Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
CS526 ISFET pH Probe
Copyright © 2009- 2014
Campbell Scientific, Inc.
Revision: 4/14
Page 2

Page 3

Limited Warranty
The CS526 ISFET pH Probe is warranted for six (6) months subject to this
limited warranty:
“Products manufactured by CSI are warranted by CSI to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal use and service for twelve months
from the date of shipment unless otherwise specified in the corresponding
product manual. (Product manuals are available for review online at
www.campbellsci.com.) Products not manufactured by CSI, but that are resold
by CSI, are warranted only to the limits extended by the original manufacturer.
Batteries, fine-wire thermocouples, desiccant, and other consumables have no
warranty. CSI’s obligation under this warranty is limited to repairing or
replacing (at CSI’s option) defective Products, which shall be the sole and
exclusive remedy under this warranty. The Customer assumes all costs of
removing, reinstalling, and shipping defective Products to CSI. CSI will return
such Products by surface carrier prepaid within the continental United States of
America. To all other locations, CSI will return such Products best way CIP
(port of entry) per Incoterms ® 2010. This warranty shall not apply to any
Products which have been subjected to modification, misuse, neglect, improper
service, accidents of nature, or shipping damage. This warranty is in lieu of all
other warranties, expressed or implied. The warranty for installation services
performed by CSI such as programming to customer specifications, electrical
connections to Products manufactured by CSI, and Product specific training, is
part of CSI's product warranty. CSI EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS AND
EXCLUDES ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. CSI hereby disclaims,
to the fullest extent allowed by applicable law, any and all warranties and
conditions with respect to the Products, whether express, implied or
statutory, other than those expressly provided herein.”
Page 4

Assistance
Products may not be returned without prior authorization. The following
contact information is for US and international customers residing in countries
served by Campbell Scientific, Inc. directly. Affiliate companies handle
repairs for customers within their territories. Please visit
www.campbellsci.com to determine which Campbell Scientific company serves
your country.
To obtain a Returned Materials Authorization (RMA), contact CAMPBELL
SCIENTIFIC, INC., phone (435) 227-9000. After an applications engineer
determines the nature of the problem, an RMA number will be issued. Please
write this number clearly on the outside of the shipping container. Campbell
Scientific's shipping address is:
CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC, INC.
RMA#_____
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321-1784
For all returns, the customer must fill out a "Statement of Product Cleanliness
and Decontamination" form and comply with the requirements specified in it.
The form is available from our web site at www.campbellsci.com/repair. A
completed form must be either emailed to repair@campbellsci.com or faxed to
(435) 227-9106. Campbell Scientific is unable to process any returns until we
receive this form. If the form is not received within three days of product
receipt or is incomplete, the product will be returned to the customer at the
customer's expense. Campbell Scientific reserves the right to refuse service on
products that were exposed to contaminants that may cause health or safety
concerns for our employees.
Page 5

Precautions
DANGER — MANY HAZARDS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH INSTALLING, USING, MAINTAINING, AND WORKING ON OR AROUND
TRIPODS, TOWERS, AND ANY ATTACHMENTS TO TRIPODS AND TOWERS SUCH AS SENSORS, CROSSARMS, ENCLOSURES,
ANTENNAS, ETC. FAILURE TO PROPERLY AND COMPLETELY ASSEMBLE, INSTALL, OPERATE, USE, AND MAINTAIN TRIPODS,
TOWERS, AND ATTACHMENTS, AND FAILURE TO HEED WARNINGS, INCREASES THE RISK OF DEATH, ACCIDENT, SERIOUS
INJURY, PROPERTY DAMAGE, AND PRODUCT FAILURE. TAKE ALL REASONABLE PRECAUTIONS TO AVOID THESE HAZARDS.
CHECK WITH YOUR ORGANIZATION'S SAFETY COORDINATOR (OR POLICY) FOR PROCEDURES AND REQUIRED PROTECTIVE
EQUIPMENT PRIOR TO PERFORMING ANY WORK.
Use tripods, towers, and attachments to tripods and towers only for purposes for which they are designed. Do not exceed design
limits. Be familiar and comply with all instructions provided in product manuals. Manuals are available at www.campbellsci.com or
by telephoning 435-227-9000 (USA). You are responsible for conformance with governing codes and regulations, including safety
regulations, and the integrity and location of structures or land to which towers, tripods, and any attachments are attached. Installation
sites should be evaluated and approved by a qualified engineer. If questions or concerns arise regarding installation, use, or
maintenance of tripods, towers, attachments, or electrical connections, consult with a licensed and qualified engineer or electrician.
General
• Prior to performing site or installation work, obtain required approvals and permits. Comply
with all governing structure-height regulations, such as those of the FAA in the USA.
• Use only qualified personnel for installation, use, and maintenance of tripods and towers, and
any attachments to tripods and towers. The use of licensed and qualified contractors is
highly recommended.
• Read all applicable instructions carefully and understand procedures thoroughly before
beginning work.
• Wear a hardhat and eye protection, and take other appropriate safety precautions while
working on or around tripods and towers.
• Do not climb tripods or towers at any time, and prohibit climbing by other persons. Take
reasonable precautions to secure tripod and tower sites from trespassers.
• Use only manufacturer recommended parts, materials, and tools.
Utility and Electrical
• You can be killed or sustain serious bodily injury if the tripod, tower, or attachments you are
installing, constructing, using, or maintaining, or a tool, stake, or anchor, come in contact
with overhead or underground utility lines.
• Maintain a distance of at least one-and-one-half times structure height, or 20 feet, or the
distance required by applicable law, whichever is greater, between overhead utility lines and
the structure (tripod, tower, attachments, or tools).
• Prior to performing site or installation work, inform all utility companies and have all
underground utilities marked.
• Comply with all electrical codes. Electrical equipment and related grounding devices should
be installed by a licensed and qualified electrician.
Elevated Work and Weather
• Exercise extreme caution when performing elevated work.
• Use appropriate equipment and safety practices.
• During installation and maintenance, keep tower and tripod sites clear of un-trained or non-
essential personnel. Take precautions to prevent elevated tools and objects from dropping.
• Do not perform any work in inclement weather, including wind, rain, snow, lightning, etc.
Maintenance
• Periodically (at least yearly) check for wear and damage, including corrosion, stress cracks,
frayed cables, loose cable clamps, cable tightness, etc. and take necessary corrective actions.
• Periodically (at least yearly) check electrical ground connections.
WHILE EVERY ATTEMPT IS MADE TO EMBODY THE HIGHEST DEGREE OF SAFETY IN ALL CAMPBELL SCIENTIFIC PRODUCTS,
THE CUSTOMER ASSUMES ALL RISK FROM ANY INJURY RESULTING FROM IMPROPER INSTALLATION, USE, OR
MAINTENANCE OF TRIPODS, TOWERS, OR ATTACHMENTS TO TRIPODS AND TOWERS SUCH AS SENSORS, CROSSARMS,
ENCLOSURES, ANTENNAS, ETC.
Page 6

