Page 1

Heritage Series
Ideal as a terrific everyday sport plane, the Skylane ARF combines docile flight characteristics with the aptitude
for super-smooth,scale flight. This ARF has been designed to keep building time to a minimum; it's 90% prebuilt, with a pre-assembled elevator and installed pushrod and wing guide tubes, and it features top-quality
hardware and premium covering. So read through these instructions, follow them carefully, and you'll soon be
flying this superb model.
WARNING
A radio-controlled model is not a toy and is not intended for persons under 16 years old. Keep
this kit out of the reach of younger children, as it contains parts that could be dangerous. A radiocontrolled model is capable of causing serious bodily injury and property damage. It is the buyer's
responsibility to assemble this aircraft correctly and to properly install the motor, radio, and all other
equipment. Test and fly the finished model only in the presence and with the assistance of another
experienced R/C flyer. The model must always be operated and flown using great care and common
sense, as well as in accordance with the Safety Code of the Academy of Model Aeronautics (5151
Memorial Drive, Muncie, IN 47302, 1-800-435-9262). We suggest you join the AMA and become properly insured prior to flying this model. Also, consult with the AMA or your local hobby dealer to find an
experienced instructor in your area. Per the Federal Communications Commission, you are required
to use only those radio frequencies specified "for Model Aircraft."
LIMITED WARRANTY
Carl Goldberg Products has inspected and certified the components of this aircraft. The company urges the buyer to perform his
own inspection, prior to assembly, and to immediately request a replacement of any parts he believes to be defective for their
intended use. The company warrants replacement of any such components, provided the buyer requests such replacement within a period of one year from the date of purchase and provided the defective part is returned, if so requested by the company.
No other warranty, expressed or implied, is made by the company with respect to this kit. The buyer acknowledges and understands that it is his responsibility to carefully assemble the finished flying model airplane and to fly it safely. The buyer hereby
assumes full responsibility for the risk and all liability for personal or property damage or injury arising out of the buyer's use of the
components of this kit.
INSTRUCTIONS
© Copyright 2006 Carl Goldberg Products LTD.
P.O. Box 818 Oakwood GA 30566 Phone #678-450-0085 Fax # 770-532-2163 www.carlgoldbergproducts.com
SSKKYYLLAANNEE 6622 AARRFF
SSKKYYLLAANNEE 6622 AARRFF
Page 2

