Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path
Copyright © 2010- 2014
Campbell Scientific, Inc.
Gas Analyzer
Revision: 6/14
Page 2

Page 3

Limited Warranty
“Products manufactured by CSI are warranted by CSI to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal use and service for twelve months
from the date of shipment unless otherwise specified in the corresponding
product manual. (Product manuals are available for review online at
www.campbellsci.com.) Products not manufactured by CSI, but that are resold
by CSI, are warranted only to the limits extended by the original manufacturer.
Batteries, fine-wire thermocouples, desiccant, and other consumables have no
warranty. CSI’s obligation under this warranty is limited to repairing or
replacing (at CSI’s option) defective Products, which shall be the sole and
exclusive remedy under this warranty. The Customer assumes all costs of
removing, reinstalling, and shipping defective Products to CSI. CSI will return
such Products by surface carrier prepaid within the continental United States of
America. To all other locations, CSI will return such Products best way CIP
(port of entry) per Incoterms ® 2010. This warranty shall not apply to any
Products which have been subjected to modification, misuse, neglect, improper
service, accidents of nature, or shipping damage. This warranty is in lieu of all
other warranties, expressed or implied. The warranty for installation services
performed by CSI such as programming to customer specifications, electrical
connections to Products manufactured by CSI, and Product specific training, is
part of CSI's product warranty. CSI EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS AND
EXCLUDES ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. CSI hereby disclaims,
to the fullest extent allowed by applicable law, any and all warranties and
conditions with respect to the Products, whether express, implied or
statutory, other than those expressly provided herein.”
Page 4

Assistance
Products may not be returned without prior authorization. The following
contact information is for US and international customers residing in countries
served by Campbell Scientific, Inc. directly. Affiliate companies handle
repairs for customers within their territories. Please visit
www.campbellsci.com to determine which Campbell Scientific company serves
your country.
To obtain a Returned Materials Authorization (RMA), contact CAMPBELL
SCIENTIFIC, INC., phone (435) 227-9000. After an application engineer
determines the nature of the problem, an RMA number will be issued. Please
write this number clearly on the outside of the shipping container. Campbell
Scientific’s shipping address is:
CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC, INC.
RMA#_____
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321-1784
For all returns, the customer must fill out a “Statement of Product Cleanliness
and Decontamination” form and comply with the requirements specified in it.
The form is available from our web site at www.campbellsci.com/repair. A
completed form must be either emailed to repair@campbellsci.com or faxed to
(435) 227-9106. Campbell Scientific is unable to process any returns until we
receive this form. If the form is not received within three days of product
receipt or is incomplete, the product will be returned to the customer at the
customer’s expense. Campbell Scientific reserves the right to refuse service on
products that were exposed to contaminants that may cause health or safety
concerns for our employees.
Page 5

Precautions
DANGER — MANY HAZARDS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH INSTALLING, USING, MAINTAINING, AND WORKING ON OR AROUND
TRIPODS, TOWERS, AND ANY ATTACHMENTS TO TRIPODS AND TOWERS SUCH AS SENSORS, CROSSARMS, ENCLOSURES,
ANTENNAS, ETC. FAILURE TO PROPERLY AND COMPLETELY ASSEMBLE, INSTALL, OPERATE, USE, AND MAINTAIN TRIPODS,
TOWERS, AND ATTACHMENTS, AND FAILURE TO HEED WARNINGS, INCREASES THE RISK OF DEATH, ACCIDENT, SERIOUS
INJURY, PROPERTY DAMAGE, AND PRODUCT FAILURE. TAKE ALL REASONABLE PRECAUTIONS TO AVOID THESE HAZARDS.
CHECK WITH YOUR ORGANIZATION'S SAFETY COORDINATOR (OR POLICY) FOR PROCEDURES AND REQUIRED PROTECTIVE
EQUIPMENT PRIOR TO PERFORMING ANY WORK.
Use tripods, towers, and attachments to tripods and towers only for purposes for which they are designed. Do not exceed design
limits. Be familiar and comply with all instructions provided in product manuals. Manuals are available at www.campbellsci.com or
by telephoning 435-227-9000 (USA). You are responsible for conformance with governing codes and regulations, including safety
regulations, and the integrity and location of structures or land to which towers, tripods, and any attachments are attached. Installation
sites should be evaluated and approved by a qualified engineer. If questions or concerns arise regarding installation, use, or
maintenance of tripods, towers, attachments, or electrical connections, consult with a licensed and qualified engineer or electrician.
General
• Prior to performing site or installation work, obtain required approvals and permits. Comply
with all governing structure-height regulations, such as those of the FAA in the USA.
• Use only qualified personnel for installation, use, and maintenance of tripods and towers, and
any attachments to tripods and towers. The use of licensed and qualified contractors is highly
recommended.
• Read all applicable instructions carefully and understand procedures thoroughly before
beginning work.
• Wear a hardhat and eye protection, and take other appropriate safety precautions while
working on or around tripods and towers.
• Do not climb tripods or towers at any time, and prohibit climbing by other persons. Take
reasonable precautions to secure tripod and tower sites from trespassers.
• Use only manufacturer recommended parts, materials, and tools.
Utility and Electrical
• You can be killed or sustain serious bodily injury if the tripod, tower, or attachments you are
installing, constructing, using, or maintaining, or a tool, stake, or anchor, come in contact with
overhead or underground utility lines.
• Maintain a distance of at least one-and-one-half times structure height, or 20 feet, or the
distance required by applicable law, whichever is greater, between overhead utility lines and
the structure (tripod, tower, attachments, or tools).
• Prior to performing site or installation work, inform all utility companies and have all
underground utilities marked.
• Comply with all electrical codes. Electrical equipment and related grounding devices should
be installed by a licensed and qualified electrician.
Elevated Work and Weather
• Exercise extreme caution when performing elevated work.
• Use appropriate equipment and safety practices.
• During installation and maintenance, keep tower and tripod sites clear of un-trained or non-
essential personnel. Take precautions to prevent elevated tools and objects from dropping.
• Do not perform any work in inclement weather, including wind, rain, snow, lightning, etc.
Maintenance
• Periodically (at least yearly) check for wear and damage, including corrosion, stress cracks,
frayed cables, loose cable clamps, cable tightness, etc. and take necessary corrective actions.
• Periodically (at least yearly) check electrical ground connections.
WHILE EVERY ATTEMPT IS MADE TO EMBODY THE HIGHEST DEGREE OF SAFETY IN ALL CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC PRODUCTS,
THE CUSTOMER ASSUMES ALL RISK FROM ANY INJURY RESULTING FROM IMPROPER INSTALLATION, USE, OR
MAINTENANCE OF TRIPODS, TOWERS, OR ATTACHMENTS TO TRIPODS AND TOWERS SUCH AS SENSORS, CROSSARMS,
ENCLOSURES, ANTENNAS, ETC.
Page 6

Page 7

Table of Contents
PDF viewers: These page numbers refer to the printed version of this document. Use the
PDF reader bookmarks tab for links to specific sections.
1. Introduction ................................................................. 1
2. Cautionary Statements ............................................... 1
3. Initial Inspection ......................................................... 2
4. Overview ...................................................................... 2
4.1 General ................................................................................................. 2
4.2 Features ................................................................................................ 2
4.3 Gas Head Memory ............................................................................... 3
4.4 Self-diagnostics and Data Integrity ...................................................... 3
4.5 Field Zero/Span Capabilities ................................................................ 3
4.6 EC100 Electronics Module .................................................................. 4
4.6.1 EC100 Communications and Control ........................................... 4
4.6.2 EC100 Outputs .............................................................................. 4
4.6.2.1 SDM Output ....................................................................... 5
4.7 Automatic Heater Control .................................................................... 5
4.8 Theory of Operation ............................................................................. 6
5. Specifications ............................................................. 7
5.1 Measurements ...................................................................................... 7
5.2 Output Signals ...................................................................................... 9
5.3 Physical Description ............................................................................ 9
5.4 Power Requirements .......................................................................... 10
6. Installation ................................................................. 11
6.1 Orientation ......................................................................................... 11
6.2 Mounting Analyzer to Support Hardware .......................................... 11
6.2.1 Preparing the mounting structure ................................................ 14
6.2.2 Mounting EC150 with optional CSAT3A ................................... 14
6.2.3 Mounting EC150 without CSAT3A ........................................... 16
6.2.4 Attaching EC100 Electronics Enclosure to Mounting
Structure .................................................................................. 17
6.2.5 Install the EC150 Temperature Probe ......................................... 18
6.3 Wiring and Connections ..................................................................... 19
6.3.1 Connecting the EC150 Gas Analyzer Head ................................ 20
6.3.2 Connect the CSAT3A Sonic Head .............................................. 20
6.3.3 Connect the EC150 Temperature Probe ...................................... 21
6.3.4 Ground the EC100 Electronics ................................................... 21
6.3.5 Connect SDM Communications to the EC100 ........................... 21
6.3.6 Wire Power and Ground the EC100 ........................................... 22
7. Zero and Span ........................................................... 22
7.1 Introduction ........................................................................................ 22
i
Page 8

Table of Contents
7.2 Zero and Span Procedure .................................................................. 23
8. Maintenance and Troubleshooting .......................... 28
8.1 Routine Site Maintenance ................................................................. 28
8.2 Gas Analyzer Wicks .......................................................................... 28
8.3 Cleaning Analyzer Windows ............................................................. 29
8.4 Zero and Span.................................................................................... 29
8.5 Replacing CO2 Scrubber Bottles ....................................................... 30
8.6 Factory Recalibration ........................................................................ 31
8.7 Troubleshooting ................................................................................ 32
8.7.1 Data Loss During Precipitation Events ...................................... 32
8.7.2 EC100 Diagnostics for Gas Analyzer Troubleshooting ............. 32
8.7.3 LED Status Lights ...................................................................... 32
8.7.4 Diagnostic Flags ......................................................................... 33
Appendices
EC150 Settings ........................................................ A-1
A.
A.1 Factory Defaults .............................................................................. A-1
A.2 Details ............................................................................................. A-1
A.2.1 SDM Address ........................................................................... A-2
A.2.2 Bandwidth ................................................................................ A-2
A.2.3 Unprompted Output ................................................................. A-2
A.2.4 Unprompted Output Rate ......................................................... A-2
A.2.5 RS-485 Baud Rate .................................................................... A-3
A.2.6 Analog Output .......................................................................... A-3
A.2.7 ECMon Update Rate ................................................................ A-3
A.2.8 Temperature Sensor ................................................................. A-3
A.2.9 Fixed Temperature Value ......................................................... A-3
A.2.10 Pressure Sensor ........................................................................ A-4
A.2.10.1 Pressure Gain ................................................................. A-6
A.2.10.2 Pressure Offset ............................................................... A-6
A.2.10.3 Fixed Pressure Value ..................................................... A-6
A.2.11 Pressure Differential Enable ..................................................... A-6
A.2.12 Heater Control .......................................................................... A-7
A.2.13 Head Power Off........................................................................ A-7
A.3 ECMon ............................................................................................ A-7
A.4 Device Configuration Utility ........................................................... A-9
A.5 EC100Configure() Instruction ......................................................... A-9
A.5.1 ConfigCmd 11 Zero-and-Span Control .................................. A-11
A.6 Example CRBasic Program ........................................................... A-12
B. Filter Bandwidth and Time Delay ........................... B-1
C. Alternate EC100 Outputs ........................................ C-1
C.1 USB or RS-485 Output.................................................................... C-1
C.1.1 Specifications ........................................................................... C-1
C.1.2 Detailed Information ................................................................ C-1
C.2 Analog Output ................................................................................. C-3
C.2.1 Specifications ........................................................................... C-3
C.2.2 Detailed Information ................................................................ C-3
ii
Page 9

Table of Contents
D. Useful Equations .................................................... D-1
E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) ..................... E-1
E.1 Magnesium Perchlorate MSDS ........................................................ E-1
E.2 Decarbite MSDS .............................................................................. E-8
F. Packing Information ............................................... F-1
F.1 EC150-GH Packing Information ...................................................... F-1
F.2 EC150-SH Packing Information ...................................................... F-2
Figures
4-1. EC100 electronics module ................................................................... 4
5-1. Optical path and envelope dimensions of EC150 analyzer head........ 10
6-1. Mounting bracket options for EC150 head only (pn 26785) or
EC150 head with CSAT3A (pn 26786) .......................................... 11
6-2. Changes in flux attenuation ratio relative to sensor height at the
most fore and aft positions .............................................................. 12
6-3. Mounting position of CSAT3A and EC155 with a 4.9 cm sensor
separation. ....................................................................................... 13
6-4. Mounting position of CSAT3A and EC155 with a 9.7 cm sensor
separation. ....................................................................................... 13
6-5. Exploded view of mounting CSAT3A and EC150 ............................ 15
6-6. Exploded view of mounting the EC150 without the CSAT3A .......... 16
6-7. EC100 enclosure mounting bracket mounted on a vertical mast
(left) and a tripod leg (right) ........................................................... 17
6-8. Exploded view of mounting the EC100 enclosure ............................. 18
6-9. EC150 temperature probe .................................................................. 19
6-10. Solar radiation shield with EC150 temperature probe ....................... 19
6-11. EC100 electronics front panel showing EC100 as shipped (left)
and after completed wiring and connections (right) ....................... 19
6-12. Bottom of EC100 enclosure ............................................................... 20
7-1. Zero-and-span shroud mounted on the zero-and-span stand .............. 24
7-2. ECMon zero-and-span window .......................................................... 26
8-1. Proper location of the gas analyzer top wick (left) and bottom
wick (right) ..................................................................................... 29
8-2. Replacing the desiccant/CO2 scrubber bottles .................................... 31
8-3. LED status during normal operation .................................................. 32
A-1. Location of EC100 basic barometer ................................................ A-4
A-2. Location of EC100 enhanced barometer ......................................... A-5
A-3. Comparison of error in basic versus enhanced barometer over
operational temperatures .............................................................. A-5
A-4. Main screen of ECMon ................................................................... A-8
A-5. Setup screen in ECMon ................................................................... A-8
B-1. Amplitude response of EC100 filter at various bandwidths ............. B-1
B-2. Frequency response comparison of EC100 10-Hz bandwidth
and a 50-msec moving average ..................................................... B-2
C-1. USB data output in terminal mode ................................................... C-2
Tables
6-1. EC100 SDM output to a Campbell Scientific CR1000, CR3000,
or CR5000 Datalogger .................................................................... 22
8-1. Rain Wick Replacement Parts ............................................................ 28
iii
Page 10

Table of Contents
8-2. Diagnostic Flags of Sonic Status LED .............................................. 33
8-3. Diagnostic Flags and Suggested Actions........................................... 34
A-1. Factory Default Settings .................................................................. A-1
A-2. ConfigCmd Values for Setting and Retrieving Settings ................ A-10
B-1. Filter Time Delays for Various Bandwidths .................................... B-3
C-1. USB and RS-485 Output Elements ................................................. C-1
C-2. Multipliers and Offsets for Analog Outputs .................................... C-4
D-1. Variables and Constants .................................................................. D-1
iv
Page 11

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas
Analyzer
1. Introduction
The EC150 is an in situ, open-path, mid-infrared absorption gas analyzer that
measures the absolute densities of carbon dioxide and water vapor. The EC150
was designed for open-path eddy covariance flux measurements as part of an
open-path eddy covariance measurement system. It is most often used in
conjunction with the CSAT3A sonic anemometer and thermometer, which
measures orthogonal wind components along with sonically determined air
temperature.
Before attempting to assemble, install or use the EC150, please study:
• Section 2, Cautionary Statements
• Section 3, Initial Inspection
• Section 6, Installation
Greater detail is available in the remaining sections.
Other manuals that may be helpful include:
• CR3000 Micrologger Operator’s Manual
• CFM100 CompactFlash Module Instruction Manual
• NL115 Ethernet and CompactFlash Module Instruction Manual
• Application Note 3SM-F, PC/CF Card Information
• LoggerNet Instruction Manual, Version 4.1
• CSAT3 Three Dimensional Sonic Anemometer Manual
• ENC10/12, ENC12/14, ENC14/16, ENC16/18 Instruction Manual
• CM106 Tripod Instruction Manual
• Tripod Installation Manual Models CM110, CM115, CM120
2. Cautionary Statements
• DANGER:
o The scrubber bottles in the EC150 contain sodium hydroxide
(NaOH) and anhydrous magnesium perchlorate (Mg(ClO
not attempt to access or remove these chemical bottles before
reviewing Section 8.5, Replacing CO
Avoid direct contact with the chemicals.
Ensure your work area is well ventilated and free of
Store used chemical bottles in a sealed container until
Dispose of chemicals and bottles properly.
• WARNING:
o Do not carry the EC150 by the arms or the strut between the
arms. Always hold it by the mounting base where the upper and
lower arms connect.
Scrubber Bottles.
2
reactive compounds and combustible materials.
disposal.
4)2
). Do
1
Page 12

