Page 1

PVS4100/4120/4150
Portable Samplers
Revision: 4/12
Copyright © 2011-2012
Campbell Scientific, Inc.
Page 2

Page 3

Warranty
The PVS4100/4120/4150 Portable Samplers are warranted for thirty-six (36)
months subject to this limited warranty:
“PRODUCTS MANUFACTURED BY CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC, INC. are
warranted by Campbell Scientific, Inc. (“Campbell”) to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal use and service for twelve (12)
months from date of shipment unless otherwise specified in the corresponding
Campbell pricelist or product manual. Products not manufactured, but that are
re-sold by Campbell, are warranted only to the limits extended by the original
manufacturer. Batteries, fine-wire thermocouples, desiccant, and other
consumables have no warranty. Campbell's obligation under this warranty is
limited to repairing or replacing (at Campbell's option) defective products,
which shall be the sole and exclusive remedy under this warranty. The
customer shall assume all costs of removing, reinstalling, and shipping
defective products to Campbell. Campbell will return such products by surface
carrier prepaid within the continental United States of America. To all other
locations, Campbell will return such products best way CIP (Port of Entry)
INCOTERM® 2010, prepaid. This warranty shall not apply to any products
which have been subjected to modification, misuse, neglect, improper service,
accidents of nature, or shipping damage. This warranty is in lieu of all other
warranties, expressed or implied. The warranty for installation services
performed by Campbell such as programming to customer specifications,
electrical connections to products manufactured by Campbell, and product
specific training, is part of Campbell’s product warranty. CAMPBELL
EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS AND EXCLUDES ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Campbell is not liable for any special, indirect,
incidental, and/or consequential damages.”
Page 4

Assistance
Products may not be returned without prior authorization. The following
contact information is for US and international customers residing in countries
served by Campbell Scientific, Inc. directly. Affiliate companies handle
repairs for customers within their territories. Please visit
www.campbellsci.com to determine which Campbell Scientific company serves
your country.
To obtain a Returned Materials Authorization (RMA), contact CAMPBELL
SCIENTIFIC, INC., phone (435) 227-9000. After an applications engineer
determines the nature of the problem, an RMA number will be issued. Please
write this number clearly on the outside of the shipping container. Campbell
Scientific's shipping address is:
CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC, INC.
RMA#_____
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321-1784
For all returns, the customer must fill out a "Statement of Product Cleanliness
and Decontamination" form and comply with the requirements specified in it.
The form is available from our web site at www.campbellsci.com/repair. A
completed form must be either emailed to repair@campbellsci.com or faxed to
(435) 227-9106. Campbell Scientific is unable to process any returns until we
receive this form. If the form is not received within three days of product
receipt or is incomplete, the product will be returned to the customer at the
customer's expense. Campbell Scientific reserves the right to refuse service on
products that were exposed to contaminants that may cause health or safety
concerns for our employees.
Page 5

PVS4100/4120/4150
Table of Contents
PDF viewers: These page numbers refer to the printed version of this document. Use the
PDF reader bookmarks tab for links to specific sections.
1. Product Overview......................................................1-1
1.1 Introduction........................................................................................ 1-1
1.2 Features.............................................................................................. 1-2
1.2.1 PVS4100 and PVS4120 Sampler Features............................... 1-2
1.2.2 PVS4150 Sampler Features...................................................... 1-4
1.2.3 Sampler Vacuum System Features........................................... 1-6
1.2.4 Signal Panel.............................................................................. 1-8
1.3 Specifications..................................................................................... 1-9
1.3.1 PVS4100 Portable Sampler Specifications............................... 1-9
1.3.2 PVS4120 Lightweight Portable Sampler Specifications........ 1-10
1.3.3 PVS4150 Ultra-Portable Sampler Specifications................... 1-11
1.3.4 Controller Specifications........................................................ 1-12
1.3.5 Vacuum System Specifications.............................................. 1-13
1.3.6 Sample Container Options...................................................... 1-14
1.3.7 Composite and Discrete Overview......................................... 1-14
1.3.8 Sample Transport Velocity..................................................... 1-15
1.3.8.1 Using Velocity to Calculate Purge Time .................... 1-16
1.3.8.2 Horizontal/Vertical Co
1.3.9 Special System
1.3.9.1 5/8 Systems................................................................. 1-17
1.3.9.2 MISA Systems – Teflon and Glass............................. 1-17
Portable Sampler Model Selection Guide ........................................ 1-18
1.4
s...................................................................... 1-17
mbinations.............................. 1-16
2. Installation .................................................................2-1
2.1 Cabinet Positioning ............................................................................ 2-1
2.2 Intake Hose ........................................................................................ 2-2
2.3 Sinker / Strainer ................................................................................. 2-2
2.4 Storage ............................................................................................... 2-2
2.5 Signal Wiring..................................................................................... 2-3
2.6 Installation Checklist.......................................................................... 2-4
3. Operation ...................................................................3-1
3.1 Operating Sequence ........................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 Sampling Sequence .................................................................. 3-1
3.1.2 Line Voltage Failure................................................................. 3-2
3.2 Operating Instructions........................................................................ 3-2
3.2.1 Sample Volume Adjustment .................................................... 3-2
3.2.2 Liquid Sensing Rod.................................................................. 3-3
3.3 Battery................................................................................................ 3-4
3.3.1 Battery: Operating and Backup (optional)................................ 3-4
3.3.2 Battery: Microprocessor........................................................... 3-5
3.4 Test Procedure ................................................................................... 3-6
3.5 Troubleshooting ................................................................................. 3-6
i
Page 6

PVS4100/4120/4150 Table of Contents
4. Maintenance.............................................................. 4-1
4.1 General Maintenance.......................................................................... 4-1
4.2 Testing System Vacuum..................................................................... 4-1
5. Programming ............................................................ 5-1
5.1 General Programming ........................................................................ 5-1
5.1.1 Guidelines................................................................................. 5-1
5.1.2
5.1.3 General Terms .......................................................................... 5-4
5.2 Quick Start Guide to Programming.................................................... 5-6
5.2.1 Automatic Sampling Program ..................................................5-6
5.2.2 Taking a Manual Sample.......................................................... 5-7
5.2.3 Viewing Program Parameters................................................... 5-7
5.2.4 Setting Program Parameters Individually................................. 5-8
5.3 Programming START DELAY.......................................................... 5-8
5.3.1 START DELAY Overview ......................................................5-8
5.3.2 START DELAY using Time/Day ............................................5-9
5.3.3 START DELAY using Pulse Input ........................................ 5-11
5.3.4 START DELAY using 4-20mA Input.................................... 5-12
5.3.5 START DELAY using External Contact................................5-14
5.3.6 START DELAY using Level Control .................................... 5-15
5.4 Programming SAMPLE INITIATION............................................. 5-16
5.4.1 SAMPLE INITIATION Overview......................................... 5-16
5.4.2 SAMPLE INITIATION using Interval Time ......................... 5-17
5.4.3 SAMPLE INITIATION using Pulse Input............................. 5-19
5.4.4 SAMPLE INITIATION using 4-20mA Input......................... 5-20
5.4.5 SAMPLE INITIATION using External Contact .................... 5-22
5.5 Programming PROGRAM TYPE .................................................... 5-23
5.5.1 PROGRAM TYPE Overview................................................. 5-23
5.5.2 PROGRAM TYPE - Composite............................................. 5-24
5.5.3 PROGRAM TYPE - Daily Cycle........................................... 5-26
5.5.4 PROGRAM TYPE - Daily Cycle for Dual Station ................5-27
5.5.5 PROGRAM TYPE - Consecutive...........................................5-29
5.5.6 PROGRAM TYPE - Multi-Composite................................... 5-31
5.5.7 PROGRAM TYPE - Timed Step............................................ 5-32
5.6 Programming OTHER OPTIONS.................................................... 5-34
5.6.1 OTHER OPTIONS Overview ................................................ 5-34
5.6.2 OTHER OPTIONS - Clock .................................................... 5-36
5.6.3 OTHER OPTIONS - Purge Time ...........................................5-37
5.6.4 OTHER OPTIONS - Pinch Valve.......................................... 5-39
5.6.5 OTHER OPTIONS - Fault Shutdown .................................... 5-40
5.7 Viewing Information ........................................................................ 5-42
5.7.1 Viewing Programmed Information......................................... 5-42
5.7.2 Viewing Generated Information............................................. 5-44
5.1.1.1 Flashing Text ................................................................ 5-1
5.1.1.2 Real Time Clock ........................................................... 5-1
5.1.1.3 Total Bottles
.................................................................. 5-1
Touchpad Keys......................................................................... 5-2
ii
Page 7

PVS4100/4120/4150 Table of Contents
Appendices
A. Principles of Operation........................................... A-1
B. Parts List.................................................................. B-1
Programming 4-20mA for Flow Proportional
C.
Sampling ...............................................................C-1
List of Figures
1-1. Highlights of the PVS4100 and PVS4120 Samplers........................... 1-2
1-2. Highlights of the PVS4150 Sampler.................................................... 1-4
1-3. Diagram of the PVS Vacuum System ................................................. 1-6
2-1. Sampler Installation............................................................................. 2-1
2-2. External Signal Cable for PVS4100 and PVS4120 ............................. 2-3
3-1. Battery Performance Curve ................................................................. 3-4
List of Tables
1-1. PVS4100 and PVS4120 Sampler Features......................................... 1-3
1-2. PVS4150 Sampler Features................................................................. 1-5
1-3. Vacuum System Features .................................................................... 1-7
1-4. PVS4100 Sampler Specifications........................................................ 1-9
1-5. PVS4120 Sampler Specifications...................................................... 1-10
1-6. PVS4150 Sampler Specifications...................................................... 1-11
1-7. Controller Specifications................................................................... 1-12
1-8. Vacuum System Specifications ......................................................... 1-13
1-9. Sample Container Options – PVS4100 and PVS4120....................... 1-14
1-10. Sample Container Options – PVS4150............................................. 1-14
1-11. Vertical Velocity ............................................................................. 1-15
1-12. Horizontal Velocity ......................................................................... 1-16
1-13. MISA System Changes.................................................................... 1-17
5-1. Touchpad Button Descriptions............................................................ 5-2
B-1. PVS Replacement Parts ......................................................................B-1
iii
Page 8

PVS4100/4120/4150 Table of Contents
iv
Page 9

Section 1. Product Overview
1.1 Introduction
The PVS4100, PVS4120 and PVS4150 Portable Samplers are automatic liquid
samplers for water and wastewater applications. PVS Samplers are capable of
gathering fluid automatically from a variety of sources, including containers,
open channels, sewers, pipes, and any open source of water.
Samplers are designed for reliable unattended sample collection. Portable units
are capable of keeping the temperature of the deposited liquid at 4ºC (39.2ºF)
for up to 24 hours using crushed ice or ice packs until the samples are gathered
and brought back to the laboratory for analysis.
There are a variety of methods for depositing samples. Composite sampling is
used where samples are deposited, over time, into one container. Discrete
systems are used when multiple bottles are needed. These are also called
“sequential” systems, and involve a stepper with distributor arm which
dispenses the liquid into a bottle, then moves to the next bottle.
Operating temperature for portable samplers is 10ºC to 50ºC (50ºF to 122ºF),
adaptable down to 0ºC (32ºF) upon request.
Samples can be triggered by a variety of means. The internal clock on the
controller can be set to sample based on time/day (e.g. sample every hour).
There are also a variety of external inputs that can be connected to control
sampling using the optional external signal cable. Pulse count is useful for
sampling after a certain number of pulses have been reached (e.g. using a rain
gauge to trigger sampling). The 4-20 mA option is useful for flow-based
sampling (e.g. using a flow meter to trigger sampling after a certain volume of
water has passed by). External contact is used to control the sampler from
another data logger or PLC, and is useful when full external control is desired.
Level control is the option to choose when the application has starts and stops
(e.g. using a float switch to trigger sampling when water is present, then stop
sampling when the water drops below the set level).
When sampling is initiated, liquid travels through the intake tube into the
metering chamber. The amount of water taken is set mechanically using the
liquid sensing rod and the volume control tube, which means sample accuracy
is precise every time, usually within +/- 2% or +/- 2ml.
Once the pre-set amount has been reached, all excess liquid is purged from the
system, and the sample is dropped into a container. Sample containers range
from 500 ml (500 cc or 2 cup) wedges in discrete systems, to 9 liters (2.3
Gallon) containers for composite systems.
Intake tube is offered in either 3/8” (9.5 mm) ID or 5/8” (15.9 mm) ID, and can
be either Nylon-reinforced PVC or Teflon-lined PVC. Transport velocity varies
depending on height and distance being sampled. For most situations the
sampler pulls at over 1.5 m/s (5 ft/sec). For an in-depth speed chart, refer to
Section 1.3.7 Sample Transport Velocity
on page 1-15.
1-1
Page 10
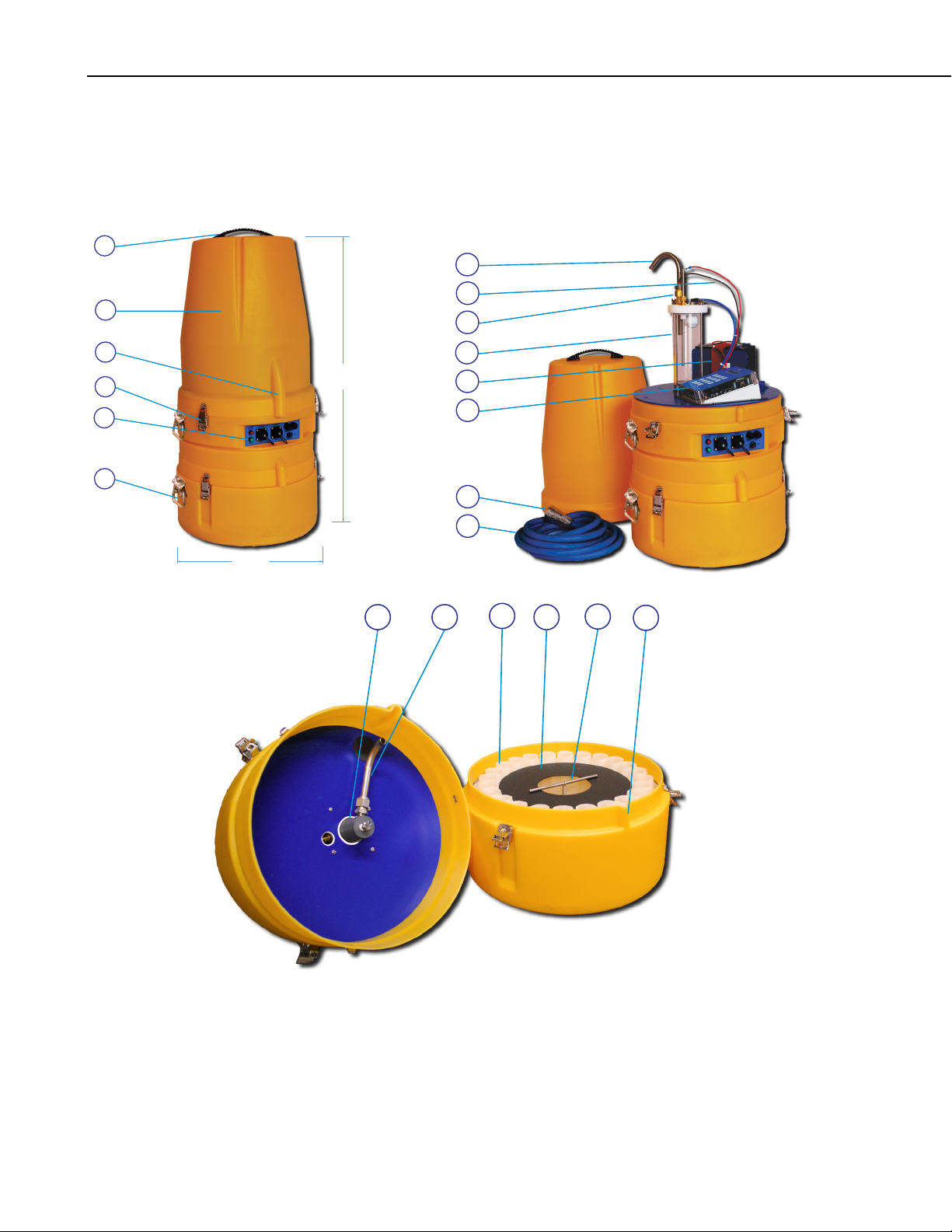
Section 1. Product Overview
1.2 Features
1.2.1 PVS4100 and PVS4120 Sampler Features
1
2
7
8
9
3
31.875”
4
5
6
(810 mm)
10
11
12
13
14
Diameter
16.375”
(416 mm)
15 16
17
18
19
20
1-2
FIGURE 1-1. Highlights of the PVS4100 and PVS4120 Samplers
Page 11