2
ITEMS NEEDED TO COMPLETE THIS AIRCRAFT
1 RADIO GUIDANCE SYSTEM (4 CHANNEL
MINIMUM REQUIRED) 7 SERVOS
2 12” AILERON SERVO EXTENSION WIRES
2 Y-HARNESS
1 ENGINE . 2-CYCLE OR . 4-CYCLE, AND
MUFFLER
1 ZAP ACCELERATOR
1 2 OZ. BOTTLE ZAP-A-GAP medium CA
1 1/2 OZ. BOTTLE ZAP Super Thin CA
1 BOTTLE ZAP 30 minute and/or 5 minute
epoxy.
1 Foam rubber 1/2”x8”x12”
1 ” Spinner 2-1/2”
TOOLS AND SUPPLIES FOR ASSEMBLY.
MODELING OR UTILITY KNIFE
WORK SURFACE (24" X70")
ELECTRIC DRILL
1/16”,5/64” 3/32”,1/8", 5/32”, 1/4” DRILL
BITS
SMALL STANDARD & PHILLIPS SCREW-
DRIVERS
MASKING TAPE
NEEDLE NOSE PLIERS
36” RULER OR TAPE MEASURE
FLEXIBLE STRAIGHT-EDGE
T-SQUARE
30-60-90° x 6" TRIANGLE
SOFT PENCIL
A FEW STRAIGHT OR "T" PINS
ADJUSTABLE WRENCH
WIRE CUTTER
OPTIONAL HEAT GUN/COVERING IRON
ACID BRUSH
You can trust ZAP™ CA (cyanoacrylate) and ZAP™ Epoxy to handle all your important
modeling needs. They're designed to withstand the high vibration levels of model aircraft, but they'll handle just about everything-dollhouse miniatures, model railroads,
arts and crafts, household repairs, building projects, and a vari ety o f industrial applications.
PROFESSIONAL-GGRADE ADHESIVES
NOTE: The Heritage Series Skylane 62 ARF is
covered in White #870 UltraCote®. The trim colors are Red #866 , BLACK #874 , and SILVER
#881.
Page 3
3
USING THIS INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Before you begin assembling your Heritage Series
Skylane 62 ARF, take some time to read through this
entire instruction book. It is designed to take you stepby-step through the process and to give you added information on engine and radio selection and set-up, balancing your aircraft, and flying your model. The time you
spend will speed the assembly process and help you
avoid problems.
PREPARING FOR ASSEMBLY
You will need a work area of approximately 24 x 70" which has
been covered to protect it from adhesive, as well as c uts and
other damage. Many people cover their work area with a
sheet of dry wall (sheet rock) and/or waxed paper t o
prevent Zap CA and Epoxy from ruining the work surface.
CONSTRUCTION TIPS
IMPORTANT: ALWAYS READ A FEW STEPS AHEAD.
This will alert you to coming instructions and will help you
plan accordingly.
Using the Parts Identification section, familiarize yourself
with the various items included in your kit box.
As you work, CHECK OFF EACH STEP in the box provided, so that you are sure you do not forget anything.
Do not hesitate to ask questions. Your local hobby dealer and area flyers will most likely be happy to help, as
they want you to have a successful flying experience.
You may also receive technical assistance from Carl
Goldberg Products via e-mail (carlgoldbergproducts.com)
INTRODUCTION
ADHESIVES & GLUING TECHNIQUES
The ZAP family of adhesives are specially formulated to
firmly glue the plywood, hardwood, and balsa used in your
model and to withstand the vibration and stresses of high
performance flight. ZAP A GAP CA is perfect for most
jobs. However, there are times, such as when you are
installing the stabilizer and fin on the fuselage and want
more set-up time for careful alignment and positioning,
then you should use ZAP ZPOXY™.. Occasionally, you
also will want to use ZAP Super Thin™, which "wicks" into
the surrounding areas. Aliphatic resin glue or similar
water-based glues can also be used, but they will add to
the assembly time because they dry so much more slowly than ZAP A GAP. Remember, whenever using any CA,
you must be careful to read instructions thoroughly, as
you will have only seconds for positioning of parts. Be
sure to trial fit parts together before gluing. Also, never
use watery THIN type CA glue for gluing plywood and
hardwood parts. Thin CA's do not adequately bond
these areas.
CAUTION
Some people may experience an allergic reaction when
exposed to fumes from CA glue or epoxy. As with paints,
thinners, and solvents, it is always important to use glues
only where there is adequate ventilation to carry fumes
away. A fan is recommended. Also, special care must
be taken when using CA, as it will bond skin as well as
other surfaces. ZAP CA remover is a CA solvent which
removes hardened glue from fingers and softens glued
joints for repositioning. Before using any CA, carefully
read all label precautions. When using CA, protective
eye-wear and care in keeping the glue away from the
face is highly recommended. If CA does happen to get
into the eye, hold lid open and flush with water only.
Seek immediate medical attention.
COVERING
The Heritage Series Skylane 62 ARF is covered in premium iron on film. It is not uncommon for ARF's to develop a few wrinkles in transit. If this is true of your model,
the situation is easily corrected. Before you begin putting
the pieces together, run over the surface of each section
with an iron (either specially designed for airplane use or
the more cumbersome household iron) or use a modeling
heat gun. Apply the heat (set at about 350° F), following
along with a soft cloth and pressing down on the covering
as you go around. This will more firmly set the covering
adhesive into the wood and keep your aircraft covering
tight and smooth in the future.
One of the great advantages of film is that it can be
applied over itself without causing gas bubbles. This
allows you to repair your aircraft, as well as to customize
it in a number of ways. If, due to a flight mishap, you get
a hole or similar covering damage, simply trim away the
ragged edges and then apply a patch, following the directions that come with replacement film , which is available
at your hobby dealer. In case of a major crash, where
large amounts of the film must be replaced, heat the
damaged covering and then slowly peel up. If you are
applying sufficient heat, the film will come up easily and
leave no color on the wood.
Page 4
4
RADIO EQUIPMENT & CARE
There are many fine radio systems on the market. Your
local hobby dealer and club members are good sources
of information on equipment and its suitability for various
projects. It is recommended that you speak to them
before making a final choice.
Today's RC systems are very well engineered and constructed.
However, they
will remain only
as good as the
way in which
they are
USED. Always
follow the rules
of proper
usage and all
manufacturer's
instructions for
your particular
piece of equipment.
TRANSMITTERS: Keep your transmitter clean and free
from fuel residue and dirt. Battery condition and RF output should be monitored, and the system should be
aligned and tuned annually. Do not transport under vibration (such as on the floor of a car) without cushioning.
RECEIVERS: Receivers must be vibration free. When
installing in the aircraft, wrap them in a minimum of ¼" soft
foam rubber (not plastic foam). Keep well clear of all
cables and batteries. Tune annually (or as recommended
by the manufacturer), as indicated below under "CheckUps."