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
o Handle the EC150 carefully. The optical source may be damaged
o Overtightening bolts will damage or deform the mounting
• CAUTION:
o Grounding the EC100 measurement electronics is critical. Proper
o Do not connect or disconnect the gas analyzer or sonic
o Resting the analyzer on its side during the zero-and-span
3. Initial Inspection
Upon receipt of your equipment, inspect the packaging and contents for
damage. File damage claims with the shipping company.
Model numbers are found on each component. On cables, the model number is
located both on the sensor head and on the connection end of the cable. Check
this information against the enclosed shipping document to verify the expected
products and that the correct accessories are included.
by rough handling, especially while the analyzer is powered.
hardware.
grounding to Earth will ensure maximum electrostatic discharge
(ESD) and lightning protection and improve measurement
accuracy.
anemometer connectors while the EC100 is powered.
procedure may result in measurement inaccuracy.
4. Overview
4.1 General
4.2 Features
The EC150 measures absolute densities of carbon dioxide and water vapor.
The EC150 analyzer was designed specifically for open-path, eddy covariance
flux measurement systems. The EC150 gas analyzer head connects directly to
Campbell Scientific’s EC100 electronics. The EC150 is commonly used with a
CSAT3A sonic anemometer head. When the CSAT3A is used in conjunction
with the EC150, the EC100 can make gas and wind measurements
simultaneously. Similarly, the EC100 can simultaneously record
measurements from temperature sensors and a pressure transducer.
The EC150 analyzer has a rugged, aerodynamic design with low power
requirements, making it suitable for field applications including those with
remote access.
The EC150 has been designed specifically to address issues of aerodynamics,
power consumption, spatial displacement, temporal synchronicity, and to
minimize sensitivity to environmental factors.
The analyzer windows are scratch resistant and treated with a durable
hydrophobic coating that facilitates shedding of raindrops from critical
surfaces. The coating also impedes the accumulation of dust and deposits, and
keeps the surfaces cleaner over longer periods of time. To minimize data loss
due to humid environments, the EC150 is provided with window wicks that
draw moisture away from the measurement path and are easily replaceable
during routine maintenance.
2
Page 13

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
• Unique design contains little obstruction surrounding the sample
volume
• 5W total power consumption
• Synchronously samples data from the EC150 and CSAT3A
• Automatically configured via a Campbell Scientific datalogger
• Minimal spatial displacement between sample volume and CSAT3A
• Slim housings located away from the measurement volume to
minimize body heating effects due to solar radiation
• Symmetrical design for improved flux measurements without a bias
for updrafts and downdrafts
• Slanted windows to prevent water from pooling and blocking the
optical path
• Scratch-resistant windows for easy cleaning
• Hydrophobic coating on windows to repel water, dust and pollen and
to prolong time between window cleaning
• Equipped with internal window heaters to keep the windows surfaces
free from condensation and frost – especially beneficial in humid
environments or conditions with frequent frost formation
• Optical layout that is not affected by solar interference
• Mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) detector for low-noise
measurements and long-term stability of factory calibration
• Chopper housing without thermal control results in significantly
reduced power consumption
4.3 Gas Head Memory
The EC100 electronics (see Section 4.6, EC100 Electronics Module) are
universal for the entire Campbell Scientific family of gas analyzer heads. In
addition to the EC150 gas analyzer head, the IRGASON or EC155 gas
analyzer head can be connected to the EC100 electronics (one gas analyzer
head per EC100). All sensor heads have dedicated, non-volatile memory,
which stores all calibration, configuration, and setting information. The EC100
electronics can be mated with any of these gas analyzers or an optional
CSAT3A sonic anemometer head.
4.4 Self-diagnostics and Data Integrity
EC100 electronics provide an extensive set of diagnostic tools which include
warning flags, status LEDs, and signal strength outputs to identify instrument
malfunctions and warn the user of compromised data. These flags are further
described in Section 8.7.4, Diagnostic Flags. The flags also prompt the user
when the instrument needs servicing and can facilitate troubleshooting in the
field. The EC150 outputs the optical strength of signals, which can be used to
filter data when the path of the instrument is obstructed due to precipitation or
dirty windows.
4.5 Field Zero/Span Capabilities
A zero/span for CO2 and H2O can be accomplished in the field with an
optional shroud. The shroud allows the flow of a gas with known composition
in the measurement path of the analyzer to account for instrument drift and
changing environmental conditions.
3
Page 14
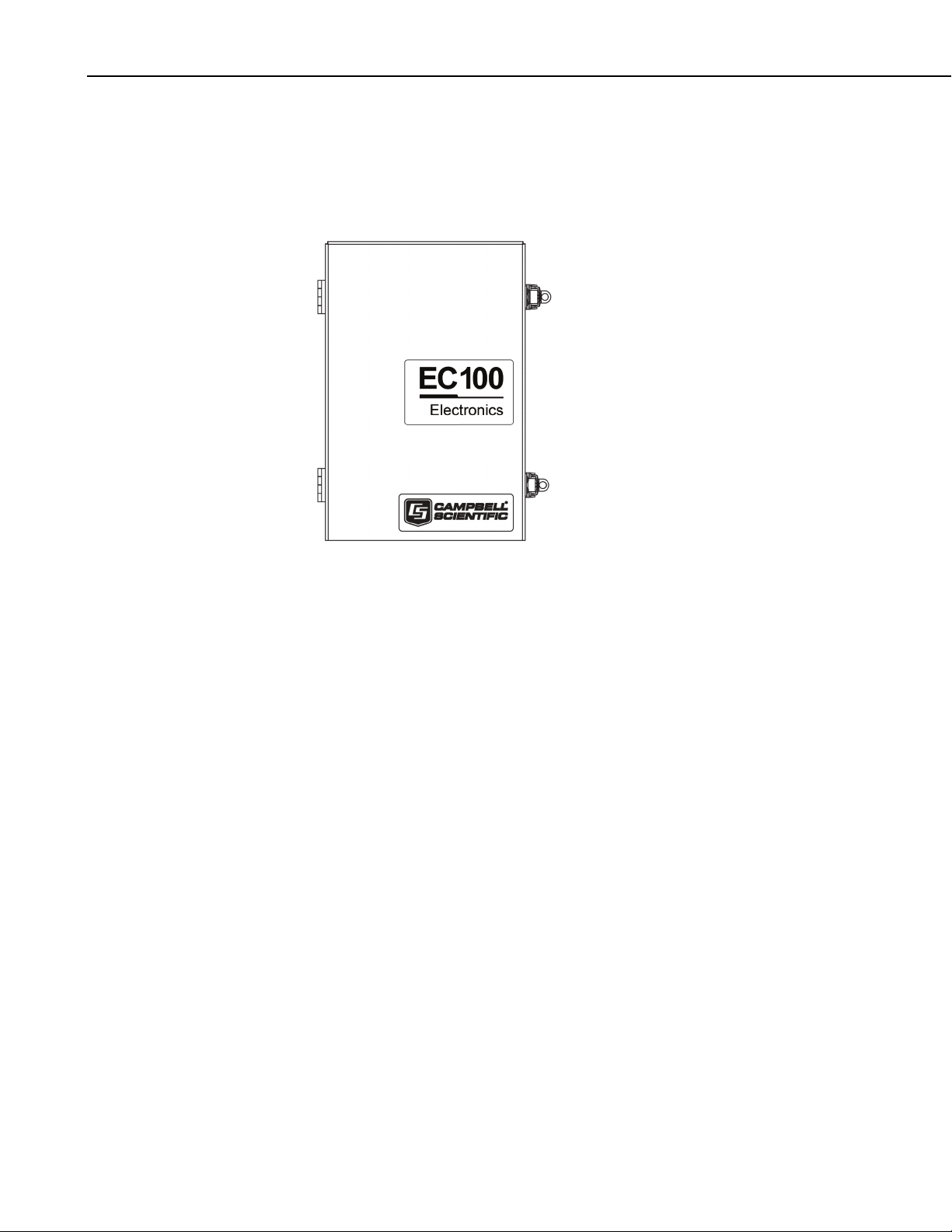
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
4.6 EC100 Electronics Module
The EC100 electronics module (shown in FIGURE 4-1) controls the EC150
and optional CSAT3A sonic anemometer head. The EC100 synchronizes
measurements and processes data from the EC150 and the CSAT3A.
FIGURE 4-1. EC100 electronics module
4.6.1 EC100 Communications and Control
The EC100 supports several serial communication interfaces, including USB,
RS-485, and Synchronous Device for Measurement (SDM). SDM is a
Campbell Scientific communication protocol that allows synchronized
measurement and rapid communication between a Campbell Scientific
datalogger and multiple devices including the EC150. Although nearly all
Campbell Scientific dataloggers support SDM, only the CR1000, CR3000, and
CR5000 dataloggers support communications with the EC100 electronics with
the EC100() instruction.
The SDM protocol allows the user to configure and control the analyzer
through CRBasic instructions in the datalogger. For example, in solar-powered
applications with limited daylight, battery power can be conserved by
programming the datalogger to turn off the EC150 at night or when conditions
are not suitable for eddy-covariance measurements. The datalogger can also be
used to change settings such as bandwidth, and perform the zero/span
procedure in the field.
4.6.2 EC100 Outputs
The EC100 outputs data in one of four types: SDM, USB, RS-485, or analog.
In general, Campbell Scientific recommends that SDM be used if a Campbell
Scientific datalogger is collecting data. However, RS-485 output is
recommended over SDM if cable lengths exceed 100 meters. If a PC is being
used as the data collection platform, USB and RS-485 are suitable outputs.
4
Information for SDM, the preferred output, is detailed below. See Appendix C,
Alternate EC100 Outputs, for USB, RS-485, and analog outputs.
Page 15

4.6.2.1 SDM Output
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
To use SDM data output, connect an SDM communications cable from the
EC100 (see Section 6.3, Wiring and Connections) to a CR1000, CR3000, or
CR5000 datalogger. On CR1000 dataloggers, the SDM protocol uses ports C1,
C2, and C3. These are multipurpose control ports that are SDM-activated
when an SDM instruction is used in the datalogger’s program. On CR3000 and
CR5000 dataloggers, the SDM protocol uses SDM-dedicated ports SDM-C1,
SDM-C2, and SDM-C3.
Each SDM device on the SDM bus must have a unique address. The EC150
has a factory default SDM address of 1, but may be changed to any integer
value between 0 and 14 (see Appendix A.2.1, SDM Address).
The sample rate for SDM output is determined by the datalogger program.
Data are output from the EC100 when a request is received from the datalogger
(for example, a prompted output mode). The number of data values sent from
the EC100 to the datalogger is also set by the user in the datalogger program.
CRBasic, the programming language used by Campbell Scientific dataloggers,
uses the EC100() instruction to get data from an EC150. This instruction is
explained in greater detail under Appendix A, EC150 Settings, and in
Appendix A.5, EC100 Configure() Instruction.
4.7 Automatic Heater Control
An advantage of the EC150’s low power consumption (5W) is that the
instrument remains at a temperature very close to ambient air temperature,
which is an important feature for eddy-covariance measurements. Under some
environmental conditions, however, the analyzer can become colder than
ambient air temperature which may increase the likelihood of frost or
condensation building on the optical windows. This will affect signal strength.
The EC150 design includes internal heaters located at the optical windows,
which aid in minimizing data loss during these specific environmental
conditions.
An automatic heater control algorithm can be activated from either Device
Configuration or ECMon by putting in a value of −2, or deactivated by putting
in a value of −1.
temperature that is a couple of degrees above the ambient dewpoint (or frost
point) to prevent condensation and icing from forming on the surface of the
optical windows.
The heater control will be disabled under any of the following conditions:
• Temperature of the detector housing is outside the −35°C to +55°C
• Temperature of the source housing exceeds 40°C
• Ambient temperature is outside the −35°C to +55°C range
• The supply voltage is below 10 V
range
i
The algorithm uses the internal heaters to maintain a
i
Automatic heater control is available in EC100 OS version 4.07 or greater and is turned on by
default starting with the OPEC program version 3.2.
5
Page 16

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
cl
o
ePP
ε
−
=
The algorithm uses the following environmental parameters to control the
heater:
• Analyzer body temperature, measured inside the source housing
(heater control does not allow the body temperature to drop below
ambient air temperature)
• Ambient relative humidity (in humidity greater than 80% heaters will
try to maintain internal temperature 2 degrees warmer than ambient)
• CO
cause the heater to turn on maximum power until the signals recover)
• Average slope of the CO
• Standard deviation of the CO
4.8 Theory of Operation
The EC150 is a non-dispersive mid-infrared absorption analyzer. Infrared
radiation is generated in the upper arm of the analyzer head before propagating
along a 15.0 cm (5.9 in) optical path as shown in FIGURE 5-1. Chemical
species located within the optical beam will absorb radiation at characteristic
frequencies. A mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) detector in the lower arm of
the gas analyzer measures the decrease in radiation intensity due to absorption,
which can then be related to analyte concentration using the Beer-Lambert
Law:
signal level (1 min average CO2 signal level; below 0.7 will
2
signal level over 1 min
2
signal over 1 min
2
where:
P is irradiance after passing through the optical path
is initial irradiance, ε is molar absorptivity, c is analyte
P
o
concentration, and
l is path length.
In the EC150, radiation is generated by applying constant power to a tungsten
lamp which acts as a 2200 K broadband radiation source. Specific
wavelengths are then selected using interference filters located on a spinning
chopper wheel. For CO
measurements, light with a wavelength of 4.3 µm is
2
selected as that corresponds to the asymmetric stretching vibrational band of
the CO
molecule. For H2O, the symmetric stretching vibration band is 2.7
2
µm.
The EC150 is a dual wavelength, single-beam analyzer. This design eliminates
the need for a separate reference cell and detector. Instead, the initial intensity
of the radiation is calculated by measuring the intensity of nearby, nonabsorbing wavelengths (4.0 µm for CO
and 2.3 µm for H2O). These
2
measurements mitigate measurement inaccuracy that may arise from source or
detector aging, as well as for low-level window contamination. For window
contamination that reduces the signal strength below 0.8, windows should be
cleaned as described in Section 8.3, Cleaning Analyzer Windows.
The chopper wheel spins at a rate of 50 revolutions per second and the detector
is measured 1024 times per revolution, resulting in a detector sampling rate of
51.2 kHz. The detector is maintained at −40°C using a three-stage
thermoelectric cooler and is coupled to a low noise pre-amp module.
6
Page 17

The EC100 electronics module digitizes and process the detector data (along
with ancillary data such as ambient air temperature and barometric pressure) to
give the CO
high measurement rate is beneficial when there is a need to synchronize the gas
measurements with additional sensors measured by the datalogger. To prevent
aliasing, measurements are filtered to a bandwidth that is specified by the user.
5. Specifications
5.1 Measurements
To compute carbon dioxide and water vapor fluxes using the eddy-covariance
method, the EC150 and a sonic anemometer measure:
These measurements are required to compute carbon dioxide and water vapor
fluxes using the:
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
and H2O density for each chopper wheel revolution (50 Hz). This
2
• Absolute carbon dioxide density (mg·m
–3
• Water vapor density (g·m
)
• Three-dimensional wind speed (m·s
–3
)
–1
; requires the CSAT3A)
• Sonic air temperature (°C; requires the CSAT3A)
• Air temperature (°C; requires an auxiliary temperature probe)
• Barometric pressure (kPa; requires an auxiliary barometer)
• Standard outputs:
o CO
density, H2O density
2
o Gas analyzer diagnostic flags
o Air temperature
o Air pressure
o CO
o H
signal strength
2
O signal strength
2
• Additional outputs from auxiliary instruments:
o u
, uy, and uz orthogonal wind components (requires the
x
CSAT3A)
o Sonic temperature (requires the CSAT3A, and is based on the
measurement of c, the speed of sound)
o Sonic diagnostic flags (from the CSAT3A)
Datalogger Compatibility: CR1000
CR3000
CR5000
Measurement
Rate: 100 Hz
ii
Output bandwidth
Output rate
ii
: 5, 10, 12.5, 20, or 25 Hz
: 10, 25 or 50 Hz
Operating temperature: −30° to 50°C
ii
user selectable
7
Page 18