Section 1. Product Overview
TABLE 1-1. PVS4100 and PVS4120 Sampler Features
Number Item Description
1 Top Handle For easy transport.
2 Enclosure Molded medium-density linear polyethylene, 3 piece
construction. Provides protection from wind and rain. Not
submersible.
3 Intake Hose Slot The hose must lie in the slot for lid to close properly. A
secondary notch is provided for lining up the sampler properly.
4 Clasps There are three clasps for each section, for a total of six. The
clasps have ringlets for attaching a suspension harness.
5 Signal Panel Red Light: Reverse Polarity, Green Light: Power
Left Plug: External Signals (to be used with optional signal
cable)
Right Plug: Power – 120VAC or 12VDC
Left Fuse: 120VAC, Right Fuse: 12VDC
Toggle Switch: Power On/Off
For detailed chart, see page 1-8.
6 Folding Handles For easy transport.
7 Intake Hose Connection The volume control tube is where the intake hose is connected to
the sampler. This stainless steel tube is raised or lowered
manually using fitting to set the sample volume (see FIGURE 1-3
n page 1-6).
o
8 Wiring Connects electricity to the rods for sampling. When replacing
metering chamber, these rods can be easily disconnected.
9 Nuts to adjust volume To adjust sample volume, twist top nut while holding bottom nut
in place. Hand tightening works for many applications, but a
wrench is advised.
10 Metering Chamber This chamber is where the sample liquid is drawn into before
dropping into the final container. The rods inside are raised and
lowered to the sample volume desired.
11 Battery Standard on all samplers. The PVS4100 battery is 15 lbs, 17AH.
The PVS4120 battery (shown) is 4 lbs, 7 AH.
12 Multi-Function Input Controller This is where sampler is controlled and programmed.
13 Sinker. Optional Strainer. Keeps the end of the intake tube in the source liquid. Optional
strainer can raise collection point above sinker.
14 Intake Hose Standard samplers come with 25 Feet of 3/8” ID PVC tube.
15 Stepper Assembly Moves the distributor arm for multiple bottle configurations. This
is not present on composite (single bottle) samplers.
16 Distributor Arm Dispenses liquid into bottles. Moves to next bottle after
sampling. On composite (single bottle) samplers, this is replaced
with discharge tube.
17 Sample Container(s) The container(s) that the sample is deposited in can be made
from a variety of materials, shapes, and sizes. In discrete
samplers, there is a distributor arm that deposits samples into
multiple containers.
18 Retaining Plate Holds sample bottles down tightly (discrete samplers only).
19 T-Bar This bar is needed to hold the retaining plate down. It is
imperative that the bottles do not lift up even a little bit, as they
can interfere with the mobility of the distributor arm (discrete
samplers only).
20 Bottle-Guide Notch This notch is the location of bottle number one. It lines up the
middle section of the sampler so that the distributor arm can be
placed at the same location.
1-3
Page 12

Section 1. Product Overview
1.2.2 PVS4150 Sampler Features
1
2
3
4
10
11
12
13
5
6
7
14
8
15
9
16
17
18
19
14.40”
(366 mm)
24.60”
(625 mm)
19.70”
(50 0 m m )
FIGURE 1-2. Highlights of the PVS4150 Sampler
1-4
Page 13

Section 1. Product Overview
TABLE 1-2. PVS4150 Sampler Features
Number Item Description
1 Signal Panel
Green Light: Integral Battery Charging (AC power connected)
Red Light: External Battery Reverse Polarity
Toggle Switch: Power On/Off
Plug: AC power (coupled with optional signal cable when
supplied).
2 Volume Control Tube
This stainless steel tube is raised or lowered manually using the
fitting to set the sample volume (see FIGURE 1-3 on
page 1-6).
3 Multi-Function Input Controller This is where sampler is controlled and programmed.
4 Metering Chamber
This chamber is where the sample liquid is drawn into before
dropping into the final container. The rods inside are raised and
lowered to the sample volume desired.
5 Pinch Valve
This valve shuts during sampling, and then releases once desired
liquid has entered the chamber.
6 Side Plug
Attached to the side of the door with Velcro. During transport of
full sample container, this plug screws into the hole where the
discharge tube enters the bottle so that the bottle can be carried
upright by its handle.
7 Sample Container
The 2.3 Gal (9L) container that the sample is deposited into is
HDPE, or can be upgraded to PP. Container has a side notch with
plug for discharge tube to enter.
8 Latches
4 Press-and-Pull Latches provide airtight seal of sampler for
transport. Sampler can operate with door open or closed.
9 Cavity Space for Cooling Pack
This space fits one large Zero-Pak cooling pack, to keep sample
cooled for 24 hours.
10 Quick Connectors Optional connectors for quick connecting and disconnecting.
11 Intake Hose Connection
Intake hose is connected to volume control tube in the absence of
quick connectors.
12 LED Indicator Lights
Green light: Power On/Sampling.
Red light: Fault.
13 Enclosure
Hardigg HPX® high performance resin. Enclosure is fully
watertight and submersible, depending on options (check with
factory).
14 Intake Hose Standard samplers come with 25 Feet of 3/8” ID PVC tube.
15 Sinker. Optional Strainer.
Keeps the end of the intake tube in the source liquid. Optional
strainer can raise collection point above sinker.
16 Telescoping Handle
Retractable handle slides up and down for easy transport by
pressing in the small lever on the right side.
17 Side Handles
Four durable soft-grip handles, one on each side, can be folded
up or down.
18 Pressure Gauge
Optional gauge on the side of the enclosure (not shown). This is
helpful for knowing what stage the sampler is at when sampling
with the door closed.
19 Wheels Two wheels for rolling on smooth surfaces.
1-5
Page 14

Section 1. Product Overview
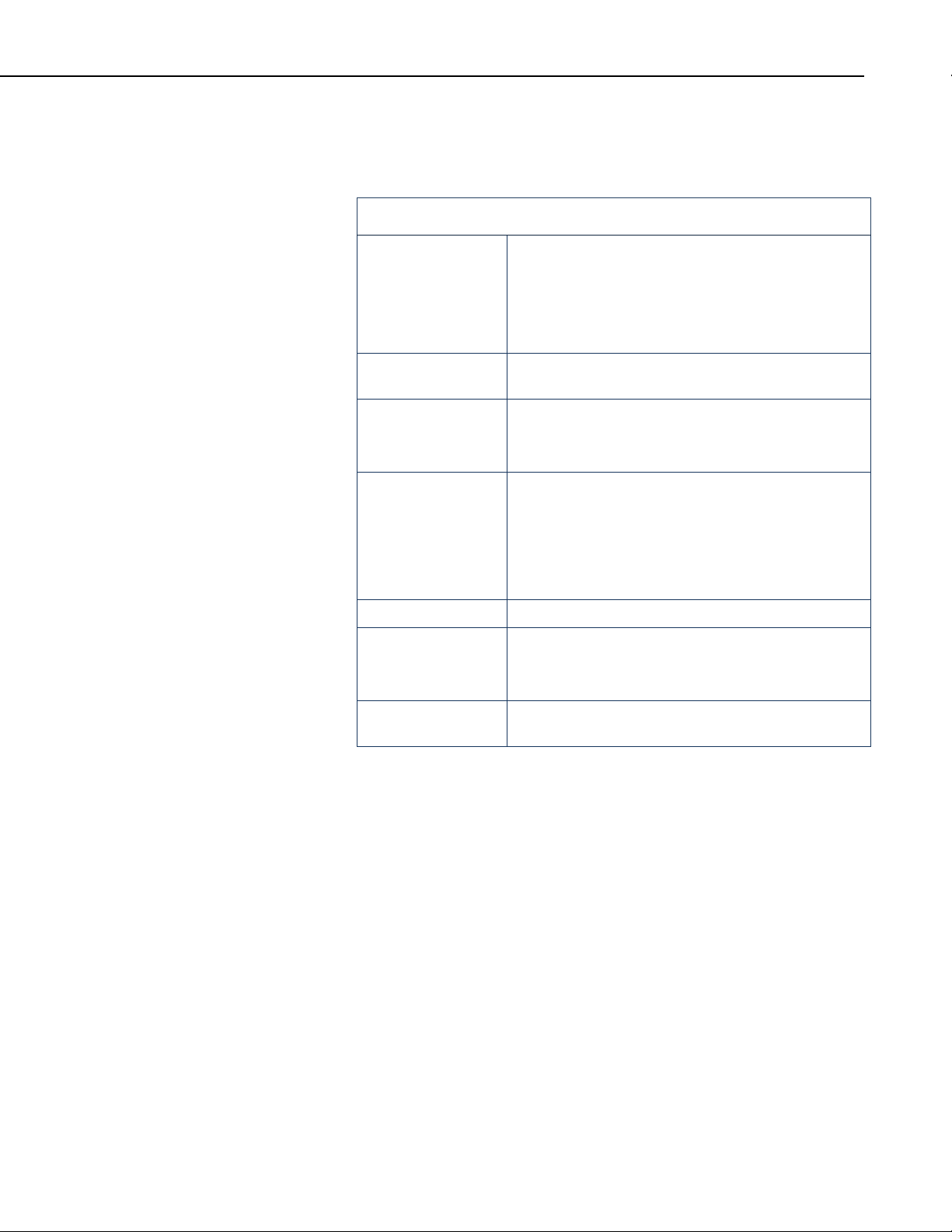
1.2.3 Sampler Vacuum System Features
1-6
FIGURE 1-3. Diagram of the PVS Vacuum System
Page 15

Section 1. Product Overview
TABLE 1-3. Vacuum System Features
Number Item Description
1 Solenoid Valves Control the air flow from pump to sampler, either purging or
sucking.
2 Pump Located behind a sheet of metal, the pump does not come into
contact with any liquid whatsoever. It does all the drawing and
purging through using a vacuum and compressor.
3 Touchpad Controller Controls sampler program and offers status feedback on LCD.
4 Sample Distributor Rotates distributor arm between multiple discrete containers.
5 Distributor Arm Dispenses liquid from metering chamber into discrete container.
6 Discrete Sample Containers Multiple containers, always in a quantity divisible into 24
(PVS4100 and PVS4120 only).
7 Pressure Gauge Visually describes sampling process in terms of
vacuum/pressure. Useful for troubleshooting a plugged/kinked
line, or signals leaks. Optional (PVS4150 only).
8 Liquid Sensing Rod This rod must remain above the volume control tube. When the
sample liquid comes into contact with the two rods it signals the
controller to stop sampling and begin purging.
9 Barrier Valve Prevents metering chamber overflow in case the liquid sensing
rod fails (e.g. completely coated with oils/grease).
10 Volume Control Tube Mechanically set the volume required for sample by using a
wrench on the fitting at the base of this stainless steel tube.
11 Metering Chamber Sample is drawn into chamber up to level set by volume control
tube, then line is purged, followed by dropping sample into
containers. Metering Chambers come in glass or acrylic, from
250cc to 500cc.
12 Pinch Valve This valve shuts during sampling, then opens during sampling to
drop sample into container, then closes to purge hose.
13 Cap with “Container Full” Shut-
off
Optional cap contains Overflow Protection Probes which signal
the sampler to halt when container is full. Can be installed in
maximum two containers, or into a discrete bottle tray.
14 Composite Sample Container A single container to hold sample liquid.
15 Intake Hose Standard samplers come with 25 Feet of 3/8” ID PVC tube.
16 Sinker. Optional Strainer. Keeps the end of the intake tube in the source liquid. Optional
strainer can raise collection point above sinker.
1-7
Page 16
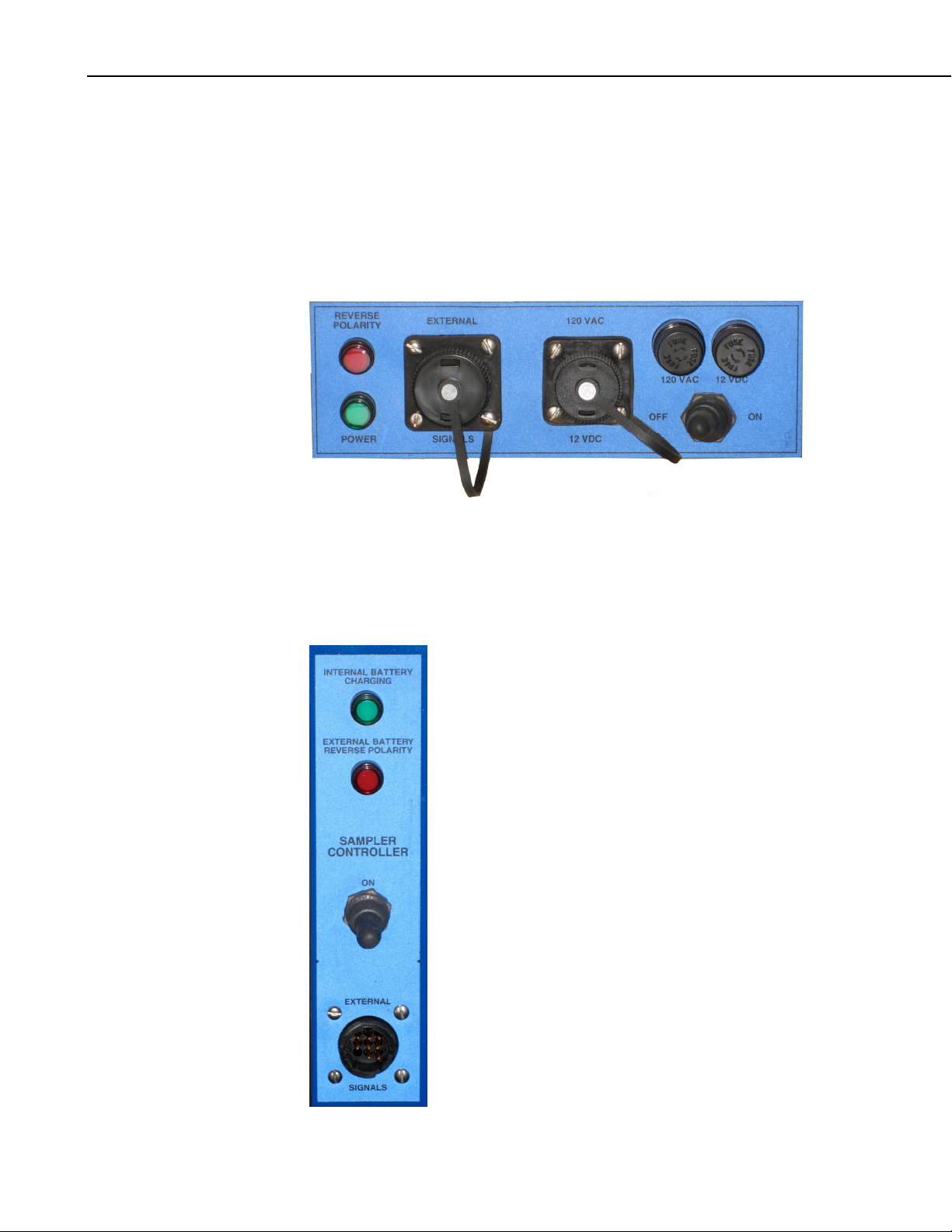
Section 1. Product Overview
1.2.4 Signal Panel
PVS4100 and PVS4120
Red Light: Reverse Polarity, Green Light: Power
Left Plug: External Signals (to be used with optional signal cable)
Right Plug: Power – 120VAC or 12VDC
Left Fuse: 120VAC, Right Fuse: 12VDC
Toggle Switch: Power On/Off
PVS4150
Green Light: Integral Battery Charging (AC power connected)
Red Light: External Battery Reverse Polarity
Toggle Switch: Power On/Off
Plug: AC power (coupled with optional signal cable when supplied).
1-8
Page 17
Section 1. Product Overview
1.3 Specifications
1.3.1 PVS4100 Portable Sampler Specifications
TABLE 1-4. PVS4100 Sampler Specifications
Dimensions
Weight
(without battery)
Enclosure
Power
Requirements
Cooling System
Operating
Temperature
Height: 809 mm (31.875 in)
Diameter: 428 mm (16.85 in)
Extended Base:
Height: 962 mm (37.875 in)
Diameter: 428 mm (16.85 in)
11.8 kg (26 lbs)
Molded medium density linear polyethylene, 3 piece
construction, all SS fittings.
Protection Rating: IP 55, Dust protection, water jets.
Sampler: DC Output: 13.6V, 10A. AC Input: 88264VAC, 50/60Hz, 2.5A (max 3A)
Integral Battery: 12VDC, 17AH, 15 lbs.
External Receptacle: 12 VDC.
Optional AC only model available (no battery).
Insulated container wall. Cavity space for ice.
Standard: 10ºC to 50ºC (50ºF to 122ºF)
* Can be modified to operate down to 0ºC (32ºF) upon
request.
Storage
Temperature
-30ºC to +60ºC (-22ºF to +140ºF)
1-9
Page 18
Section 1. Product Overview
1.3.2 PVS4120 Lightweight Portable Sampler Specifications
TABLE 1-5. PVS4120 Sampler Specifications
Dimensions
Weight
(without battery)
Enclosure
Power
Requirements
Cooling System
Operating
Temperature
Height: 31.875 in (809 mm)
Diameter: 16.85 in (428 mm)
Extended Base:
Height: 37.875 in (962 mm)
Diameter: 16.85 in (428 mm)
10.4 kg [23 lbs]
Molded medium density linear polyethylene, 3 piece
construction, all SS fittings.
Protection Rating: IP 55, Dust protection, water jets.
Integral Battery: 12 VDC, 7 AH, 4 lbs.
External Receptacle, 12 VDC.
External Charger for 115VAC (optional up to
240VAC).
Optional 120VAC/12VDC power supply with external
battery charger.
Insulated container wall. Cavity space for ice.
Standard: 10ºC to 50ºC (50ºF to 122ºF)
* Can be modified to operate down to 0ºC (32ºF) upon
request.
Storage
Temperature
-30ºC to +60ºC (-22ºF to +140ºF)
1-10
Page 19
Section 1. Product Overview
1.3.3 PVS4150 Ultra-Portable Sampler Specifications
TABLE 1-6. PVS4150 Sampler Specifications
Dimensions
Weight
(without battery)
Enclosure
Power
Requirements
Cooling System
Operating
Temperature
Storage
Temperature
H: 24.6” x W: 19.7” x D: 14.4”
[H: 625mm x W: 500mm x D: 366mm]
35.5 lbs [16.1 kg]
HPX high performance resin. Press & Pull latches, and
soft-grip handles.
Protection Rating: IP 67, Dust-tight, water-tight
(depending on options chosen).
Integral Battery: 12 VDC, 7 AH, 4 lbs.
External Charger for 115VAC (optional up to
240VAC).
Cavity space for two Zero-Pack (#12396).
Standard: 10ºC to 50ºC (50ºF to 122ºF)
* Can be modified to operate down to 0ºC (32ºF) upon
request.
-30ºC to +60ºC (-22ºF to +140ºF)
1-11
Page 20
Section 1. Product Overview
1.3.4 Controller Specifications
TABLE 1-7. Controller Specifications
Feature Function Capability
START DELAY
Time/Day Adjustable, up to 1 week in advance.
Pulse Count Adjustable, up to 9,999,999.
4-20mA Adjustable, up to 9,999,999 (4-20mA = 0-100 Pulses/min).
External Contact Momentary, 25 millisecond dry contact closure.
Level Control Adjustable up to 99 second contact duration.
SAMPLE INITIATION
Interval Time Adjustable up to 999 hours, 99 minutes
Pulse Count Adjustable, up to 9,999,999.
4-20mA Adjustable, up to 9,999,999 (4-20mA = 0-100 Pulses/min).
External Contact Momentary, 25 millisecond dry contact closure.
PROGRAM TYPE
CLOCK
PINCH VALVE
PURGE CYCLE
SUCTION CYCLE
ALARM OUTPUTS
STATUS OUTPUTS
DIRECT FUNCTION
KEYS
Manual Bottle Advance Moves distributor arm to next bottle.
AVAILABLE
DISPLAYS
Process Timing Elapsed, remaining.
Process Totals
Pulse Counting Internal/external.
Event Response With time stamp.
Flashing Text
AUTOMATIC
DISPLAYS
Fault Program not completed.
Alternating Time Stamp
Cycle(s) Abandoned
Disabled No start delay.
Disabled No sample initiation.
Composite Terminate after up to 9,999,999 samples.
Multi-Composite Adjustable, up to 99 cycles per bottle.
Consecutive Adjustable, up to 9 bottles per cycle.
Daily Cycle Adjustable, up to 9 bottles per day.
Timed Step Adjustable, up to 99 hours, 99 minutes per step.
Real Time Clock Real time operating system.
Sample release Adjustable, normally open / normally closed.
Draw and purge time Adjustable, 1 to 99 seconds.
Variable
Vacuum
Independent Container Full (Latched. Any key resets. NPN*)
Sample Fault (Latched. Any key resets. NPN*)
Cycle Abandoned (Pulsed. NPN*)
*NPN (sinking) – see Technical Appendix for details.
Independent Sample Taken (DC relay driver, sinking)
Manual Sample Samples manually when pressed twice. Does not interrupt program.
Manual Purge Purges system during second press as long as button is pressed.
Restart Re-initiates program when pressed twice.
Real-Time Clock
Multi-Level
Descriptions
Container Full Sample program complete.
Power Interrupt –
Program Resumed
Adjusts automatically to double the value of the purge time setting or
until liquid contacts level electrode in metering chamber.
System pressure range is -14 psi to +20 psi, which can be shown on
the Optional Pressure Gauge.
1-12
Page 21
1.3.5 Vacuum System Specifications
TABLE 1-8. Vacuum System Specifications
Feature Description
Switches
Sample Volume
Run/Off (SPST Toggle).
Adjustable, 50cc to 500cc [PVS4100 and
PVS4120]
Adjustable, 50cc to 250cc [PVS4150]
Section 1. Product Overview
Sample Transport
Velocity
Metering Chamber
Metering Chamber
Cover
Volume Control Tube
Metering Chamber
Level Electrode
Intake Hose
Discharge Hose
Sinker/Strainer
PVS4100: Minimum of 3 ft/sec at 20 ft of lift (3/8”
ID intake line).
PVS4100: Minimum of 3 ft/sec at 16 ft of lift (5/8”
ID intake line).
PVS4100: Maximum Vertical 27.5 ft.
PVS4120 and PVS4150: Minimum of 3 ft/sec at 13
ft of lift.
PVS4120 and PVS4150: Maximum Vertical: 18 ft
For complete charts, see page 1-15.
500cc capacity, clear acrylic, calibrated in 100cc’s.
500cc capacity, glass (Pyrex), calibrated in 100cc’s.
[OPTIONAL]
250cc capacity, clear acrylic, calibrated in 50cc’s.
[PVS4150]
Nylon
Reinforced Teflon Top. [OPTIONAL]
316 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel
Nylon-Reinforced PVC, 3/8” ID (standard 25 ft
with sinker)
Nylon-Reinforced PVC, 5/8” ID [OPTIONAL]
Teflon-lined Tygon, 1/2" ID [OPTIONAL]
Teflon-lined Tygon, 3/4" ID [OPTIONAL]
Latex, 3/8” ID
Latex, 5/8” ID [OPTIONAL]
Silicone, 3/8” ID [OPTIONAL]
Silicone, 5/8” ID [OPTIONAL]
Lead Sinker
Stainless Steel Sinker/Strainer [OPTIONAL]
Stainless Steel Sinker [OPTIONAL]
1-13
Page 22

