed at the same site, a separation of
10 ft (3 m) between the sides of the machines is required to
maintain proper airflow and minimize the chances of condenser air recirculation.
MOUNTING UNIT — The unit may be mounted on a level
pad directly on the base rails, on rails along the long axis of the
machine, or on vibration isolation springs. For all units, ensure
placement area is strong enough to support unit operating
weight. Mounting holes are provided for securing the unit to
the pad or vibration isolation springs. The base rail can be point
loaded at the mounting points. The base rail is made from steel,
which is formed into what is shown in Fig. 22. See Fig. 2-20
for locations of mounting points. At the mounting points, a Ushaped channel is welded into the base rail to provide a flat
plate for mounting. See Fig. 23 for mounting plate dimensions.
9
The 1
/16 in. (40 mm) dimension shown is to the mounting hole
from the outside edge of the rail.
NOTE: The 1
same dimension as the 1.42 in. (36 mm) flange that is turned
under the base rail in Fig. 22.
Bolt the unit securely to pad or rails. If vibration isolators
(field-supplied) are required for a particular installation, refer to
unit weight distribution in Fig. 21 to aid in the proper selection
of isolators. The 30RB units can be mounted directly on spring
isolators. For each unit or module, the final unit location must
be level so that oil will equalize properly.
RIGGING UNIT — The 30RB060-390 units are designed for
overhead rigging and it is important that this method be
used. Holes are provided in frame base channels, marked for
rigging (see rigging label on unit). It is recommended that
field-supplied shackles be used to facilitate lifting. Secure the
shackles to the base rails at the points noted on the rigging
label. See Table 2 for the number of lifting points for each unit.
Do not use a forklift truck to move the units.
9
/16 in. (40 mm) dimension in Fig. 23 is not the
2
Page 3