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
Gas analyzer
iii
Measurement precision
density: 0.2 mg·m
CO
2
O density: 0.004 g·m
H
2
–3
Factory calibrated range
: 0 to 1000 µmol·mol–1
CO
2
H
O: 0 to 72 mmol/mol (37°C dewpoint)
2
Temperature: −30° to 50°C
Barometric pressure: 70 to 106 kPa
CO
performance
2
Zero max drift
iv
: ±0.55 mg·m–3·°C–1 (± 0.3
μmol·mol·°C
Gain drift: ±0.1% of reading·°C
Sensitivity to H
H
O performance
2
Zero max drift
O: ±1.1 x 10–4 µmol CO2·mol–1 H2O (max)
2
iv
: ±0.04 g·m–3·°C–1
(± 0.05 mmol·mol
Gain drift: ±0.3% of reading·°C
Sensitivity to CO
CSAT3A sonic measurement precision
: 1.0 mm·s–1
u
x
: 1.0 mm·s–1
u
y
: 0.5 mm·s–1
u
z
: ±0.1 mol H2O·mol–1 CO2 (maximum)
2
v
Sonic temperature: 0.025°C
(0.15 µmol·mol–1)
–3
(0.006 mmol·mol–1)
–1
)
–1
(maximum)
–1
·°C–1)
–1
(maximum)
CSAT3A sonic accuracy
vi
Offset error
, uy: < ±8 cm·s–1
u
x
: < ±4 cm·s–1
u
z
Gain error
Wind vector ±5° horizontal: < ±2% of reading
Wind vector ±10° horizontal: < ±3% of reading
Wind vector ±20° horizontal: < ±6% of reading
iii
noise rms, assumes:
o 25°C
o 85 kPa
o 14 g·m-3 H2O
o 597 mg·m
o 25 Hz bandwidth
iv
−30° to 50°C
v
noise rms
vi
assumes:
o −30° to +50°C
o wind speed <30 m·s
o azimuth angles between ±170°
-3
CO2
-1
8
Page 19

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
CSAT3 sonic reporting range
Full scale wind: ±65.6 m/s
Sonic temperature: −50° to 60°C
Auxiliary sensors
Barometer
EC150 temperature sensor
5.2 Output Signals
The EC100 electronics can output data from the EC150 by several means.
• Campbell Scientific SDM
• RS-485
• USB
• Analog out
vii
Internal basic barometer
Accuracy
−30° to 0°C: ±3.7 kPa at −30°C, falling linearly to
±1.5 kPa at 0°C
0° to 50°C: ±1.5 kPa
Measurement rate: 10.0 Hz
Optional enhanced barometer
Manufacturer: Vaisala
Model: PTB110
Accuracy: ±0.15 kPa (−30°C to 50°C)
Measurement rate: 1.0 Hz
Manufacturer: BetaTherm
Model: 100K6A1A Thermistor
Accuracy: ±0.15°C (−30
o
to 50°C)
Synchronous Device for Measurement communications protocol, or SDM, is a
proprietary serial interface developed by Campbell Scientific for
communication between a datalogger and a peripheral or sensor. In almost all
cases, SDM is the preferred communications protocol with the exception of
measurement heights requiring cable lengths greater than 100 meters. In this
case, RS-485 output is recommended. See Section 4.6.2.1, SDM Output, for
details on SDM output, see Appendix C, Alternate EC100 Outputs, for greater
detail on RS-485, USB, or analog outputs.
SDM communications are output as the FLOAT data type.
5.3 Physical Description
Optical measurement path length: 15.37 cm (6.05 in)
Spatial separation from
CSAT3A sampling volume: 5.0 cm (2.0 in)
vii
refer to manufacturer’s product brochure or manual for details
9
Page 20
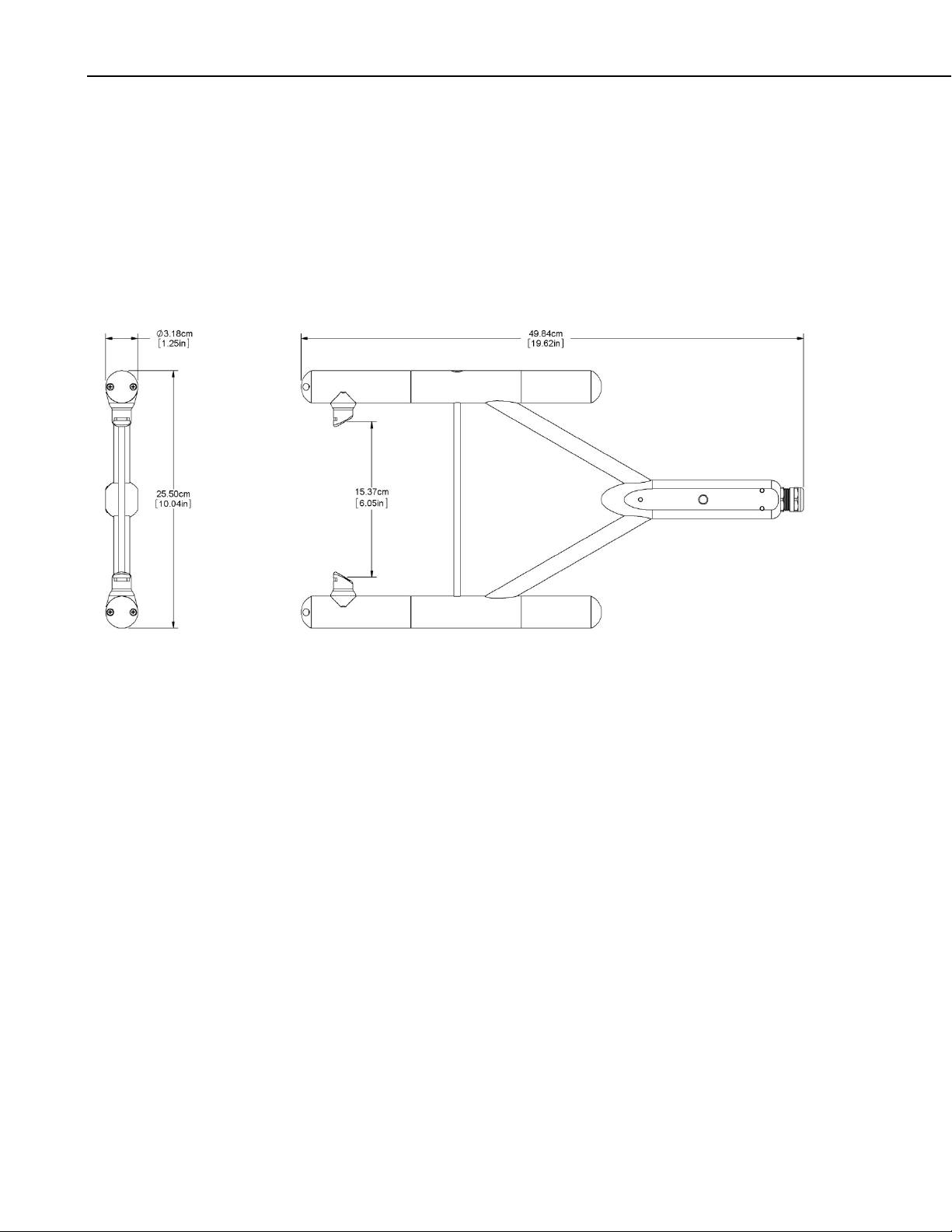
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
Dimensions
Head housing diameter: 3.2 cm (1.3 in)
Head length: 29.7 cm (11.7 in)
EC100 enclosure: 24.1 cm x 35.6 cm x 14 cm (9.5 in x
14.0 in x 5.5 in)
Weight
Analyzer and cable: 2 kg (4.4 lbs)
EC100 electronics and
EC100 enclosure: 3.2 kg (7.0 lbs)
FIGURE 5-1. Optical path and envelope dimensions of EC150 analyzer
head
5.4 Power Requirements
Voltage supply: 10 to 16 Vdc
Power at 25°C excluding CSAT3A: 4.1 W
Power at 25°C including CSAT3A: 5.0 W
Power at 25°C in power-down mode
(CSAT3A fully powered and EC150 off): 3.0 W
10
Page 21

6. Installation
NOTE
6.1 Orientation
6.2 Mounting Analyzer to Support Hardware
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
During operation, the EC150 should be positioned vertically (±15°) so that the
product label reads right side up and the upper arm (source) is directly above
the lower arm (detector). If the sensor is being used with a sonic anemometer,
the anemometer should be leveled and pointed into the prevailing wind to
minimize flow distortion from the analyzer’s arms and other supporting
structures.
The EC150 is supplied with mounting hardware to attach it to the end of a
horizontal pipe of 3.33 cm (1.31 in) outer diameter, such as the CM202 (pn
17903), CM204 (pn 17904), or CM206 crossarm (pn 17905).
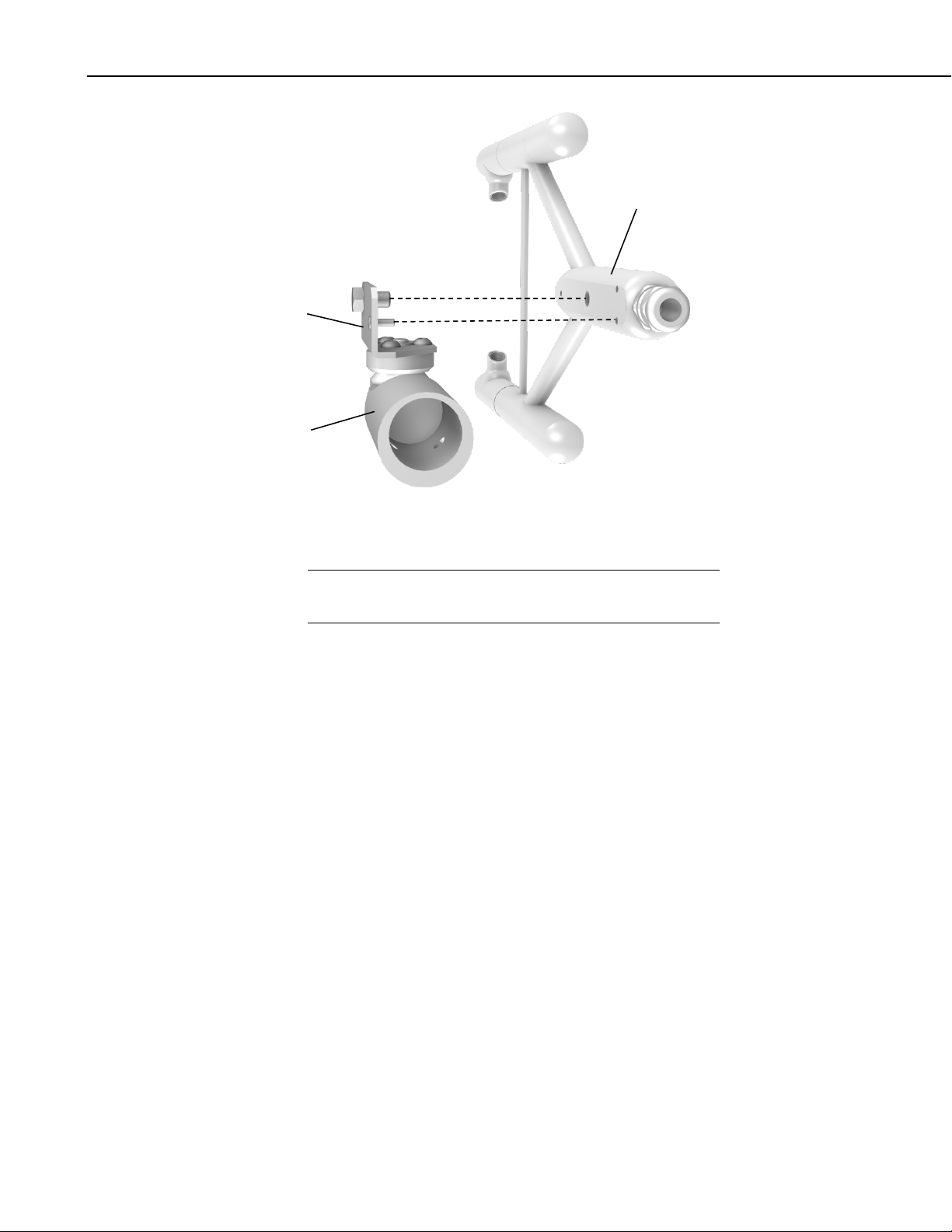
There are two different mounting brackets for the EC150. A head only
mounting bracket (pn 26785), and the EC150/CSAT3A mounting bracket (pn
26786). The two mounting brackets are shown in FIGURE 6-1.
The CSAT3A sonic anemometer head is an option when ordering the EC150
and the appropriate mounting bracket is included with the EC150 depending on
if the CSAT3A is ordered. If the user is already in possession of a CSAT3A
and intends to use it with the EC150, the proper mounting bracket should be
specified at time of order.
The screws and bolts for either mounting bracket are easily lost in
the field. Replacements are available through Campbell Scientific
or can be sourced elsewhere. For mounting bracket 26785, use pn
15807 (screw #8-32 x 0.250 socket head) and pn 26712 (screw
3/8-16 x 0.625 hex cap). For mounting bracket 26786, use pn
26711 (screw #8-32 x 0.250 shoulder cap) and pn 26712 (screw
3/8-16 x 0.625 hex cap).
FIGURE 6-1. Mounting bracket options for EC150 head only (pn
26785) or EC150 head with CSAT3A (pn 26786)
11
Page 22
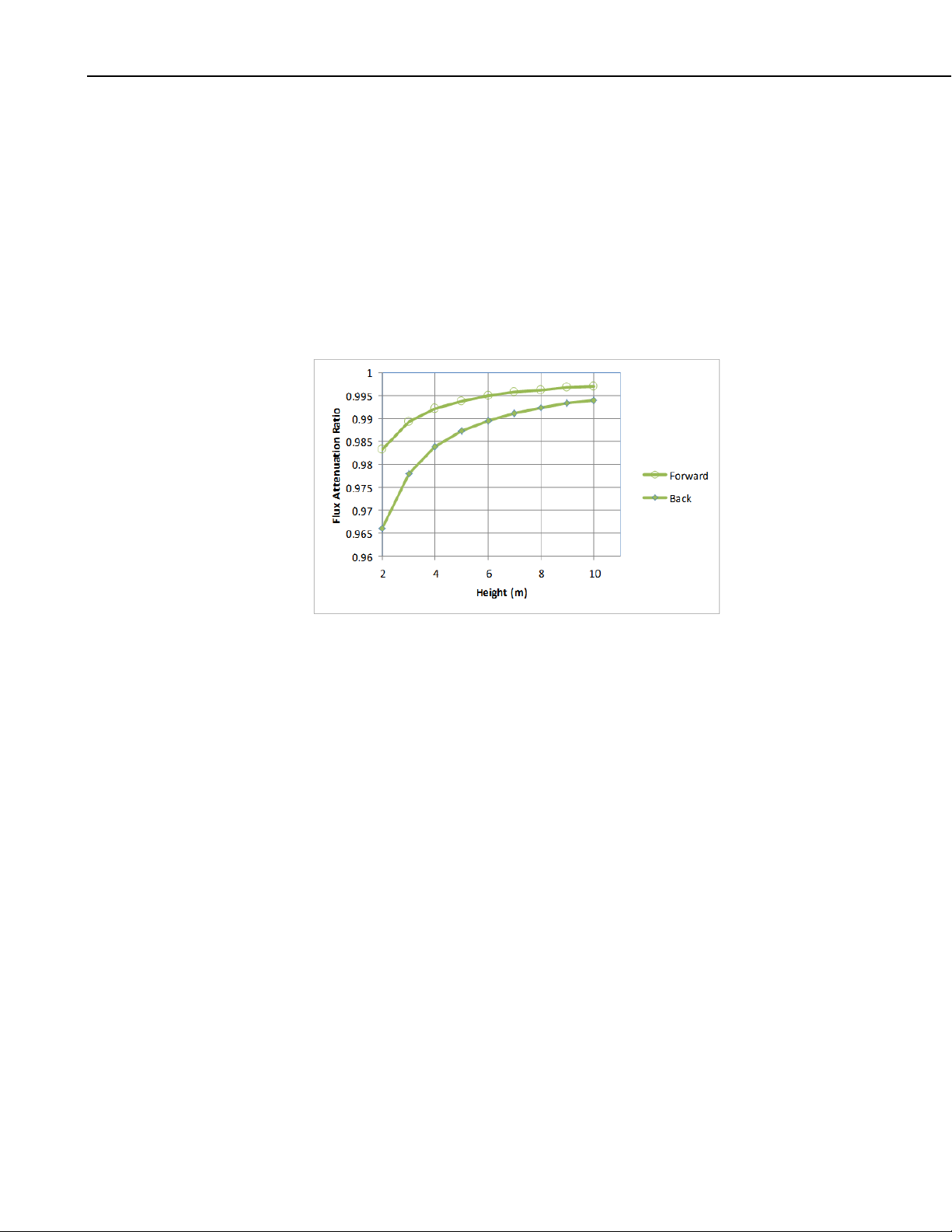
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
The mounting bracket for the EC50 with CSAT3A, pn 26786, allows the intake
source of the CSAT3A and EC150 to be positioned at varying degrees up to
approximately a 5.0 cm (2.0 in) offset. The positioning and offset is illustrated
in FIGURES 6-3 and 6-4. The change in positioning allows a small but
significant difference in the flux attenuation ratio. Campbell Scientific
generally recommends that the EC150 is positioned in the most forward
position to minimize errors caused by sensor separation. The tradeoff,
however, is greater flow distortion. The effect of spatial separation on flux
attenuation is greatest at lower measurement heights as shown in FIGURE 6-2.
A Campbell Scientific application engineer can help determine the best
positioning of the EC150 relative to the CSAT3A in scenarios where the
measurement height is below 10 meters.
FIGURE 6-2. Changes in flux attenuation ratio relative to sensor height
at the most fore and aft positions
12
Page 23
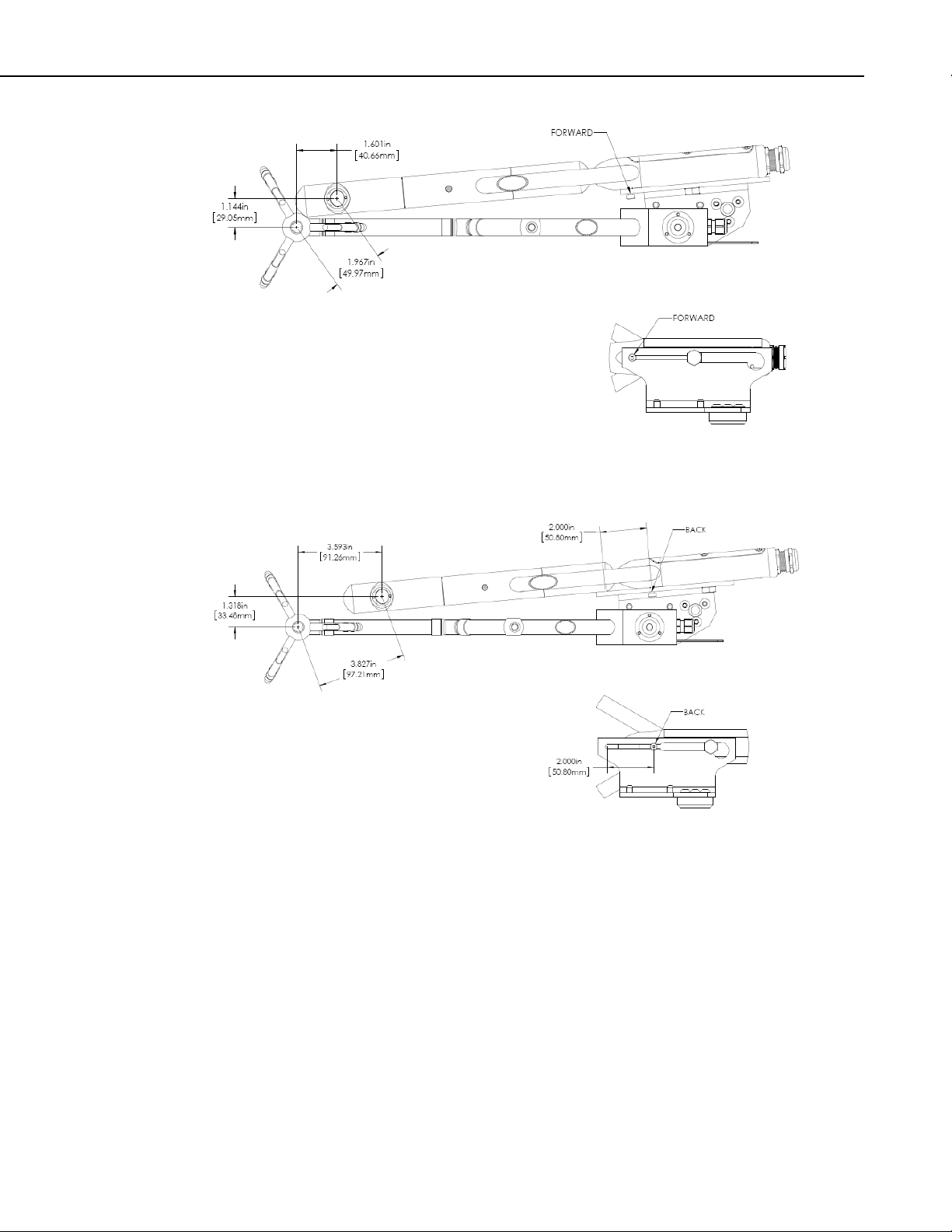
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
FIGURE 6-3. Mounting position of CSAT3A and EC155 with a 4.9 cm
sensor separation.
FIGURE 6-4. Mounting position of CSAT3A and EC155 with a 9.7 cm
sensor separation.
The following steps describe the normal mounting procedure. Refer to
FIGURE 6-5 and 6-6 throughout this section.
13
Page 24

