Page 1

CALEFFI
www.caleffi.com
38482.03
Adjustable differential pressure by-pass valve with graduated scale
© Co py right 2 01 2 Ca leffi
519 Series
Function
The differential pressure by-pass valve is used in systems with a
fixed speed circulating pump supplying several zones controlled
by two way zone valves. This valve ensures that the head pressure
of the pump is proportional to the number of two way valves being
closed. It will bypass the differential pressure created by the pump
as the zone valves close, thus eliminating water hammer noise.
Product range
Code 519502A By-pass with flow up to 9 gpm. Size 3/4" MNPT
union inlet x 3/4" MNPT union outlet
Code 519599A By-pass with flow up to 9 gpm. Size 3/4" Sweat
union inlet x 3/4" Sweat union outlet
Code 519600A By-pass with flow up to 40 gpm Size 1" FNPT
inlet x 1" MNPT union outlet
Code 519609A By-pass with flow up to 40 gpm Size 1” Female
NPT x 1” sweat outlet
Code 519700A By-pass with flow up to 45 gpm Size 1 1/4" FNPT
inlet x 1 1/4" MNPT union outlet
Code 519709A By-pass with flow up to 45 gpm Size 1 1/4" FNPT
inlet x 1 1/4" Sweat union outlet
Technical characteristics
Materials
Body: brass
Valve plug: brass
Valve plug gasket: EPDM
O-Ring seals: EPDM
Union seals: asbestos free NBR
Control knob: ABS
Spring: stainless steel
Performance
Suitable fluids: water, glycol solutions
Max percentage of glycol: 30%
Temperature range: 32–230°F (0–110°C)
Maximum working pressure: 150 psi (10 bar)
Flow rates: 3/4” flow up to 9 gpm
1” flow up to 40 gpm
1 1/4” flow up to 45 gpm
Setting range: 1 - 6 m w.g. (2 - 10 psi)
SAFETY INSTRUCTION
This safety alert symbol will be used in this manual to draw attention to safety related
instructions. When used, the safety alert symbol means ATTENTION! BECOME ALERT!
YOUR SAFETY IS INVOLVED! FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS MAY
RESULT IN A SAFETY HAZARD.
Page 2
1
2
3
4
5
Flow rate G
∆p
∆p
NOMINAL
Pump curve
∆p constant
on the circuit
Circuit resistance curve
with two-way valves
partially open
Circuit resistance curve with
two-way valves fully open
A
B
∆G
50% 100%
Two-way
TOTAL LOAD
mH2O
1
2
3
4
5
6
PARTIAL LOAD
mH2O
1
2
3
4
5
6
CAUTION: All work must be performed by qualified personnel trained in the
proper application, installation, and maintenance of systems in accordance
with all applicable codes and ordinances.
Operating principle
➪
System operation
O = open
C = close
O
O
O
O
➪
➪
O
O
➪
➪
CAUTION: Over-tightening and breakage can occur with the use of Teflon
pipe joint compounds. Teflon®provides lubricity so that care must be
exercised not to over-tighten joints. Failure to follow these instructions
could result in property damage and /or personal injury.
WARNING: System fluids are under pressure or temperature can be
hazardous. Be sure the pressure has been reduced to zero and the
system temperature is below 100°F (38°C). Failure to follow these
instructions could result in property damage and/or personal injury.
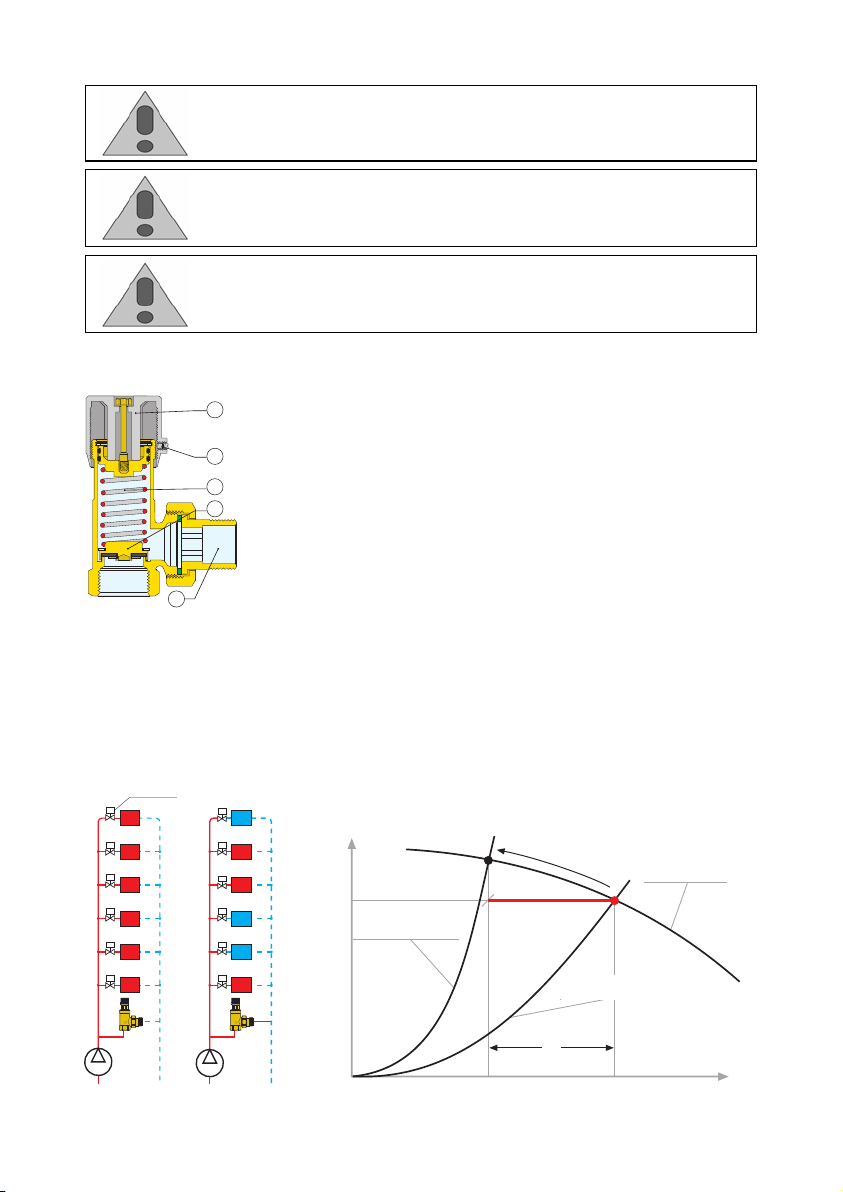
When the spring (1) compression is adjusted using the control
knob (2), the force balance acting on the valve plug (3) changes,
thus modifying the threshold pressure value
of the valve. The valve
plug opens, activating the by-pass circuit, only when it is subjected
to a differential pressure sufficient to generate a thrust greater than
the thrust exerted by the spring. This allows the flow discharge
through the outlet (4), limiting the difference in pressure between
the two points in the system where the valve is fitted.
The job of the differential pressure by-pass valve is to maintain the
➪
pump operating point as close as possible to its nominal value (point
A on the graph shown below). If the by-pass valve is not used, when
the flow rate in the circuit decreases due to partial closure of the twoway zone valves, the head loss in the circuit increases, point B.
The by-pass valve, set to the nominal head value of the pump,
limits the increase in pressure, by-passing the flow rate ∆G. This
behavior is guaranteed at any closing condition of the system twoway zone valves. In fact, once the position of the valve control
knob has been established, the threshold pressure value is more
or less constant as the discharge flow rate varies (see hydraulic
characteristic diagrams).
A proper valve sizing must guarantee a sufficient flow rate by-pass to
keep the pump at its nominal operating point in all system operating
conditions, for example when the first zone valves are closed.
C
O
O
C
C
O
➪
➪
➪
➪
®
Page 3