Table 2 — Number of Lifting Points
30RB NUMBER OF LIFTING POINTS
060-110 4
120-150 6
160-300 8
315A, 315B, 330A, 330B,
345A, 345B, 360A
360B, 390A, 390B 8
6
Use spreader bars to keep cables or chains clear of unit
sides. As further protection plywood sheets may be placed
against sides of unit, behind cables or chains. Run cables or
chains to a central suspension point so that angle from horizontal is not less than 45 degrees. Raise and set unit down carefully. See Fig. 24 and 25 for rigging centers of gravity.
Each module of the 30RB315-390 units must be rigged separately. When placing unit modules for unit sizes 315-390,
make sure modules are placed to permit access to the control
boxes for each module.
For shipping, some domestic units and all export units are
mounted on a wooden skid under entire base of unit. Skid can
be removed before unit is moved to installation site. Lift the
unit from above to remove skid. See Fig. 24 and 25 for rigging
center of gravity. On export units, the top skid can be used as
the spreader bars. If the unit was shipped with a shipping bag,
the bag must be removed to gain access to the rigging holes in
the base rail. On export units with a full crate, the crate sides
must be removed to aid in rigging.
If overhead rigging is not available, the unit can be moved
on rollers or dragged. When unit is moved on rollers, the unit
skid, if equipped, must be removed. To lift the unit, use jacks at
the rigging points. Use a minimum number of rollers to distribute the load such that the rollers are no more than 6 feet (1.8 m)
apart. If the unit is to be dragged, lift the unit as described
above, and place unit on a pad. Apply moving force to the pad,
and not the unit. When in its final location, raise the unit and
remove the pad.
If the unit was shipped with coil protection, it must be
removed before start-up. The shipping bag for export units
must be removed before start-up.
NOTE: If the application includes a remote-mounted cooler
option, follow the instructions included with the accessory for
cooler placement and refrigerant piping.
3
Page 4
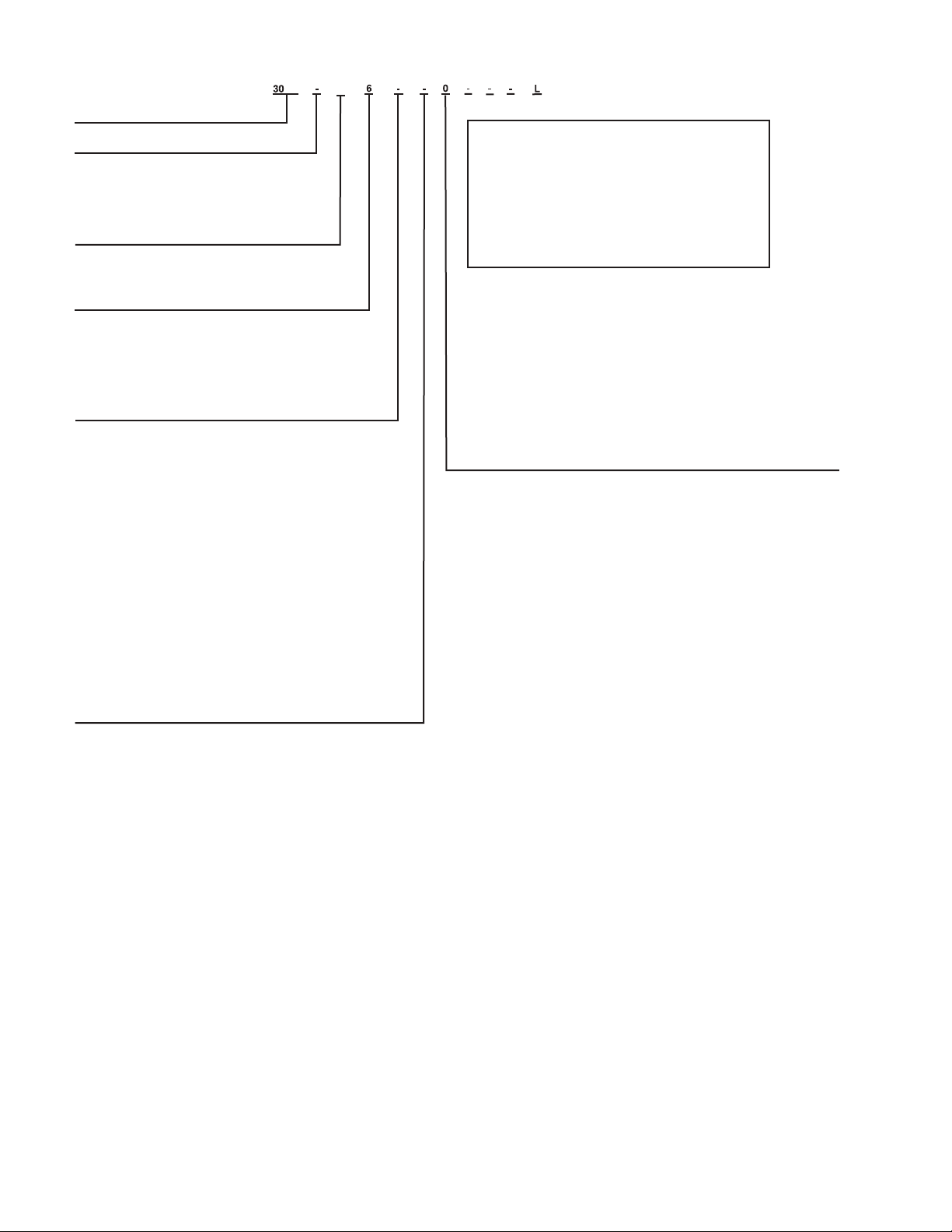
Fig. 1 — AquaSnap® Chiller Model Number Designation
LEGEND
*Refer to Table 1 on page 2 for modular unit combinations.
†Sponsored by ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and AirConditioning Engineers).
NOTE: A “Z” in position 11 indicates a special order machine. Digits following
do not correspond to tables.
CRN — Canadian Registration Number
EMM — Energy Management Module
GFI-CO — Ground Fault Interrupting Convenience Outlet
LON — Local Operating Network
SCCR — Short Circuit Curr ent Rating
VFD — Variable Frequency Device
XL — Across-the-Line Start
a30-5694
30RB – Air-Cooled AquaSnap® Chiller
Design Series
Nominal Sizes
060 110 170 275 360*
070 120 190 300 390*
080 130 210 315*
090 150 225 330*
100 160 250 345*
Voltage
1 – 575-3-60
2 – 380-3-60
Condenser Coil Options
- – Aluminum Fin/Copper Tube
0 – Copper Fin/Copper Tube
1 – Aluminum Pre-Coat Fin/Copper Tube
2 – Aluminum E-Coat Fin/Copper Tube
3 – Copper E-Coat Fin/Copper Tube
4 – Microchannel (MCHX)
5 – E-Coat, Microchannel (MCHX)
Cooler Options
- – Integral Cooler, CRN (Canada)
0 – Integral Cooler, Cooler Heater, CRN (Canada)
4 – Integral Cooler, Microchannel (MCHX), CRN (Canada)
5 – Integral Cooler, Cooler Heater, Microchannel (MCHX), CRN (Canada)
G – Integral Cooler, no CRN
H – Integral Cooler, Cooler Heater, no CRN
K – Integral Cooler, Microchannel (MCHX), no CRN
L – Integral Cooler, Cooler Heater, Microchannel (MCHX), no CRN
R – Integral Cooler, Microchannel (MCHX), Heat Recovery, no CRN
S – Integral Cooler, Cooler Heater, Microchannel (MCHX), Heat Recovery,
no CRN
T – Integral Cooler, Microchannel (MCHX), Heat Recovery, CRN (Canada)
V – Integral Cooler, Cooler Heater, Microchannel (MCHX), Heat Recovery,
CRN (Canada)
Hydronics Option†
- – No Pump Installed
0 – Single Pump, 3 HP
1 – Single Pump, 5 HP
2 – Single Pump, 7.5 HP
3 – Single Pump, 10 HP
4 – Single Pump, 15 HP
6 – Dual Pump, 3 HP
7 – Dual Pump, 5 HP
8 – Dual Pump, 7.5 HP, Low Head
9 – Dual Pump, 7.5 HP, High Head
B – Dual Pump, 10 HP
C – Dual Pump, 15 HP
F – Single Pump, 3 HP with VFD
G – Single Pump, 5 HP with VFD
H – Single Pump, 7.5 HP with VFD
J – Single Pump, 10 HP with VFD
K – Single Pump, 15 HP with VFD
M – Dual Pump, 3 HP with VFD
N – Dual Pump, 5 HP with VFD
P – Dual Pump, 7.5 HP, Low Head with VFD
T – Dual Pump, 7.5 HP, High Head with VFD
Q – Dual Pump, 10 HP with VFD
R – Dual Pump, 15 HP with VFD
Z – Special order designation
5 – 208/230-3-60
6 – 460-3-60
SEE NEXT PAGE
FOR REMAINDER
OF MODEL NUMBER
NOMENCLATURE
RB
190
318
4
Page 5
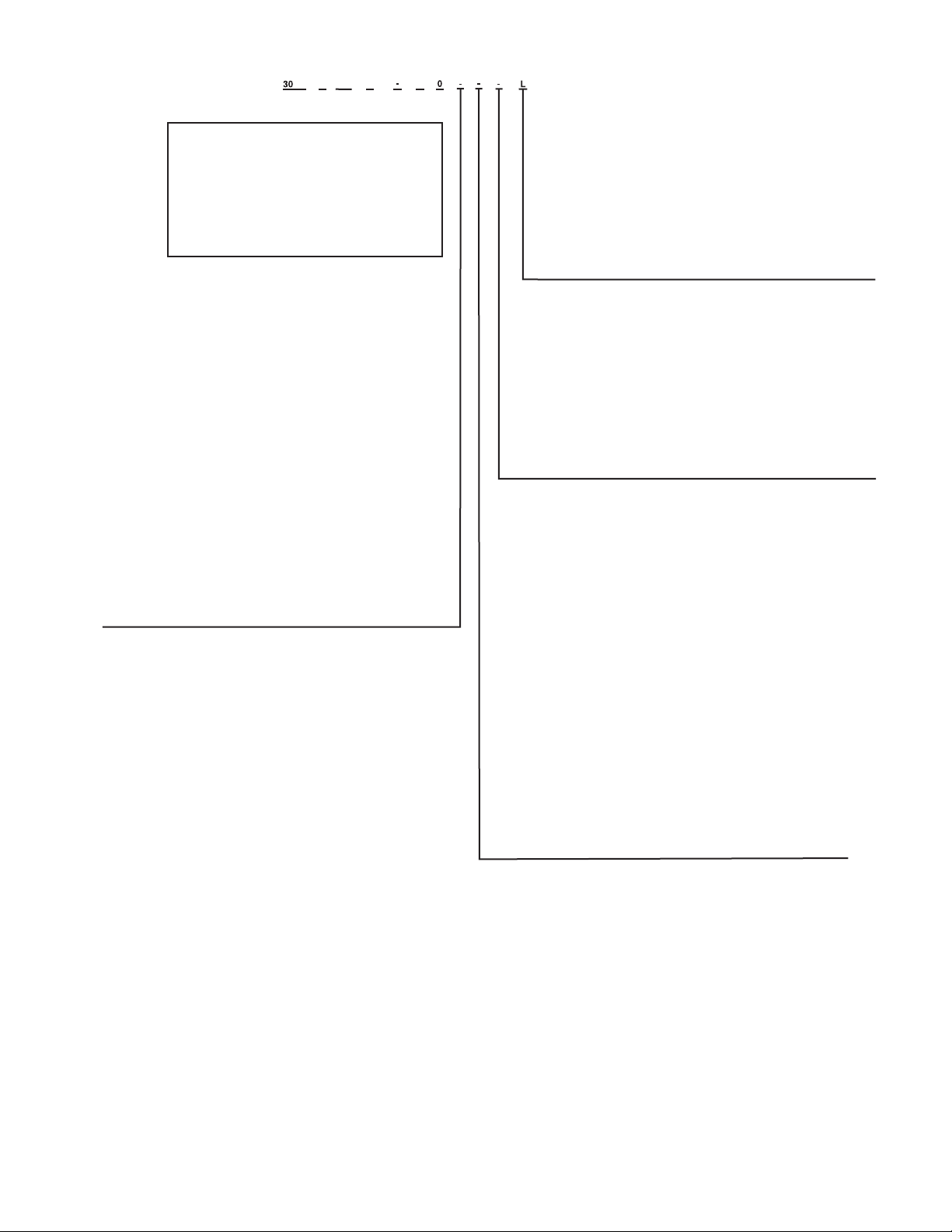
Packaging/Security Options
L – No Packaging
0 – Skid
1 – Skid, Top Crate, Bag
3 – Coil Trim Panels
4 – Skid, Coil Trim Panels
5 – Skid, Top Crate, Bag, Coil Trim Panels
7 – Coil Trim Panels, Upper and Lower Grilles
8 – Skid, Coil Trim Panels, Upper and Lower Grilles
9 – Skid, Top Crate, Bag, Coil Trim Panels, Upper and Lower Grilles
C – Trim Panels, Upper and Lower Grilles, Upper Hail Guards
D –
Skid, Trim Panels, Upper and Lower Grilles, Upper Hail Guards
F – Skid, Top Crate, Bag, Trim Panels, Upper and Lower Grilles,
Upper Hail Guards
H – Skid, Full End Covers
J – Skid, Top Crate, Bag, Full End Covers
K – Full End Covers
Controls/Communication Options
- – None
0 – EMM
1 – Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
2 – EMM, Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
3 – BACnet† Communication
4 – BACnet Communication, EMM
5 – BACnet Communication, Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
6 – BACnet Communic
ation, EMM, Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
7 – BACnet Translator
8 – BACnet Translator, EMM
9 – BACnet Translator, Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
B – BACnet Translator, EMM, Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
H – LON Translator
J – LON Translator, EMM
K – LON Translator, Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
L – LON Translator, EMM, Remote Service Port, GFI-CO
Electrical/Low Sound Options
- – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block
0 – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, High SCCR
3 – Dua
l Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block
4 – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, High SCCR
7 – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect
8 – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, High SCCR
C – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect
D – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, High SCCR
G – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, Cmpr Blankets
H – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, Cmpr Blankets, High SCCR
J – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, Cmpr Blankets
K – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Termin
al Block, Cmpr Blankets, High SCCR
L – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets
M – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets,
High SCCR
N – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets
P – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets,
High SCCR
Q – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures
R – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures, High
SCCR
S – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures
T – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Terminal Block, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures, High SCCR
V – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures
W – Single Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures, High SCCR
X – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fused Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures
W – Dual Point Power Connections, XL, Non-Fus
ed Disconnect, Cmpr Blankets,
Cmpr Enclosures, High SCCR
Refrigeration Circuit Options
- – No Suction Line Insulation
0 – Suction Insulation
1 – Suction Service Valves
2 – Low Ambient Head Pressure Control Operation
3 – Suction Insulation, Suction Service Valves
4 – Suction Insulation, Low Ambient Head Pressure Control Operation
5 – Suction Service Valves, Low Ambient Head Pressure Control Oper
ation
6 – Suction Insulation, Service Valves, Low Ambient Head Pressure
Control Operation
7 – Minimum Load Control
8 – Suction Insulation, Minimum Load Control Operation
9 – Suction Service Valves, Minimum Load Control Operation
B – Low Ambient Operation, Minimum Load Control Operation
C – Suction Insulation, Suction Service Valves, Minimum Load
Control Operation
D – Suction In
sulation, Low Ambient Head Pressure Control Operation,
Minimum Load Control Operation
F – Suction Service Valves, Low Ambient Head Pressure Control Operation,
Minimum Load Control Operation
G – Suction Insulation, Suction Service Valves, Low Ambient Head Pressure
Control, Operation, Minimum Load Control Operation
H – Suction Service Valves, High-Efficiency Variable Condenser Fans
J – Suction Insula
tion, Suction Service Valve, High-Efficiency Variable
Condenser Fans
K – High-Efficiency Variable Condenser Fans
L – Suction Insulation, High-Efficiency Variable Condenser Fans
M – Suction Service Valves, High-Efficiency Variable Condenser Fans,
Minimum Load Control Operation
N – Suction Insulation, Suction Service Valve, High-Efficiency Variable
Condenser Fans, Minimum Load Control Oper
ation
P – High-Efficiency Variable Condenser Fans, Minimum Load Control Operation
Q – Suction Insulation, High-Efficiency Variable Condenser Fans,
Minimum Load Control Operation
F
SEE PREVIOUS PAGE
FOR REMAINDER
OF MODEL NUMBER
NOMENCLATURE
RB 190
8
6
Fig. 1 — AquaSnap® Chiller Model Number Designation (cont)
a30-5704
LEGEND
*Refer to Table 1 on page 2 for modular unit combinations.
†Sponsored by ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and AirConditioning Engineers).
NOTE: A “Z” in position 11 indicates a special order machine. Digits following
do not correspond to tables.
CRN — Canadian Registration Number
EMM — Energy Management Module
GFI-CO — Ground Fault Interrupting Convenience Outlet
LON — Local Operating Network
SCCR — Short Circuit Current Rating
VFD — Variable Frequency Device
XL — Across-the-Line Start
5
Page 6
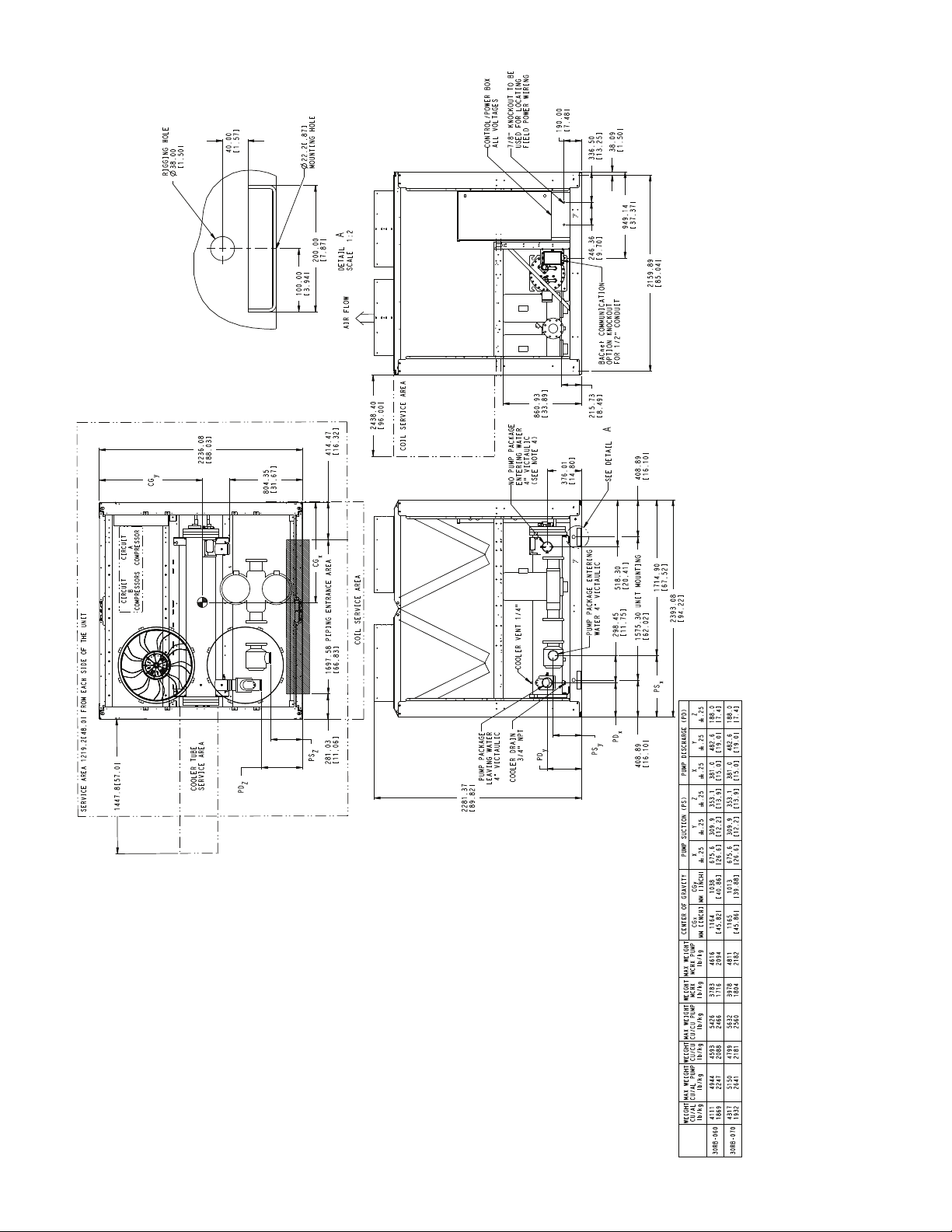
2281.37
89.82[]
UNIT MOUNTING1575.30
62.02[]
298.45
11.75[]
PS
y
376.01
14.80[]
2236.08
88.03[]
1447.8[57.0]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA1697.58
66.83[]
281.03
11.06[]
414.47
16.32[]
PD
Z
PS
Z
200.00
7.87[]
40.00
1.57[]
100.00
3.94[]
CG
x
CG
y
246.36
9.70[]
190.00
7.48[]
336.50
13.25[]
804.35
31.67[]
2393.08
94.22[]
PS
x
1714.90
67.52[]
408.89
16.10[]
408.89
16.10[]
PD
x
518.30
20.41[]
PD
y
860.93
33.89[]
2159.89
85.04[]
38.09
1.50[]
2438.40
[96.00]
RIGGING HOLE
38.00
1.50[]
949.14
37.37[]
215.73
8.49[]
WEIGHT
CU/AL
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
CU/AL PUMP
lb/kg
WEIGHT
CU/CU
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
CU/CU PUMP
lb/kg
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
MCHX PUMP
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY PUMP SUCTION (PS) PUMP DISCHARGE (PD)
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
X
.25
Y
.25
Z
.25
X
.25
Y
.25
Z
.25
30RB-060
4111
1869
4944
2247
4593
2088
5426
2466
3783
1716
4616
2094
1164
[45.82]
1038
[40.86]
675.6
[26.6]
309.9
[12.2]
353.1
[13.9]
381.0
[15.0]
482.6
[19.0]
188.0
[7.4]
30RB-070
4317
1932
5150
2641
4799
2181
5632
2560
3978
1804
4811
2182
1165
[45.86]
1013
[39.88]
675.6
[26.6]
309.9
[12.2]
353.1
[13.9]
381.0
[15.0]
482.6
[19.0]
188.0
[7.4]
COIL SERVICE AREA
NO PUMP PACKAGE
ENTERING WATER
4" VICTAULIC
(SEE NOTE 4)
COOLER VENT 1/4"
PUMP PACKAGE
LEAVING WATER
4" VICTAULIC
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT
PUMP PACKAGE ENTERING
WATER 4" VICTAULIC
SEE DETAIL
A
CONTROL/POWER BOX
ALL VOLTAGES
AIR FLOW
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
CIRCUIT
A
COMPRESSOR
CIRCUIT
B
COMPRESSORS
COIL SERVICE AREA
DETAIL
A
SCALE 1:2
22.2[.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. All pumps have drains located at the bottom of volute
for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices located on suction line,
liquid line and filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
4. Units without a pump package have the same leaving
water connection, Y and Z dimensions (entering
water), and Pump Discharge X dimensions as units
with a pump package.
5. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
6. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of
unit for condenser coil removal.
a30-4732
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 2 — 30RB060, 070 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
6
Page 7
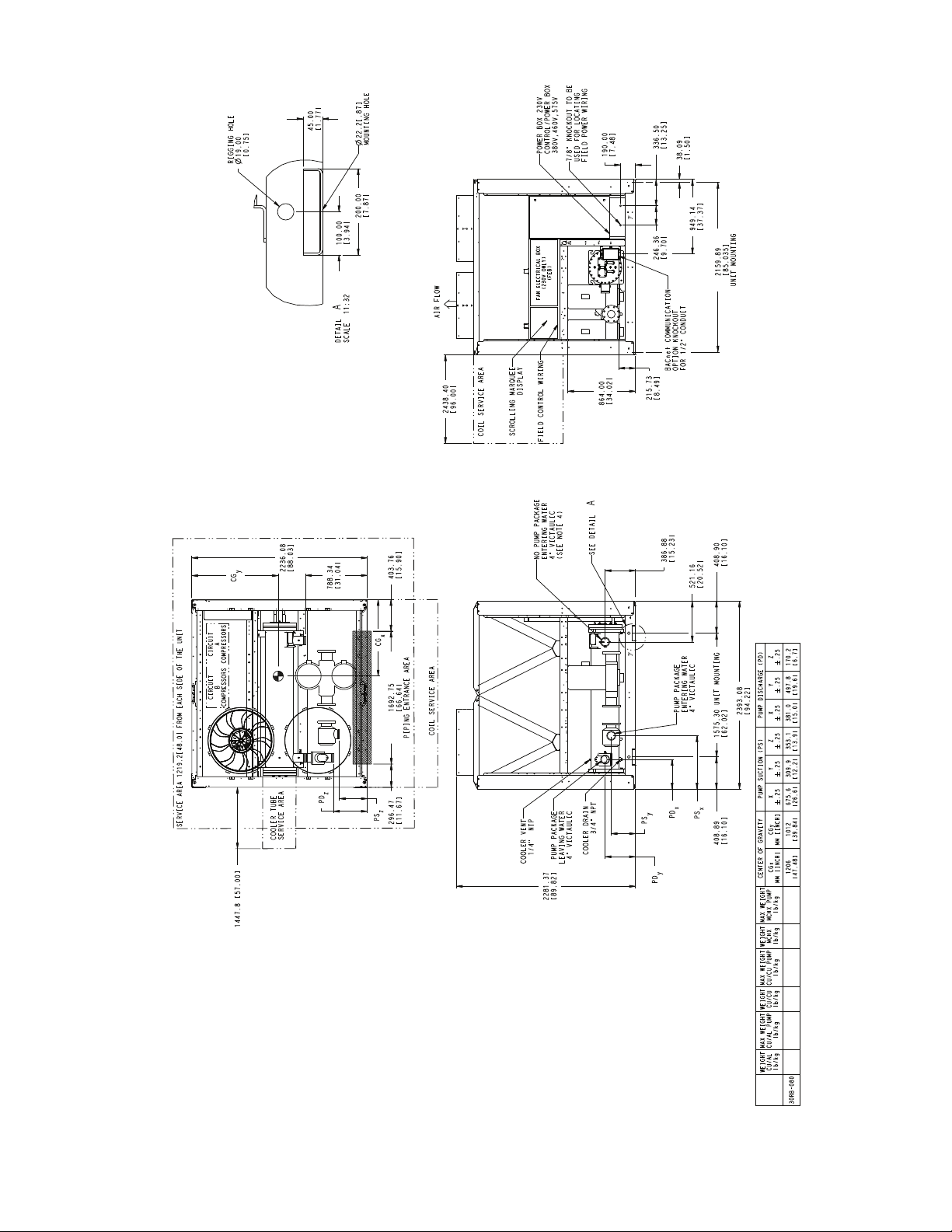
0.75[]
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from
solid surface.
2. All pumps have drains located at the
bottom of volute for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices located on
suction line, liquid line and filter drier
of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare con-
nection.
4. Units without a pump package have
the same leaving water connection, Y
and Z dimensions (entering water),
and Pump Discharge X dimensions
as units with a pump package.
5. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
6. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on
either side of unit for condenser coil
removal.
a30-4733
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 3 — 30RB080 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
19.00
RIGGING HOLE
1.77[]
45.00
22.2[.87]
200.00
3.94[]
100.00
A
SCALE 11:32
DETAIL
MOUNTING HOLE
7.87[]
AIR FLOW
2438.40
[96.00]
DISPLAY
SCROLLING MARQUEE
COIL SERVICE AREA
POWER BOX 230V
CONTROL/POWER BOX
380V,460V,575V
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(FEB)
(230V ONLY)
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
A
7.48[]
190.00
34.02[]
864.00
13.25[]
336.50
1.50[]
38.09
949.14
9.70[]
246.36
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
8.49[]
215.73
37.37[]
85.035[]
2159.89
UNIT MOUNTING
CG
A
CIRCUIT
COMPRESSORS
B
CIRCUIT
COMPRESSORS
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
1447.8 [57.00]
31.04[]
788.34
z
PD
88.03[]
2236.08
y
15.90[]
403.76
x
CG
66.64[]
1692.75
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
z
11.67[]
PS
296.47
COIL SERVICE AREA
NO PUMP PACKAGE
ENTERING WATER
4" VICTAULIC
1/4" NTP
PUMP PACKAGE
COOLER VENT
89.82[]
2281.37
SEE DETAIL
(SEE NOTE 4)
3/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN
4" VICTAULIC
LEAVING WATER
y
PS
15.23[]
386.88
PUMP PACKAGE
x
PD
y
PD
16.10[]
408.90
20.52[]
521.16
UNIT MOUNTING1575.30
ENTERING WATER
4" VICTAULIC
62.02[]
x
PS
16.10[]
408.89
Z
Y
94.22[]
X
2393.08
Z
Y
X
CGy
CGx
CENTER OF GRAVITY PUMP SUCTION (PS) PUMP DISCHARGE (PD)
MCHX PUMP
MAX WEIGHT
MCHX
WEIGHT
MAX WEIGHT
CU/CU PUMP
CU/CU
WEIGHT
.25
170.2
.25
497.8
.25
381.0
.25
353.1
.25
309.9
.25
675.6
1012
MM [INCH]
1206
MM [INCH]
5190
lb/kg
4267
lb/kg
6005
lb/kg
5082
lb/kg
[6.7]
[19.6]
[15.0]
[13.9]
[12.2]
[26.6]
[39.84]
[47.48]
2355
1934
2730
2310
7
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
CU/AL PUMP
CU/AL
lb/kg
WEIGHT
5523
2511
4600
2091
30RB-080
Page 8
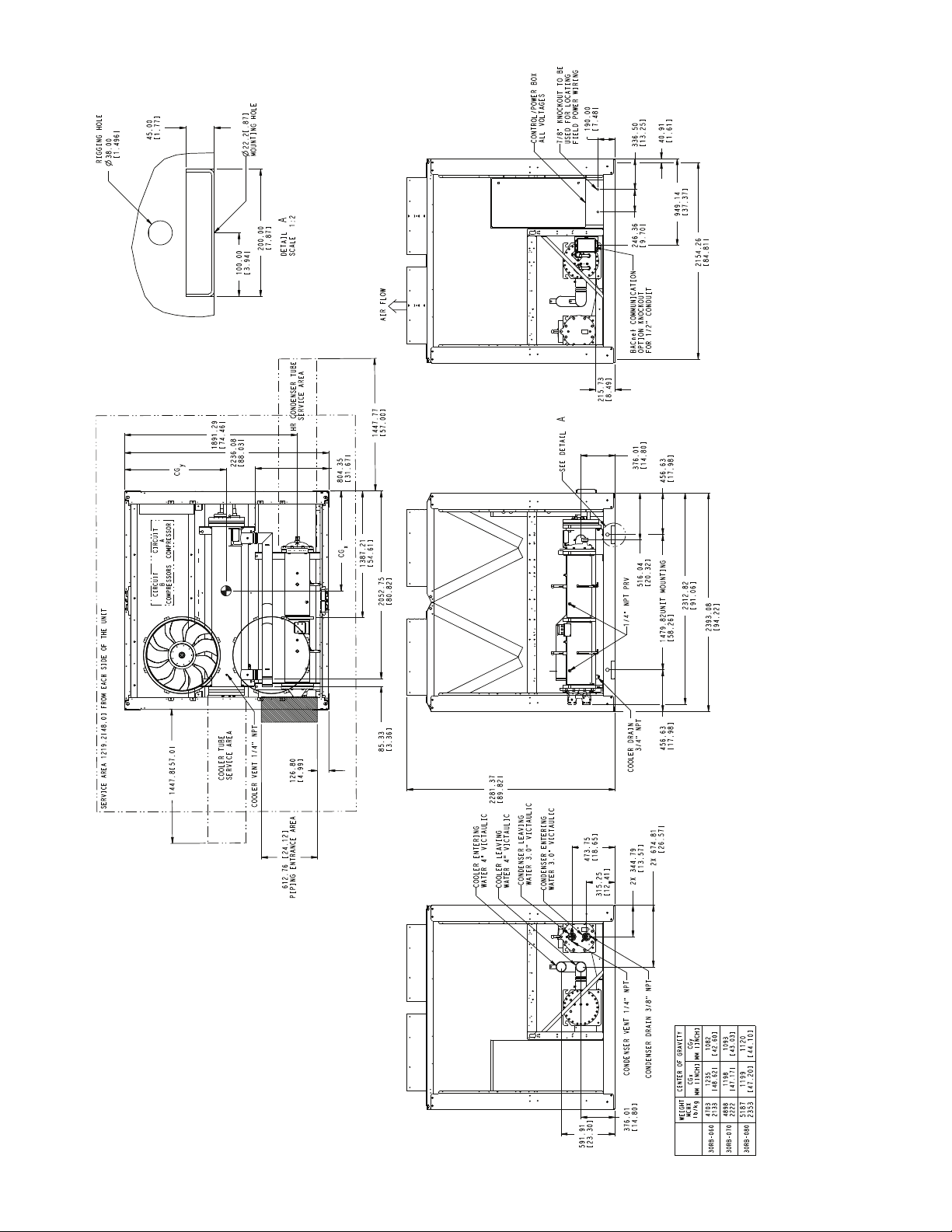
2281.37
89.82[]
UNIT MOUNTING1479.82
58.26[]
376.01
14.80[]
2236.08
88.03[]
1447.8[57.0]
200.00
7.87[]
45.00
1.77[]
100.00
3.94[]
CG
x
CG
y
246.36
9.70[]
190.00
7.48[]
336.50
13.25[]
804.35
31.67[]
2393.08
94.22[]
456.63
17.98[]
456.63
17.98[]
516.04
20.32[]
40.91
1.61[]
2154.26
84.81[]
126.80
4.99[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
612.76 24.12[]
473.75
18.65[]
315.25
12.41[]
2X 344.79
13.57[]
2312.82
91.06[]
591.91
23.30[]
2X 674.81
26.57[]
376.01
14.80[]
1447.77
57.00[]
1387.21
54.61[]
1891.29
74.46[]
85.33
3.36[]
2052.75
80.82[]
215.73
8.49[]
949.14
37.37[]
38.00
1.496[]
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-060
4703
2133
1235
[48.62]
1082
[42.60]
30RB-070
4898
2222
1198
[47.17]
1093
[43.03]
30RB-080
5187
2353
1199
[47.20]
1120
[44.10]
HR CONDENSER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT
SEE DETAIL
A
1/4" NPT PRV
CONTROL/POWER BOX
ALL VOLTAGES
AIR FLOW
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
COOLER VENT 1/4" NPT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
CIRCUIT
A
COMPRESSOR
CIRCUIT
B
COMPRESSORS
DETAIL A
SCALE 1:2
RIGGING HOLE
22.2[.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
COOLER LEAVING
WATER 4" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER ENTERING
WATER 3.0" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER LEAVING
WATER 3.0" VICTAULIC
COOLER ENTERING
WATER 4" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER DRAIN 3/8" NPT
CONDENSER VENT 1/4" NPT
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line,
liquid line and filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of
unit for condenser coil removal.
a30-4734
LEGEND
HR — Heat Reclaim
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
PRV — Pressure Relief Valve
Fig. 4 — 30RB060-080 Air-Cooled Chiller with Heat Reclaim Option Dimensions
8
Page 9
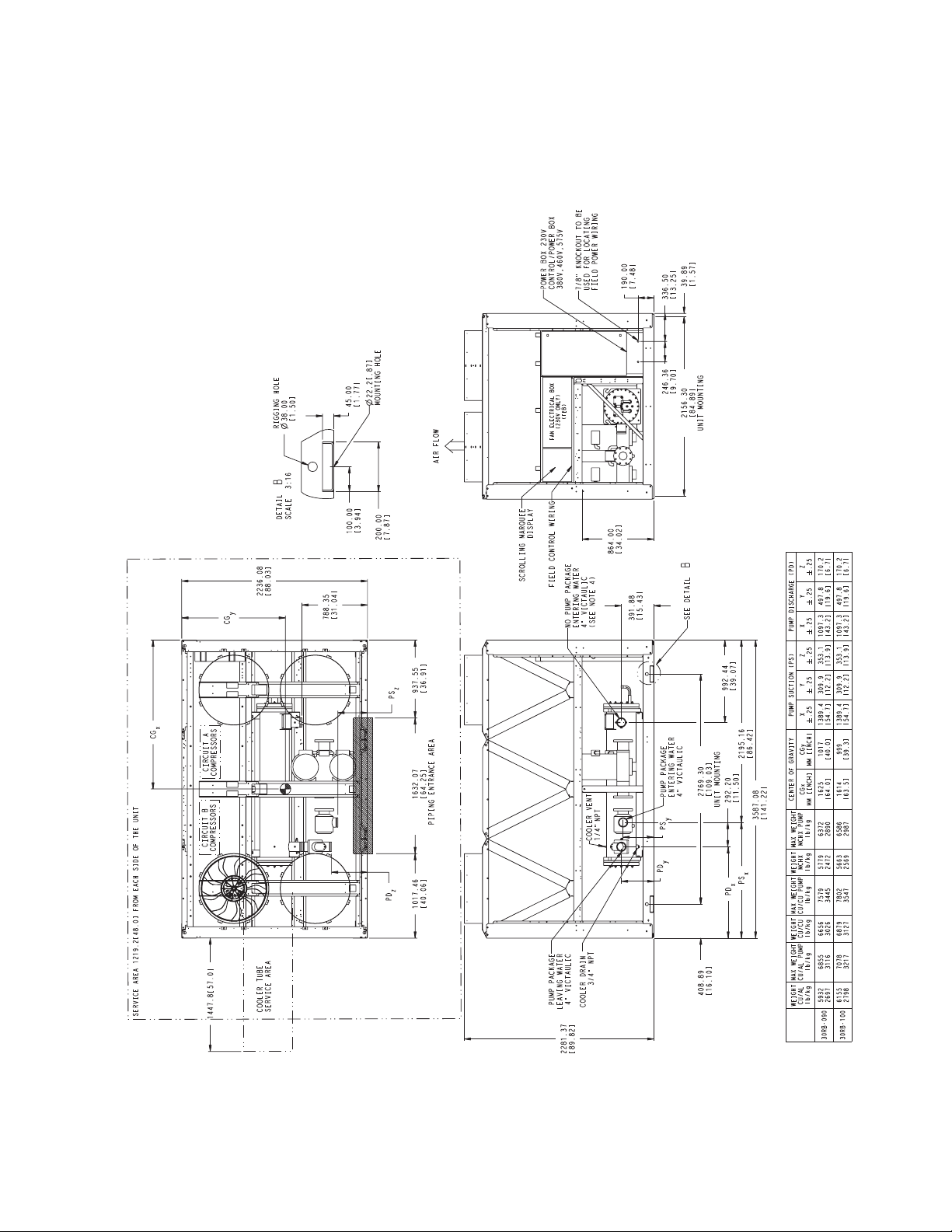
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6(1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. All pumps have drains located at the bottom of
volute for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices located on suction
line, liquid line and filter drier of each circuit and
have
1
/
4
flare connection.
4. Units without a pump package have the same
leaving water connection, Y and Z dimensions
(entering water), and Pump Discharge X dimen-
sions as units with a pump package.
5. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
6. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either
side of unit for condenser coil removal.
a30-4711
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 5 — 30RB090, 100 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
9
Page 10
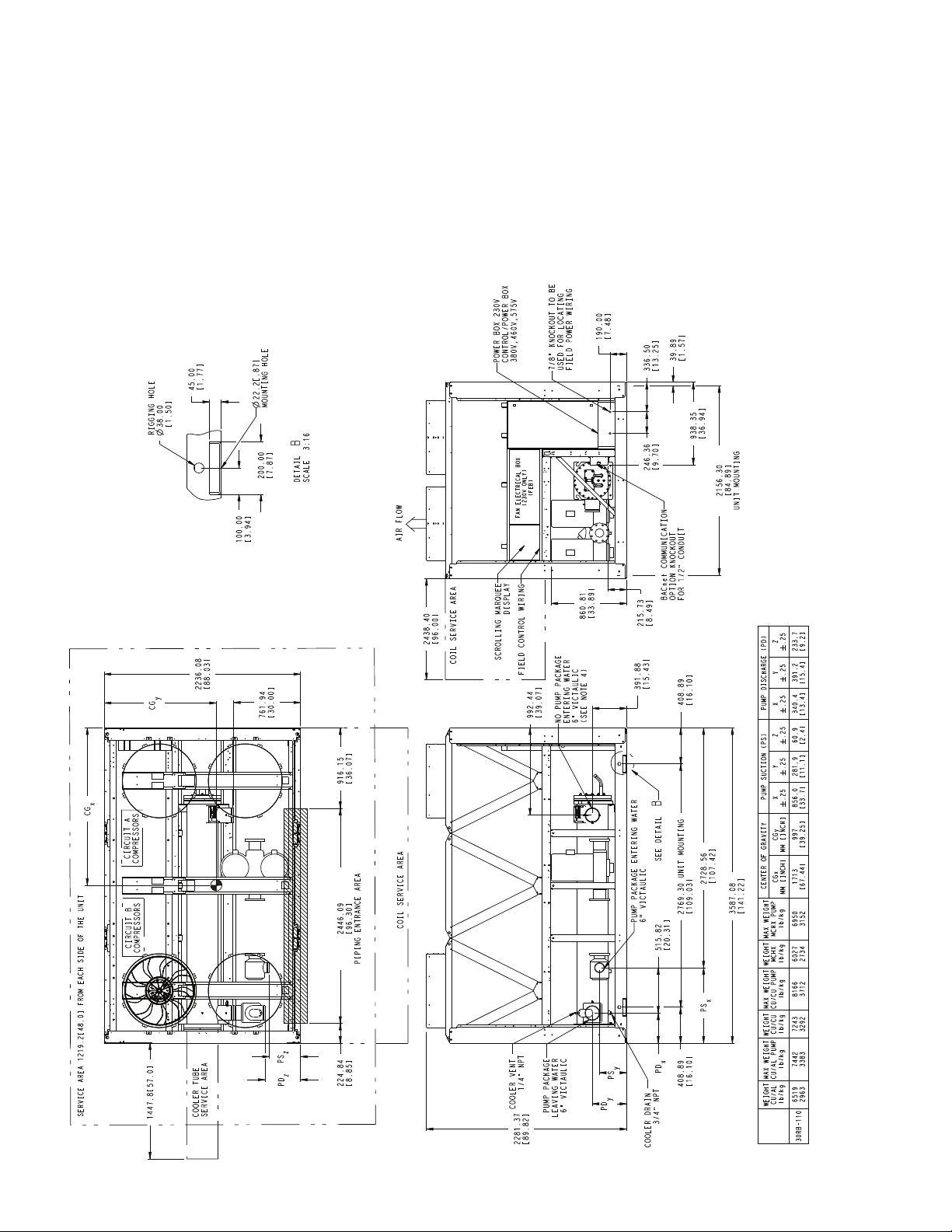
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
Airflow Side — 8 (2.4 m) required for coil service
area.
2. All pumps have drains located at the bottom of
volute for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices ocated on suction line,
liquid line and filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
4. No pump package leaving water connection is
same size and has same Y and Z dimensions as
entering water. Also has same PDx dimension as
pump package.
5. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 6 — 30RB110 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
7.48[]
190.00
1.57[]
POWER BOX 230V
CONTROL/POWER BOX
x
CG
CIRCUIT A
CIRCUIT B
1.50[]
38.00
RIGGING HOLE
y
CG
COMPRESSORS
COMPRESSORS
45.00
1.77[]
88.03[]
2236.08
22.2[.87]
200.00
3.94[]
100.00
761.94
MOUNTING HOLE
7.87[]
DETAIL B
SCALE 3:16
30.00[]
AIR FLOW
36.07[]
916.15
96.30[]
2446.09
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
2438.40
[96.00]
COIL SERVICE AREA
COIL SERVICE AREA
380V,460V,575V
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
(FEB)
(230V ONLY)
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
DISPLAY
SCROLLING MARQUEE
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
39.07[]
992.44
NO PUMP PACKAGE
FIELD POWER WIRING
33.89[]
860.81
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
(SEE NOTE 4)
39.89
13.25[]
336.50
36.94[]
938.35
9.70[]
246.36
84.89[]
2156.30
UNIT MOUNTING
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
8.49[]
215.73
15.43[]
391.88
16.10[]
408.89
B
SEE DETAIL
UNIT MOUNTING2769.30
107.42[]
2728.56
6" VICTAULIC
20.31[]
515.82
109.03[]
PUMP PACKAGE ENTERING WATER
141.22[]
3587.08
Z
.25
233.7
[9.2]
Y
.25
391.2
[15.4]
X
.25
340.4
[13.4]
Z
.25
60.9
[2.4]
Y
.25
281.9
[11.1]
X
.25
856.0
[33.7]
CGy
997
[39.25]
MM [INCH]
CGx
1713
CENTER OF GRAVITY PUMP SUCTION (PS) PUMP DISCHARGE (PD)
[67.44]
MM [INCH]
6950
3152
lb/kg
MCHX PUMP
MAX WEIGHT
MCHX
6027
2734
lb/kg
WEIGHT
PS
PD
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
1447.8[57.0]
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
8166
3712
x
PS
z
z
8.85[]
224.84
1/4" NTP
COOLER VENT
PUMP PACKAGE
89.82[]
2281.37
6" VICTAULIC
LEAVING WATER
y
PS
y
PD
x
PD
16.10[]
408.89
3/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
CU/CU PUMP
CU/CU
lb/kg
WEIGHT
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
CU/AL PUMP
CU/AL
lb/kg
WEIGHT
7243
3292
7442
3383
6519
2963
30RB-110
10
Page 11
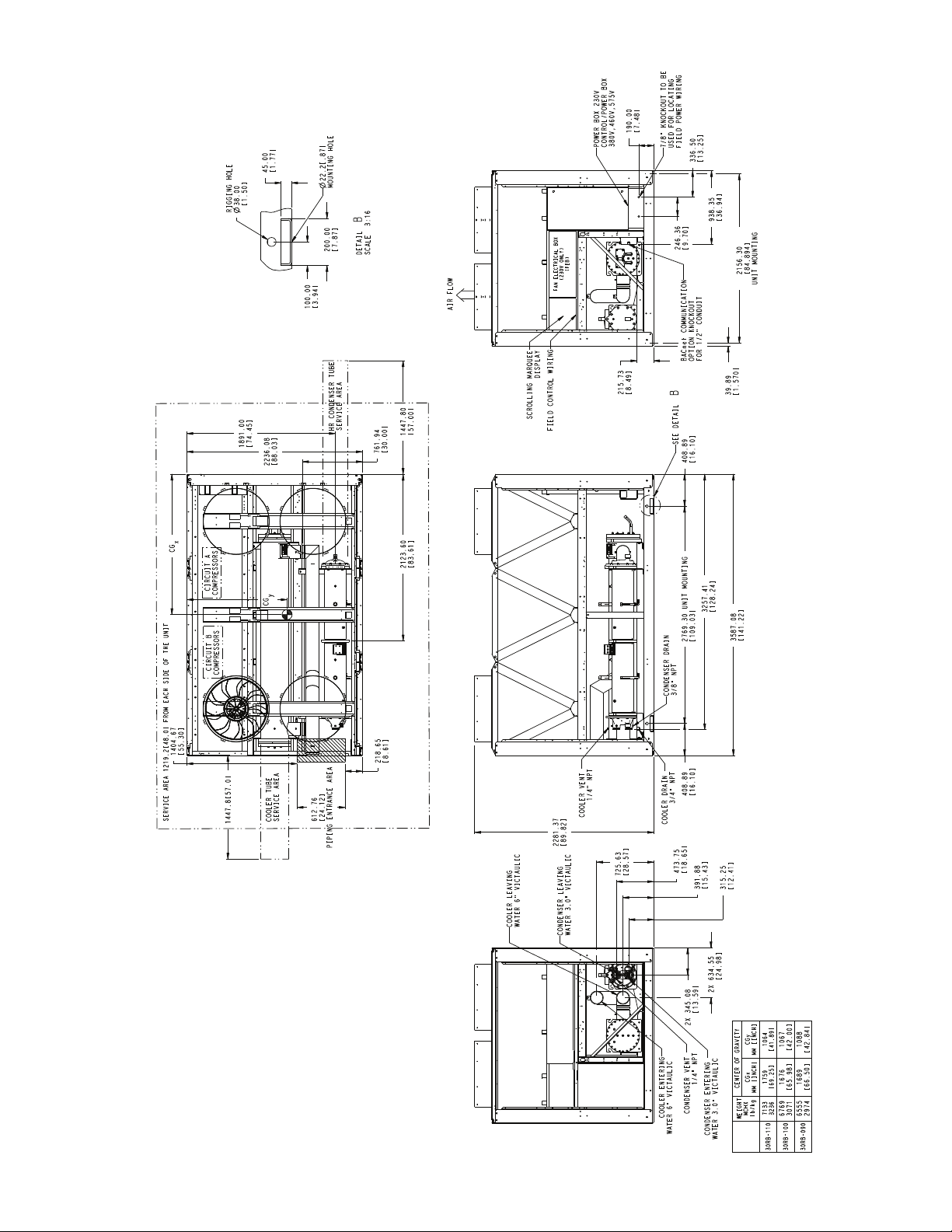
7.48[]
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line,
liquid line and filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of
unit for condenser coil removal.
a30-4735
LEGEND
HR — Heat Reclaim
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 7 — 30RB090-110 Air-Cooled Chiller with Heat Reclaim Option Dimensions
190.00
POWER BOX 230V
CONTROL/POWER BOX
380V,460V,575V
1.77[]
45.00
1.50[]
38.00
RIGGING HOLE
74.45[]
1891.00
88.03[]
2236.08
x
CG
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
y
CG
22.2[.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
7.87[]
200.00
3.94[]
100.00
HR CONDENSER TUBE
DETAIL B
SCALE 3:16
SERVICE AREA
1447.80
30.00[]
761.94
2123.60
57.00[]
83.61[]
AIR FLOW
(FEB)
(230V ONLY)
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
DISPLAY
SCROLLING MARQUEE
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
8.49[]
215.73
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
13.25[]
336.50
36.94[]
938.35
9.70[]
246.36
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
16.10[]
408.89
128.24[]
UNIT MOUNTING2769.30
3257.41
109.03[]
39.89
B
SEE DETAIL
84.894[]
2156.30
UNIT MOUNTING
1.570[]
141.22[]
3587.08
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
CONDENSER DRAIN
3/8" NPT
55.30[]
1404.67
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
1447.8[57.0]
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
24.12[]
612.76
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
8.61[]
218.65
2281.37
COOLER LEAVING
WATER 6" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER LEAVING
1/4" NPT
COOLER VENT
89.82[]
725.63
WATER 3.0" VICTAULIC
28.57[]
COOLER ENTERING
16.10[]
408.89
3/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN
18.65[]
473.75
15.43[]
391.88
24.98[]
2X 634.55
13.59[]
2X 345.08
1/4" NPT
CONDENSER VENT
WATER 6" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER ENTERING
WATER 3.0" VICTAULIC
12.41[]
315.25
CGy
MM [INCH]
CGx
CENTER OF GRAVITY
MM [INCH]
MCHX
lb/kg
WEIGHT
1064
[41.89]
1759
[69.25]
7133
3236
30RB-110
1067
[42.00]
1676
[65.98]
6769
3071
30RB-100
1088
[42.84]
1689
[66.50]
6555
2974
30RB-090
11
Page 12
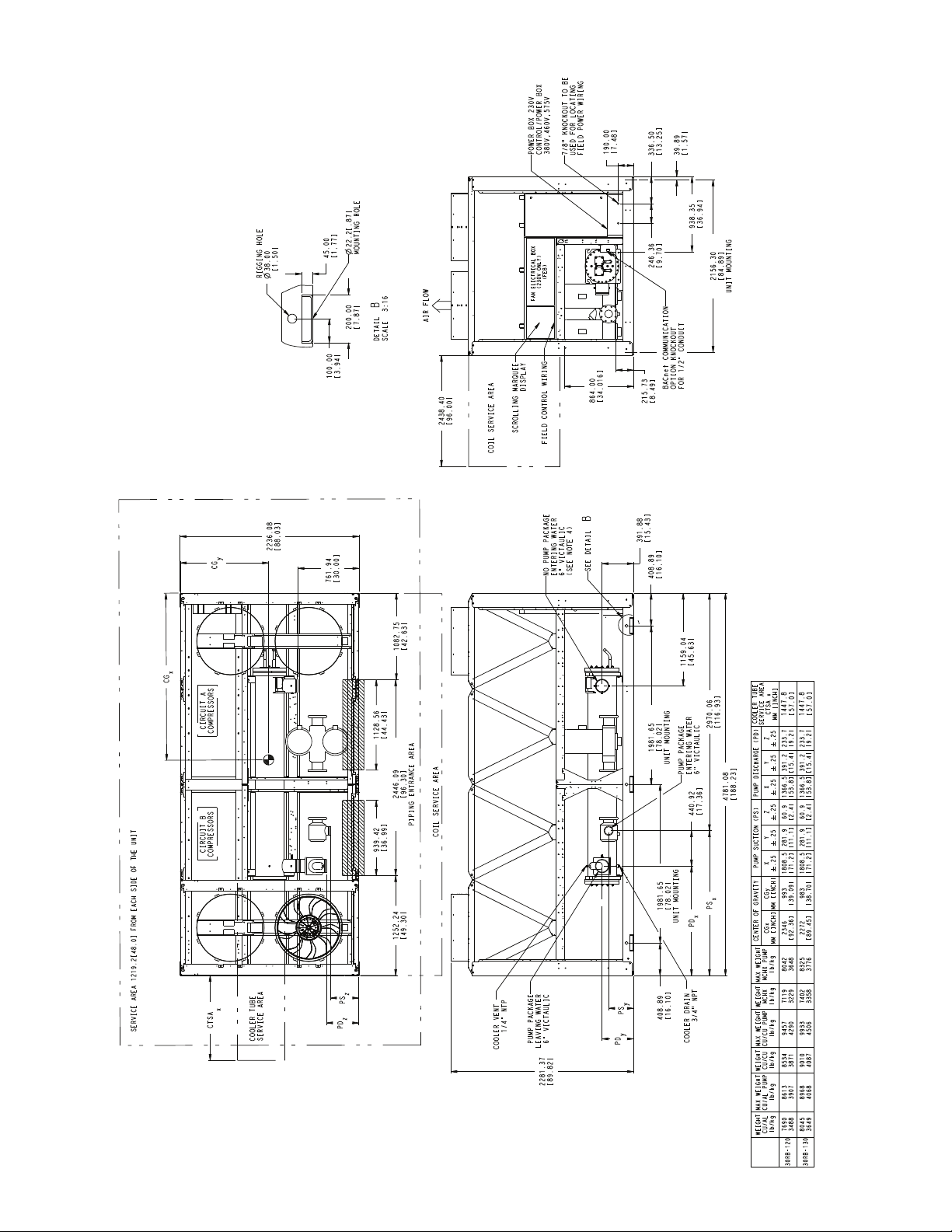
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
Airflow side — 82.4 mrequired for coil service area.
2. All pumps have drains located at the bottom of volute for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and filter drier
of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
4. No pump package leaving water connection is same size and has same Y
and Z dimensions as entering water. Also has same PDx dimension as
pump package.
5. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
a30-5333
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 8 — 30RB120, 130 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
12
Page 13
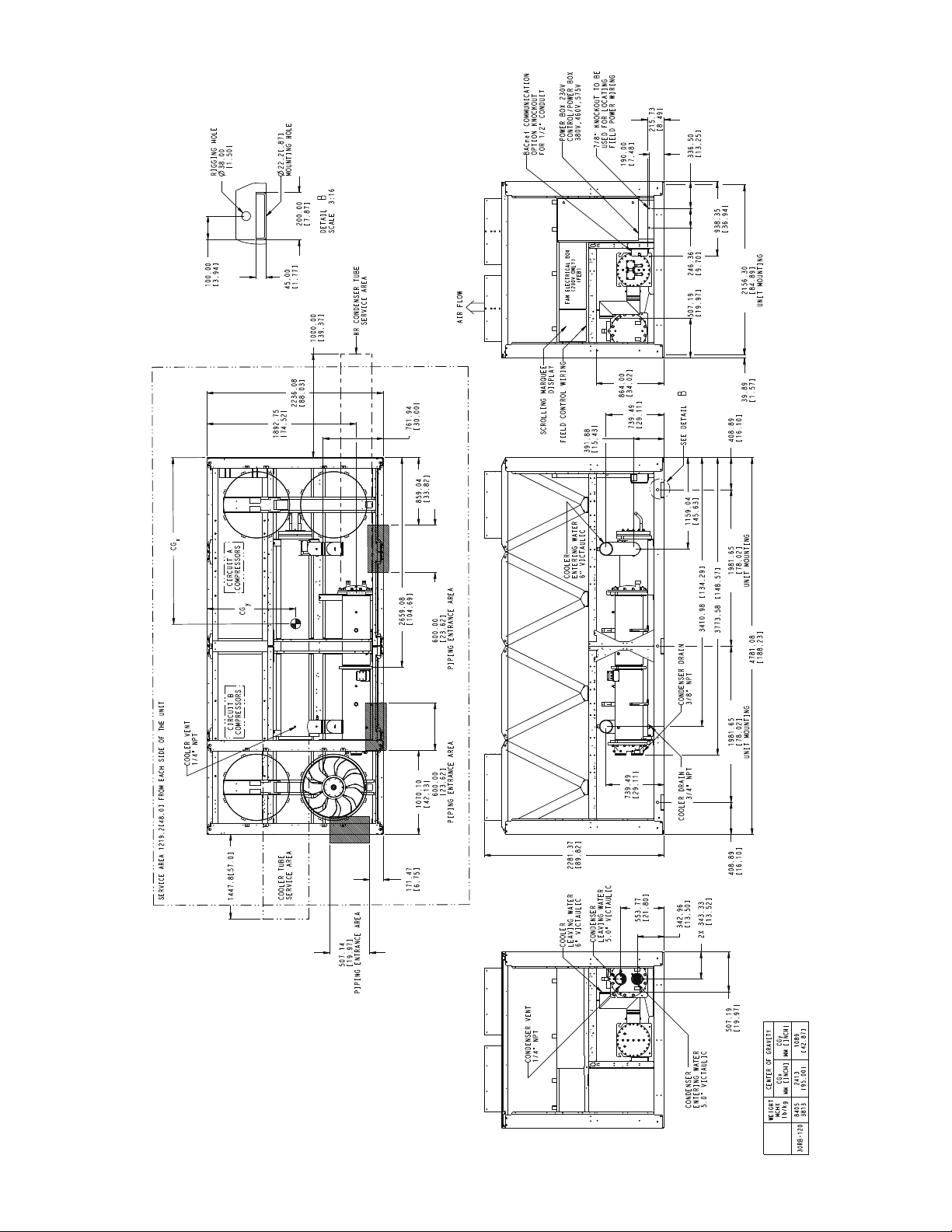
2236.08
88.03[]
761.94
30.00[]
859.04
33.82[]
CG
y
x
CG
2281.37
89.82[]
4781.08
188.23[]
1159.04
45.63[]
391.88
15.43[]
408.89
16.10[]
408.89
16.10[]
246.36
9.70[]
336.50
13.25[]
190.00
7.48[]
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
45.00
1.77[]
RIGGING HOLE
38.00
1.50[]
1447.8[57.0]
UNIT MOUNTING
1981.65
78.02[]
UNIT MOUNTING
1981.65
78.02[]
864.00
34.02[]
39.89
1.57[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.89[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
600.00
23.62[]
1070.10
42.13[]
171.47
6.75[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
507.14
19.97[]
2X 343.33
13.52[]
342.96
13.50[]
553.77
21.80[]
3410.98 134.29[]
1892.75
74.52[]
2659.08
104.69[]
1000.00
[39.37]
3773.58
148.57[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
600.00
23.62[]
507.19
19.97[]
739.49
29.11[]
739.49
29.11[]
507.19
19.97[]
215.73
8.49[]
938.35
36.94[]
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-120
8405
3813
2413
[95.00]
1089
[42.87]
HR CONDENSER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT
COOLER
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
SEE DETAIL
B
CONDENSER DRAIN
3/8" NPT
AIR FLOW
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(230V ONLY)
(FEB)
POWER BOX 230V
CONTROL/POWER BOX
380V,460V,575V
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
COOLER VENT
1/4" NPT
DETAIL
B
SCALE 3:16
22.2[.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
CONDENSER VENT
1/4" NPT
COOLER
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER
LEAVING WATER
5.0" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER
ENTERING WATER
5.0" VICTAULIC
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid sur-
face.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suc-
tion line, liquid line and filter drier of each
circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on
either side of unit for condenser coil
removal.
a30-4736
LEGEND
HR — Heat Reclaim
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 9 — 30RB120 Air-Cooled Chiller with Heat Reclaim Option Dimensions
13
Page 14
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and fil-
ter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for con-
denser coil removal.
LEGEND
HR — Heat Reclaim
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 10 — 30RB130 Air-Cooled Chiller with Heat Reclaim Option Dimensions
a30-4737
14
Page 15
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. All pumps have drains located at the bottom of volute for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and filter drier of
each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
4. Units without a pump package have the same leaving water connection, Y and Z
dimensions (entering water), and Pump Discharge X dimensions as units with a
pump package.
5. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
6. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for condenser coil
removal.
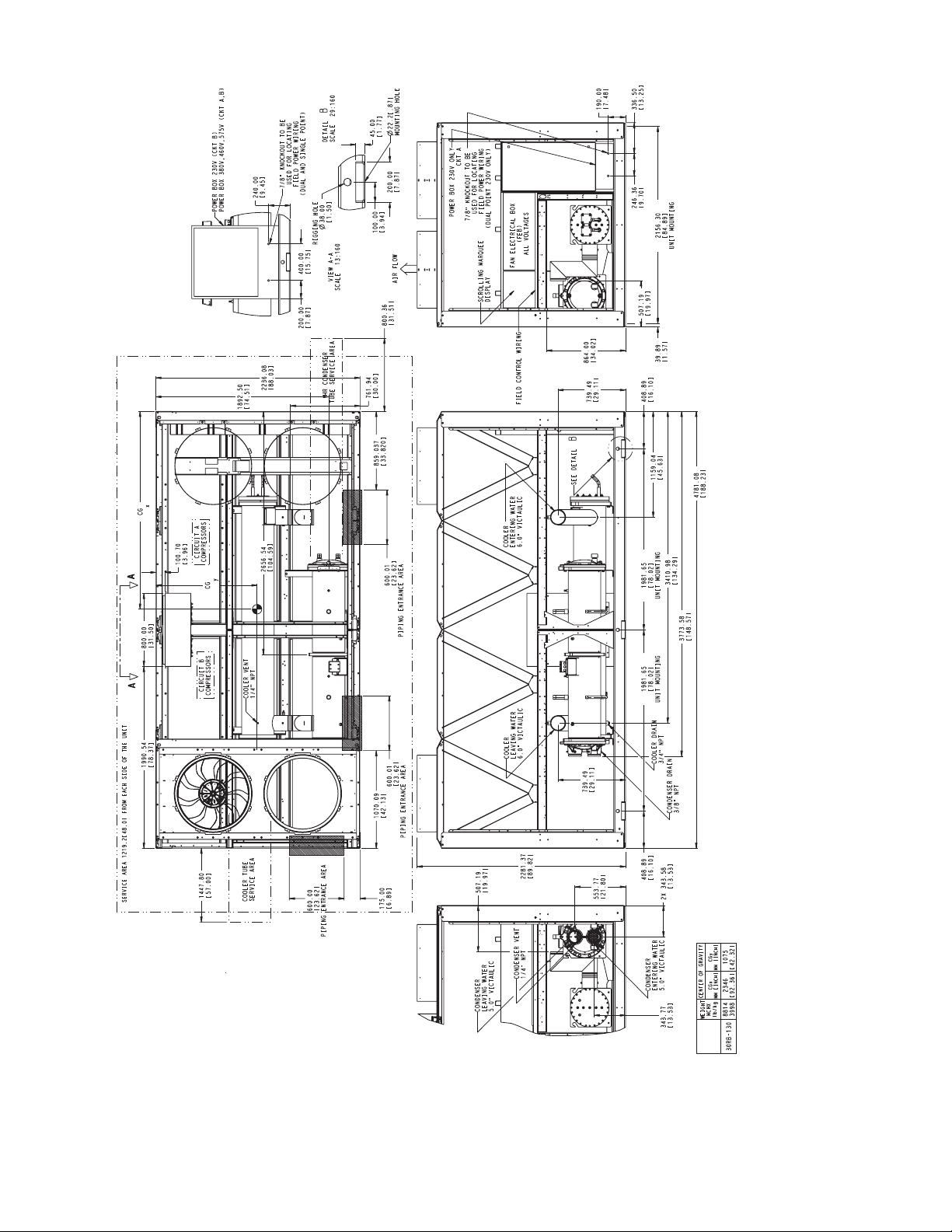
Fig. 11 — 30RB150 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
15
Page 16
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and filter drier
of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for condenser coil
removal.
a30-4738
LEGEND
HR — Heat Reclaim
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 12 — 30RB150 Air-Cooled Chiller with Heat Reclaim Option Dimensions
16
Page 17
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. All pumps have drains located at the bottom of volute for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
4. Units without a pump package have the same leaving water connection, Y and Z dimensions (entering
water), and Pump Discharge X dimensions as units with a pump package.
5. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
6. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for condenser coil removal.
a30-4715
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
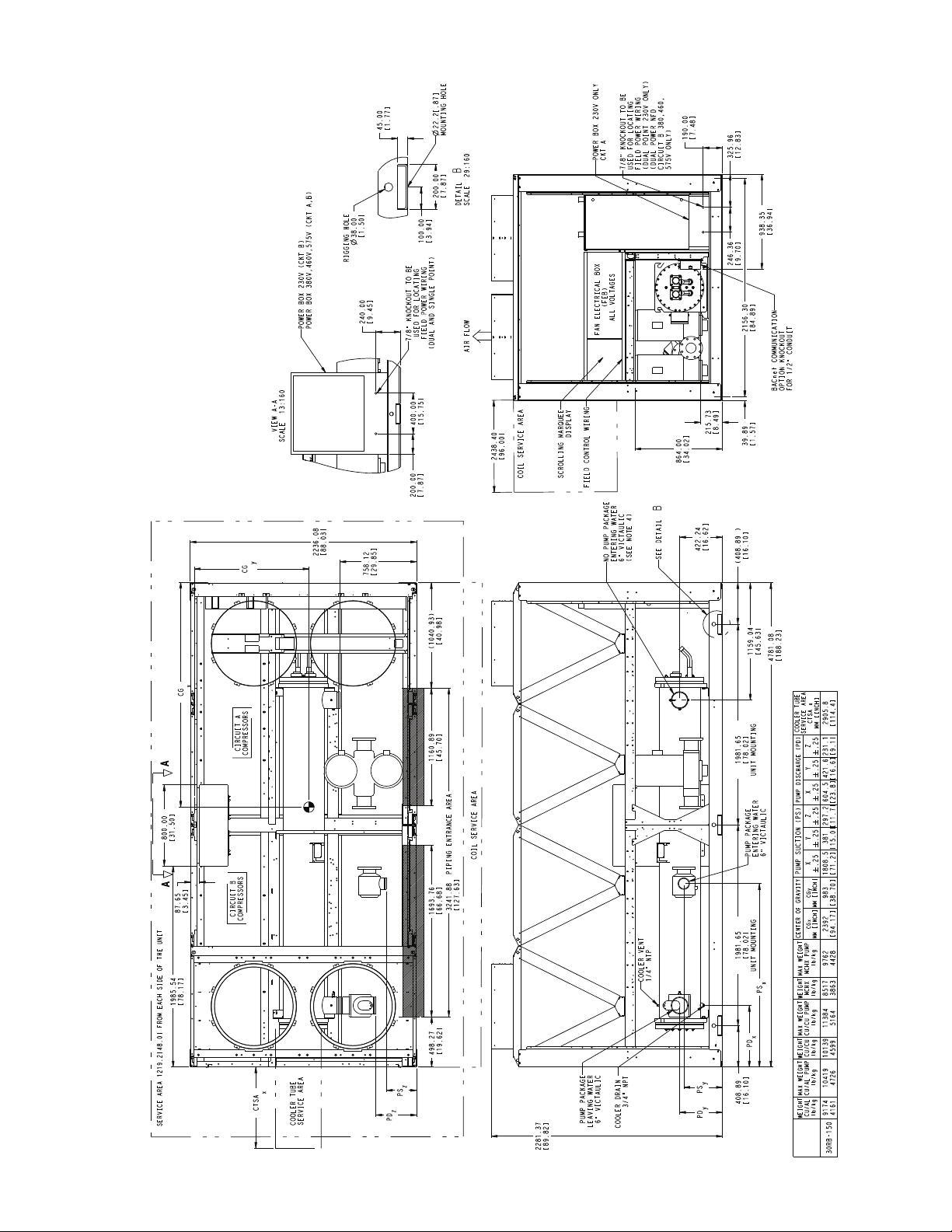
Fig. 13 — 30RB160, 170, 315A/B, 330A/B, 345A/B, 360B Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
5975.08
235.24[]
PS
x
4164.06
163.94[]
408.89
16.10[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2769.30
109.03[]
408.89
16.10[]
PD
x
923.39
36.35[]
PD
y
PS
y
422.24
16.62[]
2073.54
81.64[]
2281.37
89.82[]
864.00
34.02[]
2016.54
79.39[]
800.00
31.50[]
101.20
3.98[]
2236.08
88.03[]
PS
z
PD
z
CG
y
CG
x
1447.8
[57.00]
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
769.51
30.30[]
1483.83
58.42[]
1456.33
57.34[]
1993.25
78.47[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA3212.33
126.47[]
755.58
29.75[]
246.36
9.70[]
190.00
7.48[]
336.50
13.25[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2388.00
94.016[]
400.00
15.75[]
200.00
7.87[]
240.00
9.45[]
39.89
1.57[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.89[]
2438.40
[96.00]
RIGGING HOLE
38.00
1.50[]
938.35
36.94[]
215.73
8.49[]
WEIGHT
CU/AL
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
CU/AL PUMP
lb/kg
WEIGHT
CU/CU
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
CU/CU PUMP
lb/kg
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
MAX WEIGHT
MCHX PUMP
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY PUMP SUCTION (PS) PUMP DISCHARGE (PD)
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
X
.25
Y
.25
Z
.25
X
.25
Y
.25
Z
.25
30RB-160
315A/B,330B
10266
4666
11511
5232
11472
5215
12717
5781
9475
4297
10720
4860
3065
[120.66]
994
[39.13]
1808.48
[71.2]
381
[15.0]
297.2
[11.7]
883.92
[34.8]
421.64
[16.6]
231.14
[9.1]
30RB-170
330A,345A/B,360B
10601
4819
11846
5385
11807
5367
13052
5933
9799
4443
11044
5009
3114
[122.59]
978
[30.5]
1808.48
[71.2]
381
[15.0]
297.2
[11.7]
883.92
[34.8]
421.64
[16.6]
231.14
[9.1]
AIR FLOW
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
A
A
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(FEB)
ALL VOLTAGES
VIEW-A-A
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
COOLER VENT 1/4" NPT
PUMP PACKAGE
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT}
NO PUMP PACKAGE
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
(SEE NOTE 4)
PUMP PACKAGE
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
POWER BOX 230V ONLY (CKT A)
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL POINT 230V ONLY)
(DUAL POWER NFD
CIRCUIT B 380,460,575V
ONLY)
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
COIL SERVICE AREA
COIL SERVICE AREA
SEE DETAIL
B
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL AND SINGLE POINT)
POWER BOX 230V (CKT B)
POWER BOX
380V,460V,575V (CKT A,B)
DETAIL
B
SCALE 3:16
22.2 [.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
17
Page 18
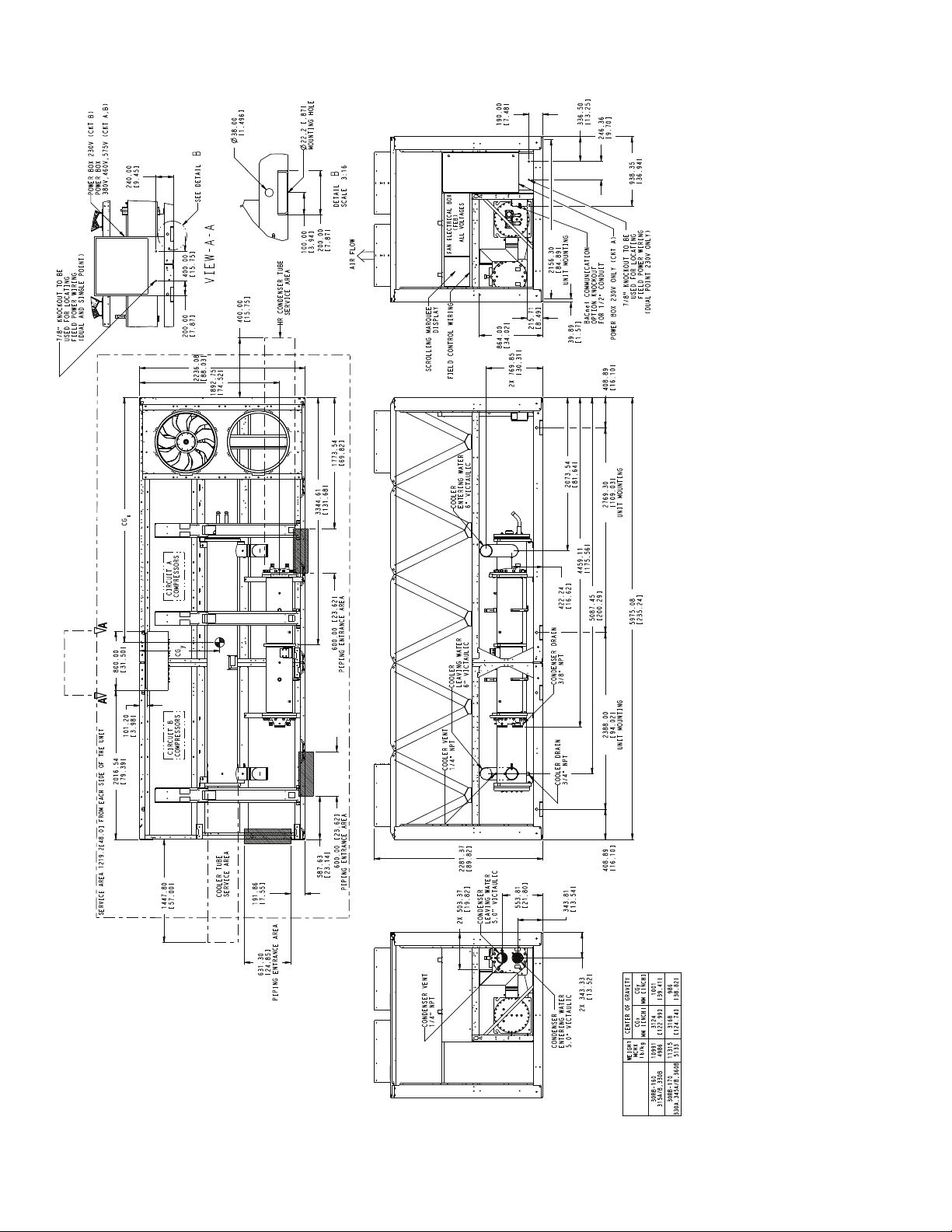
5975.08
235.24[]
408.89
16.10[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2769.30
109.03[]
408.89
16.10[]
422.24
16.62[]
2073.54
81.64[]
2281.37
89.82[]
864.00
34.02[]
2016.54
79.39[]
800.00
31.50[]
101.20
3.98[]
2236.08
88.03[]
CG
y
CG
x
1447.80
[57.00]
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
1773.54
69.82[]
246.36
9.70[]
190.00
7.48[]
336.50
13.25[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2388.00
94.02[]
400.00
15.75[]
200.00
7.87[]
240.00
9.45[]
39.89
1.57[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.89[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
600.00 23.62[]
191.86
7.55[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
631.30
24.85[]
400.00
[15.75]
553.81
21.80[]
343.81
13.54[]
2X 343.33
13.52[]
3344.61
131.68[]
1892.75
74.52[]
4459.11
175.56[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
600.00
23.62[]
587.63
23.14[]
2X 503.37
19.82[]
2X 769.85
30.31[]
5087.45
200.29[]
938.35
36.94[]
215.71
8.49[]
38.00
1.496[]
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-160
315A/B,330B
10991
4986
3124
[122.99]
1001
[39.41]
30RB-170
330A,345A/B,360B
11315
5133
3168
[124.74]
986
[38.82]
AIR FLOW
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
A
A
VIEW-A-A
COOLER VENT
1/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT
COOLER
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
COOLER
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER DRAIN
3/8" NPT
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(FEB)
ALL VOLTAGES
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
POWER BOX 230V ONLY (CKT A)
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL POINT 230V ONLY)
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
HR CONDENSER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SEE DETAIL
B
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL AND SINGLE POINT)
POWER BOX 230V (CKT B)
POWER BOX
380V,460V,575V (CKT A,B)
DETAIL
B
SCALE 3:16
22.2 [.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
CONDENSER
LEAVING WATER
5.0" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER
ENTERING WATER
5.0" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER VENT
1/4" NPT
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and filter drier
of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for condenser coil
removal.
a30-4739
LEGEND
HR — Heat Reclaim
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
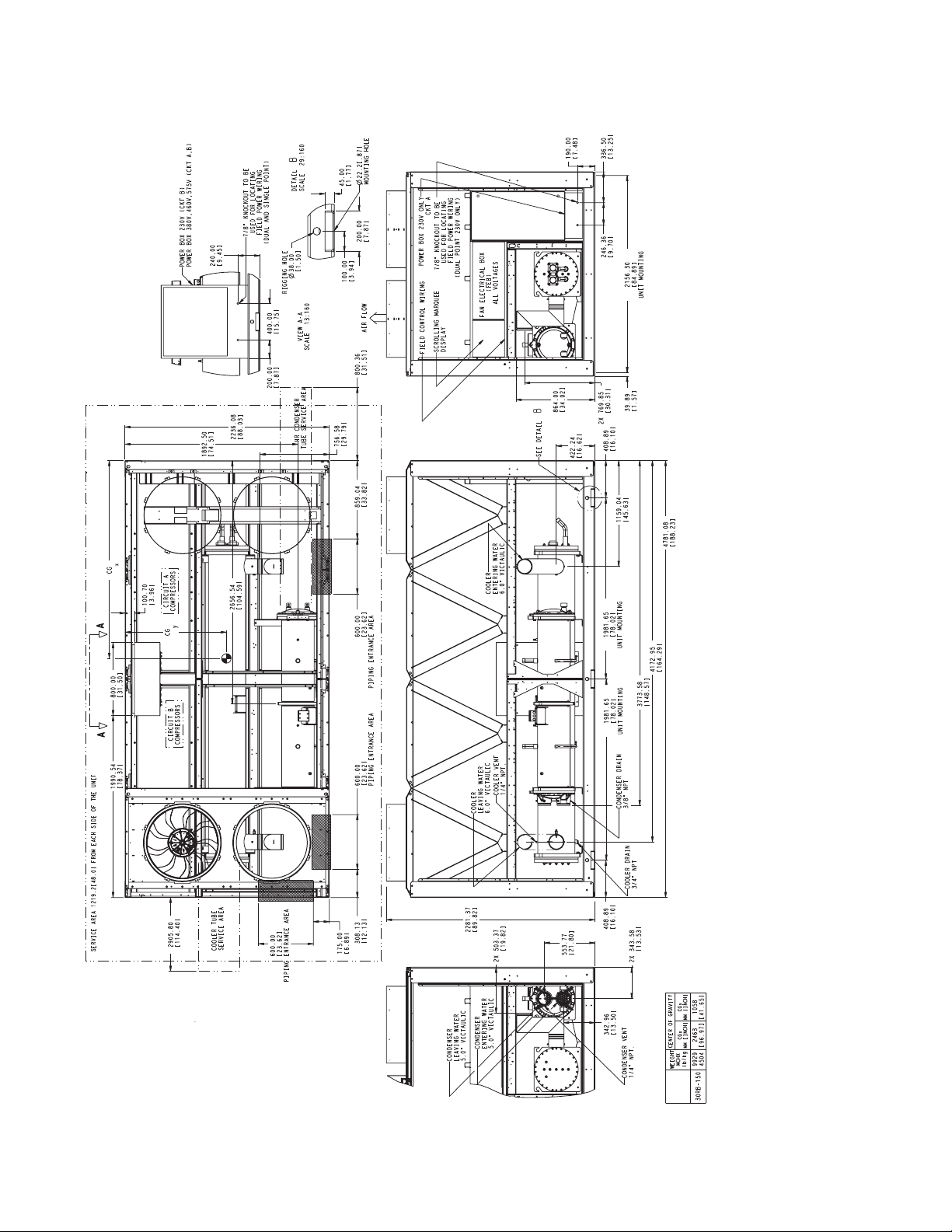
Fig. 14 — 30RB160,170 Air-Cooled Chiller with Heat Reclaim Option Dimensions
18
Page 19
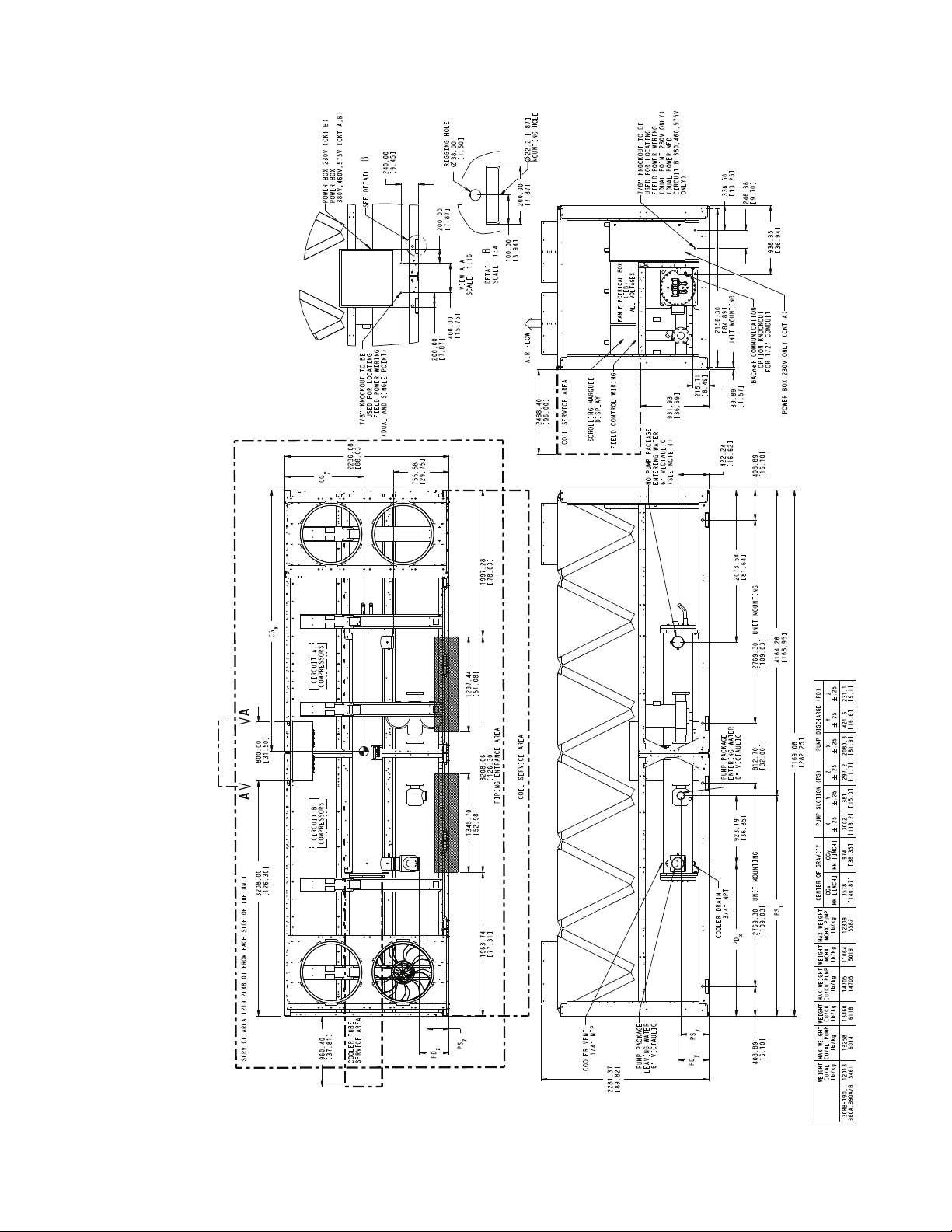
B
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. All pumps have drains located at the bottom of volute for draining.
3. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and
filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
4. Units without a pump package have the same leaving water con-
nection, Y and Z dimensions (entering water), and Pump Dis-
charge X dimensions as units with a pump package.
5. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for con-
denser coil removal.
6. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
a30-4589
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
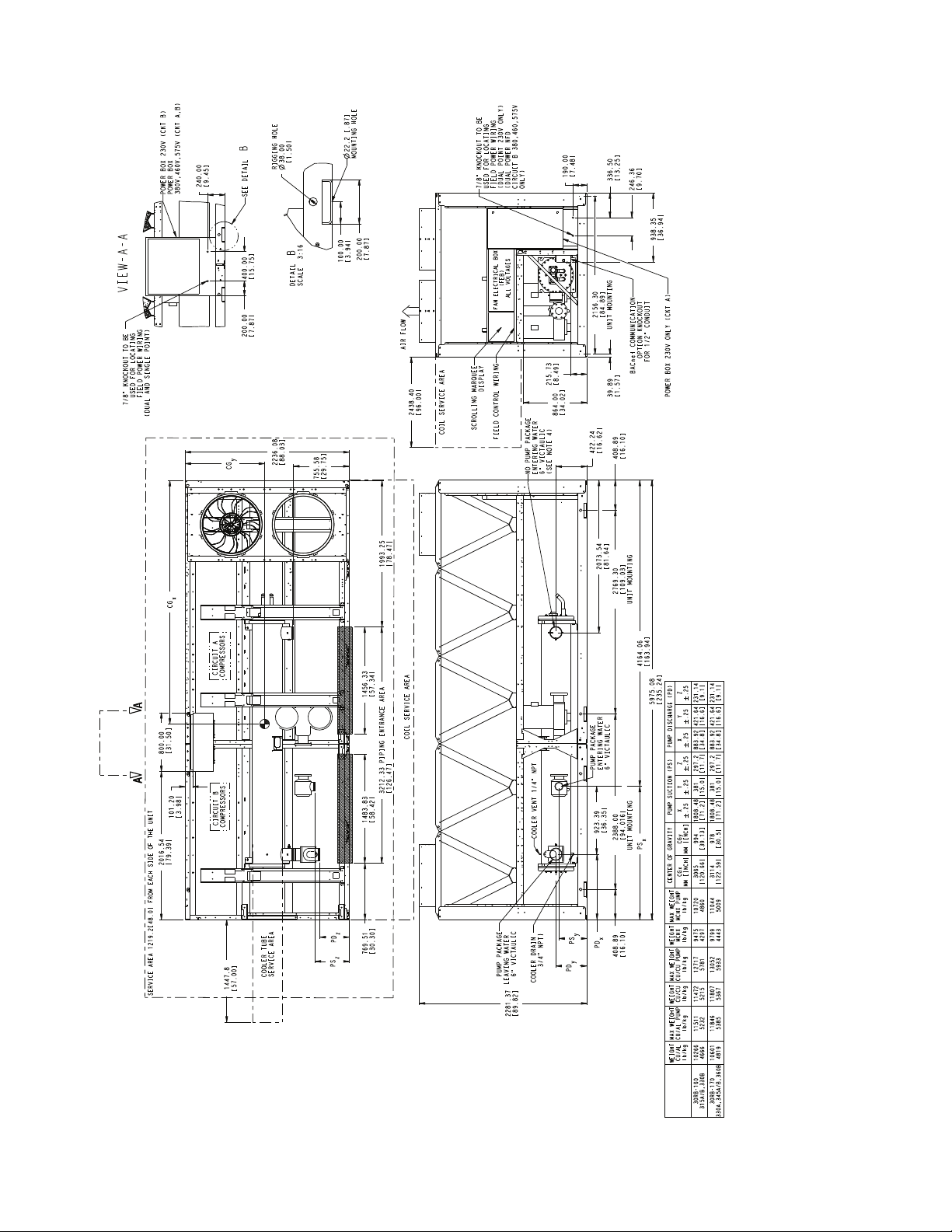
Fig. 15 — 30RB190, 360A, 390A/B Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
100.00
DETAIL
SCALE 1:4
78.63[]
1997.28
22.2 [.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
7.87[]
200.00
3.94[]
AIR FLOW
2438.40
[96.00]
COIL SERVICE AREA
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
(FEB)
ALL VOLTAGES
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
DISPLAY
SCROLLING MARQUEE
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL POINT 230V ONLY)
(DUAL POWER NFD
CIRCUIT B 380,460,575V
ONLY)
215.71
36.69[]
931.93
NO PUMP PACKAGE
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
(SEE NOTE 4)
336.50
84.89[]
2156.30
8.49[]
422.24
13.25[]
9.70[]
246.36
UNIT MOUNTING
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
BACnet COMMUNICATION
1.57[]
39.89
16.62[]
16.10[]
408.89
81.64[]
2073.54
36.94[]
938.35
POWER BOX 230V ONLY (CKT A)
1.50[]
38.00
200.00
200.00
29.75[]
755.58
RIGGING HOLE
7.87[]
VIEW A-A
15.75[]
400.00
7.87[]
SCALE 1:16
9.45[]
240.00
POWER BOX 230V (CKT B)
POWER BOX
380V,460V,575V (CKT A,B)
SEE DETAIL B
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
y
CG
(DUAL AND SINGLE POINT)
88.03[]
2236.08
x
CG
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
A
31.50[]
800.00
A
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
126.30[]
3208.00
37.81[]
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
960.40
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
UNIT MOUNTING2769.30
163.95[]
4164.26
109.03[]
51.08[]
1297.44
32.00[]
126.30[]
3208.06
COIL SERVICE AREA
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
52.98[]
1345.70
77.31[]
1963.74
y
6" VICTAULIC
LEAVING WATER
PS
y
PD
z
PS
z
PD
1/4" NTP
COOLER VENT
89.82[]
2281.37
PUMP PACKAGE
PUMP PACKAGE
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
36.35[]
923.19
3/4" NPT
x
COOLER DRAIN
PD
812.70
UNIT MOUNTING2769.30
x
PS
109.03[]
16.10[]
408.89
282.25[]
7169.08
Z
.25
231.1
[9.1]
Y
.25
421.6
[16.6]
X
.25
2080.3
[81.9]
Z
.25
297.2
[11.7]
Y
.25
381
[15.0]
X
.25
3002
[118.2]
CGy
974
[38.35]
MM [INCH]
CGx
3578
CENTER OF GRAVITY PUMP SUCTION (PS) PUMP DISCHARGE (PD)
[140.87]
MM [INCH]
5582
lb/kg
12309
MCHX PUMP
MAX WEIGHT
MCHX
5019
lb/kg
11064
WEIGHT
lb/kg
14705
14705
MAX WEIGHT
CU/CU PUMP
6118
CU/CU
lb/kg
13460
WEIGHT
6014
lb/kg
13258
MAX WEIGHT
CU/AL PUMP
5461
CU/AL
lb/kg
12013
WEIGHT
30RB-190,
360A,390A/B
19
Page 20
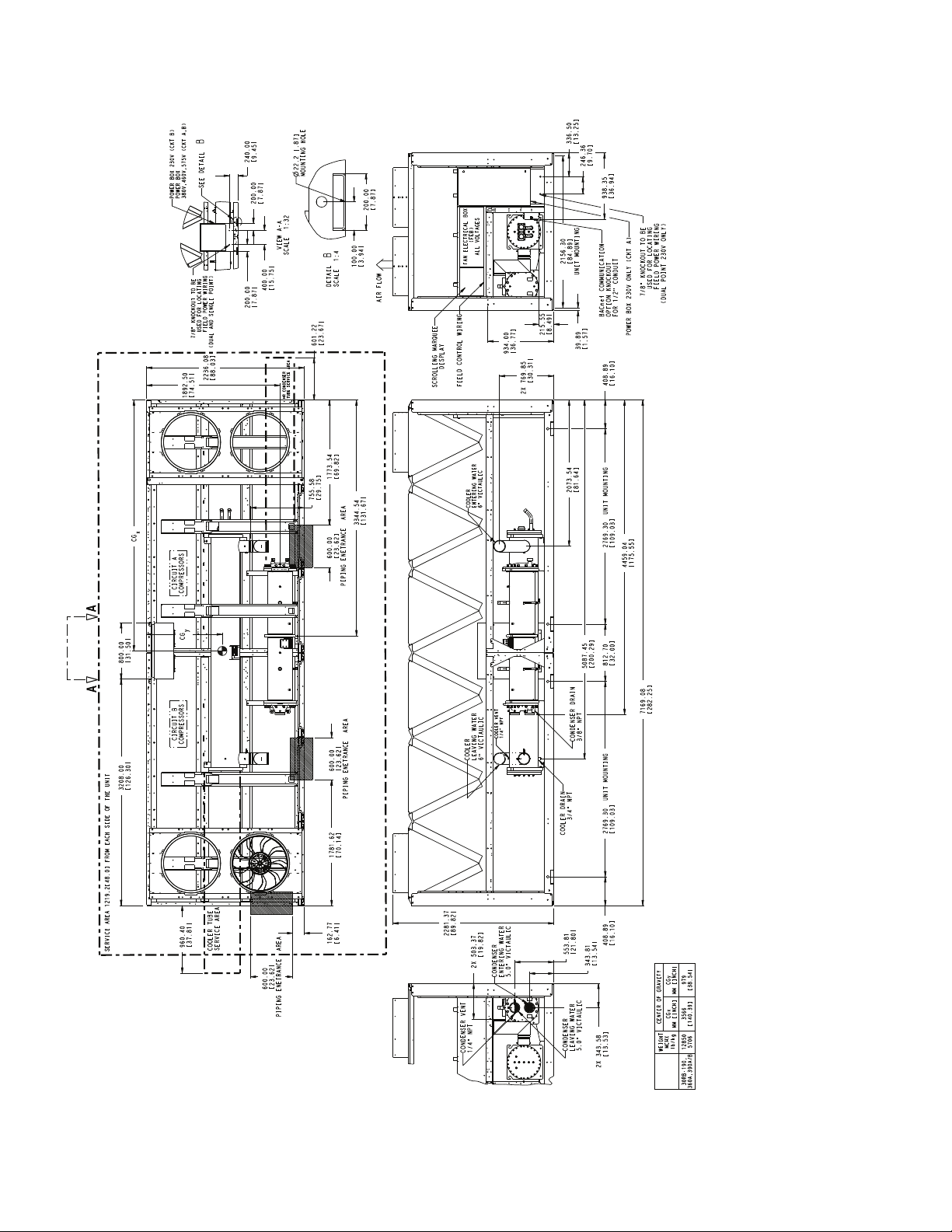
2281.37
89.82[]
408.89
16.10[]
UNIT MOUNTING2769.30
109.03[]
812.70
32.00[]
UNIT MOUNTING2769.30
109.03[]
408.89
16.10[]
2073.54
81.64[]
7169.08
282.25[]
3208.00
126.30[]
800.00
31.50[]
1781.62
70.14[]
1773.54
69.82[]
755.58
29.75[]
2236.08
88.03[]
934.00
36.77[]
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
y
CG
CG
x
960.40
37.81[]
400.00
15.75[]
240.00
9.45[]
246.36
9.70[]
336.50
13.25[]
39.89
1.57[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.89[]
200.00
7.87[]
200.00
7.87[]
2X 343.58
13.53[]
343.81
13.54[]
553.81
21.80[]
5087.45
200.29[]
3344.54
131.67[]
1892.50
74.51[]
4459.04
175.55[]
601.22
23.67[]
PIPING ENETRANCE AREA
600.00
23.62[]
PIPING ENETRANCE AREA
600.00
23.62[]
PIPING ENETRANCE AREA
600.00
23.62[]
162.77
6.41[]
2X
503.37
19.82[]
2X 769.85
30.31[]
938.35
36.94[]
215.55
8.49[]
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-190,
360A,390A/B
12850
5706
3566
[140.39]
979
[38.54]
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
A
A
HR CONDENSER
TUBE SERVICE AREA
COOLER VENT
1/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT
COOLER
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
COOLER
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER DRAIN
3/8" NPT
AIR FLOW
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(FEB)
ALL VOLTAGES
POWER BOX 230V ONLY (CKT A)
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL POINT 230V ONLY)
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
SEE DETAIL B
VIEW A-A
SCALE 1:32
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL AND SINGLE POINT)
POWER BOX 230V (CKT B)
POWER BOX
380V,460V,575V (CKT A,B)
DETAIL B
SCALE 1:4
22.2 [.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
CONDENSER
ENTERING WATER
5.0" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER
LEAVING WATER
5.0" VICTAULIC
CONDENSER VENT
1/4" NPT
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and filter drier
of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for condenser coil
removal.
a30-4740
LEGEND
HR — Heat Reclaim
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 16 — 30RB190 Air-Cooled Chiller with Heat Reclaim Option Dimensions
20
Page 21
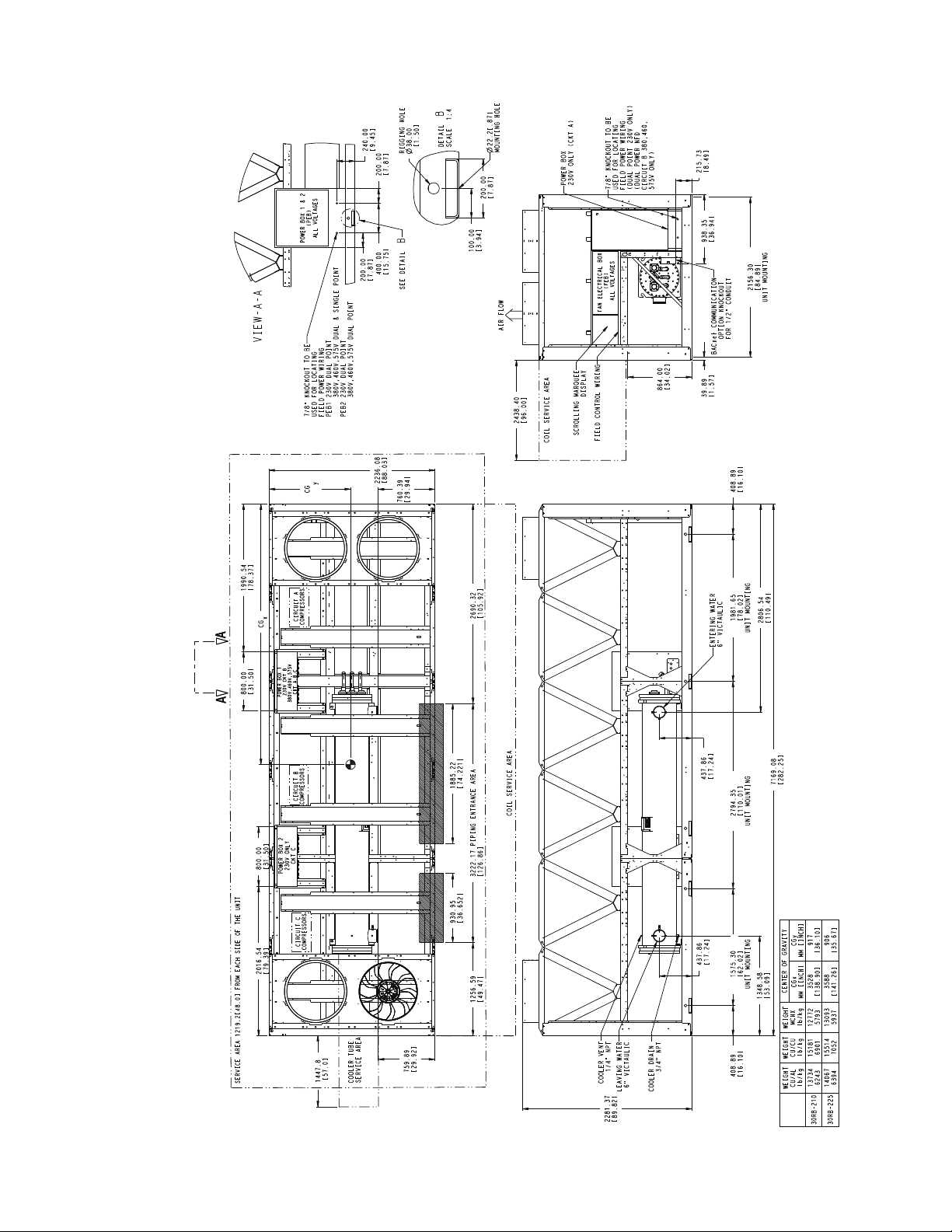
7169.08
282.25[]
2806.54
110.49[]
800.00
31.50[]
CG
x
930.95
36.652[]
1885.22
74.221[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA3222.17
126.86[]
1348.58
53.09[]
1256.59
49.47[]
2690.32
105.92[]
2236.08
88.03[]
760.39
29.94[]
1447.8
[57.0]
400.00
15.75[]
240.00
9.45[]
CG
y
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
RIGGING HOLE
38.00
1.50[]
864.00
34.02[]
408.89
16.10[]
UNIT MOUNTING
1981.65
78.02[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2794.35
110.01[]
UNIT MOUNTING
1575.30
62.02[]
408.89
16.10[]
2281.37
89.82[]
437.86
17.24[]
437.86
17.24[]
200.00
7.87[]
200.00
7.87[]
1990.54
78.37[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.89[]
39.89
1.57
[]
800.00
31.50[]
2016.54
79.39[]
759.89
29.92[]
2438.40
[96.00]
938.35
36.94[]
215.73
8.49[]
WEIGHT
CU/AL
lb/kg
WEIGHT
CU/CU
lb/kg
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-210
13734
6243
15181
6901
12772
5793
3528
[138.90]
917
[36.10]
30RB-225
14067
6394
15514
7052
13093
5937
3588
[141.26]
906
[35.67]
CIRCUIT C
COMPRESSORS
POWER BOX 2
230V ONLY
CKT C
POWER BOX 1 & 2
(PEB)
ALL VOLTAGES
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
COOLER VENT
1/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
A
A
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
POWER BOX 1
230V CKT B
380V,460V,575V
CKT A,B,C
COIL SERVICE AREA
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
PEB1 230V DUAL POINT
380V,460V,575V DUAL & SINGLE POINT
PEB2 230V DUAL POINT
380V,460V,575V DUAL POINT
SEE DETAIL
B
VIEW-A-A
DETAIL B
SCALE 1:4
22.2[.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
POWER BOX
230V ONLY (CKT A)
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(FEB)
ALL VOLTAGES
AIR FLOW
COIL SERVICE AREA
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
(DUAL POINT 230V ONLY)
(DUAL POWER NFD
CIRCUIT B 380,460,
575V ONLY)
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line
and filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for
condenser coil removal.
a30-4716
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 17 — 30RB210, 225 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
21
Page 22
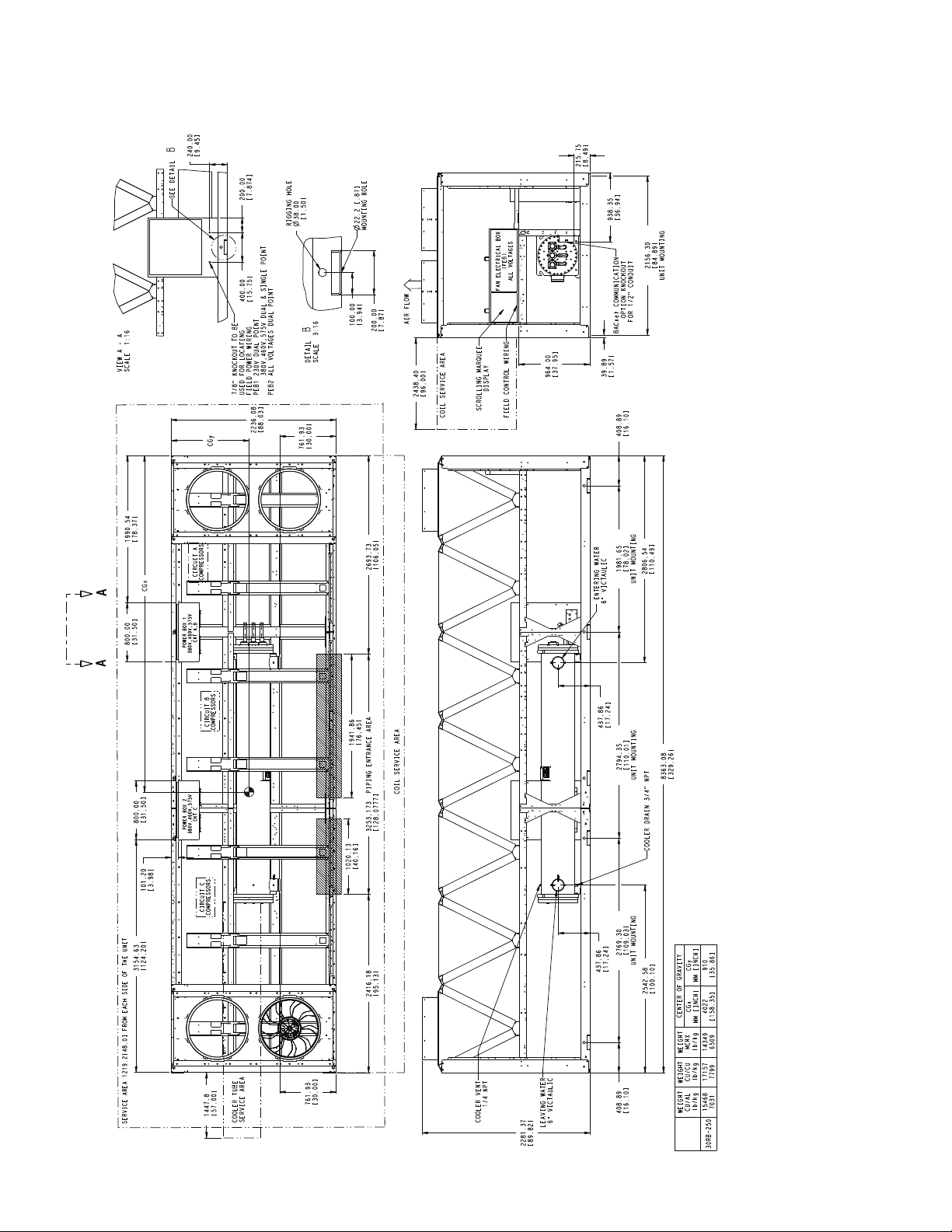
2281.37
89.82[]
408.89
16.10[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2769.30
109.03[]
UNIT MOUNTING
1981.65
78.02[]
408.89
16.10[]
2806.54
110.49[]
8363.08
329.26[]
2236.08
88.03[]
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
RIGGING HOLE
38.00
1.50[]
3154.63
124.20[]
800.00
31.50[]
800.00
31.50[]
CGx
CGy
1020.13
40.16[]
1941.86
76.45[]
2416.18
95.13[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA3253.173
128.0777[]
2693.73
106.05[]
437.86
17.24[]
2542.58
100.10[]
1447.8
[57.00]
101.20
3.98[]
964.00
37.95[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2794.35
110.01[]
39.89
1.57[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.89[]
400.00
15.75[]
240.00
9.45[]
1990.54
78.37[]
200.00
7.874[]
761.93
30.00[]
761.93
30.00[]
437.86
17.24[]
2438.40
[96.00]
938.35
36.94[]
215.75
8.49[]
WEIGHT
CU/AL
lb/kg
WEIGHT
CU/CU
lb/kg
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-250
15468
7031
17157
7799
14349
6509
4022
[158.35]
910
[35.86]
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
COOLER VENT
1/4 NPT
COOLER DRAIN 3/4" NPT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
A
A
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT C
COMPRESSORS
POWER BOX 1
380V,460V,575V
CKT A,B
POWER BOX 2
380V,460V,575V
CKT C
COIL SERVICE AREA
SEE DETAIL
B
VIEW A - A
SCALE 1:16
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
PEB1 230V DUAL POINT
380V,460V,575V DUAL & SINGLE POINT
PEB2 ALL VOLTAGES DUAL POINT
DETAIL
B
SCALE 3:16
22.2 [.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
AIR FLOW
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(FEB)
ALL VOLTAGES
COIL SERVICE AREA
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line
and filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for
condenser coil removal.
a30-4717
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 18 — 30RB250 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
22
Page 23
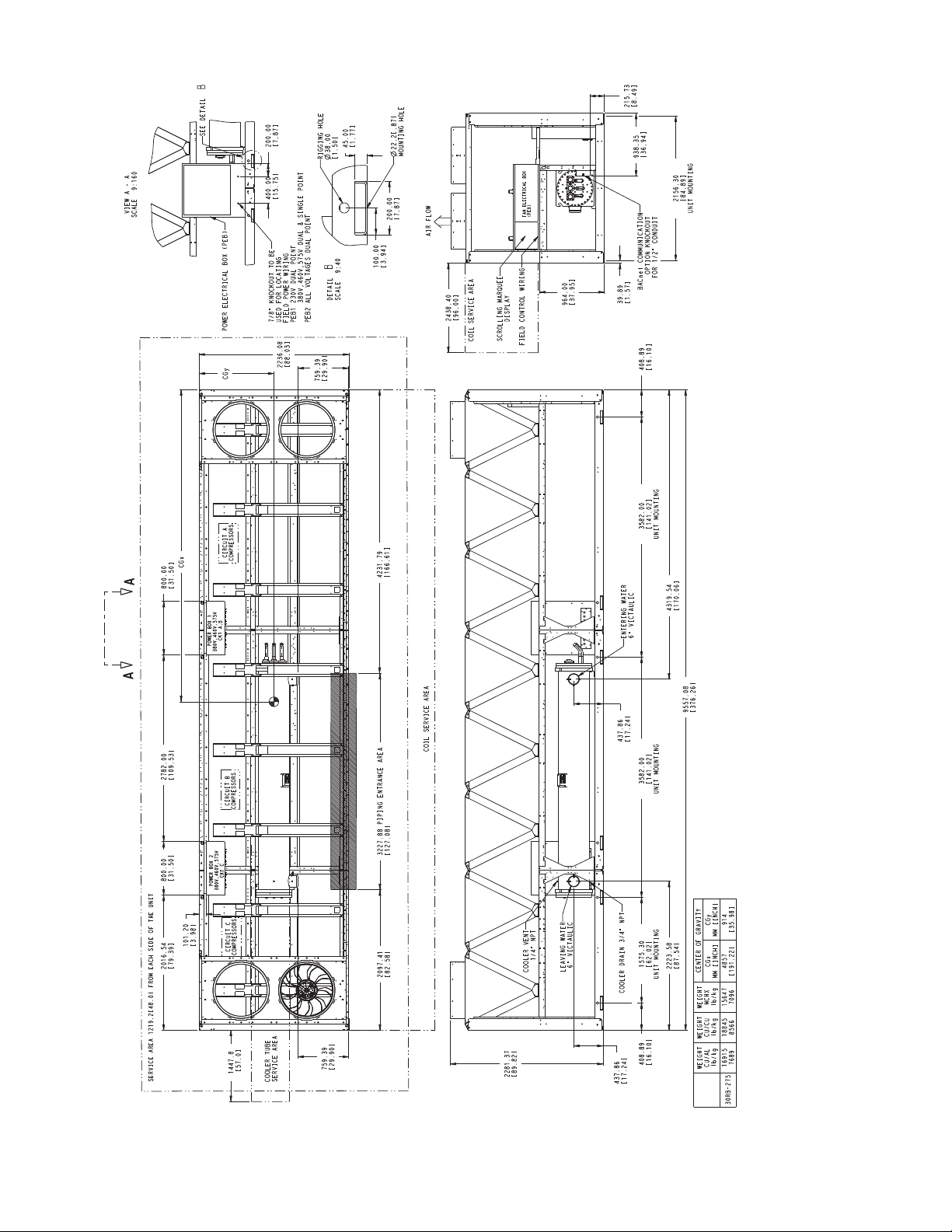
2281.37
89.82[]
4319.54
170.06[]
408.89
16.10[]
UNIT MOUNTING
1575.30
62.02[]
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
2236.08
88.03[]
2016.54
79.39[]
800.00
31.50[]
800.00
31.50[]
437.86
17.24[]
CGy
CGx
45.00
1.77[]
964.00
37.95[]
2097.41
82.58[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA3227.88
127.08[]
4231.79
166.61[]
101.20
3.98[]
2782.00
109.53[]
1447.8
[57.0]
9557.08
376.26[]
408.89
16.10[]
2223.58
87.54[]
UNIT MOUNTING
3582.00
141.02[]
UNIT MOUNTING
3582.00
141.02[]
400.00
15.75[]
200.00
7.87[]
39.89
1.57[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.89[]
759.39
29.90[]
759.39
29.90[]
437.86
17.24[]
2438.40
[96.00]
938.35
36.94[]
215.73
8.49[]
WEIGHT
CU/AL
lb/kg
WEIGHT
CU/CU
lb/kg
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-275
16915
7689
18845
8566
15647
7096
4857
[191.22]
914
[35.98]
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT C
COMPRESSORS
POWER BOX 1
380V,460V,575V
CKT A,B
POWER BOX 2
380V,460V,575V
CKT C
COIL SERVICE AREA
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
COOLER VENT
1/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN 3/4" NPT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
A
A
SEE DETAIL
B
VIEW A - A
SCALE 9:160
POWER ELECTRICAL BOX (PEB)
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
PEB1 230V DUAL POINT
380V,460V,575V DUAL & SINGLE POINT
PEB2 ALL VOLTAGES DUAL POINT
DETAIL
B
SCALE 9:40
22.2[.87]
MOUNTING HOLE
RIGGING HOLE
38.00
[1.50]
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(FEB)
AIR FLOW
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
a30-4718
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and fil-
ter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for con-
denser coil removal.
a30-4718
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 19 — 30RB275 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
23
Page 24