Page 7

Table of Contents
PDF viewers: These page numbers refer to the printed version of this document. Use the
PDF reader bookmarks tab for links to specific sections.
1. Introduction ................................................................. 1
2. Cautionary Statements ............................................... 1
3. Initial Inspection ......................................................... 2
4. Quickstart .................................................................... 2
4.1 Preparation for Use and Installation ..................................................... 2
4.2 Use SCWin to Program Datalogger and Generate Wiring Diagram .... 2
5. Overview ...................................................................... 5
6. Specifications ............................................................. 5
7. Operation ..................................................................... 6
7.1 Wiring .................................................................................................. 6
7.2 Datalogger Programming ..................................................................... 7
7.2.1 Get Data Command ....................................................................... 7
7.2.2 CRBasic Instruction Sequence ...................................................... 7
7.2.3 Instruction Descriptions ................................................................ 8
7.2.3.1 SerialOpen() Instruction ..................................................... 8
7.2.3.2 SerialOut() Instruction ........................................................ 8
7.2.3.3 SerialIn() Instruction .......................................................... 8
7.2.3.4 SplitStr() Instruction ........................................................... 9
7.2.4 Programming for Calibration ........................................................ 9
7.3 Calibration ............................................................................................ 9
8. Troubleshooting.......................................................... 9
9. Maintenance .............................................................. 10
9.1 Cleaning ............................................................................................. 10
9.1.1 When to Clean ............................................................................. 10
9.1.2 Cleaning Procedure ..................................................................... 11
9.1.2.1 Cleaning Tips ................................................................... 12
9.1.3 Revitalizing ................................................................................. 12
9.2 Storage ............................................................................................... 12
9.2.1 Short-Term Storage (2 days or less) ............................................ 12
9.2.2 Long-Term Storage (more than 2 days) ...................................... 12
Appendices
Importing Short Cut Code ...................................... A-1
A.
i
Page 8

Table of Contents
A.1 Importing Short Cut Code into a Program Editor ............................ A-1
B. Example Program .................................................... B-1
C. Calibration ............................................................... C-1
C.1 Example Calibration Program ......................................................... C-2
Figures
9-1. Tip of the CS526 probe ..................................................................... 11
Tables
7-1. Wiring .................................................................................................. 6
7-2. “Get Data” Command and Response ................................................... 7
7-3. Instruction Sequence ........................................................................... 7
7-4. Calibration Standards .......................................................................... 9
ii
Page 9

CS526 ISFET pH Probe
1. Introduction
The CS526 ISFET pH Probe measures pH from 1 to 14 in aqueous or semisolid solutions. It outputs TTL serial data that is read by compatible
dataloggers (see Section 6, Specifications).
Before using the CS526, please study
• Section 2, Cautionary Statements
• Section 3, Initial Inspection
• Section 4, Quickstart
More detailed instructions for operation, troubleshooting, and maintenance are
available in the remaining sections.
2. Cautionary Statements
• READ AND UNDERSTAND the Precautions section at the front of this
manual.
• Campbell Scientific warranty does not cover a clogged reference
diaphragm or improperly cleaned or maintained ISFET chip (see Section
9, Maintenance).
• Maximum input voltage is 5 Vdc. Incorrect wiring may cause
performance loss and irreversible damage.
• To prevent scratching the sensor chip when cleaning, first soak the sensor
in soapy water and then gently scrub with a toothbrush (see Section 9,
Maintenance). Most scratches occur when hard particles are rubbed on the
chip surface. Scratches cause irreversible damage to the probe.
• Do not use hydrofluoric acid, acetone, MEK, or similar agents to clean the
probe.
• Cable can be damaged by abrasion, rodents, sharp objects, twisting,
crimping or crushing, and pulling. Take care during installation and use to
avoid cable damage.
• The CS526 is rugged, but it should be handled as a precision scientific
instrument.
• The CS526 has no user-serviceable parts. Any attempt to disassemble the
device will void the six-month warranty.
• Care should be taken when opening the shipping package to not damage or
cut the cable jacket. If damage to the cable is suspected, consult with a
Campbell Scientific application engineer.
1
Page 10

