Page 1

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
Revision: 12/10
POWER
G 12V
RS485
Logan, Utah
CS I/O
CS I/O
NL100
RS232
RS232
SN:
MADE IN USA
LAN
LINK
10 BASE T
LAN
LINK
10 BASE T
NETWORK LINK INTERFACE
RS485
Copyright © 2000-2010
Campbell Scientific, Inc.
Page 2

Warranty and Assistance
The NL100/105 NETWORK LINK INTERFACE is warranted by Campbell
Scientific, Inc. to be free from defects in materials and workmanship under
normal use and service for twelve (12) months from date of shipment unless
specified otherwise. Batteries have no warranty. Campbell Scientific, Inc.'s
obligation under this warranty is limited to repairing or replacing (at Campbell
Scientific, Inc.'s option) defective products. The customer shall assume all
costs of removing, reinstalling, and shipping defective products to Campbell
Scientific, Inc. Campbell Scientific, Inc. will return such products by surface
carrier prepaid. This warranty shall not apply to any Campbell Scientific, Inc.
products which have been subjected to modification, misuse, neglect, accidents
of nature, or shipping damage. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties,
expressed or implied, including warranties of merchantability or fitness for a
particular purpose. Campbell Scientific, Inc. is not liable for special, indirect,
incidental, or consequential damages.
Products may not be returned without prior authorization. The following
contact information is for US and International customers residing in countries
served by Campbell Scientific, Inc. directly. Affiliate companies handle
repairs for customers within their territories. Please visit
www.campbellsci.com to determine which Campbell Scientific company
serves your country.
To obtain a Returned Materials Authorization (RMA), contact Campbell
Scientific, Inc., phone (435) 753-2342. After an applications engineer
determines the nature of the problem, an RMA number will be issued. Please
write this number clearly on the outside of the shipping container. Campbell
Scientific's shipping address is:
CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC, INC.
RMA#_____
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321-1784
For all returns, the customer must fill out a “Declaration of Hazardous Material
and Decontamination” form and comply with the requirements specified in it.
The form is available from our website at
completed form must be either emailed to repair@campbellsci.com
435-750-9579. Campbell Scientific will not process any returns until we
receive this form. If the form is not received within three days of product
receipt or is incomplete, the product will be returned to the customer at the
customer’s expense. Campbell Scientific reserves the right to refuse service on
products that were exposed to contaminants that may cause health or safety
concerns for our employees.
www.campbellsci.com/repair
. A
or faxed to
Page 3

NL100/105 Table of Contents
PDF viewers note: These page numbers refer to the printed version of this document. Use
the Adobe Acrobat® bookmarks tab for links to specific sections.
1. Introduction..................................................................1
1.1 Physical Description of the NL100/105 ...................................................1
1.2 Specifications............................................................................................2
2. Preparing to Set Up the NL100/105 ............................3
2.1 Computer to NL100/105 Physical Connection.........................................4
2.2 Communication with the NL100/105 .......................................................4
2.2.1 Setup Using the Device Configurator .............................................4
2.2.2 Setup Using a Terminal Program....................................................5
2.2.3 Establishing Communication Outside of ConfMon Mode..............5
2.3 Port Configuration ....................................................................................7
2.3.1 TCPSer............................................................................................7
2.3.2 PakBus ............................................................................................7
2.3.3 PakBusSer.......................................................................................7
2.4 NL100/105 Menu Options........................................................................7
2.4.1 Ver ..................................................................................................8
2.4.2 Show ...............................................................................................8
2.4.3 Edit..................................................................................................8
2.4.3.1 TLink Config.........................................................................8
2.4.3.2 RS485 Config........................................................................9
2.4.3.3 CS I/O Config .....................................................................10
2.4.3.4 RS-232 Config ....................................................................12
2.4.3.5 Ethernet 10 Base-T..............................................................14
2.4.3.6 PakBus Address of the NL100/105.....................................15
2.4.3.7 PakBus/Tcp Server Config..................................................15
2.4.3.8 PakBus/Tcp Client Config...................................................16
2.4.3.9 MODBUS/TCP Gateway Config ........................................16
2.4.3.10 Telnet IP Port Number ......................................................16
2.4.3.11 DevConfig Security Code .................................................16
2.4.4 Defaults.........................................................................................17
2.4.5 Reset..............................................................................................18
2.4.6 Help...............................................................................................18
2.4.7 Bye ................................................................................................18
2.4.8 Other Commands ..........................................................................18
2.4.9 Serial Server Watchdog ................................................................19
3. Connecting the NL100/105 to a Network .................19
3.1 Network to NL100 Connection ..............................................................19
3.2 Typical Configurations ...........................................................................19
3.2.1 Direct Connect from the NL100/105 to a Datalogger...................20
3.2.2 MD9 Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger........................21
3.2.3 MD485 Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger....................22
3.2.4 RF Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger ...........................22
3.2.5 Short Haul Modem Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger .23
i
Page 4

NL100/105 Table of Contents
Appendices
A. CS I/O Port ............................................................... A-1
B. Null-Modem Cable ................................................... B-1
C. 10 Base-T Cabling ................................................... C-1
Glossary
Figures
3.2.6 Phone Modem Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger........ 23
3.3 NL100/105 to Datalogger Connections - CR9000/CR5000 .................. 24
3.3.1 Software Setup ............................................................................. 24
3.3.2 Hardware Setup for NL105 Communication with the CR9000 via
TLink ...................................................................................... 25
1. NL100 ........................................................................................................ 2
2. NL100/105 Jumper Placement................................................................... 6
3. Typical NL100/105 Setups in LoggerNet................................................ 20
4. LoggerNet Setup for NL100/105 to MD9 to Datalogger Connection ..... 21
5. LoggerNet Setup for NL100/105 to RF to Datalogger Connection......... 23
6. LoggerNet Setup for NL100/105 to Phone to Datalogger Connection.... 24
7. PC9000 Setup for TCP/IP Communication ............................................. 25
ii
Page 5