CGy
CGx
2236.08
88.03[]
PIPING ENTRANCE AREA
3342.24
131.58[]
3295.57
129.75[]
4113.26
161.94[]
10751.08
423.27[]
408.89
16.10[]
UNIT MOUNTING}
2769.30
109.03[]
408.89
16.10[]
3417.58
134.55[]
4319.54
170.06[]
437.86
17.24[]
437.86
17.24[]
1447.8
[57.00]
200.00
7.87[]
100.00
3.94[]
45.00
1.77[]
RIGGING HOLE
38.00
1.50[]
864.00
34.02[]
UNIT MOUNTING
3582.00
141.024[]
UNIT MOUNTING
3582.00
141.024[]
2281.37
89.82[]
39.89
1.57[]
UNIT MOUNTING
2156.30
84.894[]
240.00
9.45[]
400.00
15.75[]
200.00
7.874[]
3158.54
124.35[]
800.00
31.50[]
800.00
31.50[]
3210.54
126.40[]
761.93
30.00[]
761.93
30.00[]
2438.40
[96.00]
938.35
36.94[]
215.73
8.49[]
WEIGHT
CU/AL
lb/kg
WEIGHT
CU/CU
lb/kg
WEIGHT
MCHX
lb/kg
CENTER OF GRAVITY
CGx
MM [INCH]
CGy
MM [INCH]
30RB-300
18306
8321
20477
9308
16893
7659
5317
[203.33]
916
[36.06]
SERVICE AREA 1219.2[48.0] FROM EACH SIDE OF THE UNIT
SCROLLING MARQUEE
DISPLAY
CIRCUIT A
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT B
COMPRESSORS
CIRCUIT C
COMPRESSORS
COIL SERVICE AREA
COIL SERVICE AREA
LEAVING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
ENTERING WATER
6" VICTAULIC
COOLER VENT
1/4" NPT
COOLER DRAIN
3/4" NPT
COOLER TUBE
SERVICE AREA
A
A
POWER BOX 1
380V,460V,575V
CKT A,B
POWER BOX 2
380V,460V,575V
CKT C
VIEW A-A
SCALE 1:10
SEE DETAIL
B
POWER ELECTRICAL BOX (PEB)
7/8" KNOCKOUT TO BE
USED FOR LOCATING
FIELD POWER WIRING
PEB1 230V DUAL POINT
380V,460V,575V DUAL & SINGLE POINT
PEB2 ALL VOLTAGES DUAL POINT
DETAIL
B
SCALE 1:5
22.2[.87]
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FAN ELECTRICAL BOX
(FEB)
AIR FLOW
BACnet COMMUNICATION
OPTION KNOCKOUT
FOR 1/2" CONDUIT
NOTES:
1. Unit must have clearances as follows:
Top — Do not restrict.
Sides and End — 6 (1.8 m) from solid surface.
2. Temperature relief devices located on suction line, liquid line and
filter drier of each circuit and have
1
/
4
flare connection.
3. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
4. Allow 8 ft (2.4 m) of service access on either side of unit for con-
denser coil removal.
a30-4719
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
Fig. 20 — 30RB300 Air-Cooled Chiller Dimensions
24
Page 25