SERVOS: Servos are vibration prone. Be sure to mount
them with grommet shock mounts in servo trays which are
also shock mounted. Also be sure to keep them clean. If
the neutral position "drifts," this is a sign of change which
should not be ignored; find out WHY before flying again.
BATTERIES: Nicads also can suffer from vibration, so
they too should be wrapped in soft foam rubber before
installing. Check their condition periodically by measuring
the voltage with a volt meter or battery tester. Charge the
batteries before EVERY flying session. When not used
for a period of time (such as during the winter months) the
batteries should be charged every 30 days. Never store
batteries in a discharged condition.
PUSHRODS: Obviously, pushrods should be installed to
operate freely, so that they place no load on the servo.
Using a servo's power to move a tight rod or heavy surface by force increases the battery drain, shortens the
electronic life, and can cause neutralizing problems. In
addition, it is important the pushrods do not flex or vibrate.
Any vibration is transferred directly to the servo, and its
gear, motor, and pot. To avoid flexing and vibration, use
guides and fairleads on the rods.
CONNECTORS: In using connectors, never pull on the
wires to disconnect; grasp the plugs instead. Clean them
by dunking in a solvent, such as dope thinner. Tape the
connectors together when installing and make sure there
is no strain on the cables.
CHECK-UPS: A full check-up by the factory or an authorized service center should be done AT LEAST ONCE A
YEAR, as well as any time something unusual occurs during usage. A malfunction or "glitch" is the first sign of an
impending failure; it should not be ignored. The checkup
should include tuning and alignment of the system, as
well as battery testing.
ENGINE & PROPELLER SELECTION
When selecting an engine, it is important to stay within
the manufacturer’s recommended range, as failure to
do so is likely to lead to less than satisfactory performance and may well lead to failure of the aircraft.
Remember, that manufacturers design and test their models for specific engine sizes. Therefore, the aircraft is
unlikely to withstand the stresses created above this
range. Many a modeler has watched all his hours of work
and many dollars worth of hardware head earthward
because he did not heed this warning: DO NOT OVER-
POWER YOUR MODEL! Doing so will automatically void
the manufacturer’s warranty.
Typically, size recommendations are for both a 2cycle or a 4-cycle engine. A 2-cycle engine has more raw
power because it has faster RPMs on the propeller. A 4cycle engine swings a bigger prop and therefore creates
more pull. It is also quieter. 4-cycle engines are generally preferred for high performance, more aerobatic planes.
However, if flying a tri-gear plane, a 2-cycle should be
used. The expense of an engine is usually related to
its efficiency. Some engines of similar cubic inch
displacements are more powerful than others. Check
with a dealer or an experienced flyer to learn about the
specific attributes of the engine you are considering.
If selecting a more sophisticated engine, you may go with
the lower recommended range However, if purchasing a
more basic engine, it is probably best to select something
in the higher recommended range. If you are a relatively
new RC pilot, it's probably a good idea to select an engine
that is popular at the flying field, so that if you have any
engine problems, other modelers will be familiar with the
engine and be able to help. REMEMBER: DON'T OVER-
POWER THE AIRCRAFT!
The propeller size must be matched to the engine. For
example, a .60 may use a 11" diameter prop while a .80
can use a 13" prop. Refer to the information that is sup-
plied with your engine for recommended propeller sizes.
It's wise to buy a few spare props, as everyone breaks
them occasionally, and particularly often when learning to
fly.
Balancing your propeller helps to protect your radio from
the damaging effects of vibration. There are good, easy
to use prop balancers on the market. Follow the instructions that are supplied with the prop balancer. Never
Page 5
5
carve or cut a prop near the hub for any reason (such as
to fit a spinner).
A " CGP 4-Pin Snap-On Spinner is available for the
Heritage Series Skylane 62 ARF. It is a rugged precision
molded spinner that does not require any special mounting nuts or screws. Carefully read the spinner instructions
and warnings included in this book. Although a spinner
helps reduce the chance of injury from a rotating prop,
extreme caution always must be used when the engine is
running.
As with other precision equipment, a new engine should
be "broken-in" to enhance performance and extend its
life. Breaking-in usually consists of running the engine
with a "rich" fuel mixture and at lower RPMs until all the
moving parts get to "know each other better." This can be
done with the engine mounted in the model or securely
clamped into a CGP Engine Test Stand or similar device.
Refer to your engine's operating manual for the recommended break-in procedure and follow it carefully.
STARTING BATTERY AND GLO-PLUG CLIP: A 1-1/2
volt battery is required to heat your engine's glo-plug for
starting. Wires connect the glo-plug clip to the battery.
Because engine starting draws a lot of electric power
from the battery, rechargeable ni-cad batteries are recommended. Although they cost more initially, they are
more economical in the long run than frequently replacing dry-cell batteries.
FUEL: For best engine performance, use the fuel recommended by your engine's manufacturer. 2 and 4cycle engines require different fuel blends. Ask your
dealer to recommend a good quality fuel.
FUEL PUMP: Needed to transfer fuel from the fuel can
to the model's fuel tank. A simple squeeze-type bulb will
do for small tanks, whereas manual crank or electric
pumps fill larger tanks more quickly.
FUEL LINE: Have about 3 feet of silicone fuel line to
make connections between the fuel pump, the fuel can,
and the model's fuel tank.
EXTRA PROPS: Experts always have a few spares on
hand, so flying doesn't have to stop due to a broken propeller.
CGP ENGINE TEST STAND
FIELD EQUIPMENT
The following equipment will be needed at the flying field
to start your engine, make adjustments, and clean your
model after flying.
FLIGHT BOX: Something sturdy in which to carry your
equipment. CGP's quick-building MiniTote carries the
basics: fuel, starter and battery, and a few essential tools.
The larger CGP SuperTote is economical, easy to build,
and pack lots of utility into little space. They hold fuel,
transmitter, starter & battery, as well as many tools, in a
balanced load that is easy to carry. The fuel tote is
designed to carry your fuel in a handy box that keeps the
jugs from rolling around in your car.
Page 6