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
1. Introduction
The NL100 and NL105 Network Link Interfaces are devices used to
communicate with Campbell Scientific dataloggers using an Ethernet 10 BaseT communications link. The NL100 includes a CS I/O port (see Appendix A)
an RS-232 port, and an RS-485 port for communication; the NL105 adds a
TLink interface for communication with a CR9000(C) system.
The NL100/105 can be configured to act as a Serial Server in a standard
TCP/IP network, to act as a PakBus node in a PakBus network, or to transfer
MODBUS/TCP packets. All of the available settings are described in Section
2.4. However, not all settings are required for all configurations. This manual
will focus mainly on setting up the NL100/105 for a standard TCP/IP network.
For PakBus and MODBUS configurations, please contact Campbell Scientific
for applications notes or other information that may be available.
Campbell Scientific's LoggerNet software is used to communicate with the
dataloggers once the NL100/105 is configured properly and connected to a
network (refer to Section 2.). Communication with CSI’s mixed-array
dataloggers (CR10X, CR510, CR23X, CR7, and 21X) and table-data
dataloggers (CR10X-TD, CR510-TD, CR23X-TD, CR5000, and CR9000)
requires LoggerNet version 2.0 or greater. Communication with CR10XTDPB, CR510TD-PB, CR23XTD-PB, and CR200 dataloggers requires
LoggerNet 2.1 or greater. Communication with the CR1000 requires
LoggerNet 3.0 or greater. Communications with the CR3000 require
LoggerNet 3.2 or greater and with the CR800 and CR850 require LoggerNet
3.3 or greater. PC208W version 3.2 or higher may also be used with mixed
array dataloggers (CR10X, CR510, CR23X, CR7, 21X). PC9000 may also be
used for CR9000 and CR5000 dataloggers.
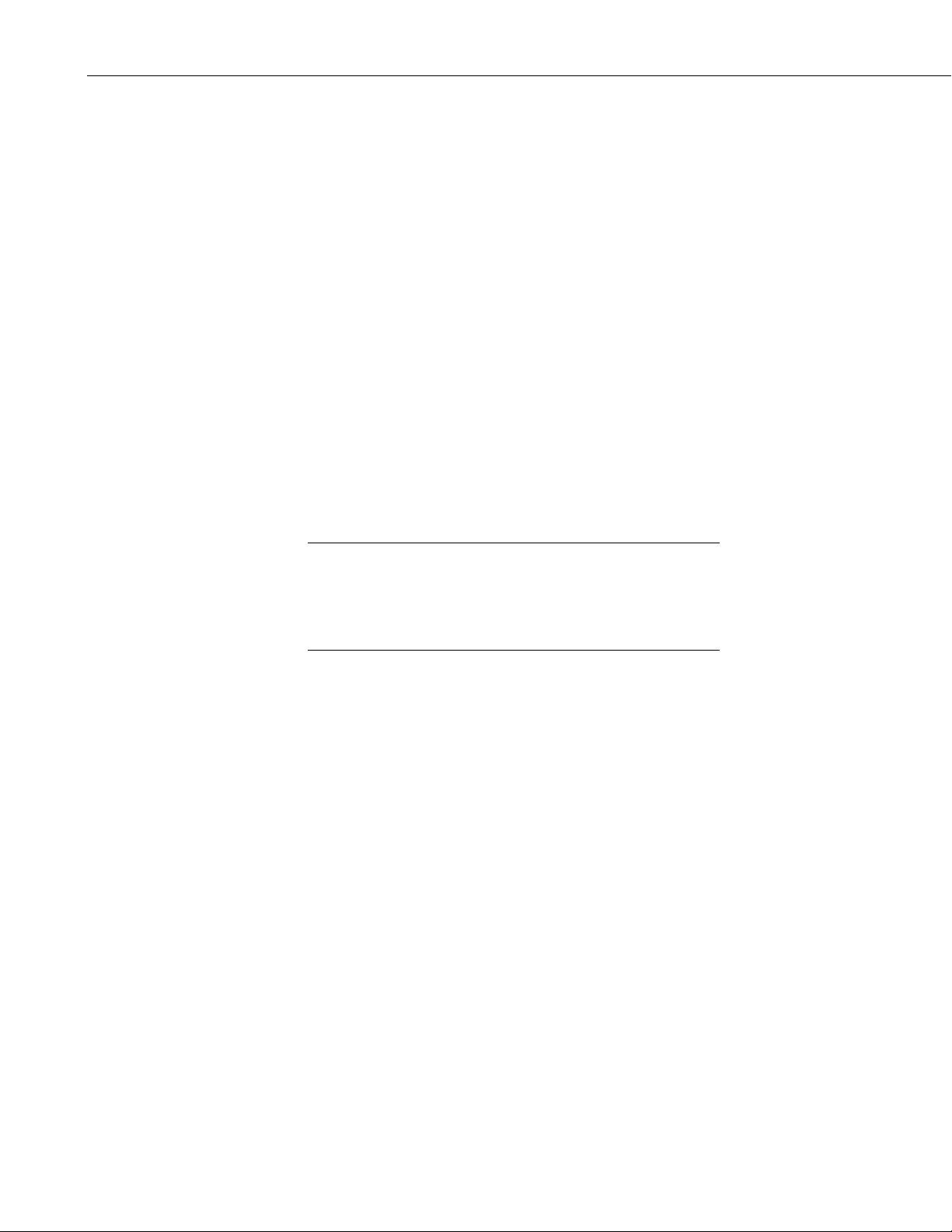
1.1 Physical Description of the NL100/105
The NL100/105 is housed in a rectangular case with all power and
communication connections on one edge. On the opposite outside edge are tabs
for mounting the NL100/105 in an enclosure. Figure 1 below shows the
position of these connections and the mounting tabs.
1
Page 6

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
t
t
Logan, Utah
Corner Screws
Mounting Tabs
12 V Power
Connection
POWER
G 12V
RS485
RS485
RS-485 Ports
CS I/O Por
1.2 Specifications
RS-485 and CS I/O Port Communication Rate
Up to 38.4 kbps
NETWORK LINK INTERFACE
NL100
CS I/O
RS232
CS I/O
RS232
RS-232
DTE Por
Communication
Indicator LEDs
FIGURE 1. NL100
LAN
LAN
LINK
MADE IN USA
LINK
10 BASE T
10 B
ASE T
SN:
10 Base-T Link
RS-232 DTE Port Communication Rate
Up to 115.2 kbps
Weight
13.3 oz (377 g)
Standards
Ethernet Standard IEEE 802.3 (CSMA/CD Access Method)
TCP/IP Protocol
Case Dimensions
9 ¼” x 4 ¼” x 1” (23.5 x 10.8 x 2.54 cm)
Temperature
-25 to +50°C
2
Page 7

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
Power Supply Requirements
The NL100/105 is powered via the green G 12V connector (11 to 16
VDC at 140 mA average current) on the front panel of the unit.
Cable Specifications
The Ethernet 10 Base-T cable should be a Category 5 twisted pair cable.
Campbell Scientific recommends the 13658. The two active pairs in an
Ethernet 10 Base-T network are pins 1 & 2 and pins 3 & 6. Use only
dedicated wire pairs (such as blue/white & white/blue, orange/white &
white/orange) for the active pairs.
RJ-45 Pin-Outs: Pin 1 = TD+, Pin 2 = TD-, Pin 3 = RD+, Pin 6 = RD-
A DB9 female to DB9 male cable such as the 10873 is used to connect
the NL100’s RS-232 port to the datalogger’s RS-232 port. A DB9 female
null modem cable such as the 13657 is used to connect the NL100’s RS232 port to a PC’s RS-232 port. The RS-232 cable should be kept at
lengths of ≤ 6 feet to maintain high data throughput rates.
The CS I/O 9 Pin cable is a straight through cable with all 9 pins
connected. Campbell Scientific’s SC12 cable is recommended.
The cable for the RS-485 connection is a 2 twisted pair, 22 awg cable.
CSI recommends the CABLE3CBL-L for use with the MD485s.
Compliance
The NL100/105 is encased in metal and meets requirements for a Class A
device under European standards:
APPLICATION OF COUNCIL DIRECTIVE(S)
89/336/EEC as amended by 89/336/EEC and 93/68/EEC.
STANDARD(S) TO WHICH CONFORMITY IS DECLARED:
ENC55022-1; 1995 AND ENC 50082-1: 1992
EUROPEAN REGULATIONS
WARNING: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment
this product may cause radio interference in which case the user may
be required to correct the interference at the user’s expense.
2. Preparing to Set Up the NL100/105
The NL100/105 must be set up by configuring one or more of the
communications ports for communication with your datalogger or other
devices in the network. To do this, you must establish a direct communication
link with the NL100/105 using a PC computer. You will need a null modem
cable to physically connect the NL100/105 to the computer. The Device
Configurator or a terminal communication software package (such as
HyperTerminal, which ships with Microsoft Windows operating system
software) is used to configure the settings in the NL100/105.
3
Page 8
NL100/105 Network Link Interface
2.1 Computer to NL100/105 Physical Connection
An RS-232 null-modem cable is required to establish communication between
the NL100/105 and your computer. One end of the cable is connected to the
computer's 9-pin RS-232 communications port and the other end is connected
to the RS-232 port of the NL100/105. If the null-modem cable does not have a
female connector on both ends, you may also need a female-to-female adapter.
For additional information on null-modem cables, refer to Appendix B.
The NL100/105 requires 12 VDC for operation. This power source can be
supplied by the datalogger's 12 V supply or by a regulated external power
source. When connecting the power leads, the ground lead should be
connected first and then the 12 V lead.
2.2 Communication with the NL100/105
2.2.1 Setup Using the Device Configurator
Campbell Scientific's datalogger support software ships with a utility called the
Device Configurator (or DevConfig). This tool is used to set up dataloggers
and other devices for communication or to download a new operating system.
DevConfig can also be downloaded from Campbell Scientific's web site.
NOTE
The NL100/105 must have at least operating system version 7 to
be compatible with DevConfig's NL100 setup. If your
NL100/105 does not have a compatible operating system, load a
new one in using DevConfig's Send OS utility or u se a terminal
emulation program to set up the device.
To use DevConfig to set up the NL100/105, first connect the NL100/105 to the
computer as noted above and follow the steps below:
1. Remove power from the NL100/105.
2. Open DevConfig.
3. Highlight the NL100 in the list of devices which appears in the left-hand
portion of the window. Select the COM port to which the NL100/105 is
connected from the drop down list box at the bottom left of the window.
4. Press the Connect button and reapply power to the NL100/105. The device
may take up to 60 seconds to respond to DevConfig, and for the current
settings to be loaded into the Settings Editor.
The Settings Editor is the active tab when you are first connected. Settings can
be changed in this window by clicking within a field and entering a new value.
If the value being set has a finite list of choices, a second click within the field
will enable a drop down list box from which to select a valid option.
4
DevConfig has built-in help for each setting, which is displayed at the bottom
of the window. Use this information, along with Section 2.4 of this manual, to
configure the settings for communication in your network. Once the settings
have been defined, press Apply to save the changes to the NL100/105.
Page 9

