Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
NL240 Wireless
Copyright © 2011- 2014
Campbell Scientific, Inc.
Network Link Interface
Revision: 9/14
Page 2

Page 3

Limited Warranty
“Products manufactured by CSI are warranted by CSI to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal use and service for twelve months
from the date of shipment unless otherwise specified in the corresponding
product manual. (Product manuals are available for review online at
www.campbellsci.com.) Products not manufactured by CSI, but that are resold
by CSI, are warranted only to the limits extended by the original manufacturer.
Batteries, fine-wire thermocouples, desiccant, and other consumables have no
warranty. CSI’s obligation under this warranty is limited to repairing or
replacing (at CSI’s option) defective Products, which shall be the sole and
exclusive remedy under this warranty. The Customer assumes all costs of
removing, reinstalling, and shipping defective Products to CSI. CSI will return
such Products by surface carrier prepaid within the continental United States of
America. To all other locations, CSI will return such Products best way CIP
(port of entry) per Incoterms ® 2010. This warranty shall not apply to any
Products which have been subjected to modification, misuse, neglect, improper
service, accidents of nature, or shipping damage. This warranty is in lieu of all
other warranties, expressed or implied. The warranty for installation services
performed by CSI such as programming to customer specifications, electrical
connections to Products manufactured by CSI, and Product specific training, is
part of CSI's product warranty. CSI EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS AND
EXCLUDES ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. CSI hereby disclaims,
to the fullest extent allowed by applicable law, any and all warranties and
conditions with respect to the Products, whether express, implied or
statutory, other than those expressly provided herein.”
Page 4

Assistance
Products may not be returned without prior authorization. The following
contact information is for US and international customers residing in countries
served by Campbell Scientific, Inc. directly. Affiliate companies handle
repairs for customers within their territories. Please visit
www.campbellsci.com to determine which Campbell Scientific company serves
your country.
To obtain a Returned Materials Authorization (RMA), contact CAMPBELL
SCIENTIFIC, INC., phone (435) 227-9000. After an application engineer
determines the nature of the problem, an RMA number will be issued. Please
write this number clearly on the outside of the shipping container. Campbell
Scientific’s shipping address is:
CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC, INC.
RMA#_____
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321-1784
For all returns, the customer must fill out a “Statement of Product Cleanliness
and Decontamination” form and comply with the requirements specified in it.
The form is available from our web site at www.campbellsci.com/repair. A
completed form must be either emailed to repair@campbellsci.com or faxed to
(435) 227-9106. Campbell Scientific is unable to process any returns until we
receive this form. If the form is not received within three days of product
receipt or is incomplete, the product will be returned to the customer at the
customer’s expense. Campbell Scientific reserves the right to refuse service on
products that were exposed to contaminants that may cause health or safety
concerns for our employees.
Page 5

Precautions
DANGER — MANY HAZARDS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH INSTALLING, USING, MAINTAINING, AND WORKING ON OR AROUND
TRIPODS, TOWERS, AND ANY ATTACHMENTS TO TRIPODS AND TOWERS SUCH AS SENSORS, CROSSARMS, ENCLOSURES,
ANTENNAS, ETC. FAILURE TO PROPERLY AND COMPLETELY ASSEMBLE, INSTALL, OPERATE, USE, AND MAINTAIN TRIPODS,
TOWERS, AND ATTACHMENTS, AND FAILURE TO HEED WARNINGS, INCREASES THE RISK OF DEATH, ACCIDENT, SERIOUS
INJURY, PROPERTY DAMAGE, AND PRODUCT FAILURE. TAKE ALL REASONABLE PRECAUTIONS TO AVOID THESE HAZARDS.
CHECK WITH YOUR ORGANIZATION'S SAFETY COORDINATOR (OR POLICY) FOR PROCEDURES AND REQUIRED PROTECTIVE
EQUIPMENT PRIOR TO PERFORMING ANY WORK.
Use tripods, towers, and attachments to tripods and towers only for purposes for which they are designed. Do not exceed design
limits. Be familiar and comply with all instructions provided in product manuals. Manuals are available at www.campbellsci.com or
by telephoning (435) 227-9000 (USA). You are responsible for conformance with governing codes and regulations, including safety
regulations, and the integrity and location of structures or land to which towers, tripods, and any attachments are attached. Installation
sites should be evaluated and approved by a qualified engineer. If questions or concerns arise regarding installation, use, or
maintenance of tripods, towers, attachments, or electrical connections, consult with a licensed and qualified engineer or electrician.
General
• Prior to performing site or installation work, obtain required approvals and permits. Comply
with all governing structure-height regulations, such as those of the FAA in the USA.
• Use only qualified personnel for installation, use, and maintenance of tripods and towers, and
any attachments to tripods and towers. The use of licensed and qualified contractors is
highly recommended.
• Read all applicable instructions carefully and understand procedures thoroughly before
beginning work.
• Wear a hardhat and eye protection, and take other appropriate safety precautions while
working on or around tripods and towers.
• Do not climb tripods or towers at any time, and prohibit climbing by other persons. Take
reasonable precautions to secure tripod and tower sites from trespassers.
• Use only manufacturer recommended parts, materials, and tools.
Utility and Electrical
• You can be killed or sustain serious bodily injury if the tripod, tower, or attachments you are
installing, constructing, using, or maintaining, or a tool, stake, or anchor, come in contact
with overhead or underground utility lines.
• Maintain a distance of at least one-and-one-half times structure height, 20 feet, or the
distance required by applicable law, whichever is greater, between overhead utility lines and
the structure (tripod, tower, attachments, or tools).
• Prior to performing site or installation work, inform all utility companies and have all
underground utilities marked.
• Comply with all electrical codes. Electrical equipment and related grounding devices should
be installed by a licensed and qualified electrician.
Elevated Work and Weather
• Exercise extreme caution when performing elevated work.
• Use appropriate equipment and safety practices.
• During installation and maintenance, keep tower and tripod sites clear of un-trained or non-
essential personnel. Take precautions to prevent elevated tools and objects from dropping.
• Do not perform any work in inclement weather, including wind, rain, snow, lightning, etc.
Maintenance
• Periodically (at least yearly) check for wear and damage, including corrosion, stress cracks,
frayed cables, loose cable clamps, cable tightness, etc. and take necessary corrective actions.
• Periodically (at least yearly) check electrical ground connections.
WHILE EVERY ATTEMPT IS MADE TO EMBODY THE HIGHEST DEGREE OF SAFETY IN ALL CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC PRODUCTS,
THE CUSTOMER ASSUMES ALL RISK FROM ANY INJURY RESULTING FROM IMPROPER INSTALLATION, USE, OR
MAINTENANCE OF TRIPODS, TOWERS, OR ATTACHMENTS TO TRIPODS AND TOWERS SUCH AS SENSORS, CROSSARMS,
ENCLOSURES, ANTENNAS, ETC.
Page 6

Page 7

Table of Contents
PDF viewers: These page numbers refer to the printed version of this document. Use the
PDF reader bookmarks tab for links to specific sections.
1. Introduction ................................................................. 1
2. Cautionary Statements ............................................... 1
3. Quickstart .................................................................... 1
3.1 Physical Setup ...................................................................................... 2
3.2 Configuring the NL240 ........................................................................ 2
3.3 LoggerNet Setup .................................................................................. 4
3.4 Connect ................................................................................................ 4
4. Overview ...................................................................... 5
5. Specifications ............................................................. 8
6. Wi-Fi ........................................................................... 10
6.1 Introduction to Wi-Fi for WLANs ..................................................... 10
6.2 Wireless Network Modes ................................................................... 10
6.3 RSSI ................................................................................................... 11
6.4 Antennas ............................................................................................ 12
6.5 Power ................................................................................................. 12
6.6 LEDs .................................................................................................. 12
7. Configuring the NL240 ............................................. 13
7.1 Configuring the NL240 with DevConfig via USB ............................. 13
7.2 Configuring the NL240 with DevConfig via Wi-Fi WLAN .............. 14
7.3 Configuring the NL240 with Telnet via Wi-Fi WLAN ...................... 14
7.4 Configuring the NL240 via RS-232 ................................................... 15
8. Operation ................................................................... 15
8.1 Wi-Fi Connection ............................................................................... 16
8.1.1 Join an Existing Network ............................................................ 16
8.1.2 Create an Ad hoc Network .......................................................... 16
8.2 Operational Mode .............................................................................. 17
8.2.1 PakBus® Router ......................................................................... 17
8.2.1.1 Physical Setup .................................................................. 17
8.2.1.2 Configuring the NL240 .................................................... 18
8.2.1.3 LoggerNet Setup ............................................................... 19
8.2.1.4 Connect ............................................................................ 20
8.2.2 Bridge Mode ............................................................................... 20
8.2.2.1 Physical Setup .................................................................. 20
8.2.2.2 Configuring the NL240 .................................................... 20
8.2.2.3 Configuring the Datalogger .............................................. 20
8.2.2.4 LoggerNet Setup ............................................................... 21
i
Page 8

Table of Contents
8.2.2.5 Connect ............................................................................ 22
8.2.3 TCP Serial Server ....................................................................... 22
8.2.3.1 Physical Setup ................................................................. 22
8.2.3.2 Configuring the NL240 ................................................... 22
8.2.3.3 LoggerNet Setup .............................................................. 23
8.2.3.4 Connect ............................................................................ 24
8.2.3.5 Serial Sensors .................................................................. 24
8.2.4 TCP Serial Client ....................................................................... 24
8.2.5 Modbus TCP/IP to RTU Gateway.............................................. 25
8.2.6 TLS ............................................................................................ 25
8.2.6.1 TLS Proxy Server ............................................................ 26
8.2.6.2 DevConfig TCP Encrypted Communication to the
NL240 .......................................................................... 28
9. Applications............................................................... 29
9.1 Working Around Firewalls ................................................................ 29
9.1.1 Configuring the NL240 .............................................................. 29
9.1.2 Configuring the Datalogger ........................................................ 30
10. Troubleshooting ........................................................ 30
11. Attribution .................................................................. 33
Appendices
Glossary ................................................................... A-1
A.
B. Cables, Pinouts, LED Function, and Jumper ....... B-1
B.1 CS I/O.............................................................................................. B-1
B.2 RS-232 ............................................................................................. B-1
B.3 USB ................................................................................................. B-2
B.4 Power............................................................................................... B-2
B.5 LEDs ............................................................................................... B-2
B.6 Power Jumper .................................................................................. B-3
C. NL240 Settings ........................................................ C-1
C.1 Main Tab ......................................................................................... C-1
C.2 Wi-Fi Tab ........................................................................................ C-4
C.3 RS-232 Tab ..................................................................................... C-8
C.4 CS I/O Tab .................................................................................... C-11
C.5 Net Services Tab ........................................................................... C-12
C.6 TLS Proxy Server Tab ................................................................... C-14
C.7 TLS Tab ........................................................................................ C-16
D. Sending a New OS to the NL240 ............................ D-1
D.1 Sending an OS via USB .................................................................. D-1
D.2 Sending an OS via Wi-Fi ................................................................. D-1
E. Radio Frequency Emission .................................... E-1
ii
Page 9

Figures
Tables
Table of Contents
3-1. NL240 with CR800 (powered through CS I/O port) ............................ 2
3-2. LoggerNet setup ................................................................................... 4
4-1. NL240 .................................................................................................. 5
4-2. Bridge Mode enabled ........................................................................... 5
4-3. Bridge Mode disabled .......................................................................... 6
5-1. NL240 dimensions ............................................................................... 8
6-1. Infrastructure network ........................................................................ 11
6-2. Ad hoc network .................................................................................. 11
8-1. PakBus® router LoggerNet setup ...................................................... 19
8-2. Bridge mode LoggerNet setup ........................................................... 22
8-3. CS I/O Serial Server LoggerNet Setup ............................................... 24
8-4. TLS proxy server configurations ....................................................... 27
9-1. Working around firewalls .................................................................. 29
B-1. CS I/O Pinout ................................................................................... B-1
B-2. RS-232 Pinout .................................................................................. B-1
B-3. USB Micro-B ................................................................................... B-2
B-4. Power In ........................................................................................... B-2
B-5. Power LED (Red) ............................................................................ B-2
B-6. Wi-Fi LED (Green) .......................................................................... B-3
iii
Page 10

Table of Contents
iv
Page 11

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
1. Introduction
The NL240 is a WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) interface that allows
Campbell Scientific dataloggers and peripherals to communicate with a Wi-Fi
network or wireless ad hoc network. This WLAN interface can be connected
to a datalogger’s CS I/O port or RS-232 port.
2. Cautionary Statements
• The first time an NL240 is attached to a datalogger and Bridge Mode is
enabled, the datalogger’s memory has to be reorganized to allow room in
memory for the IP stack. To avoid the loss of data, collect your data
before enabling Bridge Mode.
• This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. See Appendix E for
more information.
3. Quickstart
• Device Configuration Utility (DevConfig) 2.03 or higher is required to
communicate with the NL240. The latest version of DevConfig can be
downloaded from our website at www.campbellsci.com/downloads.
• The device driver for the NL240 must be installed on your computer
before you can connect to the NL240 via USB. To install the device
driver, verify you have the latest version of DevConfig (see previous
bullet). Under Device Type, select Network Peripheral | NL240. Click the
Install the device driver for the NL240 link and follow the prompts.
• CR1000, CR3000, and CR800-series dataloggers require operating system
version 25 or higher in order to operate with the NL240 in bridge mode.
(OS version 25 or higher is not required to operate as a serial server or
PakBus router.) The latest operating systems can be downloaded from our
website at www.campbellsci.com/downloads.
• Ensure maximum protection against surges. Use coaxial surge protection.
Keep RS-232 and CS I/O connections short.
• When downloading a new operating system to the NL240, do not remove
power until the red LED stops blinking.
Out of the box, the NL240 is configured for operation as a PakBus® Router.
In this mode, the NL240 can be used to communicate with Campbell Scientific
PakBus devices over a Wi-Fi network connection.
1
Page 12
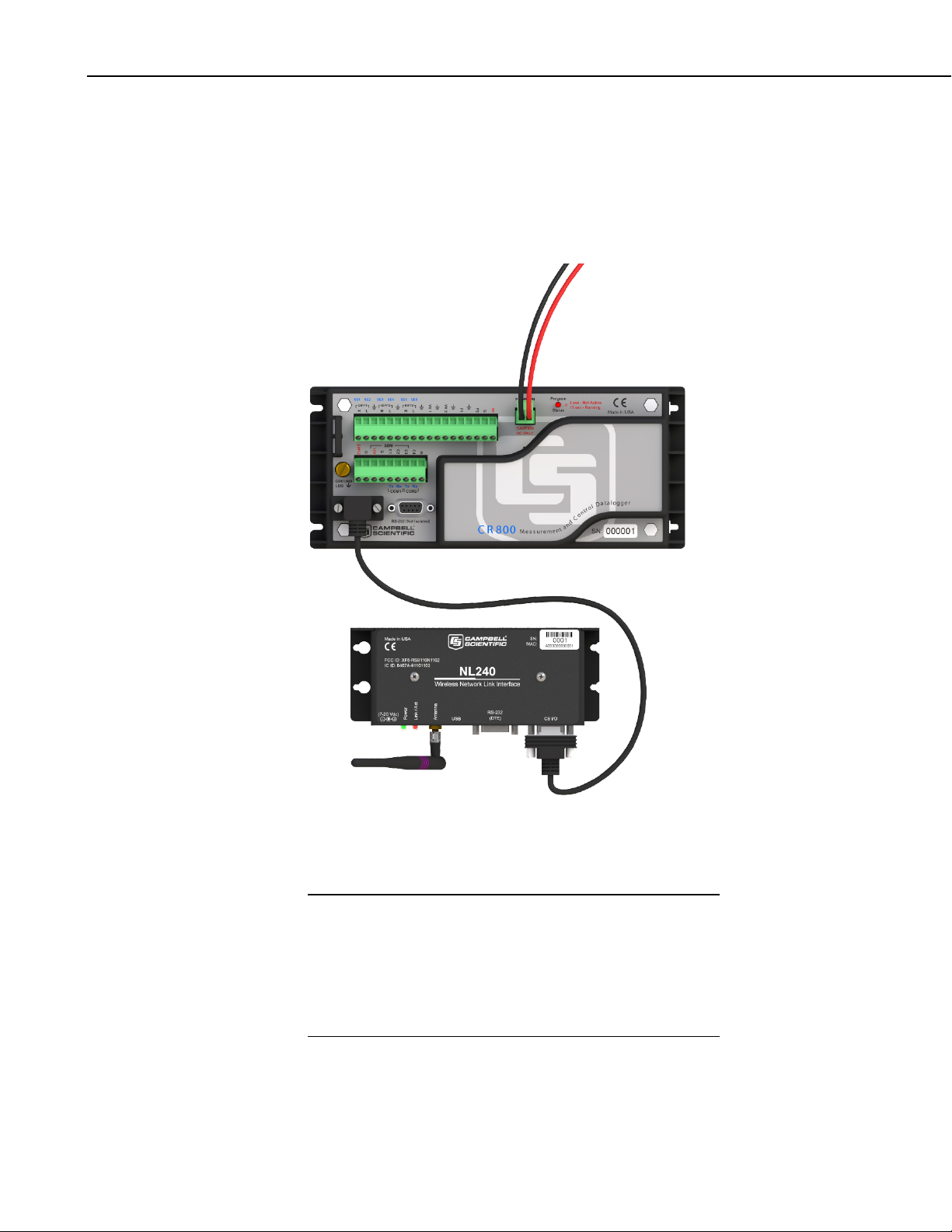
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
3.1 Physical Setup
Attach an antenna to the NL240’s antenna connector. Using the supplied serial
cable, connect the NL240’s CS I/O port to the datalogger’s CS I/O port.
Alternatively, power the NL240 through the barrel-connector jack located on
the edge of the device. Ensure that the device is powered up by inspecting the
Power LED.
2
FIGURE 3-1. NL240 with CR800 (powered through CS I/O port)
3.2 Configuring the NL240
INSTALL THE DEVICE DRIVER BEFORE plugging the
NL240 into your PC for the first time. You will need the device
driver properly installed before you can connect to the NL240 via
USB. To install the device driver, download the latest version of
DevConfig from our website. Under Device Type, select Network
Peripheral | NL240. Click the Install the device driver for the
NL240 link and follow the prompts.
Page 13