Section 1. Product Overview
1.3.6 Sample Container Options
TABLE 1-9. Sample Container Options – PVS4100 and PVS4120
Feature Description
Composite (single)
containers
Discrete (multiple)
containers
TABLE 1-10. Sample Container Options – PVS4150
Feature Description
Composite (single)
containers
9 liter (2.3 US Gal) high density polyethylene (HDPE)
9 liter (2.3 US Gal) polypropylene (PP)
10 liter (2.5 US Gal) Glass [with extended base]
500cc (0.5 L) Wedges (PP) [24 bottles]
500cc (0.5 L) Wedges (PP) [24 bottles] [with extended
base]
1 liter Glass [8 bottles] [removable bottle tray c/w
handles]
1 liter high density polyethylene (HDPE) [8 bottles]
9 liter (2.3 US Gal) high density polyethylene (HDPE)
9 liter (2.3 US Gal) polypropylene (PP)
1.3.7 Composite and Discrete Overview
Discrete Sampling (PVS4100 and PVS4120 only) is sampling wherein
samples are taken into more than one container. Inside of the cooling chamber
is a stepper assembly which revolves 360° and delivers samples into separate
containers, ranging from 8 to 24 bottles. Discrete sampling is beneficial in
situations where change over time needs to be measured, such as measuring
different water characteristics over 24 hours. Labs and monitoring personnel
tend to rely on discrete portable sampling.
1-14
Page 23
Section 1. Product Overview
Composite Sampling is for drawing water samples into one large container.
This is the simplest way of taking samples and typical for most situations
where a sampler is set up to measure effluent in one location. It is also
significantly less expensive than discrete sampling.
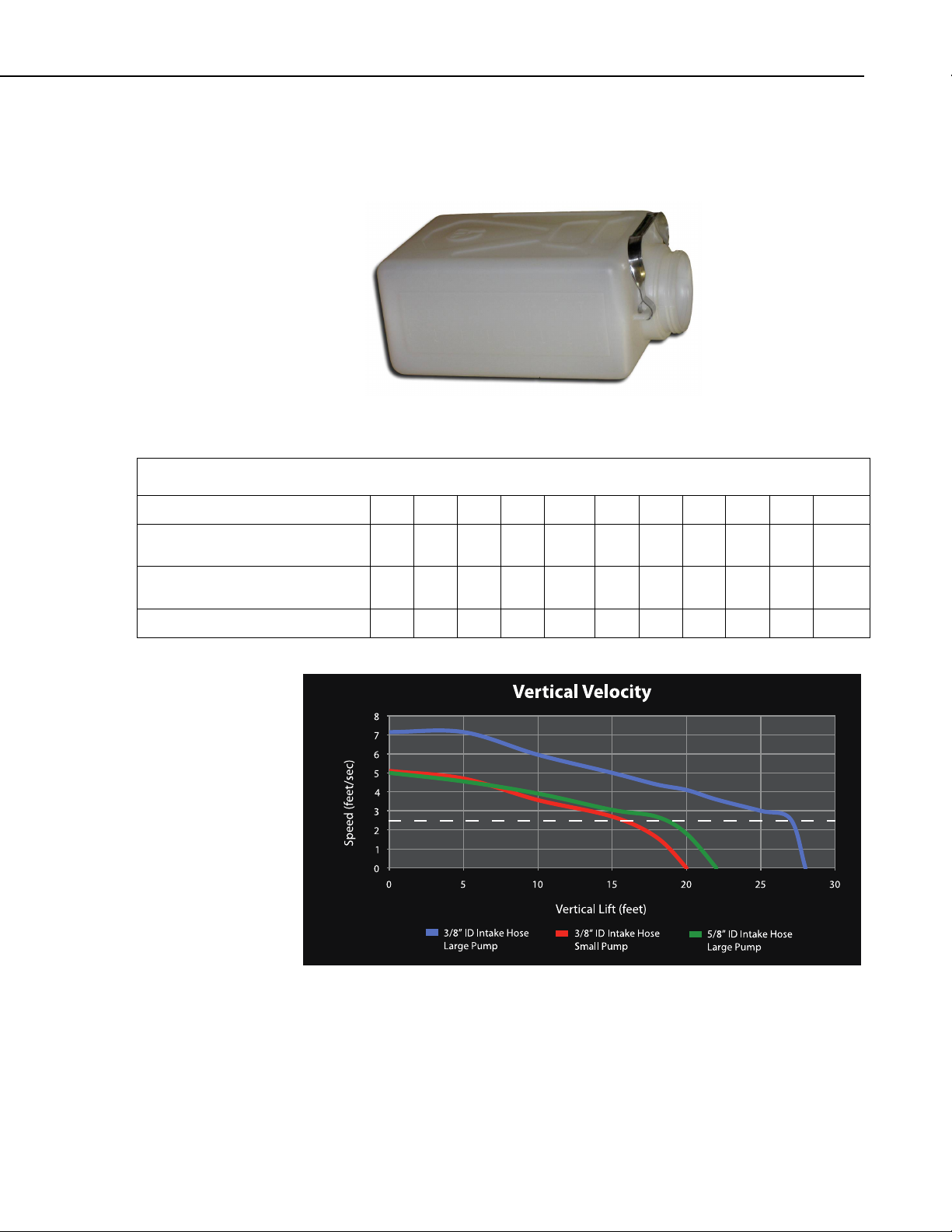
1.3.8 Sample Transport Velocity
TABLE 1-11. Vertical Velocity
0’ 5’ 10’ 15’ 18’ 20’ 22’ 25’ 27’ 28’ Height
3/8” ID Large pump
(BVS 4300, CVS 4200, PVS4100)
3/8" ID Small pump
(PVS4120, PVS4150)
5/8" ID Large pump 5 4.6 3.9 3.1 2.7 1.8 0
7.1 7.1 6.0 5 4.4 4.1 3.6 3 2.6 0 Ft/sec
5.1 4.7 3.6 2.7 1.6 0
1-15
Page 24
Section 1. Product Overview
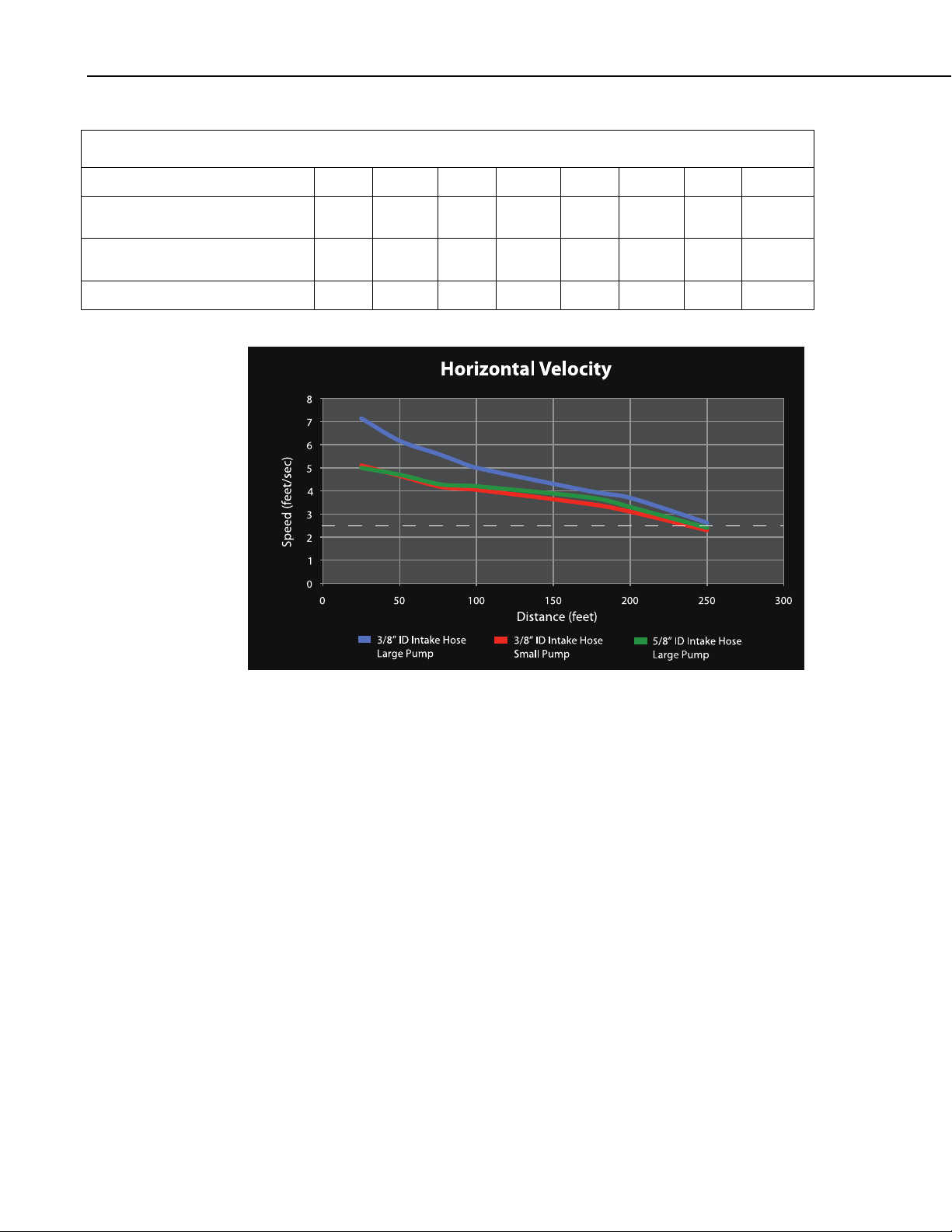
TABLE 1-12. Horizontal Velocity
25’ 50’ 75’ 100’ 175’ 200’ 250’ Distance
3/8” ID Large pump
(BVS 4300, CVS 4200, PVS4100)
3/8" ID Small pump
(PVS4120, PVS4150)
5/8" ID Large pump 5.0 4.7 4.3 4.2 3.7 3.3 2.4
7.1 6.2 5.6 5.0 4.0 3.7 2.6 Ft/sec
5.1 4.7 4.2 4.1 3.4 3.1 2.3
1.3.8.1 Using Velocity to Calculate Purge Time
Purge time of the sampler needs to be programmed based on the length of hose
and the velocity at which the liquid will travel through the hose. The formula is
l / v = p (length / velocity = min. purge time). Adding a few second to the
purge time is recommended to ensure the line is fully cleared of any
obstructions.
Example: 100 ft of hose, at 5 ft/sec, requires a minimum 20 second purge time.
100 / 5 = 20 seconds. The number input for purge time should be a minimum
of 20, but preferably 24.
Standard purge time for 25 ft of intake tube is 10 seconds. Although a standard
25 ft hose will sample in less than 4 seconds, 10 seconds is the minimum
recommended for proper clearing of the line.
1.3.8.2 Horizontal/Vertical Combinations
The velocity charts above measure only horizontal or only vertical. Most
applications will have combinations of both. With 200 feet of intake tubing,
PVS Samplers are capable of drawing a sample above 2 ft/sec at 20 feet of
vertical. At 23 feet of vertical with 200 feet of intake tubing, sampling may or
may not be successful, depending on altitude and other factors. For more
1-16
Page 25