mH2O
1
2
3
4
5
6
Installation
mH2O
1
2
3
4
5
6
mH2O
1
2
3
4
5
6
a) b)
mH2O
1
2
3
4
5
6
mH2O
1
2
3
4
5
6
c) d)
∆p
(psi)
1
2
0.5
0
1.5
G (m
3
/h) (gpm)
∆p
(psi) (m w.g.)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
0
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
1
5
4
3
2
6
7
8
9
0
The differential pressure by-pass valve can be fitted in any position,
respecting the flow direction indicated by the arrow on the valve body.
In systems with a traditional boiler it is normally fitted between the
system flow and return ends, which allows the control of the pressure
and the passage of a minimum flow through the heat generator.
In systems with a condensation boiler, it is preferable to fit the
by-pass directly between the upstream and downstream sections of
the pump, as this allows a higher ∆T in the circuit, with lower return
temperatures and therefore better operation of the system.
In the event of high by-pass flow rate levels, it is recommended to fit
the valve between the flow and return ends of each column, rather
than fitting a number of valves in parallel at the central boiler.
Adjustment
Hydraulic
characteristics
code 519502A
519599A (3/4”)
To regulate the valve, turn the knob to the required value on the
graduated scale: the values correspond to the differential pressure in
psi or meters w.g. to open the by-pass.
For a quick setup adjustment of the differential pressure by-pass
valve, use the following manual method. As an example, a hydronic
system with several zone valves: the system must be operating, the
zone valves must be fully open and the by-pass valve must be set to
the maximum value (a) (clockwise). Gradually open the differential
pressure by-pass valve using the control knob (counterclockwise).
Use a thermometer, or simply your hand, to check that the hot water
is flowing into the by-pass circuit (b). As soon as a rise in the
temperature is noted, turn control knob (clockwise) one half turn
closed so hot water stops flowing into the by-pass (c). Lock the knob
in this position (d) with the locking screw.
Setting positions
➧
10
8
6
4
2
Page 4

CALEFFI
∆p
(m w.g.)
1
2
0
3
/h) (gpm)
∆p
(m w.g.) (psi)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
5010
152520
30
3
4
5
6
403545
7
8
9
10
8
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
∆p
(m w.g.)
1
2
0
G (m
3
/h) (gpm)
∆p
(m w.g.) (psi)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
5010
152520
30
3
4
5
6
40
35
7
8
9
8
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
code 519600A 519609A (1”)
Setting positions
➧
6
5
4
3
2
1
code 519700A 519709A (1 1/4”)
Setting positions
CAUTION: If the by-pass valve is not installed, commissioned and
maintained properly, according to the instructions contained in this
manual, it may not operate correctly and may endanger the user.
CAUTION: Make sure that all the connecting pipework is water tight.
Service Instructions
There is no service required for the differential by-pass valves.
Leave this manual for the user.
➧
6
5
4
3
2
1
Caleffi North America, Inc.
3883 West Milwaukee Road
Milwaukee, WI 53208
T: 414.238.2360 F: 414.238.2366
 Loading...
Loading...