AL/CU COIL UNITS WITHOUT PUMP — ENGLISH
UNIT
30RB
060 869 913 1193 1136 4111
070 891 936 1275 1215 4317
080 982 958 1313 1346 4600
090 1159 1397 1845 1531 5932
100 1173 1431 1952 1600 6155
110 1319 1448 1964 1788 6519
UNIT
30RB
120 731 1762 809 985 2347 1056 7,690
130 728 1850 818 1168 2531 949 8,045
150 893 2085 888 1228 2864 1217 9,174
160 1106 2189 1104 1483 2923 1463 10,266
170 1142 2220 1108 1487 3039 1606 10,601
UNIT
30RB
190 1094 1388 1484 1101 1479 2004 1938 1526 12,013
210 916 1804 2139 853 1311 3044 2440 1228 13,734
225 947 1836 2144 855 1313 3049 2569 1354 14,067
250 1122 2271 2133 850 1307 3035 3166 1584 15,468
275 627 2269 2805 1292 1866 3808 3169 1080 16,915
300 899 2602 2792 1284 1859 3795 3640 1435 18,306
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
No Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) No Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) No Pump Al/Cu*
CU/CU COIL UNITS WITHOUT PUMP — ENGLISH
UNIT
30RB
060 992 1037 1311 1254 4,593
070 1014 1059 1393 1333 4,799
080 1106 1081 1431 1464 5,082
090 1342 1584 2020 1711 6,656
100 1355 1619 2126 1780 6,879
110 1503 1635 2139 1967 7,243
UNIT
30RB
120 837 1980 917 1088 2551 1161 8,534
130 850 2100 940 1288 2764 1069 9,010
150 1015 2334 1009 1348 3097 1336 10,139
160 1252 2497 1266 1642 3218 1599 11,472
170 1289 2528 1270 1645 3334 1742 11,807
UNIT
30RB
190 1257 1595 1691 1263 1638 2199 2133 1684 13,460
210 1018 2045 2410 978 1427 3297 2681 1326 15,181
225 1049 2078 2415 981 1429 3301 2810 1452 15,514
250 1283 2577 2404 976 1423 3288 3463 1744 17,157
275 732 2554 3193 1501 2059 4185 3446 1175 18,845
300 1064 2950 3179 1494 2053 4172 3974 1591 20,477
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
No Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) No Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEF G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) No Pump Cu/Cu†
MCHX COIL UNITS WITHOUT PUMP — ENGLISH
UNIT
30RB
060 800 840 1098 1045 3,783
070 821 862 1175 1120 3,978
080 911 889 1218 1249 4,267
090 1065 1283 1695 1406 5,449
100 1079 1316 1796 1472 5,663
110 1219 1339 1816 1653 6,027
UNIT
30RB
120 660 1614 737 915 2210 985 7,119
130 648 1683 738 1088 2377 870 7,402
150 810 1914 805 1146 2706 1136 8,517
160 1020 2020 1019 1368 2698 1350 9,475
170 1055 2052 1024 1374 2809 1485 9,799
UNIT
30RB
190 1007 1278 1367 1014 1362 1846 1785 1405 11,064
210 852 1677 1989 793 1219 2831 2269 1142 12,772
225 881 1709 1996 796 1222 2838 2391 1260 13,093
250 1041 2107 1979 789 1212 2815 2937 1469 14,349
275 580 2099 2594 1195 1726 3523 2931 999 15,647
300 830 2401 2576 1185 1716 3502 3359 1324 16,893
*Condenser Coil: Aluminum Fins/Copper Tubing.
†Condenser Coil: Copper Fins/Copper Tubing.
** Condenser Coil: Microchannel (MCHX) Design.
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
No Pump MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) No Pump MCHX**
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEF G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) No Pump MCHX**
AL/CU COIL UNITS WITHOUT PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 395 415 542 516 1869
070 405 425 580 552 1962
080 447 436 597 612 2091
090 527 635 839 696 2697
100 533 650 887 727 2798
110 600 658 893 813 2963
UNIT
30RB
120 332 79 9 367 447 1065 479 3488
130 330 83 9 371 530 1148 431 3649
150 405 94 6 403 557 1299 552 4161
160 503 995 502 674 1328 665 4666
170 519 1009 503 676 1381 730 4819
UNIT
30RB
190 497 631 674 500 672 911 881 694 5461
210 416 820 972 388 596 1384 1109 558 6243
225 431 835 975 389 597 1386 1168 615 6394
250 510 1032 970 386 594 1380 1439 720 7031
275 285 1032 1275 587 848 1731 1440 491 7689
300 409 1183 1269 584 845 1725 1654 652 8321
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
No Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) No Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) No Pump Al/Cu*
CU/CU COIL UNITS WITHOUT PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 451 471 596 570 2088
070 461 481 633 606 2181
080 503 491 651 665 2310
090 610 720 918 778 3026
100 616 736 966 809 3127
110 683 743 972 894 3292
UNIT
30RB
120 380 89 8 416 494 1157 527 3871
130 386 95 2 426 584 1254 485 4087
150 461 1059 458 611 1405 606 4599
160 569 1135 575 746 1463 727 5215
170 586 1149 577 748 1516 792 5367
UNIT
30RB
190 571 725 769 574 744 1000 970 765 6118
210 463 930 1095 445 649 1498 1219 603 6901
225 477 944 1098 446 650 1501 1277 660 7052
250 583 1171 1093 444 647 1494 1574 793 7799
275 333 1161 1451 682 936 1902 1566 534 8566
300 484 1341 1445 679 933 1896 1807 723 9308
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
No Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) No Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) No Pump Cu/Cu†
MCHX COIL UNITS WITHOUT PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 363 381 498 474 1716
070 372 391 533 508 1804
080 413 403 552 566 1934
090 483 582 769 638 2472
100 489 597 815 668 2569
110 553 607 824 750 2734
UNIT
30RB
120 299 732 334 415 1002 447 3229
130 294 763 335 493 1078 394 3358
150 367 868 365 520 1227 515 3863
160 463 916 492 620 1224 612 4297
170 478 931 464 623 1274 673 4443
UNIT
30RB
190 457 580 620 460 618 837 810 637 5019
210 386 761 902 360 553 1284 1029 518 5793
225 400 775 905 361 554 1287 1084 571 5937
250 472 956 898 358 550 1277 1332 666 6509
275 263 952 1176 542 783 1598 1329 453 7096
300 376 1089 1168 537 778 1588 1523 600 7659
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
No Pump MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) No Pump MCHX**
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) No Pump MCHX**
Fig. 21 — Unit Weights
25
Page 26

AL/CU COIL UNITS WITH SINGLE PUMP — ENGLISH
NOTE: Corner weights are calculated at mounting locations. Refer to Fig. 2-20 (certified drawings) for mounting locations.
Fig. 21 — Unit Weights (cont)
B
CD
A
cooler
Compressors
B
cooler
Compressors
E
C
DF
A
BD
H
A
cooler
C
E
FG
Compressors
B
cooler
Compressors
E
C
DF
A
30RB060-110
30RB160, 170, 315A, 315B, 330A, 330B,
345A, 345B, 360B
30RB190-300, 360A, 390A, 390B
30RB120-150
UNIT
30RB
060 1085 1127 1230 1184 4626
070 1107 1150 1312 1263 4832
080 1193 1164 1354 1388 5100
090 1353 1620 1885 1575 6432
100 1366 1655 1991 1644 6655
110 1565 1653 1974 1868 7059
UNIT
30RB
120 731 2062 960 961 2460 1056 8,230
130 728 2149 969 1144 2645 949 8,585
150 893 2486 1031 1165 3035 1217 9,827
160 1238 2583 1104 1483 3155 1357 10,919
170 1279 2609 1108 1487 3276 1495 11,254
UNIT
30RB
190 1094 1510 1889 1101 1479 2178 1890 1526 12,666
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
Single Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Single Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEF G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Single Pump Al/Cu*
CU/CU COIL UNITS WITH SINGLE PUMP — ENGLISH
UNIT
30RB
060 1208 1250 1348 1302 5,108
070 1230 1273 1430 1381 5,314
080 1317 1287 1472 1506 5,582
090 1537 1806 2060 1753 7,156
100 1549 1841 2166 1823 7,379
110 1749 1839 2150 2045 7,783
UNIT
30RB
120 837 2280 1068 1065 2664 1161 9,074
130 850 2399 1091 1264 2877 1069 9,550
150 1015 2735 1153 1284 3269 1336 10,792
160 1382 2894 1266 1642 3447 1495 12,125
170 1424 2920 1270 1645 3569 1633 12,460
UNIT
30RB
190 1257 1718 2095 1263 1638 2374 2084 1684 14,113
*Condenser Coil: Aluminum Fins/Copper Tubing.
†Condenser Coil: Copper Fins/Copper Tubing.
** Condenser Coil: Microchannel (MCHX) Design.
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
Single Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Single Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCD E FTotal
ABCD E F G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Single Pump Cu/Cu†
AL/CU COIL UNITS WITH SINGLE PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 493 512 559 538 2103
070 503 523 597 574 2196
080 542 529 616 631 2318
090 615 736 857 716 2924
100 621 752 905 747 3025
110 711 751 897 849 3209
UNIT
30RB
120 332 935 435 436 1116 479 3733
130 330 975 440 519 1200 431 3894
150 405 1128 468 528 1377 552 4458
160 563 1174 502 674 1434 617 4963
170 582 1186 503 676 1489 679 5116
UNIT
30RB
190 497 686 858 500 672 990 859 694 5757
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
Single Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Single Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Single Pump Al/Cu*
CU/CU COIL UNITS WITH SINGLE PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 549 568 613 592 2322
070 559 579 650 628 2415
080 599 585 669 684 2537
090 699 821 937 797 3253
100 704 837 985 828 3354
110 795 836 977 930 3538
UNIT
30RB
120 380 1034 484 483 1209 527 4116
130 386 1088 495 573 1305 485 4332
150 461 1241 523 583 1483 606 4895
160 628 1315 575 746 1567 680 5511
170 647 1327 577 748 1622 742 5664
UNIT
30RB
190 571 781 952 574 744 1079 947 765 6415
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
Single Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Single Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Single Pump Cu/Cu†
26
Page 27

MCHX COIL UNITS WITH SINGLE PUMP — ENGLISH MCHX COIL UNITS WITH SINGLE PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 1008 1047 1143 1100 4298
070 1030 1069 1220 1174 4493
080 1115 1088 1266 1298 4767
090 1251 1498 1743 1457 5949
100 1265 1532 1844 1522 6163
110 1456 1537 1836 1738 6567
UNIT
30RB
120 660 1914 887 891 2322 985 7,659
130 648 1982 888 1064 2490 870 7,942
150 810 2316 948 1083 2877 1136 9,170
160 1148 2395 1024 1376 2926 1259 10,128
170 1188 2423 1029 1381 3043 1388 10,452
UNIT
30RB
190 1012 1396 1747 1019 1368 2015 1748 1412 11,717
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
Single Pump MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Single Pump MCHX**
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEF G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Single Pump MCHX**
UNIT
30RB
060 457 475 518 499 1949
070 467 485 553 532 2037
080 506 493 574 589 2162
090 567 679 790 661 2697
100 574 695 836 690 2795
110 660 697 833 788 2978
UNIT
30RB
120 299 86 8 402 404 1053 447 3474
130 294 89 9 403 483 1129 394 3603
150 367 1051 430 491 1305 515 4160
160 521 1086 464 624 1327 571 4593
170 539 1099 467 626 1380 629 4740
UNIT
30RB
190 459 633 792 462 620 914 763 640 5313
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
Single Pump MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Single Pump MCHX**
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Single Pump MCHX**
AL/CU COIL UNITS WITH DUAL PUMP — ENGLISH
UNIT
30RB
060 1218 1259 1254 1213 4,944
070 1240 1281 1336 1293 5,150
080 1372 1339 1389 1424 5,523
090 1518 1808 1919 1611 6,855
100 1530 1843 2025 1680 7,078
110 1741 1796 1983 1922 7,442
UNIT
30RB
120 731 2281 1061 951 2534 1056 8,613
130 728 2367 1071 1133 2719 949 8,968
150 893 2864 1147 1122 3177 1217 10,419
160 1336 2962 1104 1483 3344 1282 11,511
170 1383 2983 1108 1487 3471 1415 11,846
UNIT
30RB
190 1094 1588 2288 1101 1479 2303 1879 1526 13,258
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
Dual Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Dual Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEF GHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Dual Pump Al/Cu*
CU/CU COIL UNITS WITH DUAL PUMP — ENGLISH
UNIT
30RB
060 1341 1382 1371 1331 5,426
070 1363 1405 1453 1411 5,632
080 1495 1462 1507 1541 6,005
090 1702 1994 2095 1788 7,579
100 1714 2030 2201 1858 7,802
110 1926 1982 2160 2099 8,166
UNIT
30RB
120 837 2498 1169 1054 2739 1161 9,457
130 850 2616 1193 1252 2953 1069 9,933
150 1015 3112 1270 1240 3411 1336 11,384
160 1481 3273 1266 1642 3637 1420 12,717
170 1527 3294 1270 1645 3763 1553 13,052
UNIT
30RB
190 1257 1799 2492 1263 1638 2502 2071 1684 14,705
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
Dual Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Dual Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCD E FTotal
ABCD E F G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Dual Pump Cu/Cu†
MCHX COIL UNITS WITH DUAL PUMP — ENGLISH
UNIT
30RB
060 1137 1175 1171 1133 4,616
070 1158 1197 1248 1208 4,811
080 1289 1258 1305 1338 5,190
090 1411 1680 1784 1497 6,372
100 1424 1715 1884 1563 6,586
110 1626 1677 1852 1795 6,950
UNIT
30RB
120 660 2134 987 882 2396 985 8,042
130 648 2201 989 1054 2564 870 8,325
150 810 2695 1063 1041 3017 1136 9,762
160 1244 2759 1028 1381 3114 1194 10,720
170 1289 2781 1033 1386 3236 1319 11,044
UNIT
30RB
190 1016 1474 2124 1022 1373 2138 1745 1417 12,309
*Condenser Coil: Aluminum Fins/Copper Tubing.
†Condenser Coil: Copper Fins/Copper Tubing.
** Condenser Coil: Microchannel (MCHX) Design.
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
Dual Pump MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Dual Pump MCHX**
ABCD E FTotal
ABCD E F G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Dual Pump MCHX**
AL/CU COIL UNITS WITH DUAL PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 554 572 570 552 2247
070 564 582 607 588 2341
080 624 609 631 647 2511
090 690 822 872 732 3116
100 695 838 920 764 3217
110 791 817 901 874 3383
UNIT
30RB
120 332 1035 481 431 1149 479 3907
130 330 1074 486 514 1233 431 4068
150 405 1299 520 509 1441 552 4726
160 607 1347 502 674 1520 583 5232
170 629 1356 503 676 1578 643 5385
UNIT
30RB
190 497 722 1040 500 672 1047 854 1526 6014
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
Dual Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Dual Pump Al/Cu*
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Dual Pump Al/Cu*
CU/CU COIL UNITS WITH DUAL PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 610 628 623 605 2466
070 620 638 661 641 2560
080 680 665 685 701 2730
090 774 906 952 813 3445
100 779 923 1000 845 3547
110 875 901 982 954 3712
UNIT
30RB
120 380 1133 530 478 1242 527 4290
130 386 1187 541 568 1339 485 4506
150 461 1412 576 562 1547 606 5164
160 673 1488 575 746 1653 646 5781
170 694 1497 577 748 1710 706 5933
UNIT
30RB
190 571 818 1133 574 744 1137 941 1684 6669
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
Dual Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Dual Pump Cu/Cu†
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Dual Pump Cu/Cu†
MCHX COIL UNITS WITH DUAL PUMP — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 516 533 531 514 2094
070 525 543 566 548 2182
080 585 571 592 607 2355
090 640 762 809 679 2890
100 646 778 854 709 2987
110 737 761 840 814 3152
UNIT
30RB
120 299 96 8 448 400 1087 447 3648
130 294 99 8 449 478 1163 394 3776
150 367 1223 482 472 1368 515 4428
160 564 1251 466 626 1412 541 4860
170 585 1261 468 629 1468 598 5009
UNIT
30RB
190 461 668 963 463 623 970 791 643 5582
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
Dual Pump MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Dual Pump MCHX**
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEFGHTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Dual Pump MCHX**
Fig. 21 — Unit Weights (cont)
27
Page 28

MCHX COIL UNITS WITH HEAT RECLAIM — ENGLISH
BD
H
A
cooler
C
E
FG
Compressors
30RB190-300, 360A, 390A, 390B
B
CD
A
cooler
Compressors
B
cooler
Compressors
E
C
DF
A
30RB060-110
30RB120-150
B
cooler
Compressors
E
C
DF
A
30RB160, 170, 315A, 315B, 330A, 330B,
345A, 345B, 360B
UNIT
30RB
060 1185 1175 1166 1176 4703
070 1204 1196 1245 1253 4898
080 1302 1215 1289 1381 5187
090 1507 1689 1776 1584 6555
100 1516 1723 1878 1652 6769
110 1671 1732 1899 1832 7133
UNIT
30RB
120 842 2353 889 863 2492 966 8405
130 846 2497 905 1027 2685 854 8814
150 1017 2723 969 1089 3019 1111 9929
160 1229 2841 1168 1314 3127 1312 10991
170 1268 2865 1171 1316 3245 1450 11315
UNIT
30RB
190 962 1311 1461 937 1519 2620 2296 1474 12580
*Condenser Coil: Aluminum Fins/Copper Tubing.
†Condenser Coil: Copper Fins/Copper Tubing.
** Condenser Coil: Microchannel Design.
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb)
Heat Reclaim MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Heat Reclaim MCHX**
ABCDEFTotal
ABCDEF G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (lb) Heat Reclaim MCHX**
MCHX COIL UNITS WITH HEAT RECLAIM — SI
UNIT
30RB
060 538 533 529 533 2133
070 546 542 565 568 2222
080 590 551 585 627 2353
090 683 766 805 718 2974
100 688 782 852 749 3071
110 758 786 861 831 3236
UNIT
30RB
120 382 1067 403 391 1130 438 3813
130 384 1133 411 466 1218 387 3998
150 462 1235 440 494 1370 504 4504
160 557 1289 530 596 1419 595 4986
170 575 1300 531 597 1472 658 5133
UNIT
30RB
190 436 595 663 425 689 1188 1041 669 5706
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg)
Heat Reclaim MCHX**
ABCDTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Heat Reclaim MCHX**
ABCDE FTotal
ABCDE F G HTotal
MOUNTING WEIGHT (kg) Heat Reclaim MCHX**
Fig. 21 — Unit Weights (cont)
28
Page 29

5.12" [130 mm]
1.42" [36 mm]
5.35" [136 mm]
2.56" [65 mm]
4.87" [124 mm]
2.46" [63 mm]
INNER SIDE
OF UNIT
BASE RAIL
OUTER SIDE
OF UNIT
BASE RAIL
Fig. 22 — 30RB Base Rail Cross Section
0.875 DIA. [ø22 mm]
Fig. 23 — 30RB Mounting Plate
MOUNTING HOLE
MOUNTING PLATE
0'– 1-9/16"
[39.89 mm]
REF
1.50 DIA. [ø38 mm]
RIGGING HOLE
MOUNTING
PLATE
0'– 1-3/4"
[44 mm]
BB
SIDE VIEW OF BASE RAIL
AT MOUNTING LOCATION
OUTER SIDE OF BASE RAIL
0'– 5"
[127 mm]
BOTTOM VIEW OF BASE
RAIL AT MOUNTING LOCATION
VIEW B-B
0'– 7-7/8"
[200 mm]
29
0'– 3-15/16"
[100 mm]
Page 30

Table 3A — Physical Data, 30RB060-300 — English
UNIT 30RB 060 070 080 090 100 110 120 130 150
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)*
Al-Cu Condenser Coil 4111 4317 4600 5932 6155 6519 7690 8045 9174
Cu-Cu Condenser Coil 4593 4799 5082 6656 6879 7243 8534 9010 10139
MCHX Condenser Coil 3783 3978 4267 5449 5663 6027 7119 7402 8517
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A, EXV Controlled System
Refrigerant Charge (lb)
Std Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
MCHX Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
COMPRESSORS Scroll, Hermetic
Quantity 334445566
Speed (rpm) 3500
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (2) SH240 (2) SH295 (2) SH240 (2) SH295 (2) SH295 (2) SH295 (2) SH295 (3) SH295 (3) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (1) SH240 (1) SH240 (2) SH240 (2) SH240 (2) SH295 (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH240 (3) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt C N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Oil Charge (Pt, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 26.2/13.1/— 29.2/13.1/— 26.2/26.2/— 29.2/26.2/— 29.2/29.2/— 29.2/39.4/— 29.2/43.8/— 43.8/39.4/— 43.8/43.8/—
No. Capacity Steps
Standard 334445566
Optional (Maximum) 445556677
Minimum Capacity Step (%)
Standard 33 29 25 22 25 18 20 15 17
Optional 22 19 16 14 18 12 14 10 12
Capacity (%)
Ckt A 67 71 50 56 50 45 40 56 50
Ckt B 33 29 50 44 50 55 60 44 50
Ckt C N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
COOLER Direct Expansion, Shell and Tube Type
Weight (empty, lb) 715 715 856 856 856 970 970 970 1518
Net Fluid Volume (gal) 28.2 28.2 31.3 31.3 31.3 45.8 45.8 45.8 73.5
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 445 445 445 445 445 445 445 445 445
Maximum Water Side Pressure
without Pumps (psig) 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300
Maximum Water Side Pressure
with Pumps (psig) 150 150 150 150 150 150 150 150 150
COOLER WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 444446666
Drain (NPT)
CONDENSER FANS Shrouded Axial Type, Vertical Discharge
Standard Low Noise Type
Fan Speed (rpm) Standard 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140
No. Blades...Diameter (in.) 9...30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30
No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 3/1/— 3/1/— 2/2/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/4/— 4/4/— 4/4/—
Total Airflow (cfm) 49,600 49,600 49,600 74,400 74,400 74,400 86,800 99,200 99,200
CONDENSER COILS
No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 3/1/— 3/1/— 2/2/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/4/— 4/4/— 4/4/—
Total Face Area (sq ft) 94 94 94 141 141 141 164 188 188
Max Working Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 656 656 656 656 656 656 656 656 656
OPTIONAL HEAT RECOVERY CONDENSER Flooded, Shell and Tube Type
Weight (lb) (empty) 753 753 753 872 872 872 1236 1236 1236
Net Fluid Volume (gal) 8.0 8.0 8.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 15.1 15.1 15.1
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 656 656 656 656 656 656 656 656 656
Maximum Water Side Pressure (psig) 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300
Water Connections (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 333333555
Drain (NPT)
HYDRONIC MODULE (Optional) Pump(s) with pressure/temperature taps and combination valve.
Pump Single or Dual, 1800 or 3600 rpm
CHASSIS DIMENSIONS (ft-in.)
Length 7-11 11-10 15-9
Width 7-4
Height 7-67/
LEGEND
Al-Cu — Aluminum Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
Cu-Cu — Copper Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
EXV — Electronic Expansion Valve
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
N/A — Not Applicable
*Operating weight does not include any options.
NOTES:
1. 30RB chillers with Greenspeed
2. No pumps are available for unit sizes 210-300.
®
technology are not available in unit sizes 060 and 070.
90/41/—
40/20/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
112/41/—
40/20/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
69/69/—
33/33/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
96/76/—
40/40/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
96/96/—
40/42/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
25
/
16
32
96/106/—
40/51/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
96/133/—
43/57/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
133/106/—
54/43/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
133/133/—
56/62/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
30
Page 31

Table 3A — Physical Data, 30RB060-300 — English
(cont)
UNIT 30RB 160 170 190 210 225 250 275 300
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)*
Al-Cu Condenser Coil 10,266 10,601 12,013 13,734 14,067 15,468 16,915 18,306
Cu-Cu Condenser Coil 11,472 11,807 13,460 15,181 15,514 17,157 18,845 20,477
MCHX Condenser Coil 9,475 9,799 11,064 12,772 13,093 14,349 15,647 16,893
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A, EXV Controlled System
Refrigerant Charge (lb)
Std Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
MCHX Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
COMPRESSORS Scroll, Hermetic
Quantity 7 7 8 9 9 10 11 12
Speed (rpm) 3500
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt C N/A N/A N/A (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295
Oil Charge (Pt, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 58.4/39.4/— 58.4/43.8/— 58.4/58.4/— 43.8/39.4/43.8 43.8/43.8/43.8 43.8/43.8/58.4 58.4/58.4/43.8 58.4/58.4/58.4
No. Capacity Steps
Standard 7 7 8 9 9 10 11 12
Optional (Maximum) 8 8 9 10 10 11 12 13
Minimum Capacity Step (%)
Standard 13 14 13 10 11 10 9 8
Optional 810968776
Capacity (%)
Ckt A 62 57 50 36 33 30 36 33
Ckt B 38 43 50 28 33 30 36 33
Ckt C N/AN/AN/A3633402833
COOLER Direct Expansion, Shell and Tube Type
Weight (empty, lb) 1518 1518 1518 2382 2382 2382 2382 2382
Net Fluid Volume (gal) 73.5 73.5 73.5 86.6 86.6 86.6 86.6 86.6
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 445 445 445 445 445 445 445 445
Maximum Water Side Pressure
without Pumps (psig) 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 300
Maximum Water Side Pressure
with Pumps (psig) 150 150 150 150 150 150 150 150
COOLER WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 66666666
Drain (NPT)
CONDENSER FANS Shrouded Axial Type, Vertical Discharge
Standard Low Noise Type
Fan Speed (rpm) Standard 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140
No. Blades...Diameter (in.) 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30 9…30
No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 6/4/— 6/4/— 6/6/— 4/4/4 4/4/4 4/4/6 6/6/4 6/6/6
Total Airflow (cfm) 124,000 124,000 148,800 148,800 148,800 173,600 198,400 223,200
CONDENSER COILS
No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 6/4/— 6/4/— 6/6/— 4/4/4 4/4/4 4/4/6 6/6/4 6/6/6
Total Face Area (sq ft) 235 235 282 282 282 328 375 422
Max Working Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 656 656 656 656 656 656 656 656
OPTIONAL HEAT RECOVERY CONDENSER Flooded, Shell and Tube Type
Weight (lb) (empty) 1296 1296 1296 — — — — —
Net Fluid Volume (gal) 17.4 17.4 17.4 — — — — —
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 656 656 656 — — — — —
Maximum Water Side Pressure (psig) 300 300 300 — — — — —
Water Connections (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 555—————
Drain (NPT)
HYDRONIC MODULE (Optional) Pump(s) with pressure/temperature taps
Pump Single or Dual, 1800 or 3600 rpm Not available
CHASSIS DIMENSIONS (ft-in.)
Length 19-8 23-7 27-6 31-5 35-4
Width 7-4
Height 7-67/
162/125/—
79/63/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
and combination valve.
162/133/—
79/64/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
162/162/—
79/87/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
125/125/125
59/53/64
3
/
4
125/125/125
59/59/64
3
/
4
125/125/162
59/59/89
3
/
4
162/162/125
83/87/68
3
/
4
162/162/162
83/87/94
3
/
4
—————
25
/
32
16
LEGEND
Al-Cu — Aluminum Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
Cu-Cu — Copper Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
EXV — Electronic Expansion Valve
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
N/A — Not Applicable
*Operating weight does not include any options.
NOTES:
1. 30RB chillers with Greenspeed
2. No pumps are available for unit sizes 210-300.
®
technology are not available in unit sizes 060 and 070.
31
Page 32

Table 3B — Physical Data, 30RB060-300 — SI
UNIT 30RB 060 070 080 090 100 110 120 130 150
OPERATING WEIGHT (kg)*
Al-Cu Condenser Coil 1869 1962 2091 2697 2798 2963 3488 3649 4161
Cu-Cu Condenser Coil 2088 2181 2310 3026 3127 3292 3871 4087 4599
MCHX Condenser Coil 1716 1804 1934 2472 2569 2734 3229 3358 3863
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A, EXV Controlled System
Refrigerant Charge (kg)
Std Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
MCHX Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
COMPRESSORS Scroll, Hermetic
Quantity 334445566
Speed (r/s) 58.3
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (2) SH240 (2) SH295 (2) SH240 (2) SH295 (2) SH295 (2) SH295 (2) SH295 (3) SH295 (3) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (1) SH240 (1) SH240 (2) SH240 (2) SH240 (2) SH295 (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH240 (3) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt C N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Oil Charge (L, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 12.4/6.2/— 13.8/6.2/— 12.4/12.4/— 13.8/12.4/— 13.8/13.8/— 13.8/18.6/— 13.8/20.7/— 20.7/18.6/— 20.7/20.7/—
No. Capacity Steps
Standard 334445566
Optional (Maximum) 445556677
Minimum Capacity Step (%)
Standard 33 29 25 22 25 18 20 15 17
Optional 22 19 16 14 18 12 14 10 12
Capacity (%)
Ckt A 67 71 50 56 50 45 40 56 50
Ckt B 33 29 50 44 50 55 60 44 50
Ckt C N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
COOLER Direct Expansion, Shell and Tube Type
Weight (empty, kg) 324 324 388 388 388 440 440 440 689
Net Fluid Volume (L) 106 106 118 118 118 173 173 173 278
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (kPa) 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068
Maximum Water Side Pressure
without Pumps (kPa) 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068
Maximum Water Side Pressure
with Pumps (kPa) 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 444446666
Drain (NPT)
CONDENSER FANS Shrouded Axial Type, Vertical Discharge
Standard Low Noise Type
Fan Speed (r/s) Standard 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19
No. Blades...Diameter (mm) 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762
No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 3/1/— 3/1/— 2/2/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/4/— 4/4/— 4/4/—
Total Airflow (L/s) 23 409 23 409 23 409 35 113 35 113 35 113 40 965 46 817 46 817
CONDENSER COILS
No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 3/1/— 3/1/— 2/2/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/3/— 3/4/— 4/4/— 4/4/—
Total Face Area (sq m) 8.73 8.73 8.73 13.1 13.1 13.1 15.24 17.47 17.47
Max Working Refrigeration
Pressure (kPa) 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522
OPTIONAL HEAT RECOVERY
CONDENSER
Weight (kg) (empty) 342 342 342 396 396 396 562 562 562
Net Fluid Volume (L) 30.3 30.3 30.3 37.9 37.9 37.9 57.2 57.2 57.2
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (kPa) 4523 4523 4523 4523 4523 4523 4523 4523 4523
Maximum Water Side Pressure (kPa) 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068
Water Connections (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 333333555
Drain (NPT)
HYDRONIC MODULE (Optional) Pump(s) with pressure/temperature taps and combination valve.
Pump Single or Dual, 29.2 or 58.3 r/s
CHASSIS DIMENSIONS
Length (mm) 2412 3606 4800
Width (mm) 2255
Height (mm) 2296.9
LEGEND
Al-Cu — Aluminum Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
Cu-Cu — Copper Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
EXV — Electronic Expansion Valve
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
N/A — Not Applicable
*Operating weight does not include any options.
NOTES:
1. 30RB chillers with Greenspeed
2. No pumps are available for unit sizes 210-300.
®
40.6/18.4/—
18.1/9.1/—
3
3
/
4
/
8
50.8/18.4/—
18.1/9.1/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
31.1/31.1/—
15.0/15.0/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
43.5/34.5/—
18.1/18.1/—
technology are not available in unit sizes 060 and 070.
3
/
4
43.5/43.5/—
18.1/19.1/—
3
/
4
43.5/48.1/—
18.1/23.1/—
3
Flooded, Shell and Tube Type
3
/
8
3
/
8
3
/
4
/
8
43.5/60.3/—
19.5/25.9/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
60.3/48.1/—
24.5/19.5/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
60.3/60.3/—
25.4/28.1/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
32
Page 33