detailed information for your specific application, please contact a Campbell
Scientific applications engineer.
1.3.9 Special Systems
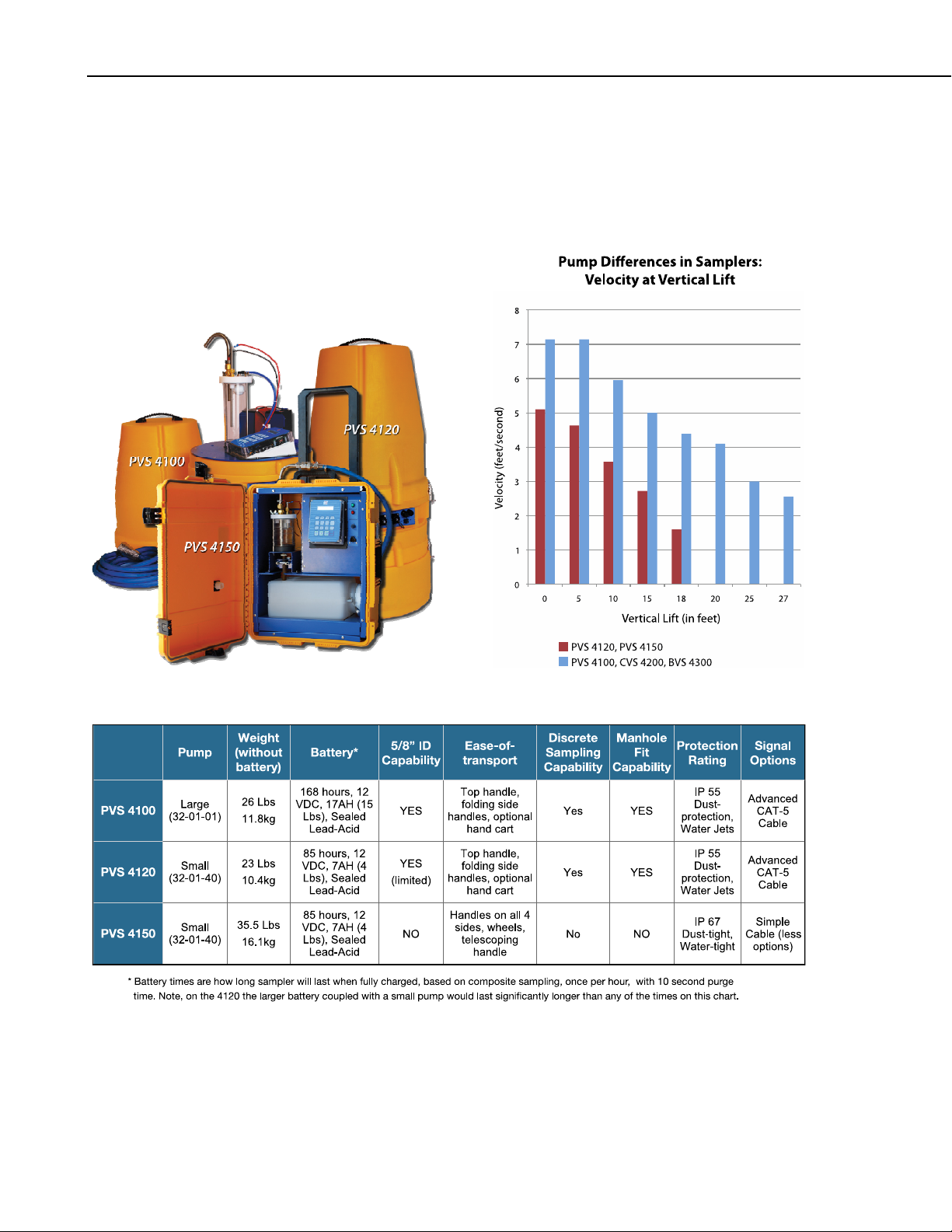
1.3.9.1 5/8 Systems
In applications with large particles or materials in the source liquid, a 5/8” ID
system will help prevent clogging. The added diameter adds 66% more volume
to the entire system. As of 2010, both composite and discrete samplers are
available in 5/8”. Smaller pump systems (PVS4120) have minimal capacity
running the larger volume of the 5/8” ID so the larger pump systems
(PVS4100) are recommended.
For a sampler to increase to a 5/8” ID, the following parts and components are
changed to allow for more volume: intake tube, volume control tube, all
fittings, metering chamber, metering chamber lid, discharge tube, sample
container cover, sinker or strainer, and the distributor assembly (for discrete
models).
1.3.9.2 MISA Systems – Teflon and Glass
Section 1. Product Overview
In applications wherein the water sample must be prevented from coming into
contact with any plastics, a MISA system is recommended. For example, when
testing for acid/base/neutral extractable organics and pesticides, the MISA
system will keep the final sample clean from any contaminants.
MISA stands for “Municipal/Industrial Strategy for Abatement,” and includes
changing all “wetted” components of the sampling system, i.e., everything that
comes in contact with the final sample. The chart below outlines the key
changes made to the sampler for a MISA system.
TABLE 1-13. MISA System Changes
Component Standard Material MISA System Material
Intake Tube PVC Teflon-Lined PVC
Sinker/Strainer Lead Sinker Stainless Steel Sinker/Strainer
Fittings Brass Stainless Steel
Metering Chamber Acrylic Pyrex
Metering Chamber Cover Delrin Teflon with Steel Bracing Ring
Discharge Tube Latex Silicone
Sample Container(s) HDPE (or PP) Glass
O-Rings Buna-N (or Viton) Silicone
1-17
Page 26
Section 1. Product Overview
1.4 Portable Sampler Model Selection Guide
PVS Samplers come in a variety of models designed for variations in weight,
pump strength, battery, larger intake hose (5/8” ID), ease-of-transport, fitting in
manholes, discrete or composite sampling, protection rating for dust and water,
signal options, and budgets.
1-18
Page 27
Section 2. Installation
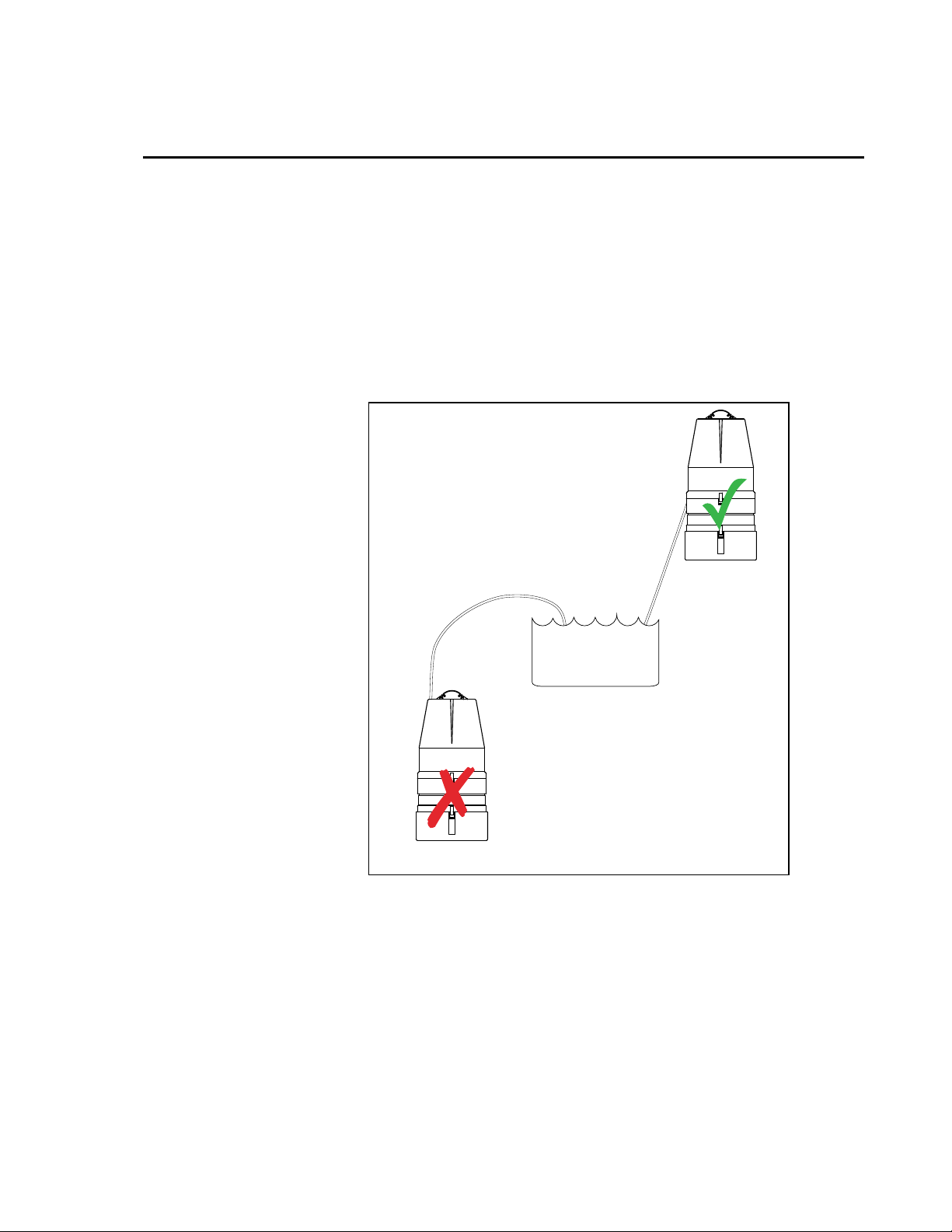
2.1 Cabinet Positioning
Place the sampler on a level surface as close as practical to the sample source.
Refer to the speed charts for maximum expected lift and draw. Manhole
installation may require 3-point suspension harness.
Sampler must be located above sample source, or liquid will flood the machine.
For situations where this is not possible, please contact a Campbell Scientific
application engineer for solutions on pressurized sources.
FIGURE 2-1. Sampler Installation
2-1
Page 28

Section 2. Installation
2.2 Intake Hose
Ensure the intake hose is submerged at all times throughout different flow
velocities.
CAUTION
Twenty-five feet of intake hose is provided with the
sampler. Shortening the hose is not recommended since
this length of hose provides sufficient back pressure to the
metering chamber, allowing the pump to efficiently expel all
solids into the sampler container. Coil any excess intake
hose in a manner to provide natural drainage away from
the sampler. To install intake hose, heat the end in hot
water and slip over volume control tube. Secure with hose
clamp provided.
Sample line should be routed so that it has a near continuous slope from the
sampler to the source liquid. This will help keep the sample line cleared and
fully drained. All excess line should be coiled neatly and without any vertical
loops.
2.3 Sinker / Strainer
Sinker or sinker/strainer is intended to keep sample line fully submerged in the
source liquid. A sinker/strainer should be used in situations with material that
clogs up a normal sinker, or where the standard sinker could stir up bottom
sediment.
Lead Sinker: SAM-23-28-01 Stainless Steel Sinker/Strainer: SAM-23-28-11
2.4 Storage
If the sampler is not to be used for an extended period of time, store the unit in
an upright position in a warm, dry location. If the unit has an integral battery,
recharge the unit prior to storage.
Acceptable storage temperature: -30ºC to +60ºC (-22ºF to +140ºF)
2-2
Page 29

2.5 Signal Wiring
External input capabilities of the sampler are implemented by the use of an
optional external signal cable plugged into an external receptacle on the side of
the sampler. External inputs of different types can be used by choosing the
appropriate pair of wires in the cable.
On the PVS4150 the signal cable is combined with the AC Power cable, thus
limiting the number of connections possible.
FIGURE 2-2. External Signal Cable for PVS4100 and PVS4120
Section 2. Installation
IMPORTANT
Wiring to remote/external functions should AVOID ALL AC
POWER LINES if possible and/or be run in shielded cable
terminating the shield at the AC ground terminal at the remote
site.
2-3
Page 30

Section 2. Installation
2.6 Installation Checklist
Check the following items prior to use of sampler:
1) Sampler is mounted securely and level.
2) Intake Hose: - Free of kinks.
- Properly installed into liquid.
- Properly connected to volume control tube on
metering chamber.
3) Discharge hose: - Free of kinks.
- Natural downward slope to sample container.
- Properly connected to (or in) sample container.
4) Power requirements: - Check battery electrical condition.
- Recharge if necessary.
2-4
Page 31

Section 3. Operation
3.1 Operating Sequence
3.1.1 Sampling Sequence
SAMPLING PROCESS:
1. High pressure air purge of intake hose.
2. Liquid is drawn into the metering chamber, up to the liquid sensing rod.
3. All excess liquid is purged from the system down to the level set by the
volume control tube.
4. The sample is then released into either one composite container or one of
several discrete containers.
The sampling sequence begins with a high pressure air purge of the intake
assembly to remove residual liquid and obstructions. Upon completion of the
pre-purge cycle, the system converts to a vacuum state, drawing the sample
through the intake hose into the metering chamber. The system then
pressurizes, ejecting excess fluid back through the intake line until the
predetermined sample volume is achieved. The sample is then deposited under
pressure into the sample container while the post purge again clears the intake
line of any residual liquid.
3-1
Page 32

Section 3. Operation
3.1.2 Line Voltage Failure
Should the sampler, for any reason, not be able to draw a sufficient volume of
fluid to obtain a sample, the unit automatically initiates a second attempt.
Should a sample still not be delivered, the sequence will be abandoned and the
unit will await the next initiation. Upon two consecutive failures, the sampler
will suspend the sampling program until manually RESTARTed.
If programmed with the FAULT SHUTDOWN “disabled”, the sampler will
not make a second attempt to draw the sample, but will simply abandon it and
await the next sample initiation. Neither will the unit suspend the sampling
program after consecutive failures. This function is provided for use in the
event that the sample source may be lacking sufficient fluid from which to
draw, for a period of time , yet allows the sampler to continue operating
without a “FAULT SHUTDOWN” occurring. The second attempt is not made
to prevent unnecessary wear on the sampler.
Should the sampler have a factory installed internal battery or have an external
battery connected, the sampler will continue operating. The duration of
operation will depend on the capability and charge level of either battery. The
frequency and the length of each sample cycle will also have an impact on how
long the batteries will last.
3.2 Operating Instructions
3.2.1 Sample Volume Adjustment
Setting the desired sample volume is accomplished by adjusting the height of
the volume control tube within the metering chamber. The tube is mounted
through the top of the chamber with a gland nut fixing the position. To adjust
the sample volume, loosen the nut until the volume control tube may be moved
freely. Raise or lower the bottom end of the tube to the desired volume using
the lines provided on the side of the chamber as a guide (lines are spaced at 100
cc intervals with the exception of one at 50 cc). Tighten the gland nut to hold
the volume control tube at the desired position.
3-2
Page 33

Section 3. Operation
IMPORTANT
NOTE
The volume control tube should always be located below the
liquid sensing rod.
Hold the bottom nut while loosening / tightening the top nut, or it
may become loosened from the metering chamber cover and
create an imperceptible leak in the vacuum system.
3.2.2 Liquid Sensing Rod
This probe, also called the “level control rod”, is used to stop the sample
intake. Always ensure that its lower end is located above the volume control
tube. Approximately 1” difference is sufficient. If the fluid intake is turbulent
within the metering chamber, more than 1” may be required to ensure
splashing of fluid does not trigger probe.
In applications with substantial oil or grease, the rods can become coated and
lose their conductivity. This is prevented by cleaning the rods regularly. In
extreme cases, extra SS wire can be wrapped around the liquid sensing rod to
increase its surface area.
IMPERATIVE: THE LIQUID SENSING ROD AND VOLUME CONTROL
TUBES MUST BE KEPT CLEAN TO ENSURE CONDUCTIVITY
NECESSARY TO DETECT THE PRESENCE OF THE FLUID.
Most PVS Samplers incorporate a Barrier Valve in the metering chamber
cover, where the tubing from the pump enters. It consists of a cage containing a
ball that will float if the sample should rise to the top of the chamber without
detection. Should rod conductivity fail, the fluid brings the float into contact
with an O-ring surrounding the pressure / vacuum port, sealing the entry to the
tubing and the pump (where the fluid may cause serious damage). This O-ring
Barrier Valve should be inspected regularly and replaced as necessary.
Due to the restriction of Wetted Materials (i.e. stainless steel, glass and
fluorocarbons etc.), some models of the sampler do not contain this barrier
valve. In these units, a secondary liquid-sensing circuit may be added as a
precaution. This circuit is connected to the pump tubing fitting on the Metering
Chamber cover.
3-3
Page 34

