Page 1
802.11g 54M WLAN
Internet Broadband Router
User Manual
#4829610ASGZ1
Page 2

Content
1. Introduction................................................................................................................................................ 3
1.1Features ...........................................................................................................3
1.2 Specification....................................................................................................4
1.3 Package Contents...........................................................................................5
2. Hardware Installation............................................................................................................................. 5
2.1 Product Description.........................................................................................5
2.1.1 Front Panel and LEDs....................................................................6
2.1.2 Rear Panel.....................................................................................6
2.2 Getting Started.................................................................................................7
2.2.1 System Requirement......................................................................7
2.2.2 Before Installation...........................................................................7
2.2.3 Setting Hardware Connection ........................................................8
2.2.4 Configure your computer................................................................9
3. Using Configuration Menu.................................................................................................................. 16
3.1 Setup Method................................................................................................17
3.2 Basic Setup ...................................................................................................20
3.2.1 Setup Router................................................................................20
3.2.2 Global Address.............................................................................22
3.2.3 Wireless .......................................................................................23
3.2.4 Tools:............................................................................................27
3.2.5 Status:..........................................................................................28
3.2.6 DHCP:..........................................................................................29
3.2.7 Log............................................................................................... 30
3.2.8 Statistics:......................................................................................31
3.2.9 Printer:..........................................................................................32
3.3 Advanced Setup ............................................................................................56
3.3.1 Virtual Servers..............................................................................56
3.3.2 Filters ...........................................................................................57
3.3.3 IP/URL Block................................................................................58
3.3.4 Special Apps(Special Applications)...............................................59
3.3.5 DMZ Host.....................................................................................60
3.3.6 MAC Clone...................................................................................61
3.3.7 Dynamic DNS...............................................................................61
3.3.8 Proxy DNS ...................................................................................62
3.3.9 Routing.........................................................................................63
3.3.10 SNMP.........................................................................................64
4. Glossary................................................................................................................................................... 65
5. TCP/IP Port List for Internet Service............................................................................................... 70
Page 3

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
1. Introduction
This 802.11g 54M Wireless LAN Broadband Router is an ideal solution for wireless/wired
Internet surfing and office resources sharing. It provides the fast, robust and flexible
features with high transmission rate up to 54Mbps bandwidth in the 2.4GHz frequency.
Not only connect with 802.11g devices, it is backward compatible with 802.11b products
and can be worked under .11b and .11g mixed environments. It employs WEP encryption to
ensure a more secure wireless connection. With web-based configure interface,
users can easily build up wire or wireless connection within minutes.
Besides, with firewall function, the Wireless LAN Broadband Router can always protect
your LAN from outsider's break-ins and yet expose your local servers such as Web Server,
E-mail Server, FTP server, for remote access by Virtual Server or DMZ setting.
1.1 Features
Wireless – Built in with IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps Access Point
. Complies with 2.4GHz 802.11g Standard
. Backward compatible with 802.11b products
. Up to 54Mbps data rate, auto fallback under noisy environment
. Support 802.1x Authentication feature and 64/128-bits WEP Encryption
Router – Built in with 4 Port 10/100M Internet Broadband Router
. 1 port 10/100M WAN and 4 ports 10/100M switch LAN (RJ-45) interface
. Quick Setup Wizard enable user to setup internet connection within 3 steps
. Advanced Access control based on URL, IP, Service Port and MAC address
. ALG function for on-line gaming, MSN, conference and P2P software
. Configurable through User-friendly web base management interface
. (Optional) With reverse SMA Antenna connector increase flexibility
. Intruder event log by packet inspection features
. DMZ and Virtual Server Mapping support
. UPnP function Supported
3
Page 4
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
1.2 Specification
Model: 802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Radio: Complies with IEEE 802.11b/g
Frequency Band: 2.412-2.462GHz (U.S.)
2.412-2.484GHz (Japan)
2.412-2.472GHz (ETSI)
Modulation TYPE: BPSK, QPSK, CCK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
Operating Channels: 11 channels (US) 13 channels (ETSI) 14 channels (Japan)
Data Rate: 1 / 2 / 5.5 / 6/9/11/12/24/36/48/54Mbps
Output Power: 18dBm@11Mbps; 14dBm@54Mbps
Receive sensitivity: Min.80dBm for 11Mbps (@BER 8%)
Min. -70dBm for 54 Mbps (@BER 10%)
Current Consumption: 3.3V, TX mode 400 mA (Max.)
RX mode 250 mA (Max.)
Media 100BASE-TX: UTP/STP Cat. 5
No. Of Port WAN: 1x 10/100M RJ-45 port, LAN: 4 x 10/100M RJ-45 ports
Reset: 1 x Reset Button , USB :1xPrinter Server
Auto MDI/MDIX Yes
PPPoE/PPTP Client Yes
Static /Fixed IP Yes
DHCP Server/Client Yes
UPnP Yes
DMZ Host Multi-DMZ Host
Routing Static, RIP I/II, Transparent mode support
Event Log System / Security Log, Remote Security Log
Firewall DoS, URL Blocking, Mac Blocking, Service Port Blocking,
IP Address Blocking, Deny/Allow Ping,
Service Time allocation
VPN PPTP, IP Sec pass through
Management Local Web-based configuration, Telnet
LED Indicator Power, Diag, WLAN, Link/Act.
4
Page 5
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Environmental Temperature
Humidity 10%~90%, non condensing
Power Consumption Input : 100V, 50/60Hz / 120V, 60Hz / 230V, 50Hz / 240V,
Conformance FCC class B, CE mark class B
1.3 Package Contents
1. One WLAN Broadband Router
2. One CD-ROM (User Manual on CD)
3. One Quick Installation Guide
4. One Power Adapter
5. (Optional)One Reverse SMA Antenna
Storage -20°C to 60°C
Operating 0°C to 45°C
50Hz
Output : DC7.5V / 1000mA
2. Hardware Installation
2.1 Product Description
You can place this Wireless LAN Broadband Router horizontally or hang it on the wall.
5
Page 6
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
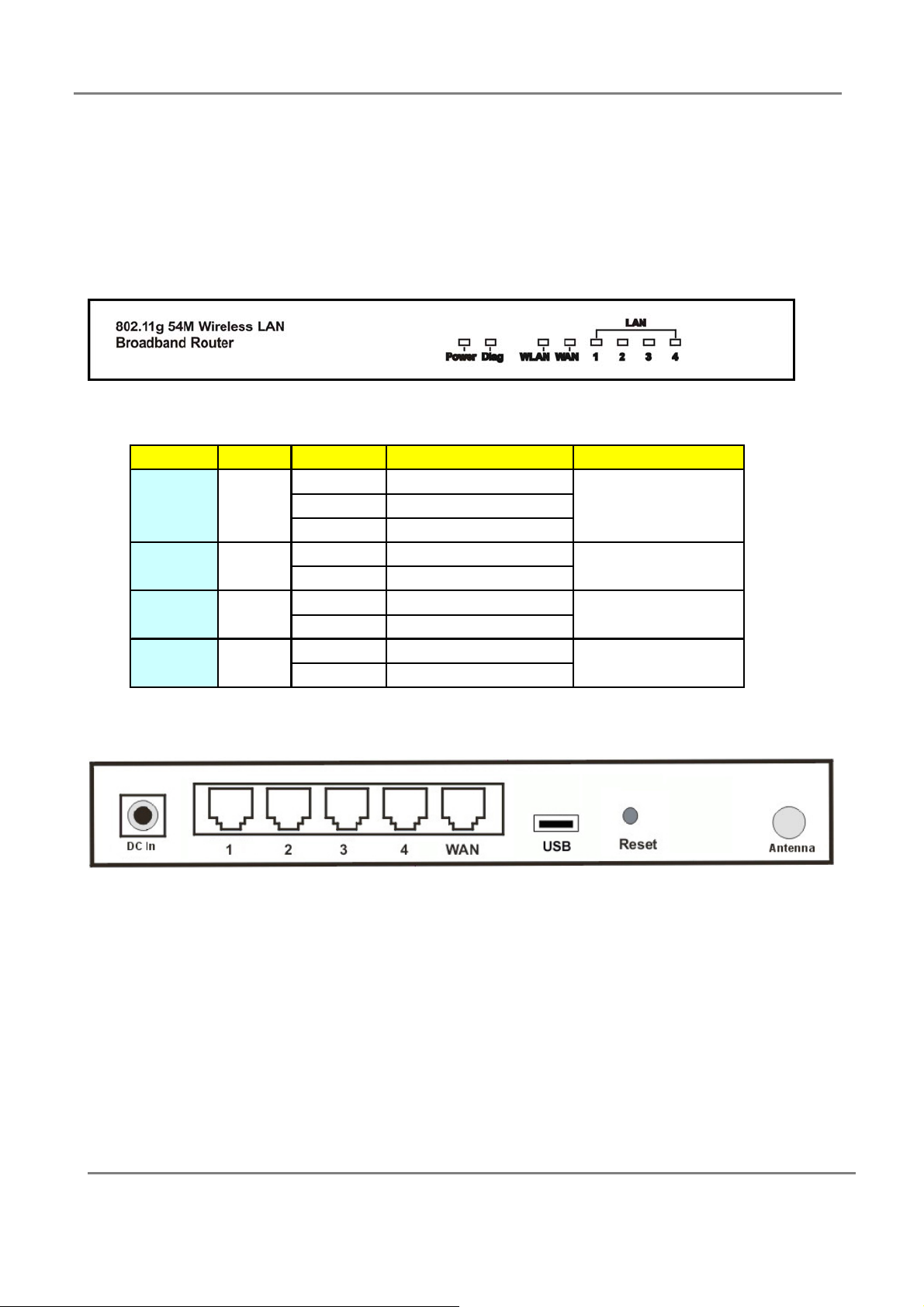
2.1.1 Front Panel and LEDs
Front Panel :
With its Diagnostic LEDs, you could easily get status information find out where the problem
is.
The LEDs are explained in the following tables.
Label Color Status Meaning Number of LEDs
On Link On
Link/Act. Green 4 x LAN,1 x WAN
Diag Green 1
WLAN
(Link)
Yellow 1
Blinking Activity
Off Link Off
On Power ON
Off Power OFF
On Work mode fail
Off Normal work mode
On Link On
Off Link Off
1Power Green
2.1.2 Rear Panel
The following graphic shows the rear panel of Wireless Router.
‧ DC In: To connect the adapter to receive power.
‧ LAN 1~4: To connect networked PC or uplink to Switch or Hub.
‧ WAN: To connect the Cabel/DSL modem via Cat.5 RJ-45 cable.
‧ USB: To connect the USB Printer
‧ Reset: Pressing the Reset button for more than 5 seconds, the router will restore to
factory default setting.
‧ Antenna Connector: (Optional, only exists in the model with reverse SMA connector)
This is standard reverse SMA connector where any antenna with reverse SMA
connector can connect to this Wireless LAN Broadband Router.
6
Page 7

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
2.2 Getting Started
Please refer to the following sections of this manual for additional information about setting
up a network.
2.2.1 System Requirement
Before you getting started, make sure that you meet the following requirements.
1. An Internet connection through a cable or DSL modem
2. A computer with an Ethernet network card
3. Your Windows CD, if your computer is running Windows 95, 98, or ME
4. UTP network cable with RJ-45 connector
5. Either Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 (or above version) or Netscape Navigator 4.0 (or
above version)
6. For Wireless Connection, you need Wireless LAN Card / USB Adapter.
2.2.2 Before Installation
Before you start to connect your router to any network device, make sure you get the
following values from your ISP. You will need those values to setup the Router and
configure you networked PCs to accept the IP address the Router chooses to assign them.
‧ PPPoE User Name and Password or Fixed Internet IP Address assigned by your local
ISP
‧ Your Subnet Mask
‧ Your Default Gateway
‧ Your Primary DNS IP address
You are supposed to have all those information mentioned above from your ISP. If not,
contact your ISP and they will be able to supply all the information you need.
7
Page 8
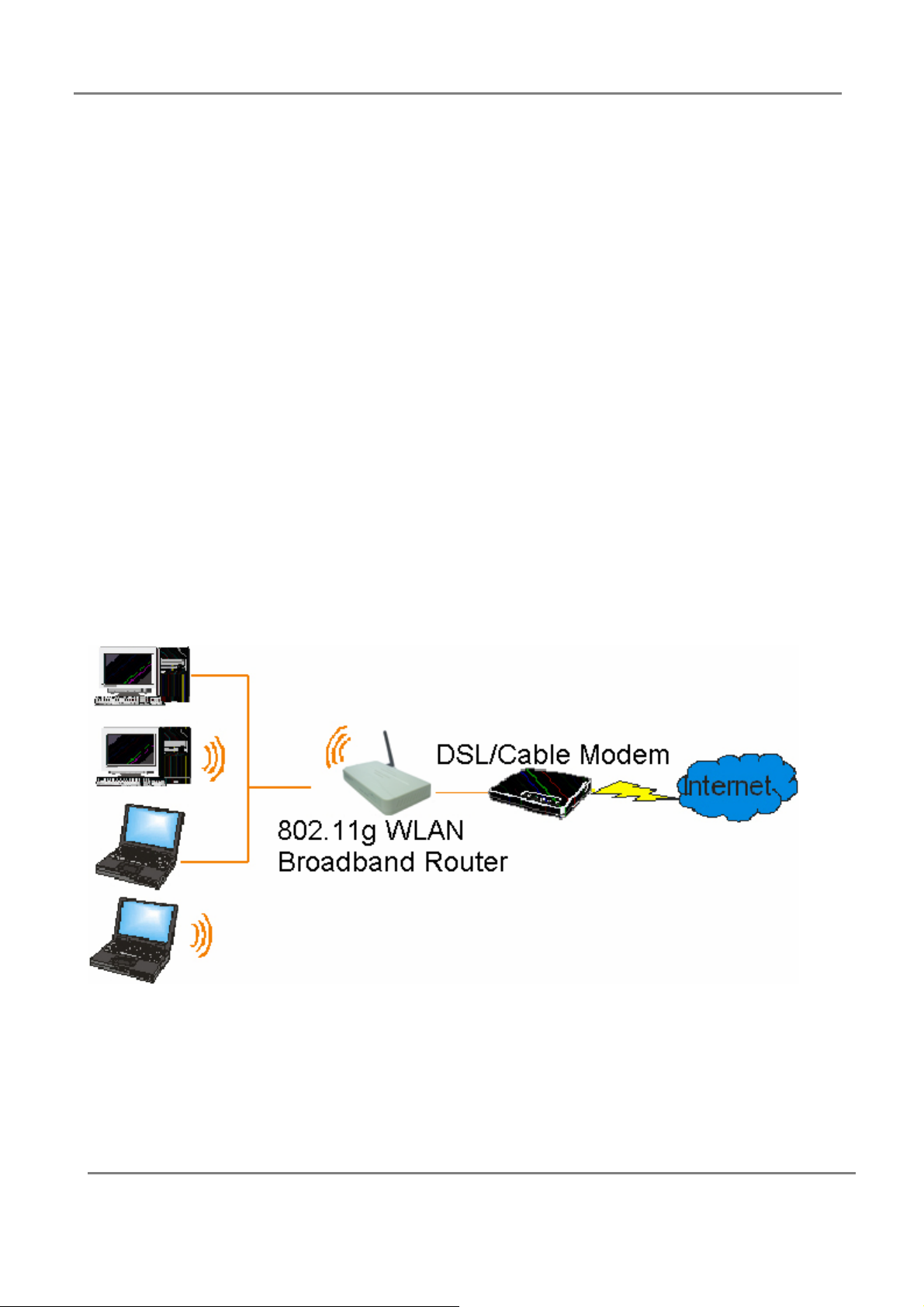
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
2.2.3 Setting Hardware Connection
Follow the steps listed below to install your Router when you have all the information
mentioned above.
Step 1. Power all devices down.
This should include your PCs, Cable or DSL modem and the Router.
Step 2. Connecting a Cable Modem or DSL Modem.
Connect your Cable or DSL modem to the WAN port on the rear panel.
Step 3. Connect the Wireless Router to your PCs.
Connect computers directly to the Router on ports 1~4 on the rear panel. If you
have more than 4 computers need to be connected, connect a hub or a switch
(using its uplink port) and connect additional computers to that device.
Step 4. Power on.
Plug the power cord into the power jack. And power on computers.
8
Page 9