Table 3B — Physical Data, 30RB060-300 — SI
(cont)
UNIT 30RB 160 170 190 210 225 250 275 300
OPERATING WEIGHT (kg)*
Al-Cu Condenser Coil 4666 4819 5461 6243 6394 7031 7686 8321
Cu-Cu Condenser Coil 5215 5367 6118 6901 7052 7799 8566 9308
MCHX Condenser Coil 4297 4443 5019 5793 5937 6509 7096 7659
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A, EXV Controlled System
Refrigerant Charge (kg)
Std Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
MCHX Coil, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C
COMPRESSORS Scroll, Hermetic
Quantity 778 9 9 10 11 12
Speed (r/s) 58.3
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
(Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt C N/A N/A N/A (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295
Oil Charge (L, Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 27.6/18.6/— 27.6/20.7/— 27.6/27.6/— 20.7/18.6/20.7 20.7/20.7/20.7 20.7/20.7/27.6 27.6/27.6/20.7 27.6/27.6/27.6
No. Capacity Steps
Standard 778 9 9 10 1112
Optional (Maximum) 8891010111213
Minimum Capacity Step (%)
Standard 13 14 13 10 11 10 9 8
Optional 8109 6 8 7 7 6
Capacity (%)
Ckt A 62 57 50 38 33 30 36 33
Ckt B 38 43 50 28 33 30 36 33
Ckt C N/A N/A N/A 36 33 40 28 33
COOLER Direct Expansion, Shell and Tube Type
Weight (empty, kg) 689 689 689 1080 1080 1080 1080 1080
Net Fluid Volume (L) 278 278 278 327 327 327 327 327
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (kPa) 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068
Maximum Water Side Pressure
without Pumps (kPa) 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068
Maximum Water Side Pressure
with Pumps (kPa) 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034 1034
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 66666666
Drain (NPT)
CONDENSER FANS Shrouded Axial Type, Vertical Discharge
Standard Low Noise Type
Fan Speed (r/s) Standard 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19
No. Blades...Diameter (mm) 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762 9…762
No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 6/4/— 6/4/— 6/6/— 4/4/4 4/4/4 4/4/6 6/6/4 6/6/6
Total Airflow (L/s) 58 521 58 521 70 226 70 226 70 226 81 930 93 634 105 339
CONDENSER COILS
No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B/Ckt C) 6/4/— 6/4/— 6/6/— 4/4/4 4/4/4 4/4/6 6/6/4 6/6/6
Total Face Area (sq m) 21.83 21.83 26.2 26.2 26.2 30.47 34.84 39.21
Max Working Refrigeration Pressure (kPa) 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522
OPTIONAL HEAT RECOVERY CONDENSER Flooded, Shell and Tube Type
Weight (kg) (empty) 589 589 589 — — — — —
Net Fluid Volume (L) 65.9 65.9 65.9 — — — — —
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (kPa) 4523 4523 4523 — — — — —
Maximum Water Side Pressure (kPa) 2068 2068 2068 — — — — —
Water Connections (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 555—————
Drain (NPT)
HYDRONIC MODULE (Optional) Pump(s) with pressure/temperature taps
Pump Single or Dual, 29.2 or 58.3 r/s
CHASSIS DIMENSIONS
Length (mm) 5994 5994 7188 7188 7188 8382 9576 10 770
Width (mm) 2255
Height (mm) 2296.9
73.5/56.7/—
35.8/28.6/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
and combination valve.
73.5/60.3/—
35.8/29.0/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
73.5/73.5/—
35.8/39.5/—
3
/
4
3
/
8
56.7/56.7/56.7
26.8/24.0/29.0
3
/
4
56.7/56.7/56.7
26.8/26.8/29.0
3
/
4
56.7/56.7/73.5
26.8/26.8/40.4
3
/
4
73.5/73.5/56.7
37.6/39.5/30.8
3
/
4
73.5/73.5/73.5
37.6/39.5/42.6
3
—————
Not available
/
4
LEGEND
Al-Cu — Aluminum Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
Cu-Cu — Copper Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
EXV — Electronic Expansion Valve
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
N/A — Not Applicable
*Operating weight does not include any options.
NOTES:
1. 30RB chillers with Greenspeed
2. No pumps are available for unit sizes 210-300.
®
technology are not available in unit sizes 060 and 070.
33
Page 34

Table 4A — Physical Data — 30RB315-390 — English
UNIT 30RB 315 330 345 360 390
OPERATING WEIGHT (Module A/Module B, lb)*
Al-Cu Condenser Coil 10,266/10,266 10,601/10,266 10,601/10,601 12,013/10,601 12,013/12,013
Cu-Cu Condenser Coil 11,472/11,472 11,807/11,472 11,807/11,807 13,460/11,807 13,460/13,460
MCHX Condenser Coil 9,475/9,475 9,799/9,475 9,799/9,799 11,064/9,799 11,064/11,064
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A, EXV Controlled System
Circuits Qty 44444
Refrigerant Charge
Std Coil, Module A Ckt A/Ckt B (lb) 162/106 162/133 162/133 162/162 162/162
Std Coil, Module B Ckt A/Ckt B (lb) 162/106 162/106 162/133 162/133 162/162
MCHX Coil, Module A Ckt A/Ckt B (lb) 83/55 83/64 83/64 83/87 83/87
MCHX Coil, Module B Ckt A/Ckt B (lb) 83/55 83/55 83/64 83/64 83/87
COMPRESSORS Scroll, Hermetic
Total Quantity 14 14 14 15 16
Speed (rpm) 3500
Module A, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
Module A, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
Module B, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
Module B, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (3) SH240 (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295
Module A Oil Charge (Pt, Ckt A/Ckt B) 52.5/39.4 52.5/39.4 52.5/39.4 52.5/52.5 52.5/52.5
Module B Oil Charge (Pt, Ckt A/Ckt B) 52.5/39.4 52.5/39.4 52.5/39.4 52.5/39.4 52.5/52.5
No. Capacity Steps
Standard 14 14 14 15 16
Optional (Maximum) 16 16 16 17 18
Minimum Capacity Step (%)
Standard 66776
Optional 54655
Capacity (%)
Module A, Ckt A 31 30 29 27 25
Module A, Ckt B 19 22 21 27 25
Module B, Ckt A 31 30 29 27 25
Module B, Ckt B 19 18 21 20 25
COOLER Direct Expansion, Shell and Tube Type
Module A Weight (empty, lb) 1518 1518 1518 1518 1518
Module B Weight (empty, lb) 1518 1518 1518 1518 1518
Net Fluid Volume (gal) Module A/Module B 73.5/73.5 73.5/73.5 73.5/73.5 73.5/73.5 73.5/73.5
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 445 445 445 445 445
Maximum Water Side Pressure (psig) 300 300 300 300 300
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 66666
Drain (NPT)
CONDENSER FANS Shrouded Axial Type, Vertical Discharge
Standard Low Noise Type
Fan Speed (rpm) Standard 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140
Module A No. Blades...Diameter (in.) Ckt A/Ckt B 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30
Module B No. Blades...Diameter (in.) Ckt A/Ckt B 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30 9...30/9...30
Total No. Fans 20 20 20 22 24
Module A No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6 6/6
Module B No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6
Total Airflow (cfm) 248,000 248,000 248,000 272,800 297,600
CONDENSER COILS
Module A No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6 6/6
Module B No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6
Total Face Area (sq ft) 470 470 470 517 564
Max Working Refrigerant Pressure (psig) 656 656 656 656 656
3
/
4
LEGEND
Al-Cu — Aluminum Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
Cu-Cu — Copper Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
EXV — Electronic Expansion Valve
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
*No pumps are available for models 30RB315-390.
3
/
4
3
/
4
3
/
4
3
/
4
34
Page 35

Table 4B — Physical Data — 30RB315-390 — SI
UNIT 30RB 315 330 345 360 390
OPERATING WEIGHT (Module A/Module B, kg)*
Al-Cu Condenser Coil 4656/4656 4808/4656 4808/4808 5448/4808 5448/5448
Cu-Cu Condenser Coil 5203/5203 5354/5203 5354/5354 6104/5354 6104/6104
MCHX Condenser Coil 4297/4297 4444/4297 4444/4444 5018/4444 5018/5018
REFRIGERANT TYPE R-410A, EXV Controlled System
Circuits Qty 44444
Refrigerant Charge
Std Coil, Module A Ckt A/Ckt B (kg) 73.5/48.1 73.5/60.3 73.5/60.3 73.5/73.5 73.5/73.5
Std Coil, Module B Ckt A/Ckt B (kg) 73.5/48.1 73.5/48.1 73.5/60.3 73.5/60.3 73.5/73.5
MCHX Coil, Module A Ckt A/Ckt B (kg) 37.6/24.9 37.6/29.0 37.6/29.0 37.6/39.5 37.6/39.5
MCHX Coil, Module B Ckt A/Ckt B (kg) 37.6/24.9 37.6/24.9 37.6/29.0 37.6/29.0 37.6/39.5
COMPRESSORS Scroll, Hermetic
Total Quantity 14 14 14 15 16
Speed (r/s) 58.3
Module A, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
Module A, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
Module B, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt A (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295 (4) SH295
Module B, (Qty) Compressor Model Number Ckt B (3) SH240 (3) SH240 (3) SH295 (3) SH295 (4) SH295
Module A Oil Charge (L, Ckt A/Ckt B) 24.8/18.6 24.8/18.6 24.8/18.6 24.8/24.8 24.8/24.8
Module B Oil Charge (L, Ckt A/Ckt B) 24.8/18.6 24.8/18.6 24.8/18.6 24.8/18.6 24.8/24.8
No. Capacity Steps
Standard 14 14 14 15 16
Optional (Maximum) 16 16 16 17 18
Minimum Capacity Step (%)
Standard 66776
Optional 54655
Capacity (%)
Module A, Ckt A 31 30 29 27 25
Module A, Ckt B 19 22 21 27 25
Module B, Ckt A 31 30 29 27 25
Module B, Ckt B 19 18 21 20 25
COOLER Direct Expansion, Shell and Tube Type
Module A Weight (empty, kg) 689 689 689 689 689
Module B Weight (empty, kg) 689 689 689 689 689
Net Fluid Volume (L) Module A/Module B 278/278 278/278 278/278 278/278 278/278
Maximum Refrigerant Pressure (kPa) 3068 3068 3068 3068 3068
Maximum Water Side Pressure (kPa) 2068 2068 2068 2068 2068
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
Inlet and Outlet, Victaulic 66666
Drain (NPT)
CONDENSER FANS Shrouded Axial Type, Vertical Discharge
Standard Low Noise Type
Fan Speed (r/s) Standard 19 19 19 19 19
Module A No. Blades...Diameter (mm) Ckt A/Ckt B 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762
Module B No. Blades...Diameter (mm) Ckt A/Ckt B 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762 9...762/9...762
Total No. Fans 20 20 20 22 24
Module A No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6 6/6
Module B No. Fans (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6
Total Airflow (L/s) 117 042 117 042 117 042 128 747 140 452
CONDENSER COILS
Module A No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6 6/6
Module B No. Coils (Ckt A/Ckt B) 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/4 6/6
Total Face Area (sq m) 43.66 43.66 43.66 48.03 52.4
Max Working Refrigerant Pressure (kPa) 4522 4522 4522 4522 4522
3
/
4
LEGEND
Al-Cu — Aluminum Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
Cu-Cu — Copper Fin/Copper Tube Condenser Coil
EXV — Electronic Expansion Valve
MCHX — Microchannel Condenser Coil
*No pumps are available for models 30RB315-390.
3
/
4
3
/
4
3
/
4
3
/
4
35
Page 36

36
Fig. 24 — Unit Rigging Label Detail 30RB060-150
Page 37

37
Fig. 25 — Unit Rigging Label Detail 30RB160-300
Page 38

Step 2 — Remove Compressor Rack Holddown
BOLT
COLLAR
Fig. 26 — Compressor Rack Holddown Bolts
Table 5 — Number of Holddown Assemblies
UNIT
30RB
CIRCUIT
A + B
CIRCUIT
A
CIRCUIT
B
CIRCUIT
C
060-070 4
——
—
080-100 4
——
—
110-120 —2 4—
130-190 —4
4
—
210-300 —4
44
MODULAR
UNIT
30RB
CIRCUIT A CIRCUIT B
Module A Module B Module A Module B
315 4
44
4
330 4
44
4
345 4444
360 44
4
4
390 44
44
REMOVE
COMPRESSOR
SHIPPING
BRACES
Fig. 27 — Compressor Shipping Braces Removal
A30-5427
INSTALL
COMPRESSOR
SOUND BLANKET
TOP COVERS
Fig. 28 — Compressor Sound Blanket Top Covers
A30-5428
Bolts —
securing the compressor rail assembly to the unit base frame.
These bolts are red and are located between the compressors in
the front and rear of the compressor rail assembly. These bolts
and holddown assemblies must be removed for the vibration
isolation system to operate properly. Using a 15mm socket,
loosen and remove the bolt and collar assembly as shown in
Fig. 26.
See Table 5 for the number of holddown assemblies for
each unit.
Isolation mounts for the compressor rail assembly are
located directly in front of and behind each compressor. Do
not loosen or remove the isolation mounts, only the shipping
bolts. There are 4 bolts that hold down each compressor. Do
not loosen these bolts.
The 30RB units are shipped with holddown bolts
Step 3 — Remove Compressor Shipping
Braces — Each unit is equipped with compressor shipping
braces tying each compressor on the circuit together. Prior to
start-up these braces must be removed. Using a 15mm socket,
loosen each bolt and nut on each compressor tab and remove
all braces before unit start-up. Remove the compressor shipping braces attached between the compressors; see Fig. 27 for
guidance.
FOR UNITS EQUIPPED WITH COMPRESSOR SOUND
BLANKETS — The sound blanket top covers are shipped inside the control box(es) for the unit. Remove the top covers
from the control boxes and install prior to start-up. Align the
discharge tube with the cutout on the top cover; see Fig. 28.
Firmly press the Velcro sections together, ensuring the top cover is held tightly against the blanket.
Step 4 — Make Cooler Fluid, Heat Reclaim and
Drain Piping Connections —
it is recommended additional field-supplied air vents be installed. Locate air vents at the highest possible point of the
chilled water and heat reclaim systems. In addition to field-supplied air vents, facilitate servicing in addition to flow balancing
by installing field-supplied shut-off valves, thermometers,
clean-out tees, pressure and temperature taps in the inlet and
outlet piping. Locate valves in return and supply cooler water
and heat reclaim lines as close to the chiller as possible.
In sound sensitive applications, consider the installation of
piping vibration isolators. Drain connections are provided in
the cooler. Refer to the dimensional drawings, Fig. 2-20 for locations. Insulate the drain piping (in the same manner as the
chilled water piping) for at least 12-in. (305 mm) from the
cooler.
FREEZE PROTECTION — Upon completion of the field
piping installation, freeze protection must be considered.
Freeze protection for the cooler is available from the factory
with a freeze protection option for the unit. Freeze protection
for the pump (hydronic) package is standard on all units with
the optional hydronic package (30RB060-190 units). External
piping freeze protection also must be considered. Since power
is sometimes lost for extended periods during winter storms,
freeze protection provided by heater tapes will be effective
only if a back-up power supply can be assured for the unit's
control circuit, heater and cooler pump. If not protected with
an antifreeze solution, draining the cooler and outdoor piping
is recommended if the system will not be used during freezing
weather conditions.
NOTE: See Freeze Protection section on page 54 for a more
detailed overview of freeze protection.
IMPORTANT: Glycol anti-freeze solutions are highly
recommended since heater tapes provide no protection
in the event of a power failure.
UNITS WITH HYDRONIC PUMP PACKAGE — The
30RB060-190 units can be equipped with a factory-installed
hydronic pump package consisting of a suction guide/strainer,
pump, combination valve, internal piping and wiring connected at the factory.
38
To facilitate servicing,
Page 39

The combination valve performs the following functions:
PT
PT
T1
T2
FS
PP
PP
D
D
V
D
PT
PT
Chilled
Water In
Chilled
Water Out
Heater (Optional)
Heater
E
PT
Air Separator with Vent*
Strainer/Suction Guide
Pump
Combination Valve
Isolation Valve*
Pressure Reducing
Fill Valve*
Flexible Connections*
Pressure Relief*
HYDRONIC PUMP PACKAGE
INSIDE
UNIT
OUTSIDE
UNIT
20 Mesh Strainer**
LEGEND
*Field-supplied and installed.
†Factory-installed option.
**Required within 10 ft (3 m) of cooler in addition
to suction strainer for open loop systems.
D—Drain,
3
/4-in. NPT
D — Drain,
1
/4-in. NPT
E—Expansion Tank Connection,
3
/4-in. NPT
FS — Flow Switch
PP — Pipe Plug,
1
/4-in. NPT
PT — Pressure/Temperature Tap
T1 — Leaving Water Thermistor
T2 — Entering Water Thermistor
V—Vent,
1
/4-in. NPT
Indicates items provided with the
optional hydronic pump package.
Fig. 29 — Typical Piping Diagram on 30RB Units with Hydronic Package — Single Pump
A30-5303
• Drip-tight shut-off valve
• Spring closure design with a non-slam check valve
• Flow-throttling valve
Refer to Fig. 2-20 for cooler connection locations. The inlet
is connected to the suction guide/strainer of the pump via a
Victaulic-type connection. The cooler supply has water-side
Victaulic-type connections (follow connection directions as
provided by the coupling manufacturer). Provide proper support for the piping. If compressor and cooler grilles have been
added, holes must be cut in the grilles for field piping and
insulation.
The suction guide/strainer is shipped from the factory with a
run-in screen. This screen is a temporary device used during
the start-up/clean-up process of the chilled water circuit to
prevent construction debris from damaging the pump or
internal tubes of cooler. After all debris has been removed or a
maximum of 24 running hours the temporary screen must
be removed. See the Controls, Start-Up, Operation, Service and
Troubleshooting guide for further information.
CAUTION
The suction guide/strainer is shipped from the factory with
a run-in screen. This temporary screen must be removed
after all debris has been removed or a maximum of 24 running hours. Failure to remove the temporary screen may
result in damage to the pump or cooler.
NOTE: Units with factory-installed hydronic pump packages
applied on open loop systems require that an additional fieldsupplied strainer with a minimum size of 20 mesh be installed
within 10 ft (3.05 m) of and ahead of the cooler inlet to prevent
debris from damaging internal tubes of the cooler.
CAUTION
Do not circulate water through unit without strainers in
place. Failure to use the strainers represents abuse and may
impair or otherwise negatively affect the Carrier product
warranty.
3
/4 in. NPT fitting is installed in the inlet piping of the
A
pump for connection to an expansion tank. Install the tank in
accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Figures 29 and 30 illustrate typical single and dual pump
packages.
Two drain connections are provided and are located at
pump volute, and the suction guide. See Fig. 2-20 for connection location.
39
Page 40

INSIDE
LEGEND
*Field-supplied and installed.
†Factory-installed option.
**Required within 10 ft (3 m) of cooler in addition to suction strainer for open loop systems.
D—Drain,
3
/4-in. NPT
D — Drain,
1
/4-in. NPT
E—Expansion Tank Connection, 3/4-in. NPT
FS — Flow Switch
PP — Pipe Plug,
1
/4-in. NPT
PT — Pressure/Temperature Tap
T1 — Leaving Water Thermistor
T2 — Entering Water Thermistor
V—Vent,
1
/4-in. NPT
Fig. 30 — Typical Piping Diagram on 30RB Units with Hydronic Package — Dual Pumps
A30-5304
UNIT
OUTSIDE
UNIT
Chilled
Water Out
D
Heater (Optional)
FS
T1
PP
HYDRONIC PUMP PACKAGE
PT
PT
D
PT
PT
E
PP
D
V
T2
PT
Chilled
Water In
Pressure Relief*
Flexible Connections*
D
Heater
Air Separator with Vent*
Strainer/Suction Guide
Reverse Flow Check
Valve/Service Valve
Service Valve
Pump
Combination Valve
Isolation Valve*
UNITS WITHOUT HYDRONIC PUMP PACKAGE — Refer
to Fig. 2-20 for cooler connection locations. It is required that a
field-supplied strainer with a minimum size of 20 mesh be
installed within 10 ft (3.05 m) of and ahead of the cooler inlet
to prevent debris from damaging internal tubes of the cooler.
CAUTION
Do not circulate water through unit without strainers in
place. Failure to use the strainers represents abuse and may
impair or otherwise negatively affect the Carrier product
warranty.
Pressure Reducing
Fill Valve*
20 Mesh Stainer**
The cooler has water-side victaulic-type connections (follow connection directions as provided by the coupling manufacturer). Provide proper support for the piping. If compressor
and cooler grilles have been added, holes must be cut in the
grilles for field piping and insulation. See Fig. 31 for a typical
piping diagram of a 30RB unit without a hydronic pump
package.
A drain connection is located at the leaving water (supply)
end of cooler. See Fig. 2-20 for connection location. Insulate
the drain piping (in the same manner as the chilled water
piping) for at least 12 in. (305 mm) from the unit.
UNITS WITH OPTIONAL HEAT RECLAIM — The
30RB060-190 units can be equipped with a factory-installed
heat reclaim package consisting of a shell and tube condenser,
40
Page 41

condenser flow switch, temperature sensors and refrigeration
T1
T2
FS
PP
PP
D
V
Heater (Optional)
Chilled Water
Out
Chilled Water
In
Isolation Valve*
20 Mesh Strainer†
Flexible Connections*
Pressure Relief*
LEGEND
*Field-supplied and installed.
D—Drain,
3
/4-in. NPT
FS — Flow Switch
PP — Pipe Plug,
1
/4-in. NPT
T1 — Leaving Water Thermistor
T2 — Entering Water Thermistor
V—Vent,
1
/4-in. NPT
Fig. 31 — Typical Piping Diagram on 30RB Units without Hydronic Package
a30-5321
Fig. 32 — Typical Piping Diagram on 30RB Units with Heat Reclaim Option
LEGEND
*Field-supplied and installed.
D* — Drain, Field Supplied
D—Drain,
3
/8-in. NPT
FS — Flow Switch
PP — Pipe Plug, 1/4-in. NPT
R—Pressure Relief
T1 — Leaving Water Thermistor
T2 — Entering Water Thermistor
V* — Vent, Field Supplied
V—Vent,
3
/8-in. NPT
devices to allow up to 100% of the condenser heat to be reclaimed for hot water. This means that this water-cooled condenser, which is in parallel with the standard air-cooled condenser, is capable of capturing all of the heat available from the
chiller condensing process. The leaving water temperature can
reach at maximum 131 F (55 C) under steady state and constant hot water flow conditions with an allowable hot water
temperature range of 68 to 131 F (20 to 55 C). The heat reclaim
condenser fluid connections are at the end of the unit opposite
the control panel. The temperature sensor and the condenser
flow switch are mounted in the nozzles and are wired in the
control box. Refer to the Controls and Troubleshooting Book
for detailed operational information.
The heat reclaim condenser has water-side Victaulic-type
connections (follow connection directions as provided by the
coupling manufacturer). Provide proper support for the piping.
If compressor and cooler grilles have been added, holes must
be cut for field piping and insulation. A field-supplied strainer
with a minimum size of 20 mesh must be installed within 10 ft
(3.0 m) of the inlet to the heat reclaim condenser. See Fig. 32
for a typical piping diagram of the heat reclaim condenser and
3-way valve location. All piping must follow standard piping
techniques. Refer to Carrier System Design Manual or appropriate ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating,
and Air-Conditioning Engineers) handbook for details.
CAUTION
Do not circulate water through unit without strainers in
place. Failure to use the strainers represents abuse and may
impair or otherwise negatively affect the Carrier product
warranty.
Two drain connections are provided, one in each head of the
condenser.
HEAD PRESSURE CONTROL — A form of head pressure
control is required while in the heat reclaim mode. In order to
meet this requirement, a properly sized 3-way valve must be
field-installed. This valve will facilitate cold water start-up
(water temperatures below 68 F [20 C]), and it also will be able
to maintain proper head pressure during heat reclaim operation.
Since the hot water temperature at start-up may be very low,
the 3-way valve is to be located as close to the heating condenser as possible so that this valve can quickly accomplish its
purpose of maintaining the minimum required head pressure.
Locate the 3-way valve within 40 ft (12.2 m) of the heating
condenser if the circulating pump is located between the 3-way
valve and the heat reclaim condenser. See Fig. 33A. If the
pumps are too far away from the condenser, a second option is
to install the 3-way control valve close to the condenser. See
Fig. 33B. The 30RB unit uses an anolog output to control this
valve.
HEAT
RECLAIM
SUPPLY
HEAT
RECLAIM
RETURN
T1
FS
PP
PP
HEAT RECLAIM CONDENSER
T2
Flexible Connections*
Pump*
Isolation Valve*
20 Mesh Strainer*, installed
within 10 ft (3 m) of condenser
inlet
Three-Way Valve*
V
D
41
V*
D*
D
R
Page 42

NOTE: Locate the 3-way valve as close as possible to the
SUPPLY
RETURN
CONSTA NT SPEED
CIRCULATING PUMPS
HEAT RECLAIM
CONDENSER
MODULATING 3-WAY
CONTROL VALVE
40 FT MAX
Fig. 33A — Three-Way Head Pressure Control
Valve Location (Preferred)
a30-4825
MODULATING 3-WAY CONTROL
VALVE (AS CLOSE TO CONDENSER
AS POSSIBLE)
HEAT RECLAIM
CONDENSER
CONSTAN T SPEED
CIRCULATING PUMPS
RETURN
SUPPLY
Fig. 33B — Three-Way Head Pressure Control
Valve Location (Alternate)
a30-4824
chiller to minimize head pressure control response time.
FOR ALL UNITS
Dual Chiller Control Option
— If the dual chiller algorithm is
used, and the machines are installed in parallel, an additional
chilled water sensor must be installed for each module. For
30RB315-390, a factory-supplied thermistor and well are
shipped in the control box of each module. Install the wells in
the common leaving water header. See Fig. 34.
Parallel chiller control with dedicated pumps is recommended. Chiller must start and stop its own water pump located in its own piping. If pumps are not dedicated for each
chiller, then isolation valves are required. Each chiller must
open and close its own isolation valve through the unit control
(the valve must be connected to the pump outputs).
See Dual Chiller Control Option section on page 58 for
more dual chiller leaving water sensor information.
Minimum Loop Volume
— The preferred minimum loop volume is dependent on the type of application. In order to obtain
leaving water temperature stability for comfort cooling applications, a minimum of 3 gallons per ton (3.25 liters per kW) is
required on all unit sizes. For process cooling applications, applications where high stability is critical, or operation at
ambient temperatures below 32 F (0° C) is expected, the loop
volume should be increased to 6 to 10 gallons per ton (6.46 to
10.76 liters per kW) of cooling.
In order to achieve this volume, it may be necessary to add a
water storage tank to the water loop. If a storage tank is added
to the system, it should be properly vented so that the tank can
be completely filled and all air eliminated. Failure to do so
could cause lack of pump stability and poor system operation.
Any storage tank that is placed in the water loop should
have internal baffles to allow thorough mixing of the fluid. See
Fig. 35. For units with heat reclaim option, a minimum condenser loop volume of 6 gallons per ton of heating (0.5 to 0.83
gallons [1.9 to 3.1 L] per 100 Btu/h of heating) capacity is necessary. In come cases, this will require the installation of a hotwater buffer tank.
System Piping
— Proper system design and installation procedures should be followed closely. The system must be
constructed with pressure tight components and thoroughly
tested for leaks.
Installation of water systems should follow sound engineering practice as well as applicable local and industry standards.
Improperly designed or installed systems may cause
unsatisfactory operation and/or system failure. Consult a water
treatment specialist or appropriate literature for information
regarding filtration, water treatment, and control devices.
Figure 29 shows a typical installation with components that
might be installed with the hydronic package of the 30RB unit.
NOTE: It is recommended for units with the hydronic package
that an inlet isolation (shutoff) valve be placed exterior to the
unit to allow removal and service of the entire pump assembly,
if necessary. The hydronic package is supplied from the factory
with a combination valve for isolation of leaving water. Also,
if the unit is isolated with valves, a properly sized pressure
relief valve is recommended and should be installed in the piping between the unit and the valves, following all applicable
local codes.
Air Separation
— For proper system operation, it is essential
that water loops be installed with proper means to manage air
in the system. Free air in the system can cause noise, reduce
terminal output, stop flow, or even cause pump failure due to
pump cavitation. For closed systems, equipment should be
provided to eliminate all air from the system.
The amount of air that water can hold in solution depends
on the pressure and temperature of the water/air mixture. Air is
less soluble at higher temperatures and at lower pressures.
Therefore, separation can best be done at the point of highest
water temperature and lowest pressure. Typically, this point
would be on the suction side of the pump as the water is returning from the system or terminals. This is generally the optimal
place to install an air separator, if possible.
1. Install automatic air vents at all high points in the system.
(If the 30RB unit is located at the high point of the system,
a vent can be installed on the piping leaving the heat exchanger on the
1
/4 in. NPT female port.)
2. Install an air separator in the water loop, at the place
where the water is at higher temperatures and lower pressures — usually in the chilled water return piping. On a
primary-secondary system, the highest temperature water
is normally in the secondary loop, close to the decoupler.
Preference should be given to that point on the system
(see Fig. 36). In-line or centrifugal air separators are readily available in the field.
It may not be possible to install air separators at the place of
the highest temperature and lowest pressure. In such cases,
preference should be given to the points of highest temperature.
It is important that the pipe be sized correctly so that free air
can be moved to the point of separation. Generally, a water
velocity of at least 2 feet per second (0.6 m per second) will
keep free air entrained and prevent it from forming air pockets.
Automatic vents should be installed at all physically elevated points in the system so that air can be eliminated during system operation. Provisions should also be made for manual
venting during the water loop fill.
IMPORTANT: Automatic vents should be located in
accessible locations for maintenance purposes and
protected from freezing.
42
Page 43

Master Chiller
Control
Box
Control
Box
Slave Chiller
Pump and Check Valve
or Isolation Valve
Dual Chiller
LWT Sensors
and Wells
Pump and Check Valve
or Isolation Valve
a30-3987ef
LEGEND
NOTE: This is a simplified piping diagram — not all hydronic specialties are shown.
Fig. 34 — Dual Chiller Control Option Thermistor
Location
LWT — Leaving Water (Fluid) Temperature
Field Wiring
Field Communication Wiring
a30-3185ef
Tank Installation
BAD
BAD
GOOD
GOOD
Fig. 35 — Tank Baffling
Distribution Pump
Expansion
Tank(s)
Air Separator
with Vent
Decoupler
Chiller 1
Chiller 2
Zone 1
Zone 2
Zone 3
NOTE: Expansion tanks for 30RB hydronic kits must be installed for chillers piped in parallel in the primary water loop.
Fig. 36 — Typical Air Separator and Expansion Tank Location on Primary-Secondary Systems
a30-4002ef
43
Page 44

Step 5 — Fill the Chilled Water and Heat
x
x
DILUTED
CLEANING
AGENT
SYSTEM
SIDE
STREAM
FILTER
POT FEEDER AND
TRANSFER PUMP
30RB UNIT
TO DRAIN
TEMPORARY
PUMP
TEMPORARY
BYPASS
x
x
DILUTED
CLEANING
AGENT
SYSTEM
POT FEEDER AND
TRANSFER PUMP
30RB UNIT
TO DRAIN
TEMPORARY
PUMP
TEMPORARY
BYPASS
Fig. 37 — Typical Set Up for Cleaning Process
Fig. 38 — Cleaning Using a Side Stream Filter
a30-3989ef
a30-3988ef
Reclaim Loop
IMPORTANT: Before starting unit, be sure all of the
air has been purged from the system.
The chilled water pump (if equipped) is rated for 150 psig
(1034 kPa) duty. The maximum cooler water-side pressure is
300 psig (2068 kPa). Check the pressure rating for all of the
chilled water devices installed. Do not exceed the lowest pressure rated device.
WATER SYSTEM CLEANING — Proper water system
cleaning is of vital importance. Excessive particulates in the
water system can cause excessive pump seal wear, reduce or
stop flow, and cause damage of other components.
CAUTION
Failure to properly clean all piping and components of the
chilled water or heat reclaim system before unit start-up
may result in plugging of the heat exchanger, which can
lead to poor performance, nuisance alarms and/or damage
from freezing. Freezing damage caused by an improperly
cleaned system represents abuse and may impair or otherwise negatively affect the Carrier product warranty.
CAUTION
A suction guide with an internal strainer is standard on all
30RB units with factory-installed hydronic packages. This
strainer allows removal of particulates from the chilled
water loop. Using the combination valve and the field-installed
isolation valve at the inlet, the strainer can be isolated from the
chilled water loop to be cleaned.
The ComfortLink controls provided have a built-in feature
to remind building owners or operators to clean the strainer at a
pre-set time interval. Properly installed, cleaned and maintained systems will rarely need the strainer cleaned after the
initial fill. This time interval is user-configurable.
Ideally, the chilled water loop will be cleaned before the unit
is connected. If the run-in screen is left in the suction guide/
strainer, it is recommended that the Service Maintenance be set
to alert the operator within 24 hours of start-up to be sure that
the run-in screen in the suction guide/strainer is not removed at
start-up.
NOTE: The suction guide/strainer must be removed after the
first 24 hours of operation.
To set the time for the parameter, go to Time Clock/MCFG/
W.FIL in the scrolling marquee or the handheld Navigator™
display. Values for this item are input in days.
WATER TREATMENT — Fill the fluid loop with water and
a corrosion-resistant inhibitor suitable for the water of the area.
Consult the local water treatment specialist for characteristics
of system water and a recommended inhibitor for the cooler or
heat reclaim fluid loop.
Do not circulate water through unit without strainers in
place. Failure to use the strainers represents abuse and may
impair or otherwise negatively affect the Carrier product
warranty.
1. Install a temporary bypass around the chiller to avoid
circulating dirty water and particulates into the pump
package and chiller during the flush. Use a temporary
circulating pump during the cleaning process. Also, be
sure that there is capability to fully drain the system after
cleaning. See Fig. 37.
2. Be sure to use a cleaning agent that is compatible with
all system materials. Be especially careful if the system
contains any galvanized or aluminum components. Both
detergent-dispersant and alkaline-dispersant cleaning
agents are available.
3. It is recommended to fill the system(s) through a water
meter. This provides a reference point for the future for
loop volume readings, and it also establishes the correct
quantity of cleaner needed in order to reach the required
concentration.
4. Use a feeder/transfer pump to mix the solution and fill the
system. Circulate the cleaning system for the length of
time recommended by the cleaning agent manufacturer.
a. After cleaning, drain the cleaning fluid and flush the
system with fresh water.
b. A slight amount of cleaning residue in the system can
help keep the desired, slightly alkaline, water pH of 8
to 9. Avoid a pH greater than 10, since this will
adversely affect pump seal components.
c. A side stream filter is recommended (see Fig. 38)
during the cleaning process. Filter side flow rate
should be enough to filter the entire water volume
every 3 to 4 hours. Change filters as often as necessary during the cleaning process.
d. Remove temporary bypass when cleaning is complete.
44
Page 45