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
• Ensure the NL240 is powered.
• Connect the supplied USB cable between a USB port on your computer
and the USB port on the NL240.
• Open DevConfig.
• Under Device Type, select Network Peripheral | NL240.
• Click the Browse button next to Communication Port.
• Select the virtual com port labeled NL240.
• Click OK.
• Click Connect.
• Click on the Wi-Fi tab.
• By default, the NL240 will attempt to connect to the strongest, unsecured
network available. This network will be shown in the Status field. If this
is not the network you wish to connect to, press the browse button next to
the SSID field. A dialog box showing all of the available wireless
networks will be displayed. Select the network you wish to connect to and
click OK. If this is a secured network, enter the password in the
Password field.
• Click on the NL240 tab.
• To enter a static IP address, select disable in the Use DHCP field. Then
input the IP Address, Network Mask, and Default Gateway. These
values can be provided by your network administrator.
• If a dynamic address is to be used, the network information acquired via
DHCP can be seen on the NL240 tab. (Note that if you have selected a
different network than the default network, you will need to press Apply
to save this change, then press the Connect button to reconnect to the
NL240 and view the network information.)
• Click Apply to save your changes.
It is recommended that a static IP address be given to the NL240
for most applications so that the path to the device is always
known. If using a dynamic IP address acquired via DHCP, you
may wish to configure the NL240 as a PakBus/TCP client.
3
Page 14
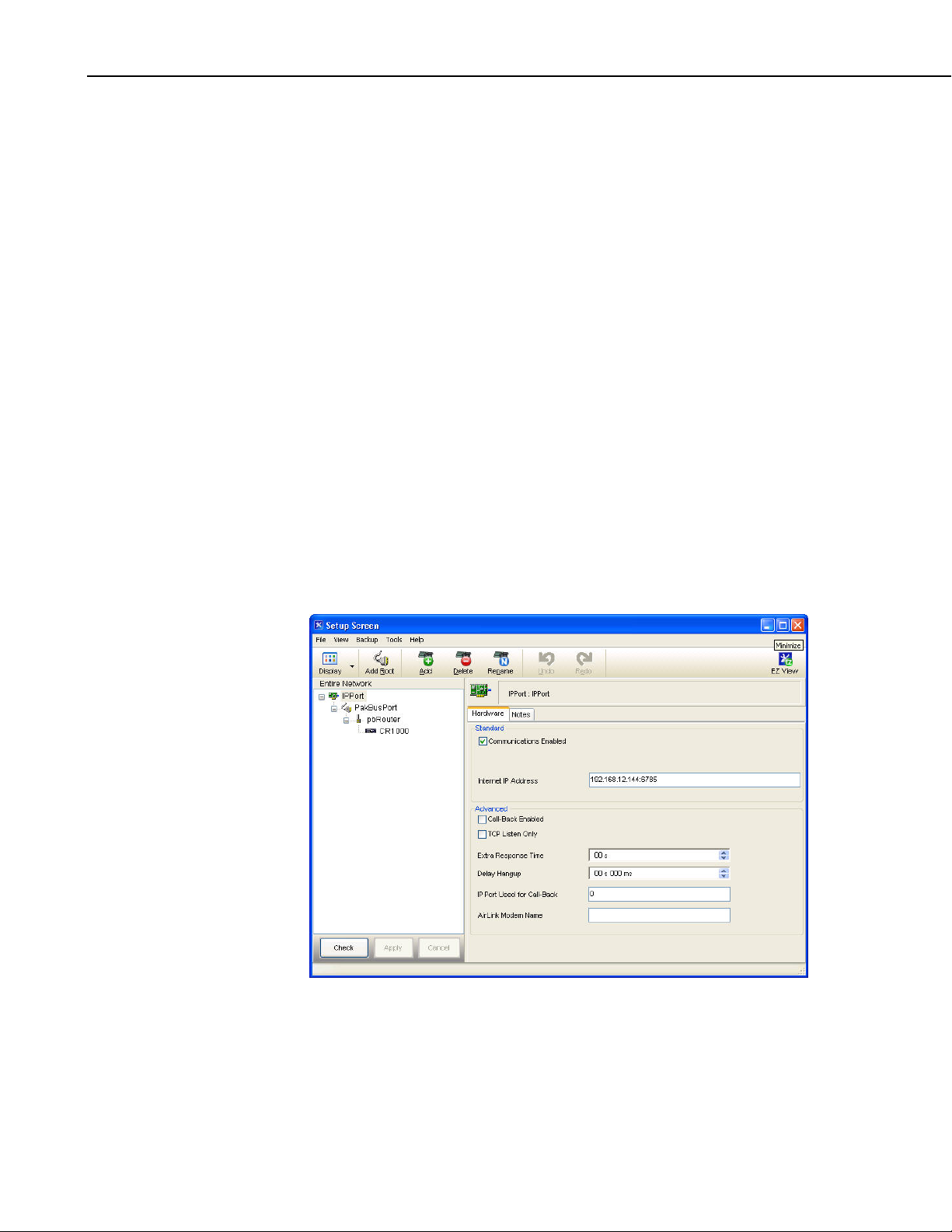
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
3.3 LoggerNet Setup
The next step is to run LoggerNet and configure it to connect to the datalogger
via the NL240.
• In the LoggerNet Setup screen, press Add Root and choose IPPort. Input
the NL240 IP address and port number. The IP address and port number
are input on the same line separated by a colon. IPv6 addresses will need
to be enclosed in square brackets when specifying a port number. An
IPv4 address may look like 192.168.1.100:6785. An IPv6 address may
look like [2001:db8::1234:5678]:6785. A fully qualified host name entry
may look like yourlogger.com:6785.
• Add a PakBus® Port (PakBusPort).
• Add a PakBus® Router (pbRouter). Input the PakBus address of the
NL240. The NL240 default PakBus address is 678.
• Add the datalogger and input the PakBus® address of the datalogger.
• Press Apply to save the changes.
• You can verify that your settings are correct by selecting the datalogger in
the Network Map, selecting the Clock tab, and pressing Check Clocks. If
your settings are correct, you should see the current clock of your server
and datalogger.
4
FIGURE 3-2. LoggerNet setup
3.4 Connect
You are now ready to connect to your datalogger using the LoggerNet Connect
screen.
Page 15
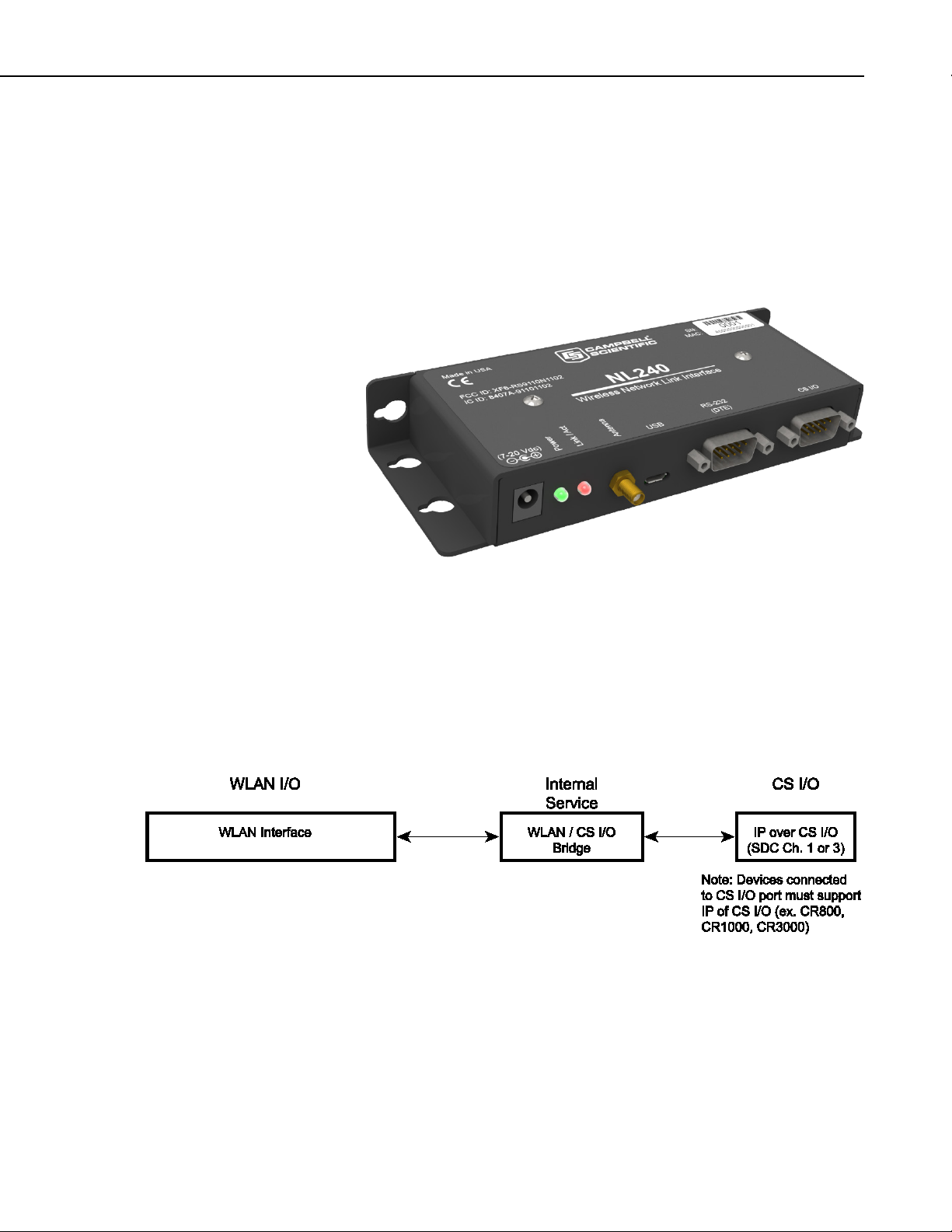
4. Overview
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
The NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface is designed for communication
with Campbell Scientific dataloggers and peripherals over a Wi-Fi network.
The Wi-Fi network can be an infrastructure network or an ad hoc (point-topoint) network. See Section 6, Wi-Fi, for more information.
The NL240 includes a CS I/O port and an RS-232 port for communication. A
USB device port is used for configuring the NL240 device.
FIGURE 4-1. NL240
Bridge Mode Enabled
The NL240 can be configured to bridge WLAN and CS I/O communications
(see FIGURE 4-2). This mode is used for providing access to the internal IP
functionality of the CR800/850, CR1000, and CR3000 (e.g., web page access,
email, FTP, etc.). Bridge mode does not use PPP. Instead, raw IP packets are
transferred between the WLAN and CS I/O connections.
FIGURE 4-2. Bridge Mode enabled
Bridge Mode Disabled
With Bridge Mode disabled (see FIGURE 4-3), the NL240 can provide
multiple services simultaneously including TCP Serial Server, TCP Serial
Client, Modbus TCP/IP Gateway, and PakBus® router. The NL240 can act as
a serial server and PakBus router simultaneously. However, each physical port
5
Page 16
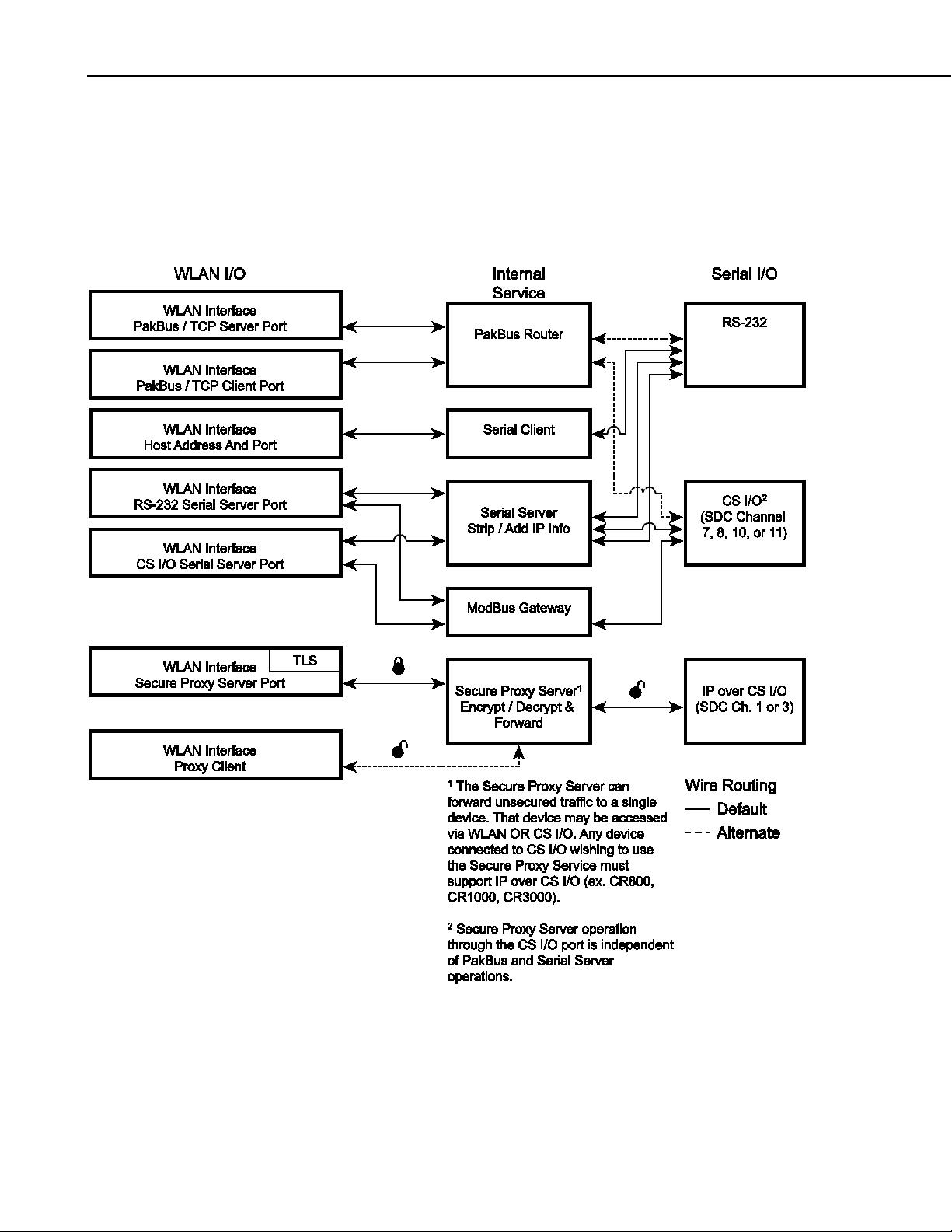
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
(R2-232 and CS I/O) is only associated with one service (PakBus router, serial
server, Modbus/TCP Gateway, etc.) at a time. For example, you can have an
RS-232 serial server and a CS I/O serial server, an RS-232 serial server and a
CS I/O PakBus router, an RS-232 PakBus router and a CS I/O serial server, or
an RS-232 PakBus router and a CS I/O PakBus router. In addition, the NL240
can act as TLS proxy server. The TLS proxy server is independent of other
modes.
6
FIGURE 4-3. Bridge Mode disabled
Some reasons you might want to use each of these modes are described below.
Refer to Section 7, Configuring the NL240, and Section 8, Operation, for
information on setting up your NL240 for each mode.
Page 17