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
2.2.4 Configure your computer
. Windows 95/98/ME
Step 1. TCP/IP Configuration
After you have completed the hardware setup by connecting your devices, you need to
configure your computer to connect to your Router.
1. From the Windows desktop, click the “Start” button and choose “Settings”,
then click “Control Panel”.
2. From “Control Panel”, double-click the “Network” icon.
3. In the “Network” window, under the “Configuration” tab, double-click the “TCP/IP” entry
that is listed with your network card.
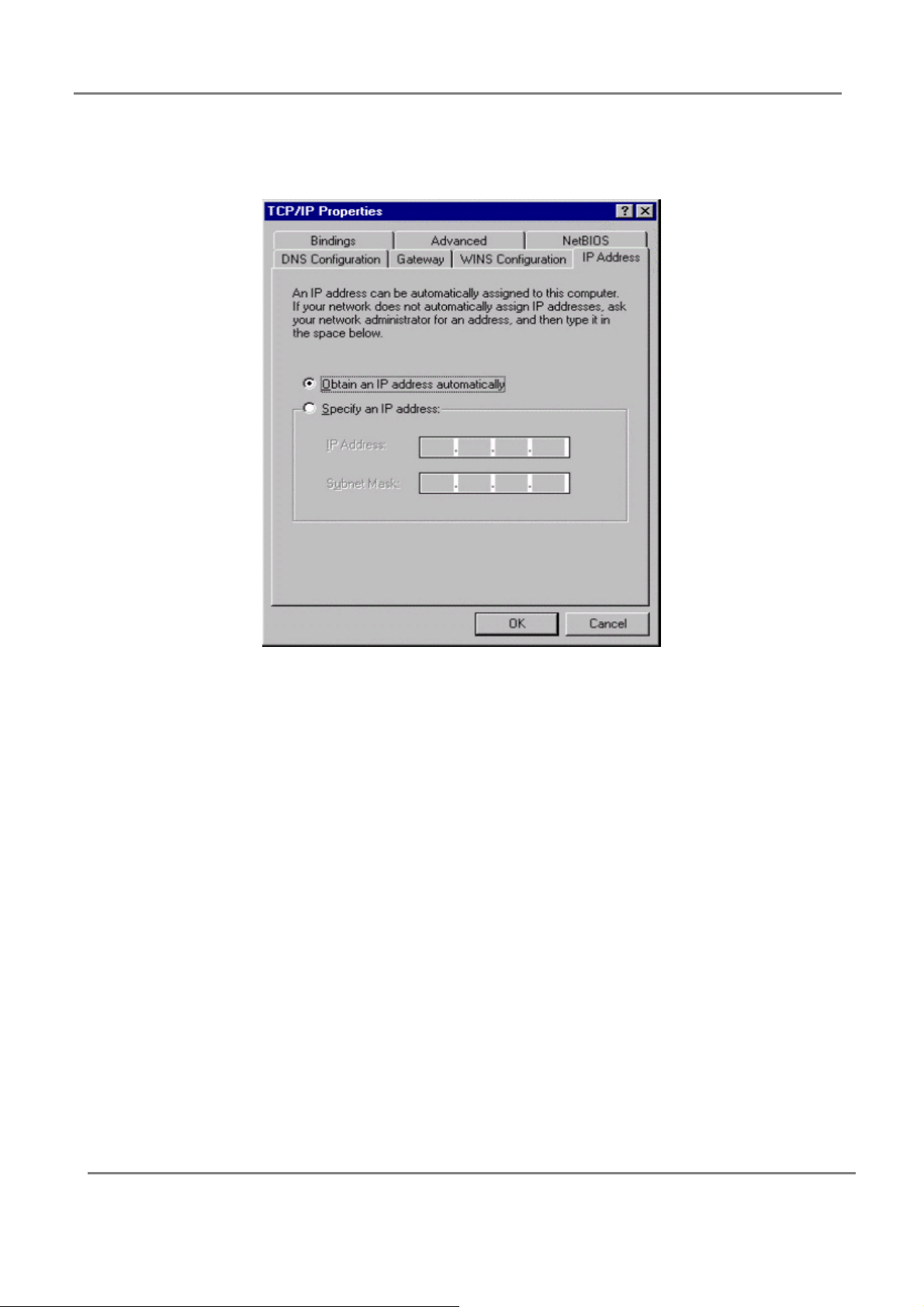
4. On the “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” dialog box, make sure “Obtain an IP
address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” are selected. If
not, select them and click “OK” and lose window.
9
Page 10
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
5. Locate your IP address and Subnet Mask. Type them in the spaces provided below.
6. Click the “Gateway” tab and record the numbers listed under “Installed gateways.”
7. Click the “DNS Configuration” tab. Locate the DNS servers listed under “DNS Server
Search Order”. And Click “OK”.
8. System may need your Windows 95/98/ME CD to copy some files. After it finishes
copying, please restart your system.
10
Page 11
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Step. 2 Disable HTTP Proxy
‧ Internet Explorer
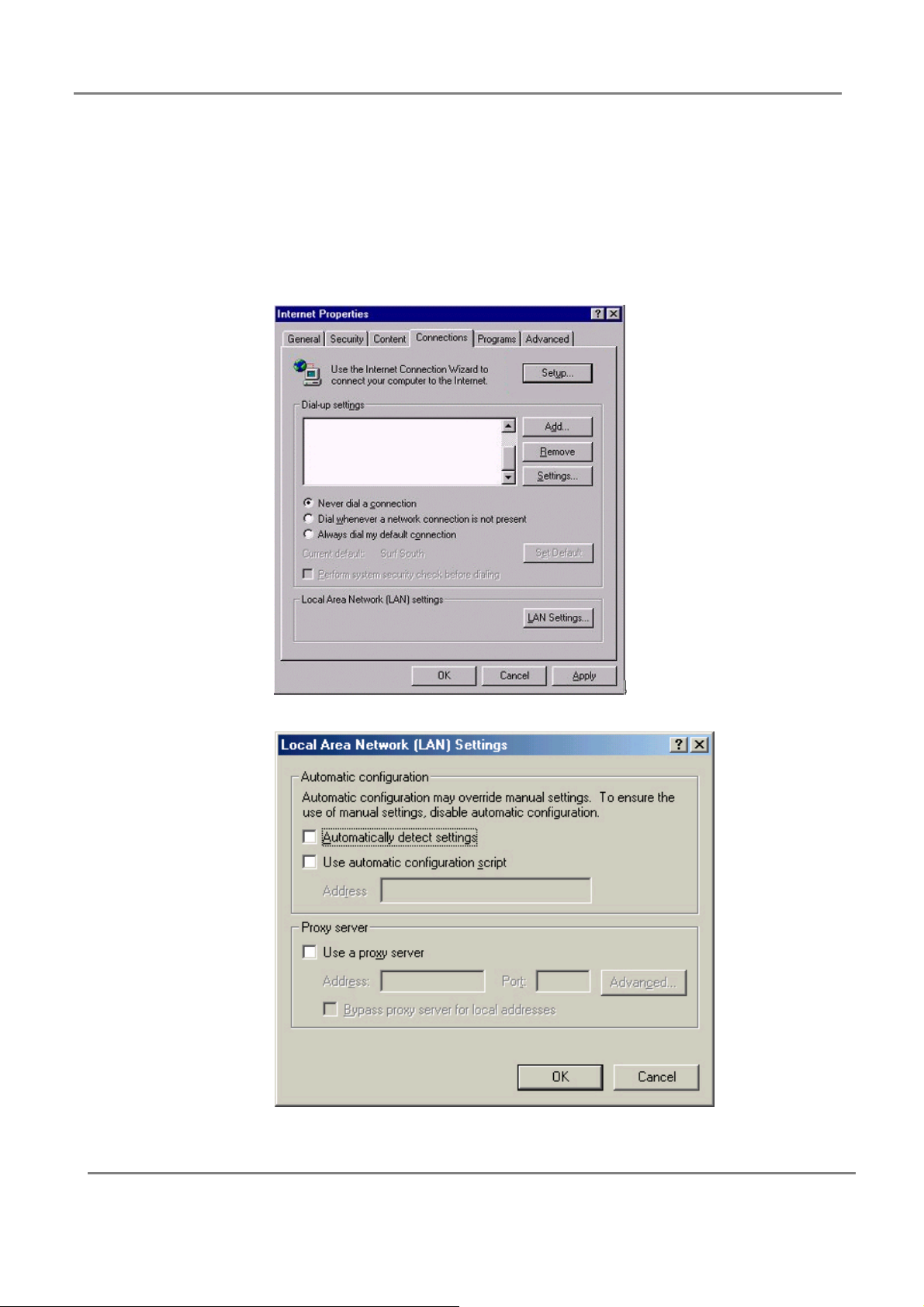
1. Open Internet Explorer and click the stop button. Click “Tools” then “Internet Options”.
2. In the “Internet Options” window click the “Connections” tab. Then click the “LAN
Settings” button.
3. Clear all the checkboxes.
11
Page 12

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
4. Click “OK”, and then click “OK” again to close the “Internet Options” window.
‧ Netscape
1. Open Netscape and click the stop button. Click “Edit”, then click “Preferences…”
2. In the “Preferences” window, under “Category” double-click “Advanced”, then click
“Proxies”. Select “Direct connection to the Internet.” Click “OK”.
Step. 3 Obtain IP Settings from Your Router
1. Click “Start”, then “Run…”. T ype “winipcfg” to open the IP Configuration utility.
2. Click the “Release All” button.
3. Click the “Renew All” button
4. Verify that your IP address is now 192.168.1.xxx, your Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0
and your Default Gateway is 192.168. 1.1. Click “OK” to close the “IP Configuration”
window.
.Windows NT/2000/XP
Step 1. TCP/IP Configuration
After you have completed the hardware setup by connecting your devices, you need to
configure your computer to connect to your Router.
1. From the Windows desktop, click the “Start” button. Choose “Settings”, then click
“Control Panel”.
2. From “Control Panel”, double-click the “Network & Dial-Up Connections” icon.
3. Double-click the icon that corresponds to the connection to your router.
4. Click “Properties” and double-click “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)”.
5. On the “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” dialog box, make sure “Obtain an IP
address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” are selected. If
not, select them and click “OK” and close window.
Step. 2 Disable HTTP Proxy
‧ Internet Explorer
12
Page 13

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
1. Open Internet Explorer and click the stop button. Click “Tools” then “Internet Options”.
2. In the “Internet Options” window click the “Connections” tab. Then click the “LAN
Settings” button.
3. Clear all the checkboxes.
4. Click “OK”, and then click “OK” again to close the “Internet Options” window.
‧ Netscape
1. Open Netscape and click the stop button. Click “Edit,” then click “Preferences…”
2. In the “Preferences” window, under “Category” double-click “Advanced”, then click
“Proxies”. Select “Direct connection to the Internet”. Click “OK”.
Step. 3 Obtain IP Settings from Your Router
1. From the Windows desktop, click the “Start” button, then “Programs“, then “Accessories”
and then click“Command Prompt”.
2. Type “IPCONFIG /RELEASE” and press “Enter”.
3. Type “IPCONFIG /RENEW” and press “Enter”.
4. Verify that your IP address is now 192.168.1.xxx, your Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0
and your Default Gateway is 192.168.1.1. Click “OK” to close the “IP Configuration”
window.
5. Type “Exit” and close window.
.MAC OS 7.X or above
Step 1. TCP/IP Configuration
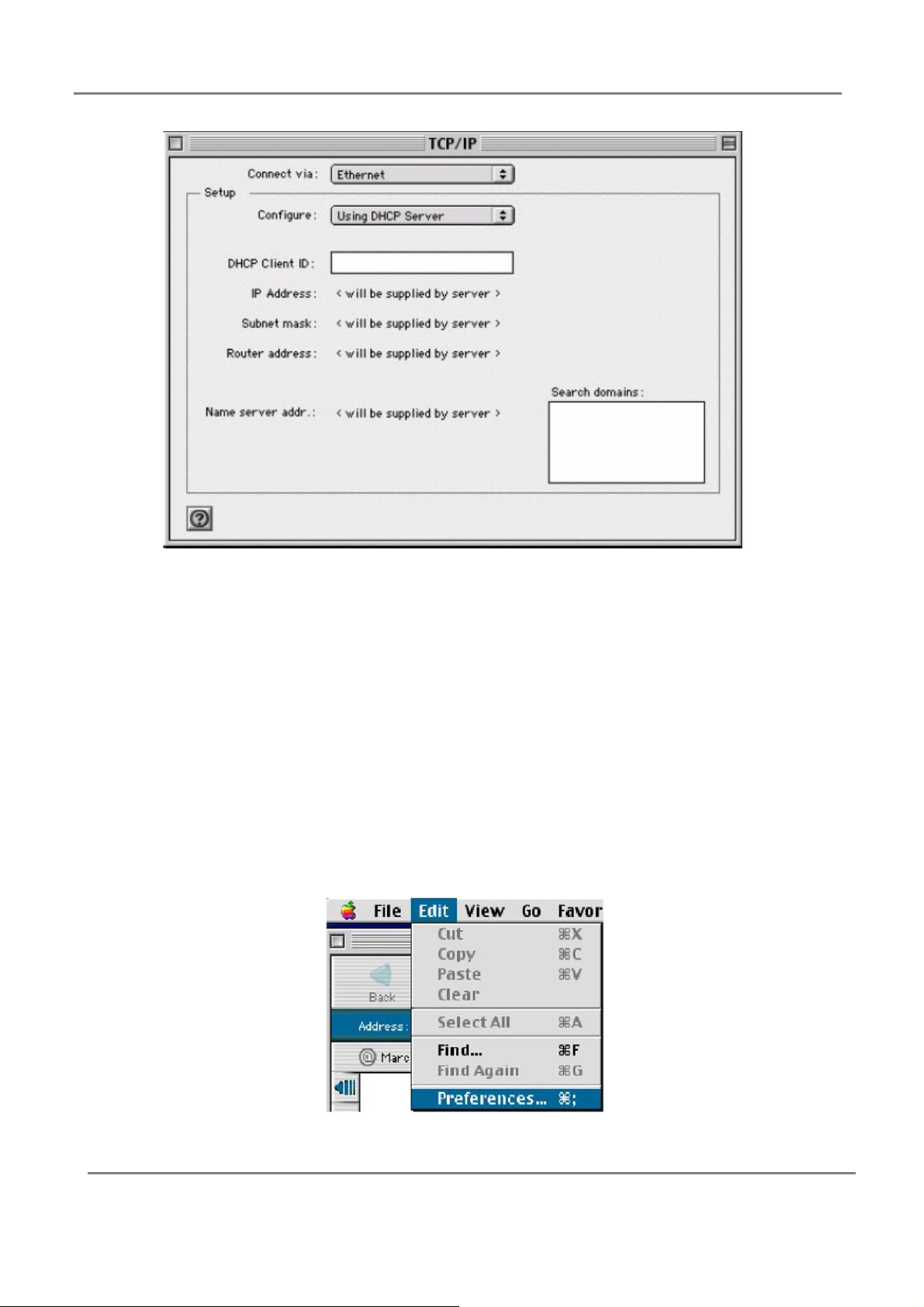
1. Pull down the Apple Menu. Click “Control Panels” and select TCP/IP.
2. In the TCP/IP dialog box, make sure that “Ethernet” is selected in the “Connect Via.”field.
Make sure “Using DHCP Server” is already selected in the “Configure” field and close
window.
13
Page 14
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
2. Another box will appear asking whether you want to save your TCP/IP settings. Click
Save.
Step. 2 Disable HTTP Proxy
‧ Internet Explorer
1. Open Internet Explorer and click the stop button. Click “Edit” then “Preferences”
14
Page 15
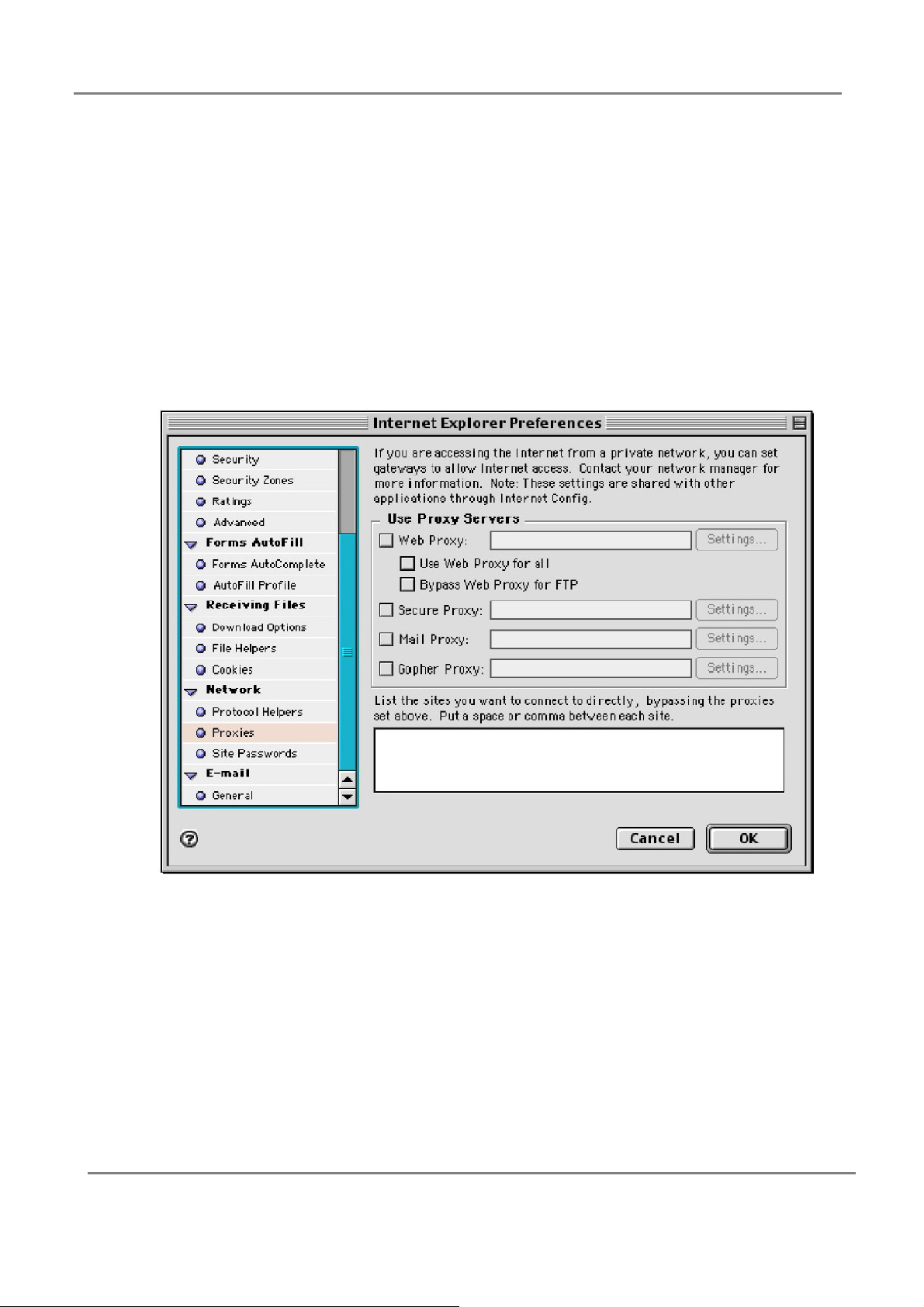
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
2. Select “Proxies” and uncheck all checkboxes and click “OK”.
‧ Netscape
1. Open Netscape and click the stop button. Click “Edit”, then click “Preferences…”
2. In the “Preferences” window, under “Category” double-click “Advanced”, then click
“Proxies”. Select “Direct connection to the Internet”. Click “OK”.
Step. 3 Obtain IP Settings from Your Router
1. Pull down the Apple Menu. Click “Control Panels” and select TCP/IP.
2. In the TCP/IP window, your new settings will be shown. Verify that your IP address is
192.168.1.xxx, Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0 and Default Gateway is 192.168.1.1.
Close Window.
15
Page 16
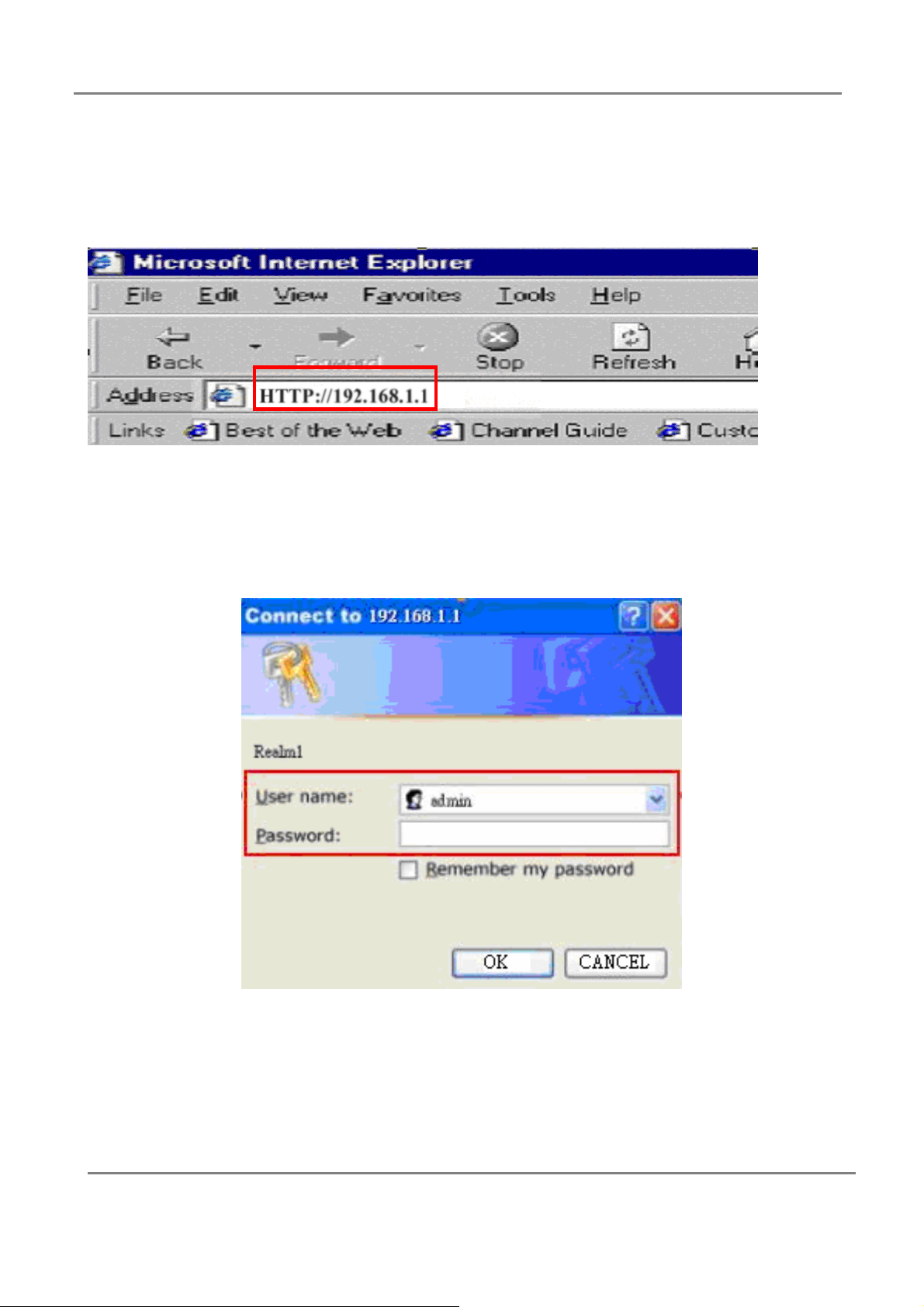
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3. Using Configuration Menu
After configuration of your network, you can access the Router via Web browser and type
the IP Address of Router. The default IP address of this Router is http://192.168.1.1.
Please note that if you have changed the default IP Address assigned to the Router, make
sure to enter the correct IP Address. The default “User Name” and “Password” are both
“admin”. Please refer to “Administrator Settings” page to check how to change your
password.
16
Page 17