Section 3. Operation
3.3 Battery
3.3.1 Battery: Operating and Backup (optional)
CHARGING AND REVERSE POLARITY PROTECTION
The sampler will charge ONLY the factory installed internal battery. This
charging takes place continually as long as there is incoming line power.
Should the need arise to only charge the internal battery, as would be required
to store the sampler for an extended period of time, simply place the “ RUN /
OFF “ toggle switch in the OFF position, and leave the sampler power breaker
on. Twenty-four (24) hours should be sufficient to fully charge the battery.
The sampler is equipped with REVERSE POLARITY PROTECTION for
checking the connection of an external battery. When attaching an external
battery, be sure to check the reverse polarity indicator. If it is ON, reverse the
connections at the battery.
3-4
FIGURE 3-1. Battery Performance Curve
Page 35

3.3.2 Battery: Microprocessor
SAMPLER CONTROLLER BACKUP BATTERY
The controller contains a 1/2AA, 3.6V lithium backup battery to maintain user
settings during loss of system power. If power is removed for any reason, the
controller will start a planned shutdown procedure which will save all user
settings while its operating voltage is reduced from 5V to approximately 3.3V.
The rate at which this voltage drops is slowed by the presence of a
supercapacitor. By the time the voltage has reached 3.3V, the controller has
safely stored all user settings and entered a “sleep” mode. This is an extremely
low-power mode which is maintained by a trickle of current from the lithium
battery, and can be maintained for many years under normal circumstances.
The battery is located on the top left hand side of the controller. It is accessible
by the removal of the clear cover, and should be changed under powered
conditions. Since the controller is a low-power device, this uncovering can be
safely done, taking care that no conductive implement contacts sensitive circuit
components.
If the controller starts to exhibit certain operating anomalies such as loss of
user settings after sustained power outages or an inability to “wake up” after a
normal shutdown, it may be due to a low or totally discharged backup battery.
To predict the probability of these events, regular examination of the battery
condition is encouraged. The battery status is easily determined while the
controller is active. The process will not affect a running program. Battery
status can be checked by use of the following touchpad sequence:
Section 3. Operation
VIEW, OTHER OPTIONS,
select MAINTENANCE, ENTER, then select B/U BATTERY TEST, ENTER
The display will then show “PASSED”, “LOW” or “FAULT”. The latter two
require battery replacement.
TO REPLACE BATTERY
1. Make sure the controller is powered.
2. Remove touchpad (clear) cover from the controller, remembering to
handle internal ribbon cable and connector with care.
3. Locate the battery holder on the normal left side of the circuit board. The
battery is a 1/2” cylinder about 1” in length. The positive (+) end of the
battery has a raised button. Note the button’s relative position in the
holder. It should be pointing away from the display side of the board.
4. Place new battery in holder, noting position of button with respect to the
polarity indicators in the holder.
5. Check battery status, as above. If necessary, locate small white button at
top of the control board (under display) and push to restore factory
defaults.
6. Replace cover securely and re-enter user settings.
3-5
Page 36

Section 3. Operation
3.4 Test Procedure
1. Set volume control tube to 200 cc.
2. Set level probe 1” above bottom of volume control tube.
3. Turn on power. Place the “RUN/OFF” switch in the “RUN” position.
After an initial delay of 15 to 20 seconds, the display will show a two line
message, the top line displaying SAMPLER HALTED and an alternating
message on the second line displaying why the sampling procedure was
interrupted as well as the event time and date.
4. Enter the following sampling program:
a) Set purge time to 10 seconds. See OTHER OPTIONS
b) Set interval time to 2 minutes. See SAMPLE INITIATION
c) Set program type to composite. See PROGRAM TYPE
d) Set to terminate after 2 samples.
e) Press RESTART, RESTART (to confirm)
5. View the following displays:
a) Samples taken - should read 0
b) Remaining time - should be counting down from 2 minutes.
6. Sampling should begin when remaining time indicator reaches 0.
7. Upon completion of sample, view the following displays:
a) Samples taken - should read 1.
b) Remaining time - should be counting down from 5 minutes.
8. Press MANUAL PURGE. Press again to confirm.
9. Press MANUAL ADVANCE. Press again to confirm.
10. Press MANUAL SAMPLE. Press again to confirm.
11. If equipped with sample container full option, short circuit level probes in
container (no dangerous voltage present - 16 Vdc). The message
“SAMPLER HALTED External Stop” should appear on the display, the
bottom line flashing.
12. Press RESTART, RESTART, the message “RESTART <Completed>”
should appear on the display.
3.5 Troubleshooting
SAMPLER INOPERATIVE: Check supply voltage.
POWER ON BUT PUMP WILL NOT START: Check wiring from
sampler controller to pump. Ensure controller is properly connected
into harness.
a) Pump defective.
b) Sampler controller defective.
3-6
Page 37

Section 3. Operation
SAMPLER WILL NOT TAKE TIMED SAMPLE:
a) Sampler controller defective.
SAMPLER WILL NOT INITIATE FROM AN EXTERNAL
CONTACT: Check wiring from terminal strip to sampler controller
plug. (Terminals 12 & 13)
a) Sampler controller is defective.
b) Sampler controller not programmed for External Contact input.
PUMP IS OPERATING, NO AIR PURGE OF INTAKE LINE: Check for
blockage of intake hose by removing hose from the metering chamber volume
control tube. Initiate manual sample and check for pressure/vacuum throughout
sample cycle.
a) If pressure/vacuum is present throughout sample cycle, intake hose is
plugged.
b) Pinch valve may not be closing the discharge hose with sufficient force
to ensure an adequate seal. Increase tension by tightening the lock nuts on
the pinch valve tension springs and/or replace discharge hose.
c) Check for disconnected air lines from pump to metering chamber.
d) Check for loose gland nuts.
e) Pump flapper valves defective.
PURGE CYCLE OPERATIVE, NO SUCTION: Pinch valve may not be
closing the discharge hose with sufficient force to ensure an adequate seal.
Increase tension by tightening the lock nuts on the pinch valve tension springs
and/or replace discharge hose.
a) Check air lines, metering chamber O-rings and fittings for leakage.
b) Solenoid valve clogged or not working.
c) Intake tube, not below water level.
SAMPLER HAS HAD AN “EXTERNAL STOP”: Contact not supplied via
terminal block.
a) Sample container Full Level Probe has been triggered.
LEVEL SENSING PROBE INOPERATIVE: Check wire contact
connections on volume control tube and level sensing probe. Check wiring to
the sampler controller plug.
a) Sampler controller defective
b) Coating on probe and/or Volume Control Tube.
3-7
Page 38

Section 3. Operation
3-8
Page 39

Section 4. Maintenance
The following maintenance procedure should be performed at regular
intervals:
4.1 General Maintenance
1. Disconnect power.
2. Open metering chamber by removing wing nuts and chamber cover.
3. Clean volume control tube and level sensing probe with mild detergent.
Alternatively, exchange tube and probe with clean set. Do not use any
cleaner which may be harmful to the metering chamber cover. Do not use
solvents such as acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride or lacquer thinners.
Grease and oil may be removed with kerosene or aliphatic naphtha (nonaromatic).
4. Check and clean O-rings in metering chamber cover.
Replace if damaged, worn or brittle.
5. Clean metering chamber using mild detergent.
Do not use any cleaner which may be harmful to the clear acrylic, (e.g.
petrochemical solvents, as noted above.) Do not use abrasives or
“scouring” compounds.
6. Check discharge tubing for wear and replace as necessary.
7. Check pinch valve to ensure free movement.
8. If possible, run sampler through several sampling sequences in clean
water.
4.2 Testing System Vacuum
Using the (optional) built-in pressure / vacuum gauge, take a reading to ensure
system has no leaks. Optimal pressure is above 28 psi. Optimal vacuum should
be 12 psi or better.
If the system is not performing at its peak, try the following:
1. Check intake hose for leaks/kinks.
2. Check discharge tube, ensure it has no leaks and is in good shape.
3. Check all fittings to ensure they are tight.
4. Make sure when tightening and loosening the gland nuts on the top of the
metering chamber that the bottom nut is held secure and does not move on
the cover. Ensure the top nut is securely tightened, and use a wrench if
necessary.
4-1
Page 40

Section 4. Maintenance
5. If still system is still not performing at its peak, inspect pump and all
pump tubing.
4-2
Page 41

Section 5. Programming
5.1 General Programming
5.1.1 Guidelines
Controller settings may be changed at any time. Changes are termed NEW
ENTRIES. No NEW ENTRIES will be acted upon unless the controller is
RESTARTed. Once RESTARTed, all NEW ENTRIES become ACTIVE
SETTINGS.
Every time the controller is RESTARTed, all accumulators (i.e. SAMPLES
TAKEN, TIME REMAINING, REMAINING PULSES, etc.) are cleared
and the ACTIVE SETTINGS are reloaded unless NEW ENTRIES have been
made.
Remember - Start Delay is reloaded too !!
5.1.1.1 Flashing Text
Flashing text is the system wide prompt that indicates an input is required from
the user. Flashing words or duel flashing digits prompt for arrow keys to be
pressed to scroll through available options. A single flashing digit prompts for
a numeric key to be pressed. When the desired option or number is shown on
the display, press the ENTER key.
5.1.1.2 Real Time Clock
The controller has two basic timing modes. The simplest of these requires no
maintenance; it simply provides a “heartbeat” for various timed functions. The
other timing mode is the REAL TIME CLOCK that is used in several functions
and must be correctly set. This is likely the first item requiring
programming. Although time may have been set at the factory, time zone shifts
may require adjustment of the Real Time Clock.
5.1.1.3 Total Bottles
Since the number of bottles is usually determined by customer requirement at
the time of purchase, this variable will normally be set at the factory to match
the actual container hardware. Choices are restricted to a single container (as in
composite) or 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 or 24. These all form instructions to the stepper
motor in how it will behave when the internal command is given to step to the
next container (as each step increment is 15°).
5-1
Page 42

Section 5. Programming
5.1.2 Touchpad Keys
TABLE 5-1. Touchpad Button Descriptions
Button Description
The VIEW key is used to review alterable parameters currently in use. It has no effect on the
program being executed at the time. Once pressed, the user is prompted for a FUNCTION to be
viewed. The parameters visible under the function can be stepped through using the ENTER key.
The SET key is used to change program settings or the entire sampling program. Changes made
have no effect on the program being executed at the time until the RESTART key is pressed twice.
To leave a programming sequence before entering it in memory either press SET or VIEW and the
sequence is aborted.
The ENTER key is used to complete either a VIEW or SET sequence, where sub-menu items are
available. Under the control of the VIEW key, parameters are scrolled onto the display, changing
with each use of the ENTER key until a complete display of the parameter is completed. Under the
control of the SET key, parameters can be displayed, with the added ability to change their values,
using the ENTER key to accept the new value until the entire parameter is displayed. (Note: New
values are not operational at this time.)
5-2
Page 43

TABLE 5-1. Touchpad Button Descriptions
Button Description
The RESTART key is used to load any new parameters into the operating program. Pressing it
twice will initialize the program and terminate any existing sample program. Any parameters
altered under the SET command are updated to the active program. If no parameters have been
changed, the program is reset to its first instruction and the same sampler program is started again.
This key requires a confirming second activation to complete its function. WARNING: Any
program in progress is ended and all data is lost.
SAMPLES TAKEN [VIEW]. The total number of samples taken can be shown on the display.
REMAINING PULSES [VIEW]. In modes using internal or external pulse counting, the current
status of the pulse count can be displayed.
REMAINING TIME [VIEW]. Various views are available dependent on the method used to
gather samples. Program variables will determine whether the displayed time is REMAINING
TIME, ELAPSED TIME or START DELAY.
START DELAY [VIEW/SET]. The start of a sample program can be made to occur at a fixed time
or event. Options: DISABLE, TIME/DAY, PULSE INPUT, 4-20mA INPUT, EXTERNAL
CONTACT, LEVEL CONTROL.
SAMPLE INITIATION [VIEW/SET]. A sample program may be initiated and controlled by
various internal and external parameters. These parameters determine how the program will begin
its actions and how the results will be recorded. Options: DISABLE, INTERVAL TIME, PULSE
INPUT, 4-20mA INPUT, EXTERNAL CONTACT.
PROGRAM TYPE [VIEW/SET]. A sample program can be made to collect samples in a fixed
style so that the results are useable in different ways. The type of program used may be hardware
dependent. This will determine the sampler’s ability to collect and store the desired samples.
Options: COMPOSITE, DAILY CYCLE, CONSECUTIVE, MULTI-COMPOSITE, TIMED
STEP.
Section 5. Programming
ACTIVE SETTINGS [VIEW]. Current sample program parameters can be reviewed by scrolling
through them using the ENTER key as a toggle.
NEW ENTRIES [SET]. Program all major program settings at once (including START DELAY,
SAMPLE INITIATION, PROGRAM TYPE, and PURGE TIME).
[VIEW]. Review parameters that have been changed since the sample program was started (only if
the changes have been properly ENTERED). Scroll through them using the ENTER key as a
toggle.
OTHER OPTIONS [VIEW/SET]. Various options relating to equipment and information retrieval
are available under this key. Changes in equipment setup can be entered here, and certain status
information is also available here. Options: CLOCK, PURGE TIME, PINCH VALVE, FAULT
SHUTDOWN, SAMPLER STATUS, CYCLES ABANDONED, BOTTLE POSITION,
MAINTENANCE.
5-3
Page 44

Section 5. Programming
TABLE 5-1. Touchpad Button Descriptions
Button Description
MANUAL PURGE. Purges the intake line independent of program control, as long as a
programmed cycle has not started. Sampler starts its pump, creating pressure in the sample intake
tube to purge it of any excess material that may be present. Button must be pressed twice to purge
line. Sustained pressure on the key during the second press will cause purging to continue until the
key is released.
MANUAL ADVANCE. Distributor arm advances one position (e.g. to next bottle), dependent on
the equipment available (discrete samplers only). This action is NOT updated to any current
sampler program. Button must be pressed twice to initiate manual advance.
MANUAL SAMPLE. Initiate a single Sample Cycle. Sampler must not be engaged in a sampling
event at the time. This action and any resulting sample collected are NOT updated to any current
sampler program. The Bottle Position is NOT advanced. Program will continue uninterrupted.
Button must be pressed twice to initiate manual sample. Whether successful or not, the display will
read “MANUAL SAMPLE Completed”.
5.1.3 General Terms
Many of the functions available on the Touchpad have a variety of options to
enhance their capabilities. These options are programmable from the Touchpad
and require only that the sampler have the correct equipment configuration to
utilize them.
DISABLE
The display showing disabled will reflect the status of any function not being
used.
TIME/DAY
The basis for several timed functions is the Real Time Operating System. Time
(of) Day will be a means of setting the timing period for the START DELAY
function. The format is on a weekly basis, requiring hour, minute, AM/PM and
day inputs (HH:MM AM SUN). This means the Start Delay can be set to any
particular minute in a week.
INTERVAL TIME
Sampler operation can be controlled by fixed time intervals which do not
require Time/Day setting. SAMPLE INITIATION has an option whereby an
interval time can be set between sample cycles. The controller will cause
samples to be taken on a timed interval basis, continuing until the sample
program is completed by a full jar or operator intercession.
5-4
PULSE INPUT
This option will allow the controller to determine the sampler operation based
on external criteria. Pulses fed to an internal accumulator in the controller will
be compared to the setting entered by the operator and will cause a sample
cycle to start. The accumulator will reset immediately and counting of pulses
Page 45

Section 5. Programming
will begin again. There is no loss of count the sample cycle. Pulse requirements
of the system are detailed in the specifications.
4-20mA INPUT
Where external devices do not themselves generate pulses in any relation to
their process but generate a current signal of 4-20 mA, this input option will
generate internal pulses proportional to the incoming 4-20 mA signal. These
can then be treated the same as the Pulse Input option and accumulated in the
controller to determine when a sample cycle will occur.
EXTERNAL CONTACT
The sampler controller can react to an external dry contact, otherwise known as
a zero-voltage contact, to activate a sample cycle on demand. This will
generally be when external conditions have caused a relay to close, requiring a
sample be taken at that time.
LEVEL CONTROL
The START DELAY function is a special case of the external contact option.
where the contact signal is required to be present for a pre-programmed time.
This enables verification of the signal where fluctuations may occur in the level
which would trigger samples at unwanted times. This is the only case in which
the START DELAY is not a single timed event. The operation of the sampler
after the level signal is verified will be controlled by whatever function is set in
the SAMPLE INITIATION. It will continue until the level drops or the
function is terminated by the controller. If the level drops before the function is
finished, any sample cycle already in progress will be completed and then the
system will shut down until the next verified level control signal.
COMPOSITE
A program option which determines that all the samples that are gathered will
be placed in a single container. The sample program terminates after a specific
number of samples.
MULTI-COMPOSITE
This option is used for discrete sampling applications, to deposit multiple
samples to one container before advancing the distributor mechanism to the
next container. The interval between each sample is controlled by the
SAMPLE INITIATION options. The multi-composite setting is
programmable up to 99 samples per container, for up to 24 containers
depending on the hardware configuration.
CONSECUTIVE
This option is used for discrete sampling applications, to successively deposit
one sample to each of a programmed number of containers on any given
sample initiation. The consecutive setting is programmable up to 99 containers
per sample initiation, although this may be severely limited by hardware
configuration.
5-5
Page 46