You can also use the Terminal tab in DevConfig to set up the NL100/105 using
the menus, as explained in the following section.
2.2.2 Setup Using a Terminal Program
Once the physical connection has been made, communication can be
established with the NL100/105 using a terminal communications package.
The steps below demonstrate configuring the NL100/105 using
HyperTerminal, which is shipped with Windows operating systems.
NL100/105 Network Link Interface
NOTE
The NL100/105 is shipped from the factory with its RS-232 port
set in the ConfMon mode (configuration monitor). Refer to
Section 2.2.3 if the RS-232 port has been set to some other
configuration and direct communication is necessary.
Ensure the NL100/105 has an appropriate power source applied. (Refer to
Section 2.1, above.)
Create a new connection in HyperTerminal. Choose the COM port to which
the null-modem cable is connected, and set the baud rate to 115,200 bps. Most
of the other settings can be left at the default (data bits = 8, parity = none, stop
bits = 1). Flow control should be set to none.
Once HyperTerminal indicates you are connected, press <Enter> a couple of
times to gain the attention of the NL100/105. When communication is
established, the current port settings will be returned, followed by the
NL100/105 prompt line:
NL100/105 (ver, show, edit, defaults, reset, help, bye):
To set up the NL100/105 for communication with the network, go into the Edit
menu (Section 2.4.3 Edit) and complete the appropriate information. Note that
the Ethernet 10 Base-T connection must be configured (Section 2.4.3.5) and at
least one of the other port options.
2.2.3 Establishing Communication Outside of ConfMon Mode
If the RS-232 port has been disabled or set to some configuration other than
ConfMon, communication can still be established with the NL100/105 using
one of two options.
When power is first applied to the NL100/NL105, there is a 0.5-second
window in which communication can be established with the NL100 using the
RS232 port, regardless of the port's configuration. Therefore, if power is
already applied, simply disconnect power and then reconnect it, then attempt to
establish communication within the 0.5-second period. Holding down the
enter key should allow you to hit this 0.5-second window.
The other option is to connect a boot jumper, which bypasses the boot
sequence of the NL100/105. To access the boot jumper, remove the
NL100/105's cover by removing the four screws at the corners.
5
Page 10
NL100/105 Network Link Interface
The boot jumper is shown in Figure 2 below. The NL100/105 ships with this
jumper connected to only one post. Place the jumper so that it connects the two
posts.
Jumper
WARNING
FIGURE 2. NL100/105 Jumper Placement
When the jumper is in place, open the HyperTerminal connection to the
NL100/105 and power up the device. The prompt "NL100 boot" will appear.
At this prompt, press <Enter> a few times to ring up the NL100/105. If
communication is successfully established, a message will be returned
indicating that the NL100/105 is initialized, along with the jumper setting (1 =
on, 0 = off), the TCP/IP address, Telnet port address, and current
communication configuration. If <Enter> is pressed again, the NL100/105
menu prompt will appear.
After reconfiguring the NL100/105 for communication,
the jumper should be disconnected. If this jumper
remains in place and power to the NL100/105 is cycled
off and back on, the NL100/105 will remain at the
"NL100 boot" prompt and will not boot up. This will
render the NL100/105 inaccessible via remote
communications.
6
Page 11

2.3 Port Configuration
An important step in configuring an NL100/105 for use is setting up the
communication port(s) that you will be using. Regardless of whether you are
connecting the datalogger (or a communication peripheral) to the RS485 port,
the CS I/O port, or the RS232 port, you must set up the port to support the
mode of communication that will be used for that portion of your network.
The three options supported are explained briefly, below.
2.3.1 TCPSer
When the port is set to TCPSer, it will act as a TCP serial server. Any packet
that is transmitted via the port will be sent using the TCP/IP protocol. This is
the simplest way to set up a port and will work in many scenarios, regardless
of whether the datalogger has a mixed-array or PakBus operating system.
One disadvantage of using this mode when communicating with PakBus
dataloggers is that no PakBus routing can occur via the port. It may also be less
efficient in some instances when communicating with PakBus dataloggers.
2.3.2 PakBus
NL100/105 Network Link Interface
2.3.3 PakBusSer
PakBus is a packet-based communications protocol developed by CSI. It is
used in the CR1000, CR800/850, CR3000, and CR200 dataloggers, as well as
CR10X, CR510, and CR23X dataloggers with a special operating system. One
of the advantages of PakBus communication is that PakBus devices in the
network can communicate directly with and route packets between other
PakBus devices in the network. In addition to the native PakBus packets, other
packet types, such as TCP/IP or ModBus, can be “wrapped” in a PakBus
packet and transferred among the PakBus devices in the network, thus
allowing for various communication protocols within one network.
By configuring a port for PakBus communication, the NL100/105 is set up as a
PakBus router in the network. The NL100/105 can then route packets to other
devices in the network that it has “learned” about through beaconing or
PakBus neighbor filters. When a port is configured for PakBus, the
NL100/105’s PakBus/TCP Server Config option must be enabled or
communication will not take place via TCP/IP with the PakBus devices on that
port.
This option is used only in a PakBus network. In this mode when a packet is
routed out the port, the PakBus framing is removed from the packet. Typically,
the attached device would be one that does not support PakBus communication
(such as a ModBus device).
2.4 NL100/105 Menu Options
The following discusses the menu options and settings that you will see when
connected to the NL100/105 using a terminal emulation package. DevConfig
provides these same options in a graphical user interface.
7
Page 12

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
The NL100/105 prompt lists all of the available menu options. Only the first
few characters of the main menu options need to be typed – the remaining
characters will be completed automatically. Press <Enter> to execute the
command. Each menu option is explained below.
2.4.1 Ver
Ver returns version information about the NL100/105. The ROM number, OS
version, Ethernet physical address, and some diagnostic statistics are
displayed. Version information may be requested by a Campbell Scientific
Applications Engineer when troubleshooting a communication problem.
NOTE
2.4.2 Show
2.4.3 Edit
The Ethernet physical address that is displayed is a hexadecimal
representation of the address assigned to this device. An Ethernet
address is unique to the specific device to which it is assigned.
This assignment is made at the factory and cannot be changed by
the user. The Ethernet physical address is not the same as the
TCP/IP address.
The Show command displays the current settings for the NL100/105.
The Edit menu option is used to set up the communications link for the
NL100/105. You should work closely with your network administrator to
determine the correct settings for your specific network.
You can progress through the menu options by pressing <Enter>. If you make
a mistake after entering a setting, press the up cursor arrow on your keyboard
to return to the previous setting. All available selections will be listed on the
prompt line enclosed in parentheses, with the current setting displayed in
brackets at the end of the selections (e.g., [disabled]). Help for a setting can be
displayed by entering the ? key and pressing <enter>, or by pressing F1.
8
Once changes have been made and you have come to the end of the prompts
for the communication options, you can choose "save" to put the new settings
into effect or "cancel" to disregard the changes and keep the current settings.
Prior to configuring one or more of the ports for communication (TLink
Config, RS485 Config, CS I/O Config, or RS232 Config) refer to the
discussion on Port Configuration above.
2.4.3.1 TLink Config
This setting is applicable to the NL105 only, and is used when communicating
with a CR9000 datalogger. TLink is an interface used to communicate with a
CR9000 datalogger over an Ethernet connection. A physical connection is
made between the TLink port on the CR9000's 9031 CPU module and the port
marked TLink on the NL105. TLink Config is used to set the TLink
communications port to one of three options:
Page 13