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.1 Setup Method
You can choose WIZARD SETUP for step-by-step Installation or choose BASIC SETUP for
basic configuration or choose ADVANCE SETUP for advanced configuration.
1. Setup Wizard
If you choose WIZARD SETUP , please refer to Quick Installation Guide for step by step
instruction.
17
Page 18
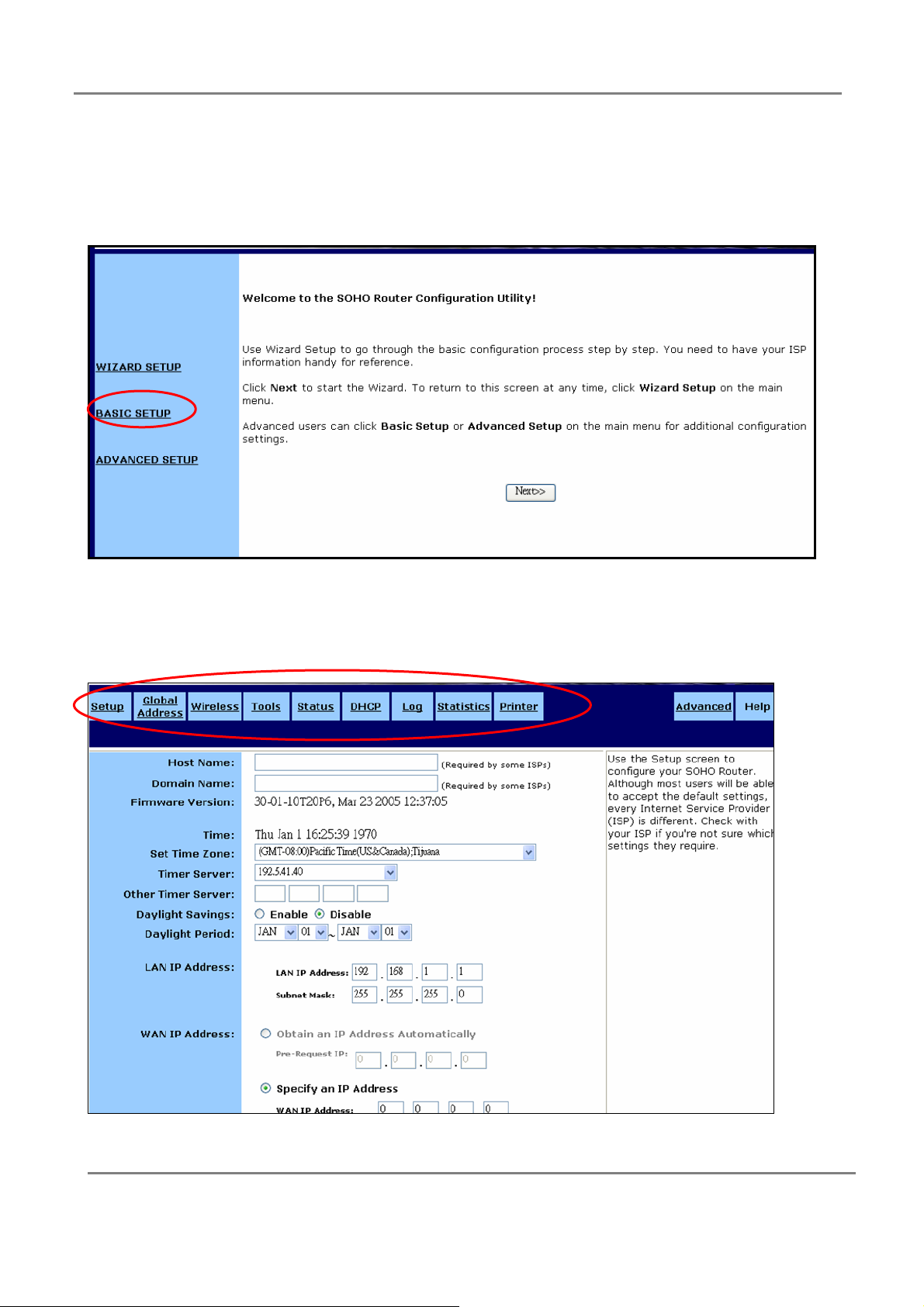
2. Basic Setup
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
If you choose BASIC SETUP , you will see setup screen as below. Click the upper frame to
change settings.
18
Page 19
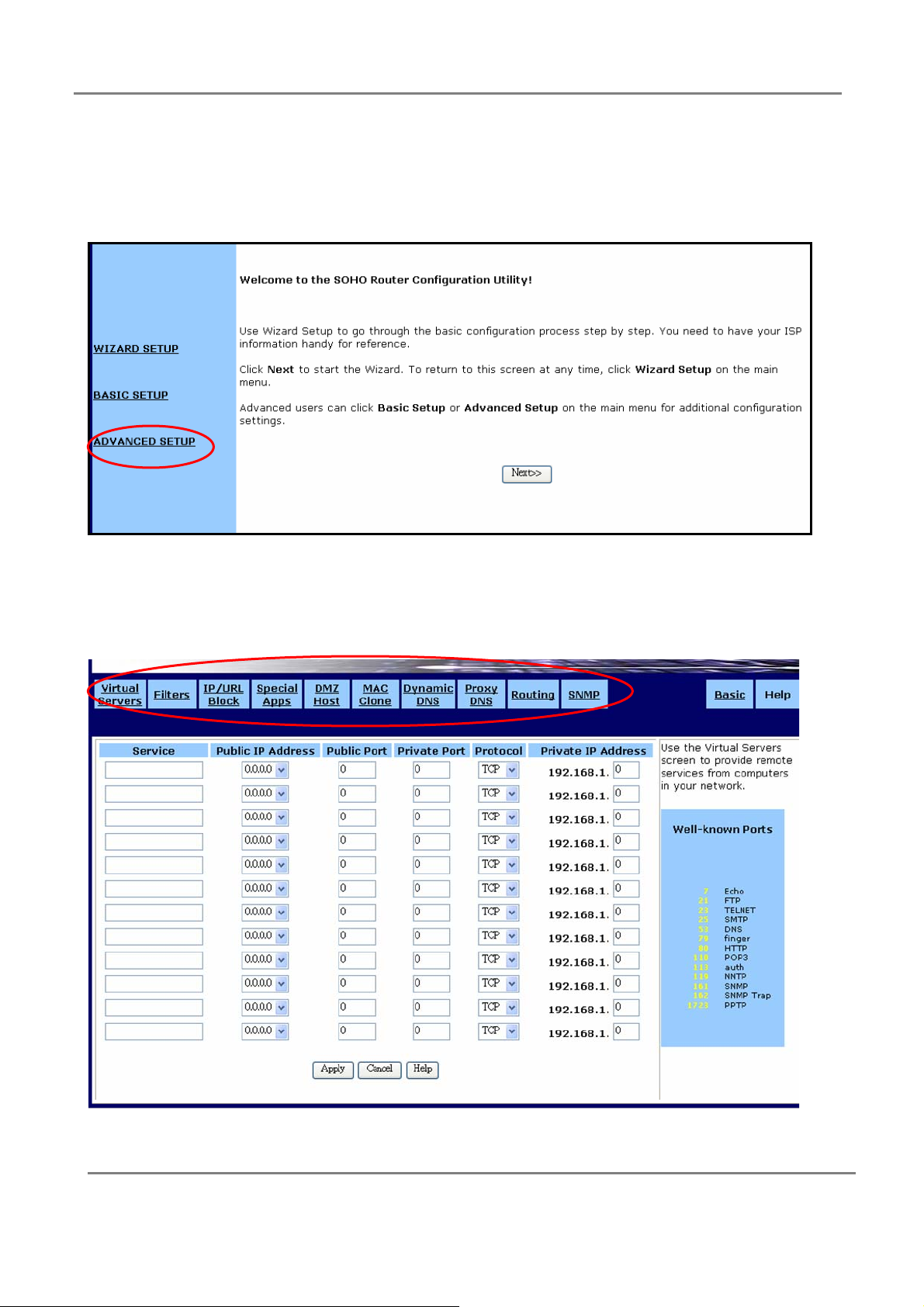
3.Advanced Setup
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
If you choose ADVANCE SETUP , you will see setup screen as below. Click the upper
frame to change settings.
19
Page 20
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.2 Basic Setup
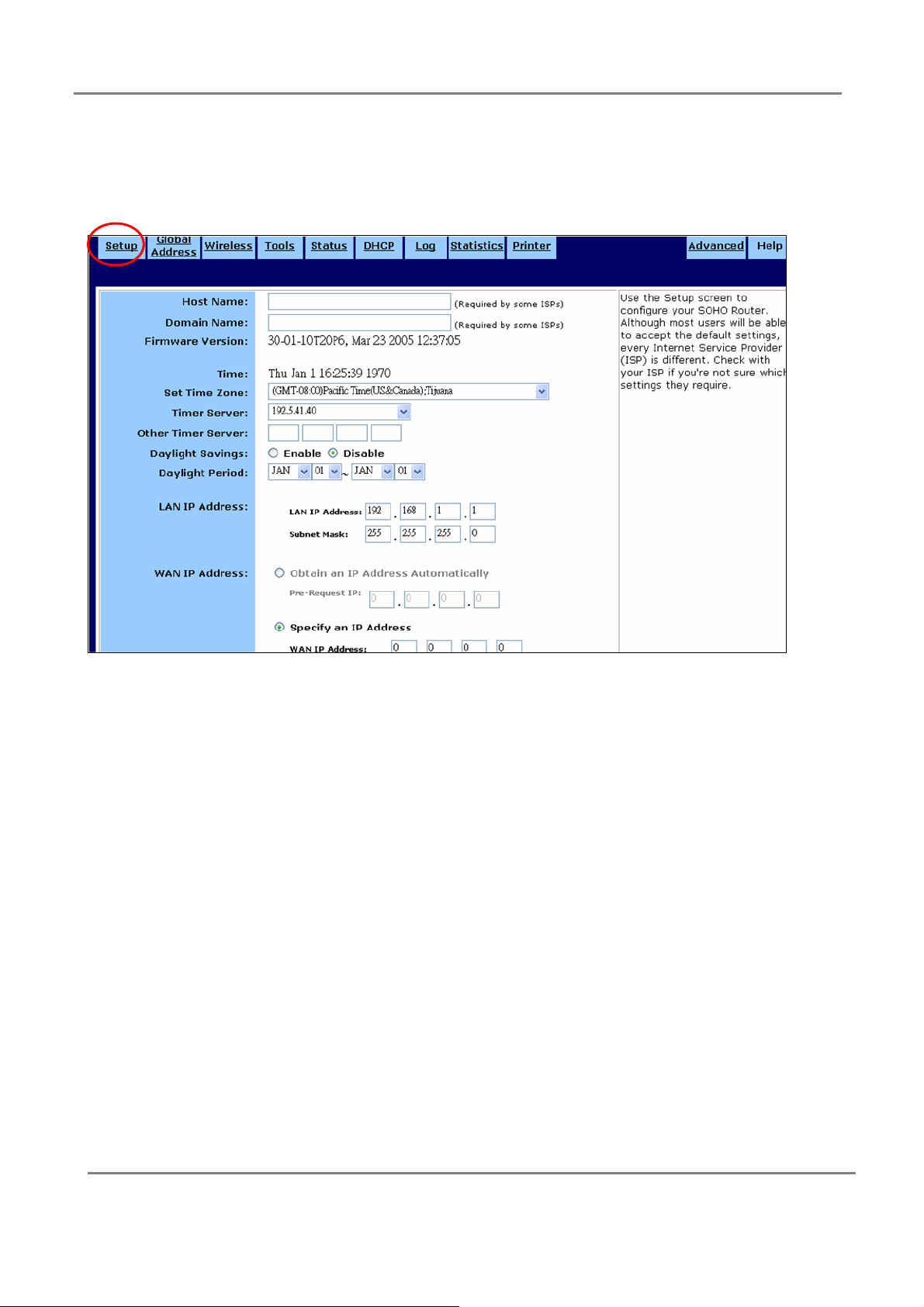
3.2.1 Setup Router
In this page, you can configure your WLAN Router.
Host Name:
Provide a host name (also called system name or account name) if your ISP requires
this information.
Domain Name:
Provide the ISP domain name (e.g. xyz.isp.com) if your ISP requires this information.
Firmware version:
The current firmware version is shown for your convenience.
Time:
Select your Time Zone and Enable or Disable the application of Daylight Savings
Time.
20
Page 21

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
LAN IP Address:
These fields show the LAN IP Address and the Subnet Mask as seen by others on
your Local Area Network (LAN). Most users will not need to change these values.
If you change the LAN IP Address with the DHCP server running, you'll need to restart
your client machines. If you change the LAN IP Address without the DHCP server
running, you'll need to manually reconfigure your clients' IP addresses.
WAN IP Address:
Choose either Obtain an IP Address Automatically (most users)(you can specify the
IP you want to get by filling the Pre-Request IP) or Specify an IP Address (if your ISP
assigns static IPs). If you choose the second option, type in the Wide Area Network
(WAN) IP Address, Subnet Mask, ISP Gateway Address, and DNS values. You can
obtain those information from your ISP.
PPPoE Login:
If your ISP uses Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE), choose Enable;
otherwise, choose Disable. PPPoE allows your ISP to authenticate your connection by
requiring you to submit a username and password.
Type the User Name and Password provided by your ISP in the boxes. For PPPoE
connection types, you can select either Connect on Demand or Connect Manually.
And moreover, if you want to limit the idling minutes, select Max Idle Time and type a
maximum number in minutes. Change MTU to specify the largest size for network
transmission. It is recommendated to use default value 1492.
UPNP:
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) enable devices such as PCs, routers or other devices
to be plugged into a network and automatically know about each other.
21
Page 22