6
HARDWARE IDENTIFICATION
GLOSSARY OF MODELING TERMS
ARF: Almost Ready to Fly
AILERON: the control surface on the wing that rolls the
plane
AIRFOIL: the shape of the wing as seen from the end
ANGLE OF ATTACK: the angle at which the wing meets
the air flow
BEVEL: to sand to an angle shape
BURR: the rough edges on a piece of wood or metal after
it is cut
CAP STRIP: a thin strip glued to the edges of the ribs to
shape the wing
CONTROL HORN: a device attached to each control sur-
face to provide an attachment point for the pushrod
COWL (COWLING): the nose section of the fuselage that
encloses the engine
DECALAGE: the difference between the incidence of the
wing and stabilizer
DIHEDRAL: the upward angle of the wings, as seen from
the front
ELEVATOR: the moveable part of the horizontal tail,
which controls pitch
EMPENNAGE: the tail of the plan
FIN: the fixed vertical part of the tail
FIREWALL: the hard wooden former at the front of the
fuselage, to which the engine is mounted
FORMER: a piece which shapes the fuselage; and to
which the sides of the fuselage are attached.
GUSSET: a small triangular piece glued into a corner to
strengthen it
INCIDENCE: the angle of the wing or the tail in relation
to the thrustline
LAMINATE: to glue two thin sheets of material together
to form a thick sheet
LEADING EDGE (L.E.): the edge of the wing that first
meets the airflow
LONGERON: a stringer that runs the length of the fuse-
lage
OUTPUT ARM: the piece that attaches to the servo and
connects it to the pushrod
PITCH: an up and down movement of the nose of the
plane, which is controlled by the elevator
PROTOTYPE: the full scale airplane from which the
model design was taken
PUSHROD: the long, stiff dowel, plastic or wire piece that
connects the servo with the control horn
RTF: Ready to Fly
RIB: the airfoil-shaped piece that connects the leading
edge, spars and trailing edge of the wing together
and holds them in shape
RETRACTS: devices for extending and retracting the
wheels on command
ROLL: tilting of the plane as viewed from the front, con-
trolled by the ailerons
RUDDER: the moveable vertical tail of the plane, which
controls yaw
SERVO: the part of the airborne radio system that
moves the control surfaces
SHEAR WEB: wood sheeting that connects the top and
bottom spars to stiffen the wing
SHIM: a thin piece of wood inserted between two other
pieces to improve their fit
SPAR: a wooden stick running lengthwise through the
wing that serves as its backbone
SPINNER: the rounded cone that fits over the propeller
hub
STABILIZER (STAB): the fixed horizontal part of the tail
STALL: a situation in which the plane is flying too slow-
ly to move sufficient air across the wing to produce
lift
STRINGER: a long piece of wood attached to the form-
ers to shape the fuselage
THRUSTLINE: a line drawn from the center of the pro-
peller hub straight through the airplane
TORQUE: a rolling tendency caused by the spinning
propeller
TRAILING EDGE (T.E.): the edge of the wing that faces
the rear of the plane
TRIM: small adjustments made to the control surfaces
to cause the plane to fly straight and level by itself
WASHIN: a twist in the wing that makes the trailing
edge lower than normal
WASHOUT: a twist in the wing that makes the trailing
edge higher than normal
WING SADDLE: the shaped part of the fuselage in
which the wing rests
WHEEL COLLAR: a metal ring that holds the wheel on
the axle
YAW: a right-to-left movement of the nose, controlled by
the rudder
BLIND NUT
EYELET
PUSHROD CONNECTOR WITH SNAP NUT.
NOSE GEAR BLOCK
SNAP LINK
LANDING GEAR
STRAP
STEERING ARM
CONTROL HORN
SOCKET HEAD
SCREW
WHEEL COLLAR
PAN HEAD
SCREW
SHEET METAL
SCREW
SET SCREW
WASHER
Page 7
7
WING ASSEMBLY & INSTALLATION
AILERON AND FLAP INSTALLATION
1. Collect the following parts:
(1) Left and right wing
(1) Left and right aileron
(1) Left and right flap
(14) CA hinge
2. Locate the pre-cut aileron and flap hinge
slots in both wing halves. Using a hobby knife
(#11 blade), slide the blade into each slot to
make sure it is cleanly cut.
Repeat this process with the ailerons and
flaps, making sure all hinge slots are clean.
3. Place a straight pin into the center of each of
the four CA hinges.
Slide each hinge into the hinge slots on one
of the wing halves. The pin will prevent the
hinges from going in further than halfway into
the wing.
4. Select the aileron for the wing on which you
are working and insert the exposed half of
each hinge into the aileron slots.
Slide the aileron toward the wing until no gap
remains between the aileron and the wing.
Install the flap in the same manner. Align the
stripes on the wing and make sure the
aileron clears the tip and the flap.
5.
When satisfied with the alignment, remove
the straight pins, being sure to keep the
aileron and flap tight to the wing. You may
wish to apply a few pieces of masking tape to
keep the pieces in place.
6. Keeping the aileron,flap, and wing in posi-
tion, apply 3 or 4 drops of thin CA to the small
exposed area of each hinge.
Turn the assembly over and again apply 3 or
4 drops of CA to the exposed hinge surfaces.
Allow to dry for 10 minutes before flexing the
aileron.
7. Repeat the above steps for the other half of
the wing and each flap.
AILERON SERVO INSTALLATION
The following pictures may not exactly match the hardware you are using. Always check the radio manufacturer's instructions when installing radio equipment.
1. Collect the following items:
(2) Wing halves
(4) Servos with rubber grommets
(16)Servo Mounting Screw (supplied with radio)
(2)12” servo extensions
Page 8
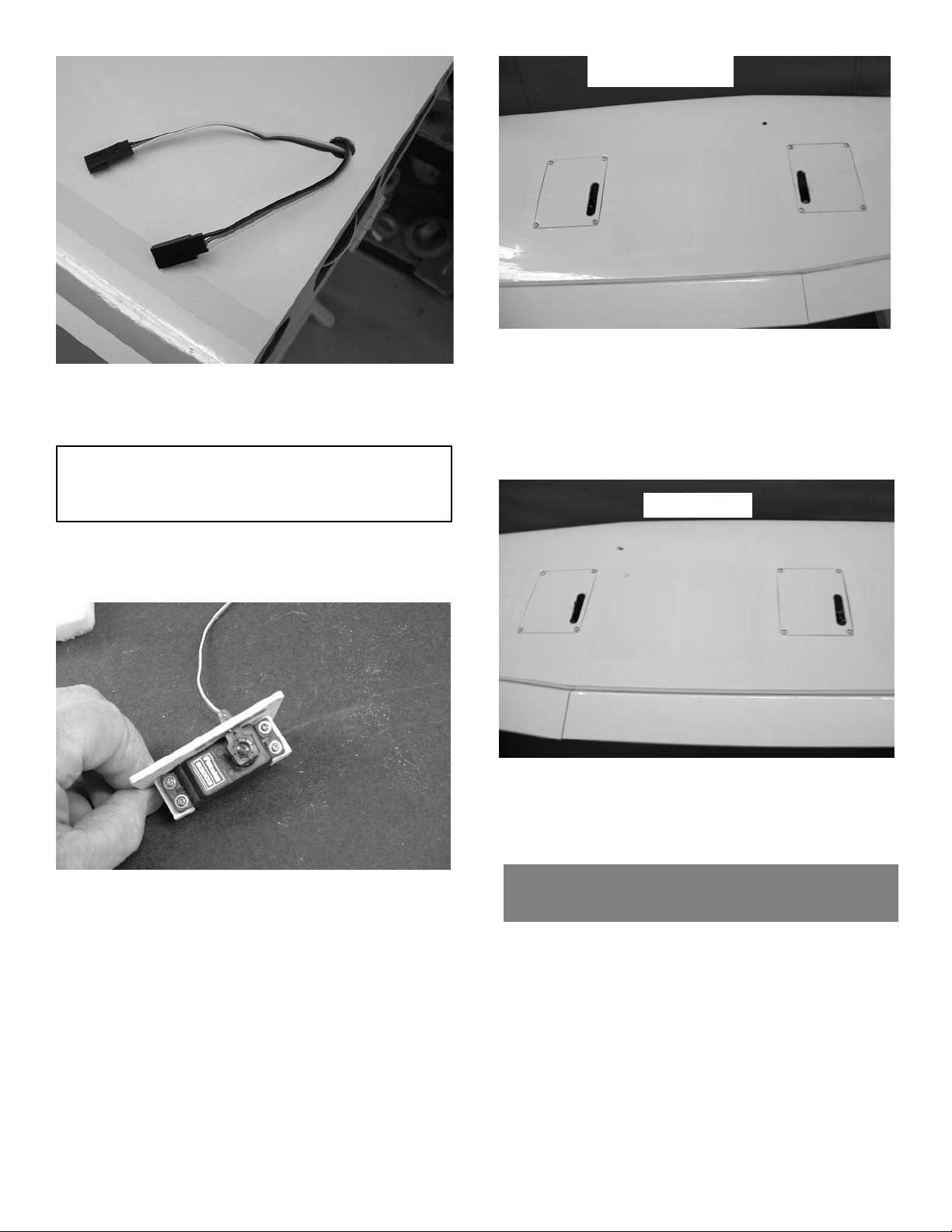
8
2. Pull the servo leads down through the wing
and exit through the hole on the bottom surface of the wing.
AILERON FLAP CONTROL HORN
INSTALLATION
1. Collect the following items
(4) Silicone clevis keepers
(4) nylon control horns
(4) nylon control horn nut plates
(4) 2-56 clevis
(4) 2-56 pushrods
(8) #2 screws
(4) Nylon swing in keepers
(4) 4-40 x 5-1/2” pushrods threaded both ends
IMPORTANT! To ensure that any connections located
inside the wing will not come loose, either when the
wires are pulled, or during flying, always tape them
securely together with electrical tape.
3. Repeat these steps for the other half of the
wing, so that both servo extensions are exiting the holes in the center of the wing.
4. Mount the aileron and flap servos using the
hardware supplied with the radio. The output
arm should go toward the trailing edge.
right wing
left wing
In order for the flaps and ailerons to work
properly the output arms for the servos must
be aligned as shown. On the left wing the
aileron servos output arm is on the inboard
side of the wing. The flap servo output arm
is on the outboard side of the wing.
On the right wing the aileron servo output
arm is on the inboard side of the wing and
the flap servo output arm is on the inboard
side of the wing also.
Page 9