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
Campbell Scientific’s LoggerNet software is used to communicate with the
dataloggers once the NL240 is configured properly and connected to a
network.
Bridge Mode
• Allows access to datalogger’s internal IP functionality when a peripheral
port is not accessible. For example, accessing the HTTP/webpage, email,
and FTP capabilities of a CR800/850, ET107, RAWS, or CS110.
Serial Server
• Allows access to a CR10X over a Wi-Fi network (RS-232 serial server)
when used in conjunction with an RS-232 to CS I/O (ME) adapter like the
SC32B or SC105.
• Allows access to a serial sensor over a Wi-Fi network (RS-232 serial
server).
• Allows access to an RF500M Base over a Wi-Fi network (RS-232 serial
server).
PakBus® Router
• Allows access to a CR10X-PB over a Wi-Fi Network.
• Allows access to a CR200X over a Wi-Fi Network.
• Allows you to connect to a PakBus® Device on the RS-232 port and a
PakBus Device on the CS I/O port using only one TCP port.
• Allows a PakBus® device on the RS-232 port and a PakBus device on the
CS I/O port to communicate with each other without routing through the
WLAN.
• Allows multiple computers to concurrently talk to PakBus® devices
connected to the RS-232 and CS I/O ports.
TLS Proxy Server
• Adds an encrypted WLAN interface to a datalogger that supports CS I/O
IP (bridge mode) communications.
7
Page 18
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
2.65
5. Specifications
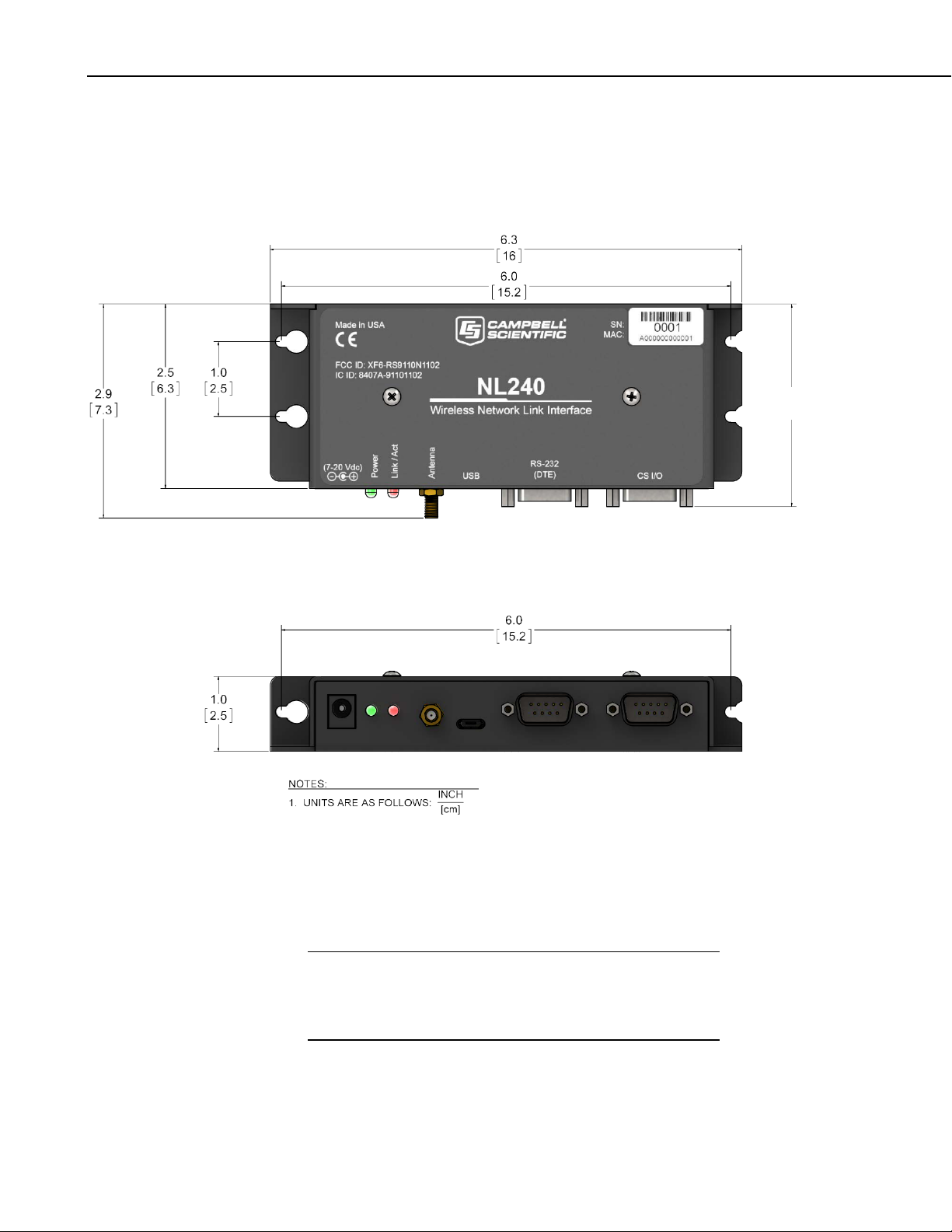
General
177 g (6.3 oz)
16 x 6.73 x 2.54 cm (6.3 x 2.65 x 1 in)
[6.73]
FIGURE 5-1. NL240 dimensions
Power
CS I/O or DC Barrel Connector (not USB)
7 to 20 Vdc
If you wish to prevent the NL240 from being powered over the CS
I/O port, you can do so by removing a jumper. See Appendix B,
Cables, Pinouts, LED Function, and Jumper, for more
information.
8
Page 19

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
Power Consumption
Maximum: 950 mW
Typical, Low Power Disabled
connected to Access Point: 600 mW idle, 670 mW communicating
searching for out of range network: 65 mW
Typical, Low Power Enabled
connected to Access Point: 73 mW idle, 480 mW communicating
searching for out of range network: 50 mW
Sleep: 16 mW
Standby power is when the IPNetPower instruction has been used
to turn off power to the Wi-Fi. See the CRBasic help for an
example of using the IPNetPower instruction. Note that the
IPNetPower instruction is only applicable when the NL240 is
configured with Bridge Mode Enabled
Operating Temperature
Standard: –25 to +50 °C
Extended: –55 to +85 °C
Configuration
DevConfig over USB or Wi-Fi
Telnet console over Wi-Fi
Terminal menu over RS-232
CS I/O Port
SDC 7, 8, 10, 11 (does not support ME)
9600 to 460.8 kbps
RS-232 Port
DTE
1200 bps to 115.2 kbps
WLAN
Antenna Connector: RPSMA
Supported Technologies: 802.11b/g/n, WPA, WPA2 (Personal
only)/TKIP or AES, WEP, WEP(open), APIPA/AutoIP, IPv4, IPv6,
ICMP/Ping, ICMPv6/Ping, TCP, DHCP Client, SLAAC, DNS Client,
HTTPS Proxy, Telnet Server, TLS, PakBus®, Modbus, TCP/IP
Topologies: infrastructure and ad hoc
Transmit Power: 5 to 50 mW, 7 dBm at low power level, 10 dBm at
medium power level, 16 to 17 dBm at high power level
Rx Sensitivity: –97 dBm (<8% PER)
Frequency: 2.4 to 2.5 GHz (2.4 GHz ISM band)
Miscellaneous
Supports 20 simultaneous TCP connections
Up to 10 of the 20 TCP connections can be used for TLS
PakBus® router supports 50 routes
Supports up to 15 concurrent Modbus server transactions
9
Page 20

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
Compliance
RoHS Compliant
Complies with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15
of the FCC Rules.
Contains an embedded radio transmitter with the following approvals:
FCC Identifier: XF6-RS9110N1102
Industry Canada: 8407A-91101102
Europe ETSI EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1:2002
Europe ETSI EN 300 328 V1.7.1:2006
6. Wi-Fi
6.1 Introduction to Wi-Fi for WLANs
Wi-Fi is a technology that allows data transfer among electronic devices using
specific radio frequencies over a wireless local area network (WLAN). A
wireless network is like a wired network, except it uses radio waves just like
cell phones, televisions, and other radios. Over-the-air speeds vary depending
on protocol, distance, and network activity. When using the NL240, please
note that your total throughput to the datalogger will generally be governed by
the speed of serial communication.
Wi-Fi transmits at frequencies around 2.4 and 5 GHz (the NL240 only uses 2.4
GHz). The high frequency allows fast rates but reduced communication
distance. These frequencies can be used by anyone and do not require a license
from the FCC to use or transmit (unlike most UHF and VHF frequencies) as
long as certain power levels are maintained.
The NL240 supports the 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n wireless network
standards.
The NL240 Wi-Fi device also supports several wireless security protocols.
These include WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), WPA (Wi-Fi Protected
Access)(personal) with TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol),
WPA(personal) with AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), WPA(personal)
with TKIP+AES, WPA2(Wi-Fi Protected Access II)(personal) with TKIP,
WPA2(Wi-Fi Protected Access II)(personal) with AES, and WPA2(Wi-Fi
Protected Access II)(personal) with TKIP+AES. These security protocols
allow network traffic to be encrypted and help protect data transmitted over the
Wi-Fi network.
6.2 Wireless Network Modes
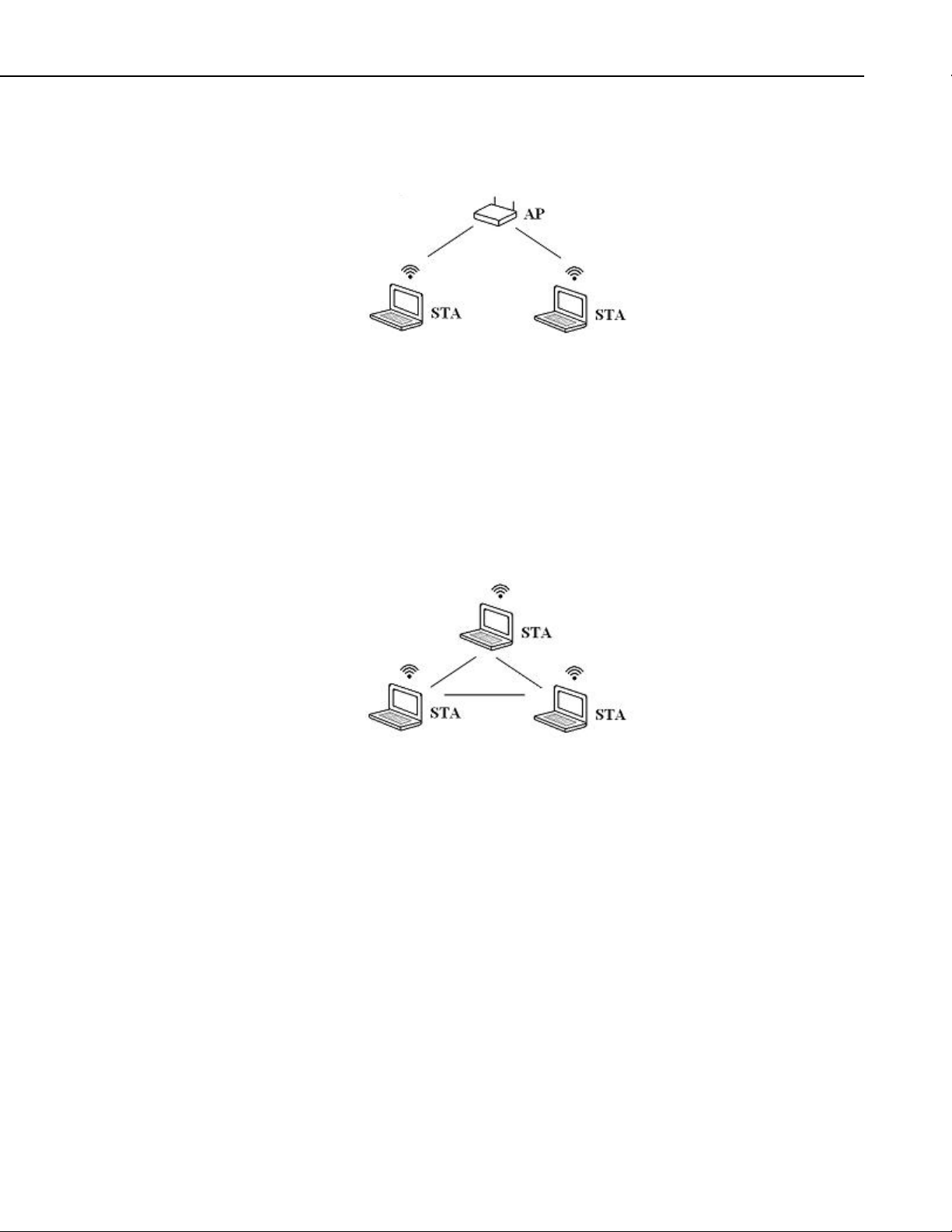
The NL240 works in two types of wireless modes, infrastructure and ad hoc.
In infrastructure mode (see FIGURE 6-1, Infrastructure network), the NL240
connects to an already established wireless network (WLAN). This wireless
network is usually controlled by a single Wireless Access Point (WAP). This
WAP will typically connect the wireless network (and the NL240) to a larger
wired company or home network and/or the internet. The WAP device also
controls and routes all the traffic on the wireless network. The WAP,
furthermore, controls security for network access, the wireless frequency
(channel) to use, and has the pre-established Service Set Identifier (SSID) for
the wireless network. Infrastructure mode wireless networks are usually the
10
Page 21
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
easiest wireless network to connect the NL240 to. (See Section 8.1, Wi-Fi
Connection, for details.) The network password/key (if required) and SSID
can be obtained from your network administrator.
FIGURE 6-1. Infrastructure network
Unlike infrastructure networks, ad hoc or peer-to-peer networks do not have a
single device (like a WAP) that controls access to the wireless network (see
FIGURE 6-2, Ad hoc network). Instead, network management and access is
decentralized. Ad hoc networks are created on the fly and all network devices
communicate directly with each other. Usually the first device on the network
(a NL240, PC, or iOS smart phone) establishes the security type, the SSID, and
the channel (frequency) that the wireless network will operate on. IP addresses
can be set statically or via AutoIP. It can take up to two minutes to find a
usable IP address using AutoIP.
6.3 RSSI
FIGURE 6-2. Ad hoc network
Once the network is established by the first wireless device, subsequent
wireless devices can connect to the ad hoc network if the correct SSID and
password (if needed) are specified in the configuration settings. Ad hoc
networks are usually small with up to five wireless devices connecting to the
wireless network. Also, ad hoc networks can only use WEP security or no
security (open). WPA security is not available in ad hoc networks.
RSSI is Received Signal Strength Indication. It is a generic radio receiver
technology metric used to determine the strength of the link between a receiver
and a transmitter. In the NL240’s case, RSSI is the measurement between the
NL240 and a wireless access point, a computer in ad hoc or another NL240 in
ad hoc. The strength of this link is recorded in dBm (power ratio in decibels)
and can be found under the Wi-Fi tab under the Settings Editor in DevConfig.
11
Page 22