Section 5. Programming
DAILY CYCLE
Allows the sampler to deposit equal sample volumes into a predetermined
number of containers per programmed day. Each day may have any number of
samples taken, dependent on the SAMPLE INITIATION mode chosen.
Deposits are made to as many as 9 containers per day, to a cumulative total of
24 containers. (e.g. Choosing a 24 bottle format, the sampler may be
programmed to deposit to Three (3) bottles on any six days of the week,
together with up to Six (6) bottles on the seventh). Timing is dependent on the
crystal-controlled Real Time Clock in the controller. The first program day will
be the current day the programming is done, unless the START DELAY
option is chosen to determine when sampling will begin.
TIMED STEP (Override)
This option will cause the sample distributor to step to a new container
regardless of the status of the SAMPLE INITIATION setting. For example,
the actual sampling may be under the control of a flowmeter and taking
samples based on the flow rate as determined by pulses or 4-20mA input to the
controller. When the user-programmed Timed interval has elapsed, the
controller will Step to a new container. The Timed Step can be set for any
interval up to 99 hours 59 minutes. Progress of the step timer can be viewed by
selecting View, Program Type and pressing ENTER twice. Thus you may
view the REMAINING TIME or the step timing.
5.2 Quick Start Guide to Programming
5.2.1 Automatic Sampling Program
To begin a new, quick program:
Press “SET”
Press “NEW ENTRIES” . Press “ENTER”
START DELAY (how you will be delaying the
sample program until certain external conditions are
met). Select, using arrows, which parameter you
would like, and adjust settings (see 5.3
Programming Start Delay). Options: DISABLE;
TIME/DAY; PULSE INPUT; 4-20mA INPUT;
EXTERNAL CONTACT; LEVEL CONTROL.
Press “ENTER” twice
5-6
Page 47

SAMPLE INITIATION (parameters for frequency
of samples). Select, using arrows, which parameter
you would like, and adjust settings (see 5.4
Programming Sample Initiation). Options:
DISABLE; INTERVAL TIME; PULSE INPUT; 420mA INPUT; EXTERNAL CONTACT.
Press “ENTER” twice.
Section 5. Programming
PROGRAM TYPE (which type of sampling
program). Select, using arrows, which parameter
you would like, and adjust settings (see 5.5
Programming Program Type). Options:
COMPOSITE; MULTI-COMPOSITE;
CONSECUTIVE; DAILY CYCLE; TIMED STEP
(override).
Press “ENTER” twice.
PURGE TIME (set how long sampler will purge
between samples, minimum of 10 seconds). Using #
keys, enter the purge time needed for application
(e.g. 100 ft draw at 5 ft/sec = 20 sec). Press
“ENTER”.
Press “RESTART” twice.
Sampling is ready to go.
5.2.2 Taking a Manual Sample
5.2.3 Viewing Program Parameters
To take a sample manually, simply press the
“Manual Sample” button twice. Manual
samples will not interrupt the current
automatic sampling program.
To view the program or remaining time,
press the “VIEW” button, followed by the
button representing what you want to see,
e.g. “REMAINING TIME”.
5-7
Page 48

Section 5. Programming
5.2.4 Setting Program Parameters Individually
5.3 Programming START DELAY
5.3.1 START DELAY Overview
To modify any of the settings individually
press the “SET” button followed by the
appropriate button based on what parameter
START DELAY is the function which will delay the beginning of a sample
program until certain external conditions are met. Upon meeting those
conditions, the sampler will initiate a sample cycle and then operate based on
the SAMPLE INITIATION parameters. Under START DELAY, flashing
text prompts the user to scroll through available options by pressing arrow
keys. These options only require that the correct equipment is present to utilize
them. The last option selected in previous programming will be the first to
appear on the display.
is being changed.
The display showing disabled will reflect
the fact that the function is not being used.
The basis for several timed functions is the
Real Time Operating System. Time (of) Day
will be a means of setting the timing period
for the START DELAY function. The
format is on a weekly basis, requiring hour,
minute, AM/PM and day inputs (HH:MM
AM SUN). This means the start of a sampler
program can be delayed up to seven days.
This option will allow the controller to
determine the sampler’s start of operation
based on external pulses. Pulses fed to an
internal accumulator in the controller will be
compared to the setting entered by the
operator. Pulse requirements of the system
are detailed in the specifications.
Where external devices do not themselves
generate pulses in any relation to their
process but generate a current signal of
4-20mA, this input option will generate
internal pulses proportional to the incoming
4-20mA signal. These can then be treated
the same as the Pulse Input option and
accumulated in the controller to determine
when a sample program should start.
5-8
Page 49

Section 5. Programming
The sampler controller can react to an
external dry contact, otherwise known as a
zero-voltage contact, to activate a sample
program on demand. This will generally be
when external conditions have caused a
relay to close, requiring a sample program
be started at that time.
This option is a special case of the external
contact option. The key difference is that
the contact closure must be present for a
pre-programmed time, thus enabling
verification of the signal. This will
accommodate fluctuations as seen in a level
switch, thereby avoiding triggering of
samples at unwanted times. This is the only
case in which the START DELAY is not a
single timed event. Should the contact open
for the same pre-programmed time, the
sampler will (after completing any sample
cycle already in progress), halt the sampling
initiation and await the next verified signal.
At this time, the sampling program will
resume.
5.3.2 START DELAY using Time/Day
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to create a future starting
time for the operation of the Sampler. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the START DELAY key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Time/Day is shown on the display.
4. Press the ENTER key.
5-9
Page 50

Section 5. Programming
When setting the time, a single flashing digit
indicates an input from a numeric key is
required. Press a number key to enter a
value. The next digits flash in succession.
Enter each as required. The format is
HH:MM.
When the four digits are entered, press
ENTER. Any wrong entries will require reentry. There are two methods of correcting a
mistake. The digit flashing “wraps around”
and begins again, at which time the correct
entry may be pressed. Alternately, the arrow
keys can be used to reposition the flashing
prompt over the error, which can then be
replaced with the correct value.
The flashing prompt advances to the
AM/PM indicator. Press the ARROW key
until the right indicator is shown. Press
ENTER.
The flashing prompt advances to the day
indicator. Press the ARROW key repeatedly
until the correct day appears. Press ENTER.
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for START DELAY. The new values
reside in the NEW ENTRIES area of the
controller memory. To make these changes
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then wait until the designated
time before starting its sampling program.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, START DELAY, ARROW(S), ENTER, #, #, #, #, ENTER,
ARROW(S), ENTER, ARROW(S), ENTER, RESTART, RESTART.
5-10
Page 51

5.3.3 START DELAY using Pulse Input
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to create a future starting
time for the operation of the Sampler. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the START DELAY key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Pulse Input is shown on the display.
Section 5. Programming
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will show a new screen
containing the option title PULSE INPUT
on the top line and a 7 digit number with the
leftmost digit flashing as an input prompt.
To set the number of pulses required to be
input before a sample program is started, use
the ARROW keys to move the flashing
prompt until it is over the digit requiring
change.
Press a number key (0-9) to replace any
existing number and advance the flashing
prompt to the next digit to change. Replace
digits as required, then press ENTER.
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
Any wrong entries will require re-entry. If
ENTER has not been pressed, reposition the
prompt over the incorrect digit and replace
it. After ENTER has been pressed, the entire
entry must be redone from the beginning
(press SET).
5-11
Page 52

Section 5. Programming
5.3.4 START DELAY using 4-20mA Input
The controller has now been given a new
value for START DELAY. The new values
reside in the NEW ENTRIES area of the
Summary of Sequence:
SET, START DELAY, ARROW(S), ENTER, #######, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
controller memory. To make these changes
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then wait until the required
pulses have been received before starting its
sampling program.
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to create a future starting
time for the operation of the Sampler. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the START DELAY key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until 4-
20mA Input is shown on the display.
4. Press the ENTER key.
5-12
Page 53

Section 5. Programming
The display will show a new screen
containing the option title 4-20mA INPUT
on the top line and a 7 digit number with the
leftmost digit flashing as a prompt for input.
The 4-20 mA input will be converted by the
controller to pulses, proportional to the span
of the input, at the rate set in the
specifications. To set the number of pulses
required to be input before a sample program
is started, use the ARROW keys to move
the flashing prompt until it is over the digit
requiring change.
Press a number key (0-9) to replace any
existing number and advance the flashing
prompt to the next digit to change. Replace
digits as required, then press ENTER.
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
Any wrong entries will require re-entry. If
ENTER has not been pressed, reposition the
flashing prompt over the incorrect digit and
replace it. After ENTER has been pressed,
the entire entry must be redone from the
beginning (press SET).
The controller has now been given a new
value for START DELAY. The new values
reside in the NEW ENTRIES area of the
controller memory. To make these changes
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then wait until the required
pulses have been received before starting its
sampling program.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, START DELAY, ARROW(S), ENTER, #######, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
5-13
Page 54

Section 5. Programming
5.3.5 START DELAY using External Contact
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to create a future starting
time for the operation of the Sampler. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the START DELAY key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
External Contact is shown on the display.
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for START DELAY. The new value
resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of the
Summary of Sequence:
SET, START DELAY, ARROW(S), ENTER, RESTART, RESTART.
controller memory. To make this change
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then wait until it receives a
contact closure (at the External Start inputs
on the terminal block) before starting its
sampling program.
5-14
Page 55

5.3.6 START DELAY using Level Control
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to create a future starting
time for the operation of the Sampler. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the START DELAY key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Level Control is shown on the display.
Section 5. Programming
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will change to read “Minimum
Contact Time: 01 seconds”. The actual time
shown may be any two digit number. The
first digit will be flashing as a prompt for
input.
Press a number key (0-9). The number will
replace the current number and advance the
flashing prompt to the next digit. Press a
second number key (0-9). Repeat this
procedure if number is wrong, until desired
time is displayed. Press the ENTER key.
The display will echo the last entry with
START DELAY, <ENTERED>.
5-15
Page 56

Section 5. Programming
5.4 Programming SAMPLE INITIATION
The controller has now been given a new
value for START DELAY. The new values
reside in the NEW ENTRIES area of the
Summary of Sequence:
SET, START DELAY, ARROW(S), ENTER, ##, ENTER, RESTART,
RESTART.
controller memory. To make these changes
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then wait until it receives a
contact closure (at the External Start inputs
on the terminal block). The contact must
remain closed for the length of time
programmed in the steps above.
5.4.1 SAMPLE INITIATION Overview
SAMPLE INITIATION is the function that will determine the frequency that
samples are drawn. There is available on the Touchpad a variety of options to
enhance the capabilities of this function. When the Sample Initiation has been
chosen to be set, a list of options is presented as flashing text below the main
heading of the function selected. The list is advanced using the ARROW keys
(any direction) until the desired option is displayed. These options are
programmable from the Touchpad and require only that the sampler have the
correct equipment configuration to utilize them. The last option selected in
previous programming will be the first to appear on the display.
The display showing disabled will reflect
the fact that the function is not being used.
Sampler operation can be started at uniform
intervals. This option allows an interval time
to be set between sample cycles.
5-16
Page 57

Section 5. Programming
This option will allow the controller to
determine the SAMPLE INITIATION
based on external pulses. Pulses fed to an
internal accumulator in the controller will be
compared to the setting entered by the
operator and will cause a sample cycle to
start. The accumulator will reset
immediately and counting of pulses will
begin again. There is no loss of count during
the sample cycle. Pulse requirements of the
system are detailed in the specifications.
Where external devices do not themselves
generate pulses in any relation to their
process but generate a current signal of
4-20mA, this input option will generate
internal pulses proportional to the incoming
4-20mA signal. These can then be treated
the same as the Pulse Input option and
accumulated in the controller to determine
when a sample cycle should occur.
The sampler controller can react to an
external dry contact, otherwise known as a
zero-voltage contact, to activate a sample
cycle on demand. This will generally be
when external conditions have caused a
relay to close, whose contact will cause a
sample to be taken.
5.4.2 SAMPLE INITIATION using Interval Time
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to form a basic operating
parameter for operation of the sampler. This
will determine the time from the start of a
sample cycle to the start of the next sample
cycle. No time is lost during the actual
sample cycle. The ACTIVE SETTINGS are
not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the SAMPLE INITIATION key.
5-17
Page 58

Section 5. Programming
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Interval Time is shown on the display.
4. Press the ENTER key.
When setting the time, a flashing digit
prompts for input from a numeric key. To
set the time, press a numeric key to enter a
value and advance to each digit in
succession. The format is HHH:MM. The
minimum time can be set to 1 minute,
however, practical considerations, such as
equipment duty cycle, maintenance and
service life suggest times of 3 minutes or
longer.
When the five digits are entered, press
ENTER. Any wrong entries will require
re-entry. There are two methods of
correcting a mistake. The digit flashing
“wraps around” and begins again, at which
time the correct entry may be pressed.
Alternately, the arrow keys can be used to
reposition the flashing prompt over the error,
which can then be replaced with the correct
value.
5-18
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for SAMPLE INITIATION. The new
values reside in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then wait the designated
time before taking a sample.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, SAMPLE INITIATION, ARROW(S), ENTER, ###:##, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
Page 59

5.4.3 SAMPLE INITIATION using Pulse Input
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to form a basic operating
parameter for operation of the sampler. This
will determine the number of pulses from
the start of a sample cycle to the start of the
next sample cycle. The ACTIVE
SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the SAMPLE INITIATION key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Pulse Input is shown on the display.
Section 5. Programming
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will show a new screen
containing the option title PULSE INPUT
on the top line and a 7 digit number with the
leftmost digit flashing to prompt for a
numeric input. To set the number of pulses
required to be input before a sample is taken,
by use of the ARROW keys, move the
flashing prompt until it is over the digit
requiring change.
Press a number key (0-9) to replace any
existing number and advance the flashing
prompt to the next digit to change. Replace
digits as required, then press ENTER.
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
Any wrong entries will require re-entry. If
ENTER has not been pressed, reposition the
prompt over the incorrect digit and replace
it. After ENTER has been pressed, the entire
entry must be redone from the beginning
(press SET).
5-19
Page 60

Section 5. Programming
5.4.4 SAMPLE INITIATION using 4-20mA Input
The controller has now been given a new
value for SAMPLE INITIATION. The new
values reside in the NEW ENTRIES area of
Summary of Sequence:
SET, SAMPLE INITIATION, ARROW(S), ENTER, #######, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then wait until the
required pulses have been received before
taking a sample.
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to form a basic operating
parameter for operation of the sampler. This
will determine the number of pulses from
the start of a sample cycle to the start of the
next sample cycle. The ACTIVE
SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the SAMPLE INITIATION key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until 4-
20mA Input is shown on the display.
4. Press the ENTER key.
5-20
Page 61

Section 5. Programming
The display will show a new screen
containing the option title 4-20mA INPUT
on the top line and a 7 digit number with the
leftmost digit flashing as a prompt for input.
The 4-20 mA input will be converted by the
controller to pulses, proportional to the span
of the input, at the rate set in the
specifications. To set the number of pulses
required to be input before a sample is taken,
use the ARROW keys to move the flashing
prompt until it is over the digit requiring
change.
Press a number key (0-9) to replace any
existing number and advance the flashing
prompt to the next digit to change. Replace
digits as required, then press ENTER.
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
Any wrong entries will require re entry. If
ENTER has not been pressed, reposition the
prompt over the incorrect digit and replace
it. After ENTER has been pressed, the
entire entry must be redone from the
beginning (press SET).
The controller has now been given a new
value for SAMPLE INITIATION. The new
values reside in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then wait until the
required pulses have been received before
taking a sample.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, SAMPLE INITIATION, ARROW(S), ENTER, #######, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
5-21
Page 62

Section 5. Programming
5.4.5 SAMPLE INITIATION using External Contact
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to form a basic operating
parameter for operation of the sampler. This
will determine the time between samples
being taken. The ACTIVE SETTINGS are
not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the SAMPLE INITIATION key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
External Contact is shown on the display.
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will echo the last entry with
<ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for SAMPLE INITIATION. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
Summary of Sequence:
SET, SAMPLE INITIATION, ARROW(S), ENTER, RESTART,
RESTART.
the controller memory. To make this change
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then wait until a contact
closure has been received before taking a
sample.
5-22
Page 63