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Click Apply when you finish choosing your settings, or click Cancel to undo your
changes.
3.2.2 Global Address
Use the Global Address screen for Network Address Translation (NAT), a process that
provides internal to external IP address mapping. If your gateway is configured to
retrieve an IP address dynamically, you will not need to use this function. On this page,
you can set up NAT (Network Address Translation) to provide internal-to-external IP
address mappings.
Default Public IP
If your gateway is configured to retrieve an IP address dynamically, you will only see
the default WAN IP address (specified in the Setup screen); you will not see the
sections below.
External-Internal Address Mapping
This section allows you to define global IP addresses for your LAN network. Use the
lines in the table to list up to six static, external IP addresses provided by your ISP.
Click Apply when you finish entering the IP addresses, or click Cancel to undo your
changes.
22
Page 23

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.2.3 Wireless
Use this screen to configure your gateway for wireless access. Note that the Wireless
settings are divided into Wireless Radio, Wireless Security and Wireless Status.
Radio Setting:
Use this screen to configure your Gateway for wireless access. If you do not know how
to change it, please leave the default value, as following table lists.
23
Page 24

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Mode:
Select the Wireless Mode your router support. It support three modes: 802.11B,
802.11G, and MIXED which supports both 802.11B and 802.11G.The default value is
MIXED
ESSID:
Unique identifier for the Extended Service Set which is shared by client stations in an
infrastructure association, such as WLAN-test. It is case-sensitive and cannot exceed
32 characters.
Channel:
Specifies the bandwidth which the wireless radio operates. AP and the client stations
that is associated work in one of channels from 1 to 14.
Beacon Interval:
Time interval between beacons broadcast by the Access Point (AP).
RTS Thresold:
Minimum size of data frames above which Request-To-Send (RTS) protocol is used.
RTS helps prevent data collision from hidden nodes.
Fragmentation Threshold:
For efficiency in high-traffic situations, large files are split into fragments. This
24
Page 25
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
parameter specifies the fragment packet size.
DTIM Interval:
Number of beacon intervals between successive Delivery Traffic Indication Maps
(DTIMs).
Preamble Type:
Shows the length of preamble, either Short (72 bits) or Long (144 bits).
Authentication Type:
Type of authentication used in your wireless network.
Enhanced Security:
Option to enable additional security measures, like hiding your Service Set Identifier
(SSID) or blocking unspecified SSIDs.
Peer AP MAC Address:
When Wireless Distribution System is enabled, wirelessly connect Access Points
using several MAC Addresses of PC cards, so that you can extend a wired
infrastructure to locations where cabling is not available.
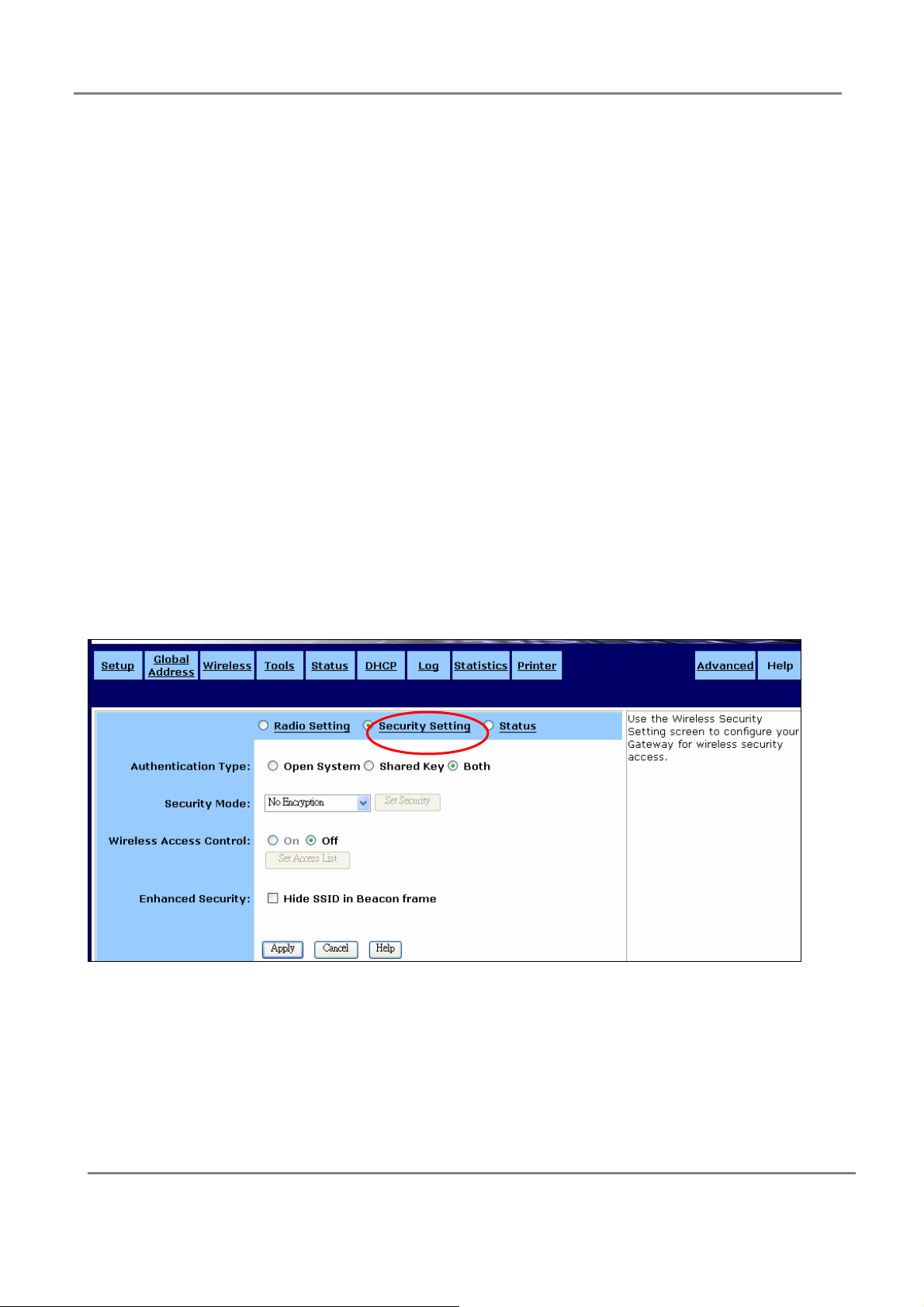
Security Setting: Use this screen to configure your Gateway for wireless security
access.
Authentication Type:
Select any of Open System, Shared Key or Both authentication algorithm which can
be supported by the Access Point.The default value is Both.
Security Mode:
25
Page 26
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
This is regard to the security for wireless access, please select one of the security
mode. The default value is No Encryption
Wireless Access Control:
If you enable Wireless Access Control, then click Set Access List to launch the
Wireless Control List window.
Enhanced Security:
If you choose Enable, you can choose to Hide SSID (Service Set Identifier) in Beacon
frame.
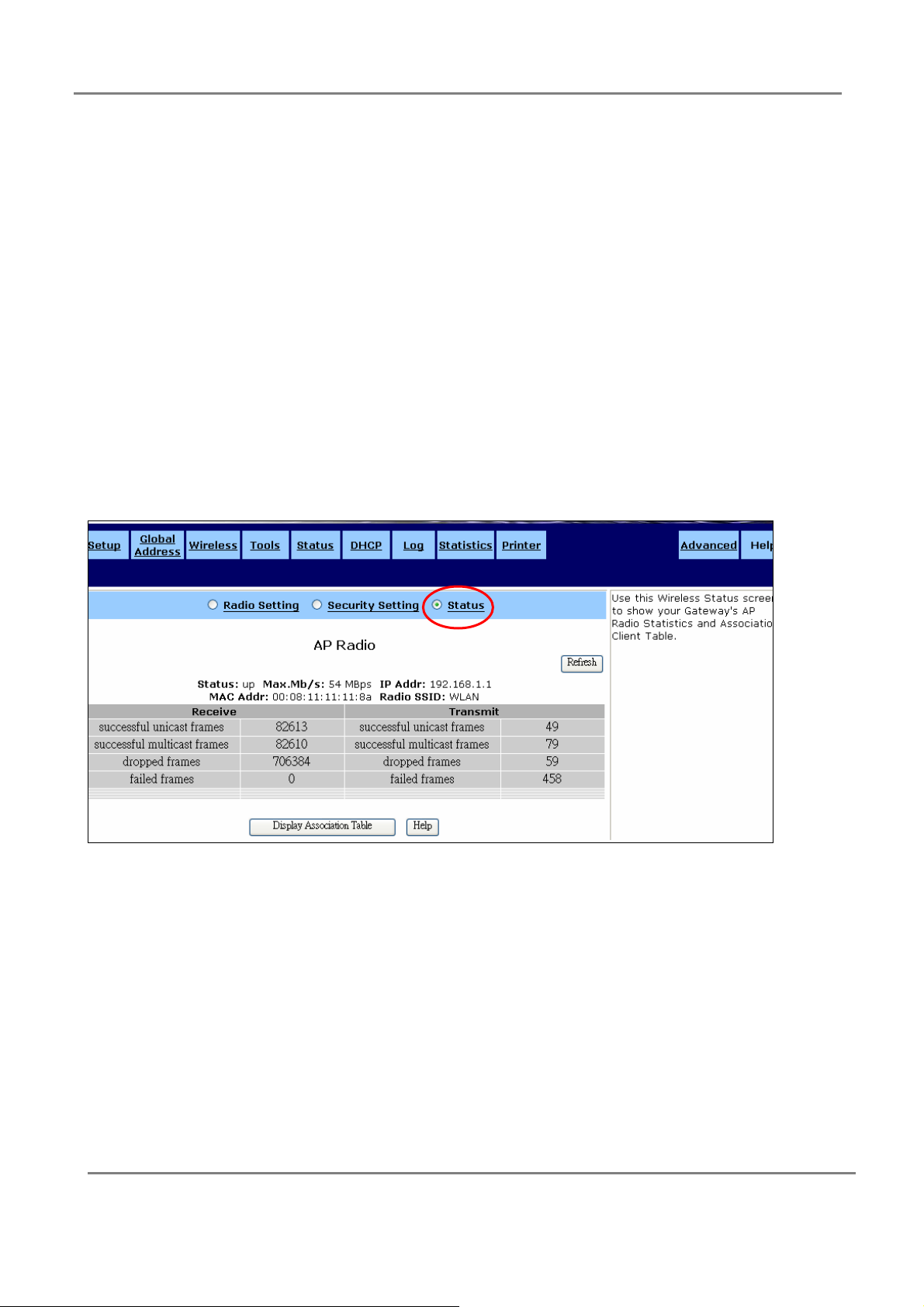
Status: This screen is to show your Gateway's AP Radio Statistics and Association
Client Table.
26
Page 27

3.2.4 Tools:
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Change Password:
Change the administrative password for your WLAN Router.
Backup Settings:
Backup the current settings to your local disk
Restore Factory Defaults:
Restore the factory default settings.
Reset Gateway:
Restart your device or reset the hardware.
Upgrade Firmware:
Upgrade firmware image file that you download from the gateway ‘s website.
27
Page 28
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
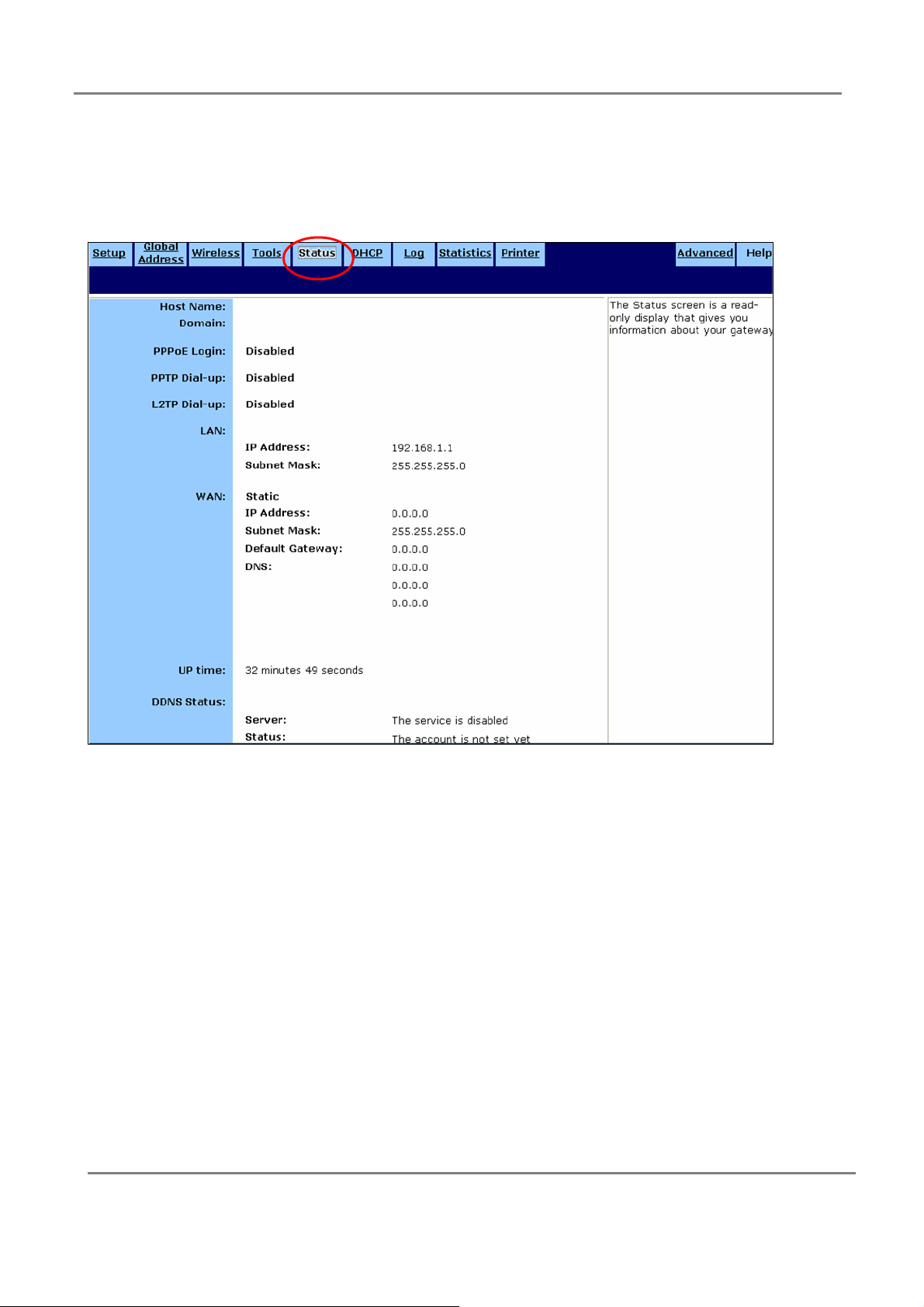
3.2.5 Status:
This page is a read-only display that gives you the information about the gateway.
28
Page 29
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
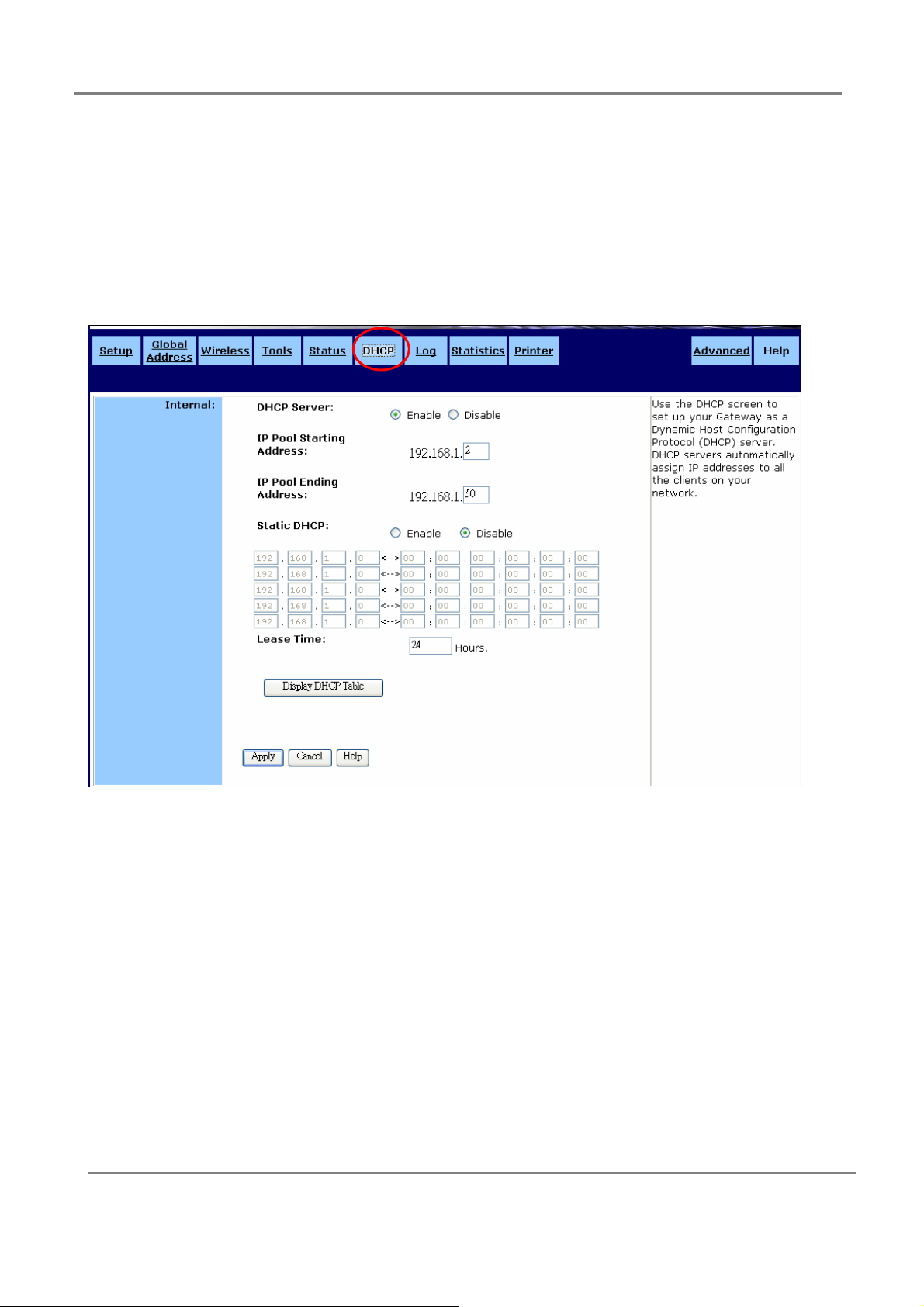
3.2.6 DHCP:
Use the DHCP screen to set up your gateway as a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) server. DHCP servers automatically assign IP addresses to all the
clients on your network.
DHCP Server
If you choose to enable DHCP, make sure there is not already a DHCP server on your
network.
If you don't enable DHCP, you'll need to manually configure an IP address for each computer on
your network. If you do enable DHCP, make sure that each computer is configured to retrieve an IP
address automatically.
IP Pool Starting Address/IP Pool Ending Address:
Specify the IP Pool Starting Address to designate the first IP address that can be
assigned to a computer on the network. Similarly, specify the IP Pool Ending
Address to designate the last IP address that can be assigned.
29
Page 30