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
RSSI in the NL240 is measured in a scale between –100 dBm and 0 dBm. The
higher the number (i.e. –12 dBm as compared to –72 dBm), the better the
connection between Wi-Fi devices. A reliable connection will be maintained if
the RSSI reading in the NL240 stays between –85 dBm and –15 dBm. A
weak, and thus intermittent, connection will have readings between –85 dBm
and –95 dBm. For every 3 dBm increase, the NL240 is receiving twice as
much signal (radiated power). For every 3 dBm lost, the NL240 is receiving
50% less signal.
To improve your RSSI readings, shorten antenna cable lengths and use
frequency matched antennas with higher gain. An NL240 with a 0 db gain
antenna can achieve ranges of up to 32 meters (120 feet) indoors and 95 meters
(300 feet) outdoors. Ranges can be improved by installing higher gain
antennas on both the NL240 and/or the wireless access point. Remember that
RSSI can also be affected by weather, vegetation, terrain, interference, and
antenna cable length and type.
6.4 Antennas
Antenna selection and placement can greatly affect the strength of the signal
you transmit and receive and therefore can impact the quality of
communications with your device. The NL240 should be paired with an
antenna designed for Wi-Fi communications at 2.4 GHz (2.401 to 2.483 GHz).
Ideally the antenna will be connected directly to the NL240 or positioned in
such a way as to minimize coaxial cable length. Note that coaxial cables
attenuate signals more as frequency increases; care should be taken when
selecting the type and length of coaxial cable used with the NL240. The
NL240 antenna connector is RPSMA male. When connecting directly to the
NL240, select a coaxial cable or antenna with a mating RPSMA female
connector.
6.5 Power
6.6 LEDs
One advantage of using the NL240 in your application is its low power
consumption capabilities. With careful planning, you can reduce your station’s
power needs while still meeting your critical communication needs. See
Section 5, Specifications (Power Consumption), and Appendix C.2, Wi-Fi Tab,
for more details.
There are two LEDs on the NL240 that serve as indicators as described below.
Normal Operation
After power-up, the red LED stays solid while the NL240 is searching for and
trying to join a Wi-Fi network (or while creating an ad hoc network).
After joining the network (or failing to join the network) the red LED will
indicate the power mode of the NL240. A double strobe indicates that the
NL240 is in low-power mode. If the red LED stays solid, low-power mode is
not enabled. If the NL240 is in Bridge Mode and the datalogger executes the
IPNetPower instruction, the NL240 will power down and the red LED will
single strobe approximately every four seconds.
12
Page 23

After the NL240 has joined a network, the green LED will flash with network
NOTE
activity. If the NL240 is configured for DHCP, the green LED will blink once
a second while it is attempting to acquire a network address from DHCP.
Operating System Upgrade
When a new operating system is sent to the NL240, the red LED will blink
repeatedly while the NL240 copies the operating system into its internal flash.
This process takes about 10 seconds. While the LED is blinking, the NL240 is
in a vulnerable state where a removal of power will leave the NL240 without a
valid operating system. Do not remove power until the LED stops blinking.
If an operating system upgrade includes an upgrade to the internal Wi-Fi
module’s firmware, after the typical re-flashing and blinking of the red LED,
the device will power up and start copying the new firmware to the Wi-Fi
module. The red LED will also blink during this process. It will start out as a
slow blink and get faster and faster as the process nears completion. This
process can take around 1.5 minutes. Again, do not remove power until the
LED stops blinking.
7. Configuring the NL240
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
The NL240 is configured using DevConfig version 2.03 or greater. You can
connect your NL240 to DevConfig using either a Wi-Fi connection or USB.
7.1 Configuring the NL240 with DevConfig via USB
INSTALL the DEVICE DRIVER BEFORE plugging the NL240
into your PC for the first time. You will need the device driver
properly installed before you can connect to the NL240 via USB.
To install the device driver, download the latest version of
DevConfig from our website. Under Device Type, select Network
Peripheral | NL240. Click the Install the device driver for the
NL240 link and follow the prompts.
• Ensure the NL240 is powered.
• Connect the supplied USB cable between a USB port on your computer
and the USB port on the NL240.
• Open DevConfig.
• Under Device Type, select Network Peripheral | NL240.
• Click the Browse button next to Communication Port.
• Select the port labeled NL240.
• Click OK.
• Click Connect.
• Configure the NL240 as needed for your application.
• Click Apply to save your changes.
13
Page 24

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
NOTE
7.2 Configuring the NL240 with DevConfig via Wi-Fi WLAN
The NL240 is configured by default to join the strongest, open WiFi network it finds. If there is no open network in the area or if the
NL240 has not been previously configured to join an existing WiFi network, it is not possible to configure the NL240 via Wi-Fi.
• Apply power to the NL240.
• The NL240 will power up and join the strongest, open Wi-Fi network it
finds or the Wi-Fi network it has already been configured to join. The
green LED on the NL240 will come on and start blinking once it has
joined the network. Once it has successfully obtained an IP address, it will
stop blinking and flicker with network activity.
• Launch DevConfig.
• Under Device Type, select Network Peripheral | NL240.
• Check the box labeled Use IP Connection.
• Enter the IP address of the device in the Communication Port field. (If
you do not know the address of the device and the device is connected to
your local area network, you may be able to use the browse button to the
right of Communication Port to discover the devices on the network.)
The IP address must be followed by :6786 (i.e., 192.168.10.55:6786) in
order to connect the device configuration service.
• Enter nl240 in the TCP Password box. (nl240 is the default administrative
password. It can be changed via the DevConfig Deployment/NL240 tab.)
• Click OK.
• Click Connect.
• Configure the NL240 as needed for your application.
• Click Apply to save your changes.
7.3 Configuring the NL240 with Telnet via Wi-Fi WLAN
The NL240 must have an IP address before connecting via Telnet.
Configuration via Telnet is not available in bridge mode.
• Ensure the NL240 is powered and connected to your network.
14
• Create a Telnet session with the device over port 23.
• Input the NL240 Admin Password (default password is nl240).
• Type help to see a list of the functionality available when connected to the
NL240 through Telnet.
Page 25

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
• Type edit and press Enter to edit the settings of the NL240.
• As each NL240 setting is shown, press Enter to accept the current value
shown in parenthesis. Type a new value and press Enter to change the
value.
• After progressing through all of the NL240 settings, type save to accept
the changes or cancel to discard the changes.
• Type bye to exit Telnet.
7.4 Configuring the NL240 via RS-232
Accessing the configuration terminal menu via RS-232 requires
the NL240 to be power cycled, so physical access to the device
will be required. A null modem serial cable will be needed; one
is not provided with the NL240.
• Using a null modem serial cable, connect your computer’s serial port to
the port labeled “RS-232” on the NL240.
8. Operation
• Connect to the NL240 using a terminal emulator. DevConfig’s “unknown”
device type or HyperTerminal are examples of simple terminal emulators.
The default settings for this interface are 115200 baud, 8 stop bits, no
parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control.
• Power cycle the NL240 and repeatedly press Enter at the terminal.
• Type help to see a list of the functionality available when connected to the
NL240 through Telnet.
• Type edit and press Enter to edit the settings of the NL240.
• As each NL240 setting is shown, press Enter to accept the current value
shown in parenthesis. Type a new value and press Enter to change the
value.
• After progressing through all of the NL240 settings, type save to accept
the changes or cancel to discard the changes.
• Disconnect your computer and power cycle the NL240.
This section describes how to configure the Wi-Fi connection and operational
mode of your NL240. See Section 6, Wi-Fi, for more information about the
types of Wi-Fi connections available. See Section 4, Overview, for help in
determining which operational mode to use.
15
Page 26

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
NOTE
8.1 Wi-Fi Connection
8.1.1 Join an Existing Network
In this configuration, the device will scan for available networks and attempt to
join the network (infrastructure or ad hoc) specified by the SSID setting.
• Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the
NL240).
• Click on the Wi-Fi tab.
• Set Configuration to Join an Existing Network.
• Press the Browse button next to the SSID field to see a list of the available
networks in the area. Select the network you wish to connect to and click
OK. If the SSID field is left blank, the device will attempt to join the
strongest unsecured network it finds.
• If this is a secured network, enter the password in the Password field.
• Under Advanced, set the TX Power Level and Lower Power mode.
(Note that these settings can often be left at their default values. See
Section 6.5, Power.)
• Click Apply to save your changes.
If for some reason the device cannot join the desired network (for
example, out of range or incorrect parameters), it will go to a lowpower state and periodically retry to join the network
approximately once every minute. If the device has successfully
joined a network and then detects a loss of connectivity with the
network, it will begin periodically searching for the network at
approximately the one-minute interval.
8.1.2 Create an Ad hoc Network
In this configuration, the device will be the creator of an ad hoc network. An
ad hoc network created by the module supports up to 4 joinees.
Please remember when joining an ad hoc network with Windows
or iOS, it can take some time to successfully join the network.
• Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the
NL240).
• Click on the Wi-Fi tab.
• Depending on whether or not you want your Ad hoc network to be
encrypted, set Configuration to Create an Open Ad hoc Network or
Create an Ad hoc Network with WEP Security.
16
Page 27

• If you have chosen WEP Security, enter the WEP key to be used for the
network in the Password field. (See Appendix C for details on the WEP
key requirements.)
• Select the Channel to be used for the network. (The Suggest Channel
button can be used to have the NL240 scan the networks for the channel
that is least likely to encounter interference from other networks.)
• Select the TX Power Level, Low Power Mode, Low Power Interval,
and Low Power On Time. (Note that these settings can often be left at
their default settings. See Section 6.5, Power.)
• Click Apply to save your changes.
8.2 Operational Mode
8.2.1 PakBus® Router
When the RS-232 or CS I/O port is configured as a PakBus® router, the
NL240 can route packets to other devices in the network that it has in its
routing table. These are devices that the NL240 has learned about through
beaconing or allowed-neighbor lists.
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
Beacon Interval – Devices in a PakBus® network may broadcast a hellomessage to other devices in order to determine “neighbor” devices. Neighbor
devices are devices that can be communicated with directly by the current
device without being routed through an intermediate device. A beacon in a
PakBus network helps to ensure that all devices in the network are aware of
which other devices are viable in the network. The beacon interval determines
how often a beacon will be sent out. Set the beacon interval to 0 to disable
beacons.
Verify Interval – This interval, in seconds, determines the rate at which the
NL240 will attempt to start a hello transaction with a neighbor if no other
communication has taken place within the interval. If Verify Interval is set to
0, the verify interval becomes 2.5 times the Beacon Interval. If both the
Beacon Interval and Verify Interval are set to 0, the verify interval becomes
300 seconds. Generally, the Verify Interval should be set greater than or equal
to the interval at which you will be talking to the attached PakBus devices. For
example, if you are using the NL240 as a PakBus router to allow scheduled
collection of a network of dataloggers every 15 minutes, consider setting the
Verify Interval to 30 minutes.
PakBus Neighbors Allowed – You can set a list of “acceptable neighbors”
which the NL240 expects to hear from within set intervals (the Verify
Interval). If the NL240 does not hear from neighbors in this list within the
Verify Interval, it will attempt to contact them on its own. It will ignore all
devices it hears that are not on the PakBus Neighbors Allowed list except if the
PakBus® address is ≥4000. Hellos from devices with PakBus address ≥4000
are automatically accepted as neighbors.
8.2.1.1 Physical Setup
Using the supplied serial cable, connect the NL240 CS I/O port or RS-232 port
to the datalogger CS I/O or RS-232 port, respectively. The NL240 will be
powered if connected via CS I/O. Alternatively, power the NL240 through the
17
Page 28

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
barrel-connector jack located on the edge of the device. Connect the NL240 to
your local wireless network by attaching an antenna to the NL240 antenna
connector. Ensure that the device is powered up by inspecting the Power LED.
8.2.1.2 Configuring the NL240
RS-232 PakBus® Router
• Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the
NL240).
• On the NL240 tab:
o Set Bridge Mode to disable.
• On the RS-232 tab:
o Set Configuration to PakBus.
o Set Baud Rate to baud rate of attached device.
o Set Beacon Interval, Verify Interval, and PakBus Neighbors
Allowed as described above. Often the default values can be used.
However, an allowed neighbors list can be useful in restricting
communication paths.
• On the Network Services tab:
o Make note of the PakBus\TCP Server Port. (The default
PakBus/TCP Server Port is 6785. Unless firewall issues exist, it is
not necessary to change the port from its default value.)
CS I/O PakBus® Router
• Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the
NL240).
• On the NL240 tab:
o Set Bridge Mode to disable.
• On the CS I/O tab:
o Set Configuration to PakBus.
o Set SDC address. (Note that if multiple peripherals are connected to
a datalogger’s CS I/O port, each must have a unique SDC address.)
o Set Beacon Interval and Verify Interval as described above. Often
the default values can be used.
18
Page 29

• On the Network Services tab:
8.2.1.3 LoggerNet Setup
• In the LoggerNet Setup screen, press Add Root and choose IPPort. Input
• Add a PakBus® Port (PakBusPort).
• Add a PakBus® Router (pbRouter). Input the PakBus address of the
• Add the datalogger and input the PakBus® address of the datalogger.
• Press Apply to save the changes.
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
o Make note of the PakBus\TCP Server Port. (The default
PakBus/TCP Server Port is 6785. Unless firewall issues exist, it is
not necessary to change the port from its default value.)
the NL240’s IP address and port number. The IP address and port number
are input on the same line separated by a colon.
NL240. The NL240 default PakBus address is 678.
FIGURE 8-1. PakBus® router LoggerNet setup
19
Page 30

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
8.2.1.4 Connect
You are now ready to connect to your datalogger using the LoggerNet Connect
screen.
8.2.2 Bridge Mode
With Bridge Mode Enabled, the device will act as a bridge from WLAN to CS
I/O. All IP packets that come into the device via WLAN will be
communicated as a complete Ethernet/TCP packet to the datalogger over the
CS I/O port. This enables the datalogger to use its TCP/IP stack to interpret the
packet and, therefore, all of the datalogger’s TCP services are available. In
bridge mode, none of the other device settings are valid and all other
functionality is disabled. All settings (that is, IP, netmask, gateway) are
configured in the datalogger. However, in bridge mode, the device will
intercept any TCP traffic on the TCP Configuration Port Number. This
allows the device to still be configured remotely by IP connection using
DevConfig. The TCP Configuration Port Number is a user setting with a
default value of 6786.
8.2.2.1 Physical Setup
Attach an antenna to the NL240 antenna connector. Using the supplied serial
cable, connect the NL240 CS I/O port to the datalogger CS I/O port. Ensure
that the device is powered up by inspecting the Power LED.
8.2.2.2 Configuring the NL240
Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the NL240). In
the NL240 tab, set Bridge Mode to enable.
In bridge mode, the IP address, subnet mask, and IP gateway to be
used by the NL240 are configured in the datalogger.
8.2.2.3 Configuring the Datalogger
• Connect a serial cable from the PC COM port to the datalogger’s RS-232
port.
• Open DevConfig. Select the device type of the datalogger (CR800,
CR1000, or CR3000), the appropriate Communication Port, and the
Baud Rate. Press Connect to connect to the datalogger.
• If using a static IP address, select the CS I/O IP tab and input the IP
address, subnet mask, and IP gateway for the correct CS I/O Interface.
The default for the NL240 is CS I/O IP Interface #2 (SDC1). DNS
server settings are shared by all active IP interfaces and can be entered on
the TCP/IP tab. These values can be provided by your network
administrator. If using DHCP, leave the CS I/O IP address settings as
0.0.0.0. You will find the information acquired by DHCP in the TCP/IP
info box on the TCP/IP tab.
20
• Press Apply to save the changes and then close DevConfig.
Page 31