5.5 Programming PROGRAM TYPE
5.5.1 PROGRAM TYPE Overview
PROGRAM TYPE is the function which determines how the sampler will
perform its program. A variety of options are available. These options are
programmable from the Touchpad and require only that the sampler have the
correct equipment configuration to utilize them. The basic function of the
Program Type is to determine the movement of the distributor.
The program option which determines that
all the samples that are gathered will be
placed in a single container. The sampler
program terminates after the specified
number of samples have been taken.
This option is used for discrete sampling
applications, to deposit one or a number of
samples to one container before advancing
to the next container. The interval between
samples is controlled by the SAMPLE
INITIATION function. The
multi-composite setting is programmable up
to 99 samples per container, for up to 24
containers depending on the hardware
configuration.
Section 5. Programming
This option is used for discrete sampling
applications, to successively deposit one
sample to each of a programmed number of
containers on any given sample initiation.
The consecutive setting is programmable up
to 99 containers per sample initiation.
Allows the sampler to deposit equal sample
volumes into a predetermined number of
containers per programmed day. Each day
may have any number of samples taken,
dependent on the SAMPLE INITIATION
mode chosen. Deposits are made to as many
as 9 containers per day, to a cumulative total
of 24 containers. Timing is dependent on the
crystal-controlled Real Time Clock in the
controller. The first program day will be the
current day the programming is done.
5-23
Page 64

Section 5. Programming
5.5.2 PROGRAM TYPE - Composite
This option will cause the sampler to step to
a new container regardless of the status of
the SAMPLE INITIATION setting. For
example, the actual sampling may be under
the control of a flowmeter and taking
samples based on the flow rate as
determined by pulses or 4-20mA input to the
controller. When the user-programmed
timed interval has elapsed, the controller
will step to a new container. The Timed
Step can be set for any interval up to 99
hours 59 minutes. Progress of the step timer
can be viewed by selecting View, Program
Type and pressing ENTER twice. Thus you
may view the step timing and the amount of
time until the next step occurs.
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to store the samples it
takes, in the hardware specified in its
configuration. The ACTIVE SETTINGS are
not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the PROGRAM TYPE key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Composite is shown on the display (for
storage in single container).
4. Press the ENTER key.
5-24
Page 65

Section 5. Programming
The display will respond with the message
“Terminate After 0000009 Samples”. The
numerical value will be whatever value was
last placed in the controller’s memory,
usually after previous programming. To
keep the previous value press ENTER, or,
to set a new value, use the ARROW keys to
advance the flashing prompt to the desired
location and replace the digits under the
prompt by using the digits (0-9) on the
Touchpad. Each new entry will
automatically advance the prompt to the next
location. In this way, the entire 7 digit
number can be changed. The ARROW keys
can be used to skip already correct digits, in
either direction.
When the 9 digit number is correctly
entered, press ENTER.
The display will echo the last entry with
PROGRAM TYPE <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for PROGRAM TYPE. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then be set to perform as
a Composite Sampler in conjunction with
the parameters programmed under the
START DELAY and SAMPLE
INITIATION variables.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, PROGRAM TYPE, ARROW(S), ENTER, #######, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
5-25
Page 66

Section 5. Programming
5.5.3 PROGRAM TYPE - Daily Cycle
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to store the samples it
takes, in the hardware specified in its
configuration. The ACTIVE SETTINGS are
not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the PROGRAM TYPE key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Daily Cycle is shown on the display (for
storage in a single container or a multiple
container array).
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will respond with the message
“DAILY CYCLE Total Bottles `nn’“. The
two digits will be flashing as a prompt that
they can be changed using the arrow keys.
Press ENTER. The second line of the
display will change to show a day of the
week. The first day that shows will be the
day the programming is being done.
Following the day of the week will be a
flashing digit, which is prompting for a
numeric input. Using the number keys (0-9)
enter the number of bottles to be utilized on
the displayed day, to a maximum of 9 or the
total number of containers not yet allocated
from the array.
Press ENTER. This will register the value
for the displayed day and change that
display to show the next day. Again, enter a
number for that particular day, remembering
that only containers not previously allocated
5-26
Page 67

Section 5. Programming
can be chosen. If no change in the displayed
value is required, the value has been
changed or the value is zero, pressing
ENTER will advance the day of the week.
Therefore...
Press ENTER. Repeat the above procedures
until all the required containers, on their
respective days, have been allocated, or the
7 days of the week are all selected. The total
number available is never allowed to be
more than the amount registered as the two
digit representation of the hardware
configuration in the “Total bottles 00” entry.
The display will echo the last entry with
PROGRAM TYPE <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for PROGRAM TYPE. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then be set to perform as
a Daily Cycle Sampler in conjunction with
the parameters programmed under the
START DELAY and SAMPLE
INITIATION variables.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, PROGRAM TYPE, ARROW(S), ENTER, ARROW(S), ENTER, #,
ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #,
ENTER, RESTART, RESTART.
5.5.4 PROGRAM TYPE - Daily Cycle for Dual Station
Dual Station – Flip Flop Application Only (Single Controller, Two Metering
Chambers)
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to store the samples it
takes, when the hardware specified is
configured to deliver Samples from two
separate sources. The ACTIVE SETTINGS
are not being altered.
5-27
Page 68

Section 5. Programming
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the PROGRAM TYPE key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Daily Cycle is shown on the display.
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will show the response “DAILY
CYCLE Total Bottles nn“. The two digits,
nn, will flash, indicating they can be
changed . In this application, the number of
bottles must be set to 24.
Press ENTER. The second line of the
display will change to show a day of the
week. The first day that shows will be the
day the programming is being done.
Following the day of the week will be a
flashing single digit, which is the prompt for
a numeric input. Using the number keys
(0-9) enter the number of bottles to be
utilized on the first day. In this application
this will be set to 2.
Press ENTER. This will register the value
for the displayed day and change that
display to show the next day. Again, enter a
number for that particular day, remembering
that in this application this will be set to 2. If
no change in the displayed value is required,
the value has been changed or the value is
zero, pressing ENTER will advance the day
of the week. Therefore...
Press ENTER. Repeat the above procedures
until all the required containers, on their
respective days, have been allocated, or the
7 days of the week are all selected. If all 7
days have been selected, then continuous
sampling will occur for up to 12 days.
5-28
Page 69

Section 5. Programming
The display will echo the last entry with
PROGRAM TYPE <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for PROGRAM TYPE. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
Summary of Sequence:
SET, PROGRAM TYPE, ARROW(S), ENTER, ARROW(S), ENTER, #,
ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #, ENTER, #,
ENTER, RESTART, RESTART.
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then be set to perform as
a Dual Station Sampler in conjunction with
the parameters programmed under the
START DELAY and SAMPLE
INITIATION variables.
5.5.5 PROGRAM TYPE - Consecutive
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to store the samples it
takes, in the hardware specified in its
configuration. The ACTIVE SETTINGS are
not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the PROGRAM TYPE key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Consecutive is shown on the display (for
storage in single multiple container array).
4. Press the ENTER key.
5-29
Page 70

Section 5. Programming
The display will show the response
“CONSECUTIVE Total Bottles nn“. The
two digits, nn, will be flashing, indicating
they can be changed by scrolling with the
arrow keys.
Press ENTER. The display now reads “nn
bottles per Sample Cycle”. A previously set
value will be displayed. One of the digits is
flashing. Using the number keys (0-9), enter
the first digit of the number of bottles that
will be used at each sampling time
determined by the programming setting, i.e.,
enter the number of samples to be taken at
each predetermined time. After the first
digit is entered, the second digit will flash
prompting for the remaining digit of the
entry. The sampler will repeat this quantity
each time the sampling is initiated, until the
“Total-Bottles” setting is reached.
Press ENTER. The display now shows
“PROGRAM TYPE <ENTERED>”.
The controller has now been given a new
value for PROGRAM TYPE. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then be set to perform as
a Consecutive Sampler in conjunction with
the parameters programmed under the
START DELAY and SAMPLE
INITIATION variables.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, PROGRAM TYPE, ARROW(S), ENTER, ENTER, ##, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
5-30
Page 71

5.5.6 PROGRAM TYPE - Multi-Composite
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to store the samples it
takes, in the hardware specified in its
configuration. The ACTIVE SETTINGS are
not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the PROGRAM TYPE key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Multi-Composite is shown on the display
(for storage in multiple container array).
Section 5. Programming
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display will respond with the message
“MULTI-COMPOSITE Total Bottles nn”.
The two digits, nn, will be flashing,
indicating they can be changed by scrolling
with the arrow keys.
Press ENTER. The display now reads
“nn Cycles per bottle”. A previously set
value is displayed. One of the digits is
flashing, prompting for a numeric entry.
Using the number keys (0-9), select the
number of times the same bottle will be used
at the times determined by the programming,
i.e., enter the number of samples to be taken
before the stepper advances to the next
bottle. After the first digit is entered, the
second digit will flash, prompting for the
second digit of the entry. Each sample
placed in a bottle will be a complete cycle.
The program will repeat this action each
time the sampling is initiated, until the
“Total Bottles” setting is reached.
5-31
Page 72

Section 5. Programming
Press ENTER. The display now reads
PROGRAM TYPE <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for PROGRAM TYPE. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then be set to perform as
a Multi-Composite Sampler in conjunction
with the parameters programmed under the
START DELAY and SAMPLE
INITIATION variables.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, PROGRAM TYPE, ARROW(S), ENTER, ENTER, ##, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
5.5.7 PROGRAM TYPE - Timed Step
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to store the samples it
takes, in the hardware specified in its
configuration. The ACTIVE SETTINGS are
not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the PROGRAM TYPE key.
5-32
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Timed Step is shown on the display (for
storage in multiple container array).
Page 73

Section 5. Programming
4. Press the ENTER key.
Press ENTER. The display will show the
response “TIMED STEP Total Bottles nn”.
The two digits, nn, will be flashing,
indicating they can be changed by scrolling
with the arrow keys.
Press ENTER. The bottom line of the
display now reads “Step Intvl 00:00”. A
previously set value is displayed. One of the
digits is flashing, prompting for first digit of
a numeric input. The format is HH:MM.
Using the number keys (0-9) enter the time
interval at which the stepper MUST
advance, regardless of SAMPLE
INITIATION settings. The program will
repeat this action at the set interval except
during an ongoing sample cycle, when it will
advance the stepper after the sample cycle is
complete.
Press ENTER. The display now reads
PROGRAM TYPE <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for PROGRAM TYPE. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then be set to perform as
a Timed Step Sampler in conjunction with
the parameters programmed under the
START DELAY and SAMPLE
INITIATION variables.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, PROGRAM TYPE, ARROW(S), ENTER, ENTER, ####, ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
5-33
Page 74

Section 5. Programming
5.6 Programming OTHER OPTIONS
5.6.1 OTHER OPTIONS Overview
SET or VIEW
This feature allows the user to SET or
VIEW the internal Real-Time clock of the
microprocessor.
This feature allows the user to SET or
VIEW the duration for which the sampler
will purge the intake line prior to drawing in
a sample to the chamber. The maximum
allowable setting is 99 seconds.
This feature allows the user to change how
the pinch valve will operate during sampling
cycles. Depending on which generation of
sampler the controller is to be used on
determines the setting. If this is a new unit,
the pinch valve action will have been factory
set. Should the controller be used as a
retrofit into an older model, the setting may
have to be changed. If the sampler has a
pinch valve that squeezes shut the discharge
tube even during an inactive state, this
model is termed as normally closed. Should
the tubing be shut only when the pinch valve
is energized, it is termed normally open.
This is the ONLY setting for the
PVSsamplers.
This feature will enable or disable the ability
of the controller to cease operations when it
encounters repeated difficulties in the
drawing of samples. The controller normally
will attempt to obtain a valid sample by
repetition of its programming with extended
purge times and vacuum cycles, also
extending the time allowed for the
acquisition of the sample. When a sample is
not obtained, this fact is noted in the
controller memory and the program resumes.
If after two (2) successive attempts have
failed, the controller will Shut Down, halting
sampling until operator intervention clears
any reason for fault and RESTARTs the
program. This is not always a required
course of action. If FAULT SHUTDOWN is
disabled, the program will record all failures
to obtain samples and without further
5-34
Page 75

VIEW ONLY
Section 5. Programming
attempts being made to obtain the failed
sample, will wait until the next sample
initiation.
The controller will remember conditions
encountered during normal operation.
Reasons for premature ending of a set
program will also be saved in memory. By
VIEWing this feature, this information can
be obtained at the time the sampler is
checked.
Values retained by the controller to indicate
number of missed samples.
When equipped with the appropriate
hardware and with the controller running the
proper program (i.e. Multi-Composite), the
current position of the distributor arm can be
determined by VIEWing this option. The
position information is relative to the
original position of the arm at the beginning
of the program start. Note: There is no
physical “Bottle 1”, any bottle can be
determined to be #1 at the beginning of a
sample program.
The following selections are all available
under the maintenance heading and are all
for VIEWing only. To check any of these
values or perform any tests, press VIEW,
then OTHER OPTIONS. Arrow left or
right as required until the flashing text
MAINTENANCE appears and press ENTER.
Once more, arrow left or right until the
desired flashing text appears, and press
ENTER.
Displays the microprocessor’s serial number.
Tests the controller’s on-board lithium
battery.
Tests the touchpad keys.
Checks the main IC’s read / write integrity.
Technicians Only! Digital Feedback from
two on-board A/D channels.
Channel 1: 4-20mA Input
Channel 2: Displays Float Voltage
5-35
Page 76

Section 5. Programming
5.6.2 OTHER OPTIONS - Clock
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to alter the Real Time
Clock, running internally in the controller,
which is the basis for all timed functions.
The ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being
altered and there are no NEW ENTRIES
generated.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the OTHER OPTIONS key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Clock is shown on the display (for updating
the internal Real Time Clock).
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display shows a time / date response in
the form of “01:23 AM SUN 01-Jan-92”.
The flashing digits are changed, if necessary,
by use of the number keys (0-9) in the same
manner as a standard watch, in the HH:MM
format. Maximum values are 01 - 12 for the
hours pair and 00 to 59 for the minutes.
However, each digit is set separately.
Press ENTER. The display will shift its
flashing prompt to the AM/PM pair. Since both
characters are flashing, the selection is made
by use of the ARROW keys. The selection
cycles through AM and PM repeatedly. Choose
one.
Press ENTER. The display will shift its
flashing prompt to the three characters forming
the day of the week. Since all three characters
are flashing, the selection is made by use of the
ARROW keys. The selection cycles through
the 7 days. Choose one.
5-36
Page 77

Section 5. Programming
Press ENTER. The bottom line of the
display shows a date in the format
DD-MM-YY. The DD pair is a pair of digits
with the normal range of 00 - 31. Set by
number keys (0-9) individually.
Press ENTER. The MM characters are set
using the ARROW keys for the choice of one
regular calendar month.
Press ENTER. The YY pair of digits are set
using the number keys again, corresponding to
the last two digits in the year. Set each digit
individually. Press ENTER. The date as
entered is now checked by the internal clock.
An invalid date will return the prompt to the
beginning of the date setting, after an error
message is displayed. It can then be corrected
and re-entered.
The display now reads CLOCK <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for the REAL TIME CLOCK. The
new value is in use immediately, once set.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, OTHER OPTIONS, ARROW(S), ENTER, ##, ##, ENTER, ,
ARROWS, ENTER, ARROWS, ENTER, ##, ENTER, ARROWS,
ENTER, ##, ENTER.
5.6.3 OTHER OPTIONS - Purge Time
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to operate some of the
hardware specified in its configuration. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
5-37
Page 78

Section 5. Programming
2. Press the OTHER OPTIONS key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Purge Time is shown on the display (for
operating time when the sampler is in the
purge mode of the Sample cycle,
pressurizing the inlet hose to clear it of
obstructions and fluid).
4. Press the ENTER key.
The display shows the response “PURGE
TIME SS seconds”. The first digit of SS is
flashing. A previously set value may be
displayed. Using the number keys (0-9)
enter the time in seconds that will represent
the basic purge time. Multiples of this time
may be used by the controller to facilitate
the removal of obstructions in the inlet hose.
Press ENTER. The display now reads
PURGE TIME <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for PURGE TIME. The new value
resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of the
controller memory. To make these changes
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then be set to perform in
conjunction with the parameters
programmed under the START DELAY,
SAMPLE INITIATION and PROGRAM
TYPE settings.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, OTHER OPTIONS, ARROW(S), ENTER, ##, ENTER, RESTART,
RESTART.
5-38
Page 79

5.6.4 OTHER OPTIONS - Pinch Valve
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to operate some of the
hardware specified in its configuration. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the OTHER OPTIONS key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Pinch Valve is shown on the display.
Section 5. Programming
4. Press the ENTER key.
The Pinch Valve option is for control of the solenoid activated pinch bar
determining vacuum / pressure modes in the sampler operation. This is a factor
usually set at the factory because it relates directly to the equipment
specification. It is alterable only to facilitate the use of the controller in plants
that have a variety of equipment configurations.
The display will show the response “PINCH
VALVE Normally Open / Closed”. All the
characters on the bottom line are flashing,
therefore the choice is made with the
ARROW keys. The choice is a toggle
between ‘Open’ and ‘Closed’. It represents
the state of the pinch valve when the
equipment is idle. Note: The sampler will
not perform properly if this setting is in
error.
Press ENTER. The display now reads
PINCH VALVE <ENTERED>,
5-39
Page 80