CS526 ISFET pH Probe
NOTE
3. Initial Inspection
Upon receipt of the CS526, inspect the packaging and contents for damage.
File damage claims with the shipping company.
The model number and cable length are printed on a label at the connection end
of the cable. Check this information against the shipping documents to ensure
the correct product and cable length are received.
4. Quickstart
For complete installation, programming, and calibration information, see
Sections 7.1 through 7.3.
4.1 Preparation for Use and Installation
1. Soak the CS526 in 7-pH buffer solution for 15 minutes.
2. Follow the calibration procedure outlined in Appendix C, Calibration.
3. Place the CS526 in the liquid being measured. The CS526 ISFET pH
probe can be installed without regard to orientation.
When installing in a well, the 7421 Split Mesh Cable grip is
recommended to center and suspend the cable, reducing cable
stretch.
4.2 Use SCWin to Program Datalogger and Generate Wiring Diagram
Short Cut is an easy way to program your datalogger to measure the CS526 and
assign datalogger wiring terminals. The following procedure shows using
Short Cut to program the CS526.
1. Install Short Cut by clicking on the install file icon. Get the install file
from either www.campbellsci.com, the ResourceDVD, or find it in
installations of LoggerNet, PC200W, PC400, or RTDAQ software.
2. The Short Cut installation should place a Short Cut icon on the desktop of
your computer. To open Short Cut, click on this icon.
2
Page 11
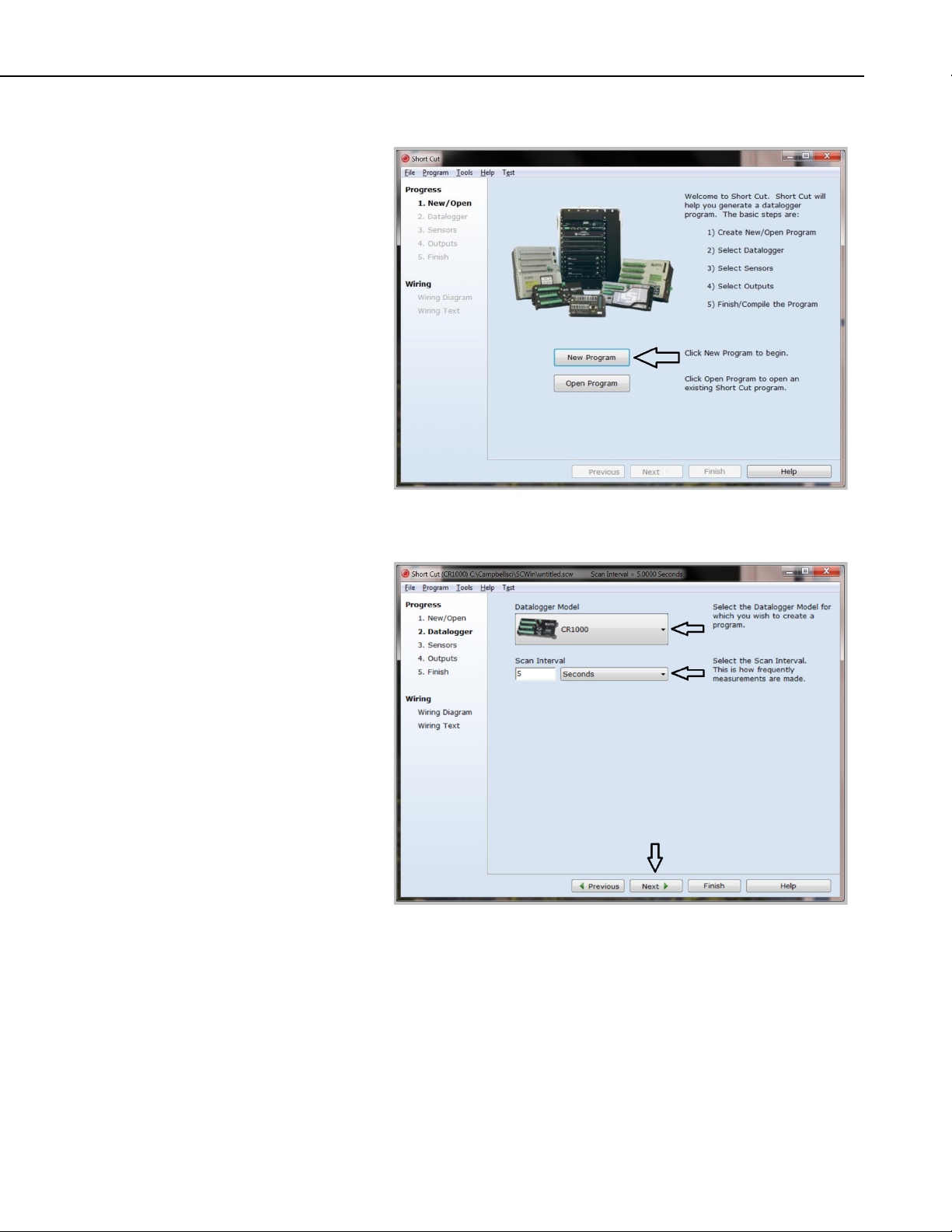
3. When Short Cut opens, select New Program.
CS526 ISFET pH Probe
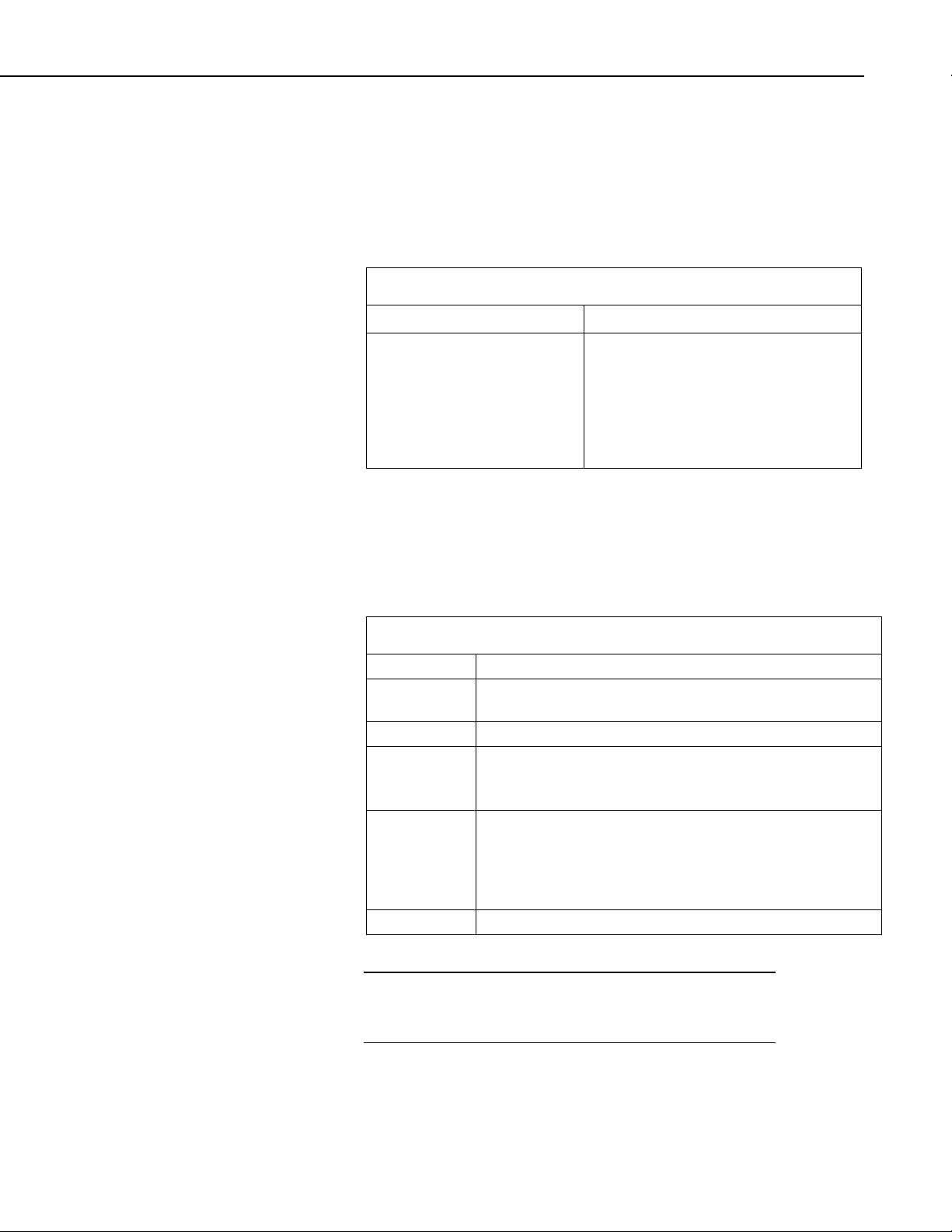
4. Select Datalogger Model and Scan Interval (default of 5 seconds is OK
for most applications). Click Next.
3
Page 12