The NL240 must be connected to the datalogger before
NOTES
configuring the datalogger with DevConfig. If it is not connected,
the TCP/IP settings will not be displayed.
By default, the NL240 uses the datalogger’s CS I/O Interface #2.
If connecting more than one NL240 to a datalogger, one NL240
can be configured to use CS I/O Interface #1. This is done by
connecting to the NL240 in DevConfig, going to the Settings
Editor tab, and changing the CS I/O IP Interface Identifier from 2
to 1. If this setting is changed, the IP address, Subnet Mask, and
IP gateway should be input under CS I/O Interface #1 on the
datalogger’s CS I/O IP tab. CS I/O Interface #2 communicates
over SDC address 1. CS I/O Interface #1 communicates over SDC
address 3.
8.2.2.4 LoggerNet Setup
The next step is to run LoggerNet and configure it to connect to the datalogger
via the Wi-Fi port. (See example in FIGURE 8-2 below.)
• In the LoggerNet Setup screen, press Add Root and choose IPPort. Input
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
the datalogger’s IP address and port number. The IP address and port
number are input on the same line separated by a colon. (The datalogger’s
default port number is 6785. It can be changed using DevConfig. Unless
firewall issues exist, the port number does not need to be changed from its
default value.)
• Add a PakBus® Port.
• Add the datalogger (CR800, CR1000, or CR3000) and input the PakBus®
address of the datalogger.
• You can verify that your settings are correct by selecting the datalogger in
the Network Map, selecting the Clock tab, and pressing Check Clocks. If
your settings are correct, you should see the current clock of your server
and datalogger.
21
Page 32

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
FIGURE 8-2. Bridge mode LoggerNet setup
8.2.2.5 Connect
You are now ready to connect to your datalogger using the LoggerNet Connect
screen.
8.2.3 TCP Serial Server
The NL240 can tunnel RS-232 and CS I/O serial communications over Wi-Fi.
Any packet sent to the configured IP port will have the IP layer removed, and
the data is then directed to the serial connection.
8.2.3.1 Physical Setup
Using the supplied serial cable, connect the NL240 CS I/O port or RS-232 port
to the datalogger CS I/O or RS-232 port, respectively. The NL240 will be
powered if connected via CS I/O. Alternatively, power the NL240 through the
barrel-connector jack located on the edge of the device. Connect the NL240 to
your local wireless network by attaching an antenna to the NL240 WLAN
connector. Ensure that the device is powered up by inspecting the Power LED.
8.2.3.2 Configuring the NL240
RS-232 Serial Server
22
• Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the
NL240).
Page 33

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
• On the NL240 tab:
o Set Bridge Mode to disable.
• On the RS-232 tab:
o Set Configuration to TCP Serial Server.
o Set Baud Rate to baud rate of attached device.
o Make note of the Service Port. (The default RS-232 Service Port is
6784. Typically, it is not necessary to change this entry from its
default.)
CS I/O Serial Server
• Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the
NL240).
• On the NL240 tab:
o Set Bridge Mode to disable.
• On the CS I/O tab:
8.2.3.3 LoggerNet Setup
The next step is to run LoggerNet and configure it to connect to the datalogger
via the Wi-Fi port. (See example in FIGURE 8-3 below.)
• In the LoggerNet Setup screen, press Add Root and choose IPPort. Input
• Add a PakBus® Port.
• Add the datalogger and input the PakBus® address of the datalogger.
• Press Apply to save the changes.
o Set Configuration to TCP Serial Server.
o Set SDC address. (Note that if multiple peripherals are connected to
a datalogger’s CS I/O port, each must have a unique SDC address.)
o Make note of the Service Port. (The default CS I/O Service Port is
6783. Typically, it is not necessary to change this entry from its
default.)
the NL240’s IP address and port number. The IP address and port number
are input on the same line separated by a colon.
• You can verify your settings are correct by selecting the datalogger in the
Network Map, selecting the Clock tab, and pressing Check Clocks. If
your settings are correct, you should see the current clock of your server
and datalogger.
23
Page 34

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
FIGURE 8-3. CS I/O Serial Server LoggerNet Setup
8.2.3.4 Connect
You are now ready to connect to your datalogger using the LoggerNet Connect
screen.
8.2.3.5 Serial Sensors
The NL240 configured as an RS-232 serial server as described above can be
used to communicate with a serial sensor. However, LoggerNet is not capable
of communicating with the serial sensor. You must have some other method of
communicating with the sensor.
8.2.4 TCP Serial Client
When the RS-232 port is configured as TCP Serial Client, the NL240 will
initiate and maintain a TCP socket connection to the IP address and port
number specified by the Serial Client Address and Serial Client Port
settings. Data received on the RS-232 port will be forwarded to this TCP
connection, and data received on the TCP connection will be forwarded to the
RS-232 port. This mode can be particularly useful when an RF base or serial
sensor is behind a firewall and needs to be the party responsible for initiating
the TCP socket connection to the data collection server.
The NL240 will attempt to open a connection with the remote server, and, if
the connection fails to open, the device will continue to retry at an interval of
60 seconds. If data arrives on the RS-232 port when no TCP connection exists,
the device will buffer the data (up to 1500 bytes) and immediately attempt to
open a connection to deliver the data. If the remote server closes the
connection due to error, the NL240 will make a best effort to save any data that
was in process and re-queue it to be sent on the next successfully-opened TCP
connection.
24
Page 35

8.2.5 Modbus TCP/IP to RTU Gateway
The NL240 can serve as a Modbus TCP/IP to RTU Gateway. It will listen for
incoming Modbus TCP/IP connections from a Modbus TCP/IP master client.
The port number of the listening connection is specified in the RS-232 Service
Port Number setting and is typically set to a value of 502. The NL240 will
convert incoming Modbus TCP/IP frames to Modbus RTU and forward them
to the RS-232 port. The NL240 will wait for a response from the Modbus RTU
device and forward that response back to the remote Modbus TCP/IP master
client over the established TCP connection. The Modbus RTU device is
generally a datalogger, such as a CR200(X), connected to the RS-232 port or a
datalogger located remotely over a transparent radio (for example, RF450)
connection, but can be any Modbus RTU device. When the NL240 is
connected directly to a CR800 series, CR1000, or CR3000 being polled by a
Modbus TCP/IP master client, the NL240 is most commonly configured with
Bridge Mode enabled instead of as a Modbus TCP/IP to RTU Gateway.
8.2.6 TLS
The NL240 supports transport layer security (TLS) for proxy functions
including HTTPS. TLS versions 1.0 and 1.1. are supported. The TLS
implementation supports symmetric algorithms AES-256, AES-128, and RC4
and RSA keys up to 4096 bits. For any TLS connection, the unit will
preferentially use AES-256, then AES-128, and finally RC4. X.509 certificates
are supported, with the exception of v3 extensions. Certificates should be PEM
format. Up to 10 certificates can be chained. 10 kB of space is provided for
certificate storage. The Private Key should also be in PEM format and, if
encrypted, use AES-256 or AES-128 (SHA).
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
The implementation of TLS in the NL240 is provided so that secure, encrypted
communications can be established between a TLS client and the NL240.
With the TLS Proxy Server enabled, the NL240 can act as a TLS proxy server
for a datalogger. The NL240’s TLS Proxy Server maintains a secure TLS
connection with a remote TLS client and forwards data onto a datalogger using
a standard TCP connection thus enabling communication with TLS clients.
The TLS client can be a web browser using HTTPS or other user-supplied TLS
client. This offloads from the datalogger the intensive computations that are
necessary for a TLS server to perform.
Also, with the NL240 configured for TLS, it can establish a secure TLS
configuration session with DevConfig.
In order to use TLS, the user must configure the NL240 with a user-supplied
TLS Private Key and TLS Certificate. The key and certificate are loaded using
DevConfig.
Using DevConfig, navigate to the Settings Editor tab and then to the TLS tab.
• Load the user-supplied, PEM-formatted TLS Private key using the Set
TLS Key … button. A file dialog will open. Navigate to the key file
and click Open.
• Load the user-supplied, PEM-formatted TLS Certificate using the Set
TLS Certificate … button. A file dialog will open. Navigate to the
certificate file and click Open.
25
Page 36

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
NOTE
• Enter the TLS Private Key Password if the TLS Private Key is
• After loading the key and certificate, click the Apply button. The
The TLS Settings described above cannot be edited over a
standard TCP DevConfig link. The TLS Private Key, TLS Private
Key Password and TLS Certificate can only be edited/transmitted
over a secure DevConfig link (USB or TLS).
If the status of the TLS stack is Initialized, the NL240 will
automatically negotiate a secure TLS connection with DevConfig
as long as the Use IP Connection option is selected.
8.2.6.1 TLS Proxy Server
A TLS proxy server is a device that acts as a secure intermediary for requests
from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the
proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or
other resource, available from a different server. The proxy server evaluates
the request according to its filtering rules. For example, it may filter traffic by
IP address or protocol. If the request is validated by the filter, the proxy
provides the resource by connecting to the relevant server and requesting the
service on behalf of the client.
encrypted. Otherwise, leave the setting blank.
NL240 will reboot. Connect with DevConfig again and navigate to
the Settings Editor tab and then to the TLS tab. The TLS Status
should say Initialized.
When the TLS Proxy Server function is enabled, the NL240’s TLS Proxy
Server maintains a secure TLS connection with a remote TLS client and
forwards data onto a datalogger using a standard TCP connection thus enabling
communication with TLS clients. The TLS client can be a web browser using
HTTPS or other user-supplied TLS client. Any other client program that
encrypts a standard TCP connection using TLS may be used to establish a
connection with the NL240 TLS Proxy Server and the NL240 will forward
unencrypted TCP data to a datalogger. In this way, a remote TLS client can
establish a TLS connection with a datalogger.
The settings found in the TLS Proxy Server and TLS tab in DevConfig are used
to configure the NL240 TLS Proxy Server.
Two physical configurations are possible and the required settings differ
depending on the configuration chosen. The possible configurations are shown
in the following figure.
26
Page 37

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
FIGURE 8-4. TLS proxy server configurations
Configuration A
In Configuration A, the NL240 decrypts TLS traffic and forwards the
unencrypted TCP traffic to the datalogger over the CS I/O port. The NL240 is
able to “learn” the IP address of the attached datalogger and will open a TCP
connection on the “learned” IP address.
Configuration B
In Configuration B, the NL240 decrypts TLS traffic and forwards the
unencrypted TCP traffic to the datalogger back out on the Wi-Fi port. The user
must specify an IP address and TCP port number for the forwarding TCP
connection.
To configure the NL240 TLS Proxy Server to communicate with a datalogger
attached to the CS I/O port or with a datalogger over an Wi-Fi connection,
open DevConfig and configure the following settings.
Settings Editor | TLS Proxy Server Tab
• Set the TLS Proxy Server setting to enable.
• Set the TLS Proxy Server Port Number. This is the TCP port number
on which the proxy server will listen for incoming connections. The TLS
Client also needs to be set to communicate on this port number. When
TLS communications are received on this port number, the NL240 will
decrypt the data and attempt to open a TCP connection to the datalogger
and forward the unencrypted data. In HTTPS communications, web
browsers use port 443. The NL240 will always listen on port 443
regardless of the value of this setting. Therefore, if HTTPS
communications are desired, it is unnecessary to configure this setting.
• Set the TLS Proxy Forward Physical Port to CS I/O Port for
Configuration A or to Wi-Fi for Configuration B.
27
Page 38

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
• For Configuration A, leave the TLS Proxy Forward IP Address set to
0.0.0.0. For Configuration B, enter the datalogger’s IP address in the TLS
Proxy Forward IP Address setting. This address must be configured in
the datalogger. It must be a unique, static IP address on the same subnet as
the NL240 IP address. For example, if the NL240 IP address is
192.168.5.1 with subnet 255.255.255.0, a valid IP address for the
datalogger would be 192.168.5.2 provided there are no other devices on
the subnet with that address.
• Set the TLS Proxy Forward Port Number. This is the TCP port number
that the proxy server will use when it opens a TCP connection to the
datalogger to forward unencrypted data. The datalogger’s TCP server port
must be set to communicate on this port number. The default value for the
datalogger’s PakBus/TCP server is 6785, so this setting can likely be left
at the default. The datalogger listens for HTTP traffic on port 80. The
NL240 will always forward TLS traffic received on port 443(HTTPS) to
port 80(HTTP) regardless of this setting. Therefore, if HTTPS
communications are desired, it is unnecessary to configure this setting.
• It is recommended to leave the TLS Proxy Timeout set to 90 seconds
although it can be changed if desired. This will determine how fast the
NL240 proxy server and client connections will timeout if no activity is
detected.
To configure the datalogger for Configuration A, connect to the datalogger
using DevConfig and select the CS I/O IP tab. Set the CS I/O Interface IP
Address to a static IP address. Use the datalogger’s CS I/O Interface that
corresponds to the NL240’s CS I/O IP Interface Identifier setting. To
configure the datalogger for Configuration B, connect to the datalogger using
DevConfig and select the TCP/IP tab. Set the Ethernet Interface IP Address
to a static IP address.
For either configuration, the IP address must not be 0.0.0.0, and it must be
unique on the same subnet as the NL240 IP address. For example, if the
NL240 IP address is 192.168.5.1 and Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0, the
datalogger address could be set as 192.168.5.2 provided there are no other
devices on the subnet with that address. Also set the datalogger’s Subnet Mask
to match that of the NL240.
The datalogger must be listening on the same TCP port that the NL240 is
configured to forward TCP traffic on (NL240 setting: TLS Proxy Forward Port
Number). The datalogger always listens on port 80 for HTTP, therefore, no
TCP port configuration is necessary for using HTTP.
8.2.6.2 DevConfig TCP Encrypted Communication to the NL240
In order to use DevConfig TCP Encrypted Communication to the NL240, you
will need to load your TLS Private Key and TLS Certificate into the NL240.
This is done from the Settings Editor | TLS tab in DevConfig. Once the private
key and certificate are loaded successfully, the TLS Status field should read
Initialized.
28
To use TCP Encrypted Communication, select the Use IP Connection check
box in DevConfig. Input the NL240’s IP address (or press the browse button
to select it from a list of NL240s connected to the network) and press Connect.
Page 39

9. Applications
NOTES
9.1 Working Around Firewalls
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
If the status of the TLS stack is Initialized, the NL240 will
automatically negotiate a secure TLS connection with DevConfig
as long as the Use IP Connection option is selected.
Encrypted Communication is required to change the TLS Private
Key and/or TLS Certificate via TCP. The private key and
certificate cannot be initialized via TCP, since the connection is
not encrypted. They must be initialized through a direct USB
connection to the NL240.
When the NL240 is in bridge mode, it cannot be configured via a
secure network connection, because in bridge mode the TLS stack
is not initialized. It can be configured via USB, RS-232, or an
unsecured network connection.
The NL240 can be used to provide a connection between LoggerNet and a
datalogger when both are behind firewalls. The NL240 must be on a public IP
address and will act as a common meeting place for all PakBus®
communications.
FIGURE 9-1. Working around firewalls
9.1.1 Configuring the NL240
• Connect to the NL240 in DevConfig (see Section 7, Configuring the
• On the NL240 tab:
NL240).
o Set Bridge Mode to disable.
o Set Use DHCP to disable.
29
Page 40

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
NOTE
o Input the IP Address, Network Mask, and Default Gateway. These
• On the Network Services tab:
o Make note of the PakBus/TCP Server Port.
9.1.2 Configuring the Datalogger
The datalogger must first be configured for internet
communication (i.e., through an NL115, an NL120, a second
NL240, or a cellular modem).
• Connect a serial cable from the PC COM port to the datalogger’s RS-232
port.
• Open DevConfig. Select the device type of the datalogger (CR800,
CR1000, or CR3000), the appropriate Communication Port, and Baud
Rate. Press Connect to connect to the datalogger.
• On the Network Services tab:
values can be provided by your network administrator.
o Under PakBus TCP Client Connections, input the NL240’s IP
• Press Apply to save the changes and then close DevConfig.
10. Troubleshooting
This section covers some common problems that might be encountered when
using the NL240. This is not comprehensive but should provide some insight
and ability to correct simple errors without a call to Campbell Scientific
technical support.
When your Campbell Scientific software cannot establish a link to a remote
datalogger that is connected to the NL240, do the following:
1. Check all your power connections.
• Your NL240 and any wireless access point (WAP) and/or wireless
2. Check all your cables and antenna.
• Verify that your antenna is securely attached to the NL240 and
address and PakBus TCP Server Port.
router being used must be connected to power. Check power indicator
lights to make sure your devices are powered.
oriented in the same direction as the antenna of your WAP. The green
Link/Act light on the NL240 should start blinking when it is
connected to a WLAN or ad hoc network. Also, the WLAN activity
light on your WAP (if it has one) should be blinking with activity as
well.
30
Page 41