9
2. Use a straight edge and make a mark at a
90º degree angle to the trailing edge and in
line with the output arm.
3. Mount the four control horns using the #2
screws and the nylon plates on the top side
of the ailerons and flaps. The holes for the
clevis should be aligned over the hinge line.
4. Mount the servos doors on the wing using the
#2 x 3/8” screws provided. Using the radio,
make sure the servo arm on the ailerons are
centered and the flap output arms are in the
fully up position.
5. Screw a metal clevis on the end of each of
the four 4” pushrods. Let the threads of the
pushrod extend into the open part of the cle
vis 1/16”. Install a silicone clevis keeper on
the clevis.
6. Install the clevis on the output arm of the
servo. Using the radio, make sure the output
arm is centered. Center the aileron and
make a mark on the pushrod where it crosses the control horn.
7. Bend the pushrod 90 degrees at the mark
and cut off at 3/8”.
Page 10

10
8. Use the nylon swing in keeper to secure the
pushrod to the control horn.
9. Repeat for the other flap and ailerons.
WING JOINING
1. Locate the dihedral brace and identify the
top and bottom.
bottom
2. Trial fit the dihedral brace in each wing half
and then slide the two wing halves together.
3. When satisfied with the fit, take the wing
apart and mix enough epoxy glue to cover
both wing roots, the dihedral brace and and
the slots in the wing that dihedral brace fit
into. Use a scrap piece of wood to work glue
down into the slots in both wing halves.
Make sure to get glue on both halves of the
tongue on the bottom side that locates the
wing. Use clamps to make sure they are
together firmly.
4. Use masking tape to hold the wing together
till the epoxy sets. Be sure to lay the wing
flat, don’t stand it on one tip or all the glue
will run to one side of the wing.
wing locating tongue
Page 11

11
TAIL ASSEMBLY & INSTALLATION
1. Collect the following parts:
(1) Stabilizer
(2) Elevators
(1) Elevator joiner wire
(1) Fin
(1) Rudder
(1) Wing/fuse assembly
(9) CA hinges
2. As with the wing and ailerons, use a model-
ing knife to make sure the hinge slots are
cleanly cut.
STAB & ELEVATOR INSTALLATION
3. Place a piece of masking tape on each wing
tip, just above the aileron hinge line.
Measure 29" out from the fuselage side to
the wing tip and mark the spot on the tape,
on both the left and the right side of the wing
CENTER JOINT
CENTERLINE
Measuring from the mark on each wing tip to
the mark on the stab tip, make sure the distance "X" on the right side and left side of the
plane are equal.
2. Install the stab in the opening in the rear of
the fuselage and fit the fin into the slot in the
top of the fuselage and into the slot in the
stab.
4. Make sure the stab is level (parallel) with the
wing and insert paper strip shims, if necessary.
Page 12