CS526 ISFET pH Probe
5. Under the Available Sensors and Devices list, select the Sensors | Water
| Quality folder. Select CS526 ISFET pH Probe. Click to move the
selection to the Selected device window.
6. After selecting the sensor, click at the left of the screen on Wiring
Diagram to see how the sensor is to be wired to the datalogger. The
wiring diagram can be printed out now or after more sensors are added.
4
7. Select any other sensors you have, then finish the remaining Short Cut
steps to complete the program. The remaining steps are outlined in Short
Cut Help, which is accessed by clicking on Help | Contents |
Programming Steps.
Page 13

5. Overview
NOTE
CS526 ISFET pH Probe
8. If LoggerNet, PC400, or PC200W is running on your PC, and the PC to
datalogger connection is active, you can click Finish in Short Cut and you
will be prompted to send the program just created to the datalogger.
9. If the sensor is connected to the datalogger, as shown in the wiring
diagram in step 6, check the output of the sensor in the datalogger support
software data display to make sure it is making reasonable measurements.
The CS526 uses SENTRON’s high-tech, Ion Sensitive Field Effect Transistor
(ISFET) semi-conductor as its pH-sensitive element, and includes a
silver/silver chloride – potassium chloride reference system.
The CS526’s design allows it to be suitable for a variety of liquid pHmonitoring applications. Its electronics are safely embedded in a durable
PEEK body. Elimination of the glass-bulb removes the possibility of broken
glass, making the CS526 more rugged and safer to use.
The CS526 is shipped dry and therefore must be soaked in pH
solution before use.
The CS526’s cable can terminate in:
6. Specifications
Features:
Measurement
Range: 2 to 12 pH
Accuracy: ±0.2 pH with 2-point calibration
24 hr drift: <0.15 pH (after 15-min soak in pH 7 at 25°C)
• Pigtails that connect directly to a Campbell Scientific datalogger
(cable termination option –PT).
• Connector that attaches to a prewired enclosure (cable termination
option –PW).
• Safety — the ISFET with durable PEEK material can be used safely
in applications where broken glass is a hazard to the user.
• Intelligent electronics — the CS526 combines the latest
developments in ISFET pH sensing technology with state-of-the-art
signal processing. This allows for accurate, fast and reliable results.
• Quality — designed and manufactured under stringent quality control
conditions in an ISO 9001 environment. Each sensor is individually
tested to the most demanding testing protocols, and the electronics
comply fully with directives and with EMC standard
IEC61326:2005.
• Compatible with Campbell Scientific CRBasic dataloggers: CR800
series, CR1000, and CR3000
5
Page 14

CS526 ISFET pH Probe
TABLE 7-1. Wiring
CAUTION
Operating
Temperature: 10° to 40°C
Water Pressure: 0 to 700 kPa (0 to 101.5 psi)
Power Requirement
Source: 5 Vdc
Load: 15 mA maximum
Output: TTL logic, 2400 bps
8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit
Maximum Cable Length: 100 m (328 ft)
7. Operation
7.1 Wiring
Cable Type: Three-twisted pair, 24-AWG cable with
Santoprene
Sensor Material: PEEK
Weight
w/10-ft cable: 318 g (11.2 oz)
Dimensions
Length: 102 mm (4 in)
Diameter: 16 mm (0.63 in)
Certifications: ISO 9001
compliant
EMC standard IEC61326:2005
If you are programming your datalogger with Short Cut, skip Section 7.1,
Wiring, and Section 7.2, Datalogger Programming. Short Cut does this work
for you. See Section 4, Quickstart, for a Short Cut tutorial.
jacket
6
Wire Color Wire Label/Function Datalogger Connections
Red (see following
caution)
Black Ground G
White Signal #1 (Rx) Control Port (Tx)
Green Signal #2 (Tx) Control Port (Rx)
Clear Shield G
This probe must be connected to the datalogger’s 5 V
terminal (not 12 V). Connecting to a higher voltage will
damage the probe beyond repair.
Power 5V 5V
Page 15
7.2 Datalogger Programming
TABLE 7-2. “Get Data” Command and Response
TABLE 7-3. Instruction Sequence
Instruction
Function
SerialOpen()
Set up a datalogger port for serial communication (see Section
NOTE
7.2.1 Get Data Command
The datalogger needs to send a “get data” serial command to the CS526 to get
the pH data. This command is sent to the CS526 via the SerialOut() CRBasic
instruction (see Section 7.2.3.2, SerialOut() Instruction). TABLE 7-2 shows
the “get data” command and its response.
Command Response
CS526 ISFET pH Probe
aMn!<CR>
Where:
a = probe address (factory
default is 1)
n = a single dummy character
(typically use 1)
7.2.2 CRBasic Instruction Sequence
A sequence of CRBasic instructions is used to measure the sensor. TABLE 7-3
shows the instruction sequence. Information about the instructions is provided
in Section 7.2.3, Instruction Descriptions, and an example program is provided
in Appendix B, Example Program.
7.2.3.1, SerialOpen() Instruction)
Scan()
SerialOut()
SerialIn()
SplitStr()
Establish a scan rate
Send “get data” command to the CS526.
See Section 7.2.1, Get Data Command, and 7.2.3.2,
SerialOut() Instruction, for more information.
Set up the COM port to receive the incoming serial data (see
Section 7.2.3.3, SerialIn() Instruction).
Please note that in the beginning of the CRBasic program, the
variable used in the SerialIn() instruction needs to be
declared as an ASCII string format.
Split out digital count value for pH from the input string.
a<value><CR><LF>
Where:
a = probe address (factory default is 1)
<value> = the probe’s reading for pH
(in digital counts).
Probe output is “Counts”. A corrected multiplier and offset are
required to provide an output in pH units (see Appendix C,
Calibration).
7
Page 16