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
WARNING
6.2.1 Preparing the mounting structure
1. Secure a CM20X crossarm to a tripod or other vertical structure using a
CM210 crossarm-to-pole bracket (pn 17767).
2. Point the horizontal arm into the direction of the prevailing wind.
3. Tighten all fitting set screws.
Do not carry the EC150 by the arms or the strut between the
arms. Always hold the sensor by the block where the upper
and lower arms connect.
6.2.2 Mounting EC150 with optional CSAT3A
The guideline below gives general instructions for mounting an EC150 and
optional CSAT3A to a mounting structure. The order of assembly will
somewhat be determined by the user’s application; primarily the height of the
tower. Steps 6, 7, and 8 should be performed in sequential order.
Please refer to all steps and the referenced figure of this section before deciding
on an assembly strategy. In general, Campbell Scientific suggests that if the
equipment is to be mounted at heights above what can be reached while
standing, to preassemble as much as possible and then hoist that assembly into
a position to be mounted on the appropriate crossarm.
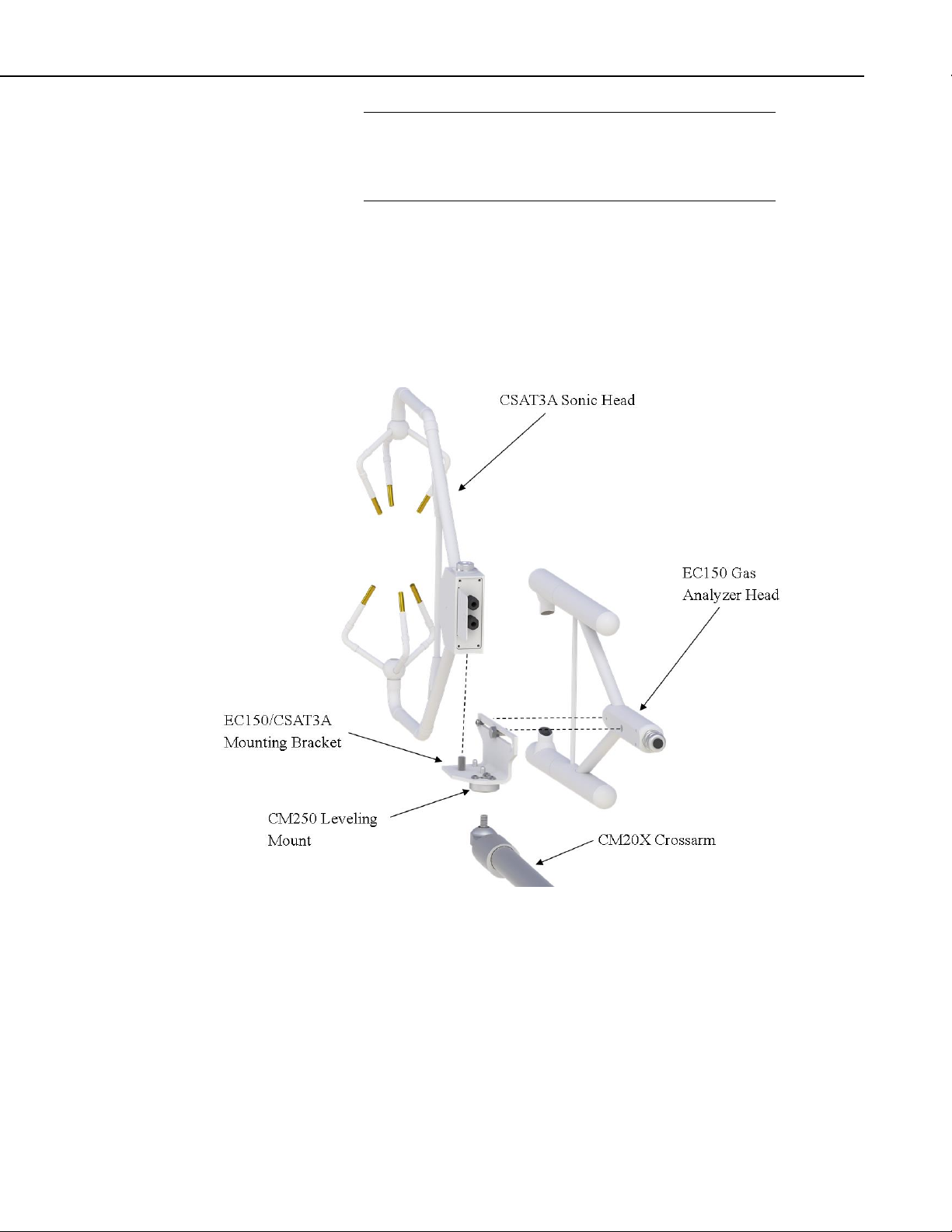
1. Bolt the EC150/CSAT3A mounting bracket (pn 26786; see FIGURE
6-1) to the CM250 leveling mount (pn 26559).
2. Install the CSAT3A sonic head to the EC150/CSAT3A mounting
bracket by aligning the threaded hole on the CSAT3A sonic head with
the hole on the bracket.
3. Insert and finger-tighten the bolt, making sure the bolt is not cross-
threaded. Finish tightening with a wrench.
4. Install the assembly to the end of the crossarm by fitting the leveling
mount over the end of the crossarm.
5. Tighten the set screws on the leveling mount.
6. Install the EC150 gas analyzer head to the EC150/CSAT3A mounting
bracket by tightening the mounting screw and loosely thread the
mounting bolt into the analyzer head.
7. Align the analyzer parallel with the vertical plate of the mounting
bracket and insert the mounting screw and bolt into the slot of the
mounting bracket.
8. Carefully slide the analyzer forward to the desired position. For a
more detailed discussion of positioning the EC150 relative to the
CSAT3A, see Section 6.2, Mounting Analyzer to Support Hardware.
14
Page 25
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
CAUTION
Avoid crashing the arms of the sensors together. The arms
of the analyzer should slide in between the claws of the
CSAT3A; the sonic head may need to be loosened and
repositioned to do this.
10. Tighten bolts and check that the analyzer is oriented vertically such
that the label is right-side-up and the upper arm (source) is directly
above the lower arm (detector).
11. If the assembly is not level, slightly loosen the bolt that holds the
mounting bracket on the leveling mount and adjust the assembly until
the leveling bubble on the top of the CSAT3A head is within the
bullseye. Retighten the bolt.
FIGURE 6-5. Exploded view of mounting CSAT3A and EC150
15
Page 26
EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
CAUTION
EC150 Gas
Analyzer Head
EC150 Head-Only
Mounting Bracket
CM250 Leveling Mount
FIGURE 6-6. Exploded view of mounting the EC150 without the
CSAT3A
Over-tightening bolts will damage or deform mounting
hardware.
6.2.3 Mounting EC150 without CSAT3A
The instructions for mounting the EC150 without the CSAT3A should
generally follow those in Section 6.2.2, Mounting EC150 with optional
CSAT3A, but requires the use of a different mounting bracket as described
below and in Section 6.2, Mounting Analyzer to Support Hardware.
1. Bolt the EC150 head-only mounting bracket (pn 26785; see FIGURE
6-1) to the CM250 leveling mount (pn 26559).
2. Mount the EC150 gas analyzer head to the EC150 head-only
mounting bracket and follow the steps outlined in Section 6.2.2,
Mounting EC150 with Optional CSAT3A, for preassembly.
3. Mount this assembly to the end of the crossarm by fitting the leveling
mount over the end of the crossarm.
4. Tighten the set screws on the leveling mount.
5. If the assembly is not level, slightly loosen the bolt that holds the
mounting bracket on the leveling mount and adjust the assembly.
Retighten the bolt.
16
Page 27

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
CAUTION
NOTE
Use caution when handling the EC150 gas analyzer head.
The optical source may be damaged by rough handling,
especially while the EC150 is powered.
The CSAT3A sonic anemometer is an updated version of the
CSAT3, designed to work with the EC100 electronics. An existing
CSAT3 may be upgraded to a CSAT3A. Contact a Campbell
Scientific application engineer for details.
6.2.4 Attaching EC100 Electronics Enclosure to Mounting Structure
The EC100 electronics enclosure can be mounted to the mast, tripod leg, or
other part of the mounting structure but must be mounted within 3.0 m (10.0 ft)
of the sensors due to restrictions imposed by the cable length.
1. Attach the EC100 enclosure mounting bracket (pn 26604) to the pipe
of the mounting structure by loosely tightening the u-bolts around the
pipe. The u-bolts are found in the mesh pocket inside the EC100
enclosure.
2. For configurations in which the pipe is not vertical (such as a tripod
leg as in FIGURE 6-7) rotate the bracket to the side of the pipe so that
when the enclosure is attached it will hang vertically upright. Make
any necessary angle adjustments by loosening the four nuts and
rotating the bracket plates relative to one another. If the necessary
angle cannot be reached in the given orientation, remove the four nuts
completely and index the top plate by 90° to allow the bracket to
travel in the other direction (see FIGURE 6-7).
FIGURE 6-7. EC100 enclosure mounting bracket mounted on a vertical
mast (left) and a tripod leg (right)
3. Tighten all nuts after final adjustments have been made.
4. Attach the EC100 enclosure to the bracket by loosening the bolts on
the back of the enclosure, hanging the enclosure on the mounting
17
Page 28

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
bracket (it should slide into place and be able to securely hang from
the bracket), and retightening the bolts (see FIGURE 6-8).
FIGURE 6-8. Exploded view of mounting the EC100 enclosure
5. Remove the EC100 enclosure desiccant from the plastic bag and put it
back in the mesh pocket of the enclosure.
6. Adhere the humidity indicator card to the inside of the door of the
enclosure.
6.2.5 Install the EC150 Temperature Probe
The temperature probe should be mounted such that it measures at the same
height as the sample volume of the EC150 and the CSAT3A.
1. Attach the R.M. Young 41303-5A 6-plate solar radiation shield (pn
4020) to the mast with the included u-bolt.
2. Insert the end of the temperature probe into the hole on the bottom of
the shield, see FIGURE 6-10.
3. Tighten screws to hold the probe in place.
18
Page 29