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
3. Power cycle the NL240 and your WAP/hub/router/PC.
• Turn off or unplug your WAP/hub/router/PC and NL240. Wait 10
seconds and then plug them back in or turn them on. A full restart
may take 30 to 60 seconds.
4. Check the settings of the NL240.
• Make sure you have entered the correct SSID and Key/Passphrase (if
needed) for your network.
• Make sure the NL240 is connected to the right WLAN (Wi-Fi Status
in DevConfig or show | Wi-Fi settings | Wi-Fi in a Telnet session).
• Make sure the Wireless Network you are connecting to has a RSSI
level of greater than (>) –90dBm (in DevConfig under the Settings
Editor tab | Wireless Networks in Area list).
• Make sure the assigned NL240 IP address (DHCP or static) and the IP
address of the PC you are trying to connect from are able to
communicate with each other. (Your network administrator can help
you with this.)
For example, the following addresses are able to communicate:
NL240: IP address: 192.168.0.2, Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
PC: IP address: 192.168.0.3, Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
• If you are using DHCP to assign an IP address to the NL240, use
DevConfig to read the IP address assigned to your NL240. This is
done through a USB connection to the NL240 while the NL240 is
connected to your network (if bridge mode is not being used).
• The IP address assigned to the NL240 must be unique on your
network.
• When Bridge Mode is enabled, the datalogger controls how the IP
address is assigned. Make sure your datalogger is connected correctly
to the NL240 via the CS I/O port and SC12 cable.
• Try to ping the NL240 from your PC. (From the Windows Start
Menu, choose Accessories | Command Prompt. Then type ping
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address of your
NL240.) If no packets are returned, this indicates that there is no
network connection to that IP address.
5. Make sure the IP address and port number entered in
LoggerNet/PC400/RTDAQ match the settings in the NL240.
• Note that PakBus® and serial server communications use different
port numbers. The default port number for PakBus communications
is 6785. The default port number for CS I/O serial server
communications is 6783. The default port number for RS-232 serial
sever communications is 6784. The correct port number must follow
31
Page 42

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
6. If you are unable to communicate with the NL240 via the USB cable,
verify that you have installed the latest drivers for the NL240. These can
be downloaded from our website at www.campbellsci.com.
7. If the NL240 is configured as a CS I/O serial server, verify that any other
SDC device attached to the datalogger is using a different SDC address.
For example, if the NL240 is configured for SDC7, any other device
attached to the datalogger cannot use SDC7.
8. If communicating over a slow or intermittent connection, it may be
necessary to lower the Maximum Packet Size of the datalogger in
LoggerNet Setup and/or add Extra Response Time to the PakBus Port in
LoggerNet Setup.
9. Reset the NL240 to its default settings.
the IP address of the NL240 in LoggerNet Setup in order for
LoggerNet to communicate through the NL240. For example, if the
NL240 is configured as a CS I/O serial server, in LoggerNet Setup,
enter the correct IP address of your NL240 followed by :6783 (e.g.,
192.168.0.3:6783).
• If none of the above steps correct your communication problems, reset
the NL240 to its default settings. This can be done using the Factory
Defaults button in DevConfig or by using the Defaults command in a
telnet session with the NL240.
10. Verify you are running the latest revision of firmware (operating system).
It is possible that an issue affecting your ability to communicate via the
NL240 is resolved in the latest version. The latest firmware version and
its revision history can be found at www.campbellsci.com/downloads.
There is no charge for this download. See Appendix D, Sending a New OS
to the NL240, for instructions on downloading the firmware revision to the
NL240.
11. If the above steps do not resolve the issue, please call Campbell Scientific,
for help. Before calling, it would be helpful to do the following:
• Obtain a detailed description of your network setup including TCP/IP
address, port number, PakBus® settings, and other pertinent
information regarding all of the devices in the NL240’s
communication network.
• Save a copy of the NL240 settings (in XML format) using DevConfig.
• Save a copy of the NL240 event log. This is low-level code that can
be used by Campbell Scientific’s engineering staff to help
troubleshoot the NL240. To obtain the event log, the NL240 must not
be in Bridge Mode. Telnet into the NL240 using your favorite telnet
program. Once you have logged in, type “eventlog” at the prompt.
Record the date and time that you did this. Copy and paste the output
into a text file.
32
Page 43

11. Attribution
NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
• If running NL240 firmware revision v.4 or greater, you can also type
“eventloga” at the prompt to obtain an ASCII version of the low-level
log. Copy and paste the output into a text file.
• Once the eventlogs have been copied, you can type “eventlog erase”
at the prompt to clear the log. If you want to add a date to indicate
when the logs were last cleared, you can enter “eventlog erase date”
where date is a string of up to 8 characters.
After calling Campbell Scientific for help, email your network description, the
newly created text files, and the saved XML settings file to the application
engineer you are working with.
PakBus is a registered trademark of Campbell Scientific, Inc.
33
Page 44

NL240 Wireless Network Link Interface
34
Page 45

Appendix A. Glossary
Beacon Interval
Devices in a PakBus® network may broadcast a hello-message to other
devices in order to determine "neighbor" devices. Neighbor devices are
devices that can be communicated with directly by the current device
without being routed through an intermediate device. A beacon in a
PakBus network helps to ensure that all devices in the network are aware
of which other devices are viable in the network.
Bridge (Bridging, Network Bridge)
In the context of this manual, bridging is the act of connecting two
network interfaces at the data link layer. The NL240 acts as a semitransparent bridge passing, without alteration, IP packets between the WiFi and CS I/O ports.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
A TCP/IP application protocol in which IP addresses are assigned
automatically by a DHCP server. Note that an IP address obtained
through DHCP is not static but is leased for a period of time set by the
network administrator. The address may change, if the NL240 is powered
down.
Hello Exchange
A communication exchange that establishes two PakBus® devices as
neighbors. A hello command packet is sent by one PakBus device (A) to
another device (B). Device (B) then sends a hello response (A). The
receipt of that packet establishes the two devices as neighbors. Only a
hello exchange can establish two devices as neighbors.
Neighbor (PakBus® Neighbor)
A device in a PakBus network that can be communicated with directly
(i.e., not via a router). Every PakBus device maintains its own Neighbor
List.
PakBus®
Campbell Scientific’s packet-switched communications protocol. Packets
of information transmitted between PakBus devices contain user data and
administrative information (a header) that routing devices use to move the
packets to their ultimate destination. PakBus devices examine the header
information and then either remove the header (at the packet’s final
destination) or forward the packet to another PakBus device.
PakBus® Node
A device in a PakBus network. Each device in a network must have a
unique PakBus address.
A-1
Page 46

Appendix A. Glossary
Port Number
A port number is a way to identify a specific process to which a network
message is to be forwarded when it arrives at the NL240.
SDC (Synchronous Device Communications)
A Campbell Scientific, addressable, and synchronous communications
protocol. The protocol allows multiple peripherals to be connected to the
same device as long as each peripheral has a unique SDC address.
Serial Server
A serial server (also referred to as a terminal server) allows serial
communication over an IP communications link.
Proxy (Proxy Server)
A device that acts as an intermediary for IP communications between two
clients. In the context of this manual, the NL240 acts an intermediary
between two or more clients requiring a secure connection (TLS) and one
client requiring an unsecured connection. Communications are encrypted
and decrypted as necessary for the two clients to communicate via the
proxy.
TLS (Transport Layer Security)
An encryption protocol allowing secure client/server communications. A
keyed, message-authentication code is used for message reliability.
Verify Interval
An interval of time that a PakBus device uses to determine when it is time
send a hello message to another device to verify that they can still
communicate.
A-2
Page 47

TABLE B-1. CS I/O Pinout
TABLE B-2. RS-232 Pinout
1
DCD
DCD
2
TXD
RXD
3
RXD
TXD
4
DTR
DTR
5
SIGNAL GND
SIGNAL GND
6
DSR
DSR
7
CTS
RTS
8
RTS
CTS
9
RING
RING
Appendix B. Cables, Pinouts, LED Function, and Jumper
B.1 CS I/O
The CS I/O cable is a 9-pin, straight-through cable with all 9 pins connected.
The supplied SC12 cable (pn 16675) is recommended.
Datalogger (DB9 Female)
Pin
Function
1 5 VDC N/C
2 SIGNAL GND SIGNAL GND
3 RING RING
4 RXD TXD
5 ME ME
6 SDE SDE
7 CLK/HS CLK/HS
8 12 VDC N/C
9 TXD RXD
Peripheral (DB9 Male)
Function
B.2 RS-232
A DB9 female to DB9 male cable (such as Campbell Scientific part number
10873) is used to connect the NL240’s RS-232 port to the datalogger’s RS-232
port. The supplied SC12 cable can also be used. A DB9 female null modem
cable (such as Campbell Scientific part number 13657) is used to connect the
NL240’s RS-232 port to a PC’s RS-232 port. The RS-232 cable should be kept
short when using high baud rates.
Datalogger (DCE, DB9 Female)
Pin
Function
Peripheral (DTE, DB9 Male)
Function
B-1
Page 48

Appendix B. Cables, Pinouts, LED Function, and Jumper
TABLE B-3. USB Micro-B
Pin
Function
1
VBUS (Not Used)
2
Data -
4
N/C
5
GND
TABLE B-4. Power In
TABLE B-5. Power LED (Red)
Double blink
Low Power Mode enabled.
Single blink
Asleep (by use of the IPNetPower instruction in the
Fast single
OS Download in progress – DO NOT DISCONNECT
B.3 USB
The USB cable is the supplied USB A to micro B style cable (Campbell
Scientific part number 27555). This is used only for device configuration.
3 Data +
B.4 Power
B.5 LEDs
Pin Function
Center 7 – 20 Vdc
Sleeve Power GND
State Description
Off Device powered off.
On solid
every two
seconds
every four
seconds
After power-up: Searching for and trying to join a Wi-Fi
network/creating an ad hoc network
Normal Operation: Low Power Mode disabled.
datalogger when in Bridge Mode)
blink
B-2
POWER
Page 49

TABLE B-6. Wi-Fi LED (Green)
State Description
Blinking once
a second
Flash with
network
activity
B.6 Power Jumper
If you wish to prevent the NL240 from being powered over the CS I/O port,
remove the two screws on the top of the NL240, remove the NL240’s top
cover, remove the jumper above the red LED and place it so that it is connected
to only one post. With the jumper connected to only one post, the NL240 can
only be powered from the barrel connector. With the jumper connected to both
posts, the NL240 can be powered from the CS I/O port or from the barrel
connector.
Appendix B. Cables, Pinouts, LED Function, and Jumper
Attempting to acquire a network address from DHCP.
Successfully connected to wireless network.
B-3
Page 50

Appendix B. Cables, Pinouts, LED Function, and Jumper
B-4
Page 51

NOTE
Appendix C. NL240 Settings
All of the NL240 settings available from the Settings Editor in DevConfig are
described below.
C.1 Main Tab
Model (read only)
Model name.
Serial Number (read only)
Specifies the NL240 serial number assigned by the factory.
OS Version (read only)
Operating system version currently in the NL240.
Compile Date (read only)
Operating system compile date.
Bridge Mode
This setting is used to configure the device's mode of operation.
Bridge Mode Disabled
With Bridge Mode disabled, the serial server (RS-232 or CS I/O),
PakBus®, and secure proxy server functionalities are available. Refer to
the respective device settings for the configuration of these functionalities.
Bridge Mode Enabled
With Bridge Mode enabled, the device will act as a bridge from Wi-Fi to
CS I/O. All IP packets that come in to the device via Wi-Fi will be
communicated to a datalogger over the CS I/O port. Some filtering is
done in order to minimize the amount of traffic on the CS I/O port but
every packet that is transmitted to the logger is sent intact as a complete
Ethernet/TCP packet. This enables the datalogger to use its TCP/IP stack
to interpret the packet, and therefore, all of the datalogger’s TCP services
are available. In bridge mode, none of the other device settings are valid
and all other functionality is disabled. All settings (i.e., IP, netmask,
gateway) are configured in the datalogger. However, in bridge mode, the
device will intercept any TCP traffic on the “TCP Configuration Port
Number.” This allows the device to still be configured remotely by IP
connection using DevConfig. The “TCP Configuration Port Number” is a
user setting with a default value of 6786.
When the device is configured in bridge mode, it is not possible to
open a telnet session with it.
C-1
Page 52

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
CS I/O IP Interface Identifier
When the device is configured to operate in Bridge Mode, the datalogger will
address the device using this identifier. The datalogger can address up to two
“CS I/O IP” devices. The corresponding CS I/O IP Address settings in the
datalogger will control the interface. CS I/O IP Interface 1 uses SDC channel
3. CS I/O IP Interface 2 uses SDC channel 1.
Bridge Mode Forward Code
When the device is configured for bridge mode, it forwards Ethernet packets to
the datalogger. Because the device is aware of the MAC address and IP
address being used by the datalogger, it is able to do some filtering on
incoming packets and only forward relevant packets. This decreases the
amount of traffic on the relatively bandwidth-limited CS I/O port and
minimizes the amount of Ethernet processing the datalogger needs to perform.
It may be desired to further reduce the amount of CS I/O traffic. This setting
allows the filtering by the device to be customized to some degree. The default
value of this setting is 65535 (0xFFFF hex) and will forward all packets that
have been determined to be relevant for proper datalogger IP communication.
If desired, other codes may be entered to filter out certain packet types.
A packet is forwarded to the datalogger if its corresponding bit is set in the
“Bridge Mode Forward Code.” It will not be forwarded if its corresponding bit
is cleared. Single bits or multiple bits may be cleared to accomplish custom
filtering. The following are example values of this code.
Forward Code Values
65535 (0xFFFF): Leave all bits set to forward all relevant packets.
65531 (0xFFFB): Clear bit 2 to forward all relevant packets except UDP
Broadcast packets. Filtering UDP broadcasts will disable the datalogger’s
ability to respond to DevConfig discovery packets but in many cases will
greatly reduce the total number of forwarded packets.
65279 (0xFEFF): Clear bit 8 to forward all relevant packets except IPv6
packets. Filtering these packets may be desired if the datalogger is on an
IPv6-enabled network but not required to respond to any IPv6-related
traffic.
DHCP
Enable if the device should be configured to use DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol) to automatically acquire an IP address, subnet mask,
and gateway from the local DHCP server. After DHCP is enabled, the device
will reboot and it may take a few moments to acquire the IP settings. In order
to see the acquired settings you may have to refresh by pressing F5.
C-2
Page 53

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
IP Address
The IP address uniquely identifies this node on an internet. If DHCP is
enabled, this is the IP address obtained from the DHCP server. If DHCP is
disabled, a static IP address must be obtained from your network administrator
for use with this device. (It is recommended to configure a static IP address.)
In bridge mode, this setting is obtained from the datalogger and
cannot be edited here. It must be edited in the datalogger settings.
If the setting has been successfully obtained from the datalogger,
this setting will show “OK”; otherwise, it will show “0.0.0.0”.
Subnet Mask
The Subnet Mask is used to select that portion of the IP address which
identifies the network. It is used to facilitate routing and should be obtained
from the network administrator along with the IP address. If DHCP is enabled,
this is the Subnet Mask obtained from the DCHP server.
In bridge mode, this setting is obtained from the datalogger and
cannot be edited here. It must be edited in the datalogger settings.
If the setting has been successfully obtained from the datalogger,
this setting will show “OK”; otherwise, it will show “0.0.0.0”.
Default Gateway
Datagrams being sent to an unknown network are routed via the Default
Gateway. This entry specifies the Internet address of the Default Gateway. If
no Default Gateway exists, set this entry to “0.0.0.0”. If DHCP is enabled, this
is the Default Gateway obtained from the DCHP server.
In bridge mode, this setting is obtained from the datalogger and
cannot be edited here. It must be edited in the datalogger settings.
If the setting has been successfully obtained from the datalogger,
this setting will show “OK”; otherwise, it will show “0.0.0.0”.
Name Servers
This setting specifies the addresses of up to three domain name servers that the
device can use to resolve domain names to IP addresses. Note that if DHCP is
used to resolve IP information, DNS addresses obtained via DHCP will
override this list.
IP Info
Reports the IP address, network mask, and default gateway of the network
interface. If DHCP is used, this setting will report the values configured by the
DHCP server.
C-3
Page 54