CS526 ISFET pH Probe
7.2.3 Instruction Descriptions
7.2.3.1 SerialOpen() Instruction
7.2.3.2 SerialOut() Instruction
The SerialOpen() instruction has the following syntax:
SerialOpen(ComPort,BaudRate,Format,TXDelay,BufferSize)
ComPort — the datalogger COM port in which the probe is connected.
BaudRate — choose 2400
Format — choose 16, which is TTL Logic; No parity, one stop bit, 8 data
bits; No error checking
TXDelay — enter 0
BufferSize — enter at least twice the number of maximum expected
characters + 1, which is 41.
The SerialOut() instruction has the following syntax:
SerialOut(ComPort,OutString,WaitString,NumberTries,TimeOut)
ComPort — the datalogger COM port in which the probe is connected.
OutString — use "1M1!"+CHR(13) for the OutString when the default
probe address of 1 is used.
WaitString — enter the null (“”) WaitString to tell the datalogger to wait
for the echo of each character in the OutString
NumberTries — enter 0
TimeOut — specifies the time, in 0.01 seconds, that the datalogger should
wait for the WaitString or echo of each character in the OutString (0
is used in the example program).
7.2.3.3 SerialIn() Instruction
The SerialIn() instruction has the following syntax:
SerialIn(Dest,ComPort,TimeOut,TerminationChar,MaxNumChars)
Dest — specifies the variable in which the incoming data will be stored.
ComPort — the datalogger COM port in which the probe is connected.
TimeOut — 20 should be adequate, which gives a 200 ms maximum delay
TerminationChar — enter 0
MaxNumChars — 20 should be adequate (specify the maximum number
Please note that in the beginning of the CRBasic program, this
variable needs to be declared as ASCII string format (see example
program in Appendix B, Example Program)
time. The TimeOut parameter is used to specify the amount of time,
in 0.01 seconds, that the datalogger should wait before proceeding to
the next instruction.
of characters to expect per input)
8
Page 17

7.2.3.4 SplitStr() Instruction
TABLE 7-4. Calibration Standards
NOTE
The SplitStr() instruction has the following syntax:
SplitStr(SplitResult,SearchString,FilterString,NumSplit,SplitOption)
SplitResult — an array in which the split string will be stored.
SearchString — the string on which this instruction will operate. This will
be the variable entered for the Dest parameter for the SerialIn()
instruction (see above).
FilterString — enter “String” (this value will be ignored because of the
SplitOption that will be used).
NumSplit — enter 2
SplitOption — enter 0. This splits out numeric values.
7.2.4 Programming for Calibration
To output in pH units instead of digital counts, enter the offset and multiplier
into the datalogger program. Simple program instructions can be used to make
the required periodic calibration easier. See Appendix C, Calibration, for an
example program.
7.3 Calibration
CS526 ISFET pH Probe
Calibration should be carried out according to the detailed procedure outlined
in Appendix C, Calibration. The calibration should use two or more pH
standards, listed in TABLE 7-4, which are available from Campbell Scientific.
pH Part Number
4 25587
7 25586
10 25588
Frequency of calibration depends on the level of accuracy required and the
coating / fouling nature of the measured samples.
8. Troubleshooting
Follow the procedure provided by the Assistance section at the
beginning of this document if the CS526 is not operating properly
and requires return to Campbell Scientific.
The most common causes for erroneous pH data include:
• poor sensor connections to the datalogger
• damaged cables
• scratched chip
• contaminated or clogged diaphragm
9
Page 18
CS526 ISFET pH Probe
CAUTION
Problem:
Output signal is at its maximum value.
Possible reasons:
o Probe is not in fluid.
o Chip is polluted.
o Diaphragm is polluted.
o Chip is scratched.
Suggestions:
o Put probe in fluid.
o Clean probe (Section 9.1, Cleaning).
o Probe cannot be fixed if chip is scratched.
Problem:
Probe response is very slow.
Possible reason:
o Diaphragm is chipped or polluted.
Suggestion:
o Clean probe (Section 9.1, Cleaning).
Problem:
Probe signal is drifting.
9. Maintenance
The CS526 needs to be periodically cleaned and calibrated
to ensure accurate readings and proper operation.
The CS526 has no user-serviceable parts.
9.1 Cleaning
Proper maintenance of a probe is important. If the probe is not properly and
regularly cleaned, the probe can malfunction due to a contaminated diaphragm
or ISFET chip. Contamination on/or blockage of the sensor and reference
electrode diaphragm surface is the most likely cause for probe failure.
Probe wear is another cause for probe failure. Probe wear is often, but not
necessarily, preceded by a period of declining calibration slope values. Probe
wear is dependent on how the probe is used and stored (see Section 9.2,
Storage). Worn probes need to be replaced.
Possible reasons:
o Diaphragm can be dried out.
o Chip is scratched.
Suggestions:
o Soak probe for 10 minutes in saturated KCl solution (pn 16349).
o Probe cannot be fixed if chip is scratched.
10
9.1.1 When to Clean
Often the probe should be cleaned daily, but the appropriate cleaning frequency
is dependent on the type of sample being measured.
Page 19

Clean the probe if any of the following occur:
CAUTION
Diaphragm
Chip
• Low slope
• Drift
• Instability of the reading
• Slow calibration
• Probe will not calibrate
• pH value doesn’t change as expected when changing samples
Additionally, when sampling colored liquids, the probe should be cleaned
when the reference diaphragm is no longer white.
9.1.2 Cleaning Procedure
Read Section 9.1.2.1, Cleaning Tips, before following this procedure.
1. Place probe in warm tap water (~60°) with a mild detergent and soak for 5
minutes, stir periodically.
2. Scrub the surface of the chip and the diaphragm (FIGURE 9-1) with a soft
toothbrush and water with a mild detergent (see Caution).
CS526 ISFET pH Probe
Never brush the probe tip, especially the ISFET chip, before
rinsing and flushing thoroughly with water. Before rinsing
debris and particles may be on the sensor surface and
brushing them into the sensor may damage it. When in
doubt, soak the probe for a while in warm water with a mild
detergent.
FIGURE 9-1. Tip of the CS526 probe
3. Rinse thoroughly with deionized water.
4. Revitalize the probe (Section 9.1.3, Revitalizing)
5. Calibrate the probe (Appendix C, Calibration).
11
Page 20

