Page 1

CarolinaTMMammal
Kidney Dissection Guide
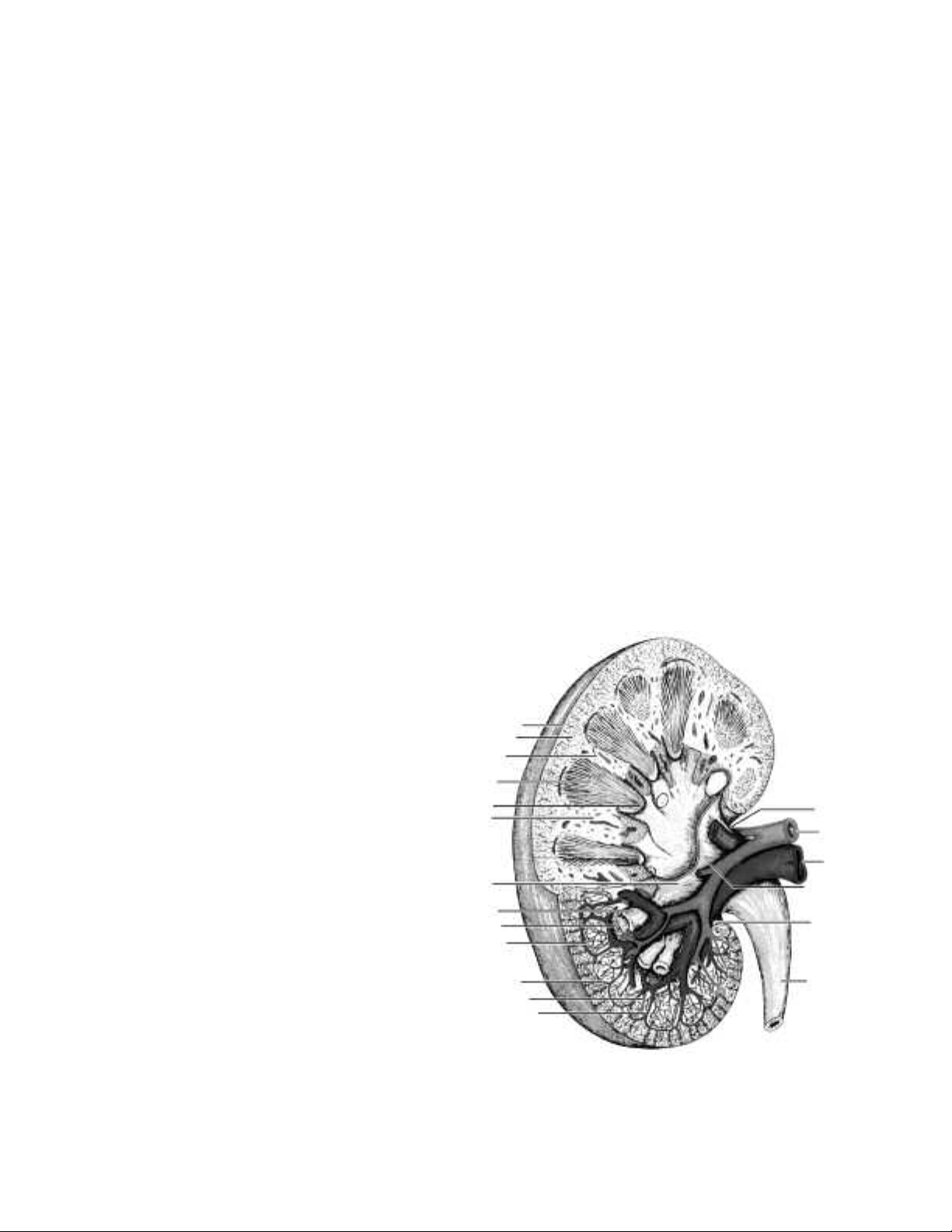
Capsule
Cortex
Medulla
Pyramid
Papilla
Column
Major calyx
Minor calyx
Pyramid
Arcuate artery
Arcuate vein
Interlobar artery
Interlobar vein
Hilus
Renal ar
Renal vein
Pelvis
Sinus
Ureter
tery
C80137
Page 2
CarolinaTMMammal Kidney Dissection Guide
Overview
The Carolina Mammal Kidney Dissection Guide is a general set of instructions for dissecting mammal
kidneys. With each type of kidney, there will be differences in the size of the structures and kidney regions,
but the general structures and their relative location will be the same or very similar.
Safety
Follow safe laboratory practices when performing any dissection. Wear safety glasses or goggles, gloves, and lab
aprons when dissecting. Perform dissections on a dissecting tray or pan to contain specimens and fluids. Be
careful when using sharp instruments, such as scalpels, forceps, teasing needles, and scissors.
Procedure
1. Review the glossary provided at the end of this dissection guide. Refer to the diagram of the kidney as
a general reference as you observe and identify e
2. Observe the renal capsule. This structure is made up of dense, irregular connective tissue and provides
protection as well as helps maintain shape. Remove any adipose tissue that may be attached to the
capsule.
xternal and internal structures.
3. Locate the hilus. This is an indentation where the ureter and blood vessels enter and e
Remove excess adipose tissue to observe the ureter more closely
. The renal artery and vein may be
xit the kidney.
difficult to locate; they were severed close to the hilus when the kidney was removed from the animal.
4. Make a frontal section through the kidney.
Locate the cortex and medulla. The
medulla lies below the cortex. Observe
and record the appearance of each region.
Capsule
5. The medulla consists of numerous conical
structures called renal pyramids. The base
of each pyramid lies next to the cortex,
while the tip forms a renal papilla. Each
papilla projects into the renal sinus.
Cortex
Medulla
Pyramid
Papilla
Column
Locate the renal pyramids, renal papilla,
and renal sinus.
6. Renal pyramids are separated by bands of
tissue called renal columns. Each column
begins in the cortex and extends through
the medulla. Examine the te
xture of this
tissue. Columns have a granular texture
similar to that of the cortex.
7. Each renal pyramid and adjacent cortical
Major calyx
Minor calyx
Pyramid
Arcuate artery
Arcuate vein
Interlobar artery
Interlobar vein
region make up a renal lobe. Urine
production occurs in the renal lobes. Each
renal papilla discharges urine into a cup
shaped minor calyx. F
-
our or five minor calyces merge to form a
major calyx. Major calyces merge to form the renal pelvis. Using a probe, trace the path of urine from the
renal pyramids to the renal pelvis.
Hilus
Renal artery
Renal vein
Pelvis
Sinus
Ureter
©2005 Carolina Biological Supply Company
Printed in USA
Page 3