2.4.3.2 RS485 Config
NL100/105 Network Link Interface
TcpSer - The NL105 acts as a serial server for the TLink port. A serial server
is a device that allows serial communication over a TCP/IP communications
link. When configured as a serial server, there is one parameter to set:
TLink Serial Server Port Number - Enter the port number, in the range of
3000 to 65000, that will be used for TLink communication. The default
port number is 6781.
232-Bridge - The NL105 transparently passes data between the TLink port and
its RS-232 ports. The 232-Bridge configuration has only one setting, RS-232
bps. This is the bits per second (bps) at which the NL105 will communicate
with the device connected to the RS-232 port. This is a fixed rate (i.e., it is not
a maximum baud rate or an autobaud rate). The default is 115k bps.
Disabled - The TLink communications port is disabled.
This option is used to configure the NL100's RS485 port for communication
with an RS485 device. Campbell Scientific offers the MD485 for
communication with its dataloggers via RS485. The port can be configured for
PakBus communication, as a TcpSer serial server, or as a PakSer serial server.
PakBus - This option is used to set up the NL100/105 to communicate with
PakBus devices over the RS485 port. Packets transferred over the port in this
mode are framed as PakBus packets; therefore, any device attached to the port
must be configured for PakBus communication also. When a port is configured
for PakBus, the NL100/105’s “PakBus/Tcp Server Config” option must be
enabled (Section 2.4.3.7) or you will no t be able to communicate with TCP/IP
through the NL100/105 to the PakBus devices on that port.
When configured for PakBus the NL100/105's RS485 port has the following
settings:
RS485 Bps - This option is used to set the bits per second (bps) at
which the NL100/105 will communicate using the RF485 port. The
default value is 38K.
RS485 Beacon Interval - The NL100/105 can be set to transmit a
beacon to a PakBus network via the selected port. The beacon allows
the NL100/105 to determine which devices in the PakBus network it
can communicate with. Note that because a beacon is broadcast to all
devices, it can interfere with other communication in the network
(such as RF), so a frequent beacon may not be desirable. If 0 is
entered, no beacon will be sent; the default beacon is 60 seconds.
RS485 Verify Interval - This is the interval at which a PakBus
communication link will be verified over the RS485 port. If
communication does not take place with a PakBus device within the
verify internal, a packet will be sent to test the communication link.
In most instances, this setting should be left at the default of 0, which
will set a verify interval of 2.5 times the Beacon Interval.
9
Page 14

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
TCPSer - This option configures the NL100 to act as a TCP/IP based serial
server when communicating with the datalogger over its RS485 port.
If both the beacon interval and verify interval are set to 0, a verify
interval of 5 minutes will be used.
RS485 Neighbor list - Enter a list of addresses for PakBus devices
with which the NL100/105 can communicate over the RS485 port.
The addresses are specified individually, with a space separating each
address, or a range of addresses can be entered by separating them
with a hyphen (e.g., 1 3 6 10-15, sets PakBus addresses 1, 3, 6, 10,
11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 as neighbors). If a Neighbor list is entered, the
NL100/105 will ignore packets from any device which is not in the
list (unless the address of the device sending the packet is 4000 or
greater). If 0 is entered for this parameter, the NL100/105 will
respond to any device that sends a packet and will automatically add
that device to its neighbor list.
RS485 Bps - This is the bits per second (bps) at which the
NL100/105 will communicate using the RS485 port. This is a fixed
rate (i.e., it is not a maximum baud rate or an autobaud rate). The
default rate is 38K bps.
NOTE
2.4.3.3 CS I/O Config
RS485 Serial server port number - Enter the port number, in the
range of 1 to 65000, that will be used for communication. The default
port number is 6782.
PakSer - The RS485 port of the NL100/105 is configured as a PakBus serial
server.
RS485 Bps - This is the bits per second (bps) at which the
NL100/105 will communicate using the RS485 port. This is a fixed
rate (i.e., it is not a maximum baud rate or an autobaud rate). The
default rate is 38K bps.
RS485 serial server AppId Number - Enter the application ID, in the
range of 1 to 65000, that will be used identify the device in the
network. The default ID is 6782.
The usual AppId for MODBUS devices is 502.
This option is used to configure the NL100/105's CS I/O port. The port can be
configured for PakBus communication, as a TcpSer serial server, or as a
PakSer serial server.
10
Page 15

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
NOTE
CR10X, CR510, CR23X, 21X, and CR7 dataloggers ship with a
mixed array operating system. Mixed array dataloggers do not
support the PakBus communications protocol. Therefore, you
cannot communicate with them over a port configured for
PakBus. However, the CR10X, CR510, and CR23X dataloggers
can be special-ordered with a PakBus operating system. Check
with your technical support representative for details.
PakBus - This option is only used when setting up the NL100/105 to
communicate with other PakBus devices in the network. Packets transferred
over the CS I/O port in this mode are framed as PakBus packets; therefore, any
device attached to the port must be capable of PakBus communication. When a
port is configured for PakBus, the NL100/105’s “PakBus/Tcp Server Config”
option must be enabled (Section 2.4.3.7) or you will not be able to
communicate with TCP/IP through the NL100/105 to the PakBus devices on
that port.
When configured for PakBus, the NL100/105's CS I/O port has the following
settings:
CS I/O SdcAddr/bps - This option is used to set up the CS I/O port to
communicate with the datalogger as an addressable SDC device or a
modem enabled device. If SDC7 or SDC8 is chosen, the NL100/105 will
use that address to communicate with the datalogger in a synchronous
communication mode. If one of the baud rates is chosen, the NL100/105
will communicate with the datalogger as a modem enabled device using
the selected baud rate. If another SDC device is connected to the
NL100/105, the two devices must use different SDC addresses.
NOTE
CS I/O Beacon Interval - The NL100/105 can be set to transmit a beacon
to a PakBus network via the selected port. The beacon allows the
NL100/105 to determine which devices in the PakBus network it can
communicate with. Note that because a beacon is broadcast to all devices,
it can interfere with other communication in the network (such as RF), so
a frequent beacon may not be desirable. If 0 is entered, no beacon will be
sent; the default beacon is 60 seconds.
CS I/O Verify Interval - This is the interval at which a PakBus
communication link will be verified over the CS I/O port. If
communication does not take place with a PakBus device within the
verify internal, a packet will be sent to test the communication link. In
most instances, this setting should be left at the default of 0, which will
set a verify interval of 2.5 times the Beacon Interval.
If both the beacon interval and verify interval are set to 0, a verify interval
of 5 minutes will be used.
A neighbor list is not specified because there is only one possible
neighbor.
TcpSer - This option configures the NL100 to act as a TCP/IP based serial
server when communicating with the datalogger over its CS I/O port.
11
Page 16