CS526 ISFET pH Probe
CAUTION
9.1.2.1 Cleaning Tips
9.1.3 Revitalizing
• To avoid scratches on the sensor surface, rinse the probe thoroughly using
water before cleaning the probe with the soft brush supplied with the meter
and tap water with a mild detergent added. Most scratches on the sensor
are caused when there are hard particles in the sample and the sample is
rubbed into the sensor when cleaning with the toothbrush.
• Proteins, fats, and oils may be removed by scrubbing in a solution of Terg-
A-Zyme (Alconox company), a pepsin solution, or a similar product.
Afterwards, rinse thoroughly with deionized or distilled water.
• Do not use hydrofluoric acid, acetone, MEK, or similar agents to clean the
probe.
Revitalization is performed to regenerate the diaphragm in the pH probe. For
best results, clean the probe first as described in Section 9.1.2, Cleaning
Procedure, before revitalizing.
1. Make sure the probe is warm (around 60°C).
2. Place the probe directly (without flushing it with deionized water or
cooling it down) in a saturated KCl-solution (pn 16349) at room
temperature and keep it in the solution for 20 minutes.
This cold KCl-dip will regenerate the reference system and the diaphragm.
9.2 Storage
9.2.1 Short-Term Storage (2 days or less)
1. Clean the probe first with water and possibly a mild detergent.
2. Place it in a clean container with fresh pH7 buffer solution (pn 25586) to
prevent contamination of the probe directly after cleaning.
9.2.2 Long-Term Storage (more than 2 days)
1. Clean the probe first with water and possibly a mild detergent.
2. Place one drop of demi-water in the probe’s protective cap.
3. Place the protective cap on the probe tip.
Always revitalize and recalibrate the probe before using it
again after long term storage (see Section 9.1.3,
Revitalizing, and Appendix C
, Calibration).
12
Page 21

NOTE
Appendix A. Importing Short Cut Code
This tutorial shows:
• How to import a Short Cut program into a program editor for
additional refinement.
• How to import a wiring diagram from Short Cut into the comments of
a custom program.
A.1 Importing Short Cut Code into a Program Editor
Short Cut creates files that can be imported into CRBasic Editor program
editor. These files normally reside in the C:\campbellsci\SCWin folder and
have the following extensions:
• .DEF (wiring and memory usage information)
• .CR1 (CR1000 datalogger code)
• .CR8 (CR800 datalogger code)
• .CR3 (CR3000 datalogger code)
Use the following procedure to import Short Cut code into CRBasic Editor
1. Create the Short Cut program following the procedure in Section 4,
Quickstart. Finish the program and exit Short Cut. Make note of the file
name used when saving the Short Cut program.
2. Open CRBasic Editor.
3. Click File | Open. Assuming the default paths were used when Short Cut
was installed, navigate to C:\CampbellSci\SCWin folder. The file of
interest has a “.CR1”, “.CR8”, or “.CR3” extension, CR1000, CR800, or
CR3000 dataloggers, respectively. Select the file and click Open.
4. Immediately save the file in a folder different from \Campbellsci\SCWin,
or save the file with a different file name.
Once the file is edited with CRBasic Editor, Short Cut can no
longer be used to edit the datalogger program. Change the name
of the program file or move it, or Short Cut may overwrite it next
time it is used.
5. The program can now be edited, saved, and sent to the datalogger.
6. Import wiring information to the program by opening the associated .DEF
file. Copy and paste the section beginning with heading “-Wiring for
CRXXX–” into the CRBasic program, usually at the head of the file.
After pasting, edit the information such that a ' character (single quotation
mark) begins each line. This character instructs the datalogger compiler to
ignore the line when compiling the datalogger code.
A-1
Page 22

Appendix A. Importing Short Cut Code
A-2
Page 23

Appendix B. Example Program
The following is a CR1000 program that measures the CS526. This program
assumes the CS526 is connected to COM1 (C1 / TX and C2 / RX) on the
CR1000.
'CR1000 Series Datalogger
'Declare variable for digital pH measurement
Public pHCount
'Declare variables for serial input from sensor
Dim rawstring As String * 20, pHDigit(2)
'Main Program
BeginProg
'Set up datalogger port for serial communication
SerialOpen ( Com1,2400,16,0,41)
'Establish program scan rate of 60 seconds
Scan (60,Sec,0,0)
'Send get data command to CS526
SerialOut (Com1,"1M1!"&CHR(13),"",0,0)
'Set up COM1 to receive incoming serial data.
'Set timeout to maximum 200 mS
SerialIn (rawstring,Com1,20,0,20)
'Split out digital count value for pH from string input
SplitStr (pHDigit(),rawstring,"String",2,0)
pHCount = pHDigit(2)
NextScan
EndProg
B-1
Page 24