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
C.2 Wi-Fi Tab
Admin Password
To help guard against unauthorized access to the NL240, it is passwordprotected by the Admin Password. This password will be required to gain
access to the NL240 via DevConfig over TCP and telnet. If the password
setting is left blank, no password is required to access the NL240. After
settings are saved, the new password will be in effect.
TCP Configuration Port Number
The default TCP port number for configuration via TCP is 6786. This entry
makes it possible for the user to change the port number used in TCP
configuration if desired. Typically, it is not necessary to change this entry
from its default. (range 1..65535)
Wi-Fi Status
Status of the Wi-Fi Module.
Wireless Network Configuration
This setting controls whether the device is configured to join an existing
network or create an Ad hoc network.
Join an Existing Network
If this mode is selected, the device will scan for available networks and
attempt to join the network specified by the SSID setting. If the SSID is
left blank the device will attempt to join the first open network it finds. If
for some reason the device cannot join the desired SSID (i.e. network out
of range or incorrect parameters), it will go to a low power state and
periodically retry. If this mode is selected, the device can join either an
Infrastructure network or an Ad hoc network.
Create an Open Ad hoc Network
If this mode is selected, the device will be the creator of an Ad hoc
network. Enter the desired name of the network in the SSID setting. An
Ad hoc network created by the module supports up to 4 joinees. The Ad
hoc network that is created will be an open network with no encryption.
If this mode is selected, the Ad hoc Channel must also be specified.
Choose a channel that is different from any surrounding wireless networks
to minimize interference.
Create an Ad hoc Network with WEP Security
C-4
Choose this option to configure the device to be the creator of an Ad hoc
network with the added security of WEP encryption. Enter the desired
name of the network in the SSID setting. An Ad hoc network created by
the module supports up to 4 joinees. The Ad hoc network that is created
will be a network with WEP encryption. The WEP Key used for the
network is entered in the Password setting. If this mode is selected, the
Page 55

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
Ad hoc Channel must also be specified. Choose a channel that is different
from any surrounding wireless networks to minimize interference.
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
The SSID is the name that identifies a wireless network (32 character
maximum). The SSID differentiates one wireless network from another, so all
devices attempting to connect to the same network must use the same SSID. If
the NL240 is configured to “Join an Existing Network”, then enter the SSID of
the network to join here. If no SSID is specified, the NL240 will join the
strongest open network it finds. If the NL240 is configured to “Create an Ad
hoc Network”, then the SSID entered here will be the SSID of the network
created.
To see a list of the available networks detected in the area, click on the browse
button or view the “Wireless Networks in Area” list on the Wi-Fi tab in the
Settings Editor.
When the browse button is clicked or the Refresh button inside the
resulting dialog is clicked, if the device is currently connected to
a network, the connection will be temporarily interrupted. The
device will disconnect, scan for available networks, then
reconnect.
Key/Passphrase
If joining a WPA or WPA2 security enabled network, then this is where the
PSK (Pre-Shared Key) is entered. If joining a WEP security enabled network
or creating an ad hoc network using WEP security, this is where the WEP key
is entered. The device supports 64-bit WEP and 128-bit WEP. For 64-bit
WEP, enter a in the form of 5 ASCII characters or 10 hexadecimal digits (0-9,
A-F). For 128-bit WEP, enter a key in the form of 13 ASCII characters or 26
hexadecimal digits (0-9, A-F).
Ad hoc Channel
Applicable only when the device is configured to create an Ad hoc network. It
specifies in which channel the network should be created. Two Wi-Fi
networks operating on the same channel will interfere with each other and will
have to compete for bandwidth. The center frequencies of adjacent channels
are 5 MHz apart and the bandwidth of each channel is 20 MHz which means
that adjacent channels overlap. To completely avoid interference, there must
be a spacing of at least 5 channels between each Wi-Fi network. It is,
therefore, recommended to use channels 1, 6, and 11. To see a list of all the
wireless networks in the area and the associated channels on which they
operate, go to the Settings Editor tab then Wi-Fi tab and see the Wireless
Networks list.
Power Level
This fixes the Transmit Power level of the module. This value can be set as
follows: Low (7dBm), Medium (10dBm), High (16 to 17dBm).
C-5
Page 56

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
This setting affects the transmission power level of the NL240,
which may affect the transmission range of the device. This
setting does not affect the overall power consumption of the
device.
Lower Power Mode
If Low Power Mode is enabled, then the device will be put into its power
saving mode. At full power the device consumes approximately 0.6W when
idle and 0.7W when communicating (USB disconnected). Enabling Low
Power will result in significant power savings. The power savings and the
behavior of the device depend on whether it is configured to join an existing
network or create an ad hoc network.
Join an Existing Network
If the device has joined an infrastructure network and Low Power Mode is
enabled, approximately 1/2W savings are observed while communications
are idle and approximately 1/3W savings are observed when doing typical
communications (i.e. data collection from a datalogger). However, power
savings are affected by the amount of traffic on the network because the
Wi-Fi module has to wake up to receive broadcast traffic from the Access
Point. Therefore, power consumption may increase slightly on a busy
network.
In typical PakBus applications, overall communication speed is not
noticeably affected by enabling Low Power Mode. However, it may be
noticeably slower in some applications because in Low Power Mode the
Wi-Fi module is put in sleep mode and occasionally wakes up to receive
data from the Access Point. This does slightly reduce the responsiveness
of the device.
If configured to join a non-existent network or a network that is not in
range, the device will periodically (~50 sec) attempt to connect with the
network while going to a low power state in between attempts. This
behavior will be observed regardless of the Low Power Mode setting.
If the device has joined an existing ad hoc network (one which it did not
create), then it will stay on at full power while the network exists and is
active. Once the network has been taken down or gone out of range, the
device will power down the Wi-Fi and go back to periodically checking
for the network to come back in existence. This behavior will be observed
regardless of the Low Power Mode setting.
Create an Ad hoc Network
If the device is configured to create an Ad hoc network and Low Power
Mode is enabled, then it will periodically power the Wi-Fi on and off in
an effort to conserve power. If Low Power Mode is disabled, then the
device will keep the Wi-Fi on at full power.
C-6
The periodic low power behavior is governed by the two settings “Ad hoc
Low Power On Time” and “Ad hoc Low Power Interval.” The device will
periodically power on according to the time configured in the “Ad hoc
Page 57

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
Low Power Interval.” It will create the Ad hoc network and it will stay on
for the amount of time configured in the “Ad hoc Low Power On Time”
setting. Then it will power of the Wi-Fi for the remainder of the interval.
This means that if you wish to join the Ad hoc network with a smartphone
or some other device, you will notice that the network may not be
available until you wait for the programmed interval to elapse. Once you
see the network become available, join it. The NL240 should recognize
traffic on the network and keep Wi-Fi powered as long as the second
device remains connected to the network. If the device takes a moment to
join the network or it takes a moment to enter a password, the NL240 may
power the Wi-Fi down in the meantime. The smartphone should still be
able to join the network and then once the Interval elapses the NL240
should power up the Wi-Fi again at which point it will recognize that the
second device has joined the network and keep Wi-Fi powered for as long
as the second device remains connected.
The user is able to configure the amount of power savings that the device
may achieve in this mode by setting the Interval and On Time settings.
While a long interval will result in greater power savings, a shorter
interval will provide more convenience for a smartphone user trying to
join the network as he will have to wait for the Low Power Interval to
elapse in order for the network to be available. The device consumes
~0.6W while it has the Wi-Fi powered and the Ad hoc network available.
It consumes ~0.02W while the Wi-Fi is powered off.
If the “Ad hoc Low Power On Time” is greater than or equal to
the “Ad hoc Low Power Interval”, then the Wi-Fi will stay
powered always and the network will always be present regardless
of the Low Power Mode setting.
Ad hoc Low Power On Time (seconds)
This setting is applicable only if the device is configured to create an Ad hoc
network and the Low Power Mode is enabled. The device will periodically
power on and off the Wi-Fi module in an effort to conserve power when there
are no other devices in the area trying to connect to the network. The Power
on/off duty cycle is governed by the Ad hoc Low Power Interval and the Ad
hoc Low Power On Time. The device powers on the Wi-Fi module every
“Low Power Interval” seconds and keeps it on for “Low Power On Time”
seconds.
Ad hoc Low Power Interval (seconds)
This setting is applicable only if the device is configured to create an Ad hoc
network and the Low Power Mode is enabled. The device will periodically
power on and off the Wi-Fi module in an effort to conserve power when there
are no other devices in the area trying to connect to the network. The Power
on/off duty cycle is governed by the Ad hoc Low Power Interval and the Ad
hoc Low Power On Time. The device powers on the Wi-Fi module every
“Low Power Interval” seconds and keeps it on for “Low Power On Time”
seconds.
C-7
Page 58

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
C.3 RS-232 Tab
Wireless Networks in Area
This is a read-only field that lists the networks available in the area.
Information listed for each network is: SSID, RSSI / Signal Strength, Channel,
Security.
If the NL240 is creating an ad hoc network, wireless networks in
the area may not be displayed.
RS-232 Configuration
This setting controls which process will be associated with the RS-232 port.
The following values are defined:
TCP Serial Server
The device will listen for an incoming TCP connection from a remote
client. The port number of the listening connection is specified in the
“RS-232 Service Port Number” setting. Data received on the TCP
connection will be forwarded to the RS-232 port, and data received on the
RS-232 port will be forwarded to this TCP connection.
TCP Serial Client
The device will maintain a TCP client connection with a remote server.
The IP address and port number of the remote server are configured in the
settings “RS-232 TCP Serial Client IP Address” and “RS-232 TCP Serial
Client Port”. Data received on the RS-232 port will be forwarded to this
TCP connection, and data received on the TCP connection will be
forwarded to the RS-232 port. The device will attempt to open a
connection with the remote server and if the connection fails to open, the
device will continue to retry at an interval of 60 seconds. If data arrives
on the RS-232 port when no TCP connection exists, the device will buffer
up the data (up to 1500 bytes) and immediately attempt to open a
connection to deliver the data. If the remote server closes the connection
due to error, the device will make a best effort to save any data that was in
process and re-queue it to be sent on the next successfully-opened TCP
connection.
PakBus
This port uses the PakBus® protocol.
Modbus/TCP Gateway
The device will listen for incoming MODBUS/TCP connections from a
remote client. The port number of the listening connection is specified in
the “RS-232 Service Port Number” setting. The device will convert
incoming MODBUS/TCP frames to MODBUS/RTU and forward them to
the RS-232 port. The device will wait for a response from the
MODBUS/RTU device and forward the response back to the remote
MODBUS/TCP client over the established TCP connection.
C-8
Disabled
This port will not be used.
Page 59

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
RS-232 Service Port Number
This setting is used when the RS-232 port is configured as a Serial Server or
MODBUS/TCP gateway. To communicate with a TCP/IP server, the client
application must open a socket to that server. The socket of a specific server is
uniquely identified by an IP address of the host where the server is running and
a port number associated with the server application on that host. This entry is
where the port number of the server is set. Ensure that the client application is
set to use the same port number as configured here. Most MODBUS/TCP
applications use port 502. (range 1..65535)
RS-232 Baud Rate
This setting specifies the baud rate of the RS-232 port. The connected device
must be set to communicate at the same baud rate.
RS-232 RTS
The NL240 asserts the RTS and DTR lines when doing RS-232 communications.
This setting allows the user to disable the RTS line if needed so that it will not be
asserted. Some hardware will not function if the RTS line is asserted, but
typically, it is not necessary to change this setting from its default (enabled).
RS-232 TCP Timeout
This setting will determine how fast the device will time out on the open TCP
connection. For Serial Server and MODBUS/gateway configurations, the
device will close the TCP connection if no activity is detected for the timeout
period. For the TCP Client configuration, the device will close the TCP client
connection if no activity is detected and then immediately open another
connection with the remote server. This behavior helps to ensure that the
connection is functional as the device does not know the frequency or nature of
the expected data. Set to 0 for no timeout (not recommended). (range 0..999)
(seconds)
RS-232 Always On
This setting controls whether the device is allowed to shut down the RS-232
port when it is not in use in order to conserve power. Typically it is not
necessary to change this setting from its default [Auto].
Auto
Based on the RS-232 port configuration, the device will decide which of
the following two modes is more likely to be desired and will operate in
the according manner.
Always On
The device will not power down the RS-232 port. The port will remain
active always. As a result the processor cannot enter its lowest power
state. Keeping the port always on may be necessary because when the
RS-232 port is powered down there is a wake-up latency and the first few
bytes that come in on the port will be missed. If this behavior is
C-9
Page 60

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
unacceptable, set this setting to “Always On” to keep the RS-232 port
always on.
Power Down Port when Inactive
The device will power down RS-232 when the port is inactive. If the
device is configured for Serial Server mode, the inactivity timeout is 40
seconds. If configured for PakBus, the device can use the PakBus
protocol’s link-state to do a more intelligent and effective inactivity
timeout. If communications are received on the port after it has been
powered down, there is a wake-up latency and the first few bytes will be
missed. PakBus has a built-in mechanism to deal with this, but if the
device is not configured for PakBus communications, the user must
decide if the application can accept this behavior. If this behavior is
unacceptable, set this setting to “Always On.” The power savings that the
device is able to achieve by powering down the RS-232 port are
significant as the processor is also able to go to a deeper sleep mode. In
an idle state with Low Power Mode enabled, an additional ~0.12W
savings are observed by setting RS-232 Always On to “Power Down Port
when Inactive.”
RS-232 PakBus Beacon Interval
This setting, in units of seconds, governs the rate at which the NL240 will
broadcast PakBus® messages on the associated port in order to discover any
new PakBus neighboring nodes. It will also govern the default verification
interval if the value of the Verify Interval setting for the associated port is zero.
RS-232 PakBus Verify Interval
This setting specifies the interval, in units of seconds, that will be reported as
the link verification interval in the PakBus® hello-transaction messages. It
will indirectly govern the rate at which the NL240 will attempt to start a hello
transaction with a neighbor if no other communication has taken place within
the interval.
Neighbors Allowed RS-232
Example: (129,129) (1084,1084)
In the example above, nodes 129 and 1084 are assigned as neighbors to the
NL240.
This setting specifies, for a given port, the explicit list of PakBus node
addresses that the NL240 will accept as neighbors. If the list is empty (the
default value), any node will be accepted as a neighbor. This setting will not
affect the acceptance of a neighbor if that neighbor's address is greater than
3999. The formal syntax for this setting follows:
C-10
neighbor := { "(" range-begin "," range-end ")" }.
range-begin := pakbus-address. ;
range-end := pakbus-address.
pakbus-address := number. ; 0 < number < 4000
Page 61

C.4 CS I/O Tab
Appendix C. NL240 Settings
RS-232 Modbus Timeout
This setting determines how long the MODBUS/TCP to MODBUS/RTU
gateway will wait for an answer from the MODBUS slave device(s) attached to
the RS-232 port. If no answer is received within the timeout period, the
MODBUS/TCP server will reply to the MODBUS/TCP client with error code
0x0B (Target Device Failed to Respond). (milliseconds)
RS-232 TCP Serial Client IP Address
This setting specifies the IP address of the outgoing TCP Serial client
connection that the device should maintain. If the connection fails, the device
will retry until the connection succeeds. No entry specifies that no client
connection will be made.
RS-232 TCP Serial Client Port
This setting specifies the TCP port of the outgoing TCP Serial Client
connection. (range 1..65535)
CS I/O Configuration
This setting controls which process will be associated with the CS I/O port.
The following values are defined:
TCP Serial Server
The device will listen for an incoming TCP connection from a remote
client. The port number of the listening connection is specified in the “CS
I/O Service Port Number” setting. Data received on the TCP connection
will be forwarded to the CS I/O port, and data received on the CS I/O port
will be forwarded to this TCP connection.
PakBus
This port uses the PakBus® protocol.
Modbus/TCP Gateway
The device will listen for incoming MODBUS/TCP connections from a
remote client. The port number of the listening connection is specified in
the “CS I/O Service Port Number” setting. The device will convert
incoming MODBUS/TCP frames to MODBUS/RTU and forward them to
the CS I/O port. The device will wait for a response from the
MODBUS/RTU device and forward the response back to the remote
MODBUS/TCP client over the established TCP connection.
Disabled
This port will not be used.
CS I/O Service Port Number
To communicate with a TCP/IP server, the client application must open a
socket to that server. The socket of a specific server is uniquely identified by
an IP address of the host where the server is running and a port number
associated with the server application on that host. This entry is where the port
C-11
Page 62