SYSTEM PRESSURIZATION — A proper initial cold fill
pressure must be established before filling of the unit. The
initial cold fill pressure is the pressure applied at the filling
point to fill a system to its highest point, plus a minimum
pressure at the top of the system (4 psig minimum [27.6 kPa])
to operate air vents and positively pressurize the system. The
expansion tank is very important to system pressurization. The
expansion tank serves several purposes:
1. Provide NPSH (net positive suction head) required for the
pump to operate satisfactorily.
2. Set system pressure.
3. Accommodate expansion or contraction of water due to
temperature changes.
4. Act as a pressure reference for the pump.
The expansion tank pressure must be set BEFORE the
system is filled. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendation
for instructions on setting the pressure in the expansion tank.
The net positive suction head pressure required information is
provided on the pump curves in Fig. 39-51 for units with factory-installed hydronic kits. See Table 6 for pump impeller sizes.
Once the system is pressurized, the pressure at the connection point of the expansion tank to water piping will not change
unless the water loop volume changes (either due to addition/
subtraction of water or temperature expansion/contraction).
The pressure at this point remains the same regardless of
whether or not the pump is running.
Since the expansion tank acts as a reference point for the
pump, there cannot be two reference points (two expansion
tanks) in a system, unless manifolded together. Where two or
more 30RB chillers with the hydronic option are installed in
parallel, there should not be more than one expansion tank in
the system, unless manifolded together as seen in Fig. 36. It is
permissible to install the expansion tank(s) in a portion of the
return water line that is common to all pumps, providing that
the tank is properly sized for combined system volume.
If the application involves two or more chillers in a primary
secondary system, a common place for mounting the expansion tank is in the chilled water return line, just before the
decoupler. See Fig. 36 for placement of expansion tank in
primary-secondary systems.
If a diaphragm expansion tank is utilized (a flexible
diaphragm physically separates the water/air interface) it is not
recommended to have any air in the water loop. See the section
on air separation on page 42 for instructions on providing air
separation equipment.
FILLING THE SYSTEM(S) — The initial fill of the chilled
water or heat reclaim system must accomplish three goals:
1. The entire piping system must be filled with water.
2. The pressure at the top of the system must be high enough
to vent air from the system (usually 4 psig [27.6 kPa] is
adequate for most vents).
3. The pressure at all points in the system must be high
enough to prevent flashing in the piping or cavitation in
the pump.
The pressure created by an operating pump affects system
pressure at all points except one — the connection of the
expansion tank to the system. This is the only location in the
system where pump operation will not give erroneous pressure
indications during the fill. Therefore, the best location to install
the fill connection is close to the expansion tank. An air vent
should be installed close by to help eliminate air that enters
during the fill procedure.
When filling the system, ensure the following:
1. Remove temporary bypass piping and cleaning/flushing
equipment.
2. Check to make sure all drain plugs are installed.
Table 6 — Pump Impeller Sizes
UNIT
30RB
060
070
080
090
100
110
120
130
150
160
170
190
*Option Code refers to the Hydronics Option (position 11) in the model number. See Fig. 1 for
option identification.
NOTE: Pump Selections are chiller size dependent. For example, dual pump “C” on a 30RB170
chiller is not the same as dual pump “C” on a 30RB130 chiller.
PUMP
Hp
3 0,F 1750 6.5 I 6,M 1750 6.5 V
5 1,G 1750 7.3 I 7,N 1750 7.3 V
7.5 2,H 1750 8.15 I
10 3,J 3450 5.4 II B,Q 3450 5.4 VI
5 1,G 1750 7.3 I 7,N 1750 7.3 V
7.5 2,H 1750 8.15 I 8,P 1750 8.15 V
10 3,J 3450 5.4 II B,Q 3450 5.4 VIIA
15 4,K 3450 6.1 II C,R 3450 6.0 VIIC
5 1,G 1750 7.3 I 7,N 1750 7.3 V
7.5 2,H 1750 8.15 I 8,P 1750 8.15 V
10 3,J 3450 5.4 II B,Q 3450 5.4 VIIA
15 4,K 3450 6.1 II C,R 3450 6.0 VIIC
5 1,G 1750 6.5 IIIA — — — —
7.5 2,H 1750 7.4 IIIB 9,T 3450 5.0 VIIB
10 3,J 3450 4.6 IVA B,Q 3450 4.6 VIIIA
15 4,K 3450 5.2 IVB C,R 3450 5.2 VIIIB
Option
Code
*
SINGLE PUMP DUAL PUMP
Rpm
Impeller Dia.
(in.)
Pump
Curve
Option
Code
8,P 1750 8.15 V
9,T 3450 5.25 VI
*
Rpm
Impeller Dia.
(in.)
Pump
Curve
45
Page 46

0
(0.00)
100
(6.31)
200
(12.62)
300
(18.93)
400
(25.24)
500
(31.54)
(gpm)
(l/s)
(0.0) 0
(9.1) 30
(18.3) 60
(27.4) 90
(36.6) 120
(45.7) 150
Head Pressure
(m) ft of fluid
Flow Rate
3450 RPM
N
P
S
H
r
5.40 in
6.10 in
77
77
74
74
70
70
62
62
52
52%
39
NPSHr
3 hp
5 hp
7.5 hp
10 hp
15 hp
20 hp
6.19 in
4.50 in
77
us
Head Pressure
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
a30-5473
a30-4388
Fig. 39 — Pump Curve I for Hydronic Package Single Pump (Fresh Water)
Fig. 40 — Pump Curve II for Hydronic Package Single Pump (Fresh Water)
(m) ft of fluid
(21.3) 70
(18.3) 60
(15.2) 50
(12.2) 40
(9.1) 30
(6.1) 20
(3.0) 10
(0.0) 0
8.19 in
7.50 in
7.00 in
6.50 in
6.00 in
0
(0.00)
40
54
65
73
78
80
81
N
P
S
H
NPSHr
r
80
(5.05)
160
(10.09)
(15.14)
Flow Rate
2 hp
240
(20.19)
80
65%
3 hp
320
1750 RPM
78
73
7.5 hp
5 hp
400
(25.24)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
46
Page 47

0
(0.00)
160
(10.09)
320
(20.19)
480
(30.28)
640
(40.38)
800
(50.47)
(gpm)
(l/s)
us
(0.0) 0
(3.7) 12
(7.3) 24
(11.0) 36
(14.6) 48
(18.3) 60
Head Pressure
(m) ft of fluid
Flow Rate
1750 RPM
N
P
S
H
r
6.50 in
77
77
73
73
67
67
59
59%
48
35
NPSHr
3 hp
5 hp
7.5 hp
10 hp
15 hp
8.19 in
6.00 in
78
Head Pressure
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
a30-4389
a30-5466
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
Fig. 41 — Pump Curve IIIA for Hydronic Package Single Pump (Fresh Water)
Fig. 42 — Pump Curve IIIB for Hydronic Package Single Pump (Fresh Water)
(m) ft of fluid
(21.3) 70
(18.3) 60
1750 RPM
(15.2) 50
(12.2) 40
(9.1) 30
(6.1) 20
(3.0) 10
(0.0) 0
0
(0.00)
(12.62)
200
400
(25.24)
Flow Rate
600
(37.85)
800
(50.47)
(gpm)
N
P
NPSHr
S
H
r
47
us
(l/s)
Page 48

Head Pressure
a30-5468
a30-5469
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
Fig. 43 — Pump Curve IVA for Hydronic Package Single Pump (Fresh Water)
Fig. 44 — Pump Curve IVB for Hydronic Package Single Pump (Fresh Water)
(m) ft of fluid
(42.7) 140
3450 RPM
(36.6) 120
(30.5) 100
(24.4) 80
(18.3) 60
(12.2) 40
(6.1) 20
(0.0) 0
0
(0.00)
N
P
S
NPSHr
H
r
200
(12.62)
400
(25.24)
600
(37.85)
Flow Rate
800
(50.47)
1000
(63.09)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
Head Pressure
(m) ft of fluid
(42.7) 140
(36.6) 120
3450 RPM
(30.5) 100
(24.4) 80
(18.3) 60
(12.2) 40
(6.1) 20
(0.0) 0
0
(0.00)
N
P
S
NPSHr
H
r
200
(12.62)
400
(25.24)
600
(37.85)
Flow Rate
800
(50.47)
1000
(63.09)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
48
Page 49

Head Pressure
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
a30-4391
a30-4392
Fig. 45 — Pump Curve V for Hydronic Package Dual Pump (Fresh Water)
Fig. 46 — Pump Curve VI for Hydronic Package Dual Pump (Fresh Water)
(m) ft of fluid
(18.3) 60
(14.6) 48
(11.0) 36
(7.3) 24
(3.7) 12
(0.0) 0
8.19 in
8.15 in
7.30 in
6.50 in
6.00 in
0
(0.00)
72
3 hp
1750 RPM
64
53
5 hp
400
7.5 hp
(gpm)
39
53
64
72
77
80
80
80
77
N
P
S
H
NPSHr
r
80
160
1 hp
240
2 hp
1.5 hp
320
us
(5.05)
(10.09)
(15.14)
Flow Rate
(20.19)
(25.24)
(l/s)
Head Pressure
(m) ft of fluid
(45.7) 150
(36.6) 120
6.19 in
5.90 in
5.25 in
4231
52
60
65
69
70
69
65
60
3450 RPM
52
15 hp
(27.4) 90
(18.3) 60
(9.1) 30
(0.0) 0
4.50 in
0
(0.00)
5 hp
N
P
S
H
NPSHr
r
60
(3.79)
120
(7.57)
3 hp
180
(11.36)
Flow Rate
7.5 hp
10 hp
240
(15.14)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
49
Page 50

0
(0.00)
100
(6.31)
200
(12.62)
300
(18.93)
400
(25.24)
500
(31.54)
(gpm)
(l/s)
us
(0.0) 0
(9.1) 30
(18.3) 60
(27.4) 90
(36.6) 120
(45.7) 150
Head Pressure
(m) ft of fluid
Flow Rate
3450 RPM
N
P
S
H
r
77
77
74
74
70
70
62
62
52
52%
39
NPSHr
3 hp
5 hp
7.5 hp
10 hp
15 hp
20 hp
6.19 in
6.10 in
5.40 in
77
Head Pressure
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
a30-4393
a30-5467
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
Fig. 47 — Pump Curve VIIA for Hydronic Package Dual Pump (Fresh Water)
Fig. 48 — Pump Curve VIIB for Hydronic Package Dual Pump (Fresh Water)
(m) ft of fluid
(42.7) 140
(36.6) 120
3450 RPM
(30.5) 100
(24.4) 80
(18.3) 60
(12.2) 40
(6.1) 20
(0.0) 0
0
(0.00)
N
P
S
NPSHr
H
r
100
(6.31)
(12.62)
200
Flow Rate
50
300
(18.93)
400
(25.24)
500
(31.55)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
Page 51

Head Pressure
a30-5472
a30-5470
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
Fig. 49 — Pump Curve VIIC for Hydronic Package Dual Pump (Fresh Water)
Fig. 50 — Pump Curve VIIIA for Hydronic Package Dual Pump (Fresh Water)
(m) ft of fluid
(42.7) 140
3450 RPM
(36.6) 120
(30.5) 100
(24.4) 80
(18.3) 60
(12.2) 40
(6.1) 20
(0.0) 0
0
(0.00)
N
P
S
H
NPSHr
r
100
(6.31)
200
(12.62)
300
(18.93)
Flow Rate
400
(25.24)
500
(31.55)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
Head Pressure
(m) ft of fluid
(42.7) 140
(36.6) 120
3450 RPM
(30.5) 100
(24.4) 80
(18.3) 60
(12.2) 40
(6.1) 20
(0.0) 0
0
(0.00)
N
P
S
NPSHr
H
r
200
(12.62)
400
(25.24)
600
(37.85)
Flow Rate
800
(50.47)
1000
(63.09)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
51
Page 52

Head Pressure
a30-5471
LEGEND
NPSHr — Net Positive Suction Head (Pressure) Required
NOTE: Refer to the 30RB nomenclature, Fig. 1, for option identification. Refer to the Pump Impeller Sizes, Table 6, for more information.
Fig. 51 — Pump Curve VIIIB for Hydronic Package Dual Pump (Fresh Water)
(m) ft of fluid
(42.7) 140
3450 RPM
(36.6) 120
(30.5) 100
(24.4) 80
(18.3) 60
(12.2) 40
(6.1) 20
(0.0) 0
N
P
S
H
0
(0.00)
NPSHr
r
200
(12.62)
400
(25.24)
600
(37.85)
Flow Rate
800
(50.47)
1000
(63.09)
(gpm)
us
(l/s)
Normally, a closed system needs to be filled only once. The
actual filling process is a fairly simple procedure. All air should
be purged or vented from the system. Thorough venting at high
points and circulation at room temperature for several hours is
highly recommended.
NOTE: Local codes concerning backflow devices and other
protection of the city water system should be consulted and
followed to prevent contamination of the public water supply.
This is critical when antifreeze is used in the system.
SET WATER FLOW RATE — Once the system is cleaned,
pressurized, and filled, the flow rate through the chiller and
heat reclaim needs to be established. Refer to the Job Submittal for flow rate requirements. See the Controls and
Troubleshooting literature for operating limits. On units
with the hydronic package, this can be accomplished by
using the balancing valve. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for setting the balancing valve. Local codes
may prohibit restricting the amount of water using the balancing valve for a given motor horsepower. In this case, use
the method listed in the Pump Modification/Trimming section. See Table 7 for the type of combination valve in 30RB
units with the optional hydronic package.
Table 7 — Combination Valve Details
30RB UNIT SINGLE/DUAL PUMP
060-130 FTV-4 in.
150-190 FTV-6 in.
NOTE: Carrier recommends a differential pressure gage when
measuring pressures across the pumps or balancing valves.
This provides for greater accuracy and reduces error build-up
that often occurs when subtracting pressures made by different
gages.
A rough estimate of water flow can also be obtained from
the pressure gages across the 30RB heat exchangers.
Figures 52-56 show the relationship between gpm and heat
exchanger pressure drop. It should be noted that these curves
are for fresh water and “clean” heat exchangers; they do not
apply to heat exchangers with fouling. To read the chart,
subtract the readings of the two pressure gages on the hydronic
kit. This number is the pressure drop across the heat exchanger.
Adjust the factory-installed balancing valve or external balancing valve (in units without hydronic package) until the correct
pressure drop is obtained for the required gpm.
PUMP MODIFICATION/TRIMMING — Since the pumps
are constant speed, the only way to obtain greater flow with a
given pump/impeller is to decrease system head. This will
allow the pump to “ride” its curve to the right, resulting in
increased flow. If greater flow is necessary, consider opening
the combination valve. Also, verify that the strainer is clean,
and that no unnecessary system resistance is present, such as
partially closed isolation valves.
Once the combination valve is set, note the stem position. If
later service work requires the valve to be closed, it will be easier
to re-balance the system, if the original balance point is known.
Increasing system resistance by closing the balancing valve
will force the pump to “ride” its curve to the left, resulting in
less flow. Although this does reduce power consumption
slightly, it may not be the desirable method of reducing the
flow, especially if a large reduction is needed.
52
Page 53

The other method for reducing flow on a constant speed
pump is impeller trimming. The impellers in the pumps provided in the 30RB hydronic kit can be easily removed for this
purpose. Refer to the vendor literature packet supplied with the
hydronic package information on Seal Replacement in the
Service Section, and follow instructions for impeller removal
and trimming. Trimming should only be done by a qualified
machine shop that has experience in this operation. Contact
your local Carrier representative for a recommended machine
shop.
CAUTION
After trimming, the impeller MUST be balanced. Failure to
balance trimmed impellers can result in excessive vibration, noise, and premature bearing failure.
Impeller trimming has the added benefit of maximum bhp
(brake horsepower) savings, which can recover the cost
incurred by performing the impeller trimming.
PUMP VFD — Pumps may be ordered with a variable frequency drive (VFD) for speed control.
SENSORLESS CONTROL (CLOSED LOOP) — ACTIVE
SETUP 1 — The VFD provided with the pump from the factory is configured for sensorless control. Default set points are
entered for the unit according to nominal tonnage of the unit.
Table 8 shows the settings from the factory. For details on operating the drive display, see the pump installation and operation manual, and for more detailed information on the drive,
see IVS 102 Operating Instructions. These manuals are supplied in the control box of the chiller.
The following set points should be verified or modified for
the actual installation.
Parameter 20-21 Setpoint, Hd, Ft-Wc
Parameter 22-89 Design Flow Setpoint, GPM
Parameter 22-87 Pressure at no-flow speed, Hmin, Ft-Wc
(40% of Hd)
When changing set points, assure values are within the
pump curve for the pump provided with the unit.
Minimum speed for the pump is set at 50 Hz, Parameter
4-12. This may be changed as long as the corresponding flow
rate meets the minimum flow requirement for the chiller.
REMOTE SENSOR (CLOSED LOOP) — ACTIVE
SETUP 2 — The drive may be set up to use a remote sensor
instead of sensorless pump control. For a remote sensor control change Active Setup on the drive from 1 to 2, Parameter
0-10. The drive will read a 0-10vdc or a 0/4-20 mA signal
from the sensor. Switch S2-01 must be set to Off (default setting) for 0-10 vdc or On for 0/4-20 mA. The switch is located
behind the display. The cover must be removed and the display
will snap off to access this switch.
The set point is defined by Parameter 20-21, Setpoint 1.
This is a percentage of the maximum signal from the sensor.
The default is 80%.
REMOTE CONTROLLER (OPEN LOOP) — ACTIVE
SETUP 3 — Drive may be controlled by external sources. For
a remote control of the drive change Active Setup on the drive
to 3, Parameter 0-10. An input signal can used to control the
drive speed. Input signal may be 0-10 vdc or 0/4-20 mA. The
setup is the same as a remote sensor.
A BACnet card is also included with the drive. For
BACnet, use Setup 3. The communication settings are in section 8 of the drive parameters. See drive manual for details.
Table 8 — Default Settings for Sensorless Control — Setup 1
SINGLE PUMP
Unit Size (tons) 60,70 80, 90, 100 110,120,130 150 160, 170, 190
Pump
HP 3 5 7.5 10 5 7.5 10 15 5 7.5 10 15 5 7.5 10 15 5 7.5 10 15
Impeller Dia (inches) 6.5 7.3 8.15 5.4 7.3 8.15 5.4 6.1 7.3 8.15 5.4 6.1 6.5 7.4 4.6 5.2 6.5 7.4 4.6 5.2
Param. Desc.
20-21 Setpoint 1 Hd ft wc 30 45 55 95 40 50 90 120 35 45 80 115 25 50 70 95 25 45 65 90
22-89
22-87
Param. Desc.
20-21 Setpoint 1 Hd ft wc 30 45 55 75 95 40 50 90 120 35 45 80 115 50 70 95 45 65 90
22-89
22-87
Flow at
Design Point
Press at No
Flow Speed
Unit Size (tons) 60,70 80, 90, 100 110, 120, 130 150 160, 170, 190
Pump
HP 3 5 7.5 7.5 10 5 7.5 10 15 5 7.5 10 15 7.5 10 15 7.5 10 15
Impeller Dia (inches) 6.5 7.3 8.15 5.25 5.9 7.3 8.15 5.4 6.0 7.3 8.15 5.4 6.0 5.0 4.6 5.2 5.0 4.6 5.2
Flow at
Design Point
Press at No
Flow Speed
gpm 150 200 270 340 410
40%
ft wc 12 18 22 38 16 20 36 48 14 18 32 46 10 20 28 38 10 18 26 36
Hd
gpm 150 200 270 340 410
40%
ft wc 12 18 22 30 38 16 20 36 48 14 18 32 46 20 28 38 18 26 36
Hd
4380
3x3x8
4382
4x4x8
4380
3x3x6
4382
3x3x6
4380
3x3x8
DUAL PUMP
4382
4x4x8
4380
3x3x6
4382
4x4x6
4380
3x3x8
4382
4x4x8
4380
3x3x6
4382
4x4x6
4380
4x4x8
4x4x6
4382
4380
4x4x6
4382
6x6x6
4380
4x4x8
4382
4x4x6
4380
4x4x6
53
Page 54

PREPARATION FOR YEAR ROUND OPERATION — If
30RB060-130
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
GPM
060, 070
080, 090, 100
110, 120, 130
(179.4kPa)
(149.5kPa)
(119.6kPa)
(89.7kPa)
(59.8kPa)
(29.8kPa)
6.3 12.6 18.9 25.2 31.5 37.8 44.2
L/s
dP (Feet)
Fig. 52 — 30RB060-130
Cooler Pressure Drop Curves
30RB150-190 and 30RB315A,B; 330A,B; 345A,B; 360A,B; 390A,B
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0 200 400 600 800 1000
GPM
dP (Feet)
(179.4kPa)
(149.5kPa)
(119.6kPa)
(89.7kPa)
(59.8kPa)
(29.8kPa)
12.6 25.2 37.8 50.5
L/s
63.1
0.0
Fig. 53 — 30RB150-190 and 30RB315A,B; 345A,B;
360A,B; 390A,B Cooler Pressure Drop Curve
0
20
40
60
(179.4kPa)
(119.6kPa)
(59.8kPa)
10
(29.8kPa)
30
(89.7kPa)
50
(149.5kPa)
70
(209.3kPa)
30RB210-300
200
400 600 800
1000
1200 1400
GPM
12.6
25.2
37.8 50.5
L/s
63.1 75.7 88.3
dP (Feet)
0.0
0
Fig. 54 — 30RB210-300
Cooler Pressure Drop Curve
the unit is in operation year-round, add sufficient suitable
inhibited antifreeze solution such as propylene or ethylene
glycol to chilled water and heat reclaim to prevent freezing
under low-ambient temperature operating conditions. Consult
local water treatment specialist on characteristics of water and
recommended inhibitor.
IMPORTANT: Glycol anti-freeze solutions are highly
recommended since heater tapes provide no protection
in the event of a power failure.
If the unit is equipped with low ambient temperature head
pressure control, field-fabricated and field-installed wind baffles are required if the wind velocity is anticipated to be greater
than 5 mph (8 km/h). Two different baffles are required, one for
the control box end and one for the opposite end of the control
box. Wind baffles should be constructed with minimum
18-gage galvanized sheet metal or other suitable corrosionresistance material with cross breaks for strength. Use fieldsupplied screws to attach baffles to the corner posts of the
machine. Be sure to hem or turn a flange on all edges to eliminate sharp edges on the baffles.
WARNING
Disconnect all power to the unit before performing maintenance or service. Unit may automatically start if power is
not disconnected. Electrical shock and personal injury
could result.
CAUTION
To avoid damage to the refrigerant coils and electrical components, use extreme care when drilling screw holes and
screwing in fasteners.
Mount the smaller height baffle on the end of the control
box. It is recommended that the upper notches be used for
mounting the baffles. This reduces the risk of damaging the
coil while drilling a mounting hole. Loosen the upper corner
post bolts and slide the baffle under the bolt and washer. Tighten the bolts. Drill holes in the bottom of the flange of the baffle
and mount with two screws to secure the bottom of the baffle to
the corner post. Repeat the process for the opposite side. See
Fig. 57.
FREEZE PROTECTION — The 30RB units are provided
with a flow switch for chilled water to protect against freezing
situations that occur from no water flow. For freeze protection
of the chiller in case of power failure during subfreezing ambient temperatures, or in other cases where water temperature
falls below the freezing mark, other methods must be used. Appropriate concentrations of inhibited propylene or ethylene glycol or other suitable inhibited antifreeze solution should be
considered for chiller protection for both chilled water and heat
reclaim, where ambient temperatures are expected to fall below
32 F (0° C). Consult local water treatment specialist on characteristics of the system water and add a recommended inhibitor
to the chilled water. The Carrier warranty does not cover damage due to freezing.
54
Page 55

HEAT RECLAIM VESSEL PRESSURE DROP CURVES
30RB 60-110 TON
0
10
(29.8kPa)
20
(59.8kPa)
30
(89.7kPa)
40
(119.6 kPa)
50
(149.5kPa)
60
(179.4kPa)
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
GPM
ft wg
L/s
0.00 6.31 12.62 18.93 25.24 31.55 37.85 44.16
a30-4822
Fig. 55 — 30RB060-110 Optional Heat Reclaim Pressure Drop Curves
a30-4823
Fig. 56 — 30RB120-190 Optional Heat Reclaim Pressure Drop Curves
HEAT RECLAIM VESSEL PRESSURE DROP CURVES
30RB 120-190 TON
50
(149.5kPa)
40
(119.6 kPa)
30
(89.7kPa)
ft wg
20
(59.8kPa)
10
(29.8kPa)
120-150ton
160-190ton
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
GPM
0.00 6.31 12.62 18.93 25.24 31.55 37.85 44.16 50.47 56.78 63.09
L/s
55
Page 56

NOTE: Do not use automobile antifreeze, or any other fluid
Cross break these faces.
Hem these 3 edges both top
and bottom.
See Detail A
1880 [74.0]
Detail A
Typical Both Flanges
X
180 [7.0]
18 [0.75]
31 [1.25]
18 [0.75]
21 [0.88]
70 [2.75]
305 [12.0]
Fig. 57 — Field-Fabricated and Field-Installed Wind Baffles
NOTES:
1. Material: 18 ga. Corrosion Resistant Sheet Metal.
2. Dimensions are in mm [inches].
POSITION BAFFLE HEIGHT (X)
Control/Power End 635 [25.0]
Opposite Control/Power End 1040 [41.0]
a30-3997ef
that is not approved for heat exchanger duty. Only use appropriately inhibited glycols, concentrated to provide adequate
protection for the temperature considered.
1. Use an electric heater tape for the external piping, if unit
will be exposed to freezing temperatures.
2. Ensure that power is available to the chiller at all times,
even during the off-season, so that the pump, cooler heaters and heat reclaim have power. Also make sure that the
piping tape heaters have power.
3. On units with pump packages, a heater is supplied with
the hydronic package that will protect this section from
freezing in outdoor-air temperatures down to –20 F
(–29 C), except in the case of a power failure. If the pump
will be subjected to freezing temperatures, steps must be
taken to prevent freeze damage. If the pump will not be
used during this time, it is recommended to drain the
pump and hydronic package and these components are
back-flushed with inhibited glycol. Otherwise, a glycolwater solution should be considered as the heat transfer
fluid. Drains are located on the pump(s) and suction
guide/strainer for units with hydronic kits. Units without
hydronic kits have a drain mounted on the bottom of the
heat exchanger near the leaving water connection of the
heat exchanger. The Carrier warranty does not cover
damage due to freezing.
4. Cooler heaters that will protect components down to
–20 F (–28.9 C) can be ordered as a factory-installed option. It should be noted that these heaters will not protect
the cooler from freezing in the event of a power failure.
The Carrier warranty does not cover damage due to
freezing.
5. Units with the heat reclaim option are supplied with a
heater to protect the reclaim condenser down to 0° F
(–18 C). If the unit controls the heat reclaim circulator
pump and or valves to allow flow through the condenser,
freeze protection to –20 F (–29 C) is provided. Again, it
should be noted that the heaters and pump control will not
protect the reclaim condenser from freezing in the event
of a power failure. The Carrier warranty does not cover
damage due to freezing.
PREPARATION FOR WINTER SHUTDOWN — If the unit
is not operational during the winter months, at the end of cooling season, perform the following:
CAUTION
Failure to remove power before draining heater equipped
coolers, heat reclaim condensers and hydronic packages
can result in heater tape and insulation damage.
CHILLED WATER SYSTEM
1. If the unit has an optional heater on the cooler and the
cooler will not be drained, do not shut off power disconnect during off-season shutdown. If the unit has an optional heater on the cooler and the cooler will be drained,
open the circuit breaker for the heater, CB-HT or shut off
power during off-season shutdown.
2. Draining the fluid from the system is highly recommended. If the unit is equipped with a hydronic package, there
are additional drains in the pump housing and strainer
56
that must be opened to allow for all of the water to drain.
Page 57

3. Replace the drain plug and add 2 gallons (7.6 liters) of a
suitable corrosion-inhibited anti-freeze solution such as
propylene glycol to the cooler to prevent freezing of any
remaining water in system. Antifreeze can be added
through the vent on top of cooler. If the unit has a hydronic pump package, the pump must also be treated in the
same manner.
4. Open one of the thermistor connections to allow air to
escape the vessel and the anti-freeze to enter.
5. At the beginning of the next cooling season, be sure that
there is refrigerant pressure on each circuit before
refilling cooler, add recommended inhibitor, and reset the
CB-HT (circuit breaker heater) (if opened) or restore
power.
HEAT RECLAIM SYSTEM — At the end of each cooling
season the fluid should be drained from the system. However,
due to the heat reclaim condenser circuiting, some fluid will remain in the condenser after draining. To prevent freeze-up
damage to the condenser tubes perform the following
procedure.
1. If the heat reclaim condenser will not be drained do not
shut off power disconnect during off-season shutdown. If
the condenser will be drained, deenergize the heaters to
prevent damage and possible safety hazards when draining, or when there is no liquid in the system. Open the
condenser heater circuit breaker, CB-CDH7 to deenergize
the heaters. Drain the fluid from the system.
2. Isolate the condenser from the rest of the system with water shut off valves.
3. Completely fill the condenser with an appropriate
amount of inhibited ethylene glycol solution (or other
suitable corrosion-inhibitive antifreeze) for 15 F
(8.3 C) below the expected low ambient conditions.
4. Leave the condenser filled with the antifreeze solution for
the winter, or drain if desired. Be sure to deenergize heaters as explained in Step 1 to prevent damages. Use an approved method of disposal when removing the antifreeze
solution.
5. At the beginning of the next cooling season, be sure that
there is refrigerant pressure on each circuit before refilling the condenser circuit, add recommended inhibitor and
reset the CB-CDHT (if opened) to restore power.
Step 6 — Make Electrical Connections
WARNING
Electrical shock can cause personal injury and death. Shut
off all power to this equipment during installation. There
may be more than one disconnect switch. Tag all disconnect locations to alert others not to restore power until work
is completed.
POWER SUPPLY — The electrical characteristics of the
available power supply must agree with the unit nameplate
rating. Supply voltage must be within the limits shown.
Some units have options for multiple power connections.
See Table 9 and Fig. 58 for elecrical connection information.
See Tables 10A-14 for electrical requirements.
IMPORTANT: Operating unit on improper supply
voltage or with excessive phase imbalance constitutes
abuse and may adversely affect Carrier warranty.
POWER WIRING — All power wiring must comply with
applicable local and national codes. Install field-supplied
branch circuit fused disconnect per NEC of a type that can be
locked OFF or OPEN. Disconnect must be within sight and
readily accessible from the unit in compliance with NEC
Article 440-14. In the power box,
power entry. The holes will need to be enlarged to accept the
appropriate conduit. NEC also requires all conduits from a
conditioned space to the power box(es) be sealed to prevent
airflow and moisture into the control box.
Duplex units require at least two separate power supplies, at
least one for each module, depending on the power supply
option ordered.
General Wiring Notes:
1. The control circuit does NOT require a separate power
source. A step-down transformer from the main threephase power supply obtains control circuit power. Be sure
that the appropriate connection tap is connected on all
transformers for the supply voltage. Up to three terminal
blocks are provided for field-wired control devices.
2. Cooler heat reclaim condenser and pump heaters (if factory installed) are wired in the control circuit so they are
operable as long as the main power supply to the unit is
ON. A factory-installed and set overload device protects
them.
NOTE: The field-supplied disconnect should never be off
except when unit is being serviced or is to be down for a prolonged period, in which case the cooler and heat reclaim condenser should be drained if not properly protected.
3. Power entry depends on the size and power entry option
ordered.
4. Maximum field wire sizes allowed by lugs on terminal
block/non-fused disconnect are listed in Tables 10 and 11.
5. Terminals for field power supply are suitable for copper
conductors. Insulation must be rated 75 C minimum.
IMPORTANT: To ensure power to the heaters, make
sure power to the unit is always on (except during service or a prolonged shutdown).
7
/8 in. holes are provided for
CAUTION
Proper rotation of condenser fan(s) and pump(s) MUST be
verified before pumps or compressors are started. Consult
the Controls, Start-Up, Operation, Service and Troubleshooting guide provided with 30RB060-390 units for correct procedure. Improper pump rotation can cause
permanent damage to pump impeller and housing. If
pump(s) have been removed for trimming, verify wiring is
reconnected in the original manner.
CONTROL POWER — Control power is obtained from the
main power supply and does NOT require a separate source. A
toggle switch (marked SW2 on the unit label diagram and by
the switch) allows the control circuit to be manually
disconnected when necessary. Cooler heat reclaim condenser
and pump heaters (if installed) are in an inoperable state when
this switch is in the Off position.
IMPORTANT: For 208-v systems, the connection tap
for all transformers must be changed. The factory
default setting is for 230-v. Failure to connect to the
proper tap may result in unreliable operation.
FIELD CONTROL OPTION WIRING — Install field control wiring options. See Fig. 58 and 59. Some options, such as
4 to 20 mA demand limit that requires the energy management
module, may require that accessories be installed first if not
factory installed for terminal connections.
57
Page 58

DUAL CHILLER CONTROL OPTION — If the dual chiller
algorithm is used and the machines are installed in parallel, an
additional chilled water sensor must be installed for each
chiller. For 30RB315-390 units, a factory-supplied thermistor
and well are shipped in the control box of each. Install the well
in the common leaving water header. See Fig 34. Do not relocate the chiller’s leaving water thermistors. They must remain
in place for the unit to operate properly.
For the non-modular units, an accessory kit, part no.
00EFN900044000A, is available. This kit includes all parts
necessary for dual chiller control.
The thermistor well is a
1
/4 in. NPT fitting for securing the
well in the piping. The piping must be drilled and tapped for
Once the well is inserted, install the thermistors. Insert the
thermistor into the well until the O-ring reaches the well body.
Use the nut on the thermistor to secure the thermistor in place.
Once the thermistor is in place, it is recommended that a
thermistor wire loop be made and secured with a wire tie to the
chilled water pipe. This will aid in thermistor retention in the
well. See Fig. 60. Attach connector (part no. HY06AM016) to
thermistor lead. Plug connector into MBB J6-CH-3.
For 30RB315-390 units, as well as all units using the dual
chiller algorithm, a Carrier Comfort Network
must be connected between the two modules. See the
Carrier Comfort Network Communication Bus Wiring section
on page 70 for additional information.
the well. Select a location that will allow for removal of the
thermistor without any restrictions. See Fig. 60 and 61.
Table 9 — Control and Power Connections, 30RB060-390
30RB UNIT SIZE VOLTAGE ELECTRICAL OPTION CONNECTIONS
Single Point Circuit 1 Combination
060,070
080-120
130-190,
315A-390A,
315B-390B
210, 225
250-300
*Dual point connection is not available when non-fused disconnect
option is selected.
†Single point connection not available.
208/230, 380,
460, 575
208/230
380, 460, 575
208/230
380, 460, 575
208/230†
380, 460, 575
208/230†
380, 460, 575
Standard (Terminal Block)
Non-Fused Disconnect Option* Single Point Circuit 1 Combination
Standard (Terminal Block)
Non-Fused Disconnect Option* Single Point Circuit 1 Power-L
Standard (Terminal Block)
Non-Fused Disconnect Option* Single Point Circuit 1 Combination
Standard (Terminal Block)
Non-Fused Disconnect Option
Standard (Terminal Block)
Non-Fused Disconnect Option
Standard (Terminal Block) Dual Point
Non-Fused Disconnect Option Dual Point
Standard (Terminal Block)
Non-Fused Disconnect Option
Standard (Terminal Block) Dual Point
Non-Fused Disconnect Option Dual Point
Standard (Terminal Block)
Non-Fused Disconnect
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 Power-L
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 Combination
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 Power-L
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 Power-L
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 PEB1
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 PEB1
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 PEB1
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 PEB1
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 PEB1
Dual Point
Single Point Circuit 1 PEB1
Dual Point
NOTES:
1. “Combination” is identified as COMB1 in Fig. 58.
2. “Power-L” is the same as COMB1 in Fig. 58.
3. “PEB” or Power Electrical Box is shown in Fig. 58.
MAIN POWER
ENTRANCE
Circuit 1 Combination
Circuit 2 Combination
Circuit 1 Power-L
Circuit 2 Power-L
Circuit 1 Combination
Circuit 2 Combination
Circuit 1 Power-L
Circuit 2 PEB1
Circuit 1 Power-L
Circuit 2 PEB1
Circuit 1 PEB1
Circuit 2 PEB1
Circuit 1 PEB1
Circuit 2 Power-L
Circuit 1 Power-L
Circuit 2 PEB2
Circuit 1 Power-L
Circuit 2 PEB2
Circuit 1 PEB1
Circuit 2 PEB1
Circuit 1 PEB1
Circuit 2 Power-L
Circuit 1 Power-L
Circuit 2 PEB2
Circuit 1 Power-L
Circuit 2 PEB2
Circuit 1 PEB1
Circuit 2 PEB2
Circuit 1 PEB1
Circuit 2 PEB2
CONTROL BOX
®
(CCN) bus
58
Page 59