12
5. When satisfied with the alignment of the
stab, temporarily tape securely in place.
Turn over the plane and mark the area on the
bottom of the stab where it rests on the fuse.
Mark along the stab on the top side next to
the fuselage.
Mark the fin on both sides where it meets the
fuselage.
Remove the stab and fin from the fuse and,
working 1/8" inside the drawn lines, carefully
remove the covering from the bottom and top
of the stab. BE CAREFUL TO AVOID CUTTING THE WOOD
6. Remove the covering on the bottom of the fin
1/8” below the ling you marked.
Spread epoxy on the stab top and bottom
and insert into the fuselage. Apply glue in
the slot on the stab and top of fuse and
install the fin. Clean up excess epoxy using
alcohol and recheck to make sure the stab
and fin are aligned properly and allow the
epoxy to set.
8. Install the elevator joiner wire in the fuselage
before installing the stab.Important:
don’t install the stab without the
elevator joiner wire in place, you
can’t install it later.
7. Remove the covering 1/16” inside the lines
on the top of the fuselage where the fin sits.
Page 13

13
OUTFITTING THE FUSELAGE
FUEL TANK ASSEMBLY
1. Gather the following items
(1) fuel tank
(1) rubber tank stopper
(1) clunk
(1) 3mm x 25mm screw
(1) cap washer large
(1) cap washer small
(1) 3mm x 40mm brass tube
(1) 3mm x 60mm brass tube
(1) silicone tube 4mm x 80mm
2. Insert the 3mm screw through the center
hole in the large washer, through the
center hole in the rubber washer against
the large side, and screw the small washer on the back side.
3. Insert the brass tubes through two or
three of the holes. They should be
arranged so as the long one (vent tube)
will be on the right side of the plane and
the short one on the left side.
The tubes should extend out the front of
the cap 5/8”. Bend the long tube up at
about a 20 degree angle. This should be
adjusted so the end of the tube almost
touches the top of the tank when
installed.
4, Install the 4mm silicone tube to the short
brass tube and install the clunk to the
other end of the silicone tube. This is the
fuel pickup and must be free to “flop”
around in the tank so it can pick up fuel in
any attitude.
Decide if you want to use a two line or a
three line tank. Most two strokes use a
two line, one to the carb and a vent tube
to the pressure fitting on the muffler. You
can get to the carb line to remove and fill
through.
On most four strokes you cannot get to
the carb easily so plumb a third line into
the tank to use as a fill line. You will fill
through it then plug it for flight. The carb
line will stay connected all the time.
Page 14

14
6. Attach the two pieces of 5mm tubing to
the two tank outlets. Use different colors
so you can tell which is the vent and
which is the fuel pickup after the tank is
installed. Make a note of which color you
attach to which tube. The short brass
with the clunk is the fuel pickup and must
go to the carburetor. The long brass tube
is the vent and should go to the pressure
outlet on the muffler.
Set tank aside till ready to install.
5. Install the assembly into the tank so the
vent tube is turned up to the top of the
tank and is positioned on the right side of
the tank. Tighten the screw to expand
the rubber cap. Don’t over tighten or you
could split the tank.
3. Position the two metal straps over the gear
legs where they turn up into the fuselage on
both sides.
Drill a 1/16” hole through each gear strap
and install the 2mm screw and flat washer.
1. Gather the following items:
(4) 2mm x 12mm screws
(4) 2mm washer
(2) Metal gear straps
(2) Main gear wire
(1) Nose Gear Wire
(6) 4mm wheel collar
(1) Nylon steering arm
(1) set screw for steering arm
(3) 2-1/2” wheels
LANDING GEAR INSTALLATION
2. Insert the main gear wires in the pre-cut
holes and slots in the bottom of the fuselage.
Page 15

15
ENGINE INSTALLATION
1. In addition to the engine collect the follow-
ing items:
(4) 4mm blind nut
(4) 4mm x 30mm" socket head bolt
(4) 4mm flat washers
5. Install a wheel collar on the nose gear and
insert into the hole in the bottom of the fuselage. Adjust the wheel collar so the gear
wire is flush with the top of the steering arm
inside the fuselage
6. Install the steering arm with the set screw on
the side next to the firewall. This means you
will have to rotate the nose gear 180
degrees, tighten the set screw, then rotate
the nose gear back into position.This is
done to give you more throw on the steering
arm before it hits the firewall. Position the
steering arm to give you enough throw and
tighten the set screw.
4. Install a wheel collar on the axle followed by
the wheel, then the other wheel collar. File a
flat spot on the axle where the outer wheel
collar set screw fit to make sure it does not
come off.
7. Install the nose wheel with a wheel collar on
both sides
Page 16

16
3. Remove the engine and drill a 5/32” hole at
the location you marked. This is the size of
the shoulder of the blind nut not the screw.
Seat the blind nuts using one of the bolts and
flat washers to pull each blind nut into the
bottom of the mount.
2. Position the engine in the mounts making
sure to leave clearance for the spinner back
plate on front. Mark the location of each hole.
4. Re-install the engine and bolt in place using
the four bolts and washers. Be sure to use
lock tite on the bolts.
PROPELLER & SPINNER INSTALLATION
The propeller size must be matched to the engine.
For example, a .60 may use a 11" diameter prop
while a .80 four stroke can use a13" prop. Follow the
engine manufacturer’s recommendation for correct
propeller sizes or speak to a knowledgeable dealer.
It's wise to buy a few spare props, as everyone
breaks them occasionally, and particularly often
when learning to fly.
Balancing your propeller helps to protect your radio
from the damaging effects of vibration. There are
good, easy to use prop balancers on the market. We
recommend sanding the heavy blade on the curved
face, out near the tip, rather than on the flat face. Try
to maintain the normal airfoil curvature. Avoid
scratches which may cause the prop to break. Never
carve or cut a prop near the hub for any reason
(such as to fit a spinner).
It is equally important to use a correctly sized spinner. The CGP 4-pin spinner (3-1/2”) for the Heritage
Series Skylane 62 ARF is a rugged precision-molded spinner which does not require any special
mounting nuts or screws. CAREFULLY READ THE
SPINNER INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
INCLUDED WITH THE SPINNER. And remember,
although a spinner helps reduce the chance of injury
from a rotating prop, extreme caution always must
be used when the engine is running.
Page 17