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
PakSer - The CS I/O port of the NL100/105 can be configured as a PakBus
serial server. This sets up the device as a serial server.
CS I/O SdcAddr/bps - This option is used to set up the CS I/O port to
communicate with the datalogger as an addressable SDC device or a
modem enabled device. If SDC7 or SDC8 is chosen, the NL100/105 will
use that address to communicate with the datalogger in a synchronous
communication mode. If one of the baud rates is chosen, the NL100/105
will communicate with the datalogger as a modem enabled device using
the selected baud rate. Note that mixed array dataloggers (CR10X,
CR510, CR23X, 21X, CR7) can be configured only as modem enabled
devices; e.g., they do not support communication using SDC7 or SDC8.
CS I/O serial server port number - Enter the port number, in the range of
1 to 65000, that will be used for communication. The default port number
is 6783.
CS I/O SdcAddr/bps - This option is used to set up the CS I/O port to
communicate with the datalogger as an addressable SDC device or a
modem enabled device. If SDC7 or SDC8 is chosen, the NL100/105 will
use that address to communicate with the datalogger in synchronous
communication mode. If one of the baud rates is chosen, the NL100/105
will communicate with the datalogger as a modem enabled device using
the selected baud rate.
NOTE
2.4.3.4 RS-232 Config
NOTE
CS I/O Serial Server AppId number - Enter the application ID, in the
range of 1 to 65000, that will be used to identify the device in the
network. The default ID is 6783.
The usual AppId for MODBUS devices is 502.
This option configures the NL100/105's RS-232 port for communication. The
port can be set up to communicate with a datalogger or other communications
device (short haul modem, RF modem, phone modem), or to be connected to
directly and configured for communication. The setup options for the port are
PakBus, TcpSer serial server, PakSer PakBus serial server, or ConfMon
(configuration monitor).
CR10X, CR510, CR23X, 21X, and CR7 dataloggers ship with a
mixed array operating system. Mixed array dataloggers do not
support the PakBus communications protocol. Therefore, you
cannot communicate with them over a port configured for
PakBus. However, the CR10X, CR510, and CR23X dataloggers
can be special-ordered with a PakBus operating system. Check
with your technical support representative for details.
12
PakBus - This option is only used when setting up the NL100/105 to
communicate with other PakBus devices in the network. Packets transferred
over the RS-232 port in this mode are framed as PakBus packets; therefore,
any device attached to the port must be capable of PakBus communication.
When a port is configured for PakBus, the NL100/105’s “PakBus/Tcp Server
Page 17

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
Config” option must be enabled (Section 2.4.3.7) or you will not be able to
communicate with TCP/IP through the NL100/105 to the PakBus devices on
that port.
When configured for PakBus, the NL100/105's RS-232 port has the following
settings:
RS-232 bps - This is the bits per second (bps) at which the NL100/105
will communicate using the RS-232 port. This is a fixed rate (i.e., it is not
a maximum baud rate or an autobaud rate). Note that the CR10XTD-PB
and the CR510TD-PB can communicate at a maximum baud rate of 9600
bps, so to communicate with one of those dataloggers, this setting must be
9600 bps or less. The default rate is 115K bps.
PakBus Beacon Interval - The NL100/105 can be set to transmit a beacon
to a PakBus network via the selected port. The beacon allows the
NL100/105 to determine which devices in the PakBus network it can
communicate with. Note that because a beacon is broadcast to all devices,
it can interfere with other communication in the network (such as RF), so
a frequent beacon may not be desirable. If 0 is entered, no beacon will be
sent; the default beacon is 60 seconds.
RS232 Verify Interval - This is the interval at which a PakBus
communication link will be verified over the RS232 port. If
communication does not take place with a PakBus device within the
verify internal, a packet will be sent to test the communication link. In
most instances, this setting should be left at the default of 0, which will
set a verify interval of 2.5 times the Beacon Interval.
If both the beacon interval and verify interval are set to 0, a verify interval
of 5 minutes will be used.
RS232 Neighbor list - Enter a list of addresses for PakBus devices with
which the NL100/105 can communicate over the RS232 port. The
addresses are specified individually, with a space separating each address,
or a range of addresses can be entered by separating them with a hyphen
(e.g., 1 3 6 10-15, sets PakBus addresses 1, 3, 6, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15
as neighbors). If a Neighbor list is entered, the NL100/105 will ignore
packets from any device which is not in the list (unless the address of the
device sending the packet is 4000 or greater). If 0 is entered for this
parameter, the NL100/105 will respond to any device that sends a packet
and will automatically add that device to its neighbor list.
TcpSer - This option configures the NL100 to act as a TCP/IP based serial
server when communicating with a datalogger over its RS-232 port.
RS-232 bps - This is the bits per second (bps) at which the NL100/105
will communicate using the RS-232 port. This is a fixed rate (i.e., it is not
a maximum baud rate or an autobaud rate). Note that the CR10(X),
CR510, and CR200 can communicate at a maximum baud rate of 9600
bps, so to communicate with one of those dataloggers, this setting must be
9600 bps or less. The default setting is 115K bps.
13
Page 18

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
PakSer - The RS-232 port of the NL100/105 can be configured as a PakBus
serial server.
RS-232 serial server port number - Enter the port number, in the range of
1 to 65000, that will be used for communication. The default port number
is 6784.
RS-232 bps - This is the bits per second (bps) at which the NL100/105
will communicate using the RS-232 port. This is a fixed rate (i.e., it is not
a maximum baud rate or an autobaud rate). Note that the CR10(X),
CR510, and CR200 can communicate at a maximum baud rate of 9600
bps, so to communicate with one of those dataloggers, this setting must be
9600 bps or less. The default setting is 115K bps.
RS-232 Serial Server AppId number - Enter the application ID, in the
range of 1 to 65000, that will be used to identify the device in the
network. The default ID is 6784.
NOTE
The usual AppId for MODBUS devices is 502.
ConfMon - Configuring the RS-232 port as a ConfMon allows you to connect
directly to the NL100/105 via a computer. There are no parameters; the baud
rate is automatically set to 115,200 bps. Refer to the previous information on
setting up the NL100/105 for communication.
2.4.3.5 Ethernet 10 Base-T
The 10 Base-T communications link is used to connect the NL100/105 to a
TCP/IP network using a Category 5 twisted pair cable. The Ethernet 10 Base-T
link must be configured or you will not be able to co mmunicate with the
NL100/105 over a TCP/IP connection. The following options must be
configured. These values should be provided by your network administrator.
10BASE-T Port IP Address - This number is the address of the
NL100/105 on a TCP/IP network. It is written as 32-bit number written in
four 8-bit decimal-equivalent syllables separated by periods, in the format
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX. The IP Address must be a static IP Address -- the
NL100/105 does not support DHCP (dynamic host configuration
protocol).
10BASE-T Port Network Mask - The network mask is used to help a
network router to more efficiently transfer information. Typically, a class
C mask will be 255.255.255.0, a class B mask will be 255.255.0.0, and a
Class A mask will be 255.0.0.0. The tighter the mask, the more the
NL100/105 will rely on the default gateway to route packets.
14
IP Address of the Default Gateway - Enter the IP address of the device
that is responsible for forwarding information to destinations outside the
internal network, defined by the network mask. To disable a default
gateway, use the default value of 0.0.0.0.
Page 19