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
For example, if you choose 10.10.10.51 as the starting address and 10.10.10.100 as the ending
address, the DHCP server will assign addresses to network clients that are between 10.10.10.51 and
10.10.10.100.
Static DHCP:
This is for static mapping of MAC address and IP address assigned by DHCP. Input
the MAC address and corresponding IP address into the boxes for each mapping
entry.
The IP address in mapping table should be within DHCP pool, otherwise that entry is
invalid.
Lease Time
This is the lease time assigned if the computer (DHCP client) requests one. If
it set to 0, the life time of IP assigned by the gateway for client computer will
be infinity. Default lease time is 24 hours.
Display DHCP Table
The DHCP Active IP Table lists information about the computers that have
been assigned IP addresses by the DHCP server.
3.2.7 Log:
On this page you can view log files that record the access activity of LAN and WAN
clients.
30
Page 31

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.2.8 Statistics:
On this page displays statistics data for LAN , WAN and AP ports.
31
Page 32
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
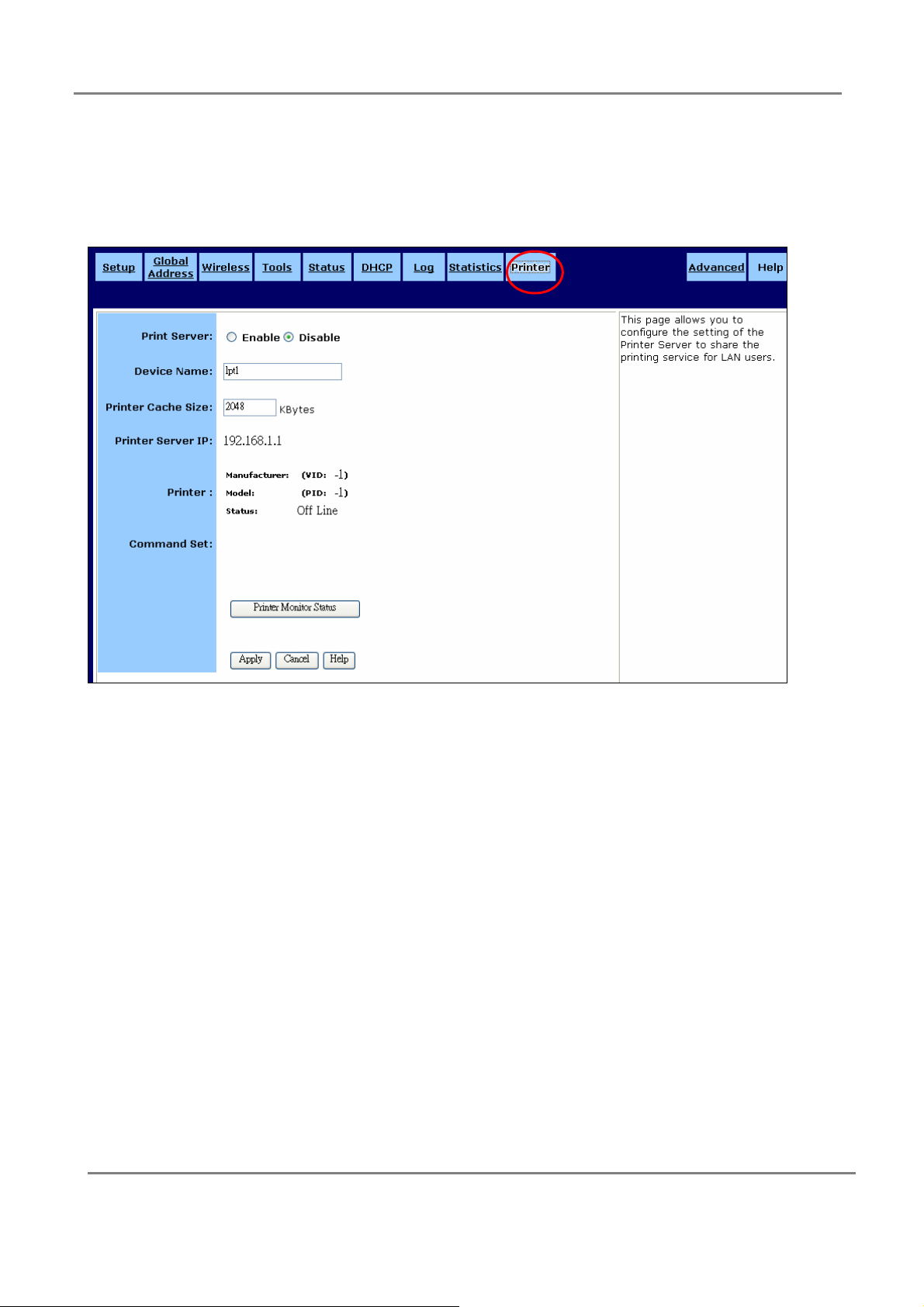
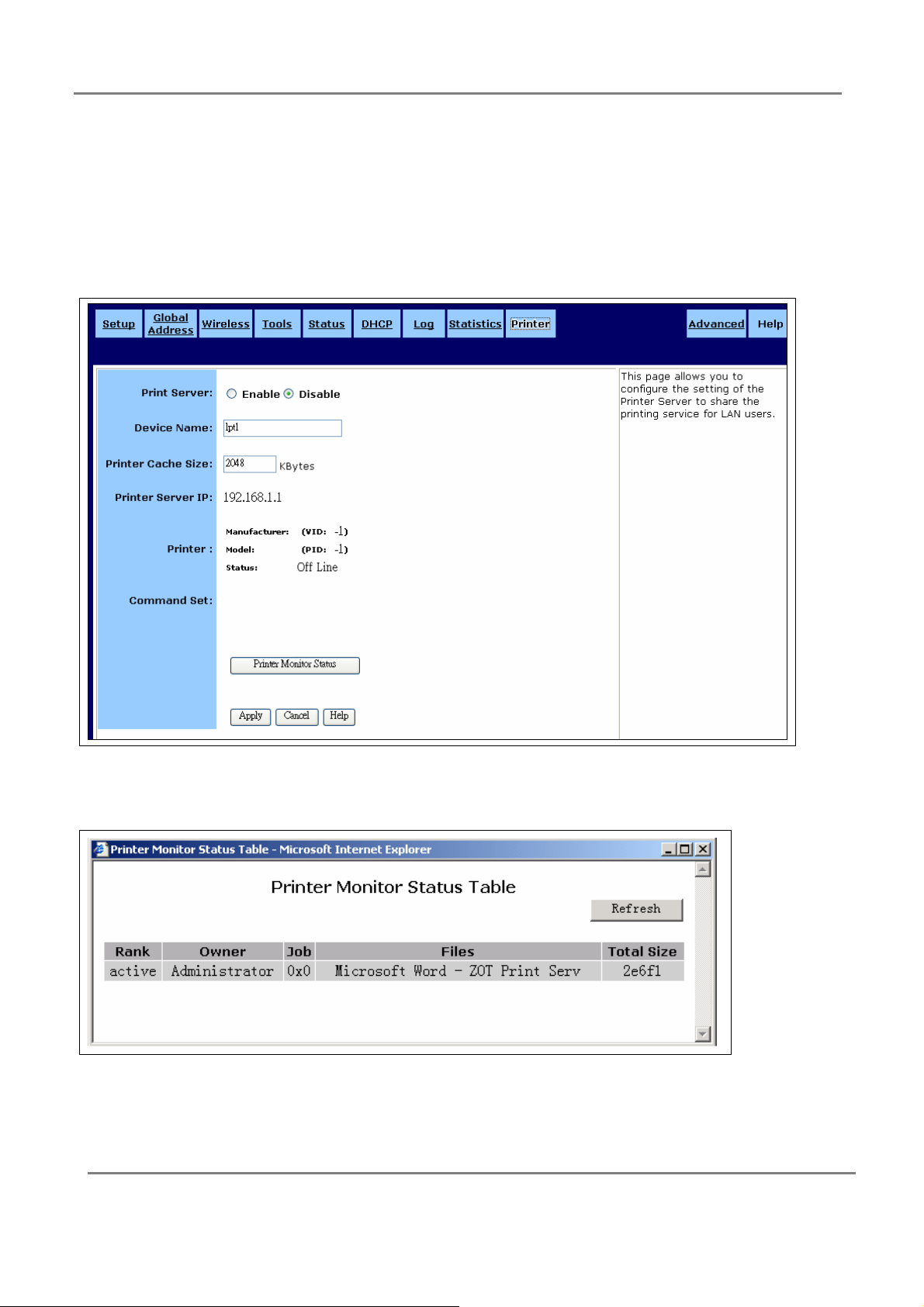
3.2.9 Printer:
This page allows you to configure the setting of the Printer Server to share the printing
service for LAN users.
Print Server:
You may choose to Enable or Disable the Print Server.
Device Name:
The name of the print server hardware used for identification purposes. Client PCs
should use this name as queue name for printing.
Printer Cache Size:
This field used for system evaluation. If the printer does not work properly, you may
augment this value, e.g. 4096, 8192. Suggest use the same value as your printer
supported.
Printer Server IP:
This field shows the Print Server IP, which equals LAN IP.
32
Page 33

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Printer:
This field shows the Manufacturer, VID(Vendor ID), Model, PID(Product ID), Status of
current Printer, which connected to the device's USB port.
Command Set:
This field shows you Command Set of the printer. When the printer connected with the
print server, it will be shown on it.
Printer Monitor Status:
Click Printer Monitor Status to launch Printer Monitor Status Table window. In this
screen the table lists all printing tasks queue. Each task has the information of Rank,
Owner, Job, Files and Total Size.
33
Page 34

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.2.9.1. Use LPD network print in window2000/window XP
3.2.9.1.1 Host setup:
Add New Printer’s driver (from the printer manufacture); If it was a new printer type (no
install in local host), please select “Control Panel / Printers / Add Printer” and complete this
procedure:
Setup procedure as below:
1.select local printer without detecting local printer;
34
Page 35
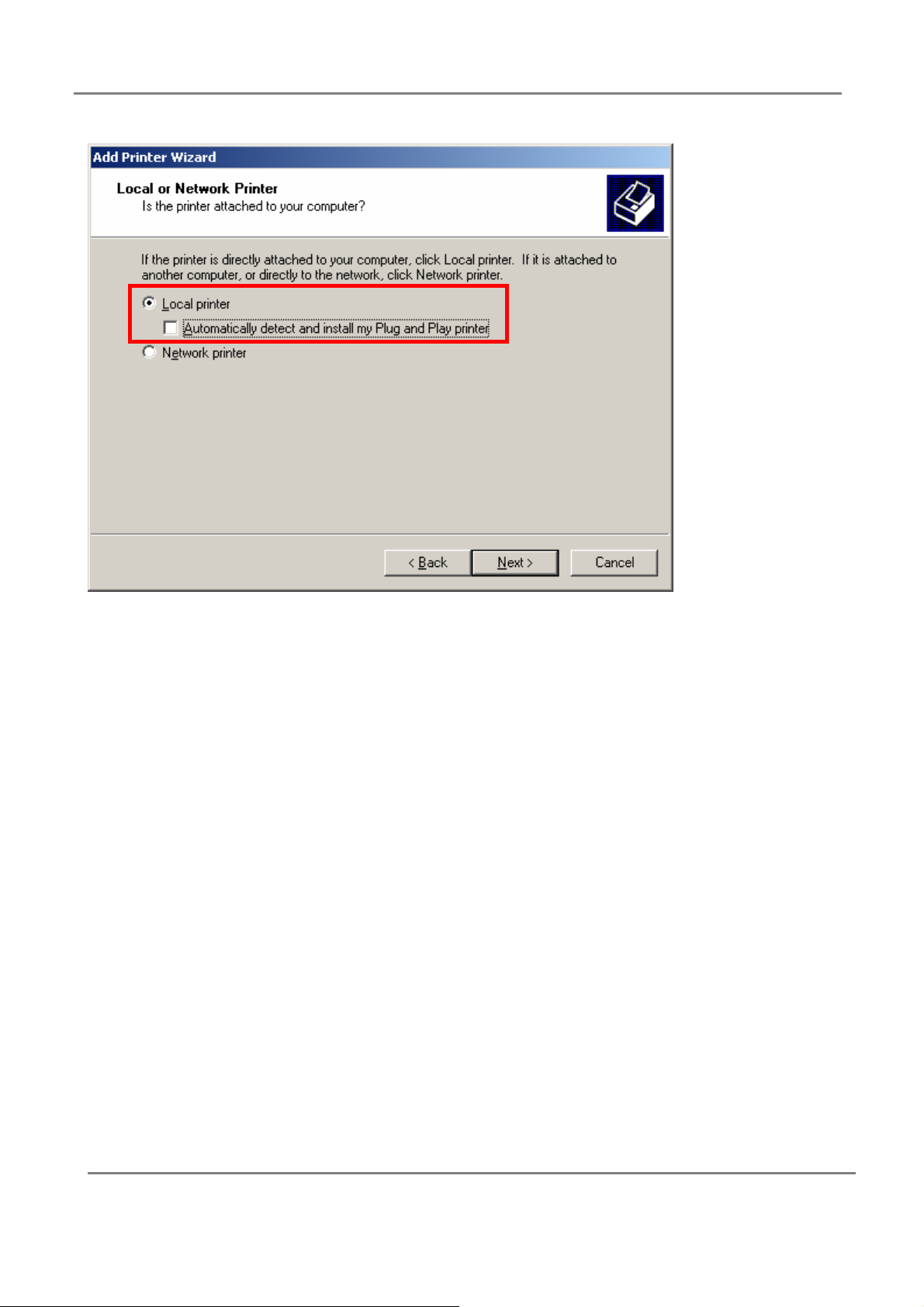
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
2.the add printer wizard screen will appear, select my computer;
3.in available port, select LPT1;
35
Page 36