17
PUSHROD INSTALLATION
RADIO INSTALLATION
1. Collect the following items:
(2) 3/8” X 16” wooden dowels
(4) 2mm x 30cm pushrods
(4) Silicone clevis keepers
(4) 1/2” x 1-1/2” shrink tubing
(4) 2mm metal clevis
(2) 2mm x 18cm metal rods
(2) EZ servo connector
(2) 4mm x 20cm nylon tubes
(2) nylon swing in keepers
2. Take two of the 2mm x 30cm pushrods and
make a 90 degree bend on the unthreaded
end 3/8” long
3. Take the two 2mm x 18cm rods, unthreaded
on both ends, and make a 90 degree bend in
one end.
4. Take the two wooden dowels and insert one
long rod and one short in each end. Fit the
3/8” leg in the hole and the wire in the
slot.Apply thick CA glue or epoxy to the wire
and then slide the shrink tubing in place.
Shrink the tubing tight.
5. Remove the covering over the rudder
pushrod exit on the top-right side of the
fuselage.
6. Remove the covering over the elevator
pushrod exit on the left-lower side of the
fuselage.
Page 18

18
7. Mount the rudder control horn the same as
we did with the ailerons and flaps. Mount it
1-1/4” up from the bottom of the rudder and
angled toward the pushrod exit.
8. Mount the elevator servo in the manner, 1-
1/8” over from the inside edge and perpendicular to the hinge line.
9. Install the pushrods in the slots in the rear of
the fuselage. Put a 2mm clevis and silicone
keeper on each rod and connect to the control horn.
SERVO INSTALLATION
1. Locate the two 3/16”x1/2”x1-5/8” wooden
blocks. Glue in place at the front and rear of
the rudder servo cutout. This will raise the
rudder servo to prevent any interference
between the rudder arm and the elevator
arm.
2. Mount the rudder, elevator,and throttle servo
in the openings provided.
Page 19

19
3. Attach one of the pushrod connectors to the
throttle servo arm.
4. Connect the other pushrod connector to the
inner hole on a double output servo arm.
5. Connect one of the2mm x 30cm pushrod
with a clevis and silicone keeper to the nose
gear steering arm. Install one of the 5mm
nylon tubes on the rod.
5. Attach the rudder output arm to the servo
and center the servo with the radio. Make
sure the rudder is centered and mark the
pushrod and bend at a 90 degree angle as
we did with the ailerons Attach to the output
arm with one of the swing in keepers.
Insert the nose gear steering rod into the
servo connector on the rudder servo, and
adjust the nose wheel till straight. Tighten
the set screw.
6. Center the elevator servo with the radio and
attach an output arm. Center the elevator
and mark the point where the pushrod
crosses the output arm and bend at a 90
degree angle. Cut off at 3/8” and attach to
the output arm using one of the nylon swing
in keepers.
Page 20

20
7. Using a long 3/16” drill, drill a hole in the fire-
wall in line with the throttle arm on the
engine.
Attach the other 2mm x 30cm pushrod to the
engine throttle arm with a clevis and silicone
keeper. Install the nylon tube on the
pushrod.
8. Attach the pushrod to the servo connector
on the throttle servo and adjust properly.
9. Both the throttle pushrod and the nose gear
steering pushrod will need to be notched
into the bulkhead where the tank fits.
TANK AND HATCH INSTALLATION
1. Install the tank through the wing opening,
through the hole in the bulkhead, and the
cap into the hole in the firewall. Foam (not
included) can be used to cushion the tank
on the sides. Connect the fuel lines from the
fuel pickup to the carburetor, and the vent
line to the muffler.
Page 21

21
2. Fit the hatch in place with the dowels in front
and secure using two 2mm screws at the
rear.
WINDSHIELD& WINDOW INSTALLATION
1. Trim the side windows leaving a 1/8” flange
all around.
2. Apply a bead of Zap canopy glue around the
1/8” flange and push the window into place
from the inside of the cockpit area. Hold with
tape till dry.
3. Trim the rear window to fit flush with the rear
of the wing saddle and overhanging the
sides 1/4” to 3/8”. Glue in place using
canopy glue and masking tape to hold in
place till the glue dries.
4. Trim the windshield to fit flush with the front
of the wing saddle and overhanging the post
1/4”. Glue in place with canopy glue and
masking tape.
Page 22

22
RECEIVER AND BATTERY INSTALLATION
1. Insert the Y-harness into the the aileron
plug in the receiver and then wrap both the
receiver and the battery in the 1/2" foam.
2. The switch can be mounted in the fuselage
side opposite the exhaust.
You can remove the tank and place the bat-
tery under the tank or it can be placed just in
front of the servo tray depending on where
you need it for balance. If the battery is
under the tank the receiver can go just in
front of the servo tray. If the battery is in front
of the servo tray you can mount the receiver
behind the servo tray under the pushrods.
Move the battery and receiver to achieve the
proper balance.
WING AND STRUT MOUNTING
1. Collect the following items:
(2) Wing Struts
(4) 3mm x 12mm socket head screws
(2) 4mm x 25mm socket head screws
(2) 4mm flat washers
2. Fit the wing into the saddle with the tongue
on the bottom of the bottom of the wing fitting into the notch at the leading edge.
Page 23