2.4.3.6 PakBus Address of the NL100/105
If the NL100/105 is to be used as a router in a PakBus network, a PakBus
Address must be assigned. If the NL100/105 will not be used to route packets
in a PakBus network, this setting can be ignored. All devices in the network
must have a unique PakBus Address. Valid addresses are 1 through 4094. The
default ID is 678.
NL100/105 Network Link Interface
NOTE
By default LoggerNet software uses PakBus Address 4094,
PC400 uses 4093, PC200W uses 4092, and PConnect/
PConnectCE uses 4091. The use of these addresses in the
NL100/105 should be avoided.
PakBus addresses of greater than 3999 are typically reserved for
PakBus routing devices and ports. This is because when a
neighbor filter is set up in a PakBus datalogger, the datalogger
will answer a Hello message from any device with an ID greater
than 3999, but it will ignore devices with IDs less than 4000 that
are not in their neighbor list.
Clock Source Address - In a PakBus network, a "neighbor" is another
PakBus device that the NL100/105 can communicate with directly
(e.g., it does not have to route data through another PakBus device to
reach the neighbor). A neighbor can be designated for the NL100/105
as the device from which the NL100/105 will accept a clock set
command. If this setting is enabled, once the NL100/105 has received
a clock set from its designated neighbor, it will broadcast its clock
information along with its beacon. Thus, the NL100/105 can be used
to set the clock of other PakBus devices in the network. Set this
address to 0 to disable the function.
Central Routers - The Central Routers setting is used to set up the
NL100/105 either as a Central Router or a Branch Router. If 0 is used
for this setting, then the NL100/105 is set up as a Central Router;
otherwise, a list of Central Routers for the NL100/105 is entered and
the device is set up as a Branch Router. While a Central Router learns
the routes of all devices in the PakBus network, a Branch Router
learns the routes for devices only within its branch. The use of
Branch Routers allows branches of the network to be isolated from
other branches. When the NL100/105 is set up as a branch router, the
addresses for the Central Routers are specified individually with a
space separating each address. A range of addresses can be entered
by separating them with a hyphen (e.g., 1 3 6 10-15, sets PakBus
addresses 1, 3, 6, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 as Central Routers).
2.4.3.7 PakBus/Tcp Server Config
This option enables the NL100/105 to use an Ethernet connection to
communicate with other PakBus devices in the network. The NL100/105 can
support up to 16 concurrent connections. The NL100/105 will listen for
incoming TCP/IP packets on the socket designated by the PakBus/Tcp server
port number setting. If the NL100/105 will not be used in a PakBus network,
or if the PakBus communication among PakBus devices in the network will
15
Page 20

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
take place over a port other than the Ethernet connection, this setting can be
disabled. When enabled, there is one option to configure:
2.4.3.8 PakBus/Tcp Client Config
Enabling this option will set up the NL100/105 to act as a client in a PakBus
network. In this mode, the NL100/105 will actively maintain a TCP/IP
connection with a PakBus/Tcp server over the 10 Base-T connection.
This option is typically used when the NL100/105 is configured to
communicate with another NL100/105 over an Ethernet connection, so that the
two PakBus networks served by the NL100/105s can be merged. In most
situations, this setting can be disabled.
PakBus/TCP server port number - Enter the port number, in the range
of 1 to 65000, that will be used for communication. The default port
number is 6785.
Server IP Address - The Server IP address is the address of the server
to which the NL100/105 will attempt to connect and act as a client.
Server IP Port Number - The Server IP port number is used to specify
the port number of the PakBus/TCP server to which the client will
attempt to connect.
2.4.3.9 MODBUS/TCP Gateway Config
When this setting is enabled, the NL100/105 will translate MODBUS/TCP
packets that arrive on the 10 Base-T link for use in a PakBus network. The
translation provided by this mode is MODBUS/TCP message format to
MODBUS RTU serial message format. Unless you are setting up a PakBus
network to also handle MODBUS communication packets, this setting can be
disabled.
2.4.3.10 Telnet IP Port Number
This setting is used to specify the IP port number that will be used for Telnet
sessions with the NL100/105. The default value is 23.
Telnet Session Password - The Telnet Session Password is the string
that must be entered to communicate with the NL100/105 over a
Telnet session. The string can range from 1 to 20 alphanumeric
characters and is case-sensitive. This security measure is
implemented to help prevent unauthorized users from gaining access
to the NL100/105 device.
2.4.3.11 DevConfig Security Code
Campbell Scientific's Device Configurator (or DevConfig) is an application
that is used to configure dataloggers and peripheral devices for communication
and to download new operating systems. A security code can be set in the
NL100/105 so that communication using DevConfig is not possible unless the
security code is sent when the application tries to communicate with the
device. This security code helps to prevent unauthorized changes to a device.
16
Page 21

2.4.4 Defaults
NL100/105 Network Link Interface
By default the address is 0. To enable security, enter a value between 1 and
65535.
The Defaults option displays the factory default settings for the different
telecommunication options. Following the display is a prompt to Save or
Cancel. If Save is selected, the NL100/105 will be reset to the factory defaults.
If Cancel is chosen, the current settings will remain in effect and the user will
be returned to the main menu prompt. The default settings are as follows:
TLink config: [disabled]
RS485 config: [disabled]
CS I/O config: [Tcp Ser]
CS I/O SdcAddr/bps: [9600]
CS I/O serial server port number [6783]
RS-232 config: [ConfMon]
EtherNet 10BASE-T: [enabled]
10BASE-T port IP address: [192.168.111.222]
10BASE-T port network mask: [255.255.0.0]
IP address of the default gateway: [0.0.0.0]
PakBus Address of the NL100/105: [678]
Clock source address: [0]
Central Routers: [0]
PakBus/Tcp server config: [disabled]
PakBus/Tcp client config: [disabled]
MODBUS/TCP gateway config: [disabled]
Telnet IP port number: [23]
Telnet session password: [nl100]
DevConfig security code: [0]
This option is different from the Reset menu item. The Default menu item
resets the NL100/105 back to the factory defaults. Reset reboots the device
using the last-saved configuration.
After the NL100/105 reboots, it may take a few moments to reestablish
communication. Press enter a few times until the NL100/105 status line is
returned.
17
Page 22

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
2.4.5 Reset
This option reboots the NL100/105, using the last saved settings that have been
programmed by the user. This option is different from the Defaults menu item.
The Defaults menu item resets the NL100/105 back to the factory defaults.
After the NL100/105 reboots, it may take a few moments to reestablish
communication. Press enter a few times until the NL100/105 status line is
returned.
NOTE
When using the NL100/105 in a PakBus network, resetting the
NL100/105 (or making other changes to the network that might
change the known route to remotes), may result in lengthy
communication interruptions until the new routes can be learned
by all the devices in the network.
2.4.6 Help
The Help option provides tips for navigating within the NL100/105 menu
prompts and gives a brief description of each menu item. Help for a particular
setting can be displayed by pressing F1 or ? at the prompt for that setting.
2.4.7 Bye
The Bye option is used to close the Socket connection at the end of a Telnet or
terminal communication session.
2.4.8 Other Commands
Additional commands are available for the NL100/105, which are not shown
on the prompt line for the device or in DevConfig. The commands are used for
troubleshooting.
18
Command Description
io This command is a toggle, which turns on or off the monitoring
of low level I/O
o (or old) This command shows historic diagnostic trace information for
the NL100/105. The object handle, name, and state are provided
for all active objects and the object handle, name, and event type
are provided for all recent events.
c (or
current)
t (or tables) This command displays the PakBus routing table information for
This command shows current diagnostic trace information for
the NL100/105. The object handle, name, and state are provided
for all active objects and the object handle, name, and event type
are provided for all recent events.
the NL100/105:
Page 23

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
2.4.9 Serial Server Watchdog
If no communication is detected for a specified number of minutes, the
NL100/105 will drop the communications link. This feature is called a
"watchdog". The watchdog alleviates the problem of a communications port
being held open, thus rendering the device inaccessible, if the NL100/105 and
the remote device failed to terminate the communications link in a "normal"
manner. The NL100/105 will wait two minutes for activity on a port before
timing out. This affects all communication modes, including when the
NL100/105 is configured as a PakBus based or TCP/IP based serial server, and
when communicating with the NL100/105 during a Telnet session.
3. Connecting the NL100/105 to a Network
3.1 Network to NL100 Connection
The connection from the computer network to the NL100/105 10 Base-T port
should be a twisted pair cable. A male RJ-45 plug connector should be on the
cable end going into the 10 Base-T port.
If the cable is to be run directly from the computer to the NL100/105, a
crossover cable is required. If the cable will be run from a hub to the
NL100/105, a straight through cable should be used. Appendix C shows the
pin-outs for these two cable types.
3.2 Typical Configurations
The cases below assume the NL100/105 is being connected to a mixed array
datalogger using the datalogger's CS I/O port (CR10X, CR510 CR23X) or RS232 port (CR23X). TD-based dataloggers (CR10X-TD, CR510-TD, and
CR23X-TD) are configured similarly. In these instances, the communication
port(s) being used on the NL100/105 should be set up as TcpSer (TCP/IP
based serial server). When communicating with PakBus devices (CR1000,
CR3000, CR800/850, CR200, CR10XPB, CR510PB, or CR23XPB), the
communication port on the NL100/105 can be configured for PakBus or
TcpSer, depending upon the role the NL100/105 is to play in the network. In
many cases, the TcpSer option can be selected.
For mixed array and TD dataloggers, the network map for the LoggerNet
software should depict an IPPort root device with the datalogger attached
directly to the IPPort (see Figure 3) unless otherwise noted. For PakBus
dataloggers, a PakBus Port must first be added to the IP Port in the network
map, and then the PakBus datalogger attached to the PakBus Port. In instances
where the NL100/105 is to be a PakBus router, a pbRouter must be added after
the PakBus Port and before the PakBus datalogger. In some instances, extra
response time (3 to 4 seconds) may need to be added to the IPPort and/or the
datalogger to account for network traffic delays over a TCP/IP connection.
NOTE
The IP Address entered in the software for the NL100/105
should not contain leading zeros. If leading zeros are used, the
communications attempts will fail.
19
Page 24