Appendix B. Example Program
B-2
Page 25

NOTE
Appendix C. Calibration
This calibration process uses 7-pH and 4-pH buffer solutions.
Protect the sensing chip from UV radiation during calibration. If
calibrating in sun or fluorescent light, shield the sensing chip from
UV radiation by using dark containers for the buffer solutions.
Load the example CRBasic program into the datalogger (Appendix C.1,
Example Calibration Program). Wire the CS526 to the datalogger according
to the following diagram.
Wire Color Datalogger Connection
Red (Caution! 5 Vdc Max!) 5V
Black G
White Control Port (Tx)
Green Control Port (Rx)
Clear G
Use the Numeric Display found in the datalogger software PC200W, PC400,
LoggerNet, PConnect, or PConnectCE to monitor the measurement in real
time.
1. Place the CS526 into a pH-7 buffer solution (pn 25586).
2. Monitor the [pHmV] reading in the Numeric Display and allow it to
stabilize.
3. Change the value in [pH7record] to -1.
4. Remove the CS526 from the pH-7 buffer solution and rinse with deionized
water.
5. Blot the CS526 dry with a soft cloth or paper towel.
6. Place the CS526 in a pH-4 buffer solution (pn 25587).
7. Allow the [pHmV] reading to stabilize.
8. Change the value in [pH4record] to –1.
9. Change the value in [pHcal] to –1.
10. The CS526 is now ready to be placed in the solution to be measured.
C-1
Page 26
Appendix C. Calibration
C.1 Example Calibration Program
Following is a simple example program to facilitate the two-point calibration.
Although this is a CR1000 program, the other dataloggers are programmed
similarly.
'CR1000 Series Datalogger
'Define Variables
Public pH, pHCount
Public PTemp, batt_volt
Public pH4record, pH4Count
Public pH7record, pH7Count
Public pHcal, pHmult1
Public pHoffset1
Dim rawstring As String * 20, pHDigit(2)
'Define Data Tables
DataTable (TenMin,1,-1)
DataInterval (0,10,Min,10)
Average (1,pH,FP2,False)
EndTable
'Main Program
BeginProg
SerialOpen (Com1,2400,16,0,41)
Scan (10,Sec,0,0)
PanelTemp (PTemp,250)
Battery (batt_volt)
SerialOut (Com1,"1M1!"&CHR(13),"",0,0)
SerialIn (rawstring,Com1,20,0,20)
SplitStr (pHDigit(),rawstring,"String",2,0)
pHCount = pHDigit(2)
'Calibration
If PH4record = -1 Then
pH4Count = pHCount
pH4record = 0
EndIf
If pH7record = -1 Then
pH7Count = pHCount
pH7record = 0
EndIf
If pHcal = -1 Then
pHmult1 = 3/(pH7Count - pH4Count)
pHoffset1 = 7 - pHmult1 * pH7Count
pHcal = 0
EndIf
pH = pHmult1 * pHCount + pHoffset1
CallTable TenMin
NextScan
EndProg
C-2
Page 27

Page 28

Campbell Scientific Companies
Campbell Scientific, Inc. (CSI)
815 West 1800 North
Logan, Utah 84321
UNITED STATES
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com
Campbell Scientific Africa Pty. Ltd. (CSAf)
PO Box 2450
Somerset West 7129
SOUTH AFRICA
www.csafrica.co.za • cleroux@csafrica.co.za
Campbell Scientific Australia Pty. Ltd. (CSA)
PO Box 8108
Garbutt Post Shop QLD 4814
AUSTRALIA
www.campbellsci.com.au • info@campbellsci.com.au
Campbell Scientific (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
8B16, Floor 8 Tower B, Hanwei Plaza
7 Guanghua Road
Chaoyang, Beijing 100004
P.R. CHINA
www.campbellsci.com • info@campbellsci.com.cn
Campbell Scientific do Brasil Ltda. (CSB)
Rua Apinagés, nbr. 2018 ─ Perdizes
CEP: 01258-00 ─ São Paulo ─ SP
BRASIL
www.campbellsci.com.br • vendas@campbellsci.com.br
Campbell Scientific Canada Corp. (CSC)
14532 – 131 Avenue NW
Edmonton AB T5L 4X4
CANADA
www.campbellsci.ca • dataloggers@campbellsci.ca
Please visit www.campbellsci.com to obtain contact information for your local US or international representative.
Campbell Scientific Centro Caribe S.A. (CSCC)
300 N Cementerio, Edificio Breller
Santo Domingo, Heredia 40305
COSTA RICA
www.campbellsci.cc • info@campbellsci.cc
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL)
Campbell Park
80 Hathern Road
Shepshed, Loughborough LE12 9GX
UNITED KINGDOM
www.campbellsci.co.uk • sales@campbellsci.co.uk
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL France)
3 Avenue de la Division Leclerc
92160 ANTONY
FRANCE
www.campbellsci.fr • info@campbellsci.fr
Campbell Scientific Ltd. (CSL Germany)
Fahrenheitstraße 13
28359 Bremen
GERMANY
www.campbellsci.de • info@campbellsci.de
Campbell Scientific Spain, S. L. (CSL Spain)
Avda. Pompeu Fabra 7-9, local 1
08024 Barcelona
SPAIN
www.campbellsci.es • info@campbellsci.es
 Loading...
Loading...