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
FIGURE 6-9. EC150 temperature probe
FIGURE 6-10. Solar radiation shield with EC150 temperature probe
6.3 Wiring and Connections
FIGURES 6-11 and 6-12 show EC100 electronics panel and the bottom of the
EC100 enclosure, respectively. Refer to these figures during the wiring and
connecting of the various auxiliary sensors.
FIGURE 6-11. EC100 electronics front panel showing EC100 as
shipped (left) and after completed wiring and connections (right)
19
Page 30

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
NOTE
FIGURE 6-12. Bottom of EC100 enclosure
6.3.1 Connecting the EC150 Gas Analyzer Head
1. Remove the black rubber cable entry plug (pn 26224) that is located on the
bottom right of the EC100 enclosure labeled Cable 3. (This plug can be
stored in the mesh pocket of the enclosure.)
2. Insert the cable entry plug that is attached to the large cable of the EC150
gas analyzer head into the vacant slot.
3. Push the connector at the end of the cable onto its mating connector
(labeled Gas Analyzer) and tighten the thumbscrews (see FIGURE 6-12).
The EC150 gas analyzer cable is approximately 3.0 m (10.0 ft) in length.
6.3.2 Connect the CSAT3A Sonic Head
Skip the following two steps if not using a CSAT3A.
1. Similar to connecting the gas analyzer head, remove the black rubber cable
entry plug found on the bottom left of the EC100 enclosure.
2. Insert the cable entry plug on the CSAT3A cable into the slot and connect
the male end to the female connector labeled Sonic Anemometer on the
EC100 electronics (see FIGURE 6-12).
20
Unlike previous models of the CSAT3 3D sonic anemometer, the
CSAT3A sonic head and the EC150 gas analyzer head have
embedded calibration information. This means that any CSAT3A
and any EC150 may be used with any EC100.
Page 31

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
CAUTION
CAUTION
6.3.3 Connect the EC150 Temperature Probe
1. Unscrew the temperature connector cover which is found on the bottom of
the EC100 enclosure labeled Temperature Probe (see FIGURE 6-12).
2. Insert the three-prong temperature probe connector into the female
connector on the enclosure and screw it firmly in place. The EC150
temperature probe cable is approximately 3.0 m (10.0 ft) in length.
6.3.4 Ground the EC100 Electronics
1. Attach a user-supplied heavy gauge wire (12 AWG would be appropriate)
to the grounding lug found on the bottom of the EC100 enclosure.
2. Earth (chassis) ground the other end of the wire using a grounding rod.
For more details on grounding, see the CR3000 datalogger manual
grounding section.
Grounding the EC100 is critical. Proper grounding to earth
(chassis) will ensure maximum electrostatic discharge
(ESD) protection and improve measurement accuracy.
Do not connect or disconnect the EC150 gas analyzer head
or CSAT3 sonic head once the EC100 is powered.
6.3.5 Connect SDM Communications to the EC100
The EC150 supports SDM communications with datalogger. SDM is the
preferred communications to the EC100. RS-485 may be necessary in some
situations. The USB is used mainly for diagnostic and trouble shooting.
Connection instructions for these modes can be found in Appendix C, Alternate
EC100 Outputs.
CABLE4CBL-L (pn 21972) is used for connecting SDM communications to
the EC100. The “L” designation denotes the length of the cable which is userspecified.
1. Loosen the nut on one of the cable entry seals (Cable 1) on the bottom of
the EC100 enclosure (refer to FIGURE 6-12).
2. Remove plastic plug and store in mesh pocket of enclosure.
3. Insert the cable while referring to TABLE 6-1 for details on which color of
wire in the cable should be connected to each terminal found on the SDM
connector of the EC100 panel.
4. Once the wires of the cable are fully connected, retighten the nut on the
appropriate cable entry.
21
Page 32

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
TABLE 6-1. EC100 SDM output to a Campbell Scientific CR1000,
EC100 Channel Description Color
SDM-C1 SDM Data Green
SDM-C2 SDM Clock White
SDM-C3 SDM Enable Brown
G Digital Ground Black
G Shield Clear
6.3.6 Wire Power and Ground the EC100
1. Feed cable CABLEPCBL-L (pn 21969-L) through Cable 2 at the bottom
of the EC100 enclosure (see FIGURE 6-12) and attach the ends into the
green EC100 power connector (pn 3768).
2. Plug the connector into the female power connector on the EC100 panel.
Ensure that the power and ground ends are going to the appropriate
terminals labeled 12V and ground, respectively.
CR3000, or CR5000 Datalogger
3. Connect the power cable to a power source. The power and ground ends
may be wired to the 12V and G ports, respectively, of a Campbell
Scientific datalogger or to another 12 Vdc source.
Once power is applied to the EC100, three LED status lights on the EC100
panel will illuminate. The power LED will be green if the power supply
voltage is between 10 to 16 Vdc. The gas LEDs will be orange until the gas
head has warmed up. The sonic LED will be red while the sonic acquires the
ultrasonic signals. The sonic and gas LEDs will turn green if there are no
diagnostic warning flags. Three green LEDs indicate that the instrument is
ready to make measurements.
The EC150 power-up sequence takes under two minutes to complete. During
power up the gas LED will be orange. If after two minutes the gas LED turns
green, power-up sequence has been completed successfully. If the gas LED
turns red, a diagnostic flag has been detected. Check the individual diagnostic
bits to determine the specific fault.
Diagnostics may be monitored using the Status window of ECMon (see
Appendix A.3, ECMon), the user interface software included with the EC150
(see Appendix A, EC150 Settings), or with a datalogger. The diagnostics may
reveal that the unit needs to be serviced (for example, cleaning the optical
windows on the EC150, cleaning the CSAT3A transducers of ice or debris, etc.
See Section 8, Maintenance and Troubleshooting).
7. Zero and Span
7.1 Introduction
Calibration of optical instrumentation like the EC150 may drift slightly from
the calibration that was performed in the factory with time and exposure to
22
Page 33

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
NOTE
CAUTION
natural elements. A zero-and span procedure should be performed after
installation of the instrument to give appropriate baseline readings as a
reference. A zero-and-span procedure should also be performed occasionally
to assess drifts from factory calibration. In many cases, a zero and span can
help resolve problems that are being experienced by the user during operating
the EC150. For example, a zero-and-span procedure should always be
performed on the analyzer after changing the internal chemicals. Before
performing a zero-and-span procedure, clean the windows of the EC150 as
described in Section 8.3, Cleaning Analyzer Windows.
After the first several zero-and-span procedures, the rate of drift in gain and
offset (explained later in this section) should be analyzed to better determine
how frequently the zero-and-span procedure should be performed once the
instrument has been put into service.
The first part of the procedure listed below simply measures the CO
span and zero without making any adjustments. This allows the CO
and H2O
2
and H2O
2
gain factors to be calculated. These gain factors quantify the state of the
analyzer before the zero-and-span procedure and, in theory, could be used to
correct recent measurements for drift. The last part of the zero-and-span
procedure adjusts internal processing parameters to correct subsequent
measurements.
If the zero-and-span procedure is being performed off site (for example, in a
laboratory), be sure to mount the EC150 on the zero-and-span stand (refer to
FIGURE 7-1). This will ensure the analyzer is in the correct upright
orientation and has the correct optical alignment.
The zero-and-span procedure must be performed correctly and not rushed.
Allocate at least one hour (preferably more) for the procedure. Ensure that the
readings are stable and all sensors are properly connected and functioning.
It is conceivable that there are circumstances in which both a zero and a span
cannot be performed by the user. In these instances, it is recommended that the
user attempt to perform a zero of the instrument even if spanning is not
possible or inconvenient. The information gained through zeroing the
instrument can help troubleshoot problems that may be encountered during
field operations.
The water vapor measurement is used in the CO2 concentration
calculations to correct instrument and pressure broadening effects.
To achieve good CO
calibration, it is imperative to maintain a
2
reasonable water vapor calibration.
7.2 Zero and Span Procedure
Resting the analyzer on its side during the zero-and-span
procedure may result in measurement inaccuracy.
This section gives instructions for performing a zero-and-span procedure, and
should be referred to any time a zero-and-span procedure is undertaken.
Check and then set the EC150 zero and span according to the following steps:
23
Page 34

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
CAUTION
1. Remove power from the EC100/EC150. Unplugging the power cable
from the EC100 is the easiest way to accomplish this.
2. Remove wicks from the snouts of the analyzer.
3. Clean windows and snouts with isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free, non-
abrasive tissue or cloth as described in Section 8.3, Cleaning Analyzer
Windows.
Make sure any residual alcohol and water completely
evaporate from the analyzer before proceeding with the
zero-and-span procedure.
4. Position the EC150 zero-and-span shroud (pn 26390) over the upper and
lower snouts. See FIGURE 7-1 for guidance with the following steps.
a. Twist the two ends of the shroud together to minimize the length of
the shroud. Make sure the rubber seals on the ends of the shroud are
clean and in good condition.
b. Position one end of the shroud over the lower snout and twist the top
part of the shroud, allowing it to extend and cover the upper snout.
c. Continue twisting the shroud until it is fully extended and covering
both snouts.
d. Twist the shroud so that the gas lines and temperature thermistor
cable are directed towards the back of the sensor.
e. Hang the lines and cable over the trunk of the sensor to alleviate any
strain on the optical arms. See FIGURE 7-1.
24
FIGURE 7-1. Zero-and-span shroud mounted on the zero-and-span
stand
Page 35

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
NOTE
5. Disconnect the EC150 temperature probe from the EC100 and connect the
shroud temperature probe in its place.
6. Connect the EC100 to a PC with the EC100 USB cable (pn 26563).
7. Resume power to the EC100/EC150.
8. Wait for all the Gas and Power LED status lights on the EC100 panel to
turn green.
9. Launch ECMon, select the appropriate USB port, and click Connect. The
main screen should now be reporting real-time CO
and H2O
2
concentrations.
10. Click Zero/Span. A graph will appear in the lower half of the zero-and-
span window showing measured CO
and H2O concentrations (see
2
FIGURE 7-2).
11. Connect a gas cylinder of known CO
concentration to a pressure
2
regulator, then to a flow controller, and finally to the intake of the shroud.
Optimally, the concentration of span CO
being measured in the field.
of CO
2
should be near the concentration
2
12. Beginning with both the pressure regulator and flow controller turned off,
use the pressure regulator to slowly increase pressure to the recommended
setting for the flow controller.
13. Set the flow between 0.2 and 0.4 LPM.
14. Monitor the ECMon zero-and-span graph and wait for the CO
2
measurement readings to stabilize (5 to 10 minutes). Once stable, record
the reported CO
concentration.
2
Use a mixture of CO2 in air (not nitrogen) for the CO2 span gas.
The use of pure nitrogen as the carrier gas will lead to errors
because the pressure-broadening of the CO
absorption lines is
2
different for oxygen and nitrogen.
25
Page 36

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
NOTE
FIGURE 7-2. ECMon zero-and-span window
15. Remove the CO
O span gas from a dew-point generator or another standard reference.
H
2
span gas from the inlet of the shroud and replace it with
2
As water molecules can adsorb to inside of the tubing and the shroud, it
may take 30 minutes or more for the H
O concentration to stabilize. The
2
user may increase the flow rate for the first several minutes to more
quickly stabilize the system before returning it to between 0.2 and 0.4
LPM to make the H
O measurement. Record the reported H2O
2
concentration. If a stable reading is not achieved within 45 to 60 minutes,
troubleshooting steps should be undertaken.
16. Remove the H
O span gas, and connect a zero air source (no CO2 or H2O)
2
to the inlet tube of the shroud. As described in step 11, use a pressure
regulator and flow controller so that zero air flows through the shroud
between 0.2 and 0.4 LPM. Wait for the measurement readings to stabilize
and record the reported values for CO
and H2O concentrations. If the
2
readings remain erratic, ensure that flow of the zero air is sufficient and
the shroud is correctly seated on the snouts.
If the quality of a zero gas is unknown or suspect, a desiccant and
CO2 scrubber should be added between the zero gas tank and the
shroud to confirm that the gas being sampled during the zero
procedure is actually a zero air source.
26
17. Along with recording the CO2 and H2O zero and span values, also record
the date and time, and temperature. With this information the user can
examine zero/span drift with time and temperature.
Page 37

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
measmeas
actual
zerospan
span
gain−=
NOTE
Compute the drift in instrument gain using the following equation:
where,
• span
• span
• zero
Note that in the zero-and-span window of ECMon, span
= known concentration of the span gas
actual
= measured concentration of the span gas
meas
= measured concentration in zero gas
meas
actual
the right of the box where the user enters the span dewpoint temperature.
The software calculates span
by taking into account the dewpoint
actual
temperature and current ambient temperature and pressure. The equations
used for this calculation may be found in Appendix D, Useful Equations.
If drift (offset or gain) for CO
replace the desiccant and CO
Scrubber Bottles).
CO
2
or H2O is excessive, it may be time to
2
scrubber bottles (see Section 8.5, Replacing
2
18. With zero air still flowing and measurements stabilized, click on the Zero
CO
and H2O button in the ECMon zero-and-span window.
2
Air flow into the shroud should be close to the recommended rate. If the
flow is too low, the shroud will not be properly flushed. If it is too high, the
air pressure within the shroud will be too high, and the analyzer will not be
zeroed and spanned properly.
19. Remove the zero air source and replace it with the CO2 span gas.
20. Allow the gas to flow through the shroud, maintaining a flow between 0.2
and 0.4 LPM. Wait for readings to stabilize.
is reported to
21. In the zero-and-span window, enter the known concentration of CO
(in
2
ppm) in the box labeled Span Concentration (dry) and press Span.
22. Replace the CO
span gas with an H2O span gas of known dewpoint.
2
Allow the gas to flow through the shroud. Higher flows may be desired
for a couple of minutes to more quickly establish equilibrium before
resuming a flow between 0.2 and 0.4 LPM. Wait for the readings to
stabilize.
23. Enter the known dewpoint (in °C) in the box labeled Span Dewpoint and
press Span.
24. The zero-and-span procedure is now complete. Remove the shroud,
reconnect the EC150 temperature probe, and prepare the site for normal
operation. Verify that readings from the instrument are reasonable.
Record the zero and span coefficients for future reference and to keep
track of the rate of the analyzer drift. Make sure that the coefficients are
between 0.9 and 1.1. Negative or numbers larger than 1.1 are usually an
indication of improper calibration.
27
Page 38

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
TABLE 8-1. Rain Wick Replacement Parts
8. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
EC150 operation requires six maintenance tasks:
• Routine site maintenance
• Wick maintenance
• Analyzer window cleaning
• Zero and span
• Replacing the analyzer desiccant/scrubber bottles
• Factory recalibration
8.1 Routine Site Maintenance
The following items should be examined periodically:
• Check the humidity indicator card in the EC100 enclosure. If the highest
dot has turned pink, replace the desiccant bags. Replacement desiccant
bags may be purchased as pn 6714.
• Make sure the Power and Gas LED status lights on the EC100 panel are
green. If not, check the individual diagnostic bits for the specific fault.
See TABLE 8-2, Diagnostic Flags of Sonic Status LED, and Section 8.7.3,
LED Status Lights, for more information.
8.2 Gas Analyzer Wicks
The windows of the EC150 gas analyzer are polished and slanted at an angle to
prevent water from collecting on their surfaces. However, due to increased
surface tension at the interface with the snout, water can pool at the edges and
partially block the optical path and attenuate the signal. To minimize the
occurrence of such events and the resulting data loss, consider using the wicks
listed in TABLE 8-1. The weave of the wicking fabric promotes capillary
action that wicks the water away from the edge of the windows. The seam and
the straight edge of the wicks are permeated with a rubberized compound to
prevent them from shifting during operation.
Proper installation of the wicks is critical. They should not block or encroach
on the optical path. Before installation, record signal strengths for both H
and CO
that these values are unchanged.
. Following installation, repeat testing of signal strength and check
2
Wick
Bottom wick 28652 Fab EC150/IRGASON rain
Top wick 28653 Fab EC150/IRGASON rain
Campbell Scientific, Inc.
Part Number
2
Campbell Scientific, Inc.
Description
wick bottom
wick top
O
The top wick has a short seam which must be aligned with the short side of the
top snout. The angled edge of the wick must closely follow the edge of the
window without encroaching on the optical path. See FIGURE 8-1 for
guidance on proper positioning of the wick.
28
Page 39