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
Some of the communication links require additional peripherals or cables that
can be purchased from Campbell Scientific. In some cases, a standard RS-232
9 to 25 pin or 25 to 25 pin cable is required. RS-232 cables can be purchased
from Campbell Scientific or from a computer accessories supplier.
FIGURE 3. Typical NL100/105 Setups in LoggerNet
3.2.1 Direct Connect from the NL100/105 to a Datalogger
Either the CS I/O port or the RS-232 port can be used to directly connect a
datalogger to the NL100/105. Cabling or additional peripherals are required as
listed below. Note that multiple dataloggers can be connected to one
NL100/105 by using combinations of the connections described below. Each
port must be assigned a unique port number.
NL100/105 CS I/O port to datalogger CS I/O port - An SC12 cable is
connected between the CS I/O ports on both devices. An SC12 is typically
shipped with all datalogger peripherals.
NL100/105 RS-232 port to datalogger RS-232 port - A standard 9 to 9 pin
communications cable should be connected between the RS-232 ports on both
devices.
NL100/105 RS-232 port to datalogger CS I/O port - A serial communications
cable should be connected to the RS-232 port of the NL100/105. This cable
should be connected to an SC32A or SC32B optically isolated interface, and
the datalogger should be connected to the 9 pin port of the SC32A/B with an
SC12 cable.
20
Page 25

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
3.2.2 MD9 Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger
Campbell Scientific's MD9 Multidrop Interface can be used to connect one or
more dataloggers to the NL100/105 via the NL100/105’s RS-232 port. A
multidrop network is capable of addressing up to 254 dataloggers, but the
actual number of dataloggers that can be connected depends upon attenuation
of the signal due to coax cable length, the number of devices on the network,
and the number of coax terminator pairs used. Refer to the MD9 manual for
determining the maximum number of dataloggers that can be connected based
on these factors.
An SC532 or SC532A Interface device should be connected to the serial port
of the NL100/105. The cable to an SC532 should be a standard 9 to 25 pin RS232 cable, with the 25 pin male connection mated to the RS-232 side of the
SC532. The cable to an SC532A should be a standard 9 to 9 pin RS-232 cable.
Note, however, that the RTS line in the cable must be disabled (pin 7 on the 9pin connector or pin 4 on the 25-pin connector). An SC12 cable is used to
connect the 9 pin peripheral connection of the SC532/SC532A to the serial I/O
port of the MD9. Coax cable, running from the coax port of the base MD9, is
run to each of the remote MD9 devices, which are connected to the dataloggers
with SC12 cables. Refer to the MD9 User's Manual for additional information.
The Setup window in LoggerNet should depict an MD9 Base modem attached
to the IPPort, with the datalogger attached to an MD9Remote Modem. Refer to
Figure 4 below.
FIGURE 4. LoggerNet Setup for NL100/105 to MD9 to Datalogger Connection
21
Page 26

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
3.2.3 MD485 Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger
Campbell Scientific's RS485 communication device, the MD485, can be
attached to an NL100/105 to provide a communication link to one or more
dataloggers. The MD485 has three communication ports: RS485 (two
terminals but the same physical port), CS I/O, and RS232. It can be configured
for communication on any two of its three ports at one time. The most typical
use of the MD485 is to set up a network of dataloggers linked together in an
RS485 network. However, you can also attach a datalogger or other
compatible peripheral to the CS I/O port or the RS-232 port of the MD485.
The MD485 can be configured to communicate in a transparent (point to point)
mode, as an MD9 emulator, or as a peripheral in a PakBus network. For
transparent or PakBus communication, the MD485 is attached to the
NL100/105's RS485 port using a 3-wire shielded cable (i.e., a 2 twisted pair
shielded cable). For MD9 emulation, at least two MD485s are required. One
MD485 is attached to the NL100/105's RS232 port using an SC12 cable. This
MD485 acts as a base MD9 device, since the NL100/105 is, in itself, not
capable of MD9 communication. A second MD485 is attached to each of the
dataloggers.
An appendix in the MD485 manual provides complete information on setting
up the NL100/105 and the MD485s for each of the above configurations, along
with information on the settings used in LoggerNet.
3.2.4 RF Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger
Interfacing the NL100/105 to an RF Base station enables wireless
communication to remote datalogger stations over a TCP/IP network. The
preferred configuration uses the NL100/105's RS-232 port (DTE) for
connection to the RF Base as follows:
For connecting to the RS-232 port (DCE) of the RF4xx series or RF450 Spread
Spectrum radios, a standard RS-232 serial cable (CSI# 10873 or equivalent) is
used.
For connecting to the RS-232 port (DTE) on an RF500M RF Modem, a nullmodem RS-232 serial cable (CSI# 13657 or equivalent) must be used. If
connecting to the CSI/O port on the RF500M, an SC532A 9-Pin Peripheral to
RS-232 interface adapter and standard serial cables are required.
NOTE
When connecting to an RF310B Base Station or its predecessors
(or directly to an RF310M RF Modem via an SC532A), the RTS
line in the standard RS-232 serial cable (pin seven on a 9-pin
connector or pin four on a 25-pin connector) must be disabled.
This is done to prevent driving the SDE signal (pin 6) on the RF
Modem's CSI/O port high and inhibiting the ME communication
cycle.
If circumstances should require the utilization of the NL100/105's CS I/O port
for connection to an RF base, please contact a Campbell Scientific
Applications Engineer for information about how this might be achieved.
22
The configuration of the Setup window in LoggerNet will vary depending on
the equipment and configuration settings employed. Please consult the
relevant manual(s) for configuration specifics. Figure 5 depicts the LoggerNet
Page 27

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
Setup window for an RF Network using VHF/UHV radios and a mixed array
datalogger.
FIGURE 5. LoggerNet Setup for NL100/105 to RF to Datalogger Connection
Refer to Campbell Scientific's Radiotelemetry Network Instruction Manual for
more information on setting up RF stations.
3.2.5 Short Haul Modem Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger
The use of Short Haul Modems (SRM-5A, SRM6-A) allows a connection to a
datalogger via TCP/IP to a twisted pair cable. The short haul modem at the
NL100/105 should be connected to the device using a standard RS-232 9 to 25
pin communication cable. It is recommended that a short haul surge protection
device (P/N 5563) be connected next and then the twisted pair cable. Another
surge protection device is recommended between the cable and the remote
short haul modem. The short haul modem should be connected to an SC932
RS-232 9 to 25 pin DCE interface, which is then connected to the datalogger's
CS I/O port via an SC12 cable.
3.2.6 Phone Modem Connection from NL100/105 to Datalogger
A Hayes-compatible phone modem can be connected to the NL100/105 to
allow a TCP/IP to phone link between a computer and a datalogger. The phone
modem should be connected to the NL100/105's RS-232 port using an
appropriate RS-232 serial cable. Connection of the remote phone modem to the
datalogger will vary, depending upon the type of remote modem used. Refer to
the user's manual for the system you purchased for additional information on
assembling the remote site.
23
Page 28