NOTES:
1. FACTORY WIRING IS IN ACCORDANCE WITH UL 1995 STANDARDS. FIELD MODIFICATIONS
OR ADDITIONS MUST BE IN COMPLIANCE WITH ALL APPLICABLE CODES.
2. WIRING FOR MAIN FIELD SUPPLY MUST BE RATED 75C MINIMUM. USE COPPER FOR ALL UNITS.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE FOR THE TERMINAL BLOCK IS #4 AWG TO 500 KCMIL.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE OF NON-FUSED DISCONNECT WITH MCA UP TO 599.9 AMPS IS 3/0 TO 500 KCMIL.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE OF NON-FUSED DISCONNECT WITH MCA FROM 600 TO 799.9 AMPS IS 1/0 TO 500 KCMIL.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE OF NON-FUSED DISCONNECT WITH MCA FROM 800 TO 1199.9 AMPS IS 250 KCMIL TO 500 KCMIL.
3. TERMINALS 9 AND 10 OF TB5 ARE FOR FIELD EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS FOR REMOTE ON-OFF.
THE CONTACTS MUST BE RATED FOR DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION CAPABLE OF HANDLING A
24VAC LOAD UP TO 50 MA.
4. TERMINALS 1 AND 2 OF TB5 ARE FOR EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS OF CHILLED WATER PUMP INTERLOCK.
THE CONTACTS MUST BE RATED FOR DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION CAPABLE OF HANDLING A
24VAC LOAD UP TO 50 MA.
5. TERMINALS 11 AND 13 OF TB5 ARE FOR CONTROL OF CHILLED WATER PUMP1 (PMP1) STARTER.
TERMINALS 13 AND 15 OF TB5 ARE FOR CONTROL OF CHILLED WATER PUMP2 (PMP2) STARTER.
THE MAXIMUM LOAD ALLOWED FOR THE CHILLED WATER PUMP RELAY IS 5 VA SEALED, 10
VA
INRUSH AT 24V. FIELD POWER SUPPLY IS NOT REQUIRED.
6. FOR CONTROL OF CHILLED WATER PUMPS, A SET OF NORMALLY OPEN CONTACTS RATED FOR DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION
MUST BE SUPPLIED FROM FIELD SUPPLIED PUMP STARTER RELAY. CONNECT CONTACTS TO VIOLET AND PINK WIRES IN
HARNESS FROM MAIN BASE BOARD CHANNEL 18. WIRES IN HARNESS ARE MARKED PMP1-13 AND PMP1-14.
7. TERMINALS 12 AND 13 OF TB5 ARE FOR A ALARM RELAY. THE MAXIMUM LOAD ALLOWED FOR THE
ALARM RELAY IS 10 VA SEALED, 25 VA INRUSH AT 24V. FIELD POWER SUPPLY IS NOT REQUIRED.
8. MAKE APPROPRIATE CONNECTIONS TO TB6 AS SHOWN FOR ENERGY MANAGEMENT BOARD OPTIONS. THE
CONTACTS FOR OCCUPANCY OVERRIDE, DEMAND LIMIT AND ICE DONE OPTIONS MUST BE RATED FOR
DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION CAPABLE OF HANDLING A 24VAC LOAD UP TO 50 MA.
9. J3 - 24 AND 25 OF EMM BOARD ARE FOR RUN RELAY AND SHUTDOWN RELAY. THE MAXIMUM
LOAD ALLOWED FOR THE RUN AND SHUTDOWN RELAY IS 10 VA SEALED, 25 VA INRUSH AT 24V.
FIELD POWER SUPPLY IS NOT REQUIRED.
ICE DONE
DEMAND LIMIT STEP 2
OCCUPANCY OVERRIDE
DUAL SETPOINT
12
3
456
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
TB5
TB6
12
3
456
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
EMM
FIOP/
ACCESSORY
REMOTE
ON/OFF
SEE
NOTE 3
A
PMP2
PMP1
+
COM
-
SHLD
DATA COM PORT
GROUND-FAULT
CIRCUIT-INTERRUPTER
OUTLET
(4 AMPS MAX.)
TRAN2
SECONDARY
115V
BLK
WHT
RESET
TEST
GRN-YEL
GFI-CO
FIOP/ACCESSORY
BRASS SCREW
SILVER SCREW
WHT
FU4
X3
X1
LOAD
LINE
SILVER SCREW
PMPI
XF
MLV-B
MLV-C
CAPACITY
LIMIT
SETPOINT
RESET
8
T8
SPACE
TEMP
(10K)
J6
R
4
3
CH
2
J4
+
2
1
CH
11A
J4
+
6
5
CH
8
J4
+
6
5
CH
9
EMM BOARD
DISPLAY LOCATION
DEMAND LIMIT STEP 1
4-20 MA
SIGNAL
GENERATOR
4-20 MA
SIGNAL
GENERATOR
+
-
GRN
BLK
REMOTE LOCKOUT SWITCH
J4
+
4
3
CH
10
1/2 WATT 250
MLV-A
DISPLAY LOCATION
MAIN POWER ENTRANCE CIRCUIT 1
060-120 ALL VOLTAGES
130-190 DUAL & SINGLE POINT 208/230V
210-300 DUAL POINT 208/230V
MAIN POWER ENTRANCE CIRCUIT 2
060-120 DUAL POINT,ALL VOLTAGES
130-190 DUAL POINT WITH DISCONNECT OPTION,380/460/575V
210,225 DUAL POINT WITH DISCONNECT OPTION,380/460/575V
MAIN POWER ENTRANCE CIRCUIT 1
130-300 DUAL & SINGLE POINT,380/460/575V
MAIN POWER ENTRANCE CIRCUIT 2
130-190 DUAL POINT,208/230V
130-190 DUAL POINT WITH TERMINAL BLOCKS,380/460/575V
210,225 DUAL POINT WITH TERMINAL BLOCKS,380/460/575V
R
S
5V
CH
6
R
S
5V
CH
5
J7B
J7A
GRA
GRA
RED
RED
BLU
BLU
ORN
ORN
VIO
GRN
VIO
BLK
TYPICAL CONTROL BOX LOCATIONS
AND MAIN POWER ENTRY
FIELD CONTROL
WIRING ENTRY
FIELD CONTROL
WIRING ENTRY
MAIN POWER ENTRANCE CIRCUIT 2
210-300 DUAL POINT,208/230V
250-300 DUAL POINT,460/575V
080-300 230V
130-300 380/460/575V
060,070 230V
060-120 380/460/575V
+
-
FEB
COMBICOMBI
OROR
POWER-LPOWER-L
PEB 1
PEB2
1/2 WATT 250
+
+
CH
25
CH
24
J3
4
3
2
1
RUN
R
SHD
R
TB5
13
C
A
B
SW2
ON/OFF
Network
Wiring
Network COM
Net+
SHIELD
Net-
BAS Port
UPC
Open
TB3
(SEE NOTE #10)
DUPLEX UNITS
SIZE STD UNIT
315A,B
330B
160
330A
345A,B
360B
170
360A
390A,B
190
LEGEND:
A - ALARM
PMPI- CHILLED WATER PUMP INTERLOCK
CWP - CHILLED WATER PUMP
EMM - ENERGY MANAGEMENT
SHD R- SHUTDOWN RELAY
RUN R- RUN RELAY
MLV - MINIMUM LOAD VALVE
TB - TERMINAL BLOCK
FIELD POWER WIRING
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FACTORY INSTALLED WIRING
a30-5708
Fig. 58 — Control and Power Wiring Schematic, 30RB060-390
59
Page 60

TERMINAL BLOCK
FIELD POWER SUPPLY
GROUND
(SEE NOTE #2)
21
11
DISCONNECT/BRANCH CIRCUIT
PROTECTION PER NEC
22
12
23
13
EQUIP
GND
TB1A (STANDARD POWER ENTRY)
TB1B/TB1C OPTIONAL DUAL POINT POWER ENTRY
NON-FUSED DISCONNECT
FIELD POWER SUPPLY
GROUND
(SEE NOTE #2)
DISCONNECT/BRANCH CIRCUIT
PROTECTION PER NEC
EQUIP
GND
CB1A ((STANDARD DISCONNECT POWER ENTRY)
CB1B (OPTIONAL DUAL POWER ENTRY POINT FOR DISCONNECT)
1
2
3
NOTES:
1. FACTORY WIRING IS IN ACCORDANCE WITH UL 1995 STANDARDS. FIELD MODIFICATIONS
OR ADDITIONS MUST BE IN COMPLIANCE WITH ALL APPLICABLE CODES.
2. WIRING FOR MAIN FIELD SUPPLY MUST BE RATED 75C MINIMUM. USE COPPER FOR ALL UNITS.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE FOR THE TERMINAL BLOCK IS #4 AWG TO 500 KCMIL.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE OF NON-FUSED DISCONNECT WITH MCA UP TO 599.9 AMPS IS 3/0 TO 500 KCMIL.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE OF NON-FUSED DISCONNECT WITH MCA FROM 600 TO 799.9 AMPS IS 1/0 TO 500 KCMIL.
INCOMING WIRE SIZE RANGE OF NON-FUSED DISCONNECT WITH MCA FROM 800 TO 1199.9 AMPS IS 250 KCMIL TO 500 KCMIL.
3. TERMINALS 9 AND 10 OF TB5 ARE FOR FIELD EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS FOR REMOTE ON-OFF.
THE CONTACTS MUST BE RATED FOR DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION CAPABLE OF HANDLING A
24VAC LOAD UP TO 50 MA.
4. TERMINALS 1 AND 2 OF TB5 ARE FOR EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS OF CHILLED WATER PUMP INTERLOCK.
THE CONTACTS MUST BE RATED FOR DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION CAPABLE OF HANDLING A
24VAC LOAD UP TO 50 MA.
5. TERMINALS 11 AND 13 OF TB5 ARE FOR CONTROL OF CHILLED WATER PUMP1 (PMP1) STARTER.
TERMINALS 13 AND 15 OF TB5 ARE FOR CONTROL OF CHILLED WATER PUMP2 (PMP2) STARTER.
THE MAXIMUM LOAD ALLOWED FOR THE CHILLED WATER PUMP RELAY IS 5 VA SEALED, 10 VA
INRUSH AT 24V. FIELD POWER SUPPLY IS NOT REQUIRED.
6. FOR CONTROL OF CHILLED WATER PUMPS, A SET OF NORMALLY OPEN CONTACTS RATED FOR DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION
MUST BE SUPPLIED FROM FIELD SUPPLIED PUMP STARTER RELAY. CONNECT CONTACTS TO VIOLET AND PINK WIRES IN
HARNESS FROM MAIN BASE BOARD CHANNEL 18. WIRES IN HARNESS ARE MARKED PMP1-13 AND PMP1-14.
7. TERMINALS 12 AND 13 OF TB5 ARE FOR A ALARM RELAY. THE MAXIMUM LOAD ALLOWED FOR THE
ALARM RELAY IS 10 VA SEALED, 25 VA INRUSH AT 24V. FIELD POWER SUPPLY IS NOT REQUIRED.
8. MAKE APPROPRIATE CONNECTIONS TO TB6 AS SHOWN FOR ENERGY MANAGEMENT BOARD OPTIONS. THE
CONTACTS FOR OCCUPANCY OVERRIDE, DEMAND LIMIT AND ICE DONE OPTIONS MUST BE RATED FOR
DRY CIRCUIT APPLICATION CAPABLE OF HANDLING A 24VAC LOAD UP TO 50 MA.
9. J3 - 24 AND 25 OF EMM BOARD ARE FOR RUN RELAY AND SHUTDOWN RELAY. THE MAXIMUM
LOAD ALLOWED FOR THE RUN AND SHUTDOWN RELAY IS 10 VA SEALED, 25 VA INRUSH AT 24V.
FIELD POWER SUPPLY IS NOT REQUIRED.
10. 250-OHM ½-WATT RESISTOR IS FIELD-SUPPLIED.
DUPLEX UNITS
SIZE STD UNIT
315A,B
330B
160
330A
345A,B
360B
170
360A
390A,B
190
LEGEND:
A - ALARM
PMPI- CHILLED WATER PUMP INTERLOCK
CWP - CHILLED WATER PUMP
EMM - ENERGY MANAGEMENT
SHD R- SHUTDOWN RELAY
RUN R- RUN RELAY
MLV - MINIMUM LOAD VALVE
TB - TERMINAL BLOCK
FIELD POWER WIRING
FIELD CONTROL WIRING
FACTORY INSTALLED WIRING
a30-5709
Fig. 58 — Control and Power Wiring Schematic, 30RB060-390 (cont)
60
Page 61

(–)
(+)
Fig. 59 — Optional Heat Reclaim Control Typical Field Wiring
NOTES:
1. Terminals 1 and 2 of TB7 are for external connection of heat
reclaim condenser water valve.
2. Terminals 3 and 4 of TB7 are for external connection of fieldsupplied heat reclaim water pump control relay.
3. The maximum load allowed for the condenser pump relay is
5 va sealed, 10 va inrush at 24 v.
4. Terminals 14 and 15 of TB7 are for external connection of
heat reclaim remote enable switch.
5. Terminals 5 through 13 of TB7 are for the connection of
factory-installed solenoid valve control wiring.
LEGEND
Field Control Wiring
Factory-Installed Wiring
a30-4742
WIRE TIE
LOOP
THERMISTOR WIRE
AND SECURE
TO CHILLED WATER PIPE
INSERT THERMISTOR UNTIL
O-RING MEETS THE
THERMISTOR WELL BODY.
Fig. 60 — Dual Leaving Water Thermistor
(Part No. 30RB660036)
5/8 in. HEX
6" MINIMUM
CLEARANCE FOR
THERMISTOR
REMOVAL
1.188 in.
2.315 in.
1/4-18 NPT
Fig. 61 — Dual Leaving Water Thermistor Well
(Part No. 00PPG000008000A)
61
Page 62

208/230
460
575 v only
Table 10A — 30RB060-190 Electrical Data — Single Point Units
UNIT 30RB
060
070
080
090
100
110
120
130
150
160
170
190
AWG — American Wire Gage MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
ICF — Instantaneous Current Flow XL — Across-the-Line Start
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
NOTES:
1. Units are suitable for use on electrical systems where voltage supplied to the unit
terminals is not below or above the listed minimum and maximum limits. Maximum
allowable phase imbalance is: voltage, 2%; amps 10%.
2. All units or modules have single point primary power connection. (Each unit or module
requires its own power supply.) Main power must be supplied from a field-supplied
disconnect.
3. Cooler heater is wired into the control circuit so it is always operable as long as the
power supply disconnect is on, even if any safety device is open.
4. For MCA that is less than or equal to 380 amps, 3 conductors are required.
For MCA between 381-760 amps, 6 conductors are required.
For MCA between 761-1140 amps, 9 conductors are required.
For MCA between 1141-1520 amps, 12 conductors are required.
Calculation of conductors required is based on 75 C copper wire.
UNIT VOLTAGE NO HYDRONIC PACKAGE 3 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM 5 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-60 187 253 291.5 350 682.8 350 300.6 350 693.6 350 306.9 350 700.5 350
380-60 342 418 150.9 175 362.9 175 156.0 175 368.8 175 159.0 175 372.6 175
460-60 414 506 127.9 150 302.0 150 132.1 150 306.9 150 135.0 150 310.0 150
575-60 518 633 102.4 125 244.7 110 105.7 125 248.6 125 107.8 125 251.1 125
208/230-60 187 253 334.7 400 777.0 400 343.8 400 787.8 400 350.1 400 794.7 400
380-60 342 418 175.5 200 428.8 200 180.8 225 434.7 200 183.6 225 438.5 200
460-60 414 506 147.9 175 355.9 175 152.1 175 360.8 175 155.0 175 363.9 175
575-60 518 633 119.8 150 287.4 150 123.1 150 291.3 150 125.2 150 293.8 150
208/230-60 187 253 366.5 400 757.8 400 — — — — 381.9 450 775.5 450
380-60 342 418 189.3 225 401.3 200 — — — — 197.4 225 411.0 225
460-60 414 506 160.6 175 334.7 175 — — — — 167.7 200 342.7 200
575-60 518 633 128.6 150 270.9 150 — — — — 134.0 150 277.3 150
208/230-60 187 253 433.6 500 875.9 500 — — — — 449.0 500 893.6 500
380-60 342 418 226.9 250 480.3 250 — — — — 235.0 250 490.0 250
460-60 414 506 191.4 225 399.4 225 — — — — 198.5 225 407.4 225
575-60 518 633 154.6 175 322.2 175 — — — — 160.0 175 328.6 175
208/230-60 187 253 472.0 500 914.3 500 — — — — 487.4 500 932.0 500
380-60 342 418 248.7 250 502.1 250 — — — — 256.8 300 511.8 300
460-60 414 506 209.2 250 417.2 225 — — — — 216.3 250 425.2 250
575-60 518 633 170.0 200 337.6 200 — — — — 175.4 200 344.0 200
208/230-60 187 253 508.6 600 950.9 600 — — — — 524.0 600 968.6 600
380-60 342 418 265.3 300 518.7 300 — — — — 273.4 300 528.4 300
460-60 414 506 224.1 250 432.1 250 — — — — 231.2 250 440.1 250
575-60 518 633 180.8 200 348.4 200 — — — — 186.2 200 354.8 200
208/230-60 187 253 578.1 600 1020.4 6 00 — — — — 593.5 600 1038.1 600
380-60 342 418 304.6 350 538.0 350 — — — — 312.7 350 567.6 350
460-60 414 506 256.2 300 464.2 300 — — — — 263.3 300 472.2 300
575-60 518 633 208.2 225 325.8 225 — — — — 213.6 225 382.2 225
208/230-60 187 253 626.7 700 1068.9 700 — — — — 642.1 700 1086.6 700
380-60 342 418 327.7 350 581.1 350 — — — — 335.8 350 590.8 350
460-60 414 506 276.5 300 484.5 300 — — — — 283.6 300 492.5 300
575-60 518 633 223.3 250 391.0 250 — — — — 228.7 250 397.4 250
208/230-60 187 253 684.3 700 1126.5 700 — — — — 699.7 700 1144.2 700
380-60 342 418 360.4 400 613.8 400 — — — — 368.5 400 623.5 400
460-60 414 506 303.2 350 511.2 350 — — — — 310.3 350 519.2 350
575-60 518 633 246.4 250 414.1 250 — — — — 251.8 300 420.5 300
208/230-60 187 253 744.8 800 1187.0 800 — — — — 760.2 800 1204.7 800
380-60 342 418 390.1 400 643.5 400 — — — — 398.2 400 653.2 400
460-60 414 506 328.9 350 536.9 350 — — — — 336.0 350 544.9 350
575-60 518 633 265.9 300 433.5 300 — — — — 271.3 300 439.9 300
208/230-60 187 253 802.4 1000 1244.6 1000 — — — — 817.8 1000 1262.3 1000
380-60 342 418 422.8 450 676.2 450 — — — — 430.9 450 685.9 450
460-60 414 506 355.6 400 563.6 400 — — — — 362.7 400 571.6 400
575-60 518 633 289.0 300 456.6 300 — — — — 294.4 300 463.0 300
208/230-60 187 253 920.5 1000 1362.7 1000 — — — — 935.9 1000 1380.4 1000
380-60 342 418 485.2 500 738.5 500 — — — — 493.3 500 748.2 500
460-60 414 506 408.0 450 616.0 450 — — — — 415.1 450 624.0 450
575-60 518 633 331.5 350 499.1 350 — — — — 336.9 350 505.5 350
Supplied MCA MOCP ICF
Min Max XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL
LEGEND
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF
5. Wiring for main field supply must be rated 75 C minimum. Use copper for all units.
a. Incoming wire size range for the terminal block is no. 4 AWG to 500 kcmil.
b. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA up to 599.9 amps is
3/0 to 500 kcmil.
c. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 600 to
799.9 amps is 1/0 to 500 kcmil.
d. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 800 to
1199.9 amps is 250 kcmil to 500 kcmil.
6. Hydronic pump packages are not available as a factory-installed option for units
30RB210-390.
7. Power draw includes both crankcase heaters and cooler heaters (where used). Each
compressor has a crankcase heater which draws 56 watts of power. Units ordered with
the cooler heater option have 1 (060-150) or 2 (160-300) cooler heaters, 825 watts
each.
Rec Fuse
MCA MOCP ICF
Size
Rec Fuse
Size
1218
62
Page 63

208/230
460
575 v only
Table 10A — 30RB060-190 Electrical Data — Single Point Units (cont)
UNIT 30RB
060
070
080
090
100
110
120
130
150
160
170
190
AWG — American Wire Gage MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
ICF — Instantaneous Current Flow XL — Across-the-Line Start
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
NOTES:
1. Units are suitable for use on electrical systems where voltage supplied to the unit
terminals is not below or above the listed minimum and maximum limits. Maximum
allowable phase imbalance is: voltage, 2%; amps 10%.
2. All units and modules have single point primary power connection. (Each unit or module requires its own power supply.) Main power must be supplied from a field-supplied
disconnect.
3. Cooler heater is wired into the control circuit so it is always operable as long as the
power supply disconnect is on, even if any safety device is open.
4. For MCA that is less than or equal to 380 amps, 3 conductors are required.
For MCA between 381-760 amps, 6 conductors are required.
For MCA between 761-1140 amps, 9 conductors are required.
For MCA between 1141-1520 amps, 12 conductors are required.
Calculation of conductors required is based on 75 C copper wire.
UNIT VOLTAGE 7.5 HP PUMP, 1750/3450 RPM 10 HP PUMP, 3450 RPM 15 HP PUMP, 3450 RPM
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-60 187 253 313.5 350 708.5 350 316.5 350 716.4 350 — — — —
380-60 342 418 163.2 200 376.9 175 164.9 200 381.3 175 — — — —
460-60 414 506 138.0 150 313.6 150 139.4 150 317.2 150 — — — —
575-60 518 633 110.5 125 254.0 125 111.6 125 256.9 125 — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 356.7 450 802.7 400 359.7 450 810.6 400 — — — —
380-60 342 418 187.8 225 442.8 225 189.5 225 447.2 225 — — — —
460-60 414 506 158.0 175 367.5 175 159.4 200 371.1 175 — — — —
575-60 518 633 127.9 150 296.7 150 129.0 150 299.6 150 — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 388.5 450 783.5 450 391.5 450 791.4 450 403.2 450 807.6 450
380-60 342 418 201.6 225 415.3 225 203.3 225 419.7 225 210.3 225 428.5 225
460-60 414 506 170.7 200 346.3 200 172.1 200 349.9 200 177.6 200 357.2 200
575-60 518 633 136.7 150 280.2 150 137.8 150 283.1 150 142.6 150 288.9 150
208/230-60 187 253 455.6 500 901.6 500 458.6 500 909.5 500 470.3 500 925.7 500
380-60 342 418 239.2 250 494.3 250 240.9 250 498.7 250 247.9 250 507.5 250
460-60 414 506 201.5 225 411.0 225 202.9 225 414.6 225 208.4 250 421.9 225
575-60 518 633 162.7 175 331.5 175 163.8 175 334.4 175 168.6 200 340.2 200
208/230-60 187 253 494.0 500 940.0 500 497.0 500 947.9 500 508.7 600 964.1 600
380-60 342 418 261.0 300 516.1 300 262.7 300 520.5 300 269.7 300 529.3 300
460-60 414 506 219.3 250 428.8 250 220.7 250 432.4 250 226.2 250 439.7 250
575-60 518 633 178.1 200 346.9 200 179.2 200 349.8 200 184.0 200 355.6 200
208/230-60 187 253 530.6 600 976.6 600 533.6 600 984.5 600 545.3 600 1000.7 600
380-60 342 418 277.6 300 532.7 300 279.3 300 537.1 300 286.3 300 545.9 300
460-60 414 506 234.2 250 443.7 250 235.6 250 447.3 250 241.1 250 454.6 250
575-60 518 633 188.9 200 357.7 200 190.0 200 360.6 200 194.8 225 366.4 225
208/230-60 187 253 600.1 700 1046.1 700 603.1 700 1054.0 700 614.8 700 1070.2 700
380-60 342 418 316.9 350 572.0 350 318.6 350 576.4 350 325.6 350 585.2 350
460-60 414 506 266.3 300 425.8 300 267.7 300 479.4 300 273.2 300 486.7 300
575-60 518 633 216.3 225 385.1 225 217.4 250 388.0 250 222.2 250 393.8 250
208/230-60 187 253 648.7 700 1094.6 700 651.7 700 1102.5 700 663.4 700 1118.7 700
380-60 342 418 340.0 350 595.1 350 341.7 350 599.5 350 348.7 350 608.3 350
460-60 414 506 286.6 300 496.1 300 288.0 300 499.7 300 293.5 300 507.0 300
575-60 518 633 231.4 250 400.3 250 232.5 250 403.2 250 237.3 250 409.0 250
208/230-60 187 253 706.3 800 1152.2 800 709.3 800 1160.1 800 721.0 800 1176.3 800
380-60 342 418 372.7 400 627.8 400 374.4 400 632.2 400 381.4 400 641.0 400
460-60 414 506 313.3 350 522.8 350 314.7 350 526.4 350 320.2 350 533.7 350
575-60 518 633 254.5 300 423.4 300 255.6 300 426.3 300 260.4 300 432.1 300
208/230-60 187 253 766.8 800 1212.7 800 769.8 800 1220.6 800 781.5 800 1236.8 800
380-60 342 418 402.4 450 657.5 450 404.1 450 661.9 450 411.1 450 670.7 450
460-60 414 506 339.0 350 548.5 350 340.4 350 552.1 350 345.9 350 559.4 350
575-60 518 633 274.0 300 442.8 300 275.1 300 445.7 300 279.9 300 451.5 300
208/230-60 187 253 824.4 1000 1270.3 1000 827.4 1000 1278.2 1000 839.1 1000 1294.4 1000
380-60 342 418 435.1 450 690.2 450 436.8 450 694.6 450 443.8 450 703.4 450
460-60 414 506 365.7 400 575.2 400 367.1 400 578.8 400 372.6 400 586.1 400
575-60 518 633 297.1 300 465.9 300 298.2 300 468.8 300 303.0 350 474.6 350
208/230-60 187 253 942.5 1000 1388.4 1000 945.5 1000 1396.3 1000 957.2 1000 1412.5 1000
380-60 342 418 497.5 500 752.5 500 499.2 500 756.9 500 506.2 600 765.7 600
460-60 414 506 418.1 450 627.6 450 419.5 450 631.2 450 425.0 450 638.5 450
575-60 518 633 339.6 350 508.4 350 340.7 350 511.3 350 345.5 350 517.1 350
Supplied MCA MOCP ICF
Min Max XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL
LEGEND
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF
5. Wiring for main field supply must be rated 75 C minimum. Use copper for all units.
a. Incoming wire size range for the terminal block is no. 4 AWG to 500 kcmil.
b. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA up to 599.9 amps is
3/0 to 500 kcmil.
c. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 600 to
799.9 amps is 1/0 to 500 kcmil.
d. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 800 to
1199.9 amps is 250 kcmil to 500 kcmil.
6. Hydronic pump packages are not available as a factory-installed option for units
30RB210-390.
7. Power draw includes both crankcase heaters and cooler heaters (where used). Each
compressor has a crankcase heater which draws 56 watts of power. Units ordered with
the cooler heater option have 1 (060-150) or 2 (160-300) cooler heaters, 825 watts
each.
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF
Rec Fuse
Size
63
1218
Page 64

Table 10B — 30RB210-390 Electrical Data — Single Point Units
208/230
460
575 v only
UNIT 30RB
210
225
250
275
300
315A
315B
330A
330B
345A
345B
360A
360B
390A
390B
AWG — American Wire Gage MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
ICF — Instantaneous Current Flow XL — Across-the-Line Start
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
NOTES:
1. Units are suitable for use on electrical systems where voltage supplied to the unit
terminals is not below or above the listed minimum and maximum limits. Maximum
allowable phase imbalance is: voltage, 2%; amps 10%.
2. All units or modules have single point primary power connection. (Each unit or module
requires its own power supply.) Main power must be supplied from a
field-supplied disconnect.
3. Cooler heater is wired into the control circuit so it is always operable as long as the
power supply disconnect is on, even if any safety device is open.
4. For MCA that is less than or equal to 380 amps, 3 conductors are required.
For MCA between 381-760 amps, 6 conductors are required.
For MCA between 761-1140 amps, 9 conductors are required.
For MCA between 1141-1520 amps, 12 conductors are required.
Calculation of conductors required is based on 75 C copper wire.
UNIT VOLTAGE NO HYDRONIC PACKAGE 3 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM 5 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-60 187 253 — — — — — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 501.8 600 755.1 600 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 422.9 450 630.9 450 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 342.3 350 509.9 350 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 — — — — — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 534.5 600 787.8 600 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 449.6 450 657.6 450 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 365.4 400 533.0 400 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 — — — — — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 596.8 600 850.2 600 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 502.0 600 710.0 600 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 408.0 450 575.6 450 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 — — — — — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 659.2 700 912.6 700 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 554.4 600 762.4 600 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 450.5 500 618.1 500 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 — — — — — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 721.6 800 975.0 800 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 606.8 700 814.8 700 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 493.0 500 660.7 500 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 744.8 800 1187.0 800 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 390.1 400 643.5 400 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 328.9 350 536.9 350 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 265.9 300 433.5 300 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 744.8 800 1187.0 800 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 390.1 400 643.5 400 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 328.9 350 536.9 350 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 265.9 300 433.5 300 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 802.4 1000 1244.6 1000 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 422.8 450 676.2 450 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 355.6 400 563.6 400 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 289.0 300 456.6 300 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 744.8 800 1187.0 800 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 390.1 400 643.5 400 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 328.9 350 536.9 350 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 265.9 300 433.5 300 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 802.4 1000 1244.6 1000 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 422.8 450 676.2 450 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 355.6 400 563.6 400 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 289.0 300 456.6 300 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 802.4 1000 1244.6 1000 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 422.8 450 676.2 450 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 355.6 400 563.6 400 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 289.0 300 456.6 300 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 920.5 1000 1362.7 1000 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 485.2 500 738.5 500 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 408.0 450 616.0 450 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 331.5 350 499.1 350 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 802.4 1000 1244.6 1000 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 422.8 450 676.2 450 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 355.6 400 563.6 400 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 289.0 300 456.6 300 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 920.5 1000 1362.7 1000 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 485.2 500 738.5 500 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 408.0 450 616.0 450 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 331.5 350 499.1 350 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 920.5 1000 1362.7 1000 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 485.2 500 738.5 500 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 408.0 450 616.0 450 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 331.5 350 499.1 350 — — — — — — — —
Supplied MCA MOCP ICF
Min Max XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL
LEGEND
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF
5. Wiring for main field supply must be rated 75 C minimum. Use copper for all units.
a. Incoming wire size range for the terminal block is no. 4 AWG to 500 kcmil.
b. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA up to 599.9 amps is
3/0 to 500 kcmil.
c. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 600 to
799.9 amps is 1/0 to 500 kcmil.
d. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 800 to
1199.9 amps is 250 kcmil to 500 kcmil.
6. Hydronic pump packages are not available as a factory-installed option for units
30RB210-390.
7. Power draw includes both crankcase heaters and cooler heaters (where used). Each
compressor has a crankcase heater which draws 56 watts of power. Units ordered with
the cooler heater option have 1 (060-150) or 2 (160-300) cooler heaters, 825 watts
each.
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF
Rec Fuse
Size
64
Page 65

Table 11A — 30RB060-190 Electrical Data — Dual Point Units
208/230
460
575 v only
30RB
UNIT
SIZE
060
070
080
090
100
110
120
130
150
160
170
190
AWG — American Wire Gage
ICF — Instantaneous Current Flow (Ckt1/Ckt2)
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (Ckt1/Ckt2)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection (Ckt1/Ckt2)
XL — Across-the-Line Start
NOTES:
1. Units are suitable for use on electrical systems where voltage supplied to the unit
terminals is not below or above the listed minimum and maximum limits. Maximum
allowable phase imbalance is: voltage, 2%; amps 10%.
2. Control power is derived from main power. No separate control power connection is
required.
3. Cooler heater is wired into the control circuit so it is always operable as long as the
power supply disconnect is on, even if any safety device is open.
4. For MCA that is less than or equal to 380 amps, 3 conductors are required.
For MCA between 381-760 amps, 6 conductors are required.
For MCA between 761-1140 amps, 9 conductors are required.
For MCA between 1141-1520 amps, 12 conductors are required.
Calculation of conductors required is based on 75 C copper wire.
UNIT VOLTAGE NO HYDRONIC PACKAGE 3 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM 5 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM
V-Hz
(3 Ph)
208/230-60 187 253 168.8/141.5 225/200 560.0/532.8 200/175 177.9/141.5 250/200 570.8/532.8 200/175 184.2/141.5 250/200 577.7/532.8 225/175
380-60 342 418 86.4/ 74.1 110/110 298.4/286.1 100/ 90 91.5/ 74.1 125/110 304.3/286.1 110/ 90 94.5/ 74.1 125/110 308.1/286.1 110/ 90
460-60 414 506 73.6/ 62.5 100/ 90 247.7/236.6 90/ 80 77.8/ 62.5 110/ 90 252.6/236.6 90/ 80 80.7/ 62.5 110/ 90 255.7/236.6 90/ 80
575-60 518 633 59.0/ 50.0 80/ 70 201.2/192.3 70/ 60 62.3/ 50.0 80/ 70 205.1/192.3 70/ 60 64.4/ 50.0 90/ 70 207.6/192.3 80/ 60
208/230-60 187 253 212.0/141.5 300/200 654.2/532.8 250/175 221.1/141.5 300/200 665.0/532.8 250/175 227.4/141.5 300/200 671.9/532.8 300/175
380-60 342 418 110.9/ 74.1 150/110 364.3/286.1 125/ 90 116.0/ 74.1 150/110 370.2/286.1 150/ 90 119.0/ 74.1 150/110 374.0/286.1 150/ 90
460-60 414 506 93.6/ 62.5 125/ 90 301.6/236.6 110/ 80 97.8/ 62.5 125/ 90 306.5/236.6 110/ 80 100.7/ 62.5 125/ 90 309.6/236.6 125/ 80
575-60 518 633 76.3/ 50.0 110/ 70 243.9/192.3 90/ 60 79.6/ 50.0 110/ 70 247.8/192.3 90/ 60 81.7/ 50.0 110/ 70 250.3/192.3 100/ 60
208/230-60187253216.5/168.8250/225607.8/560.0250/200————231.9/168.8300/225625.5/560.0300/200
380-60342418112.5/86.4150/110324.5/298.4125/100————120.6/86.4150/110334.2/298.4150/100
460-6041450695.2/73.6125/100269.3/247.7110/90————102.3/73.6125/100277.3/247.7125/90
575-6051863376.2/59.0100/80218.5/201.290/70————81.6/59.0100/80224.9/201.290/70
208/230-60187253283.6/168.8350/225725.9/560.0350/200————299.0/168.8350/225743.5/560.0350/200
380-60342418150.1/86.4175/110403.5/298.4175/100————158.2/86.4200/110413.2/298.4175/100
460-60414506126.0/73.6150/100334.0/247.7150/90————133.1/73.6150/100342.0/247.7150/90
575-60518633102.2/59.0125/80269.8/201.2125/70————107.6/59.0125/80276.2/201.2125/70
208/230-60187253283.6/212.0350/300725.9/654.2350/250————299.0/212.0350/300743.5/654.2350/250
380-60342418150.1/110.9175/150403.5/364.3175/125————158.2/110.9200/150413.2/364.3175/125
460-60414506126.0/93.6150/125334.0/301.6150/110————133.1/93.6150/125342.0/301.6150/110
575-60518633102.2/76.3125/110269.8/243.9125/90————107.6/76.3125/110276.2/243.9125/90
208/230-60187253283.6/243.8350/300725.9/635.0350/300————299.0/243.8350/300743.5/635.0350/300
380-60342418150.1/124.8175/150403.5/336.8175/150————158.2/124.8200/150413.2/336.8175/150
460-60414506126.0/106.3150/125334.0/280.4150/125————133.1/106.3150/125342.0/280.4150/125
575-60518633102.2/85.2125/110269.8/227.4125/100————107.6/85.2125/110276.2/227.4125/100
208/230-60187253295.5/306.2350/400737.8/748.4350/350————310.9/306.2400/400755.5/748.4350/350
380-60342418156.7/160.2200/200410.1/413.6175/175————164.8/160.2200/200419.7/413.6200/175
460-60414506131.4/135.2150/175339.4/343.2150/150————138.5/135.2175/175347.4/343.2150/150
575-60518633106.5/110.2125/125274.1/277.8125/125————111.9/110.2125/125280.5/277.8125/125
208/230-60187253401.7/243.8450/300843.9/635.0450/300————417.1/243.8500/300861.6/635.0450/300
380-60342418212.5/124.8250/150465.9/336.8225/150————220.6/124.8250/150475.6/336.8250/150
460-60414506178.4/106.3200/125386.4/280.4200/125————185.5/106.3225/125394.4/280.4200/125
575-60518633144.7/85.2175/110312.4/227.4175/100————150.1/85.2175/110318.8/227.4175/100
208/230-60187253401.7/306.2450/400843.9/748.4450/350————417.1/306.2500/400861.6/748.4450/350
380-60342418212.5/160.2250/200465.9/413.6225/175————220.6/160.2250/200475.6/413.6250/175
460-60414506178.4/135.2200/175386.4/343.2200/150————185.5/135.2225/175394.4/343.2200/150
575-60518633144.7/110.2175/125312.4/277.8175/125————150.1/110.2175/125318.8/277.8175/125
208/230-60187253519.8/243.8600/300962.0/635.0600/300————535.2/243.8600/300979.7/635.0600/300
380-60342418274.9/124.8300/150528.3/336.8300/150————283.0/124.8300/150538.0/336.8300/150
460-60414506230.8/106.3250/125438.8/280.4250/125————237.9/106.3250/125446.8/280.4250/125
575-60518633187.3/85.2200/110354.9/227.4200/100————192.7/85.2225/110361.3/227.4225/100
208/230-60187253519.8/306.2600/400962.0/748.4600/350————535.2/306.2600/400979.7/748.4600/350
380-60342418274.9/160.2300/200528.3/413.6300/175————283.0/160.2300/200538.0/413.6300/175
460-60414506230.8/135.2250/175438.8/343.2250/150————237.9/135.2250/175446.8/343.2250/150
575-60518633187.3/110.2200/125354.9/277.8200/125————192.7/110.2225/125361.3/277.8225/125
208/230-60187253543.7/400.4600/450985.9/842.6600/450————559.1/400.4600/4501003.6/842.6600/450
380-60342418288.0/209.5300/250541.3/462.9300/225————296.1/209.5300/250551.0/462.9300/225
460-60414506241.6/176.8250/200449.6/384.8250/200————248.7/176.8250/200457.6/384.8250/200
575-60518633195.9/144.1225/175363.5/311.7225/175————201.3/144.1225/175369.9/311.7225/175
Supplied MCA MOCP ICF Rec
Min Max XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL
LEGEND
Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF Rec
5. Wiring for main field supply must be rated 75 C minimum. Use copper for all units.
a. Incoming wire size range for the terminal block is no.4 AWG to 500 kcmil.
b. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA up to 599.9 amps is
3/0 to 500 kcmil.
c. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 600 to
799.9 amps is 1/0 to 500 kcmil.
d. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 800 to
1199.9 amps is 250 kcmil to 500 kcmil.
6. Hydronic pump packages are not available as a factory-installed option for units
30RB210-390.
7. Power draw includes both crankcase heaters and cooler heaters (where used). Each
compressor has a crankcase heater which draws 56 watts of power. Units ordered with
the cooler heater option have 1 (060-150) or 2 (160-300) cooler heaters, 825 watts
each.
Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF Rec
Fuse
Size
65
Page 66