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
The bottom wick is installed in a similar manner, except the long seam should
be aligned with the long side of the bottom snout. Once in place, the wicks
should fit snuggly over the cylindrical part of the snout without any creases or
wrinkles. The windows should be cleaned after the installation of the wicks to
ensure that there are no fingerprints left on critical surfaces. See Section 8.3,
Cleaning Analyzer Windows, for specifics on cleaning the EC150 windows.
Wicks are constructed with a UV-resistant fabric and should be functional for
an extended period of time but should be inspected every six months. Check
for contamination from dust, pollen, pitch or other debris. If needed, wash the
wicks in warm water with mild detergent or replace them.
FIGURE 8-1. Proper location of the gas analyzer top wick (left) and
bottom wick (right)
8.3 Cleaning Analyzer Windows
The windows of the analyzer should be cleaned if the signal strength for CO2
O drops below 0.7 (70% of the original value). These values may be
or H
2
monitored in the output data, or they can be viewed with ECMon.
To clean the windows, use isopropyl alcohol and a cotton swab or a lint-free
tissue or cloth. Signal strengths should be restored to values close to 1.0 after
cleaning the analyzer windows. In some cases, depending on the contaminant,
cleaning with distilled water can achieve better results. In severe cases a mild
detergent similar to ordinary hand soap can be used.
8.4 Zero and Span
As discussed in Section 7, Zero and Span, the zero-and-span procedure can
resolve many of the issues a user may encounter. Along with being a valuable
troubleshooting method, a zero-and-span procedure should be performed as
routine maintenance even when the EC150 is producing expected results.
Campbell Scientific recommends that a zero-and-span procedure be performed
at least every six months, but may be required more frequently depending on
conditions.
29
Page 40

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
DANGER
NOTE
Performing frequent zero-and-span procedures when the instrument is first put
into use to determine the drift from factory calibration, will give a good
guideline for the frequency that the procedure should be performed.
To perform a maintenance zero and span, follow the same steps as in Section 7,
Zero and Span.
8.5 Replacing CO2 Scrubber Bottles
If more than one year has passed since replacing the desiccant/scrubber or if
the zero-and-span readings have drifted excessively (see Section 7, Zero and
Span), the desiccant/scrubber bottles within the EC150 analyzer head should be
replaced. FIGURE 8-2 gives the details needed for the following steps.
The scrubber bottles contain strong oxidizing agents. Avoid
direct contact with the chemicals inside the bottles. Also
ensure your work area is well ventilated and free of any
reactive compounds, including liquid water. Store used
chemical bottles in a sealed container until disposal.
Replacing Scrubber Bottles
1. Twist the scrubber bottle covers of the upper and lower arms counter
clockwise until they detach (they should loosen by hand).
2. Remove the EC150 chemical bottles (pn 26510) from inside the
covers, and replace them with new bottles with the lid of the bottle
pointing toward the snouts of the analyzer (see FIGURE 8-2).
Before opening the covers, have the chemical bottles ready so that
the time the internal volume of the analyzer is exposed to the
environment is minimized.
3. Screw the covers back on the arms. Do not over tighten.
4. Allow the sensor to equilibrate for at least 24 hours (longer if in high
humidity).
5. After 24 hours, perform a zero-and-span procedure. If readings
continue to be suspect, the sensor may need to be recalibrated at the
factory (see Section 8.6, Factory Recalibration, below).
The chemical bottles should be disposed of according to local and federal
regulations. For more information, Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) forms
for the chemicals are included in Appendix E, Material Safety Data Sheets
(MSDS).
30
Page 41

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
FIGURE 8-2. Replacing the desiccant/CO
8.6 Factory Recalibration
When the EC150 is manufactured, it goes through an extensive calibration
process, covering a wide range of temperatures, pressures, and gas
concentrations. All CO
in ambient air that are traceable to the WMO Mole Fraction Scale
CO
2
maintained by the Central Carbon Dioxide Laboratory and the Carbon Cycle
Greenhouse Gases Group of the Global Monitoring Division/National
Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration in Boulder, CO, USA.
The long-term calibration stability of the EC150 is achieved by the use of high
quality optical and electrical components, a long lasting IR source, and a stable
MCT detector. The subtle, long-term aging effects are usually compensated by
the user with the field zero-and-span adjustments which bring the performance
of the analyzer within the original specifications. Proper handling and regular
maintenance of the instrument should make factory recalibration unnecessary
in most applications. If zero and span accessories and calibration standards are
not available, Campbell Scientific can provide two-point calibration upon
request (pn 27312).
However, if a user finds that signal strength outputs of greater than 0.75 cannot
be achieved after both cleaning the windows and a subsequent zero-and-span
procedure, contact Campbell Scientific. An application engineer will help
determine if the instrument should be returned to Campbell Scientific for a
factory recalibration.
scrubber bottles
2
calibration gases used in this process are mixtures of
2
For the CSAT3A, refer to the CSAT3 instruction manual for information on
recalibration.
31
Page 42

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
8.7 Troubleshooting
8.7.1 Data Loss During Precipitation Events
In extremely humid environments or after a precipitation event, data loss can
occur. Wicks on the analyzer windows help mitigate some of these data loss
events but cannot control for all conditions. In addition to wicking, heaters in
the snouts can aid in the prevention of data loss during precipitation and
condensation events. The heaters are automatically controlled by the EC100
electronics. The automatic heater control is activated using the Device
Configuration or ECMon software. A value of −1 turns the automatic heater
control off and a value of −2 turns it on.
8.7.2 EC100 Diagnostics for Gas Analyzer Troubleshooting
Before troubleshooting and servicing the analyzer, become familiar with
Section 2, Cautionary Statements.
The EC100 is also programmed to recognize problems with an associated gas
analyzer and reports those with LED status lights and diagnostic flags. The
two types of warnings are described in the sections that follow.
8.7.3 LED Status Lights
The EC100 has three LED status lights located in the upper left corner of the
front panel which provide immediate visual feedback and warn the user of
potential problems with the measurements. During normal operation all
STATUS LEDs should be green as shown in FIGURE 8-3.
FIGURE 8-3. LED status during normal operation
32
• POWER Status LED
The POWER status LED will turn red if the supply voltage is outside the
specified limits (see Section 5.4, Power Requirements). The user should
check the battery voltage or the power supply voltage and ensure that the
Page 43

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
TABLE 8-2. Diagnostic Flags of Sonic Status LED
power supply cable is adequate gage and does not cause excessive voltage
drop.
• SONIC Status LED
The SONIC status LED will turn red if there is no CSAT3A connected to
the EC100 electronics or if any of the six sonic diagnostic flags are set.
Please refer to TABLE 8-2 and to the CSAT3A instruction manual for
more detail information on sonic diagnostic flags.
Diagnostic
Flag Flag Name Action
0 Sonic amplitude low Clear debris from sonic
path
1 Sonic amplitude high No action
2 Poor signal lock Clear debris from sonic
Return to factory for
calibration
3 Delta temperature warning flag Return to factory for
4 Sonic acquiring signals No action
5 Signature error in reading
• GAS Status LED
The GAS status LED will turn red in the following situations:
The GAS status LED will turn orange during the initial power up
sequence, usually 1-2 min and will turn to green when the sequence is
completed and if no diagnostic flags have been set high.
8.7.4 Diagnostic Flags
calibration
Check sonic umbilical
CSAT3A sonic head calibration
o The EC150 gas head is not connected
o Any of the gas diagnostic flags are set
cable connection
Cycle power
Contact an application
engineer for a new
calibration file and upload
procedure
The EC100 operating system has extensive self-diagnostic capabilities.
TABLE 8-3 lists 23 (numbered 0 through 22) diagnostic flags that allow the
user to identify problems associated with the operation and the performance of
the EC100 electronics and the gas analyzer. There is one master flag
(BAD_DATA, or flag 0) that is set when measurements are compromised.
33
Page 44

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
TABLE 8-3. Diagnostic Flags and Suggested Actions
NOTE
If any of the remaining 22 flags are set, the master flag (BAD_DATA) is set as
well, so that the user can filter data based on this flag only. When this flag is
set, more detailed information about the nature of the problem can be obtained
from the 22 slave flags.
When a flag is set due to improper configuration of the analyzer, inadequate
power supply voltage or grounding, extreme environmental conditions, and
unreliable or missing connections, the user should try to correct the problem by
checking the instrument setup, verifying that all components are properly
connected and configured, and that operating conditions are within operational
specifications. Other flags are associated with the proper function of the
internal components of the analyzer. If any of these flags are set, consult with
a Campbell Scientific application engineer for assistance in diagnosing the
problem and, if necessary, arrange to send the instrument for repair.
If connected to a datalogger, the EC100 could be automatically
configured under CRBasic program control. The user should
verify the proper configuration in the datalogger program.
Flag
Number Flag Name Comments
0 Bad Data Set when any of flags 1 through 22 is
set. Discard all data with this flag is set.
If the flag persists, identify which of
flags 1 through 22 is set. When this flag
is set, the GAS status LED on the
EC100 electronics panel is illuminated
red.
1 General Fault Reserved for future use.
2 Startup Set during the initial power up of the
analyzer. It stays set only until all
control loops have settled. The infrared
detector temperature and the motor
speed usually stabilize in 1 to 2 minutes.
If the flag persists, verify that the
operating conditions (temperature,
pressure, supply voltage and current) are
within specified limits and that all
connections with the gas head and
peripheral sensors are made properly.
When this flag is set the GAS status
LED turns orange.
WARNING: Power off the EC100
electronics before disconnecting the gas
analyzer.
34
Page 45

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
TABLE 8-3. Diagnostic Flags and Suggested Actions
Flag
Number Flag Name Comments
3 Motor Speed Set when the motor speed is outside the
prescribed limits. It may occasionally
be set for short periods of time (10 to 15
seconds), but if it persists, the user
should consult with a Campbell
Scientific application engineer.
4 TEC Temperature Set when the infrared detector
temperature is outside the prescribed
limits. It may occasionally be set for
short periods of time (10 to 15 seconds),
but if it persists the user should consult
the factory. Verify that ambient
temperature and power supply voltage
are within the specifications.
5 Source Power Set every time the infrared source power
is outside the prescribed limits. It may
occasionally be set for short periods of
time (10 to 15 seconds), but if it persists,
the user should consult a Campbell
Scientific application engineer. Verify
that ambient temperature and power
supply voltage are within specifications.
6 Source
Temperature
Set when the internal temperature is
outside the specified safe operation
limits (−35° to 55°C). If this flag is set
the sensor head will be turned off until
the internal temperature is within the
range −30° to 50°C. If the flag is set
and ambient temperature is within the
specified range, consult with a Campbell
Scientific application engineer.
7 Source Current Set when the infrared source current is
outside the prescribed limits. It may
occasionally be set for short periods of
time, but if it persists the user should
consult with a Campbell Scientific
application engineer.
8 Off Set when the analyzer head is powered
off by the user, the datalogger program,
or the EC100 operating system when the
LIGHT_TEMP flag is set.
9 Synchronization Set when sampling errors are detected.
Sampling errors are most often caused
by strong electromagnetic interference.
If the flag persists, consult with a
Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
35
Page 46

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
TABLE 8-3. Diagnostic Flags and Suggested Actions
Flag
Number Flag Name Comments
10 Ambient
Temperature
Set when the ambient temperature is
below −30°C or above 55°C or when the
air temperature sensor is not connected.
If the user enters a fixed temperature,
this temperature must be within the
range −30° to 55°C.
11 Ambient Pressure Set when the ambient pressure is outside
the specified limits (55 to 120 kPa) or
the external pressure sensor is
configured but not connected.
12 CO2 I Set if CO2 measurement signal is outside
prescribed limits. It can be turned on
when the measurement path is
obstructed by insects, dust, precipitation,
condensation etc. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
13 CO2 Io Set if CO2 reference signal is outside
prescribed limits. It can be turned on
when the measurement path is
obstructed by insects, dust, precipitation,
condensation etc. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
14 H2O I Set if H2O measurement signal is
outside prescribed limits. It can be
turned on when the measurement path is
obstructed by insects, dust, precipitation,
condensation etc. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
15 H2O Io Set if H2O measurement signal is
outside prescribed limits. It can be
turned on when the measurement path is
obstructed by insects, dust, precipitation,
condensation etc. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
16 H2O Io Variation Set if fast changes in the CO2 reference
signal are detected. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
17 CO2 O IoH2OIo
Variation
Set if fast changes in the H2O reference
signal are detected. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
36
Page 47

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
TABLE 8-3. Diagnostic Flags and Suggested Actions
Flag
Number Flag Name Comments
18 CO2 Signal
Strength
Set if the ratio of the CO2 measurement
and the CO
reference signals are
2
outside prescribed limits. It can be
turned on when the measurement path is
obstructed by insects, dust, precipitation,
condensation etc. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
19 H2O Signal
Strength
Set if the ratio of the H2O measurement
and the H
O reference signals is outside
2
prescribed limits. It can be turned on
when the measurement path is
obstructed by insects, dust, precipitation,
condensation etc. If it persists, consult
with a Campbell Scientific application
engineer.
20 Calibration Error Set if there is a problem reading or
writing into the analyzer’s head
memory. Power off the EC100 and
reconnect the head. If the flag persists,
consult with a Campbell Scientific
application engineer. For more
information on the head memory refer to
Section 4.3, Gas Head Memory.
21 Heater Ctrl Off
22 Not Used
37
Page 48

EC150 CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer
38
Page 49

TABLE A-1. Factory Default Settings
Appendix A. EC150 Settings
Operation of the EC150 can be customized by changing the values of the
settings. Factory defaults will work well for most applications, but the user
may adjust the settings with a PC using either the ECMon software (see
Appendix A.3, ECMon) or the Device Configuration Utility (see Appendix
A.4, Device Configuration Utility), or with a datalogger using the
EC100Configure() CR Basic instruction (see Appendix A.5,
EC100Configure() Instruction).
When the EC150 is connected to a datalogger, the settings of the analyzer can
be configured automatically by the CR Basic program.
A.1 Factory Defaults
TABLE A-1 shows the default value for each of the settings.
Setting Default
A.2 Details
SDM Address 1
Bandwidth 20 Hz
Unprompted Output disabled
RS-485 Baud Rate 115200 bp
Unprompted Output Rate 10 Hz
Analog Output disabled
ECMon Update Rate 10 Hz
Temperature Sensor Auto-select (EC150 Temperature Probe)
Pressure Sensor
Pressure Differential Enable Auto-Select (Disabled for EC150)
Heater Control Disabled
This section gives an explanation for each setting. The value of each setting is
stored either in the non-volatile memory of the EC100 electronics or the EC150
gas head. The section also explains the details of where settings are stored.
For convenience all settings and calibration information associated with the
operation of the gas head are stored in non-volatile memory located in the
head.
EC100 Basic or EC100 Enhanced (depends on
initial order configuration)
Another group of settings pertinent to the operation of the EC100 electronics
are stored in non-volatile memory. These settings are the first seven in TABLE
A-1. For more details refer to the following sections.
A-1
Page 50