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
4.Select the appropriate printer manufactory;
5.Select printer type;
36
Page 37
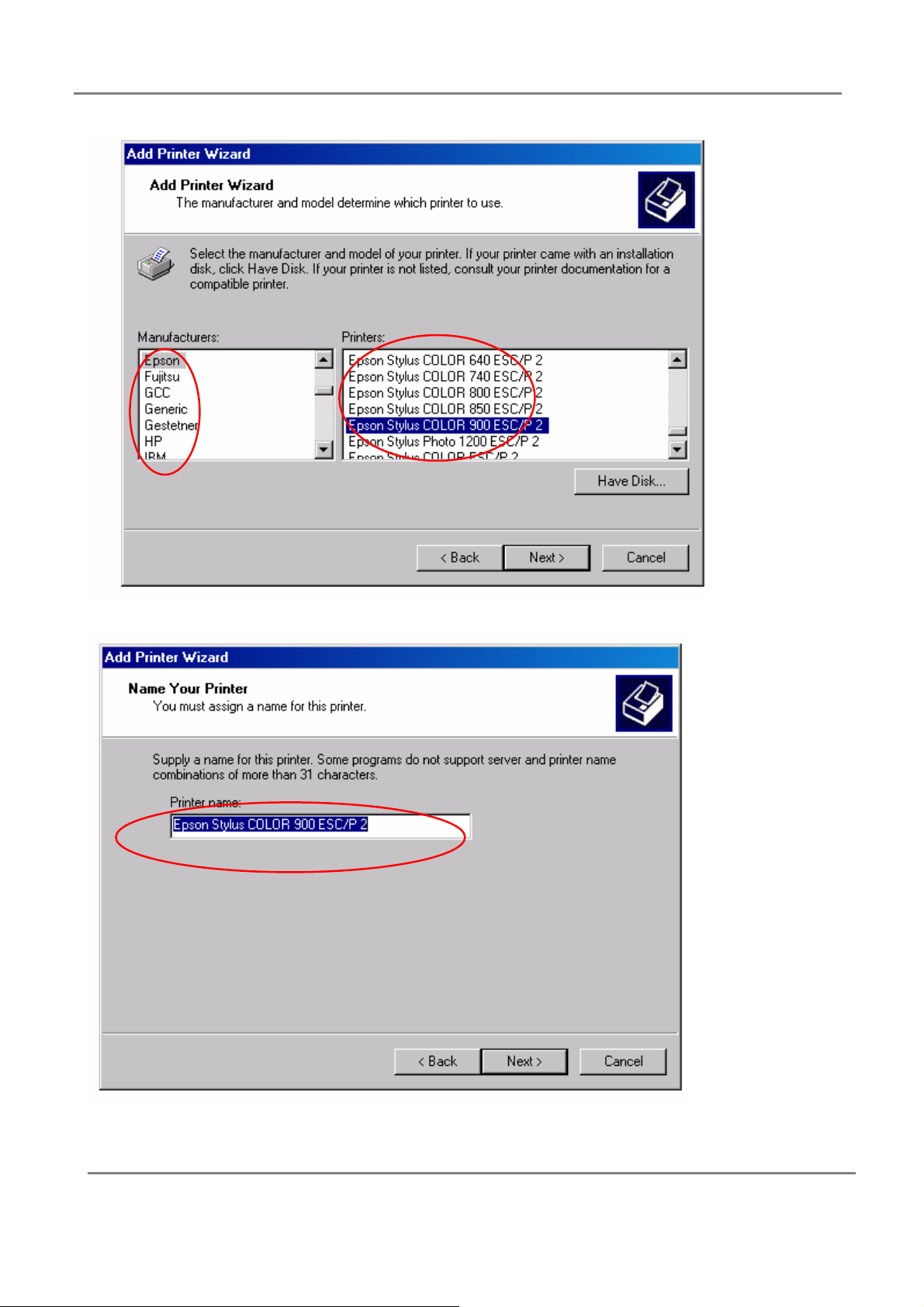
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
6.Type printer name or use default;
37
Page 38
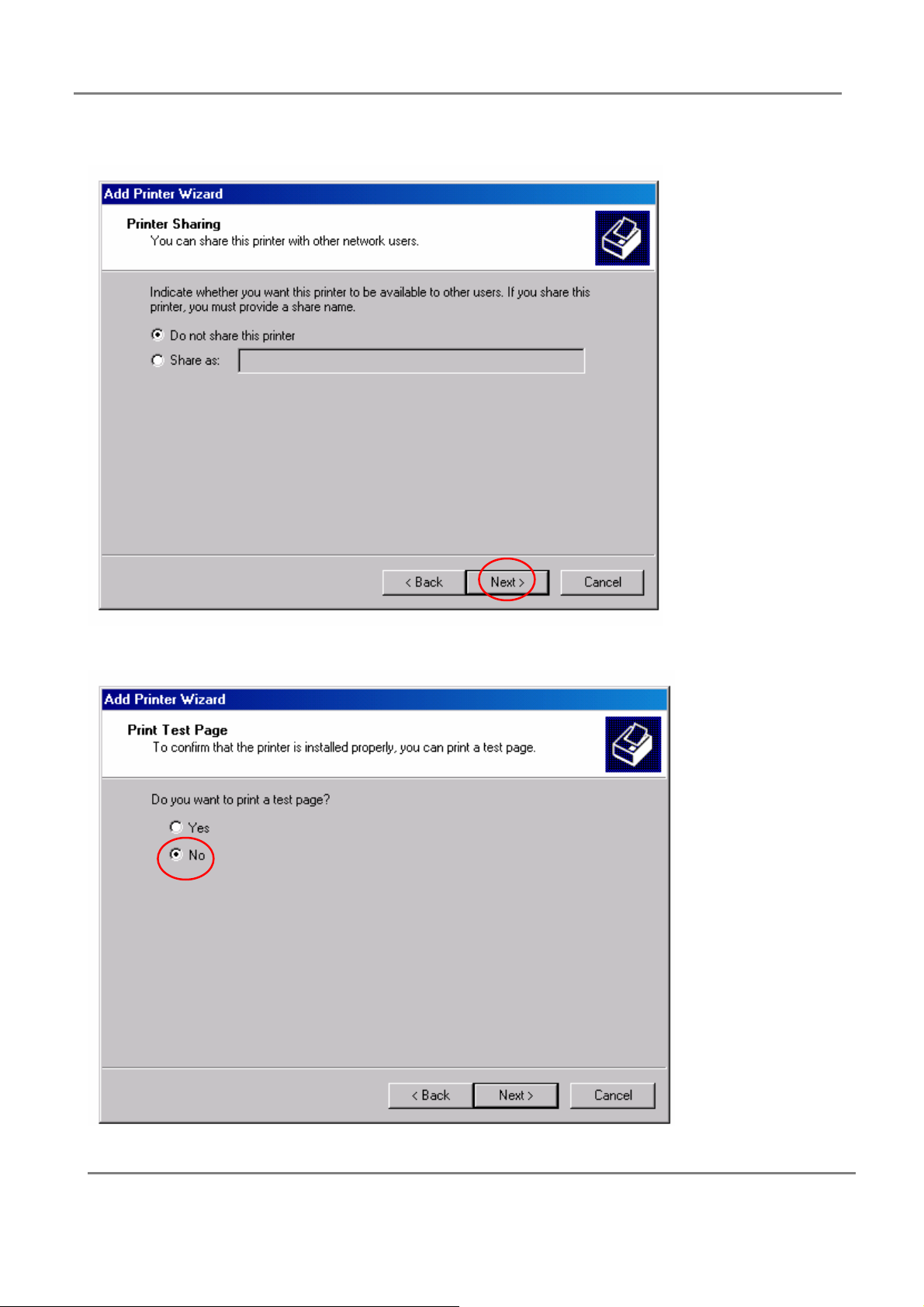
7.In printer sharing, click next;
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
8.In printing testing page, select “no”;
38
Page 39

9.Done;
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
39
Page 40
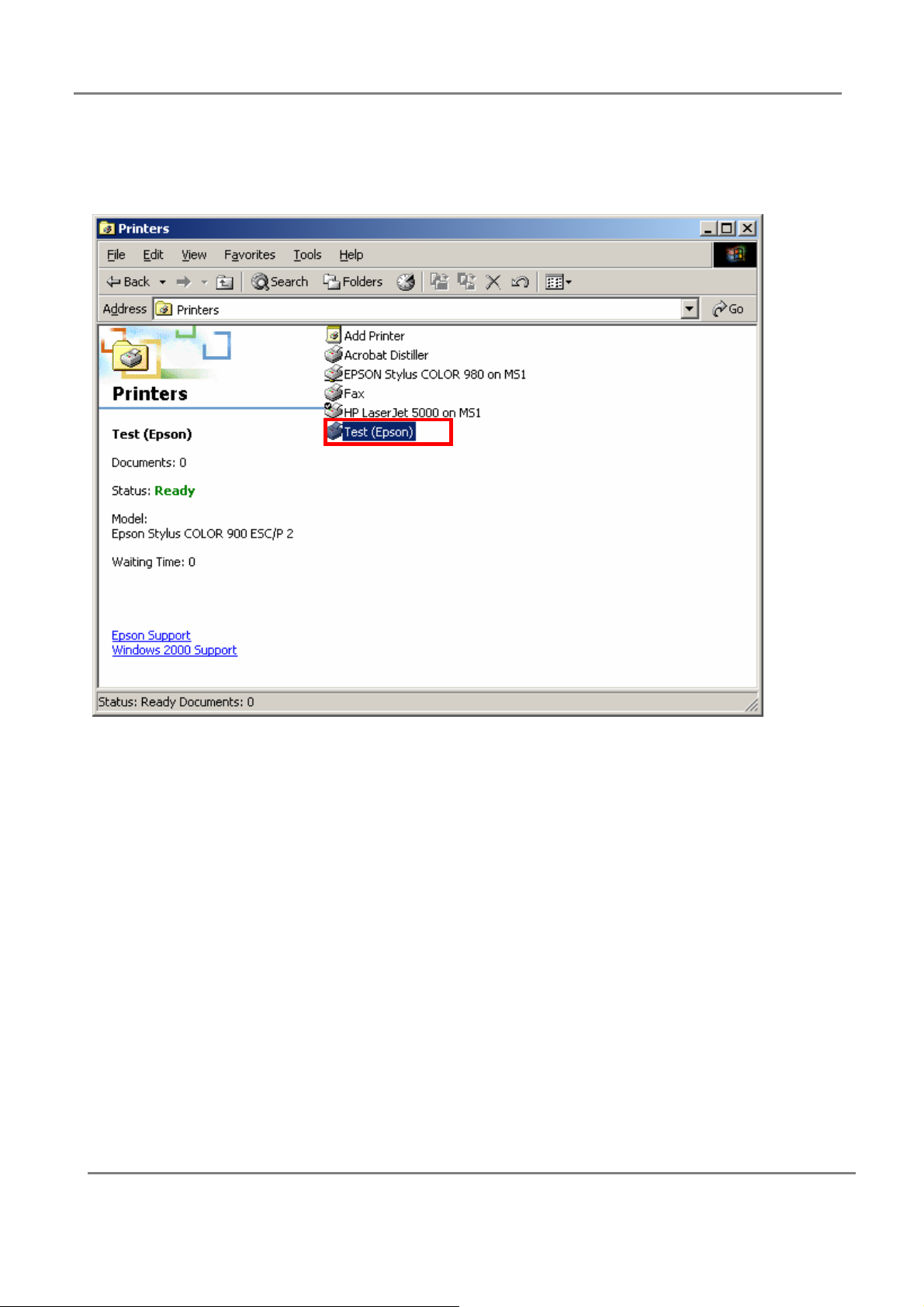
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Configure Port properties:
1.Select printer that you want to configure( setting by step 1 at local printer);
2.Select “properties”;
40
Page 41

3.Select “port”;
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
41
Page 42

4.Select “add port”;
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
5.In available ports, select “Standard TCP/IP port”, done;
42
Page 43

6.Select “add port”;
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
7.Enter network print server “IP Address” and name new port or default;
8.Finish;
43
Page 44
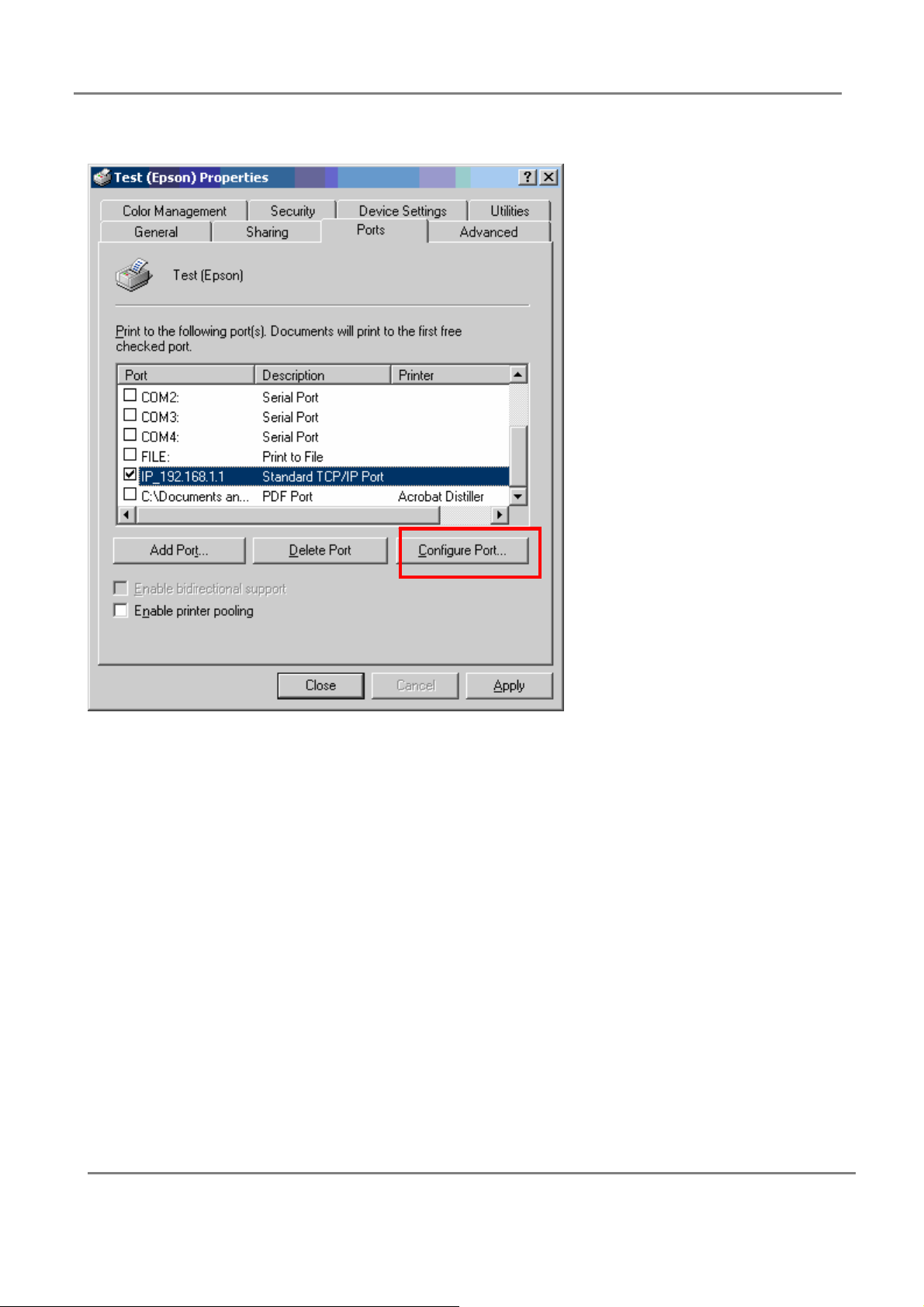
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
9.Select “properties”, and modify port setting;
44
Page 45
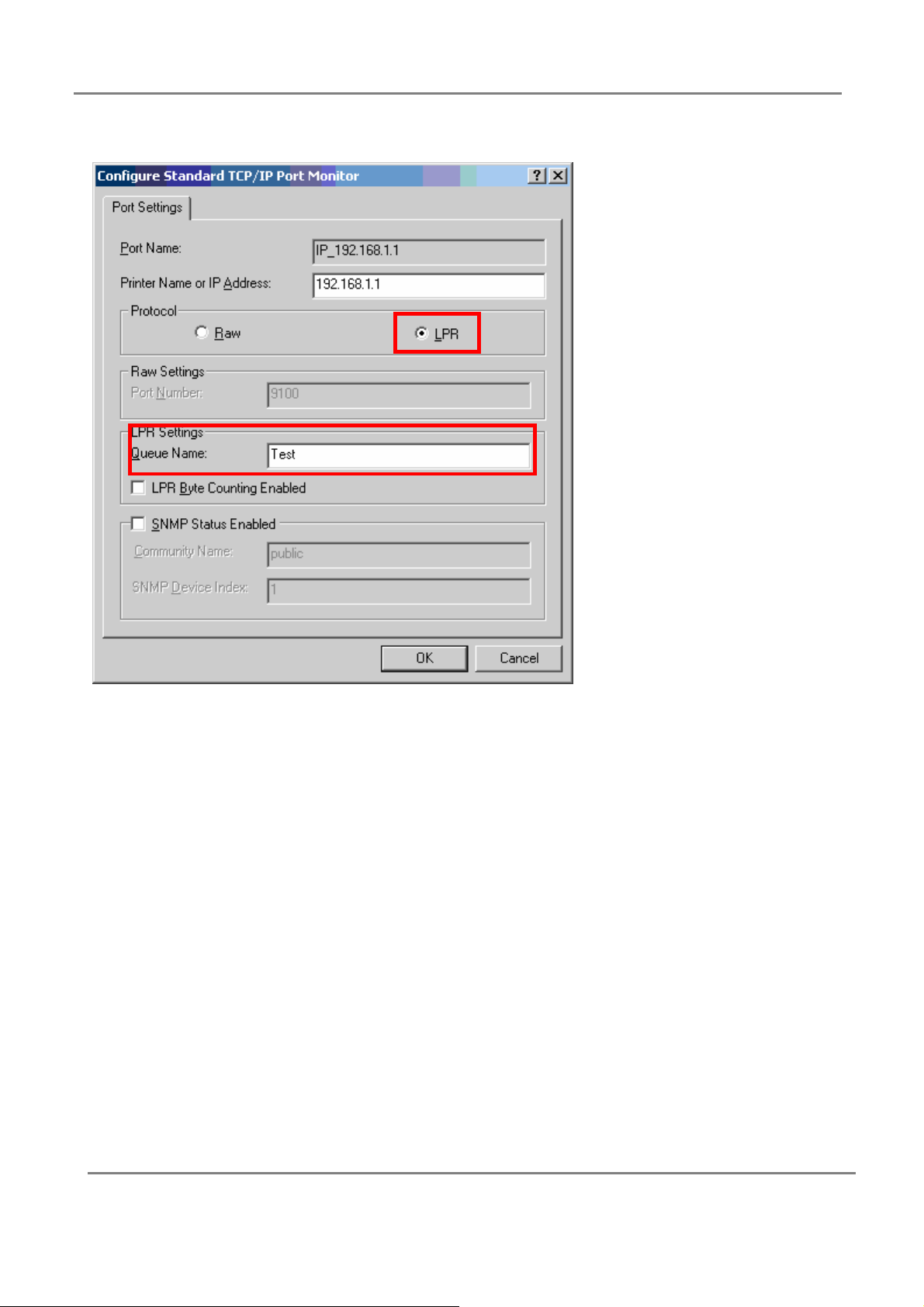
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
10.Enter you network print queue name and set port is LPR
11.Done;
45
Page 46
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.2.9.1.3 LPD Server setup
Use Web Page setting LPD server;
1.Enable the Print server
2.Enter the Device Name
The setting of Device Name must be the same as the Queue Name in host; e.g, Test, here
3.Finish.
Monitor queue list:
2. Support printer list:
ESPON Stylus C41, HP Deskjet 3820, Canon S520, Epson stylus photo 830, Epson stylus
Color 860
46
Page 47