Section 5. Programming
5.6.5 OTHER OPTIONS - Fault Shutdown
The controller has now been given a new
value for PINCH VALVE. The new value
resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of the
Summary of Sequence:
SET, OTHER OPTIONS, ARROW(S), ENTER, ARROW(S), ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
controller memory. To make these changes
active, press the RESTART key, then again
press it to confirm your choice. The
controller will then be set to perform in
conjunction with the parameters
programmed under the START DELAY,
SAMPLE INITIATION and PROGRAM
TYPE settings.
The following sequence of entries are made
on the Touchpad to describe how the
Sampler controller is to operate some of the
hardware specified in its configuration. The
ACTIVE SETTINGS are not being altered.
1. Press the SET key.
2. Press the OTHER OPTIONS key.
3. Press an ARROW key. Continue until
Fault Shutdown is shown on the display..
4. Press the ENTER key.
Fault Shutdown is used to control whether the sampler will cease taking
samples after a predetermined number of unsuccessful attempts.
5-40
Page 81

Section 5. Programming
The display will show the response “FAULT
SHUTDOWN Enabled / Disabled”. All the
characters on the bottom line are flashing,
therefore the choice is made with the
ARROW keys. The choice is a toggle
between ‘Enabled’ or ‘Disabled’. If
disabled, the controller will make a lengthy
attempt to obtain a sample, then return
control to the SAMPLE INITIATION to
try again. The controller will accumulate a
count of unsuccessful (abandoned) attempts.
Press ENTER. The display now reads
FAULT SHUTDOWN <ENTERED>.
The controller has now been given a new
value for FAULT SHUTDOWN. The new
value resides in the NEW ENTRIES area of
the controller memory. To make these
changes active, press the RESTART key,
then again press it to confirm your choice.
The controller will then be set to perform in
conjunction with the parameters
programmed under the START DELAY,
SAMPLE INITIATION and PROGRAM
TYPE settings.
Summary of Sequence:
SET, OTHER OPTIONS, ARROW(S), ENTER, ARROW(S), ENTER,
RESTART, RESTART.
5-41
Page 82

Section 5. Programming
5.7 Viewing Information
5.7.1 Viewing Programmed Information
To see current settings, press the VIEW
button, followed by the appropriate button as
described on its label.
The display will show current parameter
settings, beginning with the requested major
category.
Press the ENTER key. If more information
is available for a given parameter, it will be
displayed. Continue pressing ENTER until
no new information is presented. The display
will “wrap-around” to its first message.
Where timing or counting are used, active
values will be shown which can be used to
monitor the progress of the parameter.
START DELAY
SAMPLE INITIATION
PROGRAM TYPE
Press the VIEW key.
Press the START DELAY key.
Sequence: VIEW, START DELAY, ENTER,
(ENTER).
Press the VIEW key.
Press the SAMPLE INITIATION key.
Sequence: VIEW, SAMPLE INITIATION,
ENTER, (ENTER).
Press the VIEW key.
Press the PROGRAM TYPE key.
Sequence: VIEW, PROGRAM TYPE, ENTER,
(ENTER).
5-42
Page 83

OTHER OPTIONS
Section 5. Programming
Press the VIEW key.
Press the OTHER OPTIONS key.
Use ARROW keys to navigate to desired option on
the flashing display.
Press ENTER to view.
Available options are:
Clock - Time, Date (including Day)
Purge Time - Time in seconds
Pinch Valve - Normally Open or Closed
Fault Shutdown - Enabled or Disabled
Sampler Status - Error and system messages that
have been lost from the display by keyboard entry.
Cycles Abandoned - Counter
Bottle Position - Relative position of distributor,
Maintenance
- Serial Number - unit identification No.,
- Analog channels - A/D output display,
- Backup battery test - test of onboard Lithium
battery,
- Memory check - test of controller RAM/ROM
locations.
- Keypad Check - test of touchpad
ACTIVE SETTINGS
(Under Maintenance, ARROW to selection, then
display with ENTER.)
Press the VIEW key.
Press the ACTIVE SETTINGS key.
The display will show “ACTIVE SETTINGS
‘ENTER’ to list”.
Press the ENTER key. The display will show the
START DELAY programming.
Continuously pressing the ENTER key will display
all of the active program selections and return to the
original display.
Sequence: VIEW, ACTIVE SETTINGS,
ENTER(S)
5-43
Page 84

Section 5. Programming
5.7.2 Viewing Generated Information
NEW ENTRIES
Press the VIEW key.
Press the NEW ENTRIES key.
If no “NEW ENTRIES” have been made, the
display will show “No New Entries View Active
Set”. If new parameters have been set, but the unit
hasn’t been RESTARTed, the display will show
“NEW ENTRIES ‘ENTER’ to list”. Press the
ENTER key. The display will show the START
DELAY programming. Continuously pressing the
ENTER key will display all of the program
selections, SUBSTITUTING new parameters where
they’ve been changed, and return to the original
display.
Sequence: VIEW, NEW ENTRIES, ENTER(S)
The following sequence of entries are made on the Touchpad to examine the
sample information collected or generated by the controller and stored in its
memory.
SAMPLES TAKEN
Press the VIEW key.
Press the SAMPLES TAKEN key.
REMAINING PULSES
The display will show a count of all samples taken
during the current program. To make these changes
active, press the RESTART key, then again press it
to confirm your choice. The controller will then
wait until the designated time before starting its
sampling program.
Press the VIEW key.
Press the REMAINING PULSES key.
The display will show a countdown of incoming
pulses, decreasing from the programmed value.
Only available when either START DELAY or
SAMPLE INITIATION are using their Pulse Input
options or pulses generated by the 4-20mA input
option. The information is updated continuously
and can be left on the display as a progress
indicator.
5-44
Sequence: VIEW, REMAINING PULSES.
Page 85

REMAINING TIME
Section 5. Programming
Press the VIEW key.
Press the REMAINING TIME key.
The display will show various time counters
dependent on the programming of the START
DELAY and SAMPLE INITIATION parameters.
Priority goes to START DELAY, which will show
an incrementing time for event related delays or
decrementing time for time related delays. The
display will then yield to SAMPLE INITIATION
for an elapsed time display for event related inputs
and Remaining Time display for time related
inputs.
Sequence: VIEW, REMAINING TIME.
5-45
Page 86

Section 5. Programming
5-46
Page 87

Appendix A. Principles of Operation
Switching Methods (Sinking / NPN)
LOAD
Sensor
Sinking (NPN) Switch
The Sinking method connects or switches one side of the load to the negative
(-) side of the power supply. The positive (+) side is connected directly to the
other side of the load as shown. “NPN” refers to the type of transistor used to
act as a switch in this type of solid-state sensor.
Switching Methods (Sourcing / PNP)
Sensor
LOAD
Sourcing (PNP) Switch
The Sourcing method connects or switches one side of the load to the positive
(+) side of the power supply. The negative (-) side is connected directly to the
other side of the load as shown. “PNP” refers to the type of transistor used to
act as a switch in this type of solid-state sensor.
A-1
Page 88

Appendix A. Principles of Operation
A-2
Page 89

Appendix B. Parts List
This is a partial list of most frequently requested PVS Sampler replacement
parts.
TABLE B-1. PVS Replacement Parts
Part No.
SAMPLE CONTAINERS
27952 27-01-01 500cc Wedge (Polypropylene)
27953 27-01-02 1000cc Wedge (Polypropylene)
26897 27-03-05 2.3 Gallon (9L) Nalgene with side plug (Polyethylene)
28258 27-03-05P 2.3 Gallon (9L) Nalgene with side plug (Polypropylene)
27-03-05-4150 2.3 Gallon (9L) Nalgene with side plug for PVS4150 (HDPE)
27956 27-03-07 2.5 Gallon (10 L) Glass with Teflon Cap
26900 22-10-32 Discrete Bottle Tray (24-Bottle x 500cc)
SINKER / STRAINER
26915 23-28-01-3/8 Sinker (Lead): 3/8 System
27820 23-28-01-5/8 Sinker (Lead): 5/8 System
27821 23-28-10 Sinker Strainer (Stainless Steel): 5/8 System
26914 23-28-11 Sinker Strainer (Stainless Steel): 3/8 System
27821 23-28-12 Sinker (Stainless Steel): 3/8 System
Old Part No.
(Prior to 8-1-11) D es crip tion
27938 23-28-13 Sinker (Stainless Steel): 5/8 System
INTAKE TUBE
26904 26-01-16 PVC Standard: 3/8" ID (per foot)
27819 26-01-18 PVC Standard: 5/8" ID (per foot)
26-01-14 Teflon: 1/2" ID (Minimum 25 Ft)
26-01-09 Teflon: 3/4"ID (Minimum 25 Ft)
INTAKE TUBE WITH SINKER/STRAINER
27949 26-02-01 PVC: 3/8"ID: 25 Ft with Lead Sinker
26925-L50-E1 26-02-01-050 PVC: 3/8"ID: 50 Ft with Lead Sinker
26925-L100-E1 26-02-01-100 PVC: 3/8"ID: 100 Ft with Lead Sinker
26925-L150-E1 26-02-01-150 PVC: 3/8"ID: 150 Ft with Lead Sinker
26926-L25-E1 26-02-02 PVC: 5/8"ID: 25 Ft with Lead Sinker
B-1
Page 90

Appendix B. Parts List
26926-L50-E1 26-02-02-050 PVC: 5/8"ID: 50 Ft with Lead Sinker
26926-L100-E1 26-02-02-100 PVC: 5/8"ID: 100 Ft with Lead Sinker
26926-L150-E1 26-02-02-150 PVC: 5/8"ID: 150 Ft with Lead Sinker
26-02-03 Teflon: 1/2" ID: 25 Ft with SS Sinker
26-02-03-050 Teflon: 1/2" ID: 50 Ft with SS Sinker
26-02-11 Teflon: 3/4" ID: 25 Ft with SS Sinker/Strainer
26-02-21 Teflon: 1/2" ID: 25 Ft with SS Sinker/Strainer
DISCHARGE TUBE
26898 26-03-01 Discharge Tubing (Latex): 3/8" ID: 3 Ft
27957 26-03-06 Discharge Tubing (Latex): 5/8" ID: 3 Ft
28251 26-03-11 Discharge Tubing (Silicone): 5/8" ID: 3 Ft
26899 26-03-12 Discharge Tubing (Silicone): 3/8" ID: 3 Ft
METERING CHAMBER
50-01-01-MR Metering Chamber Assembly (complete): 3/8 System, 500cc
50-01-08-MR Metering Chamber Assembly (complete): 5/8 System, 500cc
26906 24-01-01 Metering Chamber (Acrylic): 3/8 System, 500cc
27941 24-01-02 Metering Chamber (Acrylic): 5/8 System, 500cc
26905 24-01-08 Metering Chamber (Pyrex): 3/8 System, 500cc
27942 24-01-10 Metering Chamber (Pyrex): 5/8 System, 500cc
50-21-01 Metering Chamber Cover: 3/8 Delrin
50-21-04 Metering Chamber Cover: 5/8 Delrin
50-21-06 Metering Chamber Cover: 3/8 Teflon
50-21-07 Metering Chamber Cover: 5/8 Teflon
26918 23-03-01 Volume Control Tube: 3/8 System, 500cc
26919 23-03-04 Volume Control Tube: 5/8 System, 500cc
28224 23-37-01 Liquid Sensing Rod for Metering Chamber: 500cc
26909 28-05-01 O-Ring: Barrier Valve (Buna-N)
26908 28-05-02 O-Ring: Metering Chamber (Buna-N)
26910 28-05-03 O-Ring: Barrier Valve (Viton)
26907 28-05-04S O-Ring: Metering Chamber (Silicone)
B-2
26911 28-05-04 O-Ring: Metering Chamber (Viton)
Page 91

Appendix B. Parts List
VACUUM PUMP
28006 32-01-01 Vacuum Pump - 12VDC
28009 32-02-05 Pump Assembly (including solenoids and fixtures) - 12VDC
26895 32-08-10 Brush & Lead Wire Kit (for 32-01-01)
32-10-01 Pump Kit with Flap & Diaphragms
DISTRIBUTOR / STEPPER
28287 32-04-01 Distributor (Teflon)
28011 32-05-01 Stepper Motor
28296 32-06-01 Distributor (PVC)
OTHER COMPONENTS
28005 30-DC-MFCB Multi-Function Input Controller (12VDC)
28012 50-02-13 Pinch Valve Assembly (12VDC All Systems)
27997 28-11-41 Quick Connector Stem (SS): 1/2"
27998 28-11-42 Quick Connector Body (SS): 1/2"
28-11-43 Quick Connector Stem (SS): 3/4"
28-11-44 Quick Connector Body (SS): 3/4"
MANUAL Hard Copy of Manual
26926 55-15-12 Battery: Large 12VDC, 17AH, 15 lbs
6053 55-15-40 Battery: Small 12VDC, 7AH, 4 lbs
Switching Power Supply c/w Filtering Capacitor:
INPUT: 88 - 264 VAC, 50/60 Hz. 2.5 Amps
28020 55-15-23
OUTPUT: 13.6 VDC, 10 Amps.
B-3
Page 92

Appendix B. Parts List
B-4
Page 93

m
Appendix C. Programming 4-20mA for Flow Proportional Sampling
In order to use the 4-20mA interface with a PVS Sampler, calculations must be
made based on flow. The 4-20mA input is a signal that corresponds to the flow
meter’s output. 20mA is equal to the maximum flow, and 4mA is equal to the
minimum flow. The controller requires a number which reflects the maximum
flow going through the sampler.
The PVS Controller generates 100 pulses per minute internally at the
maximum flow. This number decreases with the amount of flow proportional
to the 4-20mA scale. The Controller requires the number of pulses at maximum
flow. In order to calculate this, use the following formula:
1. Calculate Q. Q = Average flow rate divided by the maximum flow rate.
Rate Flow Average
Q =
RateFlowMaximu
2. Calculate t.
t =
samplesbetween Volume
minuteper volumeAverage
t is the number of minutes per sample you would like for an average flow rate.
Either choose how long between samples you’d like for average flow, or
calculate based on volume above.
3. Multiply Q x t x 100 (100 pulses at max flow)
This is the number you will input into the Controller at the 4-20mA dialogue.
Example
You want to collect samples every 30 minutes. On average 175gal/min flows
by. Maximum is 300gal/min.
1. Calculate Q.
Q ===
2. Calculate t.
Rate Flow Average
Rate Flow Maximum
gal/min 175
58333.
gal/min 300
or min/sample 30t =
3. Multiply Q x t x 100 pulses = 1750 pulses/sample
Enter 1750 into the Controller at the 4-20mA dialogue.
samplesbtwn Gallons 5250
gal/min 175 Average
C-1
Page 94

Appendix C. Programming 4-20mA for Flow Proportional Sampling
C-2
Page 95

Page 96

Campbell Scientific Companies
Campbell Scientific, Inc. (CSI)
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321
UNITED STATES
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com
Campbell Scientific Africa Pty. Ltd. (CSAf)
PO Box 2450
Somerset West 7129
SOUTH AFRICA
www.csafrica.co.za • cleroux@csafrica.co.za
Campbell Scientific Australia Pty. Ltd. (CSA)
PO Box 8108
Garbutt Post Shop QLD 4814
AUSTRALIA
www.campbellsci.com.au • info@campbellsci.com.au
Campbell Scientific do Brazil Ltda. (CSB)
Rua Luisa Crapsi Orsi, 15 Butantã
CEP: 005543-000 São Paulo SP BRAZIL
www.campbellsci.com.br • suporte@campbellsci.com.br
Campbell Scientific Canada Corp. (CSC)
11564 - 149th Street NW
Edmonton, Alberta T5M 1W7
CANADA
www.campbellsci.ca • dataloggers@campbellsci.ca
Campbell Scientific Centro Caribe S.A. (CSCC)
300 N Cementerio, Edificio Breller
Santo Domingo, Heredia 40305
COSTA RICA
www.campbellsci.cc • info@campbellsci.cc
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL)
Campbell Park
80 Hathern Road
Shepshed, Loughborough LE12 9GX
UNITED KINGDOM
www.campbellsci.co.uk • sales@campbellsci.co.uk
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (France)
3 Avenue de la Division Leclerc
92160 ANTONY
FRANCE
www.campbellsci.fr • info@campbellsci.fr
Campbell Scientific Spain, S. L.
Avda. Pompeu Fabra 7-9, local 1
08024 Barcelona
SPAIN
www.campbellsci.es • info@campbellsci.es
Please visit www.campbellsci.com to obtain contact information for your local US or International representative.
 Loading...
Loading...