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
NOTE
A.2.1 SDM Address
A.2.2 Bandwidth
This parameter must be set to use SDM output from the EC100. See Section
4.6.2.1, SDM Output, for details on using SDM output.
Each SDM device on the SDM bus must have a unique address. The EC150
has a factory default SDM address of 1, but may be changed to any integer
value between 0 and 14. The value 15 is reserved as an SDM group trigger.
The SDM address is stored in non-volatile memory of the EC100 electronics.
The EC100 has a user-selectable, low-pass filter to select the bandwidth (5, 10,
12.5, 20, or 25 Hz). Setting the bandwidth to a lower value will reduce noise.
However, it must be set high enough to retain the high-frequency fluctuations
and H2O, or the high frequency contributions to the flux will be lost.
in CO
2
The factory default bandwidth is set to 20 Hz which is sufficient for most flux
applications. Lower bandwidth settings may be used for higher measurement
heights which inherently have lower frequency content. Refer to Appendix B,
Filter Bandwidth and Time Delay, for more information on the digital filter
options.
If a spectral analysis is performed to evaluate the experimental setup, the
bandwidth should be set to the Nyquist frequency, which is half the datalogger
sample rate (for SDM output) or half the unprompted output rate (for USB and
RS-485 output). This ensures that the data will not be under-sampled and that
higher frequency variations will not be aliased to lower frequencies.
If too small a bandwidth is selected, high frequency fluxes will be
filtered.
The Bandwidth setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the EC100
electronics.
A.2.3 Unprompted Output
If the EC100 is to output data in one of the unprompted modes (USB or RS485, see Appendix C.1, USB or RS-485 Output), this setting must be set
accordingly. The factory default is to disable the unprompted output, assuming
data will be logged via SDM (see Section 4.6.2.1, SDM Output).
Only one unprompted output type (for example, USB or RS-485) may be
selected at a given time. The rate at which the EC100 outputs these data is
determined by the Unprompted Output Rate setting.
The Unprompted Output Rate setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the
EC100 electronics.
A-2
A.2.4 Unprompted Output Rate
When the Unprompted output is enabled, this setting determines the output rate
for unprompted output (USB or RS-485, see Appendix C.1, USB or RS-485
Output). If the unprompted output is disabled, this parameter is not used. The
factory default output rate is 10 Hz, but it may be set to 10, 25, or 50 Hz.
Page 51

The Unprompted Output setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the EC100
electronics.
A.2.5 RS-485 Baud Rate
If the unprompted output mode is set to RS-485, the RS-485 Baud Rate
parameter determines the baud rate. Otherwise this setting is not used. The
RS-485 baud rate defaults to 115200 bps, although the user may enter another
value.
The RS-485 Baud Rate setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the EC100
electronics.
A.2.6 Analog Output
The EC100 has two analog outputs for CO2 and H2O densities (see Appendix
C.2, Analog Outputs). These outputs may be enabled or disabled with this
setting. The default is for analog output to be disabled.
The Analog Output setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the EC100
electronics.
A.2.7 ECMon Update Rate
Appendix A. EC150 Settings
The ECMon Update Rate setting determines the rate at which data are sent
over the USB connection to the PC while running ECMon. The default setting
of 10 Hz should be adequate in most situations.
The ECMon Update Rate setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the
EC100 electronics.
A.2.8 Temperature Sensor
The Temperature Sensor setting configures the EC100 electronics to work
with either an EC150 open-path gas analyzer or an EC155 closed-path gas
analyzer. The EC150 measures ambient air temperature using a thermistor
probe mounted in the solar radiation shield (see Section 6.3.3, Connect the
EC150 Temperature Probe).
With the Auto-Select default setting, the EC100 will automatically detect that
an EC150 is connected to the electronics and will report ambient air
temperature measurements from the thermistor probe.
The EC150 temperature sensor is measured at 1Hz, and is not synchronized to
the CO
To diagnose problems with the temperature measurement, a fixed temperature
value may be used, or the temperature sensor may be selected manually.
The Temperature Sensor setting is stored in the non-volatile memory of the
EC150 head.
O measurements.
2/H2
A.2.9 Fixed Temperature Value
If the Temperature Sensor setting is None, the EC150 will use the value of the
Fixed Temperature Value setting for the sample temperature. This mode is
intended for troubleshooting only. In normal operation, the Temperature
Sensor is set to Auto-Select, and this setting is not used.
A-3
Page 52

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
A.2.10 Pressure Sensor
The Fixed Temperature Value setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the
EC100 electronics.
There are three options for measuring barometric pressure for the EC150 that
have different corresponding Pressure Sensor settings.
1. The EC100 has an on-board barometer that Campbell Scientific refers
to as the EC100 basic barometer. This barometer is mounted on the
EC100 electronics board as shown in FIGURE A-1.
EC100 Basic Barometer:
The EC100 always includes the EC100 basic barometer as a factory
default and the default settings is EC100 Basic.
FIGURE A-1. Location of EC100 basic barometer
2. An enhanced-performance barometer can be specified when ordering
an EC100 for any of Campbell’s gas analyzers, and is referred to as the
enhanced barometer. The enhanced barometer is installed in the
factory when specified at the time of order. It will come mounted on
the top wall of the EC100 environmental enclosure towards the left, as
shown in FIGURE A-2.
The enhanced barometer can provide greater accuracy in certain
environmental conditions that cannot be achieved with the standard
barometer. FIGURE A-3 compares the expected error relative to
environmental conditions for the two barometers. Errors related to the
altitude of the study site may also warrant the choice of one barometer
over the other. Given the various parameters that drive the decision,
the most prudent route is to provide a Campbell Scientific application
engineer sufficient detail about the expected monitoring site at the time
of order.
EC100 Enhanced Barometer:
If the EC100 is ordered with the enhanced barometer, the factory
default setting is EC100 Enhanced.
A-4
Page 53

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
FIGURE A-2. Location of EC100 enhanced barometer
FIGURE A-3. Comparison of error in basic versus enhanced barometer
over operational temperatures
A-5
Page 54

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
3. The option of a third barometer choice is also available but is rarely
used. A user-supplied barometer option can also be programmed in
the EC100 electronics. This setting determines which pressure sensor
will be used to measure the barometric pressure.
User-supplied Barometer:
When a user supplies a barometer, the setting should be changed to
User Supplied and the appropriate values for gain and offset must be
entered.
Sampling Frequency:
The enhanced barometer is sampled at 1 Hz. If the user supplies an external
pressure sensor, it is sampled at 1 Hz. The on-board pressure sensor is
measured at 10 Hz. In all cases, the pressure sensor measurement is not
synchronized to the CO
The pressure sensor also allows the setting None for the Pressure Sensor.
This mode is intended for troubleshooting only. The EC100 will use a fixed
value for pressure.
The Pressure Sensor setting is stored in non-volatile memory in the EC150
head.
and H2O measurements.
2
A.2.10.1 Pressure Gain
This setting is not used unless the Pressure Sensor is set to User Supplied.
Then this setting gives the gain factor (kPa/V) used to convert measured
voltage to pressure. If the Pressure Sensor is set to EC100 Basic or EC100
Enhanced, this setting is not used.
The Pressure Gain setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the EC100.
A.2.10.2 Pressure Offset
This setting is not used unless the Pressure Sensor is set to User Supplied.
Then this setting gives the offset (kPa) used to convert measured voltage to
pressure. If the Pressure Sensor is set to EC100 Basic or EC100 Enhanced,
this setting is not used.
The Pressure Offset setting is stored in the EC100 electronics.
A.2.10.3 Fixed Pressure Value
If the Pressure Sensor setting is None, the EC150 will use the value of this
setting for the barometric pressure. This mode is intended for troubleshooting
only. In normal operation this setting is not used.
The Fixed Pressure Value setting is stored in the EC100 electronics.
A.2.11 Pressure Differential Enable
A-6
This setting should remain disabled. It is used only for closed-path analyzers.
The Pressure Differential Enable setting is stored in non-volatile memory in
the EC150 head.
Page 55

A.2.12 Heater Control
A.2.13 Head Power Off
A.3 ECMon
Appendix A. EC150 Settings
When set to automatic, this setting applies a voltage between 0 and 4600 mV to
heaters near the optical windows of the analyzer. Heated windows inhibit the
formation of condensation, such as dew and frost, and help the analyzer
recover more quickly when precipitation has blocked the optical path.
The Heater Control setting is stored in non-volatile memory in the EC150
head.
When enabled, the EC150 gas head is turned off. The head may be turn on/off
under datalogger control to conserve power or under EC100 control if the gas
head temperature is outside the operating range. The EC100Configure()
Instructions in the CRBasic program is used to turn the gas head on/off under
datalogger control.
The Head Power Off setting is stored in non-volatile memory of the EC100.
Settings for the EC150 are easily verified and/or changed by using the
Windows PC support software ECMon (ECMon is short for Eddy Covariance
Monitor), which is found on the EC150 & EC155 Support CD (pn 27007) or at
www.campbellsci.com/downloads.
Before installing ECMon, read the file named Read.me.text found on the
EC150 & EC155 Support CD. This will direct the user to install USB drivers
(also found on the Support CD) which are required for communications
between the PC and the EC100 via the EC100 USB cable (pn 26563). Some
newer PC operating systems will automatically find and download the USB
drivers from the internet when the USB cable is connected to the PC.
Once the drivers are installed, download and run the ECMon.exe install file.
Launch ECMon and connect the EC100 electronics to the PC with the included
EC100 USB cable (pn 26563). The USB connection for the EC100 electronics
is found on the bottom of the enclosure (see FIGURE 6-12). Once connected,
select the appropriate communications port in the ECMon Main Page and click
Connect (see FIGURE A-4). Next click on the Setup button. All of the above
settings are now available for the user to change (see FIGURE A-5).
Besides changing settings, ECMon is also a useful tool for other common tasks
such as:
• Monitoring real-time data from the EC150 using the Main window
• Performing a manual zero and span of the instrument (see Section 7, Zero
and Span)
• Troubleshooting and monitoring diagnostics using the Status window
A-7
Page 56

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
FIGURE A-4. Main screen of ECMon
A-8
FIGURE A-5. Setup screen in ECMon
Page 57

A.4 Device Configuration Utility
NOTE
The Device Configuration Utility software may also be used to change settings,
although ECMon is generally preferred as the user interface is more intuitive.
Device Configuration may be downloaded from the EC150 & EC155 Support
CD (pn 27007), or at www.campbellsci.com/downloads.
Device Configuration requires a USB driver to communicate with the EC100,
similar to ECMon. See Appendix A.3, ECMon, for notes on installing a USB
driver.
After launching the Device Configuration Utility, the user should select
EC100 from the list of device types. The EC100 electronics should be
connected to the PC with the EC100 USB cable (pn 26563) and the appropriate
USB port selected before connecting. Once connected, the settings tab
displays all the current settings. The Apply button must be clicked to save any
changes.
The Device Configuration Utility is also used to send an updated operating
system to the EC100 electronics. The Send OS tab gives directions on this
procedure. For a video tutorial on updating the operating system, a video
tutorial is available at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dpRXoCv36YI.
Appendix A. EC150 Settings
A.5 EC100Configure() Instruction
EC100Configure() is an alternate way to retrieve and modify setting. While
ECmon and Device Configuration Utility software are user-interactive, the
EC100Configure() instruction allows automated control under CRBasic
datalogger programming.
EC100Configure() is a processing task instruction. When running in pipeline
mode, the datalogger will execute the instruction from the processing task.
This functionality allows the instruction to be placed in conditional statements.
Execution from processing also introduces ramifications when attempting to
execute the EC100Configure() instruction while other SDM instructions are
executing in pipeline mode. This instruction locks the SDM port during the
duration of its execution. If the pipelined SDM task sequencer needs to run
while the SDM is locked, it will be held off until the instruction completes.
This locking will likely result in skipped scans when reconfiguring an EC150.
For the EC150 to save settings, it must go through a lengthy writeread-verify process. To avoid saving the settings after each set
command, the resulting code can be used to determine if any
settings were modified from their original value. When a change
is detected, the save settings command (command code 99) can
then be sent to the EC150. The DestSource parameter variable
should be set to 2718 to save the settings. The reception of this
command is acknowledged but since it takes up to a second to
complete, a successful return code does not mean that all of the
data was successfully written to the appropriate non-volatile
memory.
A-9
Page 58

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
TABLE A-2. ConfigCmd Values for Setting and Retrieving Settings
ConfigCmd Variable
Pressure Sensor:
The instruction syntax is:
EC100Configure(Result,SDMAddress,ConfigCmd,DestSource)
Result is a variable that contains a value indicating the success or failure of the
command. A result code of 0 means that the command was successfully
executed. If reading a setting, 0 in the result code means that the value in the
DestSource variable is the value the desired setting has in the EC150. When
writing a setting, if the result code is 0, the value and setting were compatible,
but the value was not changed because it contained the same value that was
sent. A return code of 1 from the set operation means that the value was valid,
different, set and acknowledged. This allows CRBasic code to control whether
or not to save the settings. NAN (not a number) indicates that the setting was
not changed or acknowledged or a signature failure occurred.
SDMAddress defines the address of the EC150 to configure. Valid SDM
addresses are 0 through 14. Address 15 is reserved for the SDMTrigger()
instruction.
ConfigCmd is a variable that indicates whether to get or set a setting. The
options are listed in TABLE A-2.
DestSource is a variable that will contain the value to read when getting a
setting, or that will contain the value to send when writing a setting to the
EC150.
Setting Description (some settings list possible
Set Retrieve
values for the DestSource variable)
Bandwidth:
• 5 = 5 Hz
0 100
• 10 = 10 Hz
• 12 = 12.5 Hz
• 20 = 20 Hz
• 25 = 25 Hz
Unprompted Output:
1 101
• 10 = 10 Hz
• 25 = 25 Hz
• 50 = 50 Hz
• 0 = EC100 Basic
2 102
• 1 = User-supplied
• 2 = EC100 Enhanced
• 3 = None (use fixed value)
Differential Pressure:
3 103
• 0 = Disable
• 1 = Enable
4 104 Fixed Pressure Value
5 105 Pressure Offset
A-10
Page 59

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
TABLE A-2. ConfigCmd Values for Setting and Retrieving Settings
ConfigCmd Variable
PowerDown:
Setting Description (some settings list possible
Set Retrieve
values for the DestSource variable)
6 106 Pressure Gain
Temperature Sensor:
• 0 = EC150 Temperature Probe
7 107
• 1 = EC155 Sample Cell Thermistor
• 2 = EC155 Sample Cell Thermocouple
• 3 = None (use fixed value)
• 4 = Auto-Select
8 108 Fixed Temperature Value
Unprompted Output Mode:
9 109
• 0 = Disable
• 1 =USB
• 2 = RS-485
10 110 RS-485 Baud Rate
Span/Zero Control:
• 0 = Inactive
11 111
• 1 = Zero
• 2 = Span CO
• 3 = Span H
2
O (See Appendix A.5.1,
2
ConfigCmd 11 Zero-and-Span Control.)
12 112 CO2 Span Concentration
13 113 H2O Span Dewpoint Temperature
14 114 CO2 Zero
15 115 CO2 Span
16 116 H2O Zero
17 117 H2O Span
18 or 218 118 Heater Voltage (0 to 4.5375V, −1 = Off)
19 119 Reserved
Analog Output Enable:
20 120
• 0 = Disable
• 1 = Enable
21 121
99 N/A Save Settings to EEPROM memory
A.5.1 ConfigCmd 11 Zero-and-Span Control
To perform zeroing of CO2 and H2O, ConfigCmd 11 is set to 1. After the
EC150 completes the zero, it will write the value to –1. The datalogger can
poll this value or simply wait for a period of time to allow the zeroing to
• 0 = Gas Head On
• 1 = Gas Head Off
A-11
Page 60

Appendix A. EC150 Settings
complete. To perform CO2 span, the CO2 Span Concentration setting
(ConfigCmd 12) must be written to the proper value in ppm CO
setting the Span/Zero Control setting (ConfigCmd 11) to 2. After the CO
is completed, the value of the Span/Zero Control setting will change to –2.
O span is similar to CO2. First the H2O Dew Point value (ConfigCmd 13)
H
2
must be written to the desired value. Then the Span/Zero Control setting is set
to 3. After the EC150 completes the span, the span control setting is written as
–3. ConfigCmds 14 through 17 automatically store the results of the zero-and-
span procedure. Each result is a coefficient used in the gas analyzer’s
algorithms for calculating gas concentrations.
A.6 Example CRBasic Program
'CR3000 Series Datalogger
Public sonic_irga(12)
Alias sonic_irga(1) = Ux
Alias sonic_irga(2) = Uy
Alias sonic_irga(3) = Uz
Alias sonic_irga(4) = Ts
Alias sonic_irga(5) = diag_sonic
Alias sonic_irga(6) = CO2
Alias sonic_irga(7) = H2O
Alias sonic_irga(8) = diag_irga
Alias sonic_irga(9) = cell_tmpr
Alias sonic_irga(10) = cell_press
Alias sonic_irga(11) = CO2_sig_strgth
Alias sonic_irga(12) = H2O_sig_strgth
Units Ux = m/s
Units Uy = m/s
Units Uz = m/s
Units Ts = C
Units diag_sonic = arb
Units CO2 = mg/m^3
Units H2O = g/m^3
Units diag_irga = arb
Units cell_tmpr = C
Units cell_press = kPa
Units CO2_sig_strgth = arb
Units H2O_sig_strgth = arb
DataTable (ts_data,TRUE,-1)
DataInterval (0,0,mSec,10)
Sample (12,Ux,IEEE4)
EndTable
BeginProg
Scan (100,mSec,0,0)
EC100 (Ux,1,1)
CallTable ts_data
NextScan
EndProg
prior to
2
span
2
A-12
Page 61