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.2.9.2 Use LPD network print in window98/window ME
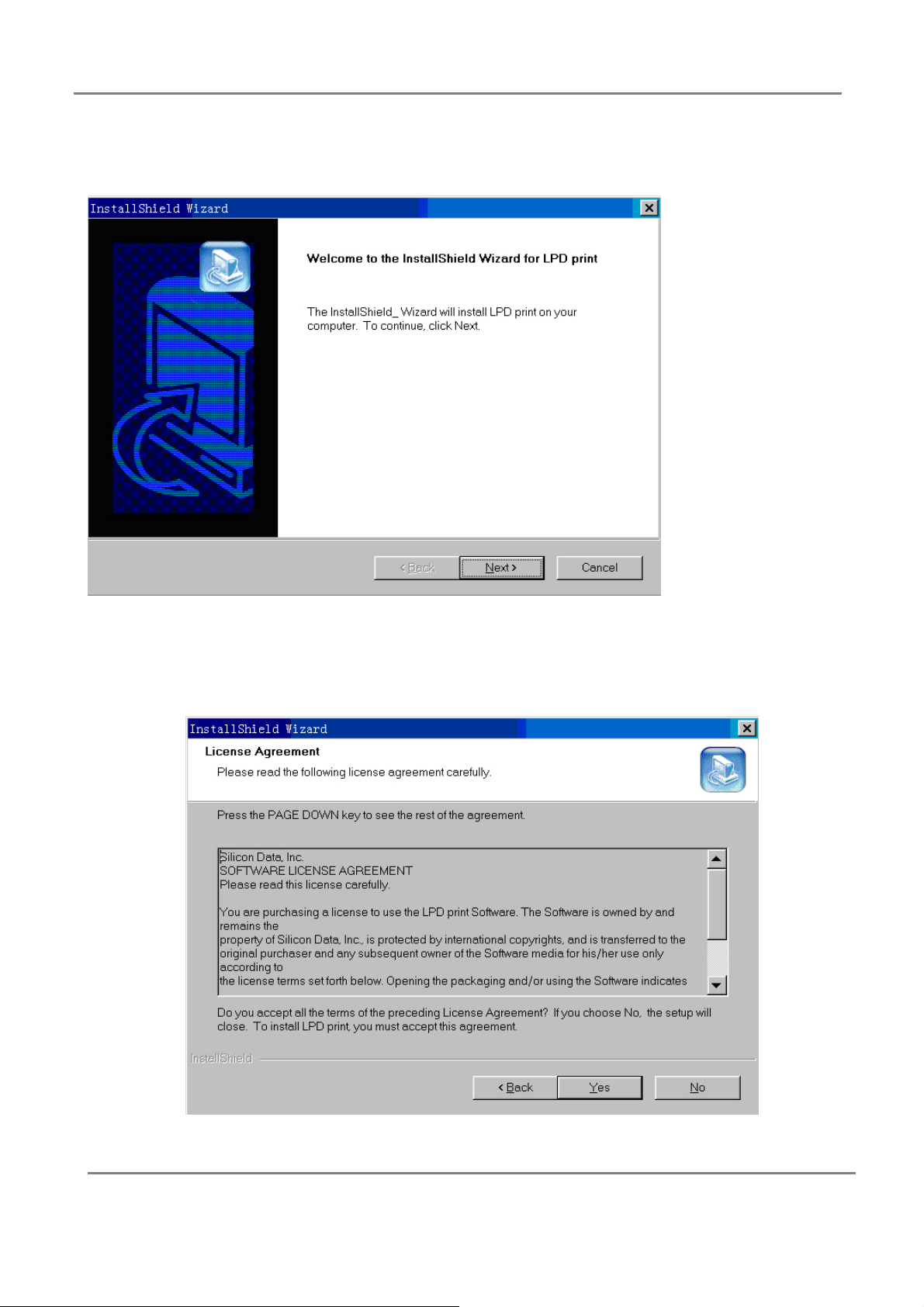
3.2.9.2.1Installation
Step 1. Double click the setup.exe in the CD.
47
Page 48
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Step 2. In the following step, click the “Next”.
Step 3. If you accept the license agreement, click “Yes”.
48
Page 49
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
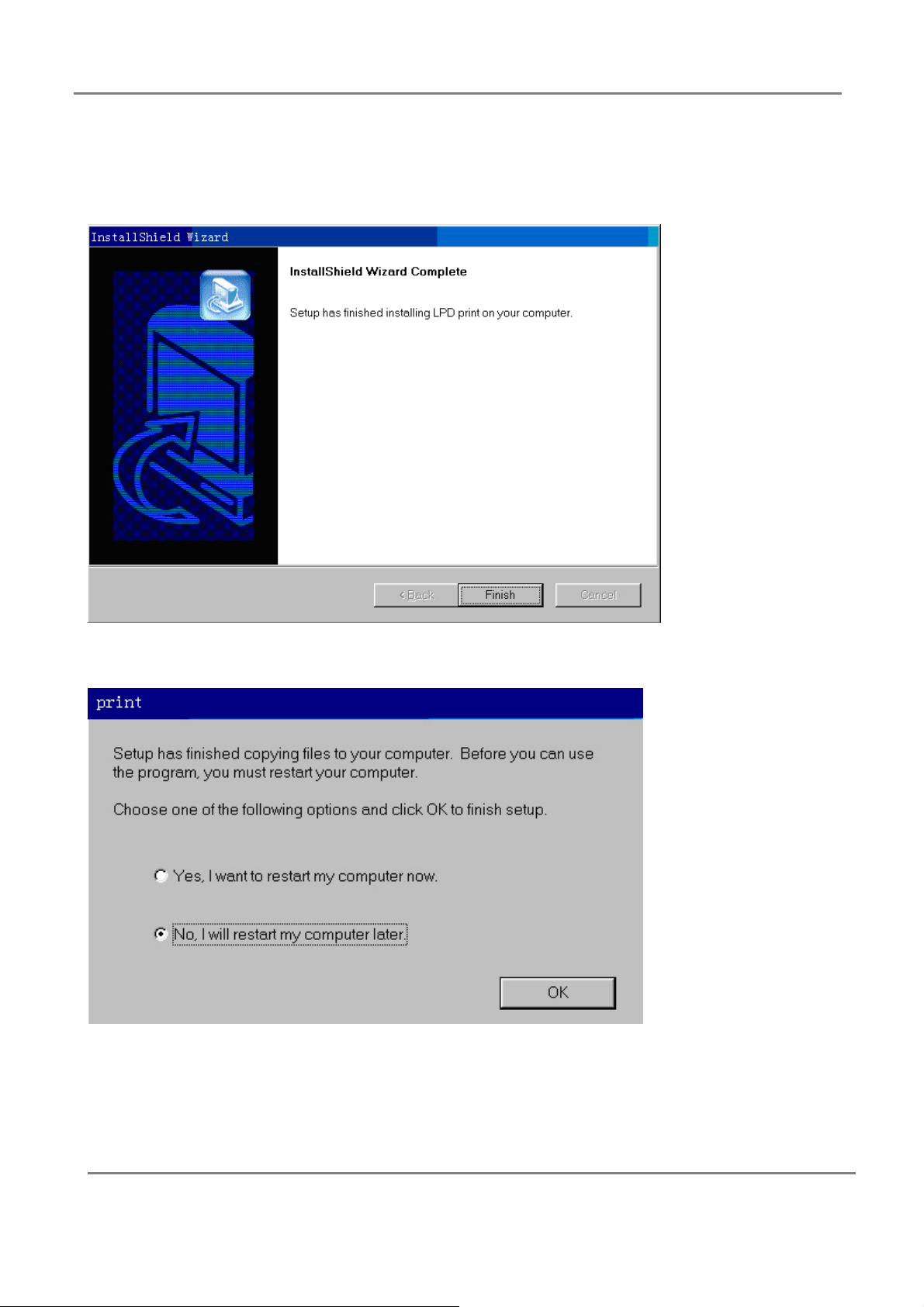
Step 4. Then click “Next”, after copying file, the following window will be displayed.
Step 5. Click “Finish”, and select “Yes”, I want to restart my computer now” to complete
the installation.
Step 6. Once you reboot system, the inst allation will be completed. And a detailed LPD print
setup manual can be found in \Program Files\LPR Clent\LPD Port Win98.
49
Page 50

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
50
Page 51
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.2.9.2.2 Configuration
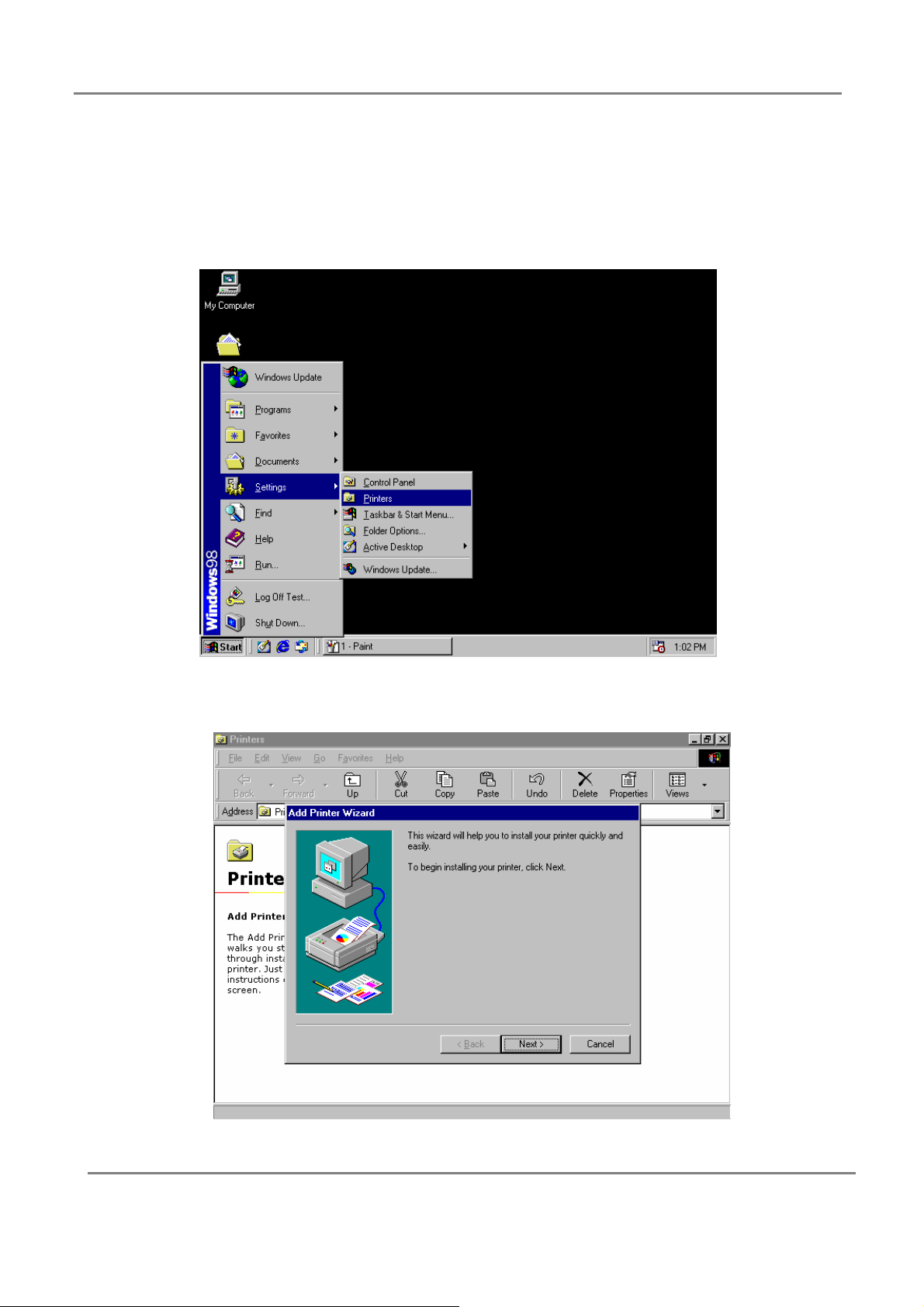
Installing the driver of your printer connected to the Printer Server gateway.
Step 1. Go to “Printers” by clicking the Start button, selecting Settings, and clicking
Printers.
Step 2: Click the “Add printer” and click “Next” in the “Adding printer wizard”
Window”.
51
Page 52
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Step 3: Select the “Local printer” and click the “next”.
Step 4: Select the Manufacturer and insert corresponding printer driver disk and
click “Install from disk…
Step 5: install printer the driver file
Step 6: Select the compatible printer, and click “Next”.
52
Page 53

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Step 8: Click “Finish”
Step 9: Click “OK” to complete the installation.
3.2.9.2.3 Printer Server Port configuration
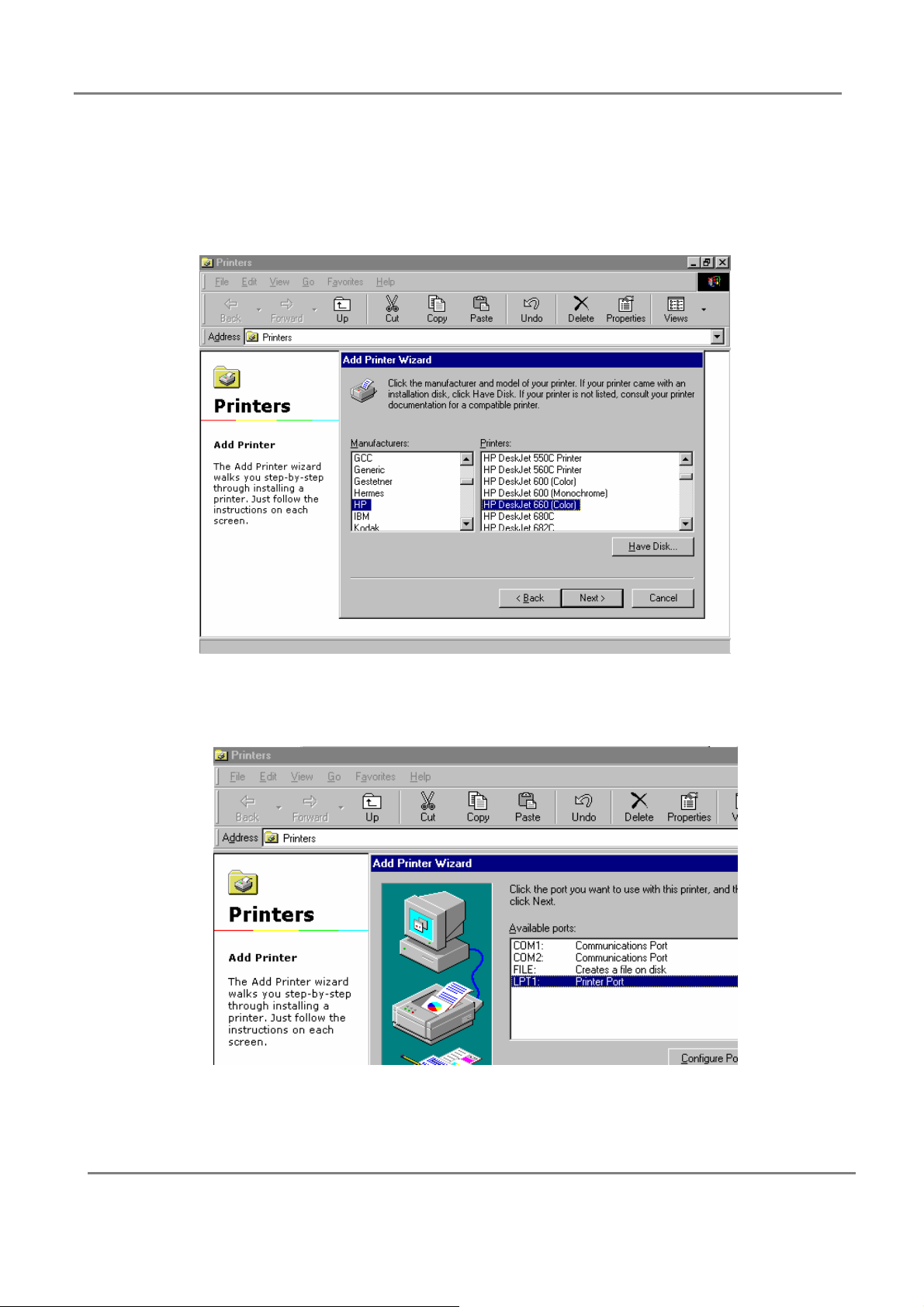
Step 1: Right click on the printer you just added, and click the “Properties”.
Step 2: Select the “Detail…” tab on the window pop up.
Step 3: Click the “Add port…”
53
Page 54
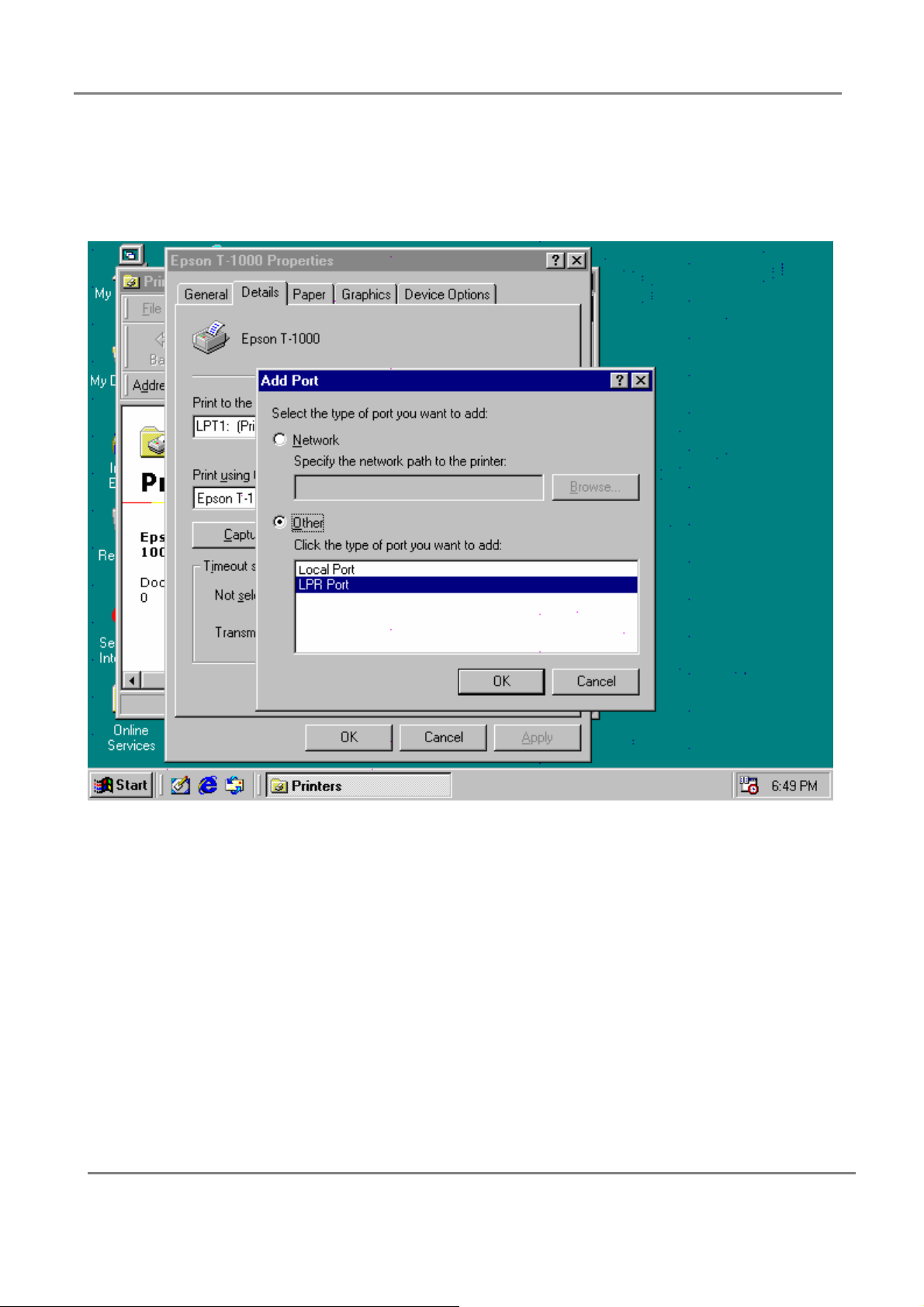
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Step 4: Select the “Others…” option from the “Adding port” window,
choose the “LPR port” item in list, then click “OK”.
54
Page 55