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
number of the serial server is set. Typically, it is not necessary to change this
entry from its default. (range 1..65535)
SDC Address
Communication with the datalogger via the CS I/O port is done using SDC
(Synchronous Device Comms). The datalogger will address the devices with
which it wishes to communicate using an SDC address. The CS I/O port can
be configured to respond to SDC address 7, 8, 10, or 11.
CS I/O TCP Timeout
This setting, in units of seconds, will determine how fast the CS I/O serial
server will time out if no activity is detected. Set to 0 for no time-out (not
recommended). (range 0..999)
CS I/O PakBus Beacon Interval
This setting, in units of seconds, governs the rate at which the NL240 will
broadcast PakBus® messages on the associated port in order to discover any
new PakBus neighboring nodes. It will also govern the default verification
interval if the value of the Verify Interval setting for the associated port is zero.
CS I/O PakBus Verify Interval
This setting specifies the interval, in units of seconds, that will be reported as
the link verification interval in the PakBus® hello-transaction messages. It
will indirectly govern the rate at which the NL240 will attempt to start a hello
transaction with a neighbor if no other communication has taken place within
the interval.
CS I/O Modbus Timeout
This setting determines how long the MODBUS/TCP to MODBUS/RTU
gateway will wait for an answer from the MODBUS slave device(s) attached to
the CS I/O port. If no answer is received within the timeout period, the
MODBUS/TCP server will reply to the MODBUS/TCP client with error code
0x0B (Target Device Failed to Respond). (milliseconds)
C.5 Net Services Tab
Telnet
Enables/Disables the telnet service.
Telnet Port Number
The default TCP port number for the configuration monitor telnet session is 23.
This entry makes it possible for the user to change the telnet session port
number if desired. Typically, it is not necessary to change this entry from its
default. (range 1..65535)
C-12
Page 63

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
Telnet Timeout
This setting, in units of seconds, will determine how fast the configuration
monitor telnet session will time out if no activity is detected. Set to 0 for no
time-out (not recommended). (range 0..999)
Ping (ICMP)
The NL240 will not respond to “Ping” requests if this setting is disabled.
PakBus Address
This setting specifies the PakBus® address for this device. The value for this
setting must be chosen such that the address of the device will be unique in the
scope of the datalogger network. Duplication of PakBus addresses in two or
more devices can lead to failures and unpredictable behavior in the PakBus
network. When a device has a neighbor list or neighbor filter setting filled in
for a port, any device that has an address greater than or equal to 4000 will be
allowed to connect to that device regardless of the neighbor filter.
PakBus/TCP Server Port
This setting specifies the TCP service port for PakBus® communications with
the datalogger. Unless firewall issues exist, this setting probably does not need
to be changed from its default value.
PakBus/TCP Password
Specifies the password that will be used to authenticate any incoming (server)
or outgoing (client) PakBus®/TCP sessions. This password is used by the
server to generate a challenge to any client that connects to the PakBus/TCP
server port. If the client fails to respond appropriately, the connection will be
terminated. If this password is blank (the default value), no such authentication
will take place.
PakBus/TCP Client Address (1-4)
This setting specifies the IP address of an outgoing PakBus®/TCP client
connection that the NL240 should maintain. If the connection fails, the NL240
will retry until the connection succeeds. No entry or a setting of 0.0.0.0
specifies that no client connection will be made.
PakBus/TCP Client Port (1-4)
This setting specifies the TCP port of the outgoing PakBus®/TCP client
connection. Typically, it is not necessary to change this entry from its default.
(range 1..65535)
PakBus Routes (read only)
This setting lists the routes that are known to the NL240. Each route known to
the NL240 will be represented by the following four components separated by
commas and enclosed in parentheses. The description of each component
follows:
C-13
Page 64

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
Port Number
Specifies a numeric code for the port that the router will use. It will
correspond with one of the following:
0 CS I/O
1 RS-232
100 PakBus/TCP Connection — If the value of the port number is
100 or greater, the connection is made through PakBus/TCP.
Via Neighbor Address
Specifies the address of the neighbor/router that will be used to send
messages for this route. If the route is for a neighbor, this value will be
the same as the address.
PakBus Address
Specifies the address that the route will reach.
Response Time
Specifies the amount of time (in milliseconds) that will be allowed for the
route.
Central Routers
This setting specifies a list of up to eight PakBus® addresses for routers that
are able to work as Central Routers. By specifying a non-empty list for this
setting, the device will be configured as a Branch Router meaning that it will
not be required to keep track of neighbors of any routers except those in its
own branch. Configured in this fashion, the device will ignore any neighbor
lists received from addresses in the central routers setting and will forward any
messages that it receives to the nearest default router if it does not have the
destination address for those messages in its routing table.
C.6 TLS Proxy Server Tab
TLS Proxy Server
Enable/Disable the TLS Proxy Server. When doing TLS proxy communications,
the device’s TLS server maintains a secure TLS connection with a remote TLS
client and forwards information onto a datalogger using a standard TCP
connection. TCP ports and physical connections are configured below.
C-14
If the TLS Proxy Server is enabled and a datalogger is connected
to the CS I/O port, the datalogger will load its TCP stack in case
it is required to do TCP communications. Running the TCP stack
causes the datalogger to use more memory, leaving less for final
storage, etc. So if TCP/TLS server capability is not required, the
TLS Proxy Server should be left disabled.
Page 65

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
TLS Proxy Server Port Number
When doing TLS Proxy communications, the NL240 TLS server maintains a
secure connection with a remote client. If the TLS Proxy Forward Physical
Port is specified to be the CS I/O port, the NL240 will then open a TCP
connection with the logger over the CS I/O port and do unecrypted data
transfer with the datalogger. If the TLS Proxy Forward Physical Port is
specified to be Wi-Fi, the NL240 will open the TCP connection over Wi-Fi on
the TLS Proxy Forward IP Address.
In order to communicate with the NL240 TLS server, the client application
must open a socket to that server. The socket of the NL240 TLS server is
uniquely identified by the IP address and a port number. This entry is where
the port number of the NL240 TLS server is set.
The TLS client needs to be set to communicate on this port number. If secure
communications come in on the Secure Proxy Server Port Number, the NL240
will attempt to open a TCP connection to the datalogger on the Secure Proxy
Forward Port Number. Also, regardless of this setting, the NL240 Secure
Proxy Server will always listen on the secure HTTP (HTTPS) port number
443. If a secure connection is established on this port, the NL240 will attempt
to communicate to the datalogger on the HTTP port 80. (range 1..65535)
TLS Proxy Forward Physical Port
When doing TLS Proxy communications, the NL240 TLS server maintains a
secure connection with a remote client. If the TLS Proxy Forward Physical
Port is specified to be the CS I/O port the NL240 will then open a TCP
connection with the logger over the CS I/O port and do unecrypted data
transfer with the datalogger. If the TLS Proxy Forward Physical Port is
specified to be Wi-Fi, the NL240 will open the TCP connection over Wi-Fi on
the TLS Proxy Forward IP Address.
TLS Proxy Forward IP Address
Secure communications received on the NL240 TLS Server will be forwarded
on a non-secure TCP connection to this IP address. If the TLS Proxy Forward
Physical Port is specified to be the CS I/O port, this setting is not set by the user
since the NL240 will obtain the IP address of the datalogger automatically. If
the TLS Proxy Forward Physical Port is specified to be Wi-Fi, the forward IP
address must be specified. Enter the IP address of the destination datalogger
here.
TLS Proxy Forward Port Number
When doing TLS Proxy communications, the NL240 TLS server maintains a
secure connection with a remote client. If the TLS Proxy Forward Physical
Port is specified to be the CS I/O port, the NL240 will then open a TCP
connection with the datalogger over the CS I/O port and do unecrypted data
transfer with the datalogger. If the TLS Proxy Forward Physical Port is
specified to be Wi-Fi, the NL240 will open the TCP connection over Wi-Fi on
the TLS Proxy Forward IP Address.
In order to communicate with the connected datalogger’s TCP server, the
NL240’s TCP client application must open a socket to that server. The socket
C-15
Page 66

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
C.7 TLS Tab
of the datalogger’s TCP server is uniquely identified by an IP address and a
port number. This entry is where the port number of the NL240’s TCP client is
set. The datalogger’s TCP server port must be set to communicate on this port
number.
If secure communications come in on the TLS Proxy Server Port Number, the
NL240 will attempt to open a TCP connection to the datalogger on the TLS
Proxy Forward Port Number. Also, regardless of this setting, the NL240 TLS
Proxy Server will always listen on the secure HTTP (HTTPS) port number
443. If a secure connection is established on this port, the NL240 will attempt
to communicate to the datalogger on the HTTP port 80.
Leave this setting at its default unless the datalogger is expecting
communications on a different port. (range 1..65535)
TLS Proxy Timeout
This setting, in units of seconds, will determine how fast the proxy server/client
sessions will time out if no activity is detected. Set to 0 for no time-out (not
recommended). (range 0..999)
TLS Status (read only)
Specifies the current status of the TLS network stack.
If the status of the TLS stack is “Initialized”, the device will
automatically negotiate a secure TLS connection with DevConfig
if the Use TCP option is selected. The TLS Private Key, Private
Key Password, and TLS Certificate can only be edited/transmitted
over a secure DevConfig link (USB or TLS). These settings
cannot be edited over a standard TCP DevConfig link.
TLS Private Key Password
Specifies the password that is used to decrypt the TLS Private Key.
This setting can only be edited/transmitted if the DevConfig link
is considered secure (USB or TLS). If the TLS stack has been
initialized, the device will automatically negotiate a secure TLS
connection with DevConfig if the Use TCP option is selected.
TLS Private Key
Specifies the private key (in PEM format) for the encryption stack.
C-16
This setting can only be edited/transmitted if the DevConfig link
is considered secure (USB or TLS). If the TLS stack has been
initialized, the device will automatically negotiate a secure TLS
connection with DevConfig if the Use TCP option is selected.
Page 67

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
NOTE
TLS Certificate
Specifies the public certificate (in PEM format) for the encryption stack.
This setting can only be edited/transmitted if the DevConfig link
is considered secure (USB or TLS). If the TLS stack has been
initialized, the device will automatically negotiate a secure TLS
connection with DevConfig if the Use TCP option is selected.
C-17
Page 68

Appendix C. NL240 Settings
C-18
Page 69

Appendix D. Sending a New OS to the NL240
Whenever a new operating system is released for the NL240, it will be
available from our website, www.campbellsci.com/downloads.
D.1 Sending an OS via USB
Follow these steps to send the new OS to the NL240 via USB:
1. Plug the wall charger into an AC outlet and the barrel connector into the
NL240’s power jack.
2. Connect a USB cable between one of your computer’s USB ports and the
USB port on the NL240.
3. Open DevConfig.
4. Select the NL240 under Device Type.
5. Select the appropriate Communication Port.
6. Go to the Send OS tab.
7. Press the Start button.
8. In the resulting dialog box, select the file that should be sent to the device
as an operating system (this file should have an .obj extension) and press
the OK button.
9. The operating system will be sent to the NL240.
10. After the file has been sent, the power LED on the NL240 will blink
repeatedly while the NL240 copies the OS into its internal flash. This
process takes about 10 seconds. While the LED is blinking, the NL240 is
in a vulnerable state where a removal of power will leave the NL240
without a valid operating system to run. DO NOT remove power until the
LED stops blinking.
D.2 Sending an OS via Wi-Fi
Follow these steps to send the new OS to the NL240 via Wi-Fi:
1. Using the supplied serial cable, connect the NL240 CS I/O port to the
datalogger CS I/O port. Alternatively, power the NL240 through the
barrel-connector jack located on the edge of the device.
2. The NL240 will power up and join the strongest, open Wi-Fi network it
finds or the Wi-Fi network it has already been configured to join. The
green LED on the NL240 will come on and start blinking once it has
joined the network. Once it has successfully obtained an IP address, it will
stop blinking and flicker with network activity.
D-1
Page 70

Appendix D. Sending a New OS to the NL240
3. Open DevConfig.
4. Select the NL240 under Device Type.
5. Ensure that the Use IP Connection box is checked on the left hand panel.
6. If the Admin Password of the device has been set, you will need to enter
that password in the TCP Password control on the left panel in order for
the connection to succeed.
7. Enter the IP address or domain name address of the device in the
Communication Port control on the left panel. If you do not know the
address of the device and the device is connected to your local area
network, you may be able to use the … button to the right of
Communication Port to discover the list of devices on the network.
Whatever address is entered, it must end with :6786 in order to connect the
device configuration service.
8. Go to the Send OS tab.
9. Press the Start button.
10. In the resulting dialog box, select the file that should be sent to the device
as an operating system (this file should have an .obj extension) and press
the OK button.
11. The operating system will be sent to the NL240.
12. After the file has been sent, the power LED on the NL240 will blink
repeatedly while the NL240 copies the OS into its internal flash. This
process takes about 10 seconds. While the LED is blinking, the NL240 is
in a vulnerable state where a removal of power will leave the NL240
without a valid operating system to run. DO NOT remove power until the
LED stops blinking
D-2
Page 71

NOTE
Appendix E. Radio Frequency Emission
Changes or modifications to the NL240 not expressly approved by Campbell
Scientific, Inc. could void the user’s authority to operate this product.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2) This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
The embedded radio transmitter approval:
FCC Identifier: XF6-RS9110N1102
Industry Canada: 8407A-91101102
Europe ETSI EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1:2002
Europe ETSI EN 300 328 V1.7.1:2006
Highest SAR value reported is: Body; 0.706 Watts/kg
E-1
Page 72

Appendix E. Radio Frequency Emission
E-2
Page 73

Page 74

Campbell Scientific Companies
Campbell Scientific, Inc. (CSI)
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321
UNITED STATES
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com
Campbell Scientific Africa Pty. Ltd. (CSAf)
PO Box 2450
Somerset West 7129
SOUTH AFRICA
www.csafrica.co.za • cleroux@csafrica.co.za
Campbell Scientific Australia Pty. Ltd. (CSA)
PO Box 8108
Garbutt Post Shop QLD 4814
AUSTRALIA
www.campbellsci.com.au • info@campbellsci.com.au
Campbell Scientific (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
8B16, Floor 8 Tower B, Hanwei Plaza
7 Guanghua Road
Chaoyang, Beijing 100004
P.R. CHINA
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com.cn
Campbell Scientific do Brasil Ltda. (CSB)
Rua Apinagés, nbr. 2018 ─ Perdizes
CEP: 01258-00 ─ São Paulo ─ SP
BRASIL
www.campbellsci.com.br • vendas@campbellsci.com.br
Campbell Scientific Canada Corp. (CSC)
14532 – 131 Avenue NW
Edmonton AB T5L 4X4
CANADA
www.campbellsci.ca • dataloggers@campbellsci.ca
Please visit www.campbellsci.com to obtain contact information for your local US or international representative.
Campbell Scientific Centro Caribe S.A. (CSCC)
300 N Cementerio, Edificio Breller
Santo Domingo, Heredia 40305
COSTA RICA
www.campbellsci.cc • info@campbellsci.cc
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL)
Campbell Park
80 Hathern Road
Shepshed, Loughborough LE12 9GX
UNITED KINGDOM
www.campbellsci.co.uk • sales@campbellsci.co.uk
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL France)
3 Avenue de la Division Leclerc
92160 ANTONY
FRANCE
www.campbellsci.fr • info@campbellsci.fr
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL Germany)
Fahrenheitstraße 13
28359 Bremen
GERMANY
www.campbellsci.de • info@campbellsci.de
Campbell Scientific Spain, S. L. (CSL Spain)
Avda. Pompeu Fabra 7-9, local 1
08024 Barcelona
SPAIN
www.campbellsci.es • info@campbellsci.es
 Loading...
Loading...