Appendix B. Filter Bandwidth and Time Delay
The EC100 measures CO2 and H2O from the EC150 gas analyzer head. It will
also measure wind velocity and sonic temperature if the optional CSAT3A
sonic head is being used. EC100 measurements occur at 100z and then a userselectable, low-pass filter is applied. The available filter bandwidths are 5, 10,
12.5, 20, and 25 Hz.
FIGURE B-1 shows the amplitude response of these filters. The EC100 filters
provide a flat pass band, a steep transition from pass band to stop band, and a
well-attenuated stop band. FIGURE B-2 compares the EC100 10-Hz filter to a
50-ms moving average filter with approximately the same bandwidth.
FIGURE B-1. Amplitude response of EC100 filter at various bandwidths
B-1
Page 62

Appendix B. Filter Bandwidth and Time Delay
FIGURE B-2. Frequency response comparison of EC100 10-Hz
bandwidth and a 50-msec moving average
The ideal eddy-covariance filter is one that is wide enough to preserve the lowfrequency signal variations that transport flux, yet narrow enough to attenuate
high-frequency noise. In addition, to minimize aliasing (defined as the
misinterpretation of high-frequency variation as lower-frequency variation), the
measurement bandwidth must be less than half of the sample rate or the
datalogger scan rate.
Two factors complicate choosing the ideal eddy-covariance bandwidth. First,
the flux signal bandwidth varies from one installation to another, and the flux
signal bandwidth varies with mean wind speed at a given installation. Second,
the fast sample rate required to anti-alias a desired signal bandwidth may result
in large, unwieldy data sets.
Fortunately, the covariance calculation itself relaxes the need for the ideal
bandwidth. The time-averaged (typically thirty minutes) covariance
calculations inherently reduce noise, and second, aliasing does not degrade the
accuracy of covariance calculations. The factory default for the EC100
bandwidth (20 Hz) is rather wide to preserve the signal variations that transport
flux. The default bandwidth is suitable for most flux applications. Additional
bandwidths are available for users desiring to match the EC100 filter
bandwidth to their data acquisition sample rate to avoid aliasing. In this case,
the selected bandwidth should be one-half of the sample rate. However, users
should be careful to avoid attenuation of flux-carrying signals.
B-2
The EC100 electronics synchronously sample the EC150 analyzer and the
CSAT3A sonic head. However, users wishing to synchronize their EC100 data
with other measurements (for example, a fine-wire thermocouple) in the data
acquisition system must account for the time delay of the EC100 filter.
TABLE B-1 shows the delay for each of the filter bandwidths. The EC100
Page 63

Appendix B. Filter Bandwidth and Time Delay
TABLE B-1. Filter Time Delays for Various Bandwidths
provides a constant time delay for all spectral components within each filter’s
pass band.
Bandwidth (Hz) Time Delay (ms)
5 800
10 400
12.5 320
20 200
25 160
The following examples show how to use TABLE B-1. To synchronize EC100
data to other datalogger measurements when the datalogger scan rate is 25 Hz
and the EC100 bandwidth is set to 20 Hz (a 200-msec time delay from TABLE
B-1), delay the non-EC100 data by five datalogger scans. Similarly, for a 10Hz datalogger scan rate and the same 20-Hz EC100 bandwidth, delay the nonEC100 data by two datalogger scans to match the EC100 data. For the best
synchronicity, choose a datalogger scan interval that is an integer multiple of
the EC100 filter delay.
The EC100 measures the gas and wind data at 150 Hz, and the 150-Hz data are
down-sampled to the datalogger’s scan rate through SDM communications (see
Section 4.6.2, EC100 Outputs). This process synchronizes the EC100 gas and
wind data with other signals measured by the datalogger to within ±3.33 ms
(plus or minus one-half of the inverse of 150 Hz).
Alternately, when sending data to a data acquisition system that is not
manufactured by Campbell Scientific, the EC100 down-samples its USB and
RS-485 outputs to a user-selectable rate of 10, 25, or 50 Hz. Although the gas
and wind data from the EC100 remain synchronized with one another, the user
must consider the down-sampled output interval when synchronizing the
EC100 data with other measurements in their system. These slower output
intervals will increase the asynchronicity of EC100 data with other system
measurements.
B-3
Page 64

Appendix B. Filter Bandwidth and Time Delay
B-4
Page 65

TABLE C-1. USB and RS-485 Output Elements
Data
Element
1
Ux
m/s 2 Uy
m/s 3 Uz
m/s 4 Sonic Temperature
°C
Appendix C. Alternate EC100 Outputs
C.1 USB or RS-485 Output
C.1.1 Specifications
Digital
RS-485
Data type: ASCII
Output Rate
Baud rate
USB
Data type: ASCII
Output rate
C.1.2 Detailed Information
In contrast to the SDM output mode, which is prompted by a datalogger, data
can also be output from the EC100 via USB or RS485 in an unprompted mode.
In this case, the EC100 sends out data without initiation from the receiving
device at a rate determined by the EC100. Only one unprompted output type
(USB or RS-485) may be selected at a given time. USB output is used to
connect a PC to the EC100 when using Device Configuration Utility or
ECMon software. RS-485 output is recommended over SDM for sending data
to a datalogger if the cable length exceeds 100 meters.
viii
: 5 to 50 Hz
viii
: 1200 to 230400 bps USB
viii
: 10, 25, or 50 Hz
To use USB or RS-485 output, connect a USB (pn 26563) or RS-485 (pn
26987) cable from the EC100 to the receiving device (see Section 6.3, Wiring
and Connections), and configure the settings.
The Unprompted Output parameter must be set to USB or RS-485.
If RS-485 is selected, the RS-485 Baud Rate must be set.
The Unprompted Output Rate must be set to the desired output rate.
All output data will be in ASCII format, with each data element separated by a
comma. Each record will terminate with a carriage return and line feed.
TABLE C-1 below lists the elements in each output array, and FIGURE C-1
shows an example USB data feed in terminal mode.
Description Units or comments
viii
user selectable
C-1
Page 66

Appendix C. Alternate EC100 Outputs
TABLE C-1. USB and RS-485 Output Elements
Data
Element
5
Sonic Diagnostic Flag
6 CO2 Density
mg·m-3
7
H2O Density
g·m-3
8
Gas Diagnostic Flag
9 Air Temperature
°C
10
Air Pressure
kPa
11
CO2 Signal Strength
Nominally 0.0 to 1.0
12
H2O Signal Strength
Nominally 0.0 to 1.0
Pressure Differential (used for EC155
only, disregard for EC150)
14
Counter
Arbitrary
Arbitrary in
hexadecimal
Description Units or comments
13
kPa
15 Signature
FIGURE C-1. USB data output in terminal mode
The final data element in each row or output array is the signature which can
be used to identify transmission errors similar to a Cyclic-Redundancy-Check
(CRC). The signature is a four character hexadecimal value that is a function
of the specific sequence and number of bytes in the output array. To check for
transmission errors, the recording device (such as a PC or datalogger)
calculates its own signature using each transmitted byte until encountering the
transmitted signature. The computed signature and the transmitted signature
are compared. If they match, the data were received correctly
C-2
If signatures do not match, the data should be disregarded.
The block of code below is an example implementation of Campbell
Scientific’s signature algorithm in the programming language C. To generate
the signature of an output array of bytes, the seed needs to be initialized to
0xaaaa and a pointer passed to the first byte of the output array. The number of
bytes in the output array should be entered in as the swath. The returned value
is the computed signature.
Page 67

//signature(), signature algorithm.
// Standard signature is initialized with a seed of 0xaaaa.
}
// Returns signature.
unsigned short signature( unsigned char* buf, int swath,
unsigned short seed ) {
unsigned char msb, lsb;
unsigned char b;
int i;
msb = seed >> 8;
lsb = seed;
for( i = 0; i < swath; i++ ) {
b = (lsb << 1) + msb + *buf++;
if( lsb & 0x80 ) b++;
msb = lsb;
lsb = b;
}
return (unsigned short)((msb << 8) + lsb);
C.2 Analog Output
Appendix C. Alternate EC100 Outputs
C.2.1 Specifications
C.2.2 Detailed Information
Analog (two outputs for CO2 and H2O densities)
Voltage range: 0 mV to 5000 mV
Resolution: 76 µV (16 bit)
Update rate: 100 Hz
Accuracy (at 25°C): ± 3 mV
density equation: mg·m-3 = 0.38632· (mV
CO
2
Full scale range: −103 to 1829 mg·m
-3
) − 102.59
out
O density equation: g·m-3 = 0.00865· (mV
H
2
Full scale range: −2 to 41 g·m
-3
) − 2.26
out
Although digital outputs are generally preferred, analog outputs are available
on the EC100 for compatibility with simple recording devices that cannot use
the digital outputs. Analog outputs are subject to additional noise and
digitization errors. Digital outputs include additional diagnostic data to assist
with data quality assessment and troubleshooting. If analog output is enabled,
the EC100 will output two analog signals that correspond to CO
O density. These signals range from 0 to +5 V. TABLE C-2 gives the
H
2
density and
2
multipliers and offsets for the analog outputs.
Analog output may also be used, however only CO
density and H2O density
2
will be output. For analog output, use cable CABLE2TP-L (pn 26986-L), the
length of which is specified by the user when ordering. The connector labeled
Analog Outputs on the EC100 panel indicates where each wire should be
connected (CO
voltage signal, H2O voltage signal, and two ground
2
connections).
C-3
Page 68

Appendix C. Alternate EC100 Outputs
TABLE C-2. Multipliers and Offsets for Analog Outputs
Density (mg·m-3)
Voltage Output Multiplier
(mg·m-3 V-1) Offset (mg·m-3)
CO2 386.32
H2O 8.65
−102.59
−2.26
C-4
Page 69

TABLE D-1. Variables and Constants
Variable or Constant
Description
Units
c
ρ
v
ρ
d
ρ
c
X
CO2 molar mixing ratio
(concentration relative to dry air)
v
X
H2O molar mixing ratio
c
M
d
M
v
M
P
Ambient pressure
kPa
R
Universal gas constant
8.3143×10–6 kPa·m3·K-1·mmol-1
T
e
f
d
T
tmpd
T
_
Temporary variable for dewpoint
calculation
( )
−
+
=
v
vc
c
c
MT
R
P
MX
ρ
ρ
15
.27310
6
( )
( )
v
vv
v
XTR
PMX
++
=
100015.
273
ρ
( )
( )
15.273+
−
=
TR
MeP
d
d
ρ
Appendix D. Useful Equations
The following table lists all the variables and constants used in the equations
below:
mass density mg·m-3
CO
2
O mass density g·m-3
H
2
-3
Mass density of dry air g·m
(concentration relative to dry air)
Molecular weight of CO
Molecular weight of dry air 0.029 g·mmol
Molecular weight of H
Ambient temperature °C
Vapor pressure kPa
Enhancement factor Arbitrary
Dewpoint temperature °C
44 mg·mmol-1
2
O 0.018 g·mmol-1
2
µmol·mol-1
mmol·mol-1
Arbitrary
-1
Mass Density from Molar Mixing Ratios
(D-1)
(D-2)
(D-3)
D-1
Page 70

Appendix D. Useful Equations
( )
15.273
1000
+
+
−
=
TR
M
X
PX
P
d
v
v
d
ρ
( )
+
−
+
=
v
v
d
d
X
X
TR
PM
1000
1
15.273
ρ
tmpd
tmpd
d
T
T
T
_
_
502.17
97.240
−
=
( )
+⋅
=
v
v
tmpd
Xf
PX
lnT
100061121.0
_
( ) ( )
295
109.5102.300072.1 PTPf
−−
×+×+=
1000
eP
e
X
v
−
=
+
⋅⋅=
d
d
T
T
EXPfe
97.240
502.17
61121.0
( )(
)
( )
++
=
d
d
v
T
T
EXP
TR
f
97.240
502.17
15.273
61121
.0018.0
ρ
(D-4)
(D-5)
Dew Point from Molar Mixing Ratio
(D-6)
(D-7)
Water Vapor Molar Mixing Ratio from Dew Point
(D-9)
(D-10)
Water Vapor Mass Density from Dew Point
(D-8)
(D-11)
D-2
Page 71

Appendix D. Useful Equations
v
v
X
PX
e
+
=
1000
( )
v
v
M
TR
e
15.273+
=
ρ
Vapor Pressure from Molar Mixing Ratio and Water Vapor Density
(D-12)
(D-13)
Equations (D-1) and (D-2) were derived from:
Leuning, R.: 2005, “Measurements of Trace Gas Fluxes in the
Atmosphere Using Eddy Covariance: WPL Corrections Revisited”,
Handbook of Micrometeorology, 29, 119-132.
Equations (D-3), (D-4), (D-5), (D-7), (D-9), and (D-13) were derived from:
Bolton, D.: 1980, “The Computation of Equivalent Potential
Temperature”, Monthly Weather Review, 108, 1046-1053.
Equations (D-6), (D-8), (D-10) and (D-11) were derived from:
Buck, A. L.: 1981; “New Equations for Computing Vapor Pressure and
Enhancement Factor”, Journal of Applied Meteorology, 20, 1528-1532.
D-3
Page 72

Appendix D. Useful Equations
D-4
Page 73

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E.1 Magnesium Perchlorate MSDS
E-1
Page 74

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-2
Page 75

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-3
Page 76

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-4
Page 77

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-5
Page 78

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-6
Page 79

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-7
Page 80

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E.2 Decarbite MSDS
E-8
Page 81

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-9
Page 82

Appendix E. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
E-10
Page 83

Appendix F. Packing Information
F.1 EC150-GH Packing Information
F-1
Page 84

Appendix F. Packing Information
F.2 EC150-SH Packing Information
F-2
Page 85

Page 86

Campbell Scientific Companies
Campbell Scientific, Inc. (CSI)
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321
UNITED STATES
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com
Campbell Scientific Africa Pty. Ltd. (CSAf)
PO Box 2450
Somerset West 7129
SOUTH AFRICA
www.csafrica.co.za • cleroux@csafrica.co.za
Campbell Scientific Australia Pty. Ltd. (CSA)
PO Box 8108
Garbutt Post Shop QLD 4814
AUSTRALIA
www.campbellsci.com.au • info@campbellsci.com.au
Campbell Scientific (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
8B16, Floor 8 Tower B, Hanwei Plaza
7 Guanghua Road
Chaoyang, Beijing 100004
P.R. CHINA
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com.cn
Campbell Scientific do Brasil Ltda. (CSB)
Rua Apinagés, nbr. 2018 ─ Perdizes
CEP: 01258-00 ─ São Paulo ─ SP
BRASIL
www.campbellsci.com.br • vendas@campbellsci.com.br
Campbell Scientific Canada Corp. (CSC)
14532 – 131 Avenue NW
Edmonton AB T5L 4X4
CANADA
www.campbellsci.ca • dataloggers@campbellsci.ca
Please visit www.campbellsci.com to obtain contact information for your local US or international representative.
Campbell Scientific Centro Caribe S.A. (CSCC)
300 N Cementerio, Edificio Breller
Santo Domingo, Heredia 40305
COSTA RICA
www.campbellsci.cc • info@campbellsci.cc
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL)
Campbell Park
80 Hathern Road
Shepshed, Loughborough LE12 9GX
UNITED KINGDOM
www.campbellsci.co.uk • sales@campbellsci.co.uk
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL France)
3 Avenue de la Division Leclerc
92160 ANTONY
FRANCE
www.campbellsci.fr • info@campbellsci.fr
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL Germany)
Fahrenheitstraße 13
28359 Bremen
GERMANY
www.campbellsci.de • info@campbellsci.de
Campbell Scientific Spain, S. L. (CSL Spain)
Avda. Pompeu Fabra 7-9, local 1
08024 Barcelona
SPAIN
www.campbellsci.es • info@campbellsci.es
 Loading...
Loading...