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Step 5: You can choose a favorite name for this port, but the IP address of the
printer server (gateway) and the printer name must match the configuration on your
gateway.
Step 6: Then the port you added is shown in the port list. Please click “Apply” and then
click “OK”.
Step 7: After you clicked the “OK”, the installation is completed.
55
Page 56
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3 Advanced Setup
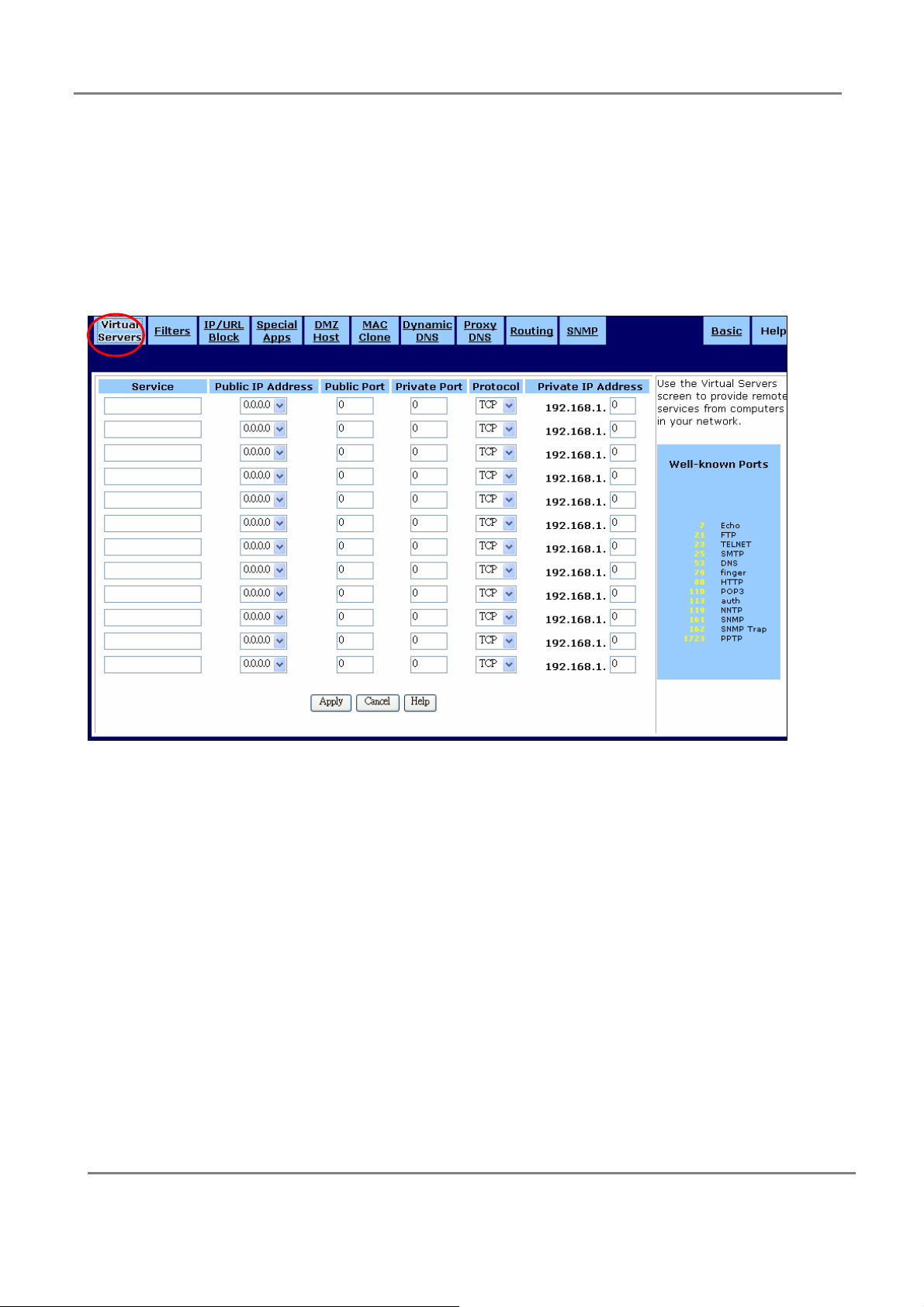
3.3.1 Virtual Servers
This provides remote services from computers in your network by virtual servers.
56
Page 57

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.2 Filters
Use this screen to create and apply filters that can selectively allow traffic to pass
in and out of your network. If no filters are enabled, all traffic will be blocked.
57
Page 58

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.3 IP/URL Block
Use the IP/URL Block screen to create and apply filters to selectively block traffic from
specific IP addresses or specific domain name from passing in and out of your
network.
58
Page 59

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.4 Special Apps(Special Applications)
Use the Special Apps screen to allow certain ports to communicate with computers
outside your network. This feature may be necessary for multi-session applications like
online gaming and video conferencing.
59
Page 60

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.5 DMZ Host
Use the DMZ Host screen to expose one or more computers on your network to the
internet. This feature is often used for online games that require unrestricted two-way
communication. Note that the computer you designate won't have any firewall protection.
60
Page 61

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.6 MAC Clone
If your ISP restricts service to PCs only, use the Mac Clone feature to copy a PC Media
Access Control (MAC) address to your Gateway. This procedure will cause the
gateway to appear as a single PC, while allowing online access to multiple
computers on your network.
3.3.7 Dynamic DNS
Use the Dynamic DNS screen to configure the router to retrieve an IP address from a
dynamic DNS provider. These providers allow you to associate a static hostname with
a dynamic IP address. This allows you to connect to the Internet with a dynamic IP
address and use applications that require a static IP address.
61
Page 62

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.8 Proxy DNS
Use the Proxy DNS screen to map a domain name to its server IP address. This
feature acts as a DNS server for the internal and DMZ networks, allowing you to
connect to local machines without using an external DNS server. This simplifies
network configuration and management.
62
Page 63

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.9 Routing
Use the Routing screen to configure the routing features. It includes static
routing and dynamic routing.
63
Page 64

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
3.3.10 SNMP
Use the SNMP screen to edit the Agent information, configure the trap receiver's IP
address and Community Names for the SNMP feature. Using SNMP, you can control
and monitor the network in a simple way.
64
Page 65

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
4. Glossary
Ad-Hoc Mode
An Ad-hoc integrated wireless LAN is a group of computers, each has a Wireless LAN
adapter, Connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad hoc wireless LAN is applicable at
a departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operation.
BSS ID
A specific Ad hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS must be
configured with the same BSS ID.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP is a protocol for dynamically assigning IP addresses to networked computers. With
DHCP, a computer can automatically be given a unique IP address each time it connects to
a network—making IP address management an easier task for network administrators.
When a computer logs on to the network, the DHCP server selects an IP address from a
master list and assigns it to the system.
DMZ Host (De-Militarized Zone Host)
DMZ is the portion of a private network that is visible through the network’s firewalls. DMZ
Host allows a local computer exposed to the Internet. Therefore, an incoming packet will be
checked by Firewall and NAT algorithms in the router then pass to the DMZ host when
packet is not sent by hacker and is not limited by Virtual Server list. Besides, there are
some IP protocols that do not have port number information. There is no way to use Virtual
Server setting to forward incoming packet. Thus, DMZ host is the way to forward such kind
of packets. If you try to enable DMZ host and setup Virtual Server, the precedence is Virtual
Server and then DMZ. For example, the incoming packet will be checked with Firewall rules,
Virtual Server rules and
then DMZ host.
DSSS (Direct-Sequencing Spread-Spectrum)
DSSS operate over the radio airwaves in the unlicensed ISM band (industrial, scientific,
medical). DSSS uses a radio transmitter to spread data packets over a fixed range of
frequency band.
Encryption
It’s a security method that applies a specific algorithm to data in order to alter the data
appearance and prevent other devices from reading the information.
Firewall
A firewall is a device that sits between your computer and the Internet that prevents
unauthorized access to or from your network. A firewall can be a computer using firewall
65
Page 66

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
software or a special piece of hardware built specifically to act as a firewall. In most
circumstances, a firewall is used to prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing
private networks or corporate LAN’s and Intranets.
A firewall watches all of the information moving to and from your network and analyzes
each piece of data. Each piece of data is checked against a set of criteria that the
administrator configures. If any data does not meet the criteria, that data is blocked and
discarded. If the data meets the criteria, the data is passed through. This method is called
packet filtering.
A firewall can also run specific security functions based on the type of application or type of
port that is being used. For example, a firewall can be configured to work with an FTP or
Telnet server. Or a firewall can be configured to work with specific UDP or TCP ports to
allow certain applications or games to work properly over the Internet.
Firmware
Program that is inserted into programmable read-only memory (programmable read-only
memory), thus becoming a permanent part of a computing device.
Fragmentation Threshold Value
Indicates how much of the network resources are devoted to recovering packet errors. The
value should remain at its default setting of 2,432. If you experience high packet error rates,
you can decrease this value but it will likely decrease overall network performance. Only
minor modifications of this value are recommended.
Fragmentation
Breaking a packet into smaller units when transmitting over a network medium that cannot
support the original size of the packet.
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IEEE 802.11b/g standard
The IEEE 802.11b/g Wireless LAN standards subcommittee formulates standards for the
industry. The objective is to enable wireless LAN hardware from different manufacturers to
communicate.
Infrastructure Mode
A client setting provides connectivity to an Access Point. As compared to Ad-Hoc mode
where PCs communicate directly with each other, clients set in Infra structure m o de all pass
data through a central Access Point. The Access Point not only mediates Wireless network
traffic in the immediate neighborhood but also pro-vides communication with the wired
network. An integrated wireless and wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure
66
Page 67

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
configuration. Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless access to central
database, or wireless application for mobile workers.
LAN (Local Area Network)
Local Area Networking (LAN) is the term used when connecting several computers
together over a small area such as a building or group of buildings. LAN’s can be
connected over large areas. A collection of LAN’s connected over a large area is called a
Wide Area Network (WAN). A LAN consists of multiple computers connected to each other.
There are many types of media that can connect computers together. The most common
media is CAT.5 cable (UTP or STP twisted pair wire.) On the other hand, wireless networks
do not use wires; instead they communicate over radio waves. Each computer must have a
Network Interface Card (NIC), which communicates the data between computers. A NIC is
usually a 10Mbps network card, or 10/100Mbps network card, or a wireless network card.
Most networks use hardware devices such as hubs or switches that each cable can be
connected to in order to continue the connection between computers. A hub
simply takes any data arriving through each port and forwards the data to all other ports. A
switch is more sophisticated, in that a switch can determine the destination port for a
specific piece of data. A switch minimizes network traffic overhead and speeds up the
communication over a network.
NAT (Network Address Translation)
For a computer to communicate with other computers on the Internet, it must have an IP
address. An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique 32-bit number that identifies the
location of your computer on a network. However, with the explosion of the Internet, the
number of available IP addresses is simply not enough.
This is where NAT comes to the rescue. Network Address Translation allows a single
device, such as a router, to act as an agent between the Internet (or “public network”) and a
local (or “private”) network. This means that only a single, unique IP address is required to
represent an entire group of computers.
Roaming
The ability to use a wireless device is able to move from one access point range to another
without losing the connection.
RTS/CTS Threshold Value
It should remain at its default setting of 2,347. A preamble is a signal used to synchronize
the transmission timing between two or more systems. A series of transmission pulses is
sent before the data to indicate that someone is about transmit data. This ensures that
systems receiving the information correctly when the data transmission starts.
67
Page 68

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Shared Key
It’s when both the sender and recipient share a secret key. Both units use this key for an
extended length of time, sometimes indefinitely. Any eavesdropper that discovers the key
may decipher all packets until the key is changed.
Signal Strength
The signal level indicates the strength of the signal as received at the wireless network
interface.
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
It’s the unique name shared among all points in a wireless network. The SSID must be
identical for all points in the network. It is case sensitive and must not exceed 32
characters.
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) with Internet Protocol (IP). The main internetworking
protocol used in the Internet.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
UDP provides a procedure for application programs to send messages to other programs
with a minimum of protocol mechanism. The protocol is transaction oriented, and delivery
and duplicate protection is not guaranteed. Applications requiring ordered reliable delivery
of streams of data should use the TCP.
What is Router?
A router is a device that forwards data packets from a source to a destination. Routers
forward data packets using IP addresses and not a MAC address. A router will forward data
from the Internet to a particular computer on your LAN. A router also determines the best
route that data packets should follow to ensure that the data p ackets are delivered properly.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
A data privacy mechanism based on a 40 bit shared key algorithm, as described in the
IEEE 802 .11 standard. The optional cryptographic confidentiality algorithm specified by
IEEE 802.11 used to provide data confidentiality that is subjectively equivalent to the
confidentiality of a wired LAN medium that does not employ cryptographic techniques to
enhance privacy.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
Wi-Fi Protected Access, a specification to improve the security level of wireless networks. It
uses 802.1x and EAP to control network access. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is
68
Page 69

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
used to secure data during transmission.
69
Page 70

802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
5. TCP/IP Port List for Internet Service
The list of TCP/IP Port for Internet service is as following table. Please note that the list is
just for your reference. You may check the service provider’s manual to see more details.
Service Name TCP UDP Notes
AOL 5190-5193 5190-5193 American OnLine
AOL ICQ 5190, dyn >=1024 Message
AOL Instant Messenger 5190 5190 American OnLine
Citrix ICA 1494, dyn >=1023 1604, dyn
>=1023
DirectX Gaming 47624, 2300-2400 47624,
2300-2400
Distributed.Net RC5/DES 2064 Distributed computation
DNS 53 Domain name Service
Doom 666 666 Network game
FTP 21 File Transfer Protocol
Glimpseserver 2001 Search engine
Gopher 70
H.323 Host Call 1720 1720 H.323 host call
HTTPs 443 Secure HTTP (SSL)
ichat client, server 4020 4020 Chat rooms
ICU II 2000-2003 Videoconferencing
iSpQ 2000-2003 Videoconference
LDAP 389 389 Lightweight Directory
Remote application
access
many network games
Access Protocol
Mirabilis ICQ dyn >=1024 4000 Locator, chat
MS ICCP 1731 1731 Audio call control
(Microsoft)
MS Netmeeting dyn >=1024, dyn >=1024 Video conference
MS NetShow 1755 1755 Streaming video
MSN Gaming Zone 28800-29000 28800-29000 Network Game
MSN Messenger 1863 Instant messenging
Netscape Conference 6498, 6502 2327 Audio conference
NNTPs 563 Secure NNTP news
(SSL)
70
Page 71
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
Palm Computing Network
Hotsync
pcAnywhere 5631 5632 Remote control
POP3 110 Post Office Protocol
QuickTime 4 RTSP RTP Streaming audio, video
Real Audio & Video RTSP, 7070 6970-7170 Streaming audio and
Remotely Possible
(ControlIT)
RTSP 554 Real Time Streaming
SMTP 25 Simple Mail Transfer
SOCKS 1080 Internet proxy
14237 14238 Data synchronization
Version 3
video
799 Remote control software
by CA
Protocol
Protocol
Squid 3128 3130 Web proxy cache
SSH 22 Secure Shell
Telnet 23
Timbuktu 1417-1420 407 Remote control
ULP 522 522 User Location Protocol
Virtual Places 1533 Conferencing
VocalTec Internet Phone 1490, 6670,
25793
Win MX 6399 6399 Peer to Peer file
Xing StreamWorks 1558 Streaming video
Yahoo Messenger –
messages
Yahoo Messenger –
Webcam
‧ Above TCP/IP Port List is from the following web page:
5050 Message
5100 Video
22555 Video conference
exchange
http://www.akerman.ca/port-table.html (The copyright is belong to the writer
of the web)
71
Page 72
802.11g 4-Port Wireless LAN Broadband Router
FCC Statement
This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instructions in this manual, may cause interference to radio communications.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class B computing device
pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of the FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable
protection against radio interference when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user, at his own
expense, will be required to take whatever measures are necessary to correct the interference.
WARNING! Any changes or modifications to this product not expressly approved by
the manufacturer could void any assurances of safety or performance and could result
in violation of Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
CE Declaration of conformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN 55022
class B for ITE and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements of the European
Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to
electromagnetic compatibility.
Trademarks
All company, brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
72
 Loading...
Loading...