8. Examine the renal pelvis. It is formed by a wall of thick fibrous tissue and forms the expanded end of the
ureter.
9. Using a scalpel, carefully cut one wall of the ureter and extend the incision to the hilus. The ureter is
continuous with the renal pelvis. Observe the fine ridges on the endothelial lining of the ureter and renal
pelvis.
10. Once you have observed all the structures of the kidney, dispose of the specimen in accordance with local
guidelines and your teacher’s instructions.
Glossary
Calyx - cup-like division found in the renal medulla; minor calyces (plural) empty into major calyces.
Hilus - depression where the renal artery, renal vein, and ureter enter and exit the kidney.
Renal artery - branch from the abdominal aorta that supplies the kidney with oxygenated blood.
Renal capsule - dense, irregular connective tissue layer that protects the kidney and helps maintain its shape.
Renal corpuscle - glomerulus enclosed within a glomerular capsule; site of filtration.
Renal cortex - outer region of the kidney.
Renal lobe - consists of a pyramid, portion of the cortex at the pyramid base, and a portion of the adjacent
renal column.
Renal medulla - inner portion of the kidney.
Renal papilla - ape
Renal pelvis - large cavity that receives urine from major calyces; continuous with ureter.
Renal pyramid - cone-shaped structure found in the medulla with its base facing the cortex and the apex
facing the hilus.
Renal vein - blood vessel exiting the kidney carrying filtered, deoxygenated blood to the inferior vena cava.
Ureter - tube that connects the kidney to the urinary bladder.
x of a renal pyramid; continuous with the minor calyx.
Carolina’s Perfect Solution
®
Independent, certified laboratory analyses of specimens fixed in Carolina’s Perfect Solution®have found it to be
xic and free of dangerous off
nonto
-gassing. This means that, for safety purposes, classrooms and labs using
Carolina’s Perfect Solution specimens do not require specialized ventilation. Carolina does recommend using
some active ventilation when working with any preserved specimens or chemicals. The safe nature of
Carolina’s Perfect Solution also means that in most localities there are no mandated disposal requirements. Be
sure to check with local sewer and landfill authorities, as local procedures may vary.
Carolina’s Perfect Solution®Specimens Available From Carolina Biological Supply Company
Carolina’s Perfect Solution®Cow Eye RN-22-8903
Carolina’s Perfect Solution®Sheep Eye RN-22-8763
erfect Solution
’s P
olina
Car
Carolina’s Perfect Solution®Pig Heart RN-22-8563
erfect Solution
’s P
olina
Car
®
Sheep Brain
®
Pig Kidney
RN-22-8703
RN-22-8573
Teacher’s Manual 3
Page 4

Carolina CarosafeTMPreservative
Carosafe™ is a holding solution for biological specimens. It contains no formaldehyde and is not a tissue fixative.
Most specimens in Carosafe are first preserved with a formalin solution and then placed in formaldehyde-free
Carosafe. This produces a formalin-preserved specimen that, when dissected, minimizes student and educator
exposure to formaldehyde.
Caropak®Packaging
Preserved animals shipped in Caropaks have been processed with Carosafe and are as “odorless” as effective
fixation and preservation techniques allow. They are packaged in vacuum-sealed, double-layered plastic barrier
bags. Specimens may be packaged one specimen per pack or many per pack.
Additional Specimens
Sheep Kidney (Carosafe™) Plain RN-22-8800
Sheep Kidney (
Sheep Kidney (
Pig Kidney (
Pig Kidney (
Pig Kidney (
Carosafe™) Double Injected RN-22-8810
osafe™
Car
Caropak®Single) Plain RN-22-8571
Caropak®Single) Double Injected RN-22-8581
Caropak®Single) Triple Injected RN-22-8591
Triple Injected RN-22-8820
)
Disposal
Because local regulations may vary from federal and state regulations, we recommend that you discuss disposal of
preserved specimens with your institution
’s or system’s environmental representative.
Carolina Biological Supply Company
2700 York Road, Burlington, North Carolina 27215
Phone: 800.334.5551 • Fax: 800.222.7112
Technical Support: 800.227.1150 • www.carolina.com
CB280980507
 Loading...
Loading...