208/230
460
575 v only
Table 11A — 30RB060-190 Electrical Data — Dual Point Units (cont)
30RB
UNIT
SIZE
060
070
080
090
100
110
120
130
150
160
170
190
AWG — American Wire Gage
ICF — Instantaneous Current Flow (Ckt1/Ckt2)
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (Ckt1/Ckt2)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection (Ckt1/Ckt2)
XL — Across-the-Line Start
NOTES:
1. Units are suitable for use on electrical systems where voltage supplied to the unit
2. Control power is derived from main power. No separate control power connection is
3. Cooler heater is wired into the control circuit so it is always operable as long as the
4. For MCA that is less than or equal to 380 amps, 3 conductors are required.
UNIT VOLTAGE 7.5 HP PUMP, 1750/3450 RPM 10 HP PUMP, 3450 RPM 15 HP PUMP, 3450 RPM
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-60 187 253 190.8/141.5 250/200 585.7/532.8 225/175 193.8/141.5 250/200 593.6/532.8 225/175 — — — —
380-60 342 418 98.7/ 74.1 125/110 312.4/286.1 110/ 90 100.4/ 74.1 125/110 316.8/286.1 110/ 90 — — — —
460-60 414 506 83.7/ 62.5 110/ 90 259.3/236.6 100/ 80 85.1/ 62.5 110/ 90 262.9/236.6 100/ 80 — — — —
575-60 518 633 67.1/ 50.0 90/ 70 210.5/192.3 80/ 60 68.2/ 50.0 90/ 70 213.4/192.3 80/ 60 — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 234.0/141.5 300/200 679.9/532.8 300/175 237.0/141.5 300/200 687.8/532.8 300/175 — — — —
380-60 342 418 123.2/ 74.1 150/110 378.3/286.1 150/ 90 124.9/ 74.1 150/110 382.7/286.1 150/ 90 — — — —
460-60 414 506 103.7/ 62.5 125/ 90 313.2/236.6 125/ 80 105.1/ 62.5 125/ 90 316.8/236.6 125/ 80 — — — —
575-60 518 633 84.4/ 50.0 110/ 70 253.2/192.3 100/ 60 85.5/ 50.0 110/ 70 256.1/192.3 100/ 60 — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 238.5/168.8 300/225 633.4/560.0 300/200 241.5/168.8 300/225 641.4/560.0 300/200 253.2/168.8 300/225 657.5/560.0 300/200
380-60 342 418 124.8/ 86.4 150/110 338.6/298.4 150/100 126.5/ 86.4 150/110 342.9/298.4 150/100 133.5/ 86.4 150/110 351.8/298.4 150/100
460-60 414 506 105.3/ 73.6 125/100 280.9/247.7 125/ 90 106.7/ 73.6 125/100 284.5/247.7 125/ 90 112.2/ 73.6 125/100 291.8/247.7 125/ 90
575-60 518 633 84.3/ 59.0 110/ 80 227.8/201.2 100/ 70 85.4/ 59.0 110/ 80 230.6/201.2 100/ 70 90.2/ 59.0 110/ 80 236.5/201.2 100/ 70
208/230-60 187 253 305.6/168.8 350/225 751.5/560.0 350/200 308.6/168.8 400/225 759.5/560.0 350/200 320.3/168.8 400/225 775.6/560.0 350/200
380-60 342 418 162.4/ 86.4 200/110 417.6/298.4 175/100 164.1/ 86.4 200/110 421.9/298.4 200/100 171.1/ 86.4 200/110 430.8/298.4 200/100
460-60 414 506 136.1/ 73.6 175/100 345.6/247.7 150/ 90 137.5/ 73.6 175/100 349.2/247.7 150/ 90 143.0/ 73.6 175/100 356.5/247.7 175/ 90
575-60 518 633 110.3/ 59.0 125/ 80 279.1/201.2 125/ 70 111.4/ 59.0 125/ 80 282.0/201.2 125/ 70 116.2/ 59.0 150/ 80 287.8/201.2 125/ 70
208/230-60 187 253 305.6/212.0 350/300 751.5/654.2 350/250 308.6/212.0 400/300 759.5/654.2 350/250 320.3/212.0 400/300 775.6/654.2 350/250
380-60 342 418 162.4/110.9 200/150 417.6/364.3 175/125 164.1/110.9 200/150 421.9/364.3 200/125 171.1/110.9 200/150 430.8/364.3 200/125
460-60 414 506 136.1/ 93.6 175/125 345.6/301.6 150/110 137.5/ 93.6 175/125 349.2/301.6 150/110 143.0/ 93.6 175/125 356.5/301.6 175/110
575-60 518 633 110.3/ 76.3 125/110 279.1/243.9 125/ 90 111.4/ 76.3 125/110 282.0/243.9 125/ 90 116.2/ 76.3 150/110 287.8/243.9 125/ 90
208/230-60 187 253 305.6/243.8 350/300 751.5/635.0 350/300 308.6/243.8 400/300 759.5/635.0 350/300 320.3/243.8 400/300 775.6/635.0 350/300
380-60 342 418 162.4/124.8 200/150 417.6/336.8 175/150 164.1/124.8 200/150 421.9/336.8 200/150 171.1/124.8 200/150 430.8/336.8 200/150
460-60 414 506 136.1/106.3 175/125 345.6/280.4 150/125 137.5/106.3 175/125 349.2/280.4 150/125 143.0/106.3 175/125 356.5/280.4 175/125
575-60 518 633 110.3/ 85.2 125/110 279.1/227.4 125/100 111.4/ 85.2 125/110 282.0/227.4 125/100 116.2/ 85.2 150/110 287.8/227.4 125/100
208/230-60 187 253 317.5/306.2 400/400 763.5/748.4 350/350 320.5/306.2 400/400 771.4/748.4 350/350 332.2/306.2 400/400 787.6/748.4 400/350
380-60 342 418 169.0/160.2 200/200 424.1/413.6 200/175 170.7/160.2 200/200 428.5/413.6 200/175 177.7/160.2 225/200 437.3/413.6 200/175
460-60 414 506 141.5/135.2 175/175 351.0/343.2 175/150 142.9/135.2 175/175 354.6/343.2 175/150 148.4/135.2 175/175 361.9/343.2 175/150
575-60 518 633 114.6/110.2 125/125 283.4/277.8 125/125 115.7/110.2 125/125 286.3/277.8 125/125 120.5/110.2 150/125 292.1/277.8 150/125
208/230-60 187 253 423.7/243.8 500/300 869.6/635.0 450/300 426.7/243.8 500/300 877.6/635.0 500/300 438.4/243.8 500/300 893.7/635.0 500/300
380-60 342 418 224.8/124.8 250/150 479.9/336.8 250/150 226.5/124.8 250/150 484.3/336.8 250/150 233.5/124.8 250/150 493.1/336.8 250/150
460-60 414 506 188.5/106.3 225/125 398.0/280.4 200/125 189.9/106.3 225/125 401.6/280.4 225/125 195.4/106.3 225/125 408.9/280.4 225/125
575-60 518 633 152.8/ 85.2 175/110 321.6/227.4 175/100 153.9/ 85.2 175/110 324.5/227.4 175/100 158.7/ 85.2 175/110 330.4/227.4 175/100
208/230-60 187 253 423.7/306.2 500/400 869.6/748.4 450/350 426.7/306.2 500/400 877.6/748.4 500/350 438.4/306.2 500/400 893.7/748.4 500/350
380-60 342 418 224.8/160.2 250/200 479.9/413.6 250/175 226.5/160.2 250/200 484.3/413.6 250/175 233.5/160.2 250/200 493.1/413.6 250/175
460-60 414 506 188.5/135.2 225/175 398.0/343.2 200/150 189.9/135.2 225/175 401.6/343.2 225/150 195.4/135.2 225/175 408.9/343.2 225/150
575-60 518 633 152.8/110.2 175/125 321.6/277.8 175/125 153.9/110.2 175/125 324.5/277.8 175/125 158.7/110.2 175/125 330.4/277.8 175/125
208/230-60 187 253 541.8/243.8 600/300 987.7/635.0 600/300 544.8/243.8 600/300 995.6/635.0 600/300 556.5/243.8 600/300 1011.8/635.0 600/300
380-60 342 418 287.2/124.8 300/150 542.3/336.8 300/150 288.9/124.8 300/150 546.7/336.8 300/150 295.9/124.8 300/150 555.5/336.8 300/150
460-60 414 506 240.9/106.3 250/125 450.4/280.4 250/125 242.3/106.3 250/125 454.0/280.4 250/125 247.8/106.3 250/125 461.3/280.4 250/125
575-60 518 633 195.4/ 85.2 225/110 364.2/227.4 225/100 196.5/ 85.2 225/110 367.1/227.4 225/100 201.3/ 85.2 225/110 372.9/227.4 225/100
208/230-60 187 253 541.8/306.2 600/400 987.7/748.4 600/350 544.8/306.2 600/400 995.6/748.4 600/350 556.5/306.2 600/400 1011.8/748.4 600/350
380-60 342 418 287.2/160.2 300/200 542.3/413.6 300/175 288.9/160.2 300/200 546.7/413.6 300/175 295.9/160.2 350/200 555.5/413.6 350/175
460-60 414 506 240.9/135.2 250/175 450.4/343.2 250/150 242.3/135.2 250/175 454.0/343.2 250/150 247.8/135.2 250/175 461.3/343.2 250/150
575-60 518 633 195.4/110.2 225/125 364.2/277.8 225/125 196.5/110.2 225/125 367.1/277.8 225/125 201.3/110.2 225/125 372.9/277.8 225/125
208/230-60 187 253 565.7/400.4 600/450 1011.6/842.6 600/450 568.7/400.4 600/450 1019.5/842.6 600/450 580.4/400.4 600/450 1035.7/842.6 600/450
380-60 342 418 300.3/209.5 350/250 555.4/462.9 350/225 302.0/209.5 350/250 559.7/462.9 350/225 309.0/209.5 350/250 568.6/462.9 350/225
460-60 414 506 251.7/176.8 300/200 461.2/384.8 300/200 253.1/176.8 300/200 464.8/384.8 300/200 258.6/176.8 300/200 472.1/384.8 300/200
575-60 518 633 204.0/144.1 225/175 372.8/311.7 225/175 205.1/144.1 225/175 375.7/311.7 225/175 209.9/144.1 225/175 381.5/311.7 225/175
terminals is not below or above the listed minimum and maximum limits. Maximum
allowable phase imbalance is: voltage, 2%; amps 10%.
required.
power supply disconnect is on, even if any safety device is open.
For MCA between 381-760 amps, 6 conductors are required.
For MCA between 761-1140 amps, 9 conductors are required.
For MCA between 1141-1520 amps, 12 conductors are required.
Calculation of conductors required is based on 75 C copper wire.
Supplied MCA MOCP ICF
Min Max
XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL
LEGEND
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF
5. Wiring for main field supply must be rated 75 C minimum. Use copper for all units.
a. Incoming wire size range for the terminal block is no. 4 AWG to 500 kcmil.
b. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA up to 599.9 amps is
3/0 to 500 kcmil.
c. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 600 to
799.9 amps is 1/0 to 500 kcmil.
d. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 800 to
1199.9 amps is 250 kcmil to 500 kcmil.
6. Hydronic pump packages are not available as a factory-installed option for units
30RB210-390.
7. Power draw includes both crankcase heaters and cooler heaters (where used). Each
compressor has a crankcase heater which draws 56 watts of power. Units ordered with
the cooler heater option have 1 (060-150) or 2 (160-300) cooler heaters, 825 watts
each.
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF
Rec Fuse
Size
1218
66
Page 67

Table 11B — 30RB210-390 Electrical Data — Dual Point Units
208/230
460
575 v only
UNIT VOLTAGE NO HYDRONIC PACKAGE 3 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM 5 HP PUMP, 1750 RPM
UNIT 30RB
AWG — American Wire Gage
ICF — Instantaneous Current Flow (Ckt1/Ckt2)
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (Ckt1/Ckt2)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection (Ckt1/Ckt2)
XL — Across-the-Line Start
NOTES:
1. Units are suitable for use on electrical systems where voltage supplied to the unit
2. Control power is derived from main power. No separate control power connection is
3. Cooler heater is wired into the control circuit so it is always operable as long as the
4. For MCA that is less than or equal to 380 amps, 3 conductors are required.
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-60 187 253 626.7/353.9 700/400 1068.9/796.2 700/400
210
225
250
275
300
315A
315B
330A
330B
345A
345B
360A
360B
390A
390B
terminals is not below or above the listed minimum and maximum limits. Maximum
allowable phase imbalance is: voltage, 2%; amps 10%.
required.
power supply disconnect is on, even if any safety device is open.
For MCA between 381-760 amps, 6 conductors are required.
For MCA between 761-1140 amps, 9 conductors are required.
For MCA between 1141-1520 amps, 12 conductors are required.
Calculation of conductors required is based on 75 C copper wire.
380-60 342 418 327.7/186.4 350/225 581.1/439.7 350/200 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 233.3/200.0 250/225 441.3/408.0 250/225 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 188.8/162.0 200/175 356.4/329.6 200/175 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 684.3/353.9 700/400 1126.5/796.2 700/400
380-60 342 418 360.4/186.4 400/225 613.8/439.7 400/200 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 260.0/200.0 300/225 468.0/408.0 300/225 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 211.9/162.0 225/175 379.5/329.6 225/175 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 684.3/472.0 700/500 1126.5/914.3 700/500
380-60 342 418 360.4/248.7 400/250 613.8/502.1 400/250 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 303.2/209.2 350/250 511.2/417.2 350/225 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 246.4/170.0 250/200 414.1/337.6 250/200 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 920.5/353.9 1000/400 1362.7/796.2 1000/400
380-60 342 418 485.2/186.4 500/225 738.5/439.7 500/200 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 408.0/156.8 450/175 616.0/364.8 450/175 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 331.5/127.5 350/150 499.1/295.1 350/150 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 920.5/472.0 1000/500 1362.7/914.3 1000/500
380-60 342 418 485.2/248.7 500/250 738.5/502.1 500/250 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 408.0/209.2 450/250 616.0/417.2 450/225 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 331.5/170.0 350/200 499.1/337.6 350/200 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 519.8/243.8 600/300 962.0/635.0 600/300 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 274.9/124.8 300/150 528.3/336.8 300/150 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 230.8/106.3 250/125 438.8/280.4 250/125 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 187.3/ 85.2 200/110 354.9/227.4 200/100 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 519.8/243.8 600/300 962.0/635.0 600/300 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 230.8/106.3 250/125 438.8/280.4 250/125 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 187.3/ 85.2 200/110 354.9/227.4 200/100 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 274.9/124.8 300/150 528.3/336.8 300/150 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 519.8/306.2 600/400 962.0/748.4 600/350 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 274.9/160.2 300/200 528.3/413.6 300/175 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 230.8/135.2 250/175 438.8/343.2 250/150 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 187.3/110.2 200/125 354.9/277.8 200/125 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 519.8/243.8 600/300 962.0/635.0 600/300 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 274.9/124.8 300/150 528.3/336.8 300/150 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 230.8/106.3 250/125 438.8/280.4 250/125 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 187.3/ 85.2 200/110 354.9/227.4 200/100 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 519.8/306.2 600/400 962.0/748.4 600/350 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 274.9/160.2 300/200 528.3/413.6 300/175 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 230.8/135.2 250/175 438.8/343.2 250/150 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 187.3/110.2 200/125 354.9/277.8 200/125 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 519.8/306.2 600/400 962.0/748.4 600/350 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 274.9/160.2 300/200 528.3/413.6 300/175 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 230.8/135.2 250/175 438.8/343.2 250/150 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 187.3/110.2 200/125 354.9/277.8 200/125 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 543.7/400.4 600/450 985.9/842.6 600/450 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 288.0/209.5 300/250 541.3/462.9 300/225 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 241.6/176.8 250/200 449.6/384.8 250/200 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 195.9/144.1 225/175 363.5/311.7 225/175 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 519.8/306.2 600/400 962.0/748.4 600/350 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 274.9/160.2 300/200 528.3/413.6 300/175 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 230.8/135.2 250/175 438.8/343.2 250/150 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 187.3/110.2 200/125 354.9/277.8 200/125 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 543.7/400.4 600/450 985.9/842.6 600/450 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 288.0/209.5 300/250 541.3/462.9 300/225 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 241.6/176.8 250/200 449.6/384.8 250/200 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 195.9/144.1 225/175 363.5/311.7 225/175 — — — — — — — —
208/230-60 187 253 543.7/400.4 600/450 985.9/842.6 600/450 — — — — — — — —
380-60 342 418 288.0/209.5 300/250 541.3/462.9 300/225 — — — — — — — —
460-60 414 506 241.6/176.8 250/200 449.6/384.8 250/200 — — — — — — — —
575-60 518 633 195.9/144.1 225/175 363.5/311.7 225/175 — — — — — — — —
Supplied MCA MOCP ICF
Min Max
XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL XL
LEGEND
Rec Fuse
Size
MCA MOCP ICF Rec
—— ——————
—— ——————
—— ——————
—— ——————
—— ——————
5. Wiring for main field supply must be rated 75 C minimum. Use copper for all units.
a. Incoming wire size range for the terminal block is no. 4 AWG to 500 kcmil.
b. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA up to 599.9 amps is
3/0 to 500 kcmil.
c. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 600 to
799.9 amps is 1/0 to 500 kcmil.
d. Incoming wire size range of non-fused disconnect with MCA from 800 to
1199.9 amps is 250 kcmil to 500 kcmil.
6. Hydronic pump packages are not available as a factory-installed option for units
30RB210-390.
7. Power draw includes both crankcase heaters and cooler heaters (where used). Each
compressor has a crankcase heater which draws 56 watts of power. Units ordered with
the cooler heater option have 1 (060-150) or 2 (160-300) cooler heaters, 825 watts
each.
Fuse
MCA MOCP ICF Rec
Size
Fuse
Size
67
Page 68

Table 12 — Condenser Fan Electrical Data
UNIT
30RB
060, 070
080
090, 100, 110
120
130, 150
160,170,
315A, 315B, 330A,
330B, 345A, 345B,
360B
190, 360A, 390A,
390B
210, 225
250
275
300
LEGEND
FLA — Full Load Amps
UNIT VOLTAGE
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-60 3 11.9 1 11.9 — —
380-60 3 6.5 1 6.5 — —
460-60 3 5.4 1 5.4 — —
575-60 3 4.3 1 4.3 — —
208/230-60 2 11.9 2 11.9 — —
380-60 2 6.5 2 6.5 — —
460-60 2 5.4 2 5.4 — —
575-60 2 4.3 2 4.3 — —
208/230-60 3 11.9 3 11.9 — —
380-60 3 6.5 3 6.5 — —
460-60 3 5.4 3 5.4 — —
575-60 3 4.3 3 4.3 — —
208/230-60 3 11.9 4 11.9 — —
380-60 3 6.5 4 6.5 — —
460-60 3 5.4 4 5.4 — —
575-60 3 4.3 4 4.3 — —
208/230-60 4 11.9 4 11.9 — —
380-60 4 6.5 4 6.5 — —
460-60 4 5.4 4 5.4 — —
575-60 4 4.3 4 4.3 — —
208/230-60 6 11.9 4 11.9 — —
380-60 6 6.5 4 6.5 — —
460-60 6 5.4 4 5.4 — —
575-60 6 4.3 4 4.3 — —
208/230-60 6 11.9 6 11.9 — —
380-60 6 6.5 6 6.5 — —
460-60 6 5.4 6 5.4 — —
575-60 6 4.3 6 4.3 — —
208/230-60 4 11.9 4 11.9 4 11.9
380-60 4 6.5 4 6.5 4 6.5
460-60 4 5.4 4 5.4 4 5.4
575-60 4 4.3 4 4.3 4 4.3
208/230-60 4 11.9 4 11.9 6 11.9
380-60 4 6.5 4 6.5 6 6.5
460-60 4 5.4 4 5.4 6 5.4
575-60 4 4.3 4 4.3 6 4.3
208/230-60 6 11.9 6 11.9 4 11.9
380-60 6 6.5 6 6.5 4 6.5
460-60 6 5.4 6 5.4 4 5.4
575-60 6 4.3 6 4.3 4 4.3
208/230-60 6 11.9 6 11.9 6 11.9
380-60 6 6.5 6 6.5 6 6.5
460-60 6 5.4 6 5.4 6 5.4
575-60 6 4.3 6 4.3 6 4.3
Circuit A Quantity FLA (each) Circuit B Quantity FLA (each) Circuit C Quantity FLA (each)
STANDARD CONDENSER FANS
Table 13 — Pump Electrical Data
PUMP HP
3
5
7.5
10
15
LEGEND
FLA — Full Load Amps
*Hydronic pump packages are not available as a factory-installed option for units 30RB210-390.
UNIT VOLTAGE
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-60 9.1
380-60 5.1
460-60 4.2
575-60 3.3
208/230-60 15.4
380-60 8.1
460-60 7.1
575-60 5.4
208/230-60 22.0
380-60 12.3
460-60 10.1
575-60 8.1
208/230-60 25.0
380-60 14.0
460-60 11.5
575-60 9.2
208/230-60 36.7
380-60 21.0
460-60 17.0
575-60 14.0
HYDRONIC SYSTEM (SINGLE/DUAL)
FLA (each)
USED ON 30RB SIZES*
060, 070
060-190
060-190
060-190
080-190
68
Page 69

UNIT
30RB
060
070
080
090
100
110
120
130
150
160, 315A, 315B, 330B
170, 330A, 345A, 345B, 360B
190, 360A, 390A, 390B
210
225
250
275
300
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
RLA — Rated Load Amps
LEGEND
Table 14 — Compressor Electrical Data
UNIT VOLTAGE
V-Hz (3 Ph)
208/230-6075.048575.0485————75.0485——————————————
380-60 38.426038.4260————38.4260——————————————
460-60 32.721532.7215————32.7215——————————————
575-60 26.217526.2175————26.2175——————————————
208/230-6094.256094.2560————75.0485——————————————
380-60 49.331549.3315————38.4260——————————————
460-60 41.626041.6260————32.7215——————————————
575-60 33.921033.9210————26.2175——————————————
208/230-6075.048575.0485————75.048575.0485————————————
380-60 38.426038.4260————38.426038.4260————————————
460-60 32.721532.7215————32.721532.7215————————————
575-60 26.217526.2175————26.217526.2175————————————
208/230-6094.256094.2560————75.048575.0485————————————
380-60 49.331549.3315————38.426038.4260————————————
460-60 41.626041.6260————32.721532.7215————————————
575-60 33.921033.9210————26.217526.2175————————————
208/230-6094.256094.2560————94.256094.2560————————————
380-60 49.331549.3315————49.331549.3315————————————
460-60 41.626041.6260————41.626041.6260————————————
575-60 33.921033.9210————33.921033.9210————————————
208/230-6094.256094.2560————75.048575.048575.0485——————————
380-60 49.331549.3315————38.426038.426038.4260——————————
460-60 41.626041.6260————32.721532.721532.7215——————————
575-60 33.921033.9210————26.217526.217526.2175——————————
208/230-6094.256094.2560————94.256094.256094.2560——————————
380-60 49.331549.3315————49.331549.331549.3315——————————
460-60 41.626041.6260————41.626041.626041.6260——————————
575-60 33.921033.9210————33.921033.921033.9210——————————
208/230-6094.256094.256094.2560——75.048575.048575.0485——————————
380-60 49.331549.331549.3315——38.426038.426038.4260——————————
460-60 41.626041.626041.6260——32.721532.721532.7215——————————
575-60 33.921033.921033.9210——26.217526.217526.2175——————————
208/230-6094.256094.256094.2560——94.256094.256094.2560——————————
380-60 49.331549.331549.3315——49.331549.331549.3315——————————
460-60 41.626041.626041.6260——41.626041.626041.6260——————————
575-60 33.921033.921033.9210——33.921033.921033.9210——————————
208/230-6094.256094.256094.256094.256075.048575.048575.0485——————————
380-60 49.331549.331549.331549.331538.426038.426038.4260——————————
460-60 41.626041.626041.626041.626032.721532.721532.7215——————————
575-60 33.921033.921033.921033.921026.217526.217526.2175——————————
208/230-6094.256094.256094.256094.256094.256094.256094.2560——————————
380-60 49.331549.331549.331549.331549.331549.331549.3315——————————
460-60 41.626041.626041.626041.626041.626041.626041.6260——————————
575-60 33.921033.921033.921033.921033.921033.921033.9210——————————
208/230-6094.256094.256094.256094.256094.256094.256094.256094.2560————————
380-60 49.331549.331549.331549.331549.331549.331549.331549.3315————————
460-60 41.626041.626041.626041.626041.626041.626041.626041.6260————————
575-60 33.921033.921033.921033.921033.921033.921033.921033.9210————————
208/230-60 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — — 75.0 485 75.0 485 75.0 485 — — 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — —
380-60 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 — — 38.4 260 38.4 260 3 8.4 260 — — 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 — —
460-60 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 — — 32.7 215 32.7 215 3 2.7 215 — — 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 — —
575-60 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 — — 26.2 175 26.2 175 2 6.2 175 — — 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 — —
208/230-60 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — — 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — — 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — —
380-60 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 — — 49.3 315 49.3 315 4 9.3 315 — — 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 — —
460-60 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 — — 41.6 260 41.6 260 4 1.6 260 — — 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 — —
575-60 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 — — 33.9 210 33.9 210 3 3.9 210 — — 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 — —
208/230-60 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — — 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — — 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560
380-60 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 — — 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 — — 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315
460-60 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 — — 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 — — 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260
575-60 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 — — 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 — — 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210
208/230-60 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 — —
380-60 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 — —
460-60 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 — —
575-60 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 — —
208/230-60 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560 94.2 560
380-60 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 49.3 315 4 9.3 315
460-60 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 41.6 260 4 1.6 260
575-60 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 33.9 210 3 3.9 210
A1 A2 A3 A4 B1 B2 B3 B4 C1 C2 C3 C4
RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPRESSOR COMPRESSOR COMPRESSOR
69
Page 70

®
(+) (COM) (-) SHIELD
CCN
RED
WHT
BLK
CCNLEN
(+) (COM) (-) SHIELD
CCN
RED
WHT
BLK
CCNLEN
TO NEXT
DEVICE
(+) (COM) (-) SHIELD
CCN
RED
WHT
BLK
CCN
LEN
SHIELD
LEGEND
Fig. 62 — TB-3 — CCN Wiring
CCN — Carrier Comfort Network®
LEN — Local Equipment Network
TB3
CARRIER COMFORT NETWORK
(CCN) COMMUNICATION BUS WIRING — The communication bus wiring is a
shielded, 3-conductor cable with drain wire and is field supplied and installed in the field.
The system elements are connected to the communication
bus in a daisy chain arrangement. The positive pin of each
system element communication connector must be wired to the
positive pins of the system elements on either side of it. This is
also required for the negative and signal ground pins of
each system element. Wiring connections for CCN should be
made at TB 3 (terminal block). Consult the CCN Contractor’s
Manual for further information. See Fig. 62.
NOTE: Conductors and drain wire must be 20 AWG
(American Wire Gage) minimum stranded, tinned copper.
Individual conductors must be insulated with PVC, PVC/
nylon, vinyl, Teflon*, or polyethylene. An aluminum/polyester
100% foil shield and an outer jacket of PVC, PVC/nylon,
chrome vinyl, or Teflon with a minimum operating temperature range of –4 F (–20 C) to 140 F (60 C) is required. Refer to
Table 15 for a list of manufacturers that produce CCN bus wiring that meets these requirements.
Table 15 — CCN Communication Bus Wiring
MANUFACTURER
Alpha 1895 —
American A21451 A48301
Belden 8205 884421
Columbia D6451 —
Manhatten M13402 M64430
Quabik 6130 —
Regular Wiring Plenum Wiring
PART NUMBER
It is important when connecting to a CCN communication
bus that a color coding scheme be used for the entire network
to simplify the installation. It is recommended that red be used
for the signal positive, black for the signal negative, and white
for the signal ground. Use a similar scheme for cables containing different colored wires. At each system element, the shields
of its communication bus cables must be tied together. If the
communication bus is entirely within one building, the resulting continuous shield must be connected to a ground at one
point only. If the communication bus cable exits from one
building and enters another, the shields must be connected to
grounds at the lightning suppressor in each building where the
cable enters or exits the building (one point per building only).
To connect the unit to the network:
1. Turn off power to the control box.
2. Cut the CCN wire and strip the ends of the red (+), white
(ground), and black (–) conductors. Substitute appropriate colors for different colored cables.
3. Connect the red wire to (+) terminal on TB3 of the plug,
the white wire to COM terminal, and the black wire to the
(–) terminal.
4. The RJ14 CCN connector on TB3 can also be used, but is
only intended for temporary connection (for example, a
laptop computer running Service Tool).
IMPORTANT: A shorted CCN bus cable will prevent
some routines from running and may prevent the unit
from starting. If abnormal conditions occur, disconnect
the machine from the CCN network. If conditions
return to normal, check the CCN connector and cable.
Run new cable if necessary. A short in one section of
the bus can cause problems with all system elements
on the bus.
NON-CCN COMMUNICATION WIRING — The 30RB units
offer several non-CCN translators. Refer to the separate installation instructions for additional wiring steps.
Step 7 — Install Accessories — A number of
accessories are available to provide the following optional features (for details, refer to the Controls, Start-Up, Operation,
Service and Troubleshooting guide).
Energy management module is used for any of the follow-
ing types of temperature reset, demand limit and ice features:
• 4 to 20 mA inputs for cooling set point reset and capacity
limit (requires field-supplied 4 to 20 mA generator)
• 0 to 10 v output for percentage total capacity running
• 24 v discrete outputs for shutdown and running relays
• 10k space temperature input
• Discrete inputs for occupancy override, demand limit
switch 2 (step 1 demand limit is wired to the base board,
requires field-supplied dry contacts), remote lockout
switch and ice done switch (requires field-supplied dry
contacts)
NAVIGATOR™ DISPLAY — The Navigator display provides hand-held, mobile capability using easy to read 4-line
display. Keypad function is the same as the scrolling marquee
display. The Navigator display features a mounting magnet for
‘hands free’ service of components.
REMOTE ENHANCED DISPLAY — For applications
where remote monitoring of the equipment is required, the
remote enhanced display provides an indoor display capable of
monitoring any equipment on the Carrier Comfort Network
(CCN) bus. A CCN bus is needed.
LOW AMBIENT TEMPERATURE OPERATION — If
outdoor ambient operating temperatures below 32 F (0° C) are
expected, refer to separate installation instructions for low
ambient temperature operation using the low ambient temperature head pressure control accessory.
MINIMUM LOAD ACCESSORY — If minimum load accessory is required, contact your local Carrier representative for
more details. For installation details, refer to separate installation instructions supplied with the accessory package.
®
* Registered trademark of DuPont.
70
Page 71

UNIT SECURITY/PROTECTION ACCESSORIES — For
applications with unique security and/or protection requirements, several options are available for unit protection.
Compressor enclosures, security grilles and hail guards are
available. Contact your local Carrier representative for more
details. For installation details, refer to separate installation
instructions supplied with the accessory package.
COMMUNICATION ACCESSORIES — A number of communication options are available to meet any requirement.
Contact your local Carrier representative for more details. For
installation details, refer to separate installation instructions
supplied with the accessory package.
SERVICE OPTIONS — Two additional accessories are
offered to aid in servicing 30RB units, a ground fault convenience outlet (GFI-CO) and a remote service port. The remote
service port is a weather-proof enclosure with a communication
port to plug in the Navigator device. Contact your local Carrier
representative for more details. For installation details, refer to
separate installation instructions supplied with the accessory
package.
Refrigerant Circuit
LEAK TESTING — Units are shipped with complete operating charge of R-410A (see Tables 3A-4B) and should be under
sufficient pressure to conduct a leak test.
CAUTION
This system uses Puron® R-410A refrigerant, which has
higher pressures than R-22 and other refrigerants. No other
refrigerant can be used in this system. Failure to use gage
set, hoses, and recovery systems designed to handle Puron
refrigerant (R-410A) may result in equipment damage or
personal injury. If unsure about equipment, consult the
equipment manufacturer.
Perform a leak test to ensure that leaks have not developed
during unit shipment. Dehydration of the system is not required
unless the entire refrigerant charge has been lost. See Controls
and Troubleshooting literature for specific torque requirements
of refrigerant fittings. Repair any leak found using good refrigeration practice.
DEHYDRATION — Refer to Carrier Standard Service Techniques Manual, Chapter 1, Refrigerants, Sections 6 and 7 for
details. Do not use compressor to evacuate system.
REFRIGERANT CHARGE (Refer to Tables 3A-4B) —
Immediately ahead of filter drier in each circuit is a factoryinstalled liquid line service valve. Each valve has a
1
/4-in.
Schrader connection for charging liquid refrigerant. Refer to
Controls, Start-Up, Operation, Service and Troubleshooting
Guide for more information.
CAUTION
When charging, circulate water through the cooler at all
times to prevent freezing. Freezing damage is considered
abuse and may impair or otherwise negatively affect the
Carrier warranty.
CAUTION
DO NOT OVERCHARGE system. Overcharging results
in higher discharge pressure possible compressor damage,
and higher power consumption.
CAUTION
Refrigerant charge must be removed slowly to prevent loss
of compressor oil that could result in compressor failure.
BACnet* Communication Option Wiring —
The BACnet communication option uses the UPC Open controller. The controller communicates using BACnet on an MS/
TP network segment communications at 9600 bps, 19.2 kbps,
38.4 kbps, or 76.8 kbps.
Wire the controllers on an MS/TP network segment in a dai-
sy-chain configuration. Wire specifications for the cable are
22 AWG (American Wire Gage) or 24 AWG, low-capacitance,
twisted, stranded, shielded copper wire. The maximum length
is 2000 ft.
Install a BT485 terminator on the first and last controller on
a network segment to add bias and prevent signal distortions
due to echoing. See Fig. 63-65.
To wire the UPC Open controller to the BAS network:
1. Pull the screw terminal connector from the controller's
BAS Port.
2. Check the communications wiring for shorts and
grounds.
3. Connect the communications wiring to the BAS port’s
screw terminals labeled Net +, Net -, and Shield.
NOTE: Use the same polarity throughout the network
segment.
4. Insert the power screw terminal connector into the UPC
Open controller's power terminals if they are not currently connected.
5. Verify communication with the network by viewing a
module status report. To perform a module status report
using the BACview keypad/display unit, press and hold
the “FN” key then press the “.” Key.
To install a BT485 terminator, push the BT485, on to the
BT485 connector located near the BACnet connector.
NOTE: The BT485 terminator has no polarity associated with
it.
To order a BT485 terminator, consult Commercial Products
®
i-Vu
Open Control System Master Prices.
MS/TP WIRING RECOMMENDATIONS — Recommendations are shown in Tables 16 and 17. The wire jacket and UL
temperature rating specifications list two acceptable alternatives. The Halar specification has a higher temperature rating
and a tougher outer jacket than the SmokeGard specification,
and it is appropriate for use in applications where the user is
concerned about abrasion. The Halar jacket is also less likely to
crack in extremely low temperatures.
NOTE: Use the specified type of wire and cable for maximum
signal integrity.
* Sponsored by ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers).
71
Page 72

Fig. 63 — UPC Open Controller
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
9
BACNET
BAUD RATE
DIP SWITCHES
ADDRESS
ROTARY
SWITCHES
POWER LED
RUN LED
ERROR LED
BACNET
CONNECTION
(BAS PORT)
BT485
TERMINATOR
Tx2 LED
Rx2 LED
Tx1 LED
Rx1 LED
EIA-485
JUMPERS
Fig. 64 — Network Wiring
72
Page 73

SPECIFICATION RECOMMMENDATION
Fig. 65 — BT485 Terminator Installation
Cable Single twisted pair, low capacitance, CL2P, 22 AWG (7x30), TC foam FEP, plenum rated cable
Conductor 22 or 24 AWG stranded copper (tin plated)
Insulation Foamed FEP 0.015 in. (0.381 mm) wall 0.060 in. (1.524 mm) O.D.
Color Code Black/White
Twist Lay 2 in. (50.8 mm) lay on pair 6 twists/foot (20 twists/meter) nominal
Shielding Aluminum/Mylar shield with 24 AWG TC drain wire
Jacket
DC Resistance 15.2 Ohms/1000 feet (50 Ohms/km) nominal
Capacitance 12.5 pF/ft (41 pF/meter) nominal conductor to conductor
Characteristic Impedance 100 Ohms nominal
Weight 12 lb/1000 feet (17.9 kg/km)
UL Temperature Rating SmokeGard 167°F (75°C), Halar -40 to 302°F (-40 to 150°C)
Voltage 300 Vac, power limited
Listing UL: NEC CL2P, or better
LEGEND
AWG — American Wire Gage
CL2P — Class 2 Plenum Cable
DC — Direct Current
FEP — Fluorinated Ethylene Polymer
NEC — National Electrical Code
O.D. — Outside Diameter
TC — Tinned Copper
UL — Underwriters Laboratories
Table 17 — Open System Wiring Specifications and Recommended Vendors
Table 16 — MS/TP Wiring Recommendations
SmokeGard Jacket (SmokeGard PVC) 0.021 in. (0.5334 mm) wall 0.175 in. (4.445 mm) O.D.
Halar Jacket (E-CTFE) 0.010 in. (0.254 mm) wall 0.144 in. (3.6576 mm) O.D.
WIRING SPECIFICATIONS RECOMMENDED VENDORS AND PART NUMBERS
Wire Type Description
22 AWG, single twisted shielded pair, low capacitance, CL2P,
TC foam FEP, plenum rated. See MS/TP Installation Guide for
MS/TP
Network (RS-485)
Rnet 4 conductor, unshielded, CMP, 18 AWG, plenum rated. W184C-2099BLB 6302UE 21450 CLP0442
LEGEND
AWG — American Wire Gage
CL2P — Class 2 Plenum Cable
CMP — Communications Plenum Rated
FEP — Fluorinated Ethylene Polymer
TC — Tinned Copper
specifications.
24 AWG, single twisted shielded pair, low capacitance, CL2P,
TC foam FEP, plenum rated. See MS/TP Installation Guide
for specifications.
Connect Air
International
W221P-22227 — 25160PV CLP0520LC
W241P-2000F 82841 25120-OR —
Belden RMCORP
73
Contractors
Wire and Cable
Page 74

Page 75

Page 76

© Carrier Corporation 2013
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53300124-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 30RB-21SI Pg 76 1218 12-13 Replaces: 30RB-20SI
 Loading...
Loading...