BALANCING THE MODEL
IMPORTANT: NEVER NEGLECT THIS STEP WITH
ANY AIRPLANE. If you try to fly a plane with the
balance point behind the recommended range, you
run the risk of having an unstable aircraft and the
strong likelihood of a crash. TAKE THE TIME TO
PROPERLY BALANCE YOUR MODEL!
To determine the Center of Gravity, measure back
on the fuselage from the leading edge of the
wing. The C.G. range for this aircraft is
3” to 3-5/8".
Place the fully assembled aircraft on a model balancing stand, as shown above. You can make this
simple set-up with a couple of ¼" dowels with rounded tops, spaced 5" apart. Alternatively, lift the model
under the wing near the fuse by your finger tips. (You
may wish to get help from a friend if using the latter
method.) Referring to the recommended balance
range for your model, move the position of the plane on
the balance stand until the model is level or the nose
slightly down.
If the is tail heavy, shift the R/C equipment away from the heavy end of the model and
recheck until the model will balance within the
acceptable range. If shifting the R/C gear still doesn't balance the model, add weight to the far end of
the nose or tail, respectively, until the model is correctly balanced. The least weight is needed when
added as far back or forward as possible. Fasten
the weight permanently in place.
3. Bolt the wing in place using the two 4mm x
25mm bolts and flat washers. The blind nuts
are pre-installed in the fuselage.
4. Connect the strut to the fuselage using one
of the 2mm bolts, don’t tighten all the way.
The blind nut is pre-installed in the fuselage.
4. Connect the other end of the strut to the
wing with another 4mm bolt. The blind nut is
pre-installed in the wing. Repeat for the
other strut and tighten all four bolts.
Page 24

24
FLYING YOUR Heritage Series Skylane 62 ARF
GETTING READY TO FLY
BEGINNING AEROBATICS
Taking time here really pays off later. Rushing the setup and testing frequently results in a model that never
performs up to its full potential and may even lead to a
crash.
CONTROL SURFACE SETTINGS. For the first few
flights, even if you are an experienced flier, it is best to
set the control surfaces at the GENTLE (LOW) settings. You can then work your way up to the higher settings. The settings for the Heritage Series Skylane 62
ARF are:
LOW HIGH
AILERONS 3/8" 1/2"
ELEVATOR 3/8” 1/2"
RUDDER 3/4”
RADIO CHECK. Many an experienced flier has rued
the day he neglected to check EVERYTHING! After
fully charging the batteries, turn on the receiver and
transmitter and actuate all controls many times to make
sure all responses are correct. Standing behind the
model, the right aileron should go up when the stick is
moved to the right. Moving the transmitter stick down
should move the elevator up, and vice versa. Also
check the wheel movement, which should move right
with the right rudder movement. Check that the throttle
opens to permit full power when the stick is moved up.
Practice steering the model on the ground, with the
throttle set at minimum, to keep model moving at a
walking pace. Before and after all tests, make sure all
gear is neatly and firmly in place - engine and servos
fastened down, receiver and battery wrapped in foam
and secured against shifting, propeller tight, and antenna extended.
Prior to the beginning of each day's flying, make a
range check of your equipment in accordance with the
manufacturer's instructions. With transmitter antenna
collapsed to 6-8", you should have at least 100 feet
range on the ground. Check this by turning on both the
receiver and transmitter and with the model heading
away from you, walk away while transmitting signals.
Watch to see that no signals are missed until you are
at least 100 feet away. Remember not to use your
transmitter when someone else is flying or testing
on the same frequency. DO NOT ATTEMPT FLIGHTS
UNLESS ALL THE EQUIPMENT WORKS PERFECTLY.
After everything checks out, check it again! When you
are satisfied with the performance of all equipment
functions, point your SKYLANE’S nose into the wind
and, gradually increasing to full power, take off for a
short (2 to 3-minute) first flight.
Before the second flight, take off the wing
and check all screws, radio equipment,
engine mounting, muffler, etc. to make
sure that nothing has come loose.
Spend the following flights getting familiar with your model and making sure it is
properly trimmed for straight and level
flight. When you feel comfortable with your model, it's
time to try aerobatics.
Almost all maneuvers are a combination of loops
and rolls, so if you can do these two things, you're off
to a good start! We highly recommend the book
Flight Training Course, Volume II, published by
R/C Modeler Magazine. Some of the following is
taken from this manual, with the gracious permission
of the magazine.
Above all, remember that top gun aerobatics are the
result of practice. The crisp, graceful movements
come from the pilot's willingness to do and do it again.
Don't give up; practice really does make perfect!
Which side is up? Learning to recognize which side
is up may sound foolish, but many a plane has bitten
the dust because the pilot lost track of the plane's
position. Other than learning to recognize the plane's
silhouette at different angles and attitudes, the best
insurance is to force yourself to concentrate on each
thing that you do, i.e. making a left turn. If your mind
strays and you forget what you're doing, coming
back to it can cause a few new grey hairs!
THE LOOP. This is a good first stunt. The model
starts flying straight and level into the wind, then
pulls up into a smooth, round loop. The up and down
portion should be straight, without the plane falling
off to the right or left, and the speed should be constant. As the plane finishes the loop, it pulls out
straight and level, at the same heading and altitude
as when it entered the maneuver.
THE HORIZONTAL ROLL. Important! Always
remember that, when the plane is inverted, the
elevator works backwards. Therefore, when the
plane is inverted, you give down elevator. Also, be
sure to fly high enough to give a good margin for
error, as your early attempts will probably end up in
a 30º dive. We also recommend you practice with
the plane in front of you, rather than overhead.
Good luck and happy flying!
WIND
(OPTIONAL, BUT
GIVES A MORE PRECISE LOOP
1. UP ELEVATOR
2. EASE OFF OF SOME
UP ELEVATOR
5. EASE OFF OF UP ELEVA-
TOR, OPEN THROTTLE
3. ADD SOME UP ELEVATOR
4. THROTTLE DOWN TO IDLE
75-150 FT.
2. DOWN ELEVATOR
4. UP ELEVATOR
3. RELEASE AILERON
CONTROL
1. FULL RIGHT OR
LEFT AILERON
WIND
 Loading...
Loading...