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
In the LoggerNet communications software, the phone modem on the
NL100/105 side should be shown attached to the IPPort. The datalogger is then
shown as connected to the remote phone modem. Refer to Figure 6 below.
FIGURE 6. LoggerNet Setup for NL100/105 to Phone to Datalogger Connection
3.3 NL100/105 to Datalogger Connections - CR9000/CR5000
3.3.1 Software Setup
As an alternative to LoggerNet, PC9000 software (version 3.5 or higher) can
be used to communicate with the CR9000 and CR5000 dataloggers via the
NL100/105 and a TCP/IP Network. To configure the software for
communication, choose the Tools | CommLink menu option. From the I/O Port
drop-down list box, select NET. On the bottom left side of the screen, there are
fields in which to type the TCP/IP address and the port number. The setup
should look similar to Figure 7, below.
24
Page 29

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
FIGURE 7. PC9000 Setup for TCP/IP Communication
3.3.2 Hardware Setup for NL105 Communication with the CR9000 via TLink
A CR9000 can be connected to a TCP/IP network by connecting the TLink
port of the CR9000 9031 CPU module to the TLink port of the NL105 (note
that the NL100 does not have this communication port). A twisted pair cable is
used to make this connection.
25
Page 30

NL100/105 Network Link Interface
26
Page 31

Appendix A. CS I/O Port
The CS I/O port is Campbell Scientific's input/output port. It is not a standard
RS-232 pin-out. The following table provides pin-out information on the port
when connected to a datalogger.
Pin Name
1 5 V (supplied by the
datalogger)
2 Signal Ground Provides reference for voltage
3 Ring Output Raised by a NL100/105 to put
4 RXD Output Serial data transmitted to the
5 Modem Enable Input Raised by the datalogger when
6 Synchronous Device
Enable
7 Clock/Handshake Input Used by the datalogger with
Signal
Type
Input Not used by NL100/105
Input Used by the datalogger to
Description
levels
the datalogger into the
telecommunications mode
datalogger
it determines that the
NL100/105 raised the ring line
address the NL100/105 when
the NL100/105 is configured
as a synchronous device
SDE and TXD lines to address
and transfer data to
synchronous devices
8 12 V (supplied by the
datalogger)
9 TXD Input Serial data received from the
Not used by the NL100/105
datalogger
A-1
Page 32

This is a blank page.
Page 33

Appendix B. Null-Modem Cable
A null-modem cable allows communication between two similar devices. It is
sometimes called a crossover cable, because the transmit and receive lines are
crossed so that the two devices can communicate. An RS-232 null modem
cable usually also crosses other handshaking lines.
An RS-232 null-modem cable can be purchased at a local computer store. The
pin-outs for this cable are provided below.
Carrier Detect
Transmit Data
Receive Data
Data Terminal Ready
Signal Ground
Data Set Ready
Request to Send
Clear to Send
Not Used 9 9 Not Used
1 ⇔ 4
2 ⇔ 3
3 ⇔ 2
4 ⇔ 1, 6
5 ⇔ 5
6 ⇔ 4
7 ⇔ 8
8 ⇔ 7
Data Terminal Ready
Receive Data
Transmit Data
Carrier Detect, Data Set Ready
Signal Ground
Data Terminal Ready
Clear to Send
Request to Send
B-1
Page 34

This is a blank page.
Page 35

Appendix C. 10 Base-T Cabling
The cable that runs from the computer to the NL100/105 should be a Category
5 twisted pair cable. If the NL100/105 will be connected directly to the
computer, a crossover cable should be used. If the NL100/105 will be
connected to the computer through a hub, a straight through cable should be
used. The pin-outs for each of these cables is shown below.
Straight Through Cable
Twisted Pair 1
1 ⇔ 1
Twisted Pair 2
Crossover Cable
Twisted Pair 1
Twisted Pair 2
2 ⇔ 2
3 ⇔ 3
6 ⇔ 6
1 ⇔ 3
2 ⇔ 6
3 ⇔ 1
6 ⇔ 2
C-1
Page 36

This is a blank page.
Page 37

Appendix D. RS-485 Connector, 3-Pin Terminal Block
The RS-485 port is for connecting an MD485 multidrop interface to the
NL100. The MD485 attaches to the NL100 via a twisted pair cable such as the
#9720. The following table shows the pin-out information for the RS-485 port.
PIN I/O FUNCTION
1 GND Signal Ground
2 I/O 485_IO- (A)
3 I/O 485_IO+ (B)
I = Signal Into the NL100, O = Signal Out of the NL100
D-1
Page 38

This is a blank page.
Page 39

Glossary
Beacon Interval - Devices in a PakBus network may broadcast a message to
other devices, in order to determine "neighbor" devices. Neighbor devices are
devices that can be communicated with directly by the current device without
being routed through an intermediate device. A beacon in a PakBus network
helps to ensure that all devices in the network are aware of which other devices
are viable in the network.
If configured to do so, a clock set command may be transmitted with the
beacon interval. This function can be used to synchronize the clocks of devices
within the PakBus network.
MODBUS - MODBUS is a communications protocol developed by Modicon
which was designed to provide a common communications protocol among
intelligent devices in the manufacturing industry.
Neighbor (PakBus Neighbor) - Neighbor devices are devices that can be
communicated with directly by the current device without being routed
through an intermediate device.
PakBus - PakBus is a packet-based communications protocol developed by
Campbell Scientific. One of the advantages of PakBus is that other
communications protocol packets, such as TCP/IP or MODBUS, can be
"wrapped" in a PakBus packet and transferred among PakBus devices in the
network, thus allowing various communication protocols within one network.
Devices that are capable of PakBus communication include the CR10XTD-PB,
CR510TD-PB, CR23XTD-PB dataloggers, the RF400 modem, and the
NL100/105.
PakBus Node - A device in the PakBus network with a unique PakBus ID.
The device can be a datalogger, a computer, or an NL100/105.
Serial Server - A serial server is a device that allows serial communication
over a TCP/IP communications link.
Page 40

This is a blank page.
Page 41

Page 42

Campbell Scientific Companies
Campbell Scientific, Inc. (CSI)
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321
UNITED STATES
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com
Campbell Scientific Africa Pty. Ltd. (CSAf)
PO Box 2450
Somerset West 7129
SOUTH AFRICA
www.csafrica.co.za • cleroux@csafrica.co.za
Campbell Scientific Australia Pty. Ltd. (CSA)
PO Box 444
Thuringowa Central
QLD 4812 AUSTRALIA
www.campbellsci.com.au • info@campbellsci.com.au
Campbell Scientific do Brazil Ltda. (CSB)
Rua Luisa Crapsi Orsi, 15 Butantã
CEP: 005543-000 São Paulo SP BRAZIL
www.campbellsci.com.br • suporte@campbellsci.com.br
Campbell Scientific Canada Corp. (CSC)
11564 - 149th Street NW
Edmonton, Alberta T5M 1W7
CANADA
www.campbellsci.ca • dataloggers@campbellsci.ca
Campbell Scientific Centro Caribe S.A. (CSCC)
300 N Cementerio, Edificio Breller
Santo Domingo, Heredia 40305
COSTA RICA
www.campbellsci.cc • info@campbellsci.cc
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL)
Campbell Park
80 Hathern Road
Shepshed, Loughborough LE12 9GX
UNITED KINGDOM
www.campbellsci.co.uk • sales@campbellsci.co.uk
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (France)
Miniparc du Verger - Bat. H
1, rue de Terre Neuve - Les Ulis
91967 COURTABOEUF CEDEX
FRANCE
www.campbellsci.fr • info@campbellsci.fr
Campbell Scientific Spain, S. L.
Avda. Pompeu Fabra 7-9, local 1
08024 Barcelona
SPAIN
www.campbellsci.es • info@campbellsci.es
Please visit www.campbellsci.com to obtain contact information for your local US or International representative.
 Loading...
Loading...